Page 1

Preface
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Introduction
Installing Device
Communication Ports
Technical Specifications
Dimension Drawings
Certification
1
2
3
4
5
6
12/2015
RC1045-EN-09
Page 2

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Copyright © 2015 Siemens Canada Ltd.
All rights reserved. Dissemination or reproduction of this document, or evaluation and communication of its contents, is not authorized
except where expressly permitted. Violations are liable for damages. All rights reserved, particularly for the purposes of patent application or
trademark registration.
This document contains proprietary information, which is protected by copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this document may be
photocopied, reproduced or translated to another language without the prior written consent of Siemens Canada Ltd..
Disclaimer Of Liability
Siemens has verified the contents of this manual against the hardware and/or software described. However, deviations between the product
and the documentation may exist.
Siemens shall not be liable for any errors or omissions contained herein or for consequential damages in connection with the furnishing,
performance, or use of this material.
The information given in this document is reviewed regularly and any necessary corrections will be included in subsequent editions. We
appreciate any suggested improvements. We reserve the right to make technical improvements without notice.
Registered Trademarks
ROX™, Rugged Operating System On Linux™, CrossBow™ and ELAN™ are trademarks of Siemens Canada Ltd. ROS® is a registered
trademark of Siemens Canada Ltd.
Other designations in this manual might be trademarks whose use by third parties for their own purposes would infringe the rights of the
owner.
Third Party Copyrights
Siemens recognizes the following third party copyrights:
• Copyright © 2004 GoAhead Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Security Information
Siemens provides products and solutions with industrial security functions that support the secure operation of plants, machines, equipment
and/or networks. They are important components in a holistic industrial security concept. With this in mind, Siemens' products and solutions
undergo continuous development. Siemens recommends strongly that you regularly check for product updates.
For the secure operation of Siemens products and solutions, it is necessary to take suitable preventive action (e.g. cell protection concept)
and integrate each component into a holistic, state-of-the-art industrial security concept. Third-party products that may be in use should also
be considered. For more information about industrial security, visit http://www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity.
To stay informed about product updates as they occur, sign up for a product-specific newsletter. For more information, visit http://
support.automation.siemens.com.
Warranty
Siemens warrants this product for a period of five (5) years from the date of purchase, conditional upon the return to factory for maintenance
during the warranty term. This product contains no user-serviceable parts. Attempted service by unauthorized personnel shall render all
warranties null and void. The warranties set forth in this article are exclusive and are in lieu of all other warranties, performance guarantees
and conditions whether written or oral, statutory, express or implied (including all warranties and conditions of merchantability and fitness for
a particular purpose, and all warranties and conditions arising from course of dealing or usage or trade). Correction of nonconformities in the
manner and for the period of time provided above shall constitute the Seller’s sole liability and the Customer’s exclusive remedy for defective
or nonconforming goods or services whether claims of the Customer are based in contract (including fundamental breach), in tort (including
negligence and strict liability) or otherwise.
For warranty details, visit www.siemens.com/ruggedcom or contact a Siemens customer service representative.
ii
Page 3

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Contacting
Address
Siemens Canada Ltd.
Industry Sector
300 Applewood Crescent
Concord, Ontario
Canada, L4K 5C7
Telephone
Toll-free: 1 888 264 0006
Tel: +1 905 856 5288
Fax: +1 905 856 1995
E-mail
ruggedcom.info.i-ia@siemens.com
Web
www.siemens.com/ruggedcom
iii
Page 4

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
iv
Page 5

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Preface ............................................................................................................... vii
Alerts ................................................................................................................................................ vii
Related Documents ............................................................................................................................ vii
Accessing Documentation .................................................................................................................. viii
Training ............................................................................................................................................ viii
Customer Support ............................................................................................................................. viii
Chapter 1
Introduction .......................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Feature Highlights ........................................................................................................................ 1
1.2 Description .................................................................................................................................. 2
1.3 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) Support ......................................................................................... 3
1.3.1 Supported Time Synchronization Sources ........................................................................... 4
1.3.2 AM and TTL Outputs ......................................................................................................... 5
1.3.3 IEEE 1588 Support ........................................................................................................... 6
Chapter 2
Installing Device .................................................................................................. 7
2.1 Mounting the Device .................................................................................................................... 7
2.1.1 Mounting the Device to a Rack .......................................................................................... 8
2.1.2 Mounting the Device on a DIN Rail .................................................................................... 9
2.1.3 Mounting the Device to a Panel ....................................................................................... 10
2.2 Connecting Power ...................................................................................................................... 11
2.2.1 Connecting AC Power ..................................................................................................... 12
2.2.2 Connecting DC Power ..................................................................................................... 13
2.2.3 Wiring Examples ............................................................................................................. 15
2.3 Installing a GPS Antenna ........................................................................................................... 17
2.4 Connecting the Failsafe Alarm Relay ........................................................................................... 19
2.5 Grounding the Device ................................................................................................................. 20
2.6 Connecting to the Device ........................................................................................................... 20
2.7 Cabling Recommendations ......................................................................................................... 21
2.7.1 Protection On Twisted-Pair Data Ports .............................................................................. 22
2.7.2 Gigabit Ethernet 1000Base-TX Cabling Recommendations ................................................. 22
v
Page 6

Table of Contents
Chapter 3
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Communication Ports ......................................................................................... 23
3.1 Copper Ethernet Ports ................................................................................................................ 24
3.2 Fiber Optic Ethernet Ports .......................................................................................................... 25
3.3 SFP Optic Ethernet Ports ........................................................................................................... 25
3.3.1 Installing an SFP Optical Port .......................................................................................... 26
3.3.2 Removing an SFP Optical Port ......................................................................................... 27
3.4 GBIC Optic Ethernet Ports .......................................................................................................... 28
3.4.1 Installing a GBIC Optical Port ........................................................................................... 28
3.4.2 Removing a GBIC Optical Port ......................................................................................... 29
3.5 BNC Ports ................................................................................................................................. 30
Chapter 4
Technical Specifications ..................................................................................... 33
4.1 Power Supply Specifications ....................................................................................................... 33
4.2 Failsafe Relay Specifications ...................................................................................................... 33
4.3 Supported Networking Standards ................................................................................................ 34
4.4 Copper Ethernet Port Specifications ............................................................................................ 34
4.4.1 Copper Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) Port Specifications ........................................................ 34
4.5 Fiber Optic Ethernet Port Specifications ....................................................................................... 35
4.5.1 10FL Ethernet Optical Specifications ................................................................................ 35
4.5.2 Fast Ethernet (10/100 Mbps) Optical Specifications ........................................................... 35
4.5.3 Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) Optical Specifications ................................................................ 36
4.6 PTP Specifications ..................................................................................................................... 37
4.7 Operating Environment ............................................................................................................... 38
4.8 Mechanical Specifications ........................................................................................................... 39
Chapter 5
Dimension Drawings .......................................................................................... 41
Chapter 6
Certification ........................................................................................................ 45
6.1 Standards Compliance ............................................................................................................... 45
6.2 Agency Approvals ...................................................................................................................... 45
6.3 EMC and Environmental Type Tests ............................................................................................ 46
vi
Page 7

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Preface
This guide describes the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288. It describes the major features of the device, installation,
commissioning and important technical specifications.
It is intended for use by network technical support personnel who are responsible for the installation,
commissioning and maintenance of the device. It is also recommended for use by network and system planners,
system programmers, and line technicians.
Alerts
The following types of alerts are used when necessary to highlight important information.
DANGER!
DANGER alerts describe imminently hazardous situations that, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury.
Preface
WARNING!
WARNING alerts describe hazardous situations that, if not avoided, may result in serious injury and/or
equipment damage.
CAUTION!
CAUTION alerts describe hazardous situations that, if not avoided, may result in equipment damage.
IMPORTANT!
IMPORTANT alerts provide important information that should be known before performing a procedure
or step, or using a feature.
NOTE
NOTE alerts provide additional information, such as facts, tips and details.
Related Documents
Other documents that may be of interest include:
• ROS User Guide for the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Alerts vii
Page 8

Preface
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Accessing Documentation
The latest user documentation for RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 v is available online at
www.siemens.com/ruggedcom. To request or inquire about a user document, contact Siemens Customer
Support.
Training
Siemens offers a wide range of educational services ranging from in-house training of standard courses on
networking, Ethernet switches and routers, to on-site customized courses tailored to the customer's needs,
experience and application.
Siemens' Educational Services team thrives on providing our customers with the essential practical skills to make
sure users have the right knowledge and expertise to understand the various technologies associated with critical
communications network infrastructure technologies.
Siemens' unique mix of IT/Telecommunications expertise combined with domain knowledge in the utility,
transportation and industrial markets, allows Siemens to provide training specific to the customer's application.
For more information about training services and course availability, visit www.siemens.com/ruggedcom or
contact a Siemens sales representative.
Customer Support
Customer support is available 24 hours, 7 days a week for all Siemens customers. For technical support or
general information, contact Siemens Customer Support through any of the following methods:
Online
Visit http://www.siemens.com/automation/support-request to submit a Support Request (SR) or check
on the status of an existing SR.
Telephone
Call a local hotline center to submit a Support Request (SR). To locate a local hotline center, visit
http://www.automation.siemens.com/mcms/aspa-db/en/automation-technology/Pages/default.aspx.
Mobile App
Install the Industry Online Support app by Siemens AG on any Android, Apple iOS or Windows mobile
device and be able to:
• Access Siemens' extensive library of support documentation, including FAQs and manuals
• Submit SRs or check on the status of an existing SR
• Contact a local Siemens representative from Sales, Technical Support, Training, etc.
• Ask questions or share knowledge with fellow Siemens customers and the support community
viii Accessing Documentation
Page 9

