Page 1

UG409: RAILtest User’s Guide
The RAILtest application (RAILtest) provides you with a simple tool
for testing the radio and the functionality of the RAIL library. For
more advanced usage, developers must write software against the
RAIL library and create a custom radio configuration.
Proprietary is supported on all EFR32FG devices. For others, check the device's data
sheet under Ordering Information > Protocol Stack to see if Proprietary is supported. In
Proprietary SDK version 2.7.n, Connect is not supported on EFR32xG22.
KEY POINTS
• Command Line Interface description
• Application features
• Protocol-s pecific features
• Testing modes
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5
Page 2

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Overview
1 Overview
The following is a summary of functionality provided as part of the RAILtest application:
• Transmit and receive packets
• Schedule transmits at a specific time in the RAIL timebase
• Configure RAIL address filtering to receive only specific packets
• Enable CCA mechanisms (CSMA/LBT) to validate that a channel is clear before transmit
• Set a timer callback in the RAIL timebase to see how the RAIL timer API works
• Change the transmit channel within the current configuration's band
• Change the transmit power level
• Enable RF energy sensing of a specified duration across the 2.4 GHz and/or Sub 1-GHz bands, and sleep to wake on this event.
• Output a continuous unmodulated tone for debugging
• Output a continuous modulated PN9 stream for debugging
• Enter into direct mode where data can be sent and received using asynchronous GPIOs as input and output
1.1 About RAILtest Versions
Gecko SDK Suite (GSDK) v3.0 contains an update to RAILtest, released as version 2.9. Users who have not yet transitioned to GSDK
v3.0 and are still working with GSDK v2.7.x will be using RAILtest version 2.8. During transition, information is supplied for both versions.
1.2 Modes
RAILtest can be in a number of different modes. Each of these modes enables a subset of the test application's functionality, so that
nonsensical commands (such as trying to transmit a tone and a packet at the same time) are ignored. The following lists supported
modes, with a short description.
• None - The app is doing nothing, but the radio may be on. Parameters can be set in this mode based on the current radio state, and
the timer can be used.
• Stream - Send a stream of pseudo-random bits.
• Tone - Send a tone at the carrier frequency.
• ContinuousTx - Send an unending stream of packets, separated by a configurable delay.
• DirectMode - Send data to and from a GPIO, without any packet handling.
• PacketTx - Send a specific number of packets, with a summary print at the end.
• ScheduledTx - Send one packet scheduled in the future.
• TxAfterRx - Schedule a packet after each RX after a specific delay.
• RxOverflow - Overflow on receive by delaying in RAILCb_RxPacketReceived.
• TxUnderflow - Underflow by not loading data for the next TX sequence.
• TxCancel - Cancel a single packet transmit to force an error callback.
• RfSense - Sense RF energy to wake the radio.
• PER (Packet Error Rate) test - A GPIO is toggled, and stats are gathered on received packets.
• BER (Bit Error Rate) test - Statistics are gathered on received bits.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 2
Page 3

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Command Line Interface
2 Command Line Interface
The most powerful way to interact with the sample application is through the provided command line interface.
2.1 Command Input
The syntax for this interface is the standard command [arg0, arg1, ...] syntax, where the number and type of arguments depend on the
specific command. Numeric values can be prefixed with 0x to indicate hexadecimal values.
In RAILtest 2.8 (GSDK v2.7.x), the maximum number of arguments to any command is set by the value of MAX_COMMAND_ARGUMENTS,
and the maximum length of each command line is set by the value of APP_COMMAND_INTERFACE_BUFFER_SIZE.
In RAILtest 2.9 (GSDK v3.0), the maximum number of arguments to any command is set by the value of
SL_CLI_MAX_INPUT_ARGUMENTS, and the maximum length of each command line is set by the value of
SL_CLI_INPUT_BUFFER_SIZE.
For a full listing of the command options see section 5.3.4 Full Help Text or use the help command.
2.2 Command Responses
All responses to commands are formatted in a human readable yet parsable format. This format has two variations: single and multiline.
Both follow these rules.
• Start and end with curly braces { }
• List the command name, enclosed in parentheses ( )
• Contain any number of tag/value pairs enclosed in curly braces { }
• Carriage returns and line feeds are treated as whitespace by any parser
2.2.1 Single Response
Used when a command has a single response.
• There is a single start/end curly brace wrapper
• Tag/value pairs are wrapped in a single set of curly braces, separated by a colon {tag:value}.
Example:
> getchannel
{{(getchannel)}{channel:4}}
2.2.2 Multi Response
Used when a command may have multiple responses, such as when reading a block of memory or receiving multiple packets.
• Response starts with a header, delimited by a hash # at the start of the line.
• Header includes the command name, followed by any tags individually wrapped with curly braces { }.
• Following the header, any number of responses can be provided.
• Data lines do not contain the command name or tags, only the values that correspond to the tags in the order described in the header.
Example:
> getmemw 0x20000000 4
#{{(getmemw)}{address}{value}}
{{0x20000000}{0x0000e530}}
{{0x20000004}{0x000051c6}}
{{0x20000008}{0x0000c939}}
{{0x2000000c}{0x0000e090}}
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 3
Page 4

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Peripherals
3 Peripherals
3.1 Buttons
When enabled, RAILtest can use up to two buttons. When pressed for a short duration (less than 1 second), the first button causes
RAILtest to transmit one packet. When pressed for a long duration (greater than 1 second), the first button causes RAILtest to continuously
transmit packets until the button is pushed again for a long duration. Pressing the second button causes RAILtest to increment the channel
number used for TX and RX until the channel number wraps around to its beginning value.
Starting in RAILtest 2.9 (GSDK v3.0), button functionality is disabled by default. In order to enable button functionality, the Simple
Button Driver software component needs to be enabled with an instance name of btn0 for the first button and btn1 for the second
button.
3.2 LEDs
When enabled, RAILtest can use up to two LEDs. The first LED toggles when a packet is successfully received, and the second LED
toggles when a packet is successfully transmitted.
Starting in RAILtest 2.9 (GSDK v3.0), LED functionality is disabled by default. In order to enable LED functionality, the Simple LED
Driver software component needs to be enabled with an instance name of led0 for the first LED and led1 for the second LED.
3.3 LCD
When enabled, RAILtest can use the LCD to show packets received and transmitted as well as the channel selected and radio activity.
Starting in RAILtest 2.9 (GSDK v3.0), LCD functionality is disabled by default. In order to enable LCD functionality, the RAILtest Ap-
plication, Graphics software component needs to be enabled.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 4
Page 5

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Application Features
4 Application Features
4.1 Packet Mode
The application starts in packet mode with the receiver enabled. In this mode the application receives and transmits packets using the
radio's frame controller hardware. To disable receive use the rx 0 command. To transmit use tx [numPackets] or press button PB0
if button support is enabled. To toggle the continuous transmit mode, hold PB0 for a couple of seconds if button support is enabled, or
run the tx 0 command. When transmitting multiple packets or infinite packets there is a configurable delay in between each transmit. By
default this is 250 ms, but it can be set with the setTxDelay command.
All received packets are printed to the console with information like CRC, RSSI, and timestamp as long as notifications are enabled.
Notifications are enabled by default, but they can be turned off with the setRxNotification 0 command.
The application by default sends a fixed packet, but it is possible to override the values through setTxPayload. The command allows
you to modify the values of the payload at specific offsets. For instance, to modify the first 4 bytes sent in the packet to be 0x01 0x02
0x03 0x04, use:
setTxPayload 0 0x01 0x02 0x03 0x04
To view the currently configured TX Packet information, use printTxPacket.
Note: The packet format depends on the current PHY configuration. If your PHY has a dynamic frame length byte then that will be
used to determine how much data should be sent.
4.2 Direct Mode
In direct mode the radio will still attempt to decode received packets, but it will only be able to transmit packets sent over the DIN pin. The
GPIOs for direct mode are fixed for now to the following pins.
DOUT - EFR32_PC11 -> EXP_HEADER16/WSTK_P13
DIN - EFR32_PC10 -> EXP_HEADER15/WSTK_P12
The data on these pins is asynchronous and can be connected directly to a UART. To enter direct mode, issue the directMode 1
command after starting the app. To leave direct mode use directMode 0. If you want to transmit, you must enable the transmitter by
issuing directTx 1 and later stop it with directTx 0. Receive is controlled using the standard rx 1/0 command, but is enabled by
default when not transmitting.
Note: Direct mode does not work in certain modulations (for example 4FSK). If you require this mode contact support to verify your
configuration.
4.3 Channels/Frequencies
The specific channel configuration depends on the PHY configuration you have chosen for your test app. To switch between channels
use the setChannel [num] command. If RX is active (rx 1) then any TX or RX in progress will be aborted and the new channel
switched to. In addition, if button support is enabled, you can use button PB1 to cycle through channels.
To modify your frequency to a value not defined in the channel list, you will need to set the application into the FREQUENCY_OVERRIDE
debug mode via setDebugMode which tells the application to ignore the current channel selection. Once in the FREQUENCY_OVERRIDE
debug mode, you can use the freqOverride command to switch to another center frequency.
Note: The freqOverride command requires you to be in FREQUENCY_OVERRIDE debug mode. The radio state must also be IDLE
for the frequency to be modified -- call rx 0 first.
setDebugMode 1
freqOverride 865000000
To leave FREQUENCY_OVERRIDE debug mode and return to normal channel-based operation, use setDebugMode 0.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 5
Page 6

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Application Features
Caution: The modem is configured to a specific band. The application will not restrict you from changing the frequency out of band but
this could cause significant issues, including forcing a chip reboot.
4.4 Command Scripting
The command scripting feature built into RAILtest allows for CLI commands to be executed without back-and-forth interaction on the
command line. The same commands that can be executed one by one can be queued up within RAILtest and executed sequentially later.
Additionally, a command script can be saved to flash, and any script saved to flash will run automatically on device boot.
In RAILtest 2.8 (GSDK v2.7.x) support is integrated into RAILtest to use a command script in RAM, but to use a command script in flash,
the Flash Data plugin must be enabled.
In RAILtest 2.9 (GSDK v3.0), to use a command script in RAM, the CLI Storage in RAM software component needs to be enabled
with an instance name of inst0. To use a command script in flash, the CLI Storage in NVM3 software component needs to be
enabled with an instance name of inst0.
This is an example of how to enter, print, and run a script from RAM. Note that the wait command needs to be used in order to allow
time for the first scripted command (that is, tx 1) to successfully run to completion before the second scripted command (that is, tx 2)
starts.
enterScript
tx 1
wait 500000
tx 2
endScript
printScript
runScript
This is an example of how to enter, print, run, and clear a script from flash.
enterScript 1
tx 1
wait 500000
tx 2
endScript
printScript 1
runScript 1
clearScript 1
This is an example of how to enter and run a script from flash on boot.
enterScript 1
tx 1
wait 500000
tx 2
endScript
reset
Note: For rapid command entry (for example, automated testing), you may need to increase the USART RX buffer from its default
value, specified by a define similar to SL_IOSTREAM_USART_VCOM_RX_BUFFER_SIZE in RAILtest 2.9, to account for long
command string entry being interrupted by chip interrupts. For lengthy (for example hours long) automated test programs, a
notable decrease in test time will come from disabling CLI command history, setting SL_CLI_NUM_HISTORY_BYTES to 0 (RAILtest 2.9).
4.5 RAIL Timebase
The microsecond RAIL timebase is used for features requiring specific timing. You can read this timebase with getTime, and you can
also set this microsecond timebase with setTime. Avoid changing the timebase when the timebase is actively being used, such as during
clear channel assessment, during scheduled TX or RX, and so on.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 6
Page 7

