Page 1

SLI-5310/SLI-5310-I IAD
User’s Manual
Rev: 1.3
2007/03/30
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form by any means without the prior written permission.
Other trademarks or brand names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies.
i
Page 2

ADSL Router User Manual
CCooppyyrriigghhtt NNoottiiccee
© 2006 All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or
by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written permission of
the seller.
DDiissccllaaiimmeerr
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations,
technical data, and recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but
are presented without express or implied warranty. The seller therefore assumes no responsibility and
shall have no liability of any kind arising from the supply or use of this document or the material
contained herein.
SSttaatteemmeenntt ooff CCoonnddiittiioonnss
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, the seller reserves
the right to make changes to the products described in this docum ent without notice.
The seller does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s)
or circuit layout(s) described herein.
In addition, the program and information contained herein are licensed only pursuant to a license
agreement that contains restrictions on use and disclosure (that may incorporate by reference certain
limitations and notices imposed by third parties).
TTrraaddeemmaarrkkss
All other product or service names mentioned in this document may be trademarks of the comp anies
with which they are associated.
ii
Page 3

SSaaffeettyy aanndd PPrreeccaauuttiioonn
For Installation
For Using
Use only the type of power source indicated on the marking labels.
Use only power adapter supplied with the product.
Do not overload wall outlet or extension cords as this may increase the
risk of electric shock or fire. If the power cord is frayed, replace it with a
new one.
Proper ventilation is necessary to prevent the product overheating. Do
not block or cover the slots and openings on the device, which are
intended for ventilation and proper operation. It is recommended to
mount the product with a stack.
Do not place the product near any source of heat or expose it to direct
sunlight.
Do not expose the product to moisture. Never spill any liquid on the
product.
Do not attempt to connect with any computer accessory or electronic
product without instructions from qualified service personnel. This may
result in risk of electronic shock or fire.
Do not place this product on unstable stand o r table.
Power off and unplug this product from the wall outlet when it is not in
use or before cleaning. Pay attention to the temperature of the power
adapter. The temperature might be high.
After powering off the product, power on the product at least 15
seconds later.
Do not block the ventilating openings of this product.
When the product is expected to be not in use for a period of time,
unplug the power cord of the product to prevent it from the damage of
storm or sudden increases in rating.
For Service Do not attempt to disassemble or open covers of this unit by yourself. Nor
should you attempt to service the product yourself, which may void the user’s
authority to operate it. Contact qualified service personnel under the following
conditions:
If the power cord or plug is damaged or frayed.
If liquid has been spilled into the product.
If the product has been exposed to rain or water.
If the product does not operate normally when the operating instructions
are followed.
If the product has been dropped or the cabinet has been damaged.
If the product exhibits a distinct change in performance.
Caution
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the authority to operate
equipment.
iii
Page 4

ADSL Router User Manual
FFCCCC
This equipment must be installed and operated in accordance with provided
instructions and a minimum 20 cm spacing must be provided between computer
mounted antenna and person’s body (excluding extremities of hands, wrist and feet)
during wireless modes of operation.
FFCCCC CCllaassss BB NNoottiiccee
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
(1) this device may not cause harmful interference;
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
Note:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment can generate, use and radiate radio frequency energy
and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined b y
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
z Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
z Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
z Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
z Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for help
iv
Page 5
Before You Use
Before You Use
Thank you for choosing this Integrated Access Device. With the asymmetric
technology, this device runs over standard copper phone lines. In addition, ADSL
allows you to have both voice and data services in use simultaneously all over one
phone line.
SLI-5310/SLI-5310-I IAD is a DSL broadband access device which allows ADSL
connectivity while providing voice over IP function for home or office users. It
supports ADSL2/ADSL2+ and is backward compatible to ADSL, even offers
auto-negotiation capability for different flavors (G.dmt, G.lite, T1.413 Issue 2, or
ADSL2/ADSL2+) according to central office DSLAM’s settings (Digital Subscriber
Line Access Multiplexer). To benefit users’ access to the Internet, 4-port 10/100
Mbps Ethernet switch hub is equipped with this IAD. Also the feature-rich routing
functions are seamlessly integrated to ADSL service for existing corporate or home
users. Now users can enjoy various bandwidth-consuming applications via the
SLI-5310/ SLI-5310-I IAD.
Unpacking
Check the contents of the package agai nst the pack contents checklist below. If any
of the items is missing, then contact the dealer from whom the equipment was
purchased.
9 Integrated Access Device
9 Power Adapter and Cord
9 RJ-11 ADSL Line Cable
9 RJ-45 Ethernet Cable
9 USB Cable
9 Phone Cable
9 PSTN Cable
9 Quick Start Guide
9 Driver & Utility Software CD
Features
ADSL Compliance
³ ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
³ ITU G.992.1 Annex A (G .dmt)
³ ITU G.992.2 Annex A (G .lit e)
³ ITU G.994.1 (G.hs)
³ Support dying gasp
³ Maximum Rate: 8 Mbps for downstream and 1 Mbps for upstream
v
Page 6

ADSL Router User Manual
ADSL2 Compliance
³ ITU G.992.3 Annex A (G .dmt.bis)
³ Maximum Rate: 12 Mbps for downstream and 1 Mbps for upstream
ADSL2+ Compliance
³ ITU G.992.5 Annex A
³ Maximum Rate: 24 Mbps for downstream and 1.2 Mbps for upstream
Voice over IP Features
³ Call Feature: basic outgoing and incoming call, Call Waiting, Three Party
Conference, Call Transfer, Caller ID
³ Call Control: support MGCP (RFC2705) or SIP (RFC3261)
³ Voice Transport: compliance to RTP (RFC1889)
³ Voice Codec: G.711 (a-law and u -la w), G.726, and G.729A
³ Tone/Ring Signal: compliance to North America, UK, France, Netherland s,
Japan, and China
³ Tone Generation: support dial tone, ring back tone, busy tone, ring tone, and
various tones on demand
³ Tone Detection: support DTMF
³ Echo Cancellation: compliance to G.168
³ Support FAX/Analog Modem function
³ Support T.38
³ Support RFC2833 RTP Payload for DT MF Digits, Telephony Tones and
Telephony Signals
³ Two VOIP (FXS) ports for VOIP phone calls
³ Both VOIP ports supporting intelligent lifeline backup
³ Manual selection of PSTN mode or VOIP mode while making a phone call
³ Automatic selection of PSTN phone call on dialing the emergency calls
³ Traffic flow control to gua rantee voice quality
Fax relay1
ATM Features
³ Compliant to ATM Forum UNI 3.1 / 4.0 Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs)
³ Support up to 16 PVCs for UBR, CBR, VBR-nrt, VBR-rt with traffic shaping
³ RFC2684 LLC Encapsulation and VC Multiplexing over AAL5
³ RFC2364 Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) over AAL5
³ RFC2225 Classical IP and ARP over ATM
³ RFC2516 PPP over Ethernet: support Relay (Transparent Forwarding) and
Client functions
³ Support PPPoA or PPPoE Bridged mode (the IP address got from ISP can be
passed to the user’s PC and behave as the IP address of the user’s PC.)
1
T.38 fax relay can be supported on demand.
vi
Page 7

Before You Use
³ OAM F4/F5 End-to-End/Segment Loopback Cells
Bridging Features
³ Supports self-learning bridge specified in IEEE 802.1d Transparent Bridging
³ Supports up to 4096 learning MAC addresses
³ Transparent Bridging among 10/100 Mb Ethernet and USB
³ Supports IGMP Snooping
³ Supports 802.1Q VLAN packet pass-through
Routing Features
³ NAT (Network Address Translation) / PAT (Port Address Translation) let
multiple users on the LAN to access the internet for the cost of only one IP
address.
³ ALGs (Application Level Gateways): such as NetMeeting, MSN Messenger,
FTP, Quick Time, mIRC, Real Player, CuSeeMe, VPN pass-through with
multiple sessions, etc.
³ Port Forwarding: the users can setup multiple virtual servers (e.g., Web, FTP,
Mail servers) on user’s local network.
³ Support DMZ
³ UPnP IGD (Internet Gateway Device) with NAT traversal capability
³ Static routes, RFC1058 RIPv1, RFC1723 RIPv2
³ DNS Relay, Dynamic DNS
³ DHCP Client/Relay/Server
³ Time protocol can be used to get current time from network time server
³ Support IGMP Proxy
³ Support port mapping function which allows you to assign all data traffic
transmitted among specific Internet connections and LAN ports
³ Support IP/Bridge QoS for prioritize the transmission of dif f erent traffic classes
³ Support 802.1Q VLAN Tagging
Security Features
³ PAP (RFC1334), CHAP (RFC1994 ), and MS-CHAP/MS-CHAP2 for PPP
session
³ Firewall support IP packets filtering based on IP address/Port number/Protocol
type
³ Bridge packet filtering (optional)
³ URL filtering (optional)
³ Support DoS (Deny of Services) which detect & protect a number of attacks
(such as SYN/FIN/RST Flood, Smurf, WinNuke, Echo Scan, Xmas Tree Scan,
etc)
Configuration and Management
³ User-friendly embedded web configuration interface with password protection
³ Remote management accesses control
³ Telnet session for local or remote management
³ Firmware upgrades through HTTP, TFTP, or FTP
vii
Page 8
ADSL Router User Manual
³ The boot loader contains very simple web page to allow the users to update the
run-time firmware image.
³ Configuration file backup and restore
³ SNMPv1/v2 agent with MIB-II, ADSL Line MIB
Subscription for ADSL Service
To use the IAD, you have to subscribe for ADSL service from your broadband
service provider. According to the service type you subscribe, you will get various IP
addresses:
Dynamic IP: If you apply for dial-up connection, you will be given an Internet
account with username and password. You will get a dynamic IP by dialing up to
your ISP, such as using PPPoA, PPPoE, or MER mode.
Static IP address: If you apply for full-time connectivity, you may get either one
static IP address or a range of IP addresses from your ISP. The IP address varies
according to different ADSL service provider, such as using IPoA or MER mode.
Notes and Cautions
Note and Caution in this manual are highlighted with graphics as below to indicate
important information.
Contains information that corresponds to a specific topic.
Note
Represents essential steps, actions, or messages that should not be
Caution
ignored.
viii
Page 9
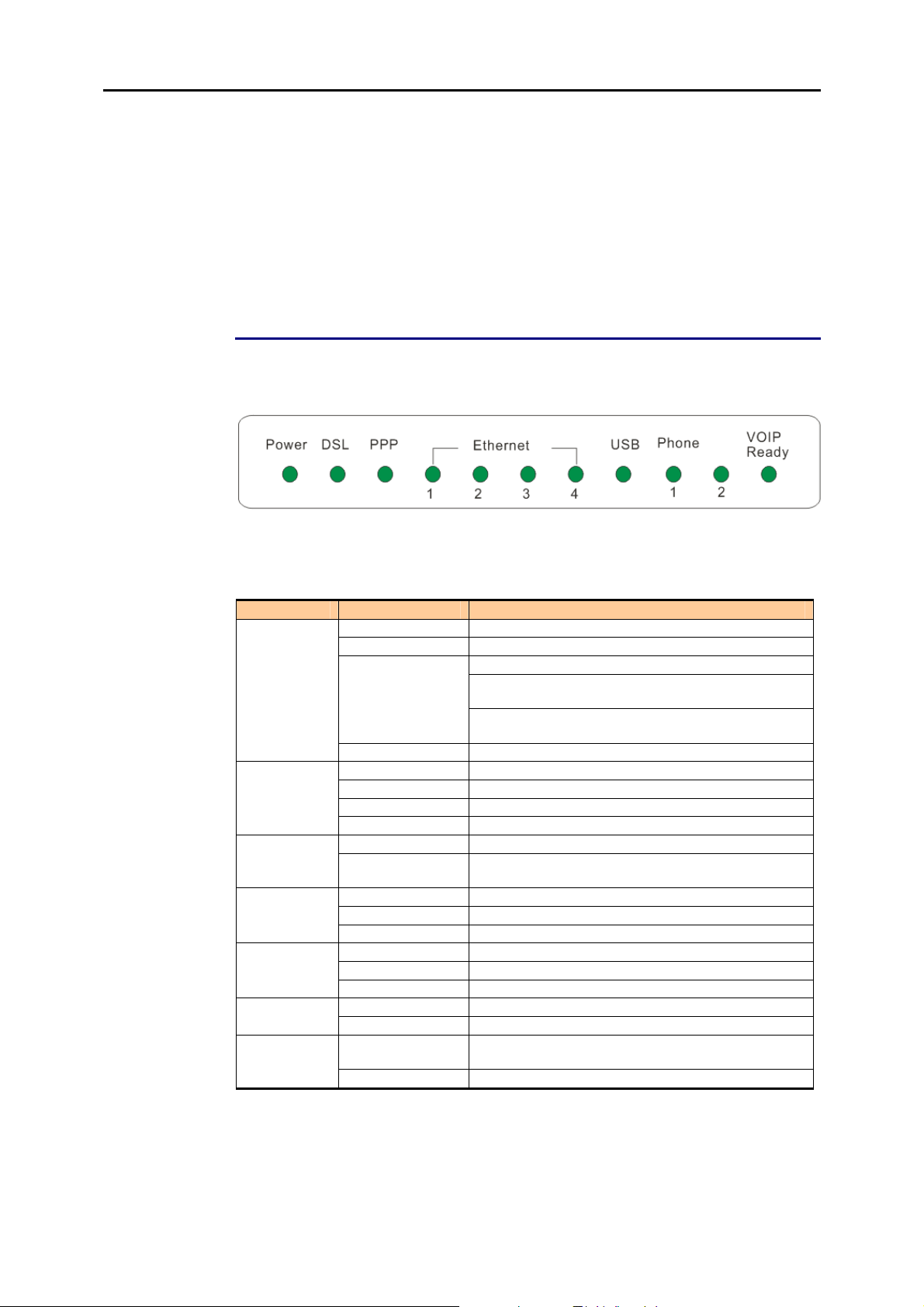
Chapter 1: Overview
Chapter 1: Overview
This chapter provides you the description for the LEDs and connectors on the front
and rear surface of the router. Before you use/install this IAD, please take a look at
the information first.
Physical Outlook
Front Panel
The following illustration displays the front panel of this IAD:
LED Indicators
This IAD is equipped with several LEDs on the front panel as described in the table
below:
Function Color Definition
Off Power is off.
Solid Green Power is on and the device operates normally.
Power on self-test in progress
The device enters the console mode of the boot
loader.
Power on self-test failure if the led always stays solid
red.
users can access the Internet now.
make PSTN phone calls only.
Power
DSL
PPP
Ethernet
USB
Phone 1 or 2
VOIP Ready
Solid Red
Flash Red Firmware upgrades in progress
Off No DSL signal is detected.
Slow Flash Green DSL line is handshaking in progress
Fast Flash Green DSL line is training in progress
Solid Green DSL line connection is up.
Off No PPPoA or PPPoE connection
Solid Green At least one PPPoA or PPPoE connection is up. The
Off No Ethernet signal is detected.
Flash Green User data is going through Ethernet port
Solid Green Ethernet interface is ready to work.
Off No USB signal is detected.
Flash Green User data is going through USB port
Solid Green USB interface is ready to work.
Off The phone is on-hook or in PSTN mode.
Solid Green VOIP phone call is in use.
Off Voice over IP service is not ready. The users can
Solid Green Voice over IP service is ready.
1
Page 10

