Page 1

SIMATIC
Preface
Basics
Installation and licensing
PCS 7 Engineering
1
2
3
4
PCS 7 process control system
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual
System configurations
OpenPCS 7 interface
Appendix
Lists and folders
5
6
A
B
05/2012
A5E02780178-02
Page 2

Legal information
Warning notice system
This manual contains notices you have to observe in order to ensure your personal safety, as well as to prevent
damage to property. The notices referring to your personal safety are highlighted in the manual by a safety alert
symbol, notices referring only to property damage have no safety alert symbol. These notices shown below are
graded according to the degree of danger.
DANGER
indicates that death or severe personal injury will result if proper precautions are not taken.
WARNING
indicates that death or severe personal injury may result if proper precautions are not taken.
CAUTION
with a safety alert symbol, indicates that minor personal injury can result if proper precautions are not taken.
CAUTION
without a safety alert symbol, indicates that property damage can result if proper precautions are not taken.
NOTICE
indicates that an unintended result or situation can occur if the relevant information is not taken into account.
If more than one degree of danger is present, the warning notice representing the highest degree of danger will be
used. A notice warning of injury to persons with a safety alert symbol may also include a warning relating to property
damage.
Qualified Personnel
The product/system described in this documentation may be operated only by personnel qualified for the specific
task in accordance with the relevant documentation, in particular its warning notices and safety instructions. Qualified
personnel are those who, based on their training and experience, are capable of identifying risks and avoiding
potential hazards when working with these products/systems.
Proper use of Siemens products
Note the following:
WARNING
Siemens products may only be used for the applications described in the catalog and in the relevant technical
documentation. If products and components from other manufacturers are used, these must be recommended or
approved by Siemens. Proper transport, storage, installation, assembly, commissioning, operation and
maintenance are required to ensure that the products operate safely and without any problems. The permissible
ambient conditions must be complied with. The information in the relevant documentation must be observed.
Trademarks
All names identified by ® are registered trademarks of Siemens AG. The remaining trademarks in this publication
may be trademarks whose use by third parties for their own purposes could violate the rights of the owner.
Disclaimer of Liability
We have reviewed the contents of this publication to ensure consistency with the hardware and software described.
Since variance cannot be precluded entirely, we cannot guarantee full consistency. However, the information in
this publication is reviewed regularly and any necessary corrections are included in subsequent editions.
Siemens AG
Industry Sector
Postfach 48 48
90026 NÜRNBERG
GERMANY
A5E02780178-02
Ⓟ 05/2012 Technical data subject to change
Copyright © Siemens AG 2012.
All rights reserved
Page 3

Table of contents
1 Preface.........................................................................................................................................................7
2 Basics...........................................................................................................................................................9
2.1 General..........................................................................................................................................9
2.2 Microsoft basics...........................................................................................................................10
2.3 OPC Foundation..........................................................................................................................11
2.4 Components of OpenPCS 7........................................................................................................12
2.5 OLE DB interface.........................................................................................................................14
2.6 COM / DCOM components of OpenPCS 7.................................................................................14
3 Installation and licensing.............................................................................................................................17
3.1 Hardware requirements...............................................................................................................17
3.2 Installing the OpenPCS 7 station.................................................................................................17
3.3 Licensing of the OpenPCS 7 station............................................................................................19
3.4 Licensing the OS-internal OPC server........................................................................................20
4 PCS 7 Engineering.....................................................................................................................................23
4.1 Configuring an OpenPCS 7 station.............................................................................................23
4.2 OpenPCS 7 and OS application on a shared PC station............................................................24
4.3 Configuring an OPC client...........................................................................................................25
4.4 Loading the OpenPCS 7 station..................................................................................................26
4.5 Configuration support with the PCS 7 project wizard..................................................................27
5 System configurations................................................................................................................................31
5.1 General configuration..................................................................................................................31
5.2 OpenPCS 7 without OS...............................................................................................................33
5.3 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS..............................................................................................34
5.3.1 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS client.....................................................................................34
5.3.2 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS server or CAS.......................................................................35
5.3.3 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS single station........................................................................36
5.4 OpenPCS 7 station for multiple PCS 7 projects..........................................................................38
5.5 DA linking of two PCS 7 projects using OpenPCS 7...................................................................39
5.6 Access to a CAS via OpenPCS 7................................................................................................40
5.7 OpenPCS 7 security concept......................................................................................................41
5.8 Settings in the Windows Firewall for Open PCS 7......................................................................42
5.9 Users and passwords in a workgroup.........................................................................................43
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 3
Page 4

Table of contents
6 OpenPCS 7 interface..................................................................................................................................45
6.1 Access options............................................................................................................................45
6.2 Data transmission........................................................................................................................45
6.3 OPC Data Access (OPC DA)......................................................................................................46
6.3.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................46
6.3.2 Introduction to the OPC Data Access interface...........................................................................46
6.3.3 How the OPC DA server works...................................................................................................47
6.4 OPC Historical Data Access (OPC HDA)....................................................................................48
6.4.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................48
6.4.2 How the OPC HDA server works.................................................................................................48
6.4.3 Data structure of the OPC HDA server........................................................................................49
6.4.4 Overview of supported attributes.................................................................................................50
6.4.5 Overview of supported aggregate functions................................................................................50
6.4.6 Overview of supported functions.................................................................................................51
6.4.7 Time format of the OPC HDA server...........................................................................................52
6.4.8 Quality codes of the OPC HDA server........................................................................................54
6.4.9 Write access supported by the OPC HDA server........................................................................54
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)..........................................................................................55
6.5.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................55
6.5.2 Introduction to OPC A&E.............................................................................................................55
6.5.3 Mapping the PCS 7 OS message system on OPC A&E.............................................................57
6.5.4 Mapping the message classes and message types of PCS 7 OS on OPC A&E........................59
6.5.5 Mapping priorities of PCS 7 OS messages to OPC A&E............................................................59
6.5.6 Attributes of the PCS 7 OS message system..............................................................................60
6.5.7 Acknowledgment concept............................................................................................................61
6.5.8 Quality codes for OPC A&E.........................................................................................................64
6.5.9 OPC A&E with hierarchical access..............................................................................................64
6.5.9.1 Differences between OPC A&E and OPC A&E with hierarchical access....................................64
6.5.9.2 Example 1: Messages are not assigned to any area...................................................................66
6.5.9.3 Example 2: Messages are assigned to an area..........................................................................69
6.5.9.4 Example 3: Messages of an area are assigned to an alarm hiding group..................................71
6.5.10 Upgrading with OPC A&E............................................................................................................73
6.5.10.1 Updating PCS 7 projects with OPC A&E.....................................................................................73
6.5.10.2 How to update an OPC project with PCS 7 V8.0.........................................................................73
6.6 OPC Historical Alarms and Events (OPC "H" A&E)....................................................................74
6.6.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................74
6.6.2 Introduction to OPC "H" A&E.......................................................................................................75
6.6.3 Reading archived messages.......................................................................................................75
6.6.4 Syntax for access to archived messages....................................................................................76
6.6.5 Read modes for archived messages...........................................................................................78
6.6.6 Identifying archived messages....................................................................................................79
6.7 OLE DB.......................................................................................................................................80
6.7.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................80
6.7.2 Basics of OLE DB........................................................................................................................81
6.7.3 Establishing the connection to the database...............................................................................82
6.7.4 Access to the OLE DB provider...................................................................................................83
6.7.5 Querying archive data.................................................................................................................85
6.7.5.1 Representation of the process value archive..............................................................................85
OpenPCS 7
4 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 5

Table of contents
6.7.5.2 Querying process value archives................................................................................................85
6.7.5.3 Representation of the message archives....................................................................................89
6.7.5.4 Querying the message archive....................................................................................................91
A Appendix.....................................................................................................................................................93
A.1 Commissioning............................................................................................................................93
B Lists and folders..........................................................................................................................................95
B.1 List of sources.............................................................................................................................95
B.2 List of abbreviations/acronyms....................................................................................................95
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 5
Page 6

Page 7

Preface
Purpose of this manual
PCS 7 is an open system that allows access to process values, archived process values and
hardware interrupts by third-party applications. PCS 7 uses the industry standard of the OPC
Foundation, OPC Data Access, OPC Alarm and Events and OPC Historical Data Access for
this purpose. PCS 7 also supports access by third-party applications using the database
mechanism, WinCC OLE DB.
This documentation describes OPC access to one or more PCS 7 OS servers using the
OpenPCS 7 station.
This documentation will familiarize you with the steps required to configure the OpenPCS 7
station in PCS 7 and demonstrate the configuration options.
To familiarize yourself in detail with the topics relating to the OPC interfaces, you will also
require the OPC-documentation from the OPC Foundation. You can download the
documentation from the Internet at www.opcfoundation.org (
Required basic knowledge
You require general knowledge of automation engineering to understand this manual. Because
OpenPCS 7 is based on the PCS 7 process control system, you should also be familiar with
the operation of PCS 7.
1
www.opcfoundation.org).
Basic knowledge of the general use of the PC/programming device and of the use of the
Windows operating system is required. If you want to develop an OPC client application, you
will also need to be able to work with Microsoft Visual Basic or Microsoft Visual C++.
Target Audience of this Documentation
This documentation is intended for PCS 7 users and SIMATIC S7 specialists.
Options for accessing PCS 7 documentation
Note
PCS 7 Readme
The information given in the
PCS 7 manuals. Please read this
and amendments on PCS 7.
● The
● After installation of PCS 7, you can find documents such as Process Control System
PCS 7 Readme
important information regarding PCS 7 and takes precedence over the PCS 7
documentation supplied.
7; PCS 7 Readme
Information > <Language>.
on the
and
What's New in PCS 7?
PCS 7 Readme
PCS 7 Readme
Process Control System; SIMATIC PCS 7
on the Internet takes precedence over all the
carefully; it contains important information
via the submenu SIMATIC > Product
DVD contains
PCS
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 7
Page 8

Preface
As of PCS 7 V8.0, you receive basic PCS 7 system documentation with the
System; SIMATIC PCS 7
The PCS 7 Internet site www.siemens.de/pcs7-dokumentation (www.siemens.com/pcs7-
documentation) provides convenient access to the complete PCS 7 documentation. You can
find the following for the latest PCS 7 versions:
● In the section "Hardware manuals for SIMATIC PCS 7 ..."
– The manuals for components approved for a PCS 7 version
● In the section "Software manuals for SIMATIC PCS 7 ..."
– The complete system documentation
– The separate setup program for PCS 7 documentation and the PCS 7 help system for
download. After the installation of the setup program, you will find the documentation at
the following locations on the Engineering Station:
- As online help (CHM file) for the SIMATIC Manager application
- As a PDF file in the Windows Start menu with the SIMATIC documentation
– The complete documentation for PCS 7 as a
Validity of the documentation
This documentation is valid for the software package
PCS 7
, V8.0 or higher.
Process Control
DVD.
Manual Collection
Process Control System; SIMATIC
OpenPCS 7
8 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 9
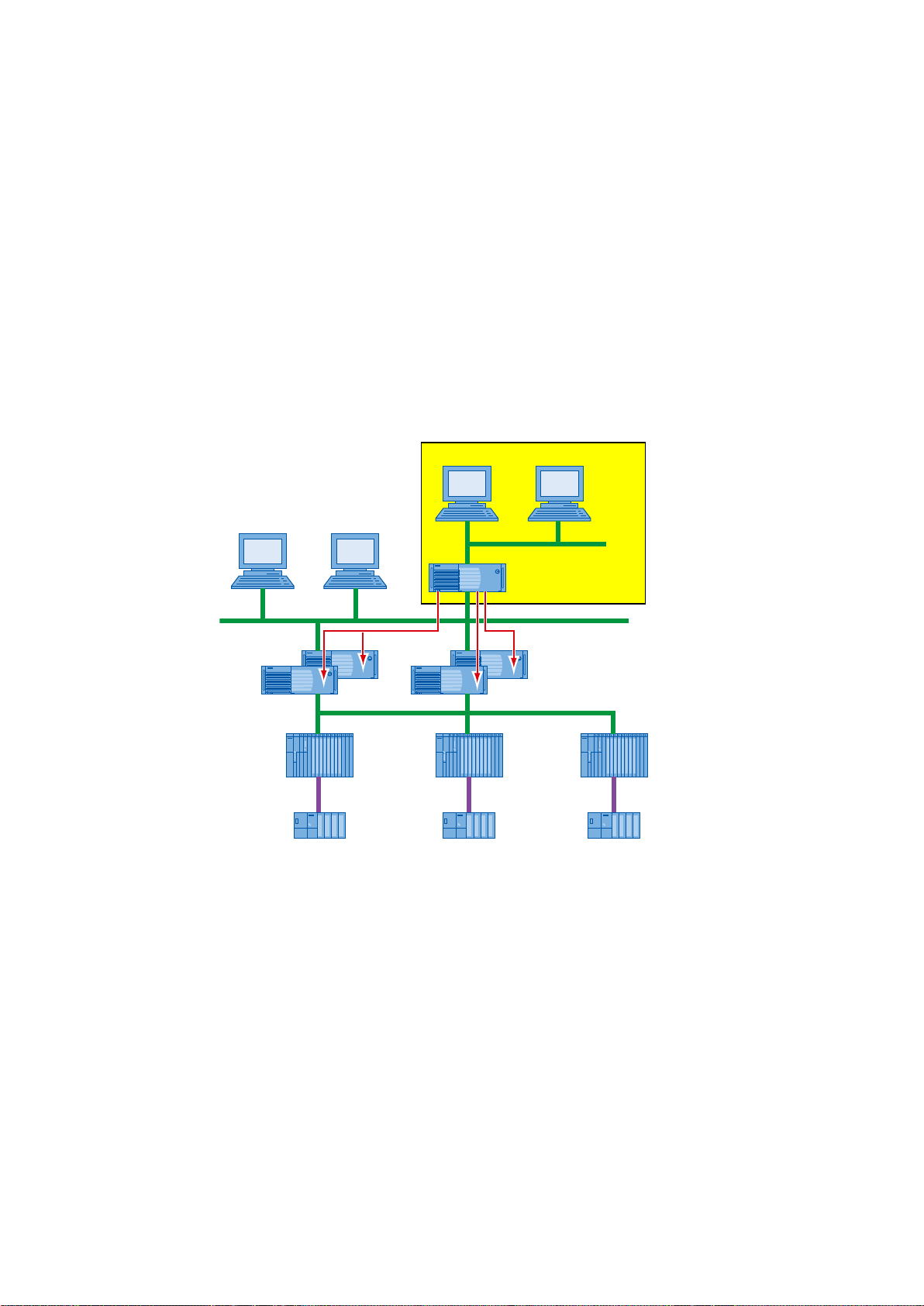
Basics
S7-400S7-400S7-400
ET 200ET 200ET 200
OpenPCS 7 Station
PCS 7 OS-Clients
OPC-Clients
PCS 7 OS-Server
Plant bus
Terminal bus
Fieldbus
2.1 General
Overview
Higher-level process control systems for production planning, process data evaluation, and
process data management can access SIMATIC PCS 7 process data via the OpenPCS 7
station. The higher-level systems are OPC clients of the OpenPCS 7 station.
2
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 9
Depending on the system configuration, the OpenPCS 7 station can provide data from various
OS servers and from the central archive server. The OpenPCS 7 station hides the distribution
of the data in terms of:
● Time period (OS1, OS2, …, CAS / Process Historian)
● Location (OS1, OS2, …, CAS / Process Historian) and
● Redundancy (OS1 master, OS1 standby …)
OpenPCS 7 replaces @PCS 7previously available in the context of SIMATIC PCS 7 and is,
at the same time, the equivalent of the Connectivity Station and the Connectivity Pack of the
WinCC SCADA system. Direct access to SIMATIC BATCH and SIMATIC Route Control data
is not possible with OpenPCS 7.
Page 10

Basics
2.2 Microsoft basics
Layout
The OpenPCS 7 station can be operated in various configurations:
● OpenPCS 7 station without OS client, based on a SIMATIC PCS 7 Industrial Workstation
in the client version. This is the recommended preferred configuration.
● OpenPCS 7 station on an OS client.
● OpenPCS 7 station on a central archive server (CAS)
● OpenPCS 7 station on an OS single station.
● OpenPCS 7 station on the OS server.
Note
The hardware and software requirements of the PC station on which OpenPCS 7 is to be
installed must be met.
2.2 Microsoft basics
Microsoft basics
The basis of OPC is provided by several Microsoft technologies. These technologies are
explained in the following section.
OPC
OPC stands for "OLE for Process Control".
OPC is a standardized, vendor-independent software interface that allows data to be
exchanged between hardware and software. One system can provide another system with
process data via OPC .
OLE
OLE means "Object Linking and Embedding", the technology for embedding objects in
documents.
COM
COM means "Component Object Model" and is necessary for the use of OPC.
COM is a central component of Windows operating systems and controls the interaction
between multiple software components. By using COM , the OPCserver effectively becomes
part of the Windows operating system and is therefore not dependent on file names, storage
locations and versions.
COM defines a standard that allows objects to be defined as self-contained units in Windows
and to access these units beyond the limits of a process.
OpenPCS 7
10 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 11

DCOM
Object
Events
Basics
2.3 OPC Foundation
COMobjects can be understood as extensions of the operating system. They are not
dependent on programming languages and are available in principle to all applications.
The data and code of the object are not directly accessible to the user of the COMobject.
DCOM is the acronym for "Distributed Component Object Model". It is based on COM
technology and provides the additional option of communicating over a network.
Objects are defined by properties and methods that can be used on objects.
An event is used to control program flow. Program execution is not linear, instead special event
handling routines are executed whenever a specific event occurs.
In terms of OpenPCS 7 and the OPC standard, Events mean messages / operation messages
of the PCS 7-system.
DLL
It is possible to use DLLs with Microsoft Visual Basic (VB) and Microsoft Visual Basic for
Applications (VBA). DLL stands for Dynamic Link Library. A DLL is a dynamic link library. Users
can link the functionalities of a DLL into their own applications. If you want to program an
OPCclient with VB, make sure that the relevant automation interface DLL is selected in the
VB Editor in "Project > References".
Collection
Collections are objects that support count and item properties. A collection consists of a certain
number of items. An item can be collection-specific, any data structure, or an object. The count
property specifies the number of items in a collection. In Microsoft Visual Basic, each item in
a collection can be identified using loops.
2.3 OPC Foundation
OPC Foundation
The aim of the OPC Foundation is to ensure compatibility between different subsystems in
automation and process control engineering. Compatibility is achieved by creating and
maintaining open specifications for the standardization of communication between subsystems
of different manufacturers. This allows process data, alarms and messages as well as archived
process data to be exchanged between subsystems regardless of their manufacturer.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 11
Page 12