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Application Features
4.6 Scheduled TX
The RAIL API has its own timebase that can be used to schedule the start of transmits. It measures time as a 32-bit integer in microseconds. As part of this change many APIs will now return the time they were run, all RX packets report the time they were received, and all
TX packets return the time that the transmit was completed. There is also the command getTime to print the current time in the RAIL
timebase.
To test scheduled transmit we provide two commands: txAt and txAfterRx. These allow you to send a packet at an absolute time in
the RAIL timebase or exactly some number of microseconds after each receive, respectively.
Note: These APIs should provide reliable timing but you may have to adjust for overhead that relates to preamble and PA ramp time
in order to transmit at the exact time you want.
4.7 Clear Channel Assessment
The RAIL API provides the ability to specify a Pre-Transmit Operation for every transmit, one of which is Scheduled Transmit discussed
above. Others are also provided to support two common medium access methodologies that delay transmission until the channel is clear:
• CSMA-CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance) -- based on IEEE 802.15.4 specification
• LBT (Listen Before Talk) -- based on ETSI EN 300 220-1 specification
Both CSMA-CA and LBT are similar: Before transmission, a device waits for a random 'backoff' period of time and then performs a CCA
(Clear Channel Assessment) for a fixed period of time. If the channel is free, the transmit proceeds; if busy, the process is repeated with
a new random backoff period. The random backoff period is determined by a randomly chosen multiple of a fixed backoff unit of time.
For CSMA-CA, the random multiplier is a power-of-2 exponential whose range increases on each try up to a limit, and the CCA period is
typically short -- smaller than a backoff unit and around the time it takes a small packet to be transmitted. For LBT, the random multiplier
is linear and typically chosen to allow the random period to range up to the CCA period, which can be quite long -- much longer than the
on-air time of the actual transmission it's gating. LBT also specifies that if the channel is found busy during CCA, the process cannot
repeat until the channel is free.
In RAIL and RAILtest, several parameters are exposed through the setLbtParams and getLbtParams commands to configure either
CSMA-CA or LBT operation. Their interpretation depends on which mode has been chosen:
• minBo -- Minimum backoff. For CSMA-CA the first try's power-of-2 random exponential range, that is the backoff multiplier, will
range from 0 to 2^minBo - 1. Subsequent tries increase minBo by 1 up to maxBo. For LBT this is the minimum backoff multiplier
for all tries, typically 0.
• maxBo -- Maximum backoff. For CSMA-CA this is the maximum power-of-2 random exponential range to which subsequent tries
can increase. For LBT this is the maximum backoff multiplier for all tries, typically maxBo * backoff = duration. If both minBo
and maxBo are 0, a non-random fixed backoff time is configured.
• tries -- The maximum number of tries ('busy' CCAs), up to 15, that the CSMA-CA or LBT operation will tolerate before declaring
the transmission a failure due to channel busy. A value of 0 will perform no CCA assessments, and always transmit immediately.
• thresh -- The CCA RSSI threshold, in dBm, above which the channel is considered 'busy'.
• backoff -- The backoff unit period, in RAIL's microsecond time base. This is multiplied by the random backoff multiplier con-
trolled by minBo and maxBo to determine the overall backoff period. For random backoffs, this value must be in the range 100
to 511 microseconds; for fixed backoffs it can go up to 65535 microseconds.
• duration -- The CCA duration, in RAIL's microsecond time base. The radio determines the maximum RSSI during this period
for comparison against the CCA threshold.
• timeout -- An overall timeout, in RAIL's microsecond time base, for the operation. If transmission does not start before this
timeout expires, the transmission will fail. This is more important for limiting LBT due to LBT's unbounded requirement that if the
channel is busy, the next try must wait for the channel to clear. A value of 0 indicates that no timeout is imposed.
Several examples:
• RAILtest's default parameters are suitable for the IEEE 802.15.4 PHY for CSMA-CA, equivalent to: setLbtParams 3 5 4 -
75 320 128 0. This specifies up to 4 CCA attempts. The 1st will choose a random multiplier of 0..7 (2^3-1), the 2nd 0..15
(2^4-1), the 3rd 0..31 (2^5-1), and the 4th 0..31 since the maxBo limit is 5.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 7
Page 8
UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Bytes: 0 - 255
0 - 8
0 - 255
0 - 8
Variable
No Match
bit0
bit1
bit2
bit3
bit4
Address 0
Address 1
Address 2
Address 3
Application Features
• ETSI EN 300 220-1 LBT's parameters in the 863 MHz band would be: setLbtParams 0 10 15 -80 500 5000 1000000.
This specifies a 5 millisecond CCA duration with random backoff period of 0..5 milliseconds (0..10 * 0.5 milliseconds) and a 1
second timeout limit in case the channel remains busy.
• A single CCA of 160 microseconds after a fixed 1024 microsecond backoff, against a -70 dBm threshold would be: setLbt-
Params 0 0 1 -70 1024 160 0.
In RAILtest, CSMA-CA and LBT are enabled as a mode applied to subsequent transmits through setLbtMode, whose choices are 'off',
'csma', and 'lbt'.
Note: On EFR32, LBT is currently implemented using the EFR32's CSMA-based hardware engine, so LBT parameters are mapped to
roughly equivalent CSMA parameters.
Note: Scheduled Transmit and Clear Channel Assessment are currently mutually exclusive, with Scheduled Transmit taking prece-
dence.
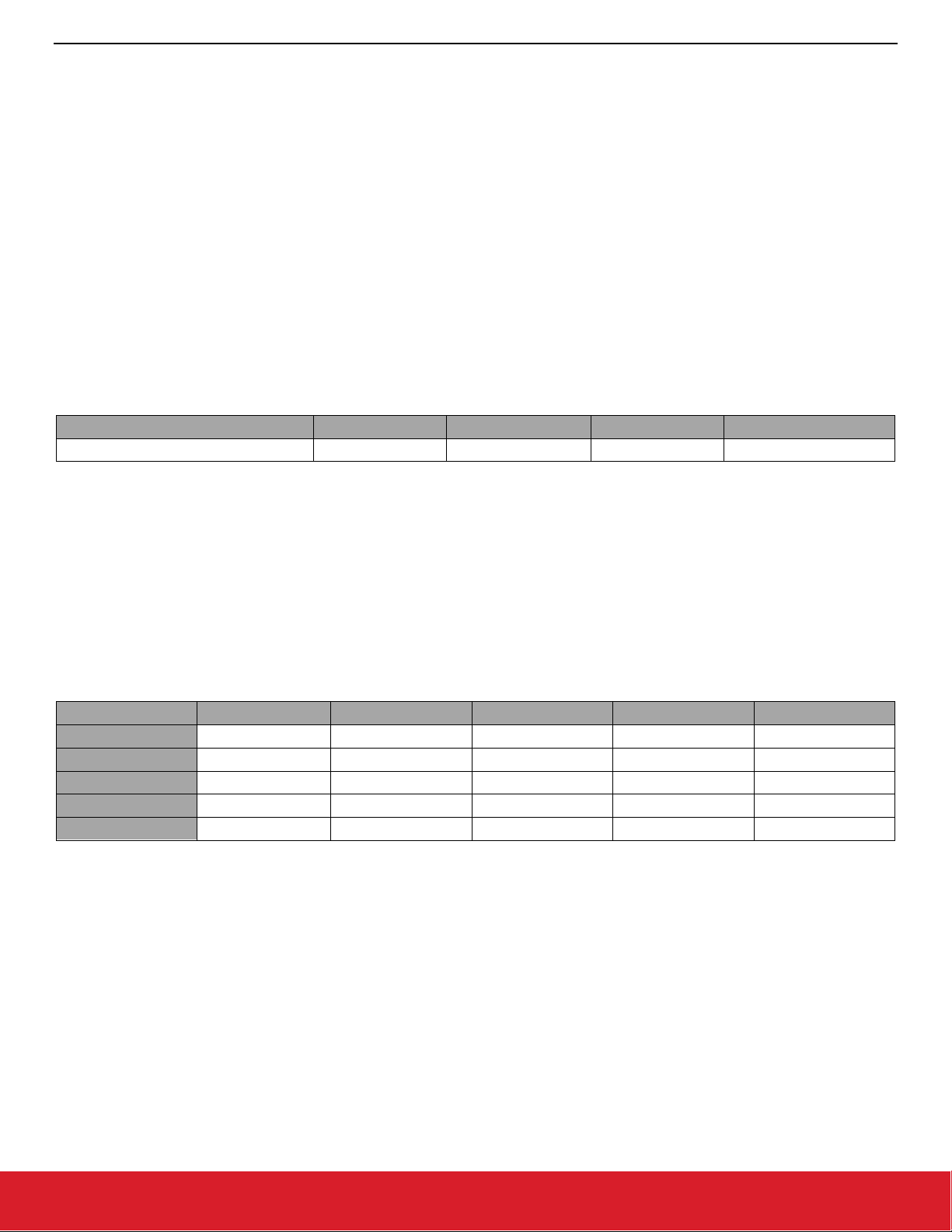
4.8 Address Filtering
The address filtering code examines the packet as follows.
Data0 Field0 Data1 Field1 Data2
In the above structure, anything listed as DataN is an optional section of bytes that will not be processed for address filtering. The FieldN
segments reference the specific sections in the packet that will be examined during filtering for addresses. There may be up to four
addresses per field and they may each have a size of up to 8 bytes. To set up address filtering, first configure where the addresses are
in the packet and how long they are. Next, configure what combinations of matches in Field0 and Field1 should constitute an address
match. Lastly, enter addresses into the tables for each field and enable them.
The configAddressFilter command can be used to set the offsets and sizes for the address fields as well as how combinations of
matches in Field0 and Field1 are combined to determine whether or not an address matches.
Configuring which combinations of Field0 and Field1 constitute a match is the most complex portion of the address filter. The easiest way
to think about this is with a truth table. If you consider each of the four possible address entries in a field, you can have a match on any
one of those or a match for none of them. This is shown in the 5x5 truth table below where Field0 matches are the rows and Field1
matches are the columns.
Fields No Match Address 0 Address 1 Address 2 Address 3
bit5 bit6 bit7 bit8 bit9
bit10 bit11 bit12 bit13 bit14
bit15 bit16 bit17 bit18 bit19
bit20 bit21 bit22 bit23 bit24
Since this is only 25 bits it can be represented in one 32bit integer, where a 1 indicates filter pass and a 0 indicates filter fail. This is the
matchTable parameter in the configAddressFilter command. For a simple one field configuration set the matchTable to 0x1fffffe
and for a two field configuration pairing indices across the fields use 0x1041040.
After you have configured address filtering you must also set which addresses are valid and enable them. This can be done with the
setAddress and setAddressEnable commands. You must also turn on the address filtering feature with the setAddressFilter-
ing command.
As an example, to configure an address of 0x00 0x01 0x02 0x03 in field0, index0 for a filter that has one field starting at offset 0 with
a length of 4 bytes, use the following commands.
configAddressFilter 0x1fffffe 0 4 0 0
setAddress 0 0 0x00 0x01 0x02 0x03
setAddressEnable 0 0 1
setAddressFiltering 1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 8
Page 9