ADSL Router User Manual
Rear Panel
The following figure illustrates the rear panel of your IAD:
Connector Description
Phone
PSTN
DSL
Ethernet 1 - 4
USB
12VAC
Phone set connector
PSTN connector
RJ-11 connector
Ethernet 10/100 Base-T auto-sensing
USB connector (for model with USB interface only)
Power Switch
Power connector
Note: For use only with power supply OEM type AA-121A5BN,
Leader type A48120150-C5.
2
Page 11
Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
System Requirement
To access the IAD via Ethernet, the host computer must meet the following
requirements:
Equipped with an Ethernet network interface.
Have TCP/IP installed.
Allow the client PC to obtain an IP address automatically or set
a fixed IP address.
With a web browser installed: Internet Explorer 5.x or later.
The IAD is configured with the default IP address of 192.168.1.1 and subnet mask
of 255.255.255.0. Considering that the DHCP server is enabled by default, the
DHCP clients should be able to access the IAD, or the host PC should be assigned
an IP address first for initial configuration.
You also can manage the IAD through a web browser-based manager: ADSL
ROUTER CONTROL PANEL. The IAD manager uses the HTTP protocol via a web
browser to allow you to set up and manage the device.
To configure the device via web browser, at least one
properly-configured PC must be connected to the network (either
connected directly or through an external hub/switch to the LAN port of
the device).
Choosing a place for the IAD
n Place the IAD close to ADSL wall outlet and power outlet for the cable to
reach it easily.
o Avoid placing the device in places where people may walk on the cables. Also
keep it away from direct sunlight or heat sources.
p Place the device on a flat and stable stand.
3
Page 12
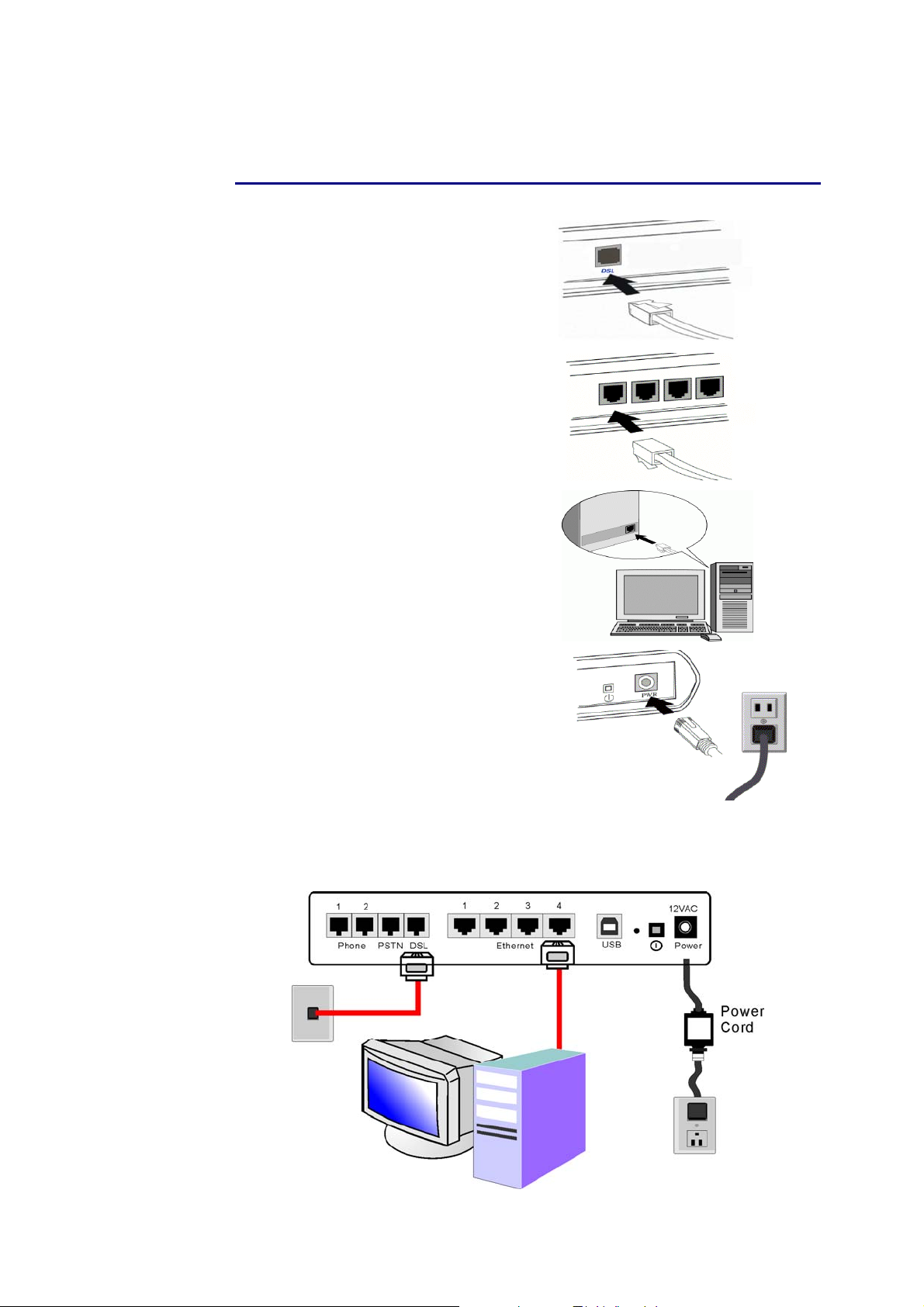
ADSL Router User Manual
Connecting the IAD
Follow the steps below to connect the related devices.
n Connecting the ADSL line:
connect the DSL port of the
device to your ADSL wall outlet
with RJ-11 cable.
o Please attach one end of the
Ethernet cable with RJ-45
connector to the LAN port of
your IAD.
p Connect the other end of the
cable to the Ethernet port of the
client PC.
q Connect the supplied power
adapter to the PWR port of your
IAD, and plug the other end to a
power outlet.
r Turn on the power switch.
Here is an example for connecting the PC to the IAD.
4
Page 13
Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
USB Driver Installation
If the IAD is connected to a PC through the USB interface, you will be prompted for
the USB drivers when plugging the USB cable to the PC. Refer to the relevant
operating system to install the USB drivers.
For Windows ME
n Run the USB installation program from the CD provided in your IAD
package.
o An InstallShield Wizard will appear. Please wait for a moment.
p When the welcome screen appears, click Next for the next step.
q When the complete window of the InstallShield Wizard appears, cli ck
Finish.
r Link your IAD and the PC with a USB cable.
s The system will detect the USB driver automatically. Then, the system will
copy the proper files for this IAD.
Note: If the USB device is not detected automatically, check the USB cable
between the PC and the device. Besides, verify that the device is power on.
t When the file copying finished, the dialog above will close. Now the USB
driver is installed properly. You can use the IAD.
For Windows 2000
n Run the USB installation program from the CD provided in your IAD
package.
o An InstallShield Wizard will appear. Please wait for a moment.
p When the welcome screen appears, click Next for the next step.
5
Page 14
ADSL Router User Manual
q When the complete window of the Inst allShield Wizard appears, click
Finish.
r Link your IAD and the PC with a USB cable.
s The system will detect the USB driver automatically. And then, the system
will copy the proper files for this IAD.
Note: If the USB device is not detected automatically, check the USB
cable between the PC and the device. Besides, make sure that the device
is power on.
t When the file copying finished, the dialog above will close. Now the USB
driver is installed properly. You can use the IAD.
To make sure that your IAD is properly installed, please do the following steps.
1. Right-click on My Computer and press Properties.
6
Page 15
Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
2. On the Hardware tap, click Device Manager.
3. Confirm that the Siemens ADSL Router USB Remote NDIS Device is on
the Network adapters list.
For Windows XP
n Run the USB installation program from the CD provided in your IAD
package.
o An InstallShield Wizard will appear. Please wait for a moment.
7
Page 16
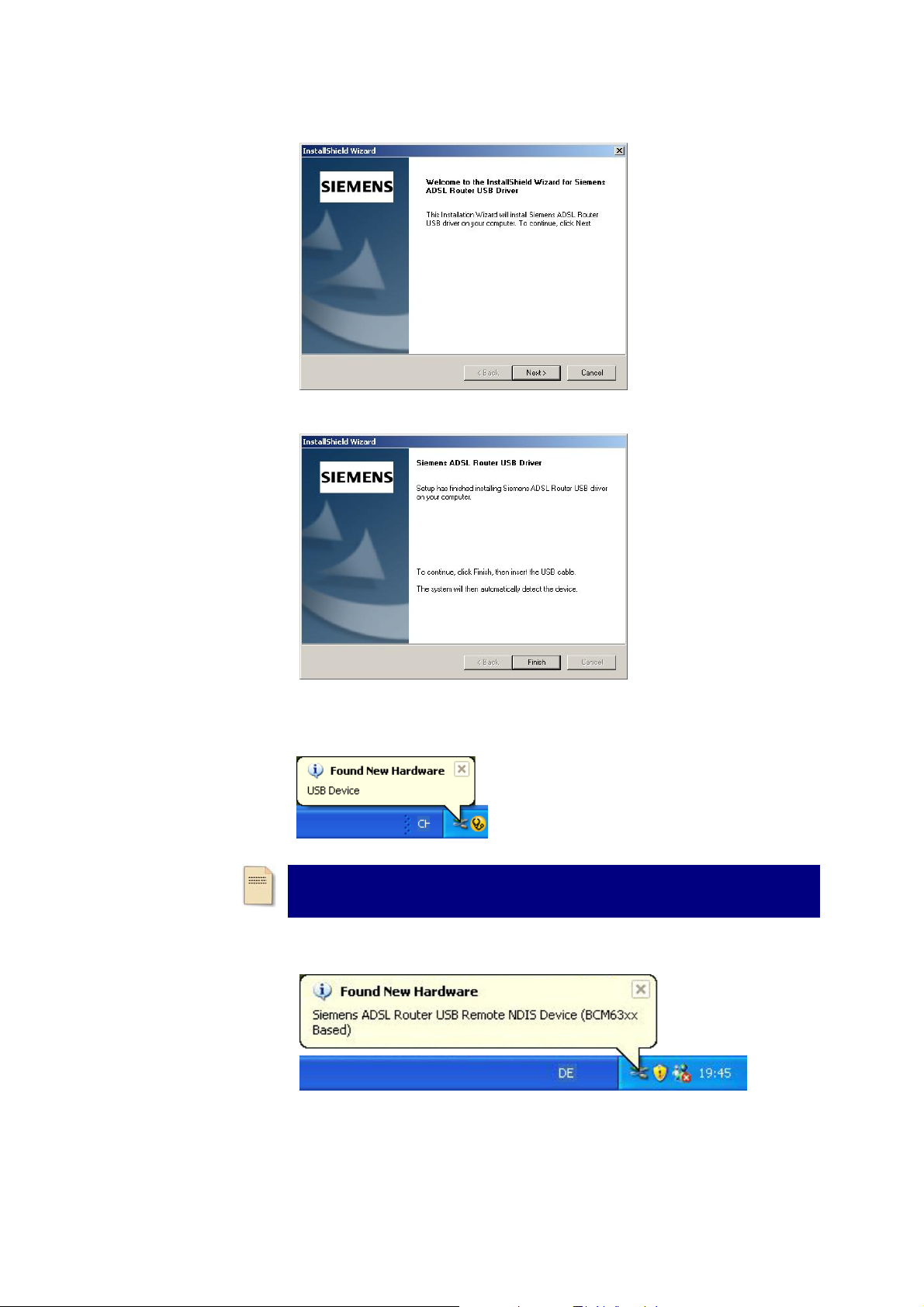
ADSL Router User Manual
p When the welcome screen appears, click Next for the next step.
q When the complete message of InstallShield Wizard appears, click Finish.
r Link your IAD and the PC with a USB cable.
s The system will detect the USB driver automatically.
Note: If the USB device is not detected, check the USB cable between the
PC and the device. Also make sure that the device is power on.
t Then the system will try to find the proper driver for your IAD and copy the
files automatically.
8
Page 17
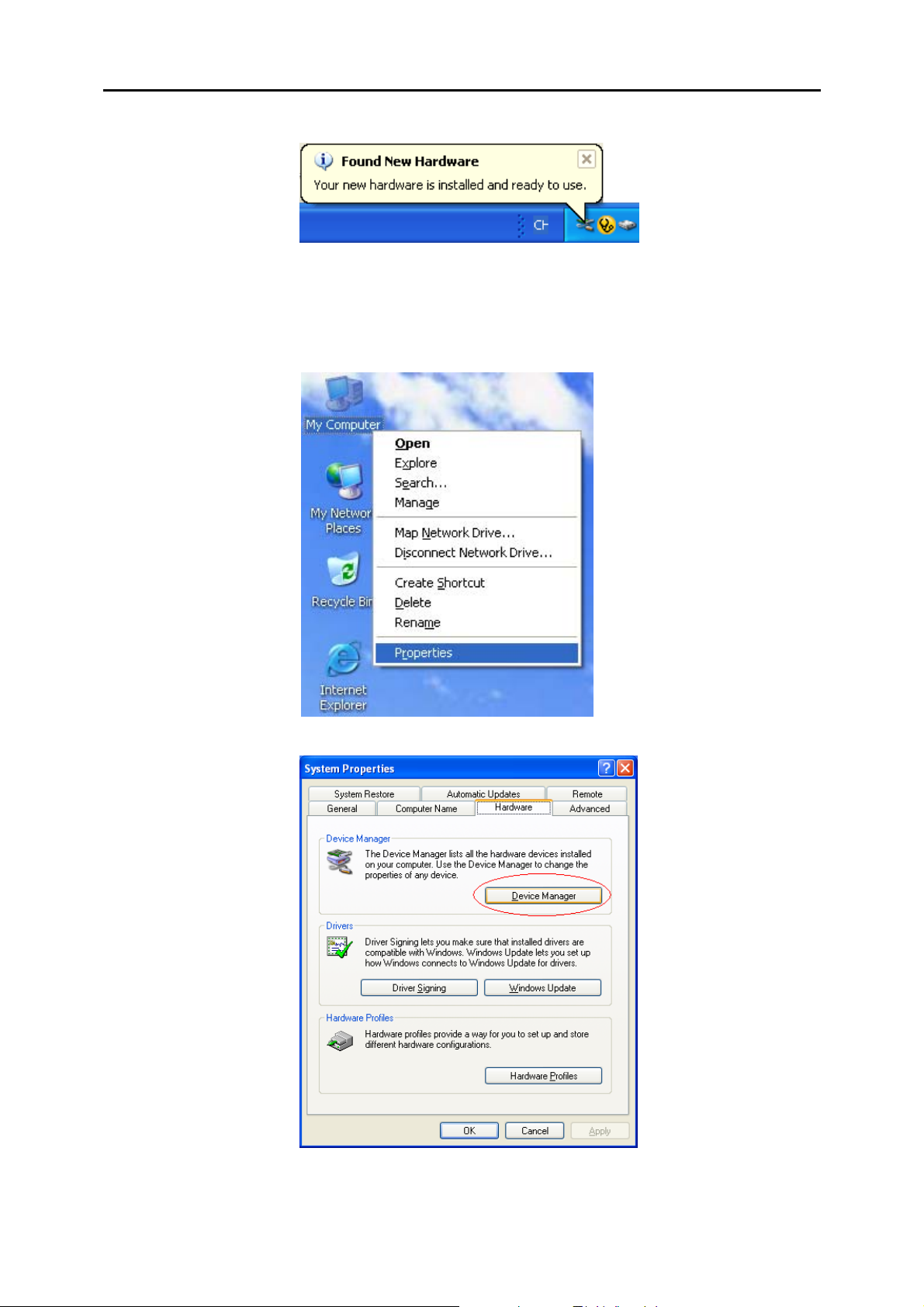
Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
u After the file copying finished, a completing message will appear.
v You can use the IAD now.
To make sure your IAD is properly installed, please do the following steps.
1. Right-click on My Computer and press Properties.
2. On the Hardware tab, click Device Manager.
9
Page 18
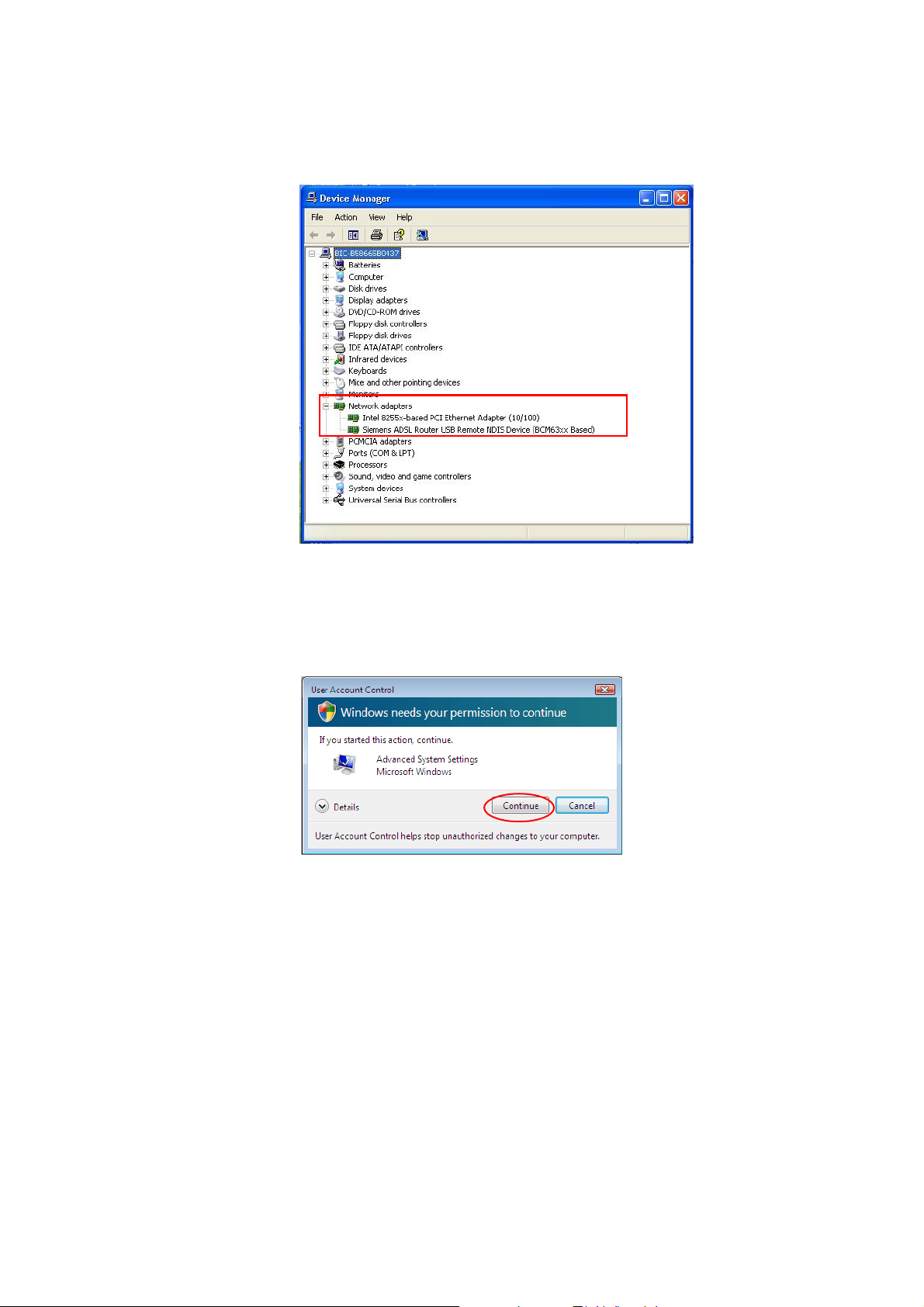
ADSL Router User Manual
3. Confirm that the Siemens ADSL Router USB Remote NDIS Device is on
the Network adapters list.
For Windows Vista
For Vista users, please press Continue whenever a prompted window asking for permission
to continue during USB driver installation pr ocess (see t he f i gu re belo w fo r example).
To install the USB driver before connect the router to the PC, here provides two methods.
Method One – Use the driver CD came with the product package.
n Run the USB installation program on the CD provided in your router package.
o An InstallShield Wizard will appear. Please wait for a moment.
10
Page 19
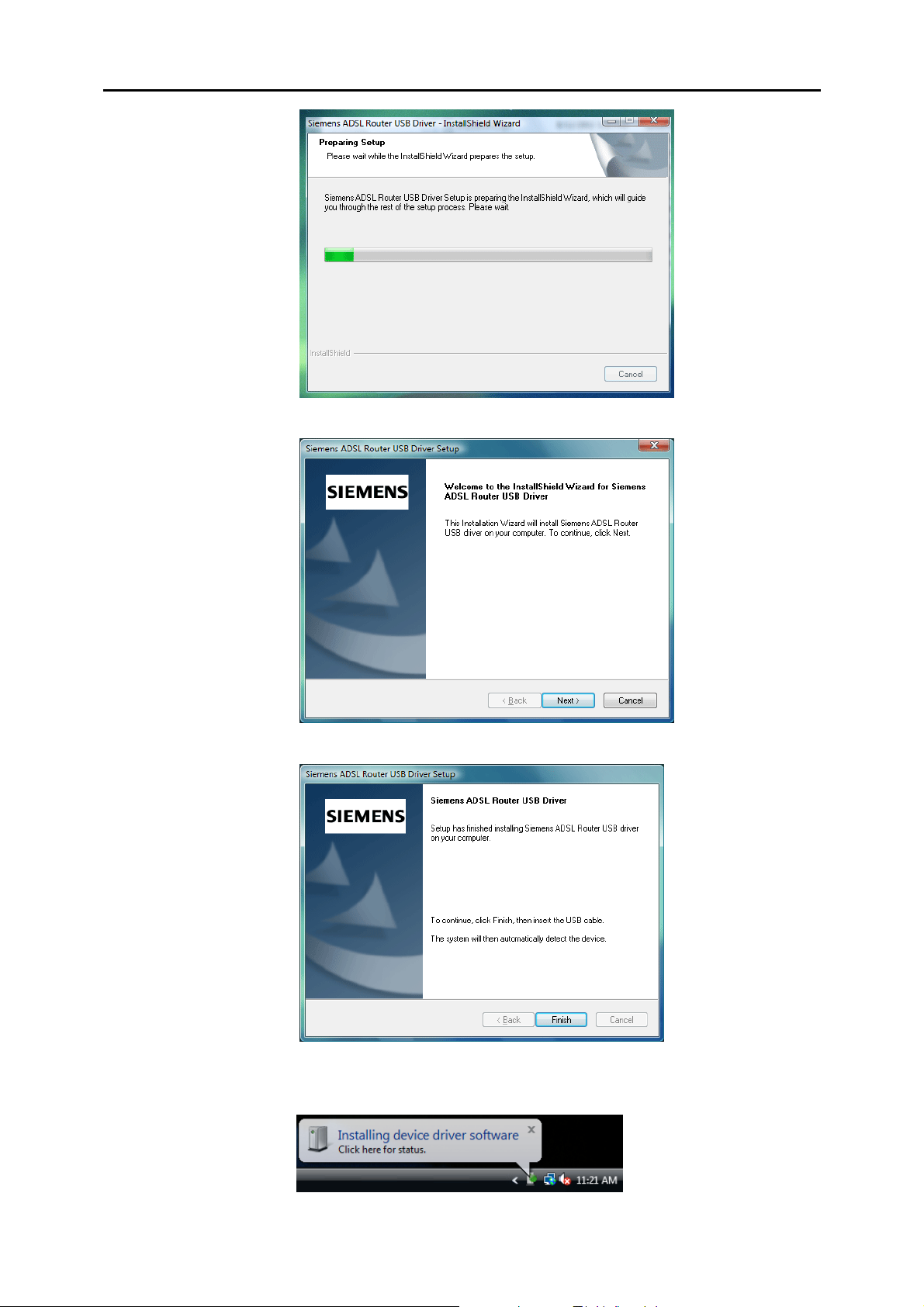
Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
p When the welcome screen appears, click Next for the next step.
q When the complete message of InstallShield Wizard appears, click Finish.
r Link your router and the PC with a USB cable.
s The system will detect the USB driver automatically.
11
Page 20

