Page 1
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm
Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
A Wireless Starter Kit with the BRD4182A Radio Board is an excellent starting point to get familiar with the EFR32™ Wireless
Gecko Wireless System-on-Chip. It also provides all necessary
tools for developing a Silicon Labs wireless application.
BRD4182A is a plug-in board for the Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard. It is a complete reference design for the EFR32xG22 Wireless SoC, with matching network and a PCB antenna for 6 dBm output power in the 2.4 GHz band.
The Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard contains an on-board J-Link debugger with a Packet
Trace Interface and a Virtual COM port, enabling application development and debugging of the attached radio board as well as external hardware. The mainboard also contains sensors and peripherals for easy demonstration of some of the EFR32's many capabilities.
This document describes how to use the BRD4182A Radio Board together with a Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard.
BRD4182A RADIO BOARD FEATURES
• EFR32xG22 Wireless Gecko Wireless
SoC with 512 kB Flash and 32 kB RAM
(EFR32MG22C224F512IM40).
• Inverted-F PCB antenna (2.4 GHz band)
• 8 Mbit low-power serial flash for over-theair upgrades
WIRELESS STK MAINBOARD FEATURES
• Advanced Energy Monitor
• Packet Trace Interface
• Virtual COM port
• SEGGER J-Link on-board debugger
• External device debugging
• Ethernet and USB connectivity
• Silicon Labs Si7021 relative humidity and
temperature sensor
• Low power 128x128 pixel Memory LCDTFT
• User LEDs / pushbuttons
• 20-pin 2.54 mm EXP header
• Breakout pads for Wireless SoC I/O
• CR2032 coin cell battery support
silabs.com
SOFTWARE SUPPORT
• Simplicity Studio™
• Energy Profiler
• Network Analyzer
ORDERING INFORMATION
• SLWSTK6021A
• SLWRB4182A
| Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0
Page 2

Table of Contents
1. Introduction ................................4
1.1 Radio Boards ..............................4
1.2 Ordering Information ............................4
1.3 Getting Started ..............................4
2. Hardware Overview .............................5
2.1 Hardware Layout .............................5
2.2 Block Diagram ..............................6
3. Connectors ................................7
3.1 J-Link USB Connector ...........................7
3.2 Ethernet Connector ............................7
3.3 Breakout Pads ..............................8
3.4 EXP Header ...............................9
3.4.1 EXP Header Pinout ...........................10
3.5 Debug Connector .............................11
3.6 Simplicity Connector ............................12
3.7 Debug Adapter ..............................13
4. Power Supply and Reset .......................... 14
4.1 Radio Board Power Selection .........................14
4.2 Board Controller Power ...........................15
4.3 EFR32 Reset ..............................15
5. Peripherals ............................... 16
5.1 Push Buttons and LEDs ...........................16
5.2 Memory LCD-TFT Display ..........................17
5.3 Serial Flash ...............................18
5.4 Si7021 Relative Humidity and Temperature Sensor..................19
5.5 Virtual COM Port .............................20
5.5.1 Host Interfaces ............................21
5.5.2 Serial Configuration ...........................21
5.5.3 Hardware Handshake ..........................22
6. Board Controller ............................. 23
6.1 Admin Console ..............................23
6.1.1 Connecting ..............................23
6.1.2 Built-in Help .............................23
6.1.3 Command Examples ..........................24
6.2 Virtual UART ..............................24
6.2.1 Target to Host .............................24
6.2.2 Host to Target .............................24
silabs.com
| Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 2
Page 3