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Application Features
In addition to the standard address filtering, if the frame length decoding algorithm is by frame type, then additional filtering functionality
is available. Address filtering can be enabled or disabled based on the frame type that is decoded. This can be set by the addressFil-
terByFrame command. This command takes an 8-bit bitmask, in which each bit represents whether addresses are present in that frame.
The least significant bit determines whether to apply the address filter to frame 0, and the most significant bit determines whether to apply
the address filter to frame 7. addressFilterByFrame must be called after configAddressFilter for it to take effect.
4.9 Automatic State Transitions
RAIL provides an API to configure state transitions to happen automatically on certain radio events:
• a successful receive
• a failed receive
• a successful transmission
• a failed transmission
All of these events can transition to a radio state of idle or receive. In addition, a transmission can be configured to happen after a
successful receive.
These states are configured through the setTxTransitions and setRxTransitions commands. Each of these commands take in
two radio states, which are passed in as single letter strings. To transition to receive after a transmission, regardless of its success, the
command is setTxTransitions r r.
When settings the receive transitions, there is also a third argument, a bitfield to configure which events count as errors. The documentation for this bitfield can be found in the RAIL library documentation. Calling setRxTransitions i i 0xFF will ignore all errors that
are possible to ignore, and transition the radio to idle after attempting to receive one packet.
In addition to the state transitions, timings can be set for the transitions. The six timings that are currently configurable are:
• idleToRx
• idleToTx
• rxToTx
• txToRx
• rxSearchTimeout
• txToRxSearchTimeout
Each of these timings configures an amount of delay between two states. The search timeouts allow you to set a maximum time that the
chip will sit in the RX search state. These can be used to implement short receive timeouts. The rxSearchTimeout is used when transitioning to receive from idle and the txToRxSearchTimeout is used when transitioning to receive from a past transmit. Setting
[rx|txToRx]SearchTimeout to zero disables the timeout and radio will stay in RX until an event changes the state. Transitions to idle simply
happen as fast as possible. Each timing is configurable in microseconds, up to a maximum of 13 ms, with the exception of txToRxSearchTimeout which could be up to a quarter of the RAIL timebase, which is 2^32/4 microseconds or 18 minutes. For example, to disable the
timeouts and set all other transitions to take 200 µs, use:
setStateTimings 200 200 200 200 0 0
4.10 Auto-Acknowledgment
RAIL contains auto-acknowledgment (ACK) APIs that are exposed through the RAILtest command interface. To initialize and enable this
functionality use autoAckConfig. For example, autoAckConfig rx 100 192 1000 will configure the 'defaultState', the state at
which the radio returns after an ACK operation, to receive. Transitions from idle will take 100 µs. Turnaround transitions will take 192 µs
and will wait for an ACK for 1000 µs. To load a custom ACK payload, call setAckPayload and setAckLength.
If a packet is received during the ACK window, then the isAck flag for that packet will be true. The ACK windows begins at the end of
the turnaround time and lasts for the timeout length. If auto acknowledgment is not enabled, then the isAck flag will always be false.
To customize ACK functionality, users can use the autoAckPause command to either skip the wait for an ACK on the transmit side or
skip the transmit of an ACK on the receive side. To modify if/how the ACK is transmitted after a receive operation, use the setTxAckOp-
tions command.
Conversely, after a transmit operation, waiting for ACK is controlled by the TX options configured by configTxOptions. When combined
with the txWithOptions command, the configuration is honored. However, whenever a simple tx is called, configured options will be
ignored and defaults will be used for the transmit (that is, do not wait for ACK, send CRC, use sync word 0).
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 9
Page 10

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Application Features
4.11 RF Energy Sensing
The EFR32 has the ability to sense the presence of RF Energy above -20 dBm within either or both the 2.4 GHz and Sub 1-GHz bands
and trigger an event if that energy is continuously present for certain durations of time.
This feature is exposed through library RAIL_RfSense() and RAIL_RfSensed() APIs, whose use is exemplified by the RAILtest
commands rfSense and sleep. Both commands allow you to specify the duration in microseconds of continuous RF energy, and which
RF band(s) to monitor. The requested duration will be mapped to the nearest duration supported by the hardware; it is not terribly precise
and can be off by a factor of 2 or more. Once RF energy of sufficient duration has been sensed, the sensing operation terminates and a
new one must be started if additional sensing is desired.
The rfSense command activates sensing in the background during normal RAILtest operation, and will report when energy of sufficient
duration has been detected through an asynchronous rfSensedCheck message. Note that sensing energy within a band on EFR32
precludes normal packet reception in that same band; this is by design.
The sleep command allows you to activate RF sensing in combination with entering one of the Energy-Saving Modes EM0..EM4. To
wake from these modes, RF energy of the specified duration and band must be sensed. Energy modes 0 through 3 will also wake and
terminate RF sensing on any serial input to the CLI. EM4 does not support waking on serial input. It will only wake on RF sense or a pin
reset.
Some examples:
RFSENSE Legacy Mode:
> rfSense 500 2 // Sense RF energy of ~0.5ms or longer in sub-GHz band
{{(rfsense)}{RfSense:MHz}{RfUs:413}} // Closest HW supports is ~0.4ms
...
{{(rfSensedCheck)}{RfSensed:MHz}{RfUs:413}}
> sleep 2 500 1 // Sleep in EM2 for RF energy of ~0.5ms in 2.4 GHz band
{{(sleep)}{EM:2}{SerialWakeup:On}{RfSense:GHz}}
...
{{(sleepWoke)}{EM:2}{SerialWakeup:No}{RfSensed:Yes}{RfUs:413}}
> sleep 4 500 3 // Sleep in EM4 for RF energy of ~0.5ms in any band
{{(sleep)}{EM:4s}{SerialWakeup:Off}{RfSense:Any}}
...
{{(reset)}{App:RAILtest}{Built:Jul 19 2019 13:36:24}}
{{(sleepWoke)}{EM:4s}{SerialWakeup:No}{RfSensed:Yes}}
RFSENSE Selective Mode (Transmit Node Setup):
> rx 0
{{(rx)}{Rx:Disabled}{Idle:Enabled}{Time:27993006}}
> configRfSenseWakeupPhy
{{(configRfSenseWakeupPhy)}{RFSense Wakeup PHY:Enabled}}
> fifoModeTestOptions 1 0 // Manually load Tx FIFO to transmit only preamble and syncword
{{(fifoModeTestOptions)}{TxFifoManual:Enabled}{RxFifoManual:Disabled}}
> setRfSenseTxPayload 0x2 0xB16F // <Syncword Size(Bytes)> <Syncword>
{{(setRfSenseTxPayload)}{RFSense Payload:Set}}
> tx 1
{{(tx)}{PacketTx:Enabled}{None:Disabled}{Time:54463886}}
{{(appMode)}{None:Enabled}{PacketTx:Disabled}{Time:57481907}}
{{(txEnd)}{txStatus:Complete}{transmitted:1}{lastTxTime:57481861}{timePos:6}{lastTxStart:57398486}{ccaSuccess:0}{failed:0}{lastTxStatus:0x000000000}{isAck:False}}
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 10
Page 11

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Application Features
RFSENSE Selective Mode (Receive Node Setup for EFR32xG22):
> sleep 2 2 0xB16F 1 // <EM Mode> <Syncword Size(Bytes)> <Syncword> <RFBand>
{{(sleep)}{RfSense:Enabled}{None:Disabled}{Time:14176659}}
...
{{(sleepWoke)}{EM:2}{SerialWakeup:No}{RfSensed:Yes}{RfUs:0}}
> rfsense 2 0xB16F 1 // <Syncword Size(Bytes)> <Syncword> <RFBand>
{{(rfsense)}{RfSense:Enabled}{None:Disabled}{Time:44817696}}
> {{(rfSensedCheck)}{RfSensed:GHz}{RfUs:0}}
4.12 Multi-Timer
If the multi-timer is never enabled (or subsequently disabled with enableMultiTimer), then the RAIL timer is a single-instance, hard-
ware timer. If the multi-timer is enabled, the RAIL timer becomes one instance of the software-based multi-timer. The multi-timer can only
be enabled or disabled when no timers are running.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 11
Page 12

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Protocol-Specific Features
5 Protocol-Specific Features
5.1 IEEE 802.15.4
RAIL provides IEEE 802.15.4-specific hardware acceleration that can be configured through RAILtest commands. To configure the IEEE
802.15.4 2.4 GHz Radio Configuration, use config2p4GHz802154. This will configure the IEEE 802.15.4 2.4 GHz modem settings as
well as channel scheme, making channels 11-26 available for use. To configure IEEE 802.15.4 hardware acceleration, use the ena-
ble802154 command. The options exposed in enable802154 allow you to configure similar parameters as autoAckConfig.
The IEEE 802.15.4 ACK payload is already loaded into the ACK buffer; do not call setAckPayload or setAckLength. However, you
will want to enable the Wait-For-ACK transmit option through configTxOptions so the hardware looks for the specific ACK correspond-
ing to the transmitted packet. RAILtest is configured to always set frame pending bit in the ACK if it successfully receives a data command
to the node. Any ACK modifications should use commands detailed in section 4.10 Auto Acknowledgment.
Further IEEE 802.15.4 configuration is done through acceptFrames, setPromiscuousMode, and setPanCoordinator. To configure
the node's address, use the setPanId802154, setShortAddr802154, or setLongAddr802154 commands. These commands map
very closely to the RAIL API that it wraps, so refer to the RAIL Library doxygen for further information.
From this point, use the normal tx and rx commands to send packets back and forth.
Transmit side:
> rx 0
{{(rx)}{Rx:Disabled}{Idle:Enabled}{Time:1846852}}
> config2p4GHz802154
{{(config2p4GHz802154)}{802.15.4:Enabled}}
> enable802154 rx 100 192 1000
{{(enable802154)}{802.15.4:Enabled}{rxDefaultState:Rx}{txDefaultState:Rx}{idleTiming:100}{turnaroundTime:192}{ackTimeout:1000}}
// Turn on transmit wait-for-ACK option
> configTxOptions 1
{{(configTxOptions)}{waitForAck:True}{removeCrc:False}{syncWordId:0}{txAntenna:Any}{altPreambleLen:False}{ccaPeakRssi:False}}
// Load packet directed towards the receive side
// Packet has the destination address set on the receive side.
> setTxLength 26
{{(setTxLength)}{TxLength:26}}
> setTxPayload 0 0x1b 0x61 0x98 0x00 0x34 0x12 0x44 0x33 0x55 0x44
{{(setTxPayload)}{len:26}{payload: 0x1b 0x61 0x98 0x00 0x34 0x12 0x44 0x33 0x55 0x44 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00}}
> setTxPayload 10 0x00 0x01 0x02 0x03 0x04 0x05 0x06 0x07 0x08 0x09
{{(setTxPayload)}{len:26}{payload: 0x1b 0x61 0x98 0x00 0x34 0x12 0x44 0x33 0x55 0x44 0x00 0x01 0x02 0x03 0x04
0x05 0x06 0x07 0x08 0x09 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00}}
> setTxPayload 20 0x0a 0x0b 0x0c 0x0d 0x0e 0x0f
{{(setTxPayload)}{len:26}{payload: 0x1b 0x61 0x98 0x00 0x34 0x12 0x44 0x33 0x55 0x44 0x00 0x01 0x02 0x03 0x04
0x05 0x06 0x07 0x08 0x09 0x0a 0x0b 0x0c 0x0d 0x0e 0x0f}}
// Assumes there is another node that will receive and ACK
> tx 1
> {{(tx)}{PacketTx:Enabled}{None:Disabled}{Time:157683158}}
{{(appMode)}{None:Enabled}{PacketTx:Disabled}{Time:157689582}}
{{(txEnd)}{txStatus:Complete}{transmitted:1}{lastTxTime:157689516}{failed:0}{lastTxStatus:0x0}{isAck:False}}
{{(rxPacket)}{len:4}{timeUs:157689914}{crc:Pass}{rssi:-20}{lqi:96}{phy:0}{isAck:True}{syncWordId:0}{antenna:0}{channelHopIdx:254}{payload: 0x05 0x02 0x00 0x00}}
// Assumes a node does not ACK
> tx 1
> {{(tx)}{PacketTx:Enabled}{None:Disabled}{Time:165139148}}
{{(rxAckTimeout)}{ackTimeoutDuration:1021}}
{{(appMode)}{None:Enabled}{PacketTx:Disabled}{Time:165187375}}
{{(txEnd)}{txStatus:Complete}{transmitted:1}{lastTxTime:165145515}{failed:0}{lastTxStatus:0x0}{isAck:False}}
Receive side:
> rx 0
{{(rx)}{Rx:Disabled}{Idle:Enabled}{Time:1846852}}
> config2p4GHz802154
{{(config2p4GHz802154)}{802.15.4:Enabled}}
> enable802154 rx 100 192 1000
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 12
Page 13

