Page 1

GM32
In-situ Gas Analyzer
Measuring Probe Version
Installation
Start-up
Maintenance
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Page 2

Document Information
Glossary
Described Product
Product name: GM32
Variants: GM32 Probe (measuring probe)
Document Identification
Title: Operating Instructions GM32
Part No.: 8012707
Version: 1.3
Release: 2009-03
Publisher
SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Nimburger Str. 11 · D-79276 Reute · Germany
Phone: +49 7641 469-0
Fax: +49 7641 469-11 49
E-Mail: info.pa@sick.de
Guarantee Information
Specified product characteristics and technical data do not serve
as guarantee declarations.
© SICK MAIHAK GmbH. All rights reserved.
CAN-Bus: Control Area Network. A field bus.
CompactFlash®-Disc: Memory card.
CUSUM board: Quality control chart (Data Sheet).
Ethernet: Computer networking technology. Basis for network pro-
tocols, e.g. TCP/IP.
Check point: Test point at approx. 70% of the upper measuring
range value.
Check cycle: Test cycle with check of the zero and check point.
OPC: Openness, Productivity, Collaboration. Standardized data
interface (OPC Foundation
QAL3: Quality monitoring according to DIN EN 14181.
Reference cycle: Test cycle with correction of internal drifts.
SCU: Operating unit for the control of several analyzers with SCU
capability.
SOPAS (SICK Open Portal for Applications and Systems): SICK
Parameter Setting and Data Calculation Software.
SOPAS ET: SOPAS PC Engineering Tool. Configuration protocol.
TM
).
2 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 3
Warning Symbols
Hazard (general)
Hazard by voltage
Hazard in potentially explosive atmospheres
Hazard by unhealthy substances
Hazard by high temperature or hot surface
Warning levels / Signal words
DANGER
Risk or hazardous situation which will result in severe personal
injury or death.
WARNING
Risk or hazardous situation which could result in severe personal
injury or death.
CAUTION
Hazard or unsafe practice which could result in personal injury or
property damage.
NOTICE
Hazard which could result in material damage.
Information Symbols
Important technical information for this product
Important information on electrical or electronic functions
Nice to know
Supplementary information
Link to information at another place
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 3
Page 4

Inhaltsverzeichnis
Operating Instructions
1 Important Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.1 Main instructions for operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.2 Intended use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.2.1 Purpose of the device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.3 Responsibility of user. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.4 Additional documentation/information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2 Product Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.1 Product identification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.2 Product description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.2.1 Device variants . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.2.2 Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.3 SOPAS ET (PC program). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.4 Reference cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.5 Check cycle. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.6 Design of GM32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.6.1 Measuring probe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.7 Purge air unit (for GMP measuring probe) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3 Preparation on the Gas Duct Side. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.1 Preparation of sampling point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.1.1 Checking the scope of delivery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.2 Overview of the installation steps (duct-side work). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.2.1 Work steps (overview) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.2.2 Installing the “flange with tube” on the gas duct . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.3 Installing the connection unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.4 Installing the purge air unit (for GMP probe) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.5 Laying the electrical connection lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.5.1 General information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.5.2 Connecting I/O interfaces (option). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.5.3 Laying the electrical connection lines to the SR-unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.5.4 Preparing the power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
4 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 5

Operating Instructions
4Start-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
4.1 Necessary technical knowledge for start-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4.2 Required material (not included in the scope of delivery) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4.3 Overview of assembly steps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.4 Transport safety devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.5 Installing the device flange on the purge air fixture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.6 Aligning the measuring probe in flow direction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
4.6.1 When the probe alignment has to be set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
4.7 For the GPP probe: Electric connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
4.8 SR-unit electric connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
4.9 Switching on the power supply of the GM32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
4.10 For GMP probe: Start-up of the purge air supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
4.11 Installing the measuring probe in the gas duct . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
4.12 Installing the SR-unit on the device flange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
4.13 Optical fine alignment of the SR-unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
5Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
5.1 Recognition of an unsafe operational state . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
5.2 Operator panel (for the “Pro” variant). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
5.2.1 Status indicators (LEDs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
5.2.2 Assignment of buttons. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
5.2.3 Contrast setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
5.2.4 Language setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
5.2.5 Menu tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
5.2.5.1 Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
5.2.5.2 Alignment check (automatic optical alignment) (option). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
5.2.5.3 Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
5.2.5.4 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
6 Putting Out of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
6.1 Putting out of operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
6.1.1 Putting out of operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
6.1.2 Disassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
6.2 Storage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
6.3 Environmentally compatible disposal/ recycling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
7Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
7.1 Maintenance plan (operator) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
7.1.1 Recommended expendable and wearing parts for 2 years operation . . . . . . . . . . . 50
7.2 Preparation work . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
7.2.1 Swiveling out and removing the SR-unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
7.3 Visual inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
7.4 Cleaning the window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
7.5 Replacing the sender lamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
7.6 Checking and replacing the drying agent cartridges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
7.7 Cleaning the purge air unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 5
Page 6

Operating Instructions
8 Clearing Malfunctions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
8.1 General hazard caused by electrical voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
8.2 Measured value blinks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
8.3 Error messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
8.3.1 Example of an error message . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
8.3.2 Error messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
8.4 Inadequate purge air supply (for GMP probe) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
8.5 Malfunctions on the connection unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
9 Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
9.1 Conformities. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
9.1.1 Electrical protection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
9.2 Technical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
6 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 7

Important Information
GM32
1 Important Information
Main safety information
Main instructions for operation
Intended use
Own responsibility
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 7
Page 8
Important Information
1.1
Main instructions for operation
WARNING: Danger resulting from escaping gas when the SR-unit is swiveled
out
Excess pressure in the gas duct can cause hot and/or noxious gases to escape
when the SR-unit is swiveled out.
b
Swivel the SR-unit out only when you have taken suitable safety measures.
CAUTION: If the hinge pin has not been correctly inserted (→p. 35, Figure 15),
the SR-unit can drop when swiveled out.
b
Check whether the hinge pin is completely pressed down before the SR-unit
is swiveled out.
CAUTION: Danger of contamination caused by purge air failure (for GM32
with GMP probe)
b
If a failure of the purge air supply occurs, take immediate measures to protect the measuring system (
1.2 Intended use
1.2.1 Purpose of the device
The GM32 serves exclusively for emission and process monitoring of gases in industrial
plants.
GM32 measures continuously directly in the gas duct (in-situ).
→
p. 59, §8.3)
1.3 Responsibility of user
Designated users
The GM32 may be operated by competent persons only who, based on their device-specific
training and knowledge of the device as well as knowledge of the relevant regulations, can
assess the tasks given and recognize the dangers involved.
Correct use
b
Use the device only as described in these Operating Instructions.
The manufacturer bears no responsibility for any other use.
b
Perform the specified maintenance work.
⊗ Do not remove, add or modify any components to or on the device unless described and
specified in the official manufacturer information.
Otherwise:
– Any warranty by the manufacturer becomes void.
– The device could become dangerous.
Special local conditions
b
Follow all local laws, regulations and company-internal operating directives applicable
at the respective installation location of the equipment.
Retention of documents
These Operating Instructions:
b
Must be available for reference.
b
Must be passed on to new owners.
8 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 9

Important Information
1.4
Additional documentation/information
b
Pay attention to the supplied documents.
Additional instructions
The following documents are applicable in addition to these Operating Instructions:
● Technical Information GM32 (option)
● Operating Instructions for purge air supply (for GMP probe)
● Technical Information “Modular I/O System” (option)
● Final inspection record
● CD-Rom with SOPAS ET PC operating program
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 9
Page 10

Important Information
10 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 11

Product Description
GM32
2 Product Description
Product identification
Functional principle
Characteristics
Variants
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 11
Page 12

Product Description
2.1
Product identification
Product name GM32
Product variant Version with measuring probe
Manufacturer SICK MAIHAK GmbH · Nimburger Str. 11
Location of type plates SR-unit: On the right and in the intermediate housing
2.2 Product description
The GM32 gas analyzer serves for continuous measurement of the gas concentrations in
industrial plants.
GM32 is an in-situ measuring system. Measurement is performed directly in the gas carrying duct.
● Components: SO
, NO, NO2 and NH3 (device-specific) as well as the temperature and
2
pressure reference values.
● Measuring principle: Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (DOAS).
2.2.1 Device variants
“Basic” variant
● Reference cycle (
● Automatic mirror tracking: Automatic adjustment of optical axis.
● System messages are recorded in a logbook.
● Ethernet interface with OPC standard.
→
p. 13, §2.4): Correction of internal drifts. Zero point check.
79276 Reute · Germany
For GMP probe: On the purge air fixture
For GPP probe: On the flange attachment
“Pro” variant
As “Basic” variant. In addition:
● “TÜV” tested for suitability.
● Check cycle (
cycle to check and output the zero and check point.
The check cycle generates the QAL3 values. These can be displayed with SOPAS ET.
● Operator panel: Measured values, operating mode and malfunction message are dis-
played in clear text on a monitor.
● QAL3 Tool (CUSUM chart)
2.2.2 Options
● I/O modules (Analog Out, Digital Out, Digital In, Analog In).
● Ethernet rail switch. Contains additional interfaces:
4 * Cu connection.
1 * fiber optics connection (sender and receiver).
● SCU: Operating unit to control several analyzers with SCU capability (→ SCU Operating
Instructions).
● Super Calibration: Several applications/calibrations. For example, for spare devices.
→
p. 13, §2.5): Reference cycle (according to “Basic” variant) followed by a
12 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 13

