Page 1
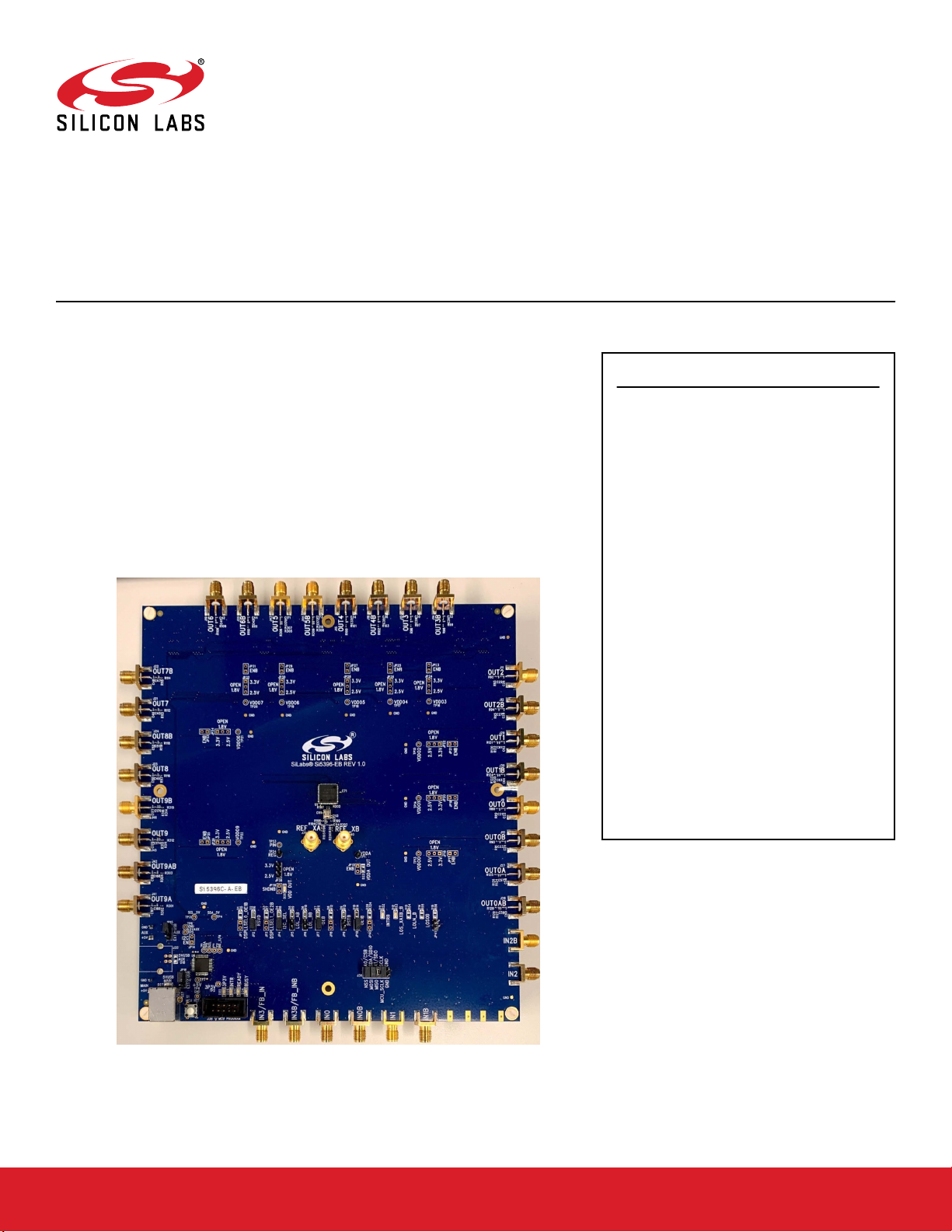
UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board
User's Guide
The Si5396C/L -EVB is used for evaluating the Si5396C/L Any-Frequency, Any-Output, Jitter-Attenuating Clock Multiplier. The Grade C board requires an external reference. The Grade L board does not require a reference because it is internal to the
chip. This user guide is intended for both the Si5396C and Si5396L EVBs. The device
grade and revision is distinguished by a white 1 x 0.187 inch label installed in the lower left corner of the board. In the example below, the label, "SI5396C-A-EB", indicates
the evaluation board has been assembled with an Si5396 device, Grade C, Revision
A, installed. (For ordering purposes only, the terms “EB” and “EVB” refer to the board
and the kit respectively. For the purpose of this document, the terms are synonymous
in context.). Note that the Si5396A/B/J/K are all 4-output, 2 PLL devices in a 44-pin
package, while the Si5396C/D/L/M are 12-output devices in a 64-pin package. This
user guide is for the Si5396C/D/L/M grade 12-output, 2 PLL devices.
KEY FEATURES
• Si5396C-A-EVB for evaluating external
reference versions Si5396C/D
• Si5396L-A-EVB for evaluating internal
reference versions Si5396L/M
• Powered from USB port or external power
supply
•
Onboard 48 MHz XTAL or Reference SMA
Inputs allow holdover mode of operation on
the Si5396C
•
ClockBuilder Pro® (CBPro) GUI
programmable VDD supply allows device to
operate from 3.3 V, 2.5 V, or 1.8 V
• CBPro GUI programmable VDDO supplies
allow each of the outputs to have its own
power supply voltage selectable from 3.3 V,
2.5 V, or 1.8 V
• CBPro GUI-controlled voltage, current, and
power measurements of VDD and all VDDO
supplies
• Status LEDs for power supplies and control/
status signals of Si5396C/L
• SMA connectors for input clocks, output
clocks, and optional external timing reference
clock to be used on external reference
grades only
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0
Page 2

