Page 1

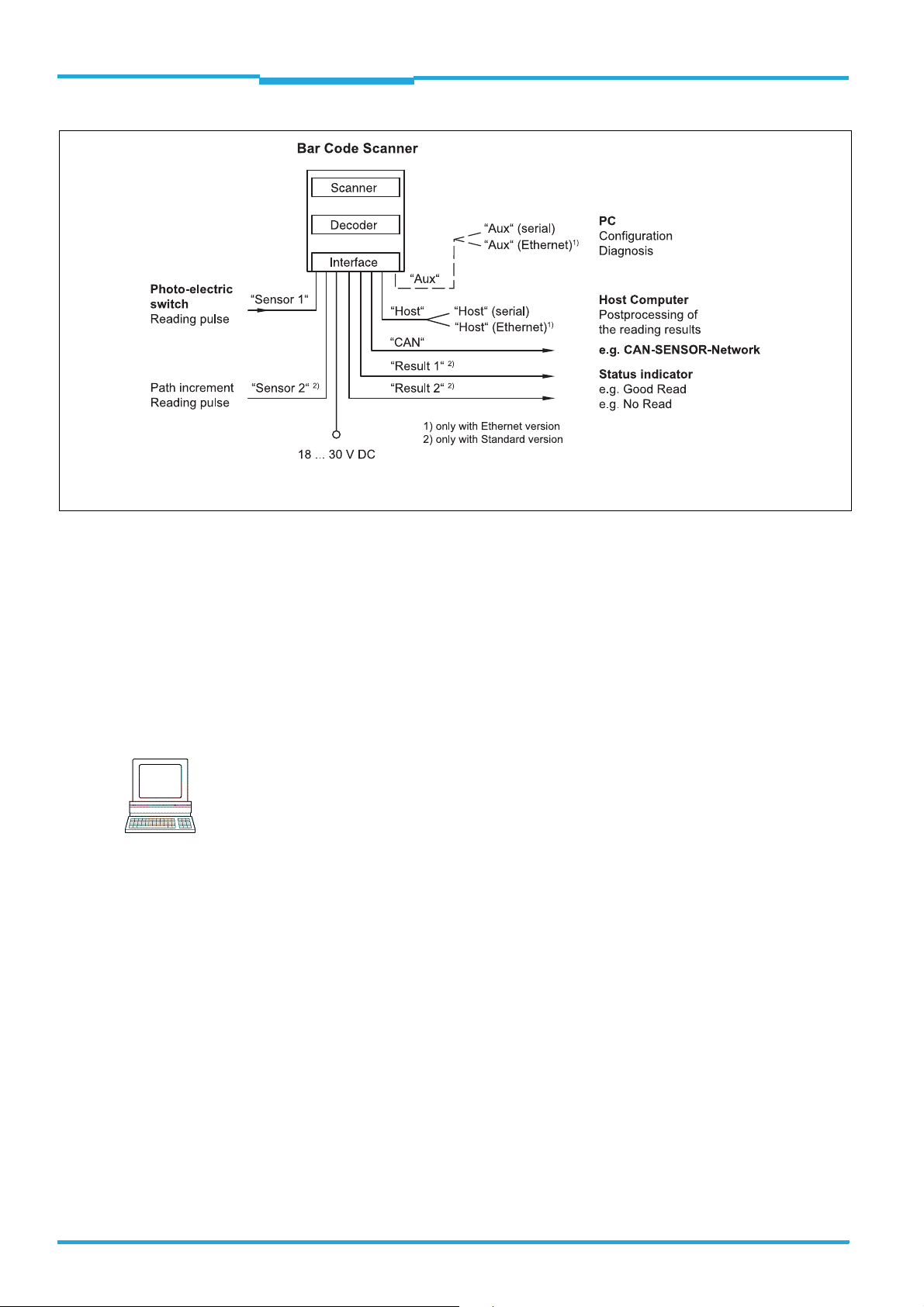
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
CLV640
Bar Code Scanner
Advanced Line
Operating Instructions
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Page 2
Software Versions
Operating Instructions
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Software Versions
Software/Tool Function Version
CLV640 Bar Code
Scanner
Device Description
CLV640
SOPAS-ET Configuration software From v 2.16
SICK firmware From v 1.0 0000
Device-specific software module for SOPAS-ET configuration software
From v 2.5
Copyright
Copyright © 2008
SICK AG Waldkirch
Auto Ident, Reute Plant
Nimburger Strasse 11
79276 Reute
Germany
Trademark
Windows 2000
TM
, XPTM, VistaTM and Internet ExplorerTM are registered trademarks or trade-
marks of the Microsoft Corporation in the USA and other countries.
Acrobat
TM
ReaderTM is a trademark of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Latest manual version
For the latest version of this manual (PDF), see www.sick.com.
2 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 3

Operating Instructions
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Contents
Table of contents
Figures and Tables............................................................................................................ 5
Abbreviations..................................................................................................... 5
Tables................................................................................................................. 6
Figures ............................................................................................................... 7
1 Notes on this document.................................................................................................11
1.1 Purpose............................................................................................................11
1.2 Target group ....................................................................................................11
1.3 Depth of information.......................................................................................11
1.4 Used symbols ..................................................................................................12
2 Safety information ..........................................................................................................13
2.1 Authorised users .............................................................................................13
2.2 Intended use ...................................................................................................14
2.3 General safety precautions and protection measures.................................14
2.4 Quick stop and quick restart ..........................................................................17
2.5 Environmental information.............................................................................18
3 Quick-Start .......................................................................................................................19
3.1 Preparing the bar code scanner for the quick start......................................19
3.2 Establishing connection with the bar code scanner.....................................19
3.3 Performing the reading...................................................................................20
4 Product description......................................................................................................... 23
4.1 Setting up the bar code scanner....................................................................23
4.2 Included in delivery .........................................................................................26
4.3 Device versions ...............................................................................................27
4.4 System requirements......................................................................................27
4.5 Product features and functions (overview) ...................................................28
4.6 Bar code scanner methods of operation.......................................................29
4.7 Indicators and control elements ....................................................................36
5 Installation .......................................................................................................................41
5.1 Overview of installation sequences ...............................................................41
5.2 Installation preparations ................................................................................41
5.3 Installation location ........................................................................................43
5.4 Installation of the bar code scanner..............................................................48
5.5 Installing external components......................................................................49
5.6 Removing the bar code scanner ....................................................................50
6 Electrical installation ......................................................................................................51
6.1 Overview of installation sequence.................................................................51
6.2 Electrical installation preparation..................................................................51
6.3 Electrical connections and cables .................................................................52
6.4 Performing electrical installation ...................................................................56
6.5 Pin assignment and wire colour assignment of the assembled cables......62
7 Startup and configuration.............................................................................................. 65
7.1 Overview of the startup procedure ................................................................65
7.2 SOPAS-ET configuration software ..................................................................65
7.3 Establish communication with the bar code scanner ..................................66
7.4 First startup .....................................................................................................68
7.5 Default setting.................................................................................................70
7.6 Adjusting the bar code scanner .....................................................................71
8 Maintenance ....................................................................................................................73
8.1 Maintenance during operation.......................................................................73
8.2 Cleaning the bar code scanner ......................................................................73
8.3 Cleaning further optical effective surfaces ...................................................76
8.4 Checking the incremental encoder................................................................76
8.5 Replacing a bar code scanner........................................................................76
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 3
Page 4
Contents
9 Troubleshooting .............................................................................................................. 79
9.1 Overview of errors and malfunctions which could occur ............................. 79
9.2 Detailed malfunction analysis ....................................................................... 79
9.3 Status protocol................................................................................................ 80
9.4 SICK Support................................................................................................... 80
10 Technical data................................................................................................................. 81
10.1 Datenblatt Barcodescanner CLV640 (Linien-/Rasterscanner) ................... 81
10.2 Data sheet for the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner (line scanner with oscillating mirror)83
10.3 Specification diagrams................................................................................... 84
10.4 CLV640 Bar Code Scanner dimensional drawings ....................................102
11 Appendix ........................................................................................................................109
11.1 Appendix overview........................................................................................ 109
11.2 Configuring the bar code scanner with command strings .........................109
11.3 Calculating the code length of a bar code ..................................................110
11.4 Ordering information for bar code scanner and accessories....................111
11.5 Dimensional drawing accessories...............................................................117
11.6 Supplementary documentation ................................................................... 121
11.7 Glossary......................................................................................................... 122
11.8 EC Declaration of Conformity.......................................................................130
11.9 Code samples of bar codes (selection).......................................................131
Operating Instructions
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
4 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 5

Operating Instructions Chapter
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Figures and Tables
Figures and Tables
Abbreviations
CAN Controlled Area Network (field bus protocol based on the CAN bus)
CDB Connection Device Basic
CDM Connection Device Modular
CLV Code-Leser V-Prinzip
CMC Connection Module Cloning
CMD Connection Module Device
CMF Connection Module Fieldbus
CMP Connection Module Power
DOF Depth Of Field
HTML Hyper Text Markup Language
IInput
LED Light Emitting Diode
MAC Medium Access Control
MTBF Mean Time Between Failure
MTTR Mean Time To Repair
OOutput
PROM Programable Read Only M
RAM Random Acces Memory
ROM Read Only Memory
RTF Rich Text Format (standardised document format with format description)
SD Secure Digital
SMART SICK Modular Advanced Recognition Technology
SOPAS-ET SICK Open Portal for Application and Systems Engineering Tool (PC software for Windows for con-
figuring the bar code scanner)
PLC Programmable Logic Controller
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
emory.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5
Page 6

Chapter Operating Instructions
Figures and Tables
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Tables
Tab. 1-1: Target group ..................................................................................................... 11
Tab. 2-1: Required qualification for starting up the bar code scanner ........................ 13
Tab. 2-2: Laser Data of CLV640 ..................................................................................... 16
Tab. 4-1: CLV640 Bar Code Scanner delivery ................................................................ 26
Tab. 4-2: Variants of the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner .................................................... 27
Tab. 4-3: Overview of the bar code scanner's product features and functions ........... 29
Tab. 4-4: Data interface function .................................................................................... 35
Tab. 4-5: LED indications ................................................................................................. 37
Tab. 4-6: Meaning of the LEDs during activation of buttons ......................................... 38
Tab. 5-1: Permitted reading angles between the scanning line and bar code ............ 45
Tab. 6-1: Electrical connections to the bar code scanner with a fixed cable and
connector (standard version) .......................................................................... 53
Tab. 6-2: Electrical connections to the bar code scanner with connector unit
(Ethernet version) ............................................................................................ 53
Tab. 6-3: Standard version: Pin assignment of the 15-pole D-Sub-HD cable
connector .......................................................................................................... 54
Tab. 6-4: Ethernet version: Pin assignment of the 4-pole M12 socket ....................... 54
Tab. 6-5: Ethernet version: Pin assignment on the 12-pole M12 plug ........................ 55
Tab. 6-6: Recommended maximum cable lengths, depending on the selected
data transfer rate ............................................................................................. 57
Tab. 6-7: Ratings for the switching inputs ..................................................................... 60
Tab. 6-8: Ratings for the switching outputs ................................................................... 61
Tab. 6-9: Pin assignment of the 4-pole M12 plug and the 6-pole RJ45 plug .............. 62
Tab. 6-10: Pin assignment of the 12-pole M12 socket and the 15-pole
D-Sub-HD plug .................................................................................................. 62
Tab. 6-11: Pin assignment of the 12-pole M12 socket and wire colours at the
open end ........................................................................................................... 63
Tab. 6-12: Pin assignment of the 5-pole M12 plug and wire colours at the
open end ........................................................................................................... 63
Tab. 6-13: Pin assignment of the 15-pole D-Sub-HD socket and wire colours
at the open cable end ...................................................................................... 64
Tab. 7-1: Default setting for the SOPAS-ET configuration software (excerpt) ............. 66
Tab. 7-2: Connection between the PC with SOPAS-ET configuration software
and the bar code scanner ............................................................................... 66
Tab. 10-1: Technical specifications for the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
(line/raster scanner)......................................................................................... 82
Tab. 10-2: Technical specifications for the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
(line scanner with oscillating mirror) ............................................................... 83
Tab. 10-3: Reading conditions for all specification diagrams ........................................ 84
Tab. 11-1: Help table for calculating the code length of a bar code.............................110
Tab. 11-2: Variants of the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner ..................................................111
Tab. 11-3: In stock accessories: Installation accessories..............................................111
Tab. 11-4: In stock accessories: Connection modules...................................................112
Tab. 11-5: In stock accessories: Extensions for connection modules ..........................114
Tab. 11-6: In stock accessories: Separate field bus modules....................................... 114
Tab. 11-7: In stock accessories: Cables and connectors for the standard
version of the bar code scanner .................................................................... 115
Tab. 11-8: In stock accessories: Cables and connectors for the Ethernet
version of the bar code scanner ...................................................................115
Tab. 11-9: In stock accessories: General cables and connectors for
bar code scanner ............................................................................................116
Tab. 11-10: In stock accessories: Memory media for CLV640 Bar Code Scanner ........117
Tab. 11-11: Supplementary documentation .....................................................................121
6 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 7

Operating Instructions Chapter
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Figures and Tables
Figures
Fig. 2-1: Outlet opening of the laser radiation at the reading window
(shown here: Ethernet version)........................................................................ 15
Fig. 2-2: Laser warning sign attached to the bar code scanner at delivery ................ 16
Fig. 3-1: Register tab Quickstart ....................................................................................20
Fig. 4-1: Housing types of the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner ........................................... 24
Fig. 4-2: Device view of the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
(shown here: Ethernet-Version)........................................................................ 25
Fig. 4-3: Bar code scanner's methods of operation in a conveyor system
(schematic)........................................................................................................ 30
Fig. 4-4: Switching the focus for CLV640: Division of the entire reading
area in distance configurations .................................................................... 31
Fig. 4-5: CLV640 Oscillating Mirror: Example of focal position control in
search run, here with 6 focus positions ......................................................... 32
Fig. 4-6: Reading operation mode for the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner in
stand-alone operation ..................................................................................... 34
Fig. 4-7: Micro SD memory card for storing the parameter set.................................... 40
Fig. 5-1: Example: Fixing the bar code scanner with the bracket no. 2042800 ........ 42
Fig. 5-2: Exchanging the laser warning sign ................................................................. 43
Fig. 5-3: Allocation of the scanning line(s) for the bar code and conveyor system .... 44
Fig. 5-4: Definition of the reading distance a and the aperture angle α ..................... 44
Fig. 5-5: Line scanner: Reading angles that occurs between the scanning line
and bar code ....................................................................................................45
Fig. 5-6: Avoiding surface reflection using the line scanner as an example:
Angle between emitting light and bar code
(tilted away from the plumb line) ..................................................................... 46
Fig. 5-7: Counting direction of the reading angle RA within the scanning l
ine and of the code angle CW with the oscillating mirror .............................. 47
Fig. 5-8: Line scanner: Installation example for positioning the external
reading pulse sensor ....................................................................................... 49
Fig. 6-1: Standard version: Electrical connections at the bar code scanner
with connection cable....................................................................................... 52
Fig. 6-2: Ethernet version: Electrical connections at the bar code scanner
with connector unit ........................................................................................... 52
Fig. 6-3: Direction of rotation of the connector unit .....................................................56
Fig. 6-4: Wiring the serial host data interfaces (RS-232 or RS-422) on the
15-pole D-Sub-HD plug .................................................................................... 58
Fig. 6-5: Function of the Ethernet interface .................................................................. 59
Fig. 6-6: Wiring the “Sensor 1“ switching input on the 15-pole D-Sub-HD plug ......... 59
Fig. 6-7: Wiring the "Sensor 2" switching input on the 15-pole D-Sub-HD plug ......... 60
Fig. 6-8: Possible wiring of the "Result 1" switching output on the 15-pole
D-Sub-HD plug .................................................................................................. 61
Fig. 7-1: Configuration with SOPAS-ET and storage the parameter set....................... 68
Fig. 8-1: Cleaning the reading window........................................................................... 75
Fig. 8-2: Cleaning of the external optical sensors (reading pulse generator) ............ 76
Fig. 10-1: Meaning of selection
elated to depth of focus diagram.....................................................................84
Fig. 10-2: Line scanner/raster scanner with front reading window: min. and
max. reading distance depending on the focus position and the aperture
angle with a resolution of 0.2 mm (8 mil)....................................................... 85
Fig. 10-3: Line scanner/raster scanner with front reading window: min. and max.
reading distance depending on the focus position and the aperture
angle with a resolution of 0.25 mm (10 mil) .................................................. 86
Fig. 10-4: Line scanner/raster scanner with front reading window: min. and max.
reading distance depending on the focus position and the aperture
angle with a resolution of 0.35 mm (14 mil) .................................................. 87
1, 2 and 3 in the reading area diagram r
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 7
Page 8