Product Description
2.3
SOPAS ET (PC program)
SOPAS ET can be used to set the GM32 parameters and provides access to the GM32 logbook.
SOPAS ET runs on an external PC connected via the Ethernet interface (
GM32.
More information on SOPAS ET:
→ Technical Information GM32
→ SOPAS ET Help menu
2.4 Reference cycle
Correction of internal drifts in an adjustable interval (standard: 1 hour, setting: SOPAS ET),
via a command (with SOPAS ET) or via an external signal (option).
Measured value output during the reference cycle: Last valid measured value.
2.5 Check cycle
The check cycle is made up of the reference cycle, followed by the check and output of the
zero and check point (70% of upper measuring range value).
It is performed in an adjustable interval (with SOPAS ET), via a command (with SOPAS ET)
or via an external signal (option).
With the check cycle, the device is capable of performing the check of the zero point and a
reference point for each component without feeding test gases. The check cycle meets the
requirements of EN14181 and makes drift monitoring with test gases according to QAL3
unnecessary.
● Zero point
An internal zero point reflector is swiveled in time-controlled in adjustable intervals. The
emitted light is reflected back in the sender/receiver unit to the detector, the zero spectrum is evaluated with the calibration function and thus the zero points of all ducts
measured and output.
If the deviation from zero is > ±2% of the FS, Maintenance request is signaled.
● Check point
An internal swivel element with two reference filters and an NO-filled cell is swiveled in
during the check cycle in addition to the zero point reflector and the reference value or
concentration value measured. These check values are scaled to 70% of the selected
measuring range.
Maintenance request is signaled if the deviation from the setpoint value is > ±2% of the
FS.
→
p. 22, Figure 4) to
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 13
Page 14
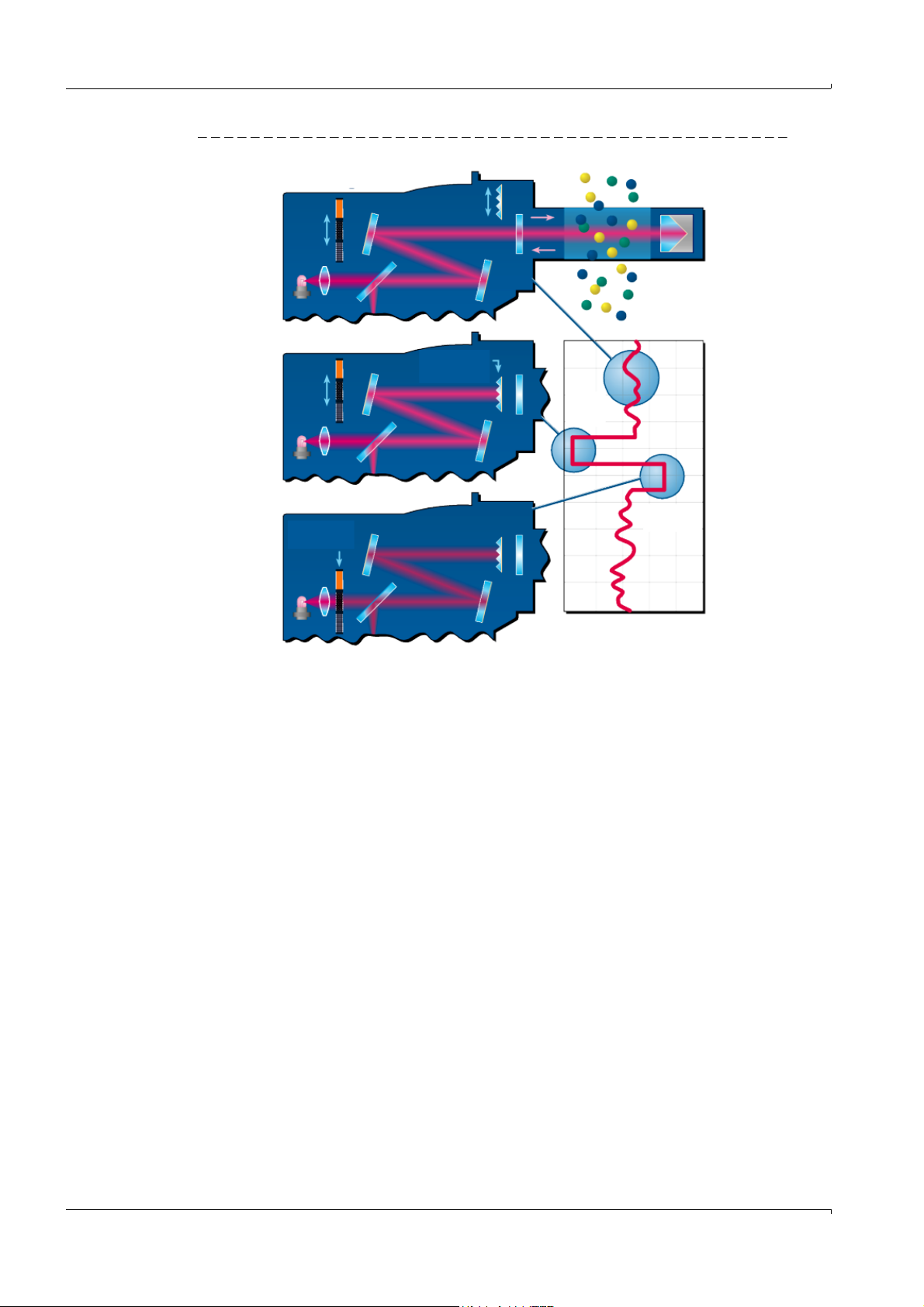
Figure 1 Check point
Measuring
Zero point
Check
Zero point
reflector
Swivel
element
Zero point
Control
point
(70% fsc)
Data recorder
Product Description
● Output of measured values during the check cycle: Last valid measured value.
● Signal during the check cycle: Not_measuring. (Optionally digital output or OPC inter-
face).
● The determined zero and reference values can be output on analog outputs depending
on the parameter settings:
– Directly after the check cycle.
– On request (via a digital input, option).
– Signal during the output: Output_control_values. (Optionally digital output or OPC
interface).
– First output of zero values for 90 s.
– Then output of reference values for 90 s.
–The Not_measuring signal is not active during the output.
● The zero and reference values of the last check cycle are displayed in SOPAS ET (menu:
Diagnosis/Check values).
The required QAL3 values can be read there.
14 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 15

Product Description
SR-unit GMP or GPP measuring probe
Measuring gap
(active measuring path)
Operator panel
(Option)
GMP probe: Purge air fixture
GPP probe: Flange attachment
Purge air unit (for GMP probe)
2.6
Design of GM32
The GM32 Probe version comprises
● Sender/receiver unit (SR-unit)
The SR-unit contains optical and electronic subassemblies.
The concentration calculation of the sample gas according to the absorption spectro-
scope principle is performed in the SR-unit.
● Measuring probe with flange resp. purge air fixture (
● Purge air unit (for GMP measuring probe) (
Figure 2 GM32 Probe (version shown: GMP measuring probe)
→
§ 2.7)
→
§ 2.6.1)
2.6.1
Measuring probe
Probe types:
● Measuring probe with open measuring gap (GMP probe)
GMP probes require a purge air supply to protect the window against contamination.
● Gas diffusion probe (GPP probe) with gas permeable ceramic filter.
GPP probes are fitted with an automatically controlled heater to prevent condensate on
the windows.
Both probe versions have an integrated temperature and pressure sensor.
2.7 Purge air unit (for GMP measuring probe)
The purge air unit supplies filtered ambient air to the purge air fixtures and protects the
windows of the SR-unit from contamination and high gas temperatures.
The purge air is blown into the gas duct through the “flange with tube”.
More information on the purge air unit → Technical Information of purge air
unit.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 15
Page 16

