Siemens SXG75 Service Manual

Service Repair Documentation
Level 3 – SXG75
Release Date Department Notes to change
1.0 19.01.2005 CC S CES New document
Page 1 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0

Table of contents:
1. Instruction 4
2. List of available spare parts 5
3. Required equipment for level 3 7
4. Required software for level 3 7
5. Radio part 8
5.1 Block diagram RF part 9
5.2 Receiver (RTR6250 and RFR6250) 10
5.2.1 GSM RX 11
5.2.2 UMTS RX 11
5.2.3 GPS 11
5.3 Transmitter (RTR6250) 12
5.3.1 GSM TX modulation 12
5.3.2 GSM dual band TX VCO 12
5.3.3 GSM power amplifier 13
5.3.4 UMTS TX 14
5.4 Antenna switch 15
6. Baseband 17
6.1 Block diagram 17
6.2 MSM6250 processor 18
6.2.1 General features 18
6.2.2 MSM6250 power supplies 19
6.2.3 Clock distribution 20
6.2.4 MSM6250 bootup and mode control 22
6.3 MSM6250 interfaces 23
6.3.1 Logic interfaces 23
6.3.2 Analogue interfaces 27
6.3.3 RF interfaces 29
7. FM radio 32
7.1 FM radio interface 32
8. Power management 34
8.1 PM6650 functional overview 34
8.2 Voltage regulators and voltage converters 36
8.3 Additional power supplies 37
8.4 PM6650 signal interfaces 38
8.5 Power On/Off sequencing 40
8.5.1 Power-On sequence 40
8.5.2 Power-Off sequence 41
Page 2 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0

9. Battery/Charging 43
9.1 Battery 43
9.2 Phone shutdown due to low battery 43
9.3 Charging 44
9.3.1 Charging concept 45
9.3.1.1 Overview 45
9.3.1.2 Measurement of battery voltage, battery type and ambient temperature 47
9.3.1.3 Timing of the battery voltage measurement 47
9.3.1.4 Recognition of the battery type 47
9.3.1.5 Trickle charging 48
9.3.1.6 Normal charging (fast charge) 48
9.3.1.7 Pulsed charging 49
9.3.1.8 USB charging 49
10. Audio interference and suspension of pulse charging 50
11. MMI 51
11.1 Display 51
11.1.1 Overview 51
11.1.2 Interface display module 51
11.1.3 Contrast and colour adjustment 53
11.1.4 Illumination 53
11.2 Keypad 54
11.2.1 Keypad mapping 54
11.2.2 Illumination 56
12. Acoustics 58
12.1 Microphone, speaker and hands-free speaker 59
12.2 Audio accessories 59
13. Cameras 60
13.1 2Mpix cameras 60
13.2 CIF camera 60
13.3 Camera bus interface 60
13.4 Camera flash trigger 61
14. Vibramotor 62
15. IrDA and fuel gauge 63
15.1 IrDA transceiver 63
15.2 Battery fuel gauge and IrDA multiplexing 64
16. Bluetooth 66
17. Accessory interface 67
17.1 Overview 67
17.2 UART and USB multiplexing 68
17.3 Connector default configuration 69
17.4 Accessory detection 69
18. UART 70
19. USB 70
20. SIM interface 71
21. MMC interface 72
22. Component placement 73
Page 3 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0

1 Instruction
This Service Repair Documentation is intended to carry out repairs on BenQ repair level 4. The
described failures shall be repaired in BenQ authorized local workshops only.
All repairs has to be carried out in an ESD protected environment and with ESD protected
equipment/tools. For all activities the international ESD regulations has to be considered.
Assembling/disassembling has to be done according to the latest SXG75 Level 2 repair
documentation. It has to be ensured that each repaired mobile phone is checked according to the
latest released General Test Instruction document (both documents are available in the technical
support section of the C-market).
Check at least weekly C-market for updates and consider all SXG75 related Customer Care
Information and Repair Information which are relevant for the SXG75.
SXG75 partnumber on IMEI label: S30880-S8900-#xxx
, while # can be any letter (A-Z) and xxx can be any number from 100, 101, 102....
Scrap handling: All scrap informations given in this manual are related to the
SCRAP-Rules and instructions.
Attention: Consider the new "LEAD-FREE" soldering rules
(available in the communication market) and avoid excessive heat.
If you do have any questions regarding the repair procedures or spare parts do not hesitate to contact
our technical support team in Kamp-Lintfort, Germany:
Tel.: +49 2842 95 4666
Fax: +49 2842 95 4302
e-mail: st-support@benq.com
Page 4 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
p
2 List of available spare parts
(according to Component Matrix V1.03 - check C-market for updates)
Com
V101 L50640-D4060-D670 DISDIODE DUAL ESD-PROTECTION SOT23
V200 L50630-C1101-D670 DISTRANS SI1555DL
N200 L50645-K280-Y337 IC FEM LMSP43MA-288TEMP GSM UMTS SMD
Z203 L50645-K280-Y323 FILTER DUPLEX WCDMA
Z200 L50645-K280-Y331 FILT SAW RX PCS1900MHZ B7846
Z201 L50645-K280-Y332 FILT SAW RX DCS1800MHZ B7844
Z202 L50645-K280-Y333 FILT SAW RX GSM900MHZ B7837
D500 L50620-L6165-D670 IC TELEC TRANSCIEVER RTR6250 QFN56
N300 Not defined yet IC MODUL PA PF0814 (PA-Type3) PB Free
V300 L50630-C1101-D670 DISTRANS SI1555DL
Z300 L50645-G100-Y108 OSCOSCI TXVCO 824-1910MHZ SMD
Z400 L50645-K260-Y93 ISOLATOR 1920MHZ-1980MHZ SMD
D400 L50651-Z2002-A66 IC TELEC ACPM-7881 SMD
V400 L50630-C1101-D670 DISTRANS SI1555DL
Z402 L50697-F5005-F88 IC TELEC RF-DETECTOR SOT23-6L
Z401 L50645-K280-Y314 FILT SAW UMTS2100 1950MHZ B7754
Z602 L50697-F5020-F34 EPCOS SAW LOW-LOSS-FILTER 2140,0MHZ LG02
X600 L36334-Z97-C334 CONNECTOR COAX SOCKET SWITCHED
Z600 L50645-K280-Y293 FILTER SAW AGPS 1575,42MHZ B7840 SMD
Z601 L50645-K280-Y304 FILSAW 1575,42 MHZ B7829 SMD
N600 L50620-L6166-D670 IC TELEC RECEIVER GPS UMTS RFR6250 QFN48
N700 L50610-U6197-D670 IC ANA STEREO-AMPLIFIER TS4975 CSP12
D800 L50620-L6164-D670 IC TELEC MSM6250 CSP409
Z1000 L50645-G200-Y27 OSCOSCI VCTCXO 19.2MHZ SMD
V1100 L50640-C3008-D670 DISTRANS PNP 0,5A 30V SOT89
V1102 L50630-C3007-D670 DISTRANS P-CH SI2333DS FDN306P SOT23
N1100 L50610-C6181-D670 IC VOLTAGE REG.TPS73601DRBR SMD ADJUSTA
V1101 L50640-D5086-D670 DISDIODE RB551V-30 PMEG3005AEA SOD323
Z1200 L50640-U6064-D670 FILTER EMI (Fi-Type7) PB Free
Z1201 L50610-C6179-D670 IC SPDT SWITCH DUAL MAX4717EBC+T UCSP12
V1303 L50640-D4043-D670 DIODENARRAY ESDA6V
Z1300 L50645-F102-Y42 OSCCRYST 32,768KHZ 7,0PF 30PPM SMD LF
N1300 L50645-J4681-Y57 IC POWER-MANAGMENT PM6650
V1301 L50640-D5086-D670 DISDIODE RB551V-30 PMEG3005AEA SOD323
D1300 L50610-C6183-D670 IC LOGIC NAND 74LVC1G00 SOT886
V1302 L50640-D5086-D670 DISDIODE RB551V-30 PMEG3005AEA SOD323
V1300 L36840-D5076-D670 DIODE SOD323 (Di-Type7)
Z1600 L50645-K280-Y328 FIL BP 2,4GHZ SMD
N1600 L50610-L6155-D670 IC TRANSCEIVER BLUETOOTH BCM2004 SMD
D1800 L50620-L6150-D670 IC TELEC TEA5764HN
V1800 L36840-D61-D670 DIODE 1SV305 (Di-Type4)
V1801 L36840-D61-D670 DIODE 1SV305 (Di-Type4)
V1900 L36840-C4057-D670 TRANSISTOR EMD12 EMT6 (Tra-Type8)
N1900 L50610-C6152-D670 IC ANA REG 2*2,85V 150MA USMD8 LP3986T
onent Ordernumber Description
Page 5 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
D1900 L50610-B6198-D670 IC LOGIC BUFFER 74ALVC16244AZQLR VBGA LF
D1901 L50610-B6198-D670 IC LOGIC BUFFER 74ALVC16244AZQLR VBGA LF
V2000 L36840-C4014-D670 TRANSISTOR BC847BS BC846S (Tra-Type7)
D2100 L50610-B6134-D670 IC LOGIC NC7WZ126L8X MAC08A
V2101 L50640-C4060-D670 DIS TRANS ARRAY EMD9 EMT6
D2200 L50610-B6186-D670 IC LOGIC 2 INPUT AND NC7SZ08L6X
N2201 L50610-C6153-D670 IC ANA RE 2.9V USMD5 PB FREE
V2200 L36840-C4014-D670 TRANSISTOR BC847BS BC846S (Tra-Type7)
V1700 L50640-D5086-D670 DISDIODE RB551V-30 PMEG3005AEA SOD323
Page 6 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0

3 Required equipment for level 3
- GSM-Tester (CMU200 or 4400S incl. options)
- PC, incl. monitor, keyboard and mouse
- USB boot cable (F30032-P465-A1)
- Troubleshooting frame SXG75
- Power supply
- Spectrum analyser
- Active RF-Probe incl. power supply
- Oscilloscope incl. probe
- RF-Connector (N<>SMA(f))
- Power supply cables
- Dongle (F30032-P28-A1). If USB-Dongle is used, a special driver for NT is required
- Soldering and BGA soldering equipment for lead free soldering.