Table of Contents
1. Functional Block Diagram ..........................3
Si5396C/L EVB Support Documentation and ClockBuilder Pro Software .........4
2.
3. Quick Start ................................5
4. Jumper Defaults ..............................6
5. Status LEDs................................7
6. External Reference Input (XA/XB)........................8
7. Clock Input Circuits (INx/INxB) .........................9
8. Clock Output Circuits (OUTx/OUTxB) .....................10
9. Installing ClockBuilder Pro Desktop Software ..................11
10. Using the Si5396C/L EVB .........................12
10.1 Connecting the EVB to Your Host PC ......................12
10.2 Additional Power Supplies .........................13
10.3 Overview of ClockBuilder Pro Applications ....................13
10.4 Common ClockBuilder Pro Workflow Scenarios ..................15
10.5 Workflow Scenario 1: Testing a Silicon Labs Default Configuration ............15
10.5.1 Verify Free-Run Mode Operation ......................18
10.5.2 Verify Locked Mode Operation .......................20
10.6 Workflow Scenario 2: Modifying the Default Silicon Labs-Created Device Configuration .....21
10.7 Workflow Scenario 3: Testing a User-Created Device Configuration ...........23
10.8 Exporting the Register Map File for Device Programming by a Host Processor ........25
11. Writing a New Frequency Plan or Device Configuration to Non-Volatile Memory (OTP) ..26
12. Serial Device Communications .......................27
12.1 Onboard SPI Support ...........................27
12.2 External I2C Support ...........................27
13. Si5396C/L EVB Schematic, Layout, and Bill of Materials (BOM) ...........28
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 2
Page 3
UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
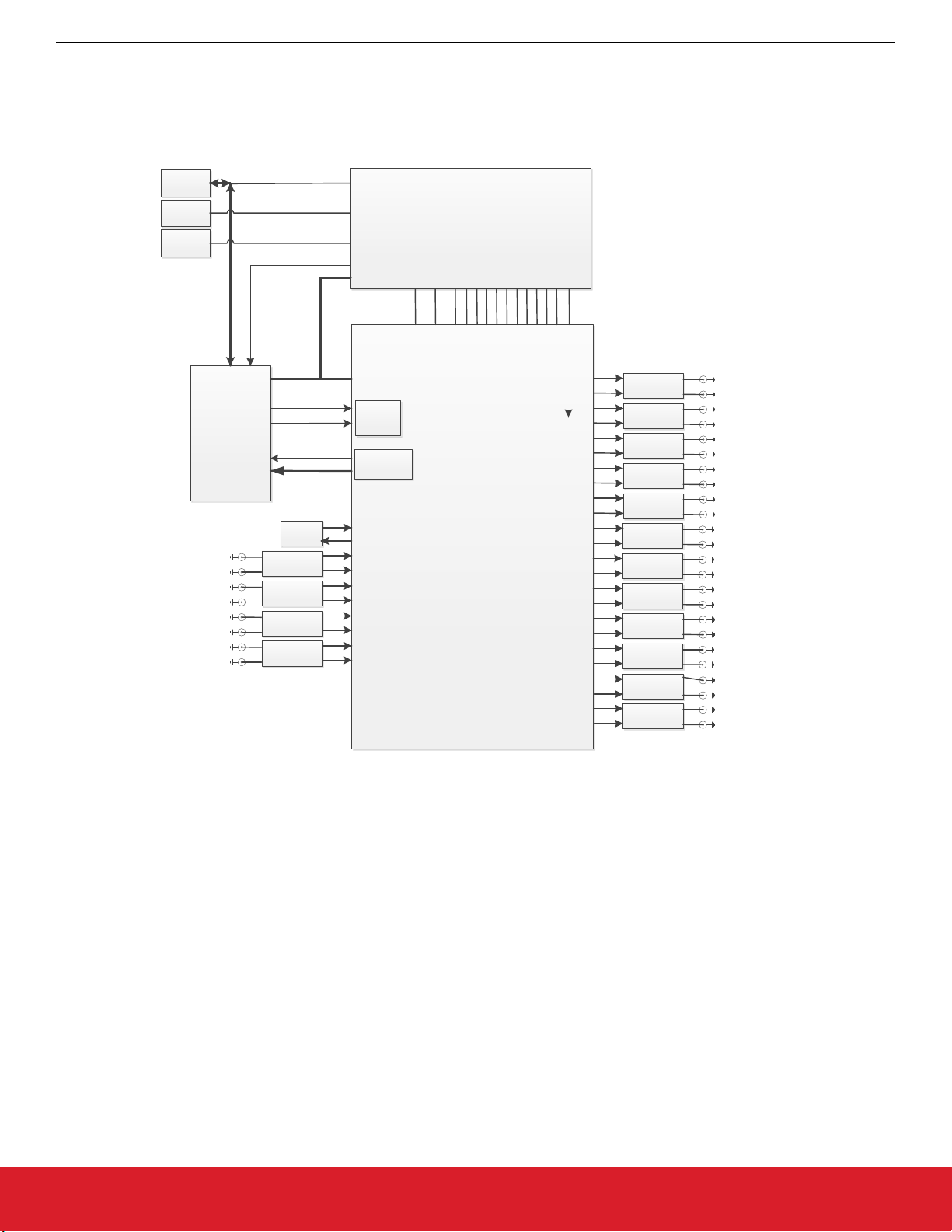
Functional Block Diagram
1. Functional Block Diagram
Below is a functional block diagram of the Si5396C EVB. Keep in mind that the Grade L board does not use an external XTAL or reference and does not use the XA/XB pins. This evaluation board can be connected to a PC via the main USB connector for programming,
control, and monitoring. See 3. Quick Start or 10.3 Overview of ClockBuilder Pro Applications for more information.
Main USB
Connector
Aux USB
Connector
Ext +5V
Connector
Input Clock 0
Input Clock 1
Input Clock 2
Input Clock 3
C8051F380
MCU
+
Peripherals
{
{
{
{
Power only
Power only
48 MHz
XTAL
Input
Termination
Input
Termination
Input
Termination
Input
Termination
+5V_USB
+5V_Aux
+5V_Ext
VDDMCU
I2C/SPI Bus
I2C/SPI Bus
Control/
Status
INTR
Alarm_Status
XA
XB
CLKIN_0
CLKIN_0B
CLKIN_1
CLKIN_1B
CLKIN_2
CLKIN_2B
CLKIN_3/FB_IN
CLKIN_3/FB_INB
Power Supply
VDD_3.3
VDD_3.3
VDDO_0
VDDO_1
VDDO_0
VDDO_1
VDDO_0A VDDO_0A
VDD_Core
VDD_Core
Si5396C
VDDO_2
VDDO_3
VDDO_2
VDDO_3
VDDO_4
VDDO_5
VDDO_4
VDDO_5
VDDO_8
VDDO_6
VDDO_7
VDDO_6
VDDO_7
VDDO_8
CLKOUT_0A
CLKOUT_0AB
CLKOUT_0
CLKOUT_0B
CLKOUT_1
CLKOUT_1B
CLKOUT_2
CLKOUT_2B
CLKOUT_3
CLKOUT_3B
CLKOUT_4
CLKOUT_4B
CLKOUT_5
CLKOUT_5B
CLKOUT_6
CLKOUT_6B
CLKOUT_7
CLKOUT_7B
CLKOUT_8
CLKOUT_8B
CLKOUT_9
CLKOUT_9B
CLKOUT_9A
CLKOUT_9AB
VDDO_9
VDDO_9A
VDDO_9
VDDO_9A
Output
Termination
Output
Termination
Output
Termination
Output
Termination
Output
Termination
Output
Termination
Output
Termination
Output
Termination
Output
Termination
Output
Termination
Output
Termination
Output
Termination
Output Clock 0A
}
Output Clock 0
}
Output Clock 1
}
Output Clock 2
}
Output Clock 3
}
Output Clock 4
}
Output Clock 5
}
Output Clock 6
}
Output Clock 7
}
Output Clock 8
}
Output Clock 9
}
Output Clock 9A
}
Figure 1.1. Si5396C EB Functional Block Diagram
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 3
Page 4