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Introduction
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 is a rugged, fully managed, modular Ethernet switch specifically designed
to operate reliably in electrically harsh and climatically demanding utility substation, railway and industrial
environments. The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 includes the IEEE 1588 v2 protocol with hardware time stamping,
allowing high precision time synchronization over the Ethernet network with accuracies of 1 μs or better. The
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288’s superior rugged hardware design coupled with the embedded Rugged Operating
System (ROS) provides improved system reliability and advanced cyber security and networking features,
making it ideally suited for creating Ethernet networks for mission-critical, real-time, control applications.
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288’s modular flexibility offers 100/1000BaseX fiber and 10/100/1000BaseTX copper
port combinations. Support for front or rear mount connectors coupled with support for multiple fiber connector
types (SFP, GBIC, LC, SC) without loss of port density makes the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 highly versatile and
suitable for any application. The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 is packaged in a rugged, galvanized steel enclosure
with industrial grade DIN, panel, or 48 cm (19 in) rack-mount mounting options.
The following sections provide more information about the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288:
• Section 1.1, “Feature Highlights”
• Section 1.2, “Description”
• Section 1.3, “Precision Time Protocol (PTP) Support”
Chapter 1
Introduction
Section 1.1
Feature Highlights
Ethernet Ports
• Up to 9 x Gigabit Ethernet ports (copper and fiber)
• Up to 9 x 100Base-FX Fiber Fast Ethernet ports (copper and fiber)
• 2-port modules for tremendous flexibility
• Non-blocking, store and forward switching
• Supports many types of fiber (multimode, single mode, bidirectional single strand)
• Full compliance with IEEE: 802.3, 802.3u & 802.3z
• Full duplex operation and flow control (IEEE 802.3x)
• Long haul optics allow Gigabit at distances up to 70 km
• Industry standard fiber optic connectors: LC, SC, SFP, GBIC
Advanced Time Synchronization
• Support for IEEE 1588 v2, GPS and IRIG-B time synchronization
• Hardware time stamping on all ports including Gigabit
• Transparent clock operation for high precision on switched networks (1us or better)
• Peer-to-peer path delay measurements
• High precision TCXO (Temperature Compensated Oscillator)
Feature Highlights 1
Page 10

Chapter 1
2
5
6
4
1
7
9
8
3
Introduction
• Supports master, slave and transparent clock modes
• Support for IRIG-B input and output
Rated for Reliability in Harsh Environments
• Immunity to EMI and heavy electrical surges
• Zero-Packet-Loss™ technology
• -40 to 85 °C (-40 to 185 °F) operating temperature (no fans)
• Conformal coated printed circuit boards (optional)
• 18 AWG galvanized steel enclosure
• Hazardous Location Certification: Class 1 Division 2
Universal Power Supply Options
• Fully integrated, dual-redundant (optional) power supplies
• Universal high-voltage range: 88-300 VDC or 85-264 VAC
• Popular low voltage ranges: 24 VDC (10-36 VDC), 48 VDC (36-72 VDC)
• Screw or pluggable terminal blocks for reliable, maintenance-free connections
• CSA/UL 60950-1 safety approved to 85 °C (185 °F)
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Section 1.2
Description
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 features various ports, controls and indicator LEDs on the display panel for
connecting, configuring and troubleshooting the device. The display panel can be located on the rear, front or top
of the device, depending on the mounting configuration.
Figure 1: RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
1. Fiber or Copper Ethernet Ports 2. Copper Ethernet Port 3. BNC Ports 4. Port Status Indicator LEDs 5. Mode Button 6. RS-232
Serial Console Port (RJ45) 7. Display Mode Indicator LEDs 8. Alarm Indicator LED 9. Power Module Indicator LEDs
• Communication Ports – Ports for communicating with other devices or accessing the RUGGEDCOM ROS
operating system are described in Chapter 3, Communication Ports.
• Port Status Indicator LEDs – Port status indicator LEDs indicate the operational status of each port,
dependent on the currently selected mode.
2 Description
Page 11

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Chapter 1
Introduction
Mode Color/State Description
Status
Duplex
Speed
Green (Solid) Link detected
Green (Blinking) Link activity
Off No link detected
Green Full duplex mode
Orange Half duplex mode
Off No link detected
Green (Solid) 100 Mb/s
Green (Blinking) 1000 Mb/s
Orange (Solid) 10 Mb/s
Off No link detected
• Display Mode Indicator LEDs – The display mode indicator LEDs indicate the current display mode for the
port status indicator LEDs (i.e. Status, Duplex or Speed).
• Mode button – The Mode button sets the display mode for the port status indicator LEDs (i.e. Status, Duplex
or Speed). It can also be used to reset the device if held for 5 seconds.
• Alarm Indicator LED – The alarm indicator LED illuminates when an alarm condition exists.
• Power Module Indicator LEDs – The power module indicator LEDs indicate the status of the power modules.
▪ Green – The power supply is supplying power
▪ Red – Power supply failure
▪ Off – No power supply is installed
• RS-232 Console Port – The serial console port is for interfacing directly with the device and accessing initial
management functions. For information about connecting to the device via the serial console port, refer to
Section 2.6, “Connecting to the Device”.
Section 1.3
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) Support
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) module adds the ability to provide time synchronization via Ethernet using
the Precision Time Protocol (PTP) and Network Time Protocol (NTP), and to synchronize with an external IRIG-B
source or GPS network.
The PTP module features BNC ports for AM OUT, TTL IN/OUT and GPS IN. It also includes an LED to indicate
when synchronization has been achieved.
NOTE
The PTP module can only be installed in slot 6. For more information, refer to Chapter 3,
Communication Ports.
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) Support 3
Page 12
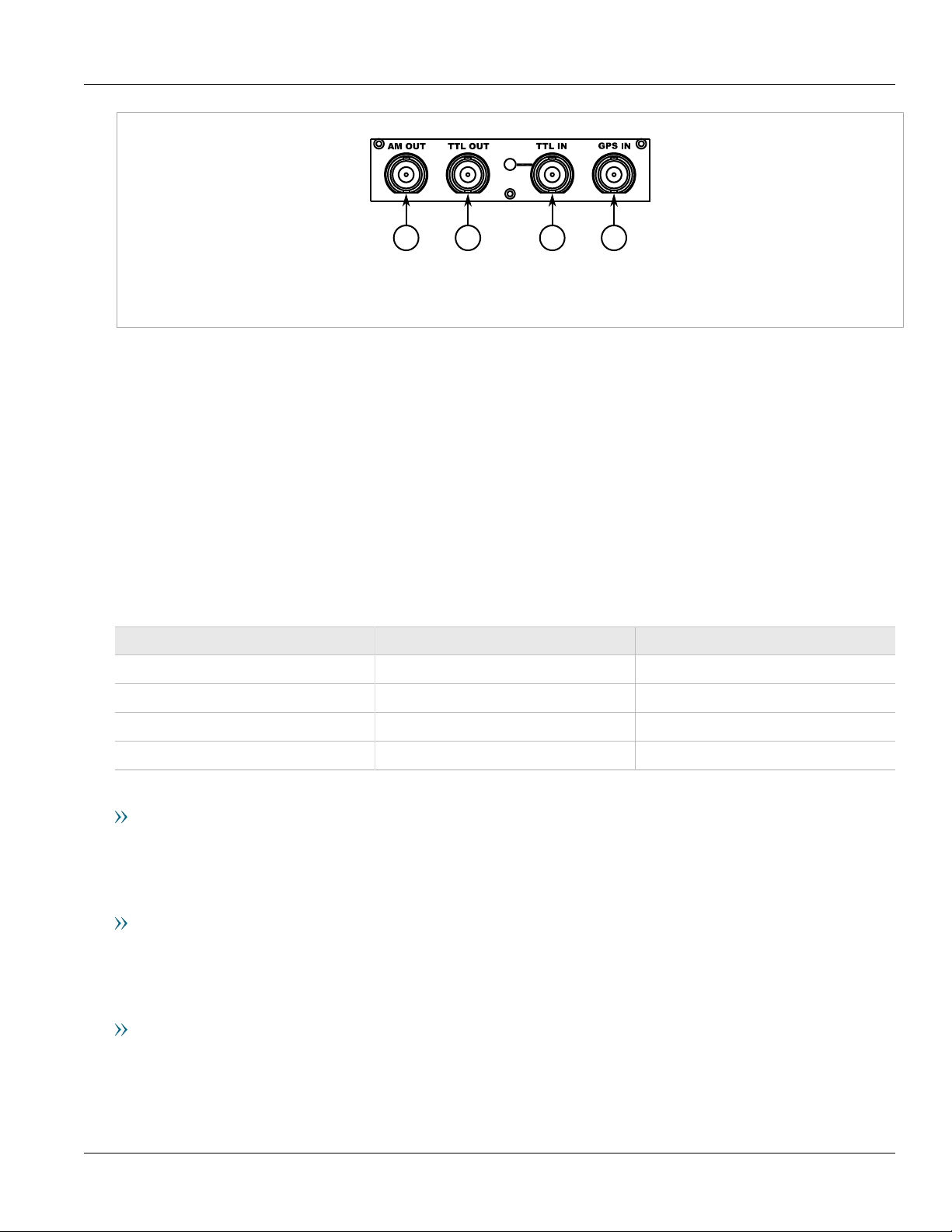
Chapter 1
1 2 3 4
Introduction
Figure 2: PTP Module
1. AM OUT Port 2. TTL OUT Port 3. TTL IN Port 4. GPS IN Port
For more information about the BNC ports, refer to Section 3.5, “BNC Ports”.
The following sections describe the PTP support in more detail:
• Section 1.3.1, “Supported Time Synchronization Sources”
• Section 1.3.2, “AM and TTL Outputs”
• Section 1.3.3, “IEEE 1588 Support”
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Section 1.3.1
Supported Time Synchronization Sources
The following time synchronization sources are supported by the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288, with or without the
PTP card:
Synchronization Source Without PTP Card With PTP Card
NTP
IEEE 1588 v2
IRIG-B PWM
GPS
NTP
NTP (Network Time Protocol) is the standard for synchronizing the clocks of computer systems throughout the
Internet and is suitable for systems that require accuracies in the order of 1 ms.
IRIG-B PWM
IRIG-B time synchronization is an even older, established, inter-device time synchronization mechanism providing
accuracy in sub-milliseconds.
ü ü
ü ü
û ü
û ü
GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), as a source of accurate time, requires an external GPS antenna input to
provide accurate time signals comparable to 500 ns. The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 can use the GPS receiver on
the PTP module to provide the time base for the system.
4 Supported Time Synchronization Sources
Page 13
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
VS
RS RC
RL/N
321
Installation Guide
IEEE 1588
IEEE 1588 is designed to provide networked, packet-based time synchronization between different networking
nodes (PTP devices). The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 supports PTP v2, which is defined in the IEEE 1588-2008
standard. IEEE 1588 is designed to fill a niche not well served by either of the two older, dominant protocols,
NTP and IRIG-B. IEEE 1588 is also designed for applications that cannot bear the cost of a GPS receiver at each
node or for which GPS signals are inaccessible.
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 supports ordinary clock, boundary clock and transparent clock modes. An ordinary
clock can be configured as either a Grandmaster Clock (GM) or a Slave Clock (SC) within the master-slave
hierarchy.
Every Ethernet port on the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 supports IEEE 1588. For more information, refer to
Section 1.3.3, “IEEE 1588 Support”.
Section 1.3.2
AM and TTL Outputs
The PTP card provides AM (Amplitude Modulated) and TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) outputs.
The AM OUT port supports the IRIG-B AM signal format, while the TTL OUT port supports the IRIG-B PWM
and PPS signal formats. Enabling/disabling the output ports and – in the case of TTL OUT – selecting the signal
format is controlled through the RUGGEDCOM ROS operating system.
Chapter 1
Introduction
IMPORTANT!
The input impedance of third-party AM inputs must be 100 Ω minimum.
The number of devices that can be connected to the AM OUT and TTL Out ports is dependent on the cabling
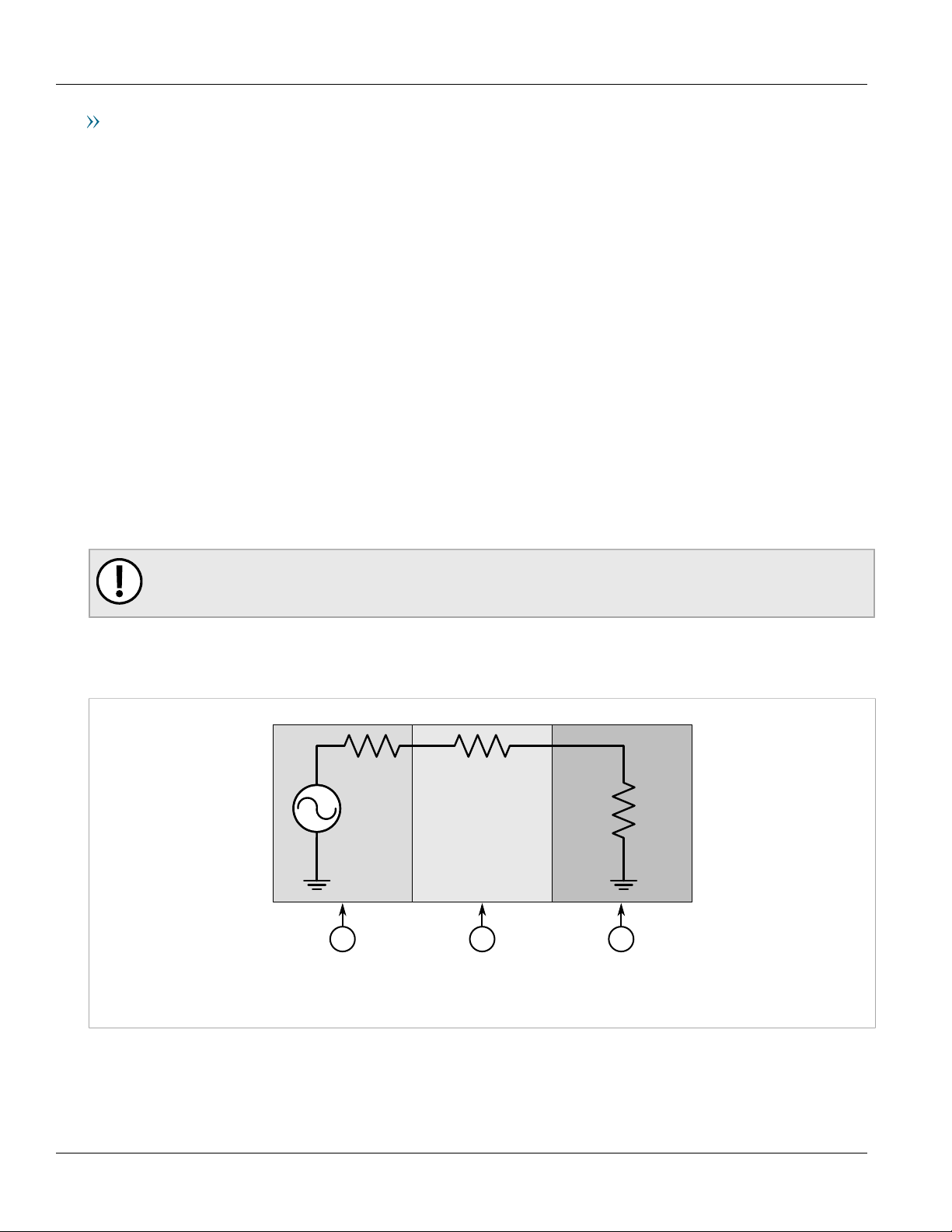
type and length, as well as the input impedances of the devices. The following simplified circuit schematic shows
the interface between an IRIG-B source and connected devices.
Figure 3: IRIG-B Simplified Circuit Schematic
1. Source 2. Cabling 3. Device
The maximum number of devices (N) that can be connected to the source is determined by checking if the source
current (IS) required to drive the connected devices is less than the maximum drive current the source can
provide, and verifying that the load voltage (VL) the connected devices see is greater than the minimum required
voltage.
AM and TTL Outputs 5
Page 14