Product Description
16 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 17

Preparation on the Gas Duct Side
GM32
3 Preparation on the Gas Duct Side
Setup
Installation
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 17
Page 18
Preparation on the Gas Duct Side
3.1
Preparation of sampling point
● The basis for the determination of the sampling point is the preceding proj-
ect planning (e.g. based on the SICK application questionnaire), the information in the final inspection record of the GM32 and the regulations of
the local authorities.
● The equipment operator is responsible for the determination of the sam-
pling point (e.g. the determination of a representative sampling point).
● The equipment operator is responsible for the preparation of the sampling
point (e.g. load carrying capacity of the welded flange).
b
Determine the installation location.
Observe the ambient conditions of the GM32 (
b
Observe the space requirements for the SR-unit (→ p. 72, §).
Provide for additional space for maintenance work (swiveling the housing door open,
pulling the measuring probe out).
b
Determine the installation location for the connection unit.
Observe the maximum line lengths (
b
Provide the power supply for the connection unit and, when necessary, for the GPP
→
p. 22, Figure 4 or as planned).
probe.
Observe the power requirements (
b
Lay the signal lines.
b
For GMP probe: Determine the installation location for the purge air unit (→p. 22,
→
p. 67, §9.2).
Figure4 resp. as planned).
Provide clearance for changing the filter element (→ Technical Data of purge air unit).
→
p. 67, §9.2).
3.1.1 Checking the scope of delivery
b
Compare the data of the final test record with the data of the order confirmation - they must be identical.
b
Check the scope of delivery according to the order confirmation/delivery note.
18 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 19
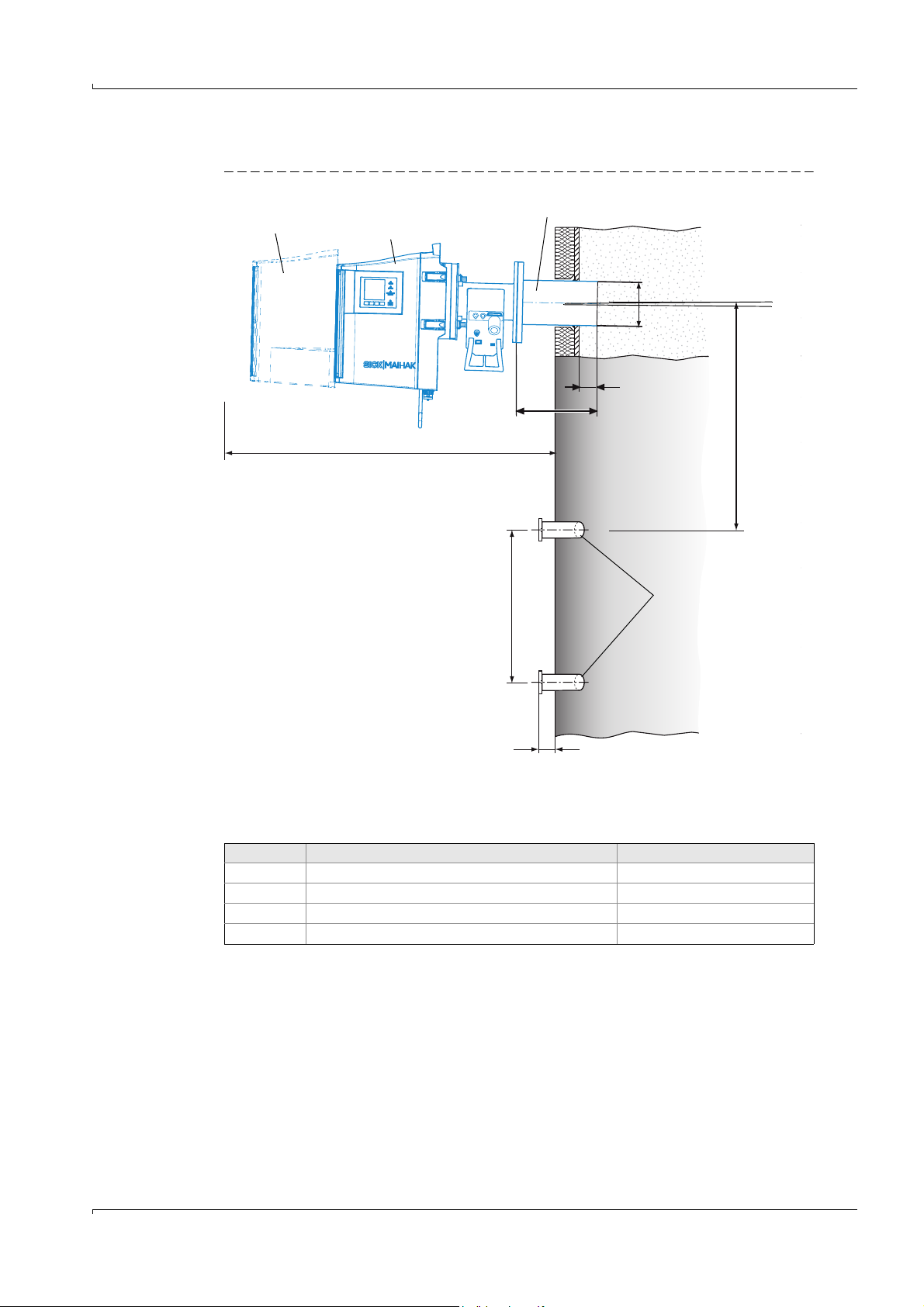
Preparation on the Gas Duct Side
30
L
50
470
Ø13
3
Weatherproof cover
“Flange with tube”: L = 240 mm (standard)
Attachment (e.g. 4 steel
pipes, 50 x 5 mm)
for purge air unit
SR-unit
Approx. 1.5 m
Min. 700 mm
Angle: Approx. 1°
3.2
Figure 3 Installation overview
Overview of the installation steps (duct-side work)
3.2.1
Work steps (overview)
Step Procedure Reference
1 Installing the “flange with tube”
2 Installing the connection unit
3 For GMP probe: Installing the purge air unit
4 Laying the electrical connection lines
→
p. 20, §3.2.2
→
p. 20, §3.3
→
p. 21, §3.4
→
p. 22, §3.5
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 19
Page 20
3.2.2 Installing the “flange with tube” on the gas duct
WARNING: Danger resulting from gases in the gas duct
Hot and/or noxious gases can escape during work on the gas duct, depending
on the equipment conditions.
b
Work on the gas duct may only be performed by skilled persons who, based
on their technical training and knowledge as well as knowledge of the relevant regulations, can assess the tasks given and recognize the hazards
involved.
1 Make a cut-out in the gas duct for the “flange with tube”.
2 Insert the “flange with tube” so that the mark (TOP)
spective of the gas duct angle) and attach the “flange with tube”.
– The tube must project at least 30 mm into the gas duct.
– Make sure the probe does not collide with other devices or fittings.
– Tilt the tube slightly downwards (approx. 1°).
This allows any condensate to drain off.
3 Now fix the “flange with tube” properly to the gas duct.
Make sure that the alignment of the flange does not change.
4 If necessary, attach duct insulation (protect GM32 from heat).
Preparation on the Gas Duct Side
▴ points upwards vertically (irre-
IMPORTANT: Observe the ambient temperature of the GM32
b
When the gas duct is hot, insulate the duct and flanges so that the
GM32 is protected from excess temperatures (
3.3 Installing the connection unit
● The length of the line to the GM32 complies with project planning.
b
Provide threaded bolts (4) to screw on the connection unit (→ p. 72, §31) and screw on
the connection unit.
⊗ Do not make the electrical connection to the connection unit yet.
→
p. 67, §9.2).
20 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 21
Preparation on the Gas Duct Side
3.4
Installing the purge air unit (for GMP probe)
● Maximum length of line to GM32 complies with project planning.
IMPORTANT: Adequate purge air pressure
b
Ensure the purge air pressure is adequate to push the purge air into the gas
duct.
If required, please contact SICK Customer Service or your local representative.
Installation of purge air unit → Data Sheet of purge air unit.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 21
Page 22
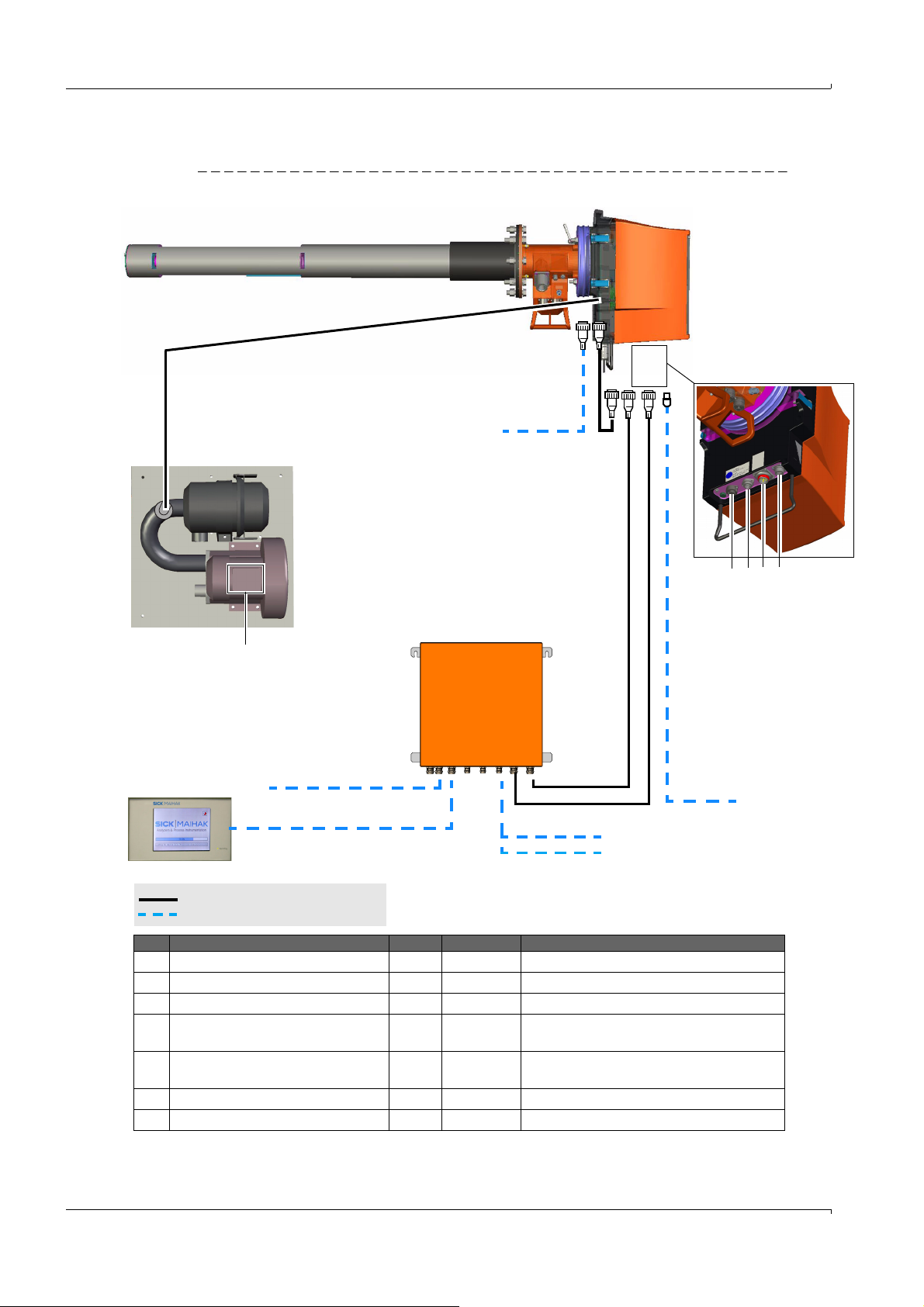
Preparation on the Gas Duct Side
Sender/
receiver unit (SR)
Measuring probe
Purge air unit SLV 4
(for GMP measuring probe)
Connection unit (AE)
Wiring and technical data,
see Data Sheet SLV4
(3) (5) (4) (6)
(3) Connection:
Purge air fixture
(4) Connection:
Power supply
(5) Connection: CAN cable
(6) Connection: PC (SOPAS
ET)
(3)
(1)
(4) (5)
(6)
For configuration and connections,
see “Operating Instructions SCU”
SCU (option)
For on-site terminal connections
(inputs/outputs), see Operating
Instructions “Modular I/O System”
(7)
Power supply:
100 ... 240 V AC, 50/60 Hz
Power supply (GPP):
115 ... 230 V AC, 50/60 Hz
(2)
No. Signal cable for connection of Length Part No. Remarks
(1) Filter monitoring 5 m 2032143 Included in the purge air fixture (probe)
(2) GPP probe power supply 10 m 2017519 Included in the GPP probe
(3) SR – purge air fixture (CAN cable) 0.8 m 2023704 Included in the purge air fixture (probe)
(4) AU – SR (CAN cable) 10 m
20 m
2028786
2045422
Order separately
(5) Power supply SR (standard) 10 m
20 m
2046548
2046549
Order separately
(6) Ethernet cable – PC/network – No, on-site
(7) CAN cable – SCU – No, on-site
Scope of delivery
On-site wiring
3.5
Figure 4 Electrical connection diagram
Laying the electrical connection lines
22 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 23
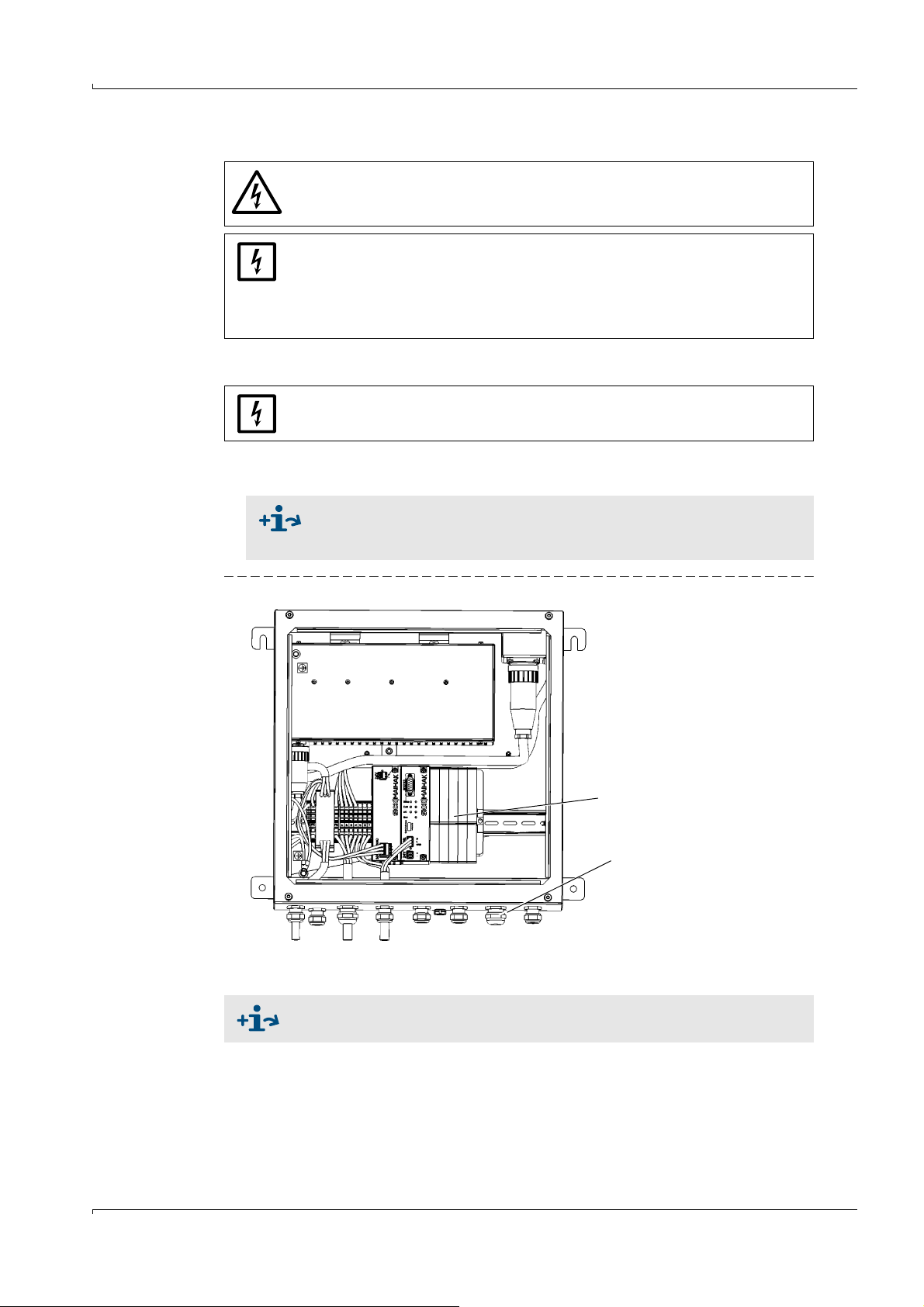
Preparation on the Gas Duct Side
I/O module
PG screw fittings
3.5.1 General information
CAUTION: Hazards caused by electric voltages
b
Only let the work described in the following be carried out by skilled electricians familiar with potential risks.
IMPORTANT:
Before signal connections are established (also with plug connections):
b
Disconnect the GM32 and any connected devices from the electrical supply.
Otherwise the internal electronics can be damaged.
3.5.2 Connecting I/O interfaces (option)
⊗ Do not lay power supply cables immediately next to signal cables.
b
Route the data lines through the PG screw fittings.
b
Connect the data line to the I/O modules.
b
Connections of I/O modules → Technical Information “Modular I/O System”.
b
Terminal assignment → final test record.
Figure 5 Connection unit (inside): Location of I/O modules
3.5.3 Laying the electrical connection lines to the SR-unit
Electrical connections on GM32 →Figure4
1 Lay the electrical connection lines from the connection unit to the SR-unit.
2 For GMP probe: Lay the signal line from the purge air unit (connection on the purge air
unit → Technical Information of the purge air unit) to the purge air fixture.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 23
Page 24