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Si5396C/L EVB Support Documentation and ClockBuilder Pro Software
2. Si5396C/L EVB Support Documentation and ClockBuilder Pro Software
Si5396C/L EVB schematics, BOMs, user’s guides, and software can be found online www.silabs.com/documents/public/schematic-files/
si539x-design-files.zip
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 4
Page 5

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
3. Quick Start
1. Install the ClockBuilder Pro desktop software from http://www.silabs.com/CBPro.
2. Connect a USB cable from Si5396C/L EVB to the PC where the software was installed.
3. Confirm jumpers are installed as shown in Table 4.1 Si5396C/L EVB Jumper Defaults1 on page 6.
4. Launch the ClockBuilder Pro Software.
5. You can use ClockBuilder Pro to create, download, and run a frequency plan on the Si5396C/L EVB.
6. Find Si5396 data sheet: https://www.silabs.com/documents/public/data-sheets/si5397-96-a-datasheet.pdf
Quick Start
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 5
Page 6
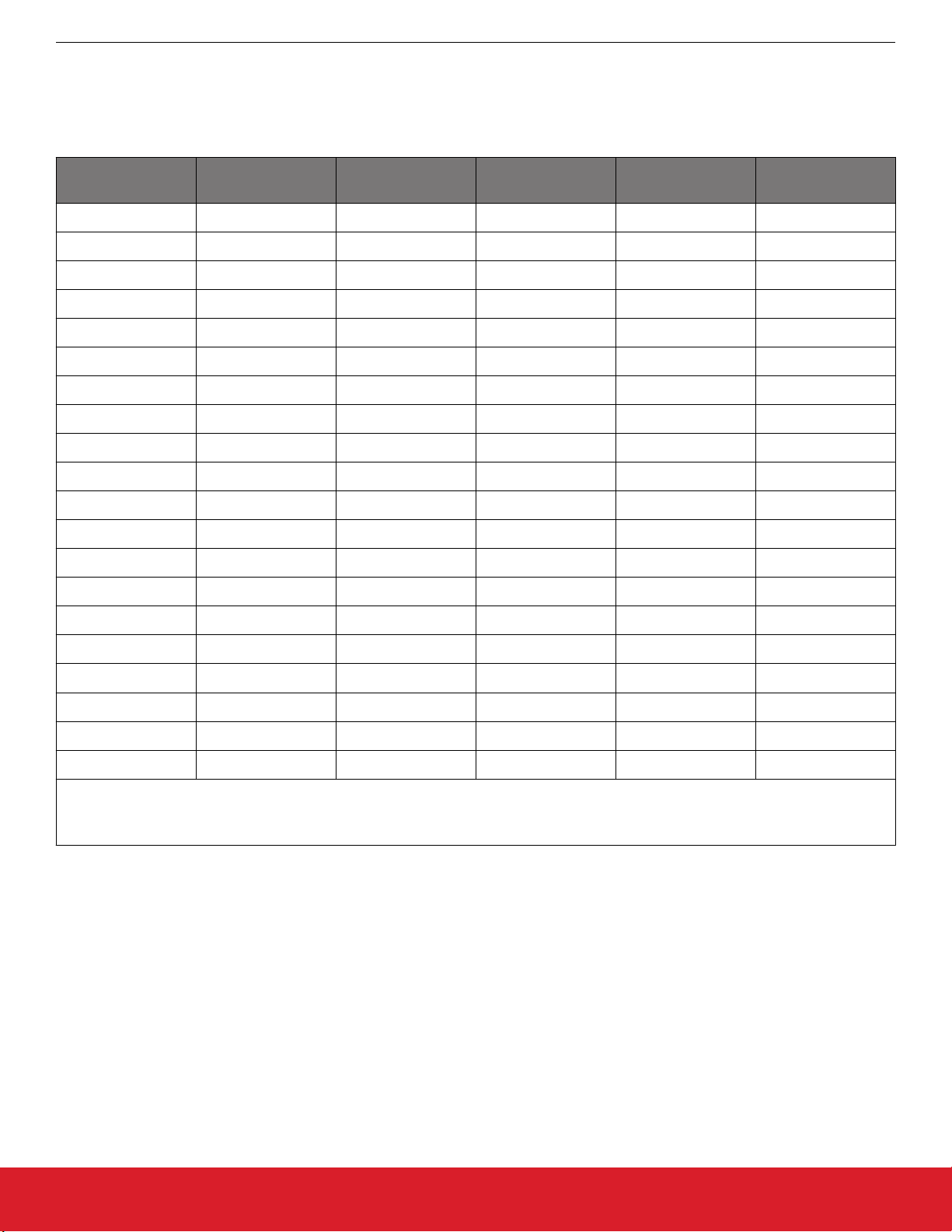
4. Jumper Defaults
UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Jumper Defaults
1
I = Installed
0 = Open
Location Type
Table 4.1. Si5396C/L EVB Jumper Defaults
I= Installed
0 = Open
Location Type
JP1 2-pin O JP23 2-pin O
JP2 2-pin I JP24 3-pin All Open
JP3 2-pin O JP25 2-pin O
JP4 2-pin I JP26 3-pin All Open
JP5 2-pin I JP27 2-pin O
JP6 2-pin I JP28 3-pin All Open
JP7 2-pin I JP29 2-pin O
JP8 2-pin O JP30 3-pin All Open
JP9 2-pin O JP31 2-pin O
JP10 2-pin I JP32 3-pin All Open
JP13 2-pin O JP33 2-pin O
JP14 2-pin I JP34 3-pin All Open
JP15 3-pin 1 to 2 JP35 2-pin O
JP16 3-pin 1 to 2 JP36 3-pin All Open
JP17 2-pin O JP38 3-pin All Open
JP18 3-pin All Open JP39 2-pin O
JP19 2-pin O JP40 2-pin O
JP20 3-pin All Open JP41 2-pin O