Reference: Equipment recommendation
(downloadable from the technical support page)
4 Required software for level 3
- Windows XP
- XFocus V2.06
- GRT V3.07
- Internet unblocking solution (JPICS)
Page 7 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0

5 Radio part
The RF section consists of three data capable transceivers and two further broadcast receivers. The
first transceiver is an IMS UMTS 2100MHz 3G solution which realizes the conversion of the RF
WCDMA signals from the antenna to the baseband and vice versa. The second transceiver is a GSM
part which realizes the conversion of the GMSK-RF-signals from the antenna to the baseband and
vice versa. The third transceiver is a Bluetooth type Personal Wireless LAN system. The first
broadcast receiver is an RDS compliant FM radio solution. The second is a GPS receiver which is
integrated into the UMTS receiver IC. The GPS software will allow assistance from a suitably enabled
network (A-GPS); standalone operation without network assistance is also supported.
The GSM part supports triple band operation in the frequency ranges EGSM900, DCS1800,
PCS1900 respectively supporting GPRS functionality up to multiclass 10. In the receiving direction,
the RF signals are filtered and then directly down-converted and split into the I- and Q-component and
led to the D/A-converter of the logic part. In the transmission direction, the GMSK-signal is generated
in an Up Conversion Modulation Phase Locked Loop by modulation of the I- and Q-signals which are
generated in the logic part. The high power Tx VCO is external to the RFIC. After that the signals are
amplified in the power amplifier. The GSM transmitter and receiver are never active at the same time
(TDMA system).
The Bluetooth solution is realized in a separate IC with an external SAW filter.
The GPS receiver is integrated into the UMTS receiver RFIC. Two stages of filtering are provided in
front of and behind the LNA. The GPS down-conversion is a direct conversion system.
The FM radio solution is also realized in a separate IC.
The RF-circuit consists of the following components:
• Qualcomm chip set
RTR6250 for GSM TX/ RX, UMTS TX, LO1, PLL for
GPS LO
• Qualcomm chip set
•
VCTCXO 19,2 MHz
RFR6250 for UMTS RX, GPS RX, UMTS VCO, GPS VCO
• GSM TX VCO
• GSM PA module
• UMTS PA module
• UMTS duplexer and isolator
• BCM2004 Bluetooth IC
• FM radio
Page 8 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
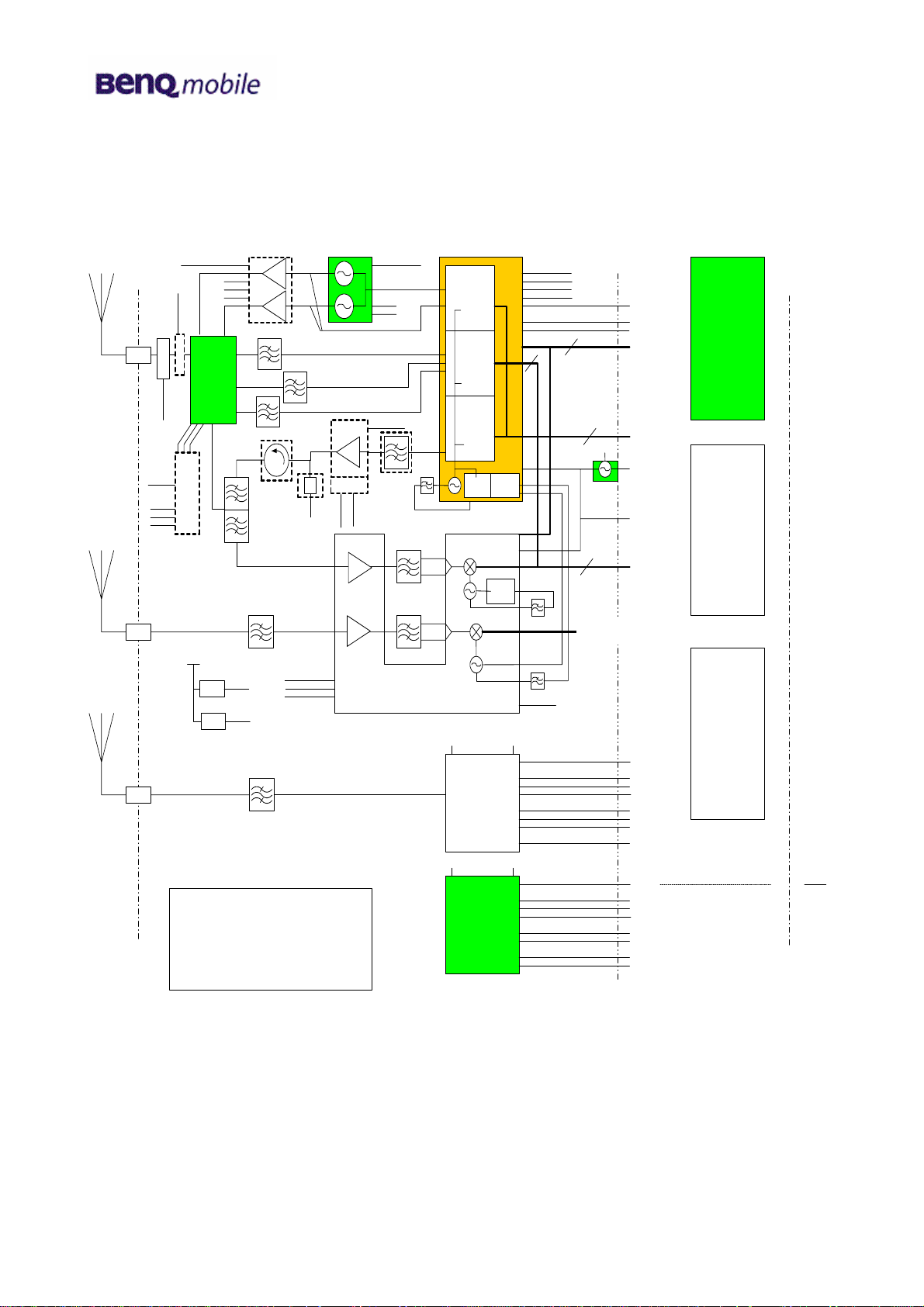
5.1 Block diagram RF part
Ant/RF
External
Cellular
Cellular
Antenna
Antenna
Connector
ANT_POSN
ANT_SEL0
ANT_SEL1
ANT_SEL2
GPS
Antenna
BT
Antenna
VREG_
RFRX_0
VBATT
GPS Bias
LMSP43MA-
288TEMP
Inte rf ac e
VREG_MSMP
GSM_PA_EN
GSM_PA_BA ND
PA_RAMP
SP6T
Murata
ESI-3EAR1.950G01-T
Renesas
PF08143B-06-TB
942.5MHz SAW
EPCOS B7837
1960MHz SAW
1575.42MHz
EPCOS
B7829
2450MHz
TDK
DEA322448BT
EPCOS B7846
Detector
AD8361
VREG_RFRX_1
VREG_TXCO
VREG_MSMP
HDET1
1920-1980MHz
Hitachi Metals