ADSL Router User Manual
Note: If the USB device is not detected, check the USB cable between the PC and
the device. Also make sure that the device is power on.
t After the file cop ying finished, a completing message will appear.
u You can use the router now.
12
Page 21

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
Uninstalling the USB Driver
For Windows ME
To uninstall the USB driver, please follow the procedures below.
Method One:
n Unplug the USB cable from the USB port on your PC.
o Choose Programs – Siemens Broadband – Uninstall Siemens ADSL
Router USB Driver from the Start menu.
p The InstallShield Wizard dialog will appear.
q A dialog appears to confirm whether you really want to remove the USB
driver or not. Please click Ok.
r When the Maintenance Complete screen appears, the USB driver is
removed successfully. Click Finish.
Method Two:
n Unplug the USB cable between your IAD and your PC. Then click OK.
o Choose Settings –Control Panel from the Start menu. Choose
Add/Remove Programs.
p A dialog appears to ask you to choose the program that you want to remove.
Please select Siemens ADSL Router USB Driver and click
Change/Remove.
q The InstallShield Wizard dialog will appear.
r When the Maintenance Complete screen appears, the USB driver is
removed successfully. Click Finish
For Windows 2000
To uninstall the USB driver, there are two ways to do it. Please do the following
procedures.
Method One:
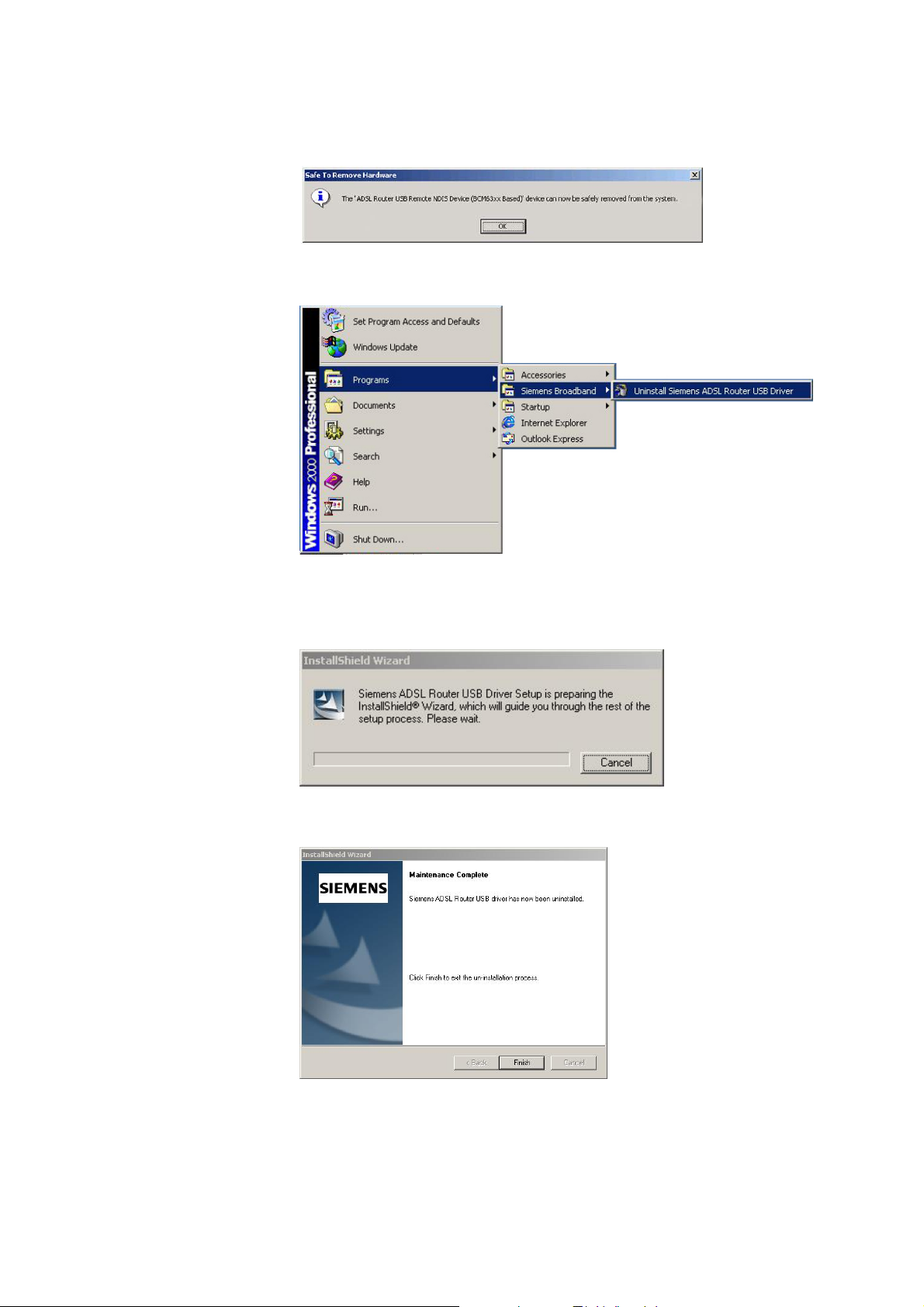
n To safely unplug the USB cable from the USB port on your PC:
1. Go to the right lower corner for Unplug and Eject Hardware and left click
on it.
2. Click the dialog for Stop Siemens ADSL Router USB Remote NDIS
Device.
13
Page 22
ADSL Router User Manual
3. The Router is safely removed, click OK to continue.
o Choose Programs – Siemens Broadband – Uninstall Siemens ADSL
Router USB Driver from the Start menu.
p The InstallShield Wizard dialog will appear.
q A dialog appe ars to confirm whether you want to remove the USB driver or
not. Please click Ok:
r When the Maintenance Complete screen appears, the USB driver is
removed successfully. Click Finish.
14
Page 23
Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
Method Two:
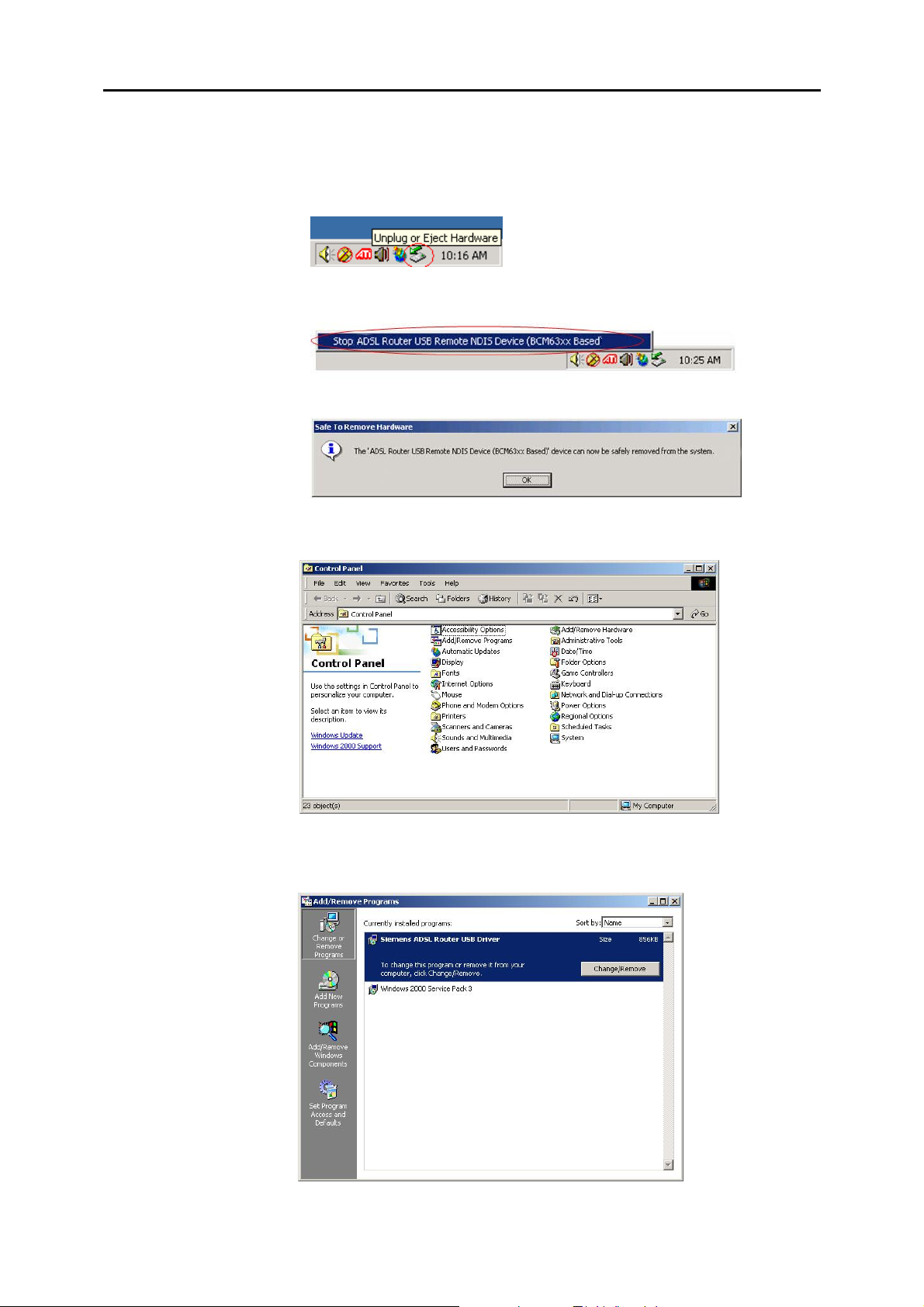
n To safely unplug the USB cable from the USB port on your PC:
1. Go to the right lower corner for Unplug and Eject Hardware and left click
on it.
2. Click the dialog for Stop Siemens ADSL Router USB Remote NDIS
Device.
3. The Router is safely removed, click OK to continue.
o Choose Settings –Control Panel from the Start menu. Choose
Add/Remove Programs.
p A dialog appears to ask you to choose the program that you want to remove.
Please select Siemens ADSL Router USB Driver and click
Change/Remove.
15
Page 24
ADSL Router User Manual
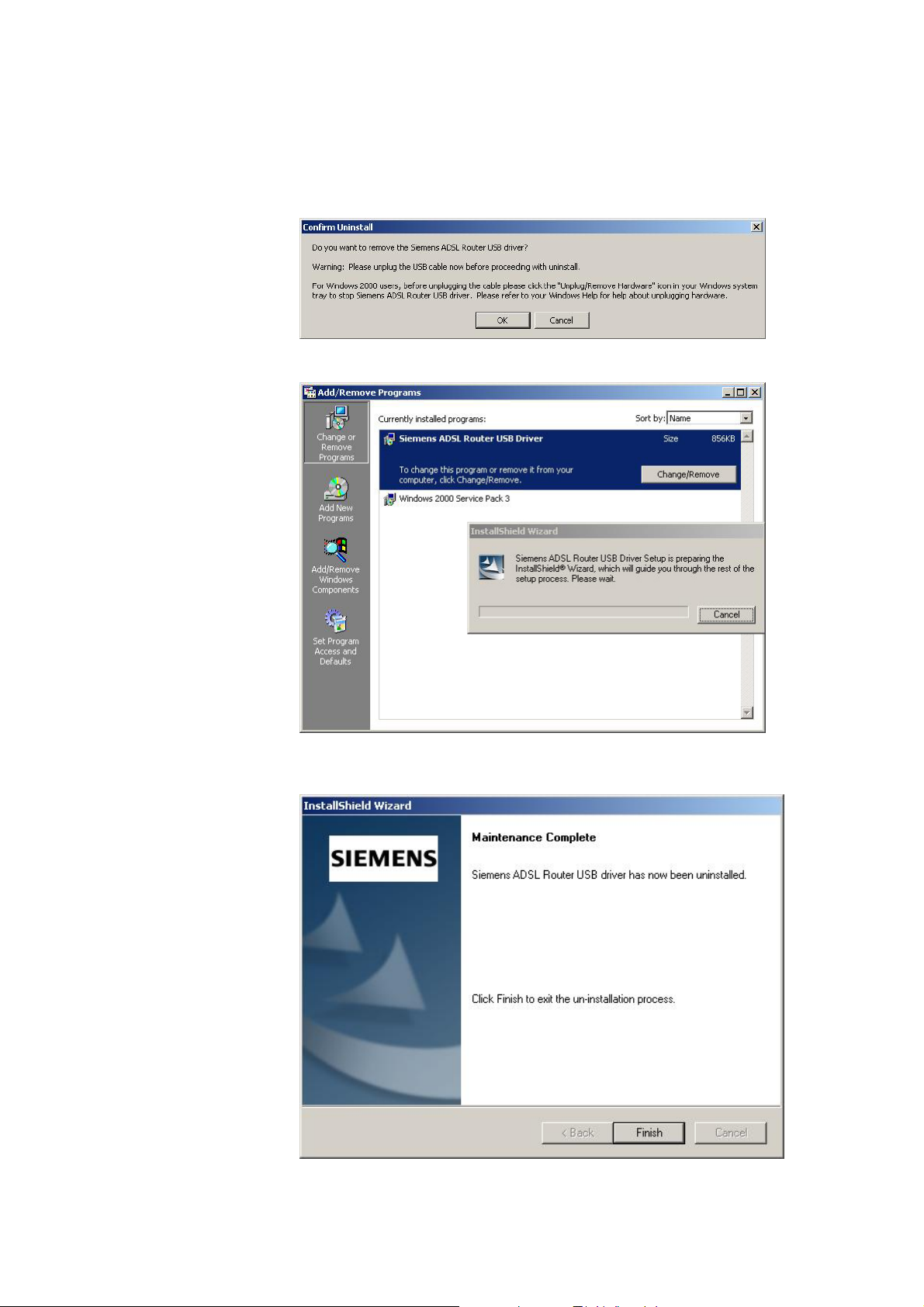
q A Confirm Un install dialog will show up, unplug your device from the USB
port and click OK.
r The InstallShield Wizard will guide you till the USB driver is removed.
s When the Maintenance Complete screen appears, the USB driver is
