Page 1

Transponder 3064
Manual
29.07.2019
Page 2

Contents
Transponder 3064 (Manual)
2 / 18
Contents
1 Safety instructions .................................................................................................................................... 3
2 General ..........................................................................................................................................................4
2.1 How it works.......................................................................................................................................................4
2.2 Incorporating the transponder in different locking systems.......................................................4
2.3 Higher-ranking locking level........................................................................................................................ 5
3 Special models ........................................................................................................................................... 7
3.1 Password transponder...................................................................................................................................7
3.2 Switch transponder .........................................................................................................................................7
3.3 Explosion protection transponder (EX protection)..........................................................................7
3.4 Bonded transponder .......................................................................................................................................7
3.5 Transponder with integrated RFID chip.................................................................................................7
3.6 Fire service key tube transponder............................................................................................................8
3.7 G2 battery replacement transponder....................................................................................................8
4 Explosion protection transponder........................................................................................................9
4.1 General..................................................................................................................................................................9
4.2 Industrial standards ........................................................................................................................................9
4.3 Classification......................................................................................................................................................9
5 Additional functions................................................................................................................................ 10
5.1 Time zone control.......................................................................................................................................... 10
5.2 Date of validity ................................................................................................................................................ 10
5.3 Activation transponder................................................................................................................................ 10
6 Battery replacement.................................................................................................................................11
6.1 Battery Replacement 3064........................................................................................................................11
7 Loss of the transponder ..........................................................................................................................12
7.1 Emergency opening .......................................................................................................................................12
7.2 Replacement transponder [G1]...............................................................................................................12
8 Overview of differences between G1 and G2 Protocols ...............................................................13
9 Technical data .......................................................................................................................................... 14
10 Declaration of conformity ......................................................................................................................15
11 Help and other information .................................................................................................................. 16
Page 3

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
1 Safety instructions
The transponder casing is protected against splash water. However, it is
not watertight!
Only use batteries which have been approved by SimonsVoss (see
Technical data [}14]
The batteries used may pose a fire or burn hazard if handled incorrectly.
Do not recharge, open, heat or burn these batteries. Do not short-circuit!
Dispose of old or used batteries correctly. Store out of children's reach.
Damage may be caused to the transponder if you reverse the polarity!
Do not touch the contacts on the new batteries with your hands when
replacing the old ones. Use cotton gloves free of fat or grease.
1. Safety instructions
3 / 18
).
The electronics must not be subject to mechanical stress or damaged in
any way.
Access through a door may be blocked due to defective or incorrectly
programmed products. SimonsVoss Technologies GmbH is not liable
for any consequences, such as blocked access to injured persons or
those at risk, physical damage or any other losses.
SimonsVoss Technologies GmbH accepts no liability for any damage
caused by incorrect fitting or installation.
Modifications or further technical developments cannot be excluded
and may be implemented without notice.
This documentation has been compiled based on the best knowledge
available to us. Nevertheless, errors cannot be ruled out. SimonsVoss
Technologies GmbH accepts no liability in such a case.
Should there be differences in the content of other language versions of
this documentation, the German version applies in cases of doubt.
Page 4