Diplexer
1950-21400MHz
EPCOSB69967N2047A760
PA_THERM
RF_THERM
Wolf 5 RF Block Diagram B1
Issue K
David Pennington
24/1/05
Commercial-in-Confidence
1842.5MHz SAW
EPCOS B7844
Agilent
ACPM 7881
Interface
VREG_
PA_ON0
VREG_RFTX
TX_VCO_1_EN
TX_VCO_0_EN
ALPS
UCVA4XW02A
V_CDMA_PA
RFTX
1950MHz
60MHz
EPCOS
B9031
2140MHz 60MHz
B7728
1575.42MHz
EPCOS
B7840
GSM Tx
GSM Rx
UMTS Tx
PLL1
PLL2
RTR6250
PLL1
RFR6250
VREG_AUX2 VREG_MSMP
BCM2004
VREG_MSMA VREG_MSMP
Philips
TEA5764HN
VREG_RFTX
VREG_SYNTH
VREG_MSMP
VREG_RFRX_0
4
GSM_PA_EN
(GPS Blank)
19.2MHz
88-106MHz
3
VREG_TXCO
19.2MHz
VCTCXO
19.2MHz
Toyocom
TCO-5871
4
4
RF/BB
TX_VCO_1_EN
TX_VCO_0_EN
TX_ON
TX_IREF
TX_AGC_ADJ
SB_**0
GSM_PA_EN
GSM_PA_BAND
PA_RAMP
ANT_SEL0
ANT_SEL1
ANT_SEL2
TX_IQ4
TRK_LO_ADJ
TXCO
PA_THERM
RF_THERM
RX_IQ_0
PA_ON0
PA_R0- Not used
HDET1
RX_IQ_1
VBATT
V_CDMA_PA
VREG_SYNTH
VREG_TXCO
VREG_RFTX
VREG_RFRX_0
VREG_RFRX_1
VREG_MSMP
VREG_AUX2
VREG_MSMA
BT_ENABLE
BT_Tx_RX_N
BT_DATA
BT_CLK
BT_SBDT
BT_SBST
BT_SBCK
BUFF_TCXO_BT
FM_IN
SLEEP_CLK
A_FM_STANDBY
A_RDS_DATA_EXIST
I2C_SCL
I2C_SDA
AUXIP
AUXIM
Memory
MSM6250
PM6650
core/rest
Battery
SIM
MMC
Screen
Camera1
Camera2
Accessory
Connect
J-TAG
Keypad
Audio
IRDa
USB
etc
FM Antenna
Page 9 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
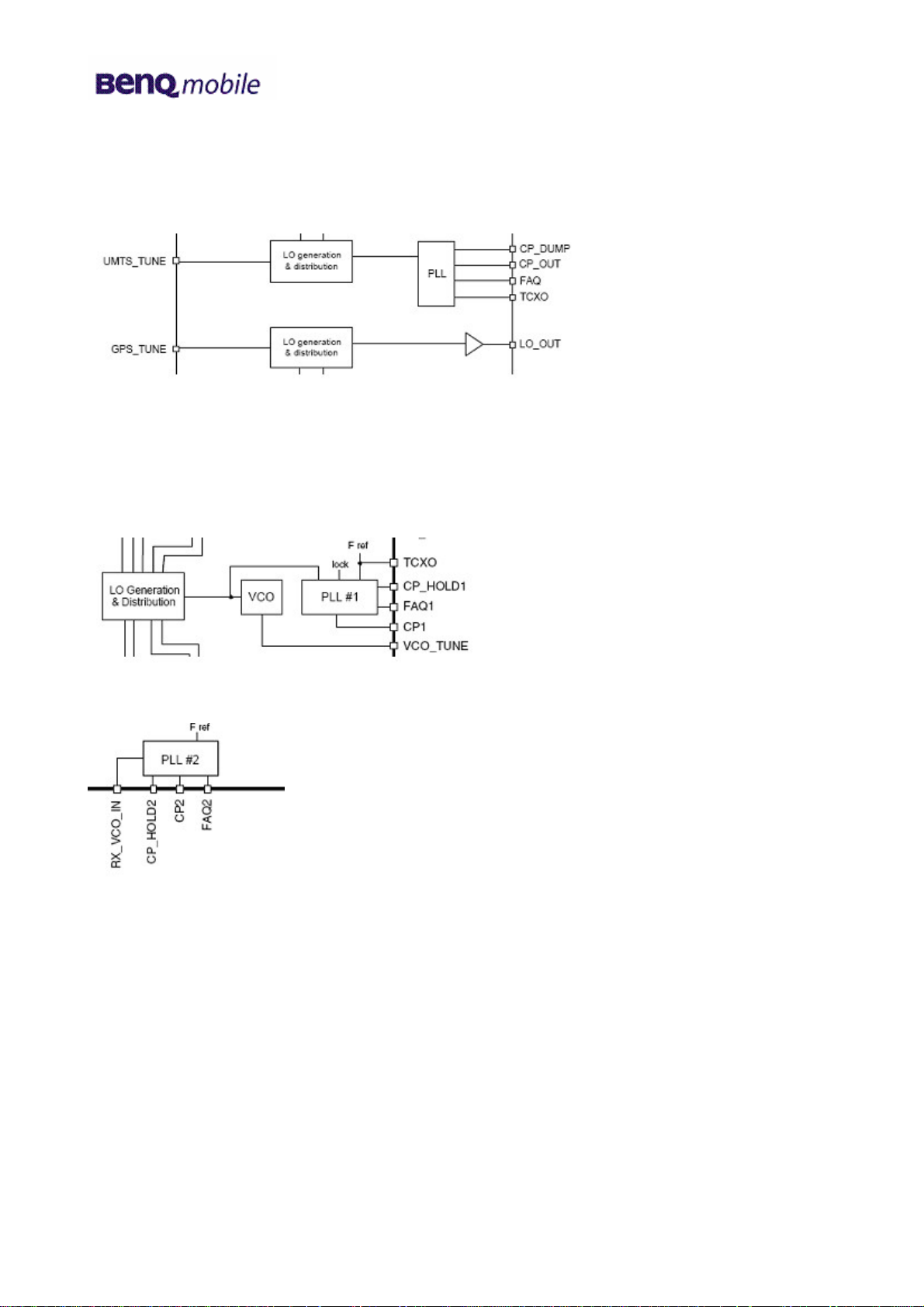
5.2 Receiver (RTR6250 and RFR6250)
The RFR6250 has two VCOs. The first is for the UMTS direct conversion receiver. The second is for
the GPS receiver and the PLL for this VCO is on the RTR6250 RFIC.
Block diagram RFR6250
The RTR6250 contains two PLLs, the first is used by the RTR for all GSM transceiver functions and
for the UMTS TX LO generation. The second PLL is used to control the GPS VCO in the sister
RFR6250 RFIC.
Block diagram RTR6250
Page 10 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0

5.2.1 GSM RX
The GSM Receiver is a zero IF architecture with direct conversion by the IC. Although the IC provides
four input paths, the GSM850 Receiver is not used in the SXG75.
Block diagram RTR6250
5.2.2 UMTS RX
The RFR6250 provides an LNA and an output to allow further input filtering. The balanced signal is
reconnected to the RFR6250 and down converted by the Zero IF Quadrature Downconverter. The
UMTS 1900 RX path (PLNA, PMIX) is not used in the SXG75.
Block diagram RFR6250
5.2.3 GPS
The GPS path is similar to the UMTS path, but uses a LNA with higher amplification to compensate
the DCS self blocking. The RFR6250 allows the GPS RX path to be switched off during GSM transmit
pulses.
Block diagram RFR6250
Page 11 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
5.3 Transmitter
5.3.1 GSM TX modulation
The GSM transmitter uses a Offset Phase Lock Loop Architecture. The high power VCO is external to
the RTR6250. A feedback signal from the VCO is down-converted and the phase compared to that of
an upconverted version of the IQ signals from the baseband. The control signal is filtered and passed
to the high power VCO.