removed successfully. Click Finish.
16
Page 25
Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
For Windows XP
To uninstall the USB driver, there are two ways to do it. Please do as follows.
Method One:
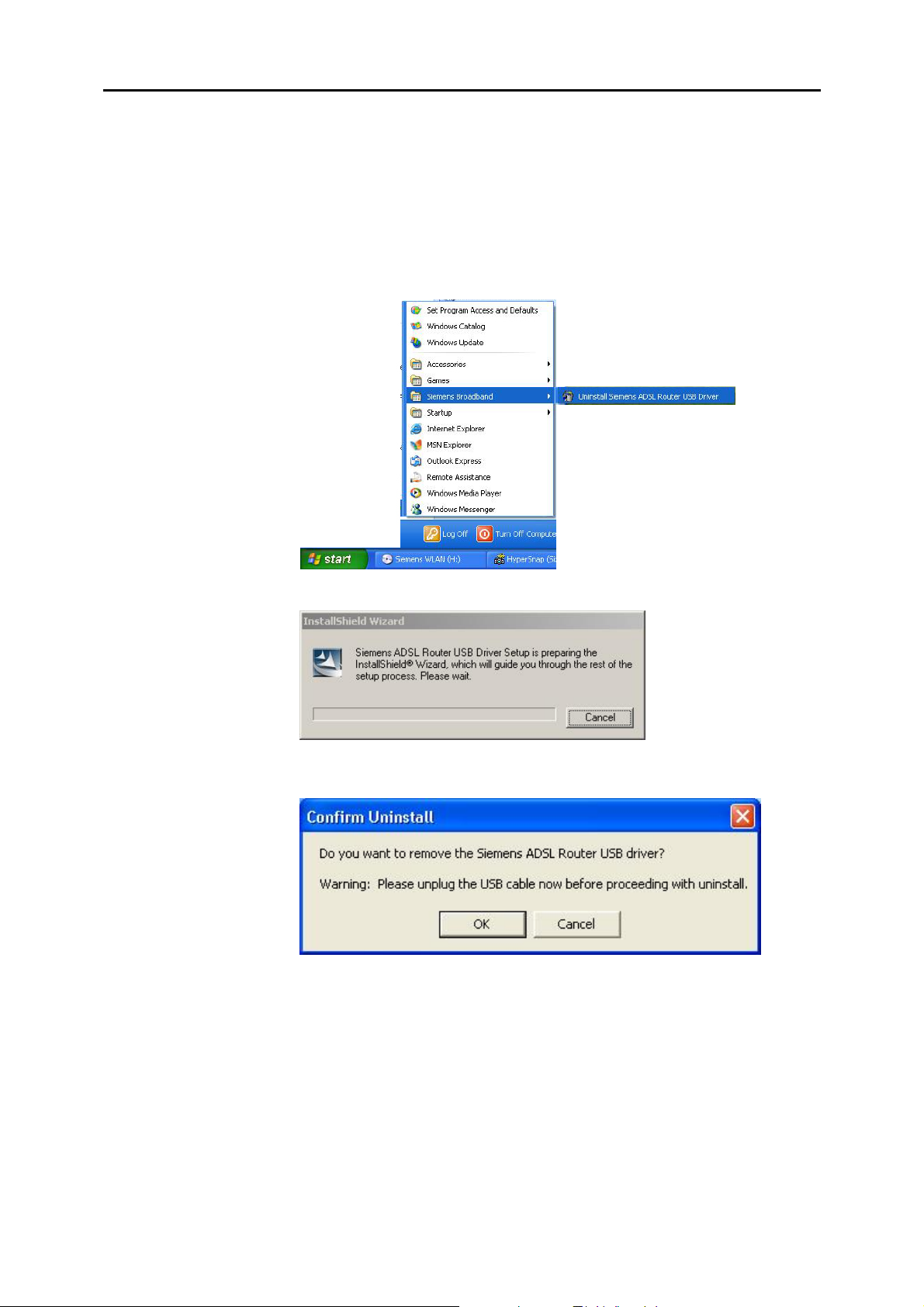
n Unplug your USB cable between your IAD and your PC.
o Choose Programs – Siemens Broadband – Uninstall Siemens ADSL
Router USB Driver from the Start menu.
p The InstallShield Wizard dialog will appear.
q A dialog appe ars to confirm whether you want to remove the USB driver or
not. Unplug the USB cable from your PC, and click Ok.
r When the Maintenance Complete screen appears, the USB driver is
removed successfully. Click Finish.
Method Two:
n Unplug your USB cable between your IAD and your PC.
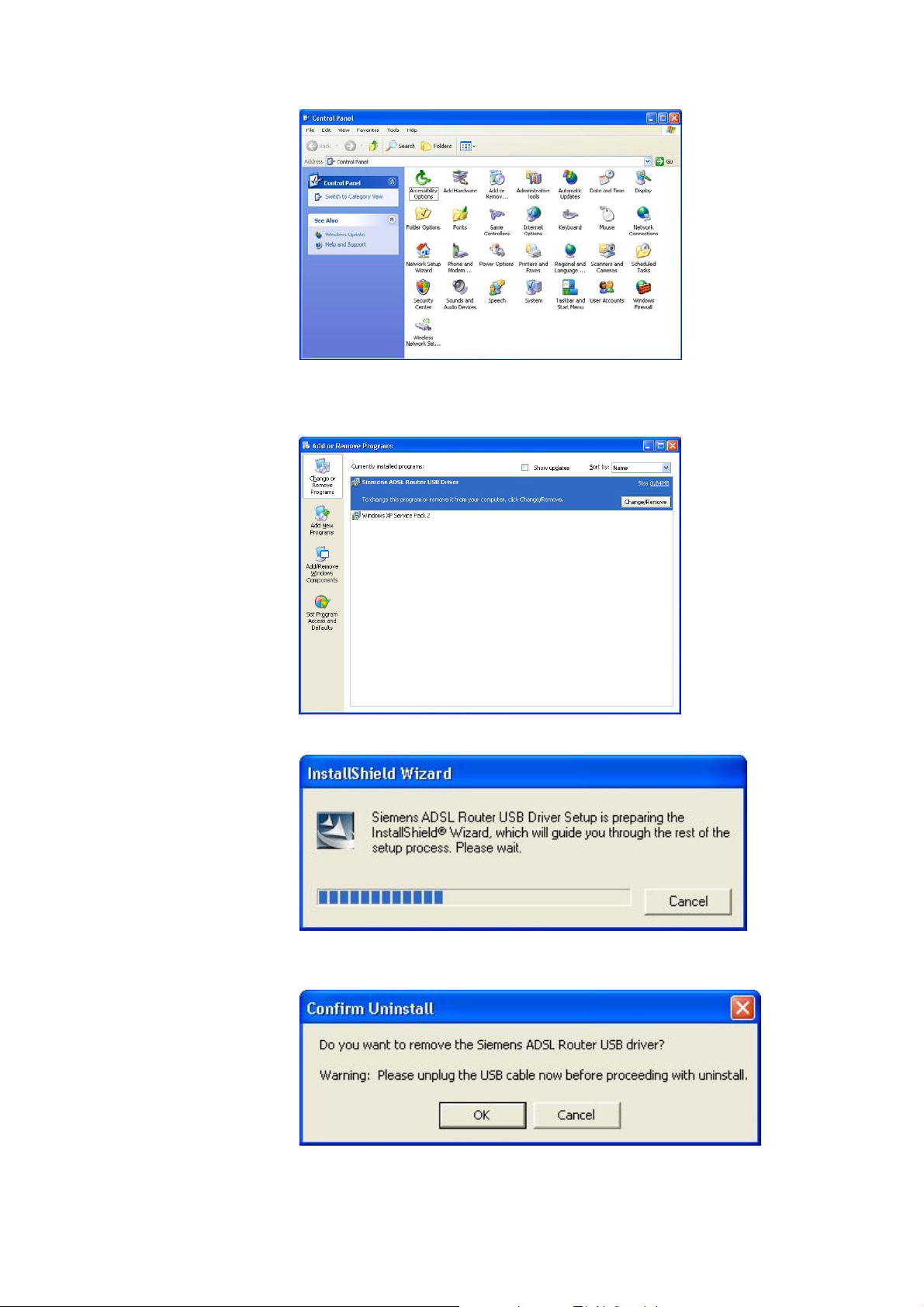
o Choose Settings –Control Panel from the Start menu. Choose Add or
Remove Programs.
17
Page 26
ADSL Router User Manual
p A dialog appears to ask you to choose the program that you want to remove.
Please select Siemens ADSL Router USB Driver and click
Change/Remove.
q The InstallShield Wizard dialog will appear.
r A dialog appe ars to confirm whether you want to remove the USB driver or
not. Unplug the USB cable from your PC, and click Ok.
18
Page 27
Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
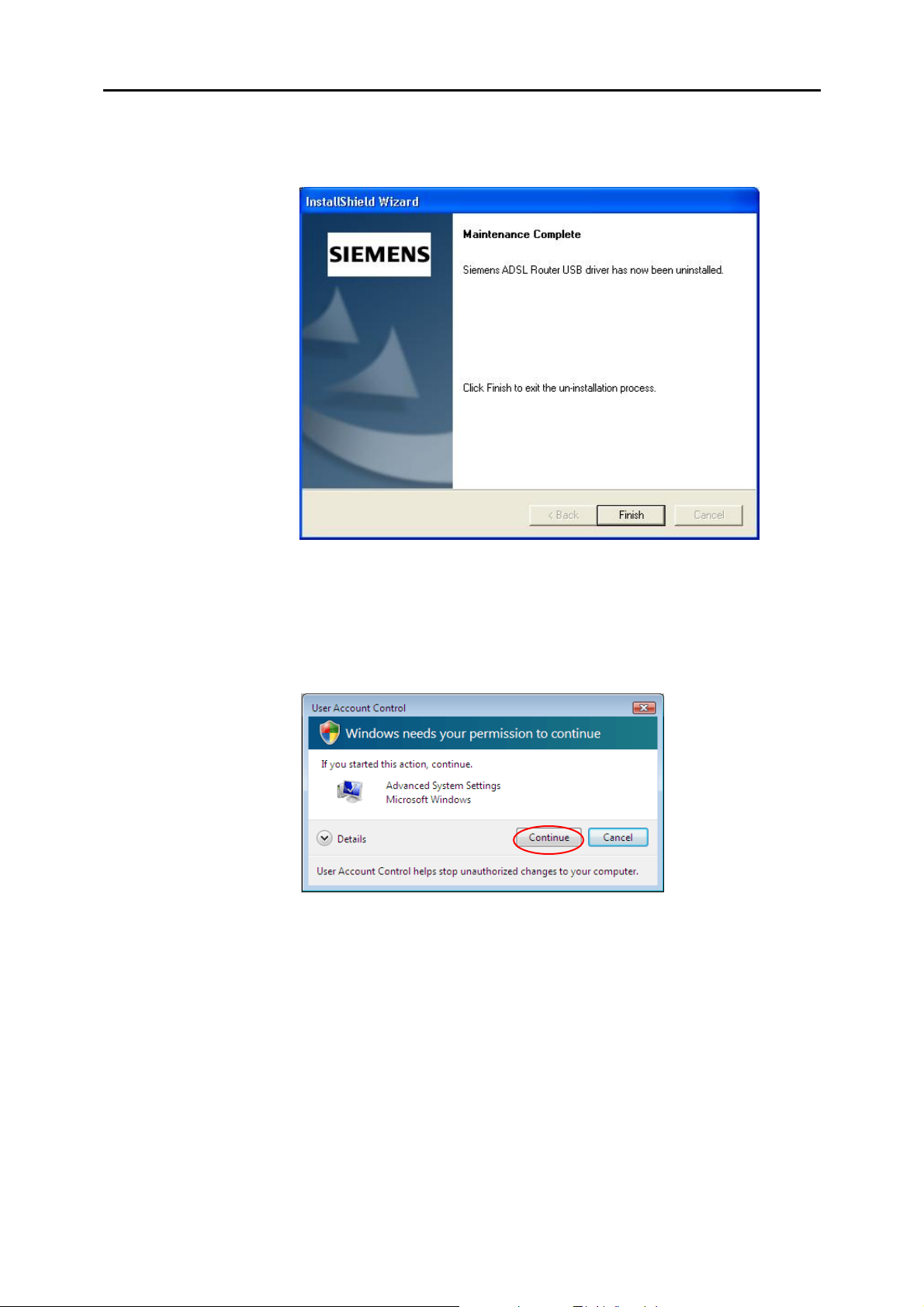
s When the Maintenance Complete screen appears, the USB driver is
removed successfully. Click Finish.
For Windows Vista
For Vista users, please press Continue whenever a prompted window asking for permission
to continue during USB driver uninstallation process (see the figure below for example).
To uninstall the USB driver, there are two ways to do it. Please follow the instructions.
Method One: Remove from Device Manager.
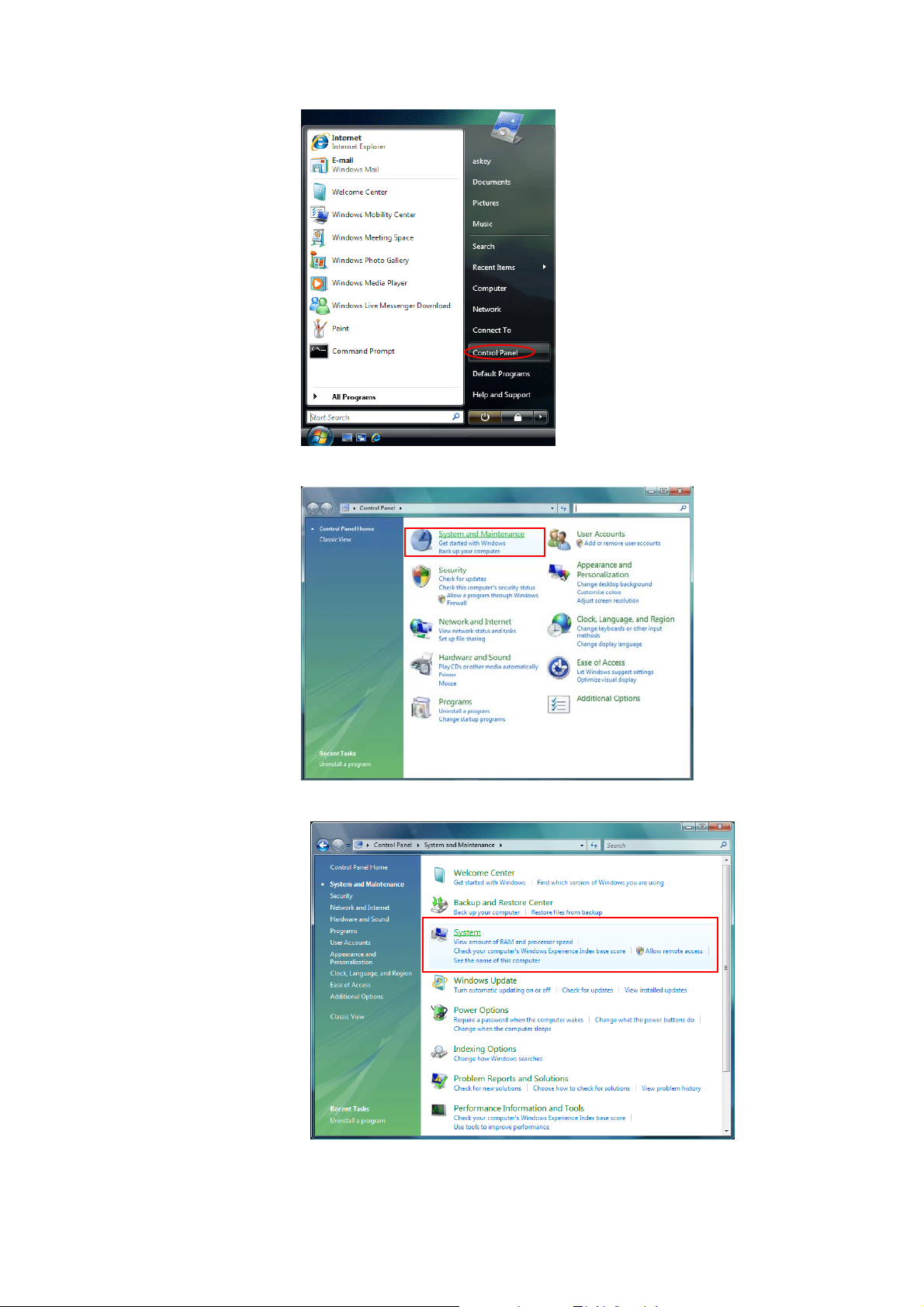
n Choose Start menu, and then select Control Panel.
19
Page 28
ADSL Router User Manual
o Click System and Maintenance.
20
p Press System.
q Click Device Manager.
Page 29
Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
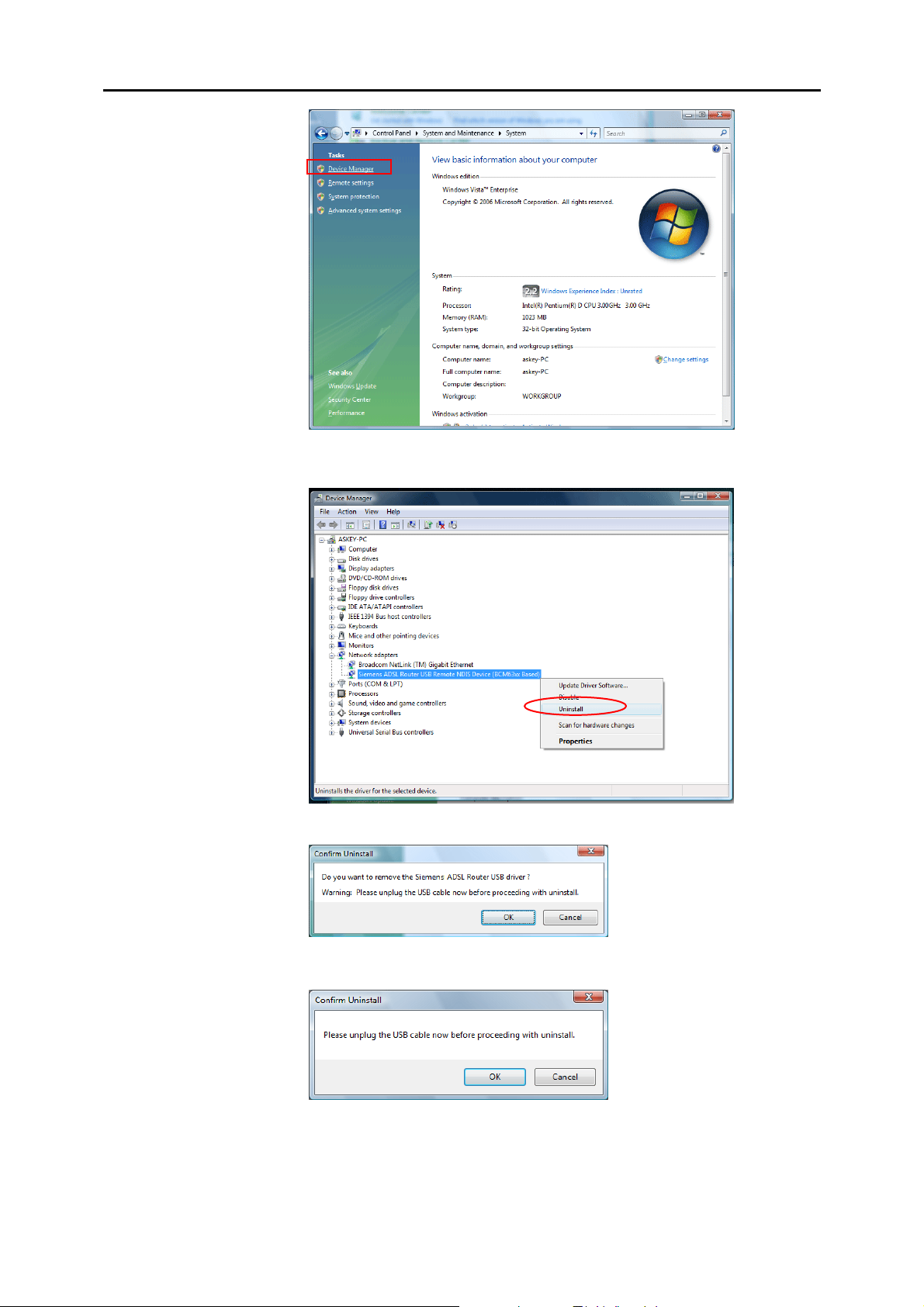
r Right click Askey ADSL Router USB Remote NDIS Device on the Network
adapters list, and press Uninstall.
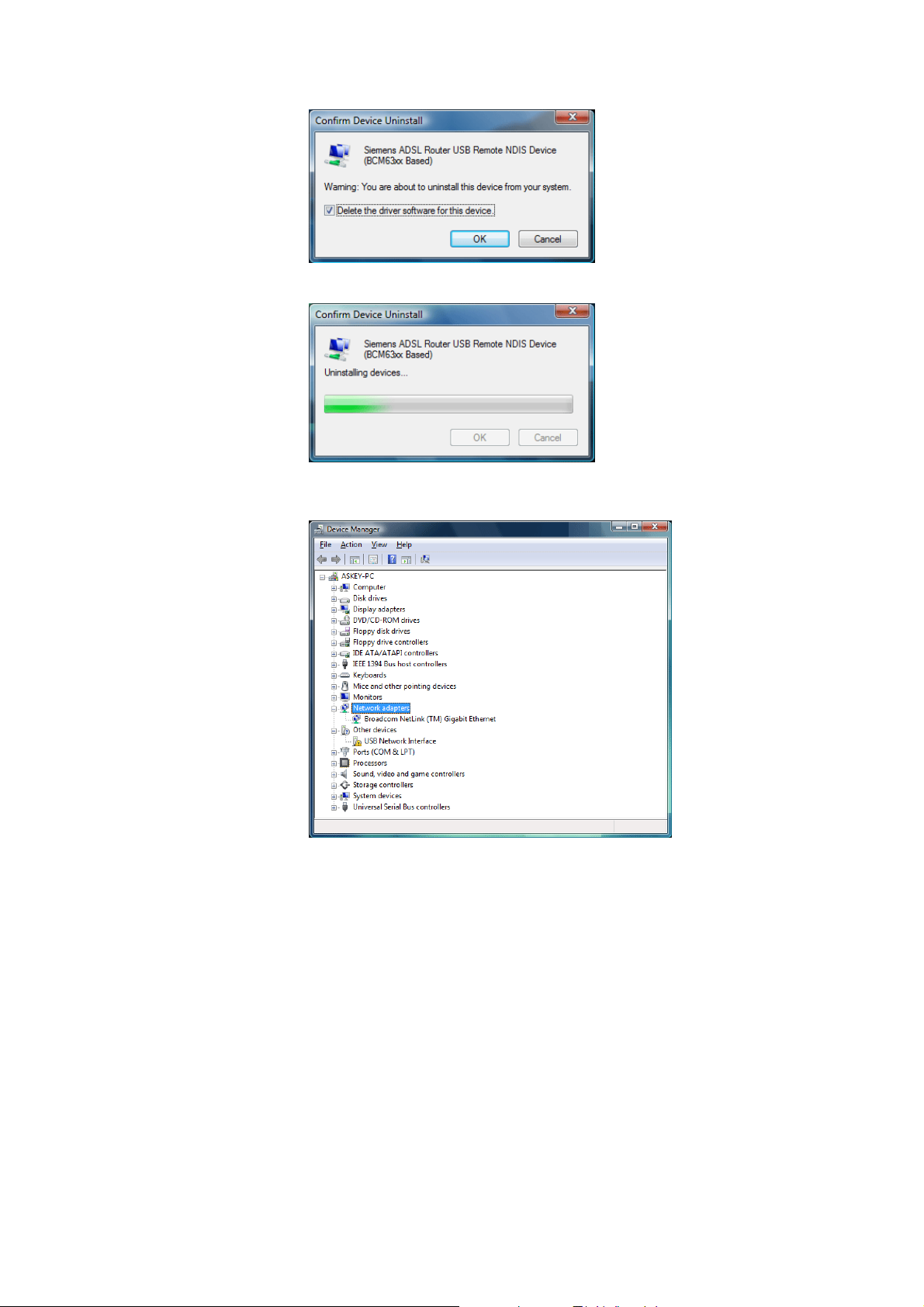
s Click OK when the Conf irm Uninstall window appears.
Remember to unplug the USB cable before continue the uninstallation, or you will
see the reminder as follows. Unplug and press OK.
t When the Confirm Device Uninstall screen show up, check Delete the driver
software for the device and click OK to continue.
21
Page 30
ADSL Router User Manual
u Wait while the system is uninstalling.
v When the uninstallation is finished, the icon of this router under network adapter
list will disappear.
22
Method T wo – uninstall from program list
Note: If your USB driver is installed by UPnP device, you can only use method one (via the
Device Manager) to uninstall, because the installed driver will not be shown on the program
list.
n Unplug your USB cable between your router and your PC.
o Choose Start menu, and open Control Panel folder. Click Uninstall a program.
Page 31

