Silicon Storage Technology Inc SST32HF802-90-4E-TBK, SST32HF802-90-4E-EK, SST32HF802-90-4C-TBK, SST32HF802-90-4C-EK, SST32HF802-70-4E-TBK Datasheet
...
Multi-Purpose Flash (MPF) + SRAM ComboMemory
SST32HF802 / SST32HF162 / SST32HF164
SST32HF802 / 162 / 164MPF (x16) + 1Mb SRAM (x16) ComboMemories
FEATURES:
Data Sheet
• MPF + SRAM ComboMemory
– SST32HF8 0 2 : 512K x16 Flash + 128K x16 SRAM
– SST32HF162: 1M x16 Flash + 128K x16 SRAM
– SST32HF164: 1M x16 Flash + 256K x16 SRAM
• Single 2.7-3.3V Read and Write Operations
• Concurrent Operation
– Read from or write to SRAM while
Erase/Program Flash
• Superior Reliability
– Endurance: 100,000 Cycles (typical)
– Greater than 100 years Data Retention
• Low Power Consumption:
– Active Current: 15 mA (typical) for
Flash or SRAM Read
– Standby Current: 20 µA (typical)
• Flexible Erase Capability
– Uniform 2 KWord sectors
– Uniform 32 KWord size blocks
• Fast Read Access Times:
– Flash: 70 ns and 90 ns
– SRAM: 70 ns and 90 ns
• Latched Address and Data for Flash
• Flash Fast Erase and Word-Program:
– Sector-Erase Time: 18 ms (typical)
– Block-Erase Time: 18 ms (typical)
– Chip-Erase Time: 70 ms (typical)
– Word-Program Time: 14 µs (typical)
– Chip Rewrite Time:
SST32HF802: 8 seconds (typical)
SST32HF162/164: 15 seconds (typical)
• Flash Automatic Erase and Program Timing
– Internal V
Generation
PP
• Flash End-of-Write Detection
– Toggle Bit
– Data# Polling
• CMOS I/O Compatibility
• JEDEC Standard Command Set
• Package Available
– 48-lead TSOP (12mm x 20mm)
– 48-ball TBGA (10mm x 12mm)
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The SST32HF802/162/164 ComboMemory devices integrate a 512K x16 or 1M x16 CMOS flash memory bank
with a 128K x16 or 256K x16 CMOS SRAM memory bank
in a Multi-Chip Package (MCP), m anufactured with SST’s
proprietary , high performance SuperFlash technology.
Featuring high performance Word-Program, the flash
memory bank provides a maximum Word-Program time of
14 µsec. The entire flash memory bank can be erased and
programmed word-by-word in typi cally 8 seconds for the
SST32HF802 an d 15 seconds for the SST32HF 162/164,
when using interface features such as Toggle Bit or Data#
Polling to indicate the completion of Program operation. To
protect against inad vertent flash write, the SS T32HF802/
162/164 devices contain on-chip hardware and software
data protection schemes.The SST32HF802/162/164
devices offer a guaranteed endurance of 10,000 cycles.
Data retention is rated at greater than 100 years.
The SST32HF802/162/164 devices consist of two independent memor y banks with re spective bank enable signals. The Flash and SRAM memory banks are
superimposed in the same memory address space. Both
memory ba nks share common address lines, data lines,
WE# and OE#. The memor y bank selection is done by
memory bank enable signals. The SRAM bank enable signal, BES# selects the SRAM bank. The flash memory
bank enable signal, B EF# s elects the f lash me mory bank.
The WE# signal has to be used with Software Data Protection (SDP) command sequence when controlling the Erase
and Program operatio ns in the flash memor y bank. The
SDP command seque nce protects the data stored in th e
flash memory bank from accidental alteration.
The SST32HF802/162/164 provide the added functionality
of being able to simultaneo usly read from or write to th e
SRAM bank while erasing or programming in the flash
memory ban k. The SRAM memo ry bank can be read or
written while the flash memory bank performs SectorErase, Bank-Erase, or Word-Program concurrently. All
flash memory Erase and Program operations will automatically latch the input address and data signals and complete
the operation in ba ckground without fur ther in put stimulus
requirement. On ce the internally contro lled erase or program cycle in the fla sh bank has c ommenced , the SRAM
bank can be accessed for read or write.
The SST32HF802/162 /164 devices are sui ted for applications that use both flash memory and S RAM memory to
store code or data. For systems requiring low power and
small form factor, the SST32HF802/162/164 devices significantly improve performance and reliability, while lowering
power consumption, when compared with multiple chip
solutions. The SST32HF802/162/164 inherently use less
energy during erase and program than alternative flash
©2001 Silicon Storage Technology, Inc.
S71171-05-000 8/01 520
1
The SST logo and SuperFlash are registered trademarks of Silicon Storage Technology, Inc.
MPF and ComboMemory are trademarks of Silicon Storage Technology, Inc.
These specifications are subject to change without notice.

Multi-Purpose Flash (MPF) + SRAM ComboMemory
SST32HF802 / SST32HF162 / SST32HF164
Data Sheet
technologies. The tota l energy consumed is a function of
the applied voltage, curre nt, and time of ap plic ation . Sinc e
for any given voltage range, the SuperFlash technology
uses less current to program and has a shorter erase time,
the total energy consumed during any Erase or Program
operation is less than alternative flash technologies.
The SuperFlash te ch nology provides fixed Erase and P r ogram times, independent o f th e numbe r of Erase/ Pro gram
cycles that have occurred. Therefore the system software
or hardware does not have to be modified or de-rated as is
necessary with al ternativ e flas h techno logies , whos e Erase
and Program times i ncrease with accumul ated Erase/P rogram cycles .
Device Operation
The ComboMemory uses BES# and BEF# to control operation of either the SRAM or the flash memory bank. When
BES# is low, the SRAM Bank is activated for Read and
Write operatio n. When BEF# is l ow the flash b ank is act ivated for Read, Program or Erase operation. BES# and
BEF# cannot be at low level at the same time. If BES# and
BEF# are both asserted to low level bus contention will
result and the device may suffer permanent damage. A ll
address, data, and control lines are shared by SRAM Bank
and flash bank whi ch minimizes power consumption and
loading. The device goes into standby when both bank
enables are high.
SRAM Operation
With BES# low and BEF# high, the SST32HF802/162
operate as 128K x16 CMOS SRAM, and the SST32HF164
operates as 256K x16 CMOS SRAM, with fully static operation requiring no external clocks or timing strobes. The
SST32HF802/162 SRAM is mapped into the first 128
KWord address space of the device, and the SST32HF164
SRAM is mapped into the first 256 KWord address space.
When BES# and BE F# are hi gh, both m emor y ba nks are
deselected and the device enters standby mode. Read and
Write cycle times are equal. The control signals UBS# and
LBS# provide access to the upper data byte and lower data
byte. See Table 3 for SRAM read a nd w rite data byte control modes of operation.