3.5.4 Preparing the power supply
Power supply
100 .. 240 V / 50 .. 60 Hz
Take precautions to prevent switching off the purge air supply accidentally.
b
Attach a clearly visible warning against accidental switching off the separation equipment for the purge air unit.
1 Provide separate external fuses for:
– Connection unit (max. power input
– For GMP probe: Purge air unit (→ Technical Data of the purge air unit)
– For GPP probe: Heater (max. power input
2 Lay the electric lines of the power supply to the connection unit and connect the power
supply in the connection unit.
Figure 6 Mains connection in the connection unit
→
p. 67, §9.2)
→
p. 67, §9.2)
Preparation on the Gas Duct Side
The power supply must remain switched off until the GM32 is to be put into
operation.
3 For GMP probe: Lay the electric lines to the purge air unit.
For GPP probe: Lay the electric lines for the probe heater.
24 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 25

Start-up
GM32
4 Start-up
Preparation
Assembly
Alignment
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 25
Page 26

Start-up
4.1
Necessary technical knowledge for start-up
The following requirements must be met for the start-up:
● You are basically familiar with GM32.
● You are familiar with the local situation, especially the potential risks
caused by gases in the gas duct (hot/noxious). You are capable of recognizing and preventing danger by possibly escaping gases.
● The specifications according to project planning have been complied with
(→ final inspection record).
● The assembly location has been prepared according to
on the Gas Duct Side«.
If one of these requirements is not met:
b
Please contact SICK Customer Service or your local representative.
WARNING: Hazard by voltage
b
All connectors of the power supply to the involved subassemblies or lines
must be disconnected before the installation work.
WARNING: Danger resulting from gases in the gas duct
Hot and/or noxious gases can escape during work on the gas duct, depending
on the equipment conditions.
b
Work on the gas duct may only be performed by skilled persons who, based
on their technical training and knowledge as well as knowledge of the relevant regulations, can assess the tasks given and recognize the hazards
involved.
→
p. 17, »Preparation
4.2 Required material (not included in the scope of delivery)
Material required Part No. Required for
Optical cleaning cloth 4003353 Cleaning the windows
Personal protective equipment --- Protection when working on the
stack
26 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 27

Start-up
Transport safety device
4.3
Overview of assembly steps
Procedure Reference
Removing the transport safety devices
Installing the device flange on the purge air fixture
Aligning the measuring probe
For the GPP probe: Electrical connection of heater
SR-unit electric connection
Switching on the power supply
For GMP probe: Purge air supply start-up
Installing the measuring probe in the gas duct
Fitting the SR-unit on the device flange
Optical fine alignment of the SR-unit
4.4 Transport safety devices
1 Remove the transport safety device of the SR-unit.
Figure 7 SR-unit transport safety device
→
p. 27, §4.4
→
p. 29, §4.5
→
p. 30, §4.6
→
p. 31, §4.7
→
p. 32, §4.8
→
p. 32, §4.9
→
p. 33, §4.10
→
p. 34, §4.11
→
p. 35, §4.12
→
p. 35, §4.13
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 27
Page 28

2 Remove the probe transport safety device.
Plugs
Stickers
The probe transport safety devices depend on the type of probe.
a) Remove the protective stickers.
b) Take out the plugs.
Figure 8 Probe transport safety devices (shown here on a GPP probe)
Start-up
3 Store the transport safety devices.
28 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 29

Start-up
Device flange
Purge air fixture
Gap: 3.5 ± 0.5 mm
Sealing ring
12 cup springs
Centering disc
Nut
4.5
Installing the device flange on the purge air fixture
Remark on the GPP probe: The procedure for the GPP probe flange attachment corresponds to the procedure shown here for the purge air fixture.
1 Recommendation: For easier handling during installation:
Remove the SR-unit from the device flange before installation (
2 Installation on the SR-unit side:
Figure 9 Installing the device flange on the purge air fixture
→
p. 51, §7.2.1).
a) Plug 12 cup springs each, individually arranged opposite each other, onto the
threaded bolts on the device flange.
b) Pull the sealing ring over the flange of the purge air fixture and hang it loosely over
the purge air unit.
c) Plug the device flange onto the purge air fixture.
d) Plug on the centering discs.
Notice: Observe the direction of the centering disc: The convex side must fit into the
groove on the purge air fixture.
e) Tighten the self-locking nuts with a wrench (19 mm) so that the cup springs are
slightly compressed and an even gap of 3...4 mm remains.
f) Install the sealing ring above the gap (
→
Figure9).
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 29
Page 30

Start-up
Flow direction sticker
Mounting ring screws (4 pcs.)
Device flange
4.6
Aligning the measuring probe in flow direction
The fitting angle of the probe is already set before delivery when the gas flow direction has
been defined during project planning for the GM32.
A sticker marks the setting.
Figure 10 Flow direction marking and setting
4.6.1
When the probe alignment has to be set
● The measuring gap must be aligned in sample gas flow direction.
● The SR-unit must be fitted vertically.
Rotate the device flange to align the probe.
To change the measuring probe alignment:
1 Loosen the 4 screws on the mounting ring (
2 Rotate the device flange:
– The measuring gap must point in flow direction.
– The device flange must be positioned so that the SR-unit can be fitted in a vertical
position.
3 Fasten the device flange in this position by tightening the screws on the mounting ring
again.
→
Figure10).
30 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 31

Start-up
Fuse holder
Switch to set voltage
4.7
For the GPP probe: Electric connection
1 Unscrew and take off the purge air fixture cover.
2 Check the switch setting for swapping the voltage to the available mains voltage and
correct when necessary.
Figure 11 Switch to select voltage and fuses
3 Check the fuses according to the available mains voltage and replace when necessary.
IMPORTANT: The fuses depend on the available mains voltage.
b
Only use the correct fuses.
– 230 V: 1.6 A (slow)
– 115 V: 2.5 A (slow)
4 Connect the power supply to the mains voltage.
Line with three wires:
– Green-yellow: PE
–Blue: N
–Brown: L1
IMPORTANT: Danger of condensation
The GPP probe must have reached its operating temperature before being
inserted in the gas duct.
b
First fit the GPP probe during final installation in the gas duct (→ p. 34,
§4.11).
b
Attach clearly visible warnings against accidental switching-off to all
switching devices where the GPP probe heater can be switched off.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 31
Page 32

Start-up
Earthing conductor
connection
4.8
SR-unit electric connection
Connecting diagram →p. 22, Figure 4
1 Connect the electric lines from the connection unit to the SR-unit.
2 For GMP probe: Connect the electric line from the purge air unit to the purge air fixture
(terminal: SLV filter).
3 Screw the earthing conductor (2.5 mm
minal (
→
Figure 12).
Figure 12 Connection of the earthing conductor at the bottom of the SR-unit
4.9 Switching on the power supply of the GM32
2
) of the equipment earth tight to the screw ter-
1 Switch on the power supply on the operator-side fuse of the connection unit.
2 An initialization screen is shown on the operator panel (for the “Pro” variant).
3 Measured values are then shown.
Ignore the displays until the start-up of the GM32 is complete.
32 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 33