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Protocol-Specific Features
{{(enable802154)}{802.15.4:Enabled}{rxDefaultState:Rx}{txDefaultState:Rx}{idleTiming:100}{turnaroundTime:192}{ackTimeout:1000}}
> setPanId802154 0x1234 // PANID: 0x1234, OTA Value: 0x34 0x12
{{(setPanId802154)}{802.15.4PanId:Success}}
> setShortAddr802154 0x3344 // Short Addr: 0x3344, OTA Value: 0x44 0x33
{{(setShortAddr802154)}{802.15.4ShortAddress:Success}}
// Long Addr (OTA): 0xDD 0xCC 0xBB 0xAA 0x99 0x88 0x77 0x66
> setLongAddr802154 0xDD 0xCC 0xBB 0xAA 0x99 0x88 0x77 0x66
{{(setLongAddr802154)}{802.15.4LongAddress:Success}}
> rx 1
{{(rx)}{Rx:Enabled}{Idle:Disabled}{Time:2070858}}
// Receive a packet and ACK it
{{(rxPacket)}{len:26}{timeUs:29662246}{crc:Pass}{rssi:-15}{lqi:82}{phy:0}{isAck:False}{syncWordId:0}{antenna:0}{channelHopIdx:254}{payload: 0x1b 0x61 0x98 0x00 0x34 0x12 0x44 0x33 0x55 0x44 0x00 0x01 0x02 0x03 0x04
0x05 0x06 0x07 0x08 0x09 0x0a 0x0b 0x0c 0x0d 0x0e 0x0f}}
5.2 Bluetooth Low Energy
RAIL provides Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)-specific hardware acceleration. RAILtest provides a few wrappers over these APIs but since
BLE is so timing-critical, not much can be done through RAILtest commands. To enable BLE hardware acceleration, use the setBleMode
1 command. You can then configure channel-specific settings with setBleChannelParams. A preset configuration to enable advertising
on channel 37 is available using the setBleAdvertising command.
RAILtest can output a BLE advertising packet on channel 37 with the following commands:
> rx 0
rx 0
{{(rx)}{Rx:Disabled}{Idle:Enabled}{Time:1999306}}
> setBleMode 1
setBleMode 1
{{(setBleMode)}{BLE:Enabled}}
> setBleAdvertising
setBleAdvertising 37
{{(setBleAdvertising)}{AdvertisingChannel:37}}
{{(setBleAdvertising)}{len:28}{payload: 0x02 0x1a 0xff 0xee 0xdd 0xcc 0xbb 0xaa 0x02 0x01 0x06 0x10 0x08 0x53
0x69 0x6c 0x61 0x62 0x73 0x20 0x52 0x41 0x49 0x4c 0x54 0x45 0x53 0x54}}
> tx 0
tx 0
> {{(tx)}{ContinuousTx:Enabled}{None:Disabled}{Time:16160500}}
After these commands, use your phone to search for available Bluetooth devices. You should see 'Silabs RAILTEST' as an available
device. RAILtest is not a connectable device.
5.3 Z-Wave
RAIL provides Z-Wave-specific hardware acceleration that can be configured through RAILtest commands. Users can use the
setZWaveMode command to enter Z-Wave mode and then setZWaveRegion to specify one of the region-specific PHYs, which gener-
ally consist of three separate channels. More about these PHYs can be found in ITU-T G.9959. In order to send packets between nodes,
the following commands must be entered on both nodes, using the same region.
RX Node:
// Turn the radio off first in order to configure it
> rx 0
{{(rx)}{Rx:Disabled}{Idle:Enabled}{Time:99647646}}
// Enable Z-Wave Mode (1) – beam detection enabled (0x2), promiscuous mode off (0x1)
> setzwavemode 1 2
{{(setZWaveMode)}{ZWAVE:Enabled}{Promiscuous:Disabled}{BeamDetect:Enabled}}
// Specify the EU Region
> setzwaveregion 0
{{(setZWaveRegion)}{ZWaveRegion:EU-European Union}{ZWaveRegionIndex:0}}
On the transmit side, the user must specify the correct Home ID of the target Z-Wave node. This can be skipped, however, by enabling
promiscuous mode on the receiver via setZWaveMode and/or setZWaveOptions. Additionally, the user must specify an accurate length
byte, otherwise the transmitter may encounter an underflow. The CRC will be calculated on the fly by the radio hardware, so there is no
need to specify it explicitly.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 13
Page 14

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Protocol-Specific Features
TX Node:
// Specify the Home ID in the packet. This is a 4-byte value, starting at byte 0
> setTxPayload 0 0xCA 0xFE 0xC0 0xDE
{{(setTxPayload)}{len:16}{payload: 0xca 0xfe 0xc0 0xde 0x33 0x44 0x55 0x66 0x77 0x88 0x99 0xaa 0xbb
0xcc 0xdd 0xee}}
// Specify the length byte (byte 7) for a packet
> setTxPayload 7 15
{{(setTxPayload)}{len:16}{payload: 0xca 0xfe 0xc0 0xde 0x33 0x44 0x55 0x0f 0x77 0x88 0x99 0xaa 0xbb
0xcc 0xdd 0xee}}
On the receiver side, for basic functionality, the node must configure its own Home ID. Note that this will set parameters for the node on
which these commands are executed – they do not set the TX packet contents for outgoing packets. To skip Home ID configuration,
promiscuous mode can also be enabled.
RX Node:
// The Home ID is CAFEC0DE, using a “don’t care” hash
setzwavehomeid 0xCAFEC0DE 0x55
{{(setZWaveHomeId)}{Status:Set}}
For more advanced receiver functionality, or to be used as a sniffer, channel hopping must be configured. As used in Z-Wave networks,
the three channels in each of the Z-Wave regions can be used in rapid succession for different purposes. For a receiving node to be able
to receive these packets on any arbitrary channel, the node uses hardware acceleration to hop through the three different channels at
specific intervals, using preamble sense mode. The following specification configures the correct hopping scheme, with the on-channel
time and preamble sense mode, as well as zero delay between channels. Note, that while this configuration is accurate for most regions,
Japan and Korea regions use 270 µs for all the channels, instead of the 270, 450, and 560 specified below. After this, packets can be
transmitted on channel 0, 1, or 2, and will be received on the receiver node, without having explicitly set the channel.
RX Node:
// Configure the channel hopping algorithm
> configRxChannelHopping 0 2 270 0 1 2 450 0 2 2 560 0
{{(configRxChannelHopping)}{numberOfChannels:3}{buffer:0x200048b0}{Success:True}}
// Enable channel hopping
> enableRxChannelHopping 1
{{(enableRxChannelHopping)}{Success:True}}
TX Node:
setChannel 0
{{(setchannel)}{channel:0}}
> tx 1
> {{(tx)}{PacketTx:Enabled}{None:Disabled}{Time:1518591782}}
{{(appMode)}{None:Enabled}{PacketTx:Disabled}{Time:1518601722}}
{{(txEnd)}{txStatus:Complete}{transmitted:1}{lastTxTime:1518601679}{timePos:6}{lastTxStart:1518597116}{ccaSuccess:0}{failed:0}{lastTxStatus:0x000000000}{isAck:False}}
setChannel 1
{{(setchannel)}{channel:1}}
> tx 1
> {{(tx)}{PacketTx:Enabled}{None:Disabled}{Time:1522247672}}
{{(appMode)}{None:Enabled}{PacketTx:Disabled}{Time:1522258337}}
{{(txEnd)}{txStatus:Complete}{transmitted:1}{lastTxTime:1522258277}{timePos:6}{lastTxStart:1522252961}{ccaSuccess:0}{failed:0}{lastTxStatus:0x000000000}{isAck:False}}
setChannel 2
{{(setchannel)}{channel:2}}
> tx 1
> {{(tx)}{PacketTx:Enabled}{None:Disabled}{Time:1526903409}}
{{(appMode)}{None:Enabled}{PacketTx:Disabled}{Time:1526930874}}
{{(txEnd)}{txStatus:Complete}{transmitted:1}{lastTxTime:1526930821}{timePos:6}{lastTxStart:1526908743}{ccaSuccess:0}{failed:0}{lastTxStatus:0x000000000}{isAck:False}}
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 14
Page 15

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Protocol-Specific Features
RX Node:
{{(rxPacket)}{len:13}{timeUs:1508290532}{timePos:4}{crc:Pass}{rssi:10}{lqi:114}{phy:0}{isAck:False}{syncWordId:0}{antenna:0}{channelHopIdx:0}{payload: 0xca 0xfe 0xc0
0xde 0x33 0x0a 0x55 0x0f 0x77 0x88 0x99 0xaa 0xbb}}
{{(rxPacket)}{len:14}{timeUs:1511945271}{timePos:4}{crc:Pass}{rssi:8}{lqi:100}{phy:0}{isAck:False}{syncWordId:0}{antenna:0}{channelHopIdx:1}{payload: 0xca 0xfe 0xc0
0xde 0x33 0x0a 0x55 0x0f 0x77 0x88 0x99 0xaa 0xbb 0xcc}}
{{(rxPacket)}{len:14}{timeUs:1516608125}{timePos:4}{crc:Pass}{rssi:10}{lqi:102}{phy:0}{isAck:False}{syncWordId:0}{antenna:0}{channelHopIdx:2}{payload: 0xca 0xfe 0xc0
0xde 0x33 0x0a 0x55 0x0f 0x77 0x88 0x99 0xaa 0xbb 0xcc}}
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 15
Page 16

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Testing Modes
6 Testing Modes
6.1 Packet Error Rate Testing
RAILtest can be used to determine the packet error rate (PER) for a given setup. To set up this test, a piece of test equipment needs to
be configured to send a packet on the rising edge of a GPIO. The specific EFR32 pin and port to be used are identified by the defines
PER_PIN and PER_PORT (RAILtest 2.8) or defines SL_RAIL_TEST_PER_PIN and SL_RAIL_TEST_PER_PORT (RAILtest 2.9). perRx
100 10000 configures the Packet Error Rate test to send 100 packets, waiting 10000 µs between each packet. At the end of the test,
the app provides an output indicating that Per mode has finished, and the statistics on the test can be recovered with perStatus and
status. Calling perRx 0 0 cancels an ongoing test, and calling perRx has the same effect as calling resetCounters.
6.2 Bit Error Rate Testing
The EFR32 hardware can enter bit error rate (BER) receive mode for diagnostic purposes. In BER mode, the chip expects to receive a
PN9 (x^9 + x^5 + 1) transmission. In order to run the BER test successfully, a radio configuration specific to BER mode must be generated
by the radio configurator.
Use the setBerConfig command to specify how many bytes to receive in BER receive mode. The maximum number of bytes is
536870911. Specifying 0 or a number greater than the maximum possible value automatically configures the BER test to receive the
maximum number of bytes for testing.
Use the berRx command to enter or exit BER receive mode. If the test is allowed to run to completion, there is no need to exit BER
receive mode.
Use the berStatus command to query for test statistics during or after a test. The statistics are reset when setBerConfig is run or
when berRx 1 is run. The statistics include:
• BitsToTest (total bits to be tested)
• BitsTested (the number of bits already received and tested)
• PercentDone (percentage of how many configured bytes have been received)
• RSSI (an instantaneous RSSI value corresponding to the last byte received)
• BitErrors (the number of received bits determined to be in error)
• PercentBitError (percentage of bit errors to bits tested)
Some examples:
> setberconfig 100000
> berrx 1
> berstatus
{{(berStatus)}{BitsToTest:800000}{BitsTested:0}{PercentDone:0.00}
{RSSI:0}{BitErrors:0}{PercentBitError:0.00}}
// PN9 transmission enabled here
> berstatus
{{(berStatus)}{BitsToTest:800000}{BitsTested:121312}{PercentDone:15.16}
{RSSI:-23}{BitErrors:0}{PercentBitError:0.00}}
> berstatus
{{(berStatus)}{BitsToTest:800000}{BitsTested:800000}{PercentDone:100.00}
{RSSI:-24}{BitErrors:0}{PercentBitError:0.00}}
> berrx 1
> berstatus
{{(berStatus)}{BitsToTest:800000}{BitsTested:363936}{PercentDone:45.49}
{RSSI:-23}{BitErrors:0}{PercentBitError:0.00}}
> setberconfig 1000000
> berrx 1
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 16
Page 17

