Page 1

Instruction
Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide
Document No.:
INS14606
Version:
7
Description:
The Z-Ware Library is a Z-Wave Plus v2 SmartStart Z-Wave for IP client.
Written By:
MIKOZIK;KAJAROSZ;ADGIELNI;JFR
Date:
2020-07-07
Reviewed By:
JCC;SCBROWNI;TRBOYD
Restrictions:
Public
Approved by:
Date CET Initials Name Justification
2020-07-07 03:07:42 NTJ Niels Johansen
This document is the property of Silicon Labs. The data contained herein, in whole or in
part, may not be duplicated, used or disclosed outside the recipient for any purpose. This
restriction does not limit the recipient's right to use information contained in the data if it
is obtained from another source without restriction.
Page 2

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page ii of vi
REVISION RECORD
Doc. Rev
DateByPages
affected
Brief description of changes
1
20190816
20190828
SNA
DCHOW
ALL
- Cloned from 14416, delelgated only API & File formats to 14416
-v9.22
-Control Firmware Update MD CC v7, Battery CC v2, Sound Switch CC v2, Door Lock Logging
CC v1
-Added text to explain Z/IP gateway supports of IPv6 Router Advertisement for IPv6 autoconfiguration and routing in section 4.1.4
-Deprecated BASIC sample app.
-Added section "Controller App"
-Added SDS14223, SDS, Z-Wave Command Class Control Specification in "References"
20191108
DCHOW
ALL
-v10.01
-Changed section "Firmware Update" to "Firmware Update and Backup"
-Removed source code sub-directory "script" as the script file "network_setup.sh" became
obsolete when Z/IP gateway supported IPv6 router advertisement.
-Added section “TYPICAL COMMAND CLASS IMPLEMENTATION”
20191120
KSUNDARAM
ALL
-Added sections on SmartStart, network health, update node, update n/w, door lock CC,
notification CC under “Controller App”
2
20191128
20191206
SNA
ALL
- rewrote Device Database section
- added Saving & Restoring Network subsection
- added CC control for Door Lock Logging, moved CC support for Multi-Cmd to ZIPGW
- upgraded ZIPGW NW MGMT PROXY CC to v3
3
20191226
20200107
SNA
3,
4,
4
CC Control: Updated NWMG_PROXY to v2, removed duplicate SENSOR_ALARM, added
ZIPGW CCs; CC Support: Overhauled table format to show security requirements
CC Support:: corrected Node Provisioning CC details
4
20200110
SNA
V7.13.1 - no change
5
20200325
SNA
Removed Portal support
5
20200416
ADGIELNI
3
Support Battery CC v3
6
20200618
MIKOZIK
v, 4
- Removed old version ”7.13” from table 3 description.
- Updated Required Security class for: FIRMAWRE_UPDATE_MD, NW_MGMT_BASIC,
NW_MGMT_INCLUSION, NW_MGMT_IMA, NW_MGMT_PROXY in table 3
7
20200701
SCBROWNI
All
Tech Pubs review
7
20200702
MIKOZIK
ALL
Changed version to 7.14.x
Page 3

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page iii of vi
Table of Contents
1 INTRODUCTION................................................................................................................1
1.1 Purpose ................................................................................................................................1
1.2 Audience and Prerequisites..................................................................................................1
2 FEATURES.........................................................................................................................2
2.1 Role.......................................................................................................................................2
2.2 Network Operations.............................................................................................................2
2.3 CC Control.............................................................................................................................3
2.4 CC Support............................................................................................................................4
2.5 Device Database...................................................................................................................5
2.6 Command Class Configuration .............................................................................................5
2.7 Network Initialization...........................................................................................................6
2.8 Node Update........................................................................................................................6
2.9 Network Update...................................................................................................................8
2.10 Background Polling...............................................................................................................8
2.11 Post-Set Polling.....................................................................................................................9
3 TYPICAL USAGE ..............................................................................................................10
3.1 Network..............................................................................................................................10
3.1.1 Initialization ..............................................................................................................10
3.1.2 Creation and Tear Down ...........................................................................................10
3.1.3 Network and Client Preference Storage ...................................................................11
3.1.4 Security 2 (S2) ...........................................................................................................11
3.1.5 SmartStart.................................................................................................................12
3.1.6 Network Health Check ..............................................................................................12
3.2 Interface Monitor/Control .................................................................................................13
3.3 Actuator Interface Multicast & Multi-endpoint Control ....................................................15
3.4 Node Identification.............................................................................................................15
3.5 Grouping.............................................................................................................................15
3.6 Firmware Update and Backup............................................................................................16
3.7 Polling Facility.....................................................................................................................16
3.8 Device Database.................................................................................................................16
3.9 Saving & Restoring the Network for Middleware Changes................................................16
4 HOW TO: ADD CONTROL FOR A CC AS AN INTERFACE.....................................................18
4.1 Initialization........................................................................................................................19
4.1.1 Global Setting............................................................................................................19
4.1.2 Loading of Door Lock Information from Persistent Storage .....................................19
4.1.2.1 Old Format Persistent Storage .............................................................................19
4.1.2.2 New Format Persistent Storage............................................................................20
4.2 Shutting Down....................................................................................................................20
4.2.1 Saving of Interface Information into Persistent Storage...........................................20
Page 4

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page iv of vi
4.2.1.1 New Format Persistent Storage............................................................................20
4.3 Node Update/Inclusion Information Gathering .................................................................20
4.4 Capability APIs....................................................................................................................21
4.4.1 zwif_dlck_cap_get.....................................................................................................21
4.4.2 zwif_dlck_cap_cache_get .........................................................................................22
4.5 Monitor APIs.......................................................................................................................22
4.5.1 zwif_dlck_op_rpt_set................................................................................................23
4.5.2 zwif_dlck_op_get ......................................................................................................23
4.5.3 zwif_dlck_op_get_poll ..............................................................................................23
4.6 Control APIs........................................................................................................................24
4.6.1 zwif_dlck_op_set ......................................................................................................24
4.6.2 zwif_dlck_op_mset ...................................................................................................25
4.7 Configuration APIs..............................................................................................................25
4.7.1 zwif_dlck_cfg_set......................................................................................................25
4.7.2 zwif_dlck_cfg_get .....................................................................................................25
4.8 Caching Implementation ....................................................................................................26
4.8.1 Door Lock Operating Mode Cache ............................................................................26
4.8.2 Door Lock Configuration Cache.................................................................................26
4.8.3 Door Lock Capability Cache.......................................................................................26
4.9 Post-Set Polling Implementation........................................................................................27
4.9.1 Supervision Get.........................................................................................................27
4.9.2 Manual Report Get ...................................................................................................27
4.10 Adjunct Notification CC Handling .......................................................................................28
4.10.1 Monitor APIs .............................................................................................................28
4.11 Device Database Upgrade for Door Lock CC version 3 and below .....................................28
5 SAMPLE APPLICATIONS ..................................................................................................30
5.1 Getting Started...................................................................................................................30
5.1.1 Prerequisites .............................................................................................................30
5.1.2 Building of Sample Applications................................................................................30
5.1.3 Installation of Sample Applications...........................................................................30
5.1.4 Configuration ............................................................................................................30
5.2 Running Sample Applications.............................................................................................32
5.2.1 ZIPGW Discovery.......................................................................................................32
5.2.2 Reset Z/IP Network ...................................................................................................32
5.2.3 Add Node into a Network .........................................................................................33
5.2.3.1 ZIPGW that Supports Security 2 (S2) ....................................................................33
5.2.3.2 ZIPGW that Does not Support Security 2 (S2) ......................................................33
5.2.4 Remove Node from a Network .................................................................................34
5.2.5 Binary Switch.............................................................................................................34
5.2.6 Basic ..........................................................................................................................35
5.2.7 Binary Sensor ............................................................................................................35
5.2.8 Controller App...........................................................................................................36
5.2.8.1 Manage Network Menu........................................................................................37
5.2.8.2 Binary Switch Menu..............................................................................................41
5.2.8.3 Binary Sensor Menu .............................................................................................41
Page 5

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page v of vi
5.2.8.4 Door Lock Menu ...................................................................................................41
5.2.8.5 Notification (Alarm) Menu....................................................................................42
6 RUNTIME AND BUILD .....................................................................................................43
6.1 Runtime System Requirements..........................................................................................43
6.2 Source Directory Structure.................................................................................................43
6.1 Build System.......................................................................................................................44
6.2 Build System Setup.............................................................................................................44
6.2.1 Target Platform Ubuntu Linux...................................................................................44
6.2.2 Target Platform RPi3B...............................................................................................45
6.3 Build Commands ................................................................................................................45
6.4 Source Code Documentation .............................................................................................45
6.4.1 Manual Generation of Documentation.....................................................................45
6.4.2 Auto Generation of Documentation in Ubuntu Linux...............................................46
REFERENCES .........................................................................................................................47
Table of Tables
Table 1. Z-Wave Example Device and Descriptors........................................................................2
Table 2.: Supported Z-Wave CCs Pushed Down from Z-Ware (No Security Requirements)..........4
Table 3. ZIPGW SDK Supported Z-Wave CCs..................................................................................4
Table 4. Node Update get/set CCs.................................................................................................7
Table 5. Node Update endpoint get/set CCs .................................................................................7
Table 6. Network Scanning APIs ..................................................................................................10
Table 7. Network Initialization API ..............................................................................................10
Table 8. Network Creation and Tear Down APIs..........................................................................11
Table 9. Network and Client Preference Storage APIs.................................................................11
Table 10. Security 2 APIs..............................................................................................................11
Table 11. Smart Start Provisioning List Management APIs..........................................................12
Table 12. Network Health Check API ...........................................................................................13
Table 13. Interface Control APIs ..................................................................................................13
Table 14 – Interface Control APIs ................................................................................................13
Table 15. Node Identification APIs ..............................................................................................15
Table 16. Grouping APIs...............................................................................................................15
Table 17. Firmware Update APIs .................................................................................................16
Table 18. Polling Facility APIs.......................................................................................................16
Table 19. Device Database APIs...................................................................................................16
Table 20. CC Implementation Programming Elements................................................................18
Table 21. Configuration file entries .............................................................................................30
Table 22. Base Memory Requirement .........................................................................................43
Table 23. Per Node Memory Requirement..................................................................................43
Table 24. Per Z-Wave Network Memory Requirement ...............................................................43
Table 25. Files ..............................................................................................................................43
Table 26. Build System Requirements .........................................................................................44
Page 6