Chapter Operating Instructions
Figures and Tables
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Fig. 10-5: Line scanner/raster scanner with front reading window: min. and max.
reading distance depending on the focus position and the aperture
angle with a resolution of 0.5 mm (20 mil)..................................................... 88
Fig. 10-6: Line scanner/raster scanner with front reading window: min. and
max. reading distance depending on the focus position and the
aperture angle with a resolution of 1.0 mm (40 mil) ..................................... 89
Fig. 10-7: Line scanner/raster scanner with side reading window: min. and
max. reading distance depending on the focus position and the
aperture angle with a resolution of 0.2 mm (8 mil)........................................ 90
Fig. 10-8: Line scanner/raster scanner with side reading window: min. and
max. reading distance depending on the focus position and the
aperture angle with a resolution of 0.25 mm (10 mil)................................... 91
Fig. 10-9: Line scanner/raster scanner with side reading window: min. and
max. reading distance depending on the focus position and the
aperture angle with a resolution of 0.35 mm (14 mil)................................... 92
Fig. 10-10: Line scanner/raster scanner with side reading window: min. and
max. reading distance depending on the focus position and the
aperture angle with a resolution of 0.5 mm (20 mil) ..................................... 93
Fig. 10-11: Line scanner/raster scanner with side reading window: min. and max.
reading distance depending on the focus position and the aperture
angle with a resolution of 1.0 mm (40 mil)..................................................... 94
Fig. 10-12: Line scanner with oscillating mirror (side reading window): min. and
max. reading distance depending on the focus position and the aperture
angle with a resolution of 0.2 mm (8 mil)....................................................... 95
Fig. 10-13: Line scanner with oscillating mirror (side reading window): min. and
max. reading distance depending on the focus position and the aperture
angle with a resolution of 0.25 mm (10 mil) .................................................. 96
Fig. 10-14: Line scanner with oscillating mirror (side reading window): min. and
max. reading distance depending on the focus position and the
aperture angle with a resolution of 0.35 mm (14 mil)................................... 97
Fig. 10-15: Line scanner with oscillating mirror (side reading window): min. and
max. reading distance depending on the focus position and the
aperture angle with a resolution of 0.5 mm (20 mil) ..................................... 98
Fig. 10-16: Line scanner with oscillating mirror (side reading window): min. and
max. reading distance depending on the focus position and the
aperture angle with a resolution of 1.0 mm (40 mil) ..................................... 99
Fig. 10-17: Deflection range depending on the reading distance, angle of
deflection and resolution with a focus position F = 280 mm (11 in).......... 100
Fig. 10-18: Deflection range depending on the reading distance, angle of
deflection and resolution with a focus position F = 215 mm (8 in) ............ 100
Fig. 10-19: Deflection range depending on the reading distance, angle of
deflection and resolution with a focus position F = 140 mm (5.5 in)......... 101
Fig. 10-20: Standard version: Dimensions of the bar code scanner with front
reading window (CLV640-0000 and CLV640-1000)....................................102
Fig. 10-21: Standard version: Dimensions of the bar code scanner with side
reading window (CLV640-2000 and CLV640-3000)....................................103
Fig. 10-22: Standard version: Dimensions of the bar code scanner with
oscilliating mirror (CLV640-6000) .................................................................104
Fig. 10-23: Ethernet version: Dimensions of the bar code scanner with
front reading window (CLV640-0120 and CLV640-1120)...........................105
Fig. 10-24: Ethernet version: Dimensions of the bar code scanner with side
reading window (CLV640-2120 and CLV640-3120)....................................106
Fig. 10-25: Ethernet version: Dimensions of the bar code scanner with
oscilliating mirror (CLV640-6120) .................................................................107
8 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 9

Operating Instructions Chapter
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Figures and Tables
Fig. 11-1: Dimensions of the fixing bracket no. 2020410 ...........................................117
Fig. 11-2: Dimensions of the quick release clamp no. 2025526 ...............................118
Fig. 11-3: Dimensions of the fixing bracket no. 2042800............................................119
Fig. 11-4: Dimensions of the round rod holder no. 2042801......................................120
Fig. 11-5: EC Declaration of Conformity for the bar code scanner
(page 1, scaled down version) ......................................................................130
Fig. 11-6: Code samples of bar codes of various module widths (print ratio 2:1) .....131
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 9
Page 10

Chapter Operating Instructions
Figures and Tables
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
10 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 11

Operating Instructions Chapter 1
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Notes on this document
1 Notes on this document
1.1 Purpose
This document provides instructions for technical staff on the installation and operation of
the bar code scanner series CLV640 with dynamic focus position in the following versions:
• Line scanner / raster scanner / line scanner with oscillating mirror
• With front / side reading window
• With cable and connector (standard version) / with connector unit (Ethernet version)
A summary of all device versions is shown in chapter 4.3 Device versions, page 27.
This document contains the following information:
• Installation
• Electrical installation
• Startup and configuration
• Maintenance
• Troubleshooting
• Replacing the bar code scanner
A step-by-step approach is taken for all tasks.
1.2 Target group
The target group of this document is persons assigned the following tasks:
Tasks Target group
Installation, electrical installation, maintenance,
replacing the device
Startup and configuration Trained staff, e.g. technicians or engineers
Operation of the conveyor system Qualified staff for start-up and operation of the
Tab. 1-1: Target group
Qualified staff, e.g. service technicians and factory electricians
conveyor system
1.3 Depth of information
This document contains all the required information for installation, electrical installation
and operation of the bar code scanner at the installation location. The factory default set-
ting (basic configuration) of the bar code scanner is prepared for the use as a stand-alone
device.
Configuration of the bar code scanner for the application-specific reading conditions and
operation is carried out using the SOPAS-ET configuration software on a Windows
SOPAS-ET configuration software contains an online help system to facilitate configuration.
TM
PC. The
Important Further information about the design of the bar code scanner as well as the bar code tech-
nology is available from SICK AG, Auto Ident division.
On the Internet at www.sick.com.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 11
Page 12

Chapter 1 Operating Instructions
Notes on this document
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
1.4 Used symbols
To gain easier access, some information in this documentation is emphasised as follows:
Notice!
¾ Indicates a potential risk of damage or impair on the functionality of the bar code scan-
ner or other devices.
Warning notice!
A warning notice indicates real or potential danger. This should protect you against accidents.
The safety symbol next to the warning notice indicates why there is a risk of accident, e.g.
due to electricity. The warning levels (DANGER, WARNING, CAUTION) indicate the seriousness of the risk.
¾ Carefully read and follow the warning notices!
Reference Italic script denotes a reference to further information.
Important This important note informs you about specific features.
Explanation An explanation provides background knowledge of technical nature.
Recommendation A recommendation helps you to carry out tasks correctly.
TIP A tip explains setting options in the SOPAS-ET configuration software.
P
ROJECT This type of script denotes a term in the user interface in the SOPAS-ET configuration soft-
ware.
A symbol indicates a button in the user interface of the SOPAS-ET configuration software.
There is a procedure which needs to be carried out. This symbol indicates operational instructions which only contain one operational step or operational steps in warning notices
which do not have to be followed in any particular order.
Operational instructions comprising several steps are denoted using consecutive numbers.
This symbol indicates a reference to other information in the glossary.
Note
This symbol denotes a section in which the operation steps with the SOPAS-ET configuration
software are described.
Important
This symbol indicates supplementary technical documentation.
12 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 13

Operating Instructions Chapter 2
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Safety information
2 Safety information
This chapter deals with your safety and operator safety in the operational area.
¾ Read this chapter carefully before using the bar code scanner.
2.1 Authorised users
For correct and safe functioning, the bar code scanner must be installed, operated and
maintained by sufficiently qualified staff.
Repairs to the bar code scanner should only be carried out by qualified and authorised
SICK AG service staff.
¾ The operating instructions should be made available to the end user.
¾ The end user should be briefed and urged to read the operating instructions by the
technicians.
The following qualifications are required for different activities:
Tasks Qualification
Installation, maintenance
Electrical installation, device
replacement
Startup, configuration
Operation of the device in
each operational area
• Practical technical training
• Knowledge of current health and safety regulations at the work-
place
• Practical electrical training
• Knowledge of current electrical safety regulations
• Knowledge of start-up and operation of the device in each opera-
tional area (e. g. conveyor system)
• Basic knowledge of the Windows
TM
operating system
• Basic knowledge of designing and setting up (addressing) Ethernet
connections for connecting the bar code system to the Ethernet
• Basic knowledge of working with an HTML browser (e. g. Internet
ExplorerTM) for using the online help
• Basic knowledge of data transfer
• Basic knowledge of bar code technology
• Knowledge of start-up and operation of the device in each opera-
tional area (e. g. conveyor system)
• Knowledge of the software and hardware environment in each op-
erational area (e. g. conveyor system)
Tab. 2-1: Required qualification for starting up the bar code scanner
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 13
Page 14

Chapter 2 Operating Instructions
Safety information
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
2.2 Intended use
The CLV640 Bar Code Scanner is an intelligent sensor for the automatic recognition and decoding of bar codes on objects e.g. in a conveyor system.
The intended use of the bar code system results from the following description of the function:
• In a reading station, the bar code scanner is installed in a holder, either on the side of
a conveyor system (side reading) or above it (reading from above).
• The bar code scanner transfers the reading data via the host interface to a superordinate host computer for further processing.
• The bar code scanner is configured/operated using the SOPAS-ET configuration software that runs on a standard client PC provided by the customer. Communication takes
place using RS-232 or Ethernet.
Important Any warranty claims against SICK AG shall be deemed invalid in the case changes to the bar
code scanner, such as opening the housing, this includes modifications during installation
and electrical installation or changes to the SICK software.
The bar code scanner is only to be operated in ambient air temperature limit.
2.3 General safety precautions and protection measures
¾ Read the general safety precautions thoroughly and observe them during all bar code
scanner activities. Also observe the warning notices above the operational instructions
of each chapter.
2.3.1 Electrical installation work
Risk of injuries due to electrical current!
The optional power supply module CMP400/CMP490 is connected to the power supply
(100 ... 250 V AC/50 ... 60 Hz) in connection module CDM420.
¾ Observe current safety regulations when working with electrical equipment.
Important Electrical installation should only be carried out by qualified staff.
Connect or release current linkages only under de-energised conditions.
Wire cross sections and their correct shields have to be selected and implemented according to valid engineering standards.
14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 15

Operating Instructions Chapter 2
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Safety information
2.3.2 Laser radiation of the bar code scanner
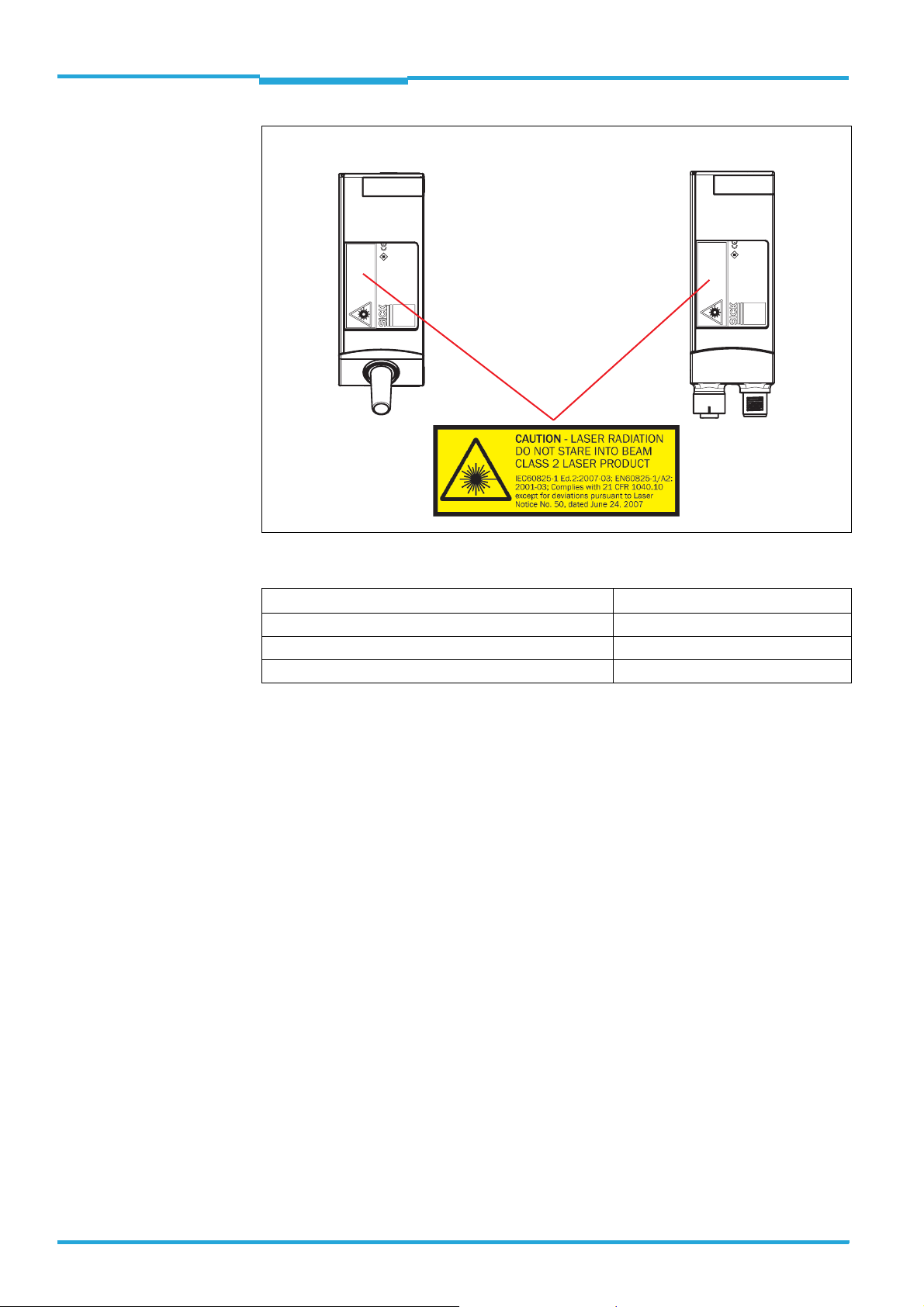
Fig. 2-1: Outlet opening of the laser radiation at the reading window (shown here: Ethernet version)
Damage to the eyes through laser radiation!
The bar code scanner operates with an red light laser of class 2. Looking at the laser's light path for a longer period of time can damage the eye's retina.
The entire reading window is the LED radiation outlet opening.
Caution - use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those
specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
¾ Never look directly into the light path (similar to sun light).
¾ Never direct the device's laser beam at the eyes of persons.
¾ When installing and aligning the bar code scanner, avoid laser beam reflections from
reflective surfaces.
¾ Do not open the housing. (Opening does not interrupt the activation of the laser diode
by the reading pulsing.)
¾ Always observe the latest valid version of laser protection regulations.
Important Bar code scanners in series CLV640 operate with a laser of wavelength λ = 655 nm (red
light). The radiation emitted is not harmful to human skin.
The product is classified in laser class 2 (laser class II) in accordance with EN 60825-1,
IEC 60825-1 and 21 CFR 1040.10 (see the warning sign on the device for the date of publication)
Maintenance is not required to ensure compliance with laser class 2.
The bar code scanner displays a black and yellow laser warning sign.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 15
Page 16
Chapter 2 Operating Instructions
Safety information
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Standard version Ethernet version
Fig. 2-2: Laser warning sign attached to the bar code scanner at delivery
Device CLV640
Laser out radiation (maximum/average) 3.2 mW/ <1.0 mW
Emitted wavelength 655 nm
Pulse duration < 300 μs
Tab. 2-2: Laser Data of CLV640
Important If the bar code scanner is installed in a machine/panelling in such a way that the bar code
scanner's laser warning sign is hidden, additional warning signs in the same language (not
included in delivery) have to be attached to the machine next to the outlet opening of the
laser radiation!
The bar code scanner works as follows in controlling the laser diodes:
• The bar code scanner has monitoring switches that deactivate the laser diode if irregularities occur in the radiation emission.
• The reading pulse (pulse source) controls the on and off mechanism of the laser diode
during the reading process.
• During reading operation with "Sensor" and "Command" reading pulses, each time level
(laser timeout) switches off the laser diode automatically after 10 minutes (default settings) when a permanent reading pulse has been started. However, it does not stop the
reading pulse.
The reading pulse can be stopped via an appropriate clock signal. The successive reading pulse switches on the laser diode.
• In SOPAS-ET on the "Illumination control" tab you can set or deactivate the laser timeout
within a range of 1 ... 1,500 min (= 25h).
16 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 17