SRAM Write
The SRAM Write operation of the SST32HF802/162/164
is controlled by WE# and BES# being low for the system
to write to the SRAM. During the Word-Write operation,
the addresses and data are referenced to the rising edge
of WE# or BES#, which ever occurs first. The write time is
measured from the last falling edge to the rising edge of
WE# or BES#. Refer to the Write cycle timing diagrams,
Figures 4 and 5, f or further details .
Flash Operation
With BEF# active, the SST32HF162/164 operate as 1M
x16 flash memory and the SST32HF802 operates as 512K
x16 flash memo ry. The flash memor y bank is re ad using
the common address lines, data lines, WE# and OE#.
Erase and Program operations are initiated with the
JEDEC standard SDP command sequences. Address and
data are latched during the SDP commands and during the
internally timed Erase and Program operations.
Flash Read
The Read operation of the SST32HF 802 /162 /164 devices
is control led by BE F# and OE #. Both have to be low, with
WE# high, for the system to obtain data from the outputs.
BEF# is used for flash memory bank selection. When
BEF# and BES# are high, both banks are deselected and
only standby power is consumed. OE# is the output control and is used to gate d ata from the ou tput pins. The data
bus is in high impedance state when OE# is high. Ref er to
Figure 6 for further details.
Flash Erase/Program Operation
SDP commands are used to initiate the flash memory bank
Program and Erase op erations of the SST32HF 802/162/
164. SDP commands are loaded to the flash memory bank
using standard microprocess or write sequences. A command is loaded by asserting WE# low while keeping BEF#
low and OE# high. The a ddress is latched on the falling
edge of WE# or BEF#, wh ichever occurs last. The dat a is
latched on the rising edge of WE# or BEF#, whichever
occurs first.
SRAM Read
The SRAM Read operation of the SST32HF802/162/164 is
controlled by OE# and BES#, both have to be low with
WE# high for the system to obtain data fr om the outputs.
BES# is used for SRAM bank se le ction. OE# is the ou tpu t
control and is used to gate data fr om the outpu t pins. The
data bus is in high impedance state when OE# is high. See
Figure 3 for the Read cycle timing diagram.
©2001 Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. S71171-05-000 8/01 520
Flash Word-Program Operation
The flash memory bank of the SST32HF802/162/164
devices is programmed on a word-by-word basis. Before
the Program operations, the memory must b e erased fi rst .
The Program operati on consists of three steps. Th e first
step is the three-byte load sequence for Software Data Protection. The second step is to load word address and word
data. During the Word-Program operation, the addres ses
2

Multi-Purpose Flash (MPF) + SRAM ComboMemory
SST32HF802 / SST32HF162 / SST32HF164
Data Sheet
are latched on the falling edge of either BEF# or WE#,
whichever occurs last. The data is latched on the rising
edge of either BEF# or W E#, whichever occurs first. The
third step is the internal Program operat ion which is initiated after the rising edge of the fourth WE# or BEF#,
whichever occurs first. The P rogram operation, once in itiated, will be completed, within 20 µs. See Figures 7 and 8
for WE# and BEF# controlled Program operation timing
diagrams and Figure 18 for flowcharts. During the Program
operation, the only valid flas h Read operations are Data#
Polling and Toggle B it. Dur ing the i nternal Program ope ration, the host is free to pe rform additio nal tasks. Any SDP
commands load ed during the inter nal Program operation
will be ignored.
Flash Sector/Block-Erase Operation
The Flash Sector/Block-Erase operation allows the system
to erase the device on a sector-by-sector (or block-byblock) basis. The SST32HF802/162/1 64 offer both SectorErase and Block-Erase mode. The sector architecture is
based on uniform sector size of 2 KWord. The Block-Erase
mode is based on uniform block size of 32 KWord. The
Sector-Erase op eration is init iated by executing a six-byte
command sequence with Sector-Erase command (30H)
and sector address (SA) in the last bus cycle. The address
lines A
, for SST32HF162/164, and A18-A11, for
19-A11
SST32HF802, ar e used to deter mine the sector ad dress.
The Block-Erase opera tion is initiated by executing a sixbyte command sequence with Block-Erase command
(50H) and block address ( BA) in the last bus cycle. The
address lines A
, for SST32HF162/164, and A18-A15,
19-A15
for SST32HF802, are used to determine the block address.
The sector or block address is latched on the falling edge of
the sixth WE# p ulse, while the command (30H or 50H) is
latched on the rising edge of the sixth WE# pulse. The
internal Era se operati on begin s after t he sixth W E# puls e.
The End-of-Erase operation can be determined using
either Data# Polling or Toggle Bit methods. See Figures 12
and 13 for timing waveforms. Any commands issued during
the Sector- or Block-Erase operation are ignored.
Flash Chip-Erase Operation
The SST32HF802/162/164 provide a Chip-Erase operation, which allows the user to erase the entire memory
array to the “1” state. This is useful when the entire device
must be quickly erased.
The Chip-Erase operation is initiated by executing a sixbyte command sequence with Chip-Erase command (10H)
at address 5555H in the last byte sequence. The Eras e
operation begins with the rising edge of the sixt h WE# or
CE#, whichever occurs first. During the Erase operation,
the only valid read is T oggle Bit or Data# Polling. See Table
4 for the command sequence, Figure 10 for timing diagram,
and Figure 21 for the flowchart. Any commands issued during the Chip-Erase operation are ignored.
Write Operation Status Detection
The SST32HF802/162/164 provide two software means to
detect the compl etion o f a wr i te (P rogram or E rase) cycle,
in order to opt imize the system wr ite cy cle time. Th e software detection includes two status bits: Data# Polling
) and Toggle Bit (DQ6). The End-of-Write detection
(DQ
7
mode is enabled after the r ising edge of WE#, which in itiates the internal program or erase operation.
The actual comple tion of the n onvolatile write is as ync hronous with the sys tem; therefore, either a Data# Polling or
Toggle Bit read may be simultaneou s with the compl etion
of the Write cycle. If this occurs, the system may possibly
get an erroneous result, i.e., valid data may appear to conflict with either D Q
or DQ6. In order to prevent spurio us
7
rejection, if an erroneous result occurs, the software routine
should include a loop to read the accessed location an
additional two (2) times. If bo th reads are valid, then the
device has completed the write cycle, otherwise the rejection is valid.
