Page 1

CLV 480
Bar Code Scanner
Advanced line
O PERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Page 2
Operating Instructions
Software versions
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Software versions
Software/Tool Function Version
CLV 480-0010/-0011 Firmware From V 3.5 O824
CLV 480-1010/-1011 Firmware From V 3.5 O824
CLV-Setup User interface (windows-based) From V 4.1 O508
CLV-Setup Help Online help (HTML) From V 4.1 O508
I-2 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Copyright
Copyright © 2005
SICK AG Waldkirch
Auto Ident, Reute Plant
Nimburger Strasse 11
79276 Reute
Germany
Trademarks
TM
Windows 95
Explorer
TM
are registered trademarks or trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation in the USA
TM
/98
, Windows NTTM, Windows 2000TM, Windows XPTM and Internet
and other countries.
Latest manual version
For the latest version of this manual (PDF), see www.sick.com.
Page 3

Operating Instructions
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Quick Finder
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Quick Finder
• What is delivered with the device
– Chapter 3.1.1 Scope of delivery, Page 3-1
• CAUTION!
– Chapter 2 Safety information, Page 2-1
• Mounting the device at the reading station
– Chapter 4 Installation, Page 4-1
• Connecting the device
– Chapter 5 Electrical installation, Page 5-1
• Overview of the device and its functions
– Chapter 3 Product description, Page 3-1
– Chapter 6.2 Default settings, Page 6-1
– Chapter 6.5 Operating modes and outputing the reading result, Page 6-25
– Chapter 9 Technical data, Page 9-1
– Chapter 10.3 Installing and operating the external parameter memory, Page 10-22
• Starting the device with the default settings
– Chapter 6.3 Quick start, Page 6-3
• Installing the "CLV-Setup" program
– Chapter 10.6 Installing and operating the "CLV-Setup" program, Page 10-29
• Adapting the device to the reading application
– Chapter 6.4 Configuring (parameterization) the CLV, Page 6-5
• Troubleshooting
– Chapter 8 Troubleshooting, Page 8-1
• Finding information
– Table of contents, Page I -5
– Index, Page 10 -68
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved I-3
Page 4

Quick Finder
Operating Instructions
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Installation procedure (overview)
CLV in stand-alone configuration (without heater)
Start/stop mode: Reading trigger via “Sensor“ switching input (default setting)
1. Check the delivery to make sure that none of the components is missing.
2. Mount the CLV at the reading station and align it with the object carrying the bar code.
3. Mount the AMV/S 60 Connection Module.
4. Connect the CLV to the AMV/S 60 Connection Module using two cables no. 2 020 302.
Alternatively, connect the device to the AMV/S 60 via the external parameter memory
no. 2 020 307.
5. Mount the sensor for starting/stopping the reading pulse.
6. Connect the reading pulse sensor to the "Sensor" switching input in the AMV/S 60.
7. Connect the host to the host interface in the AMV/S 60.
Adapt the AMV/S 60 to the host interface type of the CLV.
8. Switch on the power supply to the AMV/S 60.
The "Device Ready" LED lights up after the CLV has started.
CLV with external empty parameter memory connected:
After the CLV has started, it immediately copies the internal parameter set to the external parameter memory if the memory is empty. Then the "Device Ready“ LED lights up.
Line scanner with oscillating mirror:
In the default setting, the CLV deflects the scan line around the position CW = 50 with
a frequency of 1 Hz and an oscillating amplitude of max. ±20° (±40 CW).
9. Switch on your PC and start Windows
10. Install the "CLV-Setup" software and the online CLV-Setup Help from the CD-ROM
("Manuals & Software") on your PC.
11. Connect the PC to the terminal interface of the CLV.
To do so, connect a 3-core RS 232 data cable (null modem cable), e. g. no. 2 014 054
to the "Service plug" in the AMV/S 60.
12. Start the "CLV-Setup" program.
CLV-Setup establishes communication with the CLV and uploads the parameter set.
The parameters are then displayed on the tabs.
13. Carry out a test read using test bar codes (clock the CLV accordingly).
Display the reading result in the Terminal Emulator window of the "CLV-Setup" program.
14. Configure the CLV for the application using the settings on the tabs in CLV-Setup.
Copy (download) the modified parameter set to the CLV temporarily.
Do not switch off the power to the AMV/S 60 (CLV)!
15. Test the application under realistic conditions.
16. Check whether the data is transmitted correctly between the CLV and host.
17. If necessary, correct and optimize the parameter values.
Copy (download) the parameter set permanently to the CLV.
CLV with external parameter memory connected:
Copy the modified parameter set to the external parameter memory when CLV-Setup
asks you for confirmation.
18. Save the parameter set as a configuration file "*.scl" in the "CLV-Setup" program.
TM
(minimum requirement: Windows 95TM).
The CLV can then be operated with the application-specific settings.
I-4 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 5
Operating Instructions
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Contents
Table of contents
1 Notes on this document............................................................................................ 1-1
1.1 Purpose ....................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.2 Target audience........................................................................................................................ 1-1
1.2.1 Mounting, electrical installation, maintenance and replacement.................... 1-1
1.2.2 Startup, operation and configuration ......................................................................... 1-1
1.3 Information content................................................................................................................. 1-1
1.4 Symbols....................................................................................................................................... 1-2
2 Safety information....................................................................................................... 2-1
2.1 Authorized users ...................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.1.1 Mounting and maintenance .......................................................................................... 2-1
2.1.2 Electrical installation and replacement ..................................................................... 2-1
2.1.3 Startup, operation and configuration ......................................................................... 2-1
2.2 Intended use.............................................................................................................................. 2-1
2.3 General safety instructions and protection measures.............................................. 2-2
2.4 Quick stop and quick restart................................................................................................ 2-4
2.4.1 Stopping the CLV............................................................................................................... 2-4
2.4.2 Restarting the CLV............................................................................................................ 2-4
2.5 Environmental information....................................................................................................2-4
2.5.1 Power requirements.........................................................................................................2-4
2.5.2 Disposal after removal from service.......................................................................... 2-4
3 Product description .................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1 Design .......................................................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1.1 Scope of delivery............................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1.2 Variants................................................................................................................................. 3-1
3.1.3 System requirements for stand-alone configuration........................................... 3-1
3.1.4 Product features and functions (overview) ............................................................. 3-3
3.1.5 Design ................................................................................................................................... 3-5
3.2 Method of operation............................................................................................................... 3-6
3.2.1 Event-controlled dynamic focus control ................................................................... 3-7
3.2.2 Reading modes.................................................................................................................. 3-7
3.2.3 Scan procedure variants................................................................................................ 3-8
3.2.4 Additional components................................................................................................... 3-9
3.3 Indicators and control elements ........................................................................................ 3-9
3.3.1 Control elements............................................................................................................... 3-9
3.3.2 Function of the LEDs........................................................................................................ 3-9
4 Installation..................................................................................................................... 4-1
4.1 Installation sequence ............................................................................................................. 4-1
4.2 Preparations............................................................................................................................... 4-1
4.2.1 Required components..................................................................................................... 4-1
4.2.2 Required accessories...................................................................................................... 4-1
4.2.3 Required auxiliary parts .................................................................................................. 4-1
4.2.4 Replacing the laser warning label ............................................................................... 4-2
4.2.5 Selecting the mounting location .................................................................................. 4-2
4.2.6 Mounting accessories ..................................................................................................... 4-3
4.2.7 Distance between the CLV and the bar code........................................................ 4-4
4.2.8 Count direction of the code position CP and code angle CW.......................... 4-6
4.3 Mounting and adjusting the device................................................................................... 4-7
4.3.1 Mounting the CLV.............................................................................................................. 4-7
4.3.2 Adjusting the CLV .............................................................................................................. 4-7
4.3.3 Help functions for adjusting the CLV ......................................................................... 4-9
4.4 Mounting the external components................................................................................4-10
4.4.1 Mounting the AMV/S 60 Connection Module......................................................4-10
4.4.2 Mounting the external reading pulse sensor........................................................4-10
4.4.3 Installing incremental encoder ...................................................................................4-11
4.4.4 Mounting the sensors for detecting the object distance.................................4-12
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved I-5
Page 6
Contents
4.5 Dismantling the device........................................................................................................4-13
5 Electrical installation ................................................................................................. 5-1
5.1 Installation sequence.............................................................................................................5-1
5.1.1 SICK Connection Modules (overview)......................................................................5-1
5.2 Electrical connections and cables .....................................................................................5-2
5.2.1 Wire cross-sections ..........................................................................................................5-2
5.2.2 Prefabricated cables (overview) ..................................................................................5-2
5.2.3 Connections/cables for the AMV/S 60 Connection Module............................5-3
5.2.4 Connections/cables for the Bus Connection Modules
BMV 10 and BMS 20 ......................................................................................................5-4
5.2.5 Connections/cables for the external parameter memory
(connection to AMV/S or BMV 10/BMS 20)..........................................................5-5
5.2.6 Connections/cables for the IP 65 connector cover
(connection to AMV 100/200 or BMV 10).............................................................5-5
5.3 Connector pin assignment....................................................................................................5-7
5.3.1 Terminals on the CLV.......................................................................................................5-7
5.3.2 External parameter memory no. 2 020 307/no. 2 021 689/
no. 2 027 543 or connector cover no. 2 021 298/
no. 2 021 267 (optional accessories)......................................................................5-8
5.4 Preparations for electrical installation...............................................................................5-9
5.4.1 Requirements for the host interface..........................................................................5-9
5.4.2 Supply voltage ....................................................................................................................5-9
5.4.3 Non-SICK Power supply unit/connections without the
Connection Module........................................................................................................5-10
5.5 Electrical installation procedure.......................................................................................5-14
5.5.1 Individual steps................................................................................................................5-14
5.5.2 Tools.................................................................................................................................... 5-14
5.5.3 Connecting the supply voltage ..................................................................................5-14
5.5.4 Connecting the host interface ...................................................................................5-15
5.5.5 Connecting the CAN interface ...................................................................................5-16
5.5.6 Connecting the PC..........................................................................................................5-16
5.5.7 Connecting the "Sensor" switching input..............................................................5-17
5.5.8 Connecting the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs...............................................5-18
5.5.9 Connecting the "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching outputs...........................5-21
6 Operation ....................................................................................................................... 6-1
6.1 Overview of steps for starting up the CLV ......................................................................6-1
6.2 Default settings.........................................................................................................................6-1
6.2.1 Default settings of the line scanner CLV 480 (all variants)...............................6-2
6.2.2 Default settings of the line scanner with oscillating mirror
CLV 480 (all variants) ......................................................................................................6-2
6.3 Quick start ...................................................................................................................................6-3
6.3.1 Starting up the CLV with the factory default settings...........................................6-3
6.4 Configuring (parameterization) the CLV...........................................................................6-5
6.4.1 Configuring the CLV via the user interface of CLV-Setup...................................6-5
6.4.2 Function of the tabs in CLV-Setup (overview) ........................................................6-7
6.4.3 Guide to parameterization menu.................................................................................6-9
6.5 Operating modes and outputing the reading result .................................................6-25
6.5.1 Reading mode (standard operating mode).......................................................... 6-25
6.5.2 Percentage evaluation..................................................................................................6-28
6.5.3 Adjusting mode................................................................................................................6-30
6.5.4 Show CP-limits .................................................................................................................6-30
6.5.5 I/O monitor in increment trigger................................................................................6-31
6.5.6 Displaying and editing operating data .................................................................... 6-36
6.5.7 Reading diagnosis ..........................................................................................................6-36
6.5.8 Monitor Host Interface..................................................................................................6-37
6.5.9 Auxiliary input....................................................................................................................6-39
6.5.10 Code statistics for RDT 400....................................................................................... 6-39
Operating Instructions
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
I-6 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 7
Operating Instructions
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Contents
6.5.11 Self-test...............................................................................................................................6-40
6.5.12 Executing CLV functions interactively......................................................................6-41
6.6 CLV messages........................................................................................................................6-42
6.6.1 Displaying messages.....................................................................................................6-42
6.6.2 Error messages ...............................................................................................................6-43
6.7 Switching off the CLV............................................................................................................6-43
7 Maintenance ................................................................................................................. 7-1
7.1 Cleaning the CLV during operation.................................................................................... 7-1
7.2 Maintenance.............................................................................................................................. 7-2
7.3 Disposal....................................................................................................................................... 7-2
8 Troubleshooting ........................................................................................................... 8-1
8.1 Overview of the possible errors and malfunctions...................................................... 8-1
8.1.1 Mounting errors ................................................................................................................. 8-1
8.1.2 Electrical installation errors............................................................................................ 8-1
8.1.3 Parameter errors............................................................................................................... 8-1
8.1.4 Malfunctions........................................................................................................................ 8-1
8.2 Monitoring error and malfunctions.................................................................................... 8-1
8.3 Error messages ........................................................................................................................ 8-2
8.3.1 CLV without external parameter memory................................................................ 8-2
8.3.2 LED error messages for the external parameter memory................................ 8-3
8.3.3 Messages for errors accessing the external parameter memory ................. 8-5
8.4 ST error status in the reading result of a bar code..................................................... 8-7
8.5 Troubleshooting........................................................................................................................ 8-9
8.5.1 General malfunctions: CLV not ready........................................................................ 8-9
8.5.2 Malfunctions in Reading mode: reading trigger errors......................................8-10
8.5.3 Malfunctions in Reading mode: result output errors.........................................8-14
8.5.4 Malfunctions in Reading mode: errors in the result status output...............8-17
8.5.5 Malfunctions in Reading mode: oscillating mirror errors..................................8-17
8.6 SICK Support...........................................................................................................................8-18
9 Technical data.............................................................................................................. 9-1
9.1 Data sheet CLV 480-0010 bar code scanner............................................................. 9-1
9.2 Data sheet CLV 480-1010 bar code scanner............................................................. 9-2
9.3 Data sheet CLV 480-0011 bar code scanner............................................................. 9-2
9.4 Data sheet CLV 480-1011 bar code scanner............................................................. 9-3
9.5 Dimensioned drawings – CLV............................................................................................. 9-3
9.5.1 Line scanner (standard device) without /with heater ......................................... 9-3
9.5.2 Line scanner with oscillating mirror (without/with heater)................................. 9-4
10 Appendix ..................................................................................................................... 10-1
10.1 Overview....................................................................................................................................10-1
10.2 Specification diagrams.........................................................................................................10-1
10.2.1 Reading conditions for all diagrams.........................................................................10-1
10.2.2 Overview of diagrams....................................................................................................10-2
10.2.3 Reading performance data of line scanner...........................................................10-3
10.2.4 Reading performance data of line scanner with oscillating mirror ............10-13
10.3 Installing and operating the external parameter memory...................................10-22
10.3.1 Function ...........................................................................................................................10-22
10.3.2 Installation and electrical connection ...................................................................10-23
10.3.3 Operation.........................................................................................................................10-23
10.3.4 Switching on the device for the first time ...........................................................10-24
10.3.5 Adjusting the parameter set in the external parameter
memory after it has been downloaded to the CLV.........................................10-24
10.3.6 Meaning of the LEDs ..................................................................................................10-25
10.3.7 Error messages ............................................................................................................10-25
10.3.8 Replacing a CLV............................................................................................................10-25
10.4 Optional heating...................................................................................................................10-26
10.4.1 Features...........................................................................................................................10-26
10.4.2 Design ..............................................................................................................................10-26
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved I-7
Page 8
Contents
10.4.3 Function...........................................................................................................................10-26
10.4.4 Electrical installation ...................................................................................................10-27
10.4.5 Outdoor applications ..................................................................................................10-27
10.5 System messages .............................................................................................................10-28
10.5.1 CLV without external parameter memory .......................................................... 10-28
10.5.2 CLV with external parameter memory connected .......................................... 10-28
10.6 Installing and operating the "CLV-Setup" program................................................10-29
10.6.1 Preparations ..................................................................................................................10-29
10.6.2 Installing the software................................................................................................ 10-29
10.6.3 Starting CLV-Setup......................................................................................................10-32
10.6.4 User interface................................................................................................................10-34
10.6.5 Functions ........................................................................................................................10-35
10.6.6 Hot keys ..........................................................................................................................10-35
10.6.7 Opening and closing tabs......................................................................................... 10-36
10.6.8 CLV-Setup Help ............................................................................................................10-36
10.6.9 Transferring parameter sets between CLV-Setup and the CLV ................10-37
10.6.10 Unknown parameters................................................................................................. 10-37
10.6.11 Log file in the Terminal Emulator ........................................................................... 10-38
10.6.12 Starting CLV-Setup with an "INI file" as an argument....................................10-38
10.6.13 The CLV Assistant........................................................................................................10-38
10.7 Configuring a CLV with command strings..................................................................10-39
10.8 Calculating parameter values for setting the CLV..................................................10-41
10.8.1 Calculating the number of scans (for standard decoder)............................10-41
10.8.2 Calculating the start position and mirror speed for the
forward and return phase of the One-Shot function......................................10-43
10.8.3 Calculating the necessary bar code distance if several
bar codes are read on each object...................................................................... 10-44
10.9 Tables .....................................................................................................................................10-45
10.9.1 Calculating the code length of a bar code......................................................... 10-45
10.10 Special applications and procedures .........................................................................10-46
10.10.1 Auxiliary input via the terminal interface ............................................................. 10-46
10.10.2 Daisy-chain configuration
(data forwarding or master/slave arrangement)............................................. 10-49
10.10.3 SICK network (RS 485)............................................................................................. 10-49
10.10.4 Connection to Profibus DP....................................................................................... 10-49
10.10.5 Connection to the DeviceNet.................................................................................. 10-49
10.10.6 Connection to Interbus-S.......................................................................................... 10-49
10.10.7 Connection to Ethernet TCP/IP ..............................................................................10-49
10.10.8 Building a CAN scanner network ...........................................................................10-49
10.10.9 Integration in an OPS reading system ................................................................. 10-49
10.11 Replacing a CLV (copying the parameter set).........................................................10-50
10.11.1 Downloading the parameter set ............................................................................10-50
10.11.2 Importing the parameter set from the external memory ............................. 10-51
10.12 Accessories .......................................................................................................................... 10-52
10.12.1 Mounting accessories................................................................................................10-52
10.12.2 Connection modules ..................................................................................................10-52
10.12.3 Bus connection modules..........................................................................................10-53
10.12.4 Cables, external parameter memories and plug cover ................................ 10-53
10.12.5 Plug-in connections..................................................................................................... 10-55
10.12.6 Reading pulse generators........................................................................................ 10-55
10.12.7 Incremental encoder.................................................................................................. 10-56
10.12.8 Network controller.......................................................................................................10-56
10.13 Dimensioned drawings of the accessories ..............................................................10-57
10.13.1 Angle bracket, single no. 2 013 824...................................................................10-57
10.13.2 Articulated bracket No. 2 018 435......................................................................10-57
10.13.3 Quick clamping device No. 2 016 110............................................................... 10-57
10.14 Supplementary documentation .................................................................................... 10-58
Operating Instructions
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
I-8 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 9
Operating Instructions
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Contents
10.14.1 CLV Connect ..................................................................................................................10-58
10.15 Glossary..................................................................................................................................10-59
10.16 EC Declaration of Conformity .........................................................................................10-67
10.17 Index ........................................................................................................................................10-68
10.18 Bar code example ..............................................................................................................10-73
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved I-9
Page 10

Operating Instructions
Figures and tables
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Abbreviations
AMV/S Connection Module with signal distribution/with additional power supply pack
BMV/S Bus Connection module with signal distribution/with additional power supply
CAN Controller Area Network (standard field bus system with message-orientated data ex-
change protocol)
CLV Code-Leser V-Prinzip
DC Distance Configuration
DOF Depth Of Field
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
HD High Density
HTML Hyper Text Markup Language (page-description language on the internet)
LED Light Emitting Diode
MTBF Mean Time Between Failure
PLC Programmable Logic Controller
RAM Ramdom Acces Memory
ROM Read Only Memory
RTF Rich Text Format (standard document format with format descriptions)
SMART SICK Modular Advanced Recognition Technology
Tables
Table 3-1: CLV variants ........................................................................................................................ 3-1
Table 3-2: Meaning of LEDs: CLV without external parameter memory .........................3-10
Table 3-3: Meaning of LEDs: CLV with external parameter memory................................3-11
Table 4-1: Permissible reading angles between the scan line and bar code ................. 4-5
Table 5-1: Connection Modules for the CLV ................................................................................ 5-1
Table 5-2: Cables for connecting the CLV..................................................................................... 5-2
Table 5-3: Pin assignment of the 15-pin D Sub HD "Host/Term" plug ............................. 5-7
Table 5-4: Pin assignment of the 15-pin D Sub HD "I/O" socket........................................ 5-7
Table 5-5: Pin assignment of the 15-pin D Sub HD "Host/Term" cable plug................. 5-8
Table 5-6: Pin assignment of the 15-pin D Sub HD "I/O" cable socket............................ 5-8
Table 5-7: Maximum cable lengths between the CLV and host........................................... 5-9
Table 5-8: Power consumption of the CLV ................................................................................... 5-9
Table 5-9: Power-up delay as a function of the device number GN................................... 5-9
Table 5-10: Wire color assignment of the cable no. 2 020 303 ........................................5-10
Table 5-11: Wire color assignment of the cable no. 2 020 264..........................................5-11
Table 5-12: Wire color assignment of cable 1 for external parameter
memory no. 2 020 981 ...............................................................................................5-12
Table 5-13: Wire color assignment of cable 2 for external parameter
memory no. 2 020 981 ...............................................................................................5-12
Table 5-14: Wire color assignment cable 1 for connector cover no. 2 021 267..........5-13
Table 5-15: Wire color assignment cable 2 for connector cover no. 2 021 267..........5-13
Table 5-16: Communication parameters for the host interface (default setting)...........5-15
Table 5-17: Characteristic data of the "Sensor" switching input..........................................5-17
Table 5-18: Pin and terminal assignment for "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs..............5-19
Table 5-19: Characteristic data of the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs...........................5-19
Table 5-20: Dynamic focus control: switching inputs/distance
configuration assignment table..................................................................................5-19
Table 5-21: Combination of the functions of the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs.......5-20
Table 5-22: Pin and terminal assignment for "Result 1" to "Result 4"
switching outputs ............................................................................................................5-21
I-10 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 11

Operating Instructions
Figures and tables
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Table 5-23: Characteristic data of the "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching outputs....... 5-21
Table 6-1: Extract: Default parameter settings of the line scanner CLV 480..................6-2
Table 6-2: Extract: Default parameter settings of the line scanner with
oscillating mirror CLV 480..............................................................................................6-2
Table 6-3: Reading distances for default settings......................................................................6-4
Table 6-4: Guide: Parameterizing focus position switchover .................................................6-9
Table 6-5: Guide: Parameterizing oscillating mirror functions .............................................6-10
Table 6-6: Overview: CLV applications in stand-alone configuration or in
arrangement with OTS 400........................................................................................6-14
Table 6-7: Guide: Parameterizing the reading trigger for start/stop mode
in stand-alone configuration .......................................................................................6-15
Table 6-8: Guide: Parameterizing focus control in the CLV for master/
slave arrangement with
OTC 400.............................................................................................................................6-18
Table 6-9: Guide: Parameterizing reading trigger mode in the CLV for
master/slave arrangement with OTC 400............................................................6-19
Table 6-10: Guide: Parameterizing slave mode in the CLV for arrangement
with OTC 400 (master).................................................................................................6-19
Table 6-11: Guide: Parameterizing operation mode in the OTC 400 for
master/slave arrangement.........................................................................................6-19
Table 6-12: Guide: Parameterizing focus control in the CLV for master/slave
arrangement with OTC 400........................................................................................6-20
Table 6-13: Guide: Parameterizing reading trigger mode in the CLV for
master/slave arrangement with OTC 400............................................................6-21
Table 6-14: Guide: Parameterizing tracking mode in the CLV for Object
Tracking mode with OTC 400....................................................................................6-21
Table 6-15: Guide: Parameterizing slave mode in the CLV for Object
Tracking mode with OTC 400....................................................................................6-22
Table 6-16: Guide: Parameterizing Object Tracking mode in the OTC 400 .....................6-22
Table 6-17: Guide: Parameterizing the laser timeout ...............................................................6-23
Table 6-18: Guide: Parameterizing the separation of identical bar codes .......................6-23
Table 6-19: "Monitor Host Interface" function.............................................................................6-37
Table 8-1: Error messages output on the terminal interface .................................................8-2
Table 8-2: LED error messages for access to the external parameter memory ........... 8-3
Table 8-3: Messages for problems accessing the external parameter memory........... 8-5
Table 8-4: Meaning of the ST error status in the reading result...........................................8-7
Table 8-5: Troubleshooting: restoring operation (Reading mode) .......................................8-9
Table 8-6: Troubleshooting: reading trigger errors in Reading mode
(CLV in stand-alone configuration)...........................................................................8-10
Table 8-7: Troubleshooting: reading trigger errors in Reading mode
(CLV integrated in OTS 400 Omni Portal System).............................................8-13
Table 8-8: Troubleshooting: result output errors in Reading mode
(CLV in stand-alone configuration)...........................................................................8-14
Table 8-9: Troubleshooting: result output errors in Reading mode
(CLV integrated in OTS 400 Omni Portal System).............................................8-16
Table 8-10: Troubleshooting: errors in the result status output in Reading mode........ 8-17
Table 8-11: Troubleshooting: oscillating mirror errors in Reading mode...........................8-17
Table 9-1: Technical specifications of the CLV 480-0010 .....................................................9-1
Table 9-2: Technical specifications of the CLV 480-1010 .....................................................9-2
Table 9-3: Technical specifications of the CLV 480-0011 .....................................................9-2
Table 9-4: Technical specifications of the CLV 480-1011 .....................................................9-3
Table 10-1: Reading conditions for specification diagrams....................................................10-1
Table 10-2: Overview of specification diagrams for the line scanner.................................10-2
Table 10-3: Overview of specification diagrams for the line scanner with
oscillating mirror..............................................................................................................10-2
Table 10-4: External parameter memory ...................................................................................10-22
Table 10-5: CLV system messages..............................................................................................10-28
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved I-11
Page 12

