Page 1

LFP CUBIC
TDR level sensor
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
en
Page 2

Described product
LFP Cubic
Manufacturer
SICK AG
Erwin-Sick-Str. 1
79183 Waldkirch, Germany
Germany
Legal notices
This work is protected by copyright. The associated rights are reserved by SICK AG.
Reproduction of this document or parts of this document is only permissible within
the limits of the legal determination of Copyright Law.
Any modication, expurgation, or translation of this document is prohibited without
the express written permission of SICK AG.
The trademarks stated in this document are the property of their respective owner.
© SICK AG. All rights reserved.
Original document
This document is an original document of SICK AG.
2
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 3

Contents
1 About this document .......................................................................................6
1.1 Information on the operating instructions ................................................................ 6
1.2 Scope ..........................................................................................................................6
1.3 Explanation of symbols ..............................................................................................6
1.4 Further information ....................................................................................................7
1.5 Customer service ........................................................................................................7
2 Safety information ...........................................................................................8
2.1 Intended use ............................................................................................................... 8
2.2 Incorrect use ............................................................................................................... 8
2.3 Limitation of liability ................................................................................................... 8
2.4 Modications and conversions .................................................................................. 8
2.5 Requirements for skilled persons and operating personnel ...................................9
2.6 Operational safety and particular hazards ...............................................................9
2.7 General safety notes ................................................................................................10
2.8 Repairs ......................................................................................................................10
3 Product description ....................................................................................... 11
3.1 Product ID .................................................................................................................11
3.1.1 Information on the housing ......................................................................11
3.1.2 Type code ..................................................................................................11
3.2 Product characteristics ............................................................................................12
3.2.1 Device view ...............................................................................................12
3.2.2 Operating buttons .....................................................................................12
3.3 Product features and functions ...............................................................................12
3.3.1 Principle of operation ...............................................................................12
3.3.2 Fields of application .................................................................................13
4 Transport and storage .................................................................................. 14
4.1 Transport ...................................................................................................................14
4.2 Transport inspection ................................................................................................14
4.3 Storage ......................................................................................................................14
5 Mounting ......................................................................................................... 15
5.1 Installation conditions ..............................................................................................15
5.1.1 Installation in a container ........................................................................15
5.1.2 Installation in a metal immersion tube or metal bypass .......................16
5.1.3 Rope probe in the metallic container ......................................................17
5.2 Mounting the coaxial tube .......................................................................................18
5.3 Shortening or replacing the probe rod/rope probe ................................................18
5.3.1 Procedure ..................................................................................................18
5.3.2 Shortening the rope probe .......................................................................19
5.4 Mounting the probe rod ...........................................................................................20
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
3
Page 4

6 Electrical installation .................................................................................... 21
6.1 Safety ........................................................................................................................21
6.1.1 Notes on the electrical installation ..........................................................21
6.2 Electrical connection ................................................................................................22
6.2.1 Overview of the electrical connections ...................................................22
6.2.2 Pin assignment, M12 plug connector, 5-pin ...........................................22
6.2.3 Pin assignment, M12 plug connector, 8-pin ...........................................23
7 Commissioning .............................................................................................. 24
7.1 Quick commissioning (with factory settings) ..........................................................24
7.2 Advanced commissioning ........................................................................................24
7.3 Foam commissioning (with factory settings) ..........................................................26
8 Operation ........................................................................................................ 28
8.1 Display and pushbuttons .........................................................................................28
8.1.1 Variants with two switching outputs ........................................................28
8.1.2 Variants with four switching outputs .......................................................28
8.1.3 IO-Link .......................................................................................................28
8.2 Conguring the switching outputs ...........................................................................29
8.2.1 Switching hysteresis and window function .............................................29
8.2.2 Normally open with adjustable hysteresis ..............................................30
8.2.3 N/C output with congurable hysteresis .................................................31
8.2.4 N/O output with window function ............................................................32
8.2.5 N/C output with window function ............................................................33
8.2.6 N/O output with error signal ....................................................................34
8.2.7 N/C output with error signal ...................................................................34
8.3 Congure the analog output ....................................................................................35
8.3.1 Automated signal detection .....................................................................35
8.3.2 Current output 4 mA ... 20 mA ................................................................35
8.3.3 Voltage output 0 V ... +10 V .....................................................................35
8.4 Advanced functions ..................................................................................................36
8.4.1 Expert mode ..............................................................................................36
8.4.2 Filtering measured values ........................................................................36
8.4.3 Automated adjustment of the interference signal limit .........................37
8.4.4 Blanking the interference signals in the masked zone ..........................37
8.4.5 Selection of evaluation method ...............................................................38
8.4.6 Testing the conguration ..........................................................................38
8.4.7 Conguring the probe length ...................................................................39
8.4.8 Teaching in static interference signals ....................................................40
8.4.9 Evaluating signal quality ...........................................................................40
8.4.10 Changing the coaxial cable length .........................................................41
8.4.11 Activating the display lock ........................................................................42
8.4.12 Selecting the display unit (millimeter/inch) ............................................42
8.4.13 Setting the oset .....................................................................................43
8.4.14 Resetting the calibration ..........................................................................44
4
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 5

9 Menu overview ............................................................................................... 45
10 Overview of parameters ............................................................................... 48
11 Troubleshooting ............................................................................................. 52
11.1 Error message on the display ..................................................................................52
11.2 Operating the display ...............................................................................................53
11.3 Outputs......................................................................................................................54
11.4 Error behavior ...........................................................................................................54
12 Repair work .................................................................................................... 55
12.1 Maintenance .............................................................................................................55
12.2 Returns ......................................................................................................................55
13 Disposal .......................................................................................................... 56
14 Technical data ................................................................................................ 57
14.1 Features ....................................................................................................................57
14.2 Performance .............................................................................................................57
14.3 Mechanics/materials ...............................................................................................58
14.4 Reference conditions ...............................................................................................58
14.5 Ambient conditions ..................................................................................................58
14.6 Electrical connection values ....................................................................................59
14.7 Measurement accuracy ...........................................................................................60
15 Dimensional drawings .................................................................................. 62
16 Factory setting ............................................................................................... 65
17 Accessories .................................................................................................... 66
18 Media list ........................................................................................................ 67
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
5
Page 6

1 ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT
1 About this document
1.1 Information on the operating instructions
These operating instructions provide important notes on how to use sensors from SICK AG.
Prerequisites for safe work are:
• Compliance with all safety notes and handling instructions supplied.
• Compliance with local work safety regulations and general safety regulations for
sensor applications.
The operating instructions are intended to be used by qualied personnel and electrical
specialists.
Note:
Read these operating instructions carefully before starting any work on the device,
in order to familiarize yourself with the device and its functions.
The instructions constitute an integral part of the product and are to be stored in the
immediate vicinity of the device so they remain accessible to sta at all times. Should
the device be passed on to a third party, these operating instructions should be handed
over with it.
These operating instructions do not provide information on operating the machine
in which the sensor is integrated. For information about this, refer to the operating
instructions of the particular machine.
1.2 Scope
These operating instructions serve to incorporate a sensor into a customer system.
Instructions are given by stages for all actions required.
These instructions apply to all available device variants of the sensor. For more detailed
information for the identication of the available device types, see “3.1.2 Type code”.
Available device variants are listed on the online product page:
b www.sick.com
Various device variants are used as examples for commissioning, based on the default
parameter settings for the relevant device.
Simplied device name in the document: In the following, the sensor is referred to in
simplied form as LFP. Exceptions occur where a distinction between device variants is
required due to dierent technical features or functions. In this case, the complete type
designation (e.g. LFP Cubic) is used.
1.3 Explanation of symbols
Warnings and important information in this document are labeled with symbols.
The warnings are introduced by signal words that indicate the extent of the danger.
These warnings must be observed at all times and care must be taken to avoid
accidents, personal injury, and material damage.
DANGER
… indicates a situation of imminent danger, which will lead to a fatality or serious
injuries if not prevented.
6
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 7

WARNING
… indicates a potentially dangerous situation, which may lead to a fatality or serious
injuries if not prevented.
CAUTION
… indicates a potentially dangerous situation, which may lead to minor/slight injuries
if not prevented.
IMPORTANT
… indicates a potentially harmful situation, which may lead to material damage if
not prevented.
NOTE
… highlights useful tips and recommendations as well as information for ecient
and trouble-free operation.
1ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT
1.4 Further information
NOTE
All the documentation available for the sensor can be found on the online product
page at:
www.sick.com
The following information is available for download there:
• Model-specic online data sheets for device variants, containing technical data,
dimensional drawings and diagrams
• EU declaration of conformity for the product family
• Dimensional drawings and 3D CAD dimension models in various electronic formats
• These operating instructions, available in English and German, and in other languag-
es if necessary
• Other publications related to the sensors described here (e.g. IO-Link)
• Publications dealing with accessories
1.5 Customer service
If you require any technical information, our customer service department will be happy
to help. To nd your representative, see the nal page of this document.
NOTE
Subject to change without notice
Before calling, make a note of all sensor data such as type code, serial number, etc. to
ensure faster processing.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
7
Page 8

2 SAFETY INFORMATION
2 Safety information
2.1 Intended use
The LFP is designed for both continuous level measurement and point level measurement
in nearly all liquids (a list of the possible media can be found in the appendix).
The sensor is not aected by changes in the properties of the liquids to be measured.
The LFP can be used in metal containers or bypass/immersion pipes. A coaxial tube is
required for use in plastic containers.
2.2 Incorrect use
Any use outside of the stated areas, in particular use outside of the technical
specications and the requirements for intended use, will be deemed incorrect use.
If the operator wishes to use the sensor in other conditions or in dierent environ-
ments, then the manufacturing service may issue an operating license in consultation
with the customer and in exceptional cases.
2.3 Limitation of liability
Applicable standards and regulations, the latest state of technological development,
and our many years of knowledge and experience have all been taken into account
when assembling the data and information contained in these operating instructions.
The manufacturer accepts no liability for damage caused by:
• Failing to observe the operating instructions
• Incorrect use
• Use by untrained personnel
• Unauthorized conversions
• Technical modications
• Use of unauthorized spare parts, consumables, and accessories
With special variants, where optional extras have been ordered, or owing to the latest
technical changes, the actual scope of delivery may vary from the features and illustrations shown here.
2.4 Modications and conversions
IMPORTANT
Modications and conversions to the sensor and/or the installation may result in
unforeseeable dangers.
Interrupting or modifying the sensor or SICK software will invalidate any warranty claims
against SICK AG. This applies in particular to opening the housing, even as part of
mounting and electrical installation.
Before technical modications to and expansions of the sensor, the prior written
approval of the manufacturer must be obtained.
8
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 9

2.5 Requirements for skilled persons and operating personnel
WARNING
Risk of injury due to insucient training.
Improper handling of the sensor may result in considerable personal injury and material
damage.
• All work must only ever be carried out by the stipulated persons.
The operating instructions state the following qualication requirements for the various
areas of work:
• Instructed personnel have been briefed by the operator about the tasks assigned
to them and about potential dangers arising from improper action.
• Skilled personnel have the specialist training, skills, and experience, as well as
knowledge of the relevant regulations, to be able to perform tasks delegated to
them and to detect and avoid any potential dangers independently.
• Electricians have the specialist training, skills, and experience, as well as
knowledge of the relevant standards and provisions to be able to carry out work on
electrical systems and to detect and avoid any potential dangers independently.
In Germany, electrical specialists must meet the specications of the BGV A3 Work
Safety Regulations (e.g., Master Electrician). Other relevant regulations applicable
in other countries must be observed.
2SAFETY INFORMATION
The following qualications are required for various activities:
Activities Qualication
Mounting, maintenance
Electrical installation,
device replacement
Commissioning,
conguration
Operation of the device for
the particular application
• Basic practical technical training
• Knowledge of the current safety regulations in the workplace
• Practical electrical training
• Knowledge of current electrical safety regulations
• Knowledge of device control and operation in the particular
application concerned (e.g.conveying line)
• Basic knowledge of the control system in use
• Basic knowledge of the design and setup of the described
connections and interfaces
• Basic knowledge of data transmission
• Knowledge of device control and operation in the particular
area of application concerned (e.g. bottling plant)
• Knowledge of the software and hardware environment for the
particular application concerned (e.g. bottling plant)
2.6 Operational safety and particular hazards
Please observe the safety notes and the warnings listed here and in other chapters
of these operating instructions to reduce the possibility of risks to health and avoid
dangerous situations.
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
9
Page 10