Operating Instructions Chapter 2
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Safety information
• "Laser" LED:
During normal reading operation the "Laser" LED lights up when the laser diode is
switched on.
When calling up functions via the two buttons of the bar code scanner (aborting normal
reading operation), the LEDs have got additional display functions. The "Laser" LED will
differ from its original function. It is possible that the "Laser" LED is flashing when Autosetup is selected, although the laser diode is still switched off or the laser diode is
switched on, for example, in diagnostic mode (Read Diagn) and the "Laser" LED, however, is not flashing.
2.4 Quick stop and quick restart
The bar code scanner can be switched on or off using the main switch for connection modules CDB620 or CDM420.
2.4.1 Switching off the bar code scanner
¾ Switch off the power supply to the bar code scanner (the connection module)
- or -
Remove (pull out) the 15-pole D-Sub-HD connector of the bar code scanner's connection cable from the connection module.
When the bar code scanner is switched off, the following data is lost:
• Application-specific parameter sets in the bar code scanner that were only saved
temporarily in the device
• The last reading result of the bar code scanner
• Daily operating hours counter of the bar code scanner
2.4.2 Switching the bar code scanner back on
¾ Switch the power supply to the bar code scanner (the connection module) back on
- or -
Connect the 15-pole D-Sub-HD connector of the bar code scanner's connection cable
to the connection module.
The bar code scanner starts up using the most recent permanently saved configuration. The daily operating hours counter is reset.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 17
Page 18

Chapter 2 Operating Instructions
Safety information
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
2.5 Environmental information
The bar code scanner has been constructed with minimum environmental pollution in mind.
Excluding the housing, the bar code scanner does not contain any materials using silicone.
2.5.1 Energy requirements
The bar code scanner series CLV640 consumes the following energy:
• Line / Raster scanner: Typically 5.5 W with 24 V DC ± 10 %
• Line scanner with oscillating mirror: Typically 6.5 W with 24 V DC ± 10 %
All values with unwired switching outputs.
2.5.2 Dispose of the device after decommissioning
SICK AG will not currently accept the return of any devices which can no longer be operated
or repaired.
¾ Inoperable or irreparable devices must be disposed of in an environmentally friendly
manner and in accordance with valid country-specific waste disposal guidelines.
The design of the bar code scanner allows for its separation as recyclable secondary raw
materials and hazardous waste (electronic scrap).
18 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 19

Operating Instructions Chapter 3
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Quick-Start
3 Quick-Start
3.1 Preparing the bar code scanner for the quick start
The bar code scanner can be operated quickly and easily using the supplied SOPAS-ET configuration software.
The software offers the following options, among others:
• Fast connection with the bar code scanner
• Configuration of the most important reading parameters and display of the reading re-
sults on one clear register tab in the configuration software
System requirements for using the SOPAS-ET configuration software
See chapter 7.2.2 System requirements for the SOPAS-ET configuration software, page 65.
Additional accessories required (not in delivery)
• Connection module CDB620 or CDM420
• For the Ethernet version of the bar code scanner: Connection cable for data and func-
tion interfaces (see chapter 11.4.7 Accessories: Cables for Ethernet version,
page 115)
• 3-wire RS-232 data cable (null modem cable no. 2014054)
- or -
To connect an Ethernet version of the bar code scanner to the PC's Ethernet interface:
relevant cable (see chapter 11.4.7 Accessories: Cables for Ethernet version,
page 115).
Perform an electrical connection to the bar code scanner
1. Connect the bar code scanner to connection module CDB620/CDM420.
2. Switch on the power supply for CDB620/CDM420.
3. Switch on the PC for the configuration and install and start the supplied SOPAS-ET configuration software.
4. Connect the bar code scanner.
To achieve this, connect the PC using a 3-wire RS-232 data cable (null modem cable)
to the "Aux“ connection in CDB620/CDM420.
- or -
Connect the PC to the bar code scanner's Ethernet interface (Ethernet version).
For detailed instructions, see chapter 5 Installation, page 41 and chapter 6 Electrical in-
stallation, page 51.
3.2 Establishing connection with the bar code scanner
¾ Communicate with the bar code scanner according to the selected data interface (RS-
232 or Ethernet) (see chapter 7.3 Establish communication with the bar code scanner,
page 66) and perform a scan.
TIP To establish a connection quickly and easily via Ethernet, the SOPAS-ET configuration soft-
ware has a C
ONNECTION WIZARD in the TOOLS menu.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 19
Page 20
Chapter 3 Operating Instructions
Quick-Start
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
3.3 Performing the reading
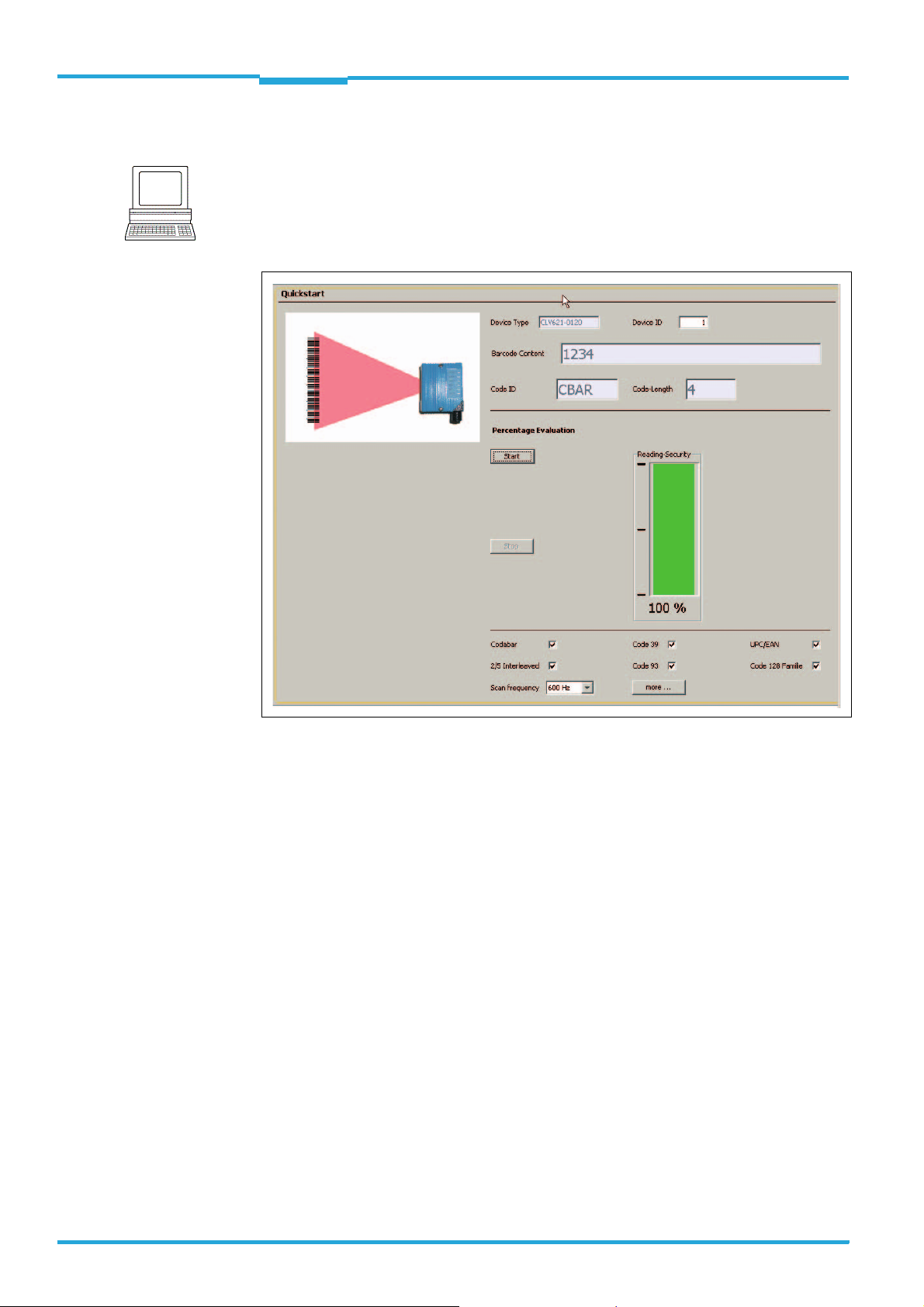
Note
With the SOPAS-ET configuration software, the QUICKSTART register tab contains the most important reading parameters for configuring and performing a bar code reading:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, QUICKSTART register tab
Fig. 3-1: Register tab Quickstart
Perform the reading:
1. Ensure that the relevant code types are activated on the register tab.
2. Carry out a test reading with a test bar code.
To achieve this, hold an object with a bar code in front of the bar code scanner's reading
window and trigger the reading by clicking S
TART. The default setting of the focus posi-
tion is 285 mm (11.2 in). If necessary, observe the bar code scanner's depth of fields
ranges in relation to the resolution (see chapter 10.3 Specification diagrams,
page 84).
During reading operation and with default settings, the line scanner with oscillating mirror deflects the scanning line by the central position with a frequency of 1 Hz and at a
max. angle of ± 20°.
The reading result is displayed in the B
ARCODE CONTENT display field.
The code reading reliability is specified in the relevant display field.
20 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 21

Operating Instructions Chapter 3
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Quick-Start
Optimise the reading conditions:
If no reading result is displayed or if you wish to increase the code reading reliability, the
reading can be repeated by taking the following measures.
¾ Install the bar code scanner in such a way that the bar code scanner's light meets the
idle object (code) at a 15° angle (skew).
¾ Correct or optimise the parameter values where necessary via the SOPAS-ET configura-
tion software.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 21
Page 22

Chapter 3 Operating Instructions
Quick-Start
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
22 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 23

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
4 Product description
This chapter describes the design, the features and the functions of the CLV640 Bar Code
Scanner.
¾ For installation, electrical installation and startup assistance as well as for the applica-
tion-specific configuration of the bar code scanner using the SOPAS-ET configuration
software, please read this chapter prior to carrying out any of the tasks.
4.1 Setting up the bar code scanner
The CLV640 Bar Code Scanner consists of a laser scanner (laser diode and lens) with dynamic focus position and an electronic unit with an integrated decoder. The laser scanner
and electronic unit are located in a housing. The light exits and enters via a reading window
in the industrial-type housing. The bar code scanner (depending on the version) is electrically connected by a cable with a connector or a revolving connector unit with two connections.
For an adaption to on-site space conditions/reading functions three housings are available:
a housing with front reading window, a housing with side reading window and a housing with
oscillating mirror. Via the integrated angle attachment/oscillating mirror, the laser beam exits through the side reading window at an angle of emergence of 105°. For the oscillating
mirror this corresponds to the central position (default settings) of the laser beam perpendicular to the scan direction.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 23
Page 24

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
4.1.1 Device view
Fig. 4-1: Housing types of the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
24 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 25

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
Fig. 4-2: Device view of the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner (shown here: Ethernet-Version)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 25
Page 26
Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
4.2 Included in delivery
Delivery of the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner includes the following components:
Piece(s) Components Comment
1 Bar code scanner CLV640
1 Set of laser warning signs for class 2 in
German/American English and French/
American English
1 Notes on device with electrical connec-
tion diagram as primary information
1 CD-ROM "Manuals & Software Auto
Ident"
CLV640 Operating Instructions in printed
form, in German and/or English
Tab. 4-1: CLV640 Bar Code Scanner delivery
Important The Micro-SD memory card is not included in delivery.
An overview of in-stock installation accessories, connection modules, cables and connectors, sensors for reading pulses as well as memory media is available in chapter 11.4 Or-
dering information for bar code scanner and accessories, page 111.
Self-adhesive to affix the warning sign to
the bar code scanner's housing (if necessary)
Included in the device packaging of the
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Optional, depending on the number of
issues explicitly ordered upon purchase
Important For save operation of the Micro-SD memory card, use only SICK approved memory card.
4.2.1 Contents of the CD-ROM
• "SOPAS-ET Engineering Tool“: Configuration software for Windows
TM
PCs with integrat-
ed online help system (HTML files)
• CLV640 operating instructions: PDF version in German and English as well as further
publications of other SICK devices
• “Acrobat Reader“: Freely available PC software for reading PDF files
Important The current versions of publications and programs on the CD-ROM can also be downloaded
at www.sick.com.
26 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 27
Operating Instructions Chapter 4
Product description
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
4.3 Device versions
The CLV640 Bar Code Scanner with a glass reading window is available in the following versions, among others:
Order no. Type Scanning method Reading
Connection (design)
window
1042014 CLV640-0000 Line scanner On front Cable with connector
1042015 CLV640-0120 Line scanner On front Connector unit on device
*)
1042016
1042017
1042018
1042019
1042020
1042021
CLV640-1000
CLV640-1120
CLV640-2000
CLV640-2120
CLV640-3000
CLV640-3120
1042022 CLV640-6000 Line scanner with
Raster scanner On front Cable with connector
*)
Raster scanner On front Connector unit on device
*)
Line scanner On side Cable with connector
*)
Line scanner On side Connector unit on device
*)
Raster scanner On side Cable with connector
*)
Raster scanner On side Connector unit on device
On side Cable with connector
oscillating mirror
1042023 CLV640-6120 Line scanner with
On side Connector unit on device
oscillating mirror
*) available from q4 2008
Tab. 4-2: Variants of the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Important Depending on the connection (design), the following interfaces are available:
• Standard version (cable with connector)
– RS-232, RS-422/485, CAN, two digital switching inputs, two digital switching out-
puts, power supply
• Ethernet version (revolving connector unit)
– Connector 1: Ethernet
– Connector 2: RS-232, RS-422/485, CAN, one digital switching input, power supply
4.4 System requirements
General system requirements are derived from the bar code scanner's technical data (see
chapter 10 Technical data, page 81).
The requirements and conditions for Installation, Electrical installation and Startup and
configuration are summarised in the respective chapters.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 27
Page 28
Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
4.5 Product features and functions (overview)
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner • Dynamic focus position
• Line scanner / raster scanner / line scanner with oscillating mirror
• Reading window on front / side
• High scan frequency
• Can be adapted to the print quality of the code
• Evaluation area of the scanning line can be restricted
User safety and convenience
Convenient operation/configuration
Reading operation modi
Reading pulse
Bar code evaluation
Data processing
Data communication
Electrical interfaces
• Robust, compact metal housing, CE mark
• Laser class 2, laser switches off if the output capacity is exceeded
• Automatic self-test on system startup
• Diagnosis tools for system setup and system (remote) monitoring
• Configurable reading diagnosis data display in two reading result formats
• Operational data retrieval, error code display on request in case of errors
• Activatable test string function (heartbeat) for signalling readiness for operation
• Password protected configuration mode
• Configured parameter values (cloning) can be additionally secured on a Micro SD
memory card (can be removed in the case of bar code scanner replacement )
• Future proof due to firmware update (flash PROM) via data interface
• Future-proof SOPAS-ET configuration software
• Low current consumption
• Extended power supply range
• Configuration (online/offline) using the SOPAS-ET configuration software (incl. help
system)
• 2 buttons on the device for calling up preset functions without connecting a PC
• Status indicators via five LEDs
• Beeper that can be switched off to confirm device functioning
• Start/Stop operation
• Pulse sources for start: switching inputs; data interface (command); automatic cycle;
CAN
• Pulse sources for stop: reading pulse source, switching inputs, command, timer, con-
dition
• All common bar code types
• Max. number of bar codes: 50 per reading pulse
• Separation of identical codes of the same code type using the reading angle
• Manipulation of the output of the reading data via event-dependent evaluation condi-
tions
• Manipulation of the output strings through filter and output sort options
• Host interface: two data output formats configurable, switchable to different physical
interfaces, parallel operation possible
• Aux interface: fixed data output format, switchable to different physical interfaces, par-
allel operation possible
• Host interface: RS-232, RS-422/485 (data format and protocol can be configured) and
Ethernet, or CAN
• Aux interface: RS-232, (fixed data format, data transfer rate and protocol) and Ether-
net
• CAN interface for integration into the SICK-specific CAN-SENSOR network
• Digital switching inputs
– Standard version: Two digital switching inputs for external reading pulse sensor(s)
or incremental encoder, using optocoupler
– Ethernet version: One digital switching input on the device
• Digital switching outputs
– Standard version: Two digital switching outputs for signalling definable results in
the reading process (reading result status)
– Ethernet version: No digital switching output on the device
28 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 29