Operating Instructions
Figures and tables
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Table 10-6: Additional CLV system messages for the connected
parameter memory .....................................................................................................10-28
Table 10-7: Default settings in CLV-Setup..................................................................................10-32
Table 10-8: Formulas for calculating the code length of a bar code ...............................10-45
Table 10-9: Communication parameters on the terminal/PC for the auxiliary input ..10-48
Table 10-10: Communication parameter settings for the SICK Hand-held
Scanner from the IT 38xx/46xx/48xx/58xx series........................................10-48
Table 10-11: Accessories: mounting accessories .....................................................................10-52
Table 10-12: Accessories: connection modules.........................................................................10-52
Table 10-13: Accessories: bus connection modules................................................................10-53
Table 10-14: Accessories: cables and connector covers for the CLV without heater.10-53
Table 10-15: Accessories: cables and connector covers for the CLV with heater .......10-55
Table 10-16: Accessories: plug-in connections ..........................................................................10-55
Table 10-17: Accessories: incremental encoder........................................................................10-56
Table 10-18: Accessories: network controller .............................................................................10-56
Table 10-19: Supplementary documentation in English language ......................................10-58
I-12 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 13

Operating Instructions
Figures and tables
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Figures
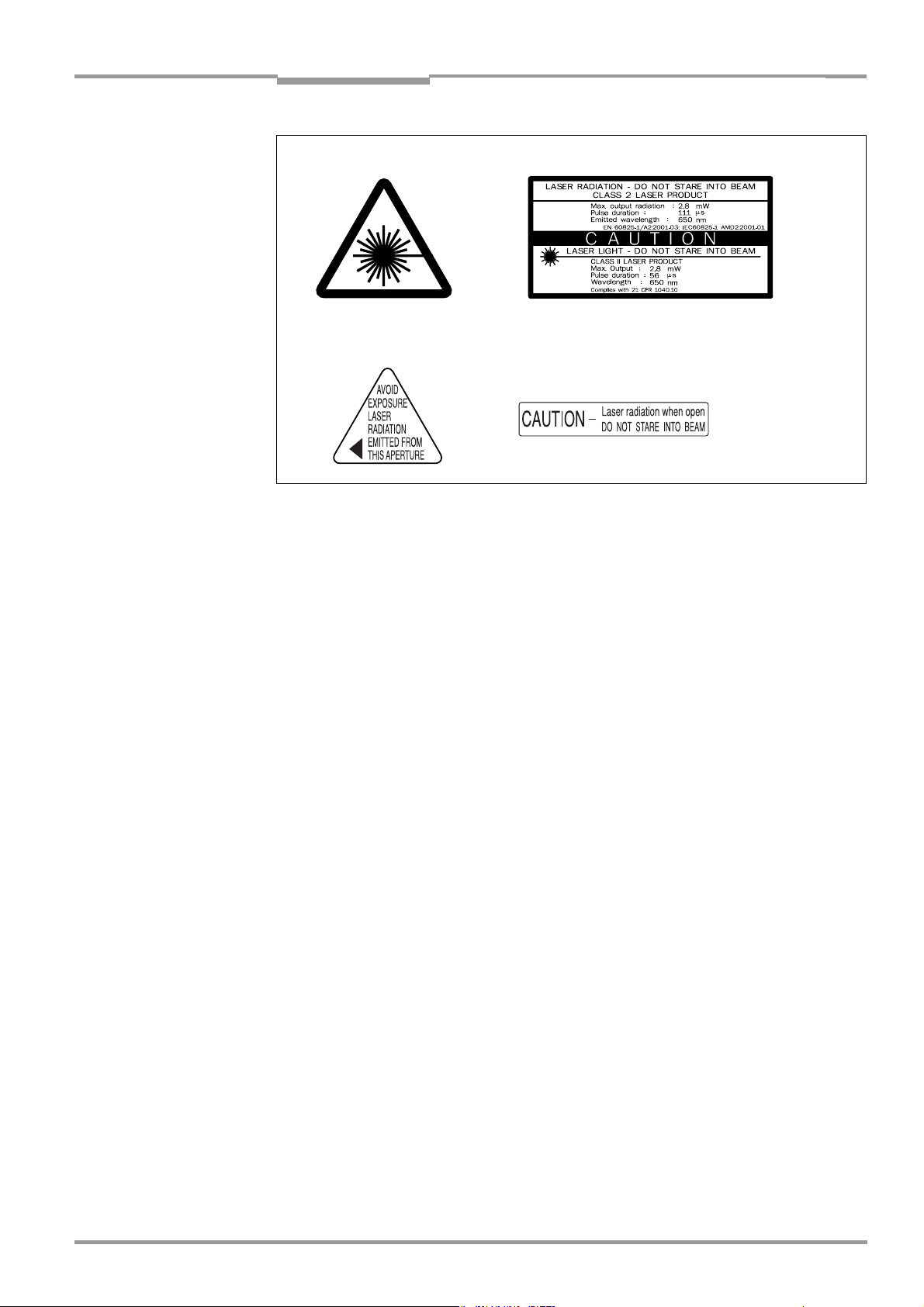
Fig. 2-1: Laser warning labels on the CLV.....................................................................................2-3
Fig. 3-1: Design of the CLV 480 .......................................................................................................3-5
Fig. 3-2: Block diagram: CLV functions...........................................................................................3-6
Fig. 3-3: Dynamic focus control: classification of the reading range in distance
configurations.........................................................................................................................3-7
Fig. 3-4: CLV in stand-alone configuration (start/stop mode) and in tracking mode ...3-8
Fig. 3-5: LEDs........................................................................................................................................3-10
Fig. 4-1: Line scanner: replacing the laser warning labels......................................................4-2
Fig. 4-2: Line scanner: position of the securing threads on the CLV..................................4-3
Fig. 4-3: Line scanner: Mounting possibilities of the CLV........................................................4-3
Fig. 4-4: Scanning methods: alignment with bar code and conveyor direction..............4-4
Fig. 4-5: Definition of the reading distance a and of the aperture angle a ......................4-4
Fig. 4-6: Line scanner: Reading angle between the scan line and the bar code...........4-5
Fig. 4-7: Avoiding surface reflections: Angle between the emitted light and the
bar code (tilted away from the vertical axis) ..............................................................4-5
Fig. 4-8: Count direction of the code position CP in the scan line and of the
code angle CW for the oscillating mirror ......................................................................4-6
Fig. 4-9: Line scanner: scan line in Adjusting mode..................................................................4-9
Fig. 4-10: Line scanner: mounting example for the external reading pulse sensor..... 4-10
Fig. 4-11: Mounting example for object distance detection ..................................................4-12
Fig. 5-1: Block diagram: Connection of the CLV to the AMV/S 60
connection module...............................................................................................................5-3
Fig. 5-2: Connecting the host interface.......................................................................................5-15
Fig. 5-3: Connecting the terminal interface ...............................................................................5-16
Fig. 5-4: Connections of the "Sensor" switching input..........................................................5-17
Fig. 5-5: Connections of the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs ..........................................5-18
Fig. 5-6: Connections of the "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching outputs.......................5-21
Fig. 6-1: Bar code pattern (Code 39; module width 0.35 mm (13.8 mil);
Print ratio 2:1) ........................................................................................................................6-3
Fig. 6-2: Oscillating mirror: "Oscillating with fixed amplitude" mode ................................ 6-11
Fig. 6-3: Oscillating mirror: "Oscillating with variable amplitude" mode ..........................6-12
Fig. 6-4: One-Shot: Object tracking (bar code read from front).........................................6-13
Fig. 6-5: CLV-Setup: Displaying the reading result in the Terminal Emulator ...............6-26
Fig. 6-6: Reading result of the terminal interface: structure for Good Read................. 6-27
Fig. 6-7: Reading result of the terminal interface: structure for No Read......................6-27
Fig. 6-8: CLV-Setup: Displaying the percentage evaluation in the
Terminal Emulator..............................................................................................................6-29
Fig. 6-9: Appearance of scan line in the "Show CP-limits" mode .....................................6-31
Fig. 6-10: CLV-Setup: Selection of the signals to be displayed in I/O Monitoring......... 6-32
Fig. 6-11: CLV-Setup: Example of output in the "I/O Monitoring" dialog box..................6-33
Fig. 6-12: CLV-Setup: "Operating Data" dialog box...................................................................6-36
Fig. 6-13: CLV-Setup: Displaying the reading result of the host interface in
the Terminal Emulator with direction identifier at the beginning
(in this case: O = Output)................................................................................................6-38
Fig. 6-14: CLV-Setup: Displaying the self-test result in the Terminal Emulator .............. 6-40
Fig. 6-15: CLV-Setup: Dialog box for executing Show limits ..................................................6-41
Fig. 6-16: CLV-Setup: Displaying the system messages in the Terminal
Emulator when starting the CLV...................................................................................6-42
Fig. 7-1: Cleaning the reading window............................................................................................7-1
Fig. 7-2: Cleaning the external optical sensors (reading pulse generator,
object-height detector) .......................................................................................................7-2
Fig. 9-1: Dimensions of the CLV 480 line scanner, front reading window .......................9-3
Fig. 9-2: Dimensions of the CLV 480: line scanner with oscillating mirror,
side reading window ............................................................................................................9-4
Fig. 10-1: CLV 480-0010/-0011 (line scanner): Reading field height as a
function of the reading distance and resolution ....................................................10-3
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved I-13
Page 14

Operating Instructions
Figures and tables
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Fig. 10-2: CLV 480-0010/-0011 (line scanner): Min. and Max. radial reading
distance as a function of the focus position at a resolution of 0.25 mm
(9.8 mil) and an aperture angle of 40°......................................................................10-4
Fig. 10-3: CLV 480-0010/-0011 (line scanner): Min. and Max. radial reading
distance as a function of the focus position at a resolution of 0.25 mm
(9.8 mil) and an aperture angle of 60°......................................................................10-4
Fig. 10-4: CLV 480-0010/-0011 (line scanner): Min. and Max. radial reading
distance as a function of the focus position at a resolution of 0.30 mm
(12 mil) and an aperture angle of 40°.......................................................................10-5
Fig. 10-5: CLV 480-0010/-0011 (line scanner): Min. and Max. radial reading
distance as a function of the focus position at a resolution of 0.30 mm
(12 mil) and an aperture angle of 60°.......................................................................10-6
Fig. 10-6: CLV 480-0010/-0011 (line scanner): Min. and Max. radial reading
distance as a function of the focus position at a resolution of 0.35 mm
(13.8 mil) and an aperture angle of 40°...................................................................10-7
Fig. 10-7: CLV 480-0010/-0011 (line scanner): Min. and Max. radial reading
distance as a function of the focus position at a resolution of 0.35 mm
(13.8 mil) and an aperture angle of 60°...................................................................10-8
Fig. 10-8: CLV 480-0010/-0011 (line scanner): Min. and Max. radial reading
distance as a function of the focus position at a resolution of 0.5 mm
(19.7 mil) and an aperture angle of 40°...................................................................10-9
Fig. 10-9: CLV 480-0010/-0011 (line scanner): Min. and Max. radial reading
distance as a function of the focus position at a resolution of 0.5 mm
(19.7 mil) and an aperture angle of 60°................................................................10-10
Fig. 10-10: CLV 480-0010/-0011 (line scanner): Min. and Max. radial reading
distance as a function of the focus position at a resolution of 1.00 mm
(39.4 mil) and an aperture angle of 40°................................................................10-11
Fig. 10-11: CLV 480-0010/-0011 (line scanner): Min. and Max. radial reading
distance as a function of the focus position at a resolution of 1.00 mm
(39.4 mil) and an aperture angle of 60°................................................................10-12
Fig. 10-12: CLV 480-1010/-1011 (line scanner with oscillating mirror): Reading
field height as a function of the reading distance and resolution.................10-13
Fig. 10-13: CLV 480-1010/-1011 (line scanner with oscillating mirror):
Min. and Max. radial reading distance as a function of the focus
position at a resolution of 0.30 mm (12 mil) and an aperture angle
of 40°...................................................................................................................................10-14
Fig. 10-14: CLV 480-1010/-1011 (line scanner with oscillating mirror):
Min. and Max. radial reading distance as a function of the focus
position at a resolution of 0.30 mm (12 mil) and an aperture angle
of 50°...................................................................................................................................10-14
Fig. 10-15: CLV 480-1010/-1011 (line scanner with oscillating mirror):
Min. and Max. radial reading distance as a function of the focus
position at a resolution of 0.35 mm (13.8 mil) and an aperture angle
of 40°...................................................................................................................................10-15
Fig. 10-16: CLV 480-1010/-1011 (line scanner with oscillating mirror):
Min. and Max. radial reading distance as a function of the focus
position at a resolution of 0.35 mm (13.8 mil) and an aperture angle
of 50°...................................................................................................................................10-16
Fig. 10-17: CLV 480-1010/-1011 (line scanner with oscillating mirror):
Min. and Max. radial reading distance as a function of the focus
position at a resolution of 0.50 mm (19.7 mil) and an aperture angle
of 40°...................................................................................................................................10-17
Fig. 10-18: CLV 480-1010/-1011 (line scanner with oscillating mirror):
Min. and Max. radial reading distance as a function of the focus
position at a resolution of 0.50 mm (19.7 mil) and an aperture angle
of 50°...................................................................................................................................10-18
I-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 15

Operating Instructions
Figures and tables
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Fig. 10-19: CLV 480-1010/-1011 (line scanner with oscillating mirror):
Min. and Max. radial reading distance as a function of the focus
position at a resolution of 1.00 mm (39.4 mil) and an aperture
angle of 40° ......................................................................................................................10-19
Fig. 10-20: CLV 480-1010/-1011 (line scanner with oscillating mirror):
Min. and Max. radial reading distance as a function of the focus
position at a resolution of 1.00 mm (39.4 mil) and an aperture
angle of 50° ......................................................................................................................10-20
Fig. 10-21: CLV 480-1010/-1011 (line scanner with oscillating mirror): deflection
range as a function of radial reading distance, deflection angle and
resolution............................................................................................................................10-21
Fig. 10-22: External parameter memory, installed on the CLV ............................................10-22
Fig. 10-23: CLV-Setup: "Device configuration" tab with the CLV start options.............. 10-23
Fig. 10-24: CLV-Setup: dialog box for adjusting the external parameter memory ....... 10-24
Fig. 10-25: CLV with heater: temperature curve inside the housing..................................10-26
Fig. 10-26: CLV-Setup: Result display of the AutoBaud Detect function..........................10-33
Fig. 10-27: User interface of the "CLV-Setup" software.........................................................10-34
Fig. 10-28: CLV-Setup: entering commands in the Terminal Emulator.............................10-39
Fig. 10-29: Line scanner: calculating the number of scans for ladder-type
bar code arrangements................................................................................................10-41
Fig. 10-30: Line scanner: calculating the number of scans for fence-type
bar code arrangements................................................................................................10-41
Fig. 10-31: Line scanner with oscillating mirror: calculating the number of
scans for fence-type bar code positioning............................................................10-42
Fig. 10-32: One-Shot: Line scanner with oscillating mirror: calculating the
number of scans for fence-type bar code positioning......................................10-43
Fig. 10-33: Required distance between the bar codes on an object ................................ 10-44
Fig. 10-34: Auxiliary input via the terminal interface of the CLV........................................... 10-46
Fig. 10-35: CLV-Setup: auxiliary input on the Terminal Emulator ........................................ 10-47
Fig. 10-36: Dimensions of the angle bracket, single No. 2 013 824................................10-57
Fig. 10-37: Dimensions of the articulated bracket No. 2 018 435 ...................................10-57
Fig. 10-38: Front view of quick clamping device No. 2 016 110 with angle
braket No. 2 0130824 ................................................................................................10-57
Fig. 10-39: Copy of the Declaration of Conformity (Page 1, scaled down) .....................10-67
Fig. 10-40: Scannable bar codes with various module widths (print ratio 2:1)............. 10-73
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved I-15
Page 16

Operating Instructions
Figures and tables
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
I-16 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 17

Operating Instructions Chapter 1
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Notes on this document
1 Notes on this document
1.1 Purpose
This document is a guide to the operation of the bar code scanner
• CLV 480 with dynamic focus
in the following variations:
• Line scanner
–CLV 480-0010
–CLV 480-0011
• Line scanner with oscillating mirror
–CLV 480-1010
–CLV 480-1011
This document provides information on
• Mounting and connecting the device
• Startup
• Operating and configuring (parametrizing) the device
• Maintenance
• Exchanging the device without losing the parameter set
• Special applications and procedures
The bar code scanner with all its variants will in this manual be referred to as the "CLV",
except where a distinction is necessary.
1.2 Target audience
This document is intended for persons who are responsible for the following activities:
1.2.1 Mounting, electrical installation, maintenance and replacement
Electricians and service technicians.
1.2.2 Startup, operation and configuration
Technicians and engineers.
1.3 Information content
This document contains all the information required to mount, install, and start up the CLV
with the factory settings.
A series of step-by-step instructions is provided for each of these activities.
Configuration of the CLV for the application-specific reading situations is carried out with
the Windows-oriented PC software "CLV-Setup".
form of the online help system CLV-Setup Help. The procedure for installing and operating
the software is described in the appendix.
For further information on the design of the bar code scanner or on bar code technology in
general, please contact the Division Auto Ident at SICK AG.
Internet address: www.sick.com.
Further assistance is also available in the
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 1-1
Page 18

Chapter 1 Operating Instructions
Notes on this document
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
1.4 Symbols
Some of the information in this document is marked specially so that you can access it
quickly:
Warning
Warnings are provided to prevent injury to operating personal or serious damage to the bar
code scanner.
¾ Always read warnings carefully and observe them at all times.
Note Indicates special features or characteristics.
Explanation Explanations provide background information on technical features.
Recommendation Recommendations help you carry out certain procedures more effectively.
Tip Tips explain settings in the user interface of the "CLV-Setup" program.
Default Marks a section containing the factory defaults.
SCANNING FREQUENCY This typeface is used to refer to a term in the "CLV-Setup" program.
Icons refer to buttons in the "CLV-Setup" program.
"Host receive fault" This typeface is used for messages output via the terminal interface of the CLV.
This symbol is used to mark sections that describe steps carried out with the "CLV-Setup"
program.
This symbol refers to additional technical documentation.
¾ An action must be performed. This symbol characterizes single-step operating instructions.
Multiple-step operating instructions are characterized by sequential numbers.
Ö Here you select a function of the "CLV-Setup" user interface.
1-2 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 19

Operating Instructions Chapter 2
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Safety information
2 Safety information
2.1 Authorized users
For the CLV to function correctly and safely, it must be mounted and operated by sufficiently
qualified personnel.
The end user must be supplied with the operating instructions.
The end user must be provided with expert tuition and is advised to read the operating
instructions.
The following qualifications are required for the various tasks involved:
2.1.1 Mounting and maintenance
• General technical training
• Knowledge of the standard guidelines relating to safety at the workplace
2.1.2 Electrical installation and replacement
• Practical training in electrical engineering
• Knowledge of the standard safety guidelines relating to electrical engineering
• Experience operating the devices in the relevant application (e. g. conveyor belt)
2.1.3 Startup, operation and configuration
• Experience operating the devices in the relevant application (e. g. conveyor belt)
• Knowledge of the hardware and software environment of the relevant application
(e. g. conveyor belt)
• Basic understanding of Windows 95TM/98TM, Windows NT4.0TM, Windows 2000TM or
Windows XP
• Ability to use an HTML browser (e. g. Internet ExplorerTM)
• Basic understanding of data transfer methods
• Basic understanding of bar code technology
TM
2.2 Intended use
The CLV is designed to detect and decode bar codes automatically. It is mounted in a
reading station and reads bar codes on objects positioned on a conveyor belt, for example.
In stand-alone configuration the CLV transfers the data content of the decoded bar codes
via its host interface to a host for further processing. Being integrated in the OTS 400 Omni
Tracking System together with other CLVs, the CLV transfers the read results via its CAN in
terface to the OTC 400 Omni Tracking Controller.
Any warranty claims vis-à-vis SICK AG will be rendered invalid if the device is used for any
other purpose or if changes are made to the device, also as part of the mounting and
electrical installation procedures.
Note Don’t open the device. The producer warranty will be forfeited if the device is opened.
-
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 2-1
Page 20

Chapter 2 Operating Instructions
Safety information
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
2.3 General safety instructions and protection measures
¾ Always read the general safety instructions carefully and observe them at all times.
Please also observe the warnings in front of the operating instructions in each chapter
of this document.
Shock hazard
Depending on the type of device, the AMS 60 Connection Module (accessory) for the CLV
is connected to a mains voltage of 230 V AC 50 Hz or 115 V AC 50/60 Hz.
¾ When working with electrical equipment, always follow the relevant safety specifications.
Laser beam can cause blindness
The CLV uses a class 2 red-light laser. Looking directly at the laser beam can seriously
damage your eyesight.
The entire glass window acts as a laser outlet aperture.
Caution – use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those
specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
¾ As with sunlight, never look directly into the laser beam.
¾ Do not direct the laser beam at other persons.
¾ Mount and align the CLV in such a way to prevent the laser beam reflecting off mirrored
surfaces.
¾ Do not open the housing.
(Opening the housing does not deactivate the laser diode).
¾ Observe the laser protection specifications (latest version).
Laser power
The laser operates at a wave length of λ = 650 nm (visible red light). The power output at
the reading window is max. 2.8 mW. The emitted radiation is not dangerous to human skin.
The product is classified in laser class 2 (laser class II) in accordance with EN 60825-1,
IEC 60825-1, and 21 CFR 1040.10 (for publication date, see the warning sign on the device)
Laser warnings
The laser warning symbols (Fig. 2-1) can be found on the CLV at the following locations:
• The laser warning symbol on line scanners is positioned beside the reading window on
the front side of the device. The laser warning in GB English/US English is located on the
side containing the electrical connections
The additional laser warnings in English applicable to the USA are positioned beside the
reading window on the front side of the device and at the bottom.
• The laser warning symbol on line scanners with oscillating mirror is located above the
reading window, on the cover of the mirror. The laser warning in GB English/US English
is located on the side containing the electrical connections
The additional laser warnings in English applicable to the USA are positioned on the cover of the mirror and on the front side of the decive at the bottom.
(see Fig. 3-1, Page 3-5).
.
2-2 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 21
Operating Instructions Chapter 2
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Safety information
black-yellow signed on device:
black-silver signed on device:
Fig. 2-1: Laser warning labels on the CLV
Note A set of laser warnings in German/US English and French/US English is included in the
delivery scope. The GB English/US English warnings can be pasted over with these if
necessary.
If the CLV is installed in a machine/panel with the result that the laser warning labels
are no longer visible, additional warnings (not included in the scope of delivery) must
be provided on the machine beside the emergence aperture of the laser beam.
Internal protective circuits
The CLV is equipped with monitoring circuits that deactivate the laser diode in the event of
a malfunction. No maintenance required to keep this product in compliance with laser
class II.
Activation and deactivation of the laser diode is controlled by the reading pulse trigger.
A timer (laser timeout) automatically deactivates the laser diode in Reading mode ("Sensor
input" and "Serial interface" trigger mode) if the reading interval has not ended after
10
minutes (default setting). However, it does not end the reading interval. In this case, the
CLV outputs the message:
"Laser safety timeout"
on the terminal interface. The reading interval must be terminated by resetting the trigger
signal. The laser diode is activated again by the next reading trigger.
The laser timeout can be set in the range of 1 min to 25 h or deactivated (see Table 6-17,
Page 6-23)
In the Percentage Evaluation mode, Adjusting mode and Show CP-limits as well as in
the Free-running Reading mode the laser diode is constantly activated.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 2-3
Page 22

Chapter 2 Operating Instructions
Safety information
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
2.4 Quick stop and quick restart
2.4.1 Stopping the CLV
¾ Switch off the power supply or remove the cables of the CLV from the connection
module.
This can result in loss of the following (at the most):
• The application-specific parameter set, if it was stored temporarily in the CLV
• The last reading result
• Daily operating data
(operating hours counter, number of reading triggers, number of Good Reads, number
of No Reads, maximum duration trigger, minimum duration trigger, number of matches
with match code 1, number of matches with match code 2, numbers of No Matches)
2.4.2 Restarting the CLV
¾ Switch on the power supply or reattach the cables of the CLV to the connection
module.
The CLV resumes operation with the parameter set that was last stored permanently
and reset the daily operating data.
2.5 Environmental information
The CLV is designed to cause minimum impact on the environment. It does not contain any
silicone-based materials on the housing surface and, therefore, does not represent any pro
blems for paint sprayers in paint shops, for example.
2.5.1 Power requirements
The power requirements depend on the variants:
• The line scanner has a typical power consumption of 11 W and max. 16 W
• The line scanner with oscillating mirror has a typical power consumption of 13 W and
max.
18 W
• The line scanner equipped with an integrated heater has a typical power consumption
of 75 W and max. 90 W
• The line scanner with oscillating mirror equipped with an integrated heater has a typical
power consumption of 75
The values are given for devices with disconnected switching outputs.
2.5.2 Disposal after removal from service
Always dispose irreparable devices in a manner that is not harmful to the environment and
in accordance with the applicable national waste disposal regulations. The CLV can be se
parated into recyclable secondary raw materials and special-category waste (electronic
scrap).
See also Chapter 7.3 Disposal, Page 7-2.
SICK AG currently does not accept delivery of unusable or irreparable devices.
W and max. 100 W
-
-
2-4 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 23