Chapter 1
Introduction
Section 1.3.3
IEEE 1588 Support
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 supports various IEEE 1588 time synchronization capabilities and provides
synchronization in 2-step mode. This mode supports the following clock types:
• Peer-to-Peer Transparent Clock
• End-to-End Transparent Clock
• End-to-End Slave Clock
• End-to-End Master Clock
• Peer-to-Peer Slave Clock
• Peer-to-Peer Master Clock
• Ordinary/Transparent Clock
• Boundary Clock
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
6 IEEE 1588 Support
Page 15

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Installing Device
The following sections describe how to install the device, including mounting the device, installing/removing
modules, connecting power, and connecting the device to the network.
DANGER!
Electrocution hazard – risk of serious personal injury and/or damage to equipment. Before performing
any maintenance tasks, make sure all power to the device has been disconnected and wait
approximately two minutes for any remaining energy to dissipate.
WARNING!
Radiation hazard – risk of serious personal injury. This product contains a laser system and is
classified as a CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of
procedures other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
IMPORTANT!
This product contains no user-serviceable parts. Attempted service by unauthorized personnel shall
render all warranties null and void.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by Siemens Canada Ltd. could invalidate
specifications, test results, and agency approvals, and void the user's authority to operate the
equipment.
Installing Device
Chapter 2
IMPORTANT!
This product should be installed in a restricted access location where access can only be gained by
authorized personnel who have been informed of the restrictions and any precautions that must be
taken. Access must only be possible through the use of a tool, lock and key, or other means of security,
and controlled by the authority responsible for the location.
• Section 2.1, “Mounting the Device”
• Section 2.2, “Connecting Power”
• Section 2.3, “Installing a GPS Antenna”
• Section 2.4, “Connecting the Failsafe Alarm Relay”
• Section 2.5, “Grounding the Device”
• Section 2.6, “Connecting to the Device”
• Section 2.7, “Cabling Recommendations”
Section 2.1
Mounting the Device
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 is designed for maximum mounting and display flexibility. It can be equipped with
connectors that allow it to be installed in a 48 cm (19 in) rack, 35 mm (1.4 in) DIN rail, or directly on a panel.
Mounting the Device 7
Page 16

