Siemens PEB4065, PEF4065 Datasheet

ICs for Communications
High Voltage Subscriber Line IC
HV-SLIC
PEB/F 4065 Version 3.0
Data Sheet 03.98
DS 1
w
m
Se
http://ww
.siem
d
n
o
ic
e
u
n
ct
s
.d
o
/
e
/
r
PEB/F 4065
Revision History: Current Version: 03.98
Previous Version: 01.96
Page
(in previous
Version)
Page
(in current
Version)
Subjects (major changes since last revision)
SLICOFI® is a registered trademark of SIEMENS AG.
For questions on technology, delivery and prices please contact the Semiconductor Group Offices
in Germany or the Siemens Companies and Representatives worldwi de: see our webpage at http:/
/www.siemens.de/Semiconductor/address/address.htm.
Edition 03 .9 8
Published by Siemens AG,
HL SP,
Balan s tr a ß e 73 ,
81541 München
© Siemens AG 1998.
All Rights Reserv ed.
Attention ple ase!
As far as patents or other rights of third parties are concerned, liability is only assumed for components, not for
applications, processes and circuits implemented within c omponents or assemblie s.
The information describes the type of component and shall not be considered as assured characteristics.
Terms of delivery and rights to change design reserved.
Due to technical requirements components may contain dangerous su bstances. For information on the types in
question please contact your nearest Siemens Office, Semiconduc tor Group.
Siemens AG i s an approved CEC C manufacturer.
Packing
Please use the recycli ng operators known to you. We can also help you – get in touch with your nearest sales
office. By agreement we will take packing material back, if it is sorted. You must bear the costs of transport.
For packi ng mat erial that is ret urned to us un sort ed or w hich w e are n ot obli ged to a ccep t, we s hall h ave to i nvoic e
you for any costs incurred.
Components used in life-support devices or systems must be express ly authorized for such purpose!
Critical componen ts
systems
1 A crit ical component is a component used in a life-support device or system whose failure can reaso nably be
2 Life support devices or systems are intended (a) to be implanted in the human body, or (b) to support and/or
2
with the ex press written approv al of the Semiconductor Group of Siemens AG.
expecte d t o c ause t he fa il ure of that l if e-s up por t devi ce or sy s tem, o r t o a ff ect i ts s af et y or ef f ec tiv en ess o f t ha t
device or system.
maintain and sustain human life. If they f ail, it is reasonabl e to assume tha t the health of the user may be endangered.
1
of the Semiconductor Group of Siemens AG, may only be used in life-support devices or

PEB/F 4065
Table of Contents Page
1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
1.2 Functional De scr iption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
1.3 Pin Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
2 Electrical Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2.2 Operating Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
2.3 Thermal Resistances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
2.4 Electrical Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
2.5 AC-Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
3 Package Outlines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Semiconductor Group 3 1998-03-01

High Voltage Subscriber Line IC
PEB/F 4065
HV-SLIC
Version 1.1 SPT 1 Overview
The High Voltage Subscriber Line IC PEB 4065 is a
rugged and reliable interface between the telephone
line and the SLICOFI, a low voltage Subscriber Line
Interface and Codec Filter IC. It is fabricated in a Smart
Power Technology offering a breakthrough voltage of
at least 170 V.
The PEB 4065 provides battery feeding between
– 24 V and – 80 V and internal ringing injection with a
differential ring voltage up to 85 Vrms. In order to
achieve these high amplitudes an auxiliary positive battery voltage is used during
ringing. This voltage can also be applied in order to drive very long telephone lines.