Start-up
SLV filter terminal
Purge air connection
(shown with protective cap)
4.10
Figure 13 Connection of the purge air supply
For GMP probe: Start-up of the purge air supply
1 Switch on the power supply of the purge air unit on the (operator-side) fuse of the purge
air unit.
– Check the function: A strong air flow must be noticeable.
If it is not noticeable: → Data Sheet of purge air unit.
– Blow out the dust that may have entered the purge air hose.
2 Check the switch function of the pressure controller in the purge air unit, e.g. by partly
closing the suction opening of the purge air unit.
The “Purge air signal” warning must be shown.
3 Switch the power supply off again.
4 Connect the purge air hose to the purge air connection with a hose clamp (
necessary, remove the protective cap from the purge air connection.
5 Switch the power supply of the purge air unit on.
→
Figure13). If
The purge air supply protects the measuring system from contamination and
overheating.
b
Ensure the purge air pressure is adequate to push the purge air into the gas
duct.
The purge air supply may not be switched off while the measuring system is on
the gas duct.
b
Attach clearly visible warnings against accidental switching-off to all switching devices where the purge air supply can be switched off.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 33
Page 34

Start-up
For GMP probe: Purge air fixture
For GPP probe: Flange attachment
Seal
“Flange with tube”
Screw
Washer
Spring sheet
Nut
4.11
Installing the measuring probe in the gas duct
IMPORTANT: With the GPP probe: Danger of condensation
The GPP probe must have reached its operating temperature before the measuring probe is inserted in the gas duct.
b
Wait until the probe has reached its operating temperature before inserting
the probe.
Do not switch the GPP probe heater off as long as the GPP probe measuring
system is in the gas duct.
b
Attach clearly visible warnings against accidental switching-off to all switching devices where the GPP probe heater could be switched off.
1 Insert the measuring probe with purge air fixture resp. flange attachment (without SR-
unit) in the “flange with tube” on the channel side.
– For GMP measuring probe: Do not interrupt the purge air feed.
– For GPP measuring probe: Do not interrupt the power supply to the measuring
probe.
2 Screw the measuring probe with purge air fixture resp. flange attachment tight to the
“flange with tube” (seal with 4 screws).
Figure 14 Fitting the probe in the gas channel
34 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 35

Start-up
Hinge pin
Hinge
Device flange
SR-unit
Lever of the
locking device
“Open” resp. “close”
marking
4.12
Installing the SR-unit on the device flange
1 Installing the SR-unit:
a) Insert the SR-unit on the device flange into the hinge (swiveling-out direction prefer-
ably to the “left”).
b) Insert the hinge pin from above.
IMPORTANT: If the hinge pin has not been correctly inserted, the SR-unit
can drop when swiveled out.
b
Figure 15 Installing the SR-unit:
Ensure that the hinge pin is fully inserted.
c) Check the window for cleanness and clean, if required (→ p. 52, §7.4).
d) Check whether the drying agent cartridge is dry (
e) Close the SR-unit with the 4 quick-release fasteners.
f) For GMP probe: Set the lever on the purge air fixture to the “open” position.
Figure 16 Lever for the locking device (for GMP probe)
4.13
Optical fine alignment of the SR-unit
Optical alignment of the SR-unit:
b
With SOPAS ET: → Leave this work to a skilled person familiar with SOPAS ET.
b
With operating unit: →p. 42
→
p. 54, §7.6).
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 35
Page 36

Start-up
36 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 37

Operation
GM32
5 Operation
Operation
Status messages
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 37
Page 38

Operation
5.1
Recognition of an unsafe operational state
CAUTION: Danger caused by unsafe operational state
If the device is or could be in an unsafe state:
b
Take the device out of operation, disconnect from the mains voltage and
signal voltage and secure against unallowed or accidental start-up.
Indication Action
Smoke escaping from the housing
Gas escaping from the housing
Water or a different liquid penetrates
into the device
Humidity or moisture condensation on
electrical connections
Electric lines are damaged or broken
Surface is damaged or deformed
Unusual noises can be heard inside the device
Malfunctions remain inexplicable despite
having been cleared
1 Immediately put the device out of operation.
2 Have the device repaired.
1 Immediately check whether the gas is noxious or
combustible.
2 If this is the case: Immediately check the local
Operating Instructions which control the behavior
during uncontrolled escape of gas.
Examples of behavior:
b
Trigger an alarm. Start emergency measures.
b
Immediately evacuate all persons from the
affected operational room.
b
Use breathing protection.
b
Stop the affected gas supply.
b
Put the measuring system out of operation.
1 Immediately put the device out of operation.
2 Locate and stop the liquid source.
3 Have the device repaired.
1 Put the device out of operation.
2 Dry the connections.
1 Put the device out of operation.
2 Have the damage repaired.
1 Put the device out of operation.
2 Have the device repaired.
b
If caused by heat from inside the device: Immediately put the device out of operation.
b
If caused by acute external influence: Locate the
heat source and protect the device provisionally
against heat.
b
Otherwise: Have the device checked immediately
by a skilled person.
1 Check malfunction displays and malfunction mes-
sages of the device.
2 Have the device checked by a skilled person.
b
Contact the manufacturer's after-sales service
department.
38 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 39

Operation
Operating mode
Status indicators (LEDs)
(
→
p. 40, §5.2.5.1)
Current menu with
menu level (numeric display)
Menu level
Significance of button
(
→
§ 5.2.2)
Contrast setting
(
→
§ 5.2.3)
MEAS button
(
→
§ 5.2.2)
Buttons
5.2
Operator panel (for the “Pro” variant)
The operator panel is located on the right side of the SR-unit housing.
Figure 17 Significance of display
5.2.1 Status indicators (LEDs)
Significance of LEDs
● The green LED goes on: Power supply is in order.
● The yellow LED goes on: Maintenance request.
● The red LED goes on: Malfunction.
More information on the significance of the LEDs → p. 40, §5.2.5.1
5.2.2 Assignment of buttons
The assignment of the buttons depends on the selected menu and is shown above the
respective button.
Assignment of buttons Significance
MEAS Back to the display of the measured value screen from any menu.
All inputs that have not been terminated with Save are discarded.
F
If the MEAS button is depressed for more than 3 seconds: The contrast setting is
displayed (
Menu Opens the main menu (menu tree)
Diag Diag is shown only when there is a message.
When this button is pressed, the current message is shown.
More information on diagnosis
List of error messages
Enter Opens the selected menu level
Save Saves the changed parameters
Start Starts the displayed action
5.2.3 Contrast setting
1 Press the MEAS button for more than 3 seconds.
2 Set the desired contrast level with both middle buttons
→
p. 39, §5.2.3)
→
p. 59, §8.3
→
p. 40, §5.2.5.1
§ and ¨.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 39
Page 40

5.2.4 Language setting
The texts of the menus are shown in English
5.2.5 Menu tree
1
1.1 Failure
1.2 Maintenance (request)→ p. 40, §5.2.5.1
1.3 Uncertain
2 Alignment check
3 Adjustments
3.1 Alignment adjust
3.2 Check cycle
3.3 Reference cycle
4 IP Configuration View the IP settings
4.1 IP IP address
4.2 M Subnetmask
4.2 GW Gateway
5 Maintenance
Diagnosis
→
p. 40, §5.2.5.1
→
p. 40, §5.2.5.1
→
p. 40, §5.2.5.1
→
p. 41, §5.2.5.2
→
p. 42, §5.2.5.3
→
p. 42
→
p. 43
→
p. 43
→
p. 44, §5.2.5.4
Operation
5.2.5.1 Diagnosis
The “Diagnosis” menu shows the current error messages.
The GM32 creates a logbook.
b
Access to the logbook is performed exclusively via SOPAS ET
→
p. 13, §2.3.
The GM32 signals a malfunction or an unsafe operational state with status signals (option) (→ electrical connection diagram).
List of error messages and measures for clearing malfunctions
→
p. 59, §8.3
40 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 41

Operation
Status messages, status indicators and system states
Status Status indicators
(LED)
Significance Measured
value dis-
Analog
outputs
play
Power On Green Power supply is in order --- --- --Uncertain Green, however,
measured value
blinks
Measured value uncertain (e.g. outside
calibration range)
Cause: Press the DIAG button
Current Current According to
All messages → SOPAS ET Logbook.
Maintenance
request
Clearing malfunctions
Yellow Irregularities (e.g. gas temperature too
high, deviation from check cycle too high)
→
p. 59, §8.3
Current Current According to
that require a review of the cause.
The measured values are valid.
Cause: Press the DIAG button
All messages → SOPAS ET Logbook.
Clearing malfunctions
Failure Red Device failure (e.g. lamp failed)
Cause: Press the DIAG button
All messages → SOPAS ET Logbook.
Clearing malfunctions
1
Option
2
Option. Refer to the delivered System Documentation for the assignment of the status outputs.
3
See SOPAS ET in the “Digital outputs” menu.
→
p. 59, §8.3
→
p. 59, §8.3
Last valid
measured
value held
Last valid measured value
held
1
nal
2,3
setting
setting
According to
setting
Status sig-
5.2.5.2 Alignment check (automatic optical alignment) (option)
The optical alignment of GM32 is automatically adjusted in this menu.
b
Perform this work only when the SR-unit is at operating temperature (in
operation for at least 30 minutes).
b
Automatic mirror adjustment - do not perform manual adjustments.
More information→ p. 42, §5.2.5.3
b
Arrow buttons: Switch from “deviation” to “performed steps of tracking mirror”
b
To exit the Menu item: Press the “Back” button.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 41
Page 42

Operation
Light energy
Focal point
Value X
Value Y
5.2.5.3
Adjustments
Alignment adjustment (manual optical alignment)
b
Perform this work only when the SR-unit is at operating temperature (in
operation for at least 30 minutes).
Figure 18 Manual alignment of optical axis
Manual optical alignment of the GM32.
1 Press the “Start” button: The GM32 goes to a defined state.
A crosshair with a focal point and X/Y values is shown on the screen.
2 Tole ranc es:
X: –0.05 ... +0.05
Y: –0.05 ... +0.05.
The focal point is then in the center of the crosshair.
Adjustment:
Adjust the optical alignment by turning both adjustment screws on the device flange of
the SR-unit (19 mm wrench).
The display on the monitor reacts to the adjustment with a delay.
b
Perform adjustments slowly and wait for approx. 20 seconds until the
display on the monitor has been updated.
42 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 43