Basics
2.4 Components of OpenPCS 7
The OPC Foundation has more than 300 members worldwide. These include the most
important manufacturers of control systems, process instrumentation and process control
systems worldwide. SIEMENS is a member of the OPC Foundation.
The declared goal of the OPC Foundation is vertical integration of information from the field
level through to the enterprise level. Using the OPC standard, this integration is possible
regardless of the system and manufacturer.
The most important standards of the OPC Foundation for OpenPCS 7
● Data Access Custom Interface Standard
● Data Access Automation Interface Standard
● Historical Data Access Specification Standard
● Historical Data Access Automation Interface Standard
● Alarms and Events Custom Interface Standard
● Alarm & Events Automation Interface Standard
2.4 Components of OpenPCS 7
Overview
OpenPCS 7 provides the following components:
● OPC DA (Data Access server)
● OPC HDA (Historical Data Access server)
● OPC A&E (Alarms & Events server)
● OPC "H" A&E (Historical Alarms & Events server)
● OLE DB
In the following graphic, you can see all the OPC components that will run on the OpenPCS
7 station. The figure also shows the PCS 7environment. OLE DB starts a direct database query
on the PCS 7 OS server.
OpenPCS 7
12 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 13
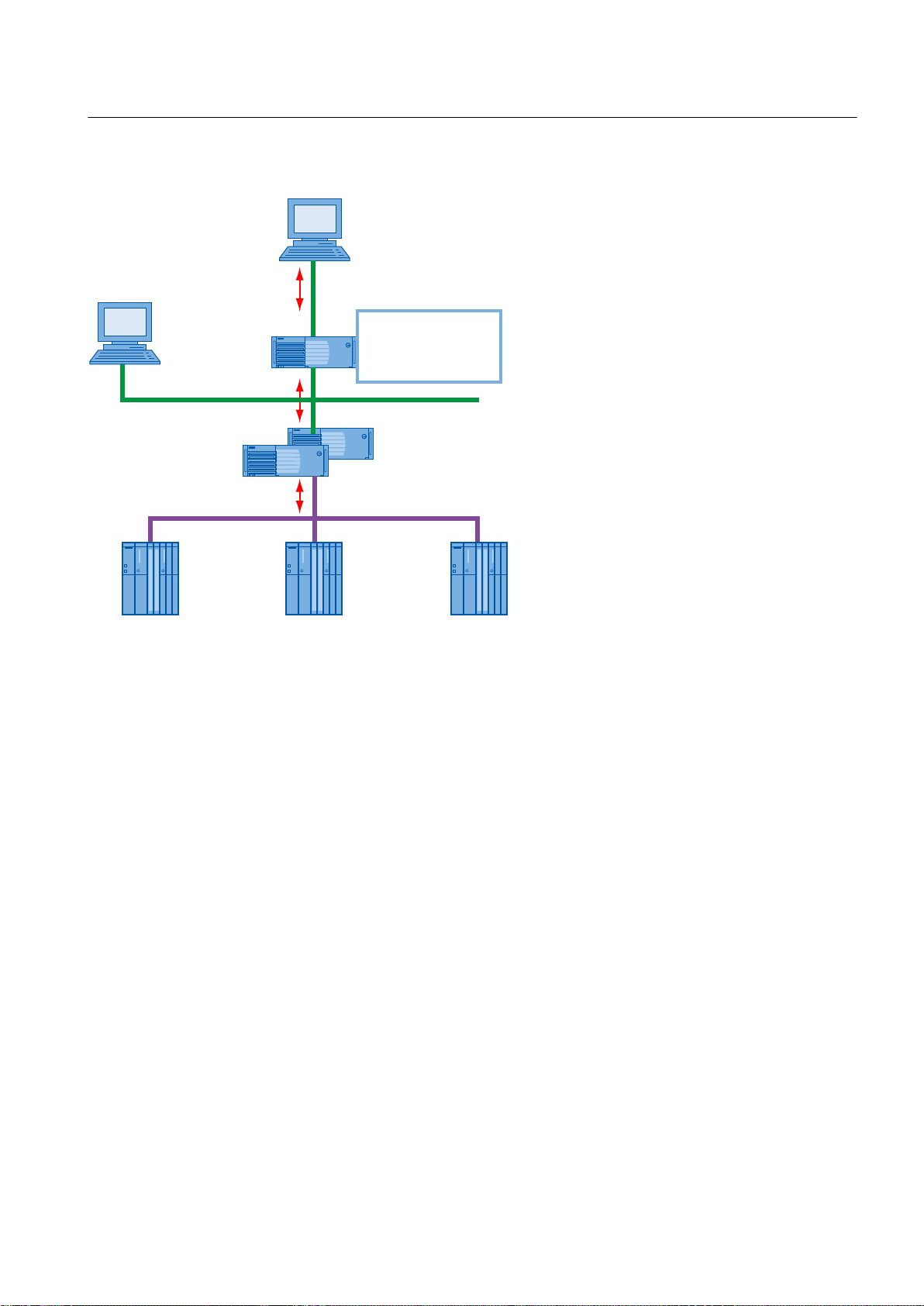
OpenPCS 7 Station
AS
Plant bus
Terminal bus
Office network
PCS 7 OS client
PCS 7 OS ser ver
OPC client
OPC DA server
OPC HDA ser ver
OPC A&E server
OPC “H” A&E ser ver
Basics
2.4 Components of OpenPCS 7
OPC DA (Data Access server)
For read and write access to process values according to the OPC specification OPC DA
V1.00, V2.05a, V3.00.
As an OPC DA server, the OpenPCS 7 station provides other applications with current data
from the OS data management. The OPC DA client can register for current changes or write
values.
OPC HDA (Historical Data Access server)
For read access to archived process values according to the OPC Specification OPC HDA
V1.20.
As an OPC HDA server, the OpenPCS 7 station provides other applications with historical data
from the OS archive system. The OPC client - for example a reporting tool - can specifically
request the data required by specifying the start and end of a period. Various aggregate
functions, such as variance, mean value, or integral, allow preprocessing by the OPC HDA
server and contribute to a reduction in the communication load.
OPC A&E (Alarms & Events server)
For read access to messages, alarms and events according to the OPC Specification OPC
A&E V1.10.
As an OPC A&E server, the OpenPCS 7 station forwards OS messages with all the associated
process values to the subscribers at the production and enterprise management level. OS
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 13
Page 14

Basics
2.6 COM / DCOM components of OpenPCS 7
messages can also be acknowledged via this server. Filter mechanisms and subscriptions
ensure that only selected, changed data is transmitted.
OPC "H" A&E (Historical Alarms & Events server)
For read access to archived alarms and messages.
Thanks to an expansion of the OPC standard interface by Siemens, the OpenPCS 7 station
is also able to transfer historical alarms and messages from the archive to the subscribers at
production and enterprise management levels.
OLE-DB
The WinCC OLE DB provider allows standardized and direct access to the archive data in the
Microsoft SQL server database on the OS server.
This setup permits access to all OS archive data, along with the associated process values,
message texts, and user texts.
2.5 OLE DB interface
OLE DB
The WinCC OLE DB Provider allows access to the process value and message archives.
Compressed process value archives are made available uncompressed. OLE DB is used to
read the PCS 7 OS or archive server database remotely.
OLE DB is an open standard for fast access to different databases. The connection between
the OLE DB level and the database is established by a database provider.
The WinCC OLE DB provider, which is integrated in the OpenPCS 7 station, enables
transparent access to archived process data of the following PCS 7 stations:
● PCS 7OS server
● Central archive server
2.6 COM / DCOM components of OpenPCS 7
COM / DCOM components used by OpenPCS 7
● OPC client runs on the OpenPCS 7 station
If the OPC client and OPC server process run on one computer, the OPC client accesses the
local OPC server object using an "in-process server" component via LRPC and a stub object.
OpenPCS 7
14 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 15
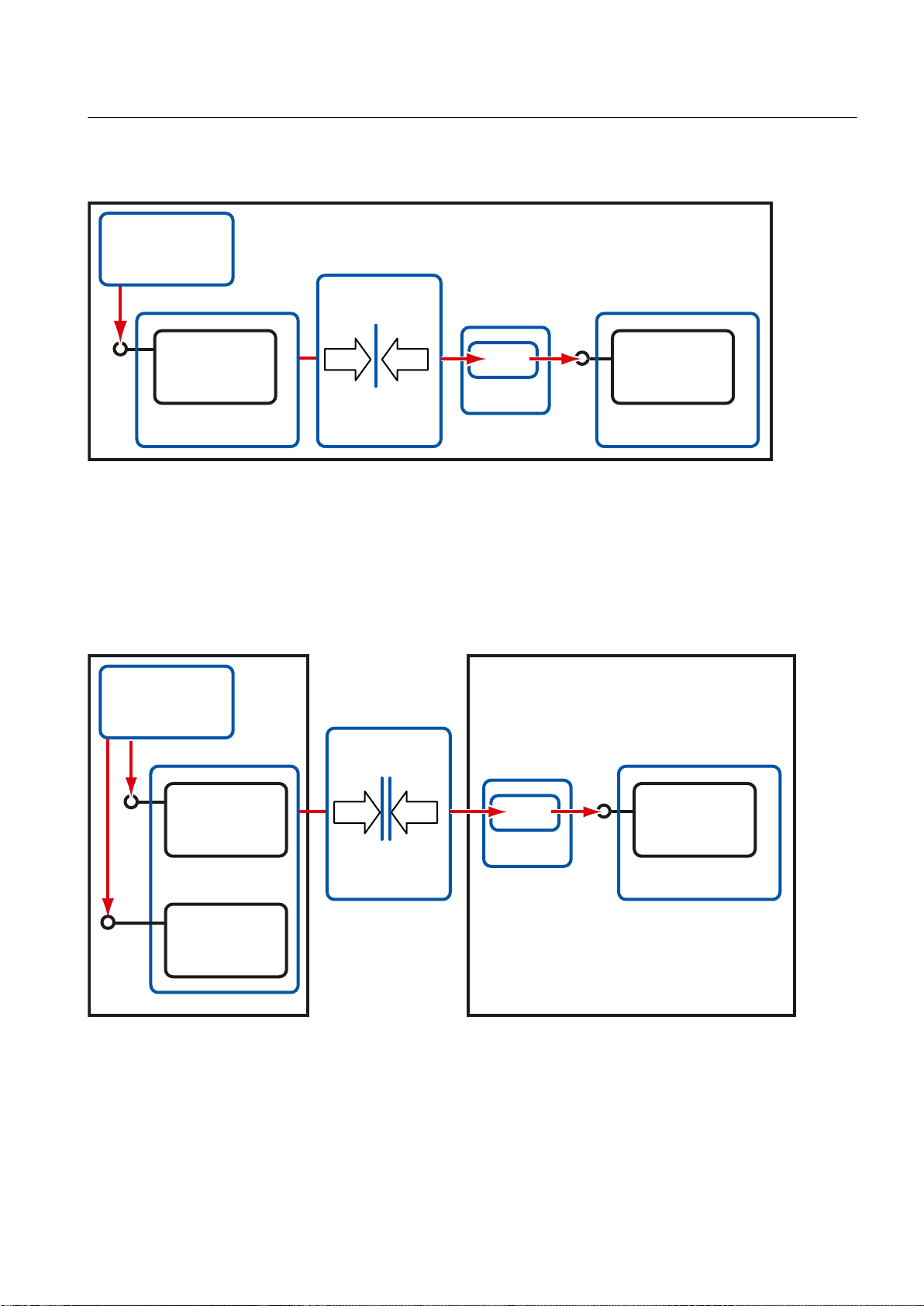
,Q3URFHVV
&20
&RPSRQHQW
,Q3URFHVV6HUYHU
/RFDO2EMHFW
/RFDO6HUYHU
&20
/53&/53&
&URVVSURFHVV
ZLWK/LJKWZHLJKW
53&
,QWHUSURFHVV
&RPPXQLFDWLRQ
&OLHQW
$SSOLFDWLRQ
2SHQ3&66WDWLRQ
6WXE
/RFDO2EMHFW
3UR[\
5HPRWH2EMHFW
3UR[\
&20
5HPRWH2EMHFW
5HPRWH6HUYHU
&20
53&53&
&URVVQHWZRUN
ZLWKWUXH53&
,QWHUSURFHVV
&RPPXQLFDWLRQ
&OLHQW
$SSOLFDWLRQ
23&&OLHQW2SHQ3&66WDWLRQ
6WXE
Basics
2.6 COM / DCOM components of OpenPCS 7
● OPC client runs on a separate computer
If the OPC client and the OPC server process run on separate computers, the OPC client
accesses a local and a remote proxy object. These objects communicate via RPC and a stub
object, with the OPC server object on a different computer.
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is a technique used for communication between different
processes. The processes typically run on different computers.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 15
Page 16

Page 17
Installation and licensing
3.1 Hardware requirements
Recommended configuration for PC stations
Use PC components according to the recommendations for SIMATIC PCS 7 PC stations.
3
For additional information, refer to the
Minimum hardware configuration of the PC stations
Parameter Performance data
Processor Intel Pentium IV
Clock-pulse rate >= 2.0 GHz
Hard disk >= 120 GB
Minimum partition size C:\ 20GB
Work memory (RAM) 1 GB
Communications interfaces for
terminal bus communication
Communications interfaces for
OPC client communication
Opt. drive DVD-ROM
RJ-45 on-board Gigabit Ethernet
INTEL PCI network adapter for connection to Industrial Ethernet
(10/100/1000 Mbps), with RJ-45 connector
3.2 Installing the OpenPCS 7 station
PCS 7readme file
.
OpenPCS 7 stations in different configurations
Configuration Requirements for installation Intended use of the software Program packages for the
installation
OpenPCS 7 station
without OS client
OpenPCS 7 station with
OS client
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 17
Installation requirements for the
SIMATIC PCS 7 Workstation with
OS client configuration
Installation requirements for the
SIMATIC PCS 7 Workstation with
OS client configuration
This serves as software for a
separate OpenPCS 7 station
without OS client functionality.
This serves to expand an
existing OS client with the
functionality of an OpenPCS 7
station.
● ""OpenPCS 7"" package
● "OpenPCS 7 with OSClient" package
(corresponds to the
software packages:
"OpenPCS 7" + "OS
Client")
Page 18
Installation and licensing
3.2 Installing the OpenPCS 7 station
Configuration Requirements for installation Intended use of the software Program packages for the
installation
OpenPCS 7 station on
the OS single station
OpenPCS 7 station on
the CAS
OpenPCS 7 station on
the OS server
Installation requirements for the
OS single station
Installation requirements for the
CAS
Installation requirements for the
OS server
This serves to expand an
existing OS single station with
the functionality of an
OpenPCS 7 station.
This serves to expand an
existing Central Archive
Server with the functionality of
an OpenPCS 7 station.
This serves to expand an
existing OS server with the
functionality of anOpenPCS 7
station.
● "OpenPCS 7" package
● Package "OS Single
Station"
● "OpenPCS 7" package
● Package "Central
Archive Server"
● "OpenPCS 7" package
● Package "OS-Server"
Requirement
Procedure
Note
If you only purchase the "OpenPCS 7 (OS Client)" software package, you will only receive
the license for OpenPCS 7 . The required licenses for OS clients must be obtained additionally
and must be available on the computer at runtime.
Message queuing must be installed.
An example procedure for the standalone variant is explained below:
1. Insert the "SIMATIC Process Control System; PCS 7" DVD in the DVD drive.
2. Run the "SETUP.exe" installation program.
3. Select the setup language and click "Next".
4. Close all programs and click "Next".
5. Read the product instructions and click "Next".
6. Accept the license conditions and click "Next".
7. Select the setup type "Install" and click "Next".
8. Enter the user information and click "Next".
9. Select the package installation and click "Next".
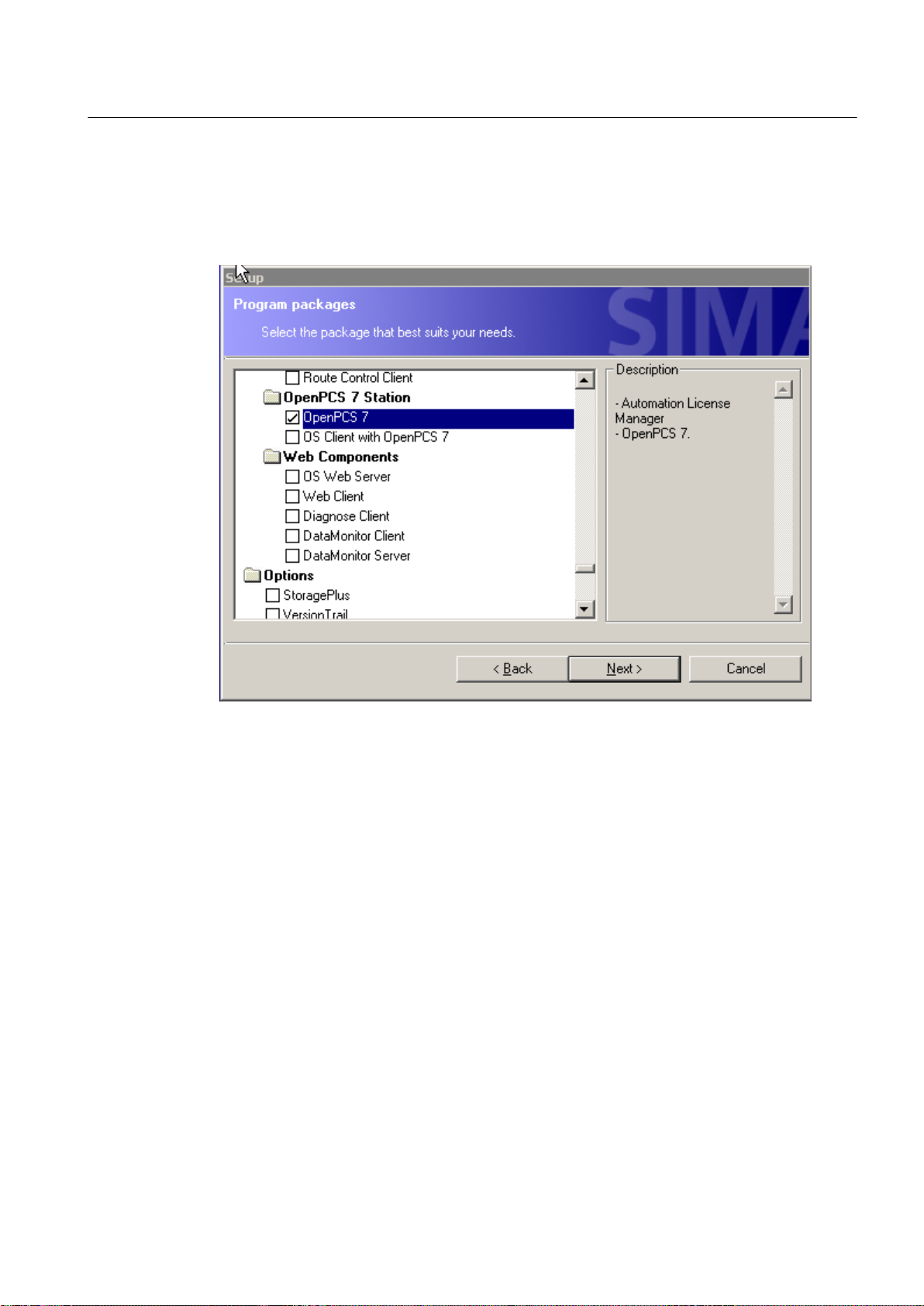
10.Select the program package and click "Next".
If, for example, you want to select the OpenPCS 7 station without OS client, click on
OpenPCS 7".
OpenPCS 7
18 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 19
3.3 Licensing of the OpenPCS 7 station
11.Check the components selected for installation and click "Next".
12.Click the "Install" button.
The following picture shows the selection for the program package:
Installation and licensing
Additional information
● You can find additional information about different modules in the manual
System PCS 7; PC Configuration and Authorization
.
Process Control
3.3 Licensing of the OpenPCS 7 station
General
Two licenses are available for OpenPCS 7. The licenses for the OpenPCS 7 station are license
keys that must be transferred directly to the machine on which the OpenPCS 7 station runs
using the Automation License Manager. A license is required for each OpenPCS 7 station.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 19
Page 20