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page vi of vi
Page 7

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 1 of 47
1 Introduction
1.1 Purpose
The Z-Ware Library is a Z/IP (Z-Wave for Internet Protocol) Gateway (ZIPGW) client and
abstracts Z-Wave Command Classes (CC) into controllable and monitorable interfaces over a C
API (Application Programming Interface) for easier development and certification of Z-Wave
controller applications. One such Z-Ware Library client is the Z-Ware Web Server.
This document describes the Library usage.
1.2 Audience and Prerequisites
This document is for Z-Wave Partners and assumes they are already comfortable with the
Z-Wave protocol and network installation. As such, the document does not go into detail on
these matters. References are also made to the Device and Command Classes and the Z/IP API,
which are what this API is built upon.
Page 8
INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 2 of 47
2 Features
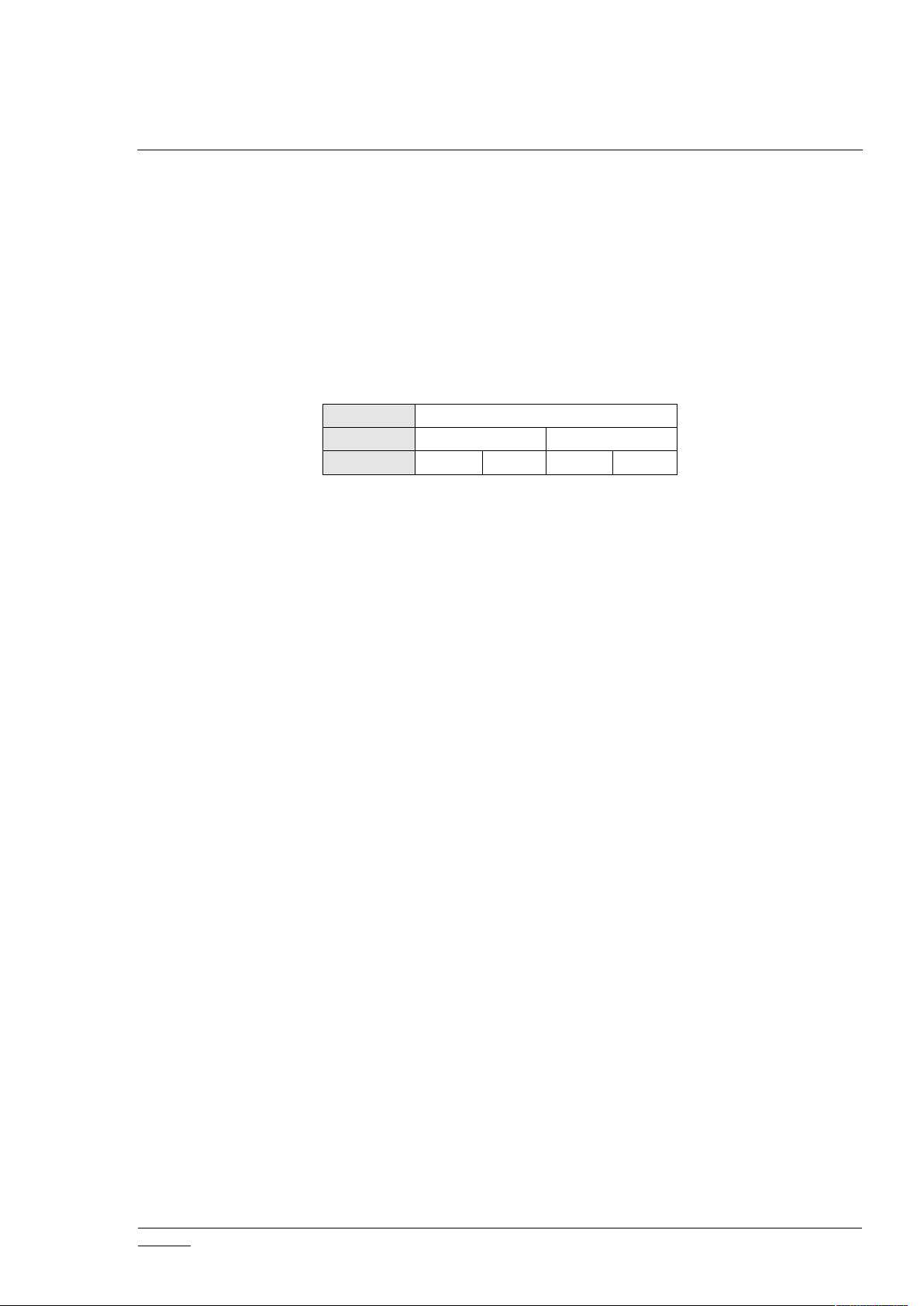
Node
Power strip
Endpoints
Power point
Power point
Interfaces
Switch
Meter
Switch
Meter
The API deals with Z-Wave through descriptors for networks, nodes, endpoints, and interfaces.
A Z-Wave Home Area Network (HAN) is uniquely identified by a Home ID encapsulated in a
network descriptor. The API views the network through its attached ZIPGW.
Nodes are Z-Wave devices in this HAN uniquely identified by a Node ID encapsulated in a node
descriptor. These nodes can be composite devices having multiple endpoints, for example a
power strip with multiple separately controllable power points. Each power point may have
multiple interfaces allowing for control and/or monitoring, e.g., a switch to set on and off and
perhaps a meter providing power consumption information.
Table 1. Z-Wave Example Device and Descriptors
2.1 Role
Z-Ware is a Z-Wave Plus version 2 Security Enabled device in the Static PC Controller class
mainly used in the roles of Static Update Controller (SUC), Identity Server (SIS), and Z-Wave
Plus Central Static Controller (CSC). As a Z/IP client, it works in conjunction with a ZIPGW. ZWare sets itself as the (first) unsolicited IP address of the ZIPGW to which it is connected.
2.2 Network Operations
Z-Ware supports Inclusion, Exclusion, Reset (Set Default), Replace/Remove Failed Node, and
Send NIF (Node Information Frame). If it is assigned a primary controller role, it will always
upgrade itself to an SIS unless there is an SUC already present. Hence, it cannot initiate
controller shift as a primary.
Z-Ware supports Set Learn mode, which allows itself to be added to or removed from a
network. Adding to a network will typically make Z-Ware an Inclusion or Secondary Controller,
in which case, some of its facilities will not be available. Set Learn mode will always attempt
classic mode before Network Wide Inclusion (NWI) mode. Controller replication (Copy) is
achieved through Inclusion and Set Learn Mode.
Z-Ware supports Node and Network Update. Z-Ware discovers a Z-Wave node’s capabilities
during inclusion through a series of comprehensive queries. This process may take some time,
especially for a secure Frequently Listening Routing Slave (FLIRs) device. This operation may be
aborted at any time. A Node Update requeries the information obtained during inclusion,
which allows discovering any changes that were not made through Z-Ware. A Network Update
requests topology from an SUC if available and then performs neighbor update if available or
node update to every node it is aware of.
Z-Ware supports SmartStart, through the NODE_PROVISIONING CC, which uses a configurable
provisioning list of devices to allow the Z-Wave network wide inclusion without having to
manually configure a new node into Z-Wave learn mode.
Page 9
INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 3 of 47
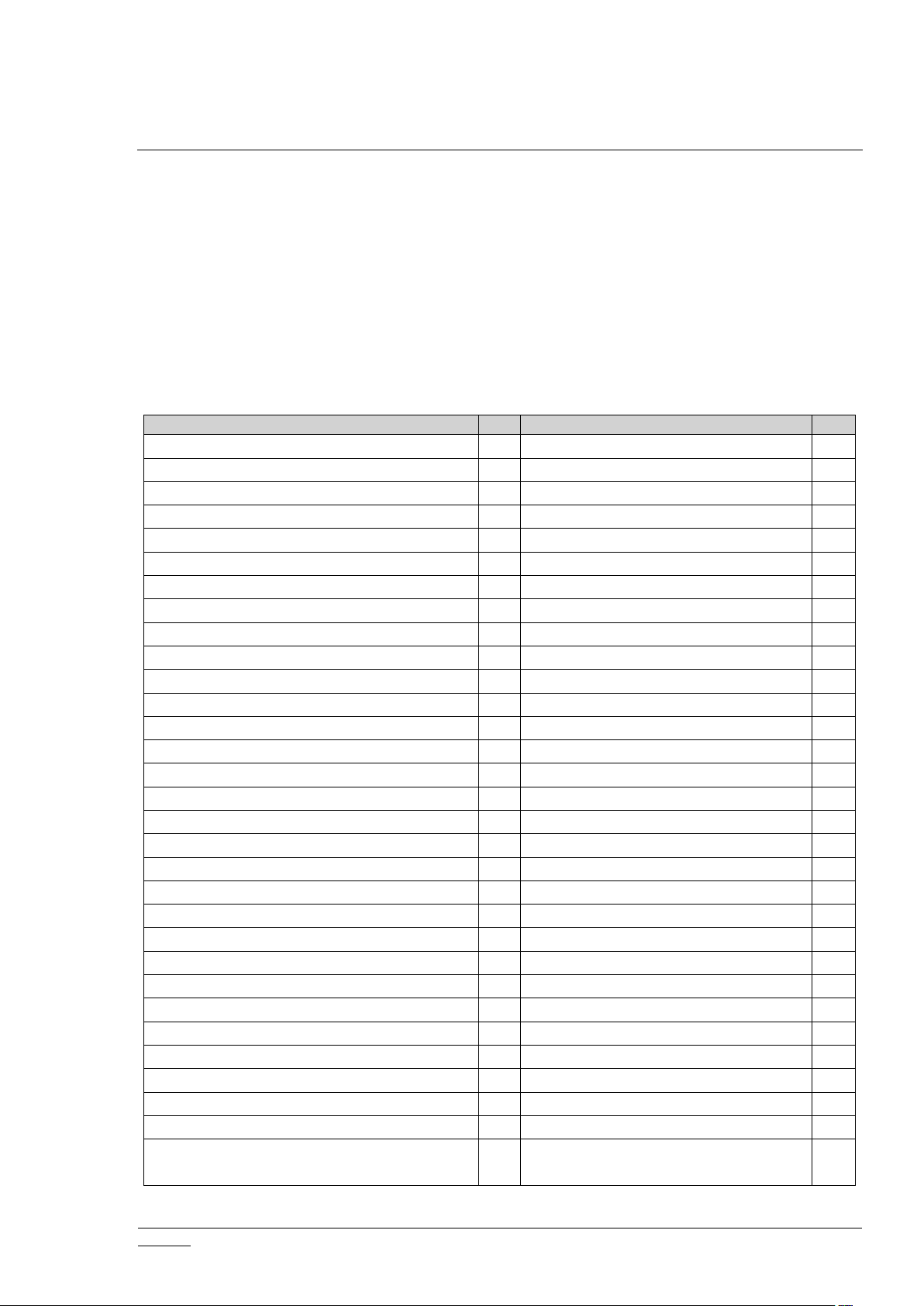
Z-Ware supports multicast operations with ZIP CC v5.
CC
VerCCVer
APPLICATION_STATUS
1
NW_MGMT_PROXY
3
ASSOCIATION
3
POWERLEVEL
1
ASSOCIATION_CMD_CFG
1
PROTECTION
2
ASSOCIATION_GRP_INFO
3
SECURITY
1
BARRIER_OPERATOR
1
SECURITY_2
1
BASIC
2
SENSOR_ALARM
1
BATTERY
3
SENSOR_BINARY
2
CENTRAL_SCENE
3
SENSOR_MULTILEVEL
11
CLIMATE_CONTROL_SCHEDULE
1
SIMPLE_AV_CONTROL
1
CLOCK
1
SOUND_SWITCH
2
CONFIGURATION
4
SUPERVISION
1
CRC16_ENCAP
1
SWITCH_ALL
1
DEVICE_RESET_LOCALLY
1
SWITCH_BINARY
2
DOOR_LOCK
4
SWITCH_COLOR
3
DOOR_LOCK_LOGGING
1
SWITCH_MULTILEVEL
4
FIRMWARE_UPDATE_MD
7
THERMOSTAT_FAN_MODE
5
INDICATOR
3
THERMOSTAT_FAN_STATE
2
MANUFACTURER_SPECIFIC
2
THERMOSTAT_MODE
3
METER
5
THERMOSTAT_OPERATING_STATE
2
METER_PULSE
1
THERMOSTAT_SETBACK
1
METER_TBL_MONITOR
1
THERMOSTAT_SETPOINT
3
MULTI_CHANNEL
4
TIME
2
MULTI_CHANNEL_ASSOCIATION
4
USER_CODE
2
MULTI_CMD
1
VERSION
3
NO_OPERATION
1
WAKE_UP
2
NODE_NAMING
1
WINDOW_COVERING
1
NODE_PROVISIONING
1
ZIP
5
NOTIFICATION/ALARM
8
ZIP_GATEWAY
1
NW_MGMT_BASIC
2
ZIP_ND
1
NW_MGMT_INCLUSION
3
ZIP_PORTAL
1
NW_MGMT_INSTALLATION_MAINTENAN
CE
2
ZWAVEPLUS_INFO
2
2.3 CC Control
Z-Ware can be operated in any Z-Wave network with other Z-Wave certified devices from
other manufacturers. All non-battery-operated nodes within the network will act as repeaters
regardless of vendor to increase reliability of the network.
Z-Ware controls/monitors Z-Wave-certified devices of different categories from various
vendors through their CCs. CCs that are automatically handled are not exposed to the user. ZWare controls the following CCs:
Table 2. Controlled Z-Wave CCs
Page 10
INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 4 of 47
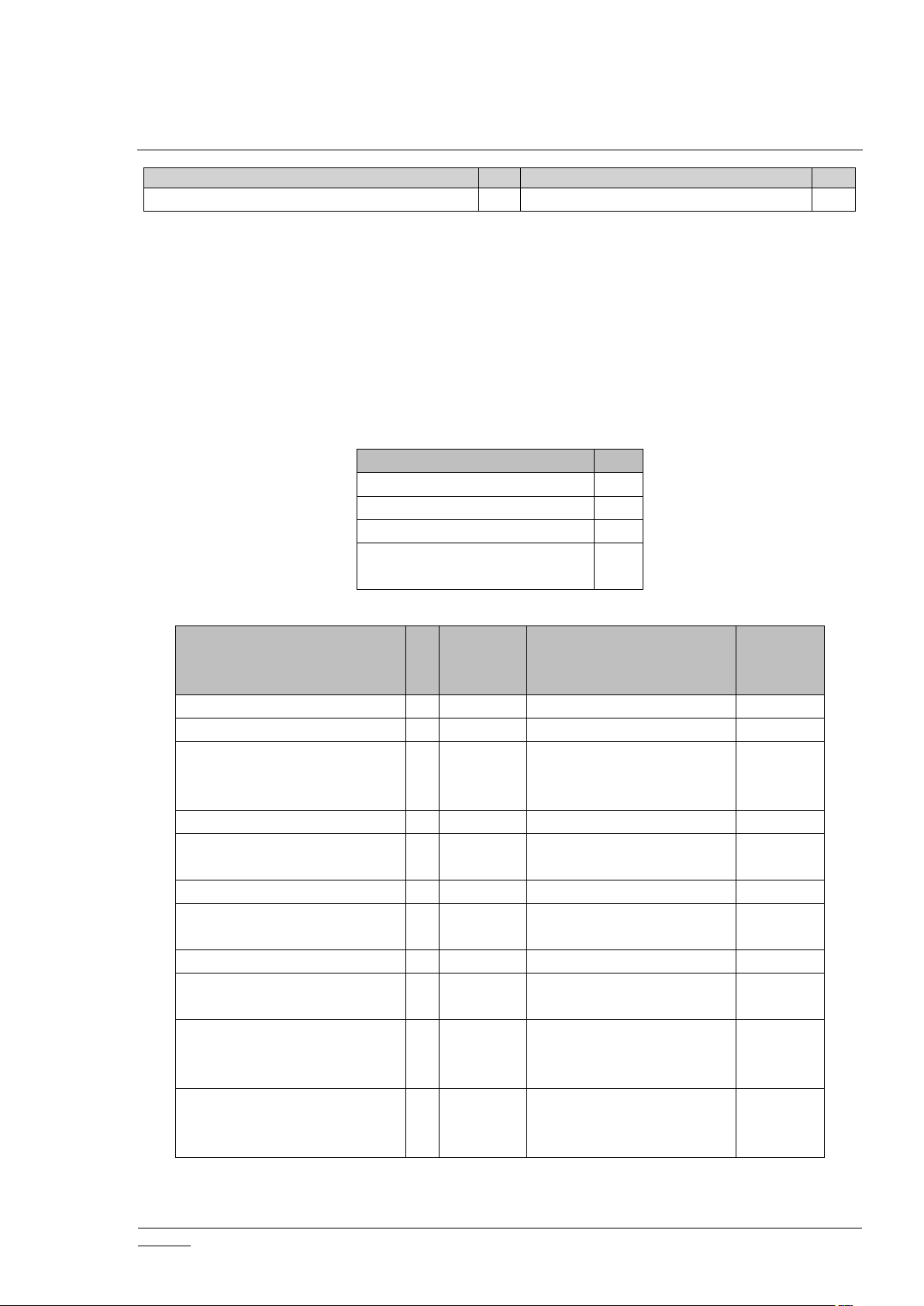
Table 2. Controlled Z-Wave CCs Inherited from ZIPGW
CC
VerCCVer
INCLUSION CONTROLLER
1
TRANSPORT_SERVICE
2
CC
Ver
ASSOCIATION
3
ASSOCIATION_GRP_INFO
3
DEVICE_RESET_LOCALLY
1
MULTICHANNEL_ASSOCIATI
ON
4
CC
Ver
Not
Added
Required Security classes
when added
On Secure
Inclusion
Failure
APPLICATION_STATUS
1
X
None
X
CRC_16_ENCAP
1
X
None
X
FIRMWARE_UPDATE_MD
5
Highest granted security
class - not supported when
included non-securely
INCLUSION_CONTROLLER
1
X
None
X
INDICATOR
3XHighest granted security
class
X
MAILBOX2LAN-side only
MANUFACTURER_SPECIFIC
2XHighest granted security
class
X
MULTI_CMD
1
X
None
X
NODE_PROVISIONING
1
Access Control, only when
SIS
NW_MGMT_BASIC
2
Highest granted security
class - not supported when
included non-securely
NW_MGMT_INCLUSION
3
Highest granted security
class - not supported when
included non-securely
NODE_PROVISIONING CC is only present when Z-Ware is operating as a Z-Wave SIS.
SUPPORT CC is automatically controlled only and only for Post Set Polling – see 2.11
Post-Set
Polling.
2.4 CC Support
For easier reference during certification, supported CCs (including those inherited from ZIPGW)
are shown below.
Table 2.: Supported Z-Wave CCs Pushed Down from Z-Ware (No Security Requirements)
Table 3. ZIPGW SDK Supported Z-Wave CCs
Page 11
INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 5 of 47
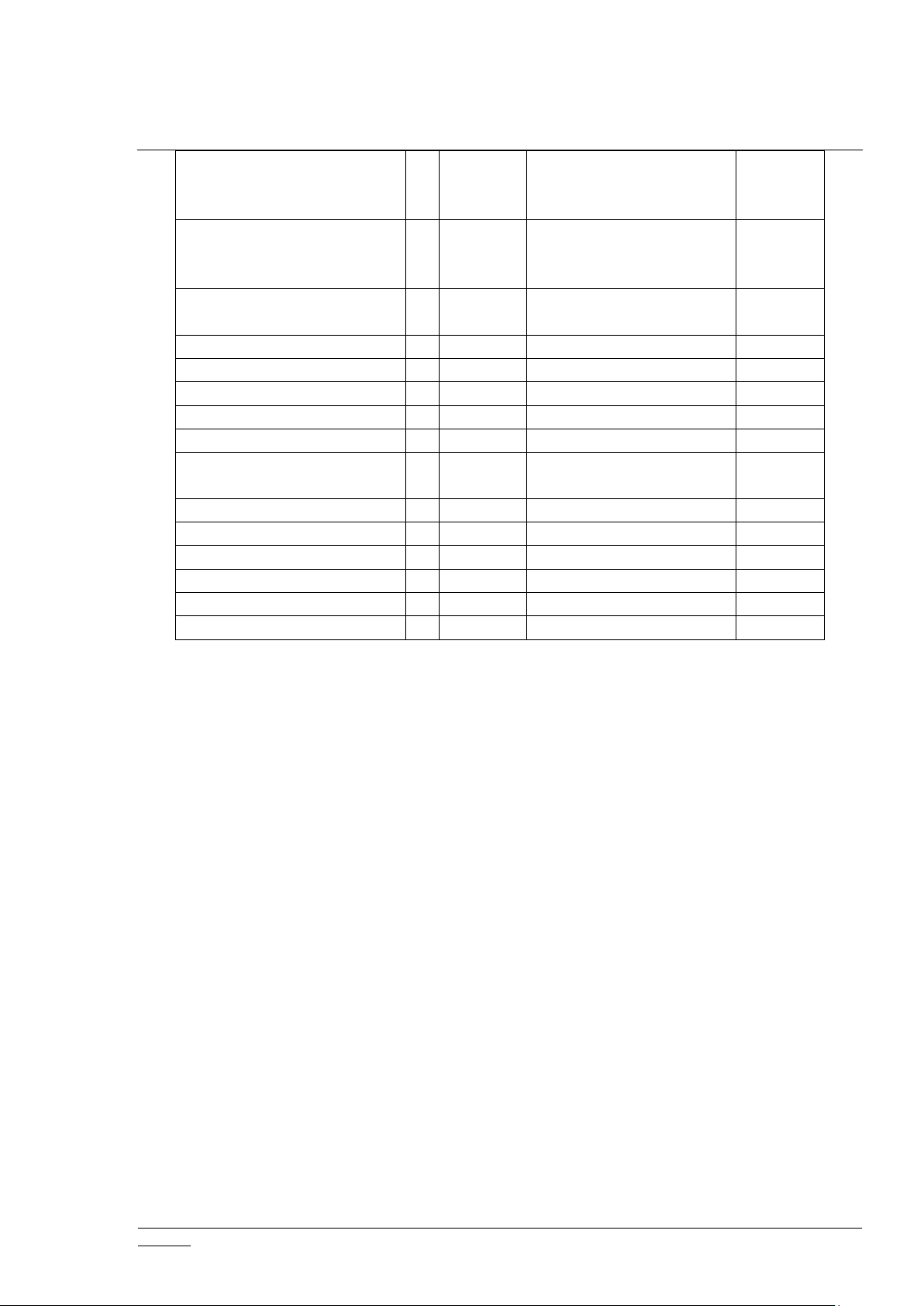
NW_MGMT_IMA
2
Highest granted security
class - not supported when
included non-securely
NW_MGMT_PROXY
3
Highest granted security
class - not supported when
included non-securely
POWERLEVEL
1XHighest granted security
class
X
SECURITY
1
X
None
SECURITY_2
1
X
None
X
SUPERVISION
1
X
None
X
TRANSPORT_SERVICE
2
X
None
X
TIME1X
None
X
VERSION
3XHighest granted security
class
X
ZIP4LAN-side only
ZIP GATEWAY
1
LAN-side only
ZIP_ND1LAN-side only
ZIP NAMING
1
LAN-side only
ZIP PORTAL
1
LAN-side only
ZWAVEPLUS_INFO
2
X
None
X
Z-Ware does nothing on receiving Basic CC Set or Get, unless Basic Set from any particular node
or endpoint is used as a Scene trigger. Z-Ware supports only 1 Association group supporting 1
node for Lifeline. This node will receive the Device Reset Locally command.
2.5 Device Database
A device database in JSON format for easier user editing is used to:
Upgrade functionality of older versions of CCs that do not support capability queries by
pre-configuring the database with the necessary information based on manufacturers’
published data sheets
Pre-configure devices automatically to optimal usage settings when dealing with
ambiguous configuration CC parameters or associations
Fix quirks in devices that are not fully compliant or compatible
Unify notification sensor implementation from Binary Sensor CC, Alarm Sensor CC,
Alarm CC v1-2, Notification CC v3-8 so tht they all look the same for an easier client API
because they essentially serve the same function
2.6 Command Class Configuration
Some library clients may want to only implement control for selected CCs of those offered.
However, this leads to Z-Wave certification form failures as the library performs background
Page 12