Flash Data# Polling (DQ7)
When the SST32HF 8 02/ 162 /16 4 f las h me mory banks a r e
in the internal Program operation, any attempt to read DQ
will produce the co mplement of the true data. Once th e
Program operation is completed, DQ
data. Note that even though DQ
will produce true
7
may have valid data
7
immediately following the completion of an inter nal Write
operation, the remai ning data outputs may still be invalid:
valid data on the entire data bus will appear in subsequent
successive Read cycles. During internal Erase operation,
any attempt to read DQ
nal Erase operation is c ompleted, DQ
will produce a ‘0’. Onc e the in ter -
7
will produce a ‘1’.
7
The Data# Polling is valid after the rising edge of the fourth
WE# (or BEF#) pulse for Program operation. For Sector- or
Block-Er a se, the Data# Polling is valid after the risi n g edge
of the sixth WE# (or BEF#) pulse. See Figure 9 for Data#
Pol ling timi ng diag ram and Fi gure 19 f or a fl owc hart.
Flash Toggle Bit (DQ6)
During the inter nal Program or Erase ope ration, any consecutive attempts to read DQ
and 0s, i.e., toggling between 1 and 0. W hen the internal
Program or Erase operation is com plete d, t he tog gling wi ll
stop. The flash memor y bank is then ready for the next
operation. The T oggle Bit is valid after the rising edge of the
fourth WE# (or BEF#) pulse for Program operation. For
will produce alter nating 1s
6
7
©2001 Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. S71171-05-000 8/01 520
3
Multi-Purpose Flash (MPF) + SRAM ComboMemory
SST32HF802 / SST32HF162 / SST32HF164
Data Sheet
Sector- or Bank-Er ase, t he Toggle Bit is v alid af ter the rising
edge of the sixth WE# (or BEF#) pul se. See F igure 10 for
Toggle Bit timing diagram and Figure 19 for a flowchart.
Flash Memory Data Protection
The SST32HF802/162/164 flash memory bank provides
both hardware and software features to protec t nonvolatile
data from inadvertent writes.
Flash Hardware Data Protection
Noise/Glitch Protection: A WE# or BEF# pulse of less than
5 ns will not initiate a Write cycle.
Power Up/Down Detection: The Write operation is
V
DD
inhibited when V
Write Inhibi t Mode:
is less than 1.5V.
DD
Forcing OE# low, BEF# high, or WE #
high will inhibit the Flash Write operation. This prevents
inadvertent writes during power-up or power-down.
Flash Software Data Protection (SDP)
The SST32HF802/162/164 provide the JEDEC approved
software data protection scheme for all flash memory bank
data alteration operations, i.e., Program and Erase. Any
Program operation requires the inclusion of a series of
three-byte sequence. The three byte-load sequence is
used to initiate the Program operation, providing optimal
protection from inadver tent Write operations, e.g., during
the system power-up or power-down. Any Erase operation
requires the inclusion of six-byte load sequence. The
SST32HF802/162/164 devices are shipped with the software data protection permanently enabled. See Table 4 for
the specific software command codes. During SDP command sequence, invalid SDP commands will abort the
device to the read mode, within Read Cycle Time (T
RC
).
Concurrent Read and Write Operations
The SST32HF802/162/164 provide the unique benefit of
being able to read from or write to SRAM, while simultaneously erasing or programming the Flash. This allows data
alteration code to be executed from SRAM, while altering
the data in Flash. The following tab le lists all v alid states.
ONCURRENT READ/WRITE STATE TABLE
C
Flash SRAM
Program/Erase Read
Program/Erase Write
The device will ig nore a ll S DP c omma nds when an Era se
or Program operation is in progress. Note that Product
Identification comman ds use SDP; therefore, these commands will also be ignored while an Erase or Program
operation is in progress.
Product Identification
The product id entification mode identifies the devices as
the SST32HFxxx and manufacturer as SST. This mode
may be accessed by software operations only. The
hardware device ID Read operation, which is typically
used by programmers, cannot be used on this device
because of the shared lines between flash and SRAM
in the multi-chip package. Therefore, application of
high voltage to pin A
may damage this device. Users
9
may use the software product identification operation to
identify the part (i.e., using the device ID) when using multiple manufacturers in the same socket. For details, see
Tables 3 and 4 for software operation, Figure 14 for the
software ID entr y and rea d timing dia gram and Figure 20
for the ID entry command sequence flowchart.
TABLE 1: PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
Address Data
Manufacture r’s ID 0000H 00BFH
Device ID
SST32HF802 0001H 2781H
SST32HF162/164 0001H 2782H
T1.1 520
Product Identification Mode Exit/Reset
In order to retur n to the sta nda rd r ead mod e, the So ftwar e
Product Identification mode must be exited. Exiting is
accomplished by issuing the Exit ID command sequence,
which returns the device to the Read operation. Please
note that the software-reset command is ignored during an
internal Pr ogram or Erase op eration. See Table 4 for software command cod es, Figur e 15 for timin g waveform and
Figure 20 for a flowchart.
Design Considerations
SST recommends a high frequency 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor to be plac ed as close as possible between V
V
, e.g., less than 1 cm away from the VDD pin of the
SS
device. Additionally, a low frequency 4.7 µF electrolytic
capacitor from V
DD
pin.