Chapter 2
Installing Device
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
NOTE
For detailed dimensions of the device with either rack, DIN rail or panel hardware installed, refer to
Chapter 5, Dimension Drawings.
The following sections describe the various methods of mounting the device:
• Section 2.1.1, “Mounting the Device to a Rack”
• Section 2.1.2, “Mounting the Device on a DIN Rail”
• Section 2.1.3, “Mounting the Device to a Panel”
Section 2.1.1
Mounting the Device to a Rack
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 can be secured to a standard 48 cm (19 in) rack using separately purchased rack
mount adapters. The adapters can be installed at the front or rear of the chassis.
Each adapter kit includes four adapters.
CAUTION!
Vibration hazard – risk of damage to the device. In high-vibration or seismically active locations, always
install four rack mount adapters (two at the front of the chassis and two at the rear).
CAUTION!
Electrical/mechanical hazard – risk of damage to the device. Before installing the device in a rack,
make sure of the following:
• When installing the device in a closed or multi-device rack, be aware that the operating ambient
temperature of the rack may be higher than the ambient temperature of the room. Make sure the
rack is installed in a suitable environment that can withstand the maximum ambient temperature
generated by the rack.
• Make sure each device in the rack is separated by at least one rack-unit of space, or 44 mm (1.75
in), to promote convectional airflow. Forced airflow is not required. However, any increase in airflow
will result in a reduction of ambient temperature and improve the long-term reliability of all equipment
mounted in the rack space.
• Do not exceed the maximum number of devices or weight restrictions specified by the rack
manufacturer.
• Do not overload the supply circuit. Refer to the over-current protection and power supply ratings
specified by the rack manufacturer.
• Make sure the rack and all devices have a proper ground-to-Earth connection. Pay particular
attention to power supply connections other than direct connections to the branch circuit (e.g. power
strips).
To secure the device to a standard 48 cm (19 in) rack, do the following:
NOTE
The device can be ordered with the communication ports located at the front or rear of the device.
Placing the ports at the rear allows all data and power cabling to be installed and connected at the rear
of the rack.
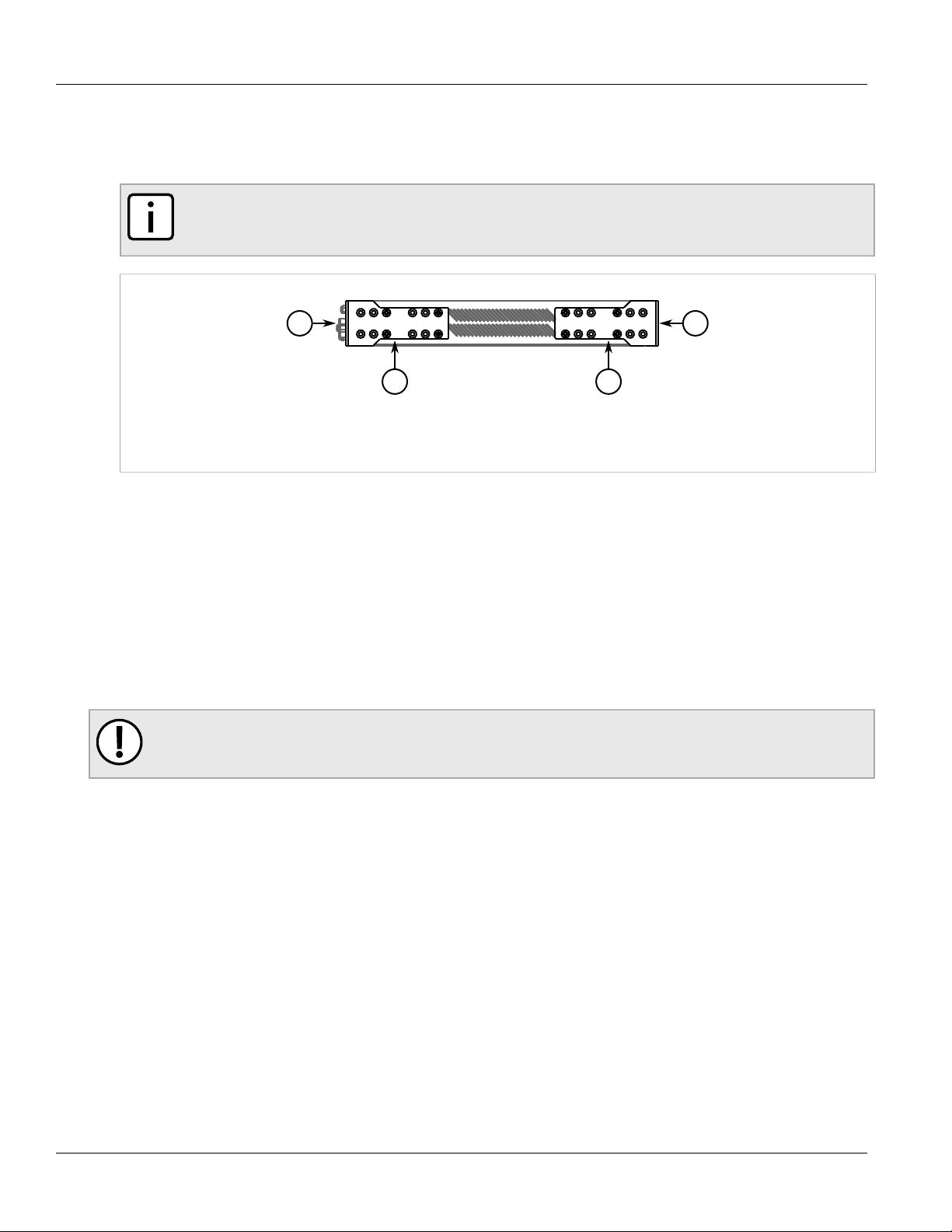
1. Make sure the rack mount adapters are installed on the correct side of the chassis.
8 Mounting the Device to a Rack
Page 17
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
1 2
3 3
Installation Guide
• To make the modules and ports accessible, install the rack mount adapters at the rear of the chassis
• To make the management ports and LEDs accessible, install the rack mount adapters at the front of the
chassis
NOTE
The chassis features multiple mounting holes, allowing the rack mount adapters to be installed up
to 25 mm (1 in) from the face of the device.
Figure 4: Rack Mount Adapters
1. Rear 2. Front 3. Rack Mount Adapter
2. If required, install adapters on the opposite side of the device to protect from vibrations.
3. Insert the device into the rack.
4. Secure the adapters to the rack using the supplied hardware.
Installing Device
Chapter 2
Section 2.1.2
Mounting the Device on a DIN Rail
For DIN rail installations, the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 can be equipped with panel/DIN rail adapters pre-installed
on each side of the chassis. The adapters allow the device to be slid onto a standard 35 mm (1.4 in) DIN rail.
IMPORTANT!
DIN rail mounting is not recommended for constant vibration environments.
To mount the device to a DIN rail, do the following:
1. Align the adapters with the DIN rails and slide the device into place.
Mounting the Device on a DIN Rail 9
Page 18

Chapter 2
2
1
2
3
3
Installing Device
Figure 5: DIN Rail Mounting
1. Panel/DIN Rail Adapter 2. DIN Rail 3. Screw
2. Install one of the supplied screws on either side of the device to secure the adapters to the DIN rails.
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Section 2.1.3
Mounting the Device to a Panel
For panel installations, the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 can be equipped with panel/DIN rail adapters pre-installed
on each side of the chassis. The adapters allow the device to be attached to a panel using screws.
To mount the device to a panel, do the following:
1. Place the device against the panel and align the adapters with the mounting holes.
10 Mounting the Device to a Panel
Page 19

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
21
1
Installation Guide
Installing Device
Chapter 2
Figure 6: Panel Mounting
1. Screw 2. Panel/DIN Rail Adapter
2. Install the supplied screws to secure the adapters to the panel.
Section 2.2
Connecting Power
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 supports a single or dual redundant AC and/or DC power supplies. The use of two
power modules is recommended to provide redundancy and load balancing.
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 can be equipped with either a screw-type or pluggable terminal block, which
provides power to both power supplies. The screw-type terminal block is installed using Phillips screws and
compression plates, allowing either bare wire connections or crimped terminal lugs. Use #6 size ring lugs for
secure, reliable connections under severe shock or vibration.
CAUTION!
Electrical hazard – risk of damage to the device. Disconnect the device from the power supply if power
input is above or below the specified input range. For more information, refer to Section 4.1, “Power
Supply Specifications”.
NOTE
• For maximum redundancy in a dual power supply configuration, use two independent power
sources.
Connecting Power 11
Page 20

Chapter 2
Installing Device
• Use only #16 gage copper wiring when connecting terminal blocks.
• For 100-240 VAC rated equipment, an appropriately rated AC circuit breaker must be installed.
• For 125/250 VDC rated equipment, an appropriately rated DC circuit breaker must be installed.
• A circuit breaker is not required for 12, 24 or 48 VDC rated power supplies.
• It is recommended to provide a separate circuit breaker for each power supply module.
• Equipment must be installed according to applicable local wiring codes and standards.
The following sections describe how to connect power to the device:
• Section 2.2.1, “Connecting AC Power”
• Section 2.2.2, “Connecting DC Power”
• Section 2.2.3, “Wiring Examples”
Section 2.2.1
Connecting AC Power
To connect a high AC power supply to the device, do the following:
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
CAUTION!
Electrical hazard – risk of damage to equipment. Do not connect AC power cables to terminals for DC
power. Damage to the power supply may occur.
CAUTION!
Electrical hazard – risk of damage to equipment. Before testing the dielectric strength (HIPOT) in the
field, remove the metal jumper. This metal jumper connects transient suppression circuitry to chassis
ground and must be removed in order to avoid damage to transient suppression circuitry during testing.
NOTE
The terminal block is divided into separate terminals for each internal power supply. Make sure to
connect the external power supply to the appropriate terminals.
NOTE
The screw-type terminal block is installed using Phillips screws and compression plates, allowing either
bare wire connections or crimped terminal lugs. Use #6 size ring lugs for secure, reliable screws, which
must be removed to make connections.
1. Remove the terminal block cover.
2. If a screw-type terminal block is installed, remove the screws from the appropriate terminals. Use these
screws along with #6 ring lugs to secure the wires to the terminal block.
3. Connect the positive wire from the power source to the positive/live (+/L) terminal on the terminal block. For
more information, refer to Section 2.2.3, “Wiring Examples”.
12 Connecting AC Power
Page 21

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
4
21
34657465
3
65746
5
Installation Guide
Figure 7: Terminal Block Wiring
1. Screw-Type Terminal Block 2. Pluggable Terminal Block 3. Jumper 4. Positive/Live (+/L) Terminal 5. Negative/Neutral (-/N)
Terminal (-/N) 6. Surge Ground Terminal 7. Chassis Ground Terminal
Installing Device
Chapter 2
4. Connect the negative wire from the power source to the negative/neutral (-/N) terminal on the terminal block.
For more information, refer to Section 2.2.3, “Wiring Examples”.
5. Install the supplied metal jumper between terminals 2, 4 and 6 to connect the surge ground terminals to the
chassis ground terminal. The surge ground terminals are used as the ground conductor for all surge and
transient suppression circuitry internal to the unit.
6. Connect the ground terminal on the power source to the chassis ground terminal on the device. For more
information, refer to Section 2.5, “Grounding the Device”
DANGER!
Electrocution hazard – risk of death, serious personal injury and/or damage to the device. Make
sure the supplied terminal block cover is always installed before the device is powered.
7. Install the terminal block cover.
Section 2.2.2
Connecting DC Power
To connect a high or low DC power supply to the device, do the following:
CAUTION!
Electrical hazard – risk of damage to equipment. Before testing the dielectric strength (HIPOT) in the
field, remove the metal jumper. This metal jumper connects transient suppression circuitry to chassis
ground and must be removed in order to avoid damage to transient suppression circuitry during testing.
NOTE
The terminal block is divided into separate terminals for each internal power supply. Make sure to
connect the external power supply to the appropriate terminals.
Connecting DC Power 13
Page 22