Installation and licensing
3.4 Licensing the OS-internal OPC server
The licenses for an OpenPCS 7 station are single licenses. This means that a license server
cannot be used for OpenPCS 7.
Note
PCS 7data can be accessed via OpenPCS 7 under the following conditions as regards license
keys:
● The OpenPCS 7 station / OS require a license for a PCS 7 OS. This is applicable for all
configurations of the OpenPCS 7 station.
● If you use the "OpenPCS 7 station" license key, you can always access PCS 7data via
OpenPCS 7.
● Access to the corresponding PCS 7data is only ensured when a license is available.
Licenses for OpenPCS 7
The following licenses are available for OpenPCS 7. The order numbers are available in the
current PCS 7 catalog or in the online catalog.
License Description
OpenPCS 7 station / OSLicense for the software for expanding an existing OS client, single station or
CAS with OpenPCS 7 station functionality.
This is a single license for one installation.
OpenPCS 7 station License for one OpenPCS 7 software installation for a separate OpenPCS 7
station based on the hardware of the SIMATIC PCS 7 workstation (client
version).
Note
This is a single license for one installation.
OPC client - server connections
On a PC with the Microsoft XP operating system, Microsoft permits 10 connections between
PCs. COM access between an OPC client and the OpenPCS 7 station does not count as a
connection in this sense.
3.4 Licensing the OS-internal OPC server
Licensing
The PCS 7 OS provides the following internal OPC servers on an OS server or an OS single
station:
● SOPCSRVRWinCC.exe for OPC DA
● SOPCAESRVRWinCC.exe for OPC A&E
● SOPCHDASRVRWinCC.exe for OPC HDA
OpenPCS 7
20 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 21

Installation and licensing
3.4 Licensing the OS-internal OPC server
These internal OPC servers can be used with OpenPCS 7-licenses. This is only possible if the
"OpenPCS 7 station / OS" or "OpenPCS 7 station" license is available on the OS station.
Note
If the internal OPC servers of an OS station are used, this represents additional load in terms
of the OS station's performance.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 21
Page 22

Page 23

PCS 7 Engineering
4.1 Configuring an OpenPCS 7 station
Introduction
The OpenPCS 7 station is configured as a SIMATIC PC station in the SIMATIC Manager. It
includes the "SPOSA application" object. SPOSA is the acronym for Single Point Of System
Access. The OPC client application can also be executed on the OpenPCS 7 station. During
configuration, the following steps need to be taken:
● Insertion of a SIMATIC PC station
● Insert and configure the SPOSA application in the hardware configuration of the SIMATIC
PC station
If you created the multiproject with the PCS 7wizard, you will already have inserted an
OpenPCS 7 station if you selected the appropriate option. You can also insert an OpenPCS
7 station by expanding the project later with the "Expand Project" PCS 7wizard. The steps
required to create an OpenPCS 7 station manually are explained in the following section.
Requirement
4
Procedure
The PCS 7 project is open. You have created the OS servers and generated the server
packages.
1. Select the project into which you want to insert the OpenPCS 7 station, in the component
view of the SIMATIC Manager.
2. Select the menu command "Insert > Station > SIMATIC PC Station".
A new SIMATIC PC station is inserted into the selected project.
3. Select the SIMATIC PC station, select the menu command "Edit > Object Properties" and
enter the desired name for the PC station and the computer name.
4. Select the SIMATIC PC station in the component view and open the hardware configuration
by double-clicking on the "Configuration" object in the detailed view.
The SIMATIC PC station hardware configuration opens.
5. If the hardware catalog is not visible, select the menu command "View > Catalog".
6. Select the SPOSA application from "SIMATIC PC Station > HMI" in the hardware catalog
and drag it to the configuration table.
7. Save and compile the hardware configuration using the menu command "Station > Save
and Compile"
8. Expand the newly created PC station and the SPOSA application in the SIMATIC Manager.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 23
Page 24
PCS 7 Engineering
4.2 OpenPCS 7 and OS application on a shared PC station
9. Open the object properties of the "Open_PCS7_Station(1)" object and enter the download
path to the OpenPCS 7 station in the "CPU" tab.
10.Right-click on the "Open_PCS7_Station(1)" object to open the shortcut menu and select
"Assign OS Server...".
11.Assign the PCS 7 OS server packages to the SPOSA application.
12.Open the hardware configuration of the OpenPCS 7 station and select the menu command
"Station > Save and Compile".
13.Right-click on the "Open_PCS7_Station(1)" object to open the shortcut menu and select
"CPU > Download".
4.2 OpenPCS 7 and OS application on a shared PC station
Configuration
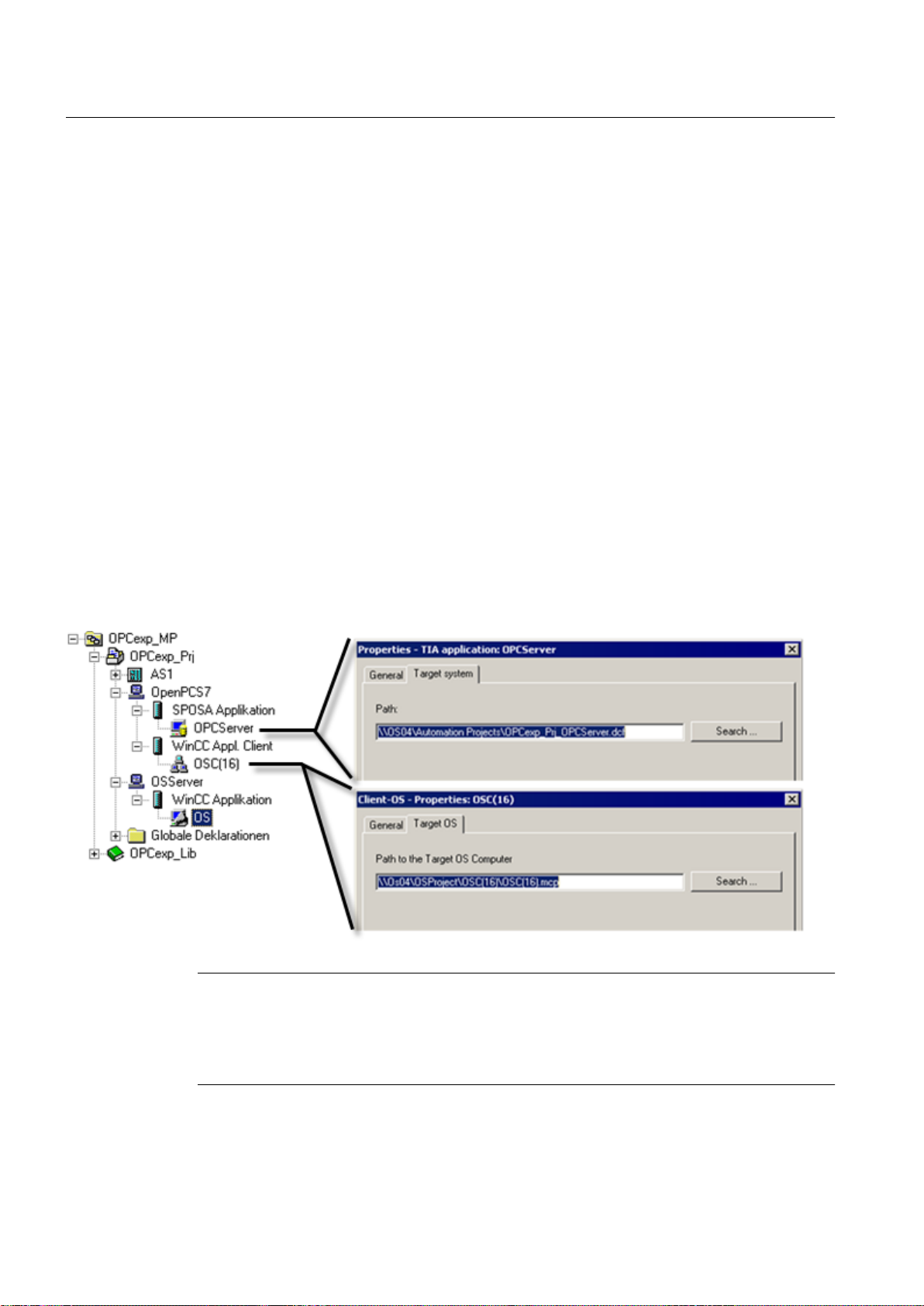
In the hardware configuration of the PC station, you configure a "SPOSA application" and a
"WinCC application client". Likewise, you can configure a "WinCC application", "CAS
application" or "CAS application standby". You specify the path to the target system of the
OpenPCS 7-computer in the object properties of the "SPOSA application". You configure the
path to the target OS computer in the object properties of the "OS client application".
Note
In a PCS 7-version lower than V7.1, a SPOSA application and an OS client cannot be
configured on the same SIMATIC PC station. In a PCS 7-version lower than V7.1, two PC
stations with the same computer name but with different PC station names must be
configured.
OpenPCS 7
24 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 25

4.3 Configuring an OPC client
OPC client engineering within PCS 7
OPC client engineering is not part of the PCS 7 engineering. No PC station is inserted and
configured in the SIMATIC Manager. In the SIMATIC Manager, only the OpenPCS 7 station
OPC client configuration outside PCS 7
is configured.
Note
If you want to use the SIEMENS OPC Automation Interfaces, the OPC client must be
executed either on the OpenPCS 7 station or you will have to take steps manually to ensure
that the required files exist and are registered on the OPC client. Refer to the section "
Configuring an OPC client computer".
An OPC client communicates with the OpenPCS 7 station via a network connection. We
recommend that you install a firewall between the OPC client and the OpenPCS 7 station if
the OPC client is on a non-secure network. So that communication between the OPC client
and OpenPCS 7 station works correctly, you need to configure the firewall and configure the
DCOM settings on the PC on which the OPC client is being executed. You will find the relevant
settings in the documentation of the OPC client and the firewall.
Note
PCS 7 Engineering
4.3 Configuring an OPC client
The DCOM and firewall settings for the Windows operating system are described in the
documentation "Using OPC via DCOM with Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2" from the
OPC Foundation.
Note
If you want to use an OPC client on a PC without an OpenPCS 7-installation, you will need
to install the OPC proxy / stub components of the OPC Foundation. You can install these
with the "OPC Core Components 3.00 Redistributable" setup of the OPC Foundation. In this
case, you should also check the installation instructions of the OPC client vendor.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 25
Page 26