Operation
Horizontal adjustment
Vertical adjustment
Figure 19 Alignment on the device flange
– Horizontal adjustment of the probe causes a horizontal adjustment of the focus.
– Vertical adjustment of the probe causes a vertical adjustment of the focus.
3 The values for the light energy V1 .. V4 must be in the range from 250 .. 500 and
approximately have the same size.
● If you cannot see a focal point or adjustment is not possible:
– Is the gap between the device flange and the purge air fixture correctly adjusted? (
p. 29, §4.5)
– For GMP probe: Diaphragm (lever) open? (
– Very much dust or humidity in the gas duct?
–Window dirty? (
– Sender lamp defective? (Replacing the sender lamp
→
p. 52, §7.4)
→
p. 35, §4.12)?
→
p. 53, §7.5)
→
Check cycle
Start the check cycle manually.
Information on the check cycle → p. 13, §2.5
Reference cycle
Start the reference cycle manually.
Information on the reference cycle → p. 13, §2.4
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 43
Page 44

Operation
5.2.5.4
Maintenance
The operating mode “Maintenance” is signaled via this menu.
● “Maintenance” is displayed in the operating mode line.
● The “Maintenance mode active” message is displayed.
● A continuous display of “*” is shown.
● The “Maintenance” status signal (→ electric connection diagram) is set.
Figure 20 “Maintenance” screen
● Assignment of buttons:
– “Back” : Show the “Measuring” menu - maintenance signal remains set.
–“MEAS”: Show the “Measuring” menu - maintenance signal is reset.
44 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 45

Putting Out of Operation
GM32
6 Putting Out of Operation
Putting out of operation
Storage
Disposal
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 45
Page 46

Putting Out of Operation
6.1
Putting out of operation
WARNING: Danger resulting from gases in the gas duct
Hot and/or noxious gases can escape during work on the gas duct, depending
on the equipment conditions.
b
Work on the gas duct may only be performed by skilled persons who, based
on their technical training and knowledge as well as knowledge of the relevant regulations, can assess the tasks given and recognize the hazards
involved.
IMPORTANT: Do not switch off the purge air immediately
⊗ Do not switch the purge air unit off as long as the SR-unit is still on the gas
duct.
IMPORTANT: With the GPP probe: Danger of condensation
⊗ Do not switch off the heater of the GPP probe as long as the probe is in the
gas duct.
6.1.1 Putting out of operation
b
Switch off the power supply of the connection unit.
The analyzer can remain on the gas duct as long as the purge air supply (for GMP probe)
resp. the heater (for GPP probe) is in operation.
IMPORTANT: In case of a failure, no message by the analyzer
The analyzer no longer outputs a message when the purge air supply resp. the
heater fails.
b
Install suitable monitoring or remove the subassemblies.
6.1.2 Disassembly
Material required Part No. Required for
Personal protective equipment --- Protection when working on the stack
Flange lid --- Covering the flange
1 Disconnect all connections between connection unit and SR-unit.
2 Remove the SR-unit (
3 Unscrew the purge air fixture or flange fixture (
the probe and lay it down
4 For GPP probe: Switch off the power supply of the heater.
5 For GMP probe: Switch the purge air supply off and disconnect the purge air hose on
the device flange.
6 Close off the flange on the gas duct with a cover.
→
p. 51, §7.2.1).
WARNING: Hazards when removing the SR-unit
b
Observe the information concerning the removal of the SR-unit (→ p. 51,
§7.2.1).
→
p. 15, Figure 2) from the flange, pull out
.
WARNING: Measuring probe can be hot
When the temperatures in the gas duct are high, the removed measuring
probe is hot.
b
Wear suitable heat-resistant gloves.
b
Provide a heat-resistant support.
46 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 47

Putting Out of Operation
6.2
Storage
1 Clean the exterior of all housings, the measuring probe and all further components
including the purge air unit (when fitted)) with damp cleaning cloths. A mild cleaning
agent can be used.
2 Check the drying agent cartridges and replace, if required (
→
3 Protect the openings of the SR-unit and measuring probe from atmospheric influences
(preferably with the transport safety devices, according to
→
p. 27, §4.4).
4 Pack the GM32 for storage or transport (preferably in the original packing).
5 Store the GM32 in a dry, clean room.
6.3 Environmentally compatible disposal/ recycling
The GM32 can be disposed off as industrial waste.
Observe the relevant local conditions for the disposal of industrial waste.
The following subassemblies could contain substances that have to be disposed of separately:
● Electronics: Capacitors, rechargeable batteries, batteries.
● Display: Liquid of LC display.
● Probes: Probes can be contaminated with pollutants.
p. 54, §7.6).
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 47
Page 48

Putting Out of Operation
48 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 49

Maintenance
GM32
7 Maintenance
Maintenance plan
Spare parts, recommended
Maintenance work
Preventative maintenance
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 49
Page 50

Maintenance
7.1
Maintenance plan (operator)
Maintenance task Reference W
Check if measured and control values (zero/test point) are valid x x
Visual inspection
Cleaning the window
Checking/drying agent cartridges, replace when necessary.
→
p. 52, §7.3 x
→
p. 52, §7.4 x
→
p. 54, §7.6 x
Replace at the latest after 6 months.
Checking the purge air unit (for GMP probe)
Checking optical alignment
1
W = weekly, Q = quarterly
7.1.1 Recommended expendable and wearing parts for 2 years operation
Spare part Number Part No.
→
p. 55, §7.7 x
→
p. 41, §5.2.5.2 x
1
Sender lamp 2 pcs 2033796
Drying agent cartridge 8 pcs 2010549
Optical cleaning cloth 8 pcs 4003353
Filter insert for purge air unit 8 pcs 5306091
1
Per piece
1
1
Q
50 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 51

Maintenance
Hinge pin
Hinge
Device flange
SR-unit
7.2
Preparation work
IMPORTANT: Some tasks cause GM32 to switch to malfunction
b
Activate the Maintenance mode before starting the work (→p. 44).
IMPORTANT: Do not switch off the purge air
⊗ Do not switch the purge air unit off as long as the SR-unit is still on the gas
duct.
IMPORTANT: With the GPP probe: Danger of condensation
⊗ Do not switch off the heater of the GPP probe as long as the probe is in the
gas duct.
7.2.1 Swiveling out and removing the SR-unit
WARNING: Danger resulting from escaping gas when the SR-unit is swiveled
out
Excess pressure in the gas duct can cause hot and/or noxious gases to escape
when the SR-unit is swiveled out.
b
Swivel the SR-unit out only when you have taken suitable safety measures.
b
For GMP probe: Set the lever on the purge air fixture to the “Close” position
(
→
p. 35, Figure 16).
CAUTION: If the hinge pin (→p. 35, Figure 15) has not been correctly inserted,
the SR-unit can drop when swiveled out.
b
Check whether the hinge pin is completely pressed down before the SR-unit
is swiveled out.
Figure 21 Swiveling out the SR-unit
1 For GMP probe: Set the lever on the purge air fixture to the “Close” position (→p. 35,
Figure 16).
2 Open the 4 quick-release fasteners of the SR-unit and swivel out the SR-unit.
3 To remove the SR-unit:
Hold the SR-unit tight, pull out the hinge pin and take the SR-unit off
IMPORTANT: The SR-unit is heavy
b
Hold the SR-unit tight when pulling out the pin.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 51
Page 52

Maintenance
Window
7.3
Visual inspection
b
Check the housings of the SR-unit housing and connection unit for mechanical damage.
b
Clean the respective housings if contaminated.
b
Check all cables for damage.
Pay attention to chafe marks and kinks on cable ducts.
b
Check flanges and screw fittings for firm seating.
7.4 Cleaning the window
Figure 22 SR-unit window
1 Swivel out the SR-unit out (→ p. 51, §7.2.1).
2 Clean the window.
Use an optical cleaning cloth for cleaning.
The cleaning cloth can be moistened with demineralized water.
Do not use cleaning agents.
3 Close the SR-unit again.
4 For GMP probe: Set the lever on the purge air fixture to the “Open” position again.
52 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 53

Maintenance
Lamp cover
Screw of plug
Screws of sender lamp
7.5
Replacing the sender lamp
1 Switch off the GM32 using the fuse on the operator side.
2 Loosen 5 screws on the rear side of the SR-unit and swivel out the rear side.
3 Pull out the lamp cover.
Figure 23 Lamp cover
Figure 24 Sender lamp
4 Loosen screw (Philips head screw) of the plug and disconnect the plug.
5 Loosen 2 screws (5 mm Allen screw) on the sender lamp and loosen the sender lamp
.
WARNING: The sender lamp is hot
b
Wear suitable heat-resistant gloves.
b
Provide a heat-resistant support.
6 Remove the cap from the new sender lamp.
7 Plug in new sender lamp and screw tight.
8 Connect the plug and screw tight.
9 Plug in the lamp cover.
10 Screw the rear cover tight.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 53
Adjustment is not required.
Page 54

Maintenance
2 drying agent cartridges
7.6
Figure 25 Drying agent cartridges
Checking and replacing the drying agent cartridges
1 Swivel out the SR-unit (→ p. 51, §7.2.1).
2 The drying agent cartridge is light blue: The drying agent cartridge is dry.
The drying agent cartridge is white: Replace the drying agent cartridge.
3 Replacing the drying agent cartridge:
a) Unscrew the drying agent cartridge.
b) Screw in the new drying agent cartridge.
4 Close the SR-unit.
5 For GMP probe: Set the lever on the purge air fixture to the “Open” position again.
54 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 55

Maintenance
7.7
Cleaning the purge air unit
IMPORTANT: Inadequate purge air supply can damage the measuring system.
b
The purge air unit must be in perfect condition.
The filter of the purge air unit must be exchanged at the latest when the low-pressure monitor on the filter outlet triggers.
Preparation
b
If the purge air unit is not immediately functional: Remove the SR-unit from the gas duct
(swiveling out is sufficient for short-time work).
Procedure
1 Put the purge air unit out of operation and completely remove the purge air hoses.
2 Replace the air filter in the purge air unit and clean the inside of the purge air unit.
Details → Data Sheet of purge air unit.
3 Fully swivel out the SR-unit so that any dust blown through the purge air hose is not
deposited on the window.
4 Put the purge air unit back into operation
→
p. 33, §4.10.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 55
Page 56