JP21 2-pin O J36 5 x 2 Hdr All 5 installed
JP22 3-pin All Open
Note:
1.
Refer to the Si5396C/L EVB schematics for the functionality associated with each jumper.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 6
Page 7
UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Status LEDs
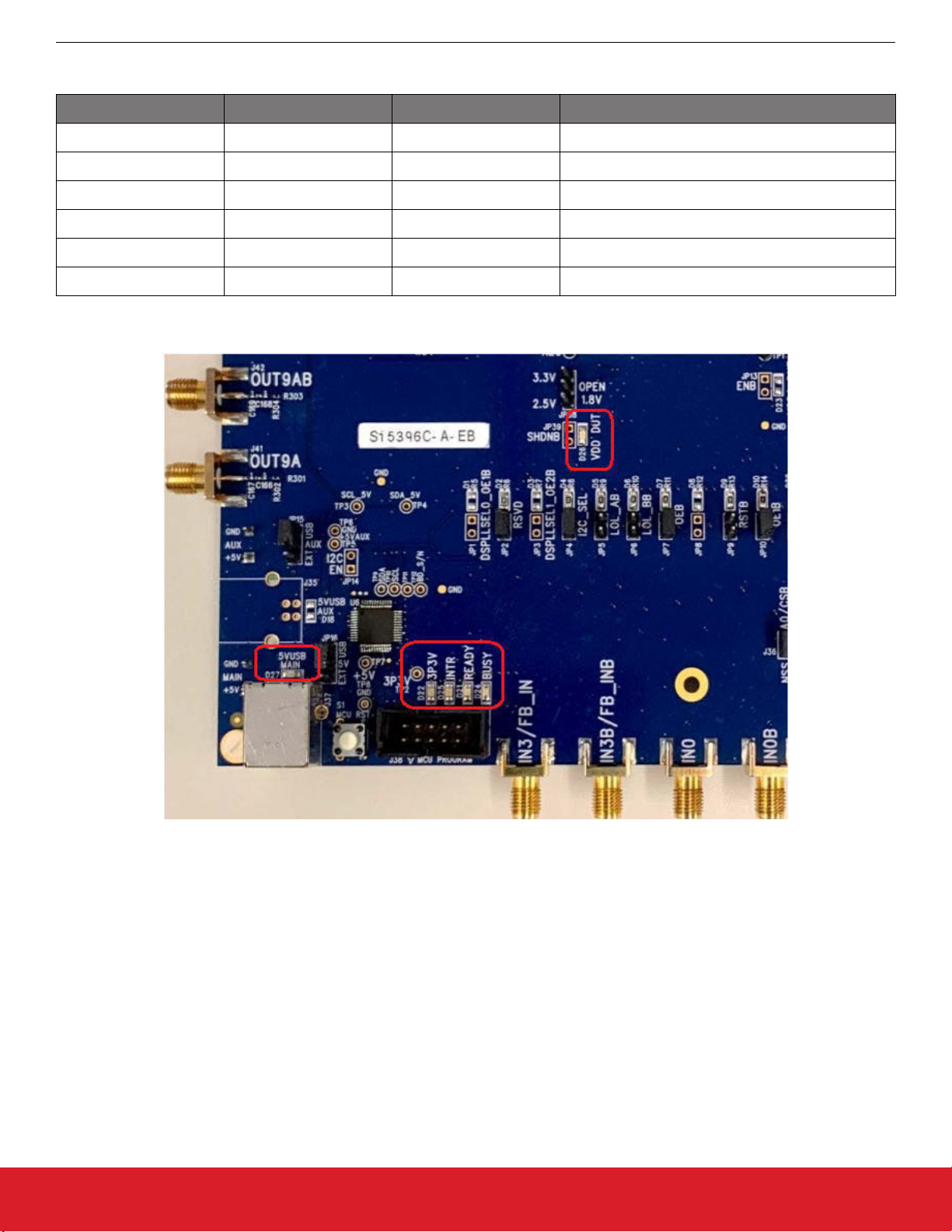
5. Status LEDs
Location Silkscreen Color Status Function Indication
D27 5VUSBMAIN Blue Main USB +5 V present
D22 3P3V Blue DUT +3.3 V is present
D26 VDD DUT Blue DUT VDD voltage present
D25 INTR Red MCU INTR (Interrupt) active
D21 READY Green MCU Ready
D24 BUSY Green MCU Busy
D27, D22, and D26 are illuminated when USB +5 V, Si5396 +3.3 V, and Si5396 VDD supply voltages, respectively, are present. D25,
D21, and D24 are status LEDs showing on-board MCU activity.
Figure 5.1. Status LEDs
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 7
Page 8
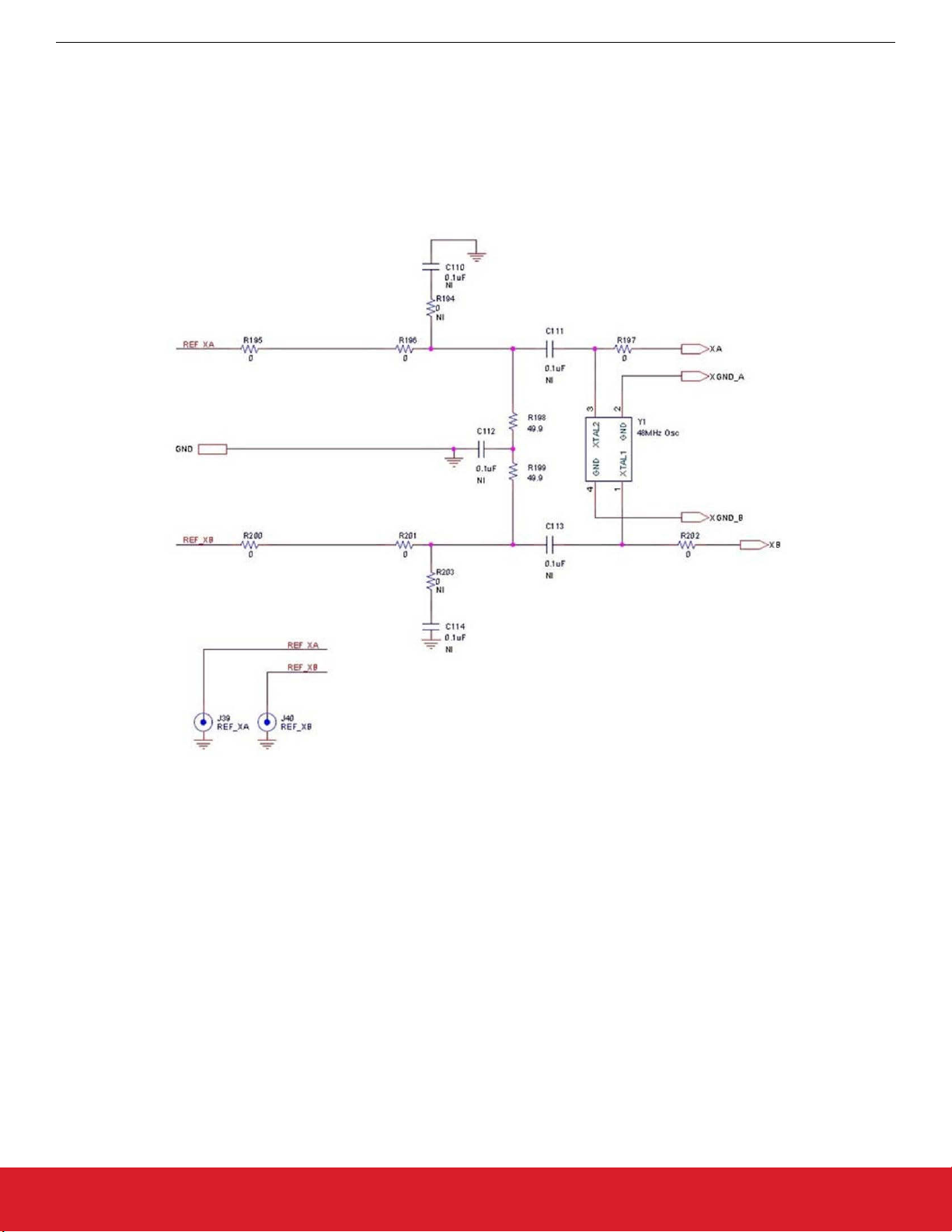
UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
External Reference Input (XA/XB)
6. External Reference Input (XA/XB)
An external reference (XTAL) is required in grade C in combination with the internal oscillator to produce an ultra-low-jitter reference
clock for the DSPLL and to provide a stable reference for the free-run and holdover modes. To evaluate the device with a REFCLK,
C111 and C113 must be populated and the XTAL removed (see the figure below). Also, R197 and R202 must be populated. The
REFCLK can then be supplied to J39 and J40.
Note: For the Si5396L-A, which is the grade with the XTAL internal to the device, there will be no external XTAL supplied on the board
and no input from Ref_XA and Ref_XB. In this case, it is advised that R197 and R202 are removed.
Figure 6.1. External Reference Input Circuit
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 8
Page 9