Operating Instructions Chapter 3
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
3 Product description
3.1 Design
3.1.1 Scope of delivery
The CLV is supplied with the following in the packing:
• An information sheet (notes on device) with terminal diagram and Quick Start instruc-
tions
• An additional set of Class 2 laser warning labels (self-adhesive) in German/US English
and French/US English
Depending on the number of devices ordered, one or more of the following:
• CD-ROM (no. 2 029 112) with
– "CLV-Setup" program for Windows
(HTML files)
– "CLV-Connect" PC software (HTML files showing terminal diagrams)
– CLV 480 Operating Instructions in English and German as PDF edition as well as
additional publications (connections module, other SICK bar code scanners)
– freely available "Acrobat Reader" PC software for reading PDF files
Note The latest versions of all the current publications/programs on the CD-ROM can also be
downloaded from
www.sick.com.
TM
and the "CLV-Setup Help" online help system
Depending on the number of copies ordered, the delivery includes (optional):
• CLV 480 Operating Instructions in English and/or German (printed edition)
Chapter 10.12 Accessories, Page 10-52 contains an overview of the available mounting
accessories, (bus) connection modules, external parameter memories, cables, connectors,
incremental encoder, and network controller as well as sensors for generating the reading
pulse.
3.1.2 Variants
The CLV is currently available in the following variants:
Type (red light) Part. no. Scanning method Reading window Heater
CLV 480-0010 1 024 065 Line scanner End No
CLV 480-1010 1 024 066 Line scanner with oscillating mirror Side Yo
CLV 480-0011 1 024 067 Line scanner End Yes
CLV 480-1011 1 024 068 Line scanner with oscillating mirror Side Yes
Table 3-1: CLV variants
3.1.3 System requirements for stand-alone configuration
CLV without heater The following are required to start up and operate the CLV 480 without heater:
1. A SICK Connection Module to provide the power supply and connect the data and
function interfaces. Available types:
–For connecting one CLV:
AMV 60-011 (no. 1 017 134) for 18 to 30 V DC, enclosure rating max. IP 54
AMS 60-013 (no. 1 017 139) for 230 V AC 50 Hz/24 V DC,
enclosure rating max. IP 54
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 3-1
Page 24

Chapter 3 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
AMS 60-012 (no. 1 017 140) for 115 V AC 50 to 60 Hz/24 V DC,
enclosure rating max. IP 54
AMS 100-011 (no. 6 021 105) for 18 to 30 V DC, enclosure rating max. IP 65
–For connecting two CLVs:
AMV 30-071 (no. 1 017 391) for 18 to 30 V DC, enclosure rating max. IP 54
AMV 200-011 (no. 6 021 106) for 18 to 30 V DC, enclosure rating max. IP 65
– or –
Alternatively, a non-SICK Power pack with a voltage output of 18 to 30 V DC pursuant
to IEC
742 (functional extra-low voltage pursuant to IEC 364-4-41) and a minimum po-
wer output of 20 W.
Cable no. 2 020 264 (3 m (9.84 ft)) with 15-pin D Sub HD connector and one open
end for connecting the CLV to the non-SICK Power pack (supply voltage).
2. The following operating voltages/power output values:
– AMV 60-011: 18 to 30 V DC (pursuant to IEC 364-4-41), min. 20 W
– AMV 30-071: 18 to 30 V DC (pursuant to IEC 364-4-41), min. 40 W
– AMV 100-011: 18 to 30 V DC (pursuant to IEC 364-4-41), min. 20 W
– AMV 200-011: 18 to 30 V DC (pursuant to IEC 364-4-41), min. 40 W
– AMS 60-013: 230 V AC ±10 % 50 Hz
– AMS 60-012: 115 V AC ±10 % 50 to 60 Hz
3. Fitting cables see Chapter 5.2.2 Prefabricated cables (overview), Page 5-2.
4. With external clock pulse (start/stop of reading interval) supply via the "Sensor"
switching input: a suitable reading pulse sensor for signaling an object with a bar code,
e.g. a photoelectric reflex switch.
5. With extended external clock pulse (stop of reading interval) supply via the “IN 4“
switching input: a suitable reading pulse sensor for generating the end of reading
intervall, e.g. a photoelectric reflex switch.
6. With object distance detection via the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs: suitable sensors
for multi-stage dynamic focus control, e. g. photoelectric reflex switches.
7. To separate bar codes with the same name (same code type, identical data content)
using the "Compare Code Position" function: a suitable incremental
e. g. no. 2 022 714.
8. A higher-level computer (host) with a data interface of type RS 422/485 or RS 232.
9. A PC (min. 80486, 66 MHz, 16 MB RAM, CD drive, a serial port (COM x), mouse
(recommended)) with Windows 95TM/98TM, Windows NT4.0TM, Windows 2000TM or
Windows XPTM.
10. A 3-core RS 232 data cable (null modem cable) with two 9-pin D Sub sockets for connecting the PC to the terminal interface of the CLV in the Connection Module, e. g. no.
2 014 054. Pin
11. An HTML browser, e. g. Internet ExplorerTM, for using the online help system "CLV-Setup
Help".
12. The appropriate bus connection module BMV/BMH 10 (available on request) for connecting the CLV to the Interbus-S, Profibus DP, the Device Net or to Ethernet.
13. For connection of the CLV to the CAN Scanner Network: the Operating Instructions
“Application of the CAN interface“ (no. 8 009 180, English edition).
2 (RxD) and Pin 3 (TxD) are crossed.
encoder,
3-2 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 25

Operating Instructions Chapter 3
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
CLV with heater The following are required to start up and operate the CLV 480 with heater:
1. A SICK Connection Module from the AMV 100 or AMV 200 series to provide the power
supply and connect the data and function interfaces.
Available types:
– For connecting one CLV: AMV 100-011 (no. 6 021 105) for 24 V DC, max. IP 65
– For connecting two CLVs: AMV 200-011 (no. 6 021 106) for 24 V DC, max. IP 65
– or –
Alternatively, a non-SICK Power pack with a voltage output of 24 V DC +20 %/–10 %
to IEC
742 (functional extra-low voltage pursuant to IEC 364-4-41) and a minimum po-
wer output of 100 W.
Cable no. 2 020 264 (3 m (9.84 ft)) with 15-pin D Sub HD connector and one open
end for connecting the CLV to the non-SICK Power pack (supply voltage).
2. The following operating voltages/power output values:
– AMV 100-011: 24 V DC +20 %/–10 % (pursuant to IEC 364-4-41), min. 100 W
– AMV 200-011: 24 V DC +20 %/–10 % (pursuant to IEC 364-4-41), min. 200 W
3. See pos. 3 under CLV without heater
3.1.4 Product features and functions (overview)
High-performance laser scanner:
• Line scanner (front-end reading window)
• Scanner variant with oscillating mirror (side reading window)
• Dynamic focus
• Dynamic focus control with external or internal trigger
• Reading range 260 to 2,050 mm (10.2 to 80.7 in)
(with oscillating mirror 220 to 1,950 mm (8.7 to 76.8 in))
• Resolution 0.25 to 1.0 mm (9.8 to 39.4 mil)
(with oscillating mirror 0.3 to 1.0 mm (12 to 39.4 mil)
• Scanning/decoding frequency 600 to 1,200 Hz
• Variable active evaluation range of the scan line
Safety and user-friendly features:
• Robust, compact metal housing, max. IP 65, CE certification
• Laser class 2, laser diode switches off if reading interval is active for too long and if the
output power is exceeded
• Automatic self-test on startup. Can also be triggered at any time
• Diagnosis tools for installing and monitoring the system
• Parameterized output of reading diagnosis data in reading mode
• Operating data query, and error messages
• Test string function for signaling readiness for operation
• Future proof thanks to firmware update via serial interface (flash PROM)
• Low power consumption, other voltage range
Easy operation/configuration:
• With "CLV-Setup" PC software for Windows
• Alternatively with simple command strings, also for use with special devices
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 3-3
Page 26

Chapter 3 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
• Four status LEDs
• External parameter (optional) simplifies device replacement
Operating modes:
• Reading mode
• Percentage evaluation - for assessing the quality of the reads
• Special functions for system installation
Bar code evaluation:
• All standard bar code types
• Max. 50 codes per reading pulse, max. 12 per scan
• Code comparison (max. 5 matchcodes), can also be used as filter or sort criterion for
the reading result
• Sort sequences: code position, FIFO, LIFO, code length list
Reading pulse (start/stop mode):
• External reading pulse, via switching input(s) or serial interface
• Timer
• Free running
• OTS mode (special application)
Object tracking (tracking mode):
• Object tracking (20 objetcs) in combination with OTS 400 Object Tracking System
Electrical interfaces:
• Serial host interface (RS 422/485 or RS 232) with variable transfer rate and telegram
structure
• Serial terminal interface (RS 232) as auxiliary data interface with special diagnosis and
statistics functions
• CAN interface for integration in the SICK CAN Scanner Network or a CANopen network,
and for OTS operation
• 6 switching inputs for external reading pulse, focus control, encoder increment and special function (teach-in)
• 4 switching outputs for signaling defined events in reading mode
Connections:
• All interfaces are connected via two 15-pin D Sub HD connections on the housing
• AMV/S 60 or AMV 100/200 connection module for connection to host, AMV 70/71 for
integration in SICK CAN scanner network
• BMS 10/BMV 10 bus connection modules for connection to field bus systems
Additional functions:
• Version with integrated heater (max. –35 °C (–31 °F))
• External parameter memory in connector cover (optional)
• Can be used in an omni-directional reading system in combination with the OTS 400
Omni Tracking System
3-4 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 27
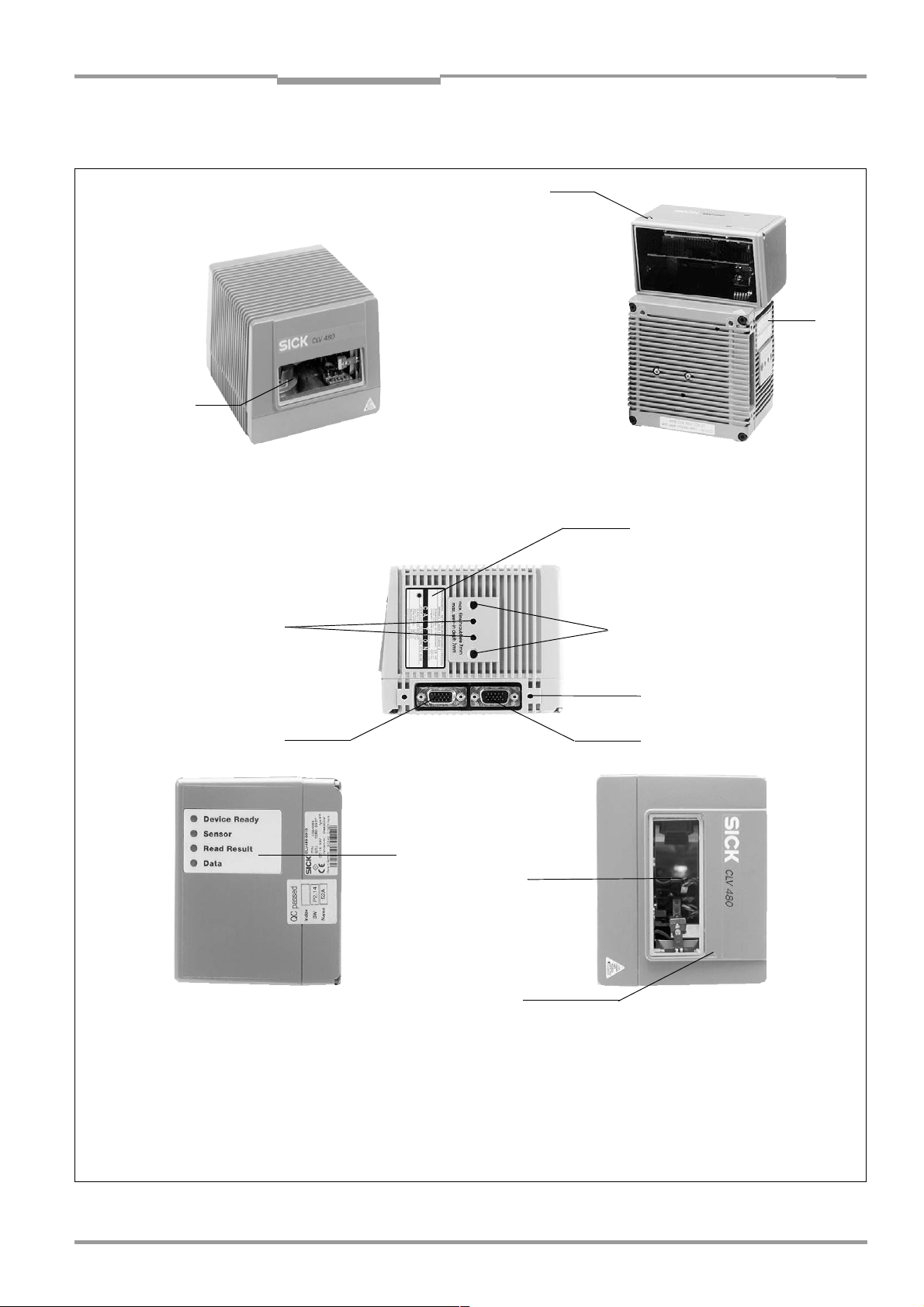
Operating Instructions Chapter 3
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
3.1.5 Design
➋
➋
➋
Line scanner
(front-end reading window)
➊
➏
Line scanner with oscillating mirror
(side reading window)
➋
➌
➍
➎
➐
➑
➒
Legend
➊ Drilled hole, Ø 3.6 mm (0.14 in),
6 mm (0.24 in) deep
➋ Laser warning labels
➌ Blind hole thread M6, 7 mm (0.28 in)
for securing the device
deep,
Fig. 3-1: Design of the CLV 480
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 3-5
➍ Blind hole thread M4,
10 mm (0.39 in) deep, for the
connector cover
➎ "Host/Term" connector
15-pin D Sub HD plug
➏ "I/O" connector,
15-pin D Sub HD socket
➐ LEDs (status indicators)
➑ Reading window
➒ Mark for count direction of the code
position (deflection direction of the
laser beam)
Page 28
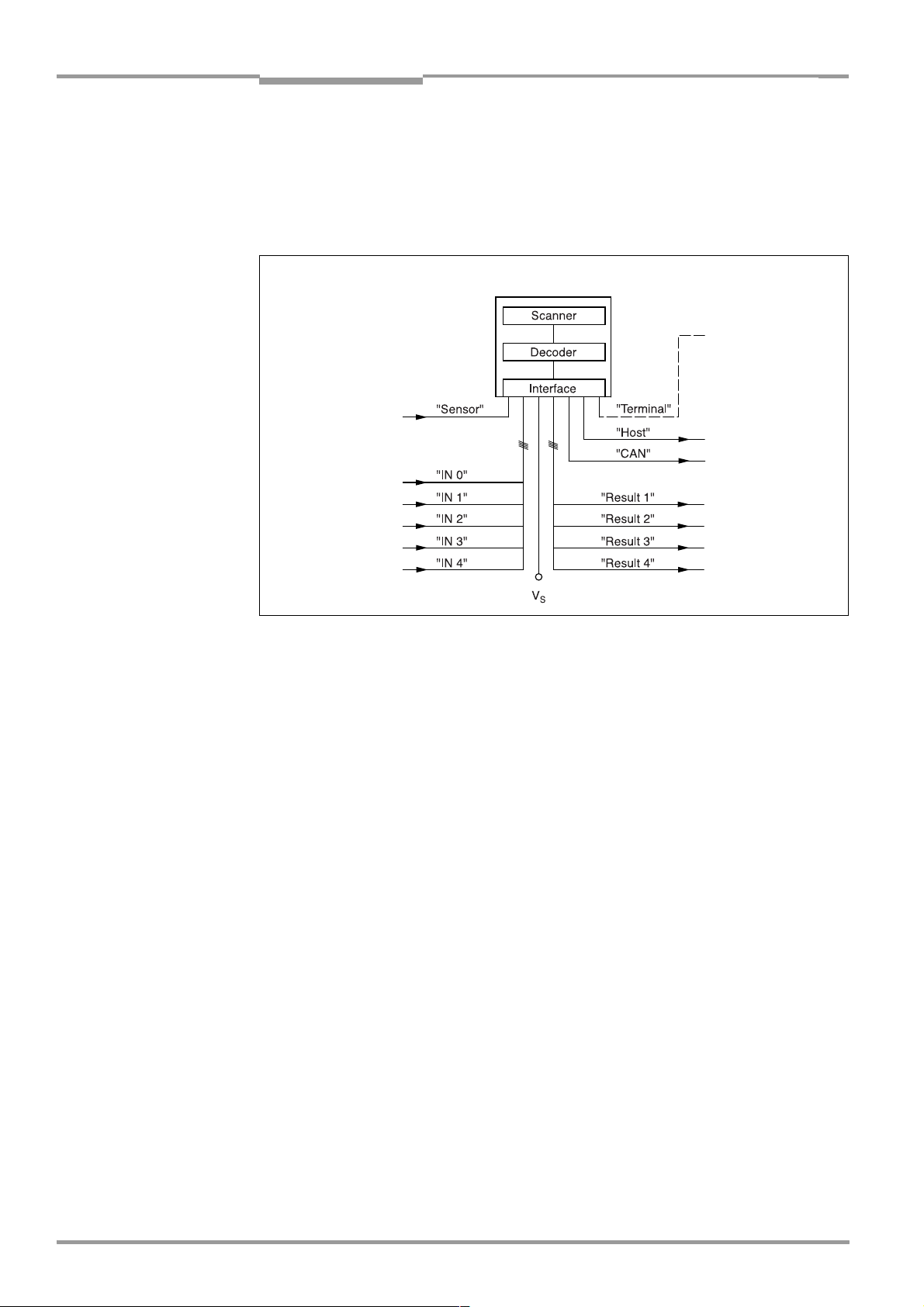
Chapter 3 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
3.2 Method of operation
The CLV first scans the bar code with a scan line and then decodes it. In stand-alone configuration, the data is forwarded via the serial host interface (main data interface) to a host/
PC for further processing, or via the CAN interface to the OTS 400 Omni Tracking System.
An overview of the CLV functions is provided in
CLV 480
Photoelectric
switch
Reading pulse
1)
Signal
Focal control
Trigger One-Shot
Conveyer increment
End of reading
interval
1) if required
Fig. 3-2.
PC
Operation
Parameterization,
etc.
HOST
Further processing
of the reading result
CAN bus
Status display
e. g. Device Ready
e. g. Good Read
e. g. No Read
e. g. Match 1
Fig. 3-2: Block diagram: CLV functions
The CLV is equipped with two decoders:
• The SMART decoder (SICK Modular Advanced Recognition Technology) for decoding
bar codes with small code height, bar codes that are dirty or damaged, as well as bar
codes that are tilted excessively (azimuth angle)
• The tried-and-tested standard decoder of the CLV series
The CLV derives useful diagnosis data from the reading process and can transfer it to also
the host. It also records operating data that can be interrogated at any time. The quality of
the read can be checked in percentage evaluation mode.
To start the reading process when an object is located in the reading field, the CLV requires
a suitable trigger. This opens an internal time window ("reading interval") in the CLV. In the
default configuration, this trigger is supplied by an external reading pulse sensor. Alternative
trigger sources include Free-running mode or a command via the host interface (for more
complex applications: OTS trigger).
The current operating status is indicated by four LEDs.
If the trigger is supplied externally, the "Sensor" switching input instructs the CLV to start the
reading process. The five "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs switch the focus position in
response to certain events, as an alternative to the autofocus function. The "IN
"IN
4” inputs can also be assigned special functions. The four "Result 1" to "Result 4"
3" and
switching outputs can be assigned to different functions for displaying the result status and
also control external devices, such as a PLC.
The CLV is operated and configured via the serial terminal interface (auxiliary interface) using
the "CLV-Setup" software or via the host interface/terminal interface using command
strings.
System and error messages help you to configure the device and to locate the source of
errors during startup and reading mode.
3-6 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 29
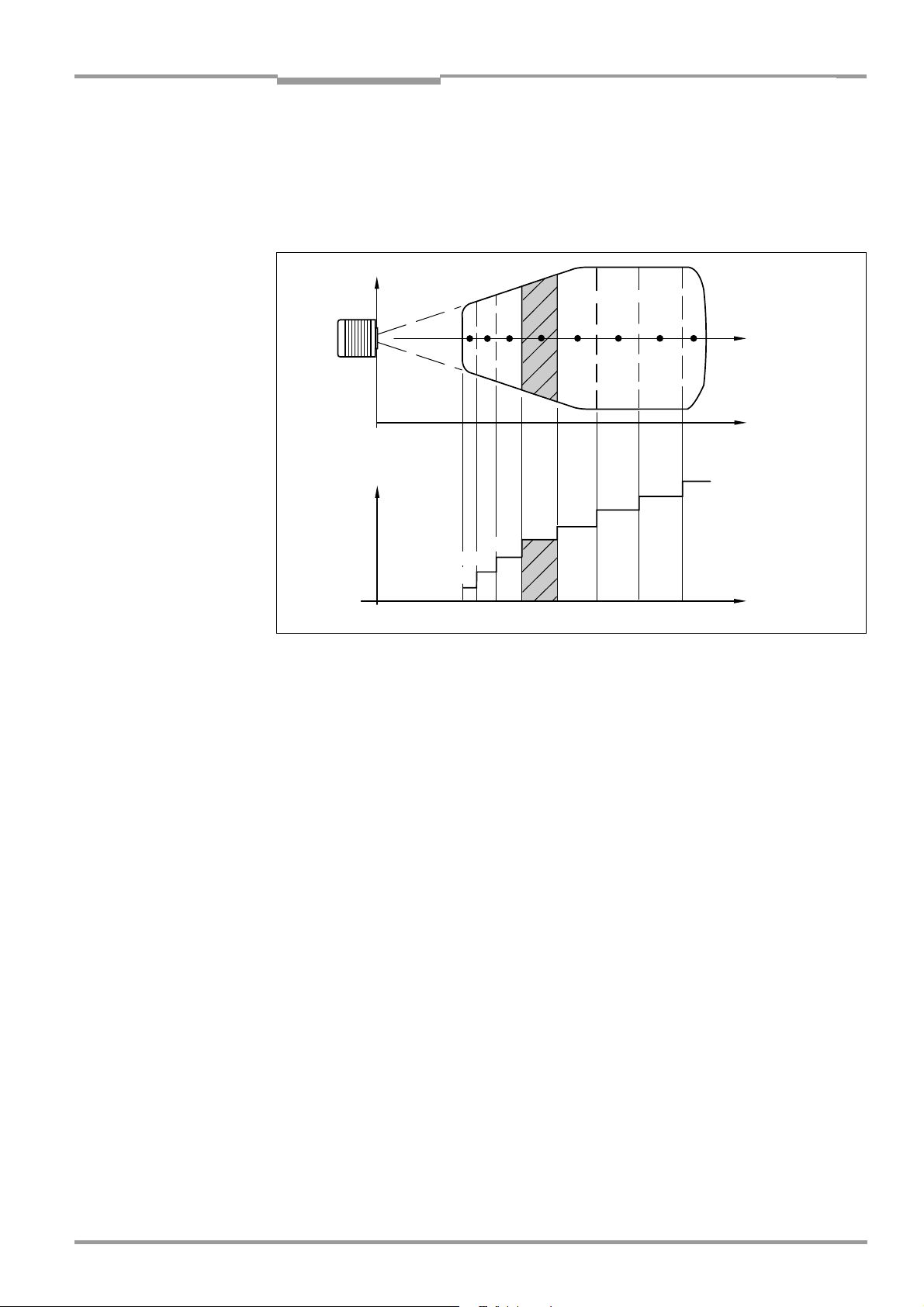
Operating Instructions Chapter 3
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
3.2.1 Event-controlled dynamic focus control
The CLV can switch its focus position in response to certain events and thus dynamically
cover a large reading range. A maximum of eight reading ranges can be defined as distance
configurations for this purpose and approached consecutively in reading mode (see
Fig. 3-3).
Reading
field height
123 5 8
Focus
position
DC 3
DC 2
DC 1
DC = Distance Configuration
Fig. 3-3: Dynamic focus control: classification of the reading range in distance configurations
4
DC 5
DC 4
6 7
DC 6
Focus position
Reading distance
DC 8
DC 7
Reading distance
The switch over takes place in response to changes in the object distance (with reads from
above: object height detection). The trigger source for the switchover can be:
• A signal combination at the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs, a command on the host
interface/terminal interface or the integrated timer (e.
g. for search mode). Additional in
the case of the line scanner with oscillating mirror also the oscillating mirror reversal
points. The distance configurations are assigned to the switchover sequence by means
of a programmable assignment table.
• In combination with the OTS 400 Omni Tracking System:
Alternatively the object height information from the OTS 400 or any other CLV via the
CAN bus.
3.2.2 Reading modes
Start/stop mode
During the reading process, only one object is located in the reading field in start/stop
mode, i. e. all read bar codes can be clearly assigned to the object. As default, two reading
pulse sensors at the beginning and at the end of the reading field control the starting and
stopping of the reading process (
Fig. 3-4). The size of the reading field is determined by the
distance between the two sensors. Alternatively, the reading process can be controlled with
command strings via the data interface or can be left free running. The CLV either outputs
the reading result at the end of the reading pulse (the back edge of the object has left the
end of reading field) or already during the reading pulse as a result of predefined (parame
trized) conditions. To separate bar codes of the same type with identical contents, an incremental encoder must be connected to the CLV.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 3-7
-
Page 30
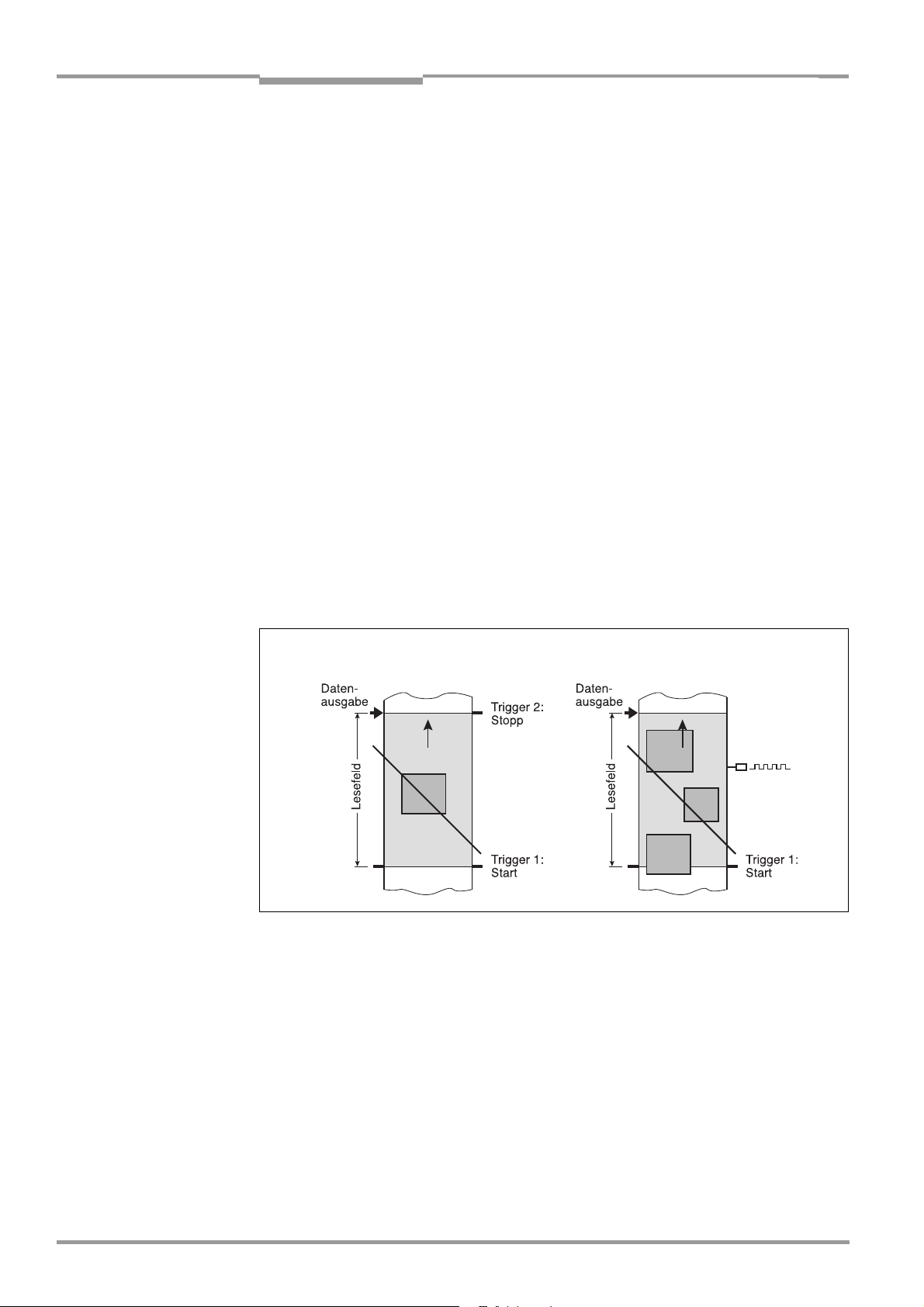
Chapter 3 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
In object polling mode, the CLV automatically detects the beginning and the end of the object located in the reading field without any help of external sensors. The minimum temporal
distance between two consecutive objetcs must not fall below 70 ms when the objects are
moved on the conveyor belt.
Tracking mode (in combination with the OTS 400 Omni Tracking System)
In tracking mode with the OTS 400 Omni Tracking System, max. 20 objects can simultaneously be located in the reading field (following each other), i. e. the CLV must be able to clearly assign the bar codes to the objects (Fig. 3-4). As default, a reading pulse sensor at the
beginning of the reading field controls the starting of the reading process. The end of the
reading field is determined by the parametrized object release point in the OTC 400 Omni
Tracking Controller. In this way, the size of the reading field is clearly determined.
In order to track the transport of the objects in the reading field, a regularly-timed pulse is
required. This is generated by an external incremental encoder for the OTC 400 which re
gularly supplies a pulse at least every 10 mm (0.39 in) of movement in conveying direction.
As a result, the the distance between the reading pulse sensor and the object release point
is clearly time-mapped in the CLV. Fluctuations when approaching the conveyor or decrea
ses in speed due to heavy load with numerous conveyor obejcts are also recorded. An internal clock in the CLV also allows operation at a constant conveyor speed. A gap of at least
50 mm (1.97 in) is necessary for the clear separation of consecutive objects. The reading
result for an object is output by the OTC 400 after the back edge of the object passes the
object release point. Alternatively, the reading process can be started with a command
strings via the data interface.
-
-
Start/stop mode
Fig. 3-4: CLV in stand-alone configuration (start/stop mode) and in tracking mode
Tracking mode
3.2.3 Scan procedure variants
Line scanner (standard device)
Generates a scan line; due to the V-principle of the beam generation, the reading field height
(the useful length of the scan line for evaluation purposes) is dependent on the reading
distance.
Line scanner with oscillating mirror
The oscillating mirror also deflects the scan line perpendicularly to the scan direction at both
sides around the neutral position with a low oscillating frequency. As a result, the CLV can
also scan larger areas for bar codes. Due to the V-principle of beam generation, the reading
field height is dependent on the reading distance.
3-8 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 31