PCS 7 Engineering
4.4 Loading the OpenPCS 7 station
Additional information
● You can find more information about PCS 7 security concepts in the manual
concept
.
4.4 Loading the OpenPCS 7 station
Requirements
● The following components are installed on the PC station:
– Operating system
– OpenPCS 7 station software
● The terminal bus is configured on the OpenPCS 7 station.
● The OpenPCS 7 station is connected to the engineering station via the terminal bus.
● The protocol for the communication on the terminal bus is set to TCP/IP.
● The OpenPCS 7 station is configured in the PCS 7project.
● The user logged in on the ES can access the shared Windows folder "\\<OpenPCS 7
Station>\Automation Projects". The folder is located on the OpenPCS 7 station in the path
"C:\Program Files\SIEMENS".
● The PCS 7multiproject is open on the ES.
PCS 7Security
Procedure
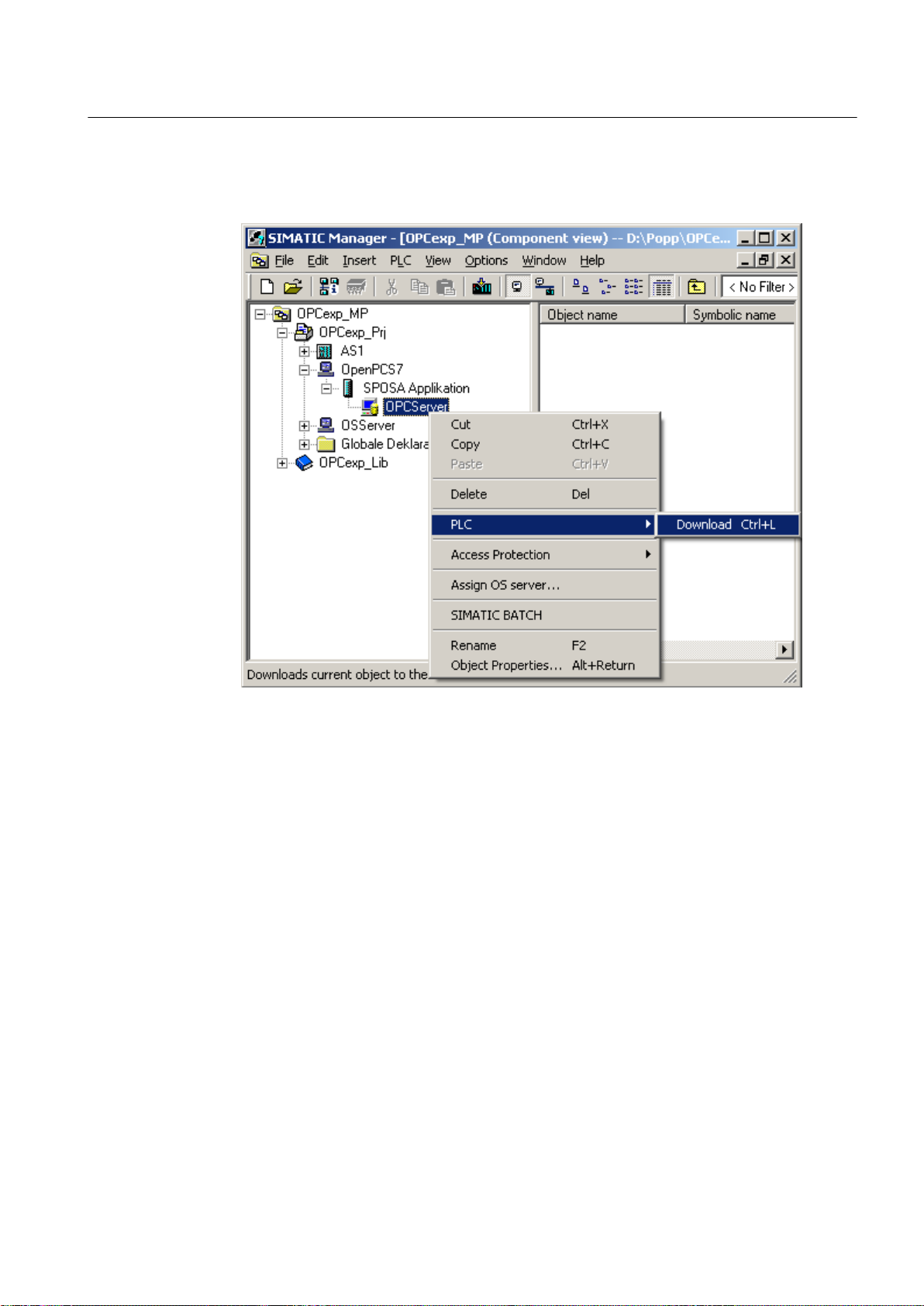
1. Expand the PC station of the OpenPCS 7 station.
2. Expand the SPOSA application.
OpenPCS 7
26 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 27
4.5 Configuration support with the PCS 7 project wizard
3. Right-click on the object below the SPOSA application.
4. Select " CPU > Download".
PCS 7 Engineering
4.5 Configuration support with the PCS 7 project wizard
The PCS 7 project wizard
The PCS 7project wizard supports you when creating a PCS 7project including an OpenPCS
7 station. In the following example, we will create the minimum configuration for a PCS 7project
with an OpenPCS 7 station. We will only deal with the configuration steps on the ES that relate
to the OpenPCS 7 station. AS / OS engineering and downloading of the project are not dealt
with at this point.
Requirement
You have an engineering station with at least a PCS 7 V8.0 installation.
Example
1. Open SIMATIC Manager.
2. Start the PCS 7project wizard in the SIMATIC manager using the " File > ' New Project'
Wizard" menu.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 27
Page 28
PCS 7 Engineering
4.5 Configuration support with the PCS 7 project wizard
3. Click the "Next" button in the "Introduction" dialog.
4. Select the required CPU in the "Which CPU are you using in your project?" dialog and then
click the "Next" button.
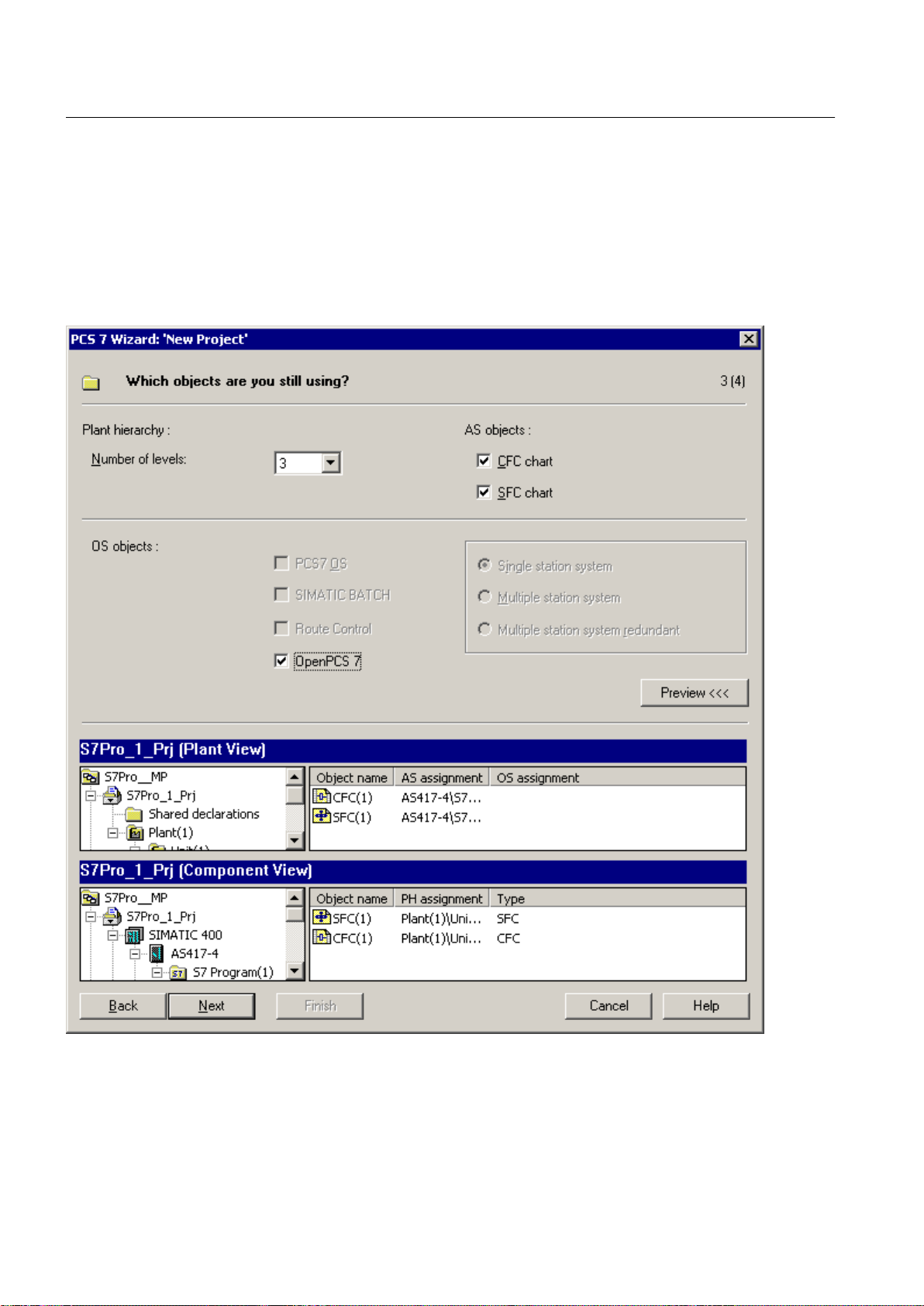
5. Click the " Preview >>>" button.
6. Select the "OpenPCS 7" option in the "Which objects are you still using?" dialog.
7. Click "Continue".
8. Enter a directory name in the "Directory name" box in the "Where do you want to store the
multiproject?" dialog.
OpenPCS 7
28 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 29
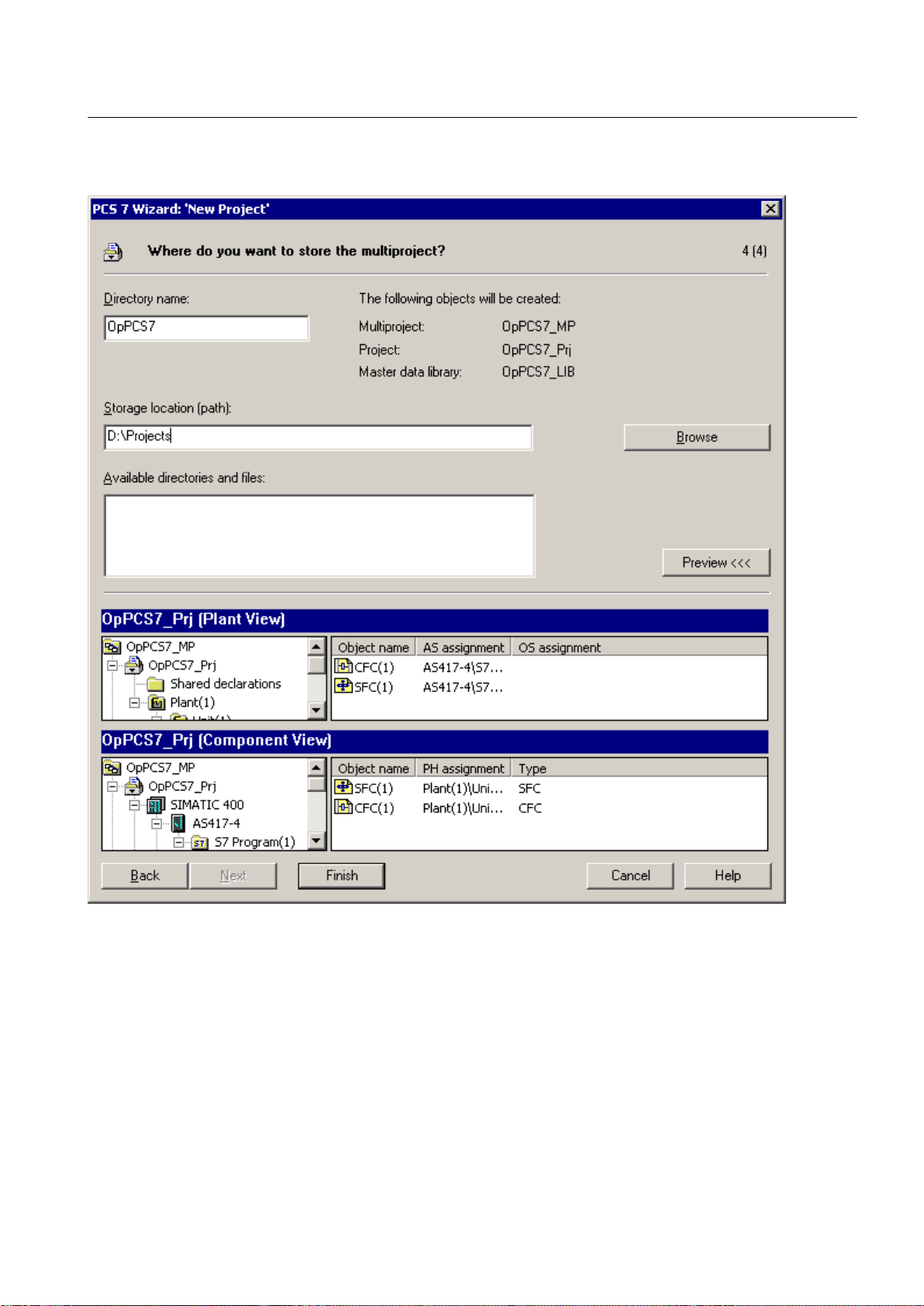
4.5 Configuration support with the PCS 7 project wizard
9. Click the "Browse" button and set the path for the storage location.
PCS 7 Engineering
10.Click the "Finish" button.
11.Click "OK" in the "Message Number Assignment" dialog.
12.Insert a new PC station in your project.
13.Enter the computer name in the object properties of the PC station.
14.Open the hardware configuration and insert an OS application.
15.Compile the OS.
16.Open the context menu of the OpenPCS 7 station.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 29
Page 30

PCS 7 Engineering
4.5 Configuration support with the PCS 7 project wizard
17.Assign the OS server to the OpenPCS 7 station.
18.Following this, you will need to complete the project with the AS and OS engineering and
download the project.
OpenPCS 7
30 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 31

System configurations
S7-400S7-400S7-400
ET 200ET 200ET 200
OpenP CS 7
Station
Plant bus
Terminal bus
Fieldb us
PCS 7 OS clients
PCS 7 OS se rver BATCH serve rRoute Co ntrol se rver Archi ve server
OPC client
5.1 General configuration
General OpenPCS 7configuration
In process mode, the OpenPCS 7 station communicates with the automation systems via the
operator station (OS server).
With the OpenPCS 7 station, you can access the data of redundant PCS 7 OS server pairs.
If the PCS 7 OS master server fails, the redundant OS server is automatically connected for
the next read job.
If the connection aborts during a read job, the OpenPCS 7 station also attempts to read the
data from the redundant OS server.
The OpenPCS 7 station cannot directly access the data of the BATCH server and Route
Control server. SIMATIC BATCH and SIMATIC Route Control use blocks in the automation
system. These blocks have OS tags for operator control and monitoring at the OS level. These
OS tags are available via OPC DA. SIMATIC BATCH and SIMATIC Route Control also use
an OS server as a message server. These messages are available via OPC A&E.
The data of the central archive server (CAS) is made available to the OpenPCS 7 station via
OPC HDA and OPC "H" A&E.
Note
5
The OS server requires the CAS package for the OpenPCS 7 station to provide OS server
alarms archived on the CAS to an OPC client.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 31
Page 32

System configurations
5.1 General configuration
OpenPCS 7
32 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 33

5.2 OpenPCS 7 without OS
Plant bus
Terminal bus
Fieldbus
PCS 7 OS clients
OPC clients
PCS 7 OS ser ver BATCH serverRoute Control server
Archive server
S7-400S7-400S7-400
ET 200ET 200ET 200
OpenPCS 7 Station
OpenPCS 7 station without installed OS client
In this configuration, the OpenPCS 7 station is installed without an OS client. The OPC clients
run on a separate PC. All OPC clients access the OpenPCS 7 station. The OpenPCS 7 station
contains the OPC DA, OPC HDA and OPC A&E servers.
This configuration is intended for large plants.
System configurations
5.2 OpenPCS 7 without OS
Construct redundant connections for OpenPCS 7 stations in PCS 7
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 33
No redundant OpenPCS 7 station is implemented in PCS 7.
You can create redundancy of sorts by running several identical OpenPCS 7 stations. This
requires that your OPC client has the following functionality:
● Determination of the OpenPCS 7 station through which the necessary information is
available.
● Detection of failure of an OpenPCS 7 station and failover to an available OpenPCS 7
station
Page 34

Plant bus
Terminal bus
Fieldbus
PCS 7 OS clients
PCS 7 OS ser ver BATCH serverRoute Control server Archive server
OpenPCS 7 station
PCS 7 OS client
OPC client
S7-400S7-400S7-400
ET 200ET 200ET 200
System configurations
5.3 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS
5.3 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS
5.3.1 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS client
OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS client
In this configuration, an OS client is also installed on the OpenPCS 7 station. The OPC client
also runs on the OpenPCS 7 station. The OpenPCS 7 station contains the OPC DA, OPC HDA
and OPC A&E servers. This configuration is intended for small plants.
The OPC client can also run on a separate computer. This configuration is intended for small
to medium-sized plants.
OpenPCS 7
34 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 35

Plant bus
Terminal bus
Fieldbus
PCS 7 OS clients
PCS 7 OS ser ver BATCH serverRoute Control server
Archive server
OpenPCS 7 station
PCS 7 OS client
OPC client
S7-400S7-400S7-400
ET 200ET 200ET 200
System configurations
5.3 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS
5.3.2 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS server or CAS
OpenPCS 7 on a server
PCS 7 supports the OpenPCS 7 station on the following servers:
● OS server
● Central archive server (CAS)
The preferred configuration for large PCS 7plants is a separate OpenPCS 7 station.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 35
Page 36

PCS 7 OS Client 1
PCS 7 OS Server 1
Plant bus
Terminal bus
Fieldbus
OPC client
PCS 7 OS Server 2
PCS 7 OS Client 2
Archive server
OpenPCS 7 station
S7-400 S7-400 S7-400
ET 200 ET 200ET 200
System configurations
5.3 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS
Example configuration for the central archive server:
Redundant configuration
5.3.3 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS single station
OpenPCS 7 on an OS single station
If the CAS is implemented redundantly, the OpenPCS 7 station can also be operated on both
servers.
Note
If the OpenPCS 7 station is operated on both CAS machines, the redundancy switchover of
the OPC client must be implemented on the OPC client.
PCS 7 supports an OpenPCS 7 station running on an OS single station. This provides the data
from one or more OS servers to OPC clients.
Configuration:
OpenPCS 7
36 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 37
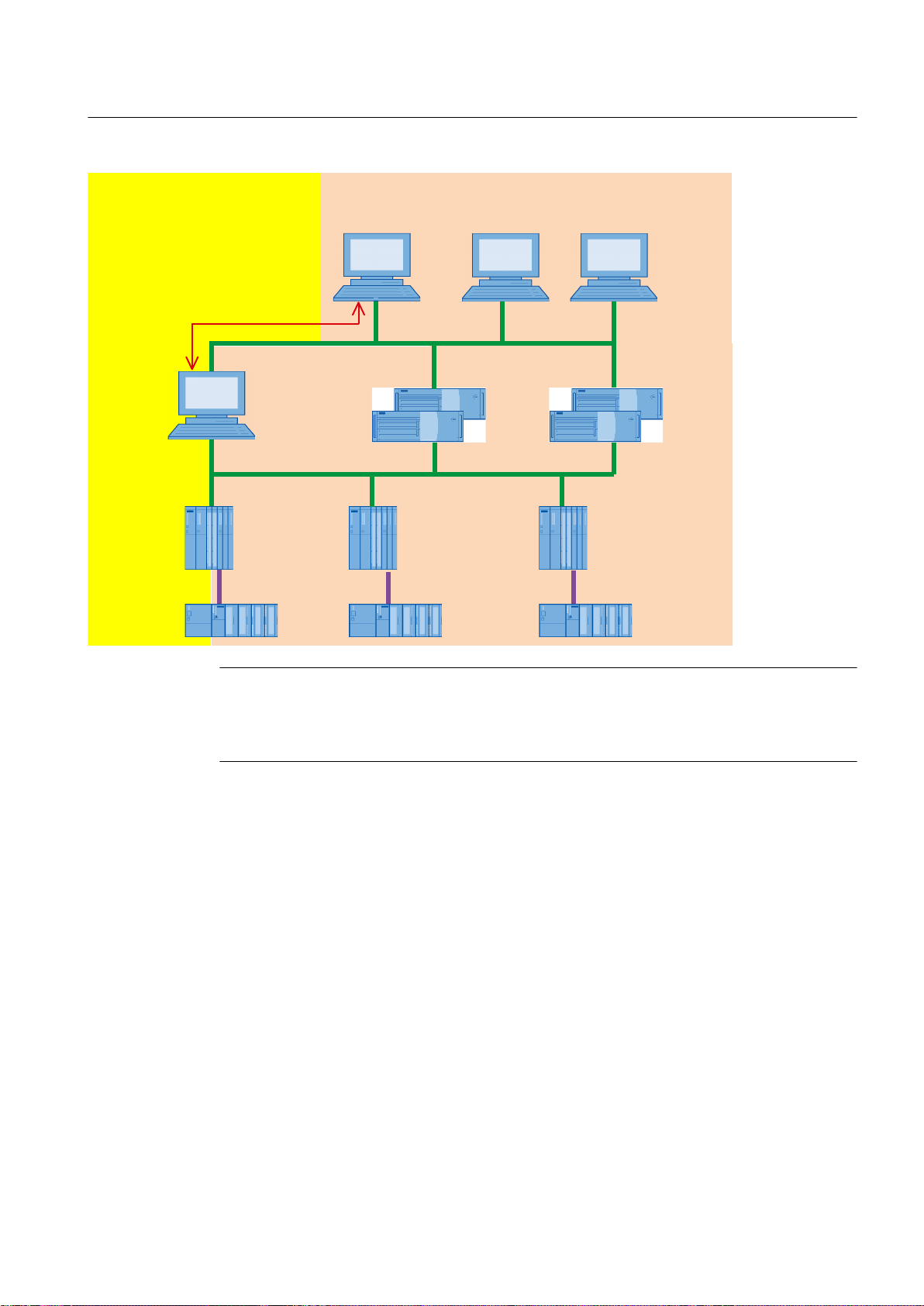
S7-400 S7-400 S7-400
ET 200 ET 200ET 200
OS single station
with parallel
OpenPCS 7 station
PCS 7 OS Client 1
PCS 7 OS Server 1
Plant bus
Terminal bus
Fieldbus
OPC client
PCS 7 OS Server 2
PCS 7 OS Client 2
OS multiple-station system
OS single-station system
System configurations
5.3 OpenPCS 7 combined with an OS
Note
An OS single station has no OS server package. This means it cannot be assigned to an
OpenPCS 7 station. For this reason, the data of an OS single station cannot be made
available to an OPC client using OpenPCS 7.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 37
Page 38

OpenPCS 7
Station
S7-400
ET 200
S7-400
ET 200
OPC client
Plant bus
Terminal bus
Fieldbus
Plant bus
Fieldbus
PCS 7 Project BPCS 7 Project A
PCS 7 OS ser ver PCS 7 OS ser ver
PCS 7 OS client PCS 7 OS client
System configurations
5.4 OpenPCS 7 station for multiple PCS 7 projects
5.4 OpenPCS 7 station for multiple PCS 7 projects
Example configuration
In this example configuration, an OpenPCS 7 station is used to make OS server data from two
PCS 7 projects available. Multiple OS servers can also be used per PCS 7project.
This example configuration has been released for identical PCS 7 versions in the PCS
7projects A and B.
Note
Hybrid configurations with regard to PCS 7versions are disabled.
Configuration
A SIMATIC PCS 7 station with a SPOSA application is configured in every PCS 7 project. The
SPOSA application is assigned to the OS server of the relevant PCS 7project. The same path
to the target system is configured and downloaded in both SPOSA applications.
38 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
OpenPCS 7
Page 39