6.2.3 Limitations ..............................24
6.2.4 Troubleshooting ............................25
7. Advanced Energy Monitor ......................... 26
7.1 Introduction ...............................26
7.2 Theory of Operation ............................26
7.3 AEM Accuracy and Performance ........................27
7.4 Usage .................................27
8. On-Board Debugger ............................ 28
8.1 Host Interfaces ..............................28
8.1.1 USB Interface .............................28
8.1.2 Ethernet Interface ...........................28
8.1.3 Serial Number Identification ........................28
8.2 Debug Modes ..............................29
8.3 Debugging During Battery Operation ......................30
9. Kit Configuration and Upgrades ....................... 31
9.1 Firmware Upgrades ............................31
10. Schematics, Assembly Drawings, and BOM .................. 32
11. Kit Revision History ........................... 33
11.1 SLWRB4182A Revision History ........................33
11.2 SLWSTK6021A Revision History .......................33
12. Document Revision History ........................ 34
silabs.com
| Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 3
Page 4
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Introduction
1. Introduction
The EFR32xG22 Wireless Gecko Wireless SoC is featured on a radio board that plugs directly into a Wireless Starter Kit (WSTK) Mainboard. The mainboard features several tools for easy evaluation and development of wireless applications. An on-board J-Link debugger enables programming and debugging on the target device over USB or Ethernet. The Advanced Energy Monitor (AEM) offers realtime current and voltage monitoring. A virtual COM port interface (VCOM) provides an easy-to-use serial port connection over USB or
Ethernet. The Packet Trace Interface (PTI) offers invaluable debug information about transmitted and received packets in wireless links.
All debug functionality, including AEM, VCOM, and PTI, can also be used towards external target hardware instead of the attached radio board.
To further enhance its usability, the mainboard contains sensors and peripherals that demonstrate some of the many capabilities of the
EFR32xG22. A 20-pin expansion header (EXP header) is also provided that allows connection of expansion boards (EXP boards) to
the kit.
1.1 Radio Boards
A Wireless Starter Kit consists of one or more mainboards and radio boards that plug into the mainboard. Different radio boards are
available, each featuring different Silicon Labs devices with different operating frequency bands.
Since the mainboard is designed to work with all different radio boards, the actual pin mapping from a device pin to a mainboard feature
is done on the radio board. This means that each radio board has its own pin mapping to the Wireless Starter Kit features, such as
buttons, LEDs, the display, the EXP header and the breakout pads. Because this pin mapping is different for every radio board, it is
important that the correct document be consulted which shows the kit features in context of the radio board plugged in.
This document explains how to use the Wireless Starter Kit when the EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Radio Board (BRD4182A) is combined with a Wireless STK Mainboard. The combination of these two boards is hereby referred to as a Wireless Starter Kit (Wireless
STK).
1.2 Ordering Information
BRD4182A can be obtained as part of SLWSTK6021A EFR32xG21 2.4 GHz Mesh Networking Starter Kit or as a separate radio board,
SLWRB4182A.
Table 1.1. Ordering Information
Part Number Description Contents
SLWSTK6021A EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz Mesh Networking Starter Kit 1x BRD4001A Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard
1x BRD4182A EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Radio Board
1x BRD4183A EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm QFN32 Radio Board
1x USB Type A to Mini-B cable
1x 10-pin 1.27mm IDC debug cable
1x BRD8010A Debug Adapter Board
SLWRB4182A EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Radio Board 1x BRD4182A EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Radio Board
1.3 Getting Started
Detailed instructions for how to get started can be found on the Silicon Labs web pages:
silabs.com/start-efr32xg22
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 4
Page 5
On-board USB and
Ethernet J-Link
Debugger
Radio Board Breakout Pads
Plug-in Radio Board
Si7021 Humidity and
Temperature Sensor
EXP-header for
expansion boards
Serial-port, packet trace and Advanced
Energy Monitoring header
ARM Coresight 19-pin
trace/debug header
Ultra-low power 128x128
pixel memory LCD,
buttons and LEDs
Battery or
USB power
USB-serial-port
Packet-trace
Advanced Energy
Monitoring
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
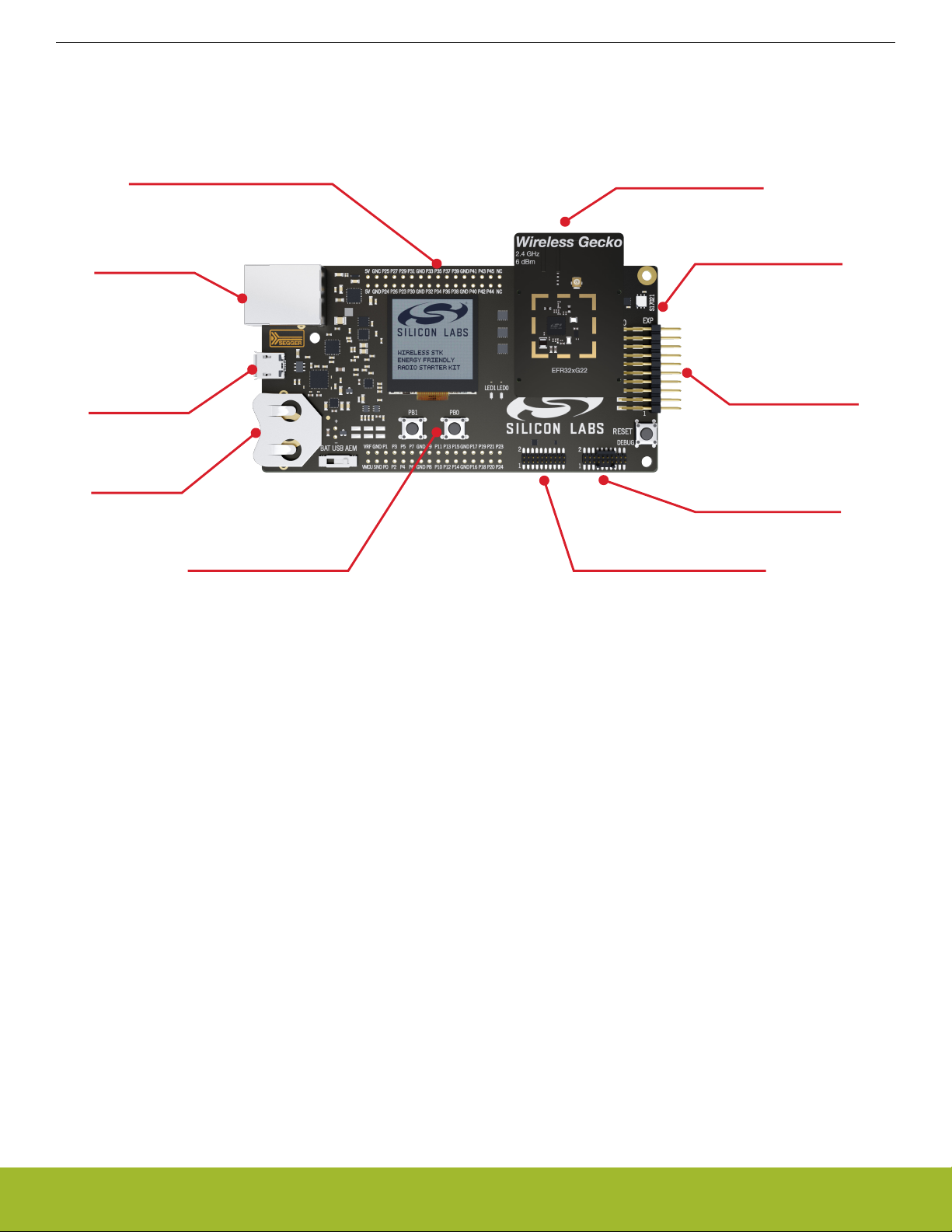
2. Hardware Overview
2.1 Hardware Layout
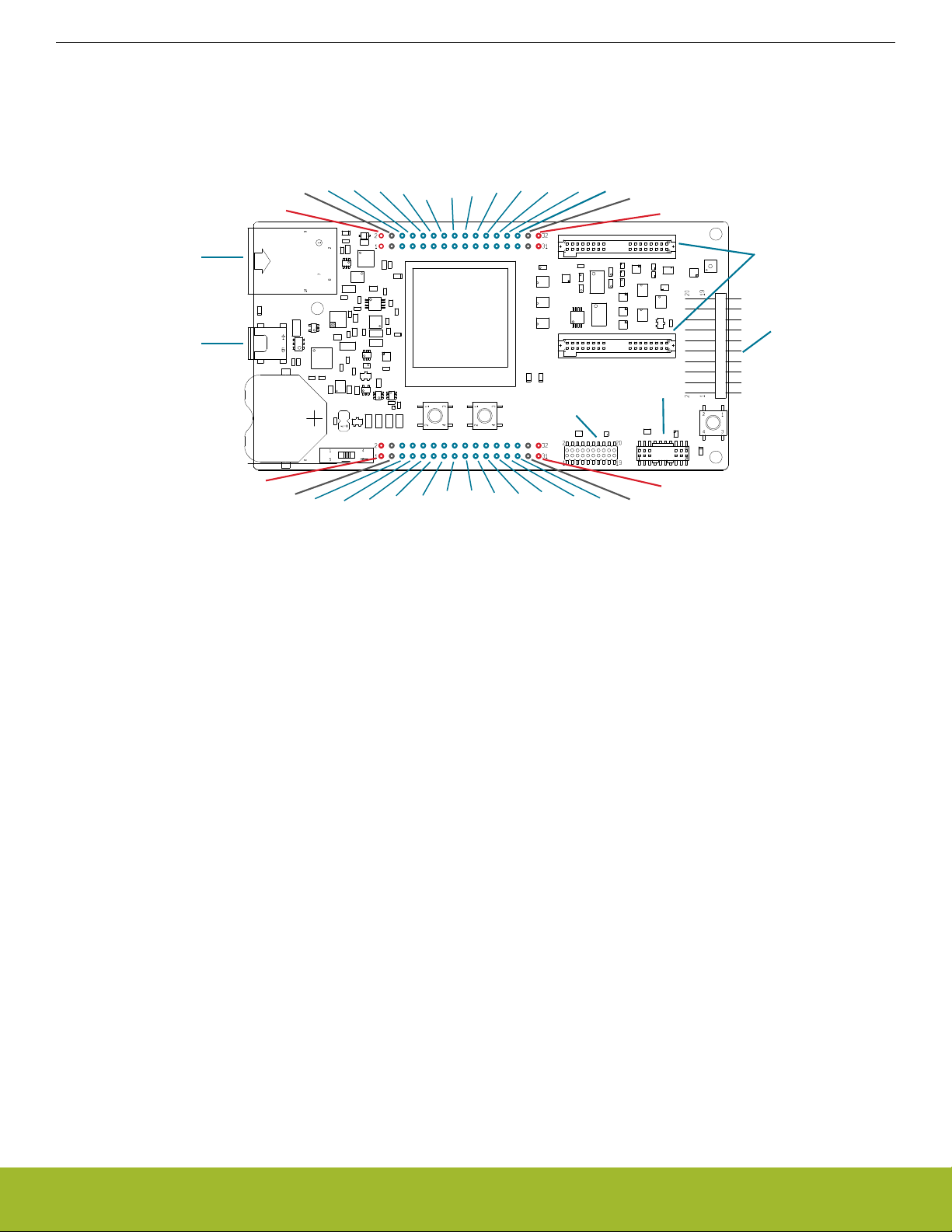
The layout of the EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit is shown in the figure below.
Hardware Overview
Figure 2.1. Kit Hardware Layout
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 5
Page 6
Debug
USB Mini-B
Connector
UART
RJ-45 Ethernet
Connector
Packet Trace
AEM
Multiplexer
Debug
UART
Packet Trace
AEM
Debug
UART
Packet Trace
AEM
Simplicity
Connector
Debug
Connector
Board
Controller
OUT
IN
MCU
SMA
Connector
2.4 GHz RF
Inverted-F
PCB Antenna
EFR32xG22
Wireless SoC
128 x 128 pixel
Memory LCD
I2C
Si7021
Temperature
& Humidity
Sensor
SPI
8 Mbit
MX25R
Serial Flash
GPI
O
EXP
Header
User Buttons
& LEDs
GPIO
ETM Trace
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
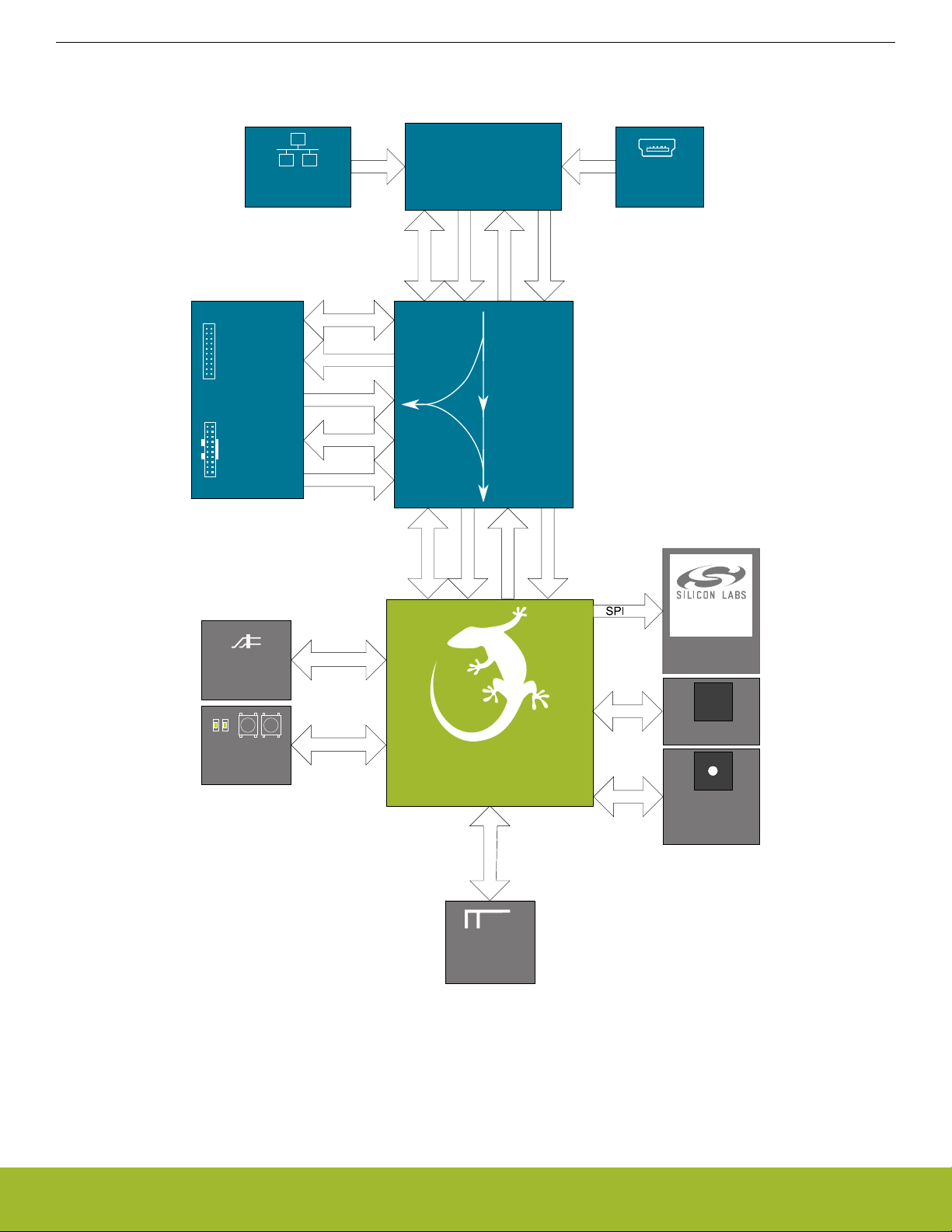
2.2 Block Diagram
An overview of the EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit is shown in the figure below.
Hardware Overview
Figure 2.2. Kit Block Diagram
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 6
Page 7
Simplicity
Connector
Debug
Connector
GND
GND
5V
5V
P25
P24
P27
P26
P29
P28
P31
P30
P33
P32
P35
P34
P37
P36
P39
P38
P41
P40
P43
P42
P45
P44
GND
GND
NC
NC
Radio Board
Connectors
EXP Header
GND
GND
VMCU
VMCU
P1
P0
P3
P2
P5
P4
P7
P6
P9
P8
P11
P10
P13
P12
P15
P14
P17
P16
P19
P18
P21
P20
GND
GND
P23
P22
VRF
VRF
3V3
3V3
Ethernet
Connector
J-Link USB
Connector
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Connectors
3. Connectors
This chapter gives you an overview of the Wireless STK Mainboard connectivity. The placement of the connectors are shown in the
figure below.
Figure 3.1. Mainboard Connector Layout
3.1 J-Link USB Connector
The J-Link USB connector is situated on the left side of the Wireless Starter Kit Mainboard. Most of the kit's development features are
supported through this USB interface when connected to a host computer, including:
• Debugging and programming of the target device using the on-board J-Link debugger
• Communication with the target device over the virtual COM port using USB-CDC
• Accurate current profiling using the AEM
In addition to providing access to development features of the kit, this USB connector is also the main power source for the kit. USB 5V
from this connector powers the board controller and the AEM. It is recommended that the USB host be able to supply at least 500 mA
to this connector, although the actual current required will vary depending on the application.
3.2 Ethernet Connector
The Ethernet connector provides access to all of the Wireless Starter Kit's development features over TCP/IP. The Ethernet interface
provides some additional development features to the user. Supported features include:
• Debugging and programming of the target device using the on-board J-Link debugger
• Communication with the target device over the virtual COM port using TCP/IP socket 4901
• "VUART" communication with the target device over the debug SWD/SWO interface using TCP/IP socket 4900
• Accurate current profiling using the AEM
• Real-time radio packet and network analysis using the Packet Trace Interface
• Access to advanced configuration options using the admin console over TCP/IP socket 4902
Note: The Wireless Starter Kit cannot be powered using the Ethernet connector, so in order to use this interface, the USB connector
must be used to provide power to the board.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 7
Page 8
GND
VMCU
P23 / NC
P21 / PA08 / VCOM_CTS
P19 / PA07 / VCOM_RTS
P17 / NC
GND
P15 / PB04 / VCOM_ENABLE
P13 / PB03 / EXP16 / SENSOR_SDA
P11 / PA06 / EXP14 / VCOM_RX
P9 / PA05 / EXP12 / VCOM_TX
P7 / PC03 / EXP10
P5 / PC02 / EXP8 / FLASH_SCLK / DISP_SCLK
P3 / PC01 / EXP6 / FLASH_MISO
P1 / PC00 / EXP4 / FLASH_MOSI / DISP_MOSI
VRF
GND
VMCU
FLASH_CS / PA04 / P22
DBG_TDO_SWO / PA03 / P20
DBG_TMS_SWDIO / PA02 / P18
DBG_TCK_SWCLK / PA01 / P16
GND
DISP_EXTCOMIN / PA00 / P14
SENSOR_SCL / EXP15 / PB02 / P12
UIF_LED1 / EXP13 / PD03 / P10
UIF_LED0 / EXP11 / PD02 / P8
UIF_BUTTON1 / EXP9 / PB01 / P6
UIF_BUTTON0 / EXP7 / PB00 / P4
NC / P2
NC / P0
VRF
J101
GNDGND
5V5V
NCNC
P45 / NCNC / P44
P43 / NCTRACED0 / PA03 / P42
P41 / NCNC / P40
3V33V3
P39 / NCNC / P38
P37 / PC07 / SENSOR_ENABLE / DISP_ENABLENC / P36
P35 / NCNC / P34
P33 / NCNC / P32
P31 / PC07 / SENSOR_ENABLE / DISP_ENABLENC / P30
P29 / PC06 / DISP_SCSNC / P28
P27 / PC05 / PTI_SYNCNC / P26
P25 / PC04 / PTI_DATANC / P24
GNDGND
J102
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Connectors
3.3 Breakout Pads
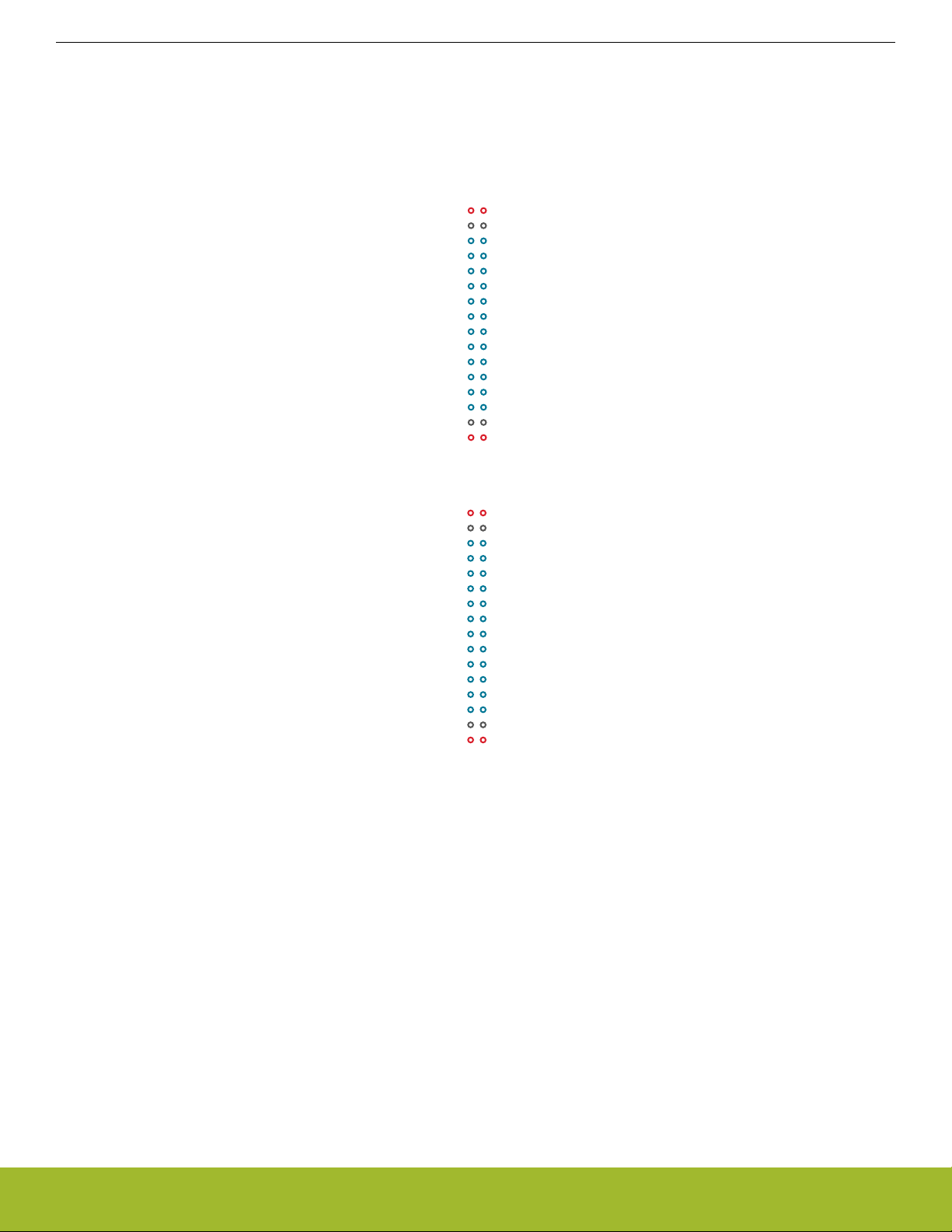
Most pins of the EFR32 are routed from the radio board to breakout pads at the top and bottom edges of the Wireless STK Mainboard.
A 2.54 mm pitch pin header can be soldered on for easy access to the pins. The figure below shows you how the pins of the EFR32
map to the pin numbers printed on the breakout pads. To see the available functions on each, refer to the data sheet for
EFR32MG22C224F512IM40.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 8
Figure 3.2. Breakout Pad Pin Mapping
Page 9
12
4
8
6
10
3
5
9
7
12
13
14
11
1516
17
18
20 19
VMCU
SPI_MOSI / PC00
SPI_MISO / PC01
SPI_CLK / PC02
SPI_CS / PC03
UART_TX / PA05
UART_RX / PA06
I2C_SDA / PB03
5V
3V3
GND
NC
NC
PB00 / GPIO
PB01 / GPIO
PD02 / GPIO
PD03 / GPIO
PB02 / I2C_SCL
BOARD_ID_SDA
BOARD_ID_SCL
Reserved (Board Identification)
EFR32 I/O Pin
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Connectors
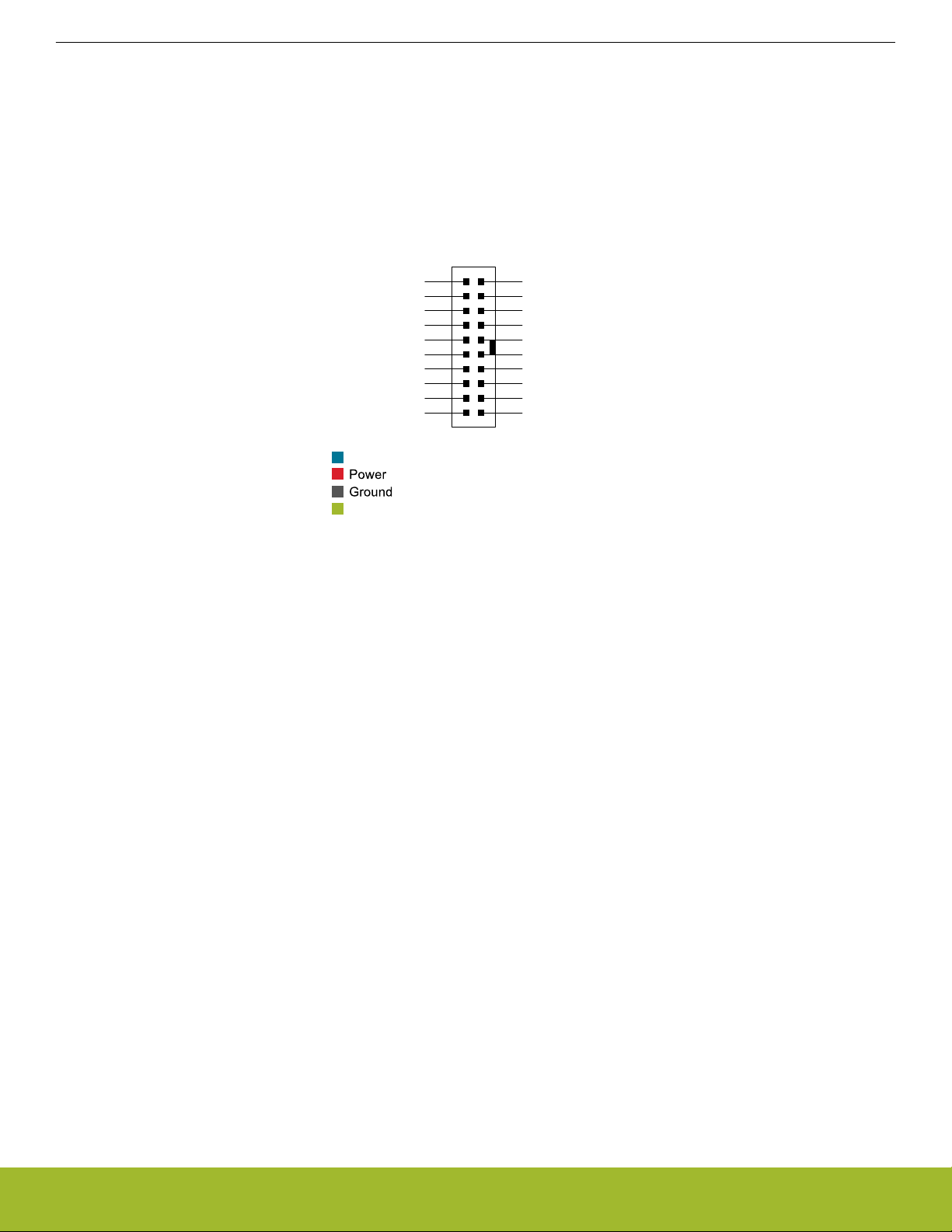
3.4 EXP Header
The EXP header is an angled 20-pin expansion header provided to allow connection of peripherals or plugin boards to the kit. It is located on the right-hand side of the mainboard, and it contains a number of I/O pins that can be used with most of the EFR32 Wireless
Gecko's features. Additionally, the VMCU, 3V3, and 5V power rails are also exported.
The connector follows a standard which ensures that commonly used peripherals, such as an SPI, a UART, and an I2C bus, are available on fixed locations in the connector. The rest of the pins are used for general purpose IO. This allows the definition of expansion
boards (EXP boards) that can plug into a number of different Silicon Labs Starter Kits.
The figure below shows the pin assignment of the EXP header. Because of limitations in the number of available GPIO pins, some of
the EXP header pins are shared with kit features.
Figure 3.3. EXP Header
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 9
Page 10
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Connectors
3.4.1 EXP Header Pinout
The pin-routing on the EFR32 is very flexible, so most peripherals can be routed to any pin. However, many pins are shared between
the EXP header and other functions on the Wireless STK Mainboard. The table below includes an overview of the mainboard features
that share pins with the EXP header.
Table 3.1. EXP Header Pinout
Pin Connection EXP Header Function Shared Feature Peripheral Mapping
20 3V3 Board controller supply
18 5V Board USB voltage
16 PB03 I2C_SDA SENSOR_SDA I2C0_SDA
14 PA06 UART_RX VCOM_RX USART1_RX
12 PA05 UART_TX VCOM_TX USART1_TX
10 PC03 SPI_CS USART0_CS
8 PC02 SPI_SCLK DISP_SCLK, FLASH_SCLK USART0_CLK
6 PC01 SPI_MISO FLASH_MISO USART0_RX
4 PC00 SPI_MOSI DISP_MOSI, FLASH_MOSI USART0_TX
2 VMCU EFR32 voltage domain, included in AEM measurements.
19 BOARD_ID_SDA Connected to board controller for identification of add-on boards.
17 BOARD_ID_SCL Connected to board controller for identification of add-on boards.
15 PB02 I2C_SCL SENSOR_SCL I2C0_SCL
13 PD03 GPIO UIF_LED1
11 PD02 GPIO UIF_LED0
9 PB01 GPIO UIF_BUTTON1
7 PB00 GPIO UIF_BUTTON0
5 NC GPIO
3 NC GPIO
1 GND Ground
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 10
Page 11
1 2
4
8
6
10
5
9
12
13 14
11
15 16
17 18
2019
TMS / SWDIO / C2D
TCK / SWCLK / C2CK
TDO / SWO
TDI / C2Dps
TRACECLK
TRACED0
TRACED1
TRACED2
TRACED3
RESET / C2CKps
GND
NC
NC
GND
GND
GND
7
GND
VTARGET
Cable Detect
NC
3
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Connectors
3.5 Debug Connector
The debug connector serves multiple purposes based on the "debug mode" setting which can be configured in Simplicity Studio. When
the debug mode is set to "Debug IN", the debug connector can be used to connect an external debugger to the EFR32 on the radio
board. When set to "Debug OUT", this connector allows the kit to be used as a debugger towards an external target. When set to "Debug MCU" (default), the connector is isolated from both the on-board debugger and the radio board target device.
Because this connector is electronically switched between the different operating modes, it can only be used when the board controller
is powered (i.e., J-Link USB cable connected). If debug access to the target device is required when the board controller is unpowered,
connect directly to the appropriate breakout pins.
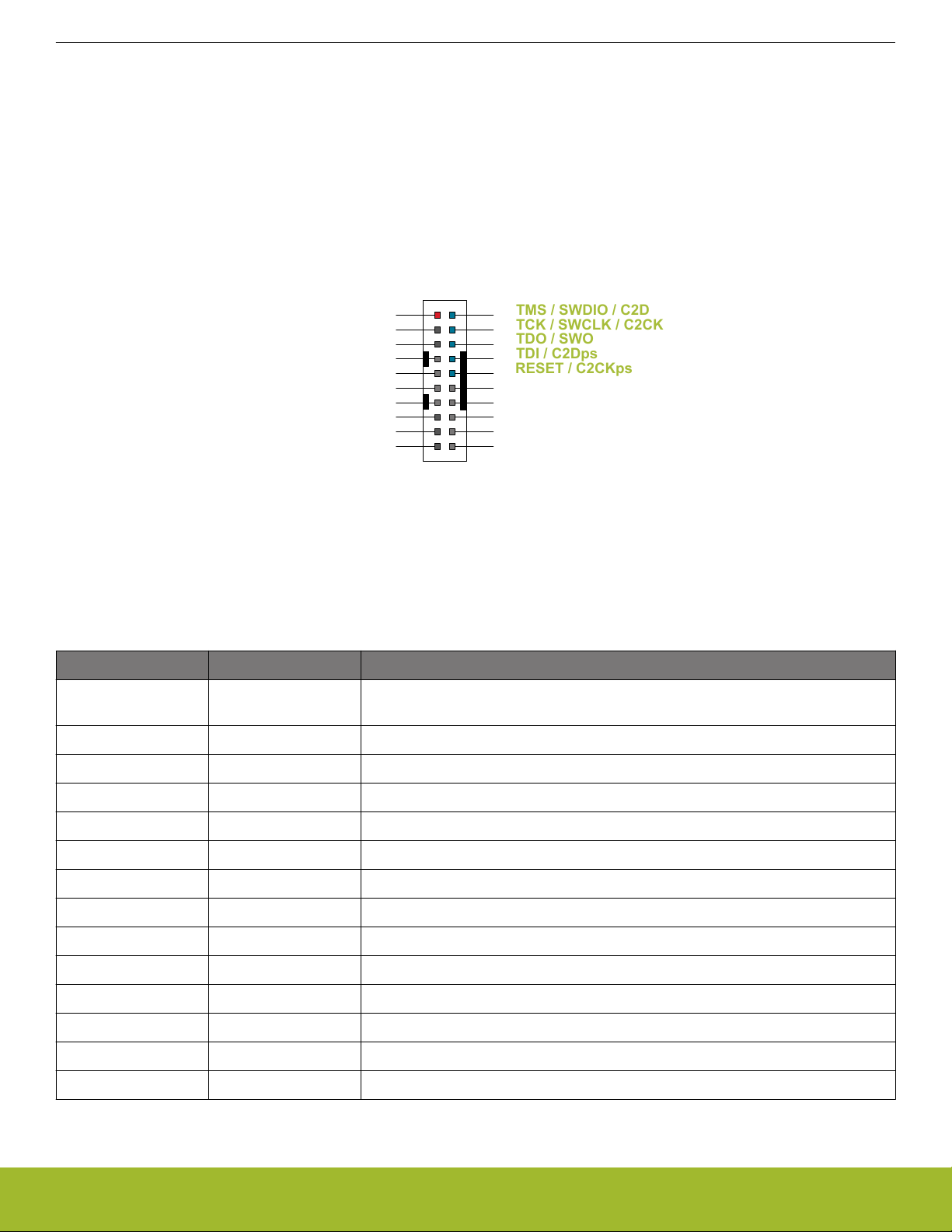
The pinout of the connector follows that of the standard ARM Cortex Debug+ETM 19-pin connector. The pinout is described in detail
below. Even though the connector has support for both JTAG and ETM Trace, it does not necessarily mean that the kit or the on-board
target device supports this.
Figure 3.4. Debug Connector
Note: The pinout matches the pinout of an ARM Cortex Debug+ETM connector, but these are not fully compatible because pin 7 is
physically removed from the Cortex Debug+ETM connector. Some cables have a small plug that prevent them from being used when
this pin is present. If this is the case, remove the plug or use a standard 2x10 1.27 mm straight cable instead.
Table 3.2. Debug Connector Pin Descriptions
Pin Number(s) Function Description
1 VTARGET Target reference voltage. Used for shifting logical signal levels between target and
debugger.
2 TMS / SDWIO / C2D JTAG test mode select, Serial Wire data, or C2 data
4 TCK / SWCLK / C2CK JTAG test clock, Serial Wire clock, or C2 clock
6 TDO/SWO JTAG test data out or Serial Wire Output
8 TDI / C2Dps JTAG test data in or C2D "pin sharing" function
10 RESET / C2CKps Target device reset or C2CK "pin sharing" function
12 TRACECLK Not connected
14 TRACED0 PA03
16 TRACED1 Not connected
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 11
18 TRACED2 Not connected
20 TRACED3 Not connected
9 Cable detect Connect to ground
11, 13 NC Not connected
3, 5, 15, 17, 19 GND Ground
Page 12