the V
to VSS should be placed within 1 cm of
DD
DD
and
©2001 Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. S71171-05-000 8/01 520
4
Multi-Purpose Flash (MPF) + SRAM ComboMemory
SST32HF802 / SST32HF162 / SST32HF164
Data Sheet
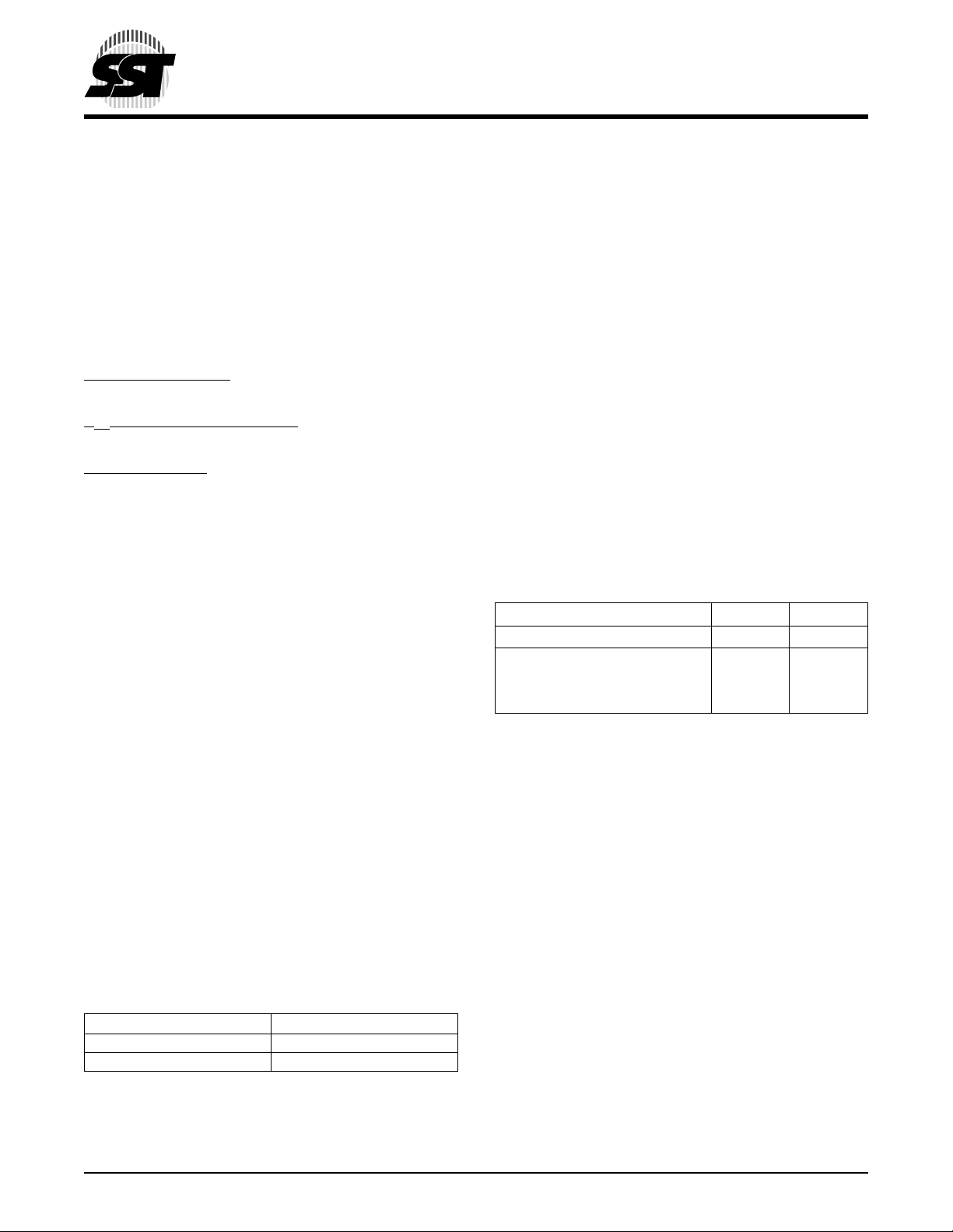
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
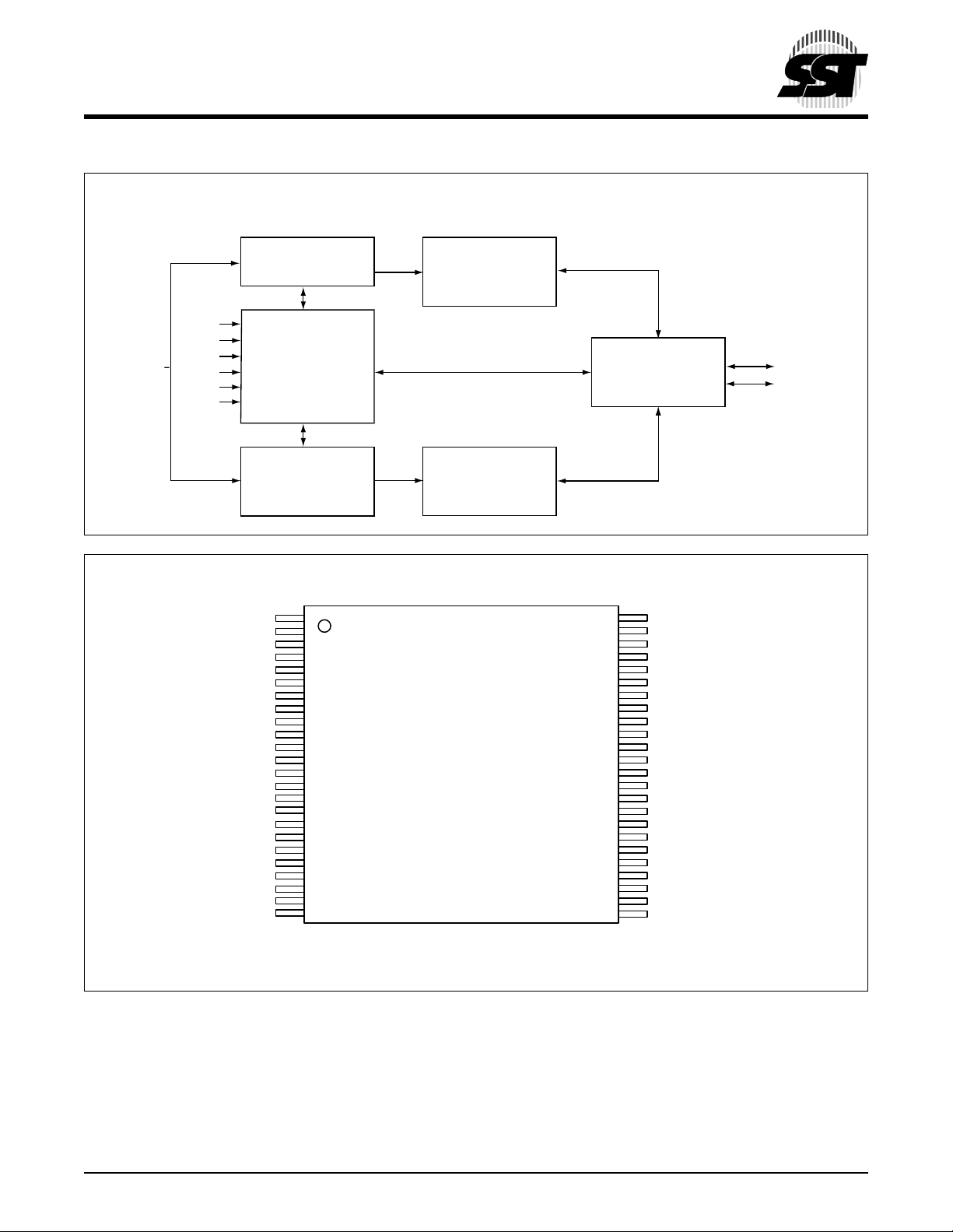
Address Buffers
SRAM
UBS#
LBS#
-A
BES#
0
BEF#
(1)
A
MS
OE#
Control Logic
I/O Buffers
DQ15 - DQ
DQ7 - DQ
8
0
WE#
Address Buffers
& Latches
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A19
WE#
V
DDS
BES#
UBS#
LBS#
A18
A17
A9
A8
NC
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
Standard Pinout
SuperFlash
Memory
T op Vie w
Die Up
520 ILL B1.1
SST32HF162/164SST32HF162/164
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
A16
NC
V
SS
DQ15
DQ7
DQ14
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
DDF
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
DQ2
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
OE#
V
SS
BEF#
A0
520 ILL F01b.1
FIGURE 1: PIN ASSIGNMENTS FOR 48-LEA D TSOP (12MM X 20MM)
©2001 Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. S71171-05-000 8/01 520
5
Multi-Purpose Flash (MPF) + SRAM ComboMemory
SST32HF802 / SST32HF162 / SST32HF164
Data Sheet
TOP VIEW (balls facing down)
6
5
4
3
2
1
BES#
A10
OE#
A11
A13
WE#
V
DQ5
DQ7
A8
A17
V
DDS
DQ1
DQ2
DQ4
A5
UBS#
A16
A1
A0
DQ0
DQ8
BEF#
V
SS
SS
A2
A3
A6
DQ3
DQ10
DQ9
A4
A7
A18
DQ12
V
DDF
DQ11
NC
NC
NC
A12
DQ6