Plant bus
Terminal bus
Fieldbus
PCS 7 Project BPCS 7 Project A
PCS 7 OS ser ver
OPC channel as
OPC client
PCS 7 OS ser ver
PCS 7 OS client
PCS 7 OS ser ver
OPC coupling
OpenPCS 7 station
PCS 7 OS client
Scalance S 612
S7-400
ET 200
S7-400
ET 200
5.5 DA linking of two PCS 7 projects using OpenPCS 7
5.5 DA linking of two PCS 7 projects using OpenPCS 7
Plant configuration of the OPC DA link
The PCS 7 OS servers can also be used as OPC clients. The "OPC" channel is the OPC client
application of the PCS 7 OS. Information on the configuration of the OPC channel is available
in the WinCC Information System in the section "WinCC Information System/Communication/
OPC Channel". In this configuration, the OpenPCS 7 station can make data from several OS
servers available for Project A via OPC.
System configurations
Application 1:
Application 2:
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 39
There are two PCS 7projects, Project A and Project B, in a plant network. For technical reasons,
Project A needs to visualize data of Project B. The OPC channel of the PCS‑7 OS can be
used for this purpose.
If PCS 7Project A and PCS 7Project B use different PCS 7versions, but support the same OPC
version: The OPC channel of the PCS 7 OS can be used for this purpose.
Page 40

System configurations
5.6 Access to a CAS via OpenPCS 7
Application 3:
This configuration can also be used if Project B is a third-party product that provides an OPC
server and not a PCS 7 project. The requirement is that both projects support the same OPC
standard.
Note
The OPC channel can only be used for OPC DA.
5.6 Access to a CAS via OpenPCS 7
Access to a central archive server (CAS) via OpenPCS 7
In a PCS 7project, the data archived on the PCS 7 OS server can be transferred to a central
archive server. You access the data on the central archive server via the OpenPCS 7 station,
OPC HDA and OPC "H" A&E.
The OpenPCS 7 station hides the communication between the OpenPCS 7 station, PCS 7 OS
server and the central archive server. The OPC client always directs its query to the OpenPCS
7 station.
The access mechanism with OPC "H" A&E is as follows:
The OPC client sends the query to the OpenPCS 7 station. The OpenPCS 7 station sends the
query to the PCS 7 OS server. The OS server sends the query to the CAS if the time period
in question is no longer available on the OS server and then forwards the data to the OpenPCS
7 station.
If, while reading messages on an operator station, you wish to use OPC Alarms & Events to
gain additional access to messages for this OS that are stored in an archive on a CAS, then
you will need to carry out the following configuration steps:
1. Assign the CAS to the OS server as well in the configuration in the SIMATIC manager.
(Right-click on the OS project, choose "Assign server", select "CAS".)
2. For all alarm controls of the OS server, you must deactivate the "All servers" check box
and select only those servers (with the exception of the CAS) whose messages are to be
displayed.
Note
When a time range is specified in an alarm control, the messages archived in the CAS
are automatically included - even if the CAS was not one of the servers selected.
The access mechanism with OPC HDA is as follows:
The OPC client sends its query to the OpenPCS 7 station. The OpenPCS 7 station accesses
the CAS directly using OPC HDA. The CAS package must be assigned to the OpenPCS 7
station.
OpenPCS 7
40 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 41

OpenPCS 7 Station
S7-400
ET 200
Terminal bus
Plant bus
Fieldbus
OPC client
PCS 7 OS ser ver Archive server
System configurations
5.7 OpenPCS 7 security concept
In the following picture OpenPCS 7 is shown with the central archive server:
5.7 OpenPCS 7 security concept
Plant configuration with firewall
The following figure shows the schematic structure of a PCS 7plant with an OpenPCS 7 station
and firewall. The PCS 7security cell is separated from the demilitarized zone (DMZ) by a
Microsoft ISA server firewall. The OpenPCS 7 station is placed in the DMZ. The DMZ is also
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 41
Page 42
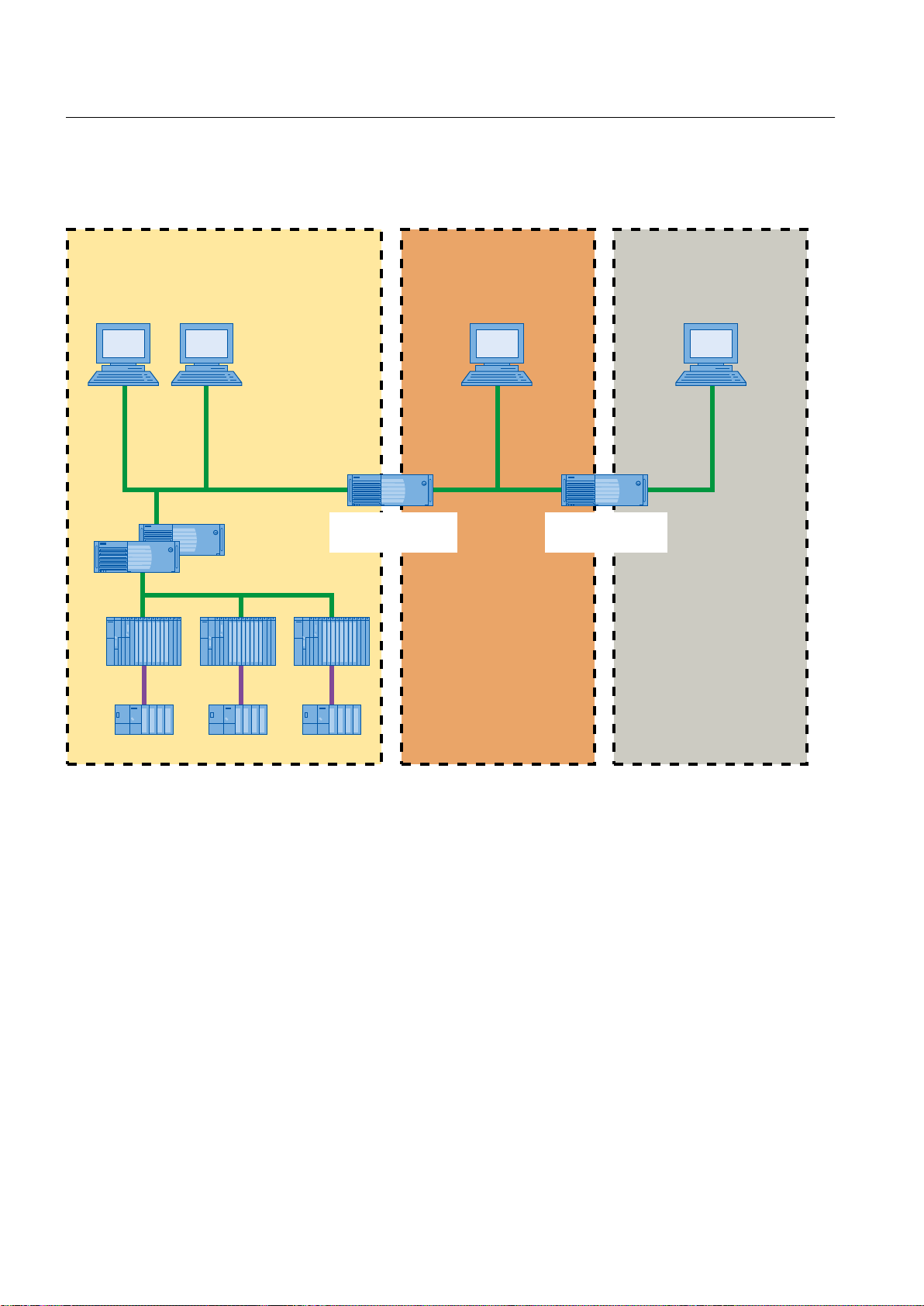
S7-400
ET 200
OpenPCS 7 Station
Microsoft ISA
Server Firewall
Microsoft ISA
Server Firewall
Office network
Plant bus
Terminal bus
Fieldbus
DMZ perimeter
network
PCS 7 security cell
PCS 7 OS ser ver
PCS 7 OS client OPC client
System configurations
5.8 Settings in the Windows Firewall for Open PCS 7
separated from the office network by a firewall. The OPC client that accesses the OpenPCS
7 station is located in the office network.
Additional information
● You can learn about the PCS 7 security concepts in the
● Documentation
Process Control System PCS 7; PC Configuration and Authorization
Security ConceptPCS 7
5.8 Settings in the Windows Firewall for Open PCS 7
Windows Firewall settings
42 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
When the OpenPCS 7 station is outside the network (subnet) of the PCS 7 system, settings
need to be made in the Windows Firewall on all OS servers which are to access to the
OpenPCS 7 station.
manual.
OpenPCS 7
Page 43

Setting location
The following table shows where the settings must be made for the respective operating
system:
Operating system Setting location
Windows XP "Exceptions" tab
Windows Server 2003
Windows 7 Inbound rules in the "Windows Firewall with
Windows Server 2008 R2
Settings for the rules
● The following rules must be adjusted depending on the type of connection:
System configurations
5.9 Users and passwords in a workgroup
Advanced Security" dialog
– The "CCEServer" rule for an OPC connection
– The "SQL Server 2005" and "SQL Browser" rules for an OLE DB connection
Expand the scope for corresponding rule(s) mentioned above from which access is to be
allowed to the subnet or IP address of the OpenPCS 7 station on the OS server.
● Make sure that bi-directional access is ensured between the OpenPCS 7 station and OS
server. Check the availability of both ends with the "ping" command. Adjust the firewall
settings if necessary.
5.9 Users and passwords in a workgroup
Users and passwords
Users and passwords of logged-on users must be created identically on the OpenPCS 7 station
and on the OPC client. Otherwise correct access by the OPC client to the OpenPCS 7 station
cannot be guaranteed.
The logged-on user should have at least power user privileges in the operating system.
Example
If the user with the user name "User1" and the password "xyz" is logged in on the OpenPCS
7 station, the user on the OPC client must be created identically. If the user with the user name
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 43
Page 44

Login / Password
Login / Password
S7-400 S7-400
ET 200 ET 200
OpenPCS 7 Station
Terminal bus
Plant bus
Fieldbus
OPC client
Microsoft workgroup
PCS 7 OS clients
PCS 7 OS ser ver
System configurations
5.9 Users and passwords in a workgroup
"User2" and the password "abc" is logged in on the OPC client, the user on the OpenPCS 7
station must also be created identically.
44 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
OpenPCS 7
Page 45

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.1 Access options
Access options
The following table lists the options for access to the PCS 7 OS server and the central archive
server via OPC:
6
Access to data
from
OS server DA Tags in process mode Reading / writing
OS server HDA Archive tags in the measured value archive
OS server A&E Alarms and messages Read/
OS server "H" A&E Alarms and messages from the message archive Read
Central archive
server
Central archive
server
Access
via OPC
"H" A&E Alarms and messages from the message archive Read
HDA Archive tags in the measured value archive
Data type Type of access
(TagLogging)
(TagLogging)
6.2 Data transmission
Type of data transfer of OPC DA, OPC HDA and OPC A&E
This section explains the various types of data transfer.
Event-driven data transfer
Read
acknowledge
Read
With event-driven data transfer, the OPC registers the required data for updating on the OPC
server. The OPC server sends the tags to the OPC client when they change.
Asynchronous data transfer
When using asynchronous data transfer, the called method is not completely processed on
the OPC server before the OPC client receives data from the OPC server. The OPC server
returns the results of the asynchronous operations using events. In this way, it is possible for
the OPC server to supply data to the OPC client automatically if the data has changed.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 45
Page 46

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.3 OPC Data Access (OPC DA)
Synchronous data transmission
When calling synchronous methods, the job is processed completely on the OPC server before
the information is transferred to the OPC client. The OPC server provides synchronous write
and read methods.
Note
You will find the asynchronous and synchronous write and read methods that are available
in the sections "SIEMENS OPC DA Automation Interface 2.0", "SIEMENS OPC HDA
Automation Interface 1.0" and " SIEMENS OPC Alarms and Events Automation Interface 1.0".
6.3 OPC Data Access (OPC DA)
6.3.1 Overview
Overview
You will find information about the following topics in the section below:
● Introduction to the OPC Data Access interface
● How the OPC DA server works
6.3.2 Introduction to the OPC Data Access interface
Introduction
The data access interface is a vendor-independent worldwide standard for reading, writing
and monitoring process data. Communication is based on the Microsoft COM protocol. This
standard has gained acceptance both with users and manufacturers. The user programs, for
example, range from office applications to sophisticated HMI (Human Machine Interface) or
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems.
OPC Data Access (OPC DA)
The OPC Data Access specification defines the interface between client and server programs
for process data communication.
Here, the OPC DA servers allow one or more OPC DA clients transparent access to an
extremely wide variety of data sources (for example temperature sensors) and data sinks (for
example controllers). The following options are typical for connecting data sources and sinks
to automation systems in a PCS 7 plant:
OpenPCS 7
46 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 47

OPC DA client
OPC DA server
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.3 OPC Data Access (OPC DA)
● Connection via PROFIBUS
● Connection using input modules or output modules
Data access clients can, for example, be Excel tables in conjunction with Visual Basic for
Applications (VBA). They may also be extensive applications created with Visual Basic or
Visual C++.
Basically an OPC DA server makes process data available to an OPC DA client for read and
write access.
OPC DA servers can be programs that, for example, allow access to an automation system
via a serial interface. More complex programs are possible that provide access to large
numbers of tags on numerous devices using extensive communications mechanisms. This is
the case with OpenPCS 7.
Access options using OPC DA
OPC Data Access is a specification for access to process data using process variables. An
OPC DA server manages the process variables and the various options for access to these
variables. The following types of access are possible:
● Reading the value of one or more process variables (tags)
● Modifying the value of one or more process variables (tags) by writing a new value
● Monitoring the value of one more process variables (tags)
● Reporting value changes
6.3.3 How the OPC DA server works
Requirement
To be able to set up successful OPC communication, the following requirements must be met:
● The PCS 7 OS project and the OPC DA server must be loaded and started.
● The computer of the OPC DA server can be reached by the OPC DA client via its IP address.
Note
In your PCS 7 OS project, variables can be grouped together in variable groups to provide
structuring. The variables must not have the same name as a variable group.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 47
Page 48

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.4 OPC Historical Data Access (OPC HDA)
How it works
The OPC DA server supports OPC data access with the following specifications:
● 1.0a
● 2.0.
● 3.0.
The OPC DA server is a DCOM application. Using this software interface, the OPC DA server
provides the OPC DA client with the necessary information about PCS 7 OS tags. The OPC
DA server becomes active when it is accessed by the OPC DA client over a connection to the
OPC DA server.
6.4 OPC Historical Data Access (OPC HDA)
6.4.1 Overview
Overview
You will find information about the following topics in the chapters below:
● How the OPC HDA server works
● Data structure of the OPC HDA server
● Overview of supported attributes
● Overview of supported aggregate functions
● Overview of supported functions
● Time format of the OPC HDA server
● Quality codes
The following chapters show the data structure and the attributes, aggregate functions and
functions supported by the OPC HDA server. This is not a detailed description but rather an
overview. Detailed information is available in the "OPC Historical Data Access Specification"
of the OPC Foundation.
6.4.2 How the OPC HDA server works
How it works
Using OPC HDA, it is possible to access archived data from the PCS 7servers. The OPC HDA
server is a DCOM application that provides the OPC HDA client with the required data from
the PCS 7 OS archive system. Data is accessed via item handles. Only read access to archived
data is approved for PCS 7. The data can also be analyzed.
OpenPCS 7
48 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 49

The OPC HDA server supports the OPC Historical Data Access 1.20 specification. This was
confirmed by the compliance test. All OPC HDA clients complying with the OPC Historical Data
Access 1.20 specification can access the OPC HDA server. The use of individually
programmed OPC HDA clients is the best way to meet the requirements.
Using the OPC HDA client
There are numerous potential applications for an OPC HDA client. The following uses are
possible:
● Analysis and evaluation of archived data.
● Static process control via archives from various OPC HDA servers.
Rules
If you request historical values with the OPC HDA client, remember the following during
configuration:
● Select the cycle for a query so that the client has received the requested data before the
next query starts. If the cycles are too short, the result can be a large time offset when
receiving the data.
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.4 OPC Historical Data Access (OPC HDA)
● The CPU load of the PCS 7 OS server depends on the number of variables per query.
6.4.3 Data structure of the OPC HDA server
Data structure
The data of the OPC HDA server is structured. The following table describes the data structure.
Element Description
Raw Data The raw data is the data transferred from the PCS 7 OS archive system for
a specified period. This data has a time stamp and a quality.
Attribute Return additional quality characteristics of the raw data. Attributes include
data type, information on archiving. Additional information is available in the
section "Overview of the supported attributes".
Aggregate Return a single value based on the raw data of a particular period. Aggregate
functions include average value, minimum and maximum. Additional
information is available in the section "Overview of the supported aggregate
functions".
StartTime/EndTime Specify the start and end time for the period.
Bounding Values Bounding values are the values recorded at the start and end time. If these
do not exist, the values closest to the time are used as the bounding values.
Item Handle The item handle is a unique assignment to a PCS 7 OS archive tag.
ItemID The ItemID is the unique identification of the PCS 7 OS archive tag. An item
handle can be fetched using the ItemID.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 49
Page 50

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.4 OPC Historical Data Access (OPC HDA)
Additional information
● Additional information on the data structure of the OPC HDA is available in the specification
OPC Historical Data Access Specification V1.2
6.4.4 Overview of supported attributes
Supported attributes
The following table lists the attributes supported by the OPC HDA server. Additional information
is available in the "OPC Historical Data Access Specification 1.20" of the OPC Foundation.
Attribute Attribute ID Description
ItemID OPCHDA_ITEMID Specifies which PCS 7 OS archive tag is accessed.
Item data type OPCHDA_DATA_TYPE Specifies the data type of the PCS 7 OS archive
Description OPCHDA_DESCRIPTION Outputs the description of the PCS 7 OS archive
Engineering
Units
OPCHDA_ENG_UNITS Specifies the labeling of the unit shown in the
of the OPC Foundation.
tag.
tag. The description is specified in PCS 7 OS
TagLogging.
display. The labeling is specified in PCS 7 OS
TagLogging.
6.4.5 Overview of supported aggregate functions
Supported aggregate functions
The following table lists the aggregate functions supported by the OPC HDA server. Additional
information is available in the "OPC Historical Data Access Specification 1.20" of the OPC
Foundation.
Aggregate function Description
OPCHDA_COUNT Obtains the number of raw data for the specified period.
OPCHDA_START Obtains the start value of the raw data at the start time.
OPCHDA_END Obtains the end value of the raw data at the end time.
OPCHDA_AVERAGE Obtains the average value of the raw data for the specified
period.
OPCHDA_TIMEAVERAGE Obtains the time-weighted average value of the raw data for
the specified period.
OPCHDA_TOTAL Obtains the total value for the specified period.
OPCHDA_STDEV Obtains the standard deviation of the raw data for the
specified period.
OPCHDA_MINIMUMACTUALTIME Obtains the highest value and the time stamp of the raw data
for the specified period.
OpenPCS 7
50 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 51