Blockdiagram RTR6250
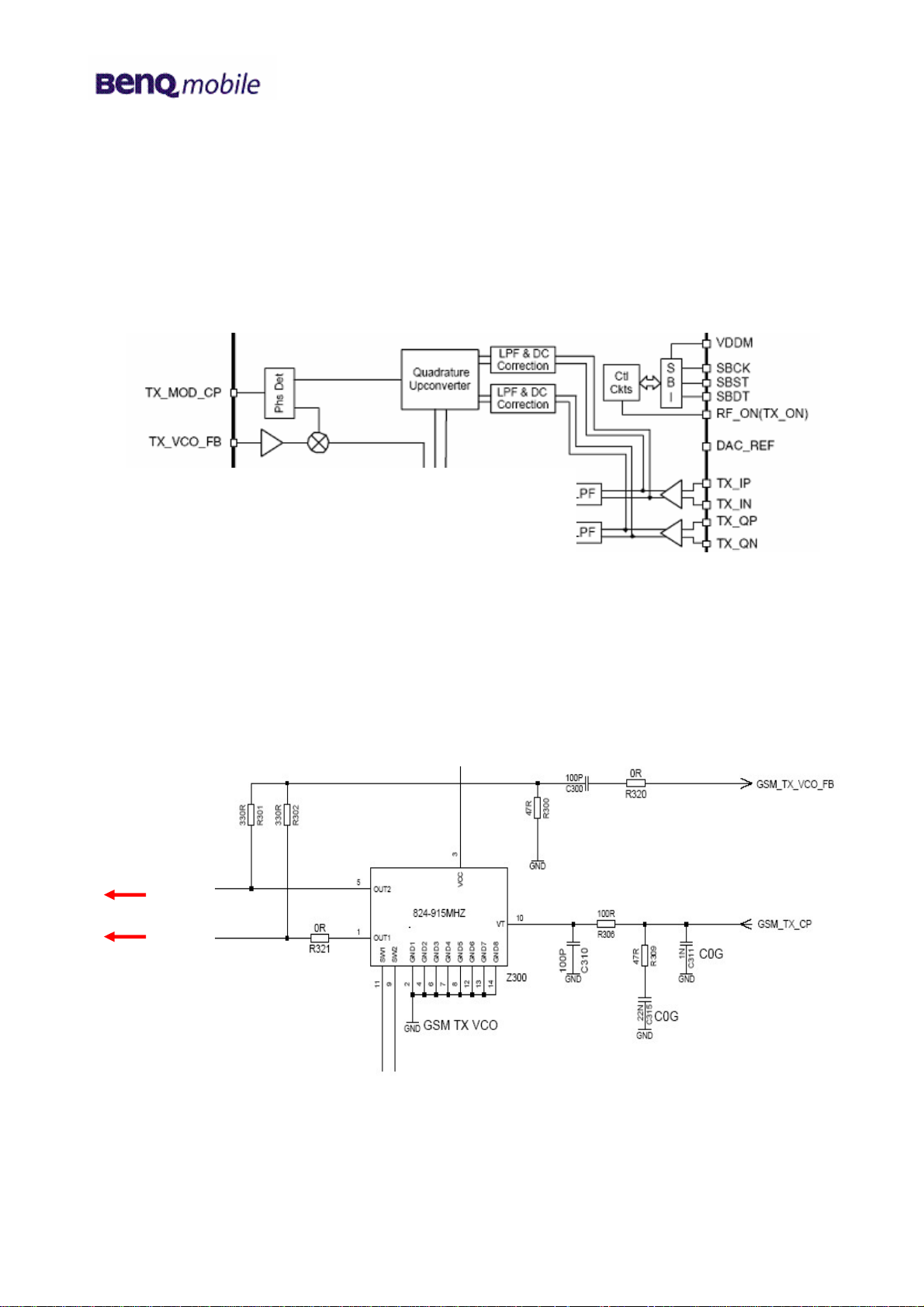
5.3.2 GSM dual band TX VCO
The GSM TX VCO (Z300) is external to the RTR6250 and uses filtered signals (GSM_TX_CP) from
the RTR6250 to provide the GMSK signal to the power amplifier.
PA
Circuit diagram (sheet 3)
Page 12 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
5.3.3
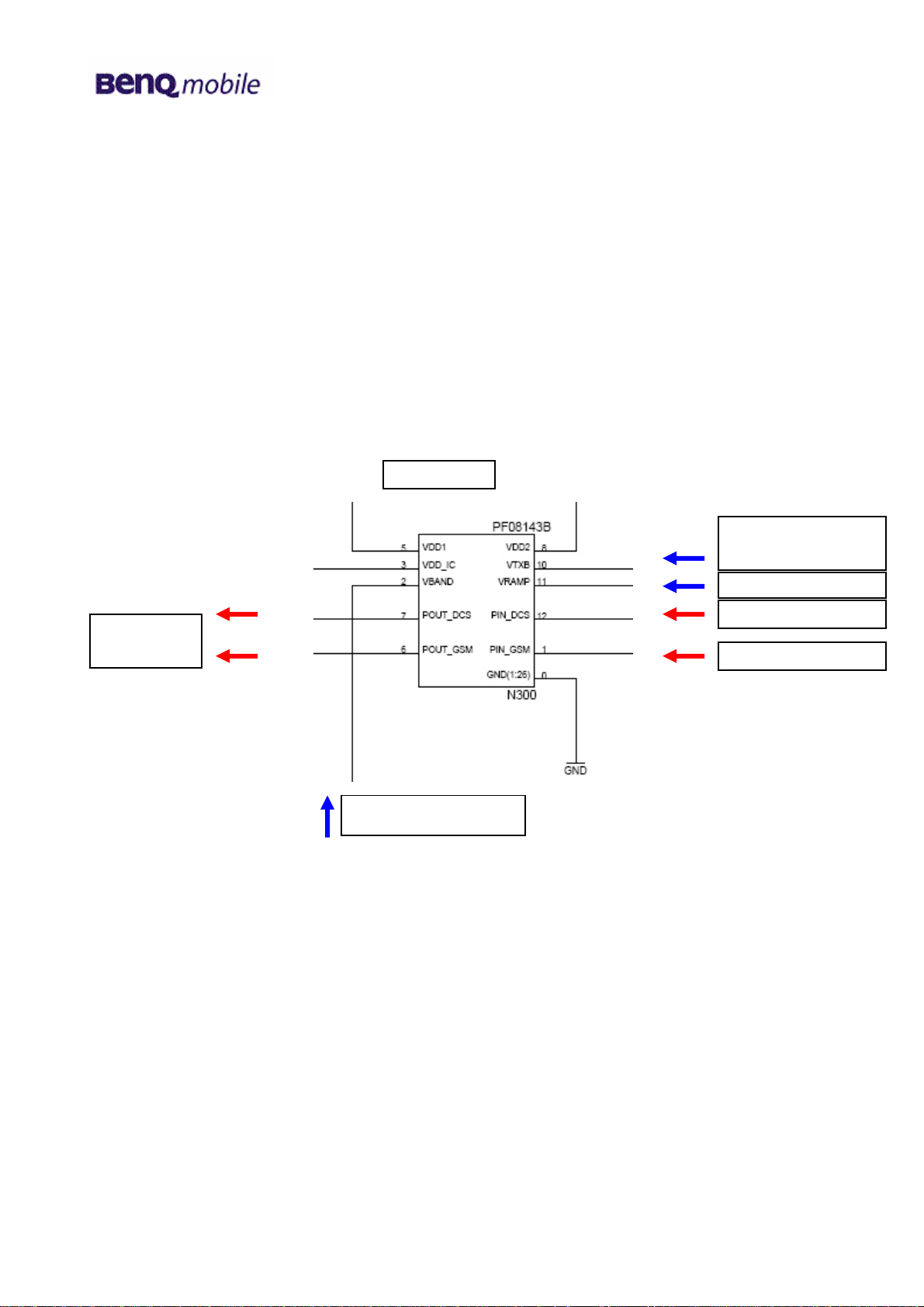
GSM power amplifier
The output signals (OUT1 and OUT2) from the GSM TX VCO are led to the power amplifier. The
power amplifier is the PA-module N300. It contains of two separate amplifier chains for GSM900 and
GSM1800/GSM1900 operation. The amplification is controlled with the signal VRAMP. The
appropriate amplifier chain is activated by the logic signal GSM_PA__BAND which is provided by the
MSM6250. The N300 is activated through the signal VTXB, which is the level shifted GSM_PA_EN
provided by the MSM6250.
The voltage VBATT is provided by the battery.