Chapter 2
4
21
34657465
3
65746
5
Installing Device
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
NOTE
The screw-type terminal block is installed using Phillips screws and compression plates, allowing either
bare wire connections or crimped terminal lugs. Use #6 size ring lugs for secure, reliable screws, which
must be removed to make connections.
1. Remove the terminal block cover.
2. If a screw-type terminal block is installed, remove the screws from the appropriate terminals. Use these
screws along with #6 ring lugs to secure the wires to the terminal block.
3. Connect the positive wire from the power source to the positive/live (+/L) terminal on the terminal block. For
more information, refer to Section 2.2.3, “Wiring Examples”.
Figure 8: Terminal Block Wiring
1. Screw-Type Terminal Block 2. Pluggable Terminal Block 3. Jumper 4. Positive/Live (+/L) Terminal 5. Negative/Neutral (-/N)
Terminal (-/N) 6. Surge Ground Terminal 7. Chassis Ground Terminal
4. Connect the negative wire from the power source to the negative/neutral (-/N) terminal on the terminal block.
For more information, refer to Section 2.2.3, “Wiring Examples”.
5. Install the supplied metal jumper between terminals 2, 4 and 6 to connect the surge ground terminals to the
chassis ground terminal. The surge ground terminals are used as the ground conductor for all surge and
transient suppression circuitry internal to the unit.
6. Connect the ground terminal on the power source to the chassis ground terminal on the device. For more
information, refer to Section 2.5, “Grounding the Device”
DANGER!
Electrocution hazard – risk of death, serious personal injury and/or damage to the device. Make
sure the supplied terminal block cover is always installed before the device is powered.
7. Install the terminal block cover.
14 Connecting DC Power
Page 23

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Section 2.2.3
Wiring Examples
The following illustrate how to connect power to single and dual power supplies.
Installing Device
Chapter 2
Figure 9: Single AC Power Supply
Figure 10: Single DC Power Supply
Wiring Examples 15
Page 24

Chapter 2
Installing Device
Figure 11: Dual AC Power Supply
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Figure 12: Dual DC Power Supply
16 Wiring Examples
Page 25

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Figure 13: Dual AC/DC Power Supply
Installing Device
Chapter 2
Section 2.3
Installing a GPS Antenna
For increased signal coverage and improved performance, the GPS antenna is intended to be installed in a
remote location separate from the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288.
IMPORTANT!
A PTP card must be installed in the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 for GPS capabilities. For more
information, refer to Section 1.3, “Precision Time Protocol (PTP) Support”.
NOTE
A specific brand of antenna is not specified.
To install the GPS antenna, do the following:
IMPORTANT!
The antenna installation must be as per Article 810 of the NEC. Specifically, the grounding conductor
must not be less than 10 AWG (Cu). The scheme should be either:
• In accordance with UL 96 and 96A Lightning Protection Components and Installation Requirements
for Lightning Protection Systems (LPS)
• Tested in accordance with UL 50 and UL 497
IMPORTANT!
A Radio Frequency (RF) site survey is recommended prior to any installation to help determine the
best location for the GPS antenna. For assistance, contact a Siemens Sales representative.
Installing a GPS Antenna 17
Page 26

Chapter 2
Installing Device
IMPORTANT!
Although it is not possible to protect the antenna from a direct lightning strike, the antenna and
connected components can be protected from secondary effects through installation location and
protection devices.
Install the antenna at least 15 meters away from and lower than any structures that attract lightning.
GPS antenna damage is usually not the result of a direct lightning strike, but due to high currents
induced by the effects of a lightning strike on a nearby structure. Siemens also recommends installing
lightning protectors in the antenna line to protect the receiver and connected devices. If a lightning
protector is installed, it is important to make sure it has a low impedance path to the ground.
NOTE
The GPS IN port provides 5 VDC at up to 10 mA to power the antenna. For best results, a total gain
of 18 dB at the antenna input is recommended, which includes the antenna gain, cable loss, lightning
protector loss, line amplifier gain and filter loss.
NOTE
For technical specifications, refer to Section 4.6, “PTP Specifications”.
1. Mount the antenna to a pole or wall in an area that provides good signal coverage and is away from any
signal noise emanating from other communications equipment. Make sure 90° of the sky is visible to the
antenna.
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
NOTE
Using any length of coaxial cable will add time delay to the GPS signal, which degrades the
accuracy of the calculated time and position. The time delay is dependent on the type of dielectric
material in the cable and ranges from 10 to 2 ns/ft. The following are examples of the day that can
be expected based on the dielectric type.
Dielectric Type Time Delay (ns/ft) Propagation Velocity (% of c)
Solid Polyethylene (PE) 1.54 65.9
Foam Polyethylene (FE) 1.27 80.0
Foam Polystyrene (FS) 1.12 91.0
Air Space Polyethylene (ASP) 1.15-1.21 84-88
Solid Teflon (ST) 1.46 69.4
Air Space Teflon (AST) 1.13-1.20 85-90
2. Using shielded, low loss 50 Ω coaxial cables, connect the antenna to a lightning protector. Make sure the
cables are routed away from any noise sources, such as Switch-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS).
18 Installing a GPS Antenna
Page 27

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
4
2
6
2
3
3
5
1
Installation Guide
Figure 14: Antenna and Lightning Protector Assembly
1. RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 2. Drain Wire 3. Shielded Coaxial Cable 4. Lightning Protector 5. Ground Wire 6. Antenna
Installing Device
Chapter 2
NOTE
Although active GPS antennas have gain, depending on the length of the coaxial cable used, the
gain may be insufficient, in which case a line amplifier is required.
Most active antennas include filters. However, if there is a high potential for electromagnetic
interference, such as from the near field of a radio transmitter, additional antenna line filtering may
be necessary.
3. [Optional] Install one or more line amplifiers, as required.
4. If installed indoors, install a lightning arrestor at the entrance to the building and one near the RUGGEDCOM
RSG2288.
5. Connect the lightning protector to the the GPS IN port.
Section 2.4
Connecting the Failsafe Alarm Relay
The failsafe relay can be configured to latch based on alarm conditions. The NO (Normally Open) contact is
closed when the unit is powered and there are no active alarms. If the device is not powered or if an active alarm
is configured, the relay opens the NO contact and closes the NC (Normally Closed) contact.
NOTE
Control of the failsafe relay output is configurable through ROS. One common application for this relay
is to signal an alarm if a power failure occurs. For more information, refer to the ROS User Guide for
the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288.
The following shows the proper relay connections.
Connecting the Failsafe Alarm Relay 19
Page 28

Chapter 2
1
3
2
2
1
3
Installing Device
Figure 15: Failsafe Alarm Relay Wiring
1. Normally Open 2. Common 3. Normally Closed
Section 2.5
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Grounding the Device
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 chassis ground terminal uses a #6-32 screw. It is recommended to terminate the
ground connection with a #6 ring lug and torque it to 1.7 N·m (15 lbf·in).
Figure 16: Chassis Ground Connection
1. Stainless Steel Stud 2. #6-32 Screw 3. #6 Ring Lug
Section 2.6
Connecting to the Device
The following describes the various methods for accessing the ROS console and Web interfaces on the device.
For more detailed instructions, refer to the ROS User Guide for the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288.
20 Grounding the Device
Page 29

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
18
Installation Guide
Installing Device
RS232 Console Port
Connect a PC or terminal directly to the RS232 console port to access the boot-time control and ROS interfaces.
The console port provides access to ROS's console and Web interfaces.
IMPORTANT!
The console port is intended to be used only as a temporary connection during initial configuration or
troubleshooting.
Connection to the console port is made using an RJ45-to-DB9 console cable. The following is the pin-out for the
console port:
Pin
Name Description Comment
a
Carrier Detect Reserved (Do
a
Data Terminal
Ready
Not Connect)
Figure 17: RJ45 Console Port Pin Configuration
RJ45
Male
DB9
Female
1 6 DSRaData Set Ready
2 1 DCD
3 4 DTR
Chapter 2
4 5 GND Signal Ground
a
The DSR, DCD and DTR pins are connected together internally.
b
The CTS and RTS pins are connected together internally.
c
RI is not connected.
5 2 RxD Receive Data
6 3 TxD Transmit Data
7 8 CTS
8 7 RTS
1 9 RI
b
b
c
(to DTE)
(from DTE)
Clear to Send
Read to Send
Ring Indicator
Communication Ports
Connect any of the available Ethernet ports on the device to a management switch and access the ROS console
and Web interfaces via the device's IP address. For more information about available ports, refer to Chapter 3,
Communication Ports.
Section 2.7
Cabling Recommendations
Before connecting the device, be aware of the recommendations and considerations outlined in the following
sections:
• Section 2.7.1, “Protection On Twisted-Pair Data Ports”
• Section 2.7.2, “Gigabit Ethernet 1000Base-TX Cabling Recommendations”
Cabling Recommendations 21
Page 30

Chapter 2
Installing Device
Section 2.7.1
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Protection On Twisted-Pair Data Ports
Siemens does not recommend the use of copper cabling of any length for critical, real-time substation automation
applications. All copper Ethernet ports on RUGGEDCOM products include transient suppression circuitry
to protect against damage from electrical transients and conform with IEC 61850-3 and IEEE 1613 Class 1
standards. This means that during a transient electrical event, communications errors or interruptions may occur,
but recovery is automatic.
Siemens also does not recommend using copper Ethernet ports to interface with devices in the field across
distances that could produce high levels of ground potential rise (i.e. greater than 2500 V), during line-to-ground
fault conditions.
Section 2.7.2
Gigabit Ethernet 1000Base-TX Cabling Recommendations
The IEEE 802.3ab Gigabit Ethernet standard defines 1000 Mbit/s Ethernet communications over distances of up
to 100 m (328 ft) using all 4 pairs in category 5 (or higher) balanced, unshielded twisted-pair cabling. For wiring
guidelines, system designers and integrators should refer to the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA)
TIA/EIA-568-A wiring standard that characterizes minimum cabling performance specifications required for proper
Gigabit Ethernet operation. For reliable, error-free data communication, new and pre-existing communication
paths should be verified for TIA/EIA-568-A compliance.
The following table summarizes the relevant cabling standards:
Cabling Category
< 5 No New wiring infrastructure required.
5 Yes Verify TIA/EIA-568-A compliance.
5e Yes No action required. New installations should be designed with Category 5e or higher.
6 Yes No action required.
> 6 Yes Connector and wiring standards to be determined.
1000Base-
TX Compliant
Required Action
Follow these recommendations for copper data cabling in high electrical noise environments:
• Data cable lengths should be as short as possible, preferably 3 m (10 ft) in length. Copper data cables should
not be used for inter-building communications.
• Power and data cables should not be run in parallel for long distances, and should be installed in separate
conduits. Power and data cables should intersect at 90° angles when necessary to reduce inductive coupling.
• Shielded/screened cabling can be used when required. Care should be taken to avoid the creation of ground
loops with shielded cabling.
22 Protection On Twisted-Pair Data Ports
Page 31