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.4 OPC Historical Data Access (OPC HDA)
Aggregate function Description
OPCHDA_MINIMUM Obtains the lowest value of the raw data for the specified
period.
OPCHDA_MAXIMUMACTUALTIME Obtains the highest value and the time stamp of the raw data
for the specified period.
OPCHDA_MAXIMUM Obtains the highest value of the raw data for the specified
period.
OPCHDA_DELTA Obtains the difference between the first and last value of the
raw data of the specified period.
OPCHDA_REGSLOPE Obtains the slope of the linear regression of the raw data for
the specified period.
OPCHDA_REGCONST Obtains the value of the linear regression of the raw data at
the start time.
OPCHDA_REGDEV Obtains the standard deviation of the linear regression of the
raw data for the specified period.
OPCHDA_VARIANCE Obtains the variance of the raw data for the specified period.
OPCHDA_RANGE Obtains the difference between OPCHDA_MAXIMUM and
OPCHDA_MINIMUM of the raw data for the specified period.
OPCHDA_DURATIONGOOD Obtains the period in which the quality of the raw data was
good. The period is entered in seconds.
OPCHDA_DURATIONBAD Obtains the period in which the quality of the raw data was
bad. The period is entered in seconds.
OPCHDA_PERCENTGOOD Obtains the portion during which the quality of the raw data
was good as a percentage.
OPCHDA_PERCENTBAD Obtains the portion during which the quality of the raw data
was bad as a percentage.
OPCHDA_WORSTQUALITY Obtains the worst quality of the raw data for the specified
period.
6.4.6 Overview of supported functions
Introduction
The following tables list the functions supported by the OPC HDA server. These functions can
be used by the OPC HDA client for data exchange. Additional information is available in the
"OPC Historical Data Access Specification 1.20" of the OPC Foundation.
Function Description
ReadRaw Specifies the raw data, its quality and its time stamp for the specified period.
ReadProcessed Returns the calculated value, the quality of the value and the time stamp
for the specified period. The calculated value depends on the selected
aggregate function.
ReadAtTime Specifies the raw data, its quality and its time stamp for a specific point in
time. If no value exists, it is interpolated for this point in time.
ReadAttribute Returns the attributes of the item and the time stamp for the specified period.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 51
Page 52

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.4 OPC Historical Data Access (OPC HDA)
6.4.7 Time format of the OPC HDA server
Period of the historical data
The period is specified by the start and end time on the OPC HDA server. The specified period
defines the period examined for the historical data. When specifying the times, you will have
to maintain certain formats. A point in time can be specified in the following ways:
● Absolute in UTC.
● Relative to the local time of the OPC HDA server.
Specified in absolute form according to UTC
As default, the OPC HDA server works with the coordinated world time UTC as the timebase.
The time corresponds to the Greenwich time zone (= central European standard time minus
one hour).
Time format
YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.msmsms
Parameter
YYYY = year
MM = month
DD = day
hh = hour
mm = minute
ss = second
ms = millisecond
Example of an entry
2011/08/10 09:27:30.000
Specifying the point in time relative to the local time
Here, the point in time is specified relative to the local time of the OPC HDA server. You set
the local time zone in the Control Panel of your computer in "Date/Time".
Time format
Keyword +/-offset1 +/-offset(n)
The offset is the deviation from local time of the OPC HDA server.
OpenPCS 7
52 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 53

Keyword
Offset
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.4 OPC Historical Data Access (OPC HDA)
NOW = current local time of the server
SECOND = current second
MINUTE = current minute
HOUR = current hour
DAY = current day
WEEK = current week
MONTH = current month (0-11)
YEAR = current year
+/-S = deviation in seconds
+/-M = deviation in minutes
+/-H = deviation in hours
Example
+/-D = deviation in days
+/-W = deviation in weeks
+/-MO = deviation in months
+/-Y = deviation in years
DAY - 1D = previous day
DAY-1D + 7H30 = previous day at 7:30 a.m.
MO-1D+5H = last day of the previous month at 5.00 a.m.
NOW-1H15M = 1 hour and 15 minutes ago
YEAR+3MO= April of this year
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 53
Page 54

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.4 OPC Historical Data Access (OPC HDA)
6.4.8 Quality codes of the OPC HDA server
Quality codes
The quality code is required to check the status and quality of the raw data. The following table
shows the quality codes of OPC HDA.
Code OPC Description Quality
0x00040000 OPCHDA_RAW Provides information on the quality of
0x00080000 OPCHDA_CALCULATED Provides information on the quality of
0x00100000 OPCHDA_NOBOUND No bounding values were found at the
0x00200000 OPCHDA_NODATA No raw data was found for the
0x00400000 OPCHDA_DATALOST Raw data was not completely archived
the value transfer of raw data.
the value transfer of calculated data.
start or end time.
specified period.
during the selected period.
GOOD
BAD
UNCERTAIN
GOOD
BAD
UNCERTAIN
BAD
BAD
BAD
Additional information is available in the "OPC Historical Data Access Specification 1.20" of
the OPC Foundation.
6.4.9 Write access supported by the OPC HDA server
Introduction
The OPC HDA specification of the OPC Foundation also defines write access to archived data.
Note
PCS 7 is a process control system. In a process control system, archived data must not be
modified. For this reason, write access to archived data using OPC HDA has not been
enabled.
OpenPCS 7
54 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 55

6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
6.5.1 Overview
Overview
You will find information on the following topics in the sections below:
● Mapping the PCS 7 OS message system on OPC A&E
● Mapping the message classes and message types of PCS 7 OS on OPC A&E
● Mapping the priorities of PCS 7 OS messages on OPC A&E
● Attributes of the PCS 7 OS message system
● Acknowledgement scheme
● Quality code for OPC A&E
● OPC A&E with hierarchical access
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
● Upgrading with OPC A&E
Note
You will find general information on these topics in the sections. Detailed information is
available in the "OPC Alarms and Events Custom Interface Standard V1.0" and "OPC
Alarm and Events Automation Interface Standard V1.01" specifications of the OPC
Foundation.
6.5.2 Introduction to OPC A&E
Functionality of the OPC A&E server
The OPC A&E server is a DCOM application. The OPC A&E client will receive information on
status changes of PCS 7 OS messages using subscriptions. Using the subscription, the OPC
A&E client can set a filter. This filter specifies which messages and attributes will be displayed.
The OPC A&E server supports the specification OPC Alarm&Event 1.10. The following chapter
explains the mapping of the PCS 7 OS message system on OPC A&E and the attributes
supported by the OPC A&E server. This is not a detailed description but rather an overview of
the specific information. Detailed information on this topic is available in the specification of
"OPC Alarms & Events 1.10".
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 55
Page 56

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
Supported events
The OPC A&E server supports the following events:
● Condition-related event
● Simple event
● Tracking event
Condition-related events
With a condition-related event server, the event is associated with a condition. A condition may
be the limit violation of a tag. On the PCS 7 OS, a message will be generated as soon as a
limit violation occurs. This message is shown as an alarm in OPC A&E.
Simple event
Simple events are messages that inform the OPC A&E client about events. Simple events
include, for example, the launching and closing of programs.
Note
Tracking event
OPC A&E client
Note the following when using redundant PCS 7 OS servers:
Simple events that are linked to internal tags are sent twice when comparing tags. The first
message is triggered by the OS master server, the second by the OS standby server.
If a change is made in the process control system, the OPC A&E client will receive a message.
A change can, for example, be a change to a control parameter in the faceplate of the controller
or the suppression of messages in the message system.
Note
When filtering for all alarms of a plant section, make sure that you replace the source with a
wildcard in the filter text, because the source is only generated in runtime for a tracking event.
For example, the filter text for all events from the "Plant1\Unit1\Tank1" area is "Server
prefix::*Plant1\Unit1\Tank1*" and not "Server prefix::Plant1\Plant1\Unit1\Tank1*".
All OPC A&E clients complying with the OPC Alarms & Events 1.10 specification can access
the OPC A&E server. On the OPC A&E client, this can involve, for example, simple or complex
Microsoft Visual Basic or Microsoft Visual C++ applications. The use of individually developed
OPC A&E clients is the best way to meet the requirements. An OPC A&E client can, for
example, be used to analyze alarms or for the common archiving of alarms from different OPC
A&E servers.
OpenPCS 7
56 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 57

When acknowledging messages, a distinction must be made between "pending" messages
and "historical" messages.
● Pending messages
● Historical messages
Additional information
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
Messages received over the path specified by OPC A&E (for example, "Refresh") can be
acknowledged.
Messages received over the "historical messages" path (extension of the Siemens OPC
A&E server) cannot be acknowledged.
● For additional information about "OPC - OLE for Open Connectivity" refer to the
Information System
● Additional information about the OPC A&E can be found in the specification
& Events 1.10
.
.
6.5.3 Mapping the PCS 7 OS message system on OPC A&E
Introduction
In PCS 7, program functionality in the automation system is configured using messaging
capable CFCblocks from the PCS 7library. After compiling the PCS 7 OS, the configuration
messages exist in the PCS 7 OS message system. These messages are mapped to the OPC
A&E standard by the OpenPCS 7 station implementation. The OS configuration defines which
event in the process triggers a message.
Mapping the OS message system on OPC A&E with hierarchical access
In PCS 7, the following standard settings in the OS message system are used for mapping
messages on OPC A&E:
● The source of a message is mapped on the OPC source.
WinCC
OPC Alarms
● The message text of a message is mapped on the OPC message.
Overview
The OPC attribute class OPCEvent is used in OPC A&E to display events. The following table
shows selected OPC attributes and their meaning in the OS message system.
The events that use the configured attributes are shown in the third column of the table:
● "S" means a simple event
● "C" means a condition-related event
● "T" means a tracking event
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 57
Page 58

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
OPC OS message system Event type
Area In PCS 7, an "area" is an area, a diagnostics area or an alarm hiding group. If there
is no area, no diagnostic area or no alarm hiding group configured for the message,
only the OPC area corresponding to the server prefix will be available.
Source Indicates the source of a message. The source has the format "<Server prefix>::Area
\Source". The server prefix of a local computer is "@LOCALMACHINE". The server
prefixes always show the top areas in the hierarchy of the server.
Time Issues a time stamp for received, sent and acknowledged messages. Issues a time
stamp in UTC (Universal Time Coordinated).
Type Indicates whether the event is a simple, tracking or condition-related event. S, C, T
Severity Displays the priority of the message. S, C, T
EventCategory Displays the message class. "Event Category" is made up of the "CategoryID" and
the "Category Description". "CategoryID" corresponds to the internal ID of the
message class. "Category Description" corresponds to the name of the message class.
Message Displays the message text of the corresponding message number. S, C, T
Condition Displays the message type. The message types "Alarm", "Warning" and "Tolerance"
are combined and called "Level" in PCS 7.
Sub Condition Corresponds to the "Condition" parameter. In PCS 7, this is identical to Condition in
single state conditions. The following subconditions are mapped for the "Level"
multistate condition in PCS 7:
● Alarm low
● Alarm high
● Warning low
● Warning high
● Tolerance low
● Tolerance high
ChangeMask Specifies the change of the condition. C
NewState Displays the current status of the condition. C
ConditionQuality Displays the quality of the message.
For additional information about quality codes refer to the system manual
WinCC/Connectivity Pack
AckRequired Indicates whether the message requires acknowledgment. C
EventAttribute Lists the attributes required for this message. C
Quality Indicates the quality code of the message. C
Cookie Does not include any usable information for the client C
ActorID Indicates which user acknowledged the message. T
.
MDM -
S, C, T
S, C, T
S, C, T
S, C, T
C
C
C
OpenPCS 7
58 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 59

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
NOTICE
The message classes and message types must be configured identically on the connected
OS servers if you operate the OPC A&E server as follows:
● On an OS client
● on a WinCCconnectivity station
● within the scope of OpenPCS 7
If the OS server is not configured identically, the OPC client that is used must access the
respective OS server directly.
6.5.4 Mapping the message classes and message types of PCS 7 OS on OPC A&E
Mapping of the message classes
The PCS 7 OS message system provides information on fault and operational states in the
process. A PCS 7 OS message always belongs to a particular message class and message
type that is in turn related to an event category.
Event category
Each combination of message class and message type is mapped to an event category on
the OPC A&E server. An event category is identified by a CategoryID and a category
description.
The CategoryID is made up of the internal PCS 7 OS ID of the message class and message
type.
The category description is made up of the name of the message class and message type.
The names of the message classes and message types can be obtained explicitly using the
alarm attributes CLASSNAME and TYPENAME.
6.5.5 Mapping priorities of PCS 7 OS messages to OPC A&E
Mapping priorities
The priority of messages is mapped by the OPC A&E server to the "Severity" attribute. When
configuring alarms in the message system, you can configure a priority from "0" to "16". The
OPC A&E specification defines a range of values from "1" to "1000" for the severity. "1" stands
for the lowest and "1000" for the highest severity. For this reason, the values of the priority are
suitably mapped to the OPC severity. In the standard mapping, priority "0" is assigned to OPC
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 59
Page 60
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
severity "1" and priority "16" to OPC severity "1000". All other priority values are obtained by
linear interpolation between "0" and "1000".
6.5.6 Attributes of the PCS 7 OS message system
Attributes of the PCS 7 OS message system
The following table lists the OPC attributes and their meaning in the PCS 7 OS message
system. A PCS 7 OS message belongs to a message class and has system attributes, user
texts and process values. Some of the attributes of a PCS 7 OS message are only for internal
use in the PCS 7 OS and are therefore not relevant for an OPC A&E client. These attributes
are not listed in the table.
OPC attribute Meaning in the PCS 7 OS message system
ClassName Displays the message class name.
Type name Displays the message type name.
ForeColor Displays the text color for the display of received, sent and acknowledged
messages.
BackColor Displays the background color for the display of received, sent and acknowledged
messages.
FlashColor Displays the flashing color.
Flags Indicates whether the message requires acknowledgment.
Text01 Displays the content in the source.
Text02 Displays the content of the area.
Text03 Displays the content in the event.
Text04 Displays the batch name.
Text05 Displays the content of the operation message.
Text06 Displays the content of the text block "free 1".
Text07 Displays the content of the text block "free 2".
Text08 Displays the content of the text block "free 3".
Text09 Displays the content of the text block "free 4".
Text10 Displays the content of the text block "free 5".
ProcessValue01 Displays the content of ProcessValueBlock01.
ProcessValue02 Displays the content of ProcessValueBlock02.
ProcessValue03 Displays the content of ProcessValueBlock03.
ProcessValue04 Displays the content of ProcessValueBlock04.
ProcessValue05 Displays the content of ProcessValueBlock05.
ProcessValue06 Displays the content of ProcessValueBlock06.
ProcessValue07 Displays the content of ProcessValueBlock07.
ProcessValue08 Displays the content of ProcessValueBlock08.
ProcessValue09 Displays the content of ProcessValueBlock09.
ProcessValue10 Displays the content of ProcessValueBlock10.
StateText Displays the status message.
OpenPCS 7
60 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 61
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
OPC attribute Meaning in the PCS 7 OS message system
InfoText Displays the information text for the message.
LoopInAlarm States if LoopInAlarm has been configured.
ClassID Displays the message class ID.
Type ID Displays the message type ID.
AG_Number Displays the number of the automation device that generated the message.
CPU_Number Displays the number of the CPU that generated the message.
Duration Displays the period of time between message received, sent and acknowledged.
QuitStateText Indicates whether the message has been acknowledged.
Priority Indicates the configured priority of the message.
OS EVENT ID Displays the message number.
IEVENT UNIQUE EVENT ID Displays the unique event ID across all messages.
OS-HIDDEN Indicates whether a message configured with the "alarm hiding" function is shown
(yes/no).
HIDDEN-COUNT Indicates the number of messages currently hidden with the "alarm hiding" function
(HIDDEN).
6.5.7 Acknowledgment concept
Mapping the acknowledgment concept
In the PCS 7 OS, the acknowledgment concept is how a message is displayed and processed
from "came in" to "went out". On the OPC A&E server, this message status is displayed in the
"ChangeMask" and "NewState" parameters.
Condition-related event, simple event and tracking event
Messages with acknowledgment are sent from the system to the client as condition-related
events. Before a message is treated as a simple event, the message class of the message
must meet the following conditions:
● "Acknowledgment came in" is not activated.
● Message without status "went out" is activated.
The following messages are sent as tracking events in PCS 7:
● Messages of the "Operation message" message class.
● Messages of "System, does not require acknowledgment" message class with the
"Operation message" message type.
NOTICE
Messages with "System, does not require acknowledgment" message class and "Process
control system" message type are transferred as simple events with the "System
message" event category.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 61
Page 62
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
ChangeMask
The "ChangeMask" parameter keeps track of where the message status was changed.
Parameter values of ChangeMask:
● OPC_CHANGE_ACTIVE_STATE
● OPC_CHANGE_ENABLE_STATE
● OPC_CHANGE_ACK_STATE
NewState
The "NewState" parameter indicates the message status after a change.
Parameter values of NewState:
● OPC_CONDITION_ACTIVE
● OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED
● OPC_CONDITION_ACKED
PCS 7 OS NewState ChangeState
Message came in OPC_CONDITION_ACTIVE
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED
Message went out with
acknowledgment
Message went out without
acknowledgment
Acknowledged messages
(message still pending)
Acknowledged messages
(message no longer
pending)
Locked message - OPC_CHANGE_ENABLED_STAT
Unlocked message OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED OPC_CHANGE_ENABLED_STAT
Came in, acknowledged
message
Came in, went out
message with
acknowledgment
OPC_CONDITION_ACKED
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED OPC_CHANGE_ACTIVE_STATE
OPC_CONDITION_ACTIVE
OPC_CONDITION_ACKED
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED
OPC_CONDITION_ACKED
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED
OPC_CONDITION_ACTIVE
OPC_CONDITION_ACKED
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED
OPC_CONDITION_ACKED
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED
OPC_CHANGE_ACTIVE_STATE
OPC_CHANGE_ACTIVE_STATE
OPC_CHANGE_ACK_STATE
OPC_CHANGE_ACK_STATE
E
E
OPC_CHANGE_ACTIVE_STATE
OPC_CHANGE_ACK_STATE
OpenPCS 7
62 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 63