GSM_PA_EN
(level shifted)
to antenna
switch
Circuit diagram (sheet 3)
OUT2 from TX VCO
OUT1 from TX VCO
GSM_PA_BAND
Page 13 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
5.3.4 UMTS TX
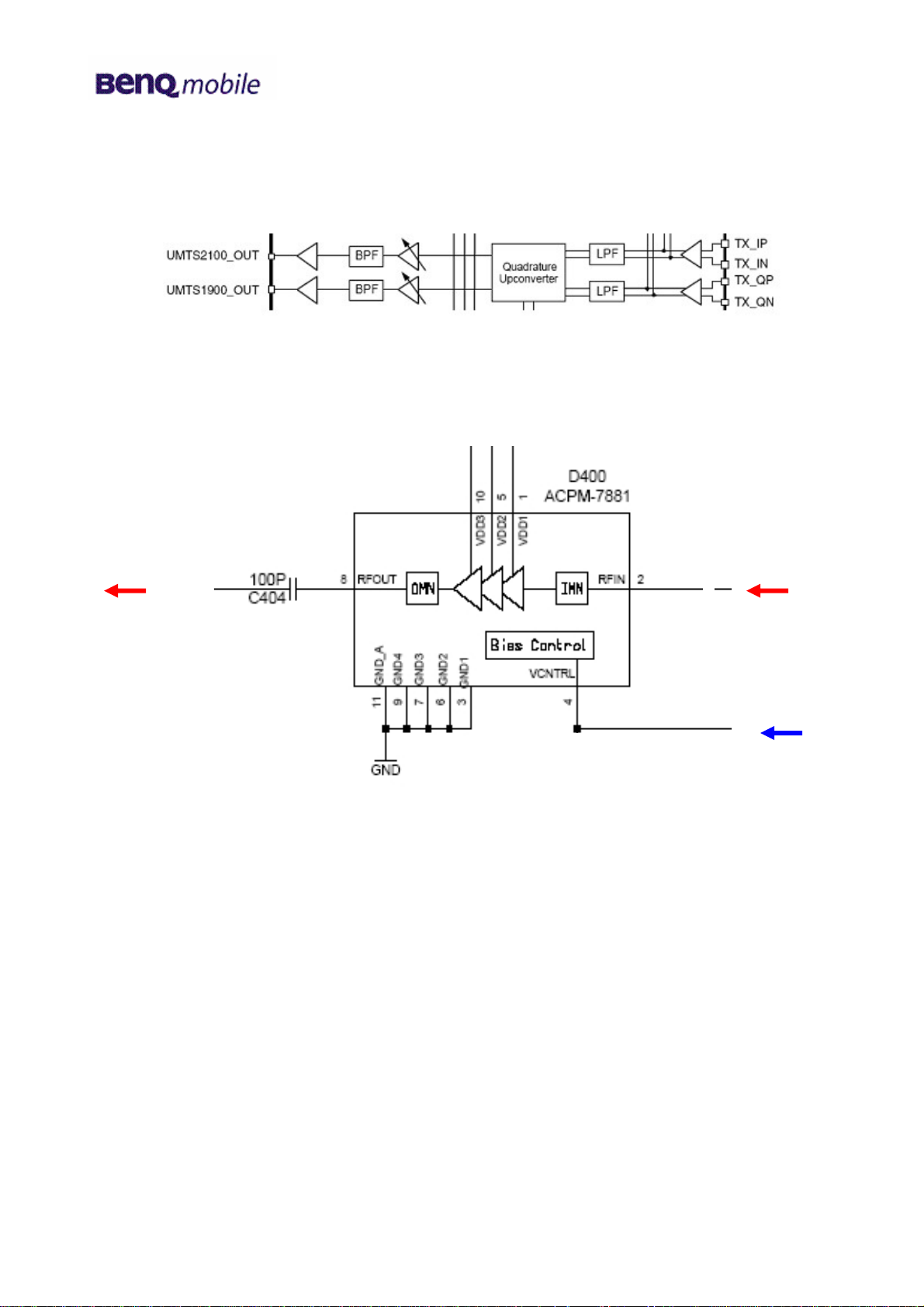
The IQ signals from the baseband are directly up-converted to the RF band by a Quadrature
Upconverter and passed to the external filter. The UMTS 1900 TX path is not used in the SXG75.
Blockdiagram RTR6250
VBATT
UMTS2100 TXWCDMA TX
PA_ON0
(level shifted)
Circuit diagram (sheet 4)
Page 14 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
5.4 Antenna switch
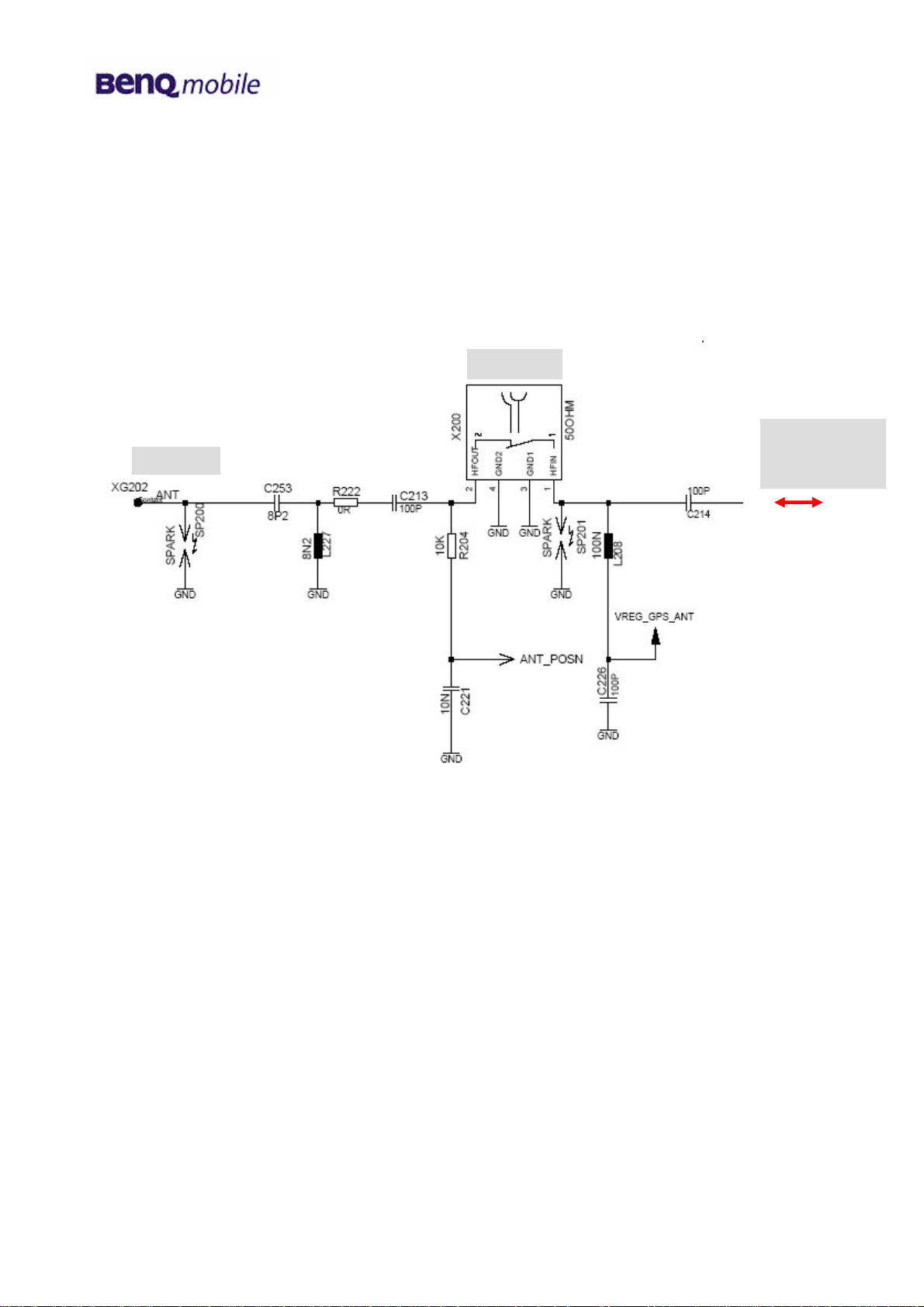
The SXG75 mobile has two antenna switches:
a) The mechanical antenna switch for the differentiation between the internal and external
antenna.