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Connection technology (design) • Standard version: Cable with 15-pole D-Sub-HD connector
Product description
• Ethernet version: Revolving connector unit on the device with two M12 circular connec-
tors
• Connection module CDB620/CDM420 for connection to the host computer (stan-
dalone) and for integrating into the SICK-specific CAN-SENSOR network
• Bus connection module CMF400
field bus systems
1) Supported by SOPAS-ET from Q4 2007
Tab. 4-3: Overview of the bar code scanner's product features and functions
1)
in connection module CDM420 for connecting to
4.6 Bar code scanner methods of operation
The CLV640 Bar Code Scanner is an intelligent sensor system for automatic and non-contact detection and decoding of bar codes. In principle, the codes can be detected on any
side of still or moving objects in a conveyor system (single-side reading).
Several bar code scanners can be combined to allow detection of several sides in one passage (multi-side reading).
The bar code scanner creates a scanning line (line scanner) to recognise the codes. In the
raster scanner version, the bar code scanner creates eight scanning lines that are moved
parallel to each other.
Line scanner with oscillating mirror
The oscillating mirror additionally deflects the scanning line from the home position to both
sides, perpendicular to the scanning direction, with a low oscillation frequency. This enables
the bar code scanner to scan larger areas for bar codes as well.
Th e leng th of the s cann ing li ne th at is used for the evaluation (reading area height) depends
on the reading distance because of the V-shaped light exit.
The light pattern that is reflected by the bar code is recorded, processed and decoded. To
control this process, external sensors deliver information via the reading pulse, the object
distance and the conveyor speed (increment). The reading results are output to the bar
code scanner's data interfaces and forwarded to a host/PC.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 29
Page 30
Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Fig. 4-3: Bar code scanner's methods of operation in a conveyor system (schematic)
The detailed wiring of the bar code scanner and the connections to the host/PC and to the
external sensors is described in chapter 6 Electrical installation, page 51.
4.6.1 Reading configuration
The bar code scanner detects bar codes with an adjustable scan frequency.
The bar code scanner can detect codes on still and moving objects.
For more rapid evaluation, the reading range of the scanning line (reading angle: RA value)
can be restricted.
Note
The SOPAS-ET configuration software can, among other things, be used to configure the
reading angle and the symbol contrast:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, READING CONFIGURATION, register tab CODELABEL PROPERTIES
30 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 31

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
4.6.2 Object trigger control
In order to start an object-related reading process, the bar code scanner requires an appropriate external signal (trigger source) for reporting an object in the reading area. The start
signal is emitted via an external reading pulse sensor (e. g. photoelectric reflex switch) as
standard. As soon as an object has passed the reading pulse sensor, a time window opens
in the bar code scanner (“reading gate“) for the reading process.
Alternatively, a command activates the reading process via a data interface or the CAN-SENSOR network. In Automatic Cycle mode, the actual bar code scanner generates the reading
gate internally with an adjustable mark-space ratio.
The reading pulse can be ended in a number of ways: With external triggering by the reading
pulse source or a command, internally by a timer or an evaluation condition to be met.
Note
The trigger source can be configured using the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, READING CONFIGURATION, OBJECT TRIGGER CONTROL, register
tab S
TART/STOP OF OBJECT TRIGGER
4.6.3 Switchable focus position
The focus position can be changed for the CLV640 thus covering a wide reading area.
You can define up to 8 reading areas for the distance configuration which can be started in
any order by the lens in reading operation.
Fig. 4-4: Switching the focus for CLV640: Division of the entire reading area in distance
configurations
The focus is shifted by changing the object position (e. g. when reading downwards: detection of object height).
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 31
Page 32

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Trigger sources for the switch-over are:
• Signal at the switching input "Sensor 2" for the max. 2-pole switching
• Command from the host interface or the integrated timer (e.g. search run) for the max.
8-pole switch-over
• Reversal points of oscillation mirror for the bilateral deflection on the line scanner with
oscillating mirror chapter 4.6.4 Oscillating mirror control, page 32
The distance configurations of the switching order are assigned via the programmable
cross-reference list.
Note
The focus position can be configured using the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, READING CONFIGURATION
PROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, READING CONFIGURATION, OSCILLATING MIRROR
PROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, READING CONFIGURATION, FOCUS CONTROL
PROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, READING CONFIGURATION, DYNAMIC READING CONFIGURATION
4.6.4 Oscillating mirror control
You can manipulate the position of the scanning line for the line scanner with oscillating mirror (CLV640-6000/CLV640-6120) by configuring the oscillating mirror.
In addition to parking (fixed scanning line position which can be adjusted) or continuous
oscillation independent of the reading pulse, controlled operation of the oscillating mirror
also enables optimised operation sequences related to the reading pulse:
• n-fold oscillation around an adjustable start position within the reading pulse
• One-shot: one-time deflection (forward and return) per reading pulse from an adjusta-
ble start position
In every oscillation mode, the amplitude can be adjusted separately for each of the two deflection directions. The deflection speed ratio of one deflection direction to the other can be
adjusted within the selected periodic time for the entire oscillation sequence.
Fig. 4-5: CLV640 Oscillating Mirror: Example of focal position control in search run, here with 6
focus positions
32 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 33

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
Note
The behaviour or the position of the oscillating mirror can be configured via the SOPAS-ET
configuration software:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, READING CONFIGURATION, OSCILLATING MIRROR, register tab
O
SCILLATING MIRROR
4.6.5 Increment configuration
The bar code scanner receives information about the conveyor speed from an external incremental encoder, for example. The incremental encoder delivers pulses which are used
to determine the current conveyor speed.
The conveyor speed results from the number of impulses and the resolution of the external
incremental encoder.
Note
The increment source and the resolution/speed can be configured using the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, INCREMENT CONFIGURATION, register tab INCREMENT
4.6.6 Code configuration
The bar code scanner can decode the following code types:
• Codabar
• Code 39
• UPC/EAN
• 2/5 Interleaved
• Code 93
• Code 128 family
• Pharmacode
Note
The code types can be selected and configured using the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, CODE CONFIGURATION, register tab SYMBOLOGIES
The selected code types can be configured individually. For this purpose, separate register
tabs are available in the configuration software SOPAS-ET.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 33
Page 34

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
4.6.7 Reading operation mode
There is only one object in the reading field during start/stop operation, i.e. all the read
codes should be unambiguously assigned to the object. The start and stop of the reading
process control one/two reading pulse sensors at the beginning and at the end of the reading field as standard. The distance between each sensor is determined by the size of the
reading field. The reading process can be alternatively controlled with command strings via
the data interface. The output of the reading results is carried out either at the end of the
reading pulse (the rear edge of the object has left the end of the reading field) or during the
reading pulse if certain configurable conditions have been fulfilled.
Fig. 4-6: Reading operation mode for the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner in stand-alone operation
Note
The reading operation mode can be configured using the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, DATA PROCESSING, register tab TRACKING
4.6.8 Data processing
Note
The output time in the reading process with regard to the reading pulse start can be configured using the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, DATA PROCESSING, OUTPUT CONTROL
P
Furthermore, the evaluation conditions and filters and sorters for data output to the host
computer can be configured:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, DATA PROCESSING, EVALUATION CONDITION
PROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, DATA PROCESSING, FILTER/SORTER FOR OUTPUT
4.6.9 Output format
The reading result (decoded codes) is displayed via selectable physical interfaces. Two different output formats (telegrams) can be defined for this task, one format for "No Read" and
one for the heartbeat (signalisation of readiness).
Note
The output formats can be configured using the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, DATA PROCESSING, OUTPUT FORMAT
34 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 35

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
4.6.10 Network / interface / IOs
All important interfaces for displaying the reading results are available on the bar code
scanner. Several bar code scanners can be connected to each other via the CAN bus in the
SICK-specific CAN-SENSOR network.
Note
The network parameters can be configured using the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, NETWORK / INTERFACE / IOS, tab pages NETWORK OPTIONS
4.6.11 Data interfaces
The following data interfaces are available on the bar code scanner depending on the version:
Data interface Function
Host interface
(RS-232 or RS-422/485
and Ethernet host port)
Auxiliary interface (RS-232
and Ethernet aux port)
CAN Networking several bar code scanners
Tab. 4-4: Data interface function
Preparation of the reading result for further processing by the host
processor
Reading diagnosis or host interface monitoring
Note
The data interfaces can be configured using the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, NETWORK / INTERFACE / IOS, SERIAL
P
PROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, NETWORK / INTERFACE / IOS, ETHERNET
PROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, NETWORK / INTERFACE / IOS, CAN
4.6.12 Digital inputs
The external sensor for the object triggering (photoelectric reflex switch) and the incremental encoder, e.g., can be connected to the digital switching inputs.
Note
The digital inputs can be configured using the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, NETWORK / INTERFACE / IOS, DIGITAL INPUTS
Important The connection "Sensor 2" is only available on the standard version of the bar code scanner.
For the Ethernet version of the bar code scanner, this input is only available with the connection module CDB620/CDM420 in combination with the parameter memory module
CMC600.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 35
Page 36

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
4.6.13 Digital outputs
With certain events in the reading process (e.g. for unsuccessful decoding "No Read"), two
independent switch signals can be generated at both digital outputs and can be used, e.g.,
to display the event status.
Note
The digital outputs can be configured using the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
P
ROJECT TREE, CLV640, PARAMETER, NETWORK / INTERFACE / IOS, DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Important The switching outputs "Result 1" and "Result 2" are only available on the standard version
of the bar code scanner. For the Ethernet version of the bar code scanner, the two outputs
are only available with the connection module CDB620/CDM420 in combination with the
parameter memory module CMC600.
4.7 Indicators and control elements
4.7.1 User interface
The bar code scanner is configured application-specifically using the SOPAS-ET configuration software (see chapter 7.4.1 Overview of the startup procedure, page 68). The software
for this runs on a PC which must be connected to one of the two data interfaces (aux interface: Ethernet or RS-232, host interface: RS-232/RS-422/485 or Ethernet) of the bar code
scanner.
As an alternative to the SOPAS-ET configuration software, command strings are available
upon which the user interface of the SOPAS-ET configuration software is based (see
chapter 11.2 Configuring the bar code scanner with command strings, page 109).
In case of an error, startup and diagnosis can be carried out via the SOPAS-ET configuration
software. The bar code scanner operates fully automated in normal operation.
36 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 37

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
4.7.2 LEDs on the bar code scanner's housing
The bar code scanner's housing has six LEDs that display the operating status, the laser diode's activity, the status of the reading result and the transfer to the RS-232/RS-422/485,
CAN and Ethernet interfaces.
In reading operation the LEDs indicate the following:
LED Colour Meaning
READY Green
• Lights up constantly after switching on and a successful self-test
• Goes out when parameter values are being uploaded from or
downloaded to the bar code scanner
Red
RESULT Green
LASER Green
DATA Green
CAN Yellow
LNK TX Green
Bar graph
(0 ... 100%)
Green
• Lights up when a hardware error has been detected
• Lights up after a successful read (Good Read, 100 ms)
• Reading operation: Lights up when the laser diode is switched on
(depends on the reading pulse)
• Lights up during the data transfer for 100 ms
• Flickers during the data transfer via the CAN interface
• Lights up when the physical Ethernet connection is o.k.
• LED´s light up according to the reading rate during diagnostic
mode.
• During normal reading mode the bar graph display is switched off.
Tab. 4-5: LED indications
Important The “Result“ LED is not coupled with one of the “Result 1“ or "Result 2" outputs.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 37
Page 38

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
4.7.3 Buttons on the bar code scanner housing
There are two yellow buttons on the bar code scanner housing in the LED area (see
chapter 4.1.1 Device view, page 24). You can call up predefined functions via these but-
tons.
After changing to the button operating mode you can select one function each by repeatedly
pressing the lower button. By pressing the upper button, you can start or stop the selected
function. The "TeachIn" function (for matchcode) and "Auto-Setup" stop the bar code scanner automatically. Currently you cannot call up user-defined functions.
The selected function is shown via the corresponding LED below the buttons.
When using both of the buttons the LEDs have different meanings than in normal reading operation:
LED Colour Function
Read Diagn Green Flashes slowly: the "Reading diagnosis/evaluation"
function is selected
Flashes rapidly: the "Reading diagnosis/evaluation"
function is started
TeachIn Green Flashes slowly: the "TeachIn matchcode" function is
selected
Flashes rapidly: the "TeachIN matchcode" function is
started
Auto-Setup Green Flashes slowly: the "Auto-Setup" function is selected
Flashes rapidly: the "Auto-Setup" function is started
Adjust Green Flashes slowly: the "Adjusting" function is selected
Flashes rapidly: the "Adjusting" function is started
Userdefined Yellow (momentarily not available)
Tab. 4-6: Meaning of the LEDs during activation of buttons
Important When using the buttons, the "Laser" LED's function differs from its original function in read-
ing operation, the display of the switched-on laser diode.
Use of the buttons
In order to use one of the possible function with the buttons, do as follows:
1. Press the upper button for approx. 3 seconds.
The bar code scanner stops the current reading operation, switches off the LEDs and
the bargraph display and changes to the button operating mode. With immediate effect
the bar code scanner ignores all the other external reading pulses. No reading results
are displayed via the host interface.
The beeper confirms this process with an ascending melody.
The "Read Diagn" function is pre-selected as first function (LED flashes slowly).
2. Repeatedly press the lower button until the LED of the required function flashes. The
bar code scanner scans all the possible functions successively without starting them
and starts over.
The beeper confirms each step with a sound.
3. Press the upper button once to start the selected function.
The LED flashes faster and the beeper confirms the start with two sounds.
38 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 39