Operating Instructions Chapter 3
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Product description
In addition to parking (fixed position) and simple deflection with maximum amplitude, optimized oscillating mirror functions are also available:
• Oscillating with variable deflection amplitude per distance configuration
• One-Shot: one-off, defined deflection per reading pulse (forward and return phase)
3.2.4 Additional components
Heater
The CLV can be permanently equipped with a heater for applications involving temperatures
up to max. –35 °C (–31 °F), e. g. in a freezer.
The design, technical data, and power-up behavior of the CLV are described in Chapter 10.4
Optional heating, Page 10-26.
External parameter memory
The external parameter memory is located in a connector cover which, when mounted,
covers the two electrical terminals on the CLV (IP 65). The parameter memory saves you
time when a CLV is replaced locally by providing a copy of the current parameter set. In other
words, you do not have to configure the new device.
For information on applications and operating procedures, see Chapter 10.3 Installing and
operating the external parameter memory, Page 10-22.
3.3 Indicators and control elements
3.3.1 Control elements
The CLV is operated and configured via the terminal interface (auxiliary interface) using the
"CLV-Setup" program or using command strings sent via the host interface/terminal inter
face. A variety of parameter options allow you to adapt the device to a wide range of applications.
The following can be defined:
• The configuration of the code types
• The read, evaluation, and output properties
• The communication parameters of the host interface/CAN interface
• The structure of the data output string for "Good Read" and "No Read" on the host in-
terface/CAN interface
• The function of the terminal interface
Chapter 10.6 Installing and operating the "CLV-Setup" program, Page 10-29 describes the
procedure for installing the "CLV-Setup" program and explains how to use it. The parameterization (configuration) procedure is explained in Chapter 6.4 Configuring (parameterizati-
on) the CLV, Page 6-5.
3.3.2 Function of the LEDs
Four LEDs indicate the operating status, activity of the laser diode, reading result status, and
data transfer on the host interface. The LEDs are located on the rear of the device (
Page 3-10).
If the optional external parameter memory is connected, the LEDs also indicate whether the
memory was successfully accessed.
Fig. 3-5,
-
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 3-9
Page 32

Chapter 3 Operating Instructions
Product description
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Device Ready
Sensor
Read Result
Data
Fig. 3-5: LEDs
The meaning of the LEDs in the various operating modes/functions is shown in Table 3-2
and Table 3-3.
CLV without external parameter memory
Operating mode LED Display Function
Start Device Ready Green • Lights up after power-up if the self-test was successful
Subsequent behavior depends on selected start option:
Start option: START WITH EXTERNAL PARAMETERS (DEFAULT)
• Lights up constantly (CLV has loaded internal parameter set)
Start option: START WITH INTERNAL PARAMETERS
• Lights up constantly (CLV has loaded internal parameter set)
Start option: START WITH COPY INTERN -> EXTERN
• Blinks constantly together with the "Read Result" LED
1)
(CLV has loaded internal parameter set)
Read Result Green
Start option: START WITH COPY INTERN -> EXTERN
• Blinks constantly together with the "Device Ready" LED
1)
Reading mode Device Ready Green • Lights up constantly
• Extinguishes with new operating mode/function
Sensor Green • Lights up if reading diode is active
(The laser diode is activated/deactivated by reading pulse)
• Lights up constantly in Free-running mode, since laser diode is always active
Read Result Green LED is linked to the "Result 2" switching output and indicates the selected result
status for the defined pulse duration of the output.
• Lights up after a successful read (default: Good Read)
• Lights up if the match code comparison is active, the bar code read matches the
specified match code(s) and the corresponding result status output is selected
for the "Result 2" output
Data Yellow • Flickers when the CLV transfers data to the host on the host interface
Percentage Sensor Green • Lights up constantly, as Free-running mode is active
evaluation Read Result Green Behavior depends on the reading quality:
• Extinguishes if reading rate < 30 %
• Blinks twice a second if reading rate 30 % to 70 %
• Blinks five times a second if reading rate 70 % to 90 %
• Lights up constantly if reading rate > 90 %
Adjusting mode Sensor Green • Lights up constantly, as Free-running mode is active
Show CP-limits Sensor Green • Blinks bright/dark alternately, in the frequency with which the scan line is (partially)
masked out
1) Set the start option to START WITH THE INTERNAL PARAMETERS on the DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab in the "CLV-Setup" program. Download to CLV!
Table 3-2: Meaning of LEDs: CLV without external parameter memory
3-10 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 33

Operating Instructions Chapter 3
Product description
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
CLV with external parameter memory connected
Operating mode LED Display Function
Start Device Ready Green • Lights up after power-up if the self-test was successful
Subsequent behavior depends on selected start option:
Start option: START WITH EXTERNAL PARAMETERS (default)
• Blinks for approx. 10 s before lighting up constantly
(CLV has loaded the parameter set from the external parameter
memory and starts reading mode straight away)
• Blinks for approx. 10 s together with the "Read Result" LED, then lights up
constantly.
(CLV has loaded the parameter set from the external parameter memory with
tolerated errors
• Lights up constantly
(CLV could not find an external parameter memory and loads the internal parameter set instead)
• Blinks constantly together with the "Read Result" LED
(The external parameter memory contains the parameter set for a different CLV
type, or is corrupt.)
CLV has loaded the internal parameter set. It starts Reading mode but does not
output data over the host interface.
Start option: START WITH INTERNAL PARAMETERS
• Lights up constantly (CLV has loaded internal parameter set)
1)
and starts reading mode straight away)
2)
Start option: START WITH COPY INTERN -> EXTERN
• Blinks alternately with the "Read Result" LED for approx. 10 s before lighting
up constantly
(CLV has successfully copied the internal parameter set to the external memory
and has reset the start option to START WITH EXTERNAL PARAMETERS).
CLV has loaded the internal parameter set.
• Blinks constantly together with the "Read Result" LED
2)
(The external parameter memory is either not connected or corrupt, or the
parameter set is too large to be copied). CLV has loaded the internal parameter
set.
Read Result Green Start option: START WITH EXTERNAL PARAMETERS (default)
• Blinks for approx. 10 s together with "Device Ready" LED
• Blinks constantly together with the "Device Ready" LED
1)
(see above) or
2)
(see above)
Start option: START WITH COPY INTERN -> EXTERN
• Blinks alternately with "Device Ready" LED for approx. 10 s (see above) or
• Blinks constantly together with the "Device Ready" LED 2) (see above)
Reading mode Device Ready Green • Lights up constantly
• Extinguishes with new operating mode/function
Sensor Green • Lights up if reading diode active
(The laser diode is activated/deactivated by the reading pulse)
• Lights up constantly in Free-running mode, since the laser diode is constantly
active
Read Result Green LED is linked to the "Result 2" output and indicates the selected result status for the
defined pulse duration of the output.
• Lights up after a successful read (Good Read)
• Lights up if the match code comparison is active, the bar code read matches the
specified match code(s) and the corresponding result output is selected for the
"Result 2" output
1) We recommend that you check the parameter set manually, e. g. by printing out the entire configuration. For troubleshooting, see also Chapter 8.3.2 LED error messages
for the external parameter memory, Page 8-3
2) Stops blinking when you switch from Reading mode to Parameterization mode
Table 3-3: Meaning of LEDs: CLV with external parameter memory
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 3-11
Page 34

Chapter 3 Operating Instructions
Operating mode LED Display Function
Product description
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Reading mode
(contd.)
Percentage Sensor Green • Lights up constantly, since Free-running mode is active
evaluation Read Result Green Behavior dependent on the reading quality:
Adjusting mode Sensor Green • Lights up constantly, since Free-running mode is active
Show CP-limits Sensor Green • Blinks bright/dark alternately, in the frequency with which the scan line is (partially)
Table 3-3: Meaning of LEDs: CLV with external parameter memory (contd.)
Data Yellow • Flickers when the CLV transmits data to the host over the host interface
• Extinguishes if reading rate < 30 %
• Blinks twice a second if reading rate 30 % to 70 %
• Blinks five times a second if reading rate 70 % to 90 %
• Lights up constantly if reading rate > 90 %
masked out
3-12 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 35

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Installation
4 Installation
4.1 Installation sequence
• Change the language version of the laser warning label (if necessary)
• Select the mounting location for the CLV
• Align the CLV with the bar code and mount the CLV
• Mount the AMV/S 60 Connection Module
• Connect the CLV to the AMV/S 60 Connection Module
• Adjust the CLV so that it is in line with the bar code
• Mount the reading pulse sensor for external triggering the reading pulse
• Option with event-controlled dynamic focus control:
mount the sensors for detecting the object distance
Note Don’t open the device. The producer warranty will be forfeited if the device is opened.
4.2 Preparations
4.2.1 Required components
• CLV Bar Code Scanner
4.2.2 Required accessories
• SICK mounting bracket for the CLV: depending on the order,
angle bracket no. 2 013 824, articulated bracket no. 2 018 435, or quick-clamping
device no. 2 016 110 with securing material for the CLV
– or –
Alternatively, if the bracket is supplied by the user
– Stable mounting device that allows the alignment of the CLV to be varied in the x and
y axes. The weight of the CLV (line scanner) is 1.5 kg (3.3 lb) and 2.2 kg (4.84 lb) as
a line scanner with oscillating mirror.
– 2 screws M6 for the CLV. The screw length depends on the wall thickness of the brak-
ket used. Depth of engagement in CLV max. 7 mm (0.28 in) from housing surface.
• AMV/S 60 Connection Module (not included in the scope of supply of the CLV)
• Reading pulse sensor(s) for external reading pulse triggering, e. g. photoelectric reflex
switch(es)/photoelectric proximity switch(es) (not included in the scope of supply)
• Option with event-controlled dynamic focus control: sensors for detecting the object
distance, e. g. photoelectric reflex switches/photoelectric proximity switches (not
included in the scope of supply of the CLV)
• Optionally for separation of bar codes with the same name (same code type, identical
data content): an incremental encoder (not included in the scope of supply of the CLV)
4.2.3 Required auxiliary parts
• 2 screws M6 for securing the SICK mounting bracket to the base. The screw length
depends on the wall thickness of the base.
• Set of laser warning labels (if necessary)
• Tool
• Measuring tape (up to 3 m (118.2 in))
• Protractor
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 4-1
Page 36

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
4.2.4 Replacing the laser warning label
If necessary, replace the GB/US laser warning label with the required language (Fig. 4-1).
The device is delivered with a set of laser warnings in:
• German/US laser warning and
• French/US laser warning
See also Chapter 2.3 General safety instructions and protection measures, Page 2-2.
Supplied laser warnings:
Fig. 4-1: Line scanner: replacing the laser warning labels
4.2.5 Selecting the mounting location
When you select the mounting location, the distance between the CLV and the host and
between the CLV and the bar code are extremely important.
Distance between the CLV and the host
The CLV can be mounted at a maximum distance of 1,200 m (3,937 ft) from the host
without a connection to the SICK network or a bus. In practice, however, the distance depends on the physical configuration of the host interface and the data transfer rate (see
Table 5-7, Page 5-9).
Distance between the CLV and the AMV/S 60 Connection Module
The AMV/S 60 Connection Module should not be located further than 10 m (32.8 ft) from
the CLV, since the "CLV-Setup" program on the PC accesses the terminal interface (RS 232)
of the CLV via this module.
4-2 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 37

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Installation
4.2.6 Mounting accessories
The CLV is secured in position using the two tapped blind holes (M6) above the electrial connections. Fig. 4-2 shows the location of the threads near the line scanner.
The dimensions of the CLV housing are shown in Fig. 9-1 to Fig. 9-2, Page 9-4.
Drilled hole, ∅ 3.6 mm,
6 mm (0.24 in) deep
Fig. 4-2: Line scanner: position of the securing threads on the CLV
Blind hole thread, M6,
7 mm (0.28 in) deep
The CLV can be mounted using the SICK bracket:
• Mounting bracket, single no. 2 013 824
• Articulated bracket (2 x mounting bracket, single) no. 2 018 435
• Quick-clamping device no. 2 016 110
The brackets are designed to support a variety of mounting positions and alignments in two
planes.
Fig. 4-3 shows two mounting examples.
The elongated holes in the mounting bracket no. 2 013 824 and in the articulated bracket
no. 2 018 435 allow the CLV to be adjusted with a freedom of rotation of
±15°.
Quick-clamping
device
Mounting
bracket
Fig. 4-3: Line scanner: Mounting possibilities of the CLV
The dimensions of the mounting brackets are shown in Chapter 10.13 Dimensioned draw-
ings of the accessories, Page 10-57
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 4-3
Page 38

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
4.2.7 Distance between the CLV and the bar code
Basic alignment between the CLV and the bar code
Depending on the application, the line scanner or line scanner with oscillating mirror versions
of the CLV is used.
Fig. 4-4 shows how the device is aligned with the bar code on the object
for each of the two scanning methods.
Line scanner Line scanner with
oscillating mirror
Fig. 4-4: Scanning methods: alignment with bar code and conveyor direction
Reading distance from the bar code and aperture angle α
The distance between the reading window of the CLV and the bar code must not exceed
the technical limits. The height of the reading field is shown as a function of the reading
distance for various resolutions (module widths) depending on the CLV type in
Chapter 10.2
Specification diagrams, Page 10-1.
Fig. 4-5 shows the definition of the reading distance a (radial measured) from the reading
window and of the aperture angle α each of the two scanning methods.
Line scanner Line scanner with oscillating mirror
α
Reading distance a
α
Reading distance a
105°
Fig. 4-5: Definition of the reading distance a and of the aperture angle α
The useful aperture angle is typically 60° for the line scanner and max. 50° for the line scanner with oscillating mirror. Due to the V-principle of beam deflection, the reading field height
(for evaluating the useful length of the scan line) depends on the readling distance.
4-4 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 39

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Installation
Angular alignment of the CLV
The alignment of the CLV is optimum when the scan line travels over the bar code lines
almost at a right angle (90
°) (Fig. 4-4). All possible reading angles that can occur between
the scan line and the bar code must be taken into consideration (Fig. 4-6 and Table 4-1).
α: Azimuth angle (tilt)
β: Angle of inclination (pitch)
Reading
range
Reading
distance
CLV
Fig. 4-6: Line scanner: Reading angle between the scan line and the bar code
γ: Angle of rotation (skew)
Angle Limit value
Tilt α (azimuth) max. 45° (limitations see reading diagrams)
Pitch β max. 45°
Skew γ max. 45°
Table 4-1: Permissible reading angles between the scan line and bar code
Note If reading from the front, mount the CLV above the conveyor belt in such a way against the
conveying direction that the scan line hits the object under a skew of approx. 10°.
Avoiding surface reflection
If the light from the scan line strikes the surface of the bar code vertically, interference may
be caused by reflections when the returned light is received. To avoid surface reflection, the
CLV must be mounted in such a way that the emitted light is tilted slightly with respect to the
vertical axis (
Fig. 4-7).
Line scanner Line scanner with oscillating mirror
15°
15°
105°
(Top view) (Side view)
Fig. 4-7: Avoiding surface reflections: Angle between the emitted light and the bar code (tilted
away from the vertical axis)
In the case of the line scanner with oscillating mirror, the laser beam is emitted at an angle
of 105
° with respect to the housing as it passes through the neutral position (CW = 50)
while oscillating. The device can only be flush-mounted with the conveyor belt with limited
deflection ranges. Otherwise, the device must also be mounted at an angle of 15
° to ensure
that the deflection ranges are symmetric.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 4-5
Page 40

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Note In oscillating mode with variable amplitude, the scan line must always sweep the neutral
position (CW
= 50). This means that oscillation is not possible in the range 60 CW to 80 CW,
for example, but is possible in the range 40 CW to 80 CW.
4.2.8 Count direction of the code position CP and code angle CW
Explanation The CLV can scan and decode several bar codes with each read. In doing so, it determines
the specific local reading diagnosis data for each bar code:
• The position (CP value) of the center of the bar code within the scan line
• (Scanning method using the oscillating mirror) also the angle of deflection of the scan
line (CW value) at which the center of the bar code is recorded
Fig. 4-8 shows the count direction of the code position and code angle. In the case of the
line scanner, the count direction of the code position is marked by a small triangle above
the reading window.
By determining this data, the device can separate identical bar codes (code type, code
length, and data content identical) and assign the bar code data in the reading result to its
position on the object.
Tip
Line scanner
100
CP
0
Scanning direction
Aperture angle α (opening angle) in the scanning direction: 1° = 1.5 CP (56° = 90 CP)
Deflection angle of the scan line crosswise to the scanning direction: 1° = 2 CW (20° = 40 CW)
Fig. 4-8: Count direction of the code position CP in the scan line and of the code angle CW for the
oscillating mirror
Line scanner with
oscillating mirror
90
CW
10
0
CP
100
In the default setting, the CLV does not output the "CP" and "CW" values (line scanner with
oscillating mirror only) in the reading result on the host interface. If this is required to
evaluate the result in the host, the values can be included in the "Code-Info/Separator"
block of the output string using the "CLV-Setup" program.
Configuring the Code-Info/Separator:
1. Choose the DATA STRINGS tab.
2. Click the CODE INFO/SEPARATOR field.
The EDIT PARAMETER TFS dialog box is displayed.
3. In the list field, click the CP and/or CW parameters.
CP and/or CW then appears in the top line.
4-6 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 41

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Installation
4. Confirm your selections with OK.
5. Download the data to the CLV by clicking in the toolbar.
The DOWNLOAD PARAMETERS dialog box is then displayed.
6. Confirm the dialog box by choosing PERMANENT.
The CLV outputs the CP value and the CW value on the host interface for each bar code
in the reading result. The values are displayed as a 3-digit number in the associated
"Code-Info/Separator" block.
4.3 Mounting and adjusting the device
4.3.1 Mounting the CLV
1. Prepare the base for mounting the bracket as described in Chapter 4.2.2 Required ac-
cessories, Page 4-1.
2. Place the object containing the bar code within the reading field of the CLV (in the position at which it is to be read) with the conveyor belt switched off.
3. Align the CLV with the bar code (in accordance with the scanning method) in such a way
that
– with the line scanner the back of the device with the LEDs is almost parallel with the
bar code surface
– with the line scanner with oscillating mirror, the broad side wall (back of the oscillating
mirror) is almost parallel with the bar code surface
All of the possible reading angles must be taken into consideration (see Fig. 4-6,
Page 4-5).
4. If it is relevant for the evaluation, note the count direction of the code position and code
angle (see
5. Mount the CLV bracket on the base.
Fig. 4-8, Page 4-6).
Risk of damage to the device
The maximum depth of engagement of the two blind hole threads M6 is 7 mm (0.28 in).
Longer screws will damage the device.
¾ Use screws with the correct length.
6. Screw the screws M6 through the bracket into the blind hole threads of the CLV.
7. Tighten the screws slightly.
8. Adjust the CLV as described below.
4.3.2 Adjusting the CLV
The CLV can be adjusted in Percentage Evaluation mode. In this mode, the CLV displays the
quality of the bar code reads that enter the CLV reading field statically (the object is not mo
ved on the conveyor belt). The CLV performs 100 scans and evaluates the reading
quality statistically. It then outputs the reading results every 2 s on the terminal interface.
The behavior of the "Read Result" LED also indicates the reading quality:
– The LED is extinguished if reading quality is < 30 %
– The LED flashes twice per second if the reading quality is 30 % to 70 %
– The LED flashes five times per second if the reading quality is 70 % to 90 %
– The LED is lit continuously if the reading quality is > 90 %
The scanning frequency in the default setting is 800 Hz.
-
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 4-7
Page 42