Maintenance
56 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 57

Clearing Malfunctions
GM32
8 Clearing Malfunctions
General malfunctions
Malfunction messages
Screen messages (for “Pro” variant)
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 57
Page 58

Clearing Malfunctions
8.1
General hazard caused by electrical voltage
CAUTION: General hazards caused by electrical voltage
b
If it is necessary to open the device for adjustment or repair: Disconnect
the device from all power sources before starting work.
b
If the open device must be live during work: This work has to be performed
by skilled persons who are familiar with potential hazards. If it is necessary
to remove or open internal components, live parts could be exposed.
b
If liquids have penetrated electrical components: Take the device out of
operation and disconnect the mains voltage externally (e.g. disconnect the
mains cable). Then contact service technicians of the manufacturer or correspondingly trained skilled persons to have the device repaired.
b
If hazard-free operation of the device is no longer possible: Take the device
out of operation and secure against unauthorized start-up.
b
Do not disconnect the protective conductor connections inside or outside
the device.
IMPORTANT: Damage by voltage
Before signal connections are established (also with plug connections):
b
Disconnect the GM32 and any connected devices from the electrical supply.
Otherwise the internal electronics can be damaged.
8.2 Measured value blinks
If a measured value blinks: Measured value is “uncertain” (e.g. calibration range
exceeded).
For GMP probe: When all measured values blink: Is the lever for the diaphragm in the
“open” position (
→
p. 35, §4.12)?
58 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 59

Clearing Malfunctions
Status (→p. 41)
Message number/
number of messages
Date (dd/mm)
Time (hh:mm:ss)
Initiator (footnote
→
p. 63)
Error message (
→
§ 8.3.2)
8.3
8.3.1 Example of an error message
Figure 26 Example of an error message
Error messages
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 59
Page 60

8.3.2 Error messages
Initiator1Tex t Classifi-
Description Possible clearance
cation
System EEPROM Failure EEPROM parameters corrupted or not com-
patible after software upgrade.
Spectro com. Communication fault with spectrometer. Error in I2C connection with spectrometer. Check
Zero com. Communication fault with zero point reflec-
tor.
Temp control
com.
Communication fault with temperature control unit.
Visor com. Communication fault with visor module. Error in I2C connection with visor module. Check
Filter com. Communication fault with control filter ele-
ment.
Mirror com. Communication fault with mirror tracking. Error in I2C connection with mirror tracking.
Lamp com. Communication fault with lamp electronics. Error in I2C connection with lamp electronics.
Visor fault Error of visor signals. Signal distorted or
zero.
Visor values Visor signals outside the valid range. Hardware defect. Electronics not adjustable
Visor no signal All 4Q signals below threshold parameter. Check alignment, reflector, contamination.
Lamp fault Lamp does not go on. Lamp is defective. Replace the lamp (
Mirror adj. End Mirror tracking has reached maximum posi-
tion.
Zero adj. mc adj. Beam tracking during adjustment not possi-
ble.
Spectro para. No correct parameters saved in spectrome-
ter.
Purge air signal Digital input signals purge air error. Check the purge air supply (
Temp control out
of range
Temperature regulation measurement out-
side the valid range.
Extinction calc Error in extinction calculation. Please contact SICK Customer Service.
Reference calc Error in reference calculation.
IIR Filter Error during IIR filtering.
Interpolation Error in interpolation calculation.
Eval modul com. Error in communication with software evalu-
ation module.
File conditions Error during condition file access.
File espec Error during extinction file access.
File cact Error during lambda coefficient file access.
File measval Error during measured value file access.
Clearing Malfunctions
2
Software upgrade: Reset parameters.
Load saved parameters.
Defect: Reload backup.
Replace hardware, if possible.
plug connector or hardware defect.
Error in I2C connection with zero point reflector.
Check plug connector or hardware defect.
Error in I2C connection.
Check plug connector or hardware defect.
plug connector or hardware defect.
Error in I2C connection with control filter element.
Check plug connector or hardware defect.
Check plug connector or hardware defect.
Check plug connector or hardware defect.
Check signals and parameters.
(amplification too high).
→
p. 53,
§7.5).
Check alignment (
Check alignment (
→
p. 41, §5.2.5.2).
→
p. 41, §5.2.5.2).
Please contact SICK Customer Service.
→
p. 55, §7.7).
Excess temperature switch-off active for temperatures > 70 °C. Switches back on automatically
when < 65 °C.
60 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 61

Clearing Malfunctions
Initiator1Text Classifi-
cation
System Lamp perfor-
mance
Maintenance
Lamp performance limit
Lamp minimum During lamp adjustment, an excess signal
Lamp 4Q max The lamp current must be set to 1000 mA
Flashcard missing
IO com. Communication fault to IO block. Connection interrupted, check the cable.
Spectro no
answer
Cycle span drift The measurement on the control filters
Cycle zero drift The zero point measurement of a measured
Cycle wavelength drift
Cycle peak position
Cycle peak width The check of the peak width of the NO cell
Cycle cell empty During the check of the NO cell it is deter-
Temp control
voltage low
Temp control
lamp fan
Temp control
optic fan
Temp control
spectro fan
Temp control
electronic temp
Temp control
spectro temp
Data logging:
writing data
Data logging:
open file
Description Possible clearance
Warning for lamp performance
Prepare to exchange the lamp (→ p. 53, §7.5).
2
Lamp performance < 20 %
→
Lamp performance too low Replace the lamp (
p. 53, §7.5).
Check the parameter settings.
was determined with minimum lamp current
and exposure.
(stop) in the alignment procedure.
Alignment, check the optics (
Possible lamp change (
→
p. 41, §5.2.5.2).
→
p. 53, §7.5) or correct
parameter settings.
No Flashcard found. Insert the Flashcard, replace a possibly defective
card.
Defective CAN-bus interface.
No data received from spectrometer. Malfunction on the interface to the spectrometer.
Check the plug.
The reference from the adjustment is not correct.
showed an excess deviation.
Check limit value parameter setting.
Check limit value parameter setting.
value showed an excess deviation.
The check of the current Lambda_C0 coeffi-
Check limit value parameter setting.
cient showed an excess deviation.
The check of the position of the peak of the
NO cell showed an excess deviation.
Check limit value parameter setting. Defective NO
cell.
Check limit value parameter setting. Defective NO
showed an excess deviation.
cell.
Cell is empty.
mined that the highest measured extinction
value in the evaluation range is smaller than
0.1.
The measured voltage supply value is too
Malfunction of temperature control unit.
small (< 20 V).
The lamp fan has a malfunction. Malfunction of the temperature control unit or fan
or cabling.
The fan of the optic carrier has a malfunc-
tion.
The fan of the spectrometer has a malfunc-
tion.
The temperature of the temperature control
Malfunction of the temperature control unit or fan
or cabling.
Malfunction of the temperature control unit or fan
or cabling.
Malfunction of temperature control unit.
electronics exceeds 100 °C.
SR-unit is too warm or too cold. In the heating phase: Normal.
When running: Check ambient temperature.
Error when writing logging data to the Flash-
Flashcard memory full, Flashcard defective.
card.
Error when opening a file for logging data on
Flashcard memory full, Flashcard defective.
the Flashcard.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 61
Page 62

Clearing Malfunctions
Initiator1Tex t Classifi-
Description Possible clearance
cation
Probe EL. too hot Mainte-
nance
Electronics too hot. Ambient temperature
too high?
Air purge low The volume flow is below the set limit. Check the purge air supply.
Filter watch Flow monitor. Check the purge air supply.
p no signal No signal from pressure sensor. Check the purge air supply.
p out of range Sample gas pressure < 500 or > 1200 hPa
(mbar).
t air no signal Broken sensor. Please contact SICK Customer Service.
[t] no signal Broken sensor.
EEPROM defect EEPROM defective.
Heat no signal Heater fault
Heater < 1.5 A
Heater defect
Heating too low
System Systemstart Xtended This message is entered during each system
start.
System Zero adjust The start of an adjustment is recorded in the
logbook.
System Boxmeasuring The start of filter box measurement is
recorded in the logbook.
P Substitute value Mainte-
nance
T Substitute value Mainte-
nance
Calculation is made with a substitute value
because of a pressure measurement error.
Calculation is made with a substitute value
because of a temperature measurement
error.
2
Allow the device to cool down.
---
Shows when the last system start was made.
Shows when the last adjustment was made.
Shows when the last filter box measurement was
made.
The set input (probe, analog input, SCU) shows
errors and the substitute value is therefore used
for calculation.
The set input (probe, analog input, SCU) of pressure measurement shows errors and the substitute value is therefore used for calculation.
62 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 63

Clearing Malfunctions
Initiator1Text Classifi-
Description Possible clearance
2
cation
Gas component
Bad Config.
(text)
Failure Error in calculation models. Please contact SICK Customer Service.
File I/O (text) Error in the file system. Restart the system.
If the error continues to exist:
Please contact SICK Customer Service.
Measurement
Xtended Current measuring range x ( x = 1 .. 8). ---
range x
Measurement
value out of
Uncertain
Measured value outside calibration range. Check measured values for plausibility.
range
Measurement
value range
Xtended Measurement beyond a warning threshold
defined during calibration.
warning
Medium pres-
sure out of range
Medium pres-
sure warning
Medium temper-
ature out of
Uncertain
Sample gas pressure outside calibrated
range.
Xtended Sample gas pressure beyond warning
threshold.
Uncertain
Sample gas temperature outside calibrated
range.
Check the sample gas pressure.
Check the sample gas temperature.
range.
Medium temper-
ature warning
Absorption
range warning
Absorption out
of range
Xtended Sample gas temperature beyond warning
threshold.
Xtended Absorption in active measuring path above
warning threshold.
Standard setting of warning threshold: 1.8
extinction units.
Failure Absorption in active measuring path too
high.
Check:
- Window dirty (
→
p. 52, §7.4)
- Dust content in sample gas too high?
- Sample gas concentration too high?
Standard setting of error threshold: 2 extinc-
tion units.
Syntax error Error in concentration calculation. Please contact SICK Customer Service.
Processing error
Numerical
Numerical error in concentration calculation.
(DivZero)
Numerical
(IppError)
Numerical
(MatSing)
OS error (text) Error in operating system. Restart the system.
If the error continues to exist:
Please contact SICK Customer Service.
Spectr. resolu-
Resolution of spectrometer wrong. Please contact SICK Customer Service.
tion out of range
Spectral evaluation
1
System = SR-unit
Probe = probe
P = pressure sensor
T = temperature sensor
Gas component
2
This Table also contains recommended solutions that can only be performed by specially trained personnel.
Uncertain
Error in calculation of spectra.
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 63
Page 64