2 SAFETY INFORMATION
2.7 General safety notes
• Read the operating instructions prior to commissioning.
• These operating instructions are valid for devices with a rmware version higher
than V4.00.
• The LFP is not a safety component under the EU Machinery Directive.
• Observe national safety and work safety regulations.
• Wiring work and the opening and closing of electrical connections may only be
carried out when the power is switched o.
• The radiated power is far lower than that from telecommunication equipment.
According to current scientic research, the operation of this device can be
classied as safe and nonhazardous.
2.8 Repairs
Repair work on the sensor may be performed only by qualied and authorized
personnel from SICK AG. Interruptions or modications to the sensor on the part
of the customer will invalidate any warranty claims against SICK AG.
10
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 11

3 Product description
3.1 Product ID
3.1.1 Information on the housing
There is information printed on the housing identifying the sensor and its
electrical connection.
3.1.2 Type code
LFP x - x x x M x
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Position Description
1 Product group
2 Probe length in mm
3 Process connection/probe version
4 Housing, display/device connection
5 Application/design
6 Signal output
7 Switching output
LFP (level sensors)
0025:
without probe
in 10 mm increments; rope probe in 1000 mm increments
0200:
4000 mm
4000:
A: G ¾ A / single-rod probe 1.4404 interchangeable, 100 °C; 10 bar
B: ¾" NPT / single-rod probe 1.4404 interchangeable, 100 °C; 10 bar
E: G ¾ A / 3 mm rope probe, 1.4404 interchangeable, 100 °C; 10 bar
F: ¾" NPT / 3 mm rope probe, 1.4404 interchangeable, 100 °C; 10 bar
4: Plastic housing with display / M12 x 1 / 5-pin male connector
5: Plastic housing with display / M12 x 1 / 8-pin male connector
B: Remote amplier; length of cable 1 m
C: Remote amplier; length of cable 2 m
D: Remote amplier; length of cable 3.3 m
N: Standard
M: 4 mA ... 20 mA / 0 V ... +10 V reversible
B: 1 x PNP + 1 x PNP/NPN
C: 1 x PNP + 3 x PNP/NPN
3PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
Subject to change without notice
Not all variants of the type code can be combined with each other!
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
11
Page 12
3 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
1
1
2
3
4
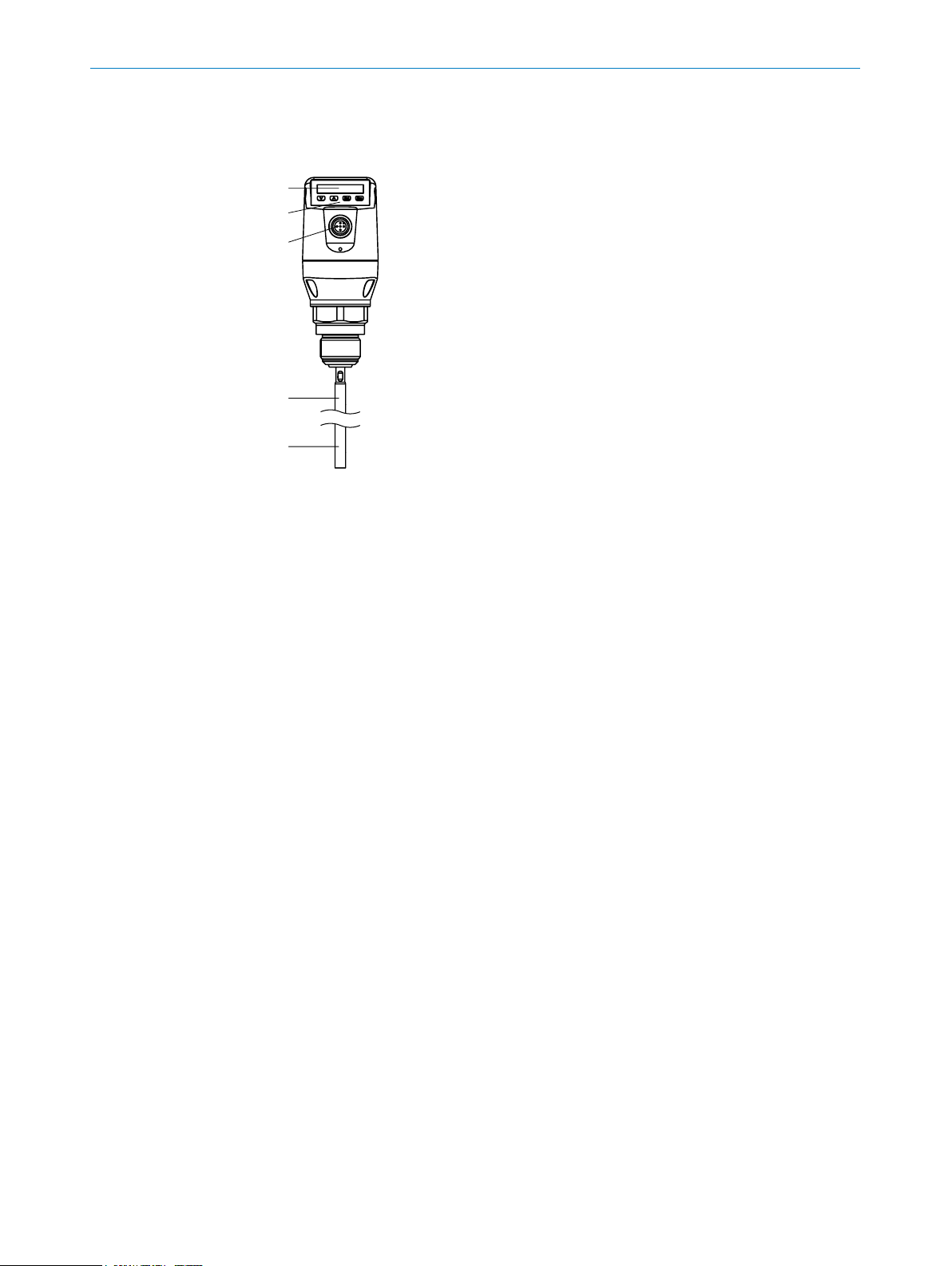
3.2 Product characteristics
3.2.1 Device view
Fig. 1: LFP Cubic (standard version)
1 Sample probe
2 Electrical connection
3 Operating buttons
4 Display
3.2.2 Operating buttons
The sensor is operated using the display and operating buttons.
For a detailed description of the pushbuttons and their functions, see “8.1 Display and
pushbuttons”.
3.3 Product features and functions
3.3.1 Principle of operation
The LFP uses TDR (Time Domain Reectometry) technology.
This is a process to determine transit times of electromagnetic waves. The sensor
electronics generate a low-energy electromagnetic pulse, which is linked to and runs
along the probe.
If this pulse strikes the surface of the liquid to be measured, a portion of the pulse
is reected there and is conducted back up along the probe path to the electronics,
which then calculate the level based on the time dierence between the sent and the
received pulse.
The sensor can output this level as a continuous measured value (analog output) and
can also derive two and/or four freely positionable switching points from it (switching
outputs).
IO-Link communication is also available for the switching output (Q1),
see “8.1.3 IO-Link”.
12
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 13

3.3.2 Fields of application
The innovative TDR technology enables reliable level measurement which is largely
application-independent. The LFP is suitable for both continuous level measurement
and point level measurement in nearly all liquids.
The sensor is not aected by changes in the properties of the liquids to be measured.
The LFP can be used in metal containers or bypass/immersion pipes. A coaxial tube is
required for use in plastic containers.
3PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
13
Page 14
4 TRANSPORT AND STORAGE
4 Transport and storage
4.1 Transport
For your own safety, please read and observe the following notes:
IMPORTANT
Damage to the sensor due to improper transport.
• The device must be packaged for transport with protection against shock and damp.
• Recommendation: Use the original packaging as it provides the best protection.
• Transport should be performed by specialist sta only.
• The utmost care and attention is required at all times during unloading and
transportation on company premises.
• Note the symbols on the packaging.
• Do not remove packaging until immediately before you start mounting.
4.2 Transport inspection
Immediately upon receipt at the receiving work station, check the delivery for
completeness and for any damage that may have occurred in transit. In the case of
transit damage that is visible externally, proceed as follows:
4.3 Storage
• Do not accept the delivery or only do so conditionally.
• Note the scope of damage on the transport documents or on the transport
company's delivery note.
• File a complaint.
Note:
Complaints regarding defects should be led as soon as these are detected. Damage
claims are only valid before the applicable complaint deadlines.
Store the device under the following conditions:
• Recommendation: Use the original packaging.
• Do not store outdoors.
• Store in a dry area that is protected from dust.
• To ensure that any residual moisture present can escape, do not store
in airtight containers.
• Do not expose to any aggressive substances.
• Protect from sunlight.
• Avoid mechanical shocks.
14
• Storage temperature: see “12 Repair work”.
• Relative humidity: see “12 Repair work”.
• For storage periods of longer than 3 months, check the general condition
of all components and packaging on a regular basis.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 15
5 Mounting
B
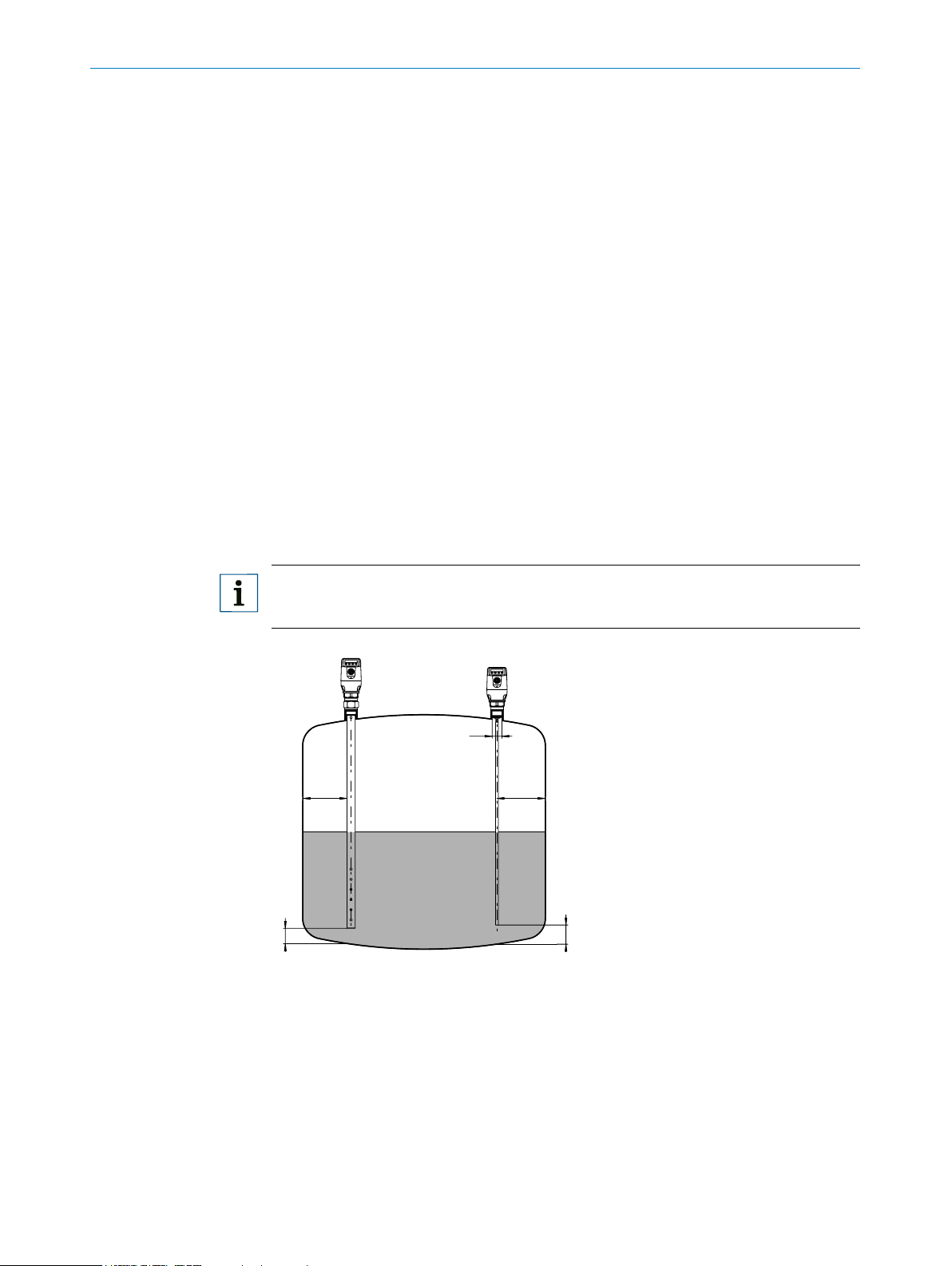
5.1 Installation conditions
The LFP is mounted vertically from above into the container or bypass, using its process
connection. The LFP level sensor has a G ¾ or ¾" NPT threaded connection. A minimum
connecting piece diameter in accordance with the diagrams below must be observed.
The LFP must be installed so that after mounting there is sucient distance to other tank
components (e.g. supply tubes, other measurement devices), the container wall or the
container bottom. These minimum distances are also specied in the diagrams.
The LFP can also be used in a metal immersion pipe or bypass. The installation
conditions are shown in the Figure on page 15.
Ensure that there is a good metallic connection between the LFP measuring device and
the tank/bypass. When operating the sensor, ensure that the ambient temperature is not
above or below the limits.
Insulating the sensor housing is not permitted for tanks with hot media.
When positioning the device, ensure that the sensor is not directly exposed to the lling ow.
The sensor housing can be rotated 360°, allowing for the cable outlet to be positioned
freely.
5MOUNTING
5.1.1 Installation in a container
Note:
The distances are identical for the sensor with remote amplier.
C A
Fig. 2: LFP Cubic
1 Mono-probe with metallic containers
Installation in the nozzle
D ≥ DN 25
Distance to container wall/container
bottom:
A ≥ 50 mm
B ≥ 10 mm
Distance to components built into the
container
≥ 100 mm
D
B
2 Coaxial tube in metallic and non-metallic
containers
C = In the case of a coaxial probe there
are no minimum distances from the container wall and built-in components to be
observed.
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
15
Page 16