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Testing Modes
> berstatus
{{(berStatus)}{BitsToTest:8000000}{BitsTested:888672}{PercentDone:11.11}
{RSSI:-23}{BitErrors:0}{PercentBitError:0.00}}
// PN9 transmission disabled here
> berstatus
{{(berStatus)}{BitsToTest:8000000}{BitsTested:4418528}{PercentDone:55.23}
{RSSI:-96}{BitErrors:960478}{PercentBitError:21.74}}
> berstatus
{{(berStatus)}{BitsToTest:8000000}{BitsTested:8000000}{PercentDone:100.00}
{RSSI:-97}{BitErrors:2752908}{PercentBitError:34.41}}
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 17
Page 18

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
7 Miscellaneous
7.1 RAM Modem Reconfiguration
RAILtest can dynamically change the modem configuration allowing for a quick evaluation of different protocols or settings without the
need to compile or flash the chip. This is enabled through the writeRmrStructure, updateConfigurationPointer and recon-
figureModem commands. These commands are intended to be used only by Simplicity Studio and not directly from the CLI.
7.2 Register/Memory Access
Note: These commands provide direct access to the chip's address space. Writing a value to an address can change RAM and register
values, and even reading from an address can change the operation of the chip. Any action taken with these commands will
potentially conflict with the running program, possibly leading to unexpected behavior or a system crash. Only use these commands when instructed to do so by your Silicon Labs support contact.
To modify any memory on the system use the getmemw and setmemw commands. To use getmemw specify the starting address and
the number of 32bit words you want to read. Using setmemw is slightly different in that you specify the starting address and the 32bit
words to write starting at the specified address. These commands operate on 32bit words so all addresses must be 32bit aligned.
7.3 Debug
• To output a tone on the current channel (or overridden frequency) use the setTxTone command.
• To output a PN9 or 101010 stream on the current channel on a certain antenna, TX_ANTENNA0 or TX_ANTENNA1, use the setTx-
Stream command.
7.4 Full Help Text
7.4.1 RAILtest 2.9 (GSDK 3.0) Help Text
Note: Each command is displayed (on the left) with its corresponding arguments and associated datatypes (on the right). Required
command arguments and their datatypes are listed first (such as uint32) with potential optional arguments and their datatypes
listed afterwards (such as uint32opt). The list of required command argument datatypes includes uint8, uint16, uint32,
int8, int16, int32, and string. The list of optional command argument datatypes includes uint8opt, uint16opt,
uint32opt, int8opt, int16opt, int32opt, and stringopt.
> help
_________________________________
____Application_Configuration____
setEventConfig Control RAIL events.
[uint32] eventsMask<31:0>
[uint32] eventsValues<31:0>
[uint32opt] eventsMask<63:32>
[uint32opt] eventsValues<63:32>
resetCounters Resets the TX and RX counters.
setPeripheralEnable Control LEDs and LCD peripherals.
[uint8] [0=Disable] 1=Enable
setNotifications Control asynchronous status prints (rxPacket,txEnd,txError).
[uint8] 0=Disable [1=Enable]
getLogLevels Show whether notifications or peripherals are enabled.
getVersion Get version information.
getVersionVerbose Get verbose version information.
setPtiProtocol Set PTI protocol for Network Analyzer.
[uint8] 0=Custom 2=Thread 3=BLE 4=Connect 5=Zigbee 6=Z-Wave
setPrintingEnable Control all printing in RAILtest, except CLI.
[uint8] 0=Disable [1=Enable]
____________________________
____Receive_and_Transmit____
rx Control receive mode.
[uint8] 0=Disable [1=Enable]
rxAt Configure scheduled receive.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 18
Page 19

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
[uint32] startTimeUs
[string] 'rel'=Relative 'abs'=Absolute
[uint32] endTimeUs
[string] 'rel'=Relative 'abs'=Absolute
[uint8opt] rxTransEndSched: [0]/1
[uint8opt] hardEnd: [0]/1
setRxOptions Show/Configure receive options (RAIL_RX_OPTIONs).
[uint32opt] rxOptionsValues: bitmask of enabled options
tx Transmit packets with current TX options.
[uint32] number of packets, 0=continuous until next 'tx 0'
txWithOptions Same tx command. This command is deprecated.
[uint32] number of packets, 0=continuous until next 'tx 0'
txAfterRx Schedule a TX with specified delay after each RX.
[uint32] delayUs: 0=Disable
configTxOptions Show/Configure transmit options (RAIL_TX_OPTIONs).
[uint32opt] txOptionsValues: bitmask of enabled options
setFixedLength Configure fixed length packet operation.
[uint16] fixedLength: payload bytes
setPower Set the transmit power. The radio must be IDLE.
[int32] power: deci-dBm unless 'raw' is added
[stringopt] 'raw'=units are raw power level
getPower Get the transmit power in deci-dBm.
setPowerConfig Set transmit PA configuration.
[uint8] paMode
[uint16] millivolts
[uint16] rampTimeUs
getPowerConfig Get the transmit PA configuration.
getPowerLimits Get min and max powerLevel for a power mode.
[uint8opt] powerMode
enablePaAutoMode Control automatic PA selection based on the TX power level.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
configPaAutoMode Configure an entry in the default PA Auto Mode plugin.
[uint8] entryIndex
[int32] min: deci-dBm
[int32] max: deci-dBm
[uint8] RAIL_TX_POWER_MODE for this power range
sweepTxPower Sweep TX power for the current PA by toning at each level.
offsetLqi Adjust the hardware's LQI value for received packets.
[int32] offset: signed value to add
The resulting LQI is capped within 0..255 range.
getRssi Get RSSI in dBm. It'll be invalid if receiver isn't ready.
[uint32opt] [0=don't wait] 1=wait for valid RSSI if possible
sweepPower Sweep power by toning low/high in a square wave fashion.
[int32] lowPower: deci-dBm
[int32] hiPower: deci-dBm
[uint32] periodUs
startAvgRssi Start AGC RSSI averaging.
[uint32] averageTimeUs
[uint16opt] channel: if different than current channel
getAvgRssi Get AGC RSSI averaging result.
setTxTone Control tone transmission.
[uint32] 0=Disable 1=Enable
[uint32opt] antenna: [0]/1
setTxStream Control stream transmission.
[uint32] 0=Disable 1=Enable
[uint32opt] streamMode: [1=PN9] 2=1010 0=tone
[uint32opt] antenna: [0]/1
status Print the current status counters.
fifoStatus Print the current FIFO-related counters.
setTxHoldOff Control transmit hold-off (blocking of transmits).
[uint32] 0=Disable 1=Enable
setTxDelay Set the inter-packet delay for repeated TX.
[uint32] delayMilliseconds
getTxDelay Get the inter-packet millisecond delay for repeated TX.
setTxPayload Set TX packet payload bytes for future transmits.
[uint16] offset
[uint8opt] byte0 byte1 ...
setTxPayloadQuiet Like setTxPayload, but less verbose.
[uint16] offset
[uint8opt] byte0 byte1 ...
setTxLength Set how much data to load into the TX FIFO for transmitting.
Actual packet length may vary based on radio configuration.
[uint16] lengthBytes
printTxPacket Print the current TX payload data and byte length.
peek Peek at the start of the receive buffer.
[uint16] bytes: 1-10
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 19
Page 20

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
[uint16opt] offset: [0]
getTime Get the current RAIL time in microseconds.
setTime Set the current RAIL time.
[uint32] timeUs
dataConfig Control the data methods for TX and RX.
[string] txMethod: 'pkt'/'fifo'
[string] rxMethod: 'pkt'/'fifo'
setRxFifo Set the receive buffer length.
[uint16] lengthBytes: range 64-RX_BUFFER_SIZE
setTxFifoThreshold Set the TX FIFO Almost Emtpy threshold.
[uint16] thresholdBytes: below which the event triggers
setRxFifoThreshold Set the RX FIFO Almost Full threshold.
[uint16] thresholdBytes: above which the event triggers
fifoModeTestOptions Manual control over RAILtest FIFO actions.
[uint8] txFifo: 1=Manual 0=Automatic
[uint8] rxFifo: 1=Manual 0=Automatic
rxFifoManualRead Read and print bytes from receive FIFO when in manual mode.
[uint8] appendedInfo: 1=include packet metadata
[uint16] bytesToRead
[uint8opt] [0=don't] 1=show timestamps with appendedInfo
txFifoManualLoad Try to load data into available TX FIFO space.
fifoReset Reset the transmit and/or receive FIFO.
[uint8] tx: 1=reset TX FIFO
[uint8] rx: 1=reset RX FIFO
abortRxPacket Idle the radio shortly after RX sync word detection.
[uint32] abortOffsetUs
printTxAcks Control printing of TX ACK packets.
[uint8] [0=Disable] 1=Enable
configRxHopping Configure an RX Channel Hopping sequence.
[uint32opt] channel hopMode param delayUs: a hop's config,
repeat for additional hops ...
Use no arguments to get Z-Wave radio config defaults.
enableRxHopping Control RX channel hopping previously configured.
[uint8] [0=Disable] 1=Enable
[uint8opt] [0=Continue] 1=Restart sequence
configRxHoppingOpts Configure options for a hop. Use configRxHopping after.
[uint8] hopIndex
[uint8] options
[int8opt] rssiThreshold: dBm for the threshold option
configRxMultiHop Configure multi-sense for a hop. Use configRxHopping after.
[uint8] hopIndex
[uint32] syncDetectUs
[uint32] preambleSenseUs
[uint32] timingSenseUs
[uint32] timingReSenseUs
getRxHoppingRssi Get the latest RSSI for a hopping channel.
[uint8] hopIndex
spectrumAnalyzer Hop across a channel range to see the RSSI distribution.
[uint8] 1=Show ASCII-Art graph (non-parseable output)
[uint16opt] minChannel: [0]-65535
[uint16opt] maxChannel: 0-[65535]
Channel range is limited by the PHY and by hopping's
MAX_NUMBER_CHANNELS.
configRxDutyCycle Configure RX Duty Cycling of the receiver.
[uint32] hopMode
[int32] parameter(s) {syncUs preamUs timingUs retimingUs}
[int32] delayUs
[int32opt] options
[int32opt] rssiThreshold: dBm for the threshold option
enableRxDutyCycle Control RX duty cycling previously configured.
[uint8] DutyCycling: 0=Disable 1=Enable
[uint8opt] ScheduledWakeup: [0=Disable] 1=Enable
setTxAltPreambleLen Set alternate TX preamble length, enabled via txOptions.
[uint32] preambleBits
configSyncWords Set sync words and their length. The radio must be off.
[uint8] bits: 2-32
[uint32] syncWord1
[uint32opt] syncWord2: [same as syncWord1]
getSyncWords Get the sync word length in bits and value(s).
printRxErrors Control printing of RX error packets.
[uint8] [0=Disable] 1=Enable
printRxFreqOffsets Control printing of RX frequency offsets.
[uint8] [0=Disable] 1=Enable
printDataRates Print the data rates of the current PHY.
stopInfinitePream Stops an infinite preamble transmission.
___________________________________
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 20
Page 21