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 6 of 47
polling and information caching for CCs not listed in the form. A CC configuration option file,
cmd_class.cfg, list all CCs offered allowing the client developer to comment out undesired CCs.
2.7 Network Initialization
The following steps are carried out during network initialization:
1. Get ZIPGW’s Z-Wave Home ID, Node ID, and Home Area Network (HAN) IP address.
2. Get ZIPGW attached controller’s cached node information.
3. Get CC versions present in the ZIPGW cached node information to create corresponding ZWare interfaces.
4. Get ZIPGW’s hardware and firmware versions if VERSION CC is Version 2 or higher.
5. Get ZIPGW’s manufacturer, product type, and product ID, if MANUFACTURER_SPECIFIC CC
presents.
6. Get node list of the HAN.
7. Turn on mailbox for ZIPGW SDK v2.1x and above. This will enable multi-client support and
receive wake-up notification from the device through mailbox ACK message.
8. Get ZIPGW dynamic DSK key for adding new node.
9. Set supported CCs in the ZIPGW attached controller’s NIF.
10. Get unsolicited destination address, and, if its IPv6 address is all zeroes, set it to the Z/IP
client IPv6 address.
11. Resolve all nodes in the node list into corresponding HAN IPv6 addresses.
12. Perform Node Update (see 2.8 Node Update) through HAN network for nodes that are not
loaded with detailed node information from persistent storage.
2.8 Node Update
The following steps are carried out to acquire detailed node information based on the CCs
present at the node and endpoint levels:
1. Get cached node information of the node of interest from the ZIPGW.
2. Assign the ZIPGW attached controller’s Z-Wave Return Route to the node.
3. Get CC versions of each CC listed in the node information.
4. Get library, protocol, and application versions.
5. Get node’s hardware and firmware versions if Version CC version is 2 or higher.
6. Get MANUFACTURER_SPECIFIC CC Manufacturer ID, Product Type, and Product ID. Based
on these, get device category from the Device Database. Get Device Serial Number if
supported.
7. If the node has just been added into the network, set the WAKEUP CC notification receiving
Node ID to SIS with/without changing the wakeup interval. The wakeup interval will be
changed if the global setting for the wakeup interval is non-zero in the Device Database.
8. For each endpoint in the node:
a) Get security supported CCs at the endpoint if the node is included securely.
b) Get version of CCs at the endpoint.
c) If the node has just been added into the network, set device-specific configuration
parameters based on the Device Database.
Page 13
INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 7 of 47
d) Get Configuration CC parameter number property if CC version is 3 or higher.
CC
CC
VERSION
MANUFACTURER_SPECIFIC
WAKE_UP
CC
CC
ASSOCIATION
SENSOR_BINARY
ASSOCIATION_GRP_INFO
SENSOR_MULTILEVEL
ALARM_SENSOR
SIMPLE_AV
BARRIER_OPERATOR
SOUND_SWITCH
BATTERY
SWITCH_BINARY
CENTRAL_SCENE
SWITCH_COLOR
CLOCK
SWITCH_MULTILEVEL
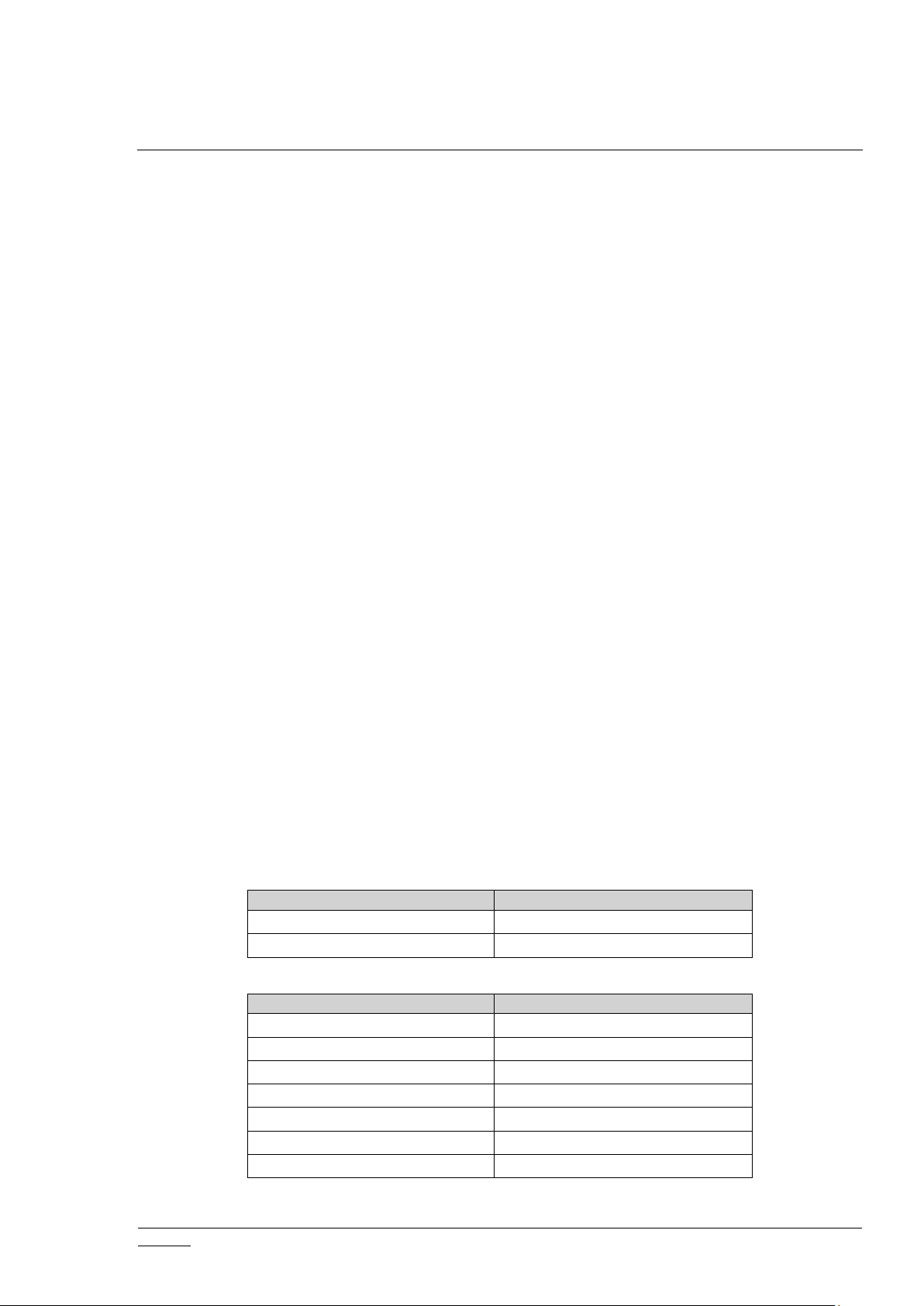
e) Get Association CC’s maximum supported group. If the node has just been added into
the network and group 1 is “Lifeline”, set the SIS node ID into group 1.
f) Get the Central Scene CC number of supported scenes. If the node has just been added
into the network and Central Scene CC version is 3 or greater, then set it to slow
refresh.
g) Get Z-Wave Plus Information.
h) Get Multilevel Sensor CC supported types, units, and current value.
i) Get Association Group Information CC details.
j) Get Indicator CC supported indicator ID, property ID, and the current property ID’s
value.
k) Get Thermostat Fan Operating Mode CC supported modes, Thermostat Mode CC
supported and current mode, Thermostat Setpoint CC supported and current type and
temperature range, Thermostat Operating State CC current state, and Thermostat Fan
State CC current state.
l) Get Multilevel Switch CC supported types and current values.
m) Get Simple AV CC supported controls.
n) Get Alarm/Notification CC supported types and events.
o) Get Protection CC supported states.
p) Get User Code CC maximum supported codes.
q) Get Meter CC capabilities and descriptors.
r) Get Binary Sensor CC supported types and current values.
s) Get Door Lock CC current state.
t) Get Alarm Sensor CC supported types and current values.
u) Get Barrier Operator CC current state.
v) Get Color Switch CC supported components and current values.
w) Get Sound Switch CC supported tone info and current configuration.
x) Get Window Covering CC supported parameter IDs and current status.
y) Get Binary Switch CC current state.
z) Get Battery CC current level.
aa) Get Node Naming CC current name and location.
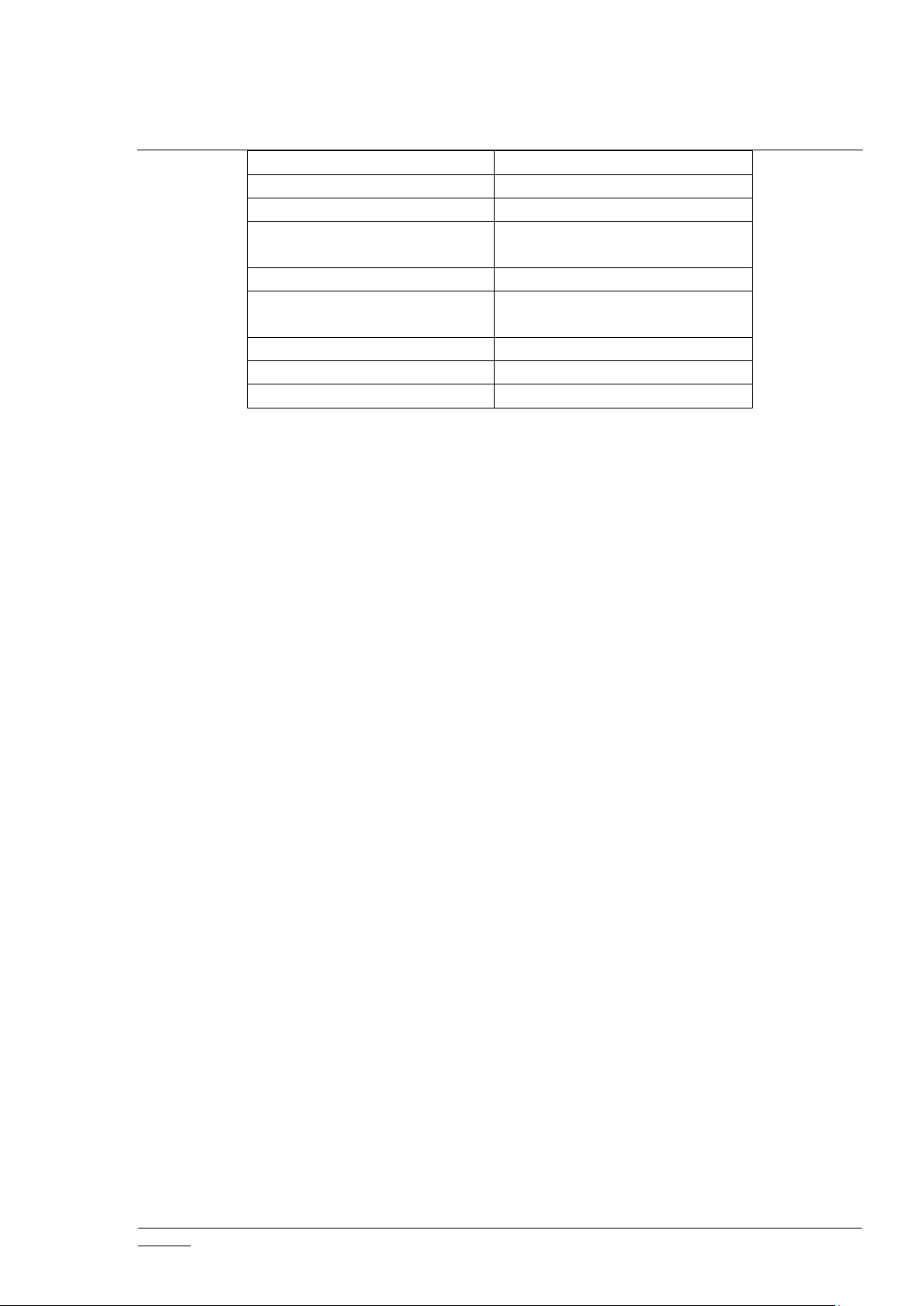
Table 4. Node Update get/set CCs
Table 5. Node Update endpoint get/set CCs
Page 14
INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 8 of 47
CONFIGURATION
THERMOSTAT_FAN_MODE
DOOR_LOCK
THERMOSTAT_FAN_STATE
INDICATOR
THERMOSTAT_MODE
METER
THERMOSTAT_OPERATING_ST
ATE
METER_TBL_MONITOR
THERMOSTAT_SETPOINT
MULTI_CHANNEL_ASSOCIATI
ON
USER_CODE
NODE_NAMING
VERSION
NOTIFICATION/ALARM
WINDOW_COVERING
PROTECTION
2.9 Network Update
The following steps are carried out to update the network:
1. Repeat steps 1 to 4 of Network Initialization (see 2.7 Network Initialization).
2. Request network update by using the command:
NETWORK_MANAGEMENT_BASIC CC-> NETWORK_UPDATE_REQUEST
3. Get node list of the HAN.
4. Resolve all nodes in the node list into corresponding HAN IPv6 addresses.
5. Request node neighbor update for each of the nodes in the node list. Repeat for up to
three iterations if the request node neighbor update failed for some nodes that may be
out-of-range.
6. Perform Node Update for each node in the network (See
2.8 Node Update).
2.10 Background Polling
Z-Ware Library performs automatic background polling to cache device-supported interface
details (e.g, as supported sensor types and units) and device values (e.g., sensor readings for
each supported type). For always-on devices, polling is carried out for all relevant interfaces in
a device followed by an interval of 10 seconds before the next device is polled. The same
device is never polled twice within an interval of 30 seconds. If the device is down or nonresponding, the next poll time will be 1 minute and double the interval each time the node is
still down or non-responding on polling until maximum of 16 minutes interval is reached. For
FLIRS (Frequently Listening Routing Slave), also known as LSS (Listening sleeping slave) devices,
polling is carried out only every 6 hours per device so as not to exhaust the device’s batteries.
For sleeping devices, polling is carried out on wake up. As sleeping devices will go to sleep
mode when they don’t receive any Z-Wave messages, this type of polling has higher priority
than the other two types of polling. The polling sequences of CCs are the same as those listed
for each endpoint in Section 2.8 Node Update.
Page 15