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
2 General
Transponder 3064 is a digital "key" which is programmed with locking plan
software and functions using contactless, wireless communication. All
functions are activated by pressing a button. These include authorisation
identification and the opening and locking of doors, gates, barriers, furniture
locks and similar items. The transponder communicates with digital
components – cylinders, SmartRelays and activation units – by sending
and receiving constantly changing crypto codes, which ensure that the
system cannot be misused.
As System 3060 functions using active transponder technology, the
transponder features its own power source, a battery. Advantages over
passive technologies include lower power requirements in the cylinder and
the greater operating range.
2. General
4 / 18
SimonsVoss supplies different transponder models. These models are
described in this document.
The second transponder generation G2 replaces the first generation G1. G2
features a more efficient communication protocol than G1. It will allow you
to create larger, more efficient locking systems. Authorisations are also
written on both the locking cylinder and the transponder, making
programming more flexible.
A G2 system can also form a virtual network, i.e. authorisations and
blocking lists are written on the transponder and transmitted to the locking
system.
This manual looks at the specific differences between transponders. Read
the G2 manual for more details.
The G2 transponder features both the G1 and G2 protocols and can thus be
programmed for both locking system generations.
2.1 How it works
To carry out an action, the user holds the transponder close to the digital
lock and presses the transponder button. The transponder may be held at
a distance of up to 40 cm for locking cylinders and SmartHandles and up
to 120 cm for SmartRelays. The transponder and locking device then
exchange keys and authorisation data. The user can only perform the
required action, such as opening or locking the door, if the transponder is
authorised for the digital lock.
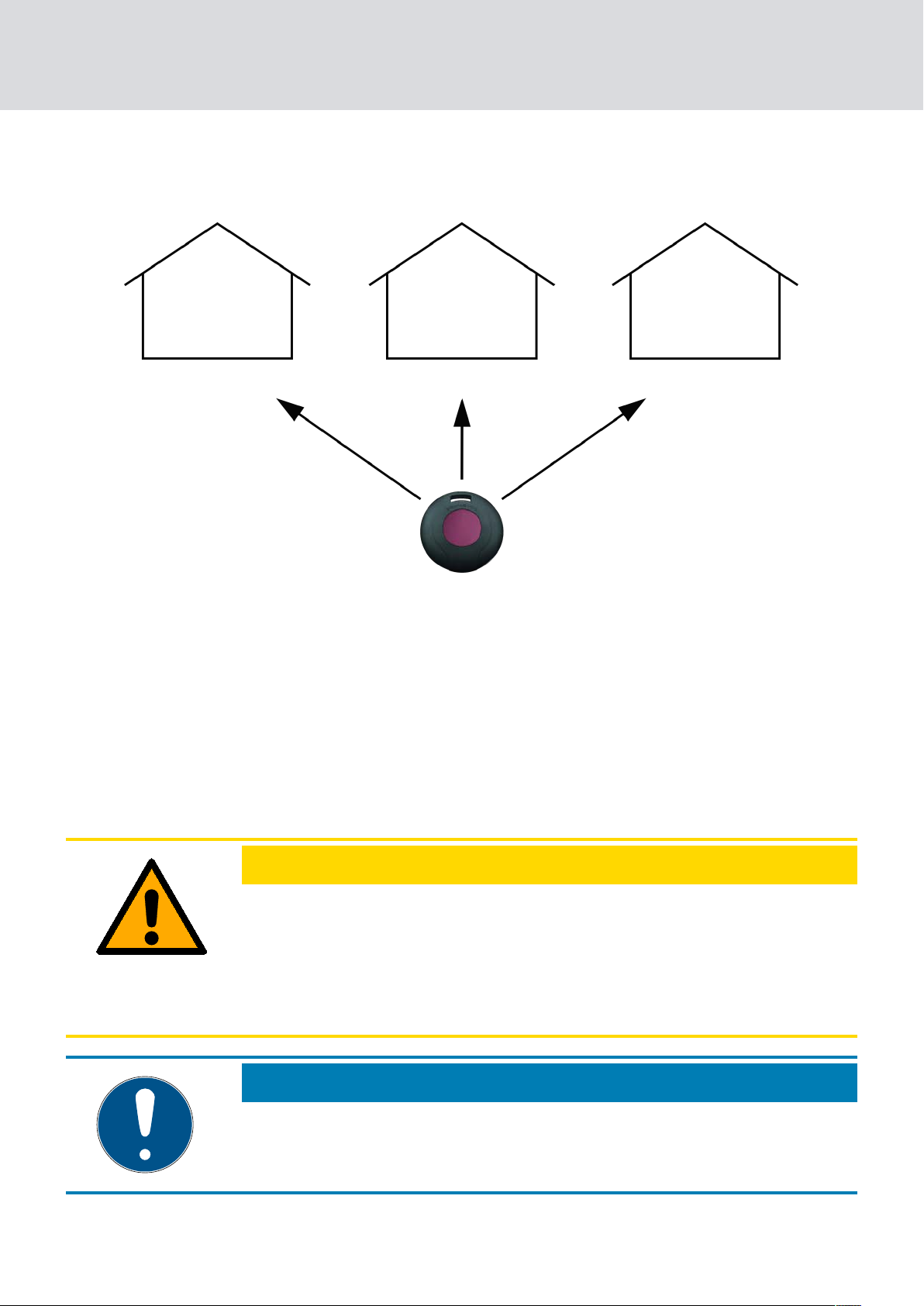
2.2 Incorporating the transponder in different locking systems
Each transponder can be used in three [G1] or four [G2] completely
separate locking systems, providing no areas of validity are programmed.