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
____Energy_Modes_and_RF_Sensing____
sleep Sleep until UART input or RF Sensed (if either configured).
[uint8] energyMode: 0-4, for EM1P use 2 with radio on
[uint32opt] Legacy: RfSenseUs
RfBand: 0=none,1=GHz,2=MHz,3=both
or Selective: SyncwordBytes Syncword RfBand
rfsense Start RfSensing.
[uint32] Legacy: RfSenseUs; Selective: SyncwordBytes
[uint32opt] Legacy: RfBand: 0=none,1=GHz,2=MHz,3=both
or Selective: Syncword RfBand: as above
configRfSenseWakeup Configure RFSense Selective Wakeup PHY for transmitting.
setRfSenseTxPayload Load TX FIFO with RfSense Selective(OOK) Mode wake packet.
[uint8] syncwordNumBytes: 1-4
[uint32] syncWord: sent from least to most significant byte
_________________________
____Address_Filtering____
configAddressFilter Configure the addresss filter.
[uint32] matchTable
[uint8opt] offset0 size0 offset1 size1 ...
Enter more offsets and sizes if required.
setAddressFiltering Control address filtering.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
getAddressFiltering Get the current state of address filtering.
printAddresses Print the current address filtering addresses.
setAddress Set a specific filtering address value.
[uint8] field: 0-1
[uint8] filterIndex: 0-3
[uint8opt] addrByte0 addrByte1 ... addrByte7
setAddressMask Set a specific filtering address mask.
[uint8] field: 0-1
[uint8opt] bitMask
setAddressEnable Control address filtering for a specific address.
[uint8] field: 0-1
[uint8] filterIndex: 0-3
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
__________________________
____Error_Rate_Testing____
perRx Start a Packet Error Rate test. 'perRx 0 0' stops test.
[uint32] number of packets
[uint32] delayUs
perStatus Get the PER test results. Also see status command.
setBerConfig Set number of bytes to receive in BER mode.
[uint32] number of bytes: 0=maximum (536870911)
berRx Control BER receive mode.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
berStatus Get status of current or last BER test.
Status is reset by setBerConfig and berRx enable.
______________________________
____Listen_Before_Talk_LBT____
setLbtMode Show/Set the LBT mode for transmits.
[stringopt] 'off'/'csma'/'lbt'
getLbtParams Get the current LBT parameters.
setLbtParams Set LBT parameters.
[uint8] minBo
[uint8] maxBo
[uint8] tries
[int32] ccaThreshold
[uint16] backoffUs
[uint16] durationUs
[uint32] timeoutUs
_____________________
____802_15_4_Mode____
enable802154 Configure and enable 802.15.4 mode.
[string] defaultState: 'idle'/'rx'
[uint16] idleToRxUs
[uint16] turnaroundTimeUs
[int16] ackTimeoutUs: to ACK's sync-detect
[uint8opt] defaultFP: [0]/1 Frame Pending for poll ACKs
config2p4GHz802154 Configure the radio for 2.4 GHz 802.15.4.
Use with enable802154.
[uint8opt] antDiv: [0=Disable] 1=Enable
[uint8opt] coex: [0=Disable] 1=Enable
config863MHz802154 Configure the radio for 863 MHz 802.15.4 GB868.
Use with enable802154.
config915MHz802154 Configure the radio for 915 MHz 802.15.4 GB868.
Use with enable802154.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 21
Page 22

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
set802154e Configure 802.15.4E options.
[uint32] RAIL_IEEE802154_EOptions_t
set802154g Configure 802.15.4G options.
[uint32] RAIL_IEEE802154_GOptions_t
set802154FpMode Control early and data frame pending lookup.
[uint8] early: [0=Disable] 1=Enable
[uint8] dataframes:[0=Disable] 1=Enable
acceptFrames Control 802.15.4 frame type acceptance.
[uint8] command: 0=Reject [1=Accept]
[uint8] ack: [0=Reject] 1=Accept
[uint8] data: 0=Reject [1=Accept]
[uint8] beacon: 0=Reject [1=Accept]
[uint8opt] multipurpose: [0=Reject] 1=Accept
setPromiscuousMode Control promiscuous mode.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
setPanCoordinator Control whether node is a PAN coordinator.
[uint8] 1=Yes 0=No
setPanId802154 Set the PAN ID for a filtering index.
[uint16] panId
[uint8opt] filterIndex: [0]-2
setShortAddr802154 Set the short address for a filtering index.
[uint16] shortAddr
[uint8opt] filterIndex: [0]-2
setLongAddr802154 Set the long address for a filtering index.
[uint8] longAddr_0
[uint8] longAddr_1
[uint8] longAddr_2
[uint8] longAddr_3
[uint8] longAddr_4
[uint8] longAddr_5
[uint8] longAddr_6
[uint8] longAddr_7
[uint8opt] filterIndex: [0]-2
setAddresses802154 Set all 802.15.4 address information.
[uint16] panId0
[uint16] shortAddr0
[stringopt] longAddr0
[stringopt] panId1 shortAddr1 longAddr1 ...
setDataReqLatency Set data request event processing latency.
[uint32] latencyUs
________________
____BLE_Mode____
setBleMode Control BLE mode.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
getBleMode Get the current BLE mode.
setBleChannelParams Configure channel parameters related to BLE.
[uint8] logicalChannel
[uint32opt] accessAddr crcInit disableWhiten
setBlePhySwitchToRx Configure BLE PhySwitchToRx parameters. RX is
entered timeDeltaUs after sync word of received packet.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
[uint32opt] phy timeDelta physicalChannel
[uint32opt] logicalChannel accessAddr crcInit
[uint32opt] disableWhiten
setBleAdvertising Configure for BLE advertising.
[uint8] advChannel: 37-39
setBle1Mbps Switch to the 1Mbps BLE PHY.
[uint8opt] 0=Legacy 1=Viterbi [chip default]
setBle2Mbps Switch to the 2Mbps BLE PHY.
[uint8opt] 0=Legacy 1=Viterbi [chip default]
setBleCoding Switch to a BLE coded PHY.
[uint8] RAIL_BLE_Coding_t value
setBleSimulscan Switch to a BLE simulscan PHY.
___________________
____Z_Wave_Mode____
setZWaveMode Show/Control Z-Wave mode.
[uint8opt] 0=Disable 1=Enable
[uint8opt] optionsBitmask
getZWaveMode Get the current Z-Wave mode.
setZWaveRegion Set the Z-Wave region.
[uint8] region: see listZWaveRegions
getZWaveRegion Get the current Z-Wave region.
listZWaveRegions List supported Z-Wave regions.
getZWaveBaudRate Get the baudrate of the current Z-Wave channel.
setZWaveNodeId Sets Z-Wave NodeId.
[uint16] nodeId
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 22
Page 23

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
setZWaveHomeId Sets Z-Wave HomeId and its hash.
[uint32] homeId
[uint8] hash
setZWaveOptions Configure Z-Wave options.
[uint8opt] optionsBitmask
setZWaveLowPower Set the transmit power for low-power ACKing.
[int32] power: deci-dBm unless 'raw' is added
[stringopt] 'raw'=units are raw power level
getZWaveLowPower Get the low power values (deci-dBm and raw).
zwaveReceiveBeam Run the Z-Wave beam detection algorithm.
__________________
____RAIL_Timer____
setTimer Set the RAIL timer timeout.
[uint32] timeout: per mode
[string] 'rel'=Relative 'abs'=Absolute
timerCancel Cancel the RAIL timer if it is active.
printTimerStats Print current timer configuration.
enableMultiTimer Control the multiTimer API.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
setMultiTimer Set a specific timer timeout.
[uint8] timer: 0..(NUM_MULTI_TIMERS-1)
[uint32] timeout: per mode
[string] 'rel'=Relative 'abs'=Absolute
multiTimerCancel Cancel a specific timer if it is active.
[uint8] timer: 0..(NUM_MULTI_TIMERS-1)
getMultiTimerStats Get information about a specific timer.
[uint8] timer: 0..(NUM_MULTI_TIMERS-1)
delayUs Do a blocking delay for a specified time.
[uint32] delayUs
____________________
____Auto_ACK_ing____
autoAckConfig Configure and enable auto-ACK functionality.
[string] defaultState: 'idle'/'rx'
[uint16] idleToRxUs
[uint16] turnaroundTimeUs
[uint16] ackTimeoutUs: to ACK's sync-detect
autoAckDisable Disable auto-ACK. Use autoAckConfig to reenable.
setAckPayload Set the ACK payload to transmit.
[uint16] offset
[uint8opt] byte0 byte1 ...
setAckLength Set how much data to load into the TXACK FIFO.
[uint16] lengthBytes
printAckPacket Print the current TXACK payload data and byte length.
getAutoAck Get the current state of auto-ACKing.
autoAckPause Pause or Resume auto-ACKing
[uint8] 1=PauseRx 0=ResumeRx
[uint8] 1=PauseTx 0=ResumeTx
setTxAckOptions Control auto-ACK response for just the next receive.
[uint8] 1=cancelAck 0=sendAck
[uint8] 1=useTxBuf 0=useTxAckBuf
______________________
____GPIO_Functions____
setGpioOutPin Set a GPIO pin data out bit.
[string] gpioPort: start from '0' or 'a' or 'A'
[uint8] gpioPin
[uint8] state: 0/1
___________________________
____Diagnostic_and_Test____
getConfigIndex Get the index of the current multi-PHY radio config.
See the entries in *channelConfigs[]. Start with index 0.
setConfigIndex Activate a multi-PHY radio configuration.
See the entries in *channelConfigs[]. Start with index 0.
[uint8] multiPhyIndex
setCtune Set the value of HFXO CTUNE. The radio must be IDLE.
[uint16] ctune
getCtune Get the value of HFXO CTUNE
setCtuneDelta Set the value of HFXO CTUNE delta
[uint16] delta
getCtuneDelta Get the value of HFXO CTUNE delta
setPaCtune Set the PACTUNE value for TX and RX.
[uint8] txPaCtune
[uint8] rxPaCtune
enablePaCal Control PA power calibration.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
setDebugSignal Configure chip specific debug output.
Use 'setDebugSignal help me' for more details.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 23
Page 24

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
[string] pin
[string] signal
[uint16opt] signalOptions
setDebugMode Control Debug mode which allows freqOverride.
[uint32] 0=Disable 1=Enable
freqOverride Set the radio frequency. Requires debug mode.
[uint32] freqHz: Only small deviations from the
current configuration are supported.
directMode Control direct mode.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
directTx Control TX in direct mode.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
txCancel Start a TX that will be cancelled.
[int32] delayUs: when to cancel it
[uint8opt] stopMode: [0=RAIL_Idle] >0=RAIL_StopMode_t
startThermistor Configures the thermistor pin and starts a measurement.
getThermistor Gets the thermistor impedance.
getRandom Get random data from the radio.
[uint16] lengthBytes
[uint8opt] [0=show them] 1=hide them
setTxUnderflow Control TX underflows by not loading the TX FIFO.
[uint8] 1=Force underflows 0=Disable
setRxOverflow Control RX overflows by delaying in the event handler.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
[uint32opt] delayUs: [0]
setCalibrations Control calibrations.
[uint8] 0=Disable 1=Enable
setTxTransitions Set the TX state transitions.
[string] txSuccess: 'idle'/'rx'
[string] txError: 'idle'/'rx'
setRxTransitions Set the RX state transitions.
[string] rxSuccess: 'idle'/'rx'/'tx'
[string] rxError: 'idle'/'rx'/'tx'
getTxTransitions Get the TX state transitions.
getRxTransitions Get the RX state transitions.
setTxTimePos Set desired TX timestamp position.
[uint8] RAIL_PacketTimePosition_t
setRxTimePos Set desired RX timestamp position.
[uint8] RAIL_PacketTimePosition_t
setTimings Set RAIL state transition timings.
[uint32] idleToRxUs
[uint32] rxToTxUs
[uint32] idleToTxUs
[uint32opt] txToRxUs
[uint32opt] rxSearchTimeoutUs
[uint32opt] txToRxSearchTimeout
forceAssert Force a RAIL assert with the given error code.
[uint32] RAIL_AssertErrorCodes_t
getAppMode Get the current RAILtest AppMode_t mode.
getRadioState Get the current RAIL_RadioState_t radio state.
verifyRadio Verify radio memory contents.
[uint32] durationUs: time limit
[uint8] 0=Resume if previously didn't finish 1=Restart
[uint8] 0=current radio config 1=external radio config
[uint8] 0=No callback 1=Use RAILCb_ConfigVerification
getChannel Get the current radio channel.
setChannel Set the radio channel.
[uint16] channel
reset Perform a reboot of the chip.
writeRmrStructure Reserved for Simplicity Studio use only.
[uint8]
[uint16]
[uint8]
[uint32opt]
updateConfigPtr Reserved for Simplicity Studio use only.
[uint8]
[uint16]
[uint8]
reconfigureModem Reserved for Simplicity Studio use only.
printEvents Show/Configure printing of RAIL events as they occur.
[uint32opt] printEvents<31:0> printEvents<63:32>
[uint32opt] mask<31:0> mask<63:32>
printChipFeatures Display RAIL features supported at compile and runtime.
getmemw Read count 32-bit words starting at address.
[uint32] address
[uint32opt] count
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 24
Page 25