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
4. Press the upper button again to stop the function.
The LED flashes more slowly again and the beeper confirms the end with two sounds.
The bar code scanner stops the "TeachIn" (for matchcode) and "Auto-Setup" function
automatically, when the presented bar code was read successfully. During this procedure, the "Ready" LED flashes in green three times and the beeper confirms it with an
ascending melody.
5. In order to return from the button operating mode to the reading operation, press the
upper button again for approx. 3 seconds.
The beeper confirms the change with a descending melody.
The "Ready" LED lights up again.
The bar code scanner is ready for reading and waits for a reading pulse.
Further behaviour of the bar code scanner when operated by buttons
• Changing into button operating mode is only possible if no other user is logged onto the
bar code scanner for changing the parameters via the SOPAS-ET configuration software. If this is the case, however, a descending melody is started by the beeper when
trying to change into the button operating mode. The bar code scanner remains in
reading operation.
• In case a user logs onto the bar code scanner in button operating mode, the bar code
scanner leaves the button operating mode and restarts the reading operation. The
beeper confirms the change with a descending melody.
• If no function is started in button operating mode or if no button operation can be performed after using a function, the bar code scanner returns into reading operation automatically after 30 seconds. The beeper confirms the change with a descending
melody.
• The bar code scanner terminates an activated continous function 5 minutes after start.
It returns to reading operation automatically. The beeper confirms the change with a
descending melody.
• If the bar code scanner could not read the bar code in the "TeachIN" (for matchcode)
as well as "Auto-Setup" functions, the "Ready" LED flashes in red for three times. The
beeper reports this with a descending melody. After this the bar code scanner remains
in button operating mode.
• You cannot switch off or turn down the beeper in button operating mode.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 39
Page 40

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Important In order to avoid data loss, the Micro SD memory card may only be removed and inserted
Product description
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
4.7.4 Parameter set on the Micro SD memory card (optional)
The bar code scanner stores configured parameter values in the internal PROM as well as
on the Micro SD memory card (cloning), provided that this card has been inserted into the
bar code scanner. If the bar code scanner needs to be replaced, the memory card enables
easy and quick transfer of the parameter set to the new device (see chapter 8.5 Replacing
a bar code scanner, page 76).
into the new device after the respective bar code scanner has been switched off and deenergized. When inserting the memory card, make sure that the contacts point backwards
and upwards (towards the inscription "mircoSD" on the box slot).
The memory card is located behind a black rubber cover attached to the bar code scanner.
Fig. 4-7: Micro SD memory card for storing the parameter set
Important To maintain the enclosure rating IP 65, the black rubber cover has to be closed and lie flush
against the device.
As an alternative to the Micro SD memory card in the bar code scanner, the external, optional parameter memory module CMC600 in connection module CDB620/CDM420 may also
be used for storing the parameter set. If both the Micro SD memory card and the parameter
memory module CMC600 are available, the bar code scanner will load the parameter set
from the CMC600.
40 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 41

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Installation
5 Installation
5.1 Overview of installation sequences
This chapter describes the installation sequences for the bar code scanner and its external
components.
The typical installation sequences are displayed below:
• Changing the language of the laser warning sign (if necessary)
• Selecting the installation location for the bar code scanner
• Aligning the bar code scanner to the object carrying the bar code
• Installing the bar code scanner
• Installing connection module CDB620 or CDM420
• Connecting the bar code scanner to connection module CDB620 or CDM420
• Adjusting the bar code scanner
• Installing the reading pulse sensor for reading pulse triggering
Important Do not open the bar code scanner's housing. If the device is opened, the SICK AG warranty
shall not apply.
5.2 Installation preparations
The following general requirements should be observed for installation:
• Typical space requirement: application specific
• Unobstructed view of the objects for the bar code scanner
• Stable installation bracket with sufficient load capacity and measurements suited to
the bar code scanner (see chapter 10.4 CLV640 Bar Code Scanner dimensional draw-
ings, page 102)
• Shock absorbent and vibration free attachment
The following tools and resources are required for installation:
• Two M5 bolts:
To fix bracket no. 2020410, quick release clamp no. 2025526 or fix bracket
no. 2042800 to the base.
The bolt length depends on the wall thickness of the base.
• Laser warning sign set (if necessary)
• Tool
• Tape measure (up to 1 m (3.28ft))
• Goniometer
5.2.1 Components to be installed
The following components have to be placed ready for installation:
• CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 41
Page 42

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
5.2.2 Accessories
The following accessories are not included in the delivery of the bar code scanner. They
have to be ordered separately and placed ready for installation:
• Mounting device, see next chapter
• Connection module CDB620 or CDM420
• Reading pulse sensor for external reading pulse triggering, e. g. photoelectric reflex
switch/photoelectric proximity switch
5.2.3 Mounting device
The bar code scanner is fixed using two blind hole taps (M5) that are each located on the
narrow sides of the device chapter 10.4 CLV640 Bar Code Scanner dimensional drawings,
page 102.
The bar code scanner can be mounter using the following SICK holders:
• Bracket no. 2020410
• Quick release clamp no. 2025526
• Bracket no. 2042800
• Round rod holder no. 2042801
The construction of the angle with adapter plate no. 2042800 supports e. g. varied mounting options and the alignment of the bar code scanner in two axis.
Fig. 5-1: Example: Fixing the bar code scanner with the bracket no. 2042800
The dimensioning of the SICK-holders is shown in chapter 11.5 Dimensional drawing acces-
sories, page 117.
Alternatively, the user can provide a holder.
The holder should meet the following requirements:
• Stable mounting device
– Adjustable alignment of the bar code scanner in the x and y axis
– The mounting device must be able to bear the weight of the bar code scanner includ-
ing its connection cable (depending on the device version) without vibrating.
• Two M5 bolts to fix the bar code scanner.
– The screw length depends on the thickness of the mounting device.
– The maximum thread reach in the bar code scanner is 5 mm (0.2 in) from the hous-
ing surface.
42 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 43

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Installation
5.2.4 Exchanging the laser warning sign
The laser warning on the bar code scanner must be in a language that the operators of the
unit in which the bar code scanner is integrated can understand.
A set of self-adhesive laser warning signs German/American English and French/American
English is included in the delivery.
¾ If necessary, replace the English laser warning sign before operating the bar code scan-
ner.
Fig. 5-2: Exchanging the laser warning sign
5.3 Installation location
The following aspects are relevant for the selection of the installation location:
• Allocation of the scanning line for the bar code
• Reading distance to the bar code and aperture angle α
• Angle alignment of the bar code scanner
• Avoiding surface reflections
• Counting direction of the reading angle (position of the bar code along the scanning
line)
Furthermore, the distance between the bar code scanner and the host computer and the
distance to the connection module has to be taken into account (see chapter 6.2 Electrical
installation preparation, page 51 and chapter 5.5.1 Installing connection module CDB620
or CDM420, page 49).
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 43
Page 44

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
5.3.1 Allocation of the scanning line for the bar code
The main allocation of the scanning line to the bar code on the object depends on the version of the bar code scanner (line scanner, raster scanner or line scanner with oscillating
mirror).
Fig. 5-3: Allocation of the scanning line(s) for the bar code and conveyor system
5.3.2 Reading distance to the bar code and aperture angle α
The maximum distance between the bar code scanner's reading window and the bar code
must not exceed the device-specific thresholds.
The usable length of the scanning line that is used for the evaluation (reading area height)
depends on the reading distance because of the V-shaped deflection of the beam.
Fig. 5-4: Definition of the reading distance a and the aperture angle α
In the specification diagrams (chapter 10.3 Specification diagrams, page 84) the depth of
field is shown depending on the adjustable focus position and the aperture angles used for
various resolutions (modul widths).
44 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 45

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Installation
5.3.3 Angle alignment of the bar code scanner
The bar code scanner is optimally aligned if the scanning line almost scans the lines of the
bar code in the right-hand angle (90°). Possible code positions that can occur between the
scanning line and bar code in all three levels in the room have to be taken into account.
β
α Azimuth angle (tilt)
β Inclination angle (pitch)
γ Step angle (skew)
a Reading distance
b Reading range
Fig. 5-5: Line scanner: Reading angles that occurs between the scanning line and bar code
Angle Threshold
Azimuth α (tilt) max. 30° (resolution 0.35 mm (13.8 mil), depending on the print
Inclination β (pitch) max. 45° (depending on module width)
Step angle γ (skew) max. 45° (depending on module width)
Tab. 5-1: Permitted reading angles between the scanning line and bar code
α
γ
image)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 45
Page 46

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
5.3.4 Avoiding surface reflections
If the light of the scanning line(s) vertically meets the surface of the bar code, this can result
in disruptive reflections when the bounced back light is received. To prevent this effect, the
bar code scanner must be installed in such a way that the light emitted is tilted down relative to the plumb line.
Fig. 5-6: Avoiding surface reflection using the line scanner as an example: Angle between emitting light and bar code (tilted away
from the plumb line)
5.3.5 Counting direction of the reading angle and code angle
The bar code scanner can scan and decode several bar codes with every read.
The location-related reading diagnosis data is determined:
• The reading angle from the reading window to the red scanning line of the deflected
scanning beam under which the middle of a bar code is detected can be displayed as
an RA (reading angle) value.
• In addition, with the line scanner with oscillating mirror, the deflection angle of the
scanning line under which the bar code scanner detects the bar code on the red scanning line can be displayed as a CW value.
The determination of the RA/CW value enables identical bar codes (code type, code length
and data contents) to be separated and the bar code data to be assigned to their position
on the object.
46 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 47

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Installation
Fig. 5-7: Counting direction of the reading angle RA within the scanning line and of the code angle CW with the oscillating mirror
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 47
Page 48

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
5.4 Installation of the bar code scanner
5.4.1 Installing the bar code scanner
Damage to the device!
The maximum thread reach of the two blind hole taps M5 is 5 mm (0.2 in). Longer bolts will
damage the device.
¾ Use bolts of a suitable length.
1. Preparing base for the installation of the bar code scanner holder, see chapter 5.2.2
Accessories, page 42.
2. Place the object with the bar code at the designated position where the reading should
be taken in the bar code scanner's visual range (no conveyor movement).
3. Visually align the bar code scanner to the bar code. Pay attention to the following
points:
– With the bar code scanner with the front reading window, ensure that the narrow re-
verse side of the device with the laser warning sign is facing the viewer and is approximately parallel to the bar code plane.
– With the bar code scanner with the side reading window, respectively the line scan-
ner with oscillating mirror, ensure that the wide side panel with the LEDs is facing
the viewer and is approximately parallel with the bar code plane.
– During the reading, consider the reading angle, see chapter 5.3.3 Angle alignment
of the bar code scanner, page 45.
– If the bar code's position within the scanning line is relevant for the evaluation, ob-
serve the reading angle's counting direction, see chapter 5.3.5 Counting direction
of the reading angle and code angle, page 46.
4. Installing the bar code scanner holder on the base.
5. Screw M5 bolts through the holder and into the bar code scanner's blind hole taps and
gently tighten them.
6. Adjusting the bar code scanner, see chapter 7.6.1 Adjusting the bar code scanner,
page 71.
48 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 49

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Installation
5.5 Installing external components
5.5.1 Installing connection module CDB620 or CDM420
Depending on the application, you can install either connection module CDB620 or
CDM420. The installation process is the same for both modules.
Important If the PC with the SOPAS-ET configuration software accesses the bar code scanner's auxil-
iary interface (RS-232; 57.6 kbd) via the connection module, the connection module should
not be installed more than 3 m (9.84 ft) cable lengths away from the bar code scanner.
1. Install the connection module close to the bar code scanner.
2. Install the connection module in such a way that the opened device can be accessed
at any time.
Important
For detailed information about installation and electrical installation, see the operating instructions "Connection Module CDB620“ (no. 8012119, German/English) or "Connection
Module CDM420-0001“ (no. 8010004, German/English).
5.5.2 Installing the external reading pulse sensor
If the bar code scanner is triggered by an external reading pulse sensor (photoelectric reflex
switch), the sensor has to be installed close to the bar code scanner.
Bar code scanner in the middle or at the end of
the conveyed material
b
Fig. 5-8: Line scanner: Installation example for positioning the external reading pulse sensor
b < a
Bar code scanner at the beginning of the con-
veyed material
b
b < a
The installation location depends on the distance (a) of the bar code to the front edge of the
object. Depending on the application, the sensor should be attached in such a way that bar
codes on different sized objects can be fully read during the evaluation (reading gate).
5.5.3 Installing the incremental encoder
An incremental encoder is required for separating bar codes with the same code type and
identical content.
The increment impulses have to come from the conveyor system area where the bar code
scanner is reading.
1. Install suitable increment encoders near to the bar code scanner, best against the direction of the conveyor system in front of the bar code scanner.
2. Ensure that the incremental encoder has direct and fixed contact with the drive system
and that the friction wheel rotates without slipping.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 49
Page 50

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
5.6 Removing the bar code scanner
Removal of the components is described in chapter 8.5.1 Removing the bar code scanner,
page 76.
50 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 51

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
6 Electrical installation
6.1 Overview of installation sequence
Important Electrical installation must be performed by qualified staff.
The following list provides an overview of a typical installation sequence:
• Connecting the bar code scanner to connection module CDB620 or CDM420
• Wiring the bar code scanner's data and function interfaces
• Connecting the connection module to the supply voltage
• Connecting a PC for start-up and configuration (RS-232 or Ethernet)
The actual installation work which has to be carried out depends on the respective system
configuration and the version of the bar code scanner (see chapter 6.2 Electrical installa-
tion preparation, page 51). Once electrical installation has been completed, the bar code
scanner is started up and configured (see chapter 7 Startup and configuration, page 65).
6.2 Electrical installation preparation
The following general requirements should be observed for the electrical installation:
• Supply voltage 18 ... 30 V DC (functional extra-low voltage in accordance with IEC 3644-41 (VDE 0100 Part 410)) and min. 10 W output power
– Using connection module CDB620/CDM420: supply voltage provided by terminals
of the connection module
- or -
– Free wiring by customer (without connection module CDB620/CDM420): connec-
tion of supply voltage e.g. by cable no. 6034418 (15-pole D-Sub-HD socket to open
end)
• With external reading pulsing
– Appropriate reading pulse sensor (start/stop), e. g. photoelectric reflex switch:
for registering an object in the reading area
– Additional appropriate reading pulse sensor (stop), e.g. photoelectric reflex switch:
For registering the end of pulse with extended external reading pulse
• Appropriate incremental encoder: For separating identical bar codes
• Host computer with RS-232, RS-422/485 data interface or Ethernet: For further
processing the reading data
• Connection cables: See chapter 11.4.7 Accessories: Cables for Ethernet version,
page 115
Important The possible distance between the bar code scanner and the host computer depends on
the physical version of the selected host interface and the set data transfer rate.
The following tools and resources are required for electrical installation:
• Tool
• Digital measuring device (current/voltage measurement)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 51
Page 52

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
6.3 Electrical connections and cables
Fig. 6-1: Standard version: Electrical connections at the bar code scanner with connection cable
Fig. 6-2: Ethernet version: Electrical connections at the bar code scanner with connector unit
52 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 53

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
6.3.1 Electrical connections at the bar code scanner
Important Prerequisites for enclosure rating IP 65:
• The black rubber cover of the memory card (optional) has to be closed and lie flush
against the device.
• The connectors attached to the used electrical connections of the Ethernet version
have to be firmly screwed.
The same applies to the EMC requirement (ESD) according to CE.
Depending on the device version, the following electrical connections are available at the
bar code scanner:
Device version Connection (design) Interfaces For connection to
CLV640-0000
CLV640-1000
CLV640-2000
CLV640-3000
CLV640-6000
Cable with connector
(D-Sub-HD, 15-pole, plug)
• RS-232
• RS-422/485
• CAN
• Two digital inputs
• Two digital outputs
e. g. connection module CDB620 or
CDM420
• Power supply
Tab. 6-1: Electrical connections to the bar code scanner with a fixed cable and connector
(standard version)
Device version Connection (design) Interfaces For connection to
CLV640-0120
CLV640-1120
CLV640-2120
CLV640-3120
CLV640-6120
Connector 1 at the connector unit
(M-12, 4-pole, socket)
Connector 2 at the connector unit
M-12, 12-pole, plug
• Ethernet Network provided by
the client
• RS-232
• RS-422/485
• CAN
e. g. connection module CDB620 or
CDM420
• One digital input
• Power supply
Tab. 6-2: Electrical connections to the bar code scanner with connector unit (Ethernet version)
Important Additional digital inputs and outputs are available at connection module CDB620/CDM420
(available from week 07/2008) in combination with the parameter memory module
CMC600.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 53
Page 54