DQ13
A B C D E F G H
A9
A14
A15
LBS#
DQ15
DQ14
520 ILL F01a.0
6
5
4
3
2
1
SST32HF802
TOP VIEW (balls facing down)
BES#
A10
OE#
A11
A13
WE#
V
DQ5
DQ7
A17
V
SS
A8
DDS
DQ1
DQ2
DQ4
A5
UBS#
A16
A1
A0
DQ0
DQ8
BEF#
V
SS
A2
A3
A6
DQ3
DQ10
DQ9
A4
A7
A18
DQ12
V
DDF
DQ11
A19
NC
NC
A12
DQ6
DQ13
A B C D E F G H
SST32HF162/SST32HF164
A9
A14
A15
LBS#
DQ15
DQ14
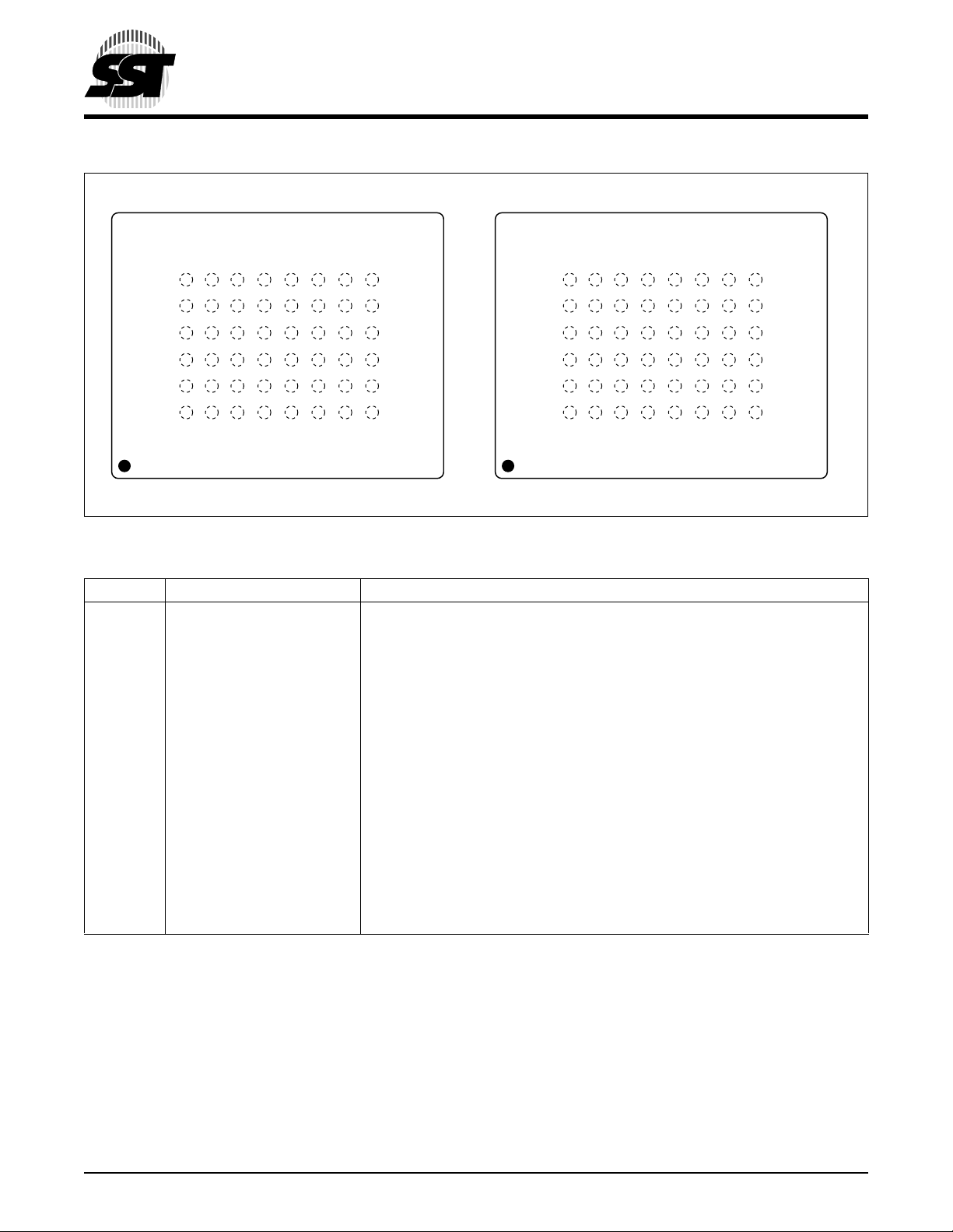
FIGURE 2: PIN ASSIGNMENTS FOR 48-BALL TBGA (10MM X 12MM)
TABLE 2: P
Symbol Pin Name Functions
1
A
-A
MS
-DQ0Data Input/output To output data during Read cycles and receive input data during Write cycles.
DQ
15
BES# SRAM Memory Bank Enable To activate the SRAM memory bank when BES# is low.
BEF# Flash Memory Bank Enable To activate the Flash memory bank when BEF# is low.
OE# Output Enable To gate the data output buffers.
WE# Write Enable To control the Write operations.
V
DDF
V
DDS
V
SS
UBS# Upper Byte Control (SRAM) To enable DQ15-DQ
LBS# Lower Byte Control (SRAM) To enable DQ7-DQ
NC No Connection Unconnected Pins
1. AMS=Most significant address
IN DESCRIPTION
Address Inputs To provide flash addresses: A19-A0 for 16M, and A18-A0 for 8M
0
SRAM addresses: A
for 2M and A17-A0 for 4M
16-A0
Data is internally latched during a flash Erase/Program cycle.
The outputs are in tri-state when OE# or BES# and BEF# are high.
Power Supply (Flash) 2.7-3.3V Po wer Supply to Flash only.
Power Supply (SRAM) 2.7-3.3V Power Supply to SRAM only
(For L3K package, V
DDF
and V
share one pin as VDD.)