5 MOUNTING
5.1.2 Installation in a metal immersion tube or metal bypass
D
B
Fig. 3: LFP Cubic
1 Centering
2 D ≥ DN 40
Distance to bypass/container bottom
B ≥ 10 mm
Centering: To prevent contact between the probe and the bypass pipe during
oscillations, the probe should be centered according to its length and depending on the
diameter of the bypass pipe. To do this, it is necessary to insert one or two centering
pieces, see “17 Accessories”.
16
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 17

5.1.3 Rope probe in the metallic container
F = 250
5MOUNTING
D
A
MX
N
max.
Fig. 4: LFP Cubic
1 Rope weight
2 Bracket rope tension
Installation in the nozzle: D ≥ DN 25
Container wall/container bottom distance: A ≥ 50 mm
Distance from components built into container: ≥ 100 mm
Mounting the mono-probe
M = Measuring range
X = No measurement is possible in this area
Container welding seams may aect the measurement accuracy.
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
17
Page 18

5 MOUNTING
5.2 Mounting the coaxial tube
See the operating instructions for the coaxial tube (8015674) at www.sick.com.
5.3 Shortening or replacing the probe rod/rope probe
If the probe rod or rope probe is too long for the application, it can be shortened to the
container height. In this case, you should not shorten the probe beyond its minimum
length of 100 mm. If the LFP is to be used in a hygienic application, then be sure that
the roughness of Ra≤0.8 µm is reestablished on the shortened machined surfaces of
the mono-probe.
5.3.1 Procedure
Shorten the probe rod and/or rope probe as desired. Adjust the new probe length in the
LFP, see “8.4.7 Conguring the probe length”. Ensure that this correction corresponds
to the probe length, because an incorrect value in the Length menu has a direct eect
on measurement accuracy and can lead to faults. The probe length L is set out in
Chapter “15 Dimensional drawings”.
The probe rod and/or the rope probe can be swapped. Use a suitable tool. If the system
experiences strong vibrations, secure the probe with thread-locking lacquer.
18
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 19

5.3.2 Shortening the rope probe
1 2 mm hexagon screw
2 Loosen the setscrews (3x)
3 Rope weight
5MOUNTING
4 New probe length
5 Shift the rope weight to the desired length
2 Setscrews* (tighten according to desired length 1.5 Nm, 3x)
*It is recommended that the setscrews be secured with a thread-locking lacquer
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
19
Page 20

5 MOUNTING
M5
5.4 Mounting the probe rod
With the LFP Cubic, the probe rod can be modied by the customer. The specications
for the probe rod should be as follows:
Probe rod diameter: 7 mm … 8 mm
Female thread on the probe rod: M5
Female thread length: min. 10 mm
Material: Stainless steel
min. 10 (0.39)
Ø 7...8 mm
( Ø 0.27... 0.31)
1 Probe rod length
Total probe length: 100 mm … 4000 mm
Total probe length = 15 mm + probe rod length
Set the total probe length as described in Chapter “8.4.7 Conguring the probe length”.
The EXPRT-Cong-Length menu is password protected. If the system experiences strong
vibrations, secure the probe with thread-locking lacquer.
100 (3.94) ... 4000 (157.48)
15 (0.59)
1 Total probe length
2 Probe rod length
20
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 21

6 Electrical installation
6.1 Safety
6.1.1 Notes on the electrical installation
IMPORTANT
Equipment damage due to incorrect supply voltage!
An incorrect supply voltage may result in damage to the equipment.
• Only operate the device using a protected low voltage and safe electrical insulation
as per protection class III.
IMPORTANT
Equipment damage or unpredictable operation due to working with live parts.
Working with live parts may result in unpredictable operation.
• Only carry out wiring work when the power is o.
• Only connect and disconnect electrical connections when the power is o.
6ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
• The electrical installation must only be performed by electrically qualied personnel.
• Standard safety requirements must be met when working in electrical systems.
• Only switch on the supply voltage for the device when the connection tasks have
been completed and the wiring has been thoroughly checked.
• When using extension cables with open ends, ensure that bare wire ends do not
come into contact with each other (risk of short-circuit when supply voltage is
switched on!). Wires must be appropriately insulated from each other.
• Wire cross-sections in the supply cable from the customer's power system must be
designed in accordance with the applicable standards. In Germany, observe the
following standards: DIN VDE 0100 (Part 430) and DIN VDE 0298 (Part 4) and/or
DIN VDE 0891 (Part 1).
• Circuits connected to the device must be designed as SELV circuits
(SELV = Safety Extra Low Voltage).
• Protect the device with a separate fuse at the start of the supply circuit.
Instructions for laying data cables:
• Use screened data cables with twisted-pair wires.
• Implement the screening design correctly and completely.
• To avoid interference, e.g. from switching power supplies, motors, clocked drives,
and contactors, always use cables and layouts that are suitable for EMC.
• Do not lay cables over long distances in parallel with voltage supply cables and
motor cables in cable channels.
Subject to change without notice
The IP67 protection class for the device is only achieved under the following conditions:
• The cable connected at the M12 connection is screwed on.
If this is not done, the device does not fulll any specied IP enclosure rating!
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
21
Page 22

6 ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
12
4 3
5
6.2 Electrical connection
6.2.1 Overview of the electrical connections
The sensor is connected using a pre-assembled female cable connector with
M12 x 1 plug connector (5/8-pin). With the power switched o, plug the female
cable connector into the sensor and screw it tight.
Connect the cable according to its function. After the supply voltage is set up, the
sensor performs a self-test. Once installed, the sensor is ready for operation upon
completion of the self-test (< 5 s). The display shows the current measured value.
Fig. 5: LFP Cubic
6.2.2 Pin assignment, M12 plug connector, 5-pin
Fig. 6: M12 x 1 plug connector, 5-pin
Contact Marking Wire color Description
1 L+ Brown Supply voltage
2 Q
3 M Blue Ground, reference potential for
4 C/Q
5 Q
A
1
2
White Analog current/voltage output
current/voltage output
Black Switching output 1, PNP/ IO-Link
communication
Gray Switching output 2, PNP/ NPN
22
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 23

6.2.3 Pin assignment, M12 plug connector, 8-pin
5
8
6ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
2
3
4
1
7
6
Fig. 7: M12 x 1 plug connector, 8-pin
Contact Marking Description
1 L+ Supply voltage
2 Q
2
Switching output 2, PNP/ NPN
3 M Ground, reference potential for current/voltage output
4 C/Q
5 Q
6 Q
7 Q
3
4
A
1
Switching output 1, PNP/IO-Link communication
Switching output 3, PNP/NPN
Switching output 4, PNP/NPN
Analog current/voltage output
8 No function
The wire colors for 8-pin cables are not standardized. Always note the pin assignment
of the sensor.
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
23
Page 24

7 COMMISSIONING
7 Commissioning
7.1 Quick commissioning (with factory settings)
Quick commissioning is used in applications under reference conditions
see “5 Mounting”.
The following rules apply:
• Use in metallic containers or immersion/bypass pipes
• Use in plastic container with a coaxial tube, see “17 Accessories”
• The liquid to be measured has a DK value of > 5, see “18 Media list”
Commissioning
1. Mount the sensor in accordance with the installation conditions, see “5 Mounting”.
2. The container must be empty and/or the level must be at least 200 mm below the
end of the probe.
3. Log in to expert mode, see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
4. After mounting, launch the AutCal menu item.
• Press and hold the Set pushbutton for at least 3 seconds.
• Use the Set pushbutton to conrm the AutCal menu item and then
use it again to conrm the “OK?” conrmation prompt.
• The AutCal function is conrmed with !CalOK.
5. Congure outputs, see “8.2 Conguring the switching outputs”.
Note:
If the AutCal function has been conrmed with !NoSig, relaunch AutCal.
If problems occur during commissioning, see “11 Troubleshooting”.
7.2 Advanced commissioning
Advanced commissioning is required when quick commissioning is not sucient or if
one of the following situations applies:
• The liquid to be measured has a DK value of < 5, see “18 Media list”.
• There are tank components which can interfere with the measurement signal
(in the case of the LFP Cubic).
• In the event of signicant ripples in the surface of the liquid.
• If there are variations in the installation conditions, see “5 Mounting”.
24
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 25

Commissioning
1. Mount the sensor in accordance with the installation conditions, see “5 Mounting”.
2. Log in to expert mode, see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
3. Select the measuring mode.
4. Teach-in the static sources of interference in the tank.
7COMMISSIONING
• Access the EXPRT-CONFIG-MeasMd menu using the arrow and Set pushbuttons.
• HiSpd: max. length = 2005 mm, response time < 400 ms.
• HiAcc: max. length = 6,005 mm, response time < 2,800 ms, more stable
measured values recommended for liquids with low DKs and where
TrsHld is < 70.
• Static sources of interference in the tank generated by tubes, beams,
couplings, or a cleaning ball are taught into the system as standard.
• Access the EXPRT-CONFIG-CalRng menu using the arrow and Set pushbuttons.
The following rules apply:
• Teach-in depth starts from the LFP process connection
• Teach-in depth should cover all interference signals
• Maximum teach-in depth (recommended) = probe length
• Set the value range between 95 mm … 6,005 mm
• If the tank cannot be emptied completely, the CalRng teach-in depth must be
adapted accordingly.
• The level must be at least 200 mm below the CalLen and/or the end of the
probe.
5. Launch the AutCal function.
• Access the AutCal menu using the arrow and Set pushbuttons.
• The following information applies: The probe must not be covered with liquid
in the CalRng set in step 4 (teach-in depth + 200 mm).
• Use the Set pushbutton to conrm the AutCal menu item and then use it again
to conrm the “Ok?” conrmation prompt.
• The AutCal function is conrmed with !CalOK.
6. Analyze the signal quality.
• The signal quality can be analyzed when the device is installed,
see “8.4.9 Evaluating signal quality”.
• In the event of problems:
• Reduce the value in the EXPRT-CONFIG-TrsHld menu.
• Set the parameter to HiAcc in the EXPRT-CONFIG-MeasMd menu.
Subject to change without notice
• Switch on the lters in the Set lters menu.
• Reduce the parameter in the EXPRT-CONFIG-MaxCol menu.
7. Congure the lter (see Chapter “8.4.2 Filtering measured values”).
8. Perform maximum change of level/plausibility check
(see Chapter “8.4.2 Filtering measured values”).
9. Congure outputs (“8.2 Conguring the switching outputs”).
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
25
Page 26