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
6.3.2 Bar code scanner connections to the cable and connector (standard version)
56
1
111015
Pin Signal Function
1 18 ... 30 V DC Operating voltage
2 RxD (Aux) Aux interface (receiver)
3 TxD (Aux) Aux interface (sender)
4 Sensor 2 Digital switching input (adjustable func-
tion, e. g. external reading pulse)
5GND Ground
6 RD+ (RS-422/485) Host interface (receiver)
7 RD– (RS-422/485);
RxD (RS-232)
8 TD+ (RS-422/485) Host interface (sender)
9 TD– (RS-422/485);
TxD (RS-232)
10 CAN H CAN bus (IN/OUT)
11 CAN L CAN bus (IN/OUT)
12 Result 1 Digital switching output, adjustable func-
13 Result 2 Digital switching output, adjustable func-
14 Sensor 1 Digital switching input for external read-
15 SensGND Common ground for the switching inputs
-– Shield
Tab. 6-3: Standard version: Pin assignment of the 15-pole D-Sub-HD cable connector
Host interface (receiver)
Host interface (sender)
tion
tion
ing pulse
6.3.3 Bar code scanner's connections with connector unit (Ethernet version)
Pin Signal Function
1TD+ Transmitter+
2RD+ Receiver+
3TD- Transmitter-
4RD- Receiver-
-- Shield
Tab. 6-4: Ethernet version: Pin assignment of the 4-pole M12 socket
54 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 55

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
Pin Signal Function
1GND Ground
2 18 ... 30 V DC Operating voltage
3 CAN L CAN bus (IN/OUT)
4 CAN H CAN bus (IN/OUT)
5 TD+ (RS-422/485) Host interface (sender)
6 TD– (RS-422/485);
TxD (RS-232)
7 TxD (Aux) Aux interface (sender)
8 RxD (Aux) Aux interface (receiver)
9 SensGND Switching input Sensor 1 ground
10 Sensor 1 Digital switching input (external reading
11 RD+ (RS-422/485) Host interface (receiver)
12 RD– (RS-422/485);
RxD (RS-232)
-– Shield
Tab. 6-5: Ethernet version: Pin assignment on the 12-pole M12 plug
Host interface (sender)
pulse)
Host interface (receiver)
Important The "Sensor 2", "Result 1" and "Result 2" connections are only available on the bar code
scanner with a cable and connector (standard version) and for the Ethernet version via the
CDB620/CDM420 connection module in combination with the parameter memory module
CMC600.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 55
Page 56

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
6.4 Performing electrical installation
Important To ensure secure fastening of the connected connectors and adherence to the enclosure
rating, the knurled nuts/coupling rings of the M12 connectors have to be tightened or the
cable connectors have to be secured.
1. Connect or release current linkages only under de-energised conditions.
2. All wire cross sections and their shields on customer side have to be selected and implemented according to valid engineering standards.
Damage to the connector unit at the bar code scanner due to overwinding.
The connector unit at the bar code scanner has two end positions.
¾ Never turn the connector unit more than 180° in one direction (comming from one of
the end positions).
¾ Always rotate the connector unit in the direction of the laser diode name.
Fig. 6-3: Direction of rotation of the connector unit
6.4.1 Connecting the power supply for the bar code scanner
The bar code scanner requires a supply voltage of 18 ... 30 V DC (functional extra-low voltage in accordance with IEC 364-4-41 (VDE 0100 (Part 410)) for operation. The functional
extra-low voltage can be created using a safety transformer in accordance with IEC 742
(VDE 0551). The maximum current consumption is 6.5 W.
The bar code scanner is supplied with 18 ...30 V DC via connection module CDB620 or
CDM420. If the power supply module CMP400/CMP490 is used, the input voltage is 100
... 250 V AC/ 50 ... 60 Hz at the module.
Important The output circuit must be electrically separated from the input circuit. This is usually crea-
ted by means of a safety transformer in accordance with IEC 742 (VDE 0551).
56 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 57

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
Connecting supply voltage
When wiring the bar code scanner using connection module CDB620 or CDM420, the bar
code scanner's data and function interfaces are contacted to the connection module together with the power supply.
1. Ensure that the connection module's supply voltage has been switched off.
2. Standard version: Connect the bar code scanner's 15-pole cable plug to the connection
module's 15-pole socket and screw it tight.
- or -
Ethernet version: Connect the bar code scanner's 12-pole plug via a corresponding cable (e.g. 2042916) to the connection module's 15-pole socket and screw it tight.
6.4.2 Wiring serial data interfaces
The maximum data transfer rate depends on the cable length and the interface type.
Interface type Transfer rate Distance to the host
RS-232 up to 19,200 Bd max. 10 m (32.8 ft)
38,400 ... 57,600 Bd max. 3 m (9.8 ft)
115,200 Bd max. 2 m (6.6 ft)
RS-422/485
1) With corresponding line termination according to specification
1)
max. 38,400 Bd max. 1,200 m (3,937 ft)
max. 115,200 Bd max. 500 m (1,640 ft)
Tab. 6-6: Recommended maximum cable lengths, depending on the selected data transfer rate
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 57
Page 58

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
RS-232
CLV
RS-422
CLV
Fig. 6-4: Wiring the serial host data interfaces (RS-232 or RS-422) on the 15-pole D-Sub-HD plug
Host
Host
Pin assignment for the serial auxiliary data interface on the 15-pole D-Sub-HD plug:
• RxD = Pin 2
• TxD = Pin 3
• GND = Pin 5
Damage to the interface module!
Incorrect wiring of the serial data interfaces can damage electronic components in the bar
code scanner.
¾ Observe information about wiring the serial data interface.
¾ Check the wiring carefully before switching on the bar code scanner.
1. Connect the bar code scanner's serial interface to the host in accordance with the EMC
regulations using shielded cables.
Adhere to the maximum cable lengths.
2. To prevent interference, do not lay cables parallel to power supply cables and motor
lines over a longer distance, e. g. in cable channels.
Important
Terminating the RS-422 data interface
Termination can be performed either in connection module CDB620 or CDM420. See operating instructions "Connection module CDB620" or "Connection module CDM420".
58 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 59

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
6.4.3 Wiring CAN interface
Important
To wire and configure the bar code scanner's CAN interface for use in the CAN-SENSOR-network, see the operating instructions "Using the CAN Interface“ (no. 8009180, English).
6.4.4 Wiring Ethernet interface
Aux and host interface communication can also be executed in parallel via the Ethernet interface.
56
$X[
5656
+RVW
&$1
3RUW$8;
(WKHUQHW
Fig. 6-5: Function of the Ethernet interface
3RUW+RVW
623$6(7
Important The Ethernet interface has an auto-MDIX function. This automatically sets the speed and
any cross connection that is required.
6.4.5 Wiring switching inputs
If the bar code scanner's reading process should be triggered by an external sensor, the
reading pulse sensor is connected to the "Sensor 1" switching input.
Fig. 6-6: Wiring the “Sensor 1“ switching input on the 15-pole D-Sub-HD plug
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 59
Page 60

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
The "Sensor 2" switching input has the following functions, among others:
Trigger source for
• Incremental encoder input
• Reading pulse generator for reading pulse end
Fig. 6-7: Wiring the "Sensor 2" switching input on the 15-pole D-Sub-HD plug
Important The ratings for "Sensor 1" and "Sensor 2" are identical.
Switching behaviour Power fed to the input opens the internal reading gate of the bar code
scanner.
(Default setting: active high; debouncing: max. 30 ms (standard))
Features – Optodecoupled, reverse polarity protected
– Can be wired with the PNP output of a sensor
Electrical values Low: |V
High: 6 V ≤ |V
| ≤ 2 V; |Iin| ≤ 0.3mA
in
| ≤ 32 V; 0.7 mA ≤ |Iin| ≤ 5.0 mA
in
Tab. 6-7: Ratings for the switching inputs
¾ Connect switching inputs depending on application.
Important
To wire the switching inputs using connection module CDB620 or CDM420, see operating
instructions "Connection Module CDB620" (no. 8012119, German/English) or "Connection
Module CDM420-0001" (no. 8010004, German/English).
60 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 61

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
Electrical installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
6.4.6 Wiring switching outputs
The two switching outputs "Result 1" and "Result 2" can be allocated various functions for
outputting the result status independently of each other. If the assigned result occurs in the
reading process, the corresponding switching output at the end of the reading pulse is live
for the selected impulse duration.
Important The "result" LED is not coupled with one of the "result" outputs.
Fig. 6-8: Possible wiring of the "Result 1" switching output on the 15-pole D-Sub-HD plug
Important The ratings of the two switching outputs are identical.
Switching behaviour PNP switching against the distribution voltage V
Features Short-circuit proof + temperature-protected,
Galvanically not separate from V
Electrical values 0 V ≤ V
Guaranteed: (VS −1.5 V) ≤ V
≤ V
out
S
S
≤ VS with I
out
Tab. 6-8: Ratings for the switching outputs
≤ 100 mA
out
S
Important Capacitance loads at the switching output affect the switching behaviour. Threshold is a
max. capacitance of 100 nF. Exeeding this value can lead to unwanted pulsing behaviour
of the output.
1. Connect switching outputs depending on application.
2. Wire the switching outputs with a load resistance to test the switching functions using
a high-resistance digital voltmeter.
Indication of incorrect voltages/switching statuses is avoided this way.
Important
To wire the switching outputs using connection module CDB620 or CDM420, see the operating instructions "Connection Module CDB620" (no. 8012119, German/English) or "Connection Module CDM420-0001" (no. 8010004, German/English).
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 61
Page 62

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
6.5 Pin assignment and wire colour assignment of the assembled cables
6.5.1 Pin assignment of the assembled cables
Cable no. 6034414, 6029630, 6034415, 6030928 (Ethernet version)
Pin (4-pole) Signal Function Pin (6-pole)
1 TD+ Transmitter+ 1
3 TD- Transmitter- 2
2RD+ Receiver+ 3
--4
--5
4RD- Receiver- 6
-- Shield -
Tab. 6-9: Pin assignment of the 4-pole M12 plug and the 6-pole RJ45 plug
Cable no. 2042916, 2041834, 2042914, 2042915 (Ethernet version)
Pin (12-pole) Signal Function Pin (15-pole)
2 18 ... 30 V DC Operating voltage 1
8 RxD (Aux) Aux interface (receiver) 2
7 TxD (Aux) Aux interface (sender) 3
-- - 4
1GND Ground 5
11 RD+ (RS-422/485) Host interface (receiver) 6
12 RD– (RS-422/485);
RxD (RS-232)
5 TD+ (RS-422/485) Host interface (sender) 8
6 TD– (RS-422/485);
TxD (RS-232)
4 CAN H CAN bus (IN/OUT) 10
3 CAN L CAN bus (IN/OUT) 11
-- - 12
-- - 13
10 Sensor 1 Digital switching input for exter-
9 SensGND Common ground for the switching
-– Shield -
Host interface (receiver) 7
Host interface (sender) 9
14
nal reading pulse
15
inputs
Tab. 6-10: Pin assignment of the 12-pole M12 socket and the 15-pole D-Sub-HD plug
62 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 63

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
6.5.2 Pin assignment and wire colour assignment of the assembled cables with an open end
Cable no. 6034605 (Ethernet version)
Pin (12-pole) Signal Function Wire colour
1 GND Ground brown
2 18 ... 30 V DC Operating voltage blue
3 CAN L CAN bus (IN/OUT) white
4 CAN H CAN bus (IN/OUT) green
5 TD+ (RS-422/485) Host interface (sender) pink
6 TD– (RS-422/485);
TxD (RS-232)
7 TxD (Aux) Aux interface (sender) black
8 RxD (Aux) Aux interface (receiver) grey
9 SensGND Common ground for the switching
10 Sensor 1 Digital switching input for external
11 RD+ (RS-422/485) Host interface (receiver) grey-pink
12 RD– (RS-422/485);
RxD (RS-232)
Host interface (sender) yellow
red
inputs
violet
reading pulse
Host interface (receiver) red-blue
Tab. 6-11: Pin assignment of the 12-pole M12 socket and wire colours at the open end
Cable no. 6012166
Pin (5-pole) Signal Function Wire colour
1– Shield -
2 +24 V DC Operating voltage red
3GND Ground black
4 CAN H CAN bus (IN/OUT) white
5 CAN L CAN bus (IN/OUT) blue
Tab. 6-12: Pin assignment of the 5-pole M12 plug and wire colours at the open end
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 63
Page 64

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Cable no. 6034418 (Standard version)
Pin (15-pole) Signal Function Wire colour
1 18 ... 30 V DC Operating voltage red
2 RxD (Aux) Aux interface (receiver) violet
3 TxD (Aux) Aux interface (sender) yellow
4 Sensor 2 Digital switching input (adjustable
function, e. g. external reading
pulse)
5GND Ground black
6 RD+ (RS-422/485) Host interface (receiver) light blue
7 RD– (RS-422/485);
RxD (RS-232)
8 TD+ (RS-422/485) Host interface (sender) light grey-turquoise
9 TD– (RS-422/485);
TxD (RS-232)
10 CAN H CAN bus (IN/OUT) grey
11 CAN L CAN bus (IN/OUT) pink
12 Result 1 Digital switching output, adjustable
13 Result 2 Digital switching output, adjustable
14 Sensor 1 Digital switching input for external
15 SensGND Common ground for the switching
Host interface (receiver) blue
Host interface (sender) green
function
function
reading pulse
inputs
red-black
brown
orange
white
white-black
Tab. 6-13: Pin assignment of the 15-pole D-Sub-HD socket and wire colours at the open cable end
64 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 65

Operating Instructions Chapter 7
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Startup and configuration
7 Startup and configuration
Startup, adjustments, configuration and diagnosis are carried out via the SOPAS-ET configuration software. A simple reading rate diagnosis (integrated bargraph display) can, among
other things, be called up independently via two buttons on the device. See chapter 4.7.3
Buttons on the bar code scanner housing, page 38.
7.1 Overview of the startup procedure
• Start up the bar code scanner with the factory default settings
• Install SOPAS-ET configuration software
• Connect the PC with the SOPAS-ET configuration software to the bar code scanner
• In order to optimise the functionality of the bar code scanner, if necessary, adjust and
configure the bar code scanner
• Check correct functioning of the bar code scanner in reading operation
7.2 SOPAS-ET configuration software
The SOPAS-ET configuration software optimises the bar code scanner to the reading conditions on site. The configuration data can be saved and archived as a parameter set (project
file) on the PC.
7.2.1 Functions of the SOPAS-ET configuration software for the bar code scanner (overview)
The online help in the SOPAS-ET configuration software describes the general functions of
the software and their operation: M
ENU, HELP, HELP F1
• Selecting the menu language (English, German)
• Setup communication with the bar code scanner
• Password protected configuration for various operating levels
• Recording of data during the current mode (recording and analyzing the data of certain
bar code scanner memory areas via the data recorder)
• Diagnosing the system
7.2.2 System requirements for the SOPAS-ET configuration software
PC system requirements:
• Recommendation: Pentium III, 500 MHz, 512 MB RAM, CD drive, RS-232 serial data
interface or Ethernet interface card, mouse (recommended) and colour monitor (recommended resolution 1,024 x 768 pixels)
• Operating system Windows 2000
TM
, Windows XPTM or Windows Vista
TM
• Free storage space on the hard drive: approx. 100 MB for SOPAS-ET (V. 2.14) configu-
ration software with help files and approx. 70 MB for "Acrobat Reader"
• PC HTML browser, e.g. Internet Explorer
TM
: For online help system for the SOPAS-ET con-
figuration software
Connection cables: See chapter 11.4.7 Accessories: Cables for Ethernet version, page 115
and chapter 11.4.8 Accessories: General cables and connectors, page 115.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 65
Page 66