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
setmemw Write 32-bit values starting at address.
[uint32] address
[uint32opt] value0 value1 ...
throughput Throughput test.
[uint32] number of packets
setRssiOffset Sets the RSSI offset.
[int32] offsetDbm
getRssiOffset Gets the RSSI offset(s) in dBm.
[uint8opt] [0=radio and protocol-specific] 1=radio only
txAt Transmit a packet at a certain time.
[uint32] time: per mode
[stringopt] ['rel'=Relative] 'abs'=Absolute
[stringopt] 'abort' RX if TX occurs during packet RX
otherwise TX is delayed to end of RX
setFreqOffset Get/Set the frequency offset adjustment.
[int32opt] offsetHz
holdRx Control holding of received packets.
[uint8] [0=Process packets immediately] 1=Hold packets
wait Suspend processing of CLI input for a while.
[uint32] waitTimeUs
[stringopt] ['rel'=Relative] 'abs'=Absolute
clearScript Clear the script entered via enterScript.
[uint8opt] [0=RAM] 1=Flash
printScript Print the script entered via enterScript.
[uint8opt] [0=RAM] 1=Flash
enterScript Enter script entry mode.
Conclude entry mode with text 'endScript'.
[uint8opt] [0=RAM] 1=Flash-script will run on boot
runScript Run the script entered via enterScript.
[uint8opt] [0=RAM] 1=Flash-script will run on boot
setRetimeOption Control retime options.
[uint8] optionBitMask: 1=HFXO | 2=HFRCO | 4=DCDC | 8=LCD
7.4.2 RAILtest 2.8 (GSDK 2.7.x) Help Text
> help
<command> <args> <help text>
u=uint8, v=uint16, w=uint32, s=int32, b=string, ?=Anything, *=0 or more of previous
--- Application Configuration ---
setEventConfig www* [mask<31:0> events<31:0> [mask<63:32> events<63:32>]] Modify
RAIL_ConfigEvents with the given mask and events
printDataRates Print the data rates of the current PHY
resetCounters Resets the Tx and Rx counters
setPeripheralEnable u [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) LEDs and LCD peripherals
setNotifications u [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) status prints that happen asynchronously
(rxPacket, txEnd, txError)
getLogLevels Get whether notifications are set or peripherals are enabled
getVersion Get version information.
getVersionVerbose Get verbose version information.
setPtiProtocol u [protocol] Set PTI protocol for Network Analyzer (0=Custom 2=Thread 3=BLE
4=Connect 5=Zigbee 6=Z-Wave)
setPrintingEnable u [enable] Universally enable or disable all printing in railtest. Enabled
by default.
--- Receive and Transmit ---
rx w [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) receive mode
rxAt wbwbu* [start mode end mode rxTransEndSched hardEnd] Configure scheduled
receive.
setRxOptions w* [rxOptionsBitField] Configure receive options, based on RAIL_RX_OPTION
defines. If called without any parameters, prints the current state of
these options.
tx w [n] Transmit n packets with tx options. If n is 0 transmit infinitely.
Defaults are don't wait for ack, send CRC, use sync word 0.
txWithOptions w [n] Same functionality as tx. This command is deprecated
txAt wb* [time mode (abort)] Transmit a packet at the time and mode specified. If
the string 'abort' is specified and the TX tries to go out during packet
reception, the TX will abort, as opposed to being postponed until the RX
completes.
txAfterRx w [time] Schedule a TX for a delay in us after each receive. 0 to disable
configTxOptions w* [txOptionsBitfield] Sets the bitmask to be used as the tx options. See
#defines starting with "RAIL_TX_OPTION_" in rail_types.h. Can be called
without any parameters to print the current state of these options.
setFixedLength v [fixedLength] Configure fixed length
setchannel v [channel] Set the current radio channel
getchannel Get the current radio channel
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 25
Page 26

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
setFreqOffset s* [(offset)] Sets the frequency offset adjustment. With no argument dis
plays the current offset setting.
setPower sb* [power raw] Set the current transmit power in deci dBm, or raw units if
'raw' is specified. The radio must be IDLE for setPower to succeed.
getPower Get the current transmit power in deci dBm
setPowerConfig uvv [mode voltage rampTime] Set the current transmit power config.
getPowerConfig Get the current transmit power config.
enablePaAutoMode u [enable] Enable automatic configuration of PA's when setting dBm power
levels.
configPaAutoMode ussu [index min max mode] Configure the entries of default PA Auto Mode
configuration provided by the PA Auto Mode plugin.
sweepTxPower Sweep power levels for the current PA and stream at each level.
offsetLqi s [offset] Add this offset value to the hardware's 8-bit hardware LQI value
before being made available to the application.
getRssi w* [wait] Get RSSI in dBm if the receiver is turned on. Optionally specify
whether or not to wait for a valid value in case it is initially invalid.
sweepPower ssw [lowPower] [hiPower] [period] Sweep power in square wave fashion. Specify
power in deci dBm, period in microseconds.
startAvgRssi wu* [averageTimeUs] [channel] Start AGC RSSI averaging
getAvgRssi Get AGC RSSI averaging result.
setRssiOffset s Sets the RSSI offset in dBm.
getRssiOffset Gets the RSSI offset.
setTxTone ww* [enable (antenna)] Enable(1) or Disable(0) a tone from the radio with
option of selecting antenna
setTxStream ww* [enable (streamMode) (antenna)] Enable(1) or Disable(0) a stream from the
radio based on selection of RAIL_StreamMode_t and antenna.(Option :
Unspecified - Any, 0 - TX_ANTENNA0, 1 - TX_ANTENNA1). Default settings
for streamMode is RAIL_STREAM_PN9_STREAM and for antenna is
RAIL_TX_OPTIONS_DEFAULT.
status Print the current status counters
fifoStatus Print the current fifo related counters
setTxHoldOff w [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) transmit hold-off (blocking of
transmits)
setTxDelay w [delay] Set the inter-packet delay in milliseconds for repeated Tx
getTxDelay Get the inter-packet delay in milliseconds for repeated Tx
setTxPayload vu* [offset byte0 byte1 ...] Set the packet bytes to be sent
setRfSenseTxPayload uw [syncwordNumBytes syncWord] Set the RfSense Wakeup Syncword (1-4 bytes)
in TX FIFO to wake up a receiving node configured for Selective(OOK)
RFSENSE.
setTxPayloadQuiet vu* [offset byte0 byte1 ...] Functions like 'setTxPayload', but outputs less
information
setTxLength v [length] Set the number of bytes to load into the FIFO before
transmitting. Actual packet length may vary based on radio configuration
printTxPacket Print the current Tx data and length
peek v* [number of bytes] [offset] Peek at the start of receive buffer.
getTime Get the current time from the RAIL timebase in microseconds
setTime w Set the current time in the RAIL timebase in microseconds
dataConfig bb [txMethod rxMethod] Choose between 'pkt' and 'fifo' data methods for RAIL
Tx and Rx
setRxFifo v [length] Set the receive buffer's length, which is used in both packet
mode and FIFO mode. The length cannot be set above RX_BUFFER_SIZE.
setTxFifoThreshold v [txFifoThreshold] Set the Tx Fifo Almost Emtpy threshold
setRxFifoThreshold v [rxFifoThreshold] Set the Rx Fifo Almost Emtpy threshold
fifoModeTestOptions uu [txFifoManual rxFifoManual] Manual control over RAILTEST fifo actions
rxFifoManualRead uvu* [appendedInfo bytesToRead printTiming] Read bytes out of receive fifo and
print
txFifoManualLoad Will attempt to load data into the fifo if there is space
fifoReset uu [tx rx] Reset the transmit or receive fifo
abortRxPacket w [abortOffset] Delay after sync word before idling radio.
printTxAcks w [printTxAcks] Enable printing of tx ack packets as they happen.
configRxChannelHopping w* [(channel mode parameter delay)...] Configure RX Channel Hopping to hop
in the sequence provided, for the given RAIL_RxChannelHoppingMode_t mode,
parameter, and interchannel delay. One mode and parameter must be
provided per channel.
enableRxChannelHopping uu* [enable (reset)] Enable/disable rx channel hopping. The channel hopping
will start again from the first member of the sequence is reset is true.
configChannelHoppingOptions uu [index options] Configure channel hopping options for the entry of
specified index. Must call configRxChannelHopping after this, for options
to take effect.
getChannelHoppingRssi u [channelIndex] Get the latest RSSI for the channel at the index of the
hopping sequence specified.
spectrumAnalyzer uv* [(graphics min max)]Emulate spectrum analyzer functionality to get the
power across min and max channels (number of channels limited by
MAX_NUMBER_CHANNELS) of the current PHY using channel hopping. Specify
graphics = 1 for an ASCII-Art graph, which will break out of the standard
RAILTest response format.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 26
Page 27

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
configRxDutyCycle www [mode parameter delay] Configure RX Duty Cycle mode to cycle the receiver
with the given parameters.
enableRxDutyCycle u [enable] Enable/disable rx duty cycle mode.
setTxAltPreambleLen w [length] Set an alternate preable length for transmit, which can be
enabled in txOptions.
configSyncWords uw* [bits sync1 (sync2)] Set the sync word bit length and value(s). It can be
only set when radio is off.
getSyncWords Get the sync word length(in bits) and value(s).
printRxErrors w [enable] Enable (1) or Disable (0) printing of Rx error packets. Defaults
to disabled.
stopInfinitePreambleTx Stops the infinite preamble transmission
--- Energy Modes and RF Sense ---
sleep uw* [EM# [RfSenseUs RfBand] or [SyncwordSize(bytes) Syncword RfBand]] Sleep
in EM# with RFSenseUs on RfBand (0=none,1=2.4GHz,2=SubGHz,3=both) (and
UART input) for Legacy Mode or SyncwordSize(bytes) and Syncword on RfBand
for Selective(OOK) Mode. To enter EM1P if supported, request EM2 with the
radio on.
rfsense ww* [[RfSenseUs RfBand] or [SyncwordSize(bytes) Syncword RfBand]] Start
RfSensing with RSenseUs on RfBand for Legacy Mode or SyncwordSize(bytes)
and Syncword on RfBand for Selective(OOK) Mode.
configRfSenseWakeupPhy Configure the transmitting node with RFSense Selective(OOK) Wakeup PHY.
--- Address Filtering ---
configAddressFilter wu* [matchTable offset0 size0 offset1 size1] Configure the addresss filter.
setAddressFiltering u [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) address filtering.
getAddressFiltering Print the current state of address filtering.
printAddresses Print the current address filtering addresses.
setAddress uuu* [field index value...] Set the address value at (field, index) to value.
setAddressEnable uuu [field index enable] Enable address filtering for the given address.
--- Error Rate Testing ---
perRx ww [packets delayUs] Start a Packet Error Rate test. 'perRx 0 0' will
disable ongoing test.
perStatus Output the results of the PER test. Also see 'status' command
setBerConfig w [number bytes] Set number of bytes to receive in BER mode; 536870911 =
max number of bytes to test; 0 = set max number of bytes to test
berRx w [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) BER receive mode
berStatus Get status of last BER test or of current running test; status
information is reset for commands setBerConfig and berRx enable
--- Listen Before Talk (LBT) ---
setLbtMode b* [modeStr] Set LBT mode off, csma, lbt
getLbtParams Get the current LBT parameters
setLbtParams uuusvvw [minBo maxBo tries thresh backoff duration timeout] Set LBT parameters
--- 802.15.4 Mode ---
enable802154 bvvvu [defaultState idleTime turnaroundTime ackTimeout (defaultFramePending)]
Enable 802.15.4 mode
config2p4GHz802154 u* [antDiv coex] Configure the radio for 2.4 GHz 802.15.4. This should be
called in addition to 'enable802154'.
config863MHz802154 Configure the radio for 863 MHz 802.15.4 GB868. This should be called in
addition to 'enable802154'.
config915MHz802154 Configure the radio for 915 MHz 802.15.4 GB868. This should be called in
addition to 'enable802154'.
set802154e w [EOptionsBitfield] Configure 802.15.4E options, based on
RAIL_IEEE802154_E_OPTION_ defines.
set802154g w [GOptionsBitfield] Configure 802.15.4G options, based on
RAIL_IEEE802154_G_OPTION_ defines.
set802154fpmode uu [early dataframes] Enable(1) or Disable(0) early frame pending lookup and
data frame pending lookup. Default settings are 0 0
acceptFrames uuuu* [command ack data beacon (multipurpose)] Enable(1) or Disable(0) 802.15.4
frame acceptance. Default settings for 802.15.4 are 1 0 1 1 0.
setPromiscuousMode u [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) promiscuous mode
setPanCoordinator u [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) the node acting as a PAN coordinator
setPanId802154 vu* [panId index] Set the PAN ID for the given index. Index defaults to 0 if
not given
setShortAddr802154 vu* [shortAddr index] Set the short address(es) for the given index. Index
defaults to 0 if not given
setLongAddr802154 uuuuuuuuu* [longAddr_0 ... longAddr_7 index] Set the long address for the given
index. Index defaults to 0 if not given
setAddresses802154 vvb* [panId0 shortAddr0 longAddr0 panId1 ... ] Set all 802.15.4 address
information.
setDataReqLatency w [us] Set data request event processing latency.
--- BLE Mode ---
setBleMode u [enable] Set BLE mode to enabled or disabled
getBleMode Get the current BLE mode
setBleChannelParams uw* [logicalChannel accessAddr crcInit disableWhiten] Configure channel
parameters related to BLE
setBlePhySwitchToRx uw* [enable phy timeDelta physicalChannel logicalChannel accessAddr crcInit
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 27
Page 28