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
1. Connect the CLV to the AMV/S 60 Connection Module and switch on the power supply
(see
Chapter 5.5.3 Connecting the supply voltage, Page 5-14).
After it has started, the CLV confirms that the self-test was successfuly and switches to
reading mode ("Device Ready" LED lights up).
2. Connect the PC to the terminal interface of CLV. To do so, connect a 3-core RS 232
data cable (null modem cable) to the internal
9-pin "Service" plug of the AMV/S 60 (see
Chapter 5.5.5 Connecting the CAN interface, Page 5-16).
3. Start Windows and the "CLV-Setup" program (see Chapter 10.6.3 Starting CLV-Setup,
Page 10-32).
Choosing the standard decoder:
4. Choose the CODE CONFIGURATION tab.
5. Click the STANDARD option in the DECODER section.
6. Download the settings to the CLV.
To do so, click again the STANDARD option with the right mouse button and choose
D
OWNLOAD PARAMETER in the context menu.
CLV-Setup copies the parameter temporary to the CLV.
The CLV operates with the standard decoder (until the CLV is switched off).
Activating Percentage Evaluation mode:
7. From the VIEW menu, choose PERCENTAGE EVALUATION.
The dialog box for entering the distance configuration appears.
8. Click the relevant distance configuration for the reading distance:
with event-controlled dynamic focus control the distance configuration that matches the
reading distance of the object (default: no. 1, focus position F = 1,200
mm
(47.3 in)).
9. Confirm the dialog box with OK.
The Terminal Emulator is launched and displays the reading result continuously (see
Chapter 6.5.2 Percentage evaluation, Page 6-28).
Monitor the reading quality (%) during each of the subsequent steps!
Line scanner with oscillating mirror:
In the "Percent Evaluation" mode, the CLV behaves in the following manner:
– in "Oscillating" mode (default setting: oscillating with a fixed amplitude), the CLV shuts
off oscillation and positions the scan line under the angle CW
an angle of deflection of 105
°). This position cannot be altered.
= 50 (corresponds to
– in "One-Shot" mode, the CLV also positions the scan line under the angle CW = 50
– in "Set Position" mode, the scan line’s selected position remains unchanged.
Performing fine adjustment:
10. Align the CLV in such a way that the angle between the scan line and the bars on the
bar code CLV is almost 90
°. The oscillating mirror must be aligned in such a way that
the scan line is located at the center of the bar code, perpendicular to the bar code li
nes, when it is in the neutral position (CW = 50).
11. To avoid interfering reflections, tilt the line scanner away from the vertical axis so that
the light strikes the bar code at an angle of approx. 105
° (see Fig. 4-7, Page 4-5).
12. If necessary, position the scan line exactly at the direct center of the bar code.
Chapter 4.3.3 Help functions for adjusting the CLV below.
13. Move objects carrying bar codes into the CLV reading field manually under realistic
conditions and check the reading result. If the objects are aligned randomly, or if the bar
-
4-8 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 43

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Installation
code is located at different positions (angles), ensure that the limit values of the
permissible reading angles are not exceeded.
14. Adjust the CLV in such a way that the good read rate is between 70 to 100 %.
With event-controlled dynamic focus control, for each defined reading range (distance
configuration), check the selected focus position and correct the parameter settings if
necessary (see
Chapter 6.4.3 Guide to parameterization menu, Page 6-9).
15. Tighten the screws on the CLV.
The CLV is aligned with the bar code.
4.3.3 Help functions for adjusting the CLV
Adjusting mode
The "Adjusting mode" helps you to position the center of the scan line on the object. To do
so, the CLV masks out one half of the scan line from the center (code position CP
CP
= 100). This is irrespective of whether the CLV is operated in Autofocus mode or with
distance configurations for event-driven dynamic focus control.
Fig. 4-9 shows the resulting
= 50 to
position of the scan line (line scanner).
Adjusting mode
Scan line
CP = 100
Range masked out
CP = 50
CP = 0
Fig. 4-9: Line scanner: scan line in Adjusting mode
Line scanner with oscillating mirror:
In "Adjusting" mode, the oscillating mirror behaves in the same manner as within the ”Percent Evaluation” mode (see Chapter Activating Percentage Evaluation mode:, Page 4-8).
1. Activate the operating mode as described in Chapter 6.5.3 Adjusting mode, Page 6-30.
2. Position the CLV in such a way that the center of the scan line, indicated by the end of
the scan line (code position CP
= 50), is located at the center of the bar code, or at the
center of the field for all codes if several bar codes are used.
Show CP Limits
The "Show CP Limits" operating mode allows you to test whether the desired effect was produced by narrowing the scan line’s active evaluation range. The CLV alternatively hides certain parts of the scan line in accordance with the selected min. and max. values of the code
position.
For activation of this operating mode and for checking, See Chapter 6.5.4 Show CP-limits,
Page 6-30.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 4-9
Page 44

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
4.4 Mounting the external components
4.4.1 Mounting the AMV/S 60 Connection Module
1. Mount the AMV/S 60 Connection Module near the CLV.
The distance between the AMV/S 60 and CLV should not exceed max. 10 m (32.8 ft).
2. Mount the AMV/S 60 in such a way that accessed to the open device is always possible. The terminal interface of the CLV is accessed via the internal "Service" plug.
Detailed information on the mounting and electrical installation procedures is provided in the
Operating Instructions "AMV/S 60 Connection Module" (order no. 8 008 296).
4.4.2 Mounting the external reading pulse sensor
If the CLV is triggered by an external reading pulse sensor, the sensor must be mounted in
the vicinity of the CLV. The "Sensor" switching input is selected as the default trigger source
for this trigger type. The default debounce time of the input is 30 ms.
Fig. 4-10 shows two examples of where a photoelectric reflex switch can be mounted. This
depends on the distance a from the bar code to the front of the object. Depending on the
application, you may need to mount the sensor in such a way that bar codes on objects of
different sizes can be read completely during the reading interval.
Bar code in the center or at the end of the object
a
b
Bar code at the start of the object
a
a
b
Fig. 4-10: Line scanner: mounting example for the external reading pulse sensor
b < a
b < a
b < a
b < a
(Top view)
a
b
(Top view)
a
b
4-10 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 45

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Installation
Installing the reading pulse sensor for start/stop mode:
1. Mount the reading pulse sensor.
2. Connect the reading pulse sensor to the "Sensor" switching input of the CLV via the
AMV/S 60 Connection Module (see
Chapter 5.5.7 Connecting the "Sensor" switching
input, Page 5-17).
3. Connect the CLV to the AMV/S 60 Connection Module and switch on the power supply
to the module (see
Chapter 5.5.3 Connecting the supply voltage, Page 5-14).
After it has started, the CLV confirms that the self-test was successfull and switches to
Reading mode ("Device Ready" LED lights up).
4. Connect the PC to the terminal interface of CLV. To do so, connect a 3-core RS 232
data cable (null modem cable) to the internal
9-pin "Service" plug of the AMV/S 60 (see
Chapter 5.5.5 Connecting the CAN interface, Page 5-16).
5. Start Windows and the "CLV-Setup" program (see Chapter 10.6.3 Starting CLV-Setup,
Page 10-32).
6. From the VIEW menu, choose READING MODE.
The Terminal Emulator is launched. The CLV is in Reading mode (default: SMART
decoder).
Monitor the reading result during each of the subsequent steps!
Line scanner with oscillating mirror:
In default setting, the CLV deflects the scan line (default setting) about the fixed position
CW
= 50 with a frequency of 1 Hz at a max. angle of ±20° (±40 CW).
50 CW corresponds to an angle of emergence of 105°.
7. Move objects with bar codes into the CLV reading field manually under realistic conditions and check whether the reading result and trigger pulse are correct.
8. Repeat the procedure with the conveyor switched on. Check whether the reading
procedure is synchronized with the objects.
Parameterizing an external sensor as a trigger source:
These settings are not required if the CLV is operated with the default configuration.
1. Choose the DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab.
2. In the READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS section click the option SENSOR INPUT (ACTIVE HIGH).
3. Download the settings to the CLV by clicking in the toolbar.
The DOWNLOAD PARAMETERS dialog box is then displayed.
4. Confirm the dialog box by choosing PERMANENT.
The CLV operates with the "Sensor" switching input as an external trigger source.
The reading pulse starts when the input is energized (high).
4.4.3 Installing incremental encoder
To separate bar codes with the same name (same code type, identical data content), an
incremental encoder is required.
1. Install the incremental encoder (e. g. no. 2 022 714) near the CLV but in front of it,
preferably against the direction of the conveyor belt. The increment pulses must
originate from the area of the conveyor belt which the CLV is reading.
2. Ensure that the incremental encoder is contacting the conveyor and that the friction
wheel turns without slipping.
3. Connect incremental encoder to "IN4" switching input of the CLV. See Chapter 5.5.8
Connecting the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs, Page 5-18.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 4-11
Page 46

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
4.4.4 Mounting the sensors for detecting the object distance
If the dynamic focus control function of the CLV is triggered by external sensors, suitable
sensors must be mounted in the vicinity of the CLV.
Fig. 4-11 shows an example of a read
operation from above. The sensors must be arranged in such a way that all of the potential
object heights are classified uniquely and overlapping reading ranges occur that can be for
med with the depths of field of the CLV. A maximum of five switching inputs are available for
this purpose. A max. of 32 switching states for 8 distance configurations (reading ranges)
can be implemented using the internal assignment table (combinations). Photoelectric reflex
switches, for example, can be used to detect the object distance. In the default setting, all
five "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs are selected for dynamic focus control.
-
DC8
LS7
Reading distance
DC2
LS2
DC1
LS1
DC = Distance Configuration
Fig. 4-11: Mounting example for object distance detection
Object distance
h7
h2
h1
1. The depths of field of the CLV for the bar code resolution in question is shown in the
graphs in
Chapter 10.2 Specification diagrams, Page 10-1 onwards. Find and note sui-
table focus positions for overlapping reading ranges.
2. Mount distance sensors (e. g. photoelectric reflex switches) one above the other in a
row at the mounting location to measure the object distance (see also assignment
Table 5-20, Page 5-19). It is advisable to mount these distance sensors opposite the
direction of motion of the conveyor belt at approx. 100 mm (3.94 in) in front of the reading pulse sensor.
3. Connect the distance sensors to the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs on the CLV via the
AMV/S 60 Connection Module (see
Chapter 5.5.7 Connecting the "Sensor" switching
input, Page 5-17).
4. Set the focus positions for the required reading ranges on the READING CONFIGURATION
tab in the "CLV-Setup" program.
down list of the
FOCUS CONTROL section.
To do so, choose the INPUTS/SERIAL option in the drop
5. Click the DISTANCE CONFIGURATION button and edit the required entries in the dialog box
that is then displayed (default: Focus position F 1 up to F 8 = 1,200 mm (47.3 in)).
6. As described in Chapter 4.3.2 Adjusting the CLV, Page 4-7, choose the standard decoder and start Percentage Evaluation mode temporarily.
7. Perform a temporarily download to the CLV.
4-12 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 47

Operating Instructions Chapter 4
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Note The CLV can switch between a maximum of 8 distance ranges for slow search runs using
Installation
8. Start Percentage Evaluation mode.
9. Check the reading quality in all distance configurations while the conveyor belt stationary.
10. Then check the distance detection function in Reading mode under realistic conditions.
To do so, monitor the reading result in the Terminal Emulator as described in
Chapter 4.4.2 Mounting the external reading pulse sensor, Page 4-10.
11. If the distance detection function operates correctly, reset the decoder to the SMART/
STANDARD option and perform a permanently download to the CLV.
the integrated timer or the oscillating mirror reversal points.
The CLV can be switched between a maximum of 8 distance ranges synchronously to the
reading process using command strings.
4.5 Dismantling the device
1. Switch off the power supply to the AMV/S 60 Connection Module.
2. Undo the screws for the cable connections on the CLV and disconnect the cables.
With mounted external parameter memory (optional):
Undo both screws and remove the cover.
3. Unscrew the CLV from the mounting device.
When removing the device from service for the last time, please dispose of it in an
environmentally-friendly manner, as described in Chapter 7.3 Disposal, Page 7-2.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 4-13
Page 48

Chapter 4 Operating Instructions
Notes
Installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
4-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 49

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
5 Electrical installation
5.1 Installation sequence
• Connect the CLV to a SICK Connection Module from the series AMV/S, BMV/BMH 10
or BMS
• Connect the data and function interfaces of the CLV in the module
• Connect the PC to the Connection Module (at the terminal interface on the CLV)
• Connect the power supply to the Connection Module
5.1.1 SICK Connection Modules (overview)
20, or using a customer-specific wiring configuration
CLV Type Temperatur
range
CLV without heater 0 to +40 °C
(+32 to +104 °F)
CLV with heater
– Line scanner
– Line scanner
with oscillating
mirror
–35 to +35 °C – Operating voltage 24 V DC +20%/–10%
–35 to +35 °C
(–31 to +95 °F)
Connection
module
AMV 60 – Connecting one CLV
AMS 60 – Connecting one CLV
AMV 100 – Connecting one CLV
BMV/BMH 10
Bus Connection
Module
BMS 20
Interbus-S
AMV 30-071 – Connecting two CLVs
AMV 200 – Connecting two CLVs
AMV 100 – Connecting one CLV 5.2.5
AMV 200 – Connecting two CLVs
Purpose see
chapter
5.2.3
– Operating voltage 18 to 30 V DC
– Enclosure rating IP 30, max. IP 54
5.2.3
– Operating voltage 230 V AC (115 V)/24 V DC
– Enclosure rating IP 30, max. IP 54
5.2.3
– Operating voltage 18 to 30 V DC
– Enclosure rating IP 52,
with connector cover max. IP 65
– Connecting one CLV to the Profibus-DP, DeviceNet
or Ethernet
– Operating voltage 20 to 30 V DC
– Enclosure rating IP 52,
with connector cover max. IP 65
– Connecting one CLV to the Interbus-S
– Operating voltage 24 V DC
– Enclosure rating max. IP 54
– Operating voltage 18 to 30 V DC
– Enclosure rating IP 30, max. IP 54
– Operating voltage 18 to 30 V DC
– Enclosure rating IP 52,
with connector cover max. IP 65
– Enclosure rating IP 52,
with connector cover max. IP 65
– Operating voltage 24 V DC +20%/–10%
– Enclosure rating IP 52,
with connector cover max. IP 65
5.2.4
5.2.4
5.2.3
5.2.3
5.2.3
Table 5-1: Connection Modules for the CLV
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5-1
Page 50

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
5.2 Electrical connections and cables
The electrical connections on the CLV consist of two 15-pin D Sub HD connections on the
housing, one plug, and one socket.
These connections are used to route the following interfaces:
• Three serial data interfaces (host interface, CAN interfaces 1 and 2, terminal interface)
• Six switching inputs (external reading pulse and multifunctional inputs)
• Four switching outputs (for result status function, for connecting to a PLC for example)
• Power supply
5.2.1 Wire cross-sections
CLV without heater:
¾ All connections must be wired with copper cables with a minimum wire diameter of
2
0.15
CLV with heater:
¾ Connect the power supply terminals (Pin 1/Pin 5) using copper wires with a minimum
cross-section of 0.75 mm
mm
(approx. 26 AWG)!
2
(approx. 20 AWG) at a maximum length of 10 m (32.8 ft)!
5.2.2 Prefabricated cables (overview)
CLV
Type
CLV
without
heater
CLV with
heater
Table 5-2: Cables for connecting the CLV
Temperature
range
0 to +40 °C
(+32 to
+104 °F)
– 35 to +35 °C
(–31 to
+95 °F)
Connection
module
AMV/S 60 2 x No. 2 020 302 or
BMV/BMH 10
Bus Connection Module
AMV 30-071 2 x No. 2 020 302 or
BMS 20
Interbus-S
Non-Sick
Power pack
AMV 100 1 x No. 2 021 298 or
AMV 200 2 x No. 2 021 298 or
Non-Sick
Power pack
Optional
cable
1 x No. 2 020 307
1 x No. 2 020 307 or
1 x No. 2 021 298
1 x No. 2 020 307
1 x No. 2 020 264 +
1 x No. 2 020 265 or
1 x No. 2 020 308
1 x No. 2 020 303 +
1 x No. 2 020 264 or
1 x No. 2 020 981 or
1 x No. 2 021 267
1 x No. 2 021 689 or
1 x No. 2 027 543
2 x No. 2 021 689 or
2 x No. 2 027 543
1 x No. 2 021 267 3 m (9.84 in) Connector cover with 2 cables (open ends)
Length Type
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
3 m (9.84 in)
Connecting cable (plug/socket)
Ext. parameter memory with 2 cables
(plug/socket)
Ext. parameter memory with 2 cables
(plug/socket)
Connector cover to connector cover
Connecting cable (plug/socket)
Ext. parameter memory with 2 cables
(plug/socket)
Connecting cable with plug/open end
Connecting cable with plug/socket
Ext. parameter memory with 2 cables
(plug/open end)
Connecting cable with socket/open end
Connecting cable with plug/open end
Ext. parameter memory with 2 cables
(open ends)
Connector cover with 2 cables (open ends)
Connector cover to connector cover
Ext. parameter memory to connector cover
Ext. parameter memory to connector cover
with wires for CAN interface 1 (IN/OUT)
Connector cover to connector cover
Ext. parameter memory to connector cover
Ext. parameter memory to connector cover
with wires for CAN interface 1 (IN/OUT)
For technical data on the cables, see Chapter 10.12.4 Cables, external parameter memo-
ries and plug cover, Page 10-53.
5-2 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 51

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
5.2.3 Connections/cables for the AMV/S 60 Connection Module
The AMV/S 60 Connection Module is suitable for connecting the CLV to peripherals (distribution function) and the power supply. The module can be used to establish a connection
to the host (point-to-point) or integrate the device in a SICK network or daisy-chain configu
ration (pass-through or master/slave configuration). The module is available in several variants (see Table 5-1, Page 5-1).
Fig. 5-1 shows the connection principle of the AMV/S 60 for one CLV.
CLV 480
AMV/AMS 60
connection module
PC
Photoelectric
switch
Reading pulse
-
Photoelectric
switch
Focal position
Trigger One-Shot
Conveyor increment
End of reading interval
– – Cable if required (if necessary)
Fig. 5-1: Block diagram: Connection of the CLV to the AMV/S 60 connection module
Connecting the CLV to the AMV/S
Two cables no. 2 020 302 are required to connect the CLV to the AMV/S. Alternatively, the
device can be connected via the external parameter memory no. 2 020 307.
See Chapter 5.2.5 Connections/cables for the external parameter memory (connection to
AMV/S or BMV 10/BMS 20), Page 5-5.
a) CLV without heater:
Connection modules: AMV/S 60 and AMV 30-071.
The cables no. 2 020 302 can be extended to 10 m (32.8 ft) (terminal interface: RS 232!).
HOST/PLC
CAN bus
PLC
18 to 30 V DC (AMV 60-011)
230 V AC 50 Hz (AMS 60-013)
115 V AC 50 to 60 Hz (AMS 60-012)
b) CLV with heater:
Connection modules: AMV 100 and AMV 200.
The cables no. 2 020 302 must not be extended!
If longer cables are required, the entire power supply system (Pin 1/Pin 5) must be
connected with a wire cross-section of at least 0.75 mm2 (approx. 20 AWG) with a maximum
length of 10 m (32.8 ft).
Recommendation Use the cable no. 2 021 298 (with two connector covers, length 3 m (9.84 ft)).
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5-3
Page 52

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
The procedures for connecting and configuring the AMV/S Connection Modules are
described in the following documentation:
• Operating Instructions for the "AMV/S 60 Connection Module" (no. 8 008 296)
• Operating Instructions for the "AMV 30-071 Connection Module" (no. 8 008 648)
• Operating Instructions for the "AMV 100/200 Connection Module" (no. 8 008 879)
5.2.4 Connections/cables for the Bus Connection Modules
BMV 10 and BMS 20
The BMV 10 Bus Connection Module (depending on the model) is used to connect a CLV
to the Profibus-DP, DeviceNet, or to the Ethernet for use in industrial applications.
The BMS 20 Bus Connection Module enables the CLV to be integrated in the Interbus-S.
Connecting the CLV to the BMV 10/BMS 20
BMV 10: two cables no. 2 020 302 are required.
BMS 20: the cables no. 2 020 265 and no. 2 020 264 are required.
Alternatively, via external parameter memory no. 2 020 307 (see Chapter 5.2.5 Connec-
tions/cables for the external parameter memory (connection to AMV/S or BMV 10/
BMS 20).
a) CLV without heater:
Connection modules: BMV 10 and BMS 20.
The cables no. 2 020 302 can be extended to 10 m (32.8 ft) for CLVs without a heater
(host and terminal interface: RS
232!).
b) CLV with heater:
Connection module: BMV 10.
The BMV 10 may only be used if it is mounted outside the refrigeration area (temperature
range 0 to +40
°C (32 to 104 °F).
The cables no. 2 020 302 must not be extended. If longer cables are required, the entire
power supply system (Pin 1/Pin 5) must be connected with a wire cross-section of at least
0.75 mm
2
(approx. 20 AWG) at a maximum of 10 m (32.8 ft).
Recommendation Use the cable no. 2 021 298 (with two connector covers, length 3 m (9.84 ft)).
The BMS 20 is not suitable for powering CLVs with heater!
The procedures for connecting and configuring the Bus Connection Modules are described
in the following documentation:
• Operating Instructions for the "BMV/BMH 10 for Profibus DP Bus Connection Module"
(no. 8 008 825)
• Operating Instructions for the "BMV/BMH 10 for DeviceNet Connection Module"
(no. 8 008 972)
• Operating Instructions for the "BMV/BMH 10 for Ethernet Connection Module"
(no. 8 009 398)
• Technical Information for the "BMS 20 for Interbus-S Bus Connection Module"
(no. 8 007 546)
5-4 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 53

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
5.2.5 Connections/cables for the external parameter memory
(connection to AMV/S or BMV 10/BMS 20)
The external parameter memory (external accessory) is located in a connector cover with
15-pin D Sub HD plug connections. The cover covers the terminals on the CLV so that the
enclosure rating IP 65 is achieved.
The connector cover with the external parameter memory is prefabricated with two cables,
each 3 m (9.84 ft) in length, and is available with four different cable ends:
• With two 15-pin D Sub HD connections (pin assignment identical to that of the CLV
terminals), no. 2 020 307
• With a connector cover, without wires for CAN interfaces, no. 2 021 689
• With a connector cover, with wires for CAN interface 1, no. 2 027 543
• With two open cable ends, no. 2 020 981
• with one 9-pin D Sub cable connector and one open end, no. 2 020308
Connecting the CLV with external parameter memory
a) CLV without heater:
Connection Modules: AMV/S 60, AMV 30-071, BMV 10
¾ Cover the terminals on the CLV with the connector cover (parameter memory)
no.
2 020 307. Connect the plug/socket on the cables ("Host/Term" and " I/O" con-
nections) with the appropriate connections on the AMV/S or BMV 10.
Connection Module: BMS 20.
¾ Cover the terminals on the CLVs with the connector cover (parameter memory)
no.
2 020 308. Connect the 9-pin plug ("Host/Term" connection) to the socket on the
BMS 20. Connect the wires of the free cable end ( "I/O" terminal) to the terminal strips
in the BMS 20.
Recommendation Use the external parameter memory no. 2 020 981 (open cable ends) for connecting the
device to non-Sick Power packs/wiring configurations.
b) CLV with heater:
Connection Module: AMV 100/200
¾ AMV 100: Cover the terminals on the CLV with the connector cover (parameter
memory) no. 2 021 689 or no. 2 027 543, labeled "SCANNER". Connect the other
connector covers, labeled "HOST" respectively "AMV/BMV", to the corresponding connections on the AMV 100.
¾ AMV 200: see AMV 100, proceed in the same way with the second CLV.
5.2.6 Connections/cables for the IP 65 connector cover
(connection to AMV 100/200 or BMV 10)
The connector cover (optional accessory) with 15-pin D Sub HD plug connections is used
to cover the terminals on the CLV so that the enclosure rating IP 65 is provided.
The connector cover is prefabricated with two cables, each of 3 m (9.84 in) in length, and
is available with two different cable ends:
• With one additional connector cover at the other end (pins assignment identical to that
of the CLV terminals, but without wires for CAN interfaces), no. 2 021 298
• With two open cable ends, without wires for CAN interfaces, no. 2 021 267
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5-5
Page 54

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Recommendation Use the external parameter memory no. 2 020 267 (open cable ends) for connecting the
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
CLV with heater:
Both connector cover variants no. 2 021 298 and no. 2 021 267 can be used with temperatures up to max. –50 °C (–58 °F) if the CLV is stationary and the cables are not moved.
If the cables are moved due to changes in the position of the CLV, the temperature must
not drop below max.
device to non-Sick Power packs/wiring configurations.
–40 °C (–40 °F).
5-6 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 55