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
p If the driver name is not on the list, click Refresh button or F5 to update the
information. To remove the driver, select it, and then press Uninstall.
Refresh button
q Then the system will start to uninstall the USB driver software automatically.
r When Maintenance Complete window shows up, click Finish to exit.
23
Page 32

ADSL Router User Manual
s The USB driver is successfully removed now.
24
Page 33

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
Setting up TCP/IP
In order to access the Internet through the IAD, each host on your
network must install/setup TCP/IP first. Please follow the steps below
to set your network adapter.
If the TCP/IP protocol has not been installed yet, please follow the steps below for
installation. In the following illustrations, we will set the PC to get an IP address
automatically at the same time.
For Windows 98
1. Open the Start menu,
point to Settings and
click on Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network icon.
25
Page 34

ADSL Router User Manual
3. The Network window appears.
On the Configuration tab, check
out the list of installed network
components.
Option 1: If there is no TCP/IP
protocol, click Add.
Option 2: If you have TCP/IP
protocol, skip to Step 6.
Your networ
interface card.
Check out if
for your NI
installed or
k
TCP/IP
C is
not.
4. Highlight Protocol and click Add.
5. Highlight Microsoft on the left
side of the window, and select
TCP/IP on the right side. Then
click OK.
6. When returning to the Network
window, highl ight TCP/IP
protocol for your NIC and click
Properties.
26
Page 35

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
7. On the IP Address tab:
Enable Obtain an IP address
automatically and click OK.
8. When returning to the Network
window, click OK
9. Wait for Windows when copying
files.
10. When prompted with System
Settings Change dialog box,
click Yes to restart your
computer.
27
Page 36

ADSL Router User Manual
For Windows ME
1. Open the Start menu, point to
Settings and click on Control
Panel.
2. Double-click the Network icon.
3. The Network window appears. On
the Configuration tab, check out
the list of installed network
components.
Option 1: If there is no TCP/IP
protocol, click Add.
Option 2: If you have TCP/IP
protocol, skip to Step 6.
Your networ
interface card.
Check out if
for your NI
installed or
k
TCP/IP
C is
not.
4. Highlight Protocol and click Add.
28
Page 37

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
5. Highlight Microsoft on the left
side of the windows, and select
TCP/IP on the right side. Then
click OK.
6. While returning to Network
window, highlight TCP/IP protocol
for your NIC and click Properties.
7. On IP Address tab:
Enable Obtain an IP address
automatically and click OK.
29
Page 38

ADSL Router User Manual
8. While returning to the Network
window, click OK.
9. Wait for Windows when copying
files.
10. When prompted with the System
Settings Change dialog box, click
Yes to restart your computer.
For Windows NT
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and
then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network icon.
30
Page 39

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
3. The Network window appears. On
the Protocols tab, check out the
list of installed network
components.
Option 1: If there is no TCP/IP
Protocol, click Add.
Option 2: If you have TCP/IP
Protocol installed, skip to Step 7.
4. Highlight TCP/IP Protocol and
click OK.
5. Insert the Windows NT CD into
your CD-ROM drive and type the
location of the CD. Then click
Continue.
31
Page 40

ADSL Router User Manual
6. When returning to the Network
window. Open the Protocols tab,
then select TCP/IP Protocol and
click Properties.
7. Enable Obtain an IP address
from a DHCP server and click
OK.
32
8. When prompted with the
message below, click Yes to
continue.
Page 41

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
9. When returning to Network
window, click Close.
10. When prompted with Network
Settings Change dialog box,
click Yes to restart your
computer.
For Windows 2000
1. From the Start menu, point to
Settings and then click Network
and Dial-up Connections.
33
Page 42

ADSL Router User Manual
2. Right-click the Local Area
Connection icon and then click
Properties.
3. On the General tab, check out
the list of installed network
components.
Option 1: If there is no TCP/IP
Protocol, click Install.
Option 2: If you have TCP/IP
Protocol, skip to Step 6.
34
4. Highlight Protocol and then click
Add.
Page 43

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
5. Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
and then click OK.
6. When returning to the Local
Area Connection Properties
window, highlight Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP) and then click
Properties.
7. Under the General tab, enable
Obtain an IP address
automatically. Then click OK.
35
Page 44

ADSL Router User Manual
For Windows XP
1. Open the Start menu, point to
Control Panel and click it.
2. Double click the Network
Connection.
3. Right click Local Area
Connection and then click
Properties.
36
Page 45

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
4. On the General tab, check out
the list of installed network
components.
Option 1: If there is no TCP/IP
Protocol, click Install.
Option 2: If you have TCP/IP
Protocol, skip to Step 7.
If th /IP
ere is no TCP
protocol installed on your
PC, press Install to continue.
5. Highlight Protocol and then click
Add.
6. Click Internet Protocol(TCP/IP)
and then click OK.
37
Page 46

ADSL Router User Manual
7. When it returns to the General
Tab on the Local Area
Connection Properties window,
highlight Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) and then click
Properties.
8. Under the General tab, select
Obtain an IP address
automatically, and Obtain DNS
server address automatically.
Then click Ok.
38
Page 47

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
For Windows Vista
9. Open the Start menu,
point to Control Panel
and click it.
10. Click Network and
Internet.
11. Select Network and
Sharing Center.
39
Page 48

ADSL Router User Manual
12. Click Manage Network
Connection on the left
side.
13. Right click Local Area
Connection and select
Properties.
14. On the Networking tab,
you will find Internet
Protocol Version 6 and
Version 4. Contact your
ISP to confirm which one
will be used. (We take
TCP/IPv4 for example
here.)
Select Internet Protocol
Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)
and press Properties.
40
Page 49

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
15. Under the General tab,
select Obtain an IP
address automatically,
and Obtain DNS server
address automatically.
Then click Ok to exit.
41
Page 50

ADSL Router User Manual
Renewing IP Address on Client PC
After the IAD gets on line, there is a chance that your PC does not renew its IP
address and thus causes the PC not able to access the Internet. To solve this
problem, please follow the procedures below to renew PC’s IP address.
For Windows 98/ME
1. Select Run from the Start menu.
2. Type winipcfg in the text box and
click OK.
3. When the figure below appears,
click Release to let go of the
address and then click the Renew
button to obtain a new IP address.
For Windows NT/2000/XP
1. Open the Start menu, and click
Run... on this menu.
42
Page 51

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
2. Type cmd in the text box that
appears and click OK. Then you
will see the command prompt
window.
Another way to open the
command prompt:
From Start menu, point to
Programs, select Accessories,
and then click Command Prompt.
3. Type ipconfig at the command
prompt window and press Enter to
view the computer’s IP information
from DHCP server.
4. If the computer is holding a
current IP address, type ipconfig
/release to let go of the address,
then type ipconfig /renew to
obtain a new one.
Released IP Address
43
Page 52

ADSL Router User Manual
For Windows Vista
1. Open the Start menu, and
type cmd in the text box then
click OK.
2. The command prompt
window will appear.
3. Type ipconfig at the
command window and press
Enter to view the computer’s
IP information from DHCP
server.
4. If the computer is holding a
current IP address, type
ipconfig /release to let go of
the address, then type
ipconfig /renew to obtain a
new one.
44
Page 53

Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
Note:
If you cannot release the IP
address successfully and see the
message “The requested
operation requires elevation,”
please go to the Start menu and
right click Command Prompt,
then set Run as administrator.
Press Continue when a dialog
asking for permission to continue
prompts.
After then, repeat the above
instruction to release and renew
the IP address.
45
Page 54

Chapter 3: Accessing the Internet
Chapter 3: Acces sing the Internet
This chapter aims to help you access the Internet in a quick and
convenient way. If you need more detailed information for web
configuration, please refer to the next chapter for the advanced
configuration.
Before configuring the IAD, you must decide whether to configure the device as a
bridge or as a router . This chapter presents some deployment examples for your
reference. Each mode includes its general configu re procedures. For more detailed
information about web configuration, refer to "Web Configuration".
PPP over ATM (PPPoA)
PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Numbered IP over ATM (IPoA)
Numbered IP over ATM (IPoA) + NAT
Unnumbered IP over ATM (IPoA)
Unnumbered IP over ATM (IPoA) + NAT
Bridge Mode
MER (Bridge Mode + NAT)
To ensure your PC accessing the Internet successfully, please check the following
first.
A netwo rk interface card is installed on your PC.
The IAD is solidly connected with your computer.
The TCP/IP protocol has been installed and the IP address setting is to
obtain IP address automatically.
When all above preparations are ready, you can open the Browser and type
“192.168.1.1” into the URL box and start to make the web configuration for different
connection modes.
This chapter is going to introduce the function of each connection mode and the
basic configuring steps that you have to do. If you do not follow the configuring steps
for using these connection modes, you might get some connection pro blems and
cannot connect to the Internet well.
46
Page 55

Chapter 3: Accessing the Internet
PPP over ATM (PPPoA) Mode
Description:
In this deployment environment, the PPPoA session is between the ADSL WAN
interface and BRAS. The IAD gets a public IP address from BRAS when connecting
to DSLAM. The multiple client PCs will get private IP address from the DHCP server
enabled on private LAN. The enabled NAT mechanism will translate the IP
information for clients to access the Internet.
Configuration:
1. Start your browser and type 192.168.1.1 as the address to access ADSL
web-based manager.
2. Go to Quick Start -Quick Setup. Uncheck Auto Scan Internet Connection
(PVC). Key in the VCI and VPI value, e.g.:
VPI – 0
VCI – 38
Click the Next button.
3. On the Configure Internet Connection -Connection Type page, select PPP
over A TM (PPPoA) then click the Next button.
4. On the WAN IP Settings page, select Obtain an IP address automatically
and check Enable NAT box. Click Next.
5. On the PPP Username and Password page, enter the PPP username and
password that you got from your ISP. Select Always on or select Dial on
Demand and key in the inactivity timeout value. (The default value is 20
minutes.) Then click Next.
6. On the Configure LAN side Settings page, key in the IP addre s s and subnet
mask for your LAN, e.g.:
Primary IP address: 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Check DHCP Server on box. And key in the start and end IP address, e.g.:
Start IP Address:192.168.1.2
End IP Address: 192.168.1.254
Then enter the leased time ( the default is 1 day), and click Next.
7. Check the network information on This Internet Connection -- Summary
page. Make sure the settings match the information provided by your ISP. Click
Finish.
47
Page 56