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
Installation Guide
Communication Ports
Communication Ports
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 can be equipped with various types of communication ports to enhance its abilities
and performance.
Figure 18: Port Assignment
Chapter 3
Each type of module has a specific location in the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 chassis:
• Slots 1 to 4 support any combination of two-port fiber or copper Ethernet modules up to 1 Gbps
• Slot 5 supports a one-port fiber or copper Ethernet module up to 1 Gbps
• Slot 6 houses the PTP Source Card
The exact configuration of the device can be determined by reading the factory data file through the ROS user
interface. For more information about how to read the factory data file, refer to the ROS User Guide for the
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288.
Each communication port is equipped with an LED that indicates the link/activity state of the port.
LED State Description
Green (Solid) Link established
Green (Blinking) Link activity
Off No link detected
Figure 19: Port LEDs
1. Port LED
The following sections describe the available communication ports:
• Section 3.1, “Copper Ethernet Ports”
• Section 3.2, “Fiber Optic Ethernet Ports”
• Section 3.3, “SFP Optic Ethernet Ports”
• Section 3.4, “GBIC Optic Ethernet Ports”
• Section 3.5, “BNC Ports”
23
Page 32

Chapter 3
18
Communication Ports
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Section 3.1
Copper Ethernet Ports
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 supports several 10/100/1000Base-TX Ethernet ports that allow connection to
standard Category 5 (CAT-5) unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cables with either RJ45 male connectors. The RJ45
connectors are directly connected to the chassis ground on the device and can accept CAT-5 shielded twistedpair (STP) cables.
WARNING!
Electric shock hazard – risk of serious personal injury and/or equipment interference. If shielded
cables are used, make sure the shielded cables do not form a ground loop via the shield wire and the
RJ45 receptacles at either end. Ground loops can cause excessive noise and interference, but more
importantly, create a potential shock hazard that can result in serious injury.
Figure 20: 1 x 10/100/1000Tx with RJ45 Ports (1CG01)
Figure 21: 2 x 10/100/1000Tx with RJ45 Ports (CG01)
Each port features an LED that indicates the state of the port.
State Description
Yellow (Solid) Link established
Yellow (Blinking) Link activity
Off No link detected
The following are the pin-out descriptions for the RJ45 connectors:
Pin
Figure 22: RJ45 Ethernet Port Pin Configuration
10/100Base-TX 1000Base-TX
1 RX+ BI_DA+ Receive Data+
2 RX- BI_DA- Receive Data-
3 TX+ BI_DB+ Transmit Data+
4 Reserved (Do
Not Connect)
Name
Description
or Bi-Directional
Pair A+
or Bi-Directional
Pair A-
or Bi-Directional
Pair B+
BI_DC+ Transmit Data+
or Bi-Directional
Pair C+
5 Reserved (Do
6 TX- BI_DB- Transmit Data-
24 Copper Ethernet Ports
Not Connect)
BI_DC- Receive Data-
or Bi-Directional
Pair C-
or Bi-Directional
Pair B-
Page 33

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
21
21
21
21
Installation Guide
Communication Ports
Chapter 3
Pin
10/100Base-TX 1000Base-TX
7 Reserved (Do
Not Connect)
8 Reserved (Do
Not Connect)
Name
Description
BI_DD+ Receive Data-
or Bi-Directional
BI_DD- Receive Data-
or Bi-Directional
For specifications on the available copper Ethernet ports, refer to Section 4.4, “Copper Ethernet Port
Specifications”.
Section 3.2
Fiber Optic Ethernet Ports
Fiber optic Ethernet ports are available with either MTRJ (Mechanical Transfer Registered Jack), LC (Lucent
Connector), SC (Standard or Subscriber Connector) or ST (Straight Tip) connectors. Make sure the Transmit (Tx)
and Receive (Rx) connections of each port are properly connected and matched to establish a proper link.
Pair D+
Pair D-
Figure 23: MTRJ Port
1. Tx Connector 2. Rx Connector
Figure 25: SC Port
1. Tx Connector 2. Rx Connector
Figure 24: LC Port
1. Tx Connector 2. Rx Connector
Figure 26: ST Port
1. Tx Connector 2. Rx Connector
For specifications on the available fiber optic Ethernet ports, refer to Section 4.5, “Fiber Optic Ethernet Port
Specifications”.
Section 3.3
SFP Optic Ethernet Ports
SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) optic Ethernet ports are available with LC (Lucent Connector) connectors.
Make sure the Transmit (Tx) and Receive (Rx) connections of each port are properly connected and matched to
establish a proper link.
Fiber Optic Ethernet Ports 25
Page 34

Chapter 3
21
Communication Ports
Figure 27: LC Port
1. Tx Connector 2. Rx Connector
NOTE
SFP modules, as well as their optical ports, can be safely inserted and removed while the chassis is
powered and operating.
The following sections describe how to install and remove SFP optical ports:
• Section 3.3.1, “Installing an SFP Optical Port”
• Section 3.3.2, “Removing an SFP Optical Port”
Section 3.3.1
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Installing an SFP Optical Port
To install an SFP optical port, do the following:
CAUTION!
Electrical hazard – risk of damage to equipment. Use only components certified by Siemens with
RUGGEDCOM products. Damage to the module and device may occur if compatibility and reliability
have not been properly assessed.
CAUTION!
Electrical hazard – risk of damage to equipment. Make sure all electrostatic energy is dissipated
before installing or removing components from the device. An electrostatic discharge (ESD) can cause
serious damage to the component once it is outside the chassis.
1. Make sure all potential electrostatic build-up has been properly discharged to prevent electrostatic
discharges (ESD). This can be accomplished by wearing an ESD wrist strap or by touching Earth or the
chassis ground.
2. Remove the dust cover from the port opening in the module.
CAUTION!
Mechanical hazard – risk of component damage. SFP optical ports are designed to insert in only
one orientation. Do not force the port into the module.
3. Remove the port from its packaging.
4. Insert the port into the module and swing the bail-latch up to lock it in place.
26 Installing an SFP Optical Port
Page 35

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
2
1
2
1
Installation Guide
Figure 28: Installing an SFP Optical Port (Typical)
1. SFP Optical Port 2. Metal Bail-Latch
5. Remove the dust cover from the port.
6. Connect a cable to the port and test the connection.
Section 3.3.2
Removing an SFP Optical Port
To remove an SFP optical port, do the following:
Communication Ports
Chapter 3
CAUTION!
Electrical hazard – risk of damage to equipment. Make sure all electrostatic energy is dissipated before
performing installing or removing components from the device. An electrostatic discharge (ESD) can
cause serious damage to the component once it is outside the chassis.
1. Make sure all potential electrostatic build-up has been properly discharged to prevent electrostatic
discharges (ESD). This can be accomplished by wearing an ESD wrist strap or by touching Earth or the
chassis ground.
2. Disconnect the cable from the port.
3. Swing the metal bail-latch down and pull the port from the module.
Figure 29: Removing an SFP Optical Port (Typical)
1. SFP Optical Port 2. Metal Bail-Latch
4. Store the port in an ESD-safe bag or other suitable ESD-safe environment, free from moisture and stored at
the proper temperature (-40 to 85 °C or -40 to 185 °F).
5. Insert a plug in the empty port opening to prevent the ingress of dust and dirt.
Removing an SFP Optical Port 27
Page 36

Chapter 3
21
Communication Ports
Section 3.4
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
GBIC Optic Ethernet Ports
GBIC (Gigabit Interface Converter) optic Ethernet ports are available with SC (Standard or Subscriber Connector)
connectors.
Figure 30: SC Port
1. Tx Connector 2. Rx Connector
The following sections describe how to install and remove GBIC optical ports:
• Section 3.4.1, “Installing a GBIC Optical Port”
• Section 3.4.2, “Removing a GBIC Optical Port”
Section 3.4.1
Installing a GBIC Optical Port
To install a GBIC optical port, do the following:
CAUTION!
Electrical hazard – risk of damage to equipment. Use only components certified by Siemens with
RUGGEDCOM products. Damage to the module and device may occur if compatibility and reliability
have not been properly assessed.
CAUTION!
Electrical hazard – risk of damage to equipment. Make sure all electrostatic energy is dissipated
before installing or removing components from the device. An electrostatic discharge (ESD) can cause
serious damage to the component once it is outside the chassis.
1. Make sure all potential electrostatic build-up has been properly discharged to prevent electrostatic
discharges (ESD). This can be accomplished by wearing an ESD wrist strap or by touching Earth or the
chassis ground.
2. Remove the dust cover from the port opening in the module.
CAUTION!
Mechanical hazard – risk of component damage. GBIC optical ports are designed to insert in only
one orientation. Do not force the port into the module.
3. Remove the port from its packaging.
4. Squeeze the latches on either side of the port and insert the port into the module.
28 GBIC Optic Ethernet Ports
Page 37

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
2
1
3
Installation Guide
Figure 31: Installing a GBIC Optical Port
1. GBIC Optical Port Module 2. GBIC Optical Port 3. Locking Latch
5. Release the latches and make sure the module is locked in place.
6. Remove the dust cover from the port.
7. Connect a cable to the port and test the connection.
Communication Ports
Chapter 3
Section 3.4.2
Removing a GBIC Optical Port
To remove an GBIC optical port, do the following:
CAUTION!
Electrical hazard – risk of damage to equipment. Make sure all electrostatic energy is dissipated before
performing installing or removing components from the device. An electrostatic discharge (ESD) can
cause serious damage to the component once it is outside the chassis.
1. Make sure all potential electrostatic build-up has been properly discharged to prevent electrostatic
discharges (ESD). This can be accomplished by wearing an ESD wrist strap or by touching Earth or the
chassis ground.
2. Disconnect the cable from the port.
3. Squeeze the latches on either side of the port and pull it from the module.
Removing a GBIC Optical Port 29
Page 38