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
5.3 Connector pin assignment
5.3.1 Terminals on the CLV
Device plug: "Host/Term" connection
5 6
10
1
11
15
Pin Signal Function
1)
1
VS Supply voltage
2 RxD (RS 232), Terminal Terminal interface (receiver)
3 TxD (RS 232), Terminal Terminal interface (transmitter)
4 Term (RS 422/485) Termination host interface
5 GND Ground
6 RD+ (RS 422/485), Host Host interface (receiver+)
7 RD– (RS 422/485), Host
Host interface (receiver–)
RxD (RS 232), Host
8 TD+ (RS 422/485), Host Host interface (transmitter+)
9 TD– (RS 422/485), Host
Host interface (transmitter–)
TxD (RS 232), Host
10 CAN H CAN interface 1 (IN/OUT)
11 n. c. –
12 CAN2 H CAN interface 2 (IN/OUT)
13 CAN2 L CAN interface 2 (IN/OUT)
14 n c. –
15 CAN L CAN interface 1 (IN/OUT)
Housing – Shield
1) Pin 1 is jumpered with Pin 1 of the "I/O" connection in the CLV
Table 5-3: Pin assignment of the 15-pin D Sub HD "Host/Term" plug
1 10
5
15 611
Device socket: "I/O" connection
L
Pin Pin Function
)
1
1
2 IN 1 Switching input (trigger for focus control)
3 Sensor Switching input (external reading pulse)
4 Result 1 Switching output, variable function
5 GND Ground
6 IN 0 Switching input (trigger for focus control)
7 IN 2 Switching input (trigger for focus control)
8 Result 2 Switching output, variable function
9 INGND Common ground for all inputs
10 Result 3 Switching output, variable function
11 IN 3 Switching input, variable function
12 IN 4 Switching input, variable function
13 I2C SDA I2C Bus (for external parameter memory)
14 I2C SCL I2C Bus (for external parameter memory)
15 Result 4 Switching output, variable function
Housing – Shield
1) Pin 1 is jumpered with Pin 1 of the "Host/Term" connection in the CLV
Table 5-4: Pin assignment of the 15-pin D Sub HD "I/O" socket
VS Supply voltage
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5-7
Page 56

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
5.3.2 External parameter memory no. 2 020 307/no. 2 021 689/no. 2 027 543
or connector cover no. 2 021 298/no. 2 021 267 (optional accessories)
Cable plug: "Host/Term" connection
5 6
10
1
11
15
Pin Signal Function
1)
1
V
S
Supply voltage
2 RxD (RS 232), Terminal Terminal interface (receiver)
3 TxD (RS 232), Terminal Terminal interface (transmitter)
4 Term (RS 422/485) Termination host interface
5 GND Ground
6 RD+ (RS 422/485), Host Host interface (receiver+)
7 RD– (RS 422/485), Host
Host interface (receiver–)
RxD (RS 232), Host
8 TD+ (RS 422/485), Host Host interface (transmitter+)
9 TD– (RS 422/485), Host
Host interface (transmitter–)
TxD (RS 232), Host
10
CAN H2)
CAN interface 1 (IN/OUT)
11 n. c. –
12
13
CAN2 H
CAN2 L
2)3)
2)3)
CAN interface 2 (IN/OUT)
CAN interface 2 (IN/OUT)
14 n. c. –
15
CAN L2)
CAN interface 1 (IN/OUT)
Housing – Shield
1) Pin 1 is jumpered with Pin 1 of the "I/O" connection in the CLV
2) not connected in no.2 021 689, no. 2 021 298 and no. 2 021 267
3) not connected in no. 2 027 543
Table 5-5: Pin assignment of the 15-pin D Sub HD "Host/Term" cable plug
1 10
5
15 611
Cable socket: "I/O" connection
Pin Signal Function
1)
1
2 IN 1 Switching input (trigger for focus control)
3 Sensor Switching input (external reading pulse)
4 Result 1 Switching output, variable function
5 GND Ground
6 IN 0 Switching input (trigger for focus control)
7 IN 2 Switching input (trigger for focus control)
8 Result 2 Switching output, variable function
9 INGND Common ground for all inputs
10 Result 3 Switching output, variable function
11 IN 3 Switching input, variable function
12 IN 4 Switching input, variable function
13
14
15 Result 4 Switching output, variable function
Housing – Shield
1) Pin 1 is jumpered with Pin 1 of the "Host/Term" connection in the CLV
2) not connected
Table 5-6: Pin assignment of the 15-pin D Sub HD "I/O" cable socket
V
S
I2C SDA2)
I2C SCL2)
Supply voltage
I2C Bus (for external parameter memory)
I2C Bus (for external parameter memory)
5-8 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 57

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
5.4 Preparations for electrical installation
5.4.1 Requirements for the host interface
The host interface of the CLV can be operated as an RS 422/485 or an RS 232 interface.
Table 5-7 shows the recommended maximum cable lengths as a function of the selected
data transfer rate.
Pin Signal Function
RS 232 Up to 19,200 bd
38 400 to 57,600 bd
RS 422/485
1) with suitable line termination according to specifications
Table 5-7: Maximum cable lengths between the CLV and host
1)
Max. 38,400 bd
Max. 57,600 bd
¾ To prevent interference, do not lay the cables parallel with power supply and motor
cables over long distances, e. g. in cable ducts.
5.4.2 Supply voltage
Max. 10 m (32.8 ft)
Max. 3 m (9.84 ft)
Max. 1 200 m (3 936 ft)
Max. 500 m (1 640 ft)
The CLV requires a power supply of 18 to 30 V DC for operation without a heater and
24
V DC +20 %/–10 % for operation with a heater (each functional extra-low voltage in
accordance with IEC 364-4-41). The functional extra-low voltage can be generated by using
a safety isloating transformer pursuant to IEC 742.
The power consumption of the individual types is as follows:
Type Voltage Scanning method Heater
CLV 480-0010/-2010/-6010 18 to 30 V DC Line scanner No 11 W (typ.)/max. 16 W AMV/S 60 or
CLV 480-1010/-3010/-7010 18 to 30 V DC Line scanner with
oscillating mirror
CLV 480-0011/-2011/-6011 24 V DC Line scanner Yes 75 W (typ.)/max. 90 W AMV 100/200
CLV 480-1011/-3011/-7011 +20 %/–10 % Line scanner with
oscillating mirror
1) switching outputs not connected
Table 5-8: Power consumption of the CLV
No 13 W (typ.)/max. 18 W AMV 30-071 or
Yes 75 W (typ.)/max. 100 W
Power consumption
1)
Connection
module
BMV/BMH 10 or
BMS 20
Power-up delay
The selected device number (default: 1) affects the power-up delay of the device. This is
useful if a large number of CLVs (e. g. in the SICK network) are to be supplied from one
power source.
Table 5-9 contains a list of the available intervals.
Device number GN Power-up delay Device number GN Power-up delay
1; 11; 21; 31 0 ms 6; 16; 26 2,000 ms
2; 12; 22 400 ms 7; 17; 27 2,400 ms
3; 13; 23 800 ms 8; 18; 28 2,800 ms
4; 14; 24 1,200 ms 9; 19; 29 3,200 ms
5; 15; 25 1,600 ms 10; 20; 30 3,600 ms
Table 5-9: Power-up delay as a function of the device number GN
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5-9
Page 58

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Tip
The device number can be selected on the DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab in the "CLV-Setup"
program.
5.4.3 Non-SICK Power supply unit/connections without the Connection Module
Power output
If an non-Sick Power supply unit is used instead of the AMS 60, it must be capable of
providing the following voltage and power values:
• For CLV without heater: 18 to 30 V DC, min. 20 W continuous power output
• For CLV with heater: 24 V DC +20 %/–10 %, min. 100 W
The non-Sick Power supply unit must provide the functional extra-low voltage in accordance
with IEC 364-4-41.
The output circuit must be reliably electrically isolated from the input circuit. To do so,
use a safety isolating transformer pursuant to IEC
742.
Wire cross-section
The wire cross-section for the power supply (Pin 1/Pin 5) should be at least 0.15 mm
2
(approx. 26 AWG), or 0.75 mm2 (approx. 20 AWG) for CLVs with heater, with a max. length
of 10 m (32.8 ft).
a) Connecting the CLV without a connector cover/external parameter memory
The two cables no. 2 020 303 and no. 2 020 264 with open cable end on one side are
required to connect the CLV. The wire color assignments are shown in
Table 5-10 and
Table 5-11, Page 5-11. The cables must not be extended for CLVs with heater.
Connection cable no. 2 020 203 ("Host/Term" connection)
15-pin D Sub HD socket and open cable end
Pin Signal Wire color
1)
1
2 RxD (RS 232), Terminal White
3 TxD (RS 232), Terminal Brown
4 Term (RS 422/485) Violet
5 GND Blue
6 RD+ (RS 422/485), Host Green
7 RD– (RS 422/485), Host
8 TD+ (RS 422/485), Host Grey
9 TD– (RS 422/485), Host
10 CAN H Grey-pink
11 n. c. Red-blue
12 CAN2 H White-green
13 CAN2 L Brown-green
14 n. c. White-yellow
15 CAN L Yellow-brown
– Shield Orange
1) Pin 1 is jumpered with Pin 1 of the "I/O" connection in the CLV
Table 5-10: Wire color assignment of the cable no. 2 020 303
V
S
RxD (RS 232), Host
TxD (RS 232), Host
Red
Yellow
Black
5-10 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 59

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
Connection cable no. 2 020 264 ("I/0" connection)
15-pin D Sub HD plug and open cable end
Pin Signal Wire color
1)
1
2 IN 1 White
3 Sensor Brown
4 Result 1 Violet
5 GND Blue
6 IN 0 Green
7 IN 2 Yellow
8 Result 2 Grey
9 INGND Black
10 Result 3 Grey-pink
11 IN 3 Red-blue
12 IN 4 White-green
13 I2C SDA Brown-green
14 I2C SCL White-yellow
15 Result 4 Yellow-brown
– Shield Orange
1) Pin 1 is jumpered with Pin 1 of the "Host/Term" connection in the CLV
Table 5-11: Wire color assignment of the cable no. 2 020 264
V
S
Red
b) Connecting the CLV with external parameter memory no. 2 020 981
CLV without heater:
¾ Cover the "Host/Term" and "I/O" connections on the CLV with the connector cover (pa-
rameter memory) no. 2 020 981. Connect the free cable ends accordingly. The wire
color assignments are shown in
Table 5-12 and Table 5-13.
CLV with heater:
Available on request.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5-11
Page 60

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Cable 1 ("Host/Term" connection)
15-pin D Sub HD socket in the connector cover and open cable end
Pin Signal Wire color
1)
1
2 RxD (RS 232), Terminal White
3 TxD (RS 232), Terminal Brown
4 Term (RS 422/485) Violet
5 GND Blue and grey-brown
6 RD+ (RS 422/485), Host Green
7 RD– (RS 422/485), Host
8 TD+ (RS 422/485), Host Grey
9 TD (RS 422/485), Host
10 CAN H Grey-pink
11 n. c. Red-blue
12 CAN2 H White-green
13 CAN2 L Brown-green
14 n. c. White-yellow
15 CAN L Yellow-brown
– Shield Orange
1) Pin 1 is jumpered with Pin 1 of the "I/O" connection in the CLV
Table 5-12: Wire color assignment of cable 1 for external parameter memory no. 2 020 981
V
S
RxD (RS 232), Host
TxD (RS 232), Host
Red and pink
Yellow
Black
Cable 2 ("I/O" connection)
15-pin D Sub HD plug in the connector cover and open cable end
Pin Signal Wire color
1)
1
2 IN 1 White
3 Sensor Brown
4 Result 1 Violet
5 GND Blue and grey-brown
6 IN 0 Green
7 IN 2 Yellow
8 Result 2 Grey
9 INGND Black
10 Result 3 Grey-pink
11 IN 3 Red-blue
12 IN 4 White-green
13 I2C SDA –
14 I2C SCL –
15 Result 4 Yellow-brown
– Shield Orange
1) Pin 1 is jumpered with Pin 1 of the "Host/Term" connection in the CLV
Table 5-13: Wire color assignment of cable 2 for external parameter memory no. 2 020 981
V
S
Red and pink
5-12 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 61

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
c) Connections with connector cover no. 2 021 267
¾ Cover the "Host/Term" and "I/O" connections on the CLV with the connector cover
no.
2 020 267 and connect the free cable ends accordingly. The wire color assign-
ments are shown in Table 5-14 and Table 5-15.
CLV with heater:
The connector cover can be used with temperatures up to max. –50 °C (–58 °F) if the CLV
is stationary and the cables are not moved. If the cables are moved due to changes in the
position of the CLV, the temperature must not drop below max. –40
°C (–40 °F).
Cable 1 (power supply)
15-pin D Sub HD socket in the connector cover and open cable end
Pin Connector cover Signal Wire color
1 Socket VS Red
5 Socket GND Black
Table 5-14: Wire color assignment cable 1 for connector cover no. 2 021 267
Cable 2 (data and function interfaces)
15-pin D Sub HD socket/plug in the connector cover and open cable end
Pin Connector cover Signal Wire color
2 Plug IN 1 White
3 Plug Sensor Brown
4 Plug Result 1 Green
6 Plug IN 0 Yellow
7 Plug IN 2 Grey
8 Plug Result 2 Pink
9 Plug INGND Blue
10 Plug Result 3 Red
11 Plug IN 3 Black
12 Plug IN 4 Violet
15 Plug Result 4 Grey-pink
2 Socket RxD (RS 232), Terminal Red-blue
3 Socket TxD (RS 232), Terminal White-green
4 Socket Term (RS 422/485) Brown-green
6 Socket RD+ (RS 422/485), Host White-yellow
7 Socket RD– (RS 422/485), Host
RxD (RS 232), Host
8 Socket TD+ (RS 422/485), Host White-grey
9 Socket TD– (RS 422/485), Host
TxD (RS 232), Host
– – Shield Orange
Yellow-brown
Grey-brown
Table 5-15: Wire color assignment cable 2 for connector cover no. 2 021 267
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5-13
Page 62

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
5.5 Electrical installation procedure
5.5.1 Individual steps
• Connect the power supply
• Connect the host interface
• Connect the PC (connect the terminal interface)
• Connect the "Sensor" and "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs
• Connect the "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching outputs
5.5.2 Tools
• Tool
• Digital measuring device (current/voltage measurement)
5.5.3 Connecting the supply voltage
a) SICK AMV/S and BMV 10 Connection Modules
If the CLV is powered via the SICK Connection Modules, the supply voltage does not have
to be wired separately.
Connecting the CLV without external parameter memory:
1. Make sure that the power supply to the Connection Module is switched off.
2. Connect the "Host/Term" and "I/O" connections on the CLV to the corresponding connections on the Connection Module using two cables no. 2 020 302 and secure them
tightly on both sides.
Connecting the CLV with external parameter memory:
1. Mount the connector cover with the external parameter memory no. 2 020 307 on the
"Host/Term" and "I/O" connections of the CLV and screw it tightly into position.
2. Connect the two free plug connections on the cables to the corresponding connections
on the Connection Module and secure them tightly.
The data and function interfaces of the CLV are connected to the Connection Module.
b) Power supply via non-SICK Power pack
Connecting the CLV without external parameter memory:
1. Connect the cable socket on cable no. 2 020 303 on the "Host/Term" connection and
screw it tightly into position.
2. Connect the cable plug on the cable no. 2 020 264 to the "I/O" connection and screw
it tightly into position.
3. Connect the power supply to the red wire (Pin 1, VS) and blue wire (Pin 5, GND) on cable
no. 2 020 303. See also
Table 5-10, Page 5-10
Connecting the CLV with external parameter memory:
1. Connect the "Host/Term" and "I/O" connections on the CLV to the corresponding connections on the Connection Module using two cables no. 2 020 981 and secure them
tightly on both sides.
2. Connect the power supply to the red/pink wire (Pin 1, VS) and the blue/grey-brown wire
(Pin 5, GND) of cable 1. See also Table 5-12, Page 5-12.
The CLV is connected to the supply voltage.
5-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 63

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
5.5.4 Connecting the host interface
AMV 60-011/AMS 60-012, -013
Terminal assignment
RS 232
( )=9-pin Sub D
( )= 9-pin D-Sub-
plug on PC
connector at PC
RS 422
RS 485: Connection diagram for SICK Network see "CLV Connect" program on CD-ROM
CAN-Network: Connection diagram for SICK CAN Scanner Network see "CLV Connect" program on CD-ROM
Fig. 5-2: Connecting the host interface
Risk of damage to the interface module
Electrical components in the CLV may be damaged if the host interface is connected
incorrectly. This also applies when the host interface connections are changed in the
Connection Modules (configuration).
¾ Connect the host interface as shown in Fig. 5-2.
¾ Check the connections carefully before you switch on the CLV.
¾ Connect the host interface on the CLV to the host using shielded cables (EMC require-
ments). Ensure that the maximum cable lengths are not exceeded (see Table 5-7,
Page 5-9).
Default In the default setting, the CLV communicates with the host via the host interface using the
values shown in
Parameter Value
Physical design RS 422/485
Data transfer rate 9,600 bd
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Protocol SICK (start character: STX, stop character: ETX, no request for repeat:
Table 5-16.
none, timeout: 50 ms)
Table 5-16: Communication parameters for the host interface (default setting)
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5-15
Page 64

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
For connecting the host interface via the AMV/S 60 Connection Module, see the Operating
Instructions "AMV/S 60 Connection Module" (no. 8 008 296).
Terminating the RS 422 interface
The interface can be terminated in the Connection Module. See the Operating Instructions
"AMV/S 60", "AMV 30.071", "AMV 100/200", or "BMS 20 Connection Modules".
Activating the RS 232 interface:
The RS 232 interface can be activated with the "CLV-Setup" program:
1. Choose the HOST INTERFACE tab.
2. Choose the RS 232 option from the HARDWARE drop-down list under DATA FORMAT.
3. Download the data to the CLV by clicking in the toolbar.
The DOWNLOAD PARAMETERS dialog box is displayed.
4. Confirm the dialog box by choosing PERMANENT.
The CLV uses the RS 232 version of the host interface.
Tip The communication parameters can be changed, if necessary, on the HOST INTERFACE tab.
To do so, change the values under DATA FORMAT and INTERFACE PROTOCOL.
RS 232
5.5.5 Connecting the CAN interface
Instructions for the connection of CAN-interface 1 and for configuration of the CLV to use
the device in the SICK-specific CAN Scanner Network or in a CANopen network see the
Operating Instructions “Application of the CAN interface“ (no. 8 009 180, English edition).
5.5.6 Connecting the PC
The CLV is operated and configured with the PC-based "CLV-Setup" program. In order to do
so, you must connect the device to the PC via the terminal interface (auxiliary interface). Un
like the host interface, the terminal interface has a permanent data format and a fixed data
transfer rate.
Fig. 5-3 shows how the terminal interface is connected. The cable length
should not be more than 10 m (32.8 ft).
AMV 60-011/AMS 60-012, -013
Terminal assignment
or 9-pin "Service"
plug
( ) = 9-pin Sub D
plug at PC
-
Fig. 5-3: Connecting the terminal interface
1. Switch off the PC and power supply to the SICK Connection Module.
2. Connect the PC to the internal, 9-pin "Service" plug on the Connection Module.
To do so, use a 3-core RS 232 data cable (null modem cable), e. g. no. 2 014 054
(RxD and TxD crossed).
– or –
Without the SICK Connection Module:
Connect the PC as shown in Fig. 5-3.
5-16 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 65

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
3. Switch on the PC and power supply to the SICK Connection Module.
4. Set the communication parameters (see Chapter 10.6.3 Starting CLV-Setup,
Page 10-32).
CLV
Tip
In the default configuration, the terminal interface outputs the reading result in reading
diagnosis mode.
You can change the operating mode to MONITOR HOST INTERFACE, to MONITOR HOST INTERFACE 2,
A
UXILIARY INPUT or EXTERNAL DATA STRING INPUT on the AUXILARY INTERFACE tab in the "CLV-
Setup" program.
5.5.7 Connecting the "Sensor" switching input
If a reading procedure is to be triggered on the CLV by an external sensor, the reading pulse
sensor must be connected to the "Sensor" switching input. This trigger type is selected in
the default setting of the CLV.
Fig. 5-4 shows the connections for the "Sensor" switching in-
put. Table 5-17 contains the characteristic data for this input.
AMV 60-011/
PNP sensor
V
S
V
2k6
Sensor
IN GND
GND
1
S
3
9
5
V
S
OUT
GND
V
S
GND
Switch
1
3
9
5
AMS 60-012, -013
Terminal assignment
V
/ 24 V
S
SENSOR
(IN) GND
GND
T. 27
T. 19
T. 20
T. 36
VS= +18 to +30 V DC for CLV without heater, 24 V DC +20 % /–10 % for CLV with heater
Fig. 5-4: Connections of the "Sensor" switching input
¾ Connect the reading pulse sensor as shown in Fig. 5-4.
Switching mode Current at the input starts the reading interval on the CLV.
(default: active high, debouncing: max. 30 ms (standard))
Properties – optodecoupled, non-interchangeable
– can be connected to PNP output on a sensor
Tip
Electrical values
Table 5-17: Characteristic data of the "Sensor" switching input
You can change the switching mode (polarity, debouncing, response for first pulse after po-
Low: –30 V ≤ VI ≤ +2 V High: +7 V ≤ VI ≤ +13 V
wer-up) of the "SENSOR" switching input on the DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab in the "CLV-Setup"
program.
¾ Click the READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS button.
Enter the values in the dialog box displayed. Download all changes to CLV.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5-17
Page 66

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
For connecting the host interface via the AMV/S 60 Connection Module, see the Operating
Instructions "AMV/S 60 Connection Module" (no. 8 008 296).
Note An external pulse is not required for Percentage Evaluation mode.
5.5.8 Connecting the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs
If the Autofocus function is not used and the CLVs dynamic focus control function is to be
triggered by external sensors, the sensors are connected to the five inputs "IN 0" to "IN 4".
Together with the internal assignment table, these can be used to configure a maximum of
32 switching states for up to 8 distance configurations. The dynamic focus control function
is selected for all inputs by default.
Additional function "IN 3":
The "IN 3" input can also be used as a trigger source for the One-Shot function of the oscillating mirror.
Additional function "IN 4":
The input "IN 4" can also be used as:
• A trigger source for the One-Shot function of the oscillating mirror
• An input for a belt increment signal in reading mode for separating bar codes of the
same symbology with identical content
• A trigger source for the end of reading interval
In this case, a maximum of 16 switching statuses can be used for dynamic focus control.
Fig. 5-5 shows the connections for the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs. Table 5-18 shows
the pin assignment on the CLV and the terminal assignment in the AMV/S 60. Table 5-19,
Page 5-19 contains the characteristic data for these inputs. Table 5-20, Page 5-19 shows
the input combinations based on the distance configurations. The interaction of the switching input functions is shown in Table 5-21, Page 5-20.
PNP sensor
V
S
CLV
V
= +18 to +30 V DC for CLV without heater, 24 V DC +20 % /–10 % for CLV with heater
S
V
2k6
IN X
IN GND
GND
1
S
Y
9
5
V
S
OUT
GND
V
S
GND
Switch
1
Y
9
5
AMV 60-011
AMS 60-012, -013
Terminal assignment
V
/ 24 V
S
IN X
(IN) GND
GND
Pin and terminal assignment
for IN X see Table 5-18
T. 28
Z
T. 20
T. 37
Fig. 5-5: Connections of the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs
5-18 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 67

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Electrical installation
Input
"IN X"
IN 0 Pin 6 T. 22
IN 1 Pin 2 T. 23
IN 2 Pin 7 T. 24
IN 3 Pin 11 T. 25
IN 4 Pin 12 T. 26
Table 5-18: Pin and terminal assignment for "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs
CLV "I/O" connection
Pin Y
AMV/S 60
Terminal Z
¾ Connect the sensors as shown in Fig. 5-5.
For connecting the host interface via the AMV/S 60 Connection Module, see the Operating
Instructions "AMV/S 60 Connection Module" (no. 8 008 296).
Function Trigger source for dynamic focus control
"IN 3" alternative: – trigger source for One Shot on oscillating mirror
"IN 4" alternative: – trigger source for One Shot on oscillating mirror
– encoder increment input
– trigger source for end of reading interval
Default setting "IN 3" and "IN 4": dynamic focus control
Switching mode Active when input energized (high)
Properties – Optodecoupled, non-interchangeable
– Can be connected to PNP output on a sensor
Electrical values
Table 5-19: Characteristic data of the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs
Low: –30 V ≤ VI ≤ +2 V High: +7 V ≤ VI ≤ +13 V
Switching inputs
Logic state1)
"IN 4 to IN 0"
inputs
0 0 0 0 0 N 1 DC 1 DC 6
0 0 0 0 1 N 2 DC 2 DC 5
0 0 0 1 0 N 3 DC 3 DC 4
0 0 0 1 1 N 4 DC 4 DC 4
0 0 1 0 0 N 5 DC 5 DC 3
0 0 1 0 1 N 6 DC 6 DC 3
0 0 1 1 0 N 7 DC 7 DC 3
0 0 1 1 1 N 8 DC 8 DC 3
0 1 0 0 0 N 9 DC 8 DC 2
0 1 0 0 1 N 10 DC 8 DC 2
0 1 0 1 0 N 11 DC 8 DC 2
0 1 0 1 1 N 12 DC 8 DC 2
0 1 1 0 0 N 13 DC 8 DC 2
0 1 1 0 1 N 14 DC 8 DC 2
0 1 1 1 0 N 15 DC 8 DC 2
0 1 1 1 1 N 16 DC 8 DC 2
1 0 0 0 0 N 17 DC 8 DC 1
1 0 0 0 1 N 18 DC 8 DC 1
1 0 0 1 0 N 19 DC 8 DC 1
1 0 0 1 1 N 20 DC 8 DC 1
1 0 1 0 0 N 21 DC 8 DC 1
1 0 1 0 1 N 22 DC 8 DC 1
Table 5-20: Dynamic focus control: switching inputs/distance configuration assignment table
Assignment
table index
Content Assignment Table Distance Config.2)
Default setting Example:
Photoelectric switches
(bright switching)
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5-19
Page 68