VMCU
1
33V3
5
5V
15
GND
13
GND
11
GND
9
GND
7
GND
17
BOARD_ID_SCL
19
BOARD_ID_SDA
2
VCOM_TX
4 VCOM_RX
6 VCOM_CTS
8
VCOM_RTS
10
PTI0_SYNC
12
PTI0_DATA
14
PTI0_CLK
16
PTI1_SYNC
18
PTI1_DATA
20
PTI1_CLK
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Connectors
3.6 Simplicity Connector
The Simplicity Connector enables the advanced debugging features, such as the AEM, the virtual COM port, and the Packet Trace
Interface, to be used towards an external target. The pinout is illustrated in the figure below.
Figure 3.5. Simplicity Connector
Note: Current drawn from the VMCU voltage pin is included in the AEM measurements, while the 3V3 and 5V voltage pins are not.
When monitoring the current consumption of an external target with the AEM, unplug the radio board from the Wireless STK Mainboard
to avoid adding the radio board current consumption to the measurements.
Table 3.3. Simplicity Connector Pin Descriptions
Pin Number(s) Function Description
1 VMCU 3.3 V power rail, monitored by the AEM
3 3V3 3.3 V power rail
5 5V 5 V power rail
2 VCOM_TX Virtual COM Tx
4 VCOM_RX Virtual COM Rx
6 VCOM_CTS Virtual COM CTS
8 VCOM_RTS Virtual COM RTS
10 PTI0_SYNC Packet Trace 0 Sync
12 PTI0_DATA Packet Trace 0 Data
14 PTI0_CLK Packet Trace 0 Clock
16 PTI1_SYNC Packet Trace 1 Sync
18 PTI1_DATA Packet Trace 1 Data
20 PTI1_CLK Packet Trace 1 Clock
17 BOARD_ID_SCL Board ID SCL
19 BOARD_ID_SDA Board ID SDA
7, 9, 11, 13, 15 GND Ground
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 12
Page 13