Clearing Malfunctions
8.4
Inadequate purge air supply (for GMP probe)
IMPORTANT: Inadequate purge air supply can damage the measuring system.
b
If there are signs of incorrect purge air supply, immediately perform the
measures listed below.
Indications of inadequate purge air supply
● Unusual noise from the area of the purge air unit.
● On systems with pressure difference sensor: An appropriate error message occurs.
● Rise of housing temperature.
● Unusually rapid contamination of the window of the GM32.
Check the purge air unit
b
Remove the purge air hose on the SR-unit: A strong air flow must be noticeable.
b
Reinstall the purge air hose immediately.
Measures if purge air supply is inadequate
b
If the purge air unit is not immediately functional: Remove the SR-unit from the gas duct
(swiveling out is sufficient for short malfunctions).
b
Immediately restore correct operation of the purge air unit or replace provisionally by a
different purge air supply with at least the same purge air throughput.
Information for fast correction of faults
● Air filter of purge air unit clogged?
● Purge air hose slipped off or broken?
● Power supply of purge air unit failed?
8.5 Malfunctions on the connection unit
A green LED lights on each power supply unit in the connection unit.
If no LED lights: Check the voltage supply of the connection unit.
Otherwise, please contact SICK Customer Service.
64 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 65

Specifications
GM32
9 Specifications
Declaration of conformity
Approvals
Technical Data
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 65
Page 66

Specifications
9.1
Conformities
The technical design of this instrument complies with the following EC
directives and EN standards:
● EU Directive NSP 2006/95/EC
● EU Directive EMC 2004/108/EC
Applied EN standards:
● EN 61010-1, Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control
and laboratory use
● EN 61326, Electrical equipment for measurement technology, control technology and
laboratory use - EMC requirements
● EN 14181, Calibration of continuously operating emission measuring devices
● EN 15267-3: Certification of automated measuring systems - Part 3
9.1.1 Electrical protection
● Insulation: Class of protection 1 according to EN 61010-1.
● Insulation coordination: Measuring category II according to EN61010-1.
● Contamination: The control unit operates safely in an environment up to contamination
level 2 according to EN 61010-1 (usual, non-conductive soiling and temporary conductivity by occasional moisture condensation).
● Electrical power: The wiring system to the voltage supply of the system must be
installed and fused according to the relevant regulations.
66 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 67

Specifications
9.2
Technical data
Tec hnic al Da ta GM32
Measuring Parameters
Measuring principle Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (DOAS)
Measured components SO
Available measuring ranges
, NO, NO2, NH3
2
thereof TÜV-tested for suitability: SO
, NO
2
Min. Max. TÜV tested for suitabil-
(calibration ranges)
SO
: 0 … 40 mg/m
2
NO: 0 … 50 mg/m
NO2: 0 … 100 mg/m
NH3: 0 … 25 mg/m
3
Operation
3
Operation
3
Operation
3
Operation
•m 0 … 20.000 mg/m
•m 0 … 2.500 mg/m
•m 0 … 2.000 mg/m
•m 0 … 50 mg/m
3
3
Operation
3
Operation
3
Operation
Operation
•m 0 … 70 mg/m
•m –
•m –
Measuring distance Active measuring path L3 →p. 70, Fig. 28 and →p. 71, Fig. 29
Measurement uncertainty
System response time t
90
● ±2 % with SO
● ±5 % with NO
● GMP measuring probe: adjustable ≥5 s; TÜV tested for suitability: adjustable >30 s
● GPP measuring probe: ≥120 s
, NO, NH3
2
2
Measuring Conditions
Measuring temperature
≤ 500 °C; higher temperatures on request
Process pressure ±60 hPa (relative)
Ambient Conditions
Ambient temperature –20 ... +55 °C; temperature change max. 10 K/h
Storage temperature –20 ... +55 °C
Rel. humidity max. 96 % rF
Moisture condensation Moisture condensation on optical interfaces not allowed
Approvals
Compliances for SO
components
and NO
2
● TÜV-tested for continuous emission control according EC regulations
(2001/80/EC, 2000/76/EC)
● EN 15267-3, EN 14181 and DIN ISO 14956
Electrical safety CE
Protection class IP 65, IP 69K
Shock & vibration According to EN 61010-1
Input/Output Signals, Interface Modules can be selected and extended as required
Analog outputs (option) 2 outputs
1
: 0/4 ... 22 mA, load max. 500 Ω; electrically isolated; max. power dissipa-
tion (for 24 V): 1.10 W; max. 16 outputs
1)
Analog inputs (option) 2 inputs
: 0/4 ... 22 mA, input resistance max. 100 Ω;
max. power dissipation (for 24 V): 0.25 W
Digital outputs (option) 4 outputs
1)
(max. 8): 48 V AC/DC, make-contact, 1.0 W (for 24 V); 0.5 A max. switch-
ing current, max. switching capacity (for 24 W): 25 VA; max. 8 outputs
1)
Digital inputs (option) 4 inputs
Interfaces
Bus protocol
Power supply
● Ethernet
● Extendable via optional SCU operating unit
● OPC
● TCP/IP via Ethernet
● 100 ... 250 V AC, 50/60 Hz; 260 VA max. power input
● Purge air unit SLV4, see Operating Instructions Separate power supply of GPP probe: 115/
: approx. 3.9 V at open contact, <4.5 mA with closed contact, 0.55 W
230 V AC; 50/60 Hz, max. 150 VA power input
ity at T = 140 °C and
active measuring path
= 1.25 m
•m 0 … 75 mg/m
3
Standard
3
Standard
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 67
Page 68

Techni cal Dat a GM32
General information
System components
● Sender/receiver unit
● Measuring probe with purge air fixture
– Type GMP with open measuring aperture or
– Type GPP, gas diffusion probe
● Flange (option)
● Purge air unit with GMP probe: See Operating Instructions SLV4
● Connction unit
● SCU operating unit: See Operating Instructions SCU
Dimensions (L x W x H)
(see Dimensions)
Weight
● Sender/receiver unit (including purge air fixture): 586 x 315 x 580 mm
● Measuring probes: See
● Connection unit: 450 x 400 mm,
● Purge air unit SLV4: 550 x 550 x 270 mm; see Operating Instructions SLV4
● Sender/receiver unit: approx. 20 kg
● Purge air attachment: 7 kg
● Connection unit: 16 kg
● Measuring probes
– GMP: 25 kg max.
– GPP: 45 kg max.
● Purge air unit: 14 kg; see Operating Instructions SLV4
Control function
1
per module
● Internal zero point control, contamination correction
● Check cycle for zero and reference point, equivalent to QAL3 (option)
→
p. 70, Fig. 28, →p. 71, Fig. 29
→
p. 72, Fig. 31
Specifications
For more information and technical information on the GM32 system and its components, see the following documents:
● Data Sheet GM32, Cross-Duct Version, Part No. 8012710
● Operating Instructions GM32, Cross-Duct Version, Part No. 8012704
● Operating Instructions GM32, Measuring Probe Version, Part No. 8012707
● Technical Information GM32, Cross-Duct Version, Part No. 8011085
● Technical Information GM32, Measuring Probe Version, Part No. 8011513
● Operating Instructions Purge Air Unit SLV4, Part No. 8008088
● Operating Unit SCU: See Operating Instructions SCU, Part No. 8011910
● Technical Information Modular I/O System, Part No. 8011913
68 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 69

Specifications
The housing of the sender/receiver unit can be swiveled
open to the left or right of the device flange
(max. 180°/105°).
Dimensions
Figure 27 GM32 sender/receiver unit
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 69
Page 70

Figure 28 GM32 measuring probe, type GMP – open measuring probe
Specifications
70 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 71

Specifications
ø 240
ø 178
ø 125
ø 133
14
240/500
8
18
4
5°
200
Fig. 29 GM32 measuring probe, type GPP – gas diffusion probe
Figure 30 Mounting flange
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 71
Page 72

Figure 31 Connection unit
Specifications
72 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 73

Stichwörter
Index
A
Additional documentation (information) . . . . . . . . . . 9
Alignment
-Automatic
-Manual
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
B
Buttons, assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
C
Check cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2, 12 - 13, 43
Check point
Cleaning the window
Compliance
Connection diagram
Contrast
CUSUM
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2, 12 - 13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 - 23
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2, 12
D
Designated users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Diagnosis (menu)
Disassembly
Disposal
Drying agent cartridges
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
E
Earth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Earthing cable
Error
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Error messages
Expendable parts
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
F
Failure (Status) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Flange attachment
Fuses (probe)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
G
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
GMP probe
GMP-Lanze
GPP probe
- Electric connection
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
I
Important Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Information concerning the Manual
Information Symbols
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Intended use
- Designated users
-Users (target group)
IR module, replacing
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
L
Lamp, replacing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Language
LEDs
Locking device lever
Logbook
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12, 40
M
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Maintenance mode active (message)
Maintenance plan
Maintenance request (Status)
Malfunctions, clearing
Measuring method
Measuring probe
Measuring probe, aligning
Menu tree
Mirror tracking
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
. . . . . . . . . . . 44
N
National language . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
O
OPC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2, 12
Operation
Operator panel
Optical alignment
-Automatic
-Manual
-SR-unit
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
P
Probe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
-GMP
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
-GPP
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Probe heater - electric connection
Probe, aligning
Product Description
Product identification
Purge air fixture
Purge air unit
Putting out of operation
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15, 55
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 - 46
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Q
QAL3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2, 12, 14
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 73
Page 74

R
Reference cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2, 12 - 13, 43
Removing the transport safety device
Responsibility of user
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . . . . . . 27
S
Scope of delivery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
SCU
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2, 12
Sender lamp, replacing
Signal words
SOPAS-ET
Specifications
Start-up
Status indicators
Status messages
Switching on
Symbols (Explanation)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2, 13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39, 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
T
Target groups (users) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Type plate
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Index
U
Uncertain (Status) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
User
- Designated users
- Responsibility of user
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
V
Visual inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
W
Warning symbols, warning levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Wearing parts
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Z
Zero point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
74 GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH
Page 75

Index
GM32 Operating Instructions V1.3 8012707 © SICK MAIHAK GmbH 75
Page 76

GM32
SICK worldwide
You will find our local subsidiary
or agency at:
www.sick.com
8012707/2009-03 (V1.3)
Your local sales and service partner
SICK MAIHAK GmbH | Germany
Nimburger Str. 11 | 79276 Reute | www.sick.com
Phone +49 7641 469-0 | Fax +49 7641 469-11 49 | info.pa@sick.de
 Loading...
Loading...