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 9 of 47
2.11 Post-Set Polling
Some devices take time to reach their target settings. This is especially true for mechanical
devices. Z-Ware Library performs post-set polling for door lock, multi-level switch motor, and
barrier operator interfaces.
For door locks, the polling intervals are 1, 2, 3 seconds, whereas for multi-level switches, the
intervals are 1, 2, 3, 4 seconds before the timeout occurs. For Barrier Operator CC, the intervals
are 1 to 7 seconds incrementally.
If the endpoint supports the Supervision CC, polling is not performed, Supervision Get
encapsulation is automatically used and notification is expected from the device on
completion. This allows the client to be informed if/when the device has reached its target
state.
Page 16
INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 10 of 47
3 Typical Usage
Action
API
Initiate network scanning for ZIPGW IP addresses. For each
valid network interface IP address, a callback will report the
result of each scanning.
zwnet_gw_discvr_start
zwnet_gw_discvr_cb
To stop the network scanning and free the resources used
in scanning.
zwnet_gw_discvr_stop
Action
API
Initialize the API and get controller node ID, home ID, HAN
address, and node list.
zwnet_init
zwnet_notify_fn
3.1 Network
3.1.1 Initialization
The first thing a client needs to do is to acquire the ZIPGW IP address either by means of
reading from the configuration file or scanning the IP network using the ZIPGW Discovery
protocol. There are APIs to help the client do the network scanning for ZIPGW IP addresses.
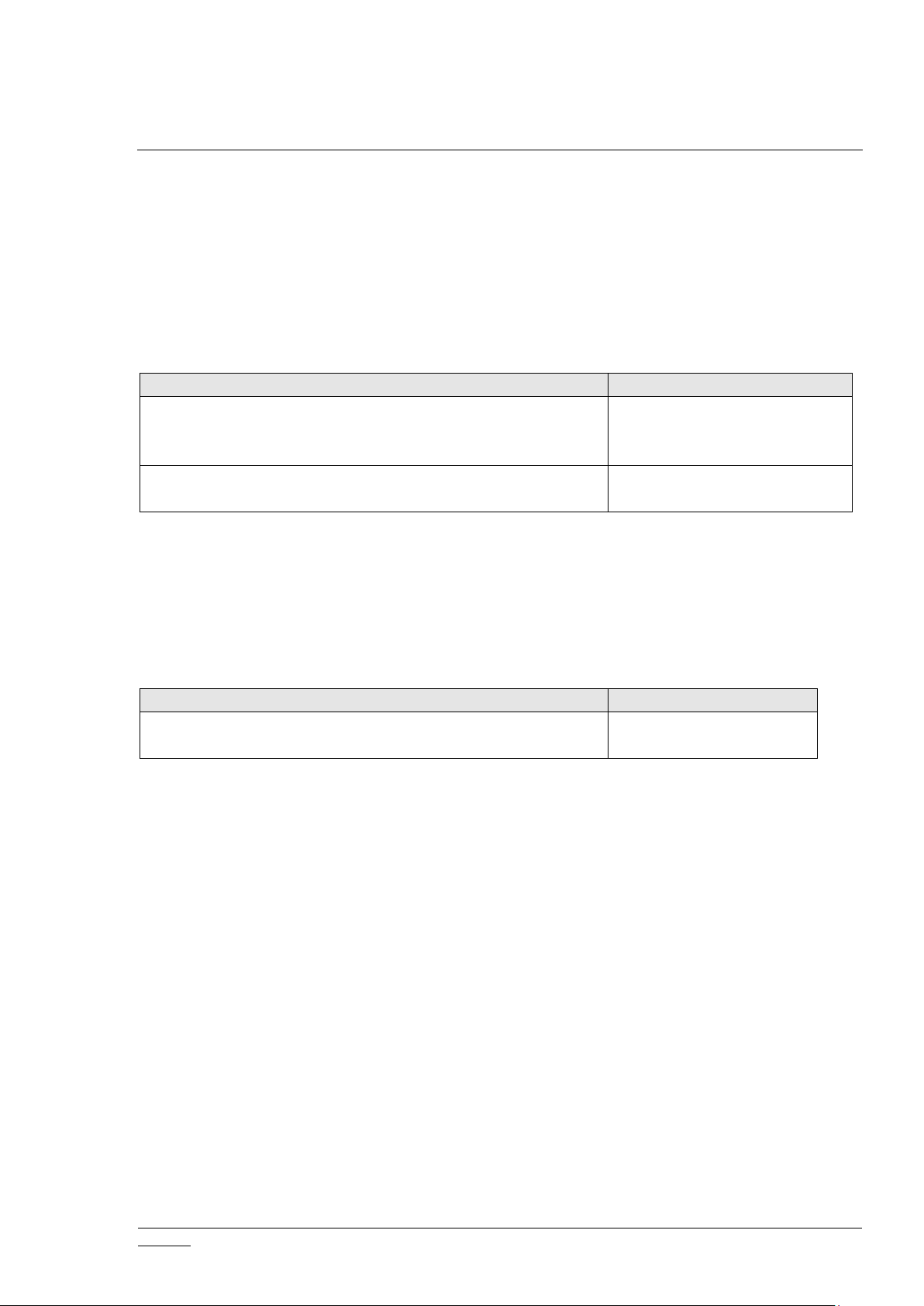
Table 6. Network Scanning APIs
The client initializes itself by querying the ZIPGW attached controller node ID, home ID, HAN
address, and the node list of all the nodes in the HAN.
After that, it loads any persistent network information from any previous sessions. This
includes information on the nodes, endpoints, and interfaces along with their versions. Home
ID is used as a unique identifier into the persistent network storage. This is analogous to the
node information stored on the non-volatile memory (NVM) of the controller.
Table 7. Network Initialization API
Sometimes, a controller that was configured on a different host is introduced to ZIPGW. In this
case, the storage on the host and the ZIPGW attached controller node information in NVM
would not match. This requires migration of the persistent network storage, a facility provided
by the client. If this migration is not performed, the information stored in the controller is used
to request further meta-information and can cause the load operation to be longer, depending
on the number of nodes discovered and their geometries, and sleeping nodes may not be
properly configured.
3.1.2 Creation and Tear Down
Typically, the client creates a network with at least two devices, one of which is a controller,
while the other can be any type of node. The user initiates the node for inclusion and uses the
controller to add the device into its network and initiate.
Now, the node can be controlled through the controller, which becomes the primary.
Similarly, more nodes can be added. Removal is identical except that the API parameter is
different. During addition, the node’s endpoints and interfaces are enumerated and populated
as descriptors for control. Security facilities are handled transparently with indications to the
client.
Page 17

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 11 of 47
The zwnet_notify_fn callback is used to notify the client of the operation’s progress while
Action
Controller
Node
Add node
zwnet_add(true)
zwnet_node_fn
zwnet_
notify_fn(progress)
zwnet_initiate
zwnet_notify_fn(progress
)
Remove node
zwnet_add(false)
zwnet_node_fn
zwnet_
notify_fn(progress)
zwnet_initiate
zwnet_notify_fn(progress
)
Action
API
Store network preference into persistent
storage.
zwnet_pref_set
Retrieve network preference from persistent
storage.
zwnet_pref_get
Store client preference into persistent storage.
zwnet_client_pref_set
Retrieve client preference from persistent
storage.
zwnet_client_pref_get
Action
API
Accept or reject newly added node into security 2
mode.
zwnet_add_sec2_accept
Grant keys to the newly added node in security 2
mode.
zwnet_add_sec2_grant_key
Get ZIPGW Device Specific Key (DSK) in security 2
mode. This is useful when ZIPGW wants to join
another S2 capable ZIPGW’s network.
zwnet_sec2_get_dsk
zwnet_node_fn callback is called in between to provide a handle to the node.
Table 8. Network Creation and Tear Down APIs
3.1.3 Network and Client Preference Storage
To facilitate storage and retrieval of network- and client-specific preferences or configurations
(which are opaque to the Z-Ware library), there are four APIs available. Each network is
restricted to one storage while there could be several client storages per network.
Table 9. Network and Client Preference Storage APIs
3.1.4 Security 2 (S2)
S2 security requires user interaction when adding new nodes and replacing failed nodes
through these APIs.
The typical interactions between the user application and Z-Ware Library through API calls and
callbacks are shown in the following figure.
Table 10. Security 2 APIs
Page 18

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 12 of 47
3.1.5 SmartStart
Action
API
Add a provisioning list entry.
zwnet_pl_add
Get a provisioning list entry information through
callback.
zwnet_pl_get
Delete a provisioning list entry.
zwnet_pl_del
Get all provisioning list entries through callback.
zwnet_pl_list_get
Delete all provisioning list entries.
zwnet_pl_list_del
As Z-Wave SmartStart inclusion does not require user interaction, APIs are provided to help
manage the provisioning list stored at the ZIPGW.
Table 11. Smart Start Provisioning List Management APIs
3.1.6 Network Health Check
Network health status is provided via an API through the NW_MGMT_IMA CC, which provides
statistics for packet error rate (PER), number of route changes (RC), number of neighbors (NB),
maximum reduction in transmit power where the last working route still works (LWRdb), and
the difference between last working route RSSI and background RSSI (LWR_RSSI) for
determination of the Network Health Value (NHV) of each node. The NHV is then translated to
Network Health Status (NHS) that is presented to the user by using a simple color code grading
system. Users can identify devices with poor network connectivity easily and take necessary
Page 19

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 13 of 47
action to remedy the situation, such as adding a repeater between devices with poor network
Action
API
Start network health check on all but sleeping
nodes.
zwnet_health_chk
Action
API
Get handle to node
zwnet_get_node, zwnode_get_next or through
zwnet_node_fn
Get handle to endpoint
zwnode_get_ep, zwep_get_next
Get handle to interface
zwep_get_if, zwif_get_next
Set up report callback
once
zwif_xxx_rpt_set (zwrep_xxx_fn), , depending on type of
interface
zwnet_appl_fn
Monitor the interface
zwif_xxx_get, depending on type of interface
zwnet_appl_fn
zwrep_level_fn
Control the interface
zwif_xxx_set, depending on type of interface
zwnet_appl_fn
Action
API
Get handle to node
zwnet_get_node, zwnode_get_next or through
zwnet_node_fn
Get handle to endpoint
zwnode_get_ep, zwep_get_next
Get handle to interface
zwep_get_if, zwif_get_next
connectivity.
Table 12. Network Health Check API
3.2 Interface Monitor/Control
With a node handle, the client can get access to its endpoints and interfaces.
Table 13. Interface Control APIs
Since interface monitoring requires a callback to receive Z-Wave reports, it is the client’s
responsibility to set up the callback. The client can solicit this report using the relevant get API
and optionally implement a timeout in case the report callback never happens.
Typically, while a zero return to an interface API indicates success, a negative return indicates
an error and that the command was not sent to the device. A positive return indicates the
command was delayed owing to the device being momentarily unavailable or asleep – in either
case the command will be sent when the device is available, but the handling may be different
as a short wait will resolve the former case.
In order to reduce unnecessary callbacks to the client application, all live reports from nodes
are compared with the cached value (if available) and callback is executed only if they are
different. However, in all cases, the timestamps on the cached values are updated.
Table 14 – Interface Control APIs
Page 20