Each locking system receives its own password and is managed separately.
Page 5
Firma:
900
Schließungen
Filiale:
85
Schließungen
Eigenheim:
3
Schließungen
Schließanlage 1 Schließanlage 2 Schließanlage 3
Transponder 3064 (Manual)
The following screen shows an example of use.
2. General
5 / 18
Fig.1:
A transponder for several separate locking systems
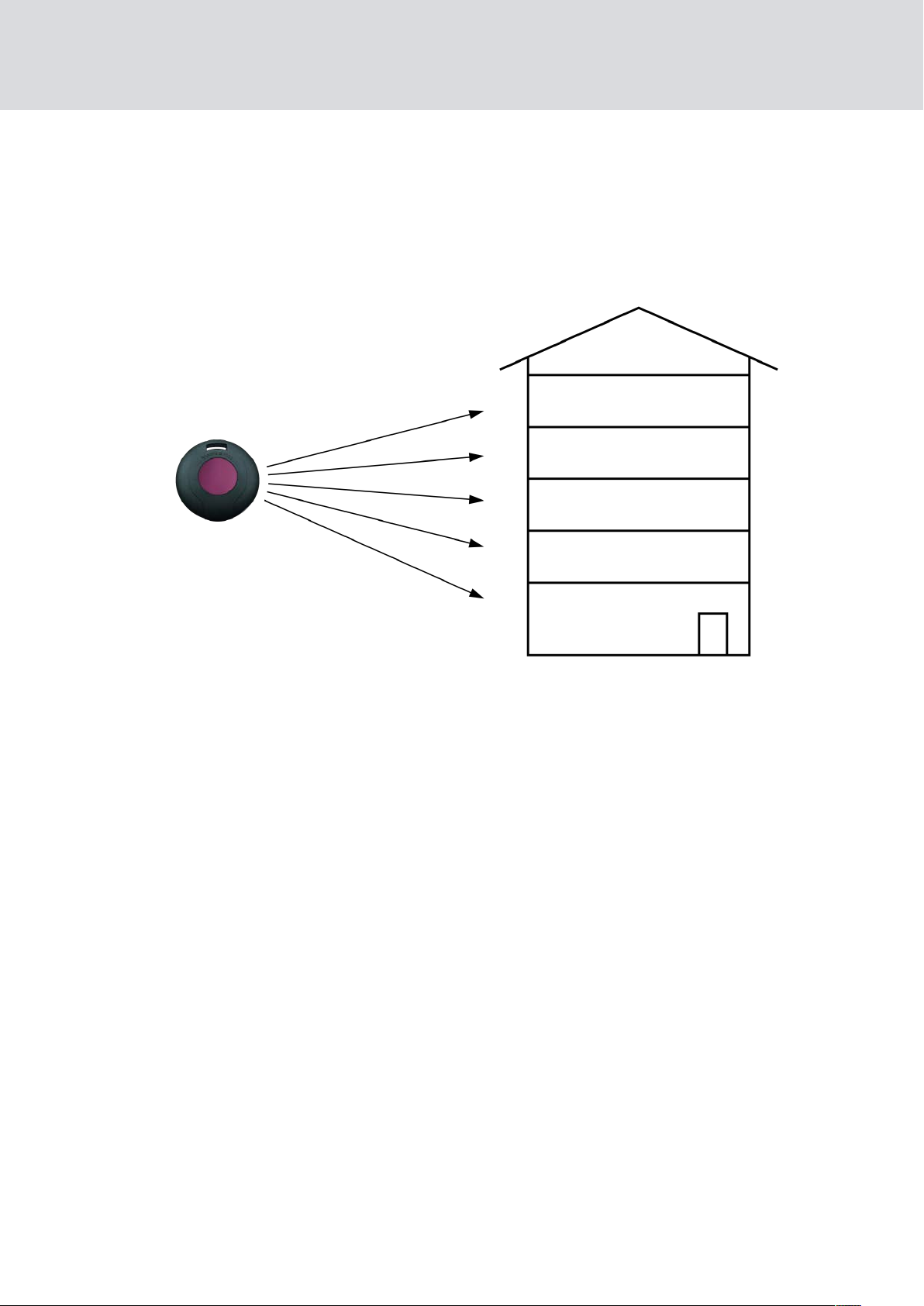
2.3 Higher-ranking locking level
Transponders can be authorised for more than three [G1] or four [G2]
locking systems. To ensure this is the case, higher-ranking locking levels
need to be set up in the locking systems concerned. A maximum of three
higher-ranking locking levels can be set up per locking system (green, blue
and red).
CAUTION
Opening deactivated locking devices using the red level
Transponders which have been assigned to the red locking level can also
open deactivated locking devices using a block lock function.
Assign the red locking level to emergency services such as the fire
service only.
IMPORTANT
Reprogramming a higher-ranking locking level
Higher-ranking locking levels can only be programmed directly on the locking device.
Page 6
Company D
Company C
Company B
Company A
Central
locking system
Transponder 3064 (Manual)
200 [G1] or 1024 [G2] transponder IDs (TIDs) are reserved for each level in
LSM. Authorisations for different transponders in the higher-ranking locking
levels may be different.
The following screen shows an example of use.
2. General
6 / 18
Fig.2:
Higher-ranking transponder
Four companies are based in an office building with a main lock which is
used by all the companies. Each company manages its own locking system
with its own password. Each employee receives a transponder which is
authorised for two locking systems, the main lock and their company's own
system. The building management or on-site technicians and cleaning staff
require access to all levels. The fire service, for example, requires a
transponder which is valid for all five locking systems in the building. They
also require access if the alarm system is activated and the block lock
function has disabled the locking cylinders. Higher-ranking locking levels
are created in each of the five locking systems to provide access to all five
locking systems. Each level receives the same password for all locking
systems.
Page 7