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Switching inputs
Logic state1)
"IN 4 to IN 0"
Assignment
table index
Content Assignment Table Distance Config.2)
Default setting Example:
inputs
1 0 1 1 0 N 23 DC 8 DC 1
1 0 1 1 1 N 24 DC 8 DC 1
1 1 0 0 0 N 25 DC 8 DC 1
1 1 0 0 1 N 26 DC 8 DC 1
1 1 0 1 0 N 27 DC 8 DC 1
1 1 0 1 1 N 28 DC 8 DC 1
1 1 1 0 0 N 29 DC 8 DC 1
1 1 1 0 1 N 30 DC 8 DC 1
1 1 1 1 0 N 31 DC 8 DC 1
1 1 1 1 1 N 32 DC 8 DC 1
1) 1 = energized (active); 0 = deenergized (inactive)
2) Distance configuration (DC): data record for focus position
Table 5-20: Dynamic focus control: switching inputs/distance configuration assignment table (contd.)
Parameter settings of switching inputs Effects
"IN 3" "IN 4"
Focus control
Focus control
)
1
1)
Focus control
One shot "IN 4" triggers the one shot
1)
"IN 3" switches the focus position in combination with "IN 0 to IN 2" and "IN 4"
"IN 3" switches the focus position in combination with "IN 0 to IN 2"
Focus control
Focus control
1
)
1
Increment
counter
"IN 4" receives increment signals
"IN 3" switches the focus position in combination with "IN 0 to IN 2"
End of reading interval "IN 4" triggers the end of reading interval
)
"IN 3" switches the focus position in combination with "IN 0 to IN 2"
One shot
Focus control
1)
"IN 0 to IN 2" switch the focus position
"IN 3" triggers the one shot
"IN 4" has no effect
One shot One shot "IN 0 to IN 2" switch the focus position
"IN 4" triggers the one shot
"IN 3" has no effect
One shot Increment
counter
"IN 0 to IN 2" switch the focus position
"IN 3" triggers the one shot
"IN 4" receives increment signals
One shot End of reading interval "IN 0 to IN 2" switch the focus position
"IN 3" triggers the one shot
"IN 4" triggers the end of reading interval
1) depending on the assignment table
Table 5-21: Combination of the functions of the "IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs
Photoelectric switches
(bright switching)
Tip
The function assigned to the "IN 3" and "IN 4" input can be modified on the DEVICE CONFI-
GURATION tab in the "CLV-Setup" program.
¾ Click the ASSIGNMENT OF INPUTS IN 3 and IN 4 drop-down list and choose the required
function. Download all changes to CLV.
5-20 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 69

Operating Instructions Chapter 5
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
5.5.9 Connecting the "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching outputs
The four switching outputs can be assigned different functions for outputting result statuses
independently of each other. If the assigned event occurs during the reading procedure, the
corresponding switching output becomes live at the end of the reading pulse for the selec
ted pulse duration. The pulse duration can be set individually for each output.
The "Read Result" LED is linked to the "Result 2" output and lights up in Reading mode for the
selected pulse duration and function of the result status display (default: Good Read, 100
ms).
Fig. 5-6, Page 5-21 shows the connections for the "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching out-
puts. Table 5-22, Page 5-21 shows the pin assignment on the CLV and the terminal assignment in the AMV/S 60. Table 5-23, Page 5-21 contains the characteristic data for these
outputs. The four outputs have the same characteristic data.
-
Fuse
V
S
Logic
Temperature
sensor
Result X
GND
5
VS= +18 to +30 V DC for CLV without heater,
24 V DC +20 %/–10 % for CLV with heater
AMV 60-011/
AMS 60-012, -013
Terminal assignment
Result XY
R
L
GND
Pin and terminal assignment
for "Result X" see Table 5-22
Fig. 5-6: Connections of the "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching outputs
Output
"Result X"
CLV "I/O" connection
Pin Y
Result 1 Pin 4 T. 31
Result 2 Pin 8 T. 32
Result 3 Pin 10 T. 33
Result 4 Pin 15 T. 34
Table 5-22: Pin and terminal assignment for "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching outputs
Z
T.35
AMV/S 60
Terminal Z
Pulse duration
depending
on setting:
– 10 ms to 900 ms
– 100 ms to 9,900 ms
–00: static
(to the end of next
reading pulse)
¾ Connect the outputs as shown in Fig. 5-6.
"
Switching mode PNP-switching with respect to the supply voltage V
S
Properties The current in the event of a short-circuit is limited to 0.7 A
Function
assignment
(default)
"Result 1": Device Ready (static), polarity: not inverted
"Result 2": Good Ready (100 ms), polarity: not inverted
"Result 3": No Ready (100 ms), polarity: not inverted
"Result 4": Match 1 (100 ms), polarity: not inverted
Electrical values
0 V ≤ VO ≤ 30 V Guaranteed: VO ≤ VS ≤ 1.3 V with I
≤ 100 mA
0
I0 ≤ 100 mA
Table 5-23: Characteristic data of the "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching outputs
Note If the "Device Ready" function is chosen, the CLV outputs a static pulse in Reading mode.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 5-21
Page 70

Chapter 5 Operating Instructions
Electrical installation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
For connecting the host interface via the AMV/S 60 Connection Module, see the Operating
Instructions "AMV/S 60 Connection Module" (no. 8 008 296).
Tip
The output function, pulse duration (timer), and polarity of the signals can be changed on
the D
EVICE CONFIGURATION tab in the "CLV-Setup" program.
¾ Click the RESULT OUTPUTS PARAMETERS button.
Enter the values in the tab displayed. Download all changes to CLV!
Recommendation ¾ To check the switching functions using a high-impedance digital voltmeter, connect a
load to the outputs to prevent incorrect voltage values/switching statuses from being
displayed.
5-22 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 71

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
6 Operation
6.1 Overview of steps for starting up the CLV
• Start up the CLV with the factory default settings (quick start).
With this configuration, the CLV can be operated without being connected to a PC.
• Connect the PC (see Chapter 5.5.5 Connecting the CAN interface, Page 5-16) and in-
stall the "CLV-Setup" program (see Chapter 10.6 Installing and operating the "CLV-Set-
up" program, Page 10-29).
• Configure (parameterize) the CLV for the application.
6.2 Default settings
Table 6-1, Page 6-2 and Table 6-2 contain an overview of the factory default settings for
the CLV. The default parameters are such that the CLV can be put into operation either
straight away or following a few minor adjustments. A PC does not need to be connected to
start up the CLV with the default settings.
The default settings are stored permanently both in the ROM of the CLV and in the CLVSetup database. They can be loaded to the RAM of the CLV at any time and displayed in the
tabs of the "CLV-Setup" program.
Displaying and printing out a complete set of default settings in CLV-Setup:
1. To save the current settings in the parameter set:
Choose FILE and SAVE AS, and enter a file name in the dialog box that appears.
CLV-Setup saves the current settings in a configuration file with the extension "*.scl".
2. Click in the toolbar.
CLV-Setup loads the default settings from its internal database and displays them in the
tabs.
3. Click in the toolbar.
The PRINT FILE dialog box is displayed.
4. If desired, a comment can be entered in the input field for the header of the printout.
Confirm the entry with OK. The PRINT dialog box for configuring the printer then is
displayed.
5. Make the appropriate entries in the dialog box and confirm these with OK.
CLV-Setup prints out the complete set of default settings in the form of a table. The header
contains the company and user names that were entered during the CLV-Setup installation
routine.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-1
Page 72

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
6.2.1 Default settings of the line scanner CLV 480 (all variants)
Parameter Default setting
Decoder SMART/standard
Active codes types Code 39, 2/5 Interleaved, Code 128
Code length Freely assignable (2/5 Interleaved: interval 4 to 50 characters)
Start/stop ratio Automatic
Min./max. code position 5/ 95 CP
No. of multiple reads 3
Min./max. no. codes 1
Scanning frequency 800 Hz
Focus control 8 distance configurations(DC)
Focus positions DC 1 to DC 8: 1,000 mm (39.4 in)
Focus control trigger Switching inputs/serial interface, switchover immediately (synchronously)
Reading pulse source Start: "Sensor" switching input (active: high); end: "Sensor" switching input
"IN 0" to "IN 4" switching inputs Focus position changeover
"Sensor" switching input Start and end of reading pulse (level: active high), debouncing 20 to 30 ms
Switching outputs Not inverted; pulse duration: 100 ms
Status output function Result 1: Device Ready (static); Result 2: Good Read; Result 3: No Read; Result 4: Match 1
CLV arrangement Stand-alone
Read result output Host interface
Device number 1
Start option Load the parameter set of the external parameter memory
Host interface (type) RS 422/485
Protocol NAK; start character: STX, stop character: ETX
Transmission rate 9,600 bd
Data format 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit
Output format Good Read: Header: blank, Code Info/Separator: blank, Splitter: blank, Terminator: blank
Reading data in case of error (no read): Output: yes; Code Info/Separator and Error string
Error string: NOREAD
Output sorting In accordance with code position
Output time Read result: end of the read interval Code Info/Separator: after code
Test string Not activated
Terminal interface RS 232, 9,600 bd, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit (values cannot be changed)
Function Reading diagnosis
Table 6-1: Extract: Default parameter settings of the line scanner CLV 480
6.2.2 Default settings of the line scanner with oscillating mirror
CLV 480 (all variants)
Default settings as for line scanner CLV 480, but with the following additional parameters:
Parameter Default setting
Oscillating amplitude ±40 CW (corresponds to an angle of deflection of –20° to +20°)
Operating mode Oscillating with fixed amplitude, mode independent of reading pulse trigger
Oscillating frequency 1 Hz
Fixed position 50 CW (corresponds to an angle of deflection of 105°)
Table 6-2: Extract: Default parameter settings of the line scanner with oscillating mirror CLV 480
6-2 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 73

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
6.3 Quick start
A PC need not to be connected when the CLV is operated with the factory default settings.
Code 39, 2/5 Interleaved, and Code 128 are the default code types enabled (free code
lenght, 2/5 Interleaved: interval 4 to 50 characters).
6.3.1 Starting up the CLV with the factory default settings
1. Connect the CLV to the AMV/S 60 Connection Module using the two cables no. 2 020 302.
2. Connect the reading pulse sensor (e. g. photoelectric reflex switch) to the "Sensor"
switching input of the CLV via the AMV/S 60 (see Chapter 5.5.7 Connecting the "Sen-
sor" switching input, Page 5-17).
3. Switch on the power supply of the AMV/S 60.
The CLV starts. The "Device Ready" LED lights up. The "Result 1" ("Device Ready")
output switches.
CLV with external parameter memory connected
(default setting: Start with external parameters):
If an external parameter memory containing a corresponding parameter set is connected to the CLV, the "Device Ready" LED blinks for 10 s when the device starts up correctly and then lights up constantly. If the external parameter memory is empty, the CLV
immediately copies its parameter set to the external parameter memory. Then the "De
vice Ready" LED lights up. The CLV is ready for operation.
Line scanner with oscillating mirror:
In the default setting, the CLV deflects the scan line around the position CW = 50 with
a frequency of 1 Hz and an oscillating amplitude of
to a deflection angle below 105
4. Start the reading pulse: block the light path of the photoelectric switch or close the
switch. The "Laser On" LED lights up. The CLV switches the laser diode on and the red
scan line appears.
5. Present the bar code pattern (Fig. 6-1) to the CLV at the reading distance specified in
Table 6-3, Page 6-4.
6. Align the bar code in such a way that the red scan line is almost at a 90° angle to the
bars (line scanner) or that the red scan line sweeps the bars at a 90
deflected (oscillating mirror).
7. End the reading pulse: unblock the light path of the photoelectric switch or open the
switch. The "Laser On" LED is extinguished. The CLV switches the laser diode off. The
CLV confirms that the bar code was read successfully (the "Read Result" LED lights up
for 100 ms). The "Result 2" ("Good Read") output is switched for a duration of 100 ms.
The CLV can now be operated with the factory default settings.
The device can be switched off without the configuration data being lost as no changes have
been made to the parameter set.
°.
±20° (±40 CW). 50 CW correspond
° angle when it is
-
0123412345
Fig. 6-1: Bar code pattern (Code 39; module width 0.35 mm (13.8 mil); Print ratio 2:1)
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-3
Page 74

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Device type Scanning method Reading distance
CLV 480 (all variants) Line scanner approx. 1,000 mm (39.4 in)
CLV 480 (all variants) Line scanner with oscillating mirror approx. 1,000 mm (39.4 in)
Table 6-3: Reading distances for default settings
6-4 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 75

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
6.4 Configuring (parameterization) the CLV
The CLV adapts to the reading situation locally with the configuration. The read, evaluation
and output characteristics can, therefore, be parameterized as required on the basis of the
factory default settings or an application-specific CLV parameter set that has already been
created.
The CLV supports two different configuration methods:
• Configuration via the "CLV-Setup" program
(parameter values are set via the serial interface)
• Configuration via command strings
(parameter values are set via the serial interface).
See Chapter 10.7 Configuring a CLV with command strings, Page 10-39.
In the Parameterization mode, the CLV outputs no reading result.
6.4.1 Configuring the CLV via the user interface of CLV-Setup
To be able to use CLV-Setup, a PC has to be connected and the program installed on it. The
procedure for connecting the PC to the CLV is described in
CAN interface, Page 5-16. The procedures for installing and starting the "CLV-Setup" pro-
gram and for starting and operating the user interface are described in the Appendix
(
Chapter 10.6 Installing and operating the "CLV-Setup" program, Page 10-29).
Chapter 5.5.5 Connecting the
Transferring a parameter set between CLV-Setup and the CLV
Upload
When the CLV is being parameterized, CLV-Setup runs in the offline mode. To be able to
modify the current parameter set of the CLV, this first has to be loaded to CLV-Setup from
the CLV. This procedure is referred to as an upload ("Upload from CLV" in the CLV
menu or [F3] key) during which CLV-Setup always loads a complete copy of the current CLV
parameter set. This parameter set remains unchanged until it is overwritten by CLV-Setup.
With the help of the context menu (right mouse button), only the parameter just edited can
be loaded ("Upload parameter") or from version 3.6 all parameters of one tab or one dialog
box ("Upload parameters of this view") from the CLV’s memory (RAM).
Download
Changes made to the current parameter set in CLV-Setup do not take effect until the
parameter set has been transferred to the CLV. CLV-Setup always sends a copy of the
complete parameter set to the CLV, i. e. all of the existing parameter values in the CLV are
overwritten. The procedure for transferring and saving the parameter values in the CLV is
referred to as a download ("Download to CLV" in the CLV
With the help of the context menu (right mouse button), only the parameter just edited
("Download parameter") or from version 3.6 all parameters of one tab or one dialog box
("Download parameters of this view") will be temporarily loaded into the CLV’s memory
(RAM). To finish the parametrization done by this way all parameters must be download
again to the CLV with the "Permanent" option.
480 menu or [F4] key).
480
Loading a complete CLV parameter set (upload)
¾ Click in the toolbar or press [F3] key.
CLV-Setup loads the current CLV parameter set from the RAM of the CLV to its database and displays the values in the tabs.
The "Device Ready" LED is extinguished during the upload.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-5
Page 76

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
If the "CLV-Setup" program does not recognize parameters transferred during the upload, it
outputs a warning message. Unknown parameters can be edited in the E
XTRAS tab by
following the conventions for command strings. When the parameter set is then saved, the
se parameters are also saved.
Transferring and saving a complete CLV parameter set (download)
1. Click in the toolbar or press [F4] key.
The "Device Ready" LED is extinguished.
CLV-Setup copies the parameter set to the RAM of the CLV. The DOWNLOAD PARAMETERS
dialog box with the storage options is then displayed.
PERMANENT: CLV-Setup copies the parameter record to the RAM and to the EEPROM of
the CLV.
TEMPORARY: CLV-Setup copies the parameter record to the RAM only. The changes are
lost when the CLV supply voltage is switched off.
2. Confirm the dialog box with the desired storage option.
The "Device Ready" LED lights up again.
The new parameter set is stored in the CLV either permanently or temporarily dependent of
the selected option
.
-
CLV with external parameter memory
If the parameter set was downloaded and stored permanently, CLV-Setup opens a further
dialog box for adjusting the parameter set in the external memory, if the start option is set
to S
TART WITH EXTERNAL PARAMETERS.
¾ Choose the COPY NOW INTERNAL PARAMETER SET TO EXTERNAL MEMORY option.
CLV-Setup then instructs the CLV to copy the new parameter set to the external
memory. The "Device Ready" LED lights up again.
The internal and external parameter sets are now identical.
See also Chapter 10.3.5 Adjusting the parameter set in the external parameter memory af-
ter it has been downloaded to the CLV, Page 10-24.
Saving a parameter set in CLV-Setup
1. To save the modified parameter set as a new configuration file in CLV-Setup, or to overwrite an existing file, choose FILE and SAVE AS.
The FILE SAVE AS dialog box is then displayed.
2. Enter the file name in the dialog box (file name extension "*.scl") and confirm the entry.
The new parameter set is now stored in CLV-Setup in the subdirectory "data".
6-6 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 77

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
6.4.2 Function of the tabs in CLV-Setup (overview)
Reading Configuration
This tab and further dialog boxes are used to set the following:
• Scanning frequency
• Start/stop ratio
• Event-controlled focus control (focus position, evaluation range of the scan line, extent
of deflection of oscillating mirror, assignment table of distance configurations)
• Trigger source for the focus control
• Adjustment to bar code quality caracteristics, code background (scattered print) and
relative module width
Device Configuration
This tab and further dialog boxes are used to set the following:
• Device number
• Source of the Reading trigger mode
• Laser timeout
• Output time of the Reading result referred to the start of the reading interval
• Scanner position parameters (the position of the CLV in the area)
• Tracking parameters
• Output filter of the reading result (host interface)
• Physical arrangement for data output via the host interface
(stand-alone, master/slave)
• Functional assignment of the "IN 3" and "IN 4" switching inputs
• Functional assignments of the "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching outputs
• Start option for accessing the parameter set
• Matchcode comparison
Code Configuration
This tab and further dialog boxes are used to set the following:
• Type of active decoder (SMART and/or standard decoder)
• Evaluation routines for individual code types
• Number of identical reads (multiple reads)
• Minimum and maximum number of bar codes to be read/output
• Type of Start/Stop recognition
• Activation of the comparison of the code position for the separation of identical codes
• special parameters for SMART decoder (e. g. in the OTS mode)
Recommendation To enhance the reading reliability with fast applications, only activate those code types and
code lengths that are actually relevant.
Host Interface
This tab and further dialog boxes are used to set the following:
• Destination of the read result date strings (host interface or CAN interface)
• Active physical interface (RS 422/485 or RS 232)
• Data format and transmission rate
• Data transmission protocol
• Start and stop characters of the interface protocol
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-7
Page 78

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Data Strings
This tab and further dialog boxes are used to set the following:
• Data output format of the host interface (telegram format)
• Constants and reading diagnosis data in the "Header", "Code Info/Separator", "Splitter"
and "Terminator" blocks
• Arrangement of the "Code info/separator" blocks in the data string
• Output format for no reads and contents of the error string
• Test string function
• Output sequence and sort criteria for reading more than one bar code per reading pulse
• Format mask and its structure
• Output format of an external data string forwarded as reading result
Auxiliary Interface
This tab and further dialog boxes are used to change the following:
• Operating mode of the terminal interface
CAN Interface
This tab and the further dialog windows are used to change the following:
• CAN interface operating mode
• Data transmission rate
• Type of logical data connection of the connected CLV
• Usage of the switch inputs/outputs of the CLV as CANopen Digital I/O
Oscillating Mirror
This tab is used to set the following:
• Operating mode of the oscillating mirror
• Oscillating frequency
• Angle of deflection (oscillating amplitude)
• Start of oscillating mode
• Trigger source for One-Shot
Extras
This tab is used to edit parameters that were not recognized by CLV-Setup after an upload.
Note CLV-Setup Online Help contains a detailed description of the functions of the parameters and
their valid entries (see
Chapter 10.6.8 CLV-Setup Help, Page 10-36 for calling up Help).
6-8 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 79

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
6.4.3 Guide to parameterization menu
Overview of parameterization steps
• a) Parameterizing focus position switchover
• b) Parameterizing optical read properties of the scanner
• c) Optional: Configuring oscillating mirror functions
• d) Parameterizing a read pulse timing
• e) Parameterizing laser timeout
• f) Parameterizing the decoder’s evaluation properties
• g) Parameterizing the output properties (data, result status)
• h) Parameterizing the terminal interface function (auxiliary interface)
• i) Parameterizing the source of the parameter set for starting up (only with external
parameter memory)
When the CLV is switched on for the first time, it is started with the factory default settings.
The following parameters must then be set:
a) Parameterizing focus position switchover
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
1. Activate focus control function (choose trigger source)
2. Set up distance
configurations
Ö READING CONFIGURATION tab
Ö FOCUS CONTROL section
– Inputs/Serial or
– Timer ÖTIMER or
– Static/No Trigger
Oscillating mirror:
– additional: Oscillating mirror extrema
Ö READING CONFIGURATION tab
Ö DISTANCE CONFIGURATION button
Ö DISTANCE CONFIGURATION tab
– Focus Position
– Minimum Code Position CP
– Maximum Code Position CP
Oscillating mirror:
– additional: Oscillating mirror amplitude CW
Ö ASSIGNMENT TABLE tab
– Index
– No. of valid configurations
3. Choose focus switchover
point (referred to reading
pulse)
4. In INPUTS/SERIAL trigger
source: choose function for
"IN 3" and "IN 4" switching
inputs
Ö READING CONFIGURATION tab
Ö FOCUS CONTROL section
Ö INPUTS/SERIAL
– Immediate or Synchronous (default) or
– Latched (special application)
Ö READING DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö ASSIGNMENT OF INPUTS section
Ö IN 3
– Focus Control
Ö IN 4
– Focus Control
Table 6-4: Guide: Parameterizing focus position switchover
Note The minimum and maximum values for the active evaluation range of the scan line (MIN. AND
M
AX. CODE POSITION) can be checked in the SHOW CP-LIMITS mode.
See Chapter 6.5.4 Show CP-limits, Page 6-30.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-9
Page 80

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
b) Parameterizing optical read properties of the scanner
• Scanning frequency Ö READING CONFIGURATION tab Ö READING PARAMETERS section
• Blank zone Ö READING CONFIGURATION tab Ö READING PARAMETERS section Ö
(Start/stop ratio)
• Poor quality bar code print (e.g. bad contrast) or scattered print Ö READING CONFIGU-
RATION tab Ö CODE LABEL CHARACTERISTICS section Ö Code label quality and Background
noise
• Reading with high tilt Ö READING CONFIGURATION tab Ö CODE LABEL CHARACTERISTICS section
Ö Relative modul width
• Reading bar codes with small height (bar length) by SMART decoder Ö CODE
CONFIGURATION tab Ö DECODER section/SMART PARAMETERS button
c) Optional: Parameterizing oscillating mirror functions
c
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
1. Choose "Oscillating with fixed amplitude"
mode
(identical amplitude for all distance
configurations)
– or –
2. Choose "Oscillating with variable amplitude"
mode
(amplitude can be chosen for each distance
configuration)
– or –
Ö OSCILLATING MIRROR tab
Ö OSCILLATING MIRROR section
– Oscillating with fixed amplitude
Ö OSCILLATING section
– Frequency
Ö OSCILLATING MIRROR tab
Ö OSCILLATING MIRROR section
– Oscillating with variable amplitude
Ö OSCILLATING section
– Frequency
Ö READING CONFIGURATION tab
Ö DISTANCE CONFIGURATION button
– Oscillating Mirror Amplitude (CW value)
3. Choose "Fixed Position" mode
– or –
Ö OSCILLATING MIRROR tab
Ö OSCILLATING MIRROR section
– Fixed Position
Ö FIXED POSITION section
– Stationary Position (CW)
4. Choose "One-Shot" mode Ö OSCILLATING MIRROR tab
Ö OSCILLATING MIRROR section
– One-Shot
Ö ONE-SHOT section
Ö PHASE 1
– Mirror Speed
– Start Position
– Distance Configuration (no.)
Ö PHASE 2
– Mirror Speed
– Start Position
– DistanceConfiguration (no.)
5. With One-Shot: choose trigger source Ö OSCILLATING MIRROR tab
Ö ONE-SHOT section
Ö TRIGGER MODE
– Reading Trigger Pulse or
– Switching input or
– Serial Interface
Table 6-5: Guide: Parameterizing oscillating mirror functions
6-10 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 81

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
6. With One-Shot and trigger source
"IN 3" or "IN 4":
Choose function for switching input
"IN 3" or "IN 4"
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö ASSIGNMENT OF INPUTS section
Ö IN 3
– One Shot or
Ö IN 4
– One Shot
see also Table 5-21, Page 5-20
7. Choose activity of oscillating mode Ö OSCILLATING MIRROR tab
Ö OSCILLATING MIRROR ACITVE section
– Continuous or
– During reading interval
Table 6-5: Guide: Parameterizing oscillating mirror functions (contd.)
Note The OSCILLATE WITH VARIABLE AMPILTUDE operating mode can only be selected from amplitudes
of min.
±10 CW and an oscillating frequency of 0.4 Hz or higher.
The scan line must always sweep the neutral position (CW = 50). This means that oscillation
is not possible in the range 60 CW to 80 CW, for example, but is possible in the range
40 CW to 80 CW.
Explanation of oscillating mirror functions
1. "Oscillating with fixed amplitude" mode
The oscillating mirror deflects the scan line up to the maximum angle of deflection of
±40 CW (corresponds to ±20°). Fig. 6-2 illustrates this mode when a bar code is read from
above.
Constant
oscillating
frequency
0 0
Scan line density depending on object height
Fig. 6-2: Oscillating mirror: "Oscillating with fixed amplitude" mode
2. "Oscillating with Variable Amplitude" mode
The deflection range can be parameterized separately for each of the maximum of 8 distance configurations/focus positions. The minimum/maximum values that can be set for
the deflection range for fast applications ensure that the scan line only sweeps areas that
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-11
Page 82