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Clock Input Circuits (INx/INxB)
7. Clock Input Circuits (INx/INxB)
The Si5396C/L EVB has eight SMA connectors (IN0, IN0B – IN3, IN3B) for receiving external clock signals. All input clocks are terminated as shown below. Note that input clocks are ac-coupled and 50 Ω terminated. This represents four differential input clock pairs. Single-ended clocks can be used by appropriately driving one side of the differential pair with a single-ended clock. For details on how to
configure inputs as single-ended, refer to the Si5396 reference manual.
Figure 7.1. Input Clock Termination Circuit
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 9
Page 10

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Clock Output Circuits (OUTx/OUTxB)
8. Clock Output Circuits (OUTx/OUTxB)
Each of the 24 output drivers (12 differential pairs) is ac-coupled to its respective SMA connector. The output clock termination circuit is
shown below. The output signal will have no dc bias. If dc coupling is required, the ac coupling capacitors can be replaced with a resistor of appropriate value. The Si5396C/L EVB provides pads for optional output termination resistors and/or low-frequency capacitors.
Note that components with the schematic “NI” designation are not normally populated on the Si5396C/L EVB and provide locations on
the PCB for optional dc/ac terminations by the end user.
Figure 8.1. Output Clock Termination Circuit
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 10
Page 11

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Installing ClockBuilder Pro Desktop Software
9. Installing ClockBuilder Pro Desktop Software
To install the CBPro software on any Windows 7 (or above) PC, go to http://www.silabs.com/CBPro and download the ClockBuilder
Pro software. Installation instructions and a user’s guide for ClockBuilder Pro are available at the download link shown above.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 11
Page 12