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
3 Special models
3.1 Password transponder
Instead of being entered manually, the locking system password can be
transmitted by radio using a special transponder. Standard transponders
cannot be used as a password transponder.
3.2 Switch transponder
For this type of transponder, a two-wire cable (about 1 m long) is
connected to the switch contacts on the button and fed to the outside.
When the two wires are connected, the transponder interconnects and is
able to trigger actions.
3. Special models
7 / 18
Examples of use:
Linking third-party systems
Remote activation of a digital locking cylinder or SmartRelay
3.3 Explosion protection transponder (EX protection)
This transponder has the same functions as a Transponder 3064, but it is
also approved for use in Explosion Protection Zone 1 (see
protection transponder [}9]
).
Explosion
3.4 Bonded transponder
This transponder is almost identical to the standard transponder, but has a
bonded casing. This prevents the end user from misusing the transponder
electronics or opening the casing.
3.5 Transponder with integrated RFID chip
Transponders can be supplied with different integrated RFID chips as an
option. These RFID Chips do not necessarily need to be programmed with
the LSM software. The active transponder and passive RFID part are
independent from one another.
The following different RFID technologies are available:
EM® 4102
HITAG® 1
HITAG® 2
MIFARE® Classic
MIFARE® DESFire
LEGIC® MIM 256
Page 8