VAEM
1
3
RST
5
VCOM_TX
9
PTI_FRAME
7
SWDIO
2
GND
4
VCOM_RX
6
SWO
8
SWCLK
10
PTI_DATA
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Connectors
3.7 Debug Adapter
The BRD8010A STK/WSTK Debug Adapter is an adapter board which plugs directly into the debug connector and the Simplicity Connector on the mainboard. It combines selected functionality from the two connectors to a smaller footprint 10-pin connector, which is
more suitable for space constrained designs.
For versatility, the debug adapter features three different 10-pin debug connectors:
• Silicon Labs Mini Simplicity Connector
• ARM Cortex 10-pin Debug Connector
• Silicon Labs ISA3 Packet Trace
The ARM Cortex 10-pin Debug Connector follows the standard Cortex pinout defined by ARM and allows the Starter Kit to be used to
debug hardware designs that use this connector.
The ISA3 connector follows the same pinout as the Packet Trace connector found on the Silicon Labs Ember Debug Adapter (ISA3).
This allows the Starter Kit to be used to debug hardware designs that use this connector.
The Mini Simplicity Connector is designed to offer advanced debug features from the Starter Kit on a 10-pin connector:
• Serial Wire Debug (SWD) with SWO
• Packet Trace Interface (PTI)
• Virtual COM port (VCOM)
• AEM monitored voltage rail
Note: Packet Trace is only available on Wireless STK Mainboards. MCU Starter Kits do not support Packet Trace.
Figure 3.6. Mini Simplicity Connector
Table 3.4. Mini Simplicity Connector Pin Descriptions
Pin Number Function Description
1 VAEM Target voltage on the debugged application. Supplied and monitored by the AEM
when power selection switch is in the "AEM" position.
2 GND Ground
3 RST Reset
4 VCOM_RX Virtual COM Rx
5 VCOM_TX Virtual COM Tx
6 SWO Serial Wire Output
7 SWDIO Serial Wire Data
8 SWCLK Serial Wire Clock
9 PTI_FRAME Packet Trace Frame Signal
10 PTI_DATA Packet Trace Data Signal
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 13
Page 14