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 14 of 47
Set up report callback
once
zwif_xxx_rpt_set (zwrep_xxx_fn), , depending on type of
interface
zwnet_appl_fn
Monitor the interface
zwif_xxx_get, depending on type of interface
zwnet_appl_fn
zwrep_level_fn
Control the interface
zwif_xxx_set, depending on type of interface
zwnet_appl_fn
Typically, the client code would map the interface handle to the UI element that the user can
If (!zwnode_get_ep(node, &ep))
{
do
{
if (!zwep_get_if(ep, &ifd))
{
do
{
switch (ifd->cls)
{
case COMMAND_CLASS_SWITCH_MULTILEVEL:
/* solicit current level */
zwif_level_get(ifd);
/* draw UI depending on capabilities */
if (ifd->ver == 3)
{
}
:
break;
:
}
}
while (!zwif_get_next(ifd, &ifd));
}
}
while (!zwep_get_next(ep, &ep));
}
manipulate. So, this enumeration happens mostly when a node is newly added and the UI
elements need to be populated.
Page 21

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 15 of 47
3.3 Actuator Interface Multicast & Multi-endpoint Control
Action
API/Structures
Get node/endpoint
type
zwnoded_t, zwepd_t
Set/get name/location
zwnoded_t, zwep_nameloc_set
Visually locate
zwnode_identify
Action
API
Get #groups in device
zwif_group_sup_get (if, zwif_group_sup_fn)
zwnet_appl_fn
zwif_group_sup_fn
Get group information
zwif_group_get (if, group#)
zwnet_appl_fn
zwif_group_fn
Modify devices in group
zwif_group_add/del
zwnet_appl_fn
The switch, level, window covering, barrier, and door lock actuator interfaces have a multicast
version of the set command named mset, where the same parameters can be sent to the same
interface type on multiple nodes if the underlying ZIPGW supports ZIP CC v5. The same APIs
can be used to have the same effect on multiple endpoints on the same node.
3.4 Node Identification
Nodes and endpoints contain information on their network and functional roles respectively,
i.e., whether they are controllers or slaves and whether they are binary switches, etc. This
allows classification of nodes by the client. Further, all endpoints (including the controller’s
endpoint) in a node have name and location fields for easier identification by the user, rather
than using the unique Node ID. Z-Wave Plus v2 nodes can also be visually located via the
Indicator CC v3 using zwnode_identify.
Table 15. Node Identification APIs
3.5 Grouping
Devices can be grouped for device-specific purposes, e.g., a motion sensor could be made to
turn on multiple lights and an alarm. In this case, it could have two groups: one for the lights
and dimmers and one for the alarm. The user can add preferred lights to the light group and
chosen alarm for the alarm group. The user may also be able to adjust the brightness to which
a dimmer is set.
Table 16. Grouping APIs
Page 22

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 16 of 47
3.6 Firmware Update and Backup
Action
API
Get firmware information.
zwif_fw_info_get
Requests firmware update operations to be carried
out.
zwif_fw_updt_req
Request for firmware download from a device into a
file for backup purposes.
zwif_fw_downld_req
Action
API
The polling variant of APIs for getting report through the polling
facility.
zwif_xxx_poll
Remove a polling request.
zwnet_poll_rm
Remove multiple polling requests.
zwnet_poll_rm_mul
Action
API
Load and store device-specific configurations.
zwdev_cfg_load
Free device-specific configuration records.
zwdev_cfg_free
Search for a match in device-specific configuration
records.
zwdev_cfg_find
In order to bring Z-wave devices in the network and the gateway up to date with the latest
features or bug fixes, there are firmware update APIs to facilitate updating. On the other hand,
backing up of firmware or non-volatile data stored in non-volatile memory (NVM) can be done
on devices that support FIRMWARE_UPDATE_MD CC version 5 or higher.
Table 17. Firmware Update APIs
3.7 Polling Facility
In order to help a user application poll the status of a device that does not support sending of
unsolicited reports, there are polling APIs to help execute the polling that conform to Z-Wave
recommendations.
Table 18. Polling Facility APIs
3.8 Device Database
The following APIs facilitate loading and unloading (freeing) the database and searching for a
specific device configuration and information. The actual format and features of the database
are documented in
[9] Silicon Labs, SDS14416, SDS, Z-Ware Library C API Reference Manual.
Table 19. Device Database APIs
3.9 Saving & Restoring the Network for Middleware Changes
Persistent storage is used to store the entire network information comprising network, nodes,
endpoints, and interfaces in JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) format for easier editing. This
Page 23

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 17 of 47
format and its features are documented in [9] Silicon Labs, SDS14416, SDS, Z-Ware Library C
API Reference Manual.
When upgrading Z-Ware or when moving from another middleware to Z-Ware, the storage can
be used to port the network seamlessly without having to repeat the tedious inclusion and
configuration of nodes. When moving from another middleware, the data required in the
storage must be filled in. Otherwise Z-Ware will solicit the missing data from the network
during start up.
Page 24

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 18 of 47
4 How To: Add Control for a CC as an Interface
File
Programming element
Type
zwnet_1_ep_sta_t
enum
zwnet_substa_t
enum
zwnet_1_ep_evt_t
enum
zip_api_pte.h
zwnet_1_ep_act_t
enum
zwnet_cls_name_t (supported_cls_map)
array
zwnet_sup_cached_cb_rpt
function
zwnet_dat_cached_cb_rpt
function
zip_api_network.c
zwnet_db_cb_rpt
function
zip_api_base.c
zwif_create
function
dlck_op_mode
array
zwif_dlck_op_set
function
zwif_dlck_op_mset
function
zwif_dlck_op_rpt_set
function
zwif_dlck_op_get_ex
function
zwif_dlck_op_get
function
zwif_dlck_op_get_poll
function
zwif_dlck_cfg_set
function
zwif_dlck_cfg_get
function
zwif_dlck_cap_get
function
zwif_dlck_cap_cache_get
function
zip_api_intf.c
zwif_dlck_cap_free
function
zw_sm_hdlr_dat_t hdlr_dat
array
zwnet_1_ep_act_t
enum
zwnet_1_ep_sm_cls_hdlr
function
zwnet_dlck_rpt_cb
function
zwnet_sm_dlck_op_get
function
zwnet_dlck_cfg_rpt_cb
function
zwnet_sm_dlck_cfg_get
function
zwnet_dlck_cap_rpt_cb
function
zwnet_sm_dlck_cap_get
function
zwnet_ep0_dedup
function
zip_api_sm.c
zwnet_1_ep_info_sm
function
zwdlck_cfg_v22_t
structure
if_dlck_cch_data_v22_t
structure
if_dlck_cch_data_v23_t
structure
if_dlck_cch_data_v24_t
structure
zip_api_util.c
zwutl_if_cch_dat_upgrd
function
Adding a Interface in the library is non-trivial and not recommended. However, if required, this
section describes how using Door Lock interface implementation as an example. The following
table shows the files and related functions and structures involved in the implementation.
Table 20. CC Implementation Programming Elements
Page 25

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 19 of 47
zwutl_if_dat_upgrd
function
zwutl_if_load
function
zwdev_if_rec_cls (cmd_cls_rec_type_tbl)
array
if_parser
array
zwdev_cfg_if_ld
function
zwdev_dlck_if_free
function
zwdev_cfg_if_free
function
zip_dev_cfg.c
zwdev_dlck_if_parser
function
ps_load_doorlck_info
function
ps_ni_load_cc_specific
function
ps_save_doorlck_info
function
zip_pstorage.c
ps_ni_save_cc_specific
function
zwif_doorlck_hdlr
function
zip_rpt_hdlr.c
zwif_rpt_hdlr_t (rpt_hdlr_map)
array
zwspoll_rpt_rcv_chk
function
zwspoll_on_rpt_rcv
function
zip_set_poll.c
zwspoll_add_poll
function
4.1 Initialization
4.1.1 Global Setting
On initialization, the Library loads the CC configuration file passed in by the client to determine
CCs that the client wishes to use. The array supported_cls_map lists the CC name as a string
and its corresponding CC constant. For door lock implemenatation, the entry
{"COMMAND_CLASS_DOOR_LOCK", COMMAND_CLASS_DOOR_LOCK} must be added into the
array.
4.1.2 Loading of Door Lock Information from Persistent Storage
Loading of persistent storage involves first loading the new JSON format persistent storage file.
If the file does not exist, loading will fallback to the old TLV (tag-length-value) format persistent
storage file for backward compatibility.
4.1.2.1 Old Format Persistent Storage
Loading of interface specific data is implemented in the zwutl_if_load function. If upgrading of
the TLV format for the command class is needed to support higher versions of the same CC,
entries must be inserted in either zwutl_if_dat_upgrd (for static cache) or/and
zwutl_if_cch_dat_upgrd (for dynamic cache) functions. Details of cache implementation will be
described in later section “Caching Implementation”. For Door Lock CC, several dynamic cache
upgrades have been implemented, each upgrade requires the copying from old cache structure
to new cache structure and initializing the new members in new cache structure to default
values. For example, the old if_dlck_cch_data_v22_t is upgraded to if_dlck_cch_data_v23_t
with addition of cfg-> blk_to_blk, cfg-> twist_asst, etc. Care must be taken to add the new
Page 26

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 20 of 47
upgrade code at the end of the case statement because the cache data may go through
multiple upgrades.
4.1.2.2 New Format Persistent Storage
Loading of interface specific data is implemented in ps_ni_load_cc_specific function. For Door
Lock CC implementation, an entry must be added in this function, which is
ps_load_doorlck_info function. This function contains implementation of loading for both
dynamic and static cache. Upgrading cache format is as easy as adding addition JSON entries
and make these entries optional (i.e., missing these entries from old JSON persistent storage
will not be considered as an error).
4.2 Shutting Down
4.2.1 Saving of Interface Information into Persistent Storage
Upon shutting down, all network info, including node info, are saved to persistent storage.
Saving into persistent storage only involves the new JSON format persistent storage file. This
will ensure seamless switch over to the new format if the loading of persistent storage was
from the old format file.
4.2.1.1 New Format Persistent Storage
Saving of interface specific data is implemented in ps_ni_save_cc_specific function. An entry
must be added in this function, which is ps_save_doorlck_info function. This function contains
implementation of saving for both dynamic and static cache.
4.3 Node Update/Inclusion Information Gathering
At node update or inclusion, a state-machine will query each interface attached to each
endpoint of the node. For door lock CC version 4 and above, the current operating mode,
configuration parameters, and capability must be queried. Thereafter, the node information is
refreshed by way of background polling in which only the variable information (dynamic
cache), such as the door lock current operating mode and configuration parameters, are
polled. The fixed information (static cache) which is door lock’s capability will only be queried if
it was not cached during the initial inclusion phase.
State, sub-state and relevant events entries are added in the single endpoint state-machine
function zwnet_1_ep_info_sm. S_EP_STA_GET_DOORLOCK is added into zwnet_1_ep_sta_t.
EVT_S_EP_DOORLOCK_OP_REPORT, EVT_S_EP_DOORLOCK_CFG_REPORT,
EVT_S_EP_DOORLOCK_CAP_REPORT and EVT_S_EP_NW_TMOUT are added into
zwnet_1_ep_evt_t. DOORLCK_SUBSTA_OP is added into zwnet_substa_t.
The entry {zwnet_sm_dlck_op_get, COMMAND_CLASS_DOOR_LOCK, 0} in array hdlr_dat in
zwnet_1_ep_sm_cls_hdlr provides the starting point for the state-machine to query Door Lock
info by calling zwnet_sm_dlck_op_get. This function implements a state-machine that sets up
a report callback function (zwnet_dlck_rpt_cb), solicits a report (zwnet_get_report), restarts
the state-machine timer, and changes state to (S_EP_STA_GET_DOORLOCK) and sub-state
Page 27

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 21 of 47
(DOORLCK_SUBSTA_OP). When zwnet_dlck_rpt_cb calls back with the event
EVT_S_EP_DOORLOCK_OP_REPORT, the state-machine will proceed to the next operation by
calling zwnet_sm_dlck_cfg_get and change its sub-state to DOORLCK_SUBSTA_CFG. This
process is repeated for the next operation by calling zwnet_sm_dlck_cap_get and changes its
sub-state to DOORLCK_SUBSTA_CAP.
For a robust state-machine implementation, the state-machine must handle timeout event
(EVT_S_EP_NW_TMOUT), which typically implements the re-transmission of report get
command based on the state-machine’s current state and sub-state.
Upon completion of operations for the current CC, the state-machine handles the next CC by
calling the zwnet_1_ep_sm_cls_hdlr with an appropriate parameter “act” value as defined in
zwnet_1_ep_act_t. Note that the entries in the enum zwnet_1_ep_act_t must be in the same
order as in the array hdlr_dat.
4.4 Capability APIs
The capability for door lock can be queried using either of the two APIs as follows:
/**
zwif_dlck_cap_get - get the supported door lock capabilities through report callback
@param[in] ifd interface
@param[in] cb report callback function
@param[in] cache flag: to get data from cached only. If set, no fetching from real device
when
cache unavailable.
@return ZW_ERR_XXX
*/
int zwif_dlck_cap_get(zwifd_p ifd, zwrep_dlck_cap_fn cb, int cache);
/**
zwif_dlck_cap_cache_get - get supported door lock capabilities from cache
@param[in] ifd interface
@param[out] cap door lock capabilities
@return ZW_ERR_XXX
@post Caller must call zwif_dlck_cap_free() to free the door lock capabilities if this call is
successful.
*/
int zwif_dlck_cap_cache_get(zwifd_p ifd, zwdlck_cap_p *cap);
The main difference between the two is the former does not return the door lock’s capability
directly to the caller, instead the capability information is delivered to the caller through
callback function. The latter returns the capability information directly to the caller if the
information is available in the cache.
4.4.1 zwif_dlck_cap_get
To implement this function, entries must be added to the device database callback function
zwnet_db_cb_rpt and capability cache callback function zwnet_sup_cached_cb_rpt. In the
door lock case, the entry is CB_RPT_TYP_DOOR_LOCK for both callback functions.
Page 28

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 22 of 47
The function first checks that the interface descriptor belongs to the right command class
which is the door lock command class. If the check fails, it returns error code
ZW_ERR_CLASS_NOT_FOUND and exits. Note that this command class checking is
implemented on all APIs, hereinafter it will not be documented on other APIs. It will then check
the real version of the interface to ensure that the Door Lock CC supported is of version 4 or
higher. If this is not the case, it tries to retrieve the capability information from the device
database and processing will stop either by returning an error code ZW_ERR_CACHE_AVAIL if
the information is found in the device database (callback will be invoked in function
zwnet_db_cb_rpt to deliver the information) or ZW_ERR_CMD_VERSION if there is no entry
found in the device database.
In the case the Door Lock CC supported is of version 4 or higher, it tries to get the capability
information from the cache. If cache is available, the function returns error code
ZW_ERR_CACHE_AVAIL else if the caller passes in the parameter “cache” with non-zero value
(i.e., the caller is only interested in getting cached value), then the error code
ZW_ERR_NO_CACHE_AVAIL will be returned. In both cases, callback will be invoked in function
zwnet_sup_cached_cb_rpt.
If cache is unavailable and the caller passes in the parameter “cache” with zero value, then as a
last resort it will get the capability information directly from the device through Z-wave.
4.4.2 zwif_dlck_cap_cache_get
To implement this function, the entry IF_REC_TYPE_DOOR_LOCK must be added into the
device database support code. Details of device database for this entry will be explained in
later section “Device Database Upgrade for Door Lock CC version 3 and below”.
The function first checks the real version of the interface to ensure that the Door Lock CC
supported is of version 4 and higher. If this is not the case, it tries to retrieve the capability
information from the device database and returns immediately the information if it is found or
ZW_ERR_CMD_VERSION if there is no entry found in the device database.
In the case the Door Lock CC supported is of version 4 and higher, it tries to get the capability
information from the cache. If the cache is available, the function returns directly the
information; else it returns error code ZW_ERR_NO_CACHE_AVAIL.
4.5 Monitor APIs
To monitor the door lock operating mode, there are APIs to get a door lock operating mode
report and the associated API to set up the report callback function as follow:
/**
zwif_dlck_op_rpt_set - Setup a door lock operation report callback function
@param[in] ifd interface descriptor
@param[in] rpt_cb report callback function
@return ZW_ERR_XXX
*/
int zwif_dlck_op_rpt_set(zwifd_p ifd, zwrep_dlck_op_fn rpt_cb) ;
/**
zwif_dlck_op_get - get the state of the door lock device through report callback
Page 29