Chapter 3
2
1
3
1 2 4 5
3
Communication Ports
Figure 32: Removing a GBIC Optical Port
1. GBIC Optical Port Module 2. GBIC Optical Port 3. Locking Latch
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
4. Store the port in an ESD-safe bag or other suitable ESD-safe environment, free from moisture and stored at
the proper temperature (-40 to 85 °C or -40 to 185 °F).
5. Insert a plug in the empty port opening to prevent the ingress of dust and dirt.
Section 3.5
BNC Ports
The following BNC ports are available on the PTP module:
Port Function
AM IN AM-level IRIG-B signal
TTL OUT IRIG-B PWM or 1 PPS signal
TTL IN TTL-level IRIG-
GPS IN GPS antenna input
Figure 33: PTP Module
1. AM OUT Port 2. TTL OUT Port 3. Sync LED 4. TTL IN
Port 5. GPS IN Port
Inputs are controlled by RUGGEDCOM ROS and only one can be active at any time. For information about
activating an input, refer to the RUGGEDCOM ROS User Guide for the RUGGEDCOM RSG2288.
The color of the Sync LED on the front panel of the PTP module indicates the status of the incoming timing
signal:
• Green – Signal locked
• Amber/Yellow – Holdover (GPS lock has been achieved, but the receiver no longer sees the minimum number
of required satellites)
input, software enabled
output, software selectable
B PWM signal input
30 BNC Ports
Page 39

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
• Red – Error
• Off – No signal detected
Communication Ports
Chapter 3
BNC Ports 31
Page 40

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Communication Ports
Chapter 3
BNC Ports 32
Page 41

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications
The following sections provide important technical specifications related to the device and available modules:
• Section 4.1, “Power Supply Specifications”
• Section 4.2, “Failsafe Relay Specifications”
• Section 4.3, “Supported Networking Standards”
• Section 4.4, “Copper Ethernet Port Specifications”
• Section 4.5, “Fiber Optic Ethernet Port Specifications”
• Section 4.6, “PTP Specifications”
• Section 4.7, “Operating Environment”
• Section 4.8, “Mechanical Specifications”
Chapter 4
Section 4.1
Power Supply Specifications
CAUTION!
Electrical hazard – risk of damage to the device. Disconnect the device from the power supply if power
input is above or below the specified input range.
Power Supply Type
24 VDC 10 VDC 36 VDC 6.3 A(F)
48 VDC 36 VDC 72 VDC 3.15 A(T)
HI (125/250 VDC)
HI (110/230 VAC)
a
(F) denotes fast-acting fuse
b
(T) denotes time-delay fuse.
c
Power consumption varies based on configuration. 10/100Base-TX ports consume roughly 1 W less than fiber optic ports.
d
The HI power supply is the same power supply for both AC and DC.
d
d
Minimum Maximum
88 VDC 300 VDC 2 A(T)
85 VAC 264 VAC 2 A(T)
Input Range
Internal Fuse Rating
ab
Maximum Power
Consumption
28 W
c
Section 4.2
Failsafe Relay Specifications
Parameter Value (Resistive Load)
Max Switching Voltage 240 VAC, 125 VDC
Power Supply Specifications 33
Page 42

Chapter 4
Technical Specifications
Parameter Value (Resistive Load)
Rated Switching Current 2 A @ 240 VAC, 0.15 A @ 125 VDC, 2 A @ 30 VDC
Maximum Switching Capacity 150 W, 500 VA
Section 4.3
Supported Networking Standards
Standard Description
IEEE 802.3 10BaseT
IEEE 802.3u 100BaseTX/100BaseFX
IEEE 802.3z 1000BaseSX/LX
IEEE 802.3ab 1000BaseTx
IEEE 802.3x Flow Control
IEEE 802.1D MAC Bridges
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN (Virtual LAN) Tagging
IEEE 802.1p Class of Service
IEEE 1588 v2 Precision Time Protocol
Section 4.4
Copper Ethernet Port Specifications
The following details the specifications for copper Ethernet ports that can be ordered with the RUGGEDCOM
RSG2288.
Section 4.4.1
Copper Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) Port Specifications
NOTE
• Maximum segment length is greatly dependent on factors such as fiber quality, and the number
of patches and splices. Consult a Siemens sales associate when determining maximum segment
distances.
• All optical power numbers are listed as dBm averages.
• F51 transceivers are rated for -40 to 85 °C (-40 to 185 °F).
Connector Duplex
RJ45 FDX/HDX > CAT-5 TIA/EIA T568A/B 100 m (328 ft) 1.5 kV
e
Auto-Negotiating
e
Cable Type
f
Wiring Standard
g
Maximum
Distance
h
Isolation
i
34 Supported Networking Standards
Page 43

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
f
Shielded or unshielded.
g
Auto-crossover and auto-polarity.
h
Typical distance. Dependent on the number of connectors and splices.
i
RMS 1 minute.
Technical Specifications
Section 4.5
Fiber Optic Ethernet Port Specifications
The following sections list specifications of the optical transceivers used in the modules available for the
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288:
• Section 4.5.1, “10FL Ethernet Optical Specifications”
• Section 4.5.2, “Fast Ethernet (10/100 Mbps) Optical Specifications”
• Section 4.5.3, “Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) Optical Specifications”
Section 4.5.1
Chapter 4
10FL Ethernet Optical Specifications
Mode
MM ST
j
Typical.
Section 4.5.2
Connector
Type
Cable
Type (µm)
62.5/125 -16 -9 18
50/125
Tx λ (nm)
850
Tx min
j
(dBm)
-19.8 -12.8
Tx max
(dBm)
Rx
Sensitivity
(dBm)
-34 -11.2 2
Rx
Saturation
(dBm)
Fast Ethernet (10/100 Mbps) Optical Specifications
Mode
MM ST
MM SC
Connector
Type
Cable
Type (µm)
62.5/125 -19 12
50/125
62.5/125 -19 12
50/125
Tx λ (nm)
1300
1300
k
Tx min.
(dBm)
-22.5
-22.5
Tx max.
(dBm)
-14 -31 -14 2
-14 -31 -14 2
Rx
Sensitivity
(dBm)
Rx
Saturation
(dBm)
Distance
(typ.) (km)
Maximum
Distance
l
(km)
Power
Budget
(dB)
14.2
Power
Budget
(dB)
8.5
8.5
MM MTRJ
SM ST 9/125 1310 -15 -8 -32 -3 20 17
SM SC 9/125 1310 -15 -8 -31 -7 20 16
SM LC 9/125 1310 -15 -8 -34 -7 20 19
62.5/125 -19 12
50/125
1300
-22.5
-14 -31 -14 2
8.5
Fiber Optic Ethernet Port Specifications 35
Page 44

Chapter 4
Technical Specifications
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Mode
Connector
Type
Cable
Type (µm)
Tx λ (nm)
Tx min.
k
(dBm)
Tx max.
(dBm)
Rx
Sensitivity
(dBm)
Rx
Saturation
(dBm)
SM SC 9/125 1310 -5 0 -34 -3 50 29
SM LC 9/125 1310 -5 0 -35 3 50 30
SM SC 9/125 1310 0 5 -37 0 90 37
SM LC 9/125 1310 0 5 -37 0 90 37
MM LC 62.5/125 1300 -19 -14 -32 -14 2 13
k
Typical.
l
Typical distance. Dependent on the cable type, number of connectors and number of splices.
Section 4.5.3
Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) Optical Specifications
Fixed Gigabit Transceivers
NOTE
These transceivers utilize a distributed feedback (DFB) type laser and are rated for -20 to 85 °C (-4 to
185 °F) operation only.
Maximum
Distance
l
(km)
Power
Budget
(dB)
Mode
Connector
Type
Cable
Type
(µm)
m
Tx λ (nm)
n
Tx
Minimum
(dBm)
o
Tx
Maximum
o
(dBm)
Rx
Sensitivity
o
(dBm)
Rx
Saturation
o
(dBm)
Maximum
Distance
p
(km)
Power
Budget
(dB)
50/125
MM LC
850 -9 -2.5 -20 0 0.5 11
62.5/125
SM SC 9/125 1310 -10 -3 -20 -3 10 10
SM LC 9/125 1310 -9.5 -3 -21 -3 10 11.5
SM SC 9/125 1310 -5 0 -20 -3 25 15
SM LC 9/125 1310 -7 -3 -24 -3 25 17
m
All cabling is duplex type unless specified otherwise.
n
Typical.
o
All optical power numbers are listed as dBm averages.
p
Typical distance. The maximum segment length is greatly dependent on factors such as fiber quality, and the number of patches and splices. Consult a Siemens
sales associates when determining maximum segment distances.
SFP Gigabit Transceivers
NOTE
SFP transceivers have a temperature range of -40 to 85 °C (-40 to 185 °F), unless specified otherwise.
36 Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) Optical Specifications
Page 45

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Technical Specifications
Chapter 4
Mode
Connector
Type
Cable
Type (µm)
Tx λ (nm)
q
Tx
Minimum
(dBm)
r
Tx
Maximum
(dBm)
r
Rx
Sensitivity
(dBm)
r
Rx
Saturation
r
(dBm)
Maximum
Distance
s
(km)
Power
Budget
(dB)
50/125 0.5
MM LC
62.5/125
850 -9 -2.5 -20 0
0.3
11
SM LC 9/125 1310 -9.5 -3 -19 -3 10 9.5
SM LC 9/125 1310 -7 -3 -23 -3 25 16
t
SM
q
Typical.
r
All optical power numbers are listed as dBm averages.
s
Typical distance. The maximum segment length is greatly dependent on factors such as fiber quality, and the number of patches and splices. Consult a Siemens
sales associates when determining maximum segment distances.
t
Operating temperature range of -20 to 85 °C (-4 to 185 °F).
LC 9/125 1550 0 5 -23 -3 70 23
GBIC Gigabit Transceivers
NOTE
GBIC transceivers have a temperature range of -40 to 85 °C (-40 to 185 °F), unless specified
otherwise.
Mode
Connector
Type
Cable
Type (µm)
Tx λ (nm)
u
Tx
Minimum
(dBm)
v
Tx
Maximum
(dBm)
v
Rx
Sensitivity
(dBm)
v
Rx
Saturation
v
(dBm)
Maximum
Distance
w
(km)
SM SC 9/125 1310 -9.5 -3 -21 -3 10 11.5
SM SC 9/125 1310 -7 -3 -24 -3 25 17
x
SM
u
Typical.
v
All optical power numbers are listed as dBm averages.
w
Typical distance. The maximum segment length is greatly dependent on factors such as fiber quality, and the number of patches and splices. Consult a Siemens
sales associates when determining maximum segment distances.
x
Operating temperature range of -20 to 85 °C (-4 to 185 °F).
SC 9/125 1550 0 5 -23 -3 70 23
Section 4.6
PTP Specifications
IRIG-B PWM Input Specifications
Parameter Typical Value
Power
Budget
(dB)
Input Voltage TTL-Compatible
Input Impedance >200 kΩ
PTP Specifications 37
Page 46