Internal/external antenna switch
External
to/ from
Internal
switch
module
Circuit diagram (sheet 2)
Page 15 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
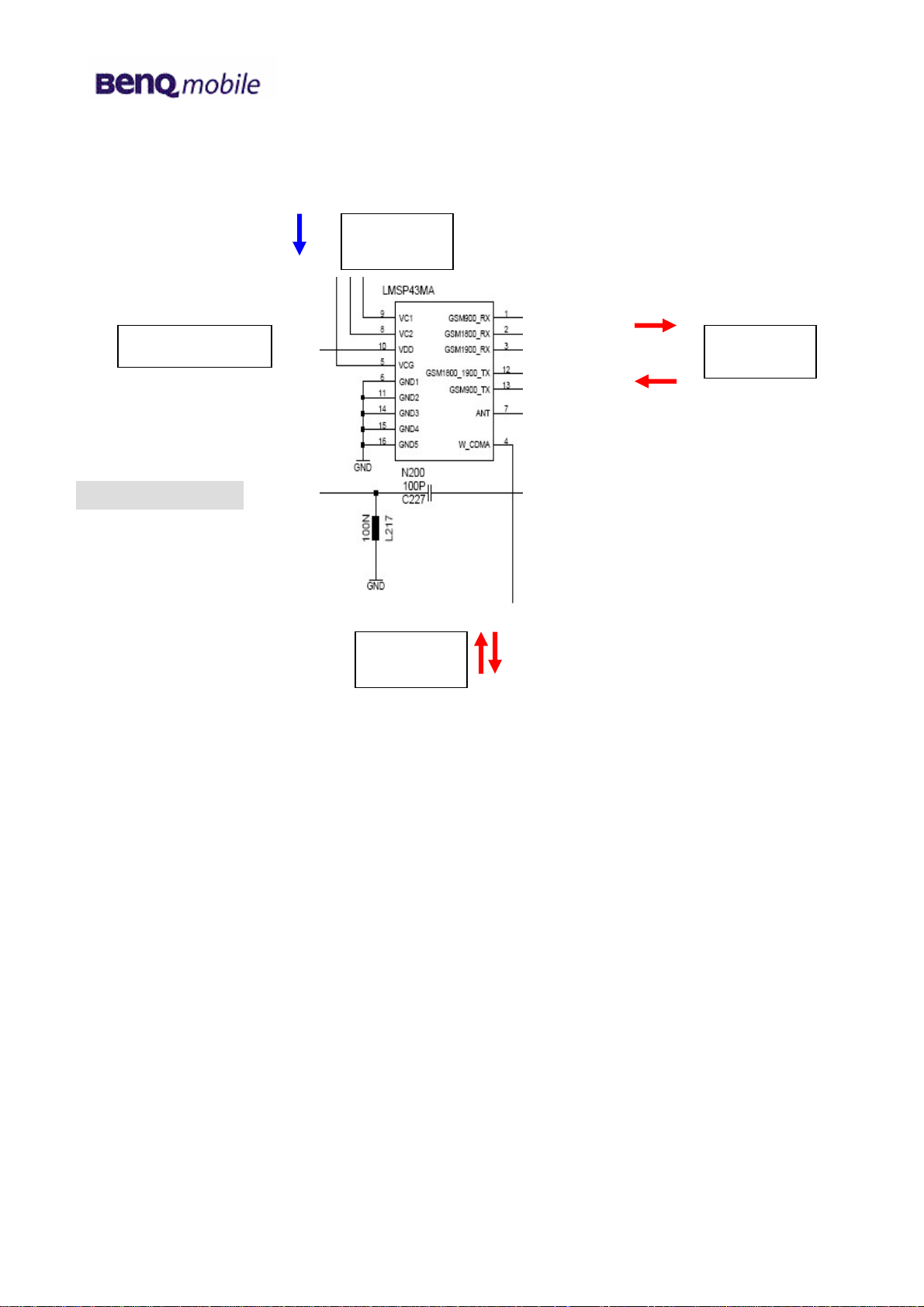
b) The electrical antenna switch for the differentiation between the GSM and UMTS
receiving respectively transmitting signals.
Signal
selection
VREG_RFRX_0
from/ to antenna
Circuit diagram (sheet 2)
GSM
signals
UMTS
signals
Page 16 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
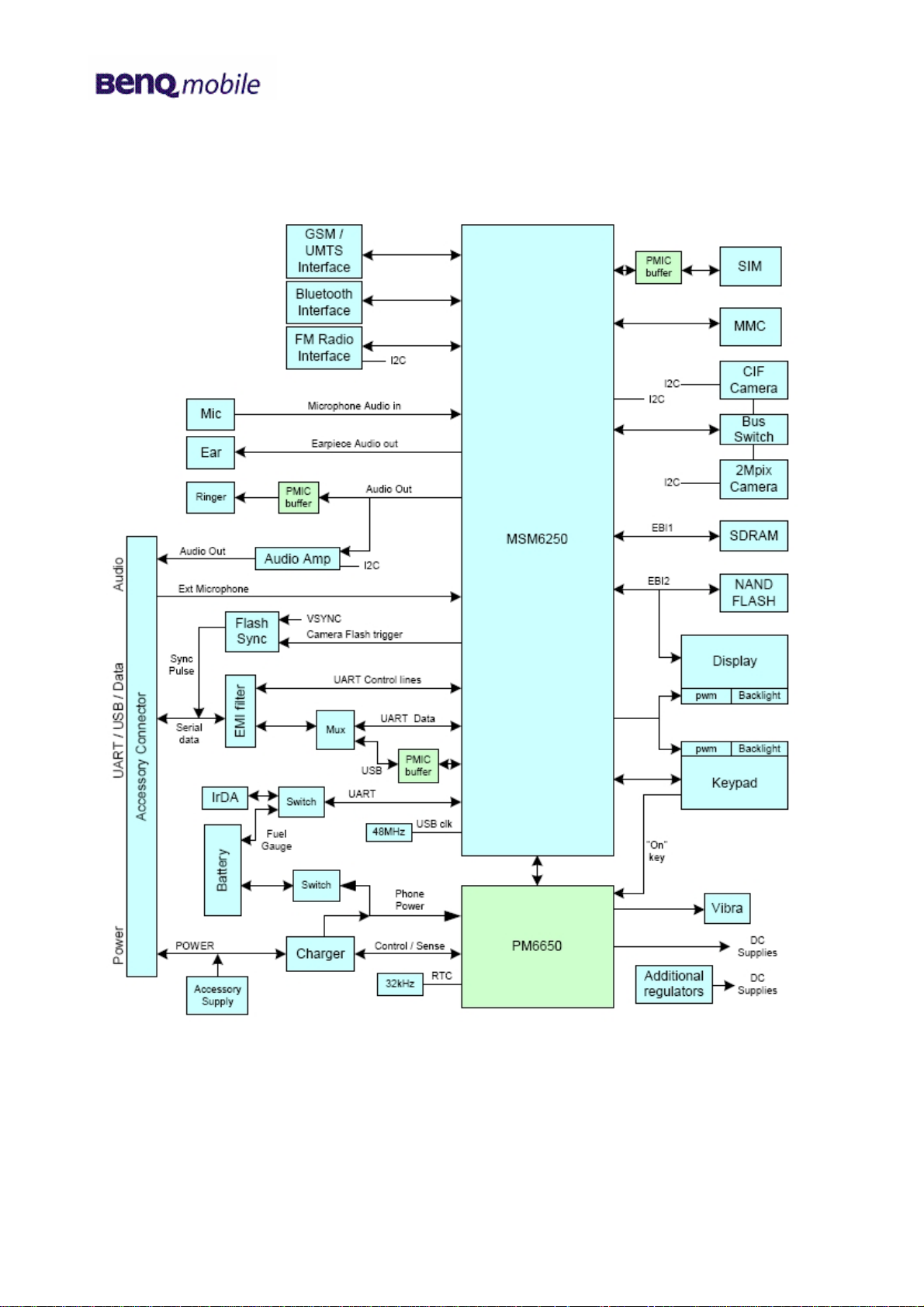
6 Baseband
6.1 Block diagram
Page 17 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
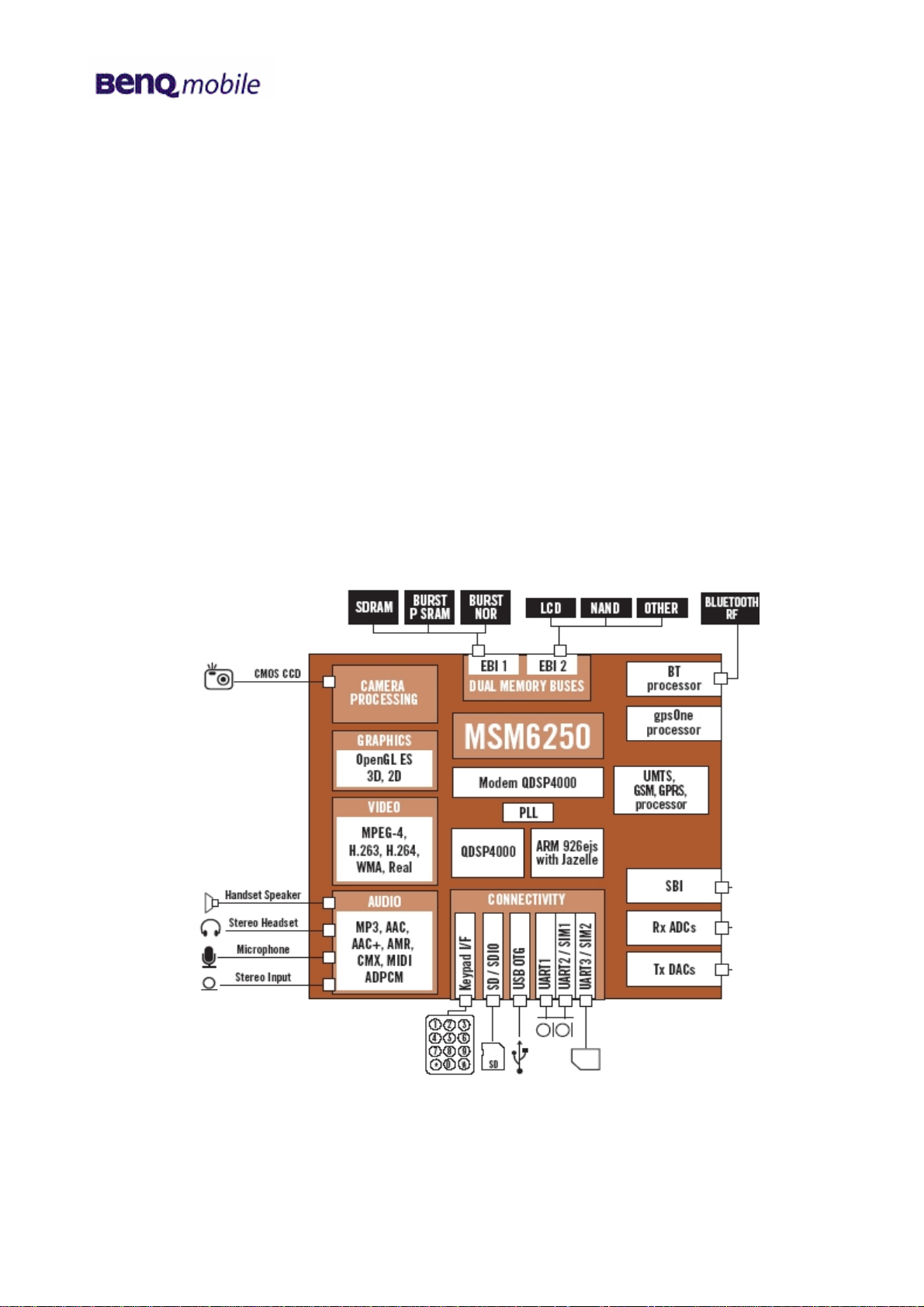
6.2 MSM6250 processor
6.2.1 General features
• Supports UMTS FDD release 99 September 2002 standard air interface
• Supports GSM/GPRS in addition to W-CDMA
• Supports low-power, low-frequency crystal to enable TCXO shutoff
• radioOne™ Zero IF interface Zero IF support - DC offset cancellation and digital variable gain
amplifier
• Software-controlled power management features
• Hardware support for inter-frequency and inter-radio access technology searching in CM
(WCDMA-GSM)
• Higher-speed serial bus interface, operating at up to 10 MHz and capable of handling four hardware
requests
• Multimedia card hardware support
• Serial bus controller: standard 100 kbps and fast 400 kbps
• MPEG4 video encoder
• 2-D and 3-D graphics accelerator for gaming applications
• Hardware acceleration supporting video capture and video telephony