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 23 of 47
@param[in] ifd interface
@param[in] flag flag, see ZWIF_GET_BMSK_XXX
@return ZW_ERR_XXX
*/
int zwif_dlck_op_get(zwifd_p ifd, int flag) ;
/**
zwif_dlck_op_get_poll - get the state of the door lock device through report callback
@param[in] ifd interface
@param[in, out] poll_req poll request
@return ZW_ERR_NONE if success; else ZW_ERR_XXX on error
*/
int zwif_dlck_op_get_poll(zwifd_p ifd, zwpoll_req_t *poll_req);
The main difference between the two monitor APIs zwif_dlck_op_get and
zwif_dlck_op_get_poll is that the former executes one-time door lock mode report get
operation, whereas the latter is meant for polling which supports multiple report get
operations.
4.5.1 zwif_dlck_op_rpt_set
To implement this function, an entry must be added in zwif_create function. This entry
(COMMAND_CLASS_DOOR_LOCK) provides all the report commands according to the Door
Lock version supported by the node. An entry must also be added to the array rpt_hdlr_map so
that the general report handler function zwif_rep_hdlr knows which command class specific
handler to call. For the case of Door Lock CC, the entry is {COMMAND_CLASS_DOOR_LOCK,
zwif_doorlck_hdlr} which indicate the report handler for Door Lock CC is zwif_doorlck_hdlr.
Hence, zwif_doorlck_hdlr must be implemented to handle all door lock related reports.
The function associates the report callback function to the report handler for
DOOR_LOCK_OPERATION_REPORT in the interface.
4.5.2 zwif_dlck_op_get
This function calls the base function zwif_dlck_op_get_ex with parameter poll_req set to NULL.
To implement the base function, an entry must be added to the dynamic data cache callback
function zwnet_dat_cached_cb_rpt. The entry COMMAND_CLASS_DOOR_LOCK must handle
the cached report callback request identified by DOOR_LOCK_OPERATION_REPORT.
The function first checks the parameter “flag” passed in by the caller. If the bitmask
ZWIF_GET_BMSK_CACHE is set, it tries to retrieve the door lock mode cache and invokes caller
provided callback function in function zwnet_dat_cached_cb_rpt regardless of whether or not
the cache is available. Subsequently, it will check if the bitmask ZWIF_GET_BMSK_LIVE is set. If
set, it will query for the door lock mode directly from the device through Z-wave. In summary,
with this API, caller has the flexibility to get the door lock state either from cache or directly
from the device or using both methods.
4.5.3 zwif_dlck_op_get_poll
This function calls the base function zwif_dlck_op_get_ex with parameter flag set to zero. To
implement the base function, no special entry needs to be added; it just needs to call the
Page 30

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 24 of 47
polling sub-system using the function zwif_get_report_poll with the report get command
DOOR_LOCK_OPERATION_GET.
The function passes the polling request parameter “poll_req” to the polling sub-system to
perform the required polling specified by the caller. The polling request parameter specifies
the interval and count of the polling as well as optional polling completion callback function
and its associated user parameter.
4.6 Control APIs
To control the door lock operation mode, there are APIs to set door lock operation mode as
follow:
/**
zwif_dlck_op_set - set door lock operation
@param[in] ifd interface
@param[in] mode operation mode (ZW_DOOR_XXX).
@param[in] cb Optional post-set polling callback function. NULL if no callback
required.
@param[in] usr_param Optional user-defined parameter passed in callback.
@return ZW_ERR_XXX
*/
int zwif_dlck_op_set(zwifd_p ifd, uint8_t mode, zw_postset_fn cb, void *usr_param);
/**
zwif_dlck_op_mset - set door lock operation using multicast addressing if available
@param[in] ifd array of interfaces
@param[in] ifd_cnt number of interfaces in "ifd" array. If value is 1, it is equivalent to
calling
zwif_dlck_op_set() with cb=NULL and usr_param=NULL
@param[in] mode operation mode (ZW_DOOR_XXX).
@return ZW_ERR_XXX
*/
int zwif_dlck_op_mset(zwifd_p *ifd, uint8_t ifd_cnt, uint8_t mode);
4.6.1 zwif_dlck_op_set
To implement this function, entry must be added to the post-set polling sub-system, but no
entry is required to be added to the Supervision Get sub-system. Details will be explained in
section “Post-set Polling Implementation”.
The function checks the parameter “mode” value for a valid operation mode. If the check fails,
it returns error code ZW_ERR_VALUE and exits. The first attempt of sending the “door lock
operation set” command is through supervision_get encapsulation. If successful, it returns
ZW_ERR_SEND_PENDING. On the other hand, if it is unsuccessful because the node does not
support supervision CC or some other error, the normal sending of the command will be
attempted, and post-set polling will be invoked after the command is sent successfully.
Page 31

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 25 of 47
4.6.2 zwif_dlck_op_mset
The implementation supports multi-cast “door lock operation set” commands to multiple
node/endpoints. This enables simultaneous locking or unlocking of door locks. Note that multicast operation does not provide post-set polling as this will flood the Z-wave network with
multiple GET and REPORT commands.
4.7 Configuration APIs
To configure the door lock, there are APIs to set and retrieve door lock configuration as follow:
/**
zwif_dlck_cfg_set - Set the configuration of the door lock device
@param[in] ifd interface
@param[in] config configuration
@return ZW_ERR_XXX
*/
int zwif_dlck_cfg_set(zwifd_p ifd, zwdlck_cfg_p config);
/**
zwif_dlck_cfg_get - get configuration parameter through report callback
@param[in] ifd interface
@param[in] cb report callback function
@param[in] flag flag, see ZWIF_GET_BMSK_XXX
@return 0 on success, else ZW_ERR_XXX
*/
int zwif_dlck_cfg_get(zwifd_p ifd, zwrep_dlck_cfg_fn cb, int flag);
4.7.1 zwif_dlck_cfg_set
To implement this function, no special entry needs to be added.
The function checks the parameter “config” value for valid configuration data. If the check fails,
it returns error code ZW_ERR_VALUE and exits; else it will prepare and send the
DOOR_LOCK_CONFIGURATION_SET command.
4.7.2 zwif_dlck_cfg_get
To implement this function, an entry must be added to the dynamic data cache callback
function zwnet_dat_cached_cb_rpt. The entry COMMAND_CLASS_DOOR_LOCK must handle
the cached report callback request identified by DOOR_LOCK_CONFIGURATION_REPORT.
The function associates the report callback function to the report handler for
DOOR_LOCK_CONFIGURATION_REPORT in the interface. It then checks the parameter “flag”
passed in by the caller. If the bitmask ZWIF_GET_BMSK_CACHE is set, it tries to retrieve the
door lock configuration cache and invokes caller provided callback function in another thread
regardless of whether or not the cache is available. Subsequently, it will check if the bitmask
ZWIF_GET_BMSK_LIVE is set. If set, it will query for the door lock configuration directly from
the device through Z-wave. In summary, with this API, the caller has the flexibility to get the
door lock configuration either from cache or directly from the device or both.
Page 32

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 26 of 47
4.8 Caching Implementation
There are two type of cache associated to an interface. One is the dynamic cache which caches
dynamic data (i.e., the data changes throughout the life cycle of the node) and the other is the
static cache which caches static data. In the case of the door lock interface, the door lock
operating mode and configuration are examples of dynamic cache, whereas the door lock
capability is an example of static cache.
The dynamic cache is stored in memory space pointed to by the member “cch_data” of
internal used interface structure “struct _zwif”, whereas the static cache is stored in memory
space pointed to by the member “data” of “struct _zwif”.
4.8.1 Door Lock Operating Mode Cache
Caching is implemented in the Door Lock report handler zwif_doorlck_hdlr for
DOOR_LOCK_OPERATION_REPORT. The implementation first checks if the interface’s cache
data “cch_data” is NULL. If so, this indicates there is no cache and therefore it allocates
memory which is big enough to store the cache data structure “if_dlck_cch_data_t” and time
stamp structure “time_t” together. The storage order for the allotted memory is the time
stamp structure first, followed by the cache data structure. Subsequently, if the cache data
“cch_data” is valid, it will update the cache’s time stamp and retrieve the cached data and
state number. Comparison between the cached data “op” member and the content of the
received report is carried out. If they are the same, no cache update is necessary except for the
time stamp which has already been updated as mentioned earlier. If they are different, and the
current door lock mode is also different from the cache, the state number is incremented by
one. Regardless whether the door lock mode is different or not, the new report content is
updated to the cache.
4.8.2 Door Lock Configuration Cache
Caching is implemented in the Door Lock report handler zwif_doorlck_hdlr for
DOOR_LOCK_CONFIGURATION_REPORT. The implementation first checks if the interface’s
cache data “cch_data” is NULL. If so, this indicates there is no cache and therefore it allocates
memory which is big enough to store the cache data structure “if_dlck_cch_data_t” and time
stamp structure “time_t” together. The storage order for the allotted memory is the time
stamp structure first, followed by the cache data structure. Subsequently, if the cache data
“cch_data” is valid, it will update the cache’s time stamp (member “cfg_ts” of the cached data
structure “if_dlck_cch_data_t”) and retrieve the cached data and state number. Comparison
between the cached data “cfg” member and the content of the received report is carried out. If
they are the same, no cache update is necessary except for the time stamp which has already
been updated as mentioned earlier. If they are different, the state number is incremented by
one and the new report content is updated to the cache.
4.8.3 Door Lock Capability Cache
Caching is implemented in the Door Lock report handler zwif_doorlck_hdlr for
DOOR_LOCK_CAPABILITIES_REPORT. The implementation first checks if the interface’s cache
data “data” is valid. If so, it will free the memory for the cache. This is to ensure that the cache
memory is reallocated later to fit the size of the report. Although door lock capability is static
Page 33

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 27 of 47
through out the life cycle of the node, there is a possibility of capability change after a
firmware update; therefore, it is wise to discard the old cache and recreate a new cache when
a report is received. The next step is to allocate memory which is big enough to store the cache
data structure “zwdlck_data_t”, number of supported operation types, and supported door
lock modes together. If the cache data “data” is valid, the new report content is updated to the
cache.
4.9 Post-Set Polling Implementation
Post-set polling is a feature to poll the device after a SET command has been sent to it in order
to ensure the SET command has been received and executed by the device. The polling is
desirable for actuator devices, like door lock, when the SET command will take a while for the
device to reach its target value due to mechanical movement. The polling can be done using
either Supervision_get encapsulation command or manual report_get commands.
4.9.1 Supervision Get
To implement this function, no entry is required to be added to the Supervision Get subsystem.
The use of this method requires the node supports Supervision CC. The implementation must
first prepare the SET command, which in the “door lock operation mode set” case is a 3-byte
buffer consisting of: [COMMAND_CLASS_DOOR_LOCK, DOOR_LOCK_OPERATION_SET, mode].
It must also prepare the 2-byte GET command buffer (which consists of
[COMMAND_CLASS_DOOR_LOCK, DOOR_LOCK_OPERATION_GET]) for retrieving the report
once the target value is hit in the device. It is necessary to get the report after the target value
is hit because the DOOR_LOCK_OPERATION_REPORT contains other info such as “outside door
handles mode” and “inside door handles mode” which cannot be known by Z-ware library if
simulated report were to be used as a means to update the user application through report
callback. The internal API zwif_supervision_get will then be invoked with the parameters of the
SET and GET buffers as well as the post-set polling completion callback and its associated user
parameter. The API checks the input parameters and whether the node supports Supervision
CC. If the node supports it, the input parameters will be submitted to the Supervision subsystem to encapsulate the SET command into Supervision_get command and waiting for the
supervision report. If the supervision report indicates status of success (0xFF), the sub-system
will send the GET command to retrieve the latest door lock operation mode. If completion
callback function is valid, the callback will also be invoked with the associated user parameter.
4.9.2 Manual Report Get
To implement this function, entry must be added to the post-set polling sub-system report
handler zwspoll_on_rpt_rcv to parse and extract useful information such as current value and
expected duration to hit target value. The entry must also be added to report checker
zwspoll_rpt_rcv_chk in which the report value extracted by function zwspoll_on_rpt_rcv is
checked against the target value of the SET command to determine whether the target set
value has been hit.
Page 34

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 28 of 47
This method serves as a fallback method from Supervision Get method. The internal API
zwif_post_set_poll is invoked with the parameters such as interface descriptor, target door
lock mode, GET command (DOOR_LOCK_OPERATION_GET) as well as the post-set polling
completion callback and its associated user parameter. The API checks the input parameters
and whether the node is a non-listening sleeping node. If the node is a non-listening sleeping
node, the processing ends with a callback with reason ZWPSET_REASON_UNSUPPORTED. For
listening node, it prepares the 2-byte GET command buffer (which consists
[COMMAND_CLASS_DOOR_LOCK, DOOR_LOCK_OPERATION_GET]) and then submits it
together with the input parameters to the Post-set Polling sub-system. For door lock, the
number of polling is 3 times with interval of 1, 2 and 3 seconds in between the pollings. If the
door lock operation report matches the target mode, polling will stop and completion callback
will be invoked with the associated user parameter and with reason
ZWPSET_REASON_TGT_HIT. If the polling has completed but the target mode had not been hit,
completion callback will be invoked with the associated user parameter and with reason
ZWPSET_REASON_TIMEOUT.
4.10 Adjunct Notification CC Handling
For complete implementation of Door Lock CC, user application needs to handle adjunct
notification (a.k.a. alarm) CC of “access control” notification type if the node supports it.
4.10.1 Monitor APIs
The zwif_alrm_rpt_set API can be used to install a callback function to the notification
interface. This is the only API needed to receive door lock events for push mode
implementation of notification CC. The other two APIs, namely zwif_alrm_get and
zwif_alrm_get_poll, can be used by both push mode and pull mode implementations of
notification CC.
The implementation of these monitor APIs is similar to those for door lock; therefore, the
implementation details will not be repeated here.
4.11 Device Database Upgrade for Door Lock CC version 3 and below
To implement this functionality, entry must be added to device database’s
cmd_cls_rec_type_tbl. The entry is {COMMAND_CLASS_DOOR_LOCK,
IF_REC_TYPE_DOOR_LOCK} which associates Door Lock command class to the device database
interface record type IF_REC_TYPE_DOOR_LOCK. An entry of device database interface parser
for door lock (zwdev_dlck_if_parser) must be added to the array if_parser in function
zwdev_cfg_if_ld. Note that the order of the entry must follow that of the IF_REC_TYPE_XXX.
The Door Lock Capability information is only available to devices which implement Door Lock
CC version 4 and above. To provide better user experience, device database allows the
capability information for lower version device to be made available to a user. The
implementation of device database is to first load the JSON format device database after the
node’s manufacturer id, product type id and product id are available either through
Page 35