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
10. Using the Si5396C/L EVB
10.1 Connecting the EVB to Your Host PC
Once ClockBuilder Pro software is installed, connect to the EVB with a USB cable as shown in the figure below:
Figure 10.1. EVB Connection Diagram
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 12
Page 13
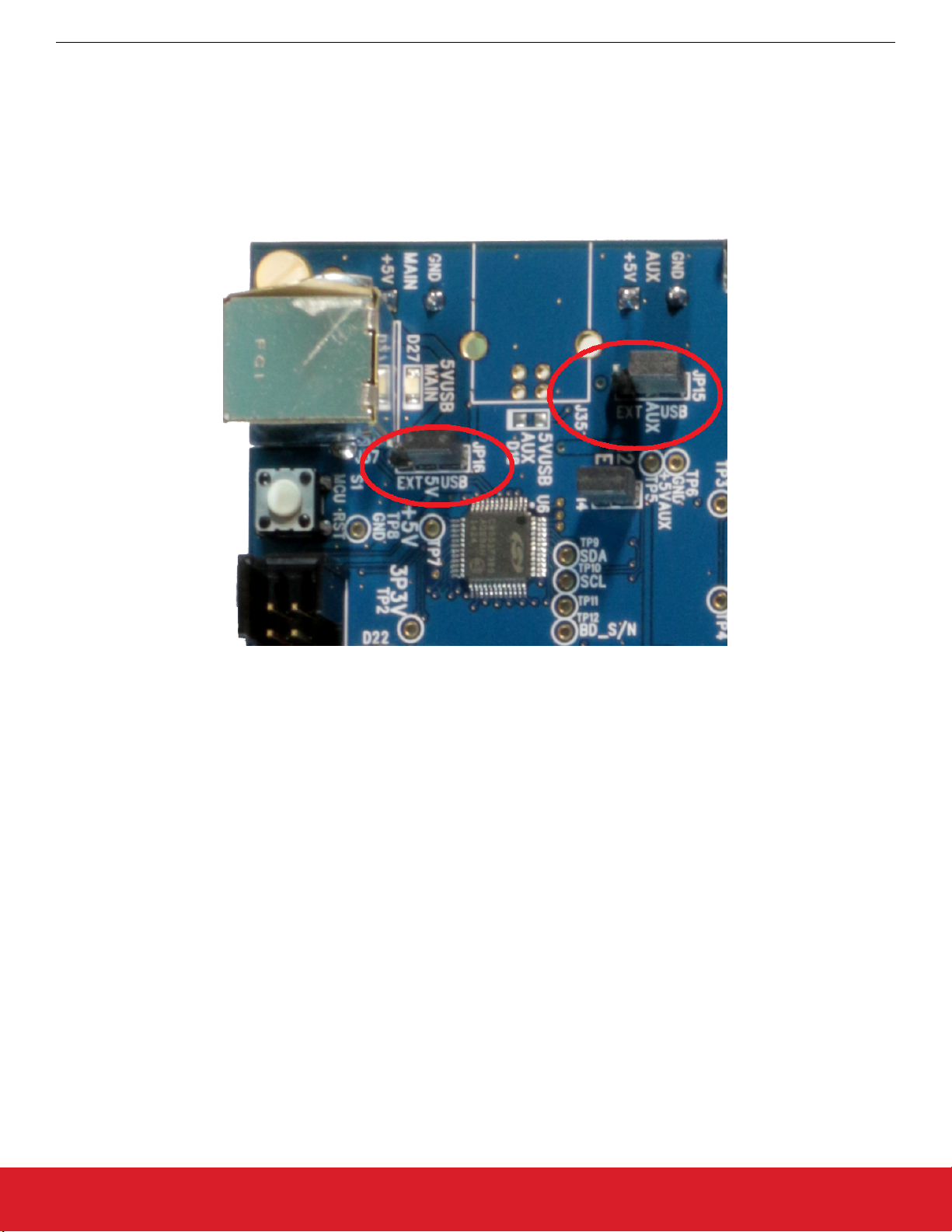
10.2 Additional Power Supplies
UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
Although additional power
(besides the power supplied by the host PC’s USB port) is not needed for most configurations, two additional
+5 VDC power supplies (MAIN and AUX) can be connected to J33 and J34 (located on the bottom of the board, near the USB connector). Refer to the Si5396C/L EVB schematic for details.
The Si5396C/L EVB comes pre-configured with jumpers installed at JP15 and JP16 (pins 1–2 in both cases) to select “USB”. These
jumpers, together with the components installed, configure the evaluation board to obtain all +5 V power solely through the main USB
connector at J37. This setup is the default configuration and should normally be sufficient.
The following figure shows the correct installation of the jumper shunts at JP15 and JP16 for default or standard operation.
Figure 10.2. JP15–JP16 Standard Jumper Shunt Installation
The general guidelines for single USB power supply operation are as follows:
• Use either a USB 3.0 or USB 2.0 port. These ports are specified to supply 900 mA and 500 mA, respectively, at +5 V.
you are working with a USB 2.0 port and you are current limited, turn off enough DUT output voltage regulators to drop the total
• If
DUT current ≤470 mA. (Note: USB 2.0 ports may supply > 500 mA. Provided the nominal +5 V drops gracefully by less than 10%,
the EVB will still work.)
• If you are working with a USB 2.0 and you are current-limited and need all output clock drivers enabled, reconfigure the EVB to drive
the DUT output voltage regulators from an external +5 V power supply as follows:
• Connect an external +5 V power supply to terminal block J33 on the back side of the PCB.
• Move the jumper at JP15 from pins 1–2 USB to pins 2–3 EXT.
10.3 Overview of ClockBuilder Pro Applications
Note: The following instructions and screen captures may vary slightly depending on the grade of your device and your version of
ClockBuilder Pro. (The screen captures below were taken for a board labeled "SI5396C-A-EB".) The ClockBuilder Pro installer will install two main applications:
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 13
Page 14

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
Use the CBPro wizard to:
• Create a new design
• Review or edit an existing design
• Export: create in-system programming
Figure 10.3. Application #1: ClockBuilder Pro Wizard
Figure 10.4. Application #2: EVBGUI
Use the EVB GUI to:
• Download configuration to EVB’s DUT (Si5396C)
• Control the EVB’s regulators
•
Monitor voltage, current, and power on the EVB
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 14
Page 15