DDS
Ground
8
0
520 ILL F01.0
T2.2 520
©2001 Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. S71171-05-000 8/01 520
6
Multi-Purpose Flash (MPF) + SRAM ComboMemory
SST32HF802 / SST32HF162 / SST32HF164
Data Sheet
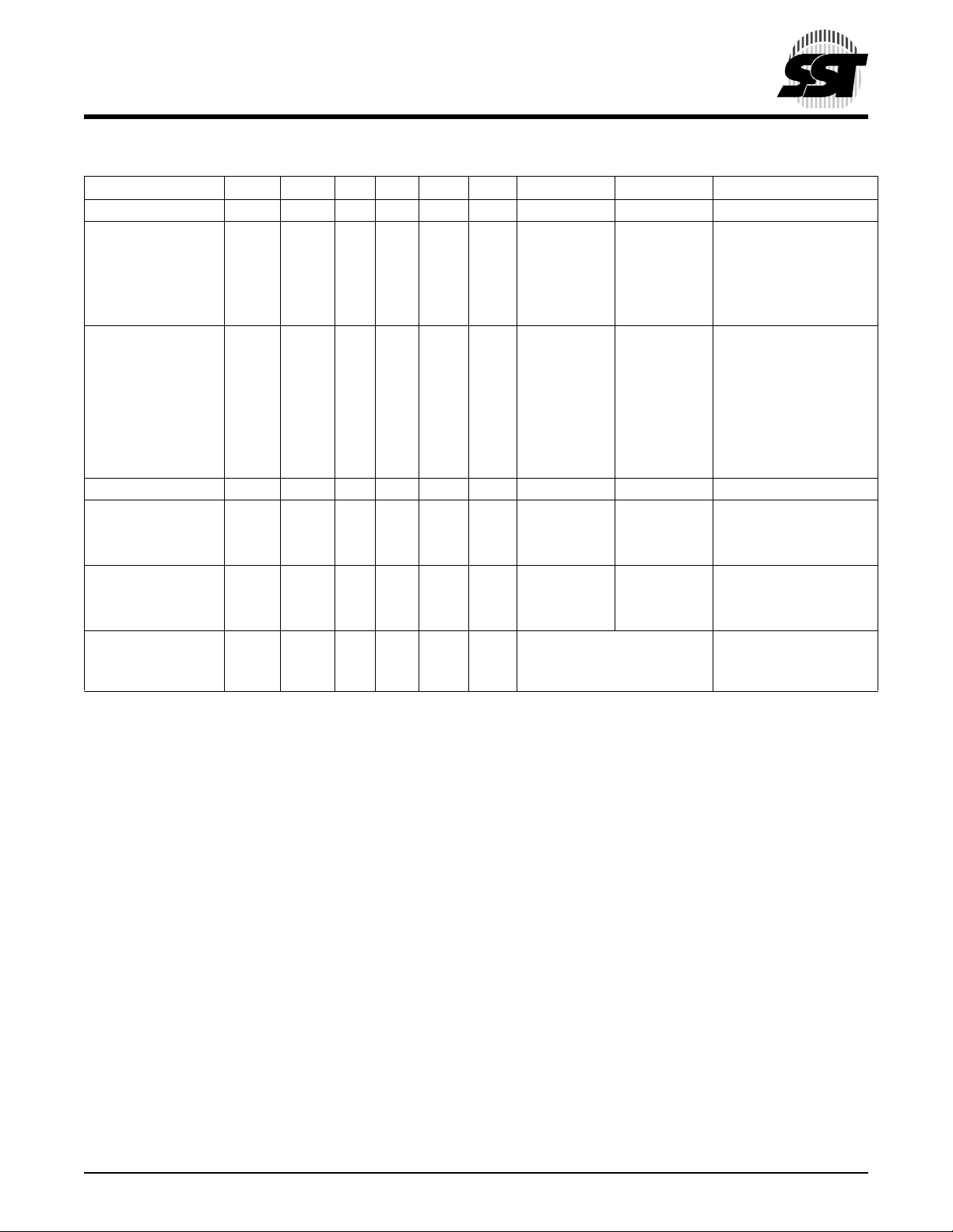
TABLE 3: OPERATION MODES SELECTION
Mode BES#1BEF#1OE# WE# UBS# LBS# DQ15 to DQ8DQ7 to DQ
Not Allowed V
V
IL
IL
Flash
Read V
Program V
IH
IH
Erase X V
V
IL
V
IL
IL
SRAM
Read V
Write V
Standby V
V
V
V
V
IHC
V
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IHC
Flash Write Inhibit X X V
XXXVIHXXHigh Z / D
Output Disable V
XV
IH
V
IL
V
IL
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
Product Identification
Software Mode V
1. Do not apply BES#=VIL and BEF#=VIL at the same time
2. X can be V
3. Device ID 2781H for SST32HF802, 2782H for SST32HF162/164
or VIH, but no other value.