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 29 of 47
interviewing the device after inclusion or retrieving from the network persistent storage.
Whenever Door Lock Capability information is required by the user application by invoking the
Capability APIs, namely zwif_dlck_cap_get and zwif_dlck_cap_cache_get, for device which
implements Door Lock CC version 1 to 3, it will check whether the node contains device
database info as indicated by the member “dev_cfg_valid” of internal node structure “struct
_zwnode”. If the device database info is available for the node, it will try to get the door lock
entry from the device database. If found, then the info will be returned to the caller; otherwise
error code ZW_ERR_CMD_VERSION will be returned.
Page 36

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 30 of 47
5 Sample Applications
The sample applications are meant for showcasing how to use the Z-Ware Library to build basic
functions of a controller, like discovery of a ZIPGW, adding node to network, removing a node
from the network, updating a node in network, updating the network, checking the network’s
health, etc.
5.1 Getting Started
5.1.1 Prerequisites
Hardware requirement for running the sample applications:
1 or more ZIPGWs
1 or more Z-Wave static bridge controllers
1 LED dimmer slave module from the Z-Wave development kit
1 Z-Wave compliant binary switch
1 Z-Wave compliant binary sensor
1 Z-Wave compliant door lock
1 Z-Wave compliant Notification/Alarm device
5.1.2 Building of Sample Applications
The first step to build the sample applications is to build the Z-Ware Library. See 6 Runtime and
Build for building the library. To build the sample applications, simply go to the sub-directory
“demos” and run:
make TARGET_PLATFORM=LINUX_ZIP2 [DEBUG=1] [SHARED=1] #To build target
binaries for Ubuntu Linux
make TARGET_PLATFORM=RASPBERRY_ZIP2 [DEBUG=1] [SHARED=1] #To build target
binaries for RPi3B
Note: Arguments in [ ] are optional. Default build options are release and static application
5.1.3 Installation of Sample Applications
To install binaries and configuration files to "install" sub-directory:
make install_all
To install binaries only to "install" sub-directory, as maybe in the case when a developer
modifies the sample application source code and does not want the configuraration files to be
overwritten by default configuration files:
make install_bin
5.1.4 Configuration
All the sample applications except “gateway discovery” sample application require a
configuration file with the name “app.cfg” to be placed in the same directory as the sample
application. For the controller_app the configuration file name is “controller_app.cfg”. The
configuration file has the following entries:
Table 21. Configuration file entries
Page 37

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 31 of 47
Entry
Name
Description
ZipLanPort
The host (where the sample application resides) listening and sending port. To
allow the OS to select the port, enter port number 0
ZipRouterIp
For sample application:
The ZIPGW IPv4 or IPv6 address.
For the controller_app:
The ZIPGW IPv4 or IPv6 address.
All-zeroes address (0.0.0.0 for IPv4 and :: for IPv6) means get the ZIPGW IP
address through Z/IP Gateway Discovery.
DTLSPSK
DTLS pre-shared key (PSK) in hexadecimal string with maximum string length
of 64 (i.e. 32 hexadecimal bytes).
An example of the configuration file:
# Host listening and sending port
# For system assigned port, enter port number 0.
ZipLanPort = 4123
# Z/IP router IPv4 or IPv6 address
ZipRouterIP = 10.40.12.67
# DTLS pre-shared key (PSK) in hexadecimal string with maximum
string
# length of 64 (i.e. 32 hexadecimal bytes).
# Note: string length must be multiple of 2 and must be at least 32. If
this
# field is empty, no DTLS will be used
# Example of PSK with string length of 10 : 03A1B2C3FF
DTLSPSK = 123456789012345678901234567890AA
#Configure local host IPv6 address
ifconfig eth0 inet6 add 2000::5/64
#Set up a default route to Z/IP PAN network
route -A inet6 add default gw 2000::3 dev eth0
If IPv6 is used in the sample applications, the host machine may require manual configuration
for an IPv6 address and setting up a route to the Z/IP PAN network. The following is an
example of the configuration commands in Linux:
Since the Z/IP gateway supports IPv6 Router Advertisement and modern Linux system is
capable of making use of the router advertisement broadcast message for IPv6 autoconfiguration and routing, the above-mentioned manual configuration is not required in most
of the use cases.
Page 38

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 32 of 47
5.2 Running Sample Applications
Scanning for Z/IP gateway ...
Press <enter> to exit.
IPv4 Address: 10.40.13.120
Join ok. sending IP:10.40.13.120
mcast IP:224.0.0.251
Received from host IP:10.40.12.84, port:5353
Received from host IP:10.40.12.84, port:5353
Received from host IP:10.40.12.84, port:5353
service:Static Controller [a2bd1fc40100]._Z-Wave._udp.local,
host:zwA2BD1FC401.local, IP:10.40.12.84
Gw discovery received 1 responses
Received report:1/1 with gw count:1
---Gateways found--(0) 10.40.12.84 [Static Controller
[a2bd1fc40100]._Z-Wave._udp.local]
Initialize network in progress, please wait for status ...
Press ENTER key to reset network
Initialization status:0
Reset network in progress, please wait for status ...
Press ENTER key to exit program
Reset status:0
5.2.1 ZIPGW Discovery
The sample application is used to discover ZIPGW IPv4/IPv6 address using mDNS protocol. To
run it, type “./gw_discovery <ip_option>” where ip_option -4 for using IPv4; -6 for using IPv6;
default to IPv6 without option given. You should see an output similar to the following lines
displayed if a gateway is discovered.
5.2.2 Reset Z/IP Network
The sample application is used to reset Z/IP network, i.e., to remove all nodes and create a new
network. Edit the “app.cfg” file to ensure the correct ZIPGW to reset. To run it, type
“./nw_reset”. You should see an output similar to the following lines displayed if the ZIPGW
was found and initialized.
Press the <ENTER> key to reset the network. You should see an output similar to the following
lines displayed if the network was reset successfully.
Page 39

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 33 of 47
5.2.3 Add Node into a Network
Initialize network in progress, please wait for status ...
Initialization status:0
(1) Add node
(x) Exit
Select your choice:
Device requested keys bit-mask 0x82:
Key (bit-mask in hex) :
Security 2 key 0 (01)
Security 2 key 1 (02)
Security 2 key 2 (04)
Security 0 (80)
Grant keys bit-mask (hex):
Add node in progress, please wait for status ...
(1) Abort add node operation
(x) Exit
Select your choice:
Node:2 added
Add node status:1
Add node status:2
Get node info 1/1 completed
Add node status:0
The sample application is used to add a node into network. Edit the “app.cfg” file to ensure the
correct ZIPGW to use. To run it, type “./add_node”. You should see an output similar to the
following lines displayed if the ZIPGW was found and initialized.
5.2.3.1 ZIPGW that Supports Security 2 (S2)
For ZIPGW that supports Security 2 (S2), press 1 and <ENTER> key to start adding node
operation. The prompt to pre-enter Device Specific key (DSK) will be displayed. If the LED
dimmer slave module supports S2, press “y” and enter the DSK; else press “n”. For S2 LED
dimmer, there will be a prompt as follows for entering security keys to grant to the LED
dimmer. In general, you should grant the device requested keys bit-mask if you wish to add the
device securely into your network.
5.2.3.2 ZIPGW that Does not Support Security 2 (S2)
Press 1 and <ENTER> key to start adding node operation. Place the LED dimmer slave module
into learn mode by pressing the button 3 times rapidly. You should see an output similar to the
following lines displayed if the slave node was added successfully.
Page 40

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 34 of 47
5.2.4 Remove Node from a Network
Initialize network in progress, please wait for status ...
(1) Remove node
(2) Abort remove node operation
(3) Exit
Select your choice:
Initialization status:0
Remove node in progress, please wait for status ...
(1) Remove node
(2) Abort remove node operation
(3) Exit
Select your choice:
Node:2 removed
Remove node status:0
Initialize network in progress, please wait for status ...
(1) Turn switch on
(2) Turn switch off
(3) Exit
Select your choice:
Initialization status:0
network ID:C3E2F8C1, Z/IP controller ID:1
Load node details in progress, please wait for status ...
Get node info 1/1 completed
Load network detail operation status:0
The sample application is used to remove a node from network. Edit the “app.cfg” file to
ensure the correct ZIPGW to use. To run it, type “./rm_node”. You should see an output similar
to the following lines displayed if the ZIPGW was found and initialized.
Press 1 and <ENTER> key to start removing node operation. At anytime, you may cancel the
operation by pressing 2 and <ENTER> key. Place the previously added LED dimmer slave
module into learn mode by pressing the button 3 times rapidly. You should see an output
similar to the following lines displayed if the slave node was removed successfully.
5.2.5 Binary Switch
The sample application is used to turn a binary switch on and off. Edit the “app.cfg” file to
ensure the correct ZIPGW to use. Use the “add_node” sample application to add a binary
switch into the network. To run the binary switch control sample application, type
“./bin_switch”. You should see an output similar to the following lines displayed if the ZIPGW
was found and initialized.
Page 41

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 35 of 47
Press 1 and <ENTER> key to turn the binary switch on. Press 2 and <ENTER> key to turn the
A controlling node MUST NOT use the Basic Command Class for controlling a node
(or endpoint) if the controlling node controls at least one actuator command class
supported by a node (or endpoint). The actuator command classes are defined in
the Application Command Class specification ([2])
Initialize network in progress, please wait for status ...
(1) Set basic value (0 ~ 255):
(2) Exit
Select your choice:
Initialization status:0
network ID:C3E2F8C1, Z/IP controller ID:1
Load node details in progress, please wait for status ...
Get node info 1/2 completed
Get node info 2/2 completed
Load network detail operation status:0
binary switch off.
5.2.6 Basic
This sample application is deprecated due to the BASIC interface is hidden in the latest Z-ware
library and hence uncontrollable by application. This is in compliant to the following clause in
[8]:
The sample application is used to control a slave device using generic Basic CC. Edit the
“app.cfg” file to ensure the correct ZIPGW to use. Use the “add_node” sample application to
add a LED dimmer slave module into the network. To run the basic control sample application,
type “./basic”. You should see an output similar to the following lines displayed if the ZIPGW
was found and initialized.
Press 1 and <ENTER> key to control the LED dimmer level. Enter the desired level (0 to 255)
and <ENTER> key to send the command to the LED dimmer.
5.2.7 Binary Sensor
The sample application is used to demonstrate the setting up of unsolicited address and port to
the ZIPGW in order to receive unsolicited sensor report. Edit the “app.cfg” file to ensure the
correct ZIPGW to use. Use the “add_node” sample application to add a binary sensor into the
network. To run the binary sensor sample application, type “./bin_sensor”. Please note that it
is important to run the binary sensor sample application in the same directory as the
“add_node” sample application in order for the binary sensor sample application to access the
post-inclusion interviewing cached data stored by the “add_node” application. You should see
an output similar to the following lines displayed if the ZIPGW was found and initialized.
Page 42

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 36 of 47
Initialize network in progress, please wait for status ...
Initialization status:0
network ID:FDB217B2, Z/IP controller ID:1
Network initialized! Setting up unsolicited address, please wait ...
(1) Setup binary sensor report
(2) Get supported binary sensor types
(3) Get live binary sensor report
(4) Get cache binary sensor report
(x) Exit
Select your choice:
Press 1 and <ENTER> key to setup callback function to receive binary sensor report.
Scanning for Z/IP gateway ...
(x) Exit program
IPv4 Address: 192.168.0.121
Join ok. sending IP:192.168.0.121
mcast IP:224.0.0.251
Rcv from host IP:192.168.0.101
Your choice:
Gw discovery received 1 responses
Received report:1/1 with gw count:1
---Select Gateway IP address--(0) 192.168.0.101 [Static Controller [d6ee06040100]._zwave._udp.local]
(x) Exit
Your choice:
Press 2 and <ENTER> key to get supported binary sensor types from the cache.
Press 3 and <ENTER> key to get live binary sensor report. If the device is a sleeping device, the
command is queued until the device is awake.
Press 4 and <ENTER> key to get cached binary sensor report.
5.2.8 Controller App
The controller app combines add/remove node, binary switch/sensor, ZIPGW discovery and
reset network sample apps into a single controller application. It also demonstrates update
node, update network, network health check, door lock, notification and SmartStart. Edit the
“controller_app.cfg” file to ensure the correct ZIPGW to use. It is recommended to use the allzeroes address for the entry “ZipRouterIP” in the configuration file in order to enable Z/IP
gateway discovery. To run it, type “./controller_app”. You should see an output like the
following lines displayed if a ZIPGW was found.
Page 43

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 37 of 47
Press (0) and <ENTER> key to select the sole ZIPGW found. You should see an output like the
Initialize network in progress, please wait for status ...
(1) Manage network
(2) Binary switch
(3) Binary sensor
(4) Door lock
(5) Notification (Alarm)
(d) Display network information
(r) Reload menu
(x) Exit program
Your choice:
Initialization status:0
Network id:D6EE0604, Z/IP controller id:1
Network initialized! Setting up unsolicited address ...
Done.
(1) Cancel current operation
(2) Add node
(3) Remove node
(4) Network update
(5) Node update
(6) Reset network
----------------------------------------------------------------(7) Add a provisioning list entry
(8) Get a provisioning list entry info
(9) Remove a provisioning list entry
(10) Get all provisioning list entries
(11) Remove all provisioning list entries
-----------------------------------------------------------------
following lines displayed if the controller app succeeded in connecting to the ZIPGW and
initialized itself which includes setting up ZIPGW unsolicited destination address as the app
listening address and port. This enable any unsolicited reports from ZIPGW and nodes be
forwarded to the app for processing.
5.2.8.1 Manage Network Menu
Press (1) and <ENTER> key to select the Manage Network menu. The menu as shown below
will be displayed. Items (1), (2), (3) and (6) are described in previous sections. The (d) Display
Network Information is new and it presents the network information to user. The example
below is the network information of a controller without any added node. Take note that the
interface marked with (^) is unsecured whereas the interface marked with (*) is secured. The
interface entry is denoted by its corresponding command class number in hexadecimal number
followed by its version. For example, 8Ah v1 means the “Time” command class is represented
by the hexadecimal number 8A and it is implemented according to “Time” command class
version 1 specification. For node that has no multi-endpoint, the interfaces are attached to
endpoint 0 which corresponds to the root device of the node.
Page 44