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
LEGIC® advant 128
3.6 Fire service key tube transponder
Almost identical to the standard transponder, but has a narrower casing
(33mm) and can be kept in a standardised fire service key tube.
3.7 G2 battery replacement transponder
A G2 battery replacement transponder can be created in the LSM software
(Version 3.0 or higher) for G2 locking systems. If the battery is low, the
locking device will switch to freeze mode and can no longer be opened with
normal transponders. The battery replacement transponder can eliminate
freeze mode when activated on the cylinder. The locking device can then
be opened with an authorised transponder. This means you no longer need
to take the programming device to enable the locking device.
3. Special models
8 / 18
CAUTION
Depleting batteries through misuse
The battery is depleted further each time it opens a locking device in conjunction with a battery replacement transponder. This may lead to the batteries being fully discharged if the transponder is not used for its intended
purpose! The batteries must be replaced immediately in such cases.
Page 9

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
4 Explosion protection transponder
4.1 General
This transponder is a special product which can be carried and used in
Zone 1 potentially explosive areas. Zone 1 refers to an area where a
potentially explosive atmosphere sometimes occurs during day-to-day
operations. The following aspects must be taken into account:
The casing must not be opened.
Unlike with Standard Transponders 3064, only SimonsVoss may
change the battery in this transponder.
As a general rule, users must comply with explosion protection
regulations such as the German Operating Regulations BGR132 when
using the device in Zone 1.
4. Explosion protection transponder
9 / 18
4.2 Industrial standards
This transponder has been tested in accordance with applicable explosion
protection standards.
Refer to the following for further information:
Directive 94/9/EC
EN 60079-0 (Equipment for explosive atmospheres)
EN 60079-11 (Equipment protection by intrinsic safety "i!")
4.3 Classification
The transponder is classified as follows:
Explosion Protection Zone 1
Intrinsic safety ib
Explosion group IIC
Temperature class T3
Device group II2 G
This applies to areas where a potentially explosive atmosphere may occur
due to gases, vapours or mist. The information given refers to an ambient
temperature between -20°C and +40°C in the area of use.
Page 10

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
5 Additional functions
The functions described below can be activated in the LSM software.
5.1 Time zone control
Transponders can be programmed to have locking authorisation for digital
access control locking devices at certain times only (time zones). Such
time zones are added to the LSM software and the transponders are then
allocated to the relevant time zone group.
Example: Mr Smith receives the following authorisations:
Monday to Friday Between 09:00 and 18:30
Saturday Between 09:00 and 12:45
Sunday No authorisation
5. Additional functions
10 / 18
5.2 Date of validity
Transponder authorisations can be linked to a validity date. The locking
device does not need to be an access control locking device.
Transponders which are valid from a specific point in time
(e.g. from 08:00 on July 12, 2005)
Transponders which are valid until a specific point in time
(e.g. until 17:00 on July 12, 2005)
Transponders which are valid for a specific time period
(e.g. between 1 July, 2003 until 31 July, 2005)
IMPORTANT
Data record creation
A data record is created each time for the activation or expiry date.
5.3 Activation transponder
As the result of a Block Lock function, all authorised transponders are
blocked for digital locking devices in a safety area when the alarm system
is activated to prevent false alarms.
Transponders can be programmed which eliminate this blocking mode and
can then be used in an emergency by the fire service, for example (see
Higher-ranking locking level [}5]
an authorised transponder.
). The door can then only be opened using
Page 11

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
6 Battery replacement
6.1 Battery Replacement 3064
The transponder battery can be replaced at any time when the battery
warning is active (see Locking Cylinder 3061 manual – Battery warning).
1. Carefully open the casing at the notches, so that you can see the battery.
2. Open the battery holder.
3. Remove the battery.
4. Insert a new battery.
5. Close the battery holder.
6. Press the casing together again.
9 Casing lid clicks back into place.
6. Battery replacement
11 / 18
9 Battery is replaced.
WARNING
Risk of explosion due to incorrect battery replacement
A battery fitted incorrectly into a explosion protection transponder may ignite an explosive atmosphere. Therefore, only SimonsVoss Technologies
GmbH may replace the battery in explosion protection transponders.
CAUTION
Lack of power supply on battery replacement
The transponder may lose data due to the interruption in power supply. Do
not interrupt the power supply for longer than two minutes. Do not press
the button when there is no power and avoid short circuits.
Page 12

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
7 Loss of the transponder
7.1 Emergency opening
You may carry out an emergency opening with the SmartCD and PDA and
by entering the locking system password.
7.2 Replacement transponder [G1]
If a transponder is lost, it can be blocked in the locking plan and a
replacement transponder added. If the locking system is operated in
overlay mode [G1], the transponder is automatically disabled as soon as
the replacement transponder is activated on the locking device (see LSM
manual for programming).
7. Loss of the transponder
12 / 18
Page 13

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
8 Overview of differences between G1 and G2 Protocols
8. Overview of differences between G1
and G2 Protocols
13 / 18
G1 G2
Locks per locking cylinder on a transponder
Number of locking systems
Max. number of TIDs per
higher-ranking locking
level
Time zone groups 5+1 100+1
Physical access lists
storable
Locking plan information
16,000 64,000
3 4 [G2] + 3 [G1]
200 1024
n/a 1000
Locking devices
Transponders or locking
devices
Page 14