7 COMMISSIONING
Note:
• Use the foam commissioning instructions for applications with foam.
• The sensor automatically quits expert mode after 5 minutes of inactivity on
the display.
• Any of the following processes voids the conguration (AutCal):
• Changing the probe length
• Changing the measuring mode
• Changing the teach-in depth
If problems occur during commissioning, see “11 Troubleshooting”.
7.3 Foam commissioning (with factory settings)
For use in applications with a signicant buildup of foam.
Performing foam calibration
1. Mount the sensor in accordance with the installation conditions, see “5 Mounting”.
2. Log in to expert mode, see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
3. Empty the tank completely.
• The probe rod must be completely free from medium and foam.
• Buildup must be removed from the probe.
• The end of the probe must not be xed to the bottom of the tank.
4. Select the measuring mode.
• Access the EXPRT-Cong-MeasMd menu using the arrow and Set
pushbuttons, and congure to HiAcc.
5. Select mode
Access the EXPRT-Cong-Mode using the arrow and Set pushbuttons, and congure to Foam.
6. Perform the empty calibration.
• Access the EXPRT-Foam-CalEmp menu using the arrow and Set pushbuttons.
• !CalOk: Proceed to step 7.
• !faild: Ensure that the tank is empty and repeat step 6.
7. Fill with medium (without foam) until the probe is covered by at least 200 mm.
The maximum level must remain 200 mm from the process connection, howeve
8. Perform EXPRT-Foam-CalMed.
• !CalOk: Everything in working order, proceed to step 9.
• !faild: Carry out step 8 again.
The LFP must now display a valid measured value.
26
9. Check the foam calibration in EXPRT-INFO-CalSta.
• FomCal: Foam commissioning was completed successfully.
• CalMis: Commissioning unsuccessful. Please repeat the process.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 27

Note:
• Measurement deviation can be higher.
• Signal quality 1 and 2 are not counted.
• The sensor automatically quits expert mode after 5 minutes of inactivity on
the display.
• Conguration (foam teach) does not take place in the following processes:
• Changing the probe length
• Changing the measuring mode
• Changing the teach-in depth
• Performing AutCal
If problems occur during commissioning, see “11 Troubleshooting”.
7COMMISSIONING
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
27
Page 28

8 OPERATION
8 Operation
8.1 Display and pushbuttons
All lengths specied in the menu refer to the end of the probe and/or, for a congured
oset (for LFP Cubic see “8.4.7 Conguring the probe length”), to the tank bottom.
You can access the menu by pressing the Set pushbutton for at least three seconds.
8.1.1 Variants with two switching outputs
Q1 Q2
1000 mm
Arrow pushbuttons: Navigating in the menu and changing values
Set pushbutton: Saving and conrming
Esc pushbutton: Exiting the operating menu step-by-step
Note:
A bar graph above the unit symbol indicates the statuses of the switching outputs
when using millimeters as the unit. This display is not available when inches are
selected as the unit.
8.1.2 Variants with four switching outputs
Q1/2/3/4
1000 mm
Arrow pushbuttons: Navigating in the menu and changing values
Set pushbutton: Saving and conrming
Esc pushbutton: Exiting the operating menu step-by-step
39,4 in
39,4 in
8.1.3 IO-Link
28
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
For operation over IO-Link, an IODD le and a description of the available telegram
parameters are available for download at www.sick.com.
Subject to change without notice
Page 29

8.2 Conguring the switching outputs
8.2.1 Switching hysteresis and window function
Depending on 2 or 4 output variants
Level
SP
RP
high
low
high
low
HNO
HNC
8OPERATION
If the level is uctuating around the
target value (e.g. ripple movement
during lling), the hysteresis keeps the
t
switching status of the outputs stable.
When the level is increasing, the
output switches when the respective
switching point (SP) is reached; if the
level sinks again, the output switches
back only after the reset switching
point (RP) has been reached.
Depending on 2 or 4 output variants
Level
The window function enables moni-
toring of a dened range. If the level
is between window high (FH) and
FH
FL
window low (FL), the output will be
active (normally open) and/or inactive
(normally closed).
t
The error status of the measuring
device reects the cable break
high
low
FNC
monitoring. During an error status,
the measuring device switches to
a safe state; i.e. the switching outputs
become inactive.
high
low
FNO
As far as the downstream signal
evaluation is concerned, this
corresponds to a cable break.
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
29
Page 30

8 OPERATION
8.2.2 Normally open with adjustable hysteresis
Applications
• Dry run protection
• Empty signal
Conguration
1. Congure the Qx switching output as normally open.
• Set the parameter in the QxMENU-OUx menu to Qx_Hno.
2. Set the switching point.
• Set the value in the QxMENU-SPx menu to the level in mm (e.g. 500 mm).
3. Set the reset point.
• Set the value in the QxMENU-RPx menu to the level in mm (e.g. 450 mm).
4. Select the electrical property (NPN/PNP/DRV (push/pull)).
Select the parameter in the QxMENU-TYPx menu.
The following rules apply:
• Qx-PNP = Switching output in PNP circuit
• Qx-NPN = Switching output in NPN circuit
• Qx-Drv = Switching output in push/pull function
Switching output behavior
Level
SP
RP
Active
Inactive
Switching output PNP NPN DRV Error status
Normally open/HNO
t
Error signal
active U
v
inactive 0 V
0 V Uv (PNP switched)
1)
Uv 2) 0 V (NPN switched)
inactive
30
1)
Pulldown only.
2)
Pullup only.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 31

8.2.3 N/C output with congurable hysteresis
Applications
• Overll protection
• Full signal
Conguration
1. Congure the Qx switching output as normally closed.
• Set the parameter in the QxMENU-OUx menu to Qx_Hnc.
2. Set the switching point.
• Set the value in the QxMENU-SPx menu to the level in mm (e.g. 500 mm).
3. Set the reset point.
• Set the value in the QxMENU-RPx menu to the level in mm (e.g. 450 mm).
4. Select the electrical property (NPN/PNP/DRV (push/pull))
Select the parameter in the QxMENU-TYPx menu.
The following rules apply:
8OPERATION
• Qx-PNP = Switching output in PNP circuit
• Qx-NPN = Switching output in NPN circuit
• Qx-Drv = Switching output in push/pull function
Switching output behavior
Level
SP
RP
Active
Inactive
Switching output PNP NPN DRV Error status
Normally closed/
HNC
Error signal
active U
inactive 0 V
t
0 V Uv (PNP switched) inactive
v
2)
1)
U
0 V (NPN switched)
v
Subject to change without notice
1)
Pulldown only.
2)
Pullup only.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
31
Page 32

8 OPERATION
8.2.4 N/O output with window function
Application
The critical lling level for the application is within the FHx
and FLx window thresholds.
Conguration
1. Congure the Qx switching output as normally open.
• Set the parameter in the QxMENU-OUx menu to Qx_Fno.
2. Set the switching point.
• Set the value in the QxMENU-FHx menu to the level in mm (e.g. 500 mm).
3. Set the reset point.
• Set the value in the QxMENU-FLx menu to the level in mm (e.g. 400 mm).
4. Select the electrical property (NPN/PNP/DRV (push/pull)).
Select the parameter in the QxMENU-TYPx menu.
The following rules apply:
• Qx-PNP = Switching output in PNP circuit
• Qx-NPN = Switching output in NPN circuit
• Qx-Drv = Switching output in push/pull function
Switching output behavior
Level
FH
FL
Active
Inactive
Switching output PNP NPN DRV Error status
Normally open/FNO
Error signal
active U
v
inactive 0 V
t
0 V Uv (PNP switched)
1)
2)
Uv
0 V (NPN switched)
inactive
1)
Pulldown only.
2)
32
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Pullup only.
Subject to change without notice
Page 33

8.2.5 N/C output with window function
Application
The critical lling level for the application is outside the FHx and
FLx window thresholds.
Conguration
1. Congure the Qx switching output as normally closed.
• Set the parameter in the QxMENU-OUx menu to Qx_Fnc.
2. Set the switching point.
• Set the value in the QxMENU-FHx menu to the level in mm (e.g. 500 mm).
3. Set the reset point.
• Set the value in the QxMENU-FLx menu to the level in mm (e.g. 400 mm).
4. Select the electrical property (NPN/PNP/DRV (push/pull)).
Select the parameter in the QxMENU-TYPx menu.
The following rules apply:
8OPERATION
• Qx-PNP = Switching output in PNP circuit
• Qx-NPN = Switching output in NPN circuit
• Qx-Drv = Switching output in push/pull function
Switching output behavior
Level
FH
FL
Active
Inactive
Switching output PNP NPN DRV Error status
Normally closed/FNC
Error signal
active U
v
inactive 0 V
t
0 V Uv (PNP switched)
1)
2)
Uv
0 V (NPN switched)
inactive
1)
Pulldown only.
2)
Subject to change without notice
Pullup only.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
33
Page 34

8 OPERATION
8.2.6 N/O output with error signal
Application
If there is an error message at the LFP, this can be transferred using a switching contact.
Conguration
1. Congure the Qx switching output as normally open.
• Set the parameter in the QxMENU-OUx menu to Qx_Eno.
2. Select the electrical property (NPN/PNP/DRV (push/pull)).
Select the parameter in the QxMENU-TYPx menu.
The following rules apply:
• Qx-PNP = Switching output in PNP circuit
• Qx-NPN = Switching output in NPN circuit
• Qx-Drv = Switching output in push/pull function
8.2.7 N/C output with error signal
Application
Conguration
If there is an error message at the LFP, this can be transferred using a switching contact.
1. Congure the Qx switching output as normally closed.
• Set the parameter in the QxMENU-OUx menu to Qx_Enc.
2. Select the electrical property (NPN/PNP/DRV (push/pull)).
Select the parameter in the QxMENU-TYPx menu.
The following rules apply:
• Qx-PNP = Switching output in PNP circuit
• Qx-NPN = Switching output in NPN circuit
• Qx-Drv = Switching output in push/pull function
34
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 35

8.3 Congure the analog output
8.3.1 Automated signal detection
The LFP can automatically detect which signal is required based on the connected
output load.
The following rules apply:
• 4 mA ... 20 mA < 500 ohms at Uv > 15 V
• 4 mA ... 20 mA < 350 ohms at Uv > 12 V
• 0 V ... +10 V > 750 ohms at Uv ≥ 14 V
Conguration
1. Access the QAMENU-TYP menu using the arrow and Set pushbuttons.
2. Set the QAMENU-TYP menu to Auto?.
Note:
Automated signal detection is only active when the device is switched on for the rst time.
After this the function can be activated again in the QAMENU-TYP menu with Auto?.
8OPERATION
8.3.2 Current output 4 mA ... 20 mA
Conguration
1. Set the upper limit value (20 mA).
• Set the value in the QAMENU-QAHIGH menu to the level in mm
(e.g. 500 mm).
2. Set the lower limit value (4 mA).
• Set the value in the QAMENU-QALOW menu to the level in mm
(e.g. 10 mm).
3. Invert the signal.
The analog signal can be inverted in the QAPOL menu.
Set the parameter in the QxMENU-QAPOL menu to QA-INV.
• QA-NRM = Analog output signal as congured
• QA-INV = Analog output signal is inverted; QAHIGH 4 mA and
QALOW 20 mA
4. Select the electrical signal.
5. Set the parameter in the QxMENU-QATYP menu to 4 mA ... 20 mA.
8.3.3 Voltage output 0 V ... +10 V
Conguration
Subject to change without notice
1. Set the upper limit value (10 V).
• Set the value in the QAMENU-QAHIGH menu to the level in mm
(e.g. 500 mm).
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
35
Page 36