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
disableWhiten] Configure parameters for BLE PhySwitchToRx. RX is entered
timeDelta us after sync word of received packet.
setBleAdvertising u [advChannel] Configure for BLE advertising on channel 37, 38, or 39
setBle1Mbps u* [isViterbi] Switch to the 1Mbps BLE PHY
setBle2Mbps u* [isViterbi] Switch to the 2Mbps BLE PHY
setBleCoding u [coding] Switch to the given RAIL_BLE_Coding_t value
--- Z-Wave Mode ---
setZWaveMode u* [enable [options]] Set Z-Wave mode to enabled or disabled
getZWaveMode Get the current Z-Wave mode
setZWaveRegion u [region] Set Z-Wave region
getZWaveRegion Get the current Z-Wave region
listZWaveRegions List supported Z-Wave regions
getZWaveBaudRate Get the baudrate of the current Z-Wave channel
setZWaveNodeId u [nodeId] Sets Z-Wave NodeId
setZWaveHomeId wu [homeId hash] Sets Z-Wave HomeId and its hash
setZWaveOptions u* [options] Enable/Disable Z-Wave options
setZWaveLowPower sb* [power raw] Set the low transmit power in deci dBm, or raw units if 'raw'
is specified. This will be used during Low Power ACKing.
getZWaveLowPower Get the deci dBm value and raw value of the Low transmit power
zwaveReceiveBeam Do the beam detection algorithm to receive Z-Wave beams.
--- RAIL Timer ---
setTimer wb [timeout mode] Set the RAIL timer timeout. You can use either an absolute
(abs) or relative (rel) timer mode.
timerCancel Cancel the RAIL timer if it's active.
printTimerStats Print current timer configuration.
enableMultiTimer u [enable] Enable (1) or disable (0) the multiTimer API for use. By default
the multiTimer is disabled for single protocol RAIL and enabled for
multiprotocol RAIL.
setMultiTimer uwb [timer timeout mode] Set a specific timer's timeout, starting with timer
0. You can use either an absolute (abs) or relative (rel) timer mode.
multiTimerCancel u [timer] Cancel a specific timer if it's active, starting with timer 0.
printMultiTimerStats u [timer] Print a specific timer's configuration, starting with timer 0.
delayUs w [delay] Blocking delay for specified number of microseconds.
--- Auto Acking ---
autoAckConfig bvvv [defaultState idleTime turnaroundTime ackTimeout] Configure and enable
auto ack functionality in RAIL.
autoAckDisable Disable auto ack. Use autoAckConfig to reenable.
setAckPayload vu* [offset byte0 byte1 ...] Set the ack bytes to be sent.
setAckLength v [length] Set the number of bytes to transmit for ack payloads
printAckPacket Print the current ack data and length
getAutoAck Print the current state of auto acking.
autoAckPause uu [RxPause TxPause] Pause(1) or Resume(0) Auto Acking
setTxAckOptions uu [cancelAck useTxBuf] Enable(1) or Disable(0) feature for one receive
--- GPIO Functions ---
setGpioOutPin buu [port pin state] Set a GPIO pin's data out bit.
--- Diagnostic and Test ---
getConfigIndex Get the index of the current radio configuration selected for use. See
the entries in *channelConfigs[]. Start with index 0.
setConfigIndex u [index] Set the index of the current radio configuration selected for
use, and associate this new configuration to the current railHandle. See
the entries in *channelConfigs[]. Start with index 0.
getmemw ww* [address count] Read count 32bit words starting at address
setmemw ww* [address value...] Write as many 32bit values as specified starting at
address
setCtune v [ctune] Set the value of CTUNE in the CMU->HFXOSTEADYSTATECTRL register.
The radio must be IDLE for setCtune to succeed.
getCtune Get the value of CTUNE in the CMU->HFXOSTEADYSTATECTRL register
setPaCtune uu [txPaCtune] [rxPaCtune] Set the value of PACTUNE for TX and RX mode
enablePaCal u [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) PA power calibration
setDebugSignal ? Configure chip specific debug output. Use 'setDebugSignal help' for more
details.
setDebugMode w [mode] 1 = Frequency Override. 0 = Disable debug mode
freqOverride w [freq] Change to freq specified in Hz. Requires debug mode to be enabled.
Only small frequency deviations from the current configuration are
supported.
directMode u [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) direct mode
directTx u [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) TX in direct mode
txCancel su* [delay (stopmode)] Start a single TX that will be cancelled in delay
microseconds using stopmode 0=RAIL_Idle(default) or >0=RAIL_StopMode_t.
startThermistorMeasurement Configures the thermistor pin and starts a thermistor measurement.
getThermistorImpedance Gets the thermistor impedance.
getRandom vu* [len hidden] Get len bytes of random data from the radio. Only print them
to the screen if hidden is 0 (default).
setTxUnderflow w [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) TX underflows
setRxOverflow w* [enable delayUs] Enable(1) or Disable(0) RX overflows. The overflow will
be caused by hanging in the interrupt handler for delayUs
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 28
Page 29

UG409: RAILtest User's Guide
Miscellaneous
setCalibrations w [enable] Enable(1) or Disable(0) RAIL calibrations
setTxTransitions bb [txSuccess txError] Set each RAIL TX state transition value to r(x) or
i(dle)
setRxTransitions bb [rxSuccess rxError] Set each RAIL RX state transition value to t(x),
r(x), or i(dle).
getTxTransitions Get the RAIL TX state transitions for success and error.
getRxTransitions Get the RAIL RX state transitions for success and error.
setTxTimePos u [RAIL_PacketTimePosition_t] Set desired Tx timestamp position.
setRxTimePos u [RAIL_PacketTimePosition_t] Set desired Rx timestamp position.
setTimings vvvv* [idleToRx txToRx idleToTx rxToTx rxSearch txToRxSearch] Set RAIL state
transition timings in microseconds
forceAssert w [errorCode] Force a RAIL assert with the given error code.
printEvents w* [printEvents<31:0> [printEvents<63:32>] [mask<31:0>] [mask<63:32>]]
Configure printing of RAIL events in chronological order as they occur.
Pass no parameters to see a list of all available event enum names and
values.
printChipFeatures Display RAIL features supported at compile and runtime on the chip.
getAppMode Print the current app mode of RAILTEST. Values printed are those to be
found in AppMode_t.
getRadioState Get the RAIL radio state. Values returned correspond to
RAIL_RadioState_t.
verifyRadio wuuu [durationUs restart override callback] Verify radio memory contents and
return after duration in microseconds. Restart (1) or resume (0) from
last run.
enterScript u* [(flash)] Enter script entry mode. Conclude entry mode with text 'end
Script'. Specify if script is saved to RAM (0, default) or RAM and flash
(1). If saved to flash, script will run on boot.
runScript u* [(flash)] Run the script entered via enterScript. Run the script in RAM
(0, default) or in flash (1).
printScript u* [(flash)] Print the script entered via enterScript. Display the script in
RAM (0, default) or in flash (1).
clearScript u* [(flash)] Clear the script entered via enterScript. Clear the script in
RAM (0, default) or in flash (1).
wait wb* [time (mode)] Suspend processing of any input until time in the future.
Optionally specify whether the time is relative (rel) (default) or
absolute (abs).
holdRx u [enable] Enable/Disable holding of received packets instead of instantly
processing them.
reset Perform a reboot of the chip
--- Antenna Commands ---
setRfPath w [rfPath] 0=Path0, 1=Path1
--- RAM Modem Reconfiguration Commands ---
writeRmrStructure uvuw* This command should only be called by Simplicity Studio and not directly
from the CI.
updateConfigurationPointer uvu This command should only be called by Simplicity Studio and not directly
from the CI.
reconfigureModem This command should only be called by Simplicity Studio and not directly
from the CI.
silabs.com | Building a more connected world. Rev. 3.5 | 29
Page 30

Simplicity Studio
One-click access to MCU and wireless
tools, documentation, software, source
code libraries & more. Available for
Windows, Mac and Linux!
IoT Portfolio
www.silabs.com/IoT
Disclaimer
Silicon Labs intends to provide customers with the la test, accurate, and in- depth document ation of all peripherals and modules available for system and software
implementers using or intending to use the Silicon Labs products. Charac terization data, available modules and peripherals, memory sizes and memor y addresses refer to
of use of the information supplied in this document. This document does not imply or expressly grant any license to design or fabricate any integrated circui ts. The
products are not designed or authorized to be used within any FDA C lass III devices, applications for which FDA premarket approval is required, or Life Support Systems
products shall under no circumstances be used in weapons of mass destruction including (but not limited to) nuclear, biological or chemical weapons, or missiles c apable
of delivering such weapons. Silicon Labs disclaims all express and implie d warranties and shall not be responsible or liable for any injur ies or damages related to use of a
Silicon Labs product in such unauthor ized applica tions.
Trademark Information
Silicon Laboratories Inc.®, Silicon Laboratories®, Silicon Labs®, Si
EFM32®, EF R, Ember®, Energy Micro, Energy Micro logo and combinations thereof, “the world ’s most energ y friendly microcontrollers”, Ember®, EZLink®, EZRadio®,
EZRadioPRO®, Gecko®, Gecko OS , Gecko OS Studio, ISOmodem®, Precision32®, ProSLIC®, Simplicit y Studio®, SiPHY®, Telegesis , the Telegesis Logo®, USBXpress®, Zentri,
the Zentri logo and Zentri DMS, Z-Wave®, and ot hers are trademarks
regis tered trademarks of ARM Holding s. Keil is a regis tered trademark of ARM Limited. W i-Fi is a registered trademark of the Wi -Fi Alliance. All other product s or brand
names mentioned herein are trademarks of their resp ective holder s.
Silicon Laboratories Inc.
400 West Cesar Chavez
Austin, T X 78701
USA
http: //www.silabs.com
www.silabs.com/simplicit y
SW/HW
Labs® and the Silicon Labs logo®, Bluegiga®, Bluegiga Logo®, ClockBuilder®, CMEMS®, DSPLL®, EFM®,
or registered trademark s of Silicon Labs. A RM, CORTEX, Cor tex-M3 and THUMB are trademarks or
Quality
www.silabs.com/quality
Support & Community
www.silabs.com/community
 Loading...
Loading...