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
9 Technical data
9. Technical data
14 / 18
Housing
Ambient conditions
Batteries
Material
Colours
Diameter 42.0 mm
Height 13.7 mm
Temperature range -20°C to 60°C
Standard protection
rating
Environmental Class III
Type CR2032
Manufacturer
Quantity 1x
Voltage 3 V
Battery life
Weatherproof plastic
(polyamide)
Casing: black
Buttons: different colours
IP65
IP66 (.SPEZ version)
Varta, (Panasonic,
Sony)
G1: up to 100,000 activations or up to 10 years
on standby
G2: up to 400,000 activations or up to 10
years on standby
Radio emissions
SRD 24.50 kHz - 25.06 kHz
RFID (depending on
equipment)
There are no geographical restrictions within the EU.
13.564 MHz - 13.564
MHz
-20 dBµA/m (10 m distance)
-19.57 dBµA/m (10 m
distance)
Page 15

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
10 Declaration of conformity
The company SimonsVoss Technologies GmbH hereby declares that
article TRA2 complies with the following guidelines:
2014/53/EU "Radio equipment"
2014/30/EU "EMC"
2011/65/EU "RoHS"
2012/19/EU "WEEE"
and regulation (EG) 1907/2006 "REACH"
The full text of the EU Declaration of conformity is available at the
following internet address:
certificates.html
.
10. Declaration of conformity
15 / 18
https://www.simons-voss.com/en/
Page 16

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
11 Help and other information
Information material/documents
You will find detailed information on operation and configuration and other
documents under Informative material/Documents in the Download
section on the SimonsVoss website (
downloads/documents.html
Declarations of conformity
You will find declarations of conformity for this product in the Certificate
section on the SimonsVoss website (
certificates.html
Information on disposal
).
11. Help and other information
16 / 18
https://www.simons-voss.com/en/
).
https://www.simons-voss.com/en/
Do not dispose the device (TRA2) in the household waste. Dispose of it
at a collection point for electronic waste as per European Directive
2012/19/EU.
Recycle defective or used batteries in line with European Directive
2006/66/EC.
Observe local regulations on separate disposal of batteries.
Take the packaging to an environmentally responsible recycling point.
Hotline
If you have any questions, the SimonsVoss Service Hotline will be happy to
help you on +49 (0)89 99 228 333 (German fixed network; call charges
vary depending on the operator).
Email
You may prefer to send us an email.
support@simons-voss.com
FAQs
You will find information and help for SimonsVoss products in the FAQ
section on the SimonsVoss website (
public.pl
).
https://faq.simons-voss.com/otrs/
Page 17

Transponder 3064 (Manual)
SimonsVoss Technologies GmbH
Feringastrasse 4
85774 Unterföhring
Germany
11. Help and other information
17 / 18
Page 18

This is SimonsVoss
SimonsVoss is a technology leader in digital
locking systems.
The pioneer in wirelessly controlled, cable-free
locking technology delivers system solutions
with an extensive product range for SOHOs,
SMEs, major companies and public institutions.
SimonsVoss locking systems unite intelligent
functions, optimum quality and award-winning
German-made design. As an innovative system
provider, SimonsVoss attaches great importan-
ce to scalable systems, effective security, reliable components, high-performance software and simple operation.
Our commercial success lies in the courage to innovate, sustainable thinking and
action, and heartfelt appreciation of employees and partners. With its headquarters in Unterföhring, near Munich, and its production site in Osterfeld, eastern
Germany, the company employs around 300 staff in eight countries.
SimonsVoss is a company in the ALLEGION Group, a globally active network in
the security sector. Allegion is represented in around 130 countries worldwide
(www.allegion.com).
© 2019, SimonsVoss Technologies GmbH, Unterföhring
All rights are reserved. Text, images and diagrams are protected under copyright
law.
The content of this document must not be copied, distributed or modified. More
information about this product can be found on the SimonsVoss website. Subject to technical changes.
SimonsVoss and MobileKey are registered brands belonging to SimonsVoss
Technologies GmbH.
 Loading...
Loading...