8 OPERATION
2. Set the lower limit value (0 V).
• Set the value in the QAMENU-QALOW menu to the level in mm
3. Invert the signal.
The analog signal can be inverted in the QAPOL menu.
Set the parameter in the QxMENU-QAPOL menu to QA-INV.
• QA-NRM = Analog output signal as congured
• QA-Inv = Analog output signal is inverted: QAHIGH 0 V and QALOW 10 V
4. Select the electrical signal.
Set the parameter in the QxMENU-QATYP menu to 0 V ... +10 V.
8.4 Advanced functions
8.4.1 Expert mode
Expert mode must rst be set in order to activate special functions.
Logging into expert mode
(e.g. 10 mm).
1. Access the PASSW menu using the arrow pushbuttons.
2. Enter the password 000537 (LFP on the mobile keypad: L=5 / F=3 / P=7).
Expert mode may be locked again if the password is entered incorrectly or if the voltage
supply is disconnected.
8.4.2 Filtering measured values
Activating ltering
Smoothing of the measured value; e.g. in the case of ripples on level surfaces. For fast
level changes, the average of the measured values over X seconds is indicated.
b Parameters in the Set lters menu.
The possible values are O, 400 ms, 600 ms, 1000 ms, 1400 ms, 2 s, 5 s, 10 s.
Maximum change of level (plausibility check)
For applications which cause level jumps as a result of signicant interference on the
LFP. Entry for the maximum level dynamic in the application and/or the maximum per-
missible change rate of the level.
1. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
2. Reduce the parameter in the EXPRT-CONFIG-MaxCol menu.
AnySpd (50 cm/s) (default), 10 cm/s, 5 cm/s, 2 cm/s
36
Note:
• For MeasMd = HiSpd, any max. change rate is possible
• For MeasMd = HiAcc, max. is 10 cm/s
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 37

8.4.3 Automated adjustment of the interference signal limit
The adjustment of the interference signal limit (TrsHld) can be carried out automatically
in many applications.
Conguration
1. Set a ll level of 30%.
2. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
3. Perform in the EXPRT-Pulse-AutoTn menu.
The sensor calculates a suitable value for TrsHld.
Note:
This setting can be used only in pulse mode.
8.4.4 Blanking the interference signals in the masked zone
To blank interference signals from the range above the maximum expected ll level,
a zone can be masked (dead zone). This zone begins at the process connection
and continues up to the congured point. If signal values above the dened limit
value (TrsHld) occur within this range, the sensor enters a safe state and signals the
error !MaskZ.
8OPERATION
MaskTr
DZ MR DZ MR DZ MR
20% x
100% x
200% x
DZ
MR
A
E
1 No reection/very weak reection
2 Weak reection (e.g. spray water)
3 Strong reection (e.g. thick layer of ketchup)
DZ Dead zone
MR Active measuring range
x No detection/measurement
Detection/measurement
1 2 3
x
x
x
x
x
x
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
37
Page 38

8 OPERATION
Conguration
1. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
2. Dene the parameter in the EXPRT-Pulse-MaskZn menu.
Note:
This setting can be used only in pulse mode.
8.4.5 Selection of evaluation method
You can switch between pulse mode and foam mode as an evaluation method.
Depending on the selected mode, other evaluation algorithms are used.
Conguration
1. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
2. In the EXPRT-Cong-Mode menu, select between Pulse and Foam.
The following rules apply:
• Mode = Pulse: The sensor measures either with or without AutCal.
• Mode = Foam: The sensor measures only with valid CalEmp+CalMed. If no valid
calibration is available, the CalPls message is displayed and the sensor enters
a safe state.
Note:
If AutCal is called up while the sensor is in foam mode, then AutCal is denied and
the error message !Denid is shown.
8.4.6 Testing the conguration
Testing outputs
Switching/analog outputs can be simulated. This makes it possible to check the wiring
and signal values on the connected systems, such as the PLC control, relay and lamps.
Conguration
Activate the Qx switching output
b Set the parameter in the QxMENU-SimQx menu to QxOn.
Additional options:
• QxO = switching output o
• QxNorm = switching output in measuring operation
38
• QxOn = switching output is active
Note:
The simulation is automatically deactivated if the supply voltage is interrupted.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 39

Activate the QA analog output
b Set the parameter in the QAMENU-SimCur or SimVol menu to the desired signal
value.
Note:
The simulation is automatically deactivated if the supply voltage is interrupted.
Simulating the level
Even if there is no liquid in the container yet, it is possible to select a lling level in the
menu in order to test the sensor conguration. When simulating a level value, all outputs on the LFP are set according to the dened conguration. The function should not
be selected until a conguration is complete.
Conguration
8OPERATION
• SimCur for current output
• SimVol for voltage output
b Set the parameter to the desired lling level as a % in the SimLev menu.
Note:
• The level simulation refers to the probe length and/or container level
(probe length + oset) if an oset is congured.
• The simulation is only active when there are no error messages.
The simulation is automatically deactivated if the supply voltage is interrupted.
Parameter selection
• SimO: O
• Filling level 0%
• Filling level 25%
• Filling level 50%
• Filling level 75%
• Filling level 100%
8.4.7 Conguring the probe length
1. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
Subject to change without notice
2. Access the EXPRT-Cong-Length menu using the arrow and Set pushbuttons.
3. Enter the probe length in the Length menu. Please note the dened probe length in
Chapter “15 Dimensional drawings”.
Note:
• HiSpd: max. length = 2005 mm, response time < 400 ms
• HiAcc: max. length = 6,005 mm, response time < 2,800 ms
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
39
Page 40

8 OPERATION
8.4.8 Teaching in static interference signals
Static interference signals in the tank generated by tubes, beams, couplings,
or a cleaning ball can be taught-in. The probe length provides the value for the
teach-in depth.
1. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
2. Access the EXPRT-Pulse-CalRng menu using the arrow and Set pushbuttons.
3. Set the value range between 95 and 6005 mm.
Note:
• The value starts from the LFP process connection.
• The value should cover all interference signals.
• Maximum value = probe length – 100 mm.
• The AutCal must then be carried out, see “7 Commissioning”.
• The CalRng parameter should always correspond to the probe length for LFPs with
remote amplier.
8.4.9 Evaluating signal quality
Parameters describe the quality of the measuring signal.
b Log in to expert mode, see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
SigQa1
Characteristic for the robustness of the EXPRT-Pulse-TrsHld setting.
Not active in foam mode. The displayed value is only valid if the sensor displays the
correct level value.
• Value range: 0% ... 100%
• Good signal: > 40% (a high pulse reserve is provided with the current
b Measures: Reduce EXPRT-Pulse-TrsHld to increase SigQa1.
Note:
• Changing TrsHld will have an impact on SigQa2 and SigQa3.
• If a satisfactory SigQa1 value cannot be achieved by adjusting TrsHld in conjunction
with the SigQa values, the installation condition must be checked. Using a coaxial
tube improves signal detection, particularly in media with low DK values (e.g. oil).
TrsHld setting.)
40
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 41

SigQa2
SigQa3
8OPERATION
Characteristic for the robustness of echo pulse detection in relation to interference
pulses.
Not active in foam mode. The displayed value is only valid if the sensor displays the
correct level value.
• Value range: 0% ... 100%
• Good signal: > 50%
b Measures: Run AutCal; check installation conditions; remove deposits from probe
and process connection.
Characteristic for signal noise and electromagnetic interference.
• Value range: 0% ... 100%
• Good signal: > 75%
• Poor signal: < 50%
Not active in foam mode. The displayed value is only valid if the sensor displays the
correct level value.
• Value range: 0% ... 100%
b Measures:
• Increase EXPRT-Cong-TrsHld
• EXPRT-Cong-MeasMd = HiAcc
• Improve ltering
• Switch on lter
• Reduce EXPRT-Cong-MaxCol
8.4.10 Changing the coaxial cable length
• Valid for versions with remote amplier.
• This setting makes it possible to congure the coaxial cable length between the
sensor head and process connection.
Conguration
Predened coaxial cable length (1,000 mm, 2,000 mm, or 3,300 mm)
1. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
2. Congure the coaxial cable length in the EXPRT-Cong-CblLen menu
(1,000 mm ... 3,300 mm).
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
41
Page 42

8 OPERATION
Note:
Only the following congurations are permitted:
Coaxial cable length [mm] Foam mode inactive Foam mode active
1,000 4,000 2,000
2,000 3,000 1,500
3,300 1,000 500
8.4.11 Activating the display lock
To prevent the sensor from being tampered with, password protection can be activated
for the display.
When the protection is active, the expert password (000537) must be entered before
the menu can be accessed.
The menu is only unlocked once the correct password is entered.
Max. probe length [mm]
Conguration
1. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
2. The protection can be (de)activated via the EXPRT-Cong-Lock menu.
Note:
• The user is logged out again after 5 minutes of inactivity.
• When the display is locked, only the congured measured value display (DspVal) can
be seen.
8.4.12 Selecting the display unit (millimeter/inch)
This setting makes it possible to display and congure all length measurements in
either millimeters or inches.
Conguration
1. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
2. Set the unit in the EXPRT-Cong-Unit menu (mm/inch).
42
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 43

8.4.13 Setting the oset
This setting makes it possible to indicate the level value on the display in relation to
the tank bottom instead of the end of the probe. The actual container level is then
indicated on the display.
Conguration
1. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
2. Set the oset in the EXPRT-Cong-Oset menu (0 mm … +3,000 mm).
8OPERATION
IA
L
O
M
IAE
Fig. 8: LFP Cubic
1 Level
2 QALOW/ QAHIGH
SPx/RPx
FHx/FI x
Can be set only in this zone
O: Oset
L: Probe length
M: Measurement length
IA: Inactive area at process connection
IAE: Inactive area at probe end
Subject to change without notice
Note:
If the oset parameter is changed, the SPx/RPx/FLx/FHx/QALOW/QAHIGH parameters
are automatically adjusted.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
43
Page 44

8 OPERATION
8.4.14 Resetting the calibration
Resetting AutCal
1. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
2. Reset AutCal in the EXPRT-Pulse-Reset menu.
Resetting CalEmp+CalMed
1. Log in to expert mode; see “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
2. Reset CalEmp+CalMed in the EXPRT-Foam-Reset menu.
44
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 45

9 Menu overview
RUN
1000 mm
9MENU OVERVIEW
3 s
Q1MENU
SP1
Value
Q2/3/4MENU
RP1
OU1
SimQ1
1)
SP2/3/4
RP2/3/4
FH2/3/4
FL2/3/4
OU2/3/4
TYP2/3/4
SimQ2/3/4
Value
Para
Para
Value
Value
Value
Value
Para
Para
Para
QAMENU
QAHIGH
QALOW
QAPOL
QATYP
QAFAIL
SimCur
SimVol
Value
Value
Para
Para
Para
2)
Para
2)
Para
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
45
Page 46

QAMENU
2)
2)
Para
TYP2/3/4
SimQ2/3/4
Para
Para
QAHIGH
QALOW
QAPOL
QATYP
Value
Value
Para
Para
QAFAIL
SimCur
SimVol
Para
Para
9 MENU OVERVIEW
DspVal
Filter
SimLev
Para
Para
Para
RstFac
EXPRT
OK? CALL..
3)
Conf ig
Lock Para
Unit Para
Offset Value
Mode Para
Pulse
MeasMd
Para
MaxCol Value
AutCal OK? Cal.OK
TrsHld Value
AutoTu OK?
Cal.OK
CalRng Value
MaskZn Value
MaskTr Value
Reset OK?
Cal.OK
46
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 47

MeasMd
Para
MaxCol Value
Mode Para
TrsHld Value
MaskZn Value
MaskTr Value
Pulse
AutCal OK? Cal.OK
AutoTu OK?
CalRng Value
Cal.OK
Reset OK?
Cal.OK
9MENU OVERVIEW
Foam
Probe
Info
CalEmp OK? Cal.OK
CalMed OK?
Limit
Reset
Length Value
CblLen Value
Type Para
FrmVer Value
SerNo Value
CalSta Value
Value
OK?
Cal.OK
Cal.OK
AppTag Value
DevTag Value
PASSW
SigQua
Value
SigQa1 Value
SigQa2 Value
SigQa3 Value
1) Visible elements depend on the OUx parameter selection
2) Visible elements depend on the QATYP parameter selection.
3) Password-protected measuring range.
Q3 and Q4 are only available for an LFP with four switching outputs.
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
47
Page 48