6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
PCS 7 OS NewState ChangeState
Came in, went out
message without
acknowledgment
Message acknowledged by
system
(message
still pending)
Message acknowledged by
system
(message
no longer pending)
Emergency acknowledged
message
(message still pending)
Emergency acknowledged
message
(message no longer
pending)
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED OPC_CHANGE_ACK_STATE
OPC_CONDITION_ACTIVE
OPC_CONDITION_ACKED
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED
OPC_CONDITION_ACKED
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED
OPC_CONDITION_ACTIVE
OPC_CONDITION_ACKED
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED
OPC_CONDITION_ACKED
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED
OPC_CHANGE_ACK_STATE
OPC_CHANGE_ACK_STATE
OPC_CHANGE_ACK_STATE
OPC_CHANGE_ACK_STATE
OpenPCS 7 interface
Note
Historical alarms and events are not acknowledged. The OPC A&E historical events interface
has read access only.
The following table shows the mapping of the "ChangeMask" and "New State" parameters to
the properties of the OPCEvent class of the "OPCSiemensAlarmEventAutomation" type library.
ChangeMask / NewState Properties of the OPCEvent class
OPC_CHANGE_ACTIVE_STATE ChangeActiveState
OPC_CHANGE_ENABLE_STATE ChangeEnableState
OPC_CHANGE_ACK_STATE ChangeAckState
OPC_CONDITION_ACTIVE ConditionActive
OPC_CONDITION_ENABLED ConditionEnabled
OPC_CONDITION_ACKED ConditionAcknowledged
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 63
Page 64

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
6.5.8 Quality codes for OPC A&E
Quality codes
The quality code is required to check the status and quality of a message. The following table
shows the quality codes of OPC A&E.
Code Quality Status
0xC0 OPC_GOOD OK
0x40 OPC_UNCERTAIN Output if there are discrepancies, for example
0x00 OPC_BAD Output if the connection to the
6.5.9 OPC A&E with hierarchical access
with a late acknowledgment.
source is interrupted.
6.5.9.1 Differences between OPC A&E and OPC A&E with hierarchical access
Representation of messages with OPC A&E
The OPC A&E server supports "conditional events" and "simple events" during access to the
message system. With "conditional events", the message numbers are shown for each source.
Since an PCS 7 OS server can hold many more message numbers, it is hard to keep an
OpenPCS 7
64 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 65

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
overview of the messages. The following figure shows an example of the display in an OPC
browser:
Representation of the messages with OPC A&E and hierarchical access
As of PCS 7 V7.0 SP1, you can use an OPC A&E server with hierarchical access in PCS 7.
The OPC A&E server with hierarchical access supports the following event types:
● Condition-related event
● Simple event
● Tracking event
With a "condition-related event," the source of the messages is determined by the area and
the source. The area can be a system area, a diagnostics area or an alarm hiding group. If the
"source" text block in WinCC is dynamic or not configured, the character string ""EventID xx"
is used for the source in OPC instead of this text. Here, "xx" represents the unique WinCC
message number. This syntax is used for the source in the Area Browser and for the message
itself. A tracking event occurs when an operation message is triggered in the system. The
following figure shows an example of the representation of a condition-related event in an OPC
browser. The "Condition" is shown in addition to "Area" and "Source":
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 65
Page 66

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
Recommendation
Use an OPC A&E server with hierarchical access when creating new projects. If you upgrade
an existing project, the OPC A&E server can be used as before or the OPC A&E server can
be converted to hierarchical access. The conversion can be undone again without any loss of
data.
6.5.9.2 Example 1: Messages are not assigned to any area
Introduction
Process control messages, messages for Batch servers and Route Control servers are not
assigned to an area or group. For these messages, no designated area is assigned in the
structure of the OPC A&E access.
OpenPCS 7
66 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 67

Requirement
● Process control messages are created on the OS servers.
● Messages for Batch servers and Route Control servers are created on the dedicated
message servers.
● No diagnostics area is present.
Structure for access to messages via the OPC A&E interface
The general mapping to the OPC A&E interface appears as follows:
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 67
Page 68

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
Example of a hierarchy without assignment
The following picture shows the hierarchy of messages in a browser that can be sent to the
client as a "conditional event".
OpenPCS 7
68 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 69

6.5.9.3 Example 2: Messages are assigned to an area
Introduction
A PCS 7project is generally divided into several system areas and diagnostic areas. This
means that messages are assigned to the areas.
The areas are shown as a hierarchy level in OPC A&E for hierarchical mapping.
Requirement
● The PCS 7project contains areas or diagnostic areas.
Structure for access to messages via the OPC A&E interface
The general mapping to the OPC A&E interface appears as follows:
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
Example of a hierarchy with an area
The following pictures show the hierarchy of messages in a browser that can be sent to the
client as a "conditional event".
Example with areas:
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 69
Page 70

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
Example with diagnostic areas:
OpenPCS 7
70 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 71

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
6.5.9.4 Example 3: Messages of an area are assigned to an alarm hiding group
Introduction
In the PCS 7project, alarm hiding groups are used to automatically hide messages. An alarm
hiding group can contain messages from several areas.
This section describes how OPC A&E accesses these messages.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 71
Page 72

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
Requirement
● Alarm hiding groups are configured in the OS project.
Access to the messages via the OPC A&E interface
The messages of an area are only shown in the alarm hiding group. The messages are no
longer visible in the area.
The general mapping to the OPC A&E interface appears as follows:
Example of a hierarchy with an alarm hiding group
The following picture shows the hierarchy of messages in a browser that can be sent to the
client as a "conditional event".
OpenPCS 7
72 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 73

6.5.10 Upgrading with OPC A&E
6.5.10.1 Updating PCS 7 projects with OPC A&E
As of PCS 7 V7.0 SP1, OPC A&E has been expanded to include hierarchical access to the
message system.
You can continue to use the non-hierarchical OPC A&E server.
Updating OPC A&E
If you use OPC A&E with hierarchical access and want to use all functions, an expansion of
the currently used OPC A&E client is necessary.
Starting from the PCS 7version of your project, various scenarios for updating projects with
OPC A&E are described below.
6.5.10.2 How to update an OPC project with PCS 7 V8.0
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.5 OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A&E)
Options
The following options are available for updating a PCS 7 project with configured access via
OPC A&E to PCS 7 V8.0 OpenPCS 7 station:
● Conversion to OPC A&E with hierarchical access
● Retain OPC A&E without hierarchical access
Requirement
The PCS 7version of the project to be updated is PCS 7 V6.1 SP2 or higher.
Preparation
Before performing the update, delete any "CCAeProvider.ini" file on the OS server or on the
ES directly in the OS project folder.
You can find the OS project folder in "wincproj" subfolder on the engineering station.
Conversion to OPC A&E with hierarchical access
No adjustments need be made for the conversion to OPC A&E with hierarchical access. OPC
A&E with hierarchical access is the default setting.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 73
Page 74

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.6 OPC Historical Alarms and Events (OPC "H" A&E)
Retain OPC A&E without hierarchical access
If you want to work with the OPC A&E server without hierarchical access, follow these steps:
1. Insert the following lines into the "CCAeProvider.ini" file in the "OPC/AlarmEvent"
subdirectory of the OS project folder on the ES:
[OpcMapping]
OpcSource =
OpcMessage =
2. Perform a full download.
OS projects in PCS 7 V6.1 SP2
Note
Modified server prefix of the local computer
For OS projects in PCS 7 V6.1 SP2, note the following change in OPC A&E:
The server prefix of the local computer is now "@LOCALMACHINE" instead of "localhost".
6.6 OPC Historical Alarms and Events (OPC "H" A&E)
6.6.1 Overview
Overview
You will find information about the following topics in the section below:
● Introduction to OPC "H" A&E
● Reading archived messages
● Syntax for access to archived messages
● Read modes for archived messages
● Identifying archived messages
OpenPCS 7
74 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 75

6.6.2 Introduction to OPC "H" A&E
OPC Historical Alarms and Events
Alarms and operating messages are stored in the database of the PCS 7 OS. With an OPC
A&E client, you can access archived messages via the OPC A&E server. When accessing
archived messages, the following methods are supported:
● Output of archived messages from a period in the past (history)
● Output of archived messages from a period in the past without an end time.
After outputting the archived messages, all additional newly generated messages are
automatically sent to the OPC A&E client.
Note
Reading archived messages using OPC "H" A&E is a Siemens expansion of the OPC A&E
standard.
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.6 OPC Historical Alarms and Events (OPC "H" A&E)
Rule
After reading archived messages, you must not use the returned "ActiveTime" of a message
either for acknowledging the message or for tracking the transitions of the message. The
"ActiveTime" is not correct for archived messages. To make sure this is recognized, the OPC
A&E client must check the "EventType" of a message for the additional flag
"OPC_HAE_HISTORICAL_EVENTFLAG".
Note
You will find information on the additional flag in "Identifying archived messages".
6.6.3 Reading archived messages
Reading archived messages using OPC A&E
Archived messages of the PCS 7system are read by the OPC A&E client via the OPC A&E
server using filters. In this situation, the term OPC "H" A&E is also used in this documentation.
Apart from the standard filters, the following filters are also available with OPC "H" A&E:
● OPC_HAE_FILTER_BY_TIMEFRAME; corresponds to the function "ReadRaw" in OPC
Historical Data Access
● OPC_HAE_FILTER_BY_STARTTIME; corresponds to the function "AdviseRaw" in OPC
Historical Data Access
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 75
Page 76

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.6 OPC Historical Alarms and Events (OPC "H" A&E)
Source filter and request for archived messages
To be able to request the archived messages, the OPC A&E client must support the "SetFilter"
functionality for a subscription. If you add the additional keyword "OPCHAEServer" in the array
of the "Source Filter" of a subscription, the OPC A&E server sends archived messages. Along
with this keyword, you can use the following parameters to specify how messages are read:
● Method
● Time period
● With or without limits
The list of sources specified in the filter can include other source names in addition to the
"OPCHAEServer" source. In this case, the subscription returns the historical events of the
specified sources. The order of the source names has no effect. After configuring the source
filter, you can call up the selected period from the OPC A&E client with a "Refresh" call.
6.6.4 Syntax for access to archived messages
Syntax for access to archived messages
OPCHAEServer hMode=(read|advise) htStartTime=szTime
[htEndTime=szTime] [bBounds=(TRUE|FALSE)]
Parameter hMode = [read|advise]
This parameter specifies how the archived messages and events are read.
htStartTime parameter
This parameter specifies the time at which the messages and events are read from the archive.
htEndTime parameter
This parameter specifies the time up to which messages and events are read from the archive.
bBounds = [TRUE|FALSE] parameter
This parameter specifies how messages close to the start and end time are handled.
OpenPCS 7
76 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 77

Example
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.6 OPC Historical Alarms and Events (OPC "H" A&E)
The following table lists the parameters and their meaning and shows suitable examples.
Parameter Meaning Example Requireme
nt
hMode =
read
hMode =
advise
htStartTime Specifies the time at which the
htEndTime Specifies the time up to which
bBounds =
FALSE
bBounds=
TRUE
Outputs archived messages and
events of a defined period in the past
(comparable with ReadRaw in OPC
Historical Data Access).
Outputs archived messages and
events starting from a defined time.
After receiving all archived
messages, new messages are sent
as with an active subscription. This
is comparable with AdviseRaw in
OPC Historical Data Access.
messages and events are read from
the archive.
messages and events are read from
the archive. if "hMode = read" ist is
set, "NOW" is used as the default
setting.
● The time stamp of the first
transferred message
>= htStartTime
● The time stamp of the last
transferred message
<= htEndTime
● The time stamp of the first
transferred message
<= htStartTime
● The time stamp of the last
transferred message
>= htEndTime
FALSE is the default setting.
Setting a filter to read archived
messages over the last 30
minutes:
OPCHAEServer hMode=read
htStartTime=NOW-30M
bBounds=TRUE
Reading archived messages as of
the last 30 minutes:
OPCHAEServer hMode=advise
htStartTime=NOW-30M
The subscription must be active
for this purpose.
htStartTime=NOW-30M Yes
htEndTime =
2011-09-10T10:00:00.000C
bBounds=FALSE optional
bBounds=TRUE optional
Yes
Yes
optional
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 77
Page 78

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.6 OPC Historical Alarms and Events (OPC "H" A&E)
Note
The following notation is supported for the "htStartTime" and "htEndTime" parameters:
● Relative notations, for example NOW
● Symbolic values, for example NOW, YEAR, MONTH
● Absolute UTC date/time specified according to XML notation:
"2011-09-10T10:00:00.000C".
The use of symbolic notation corresponds to the syntax of OPC Historical Data Access.
6.6.5 Read modes for archived messages
Read modes for archived messages
When reading archived messages, you can use the following read modes:
● Read
● Advise
"read" mode
With the "read" mode, archived messages are read from a defined period in the past. The read
order of the messages is always chronological for each OS server from which alarms are read.
By setting the start and end time, you can specify whether the oldest message is output first
or last. If the start time is lower than the end time, the oldest message is output last.
If you want to use the "read" mode, execute the following functions on the subscription:
1. SetFilter
2. Refresh
A "SetFilter" during the "Refresh" is discarded.
If you activate the subscription during "Refresh", it will not affect the running of the refresh.
The historical events are still transferred with the refresh ID. The newly generated events are
transferred according to the standard behavior of an active subscription:
● Taking into account the set filter values with the exception of the "historical" source
"OPCHAEServer"
● Without refresh ID
OpenPCS 7
78 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 79

6.6 OPC Historical Alarms and Events (OPC "H" A&E)
The following distinction is made based on the refresh ID:
● Event packages with the refresh ID contain only historical events. These events can also
still be pending.
OpenPCS 7 interface
● Event packages without the refresh ID contain only newly generated events.
"advise" read mode
With the "advise" mode, archived messages are read starting at a defined time in the past.
After reading all archived messages, new messages are sent as with an active subscription.
The archived messages are transferred in chronological order related to each OS server. First
the archived messages starting at the start time are transferred. The new archived messages
are then transferred. An active subscription is used for the "advise" read mode. If you execute
the "SetFilter" function on an active subscription, the historical alarms are transferred
immediately. If you execute the "SetFilter" function on an inactive subscription, the archived
messages are transferred only after the subscription is activated.
If you want to use the "advise" read mode with an inactive subscription, follow the steps below:
1. SetFilter
2. Set the subscription to active with SetState
If you deactivate the subscription, the transfer is interrupted. If you set the subscription to
"inactive", the transfer is stopped. A "SetFilter" is discarded while the subscription is active. A
"Refresh" on an active "historical" subscription in "advise" mode works in exactly the same
way as a with a standard subscription:
Note
An event package never contains historical and new events at the same time.
All pending condition-related events are transferred in packets with the refresh ID. The last
packet also has the "Last Refresh" ID. In "advise" mode, a "refresh" call has no influence on
the reading of historical alarms.
Note
Note that you must not specify an end time with "advise".
6.6.6 Identifying archived messages
Principle
Archived messages are distinguished by an additional flag in the EventType.
This flag is connected with the real EventType via an OR link:
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 79
Page 80
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
Name EventType EventType (archived message)
OPC_SIMPLE_EVENT 0x01 0x81
OPC_CONDITION_EVENT 0x04 0x84
OPC_TRACKING_EVENT 0x02 0x82
OPC_HAE_HISTORICAL_EVENTFLAG 0x80
Example 1
The archived messages and events of the last 30 minutes are output in "read" mode using the
following source filter. The oldest message per OS server is output first. The low limit value
will also be returned:
OPCHAEServer hmode=read htStartTime=NOW-30M bBounds=TRUE
Example 2
The archived events of September 1, 2006 from 10.00 a.m. to 12.00 a.m. are output in "read"
mode using the following source filter. The latest message per OS server is output first. The
limit values of this time range will also be returned:
OPCHAEServer hMode=read htStartTime=2006-09-01T12:00:00.000Z
htEndTime=2006-09-01T10:00:00.000Z bBounds=TRUE
Example 3
The archived messages and events of the last 30 minutes are output in "advise" mode using
the following source filter. After reading all archived messages, the newly generated messages
are transferred as with an active subscription:
OPCHAEServer hmode=advise htStartTime=NOW-30M
6.7 OLE DB
6.7.1 Overview
Overview
You will find information about the following topics in the section below:
● Basics of OLE DB
● Establishing the connection to the database
● Access to the OLE DB provider
● Representation of the process value archive
● Querying process value archives
OpenPCS 7
80 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 81

● Representation of the message archives
● Querying the message archive
6.7.2 Basics of OLE DB
Introduction
You can access process value and message archives using the OLE DB interface made
available by the PCS 7 OS and the corresponding database provider.
OLE DB
OLE DB is an open standard for fast access to different databases. It is irrelevant whether or
not the database is relational. The connection between the OLE DB level and the database is
established by an OLE DB provider. OLE DB interfaces and providers are available from
various vendors.
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
WinCC OLE DB provider
With the WinCC OLE DB provider, you have direct access to PCS 7 OS archive data stored
in the MS SQL server database. Depending on the configuration, process data of the PCS 7
OS is stored in compressed form.
The differences to Microsoft OLE DB provider are shown in the following table:
WinCC OLE DB provider Microsoft OLE DB-Provider
Transparent access to the
process data of the PCS 7 OS
Read data via multiple database
segments
Note
When the OS server closes a full archive and opens a new archive, there is a brief time when
no data is read from the message and process value archives via the WinCC OLE DB provider.
Microsoft OLE DB
The Microsoft OLE DB provider is the database provider of Microsoft. This can be implemented
with database access to the MS SQL Server database.
possible Not supported
possible Not supported
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 81
Page 82