VMCU
AEM
USB
BAT
USB Mini-B
Connector
Advanced
Energy
Monitor
3 V Lithium Battery
(CR2032 )
B
A
T
U
SB
AE
M
LDO
EFR32
5 V
3.3 V
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Power Supply and Reset
4. Power Supply and Reset
4.1 Radio Board Power Selection
The EFR32 on a Wireless Starter Kit can be powered by one of these sources:
• The debug USB cable
• A 3 V coin cell battery
• A USB regulator on the radio board (for devices with USB support only)
The power source for the radio board is selected with the slide switch in the lower left corner of the Wireless STK Mainboard. The figure
below shows how the different power sources can be selected with the slide switch.
Figure 4.1. Power Switch
With the switch in the AEM position, a low noise 3.3 V LDO on the mainboard is used to power the radio board. This LDO is again
powered from the debug USB cable. The AEM is now also connected in series, allowing accurate high speed current measurements
and energy debugging/profiling.
With the switch in the USB position, radio boards with USB-support can be powered by a regulator on the radio board itself. BRD4182A
does not contain a USB regulator, and setting the switch in the USB position will cause the EFR32 to be unpowered.
Finally, with the switch in the BAT position, a 20 mm coin cell battery in the CR2032 socket can be used to power the device. With the
switch in this position, no current measurements are active. This is the recommended switch position when powering the radio board
with an external power source.
Note: The current sourcing capabilities of a coin cell battery might be too low to supply certain wireless applications.
Note: The AEM can only measure the current consumption of the EFR32 when the power selection switch is in the AEM position.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 14
Page 15

UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Power Supply and Reset
4.2 Board Controller Power
The board controller is responsible for important features, such as the debugger and the AEM, and is powered exclusively through the
USB port in the top left corner of the board. This part of the kit resides on a separate power domain, so a different power source can be
selected for the target device while retaining debugging functionality. This power domain is also isolated to prevent current leakage from
the target power domain when power to the board controller is removed.
The board controller power domain is not influenced by the position of the power switch.
The kit has been carefully designed to keep the board controller and the target power domains isolated from each other as one of them
powers down. This ensures that the target EFR32 device will continue to operate in the USB and BAT modes.
4.3 EFR32 Reset
The EFR32 Wireless SoC can be reset by a few different sources:
• A user pressing the RESET button
• The on-board debugger pulling the #RESET pin low
• An external debugger pulling the #RESET pin low
In addition to the reset sources mentioned above, a reset to the EFR32 will also be issued during board controller boot-up. This means
that removing power to the board controller (unplugging the J-Link USB cable) will not generate a reset, but plugging the cable back in
will, as the board controller boots up.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 15
Page 16