10 OVERVIEW OF PARAMETERS
10 Overview of parameters
Parameter Description
Q1MENU, Q2MENU,
Q3MENU, Q4MENU
SPx Switching point, switching output 1 or 2 or 3 or 4
RPx Reset switching point, switching output 1 or 2 or 3 or 4.
FHx
FLx
OUx Switching output switching function.
SimQx See “8.4.6 Testing the conguration”.
TYP2/3/4 • Qx-PNP = Switching output in PNP circuit
QAMENU See “8.3 Congure the analog output”.
QAHIGH Input of the lling level in mm for 20 mA/10 V signal
QALOW Input of the lling level in mm for 4 mA/0 V signal.
QAPOL The analog output signal can be inverted.
See “8.2 Conguring the switching outputs”.
(SPx > RPx).
Note: Not displayed if the switching output in the
OUx menu is set to Error or Window.
Note: Not displayed if the switching output in the
OU2/3/4 menu is set to error or window.
• Upper threshold (high) window function, switching
output 2/3/4 (FHx > FLx)
• Lower threshold (low) window function, switching
output 2/3/4
Note: Not displayed if the switching output in the
OU2/3/4 menu is set to error or hysteresis.
• Qx-Hno = Hysteresis function, normally open
• Qx-Hnc = Hysteresis function, normally closed
• Qx-Fno = Window function, normally open (function only
available for Q2/3/4)
• Qx-Fnc = Window function, normally closed (function
only available for Q2/3/4)
• Qx-Eno = Error signal, normally open (function only
available for Q2/3/4)
• Qx-Enc = Error signal, normally closed (function only
available for Q2/3/4)
If Qx is used as an error signal, SPx/FHx and RPx/FLx are
hidden in the menu.
• Qx-NPN = Switching output in NPN circuit
• Qx-Drv = Switching output executed in push/pull function
(QAHIGH > QALOW).
• QA-Nrm = Analog output signal as congured
• QA-Inv = Analog output signal is inverted:
QAHigh 4 mA/0 V and QALow 20 mA/10 V
48
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 49

Parameter Description
QATYP Setting for the output signal.
• 4 mA ... 20 mA
• 0 V ... +10 V
• Auto V = Qa operated with voltage output of 0 V … +10 V
• Auto A = Qa operated with current output of
4 mA … 20 mA
• Auto? = Automated signal detection based on
the existing load resistance
During a menu query, either 4 mA ... 20 mA or
0 V ... +10 V is displayed.
QAFAIL Output behavior as per NE43 in the event of a fault (func-
tion only available when current output has been selected
under QATYP).
• 3.5 mA = Analog current output is set to 3.5 mA in the
event of a fault.
• 21.5 mA = Analog current output is set to 21.5 mA in
the event of a fault.
SimCur See “8.4.6 Testing the conguration”.
SimVol See “8.4.6 Testing the conguration”.
DspVal Setting the display.
• Distan = The display shows the distance in mm in
relation to the end of the probe.
• QaPerc = The display shows the ll level in % in relation
to the QA analog output with the corresponding QAHIGH
and QALOW thresholds.
• QaBarG = The display shows a bar graph in relation to
the QA analog output with the corresponding QAHIGH
and QALOW thresholds.
• QaSign = The display shows the current QA output value
in mA or V.
• QxSign = The display shows the output states.
Filter See “8.4.2 Filtering measured values”.
SimLev See “8.4.6 Testing the conguration”.
RstFac Resetting the set parameters to the factory settings.
EXPRT See “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
Lock See “8.4.11 Activating the display lock”.
Unit See “8.4.12 Selecting the display unit (millimeter/inch)”.
Oset See “8.4.13 Setting the oset”.
Mode See “8.4.5 Selection of evaluation method”.
MaxCol See “8.4.2 Filtering measured values”.
MeasMd Measuring mode.
• HiSpd: max. length = 2,005 mm,
response time < 400 ms
• HiAcc: max. length = 6,005 mm,
response time < 2,800 ms,
(more stable measured values, recommended for
liquids with low DKs and where TrsHld is < 70)
• mode-1: not supported; deactivates current AutCal/
foam calibration
10OVERVIEW OF PARAMETERS
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
49
Page 50

10 OVERVIEW OF PARAMETERS
Parameter Description
Pulse See “8.4.5 Selection of evaluation method”.
AutCal See “7 Commissioning”.
TrsHld This value describes a factor which determines how strong
AutoTn See “8.4.3 Automated adjustment of the interference
CalRng Calibration range.
an echo has to be in order to be recognized by the device.
The value range lies between 20% and 500%. The default
is 100% in this case. Only shown if password entered.
• 20% = high sensitivity
• 100% = standard
• 500% = low sensitivity
signal limit”.
• Value range: 95 mm … 6005 mm
Range starting from the process connection in which
static interference signals (coupling sections, welds, spray
balls, etc.) are hidden during the AutCal process. During
the AutCal process, there must not be any medium in the
dened area of +200 mm.
See “8.4.8 Teaching in static interference signals”.
MaskZn See “8.4.4 Blanking the interference signals in the
masked zone”.
MaskTr See “8.4.4 Blanking the interference signals in the
masked zone”.
Reset Resets the value for AutCal.
Foam See “7.3 Foam commissioning (with factory settings)”.
CalEmp See “7.3 Foam commissioning (with factory settings)”.
CalMed See “7.3 Foam commissioning (with factory settings)”.
Limit Limit between foam and uid.
• Range: 20 to 100%
• Factory setting: 90%
• Medium surface: 90%
• Foam surface: < 90%
When measuring the foam surface, it may be necessary to
reduce the limit. If the sensor displays a limit value that is
too low, it is necessary to reduce the limit.
Reset Resets the values for CalEmp and CalMed.
Probe Special settings.
Length • See “7.3 Foam commissioning (with factory settings)”
(LFP Cubic).
CblLen See “8.4.10 Changing the coaxial cable length”.
Type Choosing between rod and rope.
Info Sensor information.
FrmVer Shows the rmware version.
SerNo Shows the serial number.
CalSta Displays the status of the tank calibration.
• Pulse = AutCal (calibrated), NoCal (not calibrated)
• Foam = FomCal (calibrated), CalMis (not calibrated)
AppTag Measuring point name, can only be described via IO-Link.
50
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 51

Parameter Description
Dev Tag Device name, can only be written over IO-Link.
SigQua Parameter describes the quality of the measurement
signal.
SigQa1 See “8.4.9 Evaluating signal quality”.
SigQa2 See “8.4.9 Evaluating signal quality”.
SigQa3 See “8.4.9 Evaluating signal quality”.
PAS SW See “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
10OVERVIEW OF PARAMETERS
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
51
Page 52

11 TROUBLESHOOTING
11 Troubleshooting
11.1 Error message on the display
Error Cause Possible solution
!InvEc &
level present
!InvEc &
empty tank
AutCal not executed; interference superimposes
medium reection.
TrsHld setting is not suitable for the medium. Perform advanced commissioning
Probe length congured incorrectly. Check probe length and compare against
Probe not available. Check the probe.
Perform commissioning
(See “7.1 Quick commissioning (with factory
settings)”).
(See “7.2 Advanced commissioning”).
conguration in EXPRT-Cong-LENGTH.
!ATTNT A parameter was written outside of the valid value
range and therefore adjusted
Another parameter was automatically adjusted
due to a dependency (SPx, RPx).
!WRONG Incorrect password entered. Enter the correct password.
!NoCal Information: The AutCal process and/or foam
calibration was rejected because the probe length,
teach-in depth or measuring mode was changed.
!Denid AutCal was called up in Foam sensor mode. AutCal is available only in Pulse mode. Perform
CalPIs No valid calibrations for CalEmp and CalMed. Perform foam calibration.
!CalOk The teach-in process was successful.
!NoSig AutCal failed. Repeat commissioning.
!faild Foam-CalEmp or FoamCalMed menu item failed. Follow the foam commissioning instructions.
!SC-Q1
!SC-Q2
!SC-Q3
!SC-Q4
!SC-Qa
!IOLOf Supply voltage too low for IO-Link communication. Increase the supply voltage to achieve the desired
!QaO Supply voltage too low for analog output. Increase the supply voltage to achieve the desired
!QxO Supply voltage too low for switching outputs. Increase the supply voltage to achieve the desired
!QaOvf The ohmic load at the analog current output Qa is
!MaskZ Interference/pulse exceeds value for MaskTr. Increase MaskTr or identify and eliminate
!Range The maximum allowable measuring range was
!Cable The coaxial cable is damaged/defective. Replace the coaxial cable.
Short-circuit at the output. Remove short-circuit.
Load resistance at the output is too low. Increase the load resistance.
too high.
The analog current output Qa is not wired. Connect the load to Qa.
exceeded. Measurement in this conguration is
not possible.
The coaxial cable length was congured incorrectly. See “8.4.10 Changing the coaxial cable length”.
Rewrite the value in the valid range.
Check the parameter again.
Perform commissioning again if necessary.
foam calibration in Foam mode.
functionality.
functionality.
functionality.
Reduce the load at Qa.
interference.
Reduce the probe length and/or coaxial cable
length; see “8.4.10 Changing the coaxial cable
length”.
The display only
shows RUN. It is
otherwise empty.
52
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
The DspVal menu parameter is at QaBarG and the
level is below QALOW.
Change QALOW or DspVal.
Subject to change without notice
Page 53

Error Cause Possible solution
Display o Temperature is too high. Reduce the temperature.
Temperature is too low. Increase the temperature.
No supply voltage. Connect the sensor correctly.
!Err[xx]
System error. The device is defective and must be replaced.
!ErM[xx]
!ErI[xx]
!ErO[xx]
NVFail Memory error. The device is defective and must be replaced.
11.2 Operating the display
Error Cause Possible solution
The menu item SPx/
RPx is not displayed.
The menu item FHx/
FLx is not displayed.
QAFAIL Is not
displayed.
SimVol is not
displayed.
SimCur is not
displayed.
EXPRT-Cong-… is
not displayed.
EXPRT-Foam-… is
not displayed.
Lengths are
expressed as
decimal numbers.
The menu only
shows PASSW.
QxMENU/OUx is not
congured to Qx-Hno and/or Qx-Hnc.
QxMENU/OUx is not
congured to Qx-Fno and/or Qx-Fnc.
The analog output Qa is in voltage mode
(QATYP = 0 to 10 V).
The analog output Qa is in current mode
(QATYP = 4 to 20 mA).
The analog output Qa is in voltage mode
(QATYP = 0 to 10 V).
Congure Qx (see “8.2 Conguring the switching
outputs”).
Congure Qx (see “8.2 Conguring the switching
outputs”).
Congure Qa (see “8.3 Congure the analog
output”).
Congure Qa (see “8.3 Congure the analog
output”).
Congure Qa (see “8.3 Congure the analog
output”).
Correct password not entered. See “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
Correct password not entered. See “8.4.1 Expert mode”.
Inch is activated as the display unit. Congure the unit (see“8.4.12 Selecting the
display unit (millimeter/inch)”).
The display lock is activated. See “8.4.11 Activating the display lock”.
11TROUBLESHOOTING
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
53
Page 54

11 TROUBLESHOOTING
11.3 Outputs
Error Cause Possible solution
Switching output
does not behave as
expected
Analog output does
not behave as
expected
Conguration incorrect. Perform conguration of the switching output
(See “8.2 Conguring the switching outputs”).
An error is pending; the sensor outputs are in
a safe state.
Cable break. Check the cable.
Conguration incorrect. Congure the analog output
An error is pending; the sensor outputs are in
a safe state.
Cable break. Check the cable.
Remove the cause of the error.
(See “8.3 Congure the analog output”).
Remove the cause of the error.
11.4 Error behavior
Error Cause Possible solution
After installation, the sensor indicates
a high level although the tank is empty.
When used with a coaxial tube,
the sensor indicates a high level although the tank is empty.
Level value uctuates on the display. Medium surface unsettled. Activate ltering (see “7.1 Quick com-
The displayed level value/SPx/RPx/FHx/
FLx/QALOW/QAHIGH is greater than the
probe length.
Level occasionally jumps to a higher
value.
Level occasionally jumps to 0 mm. TrsHld set too high. Perform advanced commissioning
No measurement of low levels for media
with low DKs.
Increased measurement inaccuracy. Use of foam algorithm.
AutCal not performed. Perform commissioning
(see “7 Commissioning”).
AutCal not performed. Perform commissioning
(see “7 Commissioning”).
missioning (with factory settings)”).
An oset was congured for the level
value.
Incorrect probe length congured. Adjust the probe length
Contamination in the vicinity of the
process connection.
Spray ball or supply system wets the
probe with medium above the medium
surface.
Change in the ambient conditions
regarding the situation during the AutCal
process.
Signicant buildup of foam. Perform foam commissioning
TrsHld set too low, the echo algorithm
detects interference reections.
Signicant buildup of foam. Perform foam commissioning.
Increased inactive range at the probe
end for media with a low DK.
Adjust the oset
(see “8.4.13 Setting the oset”).
(see “8.4.7 Conguring the probe
length”).
Cleaning.
Observe the installation conditions
Congure the MaxCoL plausibility lter
(see “8.4.2 Filtering measured values”).
Perform commissioning again
(See “7 Commissioning”).
(See “7.3 Foam commissioning (with
factory settings)”).
Increase TrsHld.
(See “7 Commissioning”).
54
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 55