ADSL Router User Manual
PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) Mode
Description:
In this deployment environment, the PPPoE session is between the ADSL WAN
interface and BRAS. The IAD gets a public IP address from BRAS when connecting
to DSLAM. The multiple client PCs will get private IP address from the DHCP server
enabled on private LAN. The enabled NAT mechanism will translate the IP
information for clients to access the Internet.
Configuration:
1. Start your browser and type 192.168.1.1 in the URL box to access ADSL
web-based manager.
2. Go to Quick Start -Quick Setup. Uncheck Auto Scan Internet Connection
(PVC). Key in the VCI and VPI value, e.g.:
VPI – 0
VCI – 39
Click the Next button.
3. On the Configure Internet Connection -Connection Type page, select PPP
over Ethernet (PPPoE) then click the Next button.
4. On the WAN IP Settings page, select Obtain an IP address automatically
and check Enable NAT box. Click Next.
5. On the PPP Username and Password page, enter the PPP username and
password that you got from your ISP. Select Always on or select Dial on
Demand and key in the inactivity timeout value. (The default value is 20
minutes.) Then click Next.
6. On the Configure LAN side Settings page, key in the IP addre s s and subnet
mask for your LAN, e.g.:
Primary IP address: 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Check DHCP Server on box. And key in the start and end IP address, e.g.:
Start IP Address:192.168.1.2
End IP Address: 192.168.1.254
Then enter the leased time ( the default is 1 day), and click Next.
48
7. Check the network information on This Internet Connection -- Summary
page. Make sure the settings match the information provided by your ISP. Click
Finish.
Page 57

Chapter 3: Accessing the Internet
(
)
r
Numbered IP over ATM (IPoA)
10.3.80.81
Hub
10.3.80.82
10.3.80.83
S/W
PC(S)
ISP
Internet Service Provider
AAA
RDAIUS
Server
*BRAS: Broadband
Remote Access Serve
Default Private IP
192.168.1.1
STM-1
BRAS
DSLAM
Loop
10.3.95.233
IAD
IP over ATM
Public IP Pre-assigned
by ISP
Description:
If you apply for multiple IP addresses from your ISP, you can assign these public IP
addresses to the IAD and public server, e.g., Web or FTP server. Typically the first
IP is network address, the second is used as the IAD IP address and the last one is
for subnet broadcasting. Other remaining IP addresses can be assigned to PCs on
the LAN.
The following example uses the LAN IP address ranging from 10.3.80.81 to
10.3.80.86 and the subnet mask for LAN is 255.255.255.248. The WAN IP address
is 10.3.95.233, and the subnet mask for WAN is 255.255.255.248.
Configuration:
1. Start your browser and type 192.168.1.1 in the URL box to access ADSL
web-based manager.
2. Go to Quick Start -Quick Setup. Uncheck Auto Scan Internet Connection
(PVC). Key in the VCI and VPI value, e.g.:
VPI – 0
VCI – 32
Click the Next button.
3. On the Configure Internet Connection -Connection Type page, select IP
over A TM (IPoA) then click Next.
4. On the WAN IP Settings page, select Use the following IP address and Use
the following DNS Server Address, then key in the information that your ISP
offered, e.g.:
WAN IP Address: 10.3.95.233
WAN Subnet Mask: 2 55.255.255.248
Primary DNS server: 168.95.1.1
Secondary DNS server: 168.95.192.1
Uncheck Enable NAT and click Next.
5. On the Configure LAN side Settings page, key in the information for your
LAN, e.g.,
Primary IP Address: 192.168.1.1
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Start IP Address: 192.168.1.2
End IP Address: 192.168.1.254
49
Page 58

ADSL Router User Manual
6. Check Configure the second IP Address and Subnet Mask for LAN
Interface and enter the information needed.
Secondary IP Address: 10.3.80.81
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.248
Click Next.
7. Check the network information on the Summary page. Make sure the settings
match the settings provided by your ISP. Click Finish.
8. Refer to the TCP/IP properties, specify an IP Address, and fill in other
information needed, e.g.:
IP Address: 10.3.80.82
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248
Gateway: 10.3.80.81
Preferred DNS server: 168.95.1.1
9. Now the IAD is well-configured. You can access the Internet.
50
Page 59

Chapter 3: Accessing the Internet
Numbered IP over ATM (IPoA)+NAT
Description:
In this deployment environment, we make up a private IP network of 192.168.1.1.
NAT function is enabled (on the IAD or use another NAT box connected to hub) to
support multiple clients to access the IAD and some public se rvers (WWW, FTP).
If you apply for multiple IP addresses from your ISP, you can assign these public IP
addresses to the IAD and public server, e.g., Web or FTP server. Typically the first
IP is network address, the second is used as IAD IP address and the last one is
subnet broadcasting. Other remaining IP addresses can be assigned to PCs on the
LAN.
The following example uses the IP address ranging from 10.3.80.81 to 10.3.80.86
and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.248.
Configuration:
1. Start your browser and type 192.168.1.1 in the URL box to access ADSL
web-based manager.
2. Go to Quick Start -Quick Setup. Uncheck Auto Scan Internet Connection
(PVC). Key in the VCI and VPI value, e.g.:
VPI – 0
VCI – 32
Click the Next button.
3. On the Configure Internet Connection -Connection Type page, select IP
over A TM (IPoA) then click Next.
4. On the WAN IP Settings page, select Use the following IP address and Use
the following DNS Server Address, then key in the information that your ISP
offered, e.g.:
WAN IP Address: 10.3.80.81
WAN Subnet Mask: 2 55.255.255.248
Primary DNS server: 168.95.1.1
Secondary DNS server: 168.95.192.1
5. Check the Enable NAT box. And click Next.
51
Page 60

ADSL Router User Manual
6. On the Configure LAN side Settings page, key in the information for your
LAN, e.g.,
Primary IP Address: 192.168.1.1
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Start IP Address: 192.168.1.2
End IP Address: 192.168.1.254
7. Check the network information. Make sure the settings match the settings
provided by ISP. Click Finish.
8. Now the IAD is well configured. You can access into Internet.
52
Page 61

Chapter 3: Accessing the Internet
r
(
)
Unnumbered IP over ATM (IPoA)
ISP
Internet Service Provider
RDAIUS
Server
*BRAS: Broadband
Remote Access Serve
AAA
STM-1
BRAS
DSLAM
IP over ATM
Public IP Pre-assigned
by ISP
Default Private IP
192.168.1.1
Loop
IAD
10.3.80.81
10.3.80.83
S/W
Hub
10.3.80.82
PC(S)
Description:
If you apply for multiple IP addresses from your ISP, you can assign these public IP
addresses to the IAD and public server, e.g., Web or FTP server. Typically the first
IP is network address, the second is used as IAD IP address and the last one is
subnet broadcasting. Other remaining IP addresses can be assigned to PCs on the
LAN.
The following example uses the IP address ranging from 10.3.80.81 to 10.3.80.86
and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.248. In such circumstance, we do not assign
any WAN IP.
Configuration:
1. Start your browser and type 192.168.1.1 in the URL box to access ADSL
web-based manager.
2. Go to Quick Start -Quick Setup. Uncheck Auto Scan Internet Connection
(PVC). Key in the VCI and VPI value, e.g.:
VPI – 0
VCI – 32
Click the Next button.
3. On the Configure Internet Connection -Connection Type page, select IP
over A TM (IPoA) then click Next.
4. On the WAN IP Settings page, select None for WAN IP address settings.
Then, select Use the following DNS Server Address and key in the
information that your ISP offered, e.g.:
Primary DNS server: 168.95.1.1
Secondary DNS server: 168.95.192.1
Uncheck Enable NAT and click Next.
5. On the Configure LAN side Settings page, key in the information for your
LAN, e.g.,
Primary IP Address: 192.168.1.1
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Start IP Address: 192.168.1.2
End IP Address: 192.168.1.254
6. Check Configure the second IP Address and Subnet Mask for LAN
Interface and enter the information needed, e.g.,
Secondary IP Address: 10.3.80.81
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.248
53
Page 62

ADSL Router User Manual
Check DHCP Server Off a nd click Next.
7. Check the network information on the Summary page. Make sure the settings
match the settings provided by your ISP. Click Finish.
8. Refer to the TCP/IP properties, specify an IP Address, and fill in other
information needed, e.g.:
IP Address: 10.3.80.82
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248
Gateway: 10.3.80.81
Preferred DNS server: 168.95.1.1
9. Now the IAD is well-configured. You can access the Internet.
54
Page 63

Chapter 3: Accessing the Internet
Unnumbered IP over ATM (IPoA)+NAT
Description:
If you apply for multiple IP addresses from your ISP, you can assign these public IP
addresses to the IAD and public server, e.g., Web or FTP server. Typically the first
IP is network address, the second is used as the IAD IP address and the last one is
subnet broadcasting. Other remaining IP addresses can be assigned to PCs on the
LAN.
The following example uses the IP address ranging from 10.3.80.81 to 10.3.80.86
and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.248. In such circumstance, we enable NAT
function but not assign any WAN IP.
Configuration:
1. Start your browser and type 192.168.1.1 in the URL box to access ADSL
web-based manager.
2. Go to Quick Start -Quick Setup. Uncheck Auto Scan Internet Connection
(PVC). Key in the VCI and VPI value, e.g.:
VPI – 0
VCI – 32
Click the Next button.
3. On the Configure Internet Connection -Connection Type page, select IP
over A TM (IPoA) then click Next.
4. On the WAN IP Settings page, select None for WAN IP address settings.
Then, select Use the following DNS Server Address and key in the
information that your ISP offered, e.g.:
Primary DNS server: 168.95.1.1
Secondary DNS server: 168.95.192.1
5. Check the Enable NAT box. And click Next.
6. On the Configure LAN side Settings page, key in the information for your
LAN, e.g.,
Primary IP Address: 192.168.1.1
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Start IP Address: 192.168.1.2
End IP Address: 192.168.1.254
55
Page 64

ADSL Router User Manual
7. Check Configure the second IP Address and Subnet Mask for LAN
Interface and enter the information needed, e.g.,
Secondary IP Address: 10.3.80.81
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.248
Click Next.
8. Check the network information on the Summary page. Make sure the contents
match the settings provided by your ISP. Click Finish.
9. Now the IAD is well-configured. You can access the Internet.
56
Page 65

Bridge Mode
r
(
)
Chapter 3: Accessing the Internet
Default Private IP
192.168.1.1
ISP
Internet Service Provider
RDAIUS
Server
*BRAS: Broadband
Remote Access Serve
AAA
BRAS
STM-1
DSLAM
Bridge Mode
Loop
IAD
Hub
PPPoE
Client S/W
PC(S)
Description:
In this example, the IAD acts as a bridge which bridging the PC IP addresses from
LAN to WAN. The PC IP address can be a static public address that is pre-assigned
by the ISP or a dynamic public address that is assigned by the ISP DHCP server, or
an IP address received from PPPoE software.
Therefore, it does not require a public IP address. It only has a default private IP
address (192.168.1.1) for management purpose.
Configuration:
1. Choose a client PC and set the IP as 192.168.1.x (x is between 2 and 254) and
the gateway as 192.168.1.1.
2. Start your browser and type 192.168.1.1 in the URL box to access ADSL
web-based manager.
3. Go to Quick Start -Quick Setup. Uncheck Auto Scan Internet Connection
(PVC). Key in the VCI and VPI value, e.g.,
VPI – 0
VCI – 35
Then click the Next button.
4. On the Configure Internet Connection -Connection Type page, select
Bridging then click the Next button.
5. On the WAN IP Settings page, select None for WAN IP address settings.
6. On the Configure LAN side Settings page, enter the IP address and subnet
mask for your LAN, e.g.:
Primary IP address: 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Choose DHCP Server Off and click Next.
7. Check the network information on the Summary page. Make sure the contents
match the settings provided by your ISP. Click Finish.
8. Refer to the TCP/IP properties, specify an IP Address, and fill in other
information needed, e.g.:
IP Address: 10.3.86.81
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248
Gateway: 10.3.86.1
Preferred DNS server: 168.95.1.1
9. Click OK. Now the IAD is well-configured. You can access to the Internet.
57
Page 66

ADSL Router User Manual
R
(
)
r
MER
Default Private IP
192.168.1.1
IAD
Ethernet
Hub
PC
ISP
Internet Service Provider
AAA
RDAIUS
Server
*BRAS: Broadband
Remote Access Serve
BRAS
Public IP
assigned by BRAS
STM-1
DSLAM
ME
Loop
Description:
In this deployment environment, we make up a private IP network of 192.168.1.1.
NAT function is enabled to support multiple clients to access to Internet.
In this example, the IAD acts as a NAT device which translates a private IP address
into a public address. Therefore multiple users can share with one public IP address
to access the Internet through this IAD. The public address can be a static public
address that is pre-assigned by ISP or a dynamic public address that is assigned by
the ISP DHCP server.
Configuration:
1. Start your browser and type 192.168.1.1 in the URL box to access ADSL
web-based manager.
2. Go to Quick Start -Quick Setup. Uncheck Auto Scan Internet Connection
(PVC). Key in the VCI and VPI value, e.g.,
VPI – 0
VCI – 37
Then click the Next button.
3. On the Configure Internet Connection -Connection Type page, select
Bridging and then click the Next button.
4. On the WAN IP Settings page, select Obtain an IP address automatically;
then, select Obtain DNS server address automatically.
5. Check Enable NA T. Then click Next.
6. On the Configure LAN side Settings page, key in the IP address and subnet
mask for your LAN. Check DHCP Server On box, and enter the start and end
points, e.g.:
Primary IP address:192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask:255.255.255.0
Start IP Address:192.168.1.2
End IP Address: 192.168.1.254
Then key in the leased time that you want. And click Next
7. Check the network information on the Summary page. Make sure the contents
match the settings provided by your ISP. Click Finish.
8. Now the IAD is well-configured. You can acce ss the Internet.
58
Page 67

Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Some users might want to set specific configuration for the router such as
firewall, data transmission rate…, and so on. This chapter will provide
you advanced information of the web pages for the router for your
reference.
Using Web-Based Manager
After properly configuring you host PC, please proceed as follows:
1. Start your web browser and type
192.168.1.1, the private IP address of the
ADSL Router, in the URL field.
2. After connecting to the device, you will be
prompted to enter username and
password. By default, both the username
and the password are admin. An example
under Windows XP is shown as the left
figure.
If you login successfully, the main page will
appear. From now on, the IAD acts as a
web server sending HTML pages/forms on
your request. You can fill in these
pages/forms and apply them to the IAD.
59
Page 68

ADSL Router User Manual
Outline of Web Manager
To configure the web page, please use admin as the username and the password.
The main screen will be shown as below.
Main Menu
Title
Main Window
Title: The title of this management interface.
Main Menu: Including Quick Start, Status, Advanced, Voice, and Management.
Main Window: The current workspace of the web manager, containing
configuration or status information.
To Have the New Settings Take Effect
After selecting or adjusting the settings according to your needs, your
customizations will be saved to the flash memory before you restart the IAD. And
only after rebooting the IAD, your customizations may take effect.
Language
On the top to the right of this web page, it provides a drop-down menu for you to
choose a proper language. (However, we only offer English at present.)
60
Page 69

Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Quick Start
The pages under the Quick Start menu provide user a quick way to set up the IAD. If
you do not know much about the router, you can use the Quick Start pages to adjust
basic settings to activate your IAD.
Connect to Internet
This is a quick way to connect to the
Internet by using PPPoE interface,
please click Connect to Internet to
open the web page.
Enter the user name and password
(that you get from the ISP) for your
IAD and click Connect.
The system will connect automatically,
and then you can access the Internet.
Quick Setup
The quick setup wizard will guide you
to configure this router through some
specific steps. Yet different connection
interface will lead to different setting
pages. Refer to the following pages for
detailed information.
Auto Scan Internet Connection
(PVC):
If there is no any PVC configured in
your router, you can check this item.
Otherwise, please uncheck this box.
VPI (Virtual Path Identifier):
Identifies the virtual path between
endpoints in an ATM network. The
valid range is from 0 to 255. To enter
the setting, please refer to the setting
that the ISP offered.
VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier):
Identifies the virtual channel endpoints
in an ATM network. The valid range is
from 32 to 65535 (1 to 31 is reserved
for well-known protocols). To enter the
setting, please refer to the setting that
the ISP gave you.
After entering the VPI/VCI value,
please click Next for the following
step.
61
Page 70

ADSL Router User Manual
Connection Type
The system provides several protocols for you to choose. Your ISP will offer you the
most suitable settings of the protocol. Before you set this page, please refer to the
protocol that your ISP offered.
After clicking on the Next button from
the VPI/VCI web page, the following
screen will appear. Please choose the
connection type and encapsulation
mode that you want to use and click
Next for next page.
For instance, PPP over Ethernet
(PPPoE) is selected in this
demonstrative figure.
PPP over ATM/ PPP over Ethernet
If the connection type you choose is PPP over ATM or PPP over Ethernet, please
refer to the following information.
According to the ISP’s configuration
on the server, you can choose PPPoE
or PPPoA modes.
Choose PPPoA or PPPoE and click
Next.
On this screen, you have to make the
settings for WAN IP. To get the IP
address automatically, click the
Obtain an IP address automatically
radio button. Or click Use the
following IP address button and
enter the IP address for WA N
interface.
Check Enable NAT if you need.
MTU:
It means the maximum size of the
packet that transmitted in the network.
The packet of the data greater than
the value set here will be divided into
several packets for transmitting.
Type the value into the field of MTU.
The default setting for PPPoE is 1492;
while for PPPoA is 1500.
62
Click Next for the next procedure.
Page 71