IL
IH
V
IL
2
X
XXX X X X
V
V
IL
V
IHVIL
V
IHVIL
V
V
IL
V
V
IL
V
V
IL
XVILV
XVILV
XVILV
XX D
IH
XX D
OUT
IN
D
OUT
D
IN
X X X X Sector or Block address,
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
IL
IH
IL
IL
IH
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
D
OUT
D
OUT
D
High Z A
High Z D
D
IN
D
IN
High Z A
High Z D
OUT
OUT
D
IN
IN
X X X X High Z High Z X
XXXHigh Z / D
IL
XX X XHigh Z / D
V
IHVIH
XXVIHV
V
IHVIH
V
V
IL
X X High Z High Z X
IH
High Z High Z X
X X High Z High Z X
X X Manufacturer’s ID (00BFH)
IH
High Z / D
OUT
High Z / D
OUT
High Z / D
OUT
Device ID
3
OUT
OUT
OUT
0
Address
XXH for Chip-Erase
A19-A1=VIL, A0=V
(See Table 4)
A
IN
A
IN
A
IN
IN
A
IN
A
IN
IN
A
IN
X
X
X
IH
T3.2 520
©2001 Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. S71171-05-000 8/01 520
7
Multi-Purpose Flash (MPF) + SRAM ComboMemory
SST32HF802 / SST32HF162 / SST32HF164
Data Sheet
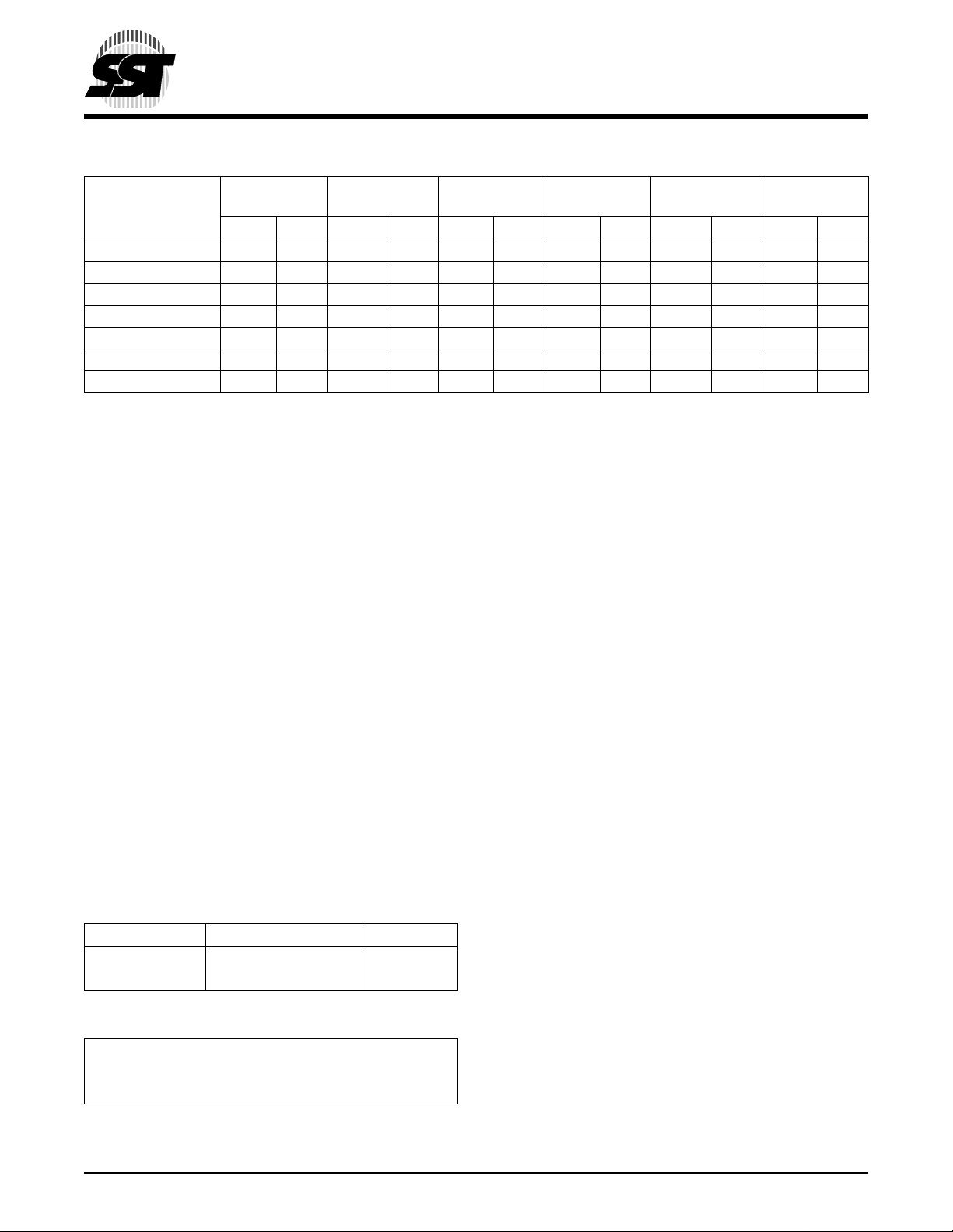
TABLE 4: SOFTWARE COMMAND SEQUENCE
Command
Sequence
Word-Program 5555H AAH 2AAAH 55H 5555H A0H WA
Sector-Erase 5555H AAH 2AAAH 55H 5555H 80H 5555H AAH 2AAAH 55H SA
Block-Erase 5555H AAH 2AAAH 55H 5555H 80H 5555H AAH 2AAAH 55H BA
Chip-Erase 5555H AAH 2AAAH 55H 5555H 80H 5555H AAH 2AAAH 55H 5555H 10H
Software ID Entry
5,6
Software ID Exit XXH F0H
Software ID Exit 5555H AAH 2AAAH 55H 5555H F0H
1. Address format A14-A0 (Hex),Address A15 can be VIL or VIH, but no other value, for the Command sequence.
2. DQ
-DQ8 can be VIL or VIH, but no other value, for the Command sequence.
15
3. WA = Program word address
4. SA
for Sector-Erase; uses AMS-A11 address lines
X
, for Block-Erase; uses A19-A15 address lines
BA
X
= Most significant address
A
MS
= A18 for SST32HF802 and A19 for SST32HF162/164
A
MS
5. The device does not remain in Software Product ID Mode if powered down.
6. With A
=0; SST Manufacturer’s ID= 00BFH, is read with A0=0,
MS-A1
1st Bus
Write Cycle
2nd Bus
Write Cycle
3rd Bus
Write Cycle
4th Bus
Write Cycle
5th Bus
Write Cycle
6th Bus
Write Cycle
Addr1Data2Addr1Data2Addr1Data2Addr1Data2Addr1Data2Addr1Data
3
Data
4
X
4
X
5555H AAH 2AAAH 55H 5555H 90H
SST32HF802 Device ID = 2781H, is read with A
SST32HF162/164 Device ID = 2782H, is read with A
0
=1.
0
=1.
30H
50H
T4.2 520
2
Absolute Maximum Stress Ratings (Applied conditions greater than those listed under “Absolute Maximum
Stress Ratings” may cause pe r manent dama ge to the device. This is a stres s rating only and funct ional operatio n
of the device at these conditions or conditions greater tha n those defined in the ope rational sections of this data
sheet is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum stress rating conditions may affect device reliability.)
Operating Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -20°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -65°C to +150°C
D. C. Voltage on Any Pin to Ground Potential . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-0.5V to V
Transient Voltage (<20 ns) on Any Pin to Ground Potential . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -1.0V to V
DD
DD
1
+0.3V
1
+1.0V
Package Power Dissipation Capability (Ta = 25°C) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0W
Surface Mount Lead Soldering Temperature (3 Seconds). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240°C