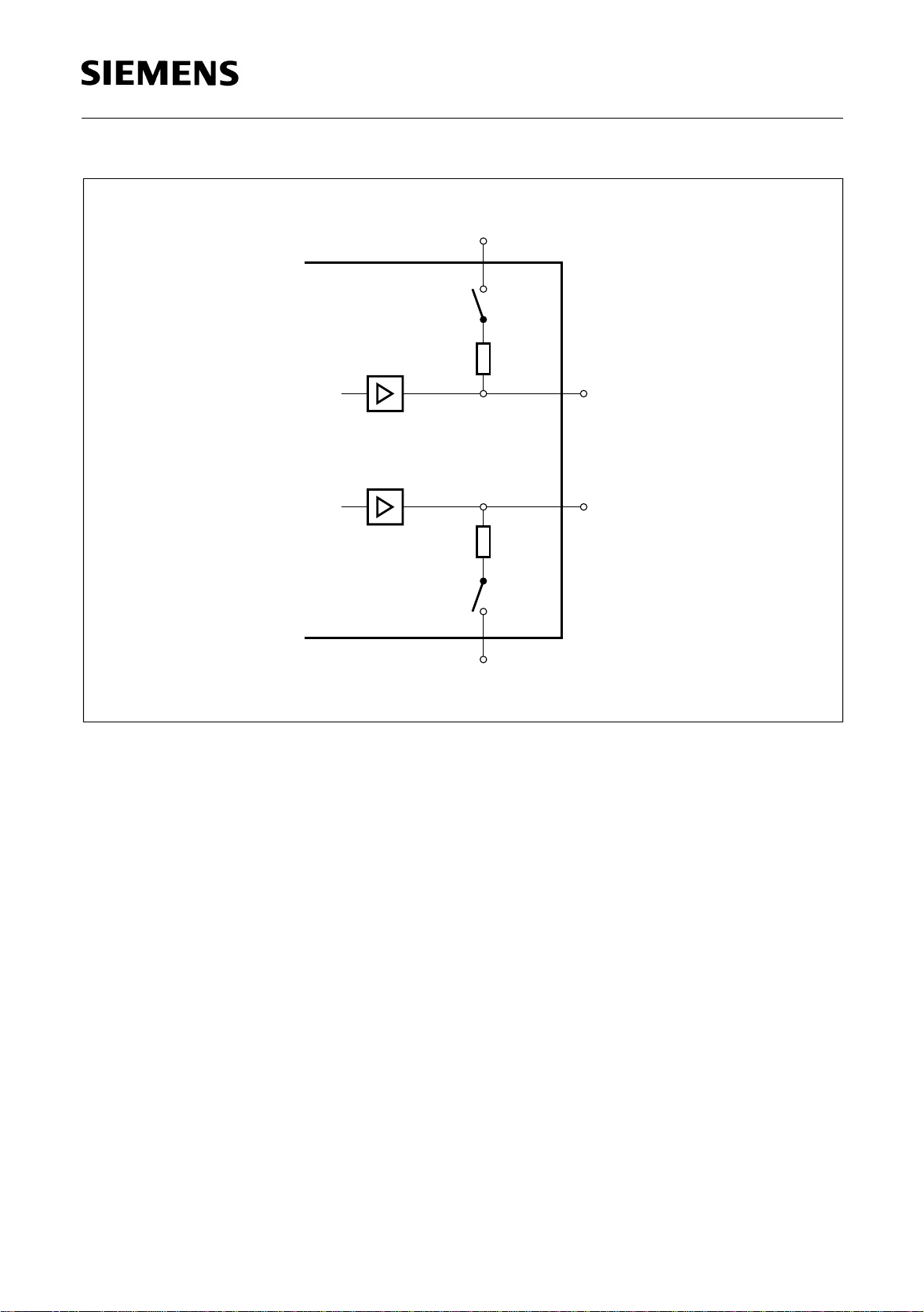
P-DSO-20-5
The SLIC is designed for a voltage feeding – current sensing line interface concept and
provides sensing of transversal and longitudinal current on both wires.
A power-down mode offers reduced power consumption at full functionality; in the power
denial mode the device is switched off turning the line outputs to a high impedance state.
1.1 Features
• High voltage line feeding
• Internal ring and metering signal injection
• Sensing of transversal and longitudinal line current
• Reliable 170 V Smart Power Technology
• Battery voltage – 24 V … – 80 V
• Boosted battery mode for long telep hone lines
and up to 85 Vrms balanced ringing
• Polarity reversal
• Small P-DSO-20-5 pow er pac kage
Type Ordering Code Package
PEB/F 4065 on request P-DSO-20-5
Semiconductor Group 4 1998-03-01
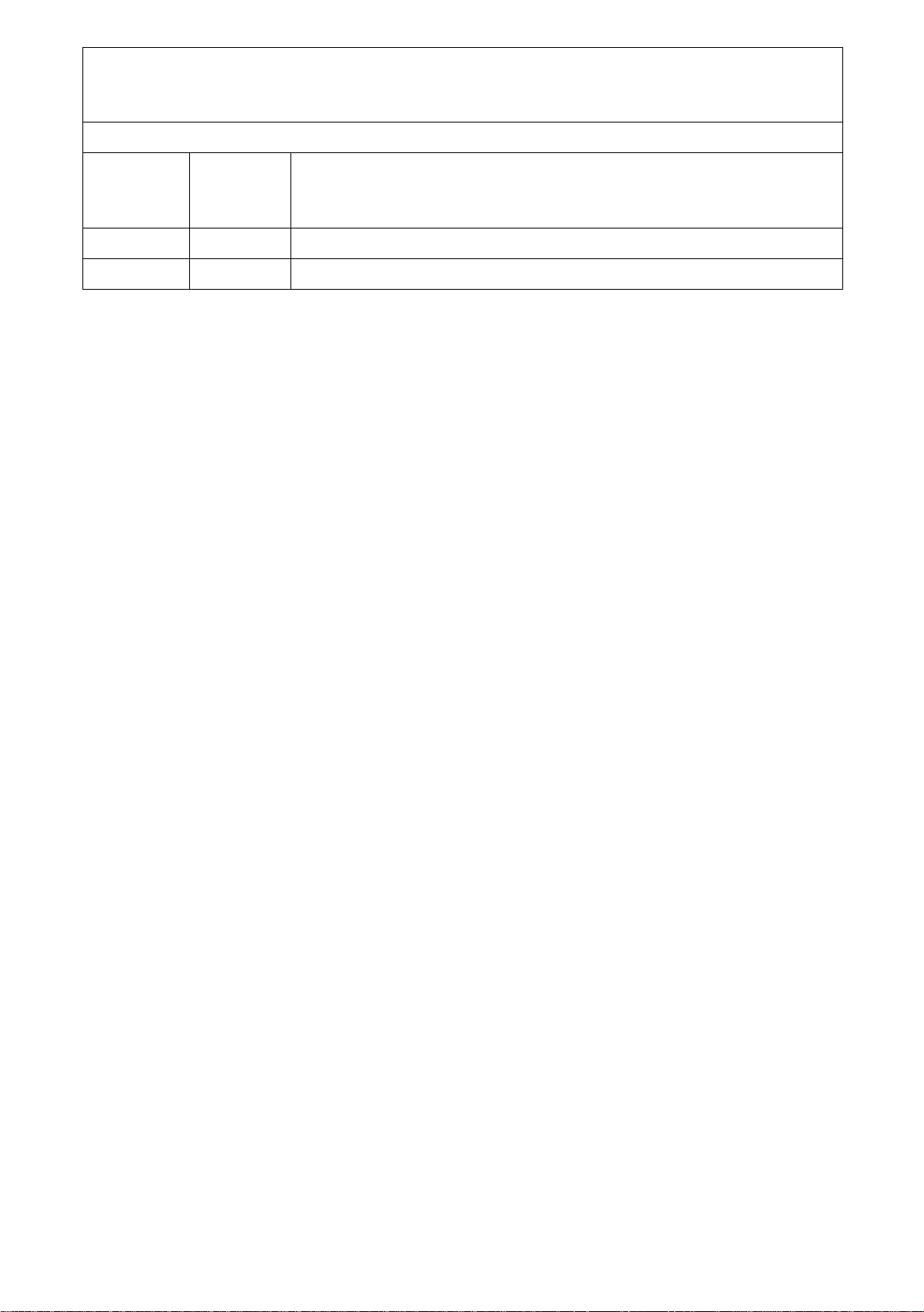
1.2 Functional Description
Ι
RING
TIP
a
V
ab
Ι
b
Buffer
Buffer
V
BGND
H
Supply
Switch
V
HINT
Differential
I/V-Converter
Control
V/I Converter
Reference
PEB/F 4065
Overview
C1
C2
V
2W
PDN
V
Current sensor
Ι
TL
Ι
BAT
Supply
VV
BAT
BIM SSVDD
AGND
V
ITB10371
Figure 1 Block Diagram
V
The PEB 4065 supports AC and DC control loops based on feeding a voltage
I
line and sensing the transversal line current
It converts a uni pol ar in put vol t age
V
into a differential output voltage Vab with an AC
2W
(Figure 2).
ab
to the
ab
receiving gain of
Gr =
V
abAC/V2WAC
= 40.
This is accomplished by converting the input voltage to a current which is used to
transpose the low voltage signals of the interface to the high voltage line feeding section.
This current is reconverted to two voltages of opp osite phase which are referenced to
the positive and negative supply voltage, respectively. Thus the differential DC
line-voltage in all normal polarity modes except ringing is related to the input voltage by
V
V
V
V
Depending on the operation mode,
BGND (
V
HINT
abDC
BAT
HINT
fix
= V
negative battery voltage
internal positive suppl y voltage
internal voltage drop of supply filter (appr. 2 V).
BAT
– V
HINT
+ V
–40× V
fix
V
is switched either to VH (V
HINT
= – 0.5 V) via the supply switch.