Chapter 7 Operating Instructions
Startup and configuration
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
7.2.3 Installing the SOPAS-ET configuration software
1. Start the PC and insert the installation CD.
2. If installation does not start automatically, call setup.exe on the CD.
3. Follow the operating instructions to conclude installation.
7.2.4 Default setting for SOPAS-ET configuration software
Parameter Value
User interface language English (the software has to be restarted after
changes)
Units of length Metric
User group (operating level) Maintenance
Download parameter for changes Immediate, temporary (bar code scanner's RAM)
Upload parameter after online switching Automatic
Window layout 3 (project tree, help, work area)
Serial communication COM 1: 9,600 Bd/19,200 Bd, 8 data bits, 1 stop
bit, no parity 1)
Tab. 7-1: Default setting for the SOPAS-ET configuration software (excerpt)
7.3 Establish communication with the bar code scanner
Prerequisite The TCP-IP protocol at the PC has to be active to enable communication via TCP-IP.
7.3.1 Connecting data interfaces
¾ Connect the PC and bar code scanner to each other.
Connection Via data interface Comment
Bar code scanner STANDARD (RS-232) Directly connect the PC (serial interface) to the AUX or
HOST connection of the bar code scanner using a suitable cable (see chapter 11.4.8 Accessories: General
cables and connectors, page 115).
Bar code scanner
(optional)
Tab. 7-2: Connection between the PC with SOPAS-ET configuration software and the bar code
scanner
ETHERNET (10/100
MBit/s)
Directly connect the PC (Ethernet interface) to the
ETHERNET connection of the bar code scanner (see
chapter 11.4.7 Accessories: Cables for Ethernet version, page 115).
66 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 67

Operating Instructions Chapter 7
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Startup and configuration
7.3.2 Starting the SOPAS-ET configuration software and calling the scan assistant
1. Switch the power supply to the bar code scanner on.
The bar code scanner performs a self-test and is initialised.
2. Switch on the PC and start the SOPAS-ET configuration software.
The SOPAS-ET configuration software opens the program window with an English program interface as standard.
3. In order to change the language setting, click on C
the program interface to e. g. G
ERMAN/DEUTSCH via the menu TOOLS/OPTIONS.
ANCEL and change the language of
4. Once the language setting has been changed, shut down the SOPAS-ET configuration
software and restart it.
5. In the dialog window, select the option C
REATE A NEW PROJECT and click on OK to confirm
it.
6. In the main window under S
The dialog window S
CAN WIZARD appears.
CAN ASSISTENT click on the CONFIGURATION button.
7.3.3 Configuring the Ethernet connection
TIP To establish a connection quickly and easily via Ethernet, the SOPAS-ET configuration soft-
ware has a C
ONNECTION WIZARD in the TOOLS menu.
Manual configuration:
1. In the dialog window N
(IP), check the check box for E
2. Click on the A
DD button.
ETWORK SCAN WIZARD under INTERNET PROTOCOL/INTERNET PROTOCOL
NABLE IP COMMUNICATION.
3. Enter the IP address of the bar code scanner and confirm it by pressing OK in the dialog
window.
The dialog window closes. A new entry appears in the IP A
DDRESS CONFIGURATION list.
4. Click on OK to confirm settings.
The dialog window A
DVANCED SCAN SETTINGS closes.
7.3.4 Configuring the serial connection
1. In the dialog window N
check the check box for E
2. Click on the A
3. Under S
DVANCED... button.
ELECT BAUDRATE(S) deactivate all the baud rates except 57.6 KBD.
4. Select the following P
ETWORK SCAN WIZARD under SERIAL PORT/STANDARD PROTOCOL,
NABLE SERIAL COMMUNICATION.
ORT SETTINGS: 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit.
5. Click on OK to confirm settings.
The dialog window A
DVANCED SCAN SETTINGS closes.
7.3.5 Carrying out a scan
1. In the dialog window S
2. Select the listed devices (CLV640) and confirm via A
CAN ASSISTENT click on the NETWORK SCAN button.
DD DEVICE.
Connected devices are searched for via the connection. The SOPAS-ET configuration
software inserts the found device in the project tree and uploads the current parameter
set (S
YNC CHECK).
3. For configuration of the devices see chapter 7.4.2 Configuring the bar code scanner,
page 69.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 67
Page 68

Chapter 7 Operating Instructions
Startup and configuration
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
7.4 First startup
The SOPAS-ET configuration software optimises the bar code scanner to the reading conditions on site. Starting point for this is the factory default setting which can be adjusted to
optimise the bar code scanner. The SOPAS-ET configuration software is used to create an
application-specific parameter set which can be loaded permanently into the bar code scanner and saved/archived as a project file (spr file with configuration data) on the PC.
Fig. 7-1: Configuration with SOPAS-ET and storage the parameter set
If the bar code scanner is optionally connected to a Micro SD memory card (see
chapter 4.7.4 Parameter set on the Micro SD memory card (optional), page 40) or connect-
ed to a module with parameter memory mode CMC600, the parameter set is saved permanently to the memory card, or to the CMC600 repectively, with every permanent storage of
the parameter set to the bar code scanner.
After the bar code scanner is restarted, the data from the memors card, repectively from the
CMC600 is automatically transferred to the bar code scanner. As such, a bar code scanner
can be exchanged, for example, without losing configuration data (see chapter 8.5 Replac-
ing a bar code scanner, page 76). If there is a memory card as well as a CMC600, the bar
code scanner takes the parameter set from the CMC600.
7.4.1 Overview of the startup procedure
• Connect data interfaces of the PC and the bar code scanner
• Start the SOPAS-ET configuration software and create a new project file
• Configure the scan assistant (activate PC communication)
• Establish communication with the bar code scanner
• Accept current configuration of the bar code scanner in the project tree
• Log on as an "Authorized client" to the bar code scanner
• Configure the bar code scanner for use
• If necessary, apply the "Event Monitor" diagnosis tool
• Load the optimised configuration into the bar code scanner and save permanently
• Save the project file with the configuration data of the bar code scanner on the PC
68 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 69

Operating Instructions Chapter 7
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Startup and configuration
7.4.2 Configuring the bar code scanner
All configurable parameters for the bar code scanner are grouped into a device description
(jar-file) for the SOPAS-ET configuration software. The device description's project tree acts
as a guideline for the configuration.
The function of each respective parameter is explained in a context-sensitive manner in an
online help (F1 key). The valid value range and the default setting list the display window
P
ARAMETER INFO (right mouse button, when the cursor is positioned over the parameter).
Note
In order to configure a device via the SOPAS-ET configuration software, the respective operating level has to be selected in advance. After the start, the SOPAS-ET configuration software functions at the operating level "M
AINTENANCE".
1. In the menu bar under T
2. In the dialog window under U
If the parameter set is password-protected, enter the password "client" in P
Activate/deactivate password protection on the P
OOLS select the command LOGIN DEVICE.
SERLEVEL in the list box select the entry AUTHORIZED CLIENT.
ASSWORD.
ARAMETER register tab.
3. Click on OK to confirm the dialog window.
The previously greyed out parameters on the register tabs are now accessible.
7.4.3 Permanently load changed parameter sets into the device
Changed parameter values are immediately transferred to the bar code scanner's main
memory (RAM) depending on the option (“Immediate download“). To ensure that the changes remain even after the bar code scanner is restarted, the configuration has to be permanently saved in the bar code scanner's PROM.
¾ In order to load the current settings permanently in the bar code scanner, select the
command P
ARAMETER/SAVE PERMANENT in the menu bar under CLV640 or click on in
the tool bar.
7.4.4 Save, display and print the current parameter set
When archiving a parameter set it is recommended to not only save the project file on the
PC but also print out the contents of the file.
1. In order to save the current parameter set, select the menu item S
menu bar under P
2. Enter a file name in the dialog window and confirm it via S
ROJECT.
AVE.
AVE PROJECT AS in the
The SOPAS-ET configuration software saves the current settings in a configuration file
“*.SPR“.
3. In order to print out the current parameter set, select the command P
in the menu bar under P
ROJECT.
RINT/PRINT PREVIEW
The SOPAS-ET configuration software displays a preview of a table with a list of all the
parameter values.
4. Click on in the tool bar at the top of the dialog window.
The dialog window P
RINT for the printer configuration appears.
5. Edit setting accordingly and confirm with OK.
The current project settings are printed as a table on several pages.
TIP To save the current parameter set as a PDF, in the menu bar under P
mand P
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 69
RINT/SAVE AS PDF FILE.
ROJECT select the com-
Page 70

Chapter 7 Operating Instructions
Startup and configuration
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
7.5 Default setting
The values of the default setting are permanently saved in the bar code scanner (ROM) and
in the database of the SOPAS-ET configuration software in the device-specific jar file (see
chapter 7.4 First startup, page 68). A PC is not required to start up the bar code scanner
with the default setting.
7.5.1 Resetting the default setting in the bar code scanner
Prerequisite The SOPAS-ET configuration software is connected online to the bar code scanner.
Two default setting types can be called up via the SOPAS-ET configuration software:
• Complete default setting (L
SOPAS-ET resets all parameter values of the bar code scanner to default. Settings
which have been previously made for the communication parameters of the Ethernet
interfaces or serial data interfaces (e.g. Ethernet address) are overwritten. The connection(s) to the bar code scanner might be interrupted and has (have) to be reconfigured.
• Application-specific default setting (L
SOPAS-ET resets the parameter values of the bar code scanner but does not change
the communication parameters. Settings which have been previously made for the
communication parameters of the Ethernet interfaces or serial data interfaces are kept
and the current connection(s) to the bar code scanner remain(s) established.
OAD FACTORY DEFAULT)
OAD APPLICATION DEFAULT)
1. In order to discard changes to the parameter set as described above, select the corresponding command in the menu bar under CLV640.
The SOPAS-ET configuration software loads the default setting from the bar code scanner and displays the parameter values in the register tabs. In the bar code scanner, the
default setting will first be active in the temporary main memory only.
The default setting can also be saved on or printed via the PC, chapter 7.4.4 Save, dis-
play and print the current parameter set, page 69.
2. In the menu bar under T
3. In the dialog window under U
OOLS select the command LOGIN DEVICE.
SERLEVEL in the list box select the entry AUTORIZED CLIENT.
If the parameter set is password-protected, enter the password "client" in P
4. Click on OK to confirm the dialog window.
5. In the menu bar under CLV640 select the command P
ARAMETER/SAVE PERMANENT.
The SOPAS-ET configuration software transfers the default setting to the permanent parameter memory (PROM) of the bar code scanner.
If the bar code scanner is equiped with the Micro SD memory card or connected to a
connection module CDB620/CDM420 with parameter memory module CMC600, the
default setting will be permanently transferred to parameter memory CMC600 or memory card respectively.
Important Once the default setting has been restored, password-protection is deactivated.
ASSWORD.
70 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 71

Operating Instructions Chapter 7
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Startup and configuration
7.6 Adjusting the bar code scanner
7.6.1 Adjusting the bar code scanner
To completely adjust the bar code scanner, the electrical installation must be complete and
the device must be operated, see chapter 6 Electrical installation, page 51 and chapter 7
Startup and configuration, page 65.
1. Align the bar code scanner in such a way that the angle between the scanning line and
the bar code's lines is almost 90°.
2. To avoid disruptive reflections, rotate the bar code scanner from the plumb line so that
the emitting light meets the bar code at an angle of approx. 105° (line scanner),
chapter 5.3.4 Avoiding surface reflections, page 46.
3. Manually bring objects with bar codes sequentially into the bar code scanner's visual
range. The default setting of the focal position is 285 mm (11.2 in) from the reading
window. Check the reading result using the SOPAS-ET configuration software.
Move objects in different positions (angles) to the reading area and ensure that the
thresholds of the permitted reading angles are not exceeded.
4. Align the bar code scanner in such a way that the good read rate is between 70 and
100%.
5. Tighten the screws on the bar code scanner.
The bar code scanner is aligned with the bar code.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 71
Page 72

Chapter 7 Operating Instructions
Startup and configuration
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
72 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 73

Operating Instructions Chapter 8
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Maintenance
8 Maintenance
8.1 Maintenance during operation
The bar code scanner functions maintenance free. Maintenance is not required to ensure
compliance with the bar code scanner's laser class 2.
Important Do not open the bar code scanner's housing. If the device is opened, the SICK AG warranty
shall not apply.
8.2 Cleaning the bar code scanner
Recommendation In or der to m ake us e of the full o ptical re ading capaci ty of th e bar c o de sca nner, t he read ing
window should be checked regularly (e. g. weekly) for soiling. This is especially recommended when operating the device in harsh conditions (dust, abrasion, humidity, finger prints,
etc.).
Damage to the eyes through laser radiation!
The bar code scanner works with an red light laser of class 2. Looking at the laser's light
path for a longer period of time can damage the eye's retina.
The entire reading window is the LED radiation outlet opening.
Caution - use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those
specified herein may result in hazardous radiaton exposure.
¾ Never look directly into the light path (similar to sun light).
¾ Never direct the device's laser beam at the eyes of persons.
¾ When installing and aligning the bar code scanner, avoid laser beam reflections from
reflective surfaces.
¾ Do not open the housing. (Opening does not interrupt the activation of the laser diode
by the reading pulsing.)
¾ Always observe the latest valid version of laser protection regulations.
The type place displays the window material used for the reading window: CLV640-xxxy
• y = 0: Glass
• y = 1: Plastic
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 73
Page 74

Chapter 8 Operating Instructions
Maintenance
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
8.2.1 Cleaning the reading window
Damage to the reading window!
Reduced reading capacity due to scratches or smears on the reading window!
The reading window for versions CLV640-xxx0 is made of glass.
¾ Do not use aggressive cleaning agents.
¾ Do not use cleaning agents which cause increased abrasion (e.g. powder).
¾ Avoid cleaning motions on the reading window which could cause scratches or abra-
sion.
Damage to the reading window!
Reduced reading capacity due to scratches or smears on the reading window!
The reading window for versions CLV640-xxx1 is made of plastic.
¾ Only clean the reading window with a damp cloth.
¾ Use mild cleansing agents without powder. Do not use strong cleansing agents such
as acetone.
¾ Avoid cleaning motions on the reading window which could cause scratches or abra-
sion.
Important Electrostatic charges cause dust particles to stick to the reading window. This effect can be
combated by using anti-static SICK synthetic cleaner (no. 5600006) in combination with a
SICK lens cloth (no. 4003353).
74 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 75

Operating Instructions Chapter 8
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Maintenance
Cleaning the reading window:
¾ Switch off the device while you are cleaning it (see Laser protection).
¾ Use a clean, soft brush to free the (glass) reading window from dust.
¾ If necessary, additionally clean the (glass) reading window with a clean, damp, lint-free
cloth and a mild, anti-static window cleaning fluid.
¾ Only clean the (plastic) reading window with a clean, damp, lint-free cloth and a mild,
anti-static window cleaning fluid.
Fig. 8-1: Cleaning the reading window
If the reading window is scratched or damaged (cracked, broken), it must be replaced.
Please contact the SICK Service.
8.2.2 Cleaning the housing
¾ Use a soft cloth to free the housing of dust.
¾ If necessary, also clean the LEDs on the housing.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 75
Page 76

Chapter 8 Operating Instructions
Maintenance
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
8.3 Cleaning further optical effective surfaces
Depending on the reading system equipment, additional external sensors with optical effective surfaces can be installed (e.g. photoelectric reflex switch for external reading pulsing).
Soiling of these sensors can cause incorrect switching behaviour.
¾ In order to prevent incorrect switching behaviour, remove soiling from the optical effec-
tive surfaces of the external sensors.
Fig. 8-2: Cleaning of the external optical sensors (reading pulse generator)
8.4 Checking the incremental encoder
If an optional incremental encoder is used, the position of the friction wheel at the drive system should be checked at regular intervals.
¾ Ensure that the incremental encoder has direct and fixed contact with the drive system
and that the friction wheel rotates without slipping.
8.5 Replacing a bar code scanner
Incorrect or damaged bar code scanners have to be removed and replaced with either new
or repaired bar code scanners.
Important Repairs to the bar code scanner should only be carried out by qualified and authorised
SICK AG service staff.
8.5.1 Removing the bar code scanner
1. Switch the power supply to the bar code scanner off.
2. Disconnect all the connection cables on the bar code scanner.
3. Remove the bar code scanner from the holder. Mark the bar code scanner's situation
and alignment on the holder or environment.
4. If available, remove the Micro SD memory card (optional) with the stored parameter set
from the faulty bar code scanner (see chapter 4.7.4 Parameter set on the Micro SD
memory card (optional), page 40). To do this, carefully open the black rubber cover and
slightly press on the memory card in order to unlock it.
5. Insert the memory card accordingly into the empty space of the new, turned-off bar
code scanner the right way round (contacts to the back and top) until it is locked.
6. Close the rubber cover.
76 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 77