Chapter 4
Technical Specifications
IRIG-B PWM Output Specifications
Parameter Typical Value
Output Current (Is) 100 mA
Output Voltage (Vs) TTL-Compatible
Output Impedance (Rs) 50 Ω
IRIG-B AM Output Specifications
Parameter Typical Value
Carrier Frequency 1 kHz
Modulation Depth 3:1±10%
Output Current (Is) 15 mA
Output Impedance (Rs) 10 Ω
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Output Voltage (Vs) 6 V
p-p
GPS Standalone Antenna Requirements
Characteristic Active Antenna
Polarization RHCP (Right-Hand Circular Polarized)
Receive Frequency 1.57542 GHz ± 1.023 MHz
Power Supply 5 VDC
DC Current < 10 mA at 3 VDC
Antenna Gain Select antenna gain based on system configuration
Total Gain at PTP GPS Input (includes antenna gain, cable loss,
lightning arrestor loss, line amplifier gain and filter loss)
Axial Ratio < 3 dB
Output VSWR < 2.5
Total Gain≤ 18 dBi
Section 4.7
Operating Environment
Parameter Range Comments
Ambient Operating Temperature -40 to 85 °C (-40 to 185 °F) Ambient Temperature as measured from a 30 cm
Ambient Relative Humidity 5% to 95% Non-condensing
Ambient Storage Temperature -40 to 85 °C (-40 to 185 °F)
radius surrounding the center of the enclosure.
38 Operating Environment
Page 47

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Section 4.8
Mechanical Specifications
Parameter Value
Dimensions Refer to Chapter 5, Dimension Drawings
Weight 4.8 kg (10.6 lbs)
Ingress Protection IP40 (1 mm or 0.04 in objects)
Enclosure 18 AWG Galvanized Steel
Technical Specifications
Chapter 4
Mechanical Specifications 39
Page 48

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Technical Specifications
Chapter 4
Mechanical Specifications 40
Page 49

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
303.28
438.15
285.24
44.45 ± 0.8
Installation Guide
Dimension Drawings
Dimension Drawings
Chapter 5
NOTE
All dimensions are in millimeters, unless otherwise stated.
NOTE
Dimensional tolerances are in accordance with ISO 2768-mK, unless otherwise stated.
Figure 34: Overall Dimensions
41
Page 50

Chapter 5
308.10
314.71
6.35
4.57
6.35
31.75
461.01
28.96
51.05
12.70
25.40
11.68
21.08
32.77
479.29
Dimension Drawings
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Figure 35: Rack Mount Dimensions
42
Page 51

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 P11 P12
MODE
STATUS
SPEED
DUPLEX
ALARM
POWER2
POWER1
57600-N-8-1
CONSOLE
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
11 12
9 10
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24
25 26 27 28
29 30 31 32
RX
TX
RX
TX
RX
TX
RX
TX
RX
TX
RX
TX
RX
TX
RX
TX
TTLIN
GPSIN
TTLOUT
AMOUT
486.4
476.3
38.9
51.6
10.4
7.4
158.0
127.5
80.0
125.5
159.8
11.4
134.4
84.1
Installation Guide
Dimension Drawings
Chapter 5
Figure 36: Panel and DIN Rail Mount Dimensions
43
Page 52

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Dimension Drawings
Chapter 5
44
Page 53

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Certification
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 device has been thoroughly tested to guarantee its conformance with recognized
standards and has received approval from recognized regulatory agencies.
• Section 6.1, “Standards Compliance”
• Section 6.2, “Agency Approvals”
• Section 6.3, “EMC and Environmental Type Tests”
Section 6.1
Standards Compliance
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 complies with the following standards:
• FCC Compliance
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation
of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be
required to correct the interference on his own expense.
• Industry Canada Compliance
CAN ICES-3 (A) / NMB-3 (A)
• Other
▪ IEC 61000-6-2 (Generic Industrial)
▪ NEMA TS-2 (Traffic Control Equipment)
▪ IEEE 1613 (Electric Utility Substations)
▪ IEC 61850-3 (Electric Utility Substations)
Chapter 6
Certification
Section 6.2
Agency Approvals
Agency Standards Comments
CSA CSA C22.2 No. 60950-1, UL 60950-1 Approved
CE EN 60950-1, EN 61000-6-2, EN
60825-1, EN 55022 Class A, EN 50581
FCC FCC Part 15, Class A Approved
FDA/CDRH 21 CFR Chapter I, Sub-chapter J Approved
Standards Compliance 45
CE Compliance is claimed via
Declaration of Self Conformity Route
Page 54

Chapter 6
Certification
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Agency Standards Comments
ISO ISO9001:2008 Designed and manufactured using an
Section 6.3
EMC and Environmental Type Tests
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 has passed the following EMC and environmental tests.
IEC 61850-3 EMC Type Tests
NOTE
• If the unit contains copper ports, the IEC 1613 conformance is Class 1, during which disturbance
errors may occur but recovery is automatic.
• If the unit contains all fiber ports, the IEC 1613 conformance is Class 2, during which no disturbance
errors will occur.
Test Description Test Levels Severity Levels
Enclosure Contact +/- 8 kVIEC 61000-4-2 ESD
Enclosure Air +/- 15 kV
ISO9001:2008 certified quality program
4
IEC 61000-4-3 Radiated RFI Enclosure Ports 20 V/m
IEC 61000-4-4 Burst (Fast Transient)
IEC 61000-4-5 Surge
IEC 61000-4-6 Induced (Conducted) RFI
IEC 61000-4-8 Magnetic Field Enclosure Ports 40 A/m, Continuous,
IEC 61000-4-29 Voltage Dips and
Interrupts (DC
Power Ports)
Signal Ports +/- 4 kV @ 2.5 kHz
DC Power Ports
AC Power Ports
Earth Ground Ports
Signal Ports +/- 4 kV Line-to-Ground,
DC Power Ports +/- 2 kV Line-to-Ground,
AC Power Ports +/- 4 kV Line-to-Ground,
Signal Ports
DC Power Ports
AC Power Ports
Earth Ground Ports
DC Power Ports 30% for 0.1 s
+/- 4 kV 4
+/- 2 kV Line-to-Line
+/- 1 kV Line-to-Line
+/- 2 kV Line-to-Line
10 V 3
1000 A/m for 1 s
60% for 0.1 s
100% for 0.05 s
4
3
4
46 EMC and Environmental Type Tests
Page 55

RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Chapter 6
Certification
Test Description Test Levels Severity Levels
AC Power Ports 30% for 1 period
60% for 50 periods
IEC 61000-4-11 Voltage Dips and
IEC 61000-4-12 Damped Oscillatory
IEC 61000-4-17 Ripple on DC
IEC 60255-5
Interrupts (A. C.
Power Ports)
Power Supply
Dielectric Strength
HV Impulse
AC Power Ports 100% for 5 periods
100% for 50 periods
Signal Ports
DC Power Ports
AC Power Ports
Signal PortsIEC 61000-4-16 Mains Frequency Voltage
DC Power Ports
DC Power Ports 10% 3
Signal Ports 2 kV (Fail-Safe
DC Power Ports 2 kV
AC Power Ports 2 kV
Signal Ports 5 kV (Fail-Safe
DC Power Ports
AC Power Ports
2.5 kV Common,
1 kV Differential
Mode @1 MHz
30 V Continuous,
300 V for 1s
Relay Output)
Relay Output)
5 kV
3
4
IEEE 1613 EMC Immunity Type Tests
NOTE
The RUGGEDCOM RSG2288 meets Class 2 requirements for an all-fiber configuration and Class 1
requirements for copper ports.
Description Test Levels
Enclosure Contact +/- 2 kV, +/-4 kV, +/-8 kVESD
Enclosure Air +/-4 kV, +/-8 kV, +/-15 kV
Radiated RFI Enclosure Ports 35 V/m
Fast Transient
Oscillatory
HV Impulse Signal Ports 5 kV (Fail-Safe Relay Output)
Signal Ports +/- 4 kV @ 2.5 kHz
DC Power Ports +/- 4 kV
AC Power Ports +/- 4 kV
Earth Ground Ports +/- 4 kV
Signal Ports 2.5 kV Common Mode @1MHz
DC Power Ports 2.5 kV common, 1 kV differential mode @ 1 MHz
AC Power Ports 2.5 kV common, 1 kV differential mode @ 1 MHz
EMC and Environmental Type Tests 47
Page 56

Chapter 6
Certification
RUGGEDCOM RSG2288
Installation Guide
Description Test Levels
DC Power Ports 5 kV
AC Power Ports 5 kV
Dielectric Strength
Damped Oscillatory
Magnetic Field
Signal Ports 2 kV
DC Power Ports 2 kV
AC Power Ports 2 kV
Enclosure Ports 100 A/m Peak
Environmental Type Tests
Test Description Test Levels
IEC 60068-2-1 Cold Temperature Test Ad -40 °C (-40 °F), 16 Hours
IEC 60068-2-2 Dry Heat Test Bd 85 °C (185 °F), 16 Hours
IEC 60068-2-30 Humidity (Damp Heat, Cyclic) Test Db 95% (non-condensing),
IEC 60068-21-1 Vibration 2g @ 10-150 Hz
IEC 60068-21-2 Shock 30 g @ 11 ms
55 °C (131 °F), 6 cycles
48 EMC and Environmental Type Tests
 Loading...
Loading...