2WDC
= VH–1V) or to
HINT
Semiconductor Group 5 1998-03-01

PEB/F 4065
Overview
Controlled by C2, the polarity of Vab can be reversed and the DC-line-voltage then is
V
abDC
=–(V
BAT
– V
HINT
+ V
–40× V
fix
2WDC
).
The transversal and longitudinal currents are measured in the buffers and scaled images
I
are provided at the
I
=(Ia+ Ib)/100 = Iab/50 IL=–(Ia– Ib)/100 = – I
T
and IL pin, respectively:
T
Long
/50.
The PEB 4065 operates in four mod es cont ro lled by ternar y lo gic sig nals at the C1 a nd
C2 input. Additionally, in the active modes a polarity reversal of the output voltage can
be programmed (see Table 1).
Power down (PD):
Power consumption is reduced by decreasing bias current levels. All
functions operate at some small perfor mance reductions. In this mode each of the line
outputs can be progr ammed to show high im pedance. HI b sw itches off the TIP buffer,
I
while the current through the RING output still can be measured by
or IL. Programming
T
HI a reverses the polarity and switches off the RING buffer.
Conversation (CONV)
teletax. The line driving section is operated between V
: This is the regular transmit and receive mode for voiceband and
and BGND.
BAT
Boosted battery (BB):
V
voltage
is used, enabling a higher DC-voltage across the line.
H
Ringing (RING):
In order to drive longer telephone lines an auxiliary positive battery
This mode also uses the auxiliary voltage VH in order to provide a
balanced ring signal of up to 85 Vrms. The ring tone wi thout any DC-component h as t o
V
be switched to the
proportional to the total supply voltage
V
H
– V
= 120 V. The current sensing functions are available for ring trip detection.
BAT
The Power Denial (PDN)
input. Internally a DC-voltage is superimposed. This voltage is
2W
V
H
– V
and amounts to typically 23 V at
BAT
state is intended to reduce power consumption of the linecard
to a minimum: the PEB 4065 is switched off completely by connecting the PDN pin to
V
, no operation is available.
DD
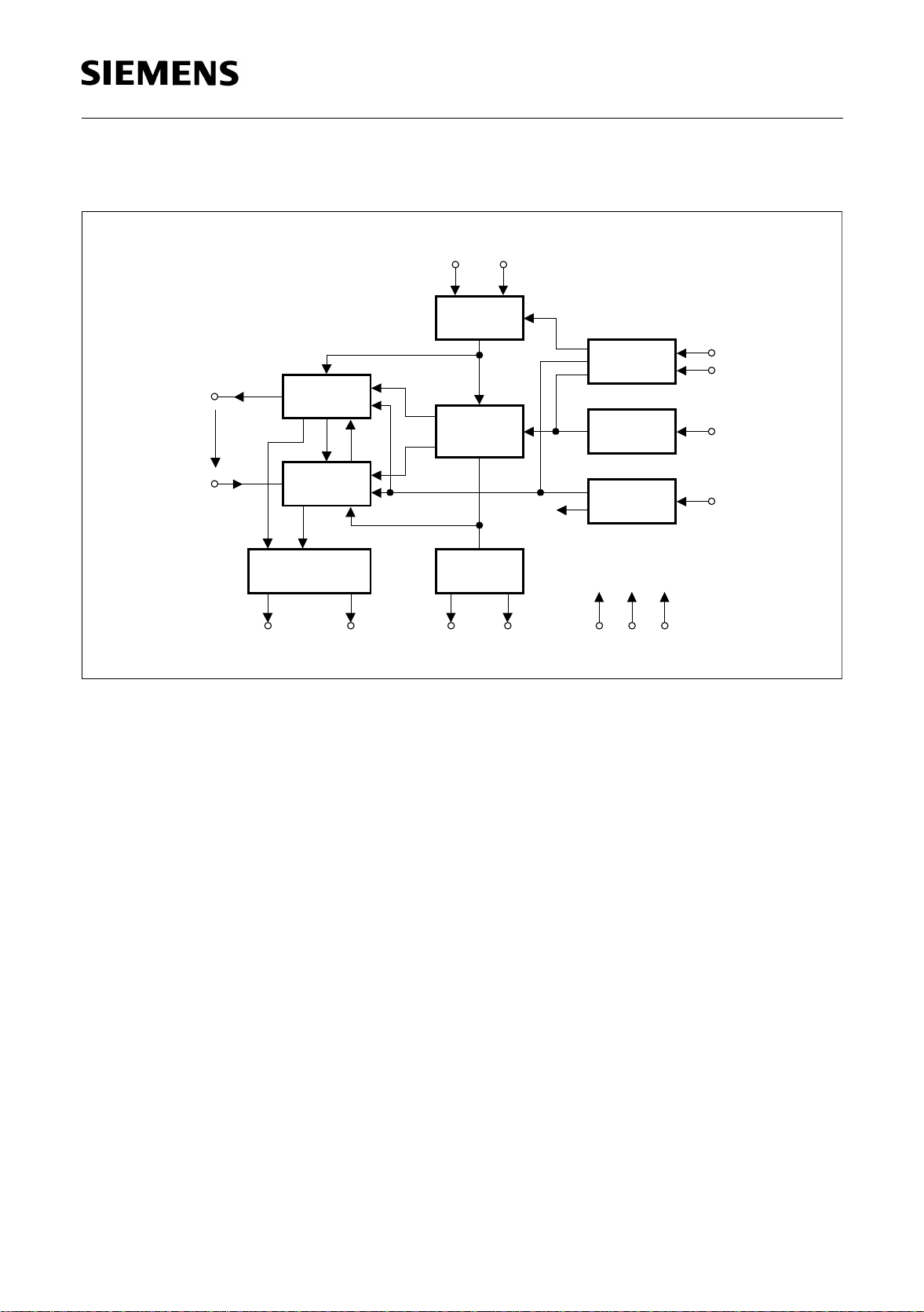
With respect to the output impedance of TIP and RING two PDN-modes have to be
distinguished. A resistive one (PDNR) provides a connection of 15 kΩ each from TIP to