PD03 (GPIO)
User Buttons
& LEDs
UIF_LED0
UIF_LED1
UIF_PB0
UIF_PB1
PB00 (GPIO)
PB01 (GPIO)
PD02 (GPIO)
EFR32
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Peripherals
5. Peripherals
The starter kit has a set of peripherals that showcase some of the features of the EFR32.
Be aware that most EFR32 I/O routed to peripherals are also routed to the breakout pads or the EXP header. This must be taken into
consideration when using these.
5.1 Push Buttons and LEDs
The kit has two user push buttons marked BTN0 and BTN1. They are connected directly to the EFR32 and are debounced by RC filters
with a time constant of 1 ms. The buttons are connected to pins PB00 and PB01.
The kit also features two yellow LEDs marked LED0 and LED1 that are controlled by GPIO pins on the EFR32. The LEDs are connected to pins PD02 and PD03 in an active-high configuration.
Figure 5.1. Buttons and LEDs
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 16
Page 17

PC02 (US0_CLK)
PC00 (US0_TX)
PC06 (US0_CS)
PA00 (GPIO)
PC07 (GPIO)
EFR32
0: Board Controller controls display
1: EFR32 controls display
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Peripherals
5.2 Memory LCD-TFT Display
A 1.28-inch SHARP Memory LCD-TFT is available on the kit to enable interactive applications to be developed. The display has a high
resolution of 128 x 128 pixels and consumes very little power. It is a reflective monochrome display, so each pixel can only be light or
dark, and no backlight is needed in normal daylight conditions. Data sent to the display is stored in the pixels on the glass, which means
no continous refreshing is required to maintain a static image.
The display interface consists of an SPI-compatible serial interface and some extra control signals. Pixels are not individually addressable, instead data is sent to the display one line (128 bits) at a time.
The Memory LCD-TFT display is shared with the kit's board controller, allowing the board controller application to display useful information when the user application is not using the display. The user application always controls ownership of the display with the
DISP_ENABLE signal:
• DISP_ENABLE = LOW: The board controller has control of the display
• DISP_ENABLE = HIGH: The user application (EFR32) has control of the display
Power to the display is sourced from the target application power domain when the EFR32 controls the display, and from the board
controller's power domain when the DISP_ENABLE line is low. Data is clocked in on DISP_SI when DISP_CS is high, and the clock is
sent on DISP_SCLK. The maximum supported clock speed is 1.1 MHz.
DISP_EXTCOMIN is the "COM Inversion" line. It must be pulsed periodically to prevent static build-up in the display itself. Refer to the
LS013B7DH03 documentation for more information on driving the display.
Figure 5.2. 128x128 Pixel Memory LCD
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 17
Page 18

PC02 (US0_CLK)
PC00 (US0_TX)
PC01 (US0_RX)
PA04 (GPIO)
EFR32
MX25R8035F
SCLK
MOSI
MISO
SCS
VMCU
VDD
8 Mbit
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Peripherals
5.3 Serial Flash
The BRD4182A Radio Board is equipped with an 8 Mbit Macronix MX25R SPI flash that is connected directly to the EFR32. The figure
below shows how the serial flash is connected to the EFR32.
Figure 5.3. Radio Board Serial Flash
The MX25R series are ultra low power serial flash devices, so there is no need for a separate enable switch to keep current consumption down. However, it is important that the flash is always put in deep power down mode when not used. This is done by issuing a
command over the SPI interface. In deep power down, the MX25R typically adds approximately 100 nA to the radio board current consumption.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 18
Page 19

SENSOR_ENABLE
Si7021
Temperature
& Humidity
Sensor
0: I2C lines are isolated, sensor is not powered
1: Sensor is powered and connected
PB02 (I2C0_SCL)
PB03 (I2C0_SDA)
PC07 (GPIO)
SENSOR_I2C_SDA
SENSOR_I2C_SCL
VMCU
VDD
SCL
SDA
EFR32
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Peripherals
5.4 Si7021 Relative Humidity and Temperature Sensor
The Si7021 I2C relative humidity and temperature sensor is a monolithic CMOS IC integrating humidity and temperature sensor elements, an analog-to-digital converter, signal processing, calibration data, and an I2C Interface. The patented use of industry-standard,
low-K polymeric dielectrics for sensing humidity enables the construction of low-power, monolithic CMOS Sensor ICs with low drift and
hysteresis, and excellent long term stability.
The humidity and temperature sensors are factory-calibrated and the calibration data is stored in the on-chip non-volatile memory. This
ensures that the sensors are fully interchangeable, with no recalibration or software changes required.
The Si7021 is available in a 3x3 mm DFN package and is reflow solderable. It can be used as a hardware- and software-compatible
drop-in upgrade for existing RH/temperature sensors in 3x3 mm DFN-6 packages, featuring precision sensing over a wider range and
lower power consumption. The optional factory-installed cover offers a low profile, convenient means of protecting the sensor during
assembly (e.g., reflow soldering) and throughout the life of the product, excluding liquids (hydrophobic/oleophobic) and particulates.
The Si7021 offers an accurate, low-power, factory-calibrated digital solution ideal for measuring humidity, dew-point, and temperature in
applications ranging from HVAC/R and asset tracking to industrial and consumer platforms.
The I2C bus used for the Si7021 is shared with the EXP header. The temperature sensor is normally isolated from the I2C line. To use
the sensor, SENSOR_ENABLE (PC07) must be set high. When enabled, the sensor's current consumption is included in the AEM
measurements.
Figure 5.4. Si7021 Relative Humidity and Temperature Sensor
Refer to the Silicon Labs web pages for more information: http://www.silabs.com/humidity-sensors
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 19
Page 20

VCOM_ENABLE
PA05 (US1_TX)
PA06 (US1_RX)
PB04 (GPIO)
VCOM_RX
VCOM_TX
Board
Controller
EFR32
USB
Host
PC
Isolation & Level Shift
PA08 (US1_CTS)
PA07 (US1_RTS)
VCOM_CTS
VCOM_RTS
ETH
or
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Peripherals
5.5 Virtual COM Port
An asynchronous serial connection to the board controller is provided for application data transfer between a host PC and the target
EFR32. This eliminates the need for an external serial port adapter.
Figure 5.5. Virtual COM Port Interface
The virtual COM port consists of a physical UART between the target device and the board controller, and a logical function in the
board controller that makes the serial port available to the host PC over USB or Ethernet. The UART interface consists of four pins and
an enable signal.
Table 5.1. Virtual COM Port Interface Pins
Signal Description
VCOM_TX Transmit data from the EFR32 to the board controller
VCOM_RX Receive data from the board controller to the EFR32
VCOM_CTS Clear to Send hardware flow control input, asserted by the board controller when it is ready to receive more data
VCOM_RTS Request to Send hardware flow control output, asserted by the EFR32 when it is ready to receive more data
VCOM_ENABLE Enables the VCOM interface, allowing data to pass through to the board controller.
The parameters of the serial port, such as baud rate or flow control, can be configured using the admin console. The default settings
depend on which radio board is used with the Wireless STK Mainboard.
Note: The VCOM port is only available when the board controller is powered, which requires the J-Link USB cable to be inserted.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 20
Page 21

UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Peripherals
5.5.1 Host Interfaces
Data can be exchanged between the board controller and the target device through the VCOM interface, which is then available to the
user in two different ways:
• Virtual COM port using a standard USB-CDC driver
• TCP/IP by connecting to the Wireless STK on TCP/IP port 4901 with a Telnet client
When connecting via USB, the device should automatically show up as a COM port. The actual device name that is associated with the
kit depends on the operating system and how many devices are or have been connected previously. The following are examples of
what the device might show up as:
• JLink CDC UART Port (COM5) on Windows hosts
• /dev/cu.usbmodem1411 on macOS
• /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux
Data sent by the target device into the VCOM interface can be read from the COM port, and data written to the port is transmitted to the
target device. Connecting to the Wireless STK on port 4901 gives access to the same data over TCP/IP. Data written into the VCOM
interface by the target device can be read from the socket, and data written into the socket is transmitted to the target device.
Note: Only one of these interfaces can be used at the same time, with the TCP/IP socket taking priority. This means that if a socket is
connected to port 4901, no data can be sent or received on the USB COM port.
5.5.2 Serial Configuration
By default, the VCOM serial port is configured to use 115200 8N1 (115.2 kbit/s, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit), with flow control disabled/ignored. The configuration can be changed using the admin console:
WSTK> serial vcom config
Usage: serial vcom config [--nostore] [handshake <rts/cts/rtscts/disable/auto>] [speed <9600,921600>]
Using this command, the baud rate can be configured between 9600 and 921600 bit/s, and hardware handshake can be enabled or
disabled on either or both flow control pins.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 21
Page 22

UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Peripherals
5.5.3 Hardware Handshake
The VCOM peripheral supports basic RTS/CTS flow control.
VCOM_CTS (target clear to send) is a signal that is output from the board controller and input to the target device. The board controller
de-asserts this pin whenever its input buffer is full and it is unable to accept more data from the target device. If hardware handshake is
enabled in the target firmware, its UART peripheral will halt when data is not being consumed by the host. This implements end-to-end
flow control for data moving from the target device to the host.
VCOM_CTS is connected to the RTS pin on the board controller and is enabled by setting handshake to either RTS or RTSCTS using
the "serial vcom config" command.
VCOM_RTS (target request to send) is a signal that is output from the target device and input to the board controller. The board controller will halt transmission of data towards the target if the target device de-asserts this signal. This gives the target firmware a means to
hold off incoming data until it can be processed. Note that de-asserting RTS will not abort the byte currently being transmitted, so the
target firmware must be able to accept at least one more character after RTS is de-asserted.
VCOM_RTS is connected to the CTS pin of the board controller. It is enabled by setting handshake to either CTS or RTSCTS using the
"serial vcom config" command in the admin console. If CTS flow control is disabled, the state of VCOM_RTS will be ignored and data
will be transmitted to the target device anyway.
Table 5.2. Hardware Handshake Configuration
Mode Description
disabled RTS (VCOM_CTS) is not driven by the board controller and CTS (VCOM_RTS) is ignored.
rts RTS (VCOM_CTS) is driven by the board controller to halt target from transmitting when input buffer is full. CTS
(VCOM_RTS) is ignored.
cts RTS (VCOM_CTS) is not driven by the board controller. Data is transmitted to the target device if CTS
(VCOM_RTS) is asserted, and halted when de-asserted.
rtscts RTS (VCOM_CTS) is driven by the board controller to halt target when buffers are full. Data is transmitted to the
target device if CTS (VCOM_RTS) is asserted, and halted when de-asserted.
Note: Enabling CTS flow control without configuring the VCOM_RTS pin can result in no data being transmitted from the host to the
target device.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 22
Page 23

UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Board Controller
6. Board Controller
The Wireless STK Mainboard contains a dedicated microcontroller for some of the advanced kit features provided. This microcontroller
is referred to as the board controller and is not programmable by the user. The board controller acts as an interface between the host
PC and the target device on the radio board, as well as handling some housekeeping functions on the board.
Some of the kit features actively managed by the board controller are:
• The on-board debugger, which can flash and debug both on-board and external targets
• The Advanced Energy Monitor, which provides real-time energy profiling of the user application
• The Packet Trace Interface, which is used in conjunction with PC software to provide detailed insight into an active radio network
• The Virtual COM Port and Virtual UART interfaces, which provide ways to transfer application data between the host PC and the
target processor
• The admin console, which provides configuration of the various board features
Silicon Labs publishes updates to the board controller firmware in the form of firmware upgrade packages. These updates may enable
new features or fix issues. See Section 9.1 Firmware Upgrades for details on firmware upgrade.
6.1 Admin Console
The admin console is a command line interface to the board controller on the kit. It provides functionality for configuring the kit behavior
and retrieving configuration and operational parameters.
6.1.1 Connecting
The Wireless Starter Kit must be connected to Ethernet using the Ethernet connector in the top left corner of the mainboard for the
admin console to be available. See Section 8.1.2 Ethernet Interface for details on the Ethernet connectivity.
Connect to the admin console by opening a telnet connection to the kit's IP address, port number 4902.
When successfully connected, a WSTK> prompt is displayed.
6.1.2 Built-in Help
The admin console has a built-in help system which is accessed by the help command. The help command will print a list of all top
level commands:
WSTK> help
*************** Root commands ****************
aem AEM commands [ calibrate, current, dump, ... ]
boardid Commands for board ID probe. [ list, probe ]
dbg Debug interface status and control [ info, mode,]
dch Datachannel control and info commands [ info ]
discovery Discovery service commands.
net Network commands. [ dnslookup, geoprobe, ip ]
pti Packet trace interface status and control [ config, disable, dump, ... ]
quit Exit from shell
sys System commands [ nickname, reset, scratch, ... ]
target Target commands. [ button, flashwrite, go, ... ]
time Time Service commands [ client, server ]
user User management functions [ login,]
The help command can be used in conjunction with any top level command to get a list of sub-commands with description. For example, pti help will print a list of all available sub-commands of pti:
WSTK> pti help
*************** pti commands ****************
config Configure packet trace
disable Disable packet trace
dump Dump PTI packets to the console as they come
enable Enable packet trace
info Packet trace state information
This means that running pti enable will enable packet trace.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 23
Page 24

UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Board Controller
6.1.3 Command Examples
PTI Configuration
pti config 0 efruart 1600000
Configures PTI to use the "EFRUART" mode at 1.6 Mb/s.
Serial Port Configuration
serial config vcom handshake enable
Enables hardware handshake on the VCOM UART connection.
6.2 Virtual UART
The Virtual UART (VUART) interface provides a high performance application data interface that does not require additional I/O pins
apart from the debug interface.
The Wireless Starter Kit makes the VUART interface available on TCP/IP port 4900.
6.2.1 Target to Host
Target to host communication utilizes the SWO-pin of the debug interface through the ITM debug peripheral. This approach allows a
sleepy target device to enter all energy modes, and still wake up intermittently to send debug information. The baud rate of the SWO
data is locked to 875 kHz.
VUART utilizes ITM stimulus port 0 for general purpose printing. Silicon Labs' networking stacks utilize ITM stimulus port 8 for debug
printing. The data on port 8 is encapsulated in additional framing and will also appear in the Simplicity Studio Network Analyzer.
6.2.2 Host to Target
Host to target communication utilizes SEGGER's Real Time Transfer (RTT) technology. A full explanation of how this works can be
found in J-Link/J-Trace User Guide (UM08001). Briefly summarized, RTT consists of a structure called the RTT Control Block, which is
located in RAM. This control block points to circular buffers that the debugger can write data into. The target application can then read
data out of this circular buffer.
The board controller will start searching for the RTT Control Block upon receiving data on TCP/IP port 4900. If the board controller is
unable to locate the RTT Control Block it will return an error message on the same connection. For the board controller to be able to
locate the RTT Control Block it has to be aligned on a 1024-byte boundary in RAM.
After initializing the RTT connection the target will only enter emulated EM2 and EM3 where the power consumption remains similar to
EM1. This is because RTT utilizes the debug interface which requires use of high frequency oscillators. Energy modes EM4S and
EM4H will work as normal. When debugging energy consumption it is therefore important to not send data on TCP/IP port 4900 as not
to instantiate the RTT connection.
6.2.3 Limitations
• Because the SWO-connection can be disabled by the debugger at will, it is important for the target application to verify that SWO is
enabled and configured before each transmission on the interface.
• After initializing host to target communication over RTT by sending data on TCP/IP port 4900 the target application will be unable to
enter EM2 and EM3. This is because RTT utilizes the debug connection of the target.
• VUART might not work reliably during an active debugging session. This is because there is contention over the target's debug interface, and the board controller will defer accessing the target until it is made available by the host debugger.
• VUART is designed with the assumption that only the board controller will access the RTT control block. If the target application
uses RTT for other purposes, such as Segger SystemView, please refrain from using VUART.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 24
Page 25

6.2.4 Troubleshooting
Problem Solution
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Board Controller
No data received after ending a
debug session.
No data received after flashing
a new application.
After certain debugger operations the host computer manually disables SWO on the target in order
to conserve power. This might cause SWO data to not appear if the target application initialized
SWO before the debugger has disconnected. Either press the RESET-button on the Wireless Starter Kit to reset the target application, or make sure that the target application verifies that SWO is
enabled and configured before sending any data.
Other issues Disconnect from TCP port 4900, press the RESET-button on the kit, then reconnect to 4900. If this
does not fix the issue, try to restart the kit by unplugging and replugging the USB cable.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 25
Page 26

EFR32
LDO
Peripherals
AEM
Processing
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Advanced Energy Monitor
7. Advanced Energy Monitor
7.1 Introduction
Any embedded developer seeking to make their embedded code spend as little energy as the underlying architecture supports needs
tools to easily and quickly discover inefficiencies in the running application. This is what the Simplicity Energy Profiler is designed to do.
In real-time, the Energy Profiler will graph and log current as a function of time while correlating this to the actual target application code
running on the EFR32. There are multiple features in the profiler software that allow for easy analysis, such as markers and statistics on
selected regions of the current graph or aggregate energy usage by different parts of the application.
7.2 Theory of Operation
The AEM circuitry on the board is capable of measuring current signals in the range of 0.1 µA to 95 mA, which is a dynamic range of
almost 120 dB. It can do this while maintaining approximately 10 kHz of current signal bandwidth. This is accomplished through a combination of a highly capable current sense amplifier, multiple gain stages, and signal processing within the kit's board controller before
the current sense signal is read by a host computer for display and/or storage.
The current sense amplifier measures the voltage drop over a small series resistor, and the gain stage further amplifies this voltage with
two different gain settings to obtain two current ranges. The transition between these two ranges occurs around 250 µA.
The current signal is combined with the target processor's Program Counter (PC) sampling by utilizing a feature of the ARM CoreSight
debug architecture. The Instrumentation Trace Macrocell (ITM) block can be programmed to sample the MCU's PC at periodic intervals
(50 kHz) and output these over SWO pin ARM devices. When these two data streams are fused and correlated with the running application's memory map, an accurate statistical profile can be built that shows the energy profile of the running application in real-time.
At kit power-up or on a power-cycle, an automatic AEM calibration is performed. This calibration compensates for any offset errors in
the current sense amplifiers.
Figure 7.1. Advanced Energy Monitor
Note: The 3.3 V regulator feedback point is after the 2.35 Ω sense resistor to ensure that the VMCU voltage is kept constant when the
output current changes. Maximum recommended output current is 300 mA.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 26
Page 27

UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Advanced Energy Monitor
7.3 AEM Accuracy and Performance
The AEM is capable of measuring currents in the range of 0.1 µA to 95 mA. For currents above 250 µA, the AEM is accurate within 0.1
mA. When measuring currents below 250 µA, the accuracy increases to 1 µA. Even though the absolute accuracy is 1 µA in the sub
250 µA range, the AEM is able to detect changes in the current consumption as small as 100 nA.
The AEM current sampling rate is 10 kHz.
Note: The AEM circuitry only works when the kit is powered and the power switch is in the AEM position.
7.4 Usage
The AEM data is collected by the board controller and can be displayed by the Energy Profiler, available through Simplicity Studio. By
using the Energy Profiler, current consumption and voltage can be measured and linked to the actual code running on the EFR32 in
realtime.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 27
Page 28

UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
On-Board Debugger
8. On-Board Debugger
The Wireless STK Mainboard contains an integrated debugger, which can be used to download code and debug the EFR32. In addition
to programming a target on a plug-in radio board, the debugger can also be used to program and debug external Silicon Labs EFM32,
EFM8, EZR32, and EFR32 devices connected through the debug connector.
The debugger supports three different debug interfaces for Silicon Labs devices:
• Serial Wire Debug is supported by all EFM32, EFR32, and EZR32 devices
• JTAG is supported by EFR32 and some EFM32 devices
• C2 Debug is supported by EFM8 devices
In order for debugging to work properly, make sure that the selected debug interface is supported by the target device. The debug connector on the board supports all three of these modes.
8.1 Host Interfaces
The Wireless Starter Kit supports connecting to the on-board debugger using either Ethernet or USB.
Many tools support connecting to a debugger using either USB or Ethernet. When connected over USB, the kit is identified by its J-Link
serial number. When connected over Ethernet, the kit is normally identified by its IP address. Some tools also support using the serial
number when connecting over Ethernet; however, this typically requires the computer and the kit to be on the same subnet for the discovery protocol (using UDP broadcast packets) to work.
8.1.1 USB Interface
The USB interface is available whenever the USB Mini-B connector on the left-hand side of the mainboard is connected to a computer.
8.1.2 Ethernet Interface
The Ethernet interface is available when the mainboard Ethernet connector in the top left corner is connected to a network. Normally,
the kit will receive an IP address from a local DHCP server, and the IP address is printed on the LCD display. If your network does not
have a DHCP server, you need to connect to the kit via USB and set the IP address manually using Simplicity Studio, Simplicity
Commander, or J-Link Configurator.
For the Ethernet connectivity to work, the kit must still be powered through the USB Mini-B connector. See Section 4.2 Board Controller
Power for details.
8.1.3 Serial Number Identification
All Silicon Labs kits have a unique J-Link serial number which identifies the kit to PC applications. This number is 9 digits and is normally on the form 44xxxxxxx.
The J-Link serial number is normally printed at the bottom of the kit LCD display.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 28
Page 29

RADIO BOARD
Board
Controller
USB
Host
Computer
DEBUG HEADER
External
Hardware
Board
Controller
USB
Host
Computer
DEBUG HEADER
External
Hardware
RADIO BOARD
Board
Controller
USB
Host
Computer
DEBUG HEADER
External Debug Probe
RADIO BOARD
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
On-Board Debugger
8.2 Debug Modes
Programming external devices is done by connecting to a target board through the provided debug connector and by setting the debug
mode to [Out]. The same connector can also be used to connect an external debugger to the EFR32 Wireless SoC on the kit by setting
debug mode to [In].
Selecting the active debug mode is done in Simplicity Studio.
Debug MCU: In this mode, the on-board debugger is connected to the EFR32 on the kit.
Figure 8.1. Debug MCU
Debug OUT: In this mode, the on-board debugger can be used to debug a supported Silicon Labs device mounted on a custom board.
Figure 8.2. Debug OUT
Debug IN: In this mode, the on-board debugger is disconnected, and an external debugger can be connected to debug the EFR32 on
the kit.
Figure 8.3. Debug IN
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 29
Page 30

UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
On-Board Debugger
Note: For "Debug IN" to work, the kit board controller must be powered through the Debug USB connector.
8.3 Debugging During Battery Operation
When the EFR32 is powered by battery and the J-Link USB is still connected, the on-board debug functionality is available. If the USB
power is disconnected, the Debug IN mode will stop working.
If debug access is required when the target is running off another energy source, such as a battery, and the board controller is powered
down, make direct connections to the GPIO used for debugging. This can be done by connecting to the appropriate pins of the breakout
pads. Some Silicon Labs kits provide a dedicated pin header for this purpose.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 30
Page 31

UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Kit Configuration and Upgrades
9. Kit Configuration and Upgrades
The kit configuration dialog in Simplicity Studio allows you to change the J-Link adapter debug mode, upgrade its firmware, and change
other configuration settings. To download Simplicity Studio, go to http://www.silabs.com/simplicity.
In the main window of the Simplicity Studio's Launcher perspective, the debug mode and firmware version of the selected J-Link adapter is shown. Click the [Change] link next to any of them to open the kit configuration dialog.
Figure 9.1. Simplicity Studio Kit Information
Figure 9.2. Kit Configuration Dialog
9.1 Firmware Upgrades
Upgrading the kit firmware is done through Simplicity Studio. Simplicity Studio will automatically check for new updates on startup.
You can also use the kit configuration dialog for manual upgrades. Click the [Browse] button in the [Update Adapter] section to select
the correct file ending in .emz. Then, click the [Install Package] button.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 31
Page 32

UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Schematics, Assembly Drawings, and BOM
10. Schematics, Assembly Drawings, and BOM
Schematics, assembly drawings, and bill of materials (BOM) are available through Simplicity Studio when the kit documentation package has been installed. They are also available from the Silicon Labs website and kit page.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 32
Page 33

SLWRB4182A
EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Radio Board
124802042
02-02-20
A00
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
11. Kit Revision History
The kit revision can be found printed on the kit packaging label, as outlined in the figure below.
Figure 11.1. Kit Label
11.1 SLWRB4182A Revision History
Kit Revision Released Description
Kit Revision History
A02 17 February 2020 Updated BRD4182A to Rev. B05
A01 18 November 2019 Updated BRD4182A to Rev. B04
A00 01 August 2019 Initial release.
11.2 SLWSTK6021A Revision History
Kit Revision Released Description
A00 19 November 2019 Initial kit release.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 33
Page 34

12. Document Revision History
Revision 1.0
21 February 2020
Initial document version.
UG430: EFR32xG22 2.4 GHz 6 dBm Wireless Starter Kit User's Guide
Document Revision History
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 1.0 | 34
Page 35

Simplicity Studio
One-click access to MCU and
wireless tools, documentation,
software, source code libraries &
more. Available for Windows,
Mac and Linux!
IoT Portfolio
www.silabs.com/IoT
Disclaimer
Silicon Labs intends to provide customers with the latest, accurate, and in-depth documentation of all peripherals and modules available for system and software implementers using or
intending to use the Silicon Labs products. Characterization data, available modules and peripherals, memory sizes and memory addresses refer to each specific device, and "Typical"
parameters provided can and do vary in different applications. Application examples described herein are for illustrative purposes only. Silicon Labs reserves the right to make changes
without further notice to the product information, specifications, and descriptions herein, and does not give warranties as to the accuracy or completeness of the included information.
Without prior notification, Silicon Labs may update product firmware during the manufacturing process for security or reliability reasons. Such changes will not alter the specifications or the
performance of the product. Silicon Labs shall have no liability for the consequences of use of the information supplied in this document. This document does not imply or expressly grant
any license to design or fabricate any integrated circuits. The products are not designed or authorized to be used within any FDA Class III devices, applications for which FDA premarket
approval is required or Life Support Systems without the specific written consent of Silicon Labs. A "Life Support System" is any product or system intended to support or sustain life and/or
health, which, if it fails, can be reasonably expected to result in significant personal injury or death. Silicon Labs products are not designed or authorized for military applications. Silicon
Labs products shall under no circumstances be used in weapons of mass destruction including (but not limited to) nuclear, biological or chemical weapons, or missiles capable of delivering
such weapons. Silicon Labs disclaims all express and implied warranties and shall not be responsible or liable for any injuries or damages related to use of a Silicon Labs product in such
unauthorized applications.
Trademark Information
Silicon Laboratories Inc.® , Silicon Laboratories®, Silicon Labs®, SiLabs® and the Silicon Labs logo®, Bluegiga®, Bluegiga Logo®, ClockBuilder®, CMEMS®, DSPLL®, EFM®,
EFM32®, EFR, Ember®, Energy Micro, Energy Micro logo and combinations thereof, "the world’s most energy friendly microcontrollers", Ember®, EZLink®, EZRadio®, EZRadioPRO®,
Gecko®, Gecko OS, Gecko OS Studio, ISOmodem®, Precision32®, ProSLIC®, Simplicity Studio®, SiPHY®, Telegesis, the Telegesis Logo®, USBXpress® , Zentri, the Zentri logo and Zentri
DMS, Z-Wave®, and others are trademarks or registered trademarks of Silicon Labs. ARM, CORTEX, Cortex-M3 and THUMB are trademarks or registered trademarks of ARM Holdings.
Keil is a registered trademark of ARM Limited. Wi-Fi is a registered trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance. All other products or brand names mentioned herein are trademarks of their respective
holders.
Silicon Laboratories Inc.
400 West Cesar Chavez
Austin, TX 78701
USA
SW/HW
www.silabs.com/simplicity
Quality
www.silabs.com/quality
Support and Community
community.silabs.com
http://www.silabs.com
 Loading...
Loading...