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
10.4 Common ClockBuilder Pro Workflow Scenarios
Three common workflow scenarios when using CBPro and the Si5396C/L EVB are:
• Workflow Scenario 1: Testing a Silicon Labs-Created Default Configuration
• Workflow Scenario 2: Modifying the Default Silicon Labs-Created Device Configuration
Workflow Scenario 3: Testing a User-Created Device Configuration
•
Each workflow scenario is described in more detail in the following sections.
10.5 Workflow Scenario 1: Testing a Silicon Labs Default Configuration
The flow for using the EVB GUI to initialize and control a device on the EVB is as follows:
Once the PC and EVB are connected, launch ClockBuilder Pro by clicking this icon on your PC’s desktop:
Figure 10.5. ClockBuilder Pro Desktop Icon
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
If an EVB is detected, click on the “Open Default Plan” button on the Wizard’s main menu. CBPro automatically detects the EVB and
device type.
Figure 10.6. Open Default Plan
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 15
Page 16

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
When you open the default plan (based on your EVB model number), a pop-up will appear:
Figure 10.7. Write Design to EVB Dialog
Select “Yes” to write the default plan to the Si5396C/L device mounted on your EVB. This ensures the device is completely reconfigured per the Silicon Labs default plan for the DUT type mounted on the EVB.
Figure 10.8. Writing Design Status
After CBPro writes the default plan to the EVB, click on “Open EVB GUI” as shown below:
Figure 10.9. Open EVB GUI
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 16
Page 17

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
The EVB GUI will appear. Note that all power supplies will be set to the values defined in the device’s default CBPro project file created
by Silicon Labs, as shown in the following figure:
Figure 10.10. EVB GUI Window
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 17
Page 18

10.5.1 Verify Free-Run Mode Operation
UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
Assuming no external
clocks have been connected to the INPUT CLOCK differential SMA connectors (labeled “INx/INxB”) located
around the perimeter of the EVB, the DUT should now be operating in free-run mode, as the DUT will be locked to the crystal in this
case.
You can run a quick check to determine if the device is powered up and generating output clocks (and consuming power) by clicking on
the highlighted "Read All" button and then reviewing the voltage, current, and power readings for each VDDx supply.
Note: Switching the VDD and VDDA supplies “Off” and then “On” will power-down and reset the DUT. Each time this is done, you must
go back to the Wizard’s main menu and select “Write Design to EVB” to reload the Silicon Labs default plan into the DUT’s register
space, as shown below.
Figure 10.11. Write Design to EVB
Failure to perform this step will cause the device to read in a pre-programmed plan from its non-volatile memory (NVM). However, the
plan loaded from the NVM may not be the latest plan recommended by Silicon Labs for evaluation.
At this point,
you should verify the presence and frequencies of the output clocks (running to free-run mode from the crystal) using appropriate external instrumentation connected to the output clock SMA connectors. To verify that the output clocks are toggling at the
correct frequency and signal format, click on View Design Report as highlighted below.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 18
Page 19

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
Figure 10.12. View Design Report
Your configuration’s design report will appear in a new window, as shown below. Compare the observed output clocks to the frequencies and formats noted in your default project’s Design Report.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 19
Page 20

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
10.5.2 Verify Locked Mode Operation
Assuming you connect
the correct input clocks to the EVB (as noted in the Design Report shown above), the DUT on your EVB will run
in “locked” mode.
Figure 10.13. Design Report Window
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 20
Page 21

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
10.6 Workflow Scenario 2: Modifying the Default Silicon Labs-Created Device Configuration
To modify the “default” configuration using the CBPro Wizard, click on the links below under “Edit Configuration with Wizard”.
Figure 10.14. Edit Configuration with Wizard
You will now be taken to the Wizard’s step-by-step menus to allow you to change any of the default plan’s operating configurations.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 21
Page 22

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
Figure 10.15. Design Wizard
Note that you can click on the icon in the lower left corner of the menu to confirm that your frequency plan is valid. After making your
desired changes, click on Write to EVB to update the DUT and reconfigure your device real-time. The Design Write status window will
appear each time you make a change.
Figure 10.16. Writing Design Status
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 22
Page 23

10.7 Workflow Scenario 3: Testing a User-Created Device Configuration
UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
To test a
Project".
previously created user configuration, open the CBPro Wizard by clicking the icon on your desktop and selecting "Open
Figure 10.17. Open Design Project File
Locate your CBPro design file (*.slabtimeproj or *.sitproj file) in the Windows file browser.
Figure 10.18. Browse to Project File
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 23
Page 24

Select "Yes" when the "Write Design to EVB" popup appears:
UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
Figure 10.19. Write Design to EVB Dialog
The progress bar will be launched. Once the new design project file has been written to the device, verify the presence and frequencies
of your output clocks and other operating configurations using external instrumentation.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 24
Page 25

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Using the Si5396C/L EVB
10.8 Exporting the Register Map File for Device Programming by a Host Processor
You can also export your configuration to a file format suitable for in-system programming by selecting "Export" as shown below:
Figure 10.20. Export Register Map File
You can now write your device’s complete configuration to file formats suitable for in-system programming:
Figure 10.21. Export Settings
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 25
Page 26

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Writing a New Frequency Plan or Device Configuration to Non-Volatile Memory (OTP)
11. Writing a New Frequency Plan or Device Configuration to Non-Volatile Memory (OTP)
Note: Writing to the device non-volatile memory (OTP) is NOT the same as writing a configuration into the Si5396C/L using ClockBuild-
er Pro on the Si5396C/L EVB. Writing a configuration into the EVB from ClockBuilder Pro is done using Si5396C/L RAM space and can
be done virtually an unlimited numbers of times. Writing to OTP is limited as described below.
Refer to the Si5397/96 Family Reference Manual and device data sheets for information on how to write a configuration to the EVB
DUT’s non-volatile memory (OTP). The OTP can be programmed a maximum of two times only. Care must be taken to ensure the
desired configuration is valid when choosing to write to OTP.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 26
Page 27