V
BGND and RING to
, respectively, while the outputs of the buffers show high
BAT
impedance (Figure 3).
The other mode (PDNH) offers high impedance at TIP and RING. It is entered when, in
V
addition to connecting PDN to
, the programming inputs C1, C2 are tied to VIL.
DD
All other combinations of C1, C2 yield the resistive power denial state PDNR.
Semiconductor Group 6 1998-03-01

Table 1 Programming of Operation Modes
PEB/F 4065
Overview
C2 (Pin 13)
V
IL
V
IL
C1 (Pin 12)
NP Normal Polarity RP...Reverse Polarity
HI a RP Ring wire set to high impedance
HI b NP Tip wire set to high impedance
V
V
IZ
IH
Buffer
RING RP RING NP HI a RP
BB RP BB NP HI b NP
CONV RP CONV NP PD NP
Ι
a
V
ab
RING
Ι
Long
V
Z
IZ
L
V
IH
2
Z
Ι
ab
Buffer
Ι
Ι
= (
ab
Long
Ι+Ι
a
= (
Ι
b
) /2
b
) /2
Ι-Ι
b
a
TIP
Ι
Long
Figure 2 Definition of Output Current Directions
L
2
~
~
ITS10372
Semiconductor Group 7 1998-03-01
HIZ
HIZ
R
15 k
R
15 k
PEB/F 4065
Overview
BGND
PDNRPDNH
TG
Ω
TIP
RING
RB
Ω
PDNRPDNH
V
BAT
Figure 3 TIP and RING Impedance in Power Denial
ITS10373
Semiconductor Group 8 1998-03-01
1.3 Pin Descriptio n
PEB/F 4065
Overview
P-DSO-20-5 (11 mm)
V
BAT
V
SS
Ι
Ι
AGND
C2 BGND
C1
AGND
PDN
V
Due to reverse bending of the leads,
the numbering of the pins is also reversed.
20 1
19
18
L
17
T
16
15
14
13
12
11
Figure 4 Pin Configuration (t op view)
Table 2 Pin Definition and Functions
Pin No. Symbol Type
Function
Input (I)
Output (O)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
ITP10374
V
BAT
RING
TIP
N.C.
V
H
V
DD
V
2W
V
BIM
V
BATBAT
1, 10, 11,
20
V
BAT
Supply Negative battery supply voltage (– 24 … – 80 V),
referred to BGND
2 RING O Subscriber loop connection, negative wire in
I
normal polarity; direction of positive
current out of
a
this pin
3 TIP O Subscriber loop connection, mor e posi tive w ire in
I
normal polarity; direction of positive
current into
b
this pin
4 – N.C. Not connecte d
5
V
H
Supply Auxiliary positive battery supply voltage
(0 … + 90 V) used in ringing and boosted battery
mode
V
6 BGND Supply Battery ground: TIP, RING,
and VH refer to this
BAT
pin
7
V
DD
Semiconductor Group 9 1998-03-01
Supply Positive supply voltage (+ 5 V), referred to AGND
 Loading...
Loading...