• USB slave functionality
• Integrated wideband stereo CODEC for digital audio application
Block diagram MSM6250
Page 18 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
6.2.2 MSM6250 power supplies
The supplies used by the MSM6250 are generated by the PM6650 (Section 5).
They are as follows:
Supply Name Value Power Domain
VREG_MSMC 1.375 V (±3%) Digital Core only.
VREG_MSME 1.850 V (±3%)
VREG_MSMA 2.600 V (±3%) Analog circuits
VREG_MSMP 2.600 V (±3%) Supply voltage for IO pad group 3
SDRAM interface (EBI1 bus), NAND FLASH
and LCD interface (EBI2 bus), supply voltage
for IO Pad group 2
MSM6250 power supplies
Each supply has a zero-ohm series resistor (R804, R805, R806, R808) before the MSM6250
decoupling capacitors. The supplies become active while the phone is in the reset state during
“Phone On” operation (PON_RST_N from the PM6650 is low). They remain active until the phone is
turned off.
Page 19 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
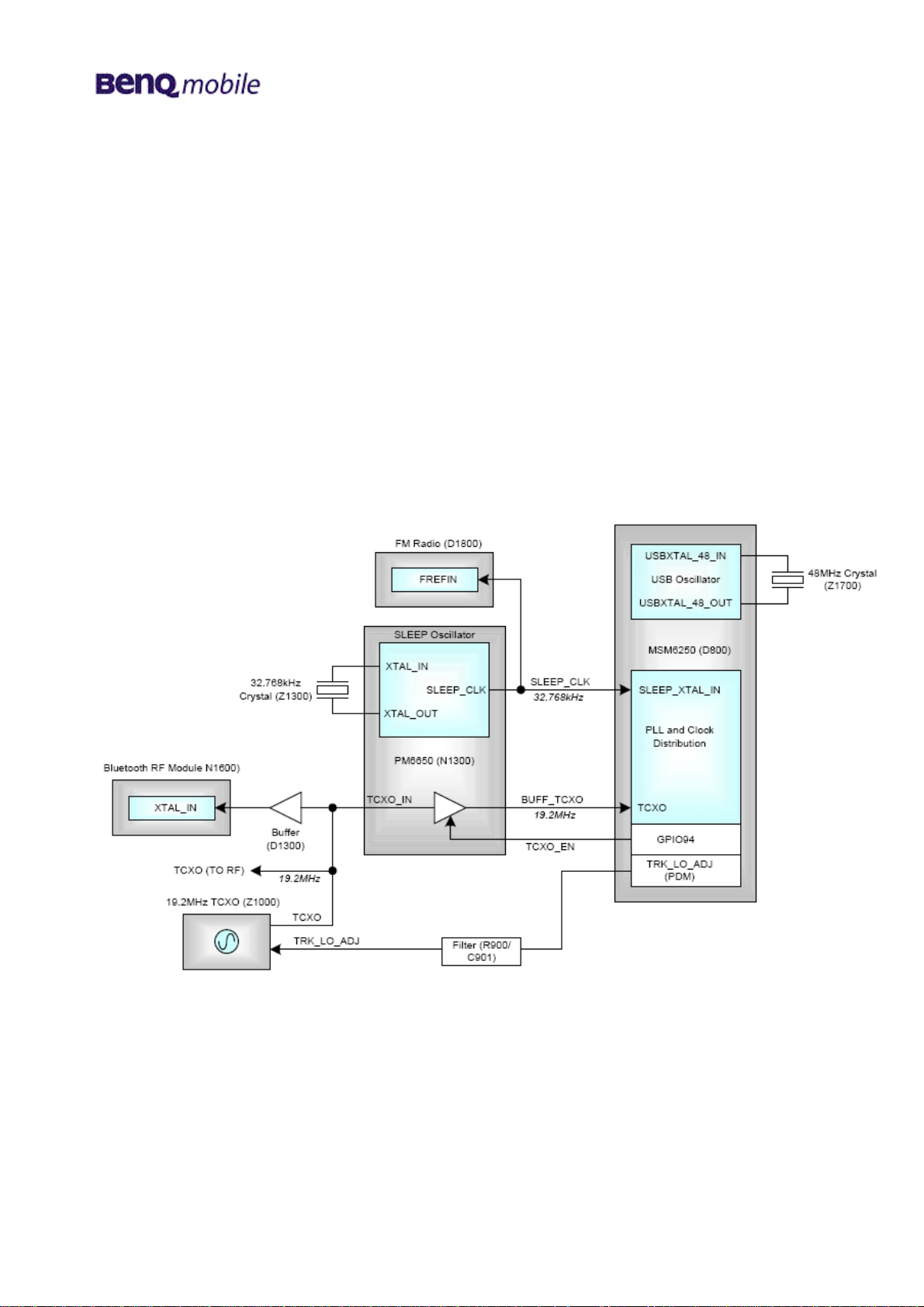
6.2.3 Clock distribution
The master clock for Wolf 5 baseband and RF systems runs at 19.2MHz. The clock is generated by
Voltage-Controlled-Temperature-Compensated-Crystal-Oscillator Z1000. The clock is buffered to
VREG_MSMP (2.6V) levels within the PM6650, and then sent to the MSM6250. The PM6650 buffer is
enabled by logic control TCXO_EN from the MSM6250. The MSM6250 integrates a phase-locked
loop and digital dividers to derive internal clocks from the TCXO clock input.