2
Output Short Circ uit Curr ent
1. VDD = V
2. Outputs shorted for no more than one second. No more than one output shorted at a time.
DDF
and V
DDS
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 mA
OPERATING RANGE
Range Ambient Temp V
Commercial 0°C to +70°C 2.7-3.3V
Extended -20°C to +85°C 2.7-3.3V
DD
AC CONDITIONS OF TEST
Input Rise/Fall Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 ns
Output Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . CL = 30 pF
See Figures 16 and 17
©2001 Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. S71171-05-000 8/01 520
8
Multi-Purpose Flash (MPF) + SRAM ComboMemory
SST32HF802 / SST32HF162 / SST32HF164
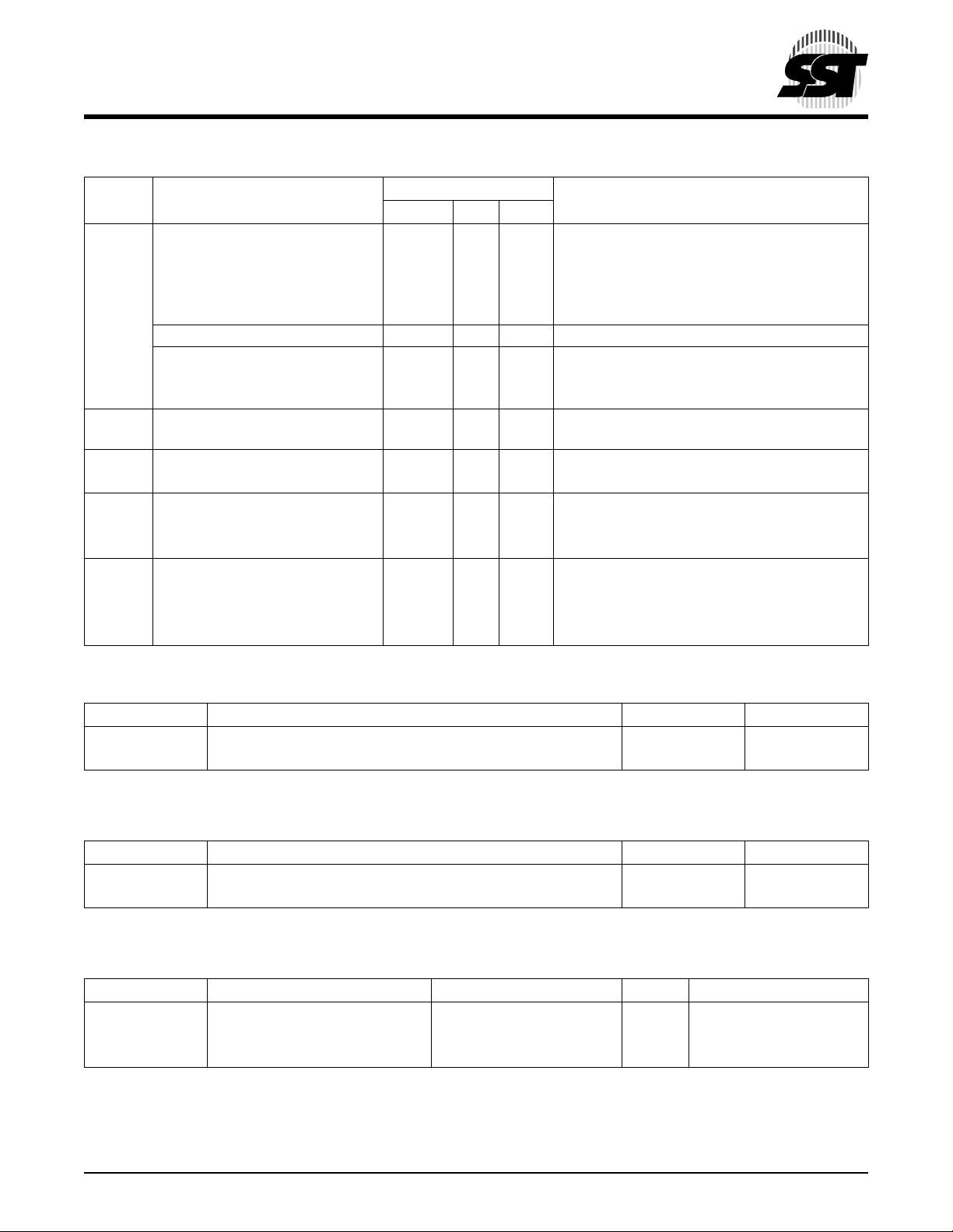
Data Sheet
TABLE 5: DC OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS (VDD = V
Limits
Symbol Parameter
I
I
I
I
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
DD
SB
LI
LO
IL
IH
IHC
OL
OH
OLS
OHS
Power Supply Current Address input = VIL/VIH, at f=1/TRC Min,
Read
Flash
SRAM 20 mA BEF#=VIH, BES#=V
Concurrent Operation 45 mA BEF#=VIH, BES#=V
Write
Flash 25 mA
SRAM 20 mA BEF#=VIH, BES#=V
Standby VDD Current 3.0V
3.3V
Input Leakage Current 1 µA VIN=GND to VDD, VDD=VDD Max
Output Leakage Current 1 µA V
Input Low Voltage 0.8 V VDD=VDD Min
Input High Voltage 0.7V
DD
Input High Voltage (CMOS) VDD-0.3 V VDD=VDD Max
Flash Output Low Voltage 0.2 V IOL=100 µA, VDD=VDD Min
Flash Output High Voltage VDD-0.2 V IOH=-100 µA, VDD=VDD Min
SRAM Output Low Voltage 0.4 V IOL=1 mA, VDD=VDD Min
SRAM Output High Voltage 2.2 V IOH=-500 µA, VDD=VDD Min
AND V
DDF
20 mA
40
µA VDD = VDD Max, BEF#=BES#=V
75
VVDD=VDD Max
= 2.7-3.3V)
DDS
Test ConditionsMin Max Units
V
DD=VDD
OE#=V
Max, all DQs open
, WE#=V
IL
BEF#=VIL, BES#=V
WE#=V
IL
BEF#=VIL, BES#=V
=GND to VDD, VDD=VDD Max
OUT
IH
IH
IL
IL
IH,
IL
OE#=V
IH
IHC
T5.5 520
TABLE 6: RECOMMENDED SYSTEM POWER-UP TIMINGS
Symbol Parameter Minimum Units
T
T
1
PU-READ
PU-WRITE
1
1. This parameter is measured only for initial qualification and after a design or process change that could affect this parameter.
Power-up to Read Operation 100 µs
Powe r-up to Program/Erase Operation 100 µs
TABLE 7: CAPACITANCE (Ta = 25°C, f=1 Mhz, other pins open)
Parameter Description Test Condition Maximum
1
C
I/O
1
C
IN
1. This parameter is measured only for initial qualification and after a design or process change that could affect this parameter.
I/O Pin Capacitance V
= 0V 12 pF
I/O
Input Capacitance VIN = 0V 12 pF
TABLE 8: FLASH RELIABILI TY CHARACTERISTICS
Symbol Parameter Minimum Specification Units Test Method
1
N
END
1
T
DR
1
I
LTH
1. This parameter is measured only for initial qualification and after a design or process change that could affect this parameter.
Endurance 10,000 Cycles JEDEC Standard A117
Data Retention 100 Years JEDEC Standard A103
Latch Up 100 + I
DD
mA JEDEC Standard 78
T6.0 520
T7.0 520
T8.1 520
©2001 Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. S71171-05-000 8/01 520
9
 Loading...
Loading...