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Serial Device Communications
12. Serial Device Communications
12.1 Onboard SPI Support
The MCU onboard the Si5396C/L EVB communicates with the Si5396C/L device through a 4-wire Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) link.
The MCU is the SPI master and the Si5396C/L device is the SPI slave. The Si5396C/L device can also support a 2-wire I2C serial
interface, although the Si5396C/L EVB does NOT support the I2C mode of operation. SPI mode was chosen for the EVB because of
the relatively higher speed transfers supported by SPI vs. I2C.
12.2 External I2C Support
I2C can be supported if driven from an external I2C controller. The serial interface signals between the MCU and Si5396C/L pass
through shunts loaded on header J36. These jumper shunts must be installed in J36 for normal EVB operation using SPI with CBPro. If
testing of I2C operation via external controller is desired, the shunts in J36 can be removed thereby isolating the onboard MCU from the
Si5396C/L device. The shunt at J4 (I2C_SEL) must also be removed to select I2C as Si5396C/L interface type. An external I2C controller connected to the Si5396 side of J36 can then communicate to the Si5396C/L device. For more information on I2C signal protocol,
refer to the Si5396 data sheet.
The figure below illustrates the J36 header schematic. J36 even numbered pins (2, 4, 6, etc.) connect to the Si5396C/L device, and the
odd numbered pins (1, 3, 5, etc.) connect to the MCU. When the jumper shunts have been removed from J36 and J4, I2C operation
should use J36 pin 4 (DUT_SDA_SDIO) as the I2CSDA and J36 pin 8 (DUT_SCLK) as the I2CSCLK. Note that the external I2C controller will need to supply its own I2C signal pull-up resistors.
Figure 12.1. Serial Communications Header J36
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 27
Page 28

UG467: Si5396C/L Evaluation Board User's Guide
Si5396C/L EVB Schematic, Layout, and Bill of Materials (BOM)
13. Si5396C/L EVB Schematic, Layout, and Bill of Materials (BOM)
The Si5396C/L EVB Schematic, Layout, and Bill of Materials (BOM) can be found online at:
www.silabs.com/documents/public/schematic-files/si539x-design-files.zip
Note: Please be aware
format.
This document supports the evaluation board silkscreened Si5396C/L EVB for the following configurations as described in the table
below. The data sheet documents the different Si5396C/L grades.
that the Si5396C/L EVB schematic is in OrCad Capture hierarchical format and not in a typical “flat” schematic
Table 13.1. Evaluation Board Configurations
1
Config # Eval Board Label Si5396 Notes
Grade Revision
1 Si5396C-A-EB C A Crystal and related components installed.
2 Si5396L-A-EB L A Crystal and related components not installed. Only the DUT
and label differ versus Si5396C-A-EB.
Note:
1.
Note that it is not possible to load an Si5396C project onto an Si5396L-A-EB or vice-versa. Use Si5396C/D plans for Si5396C-AEB and Si5396L/M plans for Si5396L-A-EB.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 28
Page 29

ClockBuilder Pro
One-click access to Timing tools,
documentation, software, source
code libraries & more. Available for
Windows and iOS (CBGo only).
www.silabs.com/CBPro
Timing Portfolio
www.silabs.com/timing
SW/HW
www.silabs.com/CBPro
Quality
www.silabs.com/quality
Support and Community
community.silabs.com
http://www.silabs.com
Silicon Laboratories Inc.
400 West Cesar Chavez
Austin, TX 78701
USA
Disclaimer
Silicon Labs intends to provide customers with the latest, accurate, and in-depth documentation of all peripherals and modules available for system and software implementers using or
intending to use the Silicon Labs products. Characterization data, available modules and peripherals, memory sizes and memory addresses refer to each specific device, and "Typical"
parameters provided can and do vary in different applications. Application examples described herein are for illustrative purposes only. Silicon Labs reserves the right to make changes without
further notice to the product information, specifications, and descriptions herein, and does not give warranties as to the accuracy or completeness of the included information. Without prior
notification, Silicon Labs may update product firmware during the manufacturing process for security or reliability reasons. Such changes will not alter the specifications or the performance
of the product. Silicon Labs shall have no liability for the consequences of use of the information supplied in this document. This document does not imply or expressly grant any license
to design or fabricate any integrated circuits. The products are not designed or authorized to be used within any FDA Class III devices, applications for which FDA premarket approval is
required, or Life Support Systems without the specific written consent of Silicon Labs. A "Life Support System" is any product or system intended to support or sustain life and/or health,
which,
if it fails, can be reasonably expected to result in significant personal injury or death. Silicon Labs products are not designed or authorized for military applications. Silicon Labs
products shall under no circumstances be used in weapons of mass destruction including (but not limited to) nuclear, biological or chemical weapons, or missiles capable of delivering
such weapons. Silicon Labs disclaims all express and implied warranties and shall not be responsible or liable for any injuries or damages related to use of a Silicon Labs product in such
unauthorized applications.
Trademark Information
Silicon Laboratories Inc.®, Silicon Laboratories®, Silicon Labs®, SiLabs® and the Silicon Labs logo®, Bluegiga®, Bluegiga Logo®, ClockBuilder®, CMEMS®, DSPLL®, EFM®, EFM32®,
EFR, Ember®, Energy Micro, Energy Micro logo and combinations thereof, "the world’s most energy friendly microcontrollers", Ember®, EZLink®, EZRadio®, EZRadioPRO®, Gecko®,
Gecko OS, Gecko OS Studio, ISOmodem®, Precision32®, ProSLIC®, Simplicity Studio®, SiPHY®, Telegesis, the Telegesis Logo®, USBXpress® , Zentri, the Zentri logo and Zentri DMS, ZWave®, and others are trademarks or registered trademarks of Silicon Labs. ARM, CORTEX, Cortex-M3 and THUMB are trademarks or registered trademarks of ARM Holdings. Keil is a
registered trademark of ARM Limited. Wi-Fi is a registered trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance. All other products or brand names mentioned herein are trademarks of their respective holders.
 Loading...
Loading...