PPP Username & PPP Password:
Key in the username and password
that you received from your ISP. (e.g.,
Siemens4/Siemens4)
Always On:
Select this item to make the
connection active all the time.
Dial on Demand:
Select this item to make a connection
automatically while in demand. Enter
the timeout to cut off the network
connection if there is no activity for
this IAD.
Manually Connect:
Select this item to make a connection
by pressing the Connect
the Advanced Setup- Internet-
Connections web page.
On the Configure LAN side Settings
page, you have to fill in the data
requested.
hyperlink on
Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Primary IP Address & Subnet Mask:
Key in the information that offered by
your ISP for the LAN connection.
Configure the secondary IP
Address and Subnet Mask:
Check this box to set up a secondary
IP Address to connect to your IAD if
they are not included in the range that
DHCP server accepts. See the next
figure for the secondary IP address
and subnet mask.
Secondary IP Address & Subnet
Mask:
Key in the second IP address and the
subnet mask received from the ISP for
your LAN connection.
MTU: (refer to the WAN section)
The default MTU value for LAN side
Settings is 1500. You may modify it if
necessary.
DHCP Server On:
Check this item if DHCP service is
needed on the LAN side. The IAD will
assign IP address and gateway
address for each of your PCs.
On this web page, the primary IP
address and subnet mask will be
shown on it. You can modify them
if needed.
Start IP Address & End IP Address:
Enter the information needed.
Lease Time:
Key in the duration for the time. The
default is 1day.
DHCP Server Off:
Check this item if DHCP service is not
needed on the LAN.
Key in all the necessary settings
and click Next for the coming
page.
63
Page 72

ADSL Router User Manual
You can check the contents on the
Summary page.
If you find anything incorrect, click
Back to modify the settings.
If everything is OK, click Finish to
accept these settings.
Now, the system will reboot to activate
the new settings that you have set in
this section.
Please wait for 2 minutes before
restarting the router.
64
Page 73

Chapter 4: Web Configuration
IP over ATM
If the type you have to choose is IP over ATM, please refer to the following
information.
IPoA is an alternative of LAN
emulation. It allows TCP/IP network to
access ATM network and uses ATM
quality of service’s features.
Choose IPoA and click Next.
None:
If it is not necessary to set the WAN IP
address, please click this button.
Obtain an IP address automatically:
Click this button to allow the system to
get an IP address automatically.
WAN IP Address & WAN Subnet
Mask:
If you choose Use the following IP
address, you have to enter the IP
address and subnet mask information
that you received from the ISP for the
WAN interface.
Obtain DNS server address
automatically:
Only when you select Obtain an IP
address automatically that this
option is available. You may click this
button to allow the system to get DNS
server address automatically.
After setting up the WAN IP and
DNS server information, click Next
to open the following page.
Use the following DNS server
addresses:
Select this item to set the DNS server
addresses manually, type the
information provided by your ISP in
the following Primary DNS and
Secondary DNS server entries, e.g.
168.95.1.1 and 168.95.192.1.
Click Enable NA T if you want.
65
Page 74

ADSL Router User Manual
On the Configure LAN side Settings
page; you have to fill in the data
requested.
Primary IP Address & Subnet Mask:
Key in the information offered by your
ISP for the LAN connection, e.g.,
192.168.1.1 for primary IP address
and 255.255.255.0 for subnet mask.
MTU:
(Please refer to the PPPoA/ PPPoE
section.) The default MTU setting is
1500. You may modify it if necessary.
Configure the secondary IP
Address and Subnet Mask:
Check this box to set up a secondary
IP address to connect to your IAD if
they are not included in the range that
DHCP server accepts. You have to
key in the information received from
your ISP for the LAN connection, e.g.,
the secondary IP is 10.3.80.81 and the
mask is 255.255.255.248 in the
example illustrated in the figure.
The primary IP address and subnet
mask will be shown on it. You can
modify them if needed.
DHCP Server On:
Check this item if DHCP service is
needed on the LAN side. The IAD will
assign IP address and gateway
address for each of your PCs.
Start IP Address & End IP Address:
Enter the information needed.
Lease Time:
Key in the duration for the time. The
default is 1day.
DHCP Server Off:
Check this item if DHCP service is not
needed on the LAN.
You can check the settings on the
Summary page.
If you find anything incorrect, click
Back to modify the settings.
If everything is OK, click Finish to
accept these settings.
And the following page will appear.
Key in all the necessary settings.
Click Next for the coming page.
66
Now, the system will reboot to activate
the new settings that you have set in
this section.
Please wait for 2 minutes before
restarting the IAD.
Page 75

Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Bridging
If the mode you choose is Bridging (or MER), please refer to the following
information.
The bridging mode can configure your
IAD to send and receive packets
between LAN and WAN interfaces.
The WAN interface is ATM PVC; the
LAN interface can be Ethernet or
USB.
Choose Bridging and click Next.
None:
If it is not necessary to set the WAN IP
address, please click this button. In
our example, we select this item.
Obtain an IP address automatically:
Click this button to allow the system to
get an IP address automatically.
WAN IP Address, WAN Subnet
Mask, and Default Gateway:
When choosing Use the following IP
address, you have to key in the IP
address, the subnet mask, and the
default gateway provided by your ISP
for the WAN interface.
While you choose to obtain the IP
address automatically or use specific
IP address, you have to decide
whether to select Obtain DNS server
address automatically or Use the
following DNS server address and
enter the information provided by you
ISP.
You may check Enable NAT if
necessary.
Press Next to continue.
Primary IP Address & Subnet Mask:
Key in the IP address and the subnet
mask that provided by your ISP for
LAN interface. The primary IP address
and subnet mask for our example are
192.168.1.1 and 255.255.255.0,
respectively.
The default setting is none, shown
as the figure above. While
selecting Obtain an IP address
automatically or Use the
following IP address, the DNS
setting appears, shown as the
figure below.
MTU: Please refer to PPPoA/ PPPoE.
DHCP Server On:
Check this item if DHCP service is
needed on the LAN. The IAD will
assign IP address and gateway
address for each of your PCs. If you
enable this function, you have to enter
the information for Start IP, End IP
and Lease Time. The default value for
lease time is one day.
67
Page 76

ADSL Router User Manual
DHCP Server Off:
Check this item if DHCP service is not
needed on the LAN. We choose this
item in our example.
You can check the settings on the
Summary page now.
If you find anything incorrect, click
Back to modify the settings.
If everything is OK, click Finish to
accept these settings.
And the following page will appear.
Now, the system will reboot to activate
the new settings that you have done in
this section.
Please wait for 2 minutes before
restarting the IAD.
68
Page 77

Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Status
Overview
This page displays the current status for the ADSL connection, including the System
Up Time, ADSL speed, LAN IP address, default gateway, DNS server, firmware
version, driver version, Ethernet MAC address, and so on. The system st atus will be
different according to the settings that you configured in the web pages.
69
Page 78

ADSL Router User Manual
ADSL Line
This page shows all information for
ADSL.
For knowing the quality of the ADSL
connection, please click ADSL BER
Test button to have advanced
information.
Click More Information
show more detailed information about
ADSL Line Status.
ADSL BER Test
This test determines the quality of the
ADSL connection. It is done by
transferring idle cells containing a
known pattern and comparing the
received data with this known pattern
to check for errors.
After selecting the test duration time
and click Start, the following dialog
appears to tell you the test is running.
You can stop the test by clicking Stop
or close this dialog window by
pressing Close.
hyperlink to
70
When the test is over, the result will be
shown on the following dialog window
for your reference. Click Close to
close this window.
Page 79

Internet Connection
This page displays the connection
information for your IAD, such as the
PVC name, VPI/VCI value, service
category, protocol, invoking NAT and
Qos or not, IP address, linking status,
and so on.
Traffic Statistics
This table shows the records of data
going through the LAN and WAN
interface. For each interface,
cumulative totals are displayed for
Received and Transmitted.
You may click Reset to reset the
amount.
DHCP Table
This table shows all DHCP clients who
get their IP addresses from your IAD.
For each DHCP client, it shows the
Host Name, MAC Address, IP
Address and the Lease Time.
Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Routing Table
This table shows the routing rules that
your router uses.
ARP Table
This table shows the IP address
record for IP-to-Physical translation in
your router.
71
Page 80

ADSL Router User Manual
Advanced Setup
Local Network – IP Address
This page is the same as you can see on the Configure LAN side Settings page
while running the Quick Setup. It allows you to set IP Address and Subnet Mask
values for LAN interface.
Primary IP Address:
Key in the first IP address that you
received from your ISP for the LAN
connection.
Subnet Mask:
Key in the subnet mask that you
received from your ISP for the LAN
connection.
Host Name:
List the host name of this device.
Domain Name:
List the name of the domain.
Configure the second IP Address
and Subnet Mask:
Check this box to enter another set
of IP Address and Subnet Mask to
connect to your IAD if they are not
included in the range that DHCP
server accepts.
After checking this box, the
secondary IP address a nd subnet
mask entries will show up, as shown
in the right figure.
Secondary IP Address & Subnet
Mask: Enter the information provided
by your ISP for your LAN connection.
MTU:
It means the maximum size of the
packet that transmitted in the
network. The packet of the data
greater than the number set here will
be divided into several packets for
transmitting. Type the value into the
field of MTU. The default setting is
1500.
Apply:
Click this button to activate the
settings listed above.
72
Page 81

Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Local Network – DHCP Server
This allows you to set DHCP server on LAN interface.
DHCP Server On:
Check this item if DHCP service is
needed on the LAN. The IAD will
assign IP address and gateway
address for each of your PCs.
You have to key in Start IP Address,
End IP Address, and Lease Time.
The default lease time is 1day.
Relay On:
Click this button to have a relay
setting. And type the Server IP in the
IP field.
When the DHCP server is served by
another device rather than the IAD
itself, you can relay to that specific
server and enter the IP address of it,
as 10.3.95.2 in our example.
Server and Relay Off:
Check this item if DHCP service isn’t
needed on the LAN.
Apply:
Click this button to activate the
settings listed above.
You can reserve one specific IP
address for a certain PC for particula r
purpose. Simply add a mapping entry
of MAC address & IP address for that
PC by pressing the Reserved IP
Address List button. The window as
the one shown in the right column will
appear.
Click the Add button to open another
dialog window , shown as the right. On
PC’s MAC Address and Assigned IP
Address boxes, please type the
correct information according to your
need and click Apply.
73
Page 82

ADSL Router User Manual
The information added will be shown
on the window right away, as the right
figure illustrates. That is, the specified
address will be reserved and not be
assigned by DHCP for other
computer(s).
You may click Add button to add
another set or click Close to exit.
Local Network – UPnP
The UPnP is only available for Windows XP. If you are not a Windows XP user, you
may ignore this page.
Enabling the UPnP IGD and NAT
traversal function allows the users to
perform more applications behind NAT
without additional configuration
settings or ALG support on your
router.
You can enable the UPnP function
through this web page by checking
Enable UPnP and press Apply.
Local Network – IGMP Snooping
Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1 sender
to 1 recipient) or Broadcast (1 sender to everyone on the network). Multicast delivers
IP packets to just a group of hosts on the network.
Without IGMP snooping, multicast traffic is treated in the same manner as broadcast
traffic, that is, it is forwarded to all ports. With IGMP snooping, multicast traffic of a
group is only forwarded to ports that have members of that group. IGMP snooping
generates no additional network traffic, allowing you to significantly reduce multicast
traffic passing through your switch.
The figure below shows a simple network connected via the ADSL router. There are
four Ethernet clients and one USB client on the LAN interface.
74
Page 83

Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Now suppose the video server is the multicast transmitter and host A and D are
multicast receivers. If we do not turn on the IGMP snooping function, the router will
forward the multicast traffic to all hosts connecting to this router and consequently
block and interrupt the traffic of the other users who do not want to receive the
multicast service, shown as the following figure.
When IGMP snooping is invoked, it makes the system aware to establish the best
path for multicast service to save LAN bandwidth. Refer the figure below, just as
desired, only host A and D will actually receive multicast traffic when IGMP snooping
is enabled.
While IGMP snooping is enabled, the
IGMP packets will be monitored, the
membership information will be
recorded and processed, and the
multicast traffic will only be forwarded
to those LAN interfaces, such as
Ethernet and USB, which are bonded
to the subscribed multicast groups.
Thus it helps to save the bandwidth
and helps the devices to perform
more effectively.
Check Enable IGMP Snooping and
click Apply to invoke this function.
Note that the IGMP proxy must be
enabled first. If the IGMP Snooping
function is not available as shown in the
following figure, you have to enable the
IGMP Proxy first.
If the PVC you’re using is NAT
enabled, remember to turn on the
IGMP Proxy at the same time.
Please refer to Internet – IGMP
Proxy for more information.
75
Page 84

ADSL Router User Manual
Internet – Connections
To set WAN settings for each service, please open Advanced– Internet. This page
allows you to edit, to remove, or to add WAN settings.
If you click the Connect
under the PVC Name item, the system
will connect to WAN automatically. If
the WAN connection is OK, you can
check the detailed information directly.
You can add new PVC(s) by clicking
the Add button, edit the settings for
the present PVC by clicking
Edit column, or delete the existing
PVC by pressing
Adding a New One
To add a new WAN connection, please click the Add button. The following screen
appears.
VPI (Virtual Path Identifier):
Identifies the virtual path between
endpoints in an ATM network. The
valid range is from 0 to 255. Please
refer to the value that your ISP
provides.
VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier):
Identifies the virtual channel endpoints
in an ATM network. The valid range is
from 32 to 65535 (1 to 31 is reserved
for well-known protocols). Please refer
to the value that your ISP provides.
hyperlink
in the
icon.
Service Category:
It decides the size and rate for the
packets of the data in different service
type. There are five categories
provided here for your selection,
shown as the drop-down menu in the
right column.
If you select UBR with PCR or CBR,
you have to offer the value for the
peak cell rate.
If you choose Non Realtime VBR, or
Realtime VBR, you have to key in the
value for the peak cell rate,
sustainable cell rate, and maximum
burst size.
As you can see in the right figure, the
range for Peak Cell Rate is from 1 to
2500; the value for Sustainable Cell
Rate ranges from 1 to 2499 and must
be smaller than Peak Cell Rate, and
the range for Maximum Burst Size is
from 1 to 1000000.
76
Page 85

After pressing Next, you will see the
web page listed as the right one.
Choose the protocol that you would
like to use.
Please refer to Quick Setup for more
information if you don’t know how to
set the configuration.
Enable QoS:
Check this item to enable IP QoS for a
PVC. It can improve performance for
selected classes of applications. For
more details please refer to
Advanced/Quality of Service
section.
If you choose PPPoE (or Bridging),
you will see the option for 802.1Q
VLAN T aggi ng.
802.1Q VLAN Tagging:
802.1Q-compliant switch ports can be
configured to transmit tagged or
untagged frames. A tag field
containing VLAN (and/or 802.1p
priority) information can be inserted
into an Ethernet frame. If a port has an
802.1Q-compliant device attached
(such as another switch), these
tagged frames can carry VLAN
membership information between
switches, thus letting a VLAN span
multiple switches. However, it is
important for network administrators to
ensure ports with non-802.1Q-
compliant devices attached are
configured to transmit untagged
frames. Many NICs for PCs and
printers are not 802.1Q-compliant. If
they receive a tagged frame, they will
not understand the VLAN tag and will
drop the frame. Also, the maximum
legal Ethernet frame size for tagged
frames was increased in 802.1Q (and
its companion, 802.3ac) from 1,518 to
1,522 bytes.
Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Notice that 802.1Q VLAN
Tagging function can only be
invoked under PPPoE and
Bridging Mode; the system will
not provide this option while
setting PPPoA or IPoA mode.
After checking Enable 802.1Q VLAN
Tagging, you will have to enter a
VLAN ID, as shown in the figure.
VLAN ID:
The VLAN Identifier is a 12 bit field. It
uniquely identifies the VLAN to which
the frame belongs to and can have a
value between 0 and 4095.
Click Next to continue.
77
Page 86

ADSL Router User Manual
The WAN IP settings page will differ
slightly according to the protocol that
you choose.
This graphic is the one that you will
see if you choose the PPPoE mode in
the previous step. You can select
Enable NA T or change the MTU value
according to your needs.
The next figure following the WAN IP
Settings in the PPPoE mode is shown
at the right. You may refer to the
Quick Setup for further information.
If you choose IP over ATM from the
Connection T ype web page, you will
get a web page as the figure.
You may refer to Quick Start-
Connection T ype- IPoA section for
more information.
Add Default Route:
Check this item to add a default IPoA
route.
After rebooting your IAD, the default
route will be shown on the Routing
Table under Status menu, you may
check it.
If you choose Bridging from the
Connection T ype web page, you will
get a web page as the figure listed at
the right side.
Please refer to Quick Setup for more
information.
78
Page 87

Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Internet – DNS Server
If Enable Automatic Assigned DNS checkbox is selected, this router will accept
the first received DNS assignment from one of the PPPoA, PPPoE or MER/DHCP
enabled PVC(s) during the connection establishment. If the checkbox is not selected,
it is necessary for you to enter the primary and optional secondary DNS server IP
addresses. Finish your setting and click the Apply button to save it and invoke it.
Enable Automatic Assigned DNS:
Check this box to enable this function,
or uncheck this box to disable it. The
default setting is checked. When this
function is disabled, you have to offer
the Primary DNS server and
Secondary DNS server.
If you are satisfied with the settings,
click Apply.
Internet – IGMP Proxy
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is an Internet protocol that
provides a way for an Internet computer to report its multicast group membership to
adjacent routers.
The hosts interact with the system through the exchange of IGMP messages. When
you want to configure IGMP proxy, the system will interact with other routers through
the exchange of IGMP messages. However, when acting as the proxy, the system
performs the host portion of the IGMP task as follo ws:
¾ When being queried, the system will send membership reports to the group.
¾ When one of the hosts joins a multicast address group which none of other
hosts belongs to, the system will send unsolicited membership reports to that
group.
¾ When the last host in a particular multicast group leaves the group, the system
will send a leave group membership report to the router’s group.
Internet Connection:
This field displays the internet
connection(s) set in this router.
IGMP Proxy Enabled:
Check this box to enable this function
or uncheck this box to disable this
function.
After finish the settings, click Apply.
79
Page 88

ADSL Router User Manual
Internet – ADSL
Enable ADSL Port:
Check this box to enable this function.
It simply invokes the line mode that
you choose here for the IAD.
Select the support of line modes:
There are several selections, and you
may select them according to the line
modes supported by your ISP and
your needs.
Capability Enabled:
Two items are provided here for you to
choose.
Bitswap:
It is a mandatory receiver initiated
feature to maintain the operating
conditions of the modem during
changing environment conditions. It
reallocates the data bits and power
among the allowed carriers without
modification of the higher layer control
parameters in the ATU. After a bit
swapping reconfiguration, the total
data rate and the data rate on each
latency path is unchanged. Check this
box to enable the function. If not,
uncheck this box to close the function.
Seamless Rate Adaptation:
It enables the ADSL2/ ADSL2+ Router
to change the data rate of the
connection while in operation without
any service interruption or bit errors.
Check this box to enable the function.
If not, uncheck this box to close the
function.
80
Page 89

Chapter 4: Web Configuration
IP Routing – Static Route
The table shows all static route status and allows you to add new static IP route or
delete static route. A Static IP Routing is a manually defined path, which determines
the data transmitting route. If your local network is composed of multiple subnets,
you may want to specify a routing path to the routing table.
Destination Network Address:
Display the IP address that the data
packets are to be sent.
Netmask, Gateway, WAN Interface:
Display the subnet mask, gateway,
and WAN interface information that
the transmitting data will pass through.
Delete:
Allow you to remove the static route
settings.
Adding a New One
To add a static route, please click Add. Ty pe the destination network address,
subnet mask and gateway that you received from the ISP and click Apply.
This page shows all the routing
table of data packets going
through your ADSL Router.
Destination IP Addre ss:
The destination IP address of the
network indicates where data packets
are to be sent. You may specify an IP,
type 0.0.0.0, or leave it blank.
Netmask:
Enter the Netmask that you got from
the ISP, type 0.0.0.0, or leave it blank.
Gateway IP Address:
Check it to forward packets to the
specific gateway. Enter the gateway IP
address that you want to use.
WAN Interface:
Click this button to forward packets to
a specific WAN interface. Choose on e
from the drop-down menu.
If you have added an IPoA PVC from
Advanced- Internet Connections
webpage, you can forward packet s to
it now. Just select it from the WAN
Interface drop down menu.
Click Apply to save the setting.
You will see the result shown as the
right figure.
For example, type 192.168.1.1 in
the field of the gateway IP address
and leave the destination network
blank.
Click Apply to view the routing result.
If you don’t want the static route that
you created, please click the
the Delete column from the table.
A dialog window will appear to confirm
your action. Click OK to remove the
static route, or click Cancel to keep
the setting.
icon in
81
Page 90

ADSL Router User Manual
Example – Static Route
Here provides you an example of Static Route.
For the LAN shown above, if the PC in the subnet of 192.168.1.x wants to access
the PC in the subnet of 192.168.10.x, we can set a static route in the ADSL router, in
which the destination is the PC in the subnet 192.168.10.x and the gateway is router
B. The setting would be as follows:
Destination: 192.168.10.0
Netmask: 255.255.255.0 (Standard Class C)
Gateway: 192.168.1.254 (Router B)
IP Routing – Dynamic Routing
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is utilized by means of exchanging routing
information between routers. It helps the routers to determine optimal routes. This
page allows you to enable/disable this function.
RIP Version:
It incorporates the RIP information
when receiving and broadcasting the
RIP packets. From the drop down
menu, select a RIP version to be
accepted, 1, 2 or both.
Operation:
There are two modes for you to
choose, Active and Passive. Select
Active for transmitting and receiving
data, or select Passive for receiving
data only.
82
Enabled:
Check Enabled to enable the RIP
function on different interface.
Otherwise, disable this function.
Click Apply to invoke the settings set
here.
Page 91

Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Virtual Server – Port Forwarding
The Router implements NAT to make your entire local network appear as a single
machine to the Internet. The typical situation is that you have local servers for
different services and you want to make them publicly accessible. With NAT applied,
it will translate the internal IP addresses of these servers to a single IP address that
is unique on the Internet. NAT function not only eliminates the need for multiple
public IP addresses but also provides a measure of security for your LAN.
When the router receives an incoming IP packet requ esting for accessing your local
server, the router will recognize the service type according to the port number in this
packet (e.g., port 80 indicates HTTP service and port 21 indicates FTP service). By
specifying the port number, the router knows which service should be forwarded to
the local IP address that you specified.
After setting the virtual server, you should modify the filter rule about the port and
service information which you set on the virtual server. Because the firewall protects
the router by the filter rule, you should update the filter rule after you set up the
virtual server.
Virtual Server function allows you to make servers on your LAN accessible to
Internet users. Normally, Internet users would not be able to access a server on your
LAN because:
Your server does not have a valid external IP Address.
Attempts to connect to devices on your LAN are blocked by the firewall in this
device.
The Virtual Server feature solves these problems and allows Internet users to
connect to your servers, as illustrated below:
IP Address seen by Internet Users
Once configured, anyone on the Internet can connect to your Virtual Servers.
Please note that, in the above picture, both Internet users are connecting to the
same IP address, but using different protocols, such as Http://203.70.212.52 and
Ftp://203.70.212.52.
To Internet users, all virtual servers on your LAN have the same IP Address. This IP
Address is allocated by your ISP. This address should be static, rather than dynamic,
to make it easier for Internet users to connect to your Servers. However, you can
use Dynamic DNS feature to allow users to connect to your virtual servers by using
a URL, instead of an IP address.
83
Page 92

ADSL Router User Manual
IP addresses can be automatically redirected to local servers configured with private
IP addresses. In other words, depending on the requested service (TCP/UDP port
number), the router redirects the external service request to the appropriate serve r
(located at another internal IP address).
Add New Port Forwarding
To set a virtual server, please open the
Virtual Server item from the
Advanced setup menu.
To add a new Port Forwarding, please
click Add from the Port Forwarding
web page.
Pre-defined:
Choose one of the service types from
the first drop-down list, such as
Audio/Video, Games, and so on. In
the second drop-down list, choose the
name of the application that you want
to use with the type that you select in
the first list.
For example, if you choose
Audio/Video in the first field, the
corresponding contents of the second
field would be like the drop-down list
shown as the following figure.
User defined:
Type a new service name for building
a customized service for specific
purpose.
There are three lines that you can
enter settings into on this page. If you
need more lines, just apply the
settings and then add a new port
forwarding rule.
From Internet Host IP Address:
Select the initial place for port
forwarding. If you choose SINGLE, a
box will appear for you to fill in the IP
address for the specific host. And, if
you choose SUBNET, the boxes for IP
address and Netmask will appear for
you to fill in the IP address and subnet
mask for the specific subnet.
84
Forward to Internal Host IP
Address:
Key in the address for the host used
as the destination that information will
be forwarded to.
Page 93

For example, select the predefined
application name Audio/Video – Media
Player 7, set from ALL internet host IP
addresses, and forward to
192.168.1.200. Click Apply. Be sure
to reboot your router for these
changes to take effect.
The result will be displayed as the
following figure.
If you do not want the server that you
created, check the Delete box of that
application and click the Delete button
to discard it.
Or if you want to add another one,
click Add to add a new one.
Virtual Server – Port Triggering
When the IAD detects outbound traffic
on a specific port, it will set up the port
forwarding rules temporarily on the
port ranges that you specify to allow
inbound traffic. It is supposed to
increase the support for Internet
gaming, video conferencing, and
Internet telephony due to the
applications require multiple
connection.
Chapter 4: Web Configuration
To add a new port triggering rule, click
Add to open this web page. Then
choose an application name from the
Pre-defined list box.
The system provides 10 items for you
to choose.
You may also define by yourself, just
type the name into the field of User
defined.
Click Apply to complete the setting.
If you select AIM Talk, the result page
will be like the demo figure in the right
column.
You may delete the application by
checking the delete box and pressing
Delete.
85
Page 94

ADSL Router User Manual
Virtual Server – DMZ Host
In computer networks, a DMZ (demilitarized zone) is a computer host or small
network inserted as a "neutral zone" between a company's private network and the
outside public network. It prevents outside users from getting direct access to a
server that has company data. A DMZ is an optional and more secure approach to a
firewall and effectively acts as a proxy server as well.
To close the function of DMZ Host,
please click Discarded.
To activate a DMZ host, please click
Forwarded to the DMZ host radio
button, and enter the IP Address of
DMZ host.
Click Apply.
Once this feature is enabled, you must specify an IP address. It allows unrestricted
2-way communication between the specified IP address and other Internet users or
Servers.
This allows almost any application to be used on the specified IP address.
The specified IP address will receive all “Unknown” connections an d data.
The DMZ feature only works when the NAT function is enabled.
86
Page 95

Chapter 4: Web Configuration
Virtual Server – Dynamic DNS
The Dynamic DNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) combines both functions of
DNS and DHCP to map a dynamic IP to a fixed domain name. This page allows you
to access the virtual servers with a domain name and password.
Dynamic DNS:
Select Enable to enable DDNS; select
Disabled to disable this function.
Dynamic DNS Provider:
Choose a provider (DynDNS.org or
TZO.com) from the drop-down list.
Internet Connection:
Select the interface from the
drop-down list that you want to use for
connecting the Internet.
User Name:
Type the user name that you
registered with the provider.
Password:
Type the p assword that you registered
with the provider.
Domain Name:
Key in the domain name that you
registered. You can use letters and
dash for naming, yet other characters
are not allowed to use for preventing
from making troubles.
Status:
It displays current status.
Virtual Server – Static DNS
This page allows you to configure DNS mapping between Domain name and IP
address for your local hosts. In case you want to access the local servers with
domain names from the local network, you can configure the mapping information
on the page.
Domain Name:
Key in the domain name that you
registered at the provider . You can use
letters and dash for naming, yet other
characters are not allowed to use for
preventing from making troubles.
IP Address:
Key in the IP address for the domain
name to map.
Click Apply to upload your setting.
87
Page 96

ADSL Router User Manual
Firewall
The firewall is a kind of software that interrupts the data between the Internet and
your computer. It is the TCP/IP equivalent of a security gate at the entrance to your
company. All data must pass through it, and the firewall (function s as a security
guard) will allow only authorized data to be passed into the LAN.
What the firewall can do? It can:
deny or permit any packet from passing through explicitly
distinguish between various interfaces and match on the following fields:
source and destination IP address
port
To keep track of the performance of IP Filter, a logging device is used. The device
supports logging of the TCP/UDP and IP packet headers and the first 129 bytes of
the packet (including headers) whenever a packet is su ccessfully passed through or
blocked, and whenever a packet matches a rule being setup for suspicious packets.
An example for firewall setup:
This picture shows the most common and easiest way to employ the firewall.
Basically, you can install a packet-filtering router at the Internet gateway and then
configures the filter rule in the router to block or filter protocols and addresses. The
systems behind the router usually have a direct access to the Internet; however
some dangerous services such as NIS and NFS are usually blocked.
For the security of your router, set the firewall is an important issue.
Firewall – IP Filtering
This page allows you to specify the IP packet filtering rules to prevent the se rvices
accessed from the Internet hosts or limit the Internet access for local hosts.
Choose Disabled to disable the
firewall function. Click Enabled to
invoke the settings that you set in this
web page.
To initiate the IP Filtering, select the
Enabled radio button and click Apply.
Select the direction to filter
packets: Inbound means the data is
transferred from outside onto your
computer. Outbound means the data
is transferred from your computer onto
outside through Internet. Please
choose Outbound traffic or Inbound
traffic as the direction for filtering
packets.
88
Click Add to add a new IP Filtering
rule.
Page 97

This page provides some settings for
you to adjust for adding a new
outbound IP Filtering.
Allow Traffic:
Choose No to stop the data
transmission, Yes to permit the data
pass through.
Protocol:
Here provides several default policies
for security levels for you to choose. If
you don’t want to use the predefined
setting, you can use User Defined to
set a customized protocol according to
the necessity.
When you choose User Defined
setting, you have to enter a port
number in the “as” field.
Source/Destination IP address:
To specify IP address to allow or deny
data transmission, please pull down
the drop-down menu to choose a
proper one.
Chapter 4: Web Configuration
The setting All means that all the IP
addressed in the network are allowed
or denied to pass through in Internet.
If you choose Single, you will have to
key in the specific IP address as the
start/end point to let the router identify
for granting or denying passing
through.
If you choose Subnet, you will have to
enter the specific IP address and
netmask as the start/end point to let
the router identify for granting or
denying passing through.
Port Range:
The port range is from 0 to 65535.
Please key in the start point and end
point for the IP Filtering.
After finish the settings, click Apply.
Here provides an example shown in
the right column. Select TCP as the
Protocol type, and make the Source
and Destination IP address to
include All, then type 0 and 65535 as
the start and end port.
89
Page 98

ADSL Router User Manual
A new IP filtering setting for Outbound
traffic is created in the web page. To
edit the setting, please click
into the editing page. To delete the
setting, click
another IP filtering, click Add again.
To add a new Inbound IP Filtering,
click Inbound traffic in the item of
Select the direction to filter packets
on the IP Filtering page. Use the
same way to add a new one as stated
above.
Quality of Service
QoS (Quality of Service) is an industry-wide initiative to provide preferential
treatment to certain subsets of data, ena bling that data to traverse the Internet or
intranet with higher quality transmission service.
to erase it. To set
to get
Quality of Service – Bridge QoS
To classify the upstream traffic by
assigning the transmission priority for
different users’ data, please use
Bridge QoS to prioritize the data
transmission.
The Bridge QoS allows you to set the
settings based on layer two bridge
packets.
Traffic Class Name:
Key in a name as the traffic class for
identification.
802.1p Priority:
Each incoming packet will be mapped
to a specific priority level, so that
these levels may be acted on
individually to deliver traffic
differentiation. Please choose the
number (from 0 to 7, low to high
priority) for the 802.1p Priority.
Traffic Priority:
There are three options – Low,
Medium, and High that you can
choose.
90
Page 99

IP Precedence:
The number you choose here decides
the type of the IP address processed.
No change is the default setting.
IP type of Service:
The system provides some types of
service for you to choose. The
meaning of each type is the same as
the denotation. The default one is No
change.
If you set the LAN 802.1p Priority 0
as the traffic condition, choose Low
traffic priority for this rule, and set IP
Precedence, IP type of service, and
WAN 802.1p as no change , after
clicking Apply, you will get the result
as the figure in the right column.
Thus when the users’ data matches
the traffic condition, the transmission
will get a low traffic priority.
Chapter 4: Web Configuration
You may check the Delete box and
press Delete to discard it, or click Add
to create more.
Quality of Service – IP QoS
To classify the upstream traffic by
assigning the transmission priority of
the data for different users, please use
IP QoS to prioritize the data
transmission.
The IP QoS allows you to set the
settings based on layer three IP
packets.
To add a new IP QoS setting, press
Add in the page of Quality of
Service – IP QoS, a page same as
the right side will appear.
Traffic Class Name:
Type a name as the traffic class for
identification.
Protocol:
Choose a proper interface for this
function. If you don’t know how to
select, simply use the default one.
91
Page 100

ADSL Router User Manual
Source IP/ Subnet Mask/ Port:
Key in the source IP address (ex.:
192.168.1.0) and subnet mask (ex.:
255.255.255.0) for the application (ex.:
FTP, HTTP, and so on) that you want
to invoke the QoS traffic rule. You may
simply enter the source port, ranging
from 0 to 65535, as the traffic
condition.
Destination IP/ Subnet Mask/ Port:
Enter the destination IP address
(ex.: 168.95.1.88) and subnet mask
(ex.:255.255.255.0) for the application
that you want to invoke the QoS traffic
rule. Or simply enter the destination
port for the traffic condition; it ranges
from 1 to 65535.
Traffic Priority/ IP Precedence/ IP
type of Service: Please refer to
Bridge QoS.
After you click Apply, the new QoS
setting will be shown as the graphic on
the right side.
According to the example, we set four
rules for IP QoS. In traffic A, we set
1-1024 as the destination port, and
the traffic priority is low; in traffic B, the
source port is from 201 to 8000, and
the priority is medium; in traffic C,
when the source IP is 192.168.1.0,
subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, the
traffic priority is high; in traffic D, when
the traffic is heading to 168.95.1.88,
the priority is high.
To delete the rules you set, simply
click the check button below Delete
item and click Delete button.
According to our example, the IP QoS configuration can be illustrated by the
following figure.
While there are many PCs
getting online, the PCs using
port 201-8000 to access the
internet will have medium
traffic priority, the PCs
carrying 192.168.1.x/
255.255.255.0 as IP address
will have high traffic priority.
In addition, PCs heading to
port 1-1024 will have a low
priority, while the PCs
accessing 168.95.1.88 will
have a high priority.
92
 Loading...
Loading...