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 38 of 47
(12) Start network health check
----------------------------------------------------------------(d) Display network information
(x) Exit menu
Your choice:
Network Information
Network id:D6EE0604, controller node id:1
___________________________________________________
Node id:1
Node security 2 granted keys bitmask: 87h
S2 Unauthenticated,
S2 Authenticated,
S2 Access Control,
S0 Unauthenticated,
Node is capable to identify itself
Node is security S0 capable
Node is security S2 capable
Node was added securely to the Z-wave network
Vendor id:0000h
Product type id:0001h
Product id:0001h
Z-wave library type:7
Z-wave protocol version:7.11
Application version:7.11
Endpoint id:0
Device class: generic:02h, specific:07h
Endpoint name:
Endpoint location:
Interface: 8Ah v1:COMMAND_CLASS_TIME ^
Interface: 5Fh v1:COMMAND_CLASS_ZIP_GATEWAY *
Interface: 7Ah
v5:COMMAND_CLASS_FIRMWARE_UPDATE_MD *
Interface: 61h v1:COMMAND_CLASS_ZIP_PORTAL *
Your choice:4
Network update in progress, please wait for status ...
Network update status:1
Network update status:2
Network update status:3
5.2.8.1.1 Update a Network
Press 4 and <ENTER> key to start network update operation. At anytime, you may cancel the
operation by pressing 1 and <ENTER> key. You should see an output similar to the following
lines displayed if the network was updated successfully.
Page 45

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 39 of 47
Get node info 1/1 completed
Network update status:0
5.2.8.1.2 Update Node in a Network
Your choice:5
Node id:16
Node update in progress, please wait for status ...
Get node info 1/1 completed
Node update status:0
Your choice:7
DSK:08337-30732-53363-34149-12388-19368-50935-56233
Enter device name (y/n)?:n
Enter device location (y/n)?:n
Enter product type (y/n)?:n
Enter product id (y/n)?:n
Enter Smart Start inclusion request interval (y/n)?:n
Enter UUID (y/n)?:n
Enter inclusion status (y/n)?:n
Enter S2 grant keys (y/n)?:n
Boot mode (y/n)?:n
Node <testing only> (y/n)?:n
Your choice:8
DSK:08337-30732-53363-34149-12388-19368-50935-56233
Device DSK:08337-30732-53363-34149-12388-19368-50935-56233
Boot mode:1 where 0=S2; 1=Smart Start
Inclusion status:0 where 0=pending; 2=passive; 3=ignored
Node id:0
Network status:0 where 0=not included; 1=included; 2=failed
--------------------------------------------------------------
Press 5 and <ENTER> key to start node update operation. Enter node id of the slave node being
updated. At anytime, you may cancel the operation by pressing 1 and <ENTER> key. You should
see an output similar to the following lines displayed if the slave node was updated
successfully.
5.2.8.1.3 Add a Provisioning List Entry (SmartStart)
Press 7 and <ENTER> key to add an entry to provisioning list. Enter DSK of the device and enter
'n' (or valid values) for rest of the prompts.
5.2.8.1.4 Get a Provisioning List Entry Info (SmartStart)
Press 8 and <ENTER> key to get an entry from provisioning list. Enter DSK of the device entry to
be fetched.
Page 46

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 40 of 47
5.2.8.1.5 Remove a Provisioning List Entry (SmartStart)
Your choice:9
DSK:08337-30732-53363-34149-12388-19368-50935-56233
Your choice:7
DSK:08337-30732-53363-34149-12388-19368-50935-56233
…
Your choice:10
===============================================
============== Provisioning list ==============
===============================================
Device DSK:08337-30732-53363-34149-12388-19368-50935-56233
Boot mode:1 where 0=S2; 1=Smart Start
Inclusion status:0 where 0=pending; 2=passive; 3=ignored
Node id:0
Network status:0 where 0=not included; 1=included; 2=failed
-------------------------------------------------------------…
Your choice:11
Your choice:10
The provisioning list is empty
Your choice:12
Network health check in progress, please wait for status ...
Network health check status:1
Network health check status:2
Network health check 1/1 completed
Press 9 and <ENTER> key to remove an entry from provisioning list. Enter DSK of the device
entry to be removed.
5.2.8.1.6 Get all Provisioning List Entries (SmartStart)
Press 7 and <ENTER> key to add an entry to the provisioning list. Repeat this with different
DSKs.
Then Press 10 and <ENTER> key to get all entries from provisioning list.
5.2.8.1.7 Remove all Provisioning List Entries (SmartStart)
Press 11 and <ENTER> key to remove all entries from provisioning list.
Then Press 10 and <ENTER> key to get all entries from provisioning list. The list shall be empty.
5.2.8.1.8 Check health of a Network
Press 12 and <ENTER> key to start network health check operation. At anytime, you may cancel
the operation by pressing 1 and <ENTER> key. You should see an output similar to the
following lines displayed if the network health check was completed successfully.
Page 47

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 41 of 47
Network health check status:3
Network health check report (1 nodes):
Node id: 6, NHV: 6, Category:0
Network health check status:0
5.2.8.2 Binary Switch Menu
(1) Select the binary switch to control
(2) Turn on switch
(3) Turn off switch
(d) Display network information
(x) Exit menu
Your choice:
(1) Select the binary sensor to control
(2) Get supported binary sensor types
(3) Get live binary sensor report
(4) Get cache binary sensor report
(d) Display network information
(x) Exit menu
Your choice:
(1) Select the door lock to control
(2) Lock door lock
(3) Unlock door lock
(d) Display network information
(x) Exit menu
Your choice:
Press (2) and <ENTER> key to select the Binary Switch menu. The menu as shown below will be
displayed. Before a user can control a binary switch, it must select the binary switch to control
using item (1). The user will be prompted for the node id and endpoint id where the binary
switch interface is located. Use item (d) to display network information in order to know which
binary switch interface to control. The items (2) to (3) are described in previous sections.
5.2.8.3 Binary Sensor Menu
Press (3) and <ENTER> key to select the Binary Sensor menu. The menu as shown below will be
displayed. Before a user can control a binary sensor, it must select the binary sensor to control
using item (1). The user will be prompted for the node id and endpoint id where the binary
sensor interface is located. Use item (d) to display network information in order to know which
binary sensor interface to control. The items (2) to (4) are described in previous sections.
5.2.8.4 Door Lock Menu
Press (4) and <ENTER> key to select the Door Lock menu. The menu as shown below will be
displayed. Before a user can control a door lock, it must select the door lock to control using
item (1). The user will be prompted for the node id and endpoint id where the door lock
interface is located. Use item (d) to display network information in order to know which door
lock interface to control.
Page 48

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 42 of 47
Press 2 and <ENTER> key to lock the door lock.
(1) Select the notification device to control
(2) Get supported vendor specific alarm types
(3) Get supported Z-Wave alarm types
(4) Get supported Z-Wave alarm events
(5) Get live notification report
(6) Get cache notification report
(7) Set alarm activity
(d) Display network information
(x) Exit menu
Your choice:
Press 3 and <ENTER> key to unlock the door lock.
5.2.8.5 Notification (Alarm) Menu
Press (5) and <ENTER> key to select the Notification (Alarm) menu. The menu as shown below
will be displayed. Before a user can control a notification/alarm device, it must select the
device to control using item (1). The user will be prompted for the node id and endpoint id
where the notification interface is located. Use item (d) to display network information in order
to know which notification interface to control.
Press 2 and <ENTER> key to get supported vendor specific alarm types.
Press 3 and <ENTER> key to get supported Z-Wave alarm types.
Press 4 and <ENTER> key to get supported Z-Wave alarm events.
Press 5 and <ENTER> key to get live alarm report. If the device is a sleeping device, the
command is queued until the device is awake.
Press 6 and <ENTER> key to get cached alarm report.
Press 7 and <ENTER> key to set the state of a Z-Wave alarm type (push mode) or clear a
persistent notification (pull mode).
Page 49

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 43 of 47
6 Runtime and Build
Type
Size
Usage
Flash
3MB
Storage of executable binary
RAM
2.3MB
Run time requirement
Type
Size
Usage
Disk/Flash
900B
Storage of node specific data
RAM
50KB
Run-time data storage requirement
Type
Size
Usage
RAM
480KB
Run-time requirement
Directory
Description
include/
Header sources. Including zip_api.h will include the rest.
lib/
Source files for low level transport, Z/IP packetization/depacketization, utilities,
multi-platform support, etc.
src/
Source files for network management state-machines, Z-Wave CC interfaces,
device database, configuration and polling system support.
demos/
Sample application source files.
doc/
Configuration files used by Doxygen for auto source code documentation
generation.
config/
Sample configuration files:
sample_device_rec_with_comment.txt – Sample device specific configurations
file (a.k.a device database) with c-style comments.
sample_device_rec.txt – Sample device database with c-style comments
removed using the utility program “RmComment.exe”.
RmComment.exe – Utility program to remove c-style comments.
zwave_device_rec.txt – Sample device database based on real devices. This file
can be used as parameter for “dev_cfg_file” in zwnet_init_t structure when
calling zwnet_init API.
device_rec_constants.txt – Numeric constants needed to edit the device
database
6.1 Runtime System Requirements
The target platform that runs the application which is built on top of the Z-Ware Library must
satisfy the following requirements:
I. Support of IPv4 and IPv6.
II. Minimum memory size based on the intended use case for 32-bit Linux:
Table 22. Base Memory Requirement
Table 23. Per Node Memory Requirement
Table 24. Per Z-Wave Network Memory Requirement
6.2 Source Directory Structure
The following files are distributed:
Table 25. Files
Page 50

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 44 of 47
cmd_class.cfg – Command class configurable file to enable probing of new node
after inclusion and during background polling. This file can be used as parameter
for “cmd_cls_cfg_file” in zwnet_init_t structure when calling zwnet_init API.
external/
Source files of external libraries and the patch files required for the modification
of external libraries to suit the Z-Ware Library use case.
<Install
root
directory>
readme.txt for version history.
INSTALL for instructions to compile the project.
cmdclass_info.txt to document support and control of CCs.
install_openssl_lib.sh to install external library source files.
build_openssl_lib.sh to build external library from source.
External library source files need to be installed before building any of the executables for
Target
platform
Toolchain
Libraries
Ubuntu
Linux
gcc
libpthread
and librt
Raspberry
Pi 3B
(RPi3B)
Platform Image, from:
http://vx2downloads.raspberrypi.org/raspbian_lite/images/raspbian_lite2017-04-10/2017-04-10-raspbian-jessie-lite.zip
Linaro Toolchain Binaries (32-bit), from:
https://releases.linaro.org/components/toolchain/binaries/6.2-
2016.11/arm-linux-gnueabihf/gcc-linaro-6.2.1-2016.11i686_arm-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz
Linaro Toolchain Binaries (64-bit), from:
https://releases.linaro.org/components/toolchain/binaries/6.2-
2016.11/arm-linux-gnueabihf/gcc-linaro-6.2.1-2016.11x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz
libpthread
and librt
target platform. To install external library, run the script file using the command:
source install_openssl_lib.sh
6.1 Build System
The build system must install the necessary toolchain for compiling source code into target
platform executable binaries. The required toolchain and libraries are shown in the following
tables:
Table 26. Build System Requirements
6.2 Build System Setup
6.2.1 Target Platform Ubuntu Linux
The build system should be run on Ubuntu Linux 14.04 LTS or higher version. The operating
system has already pre-installed with the gcc toolchain. No further installation of toolchain is
required.
Page 51

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 45 of 47
6.2.2 Target Platform RPi3B
source build_openssl_lib.sh { raspberry | linux} {debug | release} [shared] #build for RPi3B+
or Ubuntu PC, debug or release, optionally shared openssl library version
make TARGET_PLATFORM={LINUX_ZIP2 | RASPBERRY_ZIP2 } [DEBUG=1] [SHARED=1] #build
for RPi3B+ or Ubuntu PC, optionally debug, optionally shared Z-Ware library
The build system should be run on Ubuntu Linux 14.04 LTS or higher version. The following
steps show the installation of the required toolchain, namely Linaro Toolchain:
1. Download the toolchain binary from
https://releases.linaro.org/components/toolchain/binaries/6.2-2016.11/arm-linuxgnueabihf/gcc-linaro-6.2.1-2016.11-i686_arm-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz (for 32-bit Linux
build system) or
https://releases.linaro.org/components/toolchain/binaries/6.2-2016.11/arm-linuxgnueabihf/gcc-linaro-6.2.1-2016.11-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz (for 64-bit Linux
build system)
2. Uncompress the toolchain using the command: tar xf <download toolchain file in step
1>.tar.xz
3. Edit the file <your home directory>/.bashrc to add the PATH environment into it. For
example, if the toolchain binary was uncompressed to <your home directory>/gcclinaro-arm-linux-gnueabihf, add the following lines to your .bashrc file:
PATH=<your home directory>/gcc-linaro-arm-linux-gnueabihf/bin:$PATH
export PATH
4. Make the PATH environment variable take effect using the command: source ~/.bashrc
6.3 Build Commands
Execute the following commands:
Note: arguments in { } are compulsory; those in [ ] are optional.
6.4 Source Code Documentation
Source code documentation can be generated using Doxygen and Graphviz (for call graph
generation). The Doxygen configuration files (for Doxygen version 1.8.x) and an autogeneration script file are located in the doc/doxygen directory of the install path. There are two
methods to generate the documentation from source codes as follows:
6.4.1 Manual Generation of Documentation
a) Edit the configuration files to change the directory paths according to your installation
path. The variables in configuration files that need to be edited are:
OUTPUT_DIRECTORY, INPUT, PROJECT_NUMBER and DOT_PATH (if call graph is
required, see Doxyfile_call_graph_*.cfg).
Page 52

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 46 of 47
b) The following is a brief description of each of the configuration files:
i. Doxyfile_headers_*.cfg -- The minimal configuration that generate
documentation based on header files only.
ii. Doxyfile_no_graph_*.cfg -- Moderate configuration that generate
documentation based on header and source files.
iii. Doxyfile_call_graph_*.cfg -- Configuration that include call graphs. It may take a
long time to run.
6.4.2 Auto Generation of Documentation in Ubuntu Linux
a) Change the script file "generate_doc.sh" to executable by typing the following
command in a terminal:
chmod +x generate_doc.sh
b) Run the script file:
./generate_doc.sh ce [min | moderate | max]
where: min, moderate and max are the level of depth of documentation
Page 53

INS14606-7 Z-Ware SDK 7.14.x Library User Guide 2020-07-07
silabs.com | Building a more connected world.
Page 47 of 47
References
[1] Silicon Labs, SDS10243, SDS, Z-Wave Protocol Overview
[2] Silicon Labs, INS10244, INS, Z-Wave Node Type Overview and Network Installation Guide
[3] Silicon Labs, SDS10242, SDS, Z-Wave Device Classes
[4] Silicon Labs, SDS13781, SDS, Z-Wave Application Command Class Specification
[5] Silicon Labs, SDS13782, SDS, Z-Wave Management Command Class Specification
[6] Silicon Labs, SDS13783, SDS, Z-Wave Transport-Encapsulation Command Class
Specification
[7] Silicon Labs, SDS13784, SDS, Z-Wave Network-Protocol Command Class Specification
[8] Silicon Labs, SDS14223, SDS, Z-Wave Command Class Control Specification
[9] Silicon Labs, SDS14416, SDS, Z-Ware Library C API Reference Manual
 Loading...
Loading...