The TCXO is also buffered by D1300 to feed the Bluetooth RF Module, N1600. This buffer is only
enabled when the Bluetooth supply (VREG_AUX2) is active.
A 32.768 kHz clock (SLEEP_CLK) is generated by the PM6650, and fed to the MSM6250. This clock
is used for low-power operation during phone idle periods when the TCXO is disabled. It also drives a
Real-Time-Clock circuit in the PM6650. The power supply for the Sleep Oscillator and associated
Real-Time-Clock is derived from the battery voltage and backup capacitor C1312. This means the
clock is active when the phone is powered off, and for 40 seconds when the battery is removed.
A 48MHz clock is provided by Z1700. This is used internally by the MSM6250 to control USB
functions.
Block diagram
Page 20 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
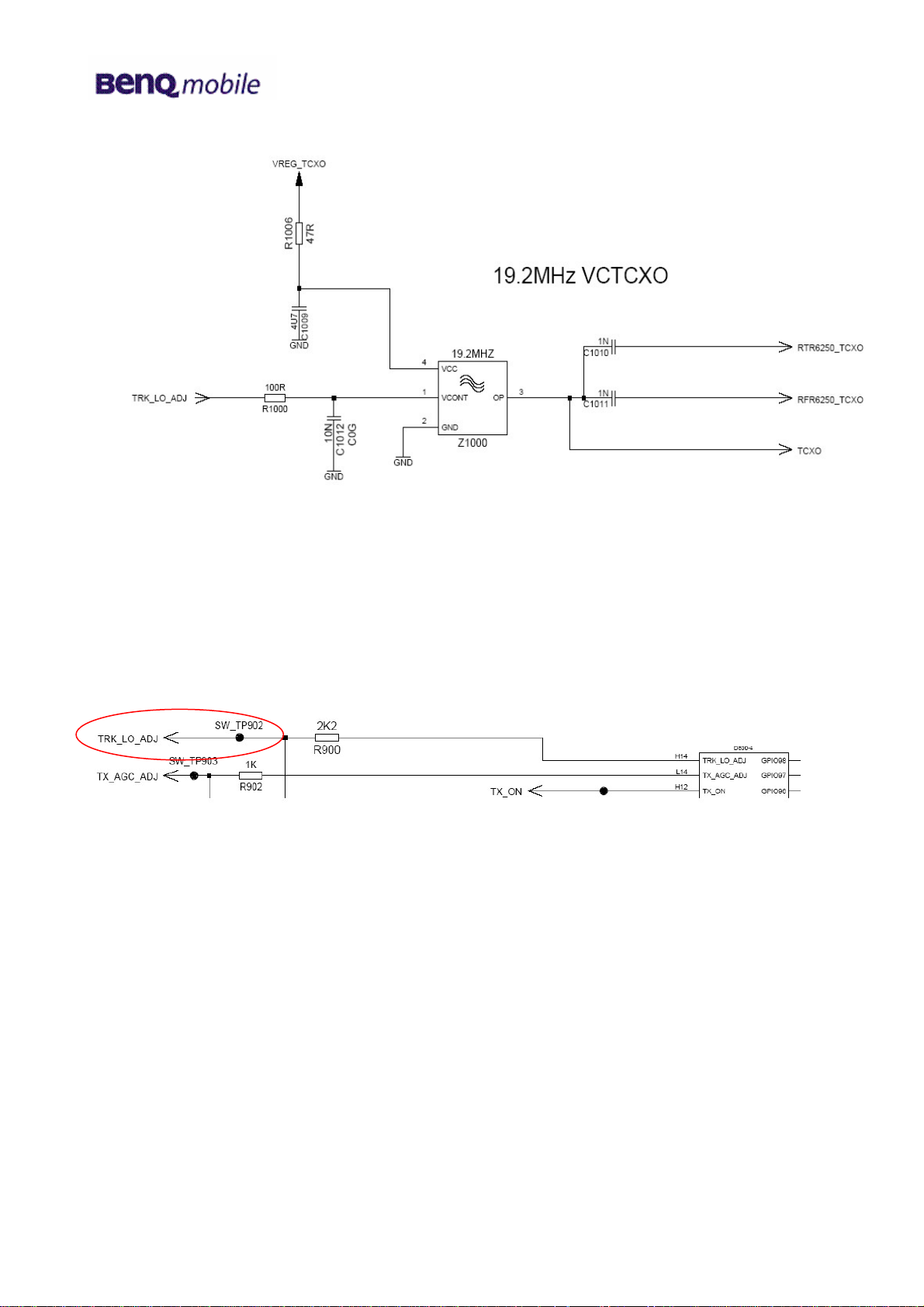
Circuit diagram (sheet 10)
The oscillator output signal TCXO is connected to the power management IC (PMIC, N1300, Pin 58).
The oscillator output signals RFR6250_TCXO and RTR6250_TCXO are connected to the RF chips
RFR6250 (N600, Pin 33) resp. RTR6250 (D500, Pin 6).
To compensate frequency drifts the oscillator frequency is controlled by the TRX_LO_ADJ signal,
generated through the MSM6250 (D800, SW_TP902).
Circuit diagram (sheet 9)
Page 21 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
6.2.4 MSM6250 bootup and mode control
The MSM6250 supports booting from the NAND FLASH memory. The high pull-up (R1700) on the
bootmode input pin is used to indicate to the MSM hardware that FLASH boot-up is required. After
power-on reset, the MSM hardware automatically loads the boot code from NAND flash to an on-chip
boot SRAM, and then releases the ARM to execute from this boot SRAM. By executing the boot code,
the ARM processor transfers the entire phone software to the SDRAM, and then branches to the
SDRAM to execute the phone software and completes the boot-up process.
The MSM6250 runs in “Native” mode. This mode is selected by the Mode 0, Mode 1 and Mode 2 pins
(Schematic sheet 17). The pins are left floating (internal pulldown resistors) to select Native mode.
Note that the Mode pins are connected to additional MSM6250 pins. This is a requirement of the
device – the signals are not required for any external functions.
MSM6250 Function Signal Function
TCXO BUFF_TCXO TCXO clock input from PM6650
USB_XTAL48_IN (48MHz crystal) 48 MHz crystal oscillator input
USB_XTAL48_OUT (48MHz crystal) 48 MHz crystal oscillator
SLEEP_XTAL_IN
SLEEP_CLK
Low-power sleep crystal oscillator from PM6650
SLEEP_XTAL_OUT
RESIN_N PON_RST_N Hardware reset input from PM6650
RESOUT_N
RESOUT_N_EBI1 RESOUT1_N
WDOG_EN
MODE[2]
MODE[1]
MODE[0]
BOOT_MODE
MSM6250 clocks and mode control
(not used)
(not used)
Reset output generated by RESIN_N and by
wdog_reset. Reset to LCD, NAND FLASH
(not used)
(not used)
(not used)
(not used)
pull-up to VREG_MSMP (boot from NAND)
Page 22 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
6.3 MSM6250 interfaces
6.3.1 Logic interfaces
Each IO pin on the MSM6250 has an associated pad group. The pad group, and hence the IO pin, is
powered from the supplies as below:
Pad
Group
1 VREG_MSME 1.850 V (±3%) EBI1 bus to SDRAM
2 VREG_MSME 1.850 V (±3%) EBI2 bus to NAND FLASH and LCD. Plus some GPIO
3 VREG_MSMP 2.600 V (±3%) Most peripheral interfaces
4 VREG_MSMP 2.600 V (±3%) SIM bus (to PM6650). Plus one GPIO.
Supply Name Value Pad Group Connections
MSM6250 pad group supplies
The maximum and minimum possible logic levels seen on the I/O pins (allowing for maximum supply
variation and loading) should be within:
Pad
Group
VOL
min
(V)
VOL
max
(V)
VOH
min
(V)
VOH
max
(V)
ViL
min
(V)
ViL
max
(V)
ViH
min
(V)
ViH
max
(V)
1, 2 0 0.45 1.344 1.906 -0.3 0.628 1.239 2.085
2, 3 0 0.45 2.027 2.678 -0.3 0.883 1.741 2.822
MSM6250 logic specification
Peripheral systems on the phone are controlled by the MSM6250 logic signals listed below. These
signals uses General Purpose IO (GPIO) pins on the MSM6250 and are configured to perform the
required function by software.
A brief description of the signals is given in the following table:
Page 23 of 74
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Release 1.0
 Loading...
Loading...