Operating Instructions Chapter 8
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Maintenance
8.5.2 Replacing the bar code scanner
1. Align and install the new or repaired bar code scanner (see chapter 5 Installation,
page 41). Observe any marks made previously on the holder or the environment
(chapter 8.5.1 Removing the bar code scanner, page 76).
2. Reconnect connection cables to the bar code scanner (see chapter 6 Electrical instal-
lation, page 51).
3. Switch the power supply to the bar code scanner back on.
The bar code scanner starts with the default setting.
4. If, as an option, a Micro SD memory card has been inserted into the bar code scanner
or a parameter memory module CMC600 into connection module CDB620/CDM420,
the new bar code scanner will automatically load the stored parameter set from the
memory card or CMC600 into its permanent memory. If both a memory card and a
CMC600 are available, the bar code scanner will load the parameter set from the
CMC600.
- or -
Without Micro SD memory card /parameter memory module CMC600: Connect to the
bar code scanner via the SOPAS-ET configuration software, transfer the configuration
stored on the PC via download to the bar code scanner and permanently store the configuration there.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 77
Page 78

Chapter 8 Operating Instructions
Maintenance
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
78 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 79

Operating Instructions Chapter 9
T
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
roubleshooting
9 Troubleshooting
This chapter describes how errors at the bar code scanner can be recognised and eliminated.
9.1 Overview of errors and malfunctions which could occur
9.1.1 Installation error
• The bar code scanner has been unsuitably aligned to objects with bar codes (e.g. visual
glare)
• Reading pulse sensor has been incorrectly positioned (e.g. internal reading gate opens
too late or shuts too early)
• Incremental encoder (optional) positioned incorrectly
9.1.2 Electrical installation error
• Interfaces of the bar code scanner wired incorrectly
9.1.3 Configuration error
• Functions have not been adjusted to the local conditions, e.g. parameters for the data
interface set incorrectly
• Device-related limits have not been considered, e.g. reading distance, aperture angle
• Selected trigger source for reading pulse incorrect
9.1.4 Malfunctions during operation
• Start/Stop operation: External reading pulse is missing, more than one object is in the
reading area
• Device error (hardware/software)
9.2 Detailed malfunction analysis
9.2.1 LEDs on the bar code scanner
The following statuses can, among other things, be read from the LEDs on the bar code
scanner's housing (see chapter 4.7.2 LEDs on the bar code scanner's housing, page 37):
• Reading reliability (Bar graph, diagnostic mode)
• Ready
• Status of the reading result (Result)
• Data trafic on the Host-, Aux- and CAN-interface
The LEDs can display possible malfunctions or errors. Please refer to the system information for further details.
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 79
Page 80

Chapter 9 Operating Instructions
Troubleshooting
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
9.2.2 System information
The bar code scanner displays errors in various ways. The error output is hierarchised and
always allows a detailed analysis:
• Communication errors can occur while transferring telegrams to the bar code scanner.
In this case, the bar code scanner returns an error code.
• Error codes are written into a status protocol for errors which occur during a reading
(chapter 9.3 Status protocol, page 80).
9.3 Status protocol
Important The status protocol remains even after switching the bar code scanner off and on again.
The bar code scanner differentiates between four error types:
• Information
• Warning
• Error
• Fatal error
The bar code scanner only saves the last five entries for each of the error types.
9.3.1 Displaying the status protocol using the SOPAS-ET configuration software
In order to display the status protocol, the SOPAS-ET configuration software has to be online
and connected to the bar code scanner.
1. Connect the SOPAS-ET configuration software with the device.
2. Open the project tree CLV640, S
ERVICE, SYSTEMSTATUS, register tab SYSTEMINFORMATION.
9.4 SICK Support
If an error cannot be eliminated, it is possible that the bar code scanner is defective. The
bar code scanner cannot be repaired by the user, meaning that it is not possible to re-establish functions after a failure. However, the bar code scanner can be rapidly replaced by
the user. See chapter 8.5 Replacing a bar code scanner, page 76.
¾ If an error occurs which cannot be eliminated, please contact SICK Service:
• International: Competent SICK branch office or SICK subsidiary
– Telephone numbers and e-mail addresses on the reverse side of these operating in-
structions
– For the postal address please visit www.sick.com
¾ Only return devices after consultation with the SICK Service.
Important Repairs to the bar code scanner should only be performed by qualified and authorised SICK
AG service staff.
80 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 81

Operating Instructions Chapter 10
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Technical data
10 Technical data
10.1 Datenblatt Barcodescanner CLV640 (Linien-/ Rasterscanner)
Type CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Focus Dynamic focus position
Reading window Line / Raster scanner: With front/side reading window (with angle attachment: light entrance/exit
under 105°)
Laser diode (wavelength) Red light (λ = 655 nm)
MTTR of the laser diode 20,000 h
Device laser class Class 2 in accordance with IEC 60825-1 and EN 60825-1, see warning sign on device for date of
publication
Useable aperture angle max. 50° (front reading window and side reading window)
Scan/decoder frequency 400 ... 1,200 Hz
Resolution 0,20 ... 1.0 mm (5.9 ... 39.5 mil) (type-dependent)
Raster height 15 mm (0.6 in) (8 lines) with 200 mm (7.9 in) reading distance (front reading window)
Bar code print contrast (PCS) ≥ 60 %
Ambient light compatibility 2,000 lx (on bar code)
Number of bar codes per scan 1 ... 20 standard decoder; 1 ... 6 SMART decoder
Number of bar codes per reading
1)
gate
Bar code types Code 39, Code 128, Code 93, Codabar, EAN, EAN 128, UPC, 2/5 Interleaved, Pharmacode
Bar code lengths Max. 50 characters (max. 5,000 characters across all bar codes per reading gate, 500 characters
Print ratio 2:1 ... 3:1
Number of multireads 1 ... 99
Memory card for parameters
(cloning)
Optical indicators 6 LEDs: Ready, Result, Laser, Data, CAN, LNK TX and bargraph display
Acoustic display Beeper, can be switched off, with function for result status display
Control elements 2 buttons (selecting and starting/stopping functions)
Reading pulsing
"Host" data interface Serial: RS-232 or RS-422/485; Ethernet (port 2112),
Data transfer rate 2,4 ... 115.2 kbd
Protocols SICK standard (SOPAS-Cola-A)
Physical configurations Stand-alone
"Aux" data interface Serial: RS-232 (57.6 kbd; 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit); Ethernet (port 2111); fixed data output
"Ethernet" data interface Only for Ethernet version: 10/100 MBit/s, TCP/IP, half/full duplex
"CAN" data interface 20 kBit/s ... 1 MBit/s, SICK CAN-SENSOR network (Master, Slave, Multiplexer)
Digital switching inputs Standard version: 2 ("Sensor 1", "Sensor 2"), 2 additional inputs via CMC600 in CDB620
1 ... 50 bar codes (auto-discriminating)
with multiplexer function (CAN))
Micro SD card (flash card) 512 MB, optional
2)
Pulse sources for start: Switching inputs "Sensor 1"
Cycle; CAN
Pulse sources for stop: Reading pulse source, "Sensor 1", "Sensor 2", command, timer, good read,
condition
adjustable data format (serial) and data output format
format
Ethernet version: 1 ("Sensor 1"), 2 additional inputs via CMC600 in CDB620, optodecoupled, V
max. 32 V, reverse polarity protected, can be wired with PNP output, configurable debouncing 0
...10.000 ms
and/or "Sensor 2"; command; Automatic
=
in
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 81
Page 82

Chapter 10 Operating Instructions
Technical data
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Type CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Digital switching outputs Standard version: 2 ("Result 1", "Result 2"), 2 additional outputs via CMC600 in CDB620
Ethernet version: no output, 2 outputs via CMC600 in CDB620
PNP, I
= max. 100 mA, short circuit-proof, configurable impulse duration (static, 10 ... 1.000 ms)
out
Electrical connection Standard version: Cable (0.9 m (3 ft)) with 15-pole D-Sub-HD plug
Ethernet version: Revolving connector unit with two M12 circular connectors
(12-pole plug, 4-pole socket)
Operating voltage 18 ... 30 V DC in accordance with IEC 364-4-41 (SELV respectively PELV acc. to IEC 60364-4-41
(2005))
Current consumption Line / Raster scanner: typically 5.5 W with DC 24 V ± 10%
Housing Die-cast aluminium
Reading window material Glass or plastic, see type plate CLV640-xxxy
(y = 0: glass, y = 1: plastic)
Electrical safety according to EN 60950-1 (2006-04)
Safety class III, according to EN 61140 (2002-03)
Enclosure rating IP 65, according to EN 60529 (1991-10); A1 (2002-02)
EMC test Emission: according to EN 61000-6-3 (2001-10); immunity: according to EN 61000-6-2 (2005-08)
Vibration-/ shock-test according to EN 60068-2-6 (1995) / according to EN 60068-2-27 (1993)
Weight Standard version:
320 g with connection cable (front reading window), 340 g (side reading window)
Ethernet version:
250 g without connection cables (front reading window), 270 g (side reading window)
Ambient operating temperature/
0 ... +40 °C/–20 ... +70 °C
storage temperature
Max. rel. humidity 90%, no condensation
Housing colour SICK Blue (light blue according to RAL 5012)
1) Reading gate: code evaluation time window created internally by the reading pulse
2) Ethernet version: only switching input "Sensor 1"
Tab. 10-1: Technical specifications for the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner (line/raster scanner)
82 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 83

Operating Instructions Chapter 10
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Technical data
10.2 Data sheet for the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner (line scanner with oscillating mirror)
The technical specifications correspond to those of the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner (line/raster scanner), except for the following variations:
Type CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Reading window side reading window, light exit under 105° (default setting)
Useable aperture angle max. 50°
Oscillating mirror functions Uncontrolled operation:
• Fixed (position can be adjusted) or
• Continuous, free oscillation
Controlled operation (start/stop condition can be adjusted):
• Triggered oscillation (start position and number of oscillations can be adjusted)
• One-shot: One-time oscillation in forward and return motion (start position can be adjusted)
In every oscillation mode, the amplitude can be adjusted separately for each of the two deflection
directions. The deflection speed ratio of one deflection direction to the other can be adjusted within
the selected periodic time for a complete oscillation sequence.
Oscillation frequency / Periodic
time
Max. angle of deflection (amplitude)
Current consumption Typically 6.5 W with DC 24 V ±10 %
Weight Standard version: 420 g
0.5 ... 6.25 Hz / 2,000 ... 160 ms
+20° ... –20°
Ethernet version: 350 g
Tab. 10-2: Technical specifications for the CLV640 Bar Code Scanner (line scanner with oscillating mirror)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 83
Page 84

Chapter 10 Operating Instructions
Technical data
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
10.3 Specification diagrams
Test code Code 39/ITF
Print ratio 2:1
Print contrast > 90 %
Tilt ±10°
Ambient light < 2 000 lx
Good read rate > 75 %
Tab. 10-3: Reading conditions for all specification diagrams
Fig. 10-1: Meaning of selection
1, 2 and 3 in the reading area diagram related to depth of focus diagram.
Observing the reading area diagram (see figure) of the CLV640 of a module width at a focal
position from the top, the selections
diagram for this module width as follows. Therefore, the depth of focus diagram consists of
a slice-shaped sequence of many reading area diagrams along the focal position.
1, 2 and 3 can be transferred to the depth of focus
84 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 85

Operating Instructions Chapter 10
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Technical data
10.3.1 Depth of field ranges of the line scanner/raster scanner with front reading window
Fig. 10-2: Line scanner/raster scanner with front reading window: min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.2 mm (8 mil)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 85
Page 86

Chapter 10 Operating Instructions
Technical data
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Fig. 10-3: Line scanner/raster scanner with front reading window: min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.25 mm (10 mil)
86 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 87

Operating Instructions Chapter 10
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Technical data
Fig. 10-4: Line scanner/raster scanner with front reading window: min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.35 mm (14 mil)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 87
Page 88

Chapter 10 Operating Instructions
Technical data
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Fig. 10-5: Line scanner/raster scanner with front reading window: min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.5 mm (20 mil)
88 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 89

Operating Instructions Chapter 10
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Technical data
Fig. 10-6: Line scanner/raster scanner with front reading window: min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 1.0 mm (40 mil)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 89
Page 90

Chapter 10 Operating Instructions
Technical data
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
10.3.2 Depth of field ranges of the line scanner/raster scanner with side reading window
Fig. 10-7: Line scanner/raster scanner with side reading window: min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.2 mm (8 mil)
90 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 91

Operating Instructions Chapter 10
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Technical data
Fig. 10-8: Line scanner/raster scanner with side reading window: min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.25 mm (10 mil)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 91
Page 92

Chapter 10 Operating Instructions
Technical data
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Fig. 10-9: Line scanner/raster scanner with side reading window: min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.35 mm (14 mil)
92 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 93

Operating Instructions Chapter 10
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Technical data
Fig. 10-10: Line scanner/raster scanner with side reading window: min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.5 mm (20 mil)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 93
Page 94

Chapter 10 Operating Instructions
Technical data
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Fig. 10-11: Line scanner/raster scanner with side reading window: min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 1.0 mm (40 mil)
94 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 95

Operating Instructions Chapter 10
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Technical data
10.3.3 Depth of field ranges of the line scanner with oscillating mirror (side reading window)
Fig. 10-12: Line scanner with oscillating mirror (side reading window): min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.2 mm (8 mil)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 95
Page 96

Chapter 10 Operating Instructions
Technical data
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Fig. 10-13: Line scanner with oscillating mirror (side reading window): min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.25 mm (10 mil)
96 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 97

Operating Instructions Chapter 10
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Technical data
Fig. 10-14: Line scanner with oscillating mirror (side reading window): min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.35 mm (14 mil)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 97
Page 98

Chapter 10 Operating Instructions
Technical data
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
Fig. 10-15: Line scanner with oscillating mirror (side reading window): min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 0.5 mm (20 mil)
98 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
Page 99

Operating Instructions Chapter 10
Technical data
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
(11.82)
(11.82) (13.79)(9.85) (15.76) (17.73)
300250 350 400 450
(3.94)
0
100
(7.88)
200
(15.76)
300
400
(19.70)
500
(23.64)
600
(27.58)
700
(31.52)
800
1200 Hz
(35.46)
900
All dimensions in mm (inch)
Focus position
0
100
min. reading distance
300
200
400
500
600
700
800
max. reading distance
(aperture angle 50°)
1000
900
1100
1200 Hz
max. reading distance
(aperture angle 25°)
1300
1200
Resolution: 1.0 mm (39.4 mil) Scanning frequency (Hz)Reading distance
1400
Fig. 10-16: Line scanner with oscillating mirror (side reading window): min. and max. reading distance depending on the focus position
and the aperture angle with a resolution of 1.0 mm (40 mil)
8011975/0000/2008-04-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 99
Page 100

Chapter 10 Operating Instructions
Technical data
CLV640 Bar Code Scanner
10.3.4 Deflection range of line scanner with oscillating mirror
Fig. 10-17: Deflection range depending on the reading distance, angle of deflection and resolution with a focus position F = 280 mm
(11 in)
Fig. 10-18: Deflection range depending on the reading distance, angle of deflection and resolution with a focus position F = 215 mm
(8 in)
100 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8011975/0000/2008-04-14
 Loading...
Loading...