12 Repair work
12.1 Maintenance
The LFP is maintenance-free. We recommend doing the following regularly:
b Checking the probe for contamination.
b Checking the screw connections and plug connections
12.2 Returns
Rinse o and/or clean removed devices before returning them in order to protect
our employees and the environment from dangers posed by residue from measured
materials. Faulty devices can only be examined when accompanied by a completed
return form. A declaration of this type includes information about all materials which
have come into contact with the device, including those which were used for testing purposes, operation, or cleaning. The return form is available on our website
(www.sick.com).
12REPAIR WORK
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
55
Page 56

13 DISPOSAL
13 Disposal
Dispose of device components and packaging materials in compliance with applicable
country-specic waste treatment and disposal regulations of the region of use.
56
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 57

14 Technical data
14.1 Features
Medium Liquids
Detection type Limit, continuous
Probe length
Adjustable measuring range 95 mm … 6,005 mm
Process pressure –1 bar … +10 bar
Process temperature –20 °C … +100 °C
GOST certicate
RoHS certicate
IO-Link
UL certicate
14.2 Performance
Accuracy
Reproducibility
Resolution
Response time
Dielectric constant
Conductivity
Maximum level change
Inactive area at end of probe
14TECHNICAL DATA
Mono-rod probe
Cable probe
1)
1)
2)
3)
1)
200 mm … 2,000 mm
1,000 mm, 2,000 mm, 3,000 mm, 4,000 mm
± 5 mm
≤ 2 mm
< 2 mm
< 400 ms
≥ 5 for mono-rod probe/rope probe
≥ 1.8 with coaxial tube
No limitation
500 mm/s
10 mm
1)
With water under reference conditions, see “14.7 Measurement accuracy”.
2)
Depends on measuring mode (high-speed < 400 ms, high accuracy < 2,800 ms)
3)
Depends on configuration (MaxCol - maximum change of level)
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
57
Page 58

14 TECHNICAL DATA
14.3 Mechanics/materials
Materials in contact with media: 1.4404, PTFE
Process connection G 3/4 A,
Housing material Plastic PBT
Max. probe load ≤ 6 Nm
Enclosure rating IP67: EN 60529
Weight Max. 1.3 kg
Coaxial cable insulation PVC
14.4 Reference conditions
3/4'' NPT
Container with diameter
Minimum distance to built-in components
Distance from end of probe to tank bottom
Air humidity
Temperature
Pressure
Medium Water, DK = 80
Centered installation of sensor
Container parameterization carried out
14.5 Ambient conditions
Ambient temperature, operation
Ambient temperature, warehouse –40 °C ... +80 °C
1)
According to UL listing: degree of contamination 3 (UL61010-1: 2012-05); air humidity: 80%
at temperatures up to 31 °C; installation height: max. 3,000 m above sea level; only for indoor
applications
m
1
>
300 mm
> 15 mm
65% ±
20%
+20 °C ±
1,013
5 °C
mbar abs. ± 20 mbar
1)
–20 °C … +60 °C
58
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 59

14.6 Electrical connection values
Supply voltage. 12 V DC ... 30 V DC
Current consumption ≤ 100 mA at 24 V without output load
Initialization time ≤ 5 s
Protection class III
Connection type M12 x 1, 5-pin
hysteresis Min. 3 mm, freely congurable
Output signal
Signal voltage HIGH Uv –2 V
Signal voltage LOW ≤ 2 V
Output current < 100 mA
Inductive load < 1 H
Capacitive load 100 nF
Temperature drift < 0.1 mm/K
Output load 4 mA ... 20 mA < 500 ohms at Uv > 15 V
Lower signal level 3.8 mA ... 4 mA
Upper signal level 20 mA ... 20.5 mA
EMC EN 61326-2-3, 2014/30/EU
1)
M12 x 1, 8-pin
4 mA ... 20 mA / 0 V ... +10 V automatically
switchable depending on output load1)
1 PNP transistor output (Q1) and 1 PNP/NPN
transistor output (Q2) switchable, or 1 PNP
transistor output (Q1) and 3 PNP/ NPN transistor
outputs (Q2 to Q4) switchable (type-dependent)
4 mA ... 20 mA < 350 ohms at Uv > 2 V
0 V ... +10 V > 750 ohms at Uv ≥ 14 V
14TECHNICAL DATA
1)
1)
All connections are reverse polarity protected. All outputs are overload and short-circuit protected.
2)
Use an energy-limited circuit for the voltage supply as per UL61010-1 3rd Ed., Section 9.3
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
59
Page 60

14 TECHNICAL DATA
L
L
0
L-180
10
L-25 L-180
100
0
0
L
L
14.7 Measurement accuracy
14.7.1 Measurement accuracy with parameterized container
25
5
0
-5
-25
25
5
0
-5
-25
1 Accuracy in mm
2 Level in mm
L-25
0
60
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 61

14.7.2 Measurement accuracy without parameterized container
L
L
0
0
L-180L-40
10
L-180
100
0
0
L
L
50
20
5
0
-5
-20
-50
14TECHNICAL DATA
50
5
0
-5
-50
1 Accuracy in mm
2 Level in mm
3 Inactive area
L-40
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
61
Page 62

15 DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS
50
IAE
15 Dimensional drawings
15.7.1 LFP Cubic with rod probe
(1.97)
104
(4.09)
126
(4.96)
G 3/4 A
3/4" NPT
L
20 (0.79)
32
(1.26)
15
22
(0.87)
L
5
(0.20)
36 (1.42)
IA
M
IAE
71
(2.80)
G 3/4 A
3/4" NPT
7 (0.28)
Mono-probe with coaxial tube
M Measuring range
L Probe length
IA Inactive area at process connection 25 mm
IAE Inactive area at probe end 10 mm
22
IA
M
33
(0.87)
(1.30)
43
(1.69)
M
12
x1
62
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 63

15.7.2 LFP Cubic with cable probe
IAE
104
(4.09)
36 (1.42)
22
(0.87)
5
(0.20)
3 (0.11)
3
IA
G 3/4 A
3/4" NPT
71
(2.80)
33
(1.30)
50
(1.97)
M12x1
43
15DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS
(1.69)
L
100
(3.93)
24
M
12
(0.47)
M Measuring range
L Probe length
IA Inactive area at process connection 25 mm
IAE Inactive area at probe end 10 mm
M6
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
63
Page 64

15 DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS
40
(1.57)
6,5 (0.26)
14
(0.55)
83
(3.27)
121
(4.76)
36 (1.42)
120
(4.72)
min. R50
22
(0.87)
L
7 (0.28)
G 3/4 A
3/4" NPT
IAE
IA
M
45
(1.77)
5
(0.20)
36
(1.42)
70 (2.76)
73
M12x1
43 (1.69)
33
(1.30)
50
C
5 (0.20)
40
(1.57)
LFP Cubic with remote amplier
C Length of cable
M Measuring range
L Probe length
IA Inactive area at process connection 20 mm/40 mm
IAE Inactive area at probe end 10 mm
64
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 65

16 Factory setting
Parameter Factory setting
SP1 80% of the probe length measured from the end of the probe
RP1 5 mm below SP1
OU1 Q1_Hno
SP2
RP2 5 mm below SP2
OU2 Q2_Hno
TYP2 Q2_PNP
SP3 40% of probe length measured from end of probe
RP3 5 mm below SP3
OU3 Q3_Hno
SP4 20% of the probe length measured from the end of the probe
RP4 5 mm below SP4
OU4 Q4_Hno
TYP3 Q3_PNP
TYP4 Q4_PNP
QAHigh 50 mm below start of probe
QALOW 10 mm above end of probe
QAPOL QA_Nrm
QATYP Auto
QAFAIL 3.5 mA
SimCur SimO
SimVol SimO
DspVal Distan
Filter O
SimLev SimO
TrsHld 100
MaskZn 0 mm
MaskTr 50%
Mode Pulse
CalSta noCal
Probe/Type Depending on probe type: Rod/Rope
MaxCol Depending on measuring mode: HiSped = AnySped, HiAcc = 10 cm/s
MeasMd HiSpd
CalRng 6,005 mm
FomSta Inactive
Limit 90
Oset 0 mm
Unit mm
Lock Inactive
16FACTORY SETTING
For 5-pin versions: 20% of the probe length measured from the end of the probe
For 8-pin versions: 60% of the probe length measured from the end of the probe
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
65
Page 66

17 ACCESSORIES
17 Accessories
b Accessories can be found online at www.sick.com
66
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 67

18 Media list
This list of media provides a guide to the DK values of liquids. Water-based liquids always have a DK value > 5,
which makes it easy to use the LFP. For DK values < 5, a coaxial tube or a metallic immersion tube/bypass is
always required.
18MEDIA LIST
Substance DK
value
Acetal (25 °C) 3.8
Acetaldehyde 15
Acetamide (77 °C) 59.2
Acetoacetic acid ethyl ester 15
Acetone 21.5
Acetophenone 18
Acetylacetone 23
Acetyl bromide 16.2
Acetyl chloride 15.9
Acetylene dibromide 7.2
Acetylene tetrabromide 5.6
Aconite acid ester 6.3
Adipic acid 1.8
Aerosile 1
Substance DK
value
Amyl amine 4.5
Aniline 7
Anisaldehyde 22.3
Anisole 4.5
Anthracite 3.2
Antimony hydride 1.8
Malic acid diethylester 10
Argon 1.5
Arsine 2.1
Arsole 2.3
Asbestos 10
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) 2.1
Azelaic acid diethylester 5
Azoxybenzene (36 °C) 5.2
Substance DK
value
Hydrogen cyanide 158
Bore oil emulsion 25
Bornylacetate 4.6
Bromine 3.1
Butanoic acid 3
Camphene 2.3
Caproic acid (71 °C) 2.6
Caprylic acid 2.5
Carbazole 1.3
Carbonylcyanide 10.7
Cellite 1.6
Cetyl alcohol (60 °C) 3.6
Quinoline 8.8
Chlorine, liquid 2.1
Activated carbon 12
Alums (60 °C) 4.2
Allyl alcohol 20.6
Allyl chloride 8.2
Allyl iodide 6.1
Aluminum bromide (100 °C) 3.4
Aluminum foil 10.8
Aluminum hydroxide 2.5
Aluminum splinters 7.3
Aluminum sulfate 2.6
Formic acid 57.9
Ammonia 15
Ammonia solution (25%) 31.6
Ammonia salt 4.3
Pentanol 14.8
Basalt 2.5
Cotton ber our 3.2
Bauxite 2.5
Bentonite 8.1
Benzal chloride 6.9
Benzaldehyde 17.6
Benzil (80 °C) 10
Benzine 2
Benzene 2.3
Benzene, heavy 3.2
Benzyl alcohol 13.5
Benzyl amine 4.6
Benzyl chloride 7
Beer brew 25
Bitumen 2.8
Chloral 6.7
Chlorobenzine 5.7
Chloracetic acid 33.4
Chlorohydrin 31
Chlorinated lime 2.3
Chloroform (trichlormethane) 4.8
Cola essence 17.3
Cream (skin) 19
Cuminaldehyde 10.7
Cyanogen 2.5
Decalin 2.1
Degalan 3.1
Desmodur 10
Diacetone alcohol 18.2
Diamylether 3
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
67
Page 68