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
The administrator of the databases can take suitable measures to protect the databases from
unauthorized access via Microsoft OLE DB.
Note
With Microsoft OLE DB, only access to WinCC user archives has been tested and released,
but not access to message and process value archives. Use the WinCC OLE DB Provider to
access message and process value archives.
Additional information
● Detailed information on "Security settings when accessing SQL databases via MS OLE
DB" is available in the system manual
MDM - WinCC/Connectivity Pack
6.7.3 Establishing the connection to the database
.
ConnectionString
The connection between the application, which reads data via the OLE DB, and the archive
database, is established via the Connection object with ActiveX Data Objects (ADO). One of
the important parameters here is the ConnectionString. The ConnectionString contains all
information necessary for access to the database using the OLE DB provider.
Structure of the ConnectionString
"Provider = name of the OLE DB provider; Catalog=database name;
Data Source=Package name + "\WinCC";"
The "Package name" is made up of the symbolic computer name and "::" e.g.
"OSPro_1_Prj_OS::".
OpenPCS 7
82 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 83
Parameter Description
Provider Name of the OLE DB provider: e.g. WinCCOLEDBProvider
Catalog The "CC_ExternalBrowsing" database can also be used.
Note
For transparent access, enter the name of the PCS 7 OS project for "Catalog", for
example: "Catalog=WinCC_Project_Name".
Note
If you access message archives or swapped archives with "CC_ExternalBrowsing",
access can take several minutes.
Data
Source
For transparent access to the central archive server or with redundant servers using the
OLE DB provider, enter the following for "Data Source": <Symbolic computer name>::
\WinCC.
Note
If you access an archive tag in the long-term server "CAS", use the name of the archive
tag. The long-term archive server "CAS" returns the CAS-ID as the ID and not the ID of
the archive tag:
<Symbolic computer name>\\<Archive_Var_Name>
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
Example of a VBA application:
In the following example, a connection object is generated and then the connection to the
WinCCdatabase (process value or message archive) is opened.
Dim sPro As String
Dim sDsn As String
Dim sSer As String
Dim sCon As String
sPro = "Provider=WinCCOLEDBProvider.1;"'Provider
SDsn = "Catalog=CC_OS_06_09_25_13_36_53;"'Catalog
SSer = "Data Source=OSPro_1_Prj_OS::\WinCC"'Data Source
SCon = sPro + SDsn + SSer 'Connection String
'Connection
Set conn = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
conn.ConnectionString = SCon
conn.CursorLocation = 3
conn.Open
6.7.4 Access to the OLE DB provider
Access options
With OLE DB, you have the following options to access PCS 7 OS archive data:
● Access with the WinCC OLE DB provider
● Access with Microsoft OLE DB
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 83
Page 84

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
Access with the WinCC OLE DB provider
With WinCC OLE DB, you can access all PCS 7 OS archive data. Depending on the
configuration, process data of the PCS 7 OS is stored in compressed form. The WinCC OLE
DB provider allows transparent access to this data.
Access with Microsoft OLE DB
With Microsoft OLE DB, you can access the WinCC user archives. User archives are part of
WinCC, not of PCS 7 OS. The user archives can be used within the framework of TIA (Totally
Integrated Automation). However, the licenses must be obtained separately for WinCC .
Note
With Microsoft OLE DB, only access to WinCC user archives has been tested and released,
but not access to message and process value archives. Use the WinCC OLE DB Provider to
access message and process value archives.
Configuration options
Basic procedure
To access the databases with the WinCC OLE DB provider, you can write your own
applications. For communication with the WinCC OLE DB provider, ADO DB is used in
applications. ADO DB can, for example, be used with Visual Basic or VBA.
Note
Special characters in tag names
In terms of the tag names, remember that programming languages such as Visual Basic,
VBScript or VBA only permit the following characters in tag names:
"A...Z", "a...z", "0...9" and "_". If you use special characters such as "," or ";" in tag names in
WinCC , the script will abort with an error message. In this case, use the "Tag ID" to address
a tag in the script if it has special characters in the name. We also recommend that you use
the "Tag ID" to improve performance.
1. The OLE DB application must always run on the OpenPCS 7 station. Remote access is
not possible.
2. With swapped archives, establish the connection between the SQL database and the
swapped archives with the WinCC Archive Connector.
Note
The WinCC RT archives in the directory "<project directory> \ ArchiveManager" and the
subdirectories belonging to it must not be connected or disconnected using the Archive
Connector because the connection to the SQL Server is managed by the WinCC basic
system.
OpenPCS 7
84 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 85

3. Establish the connection to the database, for example, by using MS Excel or your own
application. Specify the required selection criteria and read the archive data.
4. For example, you can display the results of the query in MS Excel or export it as a CSV file.
6.7.5 Querying archive data
6.7.5.1 Representation of the process value archive
Recordset for process value archives
The result of the query is returned as a recordset. This chapter describes the structure of the
recordset for process value archives.
Field name Data type Comment
ValueID Integer 4 bytes Unique identification of the value
TimeStamp Datetime Time stamp
RealValue Real 8 bytes Tag value
Quality Integer 4 bytes Quality code of the value (e.g. "good" or "bad")
Flags Integer 4 bytes Internal control parameter
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
6.7.5.2 Querying process value archives
Principle
You can access a process value archive with the following query. The data can be selected
using filter criteria. The queries are transferred to the database with the command object.
Syntax
TAG:R, <ValueID oder ValueName>,<TimeBegin>,<TimeEnd>[,<SQL_clause>]
[,<TimeStep>]
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 85
Page 86

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
Table 6-1 Parameter
Parameter Description
ValueID ValueID from the database table. Can be named more than once, for example:
ValueName ValueName in the format 'ArchiveName\Value_Name'. The <ValueName> parameter
TimeBegin Start time in the format:
TimeEnd End time in the format:
"TAG:R,(ValueID_1;ValueID_2;ValueID_x),<TimeBegin>,<TimeEnd>"
must be enclosed in single quotes. Multiple naming is possible, for example:
"TAG:R,('ValueName_1';'ValueName_2';'ValueName_x'), <TimeBegin>,<TimeEnd>"
Note
With tag names, remember that programming languages such as Visual Basic,
VBScript or VBA only permit the following characters in tag names:
"A...Z", "a...z", "0...9" and "_".
If you use special characters such as "," or ";" in tag names in WinCC , the script will
abort with an error message. In this case, use the "Tag ID" to address a tag in the script
if it has special characters in the name.
'YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.msc'
If you use <TimeStep> , then <TimeBegin> must be specified as real time. Relative
times or "0000-00-00 00:00:00.000" are not possible.
'YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.msc'
OpenPCS 7
86 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 87

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
Parameter Description
SQL_Clause Filter criterion in SQL syntax:
[WHERE search_condition] [ORDER BY {order_expression [ASC|DESC] } ]
The criterion "ORDER BY" can only be used with a specified sort order
"{order_expression [ASC|DESC] }" .
TimeStep Values in the specified time interval are grouped together beginning at the start time
<TimeBegin>.
Format: 'TIMESTEP=x,y'
x = period in seconds
y = aggregate function type
The interval result is returned for an interval depending on the type of aggregate
function. The following values are possible for the type of aggregate function:
● Without interpolation:
If there are no values in the period, no period result will be returned.
1 (FIRST): First value
2 (LAST): Last value
3 (MIN): Minimum value
4 (MAX): Maximum value
5 (AVG): Average
6 (SUM): Sum
7 (COUNT): Number of values
● With interpolation:
An interval result is returned for every interval. This is done with linear interpolation.
There is no extrapolation.
257 (FIRST_INTERPOLATED): First value
258 (LAST_INTERPOLATED): Last value
259 (MIN_INTERPOLATED): Minimum value
260 (MAX_INTERPOLATED): Maximum value
261 (AVG_INTERPOLATED): Average
262 (SUM_INTERPOLATED): Sum
263 (COUNT_INTERPOLATED): Number of values
Example: With TIMESTEP=60,257 , an interpolated value is returned for each 60
second period:
"TAG:R,1,'2004-07-09 09:03:00.000','0000-00-00 00:10:00.000','TIMESTEP=60,257'"
Rule
Note the following:
● <TimeBegin> and <TimeEnd> may not both be "ZERO" = "0000-00-00 00:00:00.000".
● In order to read data, <TimeBegin> must come before <TimeEnd>. For reverse sorting,
use the parameter "Order by-Clause" .
● To improve performance, use the "ValueID" in the query instead of "ValueName". You can
get the "ValueID" from the "Archive" table.
● With process values, some applications cannot handle the time with a resolution of 1 ms
and this can lead to inaccuracies.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 87
Page 88

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
Selecting an absolute time period
Read from start time <TimeBegin> to end time <TimeEnd>.
Example 1:
Reads the values of ValueID 1 from start time 9:03 a.m. to end time 9:10 a.m.
"TAG:R,1,'2004-07-09 09:03:00.000','2004-07-09 09:10:00.000'"
Selecting a relative time period
Reading from the start of the recording:
<TimeBegin> = '0000-00-00 00:00:00.000'
Reading to the end of the recording:
<TimeEnd> = '0000-00-00 00:00:00.000'
Example 2:
Example 3:
However, <TimeBegin> and <TimeEnd> may not both be "ZERO" = '0000-00-0000:00:00.000' .
Note
If you want to query a relative period from a connected archive database, enter this in the
following format:
0000-00-DD hh:mm:ss.msc
If you specify a period in months, the content may be incorrect since a month can have
between 28 and 31 days.
Reads starting from the absolute time of "TimeBegin" to the end of the recording, in other
words, to the last archived value.
<TimeBegin> = '2003-02-02 12:00:00.000',
<TimeEnd> = '0000-00-0000:00:00.000'
Reads 10 seconds further starting from the absolute time of "TimeBegin" .
<TimeBegin> = '2003-02-02 12:00:00.000',
<TimeEnd> = '0000-00-00 00:00:10.000'
Example 4:
Reads 10 seconds back starting from the absolute time of "TimeEnd".
<TimeBegin> = '0000-00-00 00:00:10.000',
<TimeEnd> = '2003-02-02 12:00:00.000'
OpenPCS 7
88 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 89

Example 5:
Reads the values of the last hour for several ValueIDs (1;3;5;6) , starting at the time of the last
archived value.
"TAG:R,(1;3;5;6),'0000-00-00 01:00:00.000',
'0000-00-0000:00:00.000'"
Multiple return values for one query by filtering the tag value
Example 6:
The following query also uses the <SQL_Clause> parameter and returns all values of tags
with the ValueID "3" and "6" that are below 50 or over 100.
"TAG:R,(3;6),<TimeBegin>,<TimeEnd>,'WHERE RealValue > 100 OR
RealValue < 50'"
Query with the <TimeStep>parameter
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
Example 7:
The following query uses the <TimeStep> parameter and returns all values of the ValueID "1" ,
starting at "TimeBegin" for the next 5 minutes at intervals of "60" seconds with aggregate
function type "5" = "average value without interpolation".
"TAG:R,1,'2004-10-13 17:00:00.000','0000-00-00 00:05:00.000',
'TIMESTEP=60,5'"
Example 8:
The following query uses the <TimeStep> parameter and returns all values of theValueIDs "1"
and "2" , starting at "TimeBegin" until 2 minutes later at intervals of "15" seconds with aggregate
function type "261" = "average value without interpolation".
"TAG:R,(1;2),'2004-10-13 17:00:00.000','0000-00-00 00:02:00.000',
'TIMESTEP=15,261'"
6.7.5.3 Representation of the message archives
Structure of the recordset
The result of the query is returned as a recordset. The following table describes the structure
of the recordset for message archives. Information on the status of messages is available in
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 89
Page 90

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
the WinCC Information System in "Working with WinCC > ANSI-C Function Descriptions >
Appendix > Structure Definitions > MSG_RTDATA_STRUCT Structure Definition".
Position Field name Type Comment
1 MsgNo Integer 4 bytes Message number
2 State Small integer 2
3 DateTime DateTime 8 bytes Time stamp of the message (date/time without
4 Ms Small integer 2
5 Instance VarChar(255) Instance name of the message
6 Flags1 Integer 4 bytes (for internal use only)
7 PValueUsed Integer 4 bytes Process values used
8 to 17 PValue1 to
18 to 27 PText1 to
28 Computer name VarChar(255) Computer name
29 Application VarChar(255) Application name
30 Comment VarChar(255) Comment
31 Username VarChar(255) User name
32 Counter Integer 4 bytes Continuous message counter
33 TimeDiff Integer 4 bytes Time difference to the "came in" status
34 Classname VarChar(255) Name of the message class
35 Type name VarChar(255) Name of the message type
36 Class Small integer 2
37 Type Small integer 2
38 to 47 Text1 to Text10 VarChar(255) Message text 1 to 10
48 AG_NR Small integer 2
49 CPU_NR Small integer 2
50 CrComeFore Integer 4 bytes Foreground color for the "came in" status
51 CrComeBack Integer 4 bytes Background color for the "came in" status
52 CrGoFore Integer 4 bytes Foreground color for the "went out" status
53 CrGoBack Integer 4 bytes Background color for the "went out" status
54 CrAckFore Integer 4 bytes Foreground color for the "acknowledged" status
55 CrAckBack Integer 4 bytes Background color for the "acknowledged" status
56 LocaleID Integer 4 bytes Location of the alarm
57 Priority Integer 4 bytes Priority
58 AP_type Integer 4 bytes Loop in Alarm
Message status
Byte
milliseconds)
Time stamp of the message (milliseconds)
Byte
Real 8 bytes Numerical process value 1 to 10
PValue10
VarChar(255) Process value text 1 to 10
PText10
ID of the message class
Byte
ID of the message type
Byte
Number of the PLC
Byte
Number of the CPU
Byte
OpenPCS 7
90 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 91

Position Field name Type Comment
59 AP_name VarChar(255) Loop in Alarm function name
60 AP_PAR VarChar(255) Loop in Alarm screen
61 InfoText VarChar(255) Info text
62 TxtCame VarChar(255) Text came in
63 TxtWent VarChar(255) Text went out
64 TxtCameNWent VarChar(255) Text came in and went out
65 TxtAck VarChar(255) Text acknowledged
66 AlarmTag Integer 4 bytes Message tag
67 AckType Small integer 2
68 Params Integer 4 bytes Parameter
6.7.5.4 Querying the message archive
Principle
OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
Acknowledgment type
Byte
Syntax
Use the following query to access a message archive. The data can be selected using filter
criteria. The query is transferred to the database with the command object.
Information on the status of messages is available in the WinCC Information System in
"Working with WinCC > ANSI-C Function Descriptions > Appendix > Structure Definitions >
MSG_RTDATA_STRUCT Structure Definition".
ALARMVIEW:SELECT * FROM <ViewName>[WHERE <Condition>...., optional]
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 91
Page 92

OpenPCS 7 interface
6.7 OLE DB
Parameter Description
ViewName Name of the database table.
Condition Filter criterion e.g.:
The table must be specified in the required language. The "ViewName" for the five
European languages is, for example:
ALGVIEWDEU: German message archive data
ALGVIEWENU: English message archive data
ALGVIEWESP: Spanish message archive data
ALGVIEWFRA: French message archive data
ALGVIEWITA: Italian message archive data
Note
The languages that are installed on the PCS 7 OS or configured in the PCS 7 OS Text
Library are supported. Information on the possible query languages and the
corresponding "ViewName" in the SQL server is available in the connected message
archives in "Views". Here, all languages and their identifications, such as
"ALGVIEWENU", are displayed that are supported in the particular archive.
DateTime>'2003-06-01' AND DateTime<'2003-07-01'
DateTime>'2003-06-01 17:30:00'
MsgNo = 5
MsgNo in (4, 5)
State = 2
With DateTime, the time can only be specified in absolute format.
Example 1:
Example 2:
Reads all entries of message number 5 that were recorded after July 05, 2003.
"ALARMVIEW:SELECT * FROM ALGVIEWENU WHERE MsgNo = 5 AND
DateTime>'2003-07-05'"
Reads all messages with the time stamp between July 03, 2003 and July 05, 2003.
"ALARMVIEW:SELECT * FROM ALGVIEWENU WHERE DateTime>'2003-07-03' AND
DateTime<'2003-07-05'"
OpenPCS 7
92 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
Page 93

Appendix
A.1 Commissioning
List of checkable points when commissioning the OpenPCS 7 station
The following list contains the points that can be checked when you are setting up a connection
from the OPC client to the OpenPCS 7 station.
1. Check that all necessary OpenPCS 7 licenses are available and valid.
2. Check that the OpenPCS 7 station can be reached from the OPC client computer using a
ping.
3. Check whether it is possible to access the path "\\<OpenPCS 7 Station>\Automation
Projects" over the network and that the files "SPOSA.dcf" and "<ProjectName_PCStationName>.dcf" exist.
4. Check that the OS servers and automation systems are working properly.
5. Check the installation and version of the OpenPCS 7 station
6. Check the installation of the OPC client. Information on the correct installation of the OPC
client must be supplied by the vendor of the OPC client.
A
7. Check the Windows firewall settings. The firewall settings are made during installation.
Enter the following OpenPCS 7 components in the "Exceptions" tab of the firewall:
– "SIMATIC PCS7 OPC AE Server"
– "SIMATIC PCS7 OPC DA Server" and
– "SIMATIC PCS7 OPC HDA Server
8. Implement the DCOM settings using the SecurityController on the OpenPCS 7 station.
9. Check that the following processes are executed on the OpenPCS 7 station during OPC
client runtime:
– OpcEnum.exe is started by the system.
– SOPCDASVRPCS7.exe is started by the OPC client on the OpenPCS 7 station.
– SOPCAESVRPCS7.exe is started by the OPC client on the OpenPCS 7 station.
– SOPCHDASVRPCS7.exe is started by the OPC client on the OpenPCS 7 station.
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 93
Page 94

Page 95

Lists and folders
B.1 List of sources
Sources
[1] OPC Foundation, Data Access Custom Interface Specification 3.0
[2] OPC Foundation, Data Access Automation Interface Standard 2.02
[3] OPC Foundation, Alarms and Events Custom Interface Standard 1.10
[4] OPC Foundation, Alarm & Events Automation Interface Standard 1.01
[5] OPC Foundation, Historical Data Access Specification 1.20
[6] OPC Foundation, Historical Data Access Automation Interface Standard 1.0
[7] WinCC V6.2 SP2, OPC - OLE for Process Control
[8] WinCC V6.2, OPC Channel
[9] WinCC V6.2, Connectivity Pack
[10] SIMATIC NET, Industrial Communication with PG/PC Volume 1 - Basics
B
B.2 List of abbreviations/acronyms
List of abbreviations/acronyms
Abbreviation/
acronym
APC Advanced Process Control
AS Automation System
CAL Client Access License
CAS Central Archive System
COM Component Object Model
CPU Central Processor Unit
DA Data Access
DCOM Distributed Component Object Model
DLL Dynamic Link Library
ES Engineering system
HDA Historical Data Access
HMI Human Machine Interface
HW Hardware
LRPC Lightweight Remote Procedure Call
Description
OpenPCS 7
Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02 95
Page 96

Lists and folders
B.2 List of abbreviations/acronyms
Abbreviation/
acronym
OLE Object Linking and Embedding
OLE DB Object Linking and Embedding for Data Base
OPC previously: OLE for Process Control, now: Openess, Productivity and Collaboration
OS Operating System
PC Personal Computer
PCS 7 Process Control System 7
RPC Remote Procedure Call
SFC Sequential Function Chart
SP Service pack
SPOSA Single Point of System Access
SQL Structured Query Language
WinCC Windows Control Center
APC Advanced Process Control
Description
OpenPCS 7
96 Function Manual, 05/2012, A5E02780178-02
 Loading...
Loading...