18 MEDIA LIST
Substance DK
value
Dibenzofuran (100 °C) 3
Dibenzyl (60 °C) 2.5
Diesel fuel 2.1
Diethylamine 3.8
Dimethylether (methyl ether) 5
Diofan 32
Dioxane 2
Diphenyl (75 °C) 2.5
Printing ink 4.6
Ice cream (–20 °C) 16.5
Iron (III) oxide red 1.9
Emulphor 4
Epichlorhydrin 23
Peanuts, dried 3.1
Substance DK
value
Ferrous sulfate (80 °C) 32.4
Ferrozell 18.3
Fat coal 3.4
Fatty acid (35 °C) 1.7
Fish oil 2.6
Flax pellets 1.4
Meat and bone meal 1.9
Tankage 1.9
Fly ash 3.3
Fluorine 1.5
Fluorbenzene 6.4
Hydrogen uoride (0 °C) 83.6
Calcium uoride 2.5
Formamide 109
Substance DK
value
Urea 2.9
Resin 1.5
Hazelnuts 2
Hot glue (150 °C) 2.3
Heating oil 2.1
Helium 1.1
Heptane 1.9
Heptanal 9.1
Heptanoic acid (71 °C) 2.6
Heptene 2.1
Hexane 1.9
Hexene 2.1
Hexanol 12.5
Hibiscus 2.8
Peanut expeller 2.4
Vinegar 24
Acetic acid 6.2
Cement asbestos 3.2
Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) 16.2
Ether 4
Ethyl acetate 6
Ethylamine 6.9
Ethyl benzoate 6
Ethyl benzene 2.4
Ethylene chlorohydrin 25
Ethylene chloride 10.6
Ethylenediamine 15
Ethylene oxide (–1 °C) 13.9
Ethyl mercaptan 6.9
Furan 3
Furfurol 41.7
Animal feed grist 2.4
Germanium tetrachloride 2.4
Grain grist 3
Gypsum 1.8
Fiber glass powder 1.1
Glass granulate 4
Cullet 2
Glucose (50 °C) 30
Glycerol 13.2
Glycerol water 37
Glycol 37
Glysantin 25
Granuform 4
Wood chips 2.3
Charcoal 1.3
Wood swarf 1.5
Splints 1.1
Honey 24
Hydrazine 58
Imidazole, pure (100 °C) 23
Isoamyl acetate 4.8
Isoamyl alcohol 15.6
Isoamyl bromide 6
Isoamyl chloride 6.1
Isoamyl ether 2.8
Isoamyl iodide 5.6
Isobutanoic acid 2.6
Isobutyl alcohol 18.1
Fenchone 12.8
Ferrite pellets 21
Ferrosilicone 10
68
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Guaiacol 11
Guano (phosphate rock) 2.5
Oat 4.9
Isobutyl amine 4.4
Isobutyl benzene 2.3
Isobutyl bromide 7.2
Subject to change without notice
Page 69

18MEDIA LIST
Substance DK
value
Isobutyl chloride 6.5
Isobutyl cyanide 18
Isobutyl iodide 6.5
Isobutyl nitrate 11.7
Isobutyl silane 2.5
Isoquinoline 10.7
Isocyanate 6.1
Isoprene 2.1
Isopropanol 18
Isosafrol 3.3
Iodine 11.1
Iodobenzene 4.6
Methyl iodide 7.1
Hydrogen iodide 2.9
Substance DK
value
Coke 3
Cork powder 1.7
Concentrated feed 3.2
Chalk 2.1
Cresol 11
Cresol resin 18.3
Crystal sugar 2
Fertilizer 4.3
Plastic pellets 1.2
Copper ore 5.6
Nitrous oxide 1.5
Lanolin 4.2
Latex 24
Lauric acid ethyl ester 3.4
Substance DK
value
Methylene bromide 7
Methylene chloride 9
Methylene chloride 9.1
Methylene iodide 5.3
Methyl nitrate 23.5
Methyl cellulose 3
Monochloremethane 9.8
Morpholine 7.3
Naphthenic acid 2.6
Naphthalene 2.5
Sodium carbonate 3
Sodium methylate 1.5
Sodium perborate 2.2
Sodium peroxide 2.7
Coee beans 1.5
Cocoa beans 1.8
Caustic potash 3.3
Potash salt 2
Lime 2
Potato starch 1.7
Ceramic compound 17
Ketchup 24
Gravel 2.6
Diatomaceous earth 1.4
Silicic acid 2
Bone fat 2.7
Bonemeal 1.7
Sodium chloride 23
Coal, 15% moisture 4
Diethyl carbonate 2.8
Coal dust 2.5
Coconut oil (rened) 2.9
Glue 2
Linoleic acid 2.7
Solvent 18
Skim milk powder 2.3
Corn 3.6
Corn grist 2.1
Corn starch syrup 18.4
Malt 2.7
Mandelic acid nitril 18
Small marble stones
2.5
(grain size of 2-)
Mice feed 2.3
Flour 2.5
Molasses 31.3
Menthol (42 °C) 4
Mesityl oxide 15
Metal powder 6
Methanol (methyl alcohol) 33
Methyl acetate 8
Sodium sulfate 2.7
Nitrobenzene 35
Nitroethane 29
Nitroglycol 28.3
Nitroglycerin 19.3
Nitro varnish 5.2
Nitromethane 39
Nitrophoska 5,4
Nitrosyl bromide (13 °C) 15.2
Nitrosyl chloride 19
Pasta, milled durum 1.9
Octane 2
Octene 2.1
Octyl bromide 5
Oil 2
Oileic acid 2.5
Water-in-oil emulsion 24.2
Oxalo ethyl acetate 6
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
69
Page 70

18 MEDIA LIST
Substance DK
value
Palmitic acid 2.3
Palm tree nuts 2.2
Palm tree nuts 2.8
Palm seed oil 1.8
Paper scraps 1.2
Paran 1.6
Paraldehyde 15.1
Pelargon 2.8
Penta borane 21
Penta ethyl chloride 3.8
Penta chlorotoluene 4.8
Pentane 1.8
Pentanal (15 °C) 11.8
Pentene 2
Perchlorate 3.6
Hexachlorobutadiene 2.6
Perlite 1.7
PET powder 1.5
Phenetole 4.2
Phenol 8
Phenol resin 7.4
Phosgene 4.3
Phosphate 4
Phosphorus, liquid 3.9
Phosphorus salt 4
Pinane 2.1
Piperidine 5.8
Polyamide pellets 1.7
Polyethylene 1.2
Polypropylene 1.6
Polyrol 2.8
Polyvinyl acetals 2.8
Substance DK
value
Popcorn 1.1
Pril (liquid detergent) 1.2
Propanal (15 °C) 14.4
Propanol (propyl alcohol) 2.2
Propanoic acid 3.2
Propylamine 3
Propylene, liquid 1.9
Propylene chloride 9
Propylether 3.3
PVC powder, pure 1.3
Pyridine 13.2
Pyrrol 8
Silica sand 2
Quartz stone meal 2.7
Mercury diethyl 2.1
Rapeseed 3.3
Rapeseed grist 2.1
Rice 3
Rye 6
Rye bran 2.2
Beetroot seeds 3.5
Beetroot cuttings 7.3
Carbon black 18.8
Saccharose solution 20
Sawdust 1.3
Nitric acid (98%) 19
Hydrochloric acid 5
Salt water 32
Oxygen 1.5
Chamotte 1.8
Foam akes 1.1
Lard (80 °C) 2.1
Substance DK
value
Soft soap 32
Chocolate powder 2
Black liquor 32
Sulfur 3.5
Sulfur dioxide
14
(sulfurous acid)
Carbon disulde, pure 2.6
Sulfuric acid 21.9
Sulfuric acid (15%) 31
Sulfuric acid (97%) 8.6
Sulfur trioxide 3.1
Hydrogen sulde 6
Heavy fuel oil 2.2
Soap akes 9.2
Soap pellets 3.5
Mustard 24
Mustard seeds 3.6
Silicone oil 2.7
Silicone rubber 2.9
Soy our 4.5
Soy grains 2.9
Sunower seeds 2
Cha 1.5
Stearic acid 2.3
Rock salt (0–25 mm) 4.3
Styrene 2.4
Tobacco dust 1.8
Talcum 1.5
Tea powder 2
Tar, raw 4
Terephthalic acid 1.5
White spirit 2
Terpinene 2.7
70
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918/ZJA6 / 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
Page 71

18MEDIA LIST
Substance DK
value
Terpinolene 2.3
Tetrachloroethylene 2.5
Carbon tetrachloride 2.3
Thomaskali dust 3.4
Thujone (0 °C) 10.8
Meat and bone meal 2.2
Titan tetrachloride 2.8
Toluene 2.4
Clay 2.3
Transformer oil 2.1
Trichloroethylene 3.2
Triethyl aluminum 2.9
Triptan 1.9
Dry yeast 2
Substance DK
value
Xylitol 40
Xylene 2.3
Toothpaste 18.3
Cellulose 1.2
Cement 2.2
Zinc oxide 1.5
Zinc powder 4.4
Sugar 1.8
Tinder 12
Ultrasil 1.4
Undecan 2
Valeric acid 2.7
Viscose 34.5
Wax 1.8
Benzine 2
Water 80.3
Water (360 °C) 10
Water, demineralized 29.3
Water, heavy 78.3
Sodium silicate 16
Hydrogen 1.2
Hydrogen peroxide,
84.2
pure (0 °C)
Wine 25
Tartaric acid 35.9
Wheat 4
Wheat starch 2.5
Subject to change without notice
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS | LFP CUBIC 8019918 /ZJA6/ 2017-07-20 | SICK AG
71
Page 72

8019918/ZJA6 /2017-07-20 ∙ COMAT/ITL (2016-05) ∙ A4 4c int47
Australia
Phone +61 3 9457 0600
1800 334 802 – tollfree
E-Mail sales@sick.com.au
Austria
Phone +43 22 36 62 28 8-0
E-Mail office@sick.at
Belgium/Luxembourg
Phone +32 2 466 55 66
E-Mail info@sick.be
Brazil
Phone +55 11 3215-4900
E-Mail marketing@sick.com.br
Canada
Phone +1 905 771 14 44
E-Mail information@sick.com
Czech Republic
Phone +420 2 57 91 18 50
E-Mail sick@sick.cz
Chile
Phone +56 2 2274 7430
E-Mail info@schadler.com
China
Phone +86 20 2882 3600
E-Mail info.china@sick.net.cn
Denmark
Phone +45 45 82 64 00
E-Mail sick@sick.dk
Finland
Phone +358-9-2515 800
E-Mail sick@sick.fi
France
Phone +33 1 64 62 35 00
E-Mail info@sick.fr
Germany
Phone +49 211 5301-301
E-Mail info@sick.de
Hong Kong
Phone +852 2153 6300
E-Mail ghk@sick.com.hk
Hungary
Phone +36 1 371 2680
E-Mail office@sick.hu
India
Phone +91 22 6119 8900
E-Mail info@sick-india.com
Israel
Phone +972 4 6881000
E-Mail info@sick-sensors.com
Italy
Phone +39 02 274341
E-Mail info@sick.it
Japan
Phone +81 3 5309 2112
E-Mail support@sick.jp
Malaysia
Phone +6 03 8080 7425
E-Mail enquiry.my@sick.com
Mexico
Phone +52 (472) 748 9451
E-Mail mario.garcia@sick.com
Netherlands
Phone +31 30 2044 000
E-Mail info@sick.nl
New Zealand
Phone +64 9 415 0459
0800 222 278 – tollfree
E-Mail sales@sick.co.nz
Norway
Phone +47 67 81 50 00
E-Mail sick@sick.no
Poland
Phone +48 22 539 41 00
E-Mail info@sick.pl
Romania
Phone +40 356 171 120
E-Mail office@sick.ro
Russia
Phone +7 495 775 05 30
E-Mail info@sick.ru
Singapore
Phone +65 6744 3732
E-Mail sales.gsg@sick.com
Slovakia
Phone +421 482 901201
E-Mail mail@sick-sk.sk
Slovenia
Phone +386 591 788 49
E-Mail office@sick.si
South Africa
Phone +27 11 472 3733
E-Mail info@sickautomation.co.za
South Korea
Phone +82 2 786 6321
E-Mail info@sickkorea.net
Spain
Phone +34 93 480 31 00
E-Mail info@sick.es
Sweden
Phone +46 10 110 10 00
E-Mail info@sick.se
Switzerland
Phone +41 41 619 29 39
E-Mail contact@sick.ch
Taiwan
Phone +886 2 2375-6288
E-Mail sales@sick.com.tw
Thailand
Phone +66 2645 0009
E-Mail Ronnie.Lim@sick.com
Turkey
Phone +90 216 528 50 00
E-Mail info@sick.com.tr
United Arab Emirates
Phone +971 4 88 65 878
E-Mail info@sick.ae
United Kingdom
Phone +44 1727 831121
E-Mail info@sick.co.uk
USA
Phone +1 800 325 7425
E-Mail info@sick.com
Vietnam
Phone +84 945452999
E-Mail Ngo.Duy.Linh@sick.com
Further locations at www.sick.com
SICK AG | Waldkirch | Germany | www.sick.com
 Loading...
Loading...