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
contain bar codes during the time available. This also ensures that the scan line density on
the object is, for the most part, constant.
Fig. 6-3 illustrates this mode when a bar code is
read from above.
Constant
oscillating
0 0
frequency
Scan line density equal, independant of object height
Fig. 6-3: Oscillating mirror: "Oscillating with variable amplitude" mode
Limitation of the
deflection range
(CW value)
1
3. "Fixed Position" mode
The CLV parks the oscillating mirror at the desired position. 10 CW corresponds to –20°,
and 90 CW to +20
° (see Fig. 4-8, Page 4-6). In the default setting, the fixed position is set
to 50 CW (corresponds to an angle of deflection below 105°). The Oscillating mode is switched off.
4. "One-Shot" mode
In the "One-Shot" mode, the oscillating mirror only performs one specific oscillating movement per reading interval. This movement consists of a forward phase and a return phase.
The start position of the scan line, the mirror speed and the valid distance configuration can
be parameterized separately for each phase. The end position of the one phase forms the
start position of the other phase.
Fig. 6-4 illustrates this mode with object tracking. During
the forward phase, the front of the object that moves towards the oscillating mirror is swept
once by the scan line from top to bottom in accordance with the conveyor speed. Multiple
focus position switchovers are not necessary as the required reading range (DOF) is much
smaller than with the line scanner.
Fig. 10-32, Page 10-43 explains how the start position
and mirror speed are calculated for a given conveyor speed.
Possible trigger sources for One-Shot:
• "IN 3" or "IN 4" switching input
• Command string (via serial interface)
• Start of reading interval
6-12 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 83

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Conventionally required reading range
t
0
n
a
r
g
n
i
d
a
e
R
Reduced reading range through One-Shot function
t
1
e
g
n
a
r
g
n
i
d
a
e
R
Line scanner
e
g
Line scanner with
oscillating mirror
Fig. 6-4: One-Shot: Object tracking (bar code read from front)
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-13
Page 84

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
d) Parameterizing the reading trigger
The selected reading mode depends on the number of objects that are simultanously in the
reading field of the CLV during each reading interval. This is independent of the number of
bar codes on the actual object.
Table 6-6 shows an overview of the configurations and ap-
plications.
Configuration Application See page
A. Stand-alone Start/stop mode
• One object in reading field per reading interval, reading one side
B. Used in Omni Portal System
(arrangement with OTS 400 and other
CLVs)
Table 6-6: Overview: CLV applications in stand-alone configuration or in arrangement with OTS 400
Start/stop mode
• One object in reading field per reading interval, CLV involved in read-
ing one side or more sides, master/slave arrangement with OTC 400
controller
Tracking mode (controlled by increment)
• Max. 20 objects in reading field per reading interval, CLV involved in
reading one or more sides, object tracking by OTC 400 controller
6-14
6-18
6-20
A. CLV in stand-alone configuration
A1. Start/Stop mode
• One object in the reading field per reading interval, reading on one side
Possible reading triggers:
• One external sensor (e. g. photoelectric reflex switch)
• Two external sensors
• Command strings
• Free-running mode
Further preparations:
¾ Configuring distance configurations:
see Chapter a) Parameterizing focus position switchover, Page 6-9
¾ Configuring oscillating mirror (optional):
see Chapter c) Optional: Parameterizing oscillating mirror functions, Page 6-10
¾ Configuring no. of bar codes to be read:
see Chapter f) Parameterizing the evaluation characteristics, Page 6-23
Note The size of the reading field is determined by the distance between the start and stop sen-
sors in conveying direction (see Fig. 3-4, Page 3-8).
6-14 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 85

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
Parameterize reading trigger:
one external sensor
– or –
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Start:
Ö READING TRIGGER SOURCE section
– Sensor Input (Active High) or
– Sensor Input (Active Low)
Ö READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS button
Ö DEBOUNCING SENSOR section
– Standard or
– Fast or
– Time controlled: value or
– Track contolled: value
(with connected increment sensor)
Ö FIRST TRIGGER SENSOR section
– Edge or
– Level
Stop:
Ö END OF READING INTERVAL section
– generated by Trigger Source or
– Timer: Timeout (referred to beginning of reading interval)
Output of reading result referred to beginning of reading
interval:
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö OUTPUT ON GOOD READ section
– End of reading gate or
– Immediate or
– End of Label
Ö Using End of label: READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS button
Ö END OF LABEL/FREE-RUNNING section
– Timeout
Note:
Connect the external sensor to "Sensor“ switching input!
Table 6-7: Guide: Parameterizing the reading trigger for start/stop mode in stand-alone
configuration
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-15
Page 86

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
Parameterize reading trigger:
two external sensors
– or –
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Start (sensor 1):
Ö READING TRIGGER SOURCE section
– Sensor Input (Active High) or
– Sensor Input (Active Low)
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Ö READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS button
Ö DEBOUNCING SENSOR section (also for sensor 2 on "IN 4")
– Standard or
– Fast or
– Time controlled: value
Ö FIRST TRIGGER SENSOR section
– Edge or
– Level
Stop (sensor 2):
Ö END OF READING INTERVAL section
– generated by IN 4
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö ASSIGNMENT OF INPUTS section
Ö IN 4
– Reading Trigger Stop (Active High) or
– Reading Trigger Stop (Active Low)
Output of reading result referred to beginning of reading
interval:
Ö OUTPUT ON GOOD READ section
– End of reading gate or
– Immediate or
– End of Label
Ö Using End of label: READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS button
Ö END OF LABEL/FREE-RUNNING section
– Timeout
Note:
Connect sensor 1 to "Sensor“ switching input and sensor 2 to
"IN 4“ switching input!
Table 6-7: Guide: Parameterizing the reading trigger for start/stop mode in stand-alone
configuration (contd.)
6-16 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 87

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
Parameterize reading trigger:
command strings
– or –
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Start:
Ö READING TRIGGER SOURCE section
– Serial Interface
Stop:
Ö READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS button
Ö END OF READING INTERVAL section
– generated by Trigger Source or
– Timer: Timeout (referred to beginning of reading interval)
Trigger characters:
Ö SERIAL INTERFACE section
– Standard Trigger or
– Single character
Ö Using single character: start and stop characters
Ö Echo on/off
Output of reading result referred to beginning of reading
interval:
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö OUTPUT ON GOOD READ section
– End of reading gate or
– Immediate or
– End of Label
Ö Using End of label: READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS button
Ö END OF LABEL/FREE-RUNNING section
– Timeout
Parameterize reading trigger:
free-running
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Start:
Ö READING TRIGGER SOURCE section
– Free-running with Timeout: Timeout
Stop (generated by reading trigger source):
Ö READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS button
Ö END OF LABEL/FREE-RUINNING section
– Timeout
Output of reading result referred to beginning of reading
interval:
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö OUTPUT ON GOOD READ section
– End of reading gate or
– Immediate
Note:
No laser timeout function (defined switching off of laser diode
due to too long active reading gate) in this trigger mode!
Table 6-7: Guide: Parameterizing the reading trigger for start/stop mode in stand-alone
configuration (contd.)
Note To separate bar codes of the same type with identical contents, connect an incremental en-
coder and activate the "Compare Code Position" function. See also Chapter f) Parameteri-
zing the evaluation characteristics, Page 6-23.
If you are using an incremental encoder, the "Sensor“ and "IN 4" switching inputs for the
beginning and end of the reading interval can also be debounced for specific paths.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-17
Page 88

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
B. CLV integrated in Omni Portal System
B1. Start/Stop mode
Prerequisites:
• One object in the reading field per reading interval.
Example: omni-directional 2-side reading with 4 CLVs (slaves) and OTC 400 controller
(master)
• Minimum object distance > size of reading field
(size of reading field = distance between sensors for start and stop of reading trigger)
• Dynamic focus control according to application:
– with OTS height information (distance) via CAN bus for reading from top
– one distance configuration (fixed focus) for e. g. reading from side and sufficient
depth of field (DOF)
• Two reading trigger sensors connected to OTC 400 (start and stop)
• Master/slave arrangement using the CAN interface
Possible reading triggers:
• via OTS trigger
Further preparations for each CLV:
¾ Configuring oscillating mirror (optional):
see Chapter c) Optional: Parameterizing oscillating mirror functions, Page 6-10
¾ Configuring no. of bar codes to be read:
see Chapter f) Parameterizing the evaluation characteristics, Page 6-23
Note To separate bar codes of the same type with identical contents, connect an incremental
encoder to the OTC 400 and activate the "Compare Code Position" function in the CLV.
See also Chapter f) Parameterizing the evaluation characteristics, Page 6-23.
Parameterizing focus control in the CLV:
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
Use distance information of
OTC 400 (master)
– or –
Coose fixed focus and set up
one distance configuration
Ö READING CONFIGURATION tab
Ö FOCUS CONTROL section
– OTS height information
Ö READING CONFIGURATION tab
Ö FOCUS CONTROL section
– Static (No Trigger)
Ö DISTANCE CONFIGURATION button
Ö DISTANCE CONFIGURATION tab
– Focus Position
– Minimum Code Position CP
– Maximum Code Position CP
Oscillating mirror:
– additional: Oscillating mirror amplitude CW
Ö ASSIGNMENT TABLE tab
– Index
– No. of valid configurations: 1
Table 6-8: Guide: Parameterizing focus control in the CLV for master/slave arrangement with
OTC 400
6-18 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 89

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
Parameterizing reading trigger in the CLV:
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
Choose reading trigger Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö READING TRIGGER SOURCE section
– OTS Trigger
Table 6-9: Guide: Parameterizing reading trigger mode in the CLV for master/slave arrangement
with OTC 400
Parameterizing slave mode in the CLV:
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
1. Enable slave mode in CLV for
OTC 400 (master)
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö TRACKING PARAMETERS button
Ö RELEASE POINTS section
– Object release point: 0 mm!
(controll box "Master/Slave via OTC" active)
2. Forwarding reading results to
the CAN interface
3. Parameterize CAN interface Ö CAN INTERFACE tab
Ö HOST INTERFACE tab
Ö DESTINATION OF RESULT DATA STRINGS section
– CAN interface
Ö CAN INTERFACE FUNCTION section
– OTS Slave
Ö CAN DATA RATE section
– 500 kBit/s
Table 6-10: Guide: Parameterizing slave mode in the CLV for arrangement with OTC 400 (master)
Note When in slave mode, the CLV receives the trigger signals for the reading pulse (start and
stop) from the OTC 400 via the CAN bus along with (depending on the parameter settings)
the distance information required for focus position switchover. The distance information
can be generated, for example, by the OTC 400 by means of height-control photoelectric
switches or can originate from another CLV.
Immediately after successful reading the CLV sends the reading result (contents of barcode(s)) to the OTC 400 via the CAN bus. The OTC 400 compiles the results received from
all the slaves and evaluates them accordingly before sending them to the host.
OTC 400 Controller:
Besides other function parameterize the following function in the OTC 400:
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
Choose operation mode in the
OTC 400 (master)
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS button
Ö OPERATION MODE section
– Time controlled (Master/Slave) output at end of reading
gate
or
– Time controlled (Master/Slave) output immediate if...
Table 6-11: Guide: Parameterizing operation mode in the OTC 400 for master/slave arrangement
For functions to be parametrized in the OTC 400: see "OTS 400 Omni Tracking System“
Operatings Instructions (no. 8 008 869, English edition).
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-19
Page 90

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
B2. Tracking mode (controlled by increment)
Note SICK AG can design and preconfigure more complex omni-portal systems to fulfill the
customer's reading requirements and then provide appropriately trained personnel to
install, test and put these systems into operation.
An overview of the parameterization steps for an example situation is given below (the
overview does not include all available parameterization options).
Prerequisites:
• Max. 20 objects consecutively, simultanously in the reading field.
Example: Omni-directional 3-side reading with groups of CLVs (slaves) and OTC 400
controller (master)
• Minimum object gap between two objects in conveyor direction: 50 mm
• Size of reading field = distance between sensor for beginning/end of object and object
release point parameterized in the OTC 400 (data output)
• Dynamic focus control according to application:
– with OTS height information (distance) via CAN bus for reading from top
– one distance configuration (fixed focus) for e. g. reading from side and sufficient
depth of field (DOF)
• Sensor for beginning of object and incremental encoder connected to the OTC 400
• Master/slave arrangement using the CAN interface
Possible reading triggers:
• via OTS trigger
Further preparations for each CLV:
¾ Configuring oscillating mirror (optional):
see Chapter c) Optional: Parameterizing oscillating mirror functions, Page 6-10
¾ Configuring no. of bar codes to be read:
see Chapter f) Parameterizing the evaluation characteristics, Page 6-23
Note To separate bar codes of the same type with identical contents, connect an incremental en-
coder to the OTC 400 and activate the "Compare Code Position" function in the CLV.
See also Chapter f) Parameterizing the evaluation characteristics, Page 6-23.
Parameterizing focus control in the CLV:
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
Use distance information of
OTC 400 (master)
– or –
Table 6-12: Guide: Parameterizing focus control in the CLV for master/slave arrangement with
OTC 400
Ö READING CONFIGURATION tab
Ö FOCUS CONTROL section
– OTS height information
6-20 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 91

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
Coose fixed focus and set up
one distance configuration
Ö READING CONFIGURATION tab
Ö FOCUS CONTROL section
– Static (No Trigger)
Ö DISTANCE CONFIGURATION button
Ö DISTANCE CONFIGURATION tab
– Focus Position
– Minimum Code Position CP
– Maximum Code Position CP
Oscillating mirror:
– additional: Oscillating mirror amplitude CW
Ö ASSIGNMENT TABLE tab
– Index
– No. of valid configurations: 1
Table 6-12: Guide: Parameterizing focus control in the CLV for master/slave arrangement with
OTC 400 (contd.)
Parameterizing reading trigger in the CLV:
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
Choose reading trigger Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö READING TRIGGER SOURCE section
– OTS Trigger
Table 6-13: Guide: Parameterizing reading trigger mode in the CLV for master/slave arrangement
with OTC 400
Parameterizing tracking mode in the CLV:
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
1. Define position of CLV
referred to conveyor belt
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö SCANNER POSITION PARAMETERS button
Ö ANGLES section
– alpha, beta and gamma
Ö COORDINATS section
– x-, y- and z-coordinate
2. Parameterize scale factor
for increment pulse
3. Define release points Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö DISTANCE PER ENCODER PULSE section
– Value
(in agreement with increment sensor and OTC 400)
Ö TRACKING PARAMETERS button
Ö RELEASE POINTS section
– Focus release point: value
– Object release point: value
4. Define label assignment
tolerance for object gaps
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö TRACKING PARAMETERS button
Ö LABEL ASSIGNMENT TOLERANCE section
– Automatic or
– Fixed Tolerance: value
Table 6-14: Guide: Parameterizing tracking mode in the CLV for Object Tracking mode with OTC 400
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-21
Page 92

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Explanation In a network configuration, object tracking is carried out by each CLV using an internal con-
tinuous object list. The CLV slave receives the necessary tracking information for the objects
in the reading field (current object number, start and end of object, incremental decoder va
lue) from the OTC 400 via the CAN bus. Depending on the parameter settings, this information can also include distance information for focus control. The position of the CLVs along
the conveyor system must be accurately defined so that the bar code(s), object, and scan
ner can be assigned correctly. A variable tolerance range in the conveyor direction between
two objects (end of one object and start of the next object) enables the reading results to
be assigned to the objects more easily.
Once the information has been read successfully, the CLV sends the reading results (object
number and position of the bar code(s) on the object in the conveyor direction) immediately
to the OTC 400 via the CAN bus. The OTC 400 also collects results with the same name
(identical bar code contents) from each slave to verify them. It then sends the filtered overall
result (for each object relative to the output time in the reading procedure) to the host. The
object enable point (data output) configured in the OTC 400 forms the end of the reading
field. The object enable point configured in the CLV must always be smaller than that in the
OTC 400. The configured focus enable point depends on whether the device is used in a
group and on the arrangement of the CLVs relative to the conveyor system. The focus ena
ble point is the point CLV allows a new focus switchover when the tracked object has passed
this point, even if the number of bar codes to be read has not yet been reached.
-
-
-
Parameterizing slave mode in the CLV:
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
1. Forwarding reading results to
the CAN interface
2. Parameterize CAN interface Ö CAN INTERFACE tab
Ö HOST INTERFACE tab
Ö DESTINATION OF RESULT DATA STRINGS section
– CAN interface
Ö CAN INTERFACE FUNCTION section
– OTS Slave
Ö CAN DATA RATE section
– 500 kBit/s
Table 6-15: Guide: Parameterizing slave mode in the CLV for Object Tracking mode with OTC 400
OTC 400 Controller:
Besides other function parameterize the following function in the OTC 400:
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
Choose operation mode in the
OTC 400 (master)
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS button
Ö OPERATION MODE section
– Increment controlled (Tracking)
Table 6-16: Guide: Parameterizing Object Tracking mode in the OTC 400
For functions to be parametrized in the OTC 400: see "OTS 400 Omni Tracking System“
Operatings Instructions (no. 8 008 869, English edition).
6-22 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 93

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
e) Parameterizing the laser timeout (for trigger source "Sensor input"/"Ser. interface")
Action Settings in CLV-Setup
1. Choose laser timeout duration
– or –
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö READING TRIGGER PARAMETERS button
Ö LASER TIMEOUT section
– Duration
2. Deactivate laser timeout
(The laser diode is always active, independent of the pulse duration)
Table 6-17: Guide: Parameterizing the laser timeout
Ö LASER TIMEOUT section
– Click (deactivate) the control box
INTERVAL ACTIVE
f) Parameterizing the evaluation characteristics
• Choose decoder type Ö CODE CONFIGURATION tab Ö DECODER section
• Activate code types for evaluation Ö CODE CONFIGURATION tab Ö SYMBOLOGIES section
and E
DIT button
• Activate code comparison Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab Ö MATCH CODES PARAMETERS
button
• Define output time of reading result Ö CODE CONFIGURATION tab Ö OUTPUT ON GOOD READ
section
Separation of identical bar codes (same code type/identical contents):
Number of bar codes
per object
Number n > 1:
– Same code type
– Contents
different or identical
Stationary conveyor object
Ö CODE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö CODE POSITION section
– Activate "Compare"
– Min. distance between
labels
Ö NUMBER OF CODES section
– Minimum
–Maximum
Moving conveyor object
Ö CODE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö CODE POSITION section
– Activate "Compare"
– Min. distance between
labels
Ö NUMBER OF CODES section
– Minimum
– Maximum
Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab
Ö SCANNER POSITION PARAMETERS
button
Ö ANGLES tab
– Angle alpha
Ö DISTANCE PER ENCODER PULSE
section
– Value
Table 6-18: Guide: Parameterizing the separation of identical bar codes
Note If the number n > 1, minimum clearances must be provided in the following cases:
• The SMART decoder is to read bar codes that originate from the same code type and
have identical or different data contents
• The standard decoder is to read and distinguish bar codes with the same name (iden-
tical code type and data content)
The necessary calculations are provided in Chapter 10.8.3 Calculating the necessary bar
code distance if several bar codes are read on each object, Page 10-44.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-23
Page 94

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
g) Parameterizing the output characteristics
Result status of switching outputs:
• Define function of result status output of "Result 1" to "Result 4" ("Read Result" LED:
Result 2) switching outputs Ö D
EVICE CONFIGURATION tab Ö RESULT OUTPUT PARAMETERS
button
Main Data Interface general:
• Destination of result data strings Ö HOST INTERFACE tab Ö DESTINATION OF RESULT DATA
STRINGS section
• Filter reading result Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab Ö ODETTE FILTER section
• Sort reading result Ö DATA STRINGS tab Ö OUTPUT SEQUENCE SORT section
• Mask reading result Ö DATA STRINGS tab Ö FORMAT MASK section
Host Interface:
• Arrangement in data network Ö DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab Ö SCANNER ARRANGEMENT
section
• Physical interface Ö HOST INTERFACE tab Ö DATA FORMAT section
• Communication parameters Ö HOST INTERFACE tab Ö DATA FORMAT section
• Protocol Ö HOST INTERFACE tab Ö INTERFACE PROTOCOL section
Function of the CAN interface (alternative):
See the Operating Instructions ”Application of the CAN interface” (no. 8 009 180)
Data output string of host interface:
• Choose contents of "Header", "Code Info/Separator", "Splitter" and "Terminator"
blocks Ö D
ATA STRINGS tab Ö OUTPUT FORMAT section
• Position of "Code Info/Separator" blocks in data output string Ö DATA STRINGS tab
Ö POSITION OF CODE INFO/SEPARATOR section
• Set wrong read format Ö DATA S TRINGS tab Ö Wrong read format, number of characters
and Error String
• If necessary, parameterize/activate test string Ö DATA STRINGS tab Ö TEST STRING
section
• Parameterize special functions Ö DATA STRINGS tab Ö SPECIALS button
• Output external data string as reading result Ö DATA STRINGS tab Ö EXTERNAL DATA
S
TRING PARAMETERS button
h) Parameterizing the terminal interface (auxiliary interface)
• AUXILIARY INTERFACE tab
i) Defining the start option for accessing the parameter set
• DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab Ö START WITH ...
6-24 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 95

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
6.5 Operating modes and outputing the reading result
The following CLV operating modes/functions (and more) can be selected in CLV-Setup:
Standard operating mode:
• Reading mode
For setup:
• Percentage evaluation
• Adjusting mode
For adapting the device to the application at hand:
• Configuring (parameterizing ) the CLV.
See Chapter 6.4.1 Configuring the CLV via the user interface of CLV-Setup, Page 6-5
• Show CP-limits
For monitoring purposes/trouble shooting:
• I/O monitor in incremental pulse
• Display and edit operating data
• Reading diagnosis
• Monitor host interface
• Auxiliary input
• Self-test
6.5.1 Reading mode (standard operating mode)
The CLV performs a self-test after it has been switched on. It switches to Reading mode
("Device Ready" LED lights up). In the default setting the "Sensor" switching input is the (ex
ternal) trigger source of the reading pulse. The reading result is output by the CLV at the end
of the reading pulse via the host interface (default setting) and terminal interface.
Depending of the configuration, the "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching outputs become live
for the predefined pulse length when defined events occur during the reading process (e. g.
Good Read).
The reading result of the terminal interface can be displayed in the CLV-Setup Terminal
Emulator. The CLV terminal interface must be set to the R
EADING DIAGNOSIS mode for this pur-
pose. This mode is selected for the default setting. The reading result of the terminal interface has a fixed, invariable format.
The Reading mode can be called up by choosing VIEW in the menu bar or via the Terminal
Emulator.
Line scanner with oscillating mirror:
In the Reading mode the CLV deflects (by default) the scan line about the position CW = 50
at a frequency of 1
deflection of 105
Hz and a maximum angle of ±20°. 50 CW corresponds to an angle of
°.
-
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-25
Page 96

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Note On the host interface the CLV only outputs several bar codes in the reading result if the
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Displaying the reading result in the Terminal Emulator:
1. Click in the toolbar.
The Terminal Emulator window is then displayed.
2. In the DEVICE MODE section, choose READING MODE.
3. Present the bar code pattern from Fig. 6-1, Page 6-3 to the CLV and activate the rea-
ding pulse. The "Sensor" LED lights up and the red scan line appears.
4. Ending the reading pulse.
The CLV displays the reading result in the output window of the Terminal Emulator.
The "Read Result" LED lights up for a duration of 100 ms (default setting).
Fig. 6-5 shows two examples of the output of a reading result: Good Read and No Read.
The reading result comprises the data contents of the bar code(s) and the reading diagnosis
data.
Fig. 6-6 explains the structure and function of the reading diagnosis data for Good
Read, and Fig. 6-7 for No Read.
parameterized minimum and maximum number of bar codes is > 1, and several bar codes
have been presented to it. The number of bar codes to be read/output for each reading in
terval can be selected in the CODE CONFIGURATION tab in the NUMBER OF CODES section.
The reading result of the host interface can also be displayed. Chapter 6.5.8 Monitor Host
Interface, Page 6-37 describes the procedure for this and the structure of the reading result
in the default setting.
-
Fig. 6-5: CLV-Setup: Displaying the reading result in the Terminal Emulator
6-26 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 97

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
Good Read:
TT=_ _380 ms MG=_52 % n=_1 AK=1
LS= _ _ _0 FL= _ _ _0 SB= _ _0 MB= _ 11 RM= _ _ _0
0123412345
C39 100% ST=0 CL=10 CP=_52 CD=_500 CS= 300 CA=300 CK=999 DI=F
PO=+_14 OW=+_ _0 FC=_500 CX=_913 CY=_612 CZ=1408 ON= _ _ _0
MW= _ _40 VL= _ _ _0 CI= _ _0
With:
1st. line: TT = Duration of the reading interval (ms)
MG = Temporal mean value of the identification quality (%)
n = Number of detected bar codes
AK = No. of the used distance configuration
2nd. line: LS = Special parameter for SICK-Service
FL = Special parameter for SICK-Service
SB = Special parameter for SICK-Service
MB = Special parameter for SICK-Service
RM = Special parameter for SICK-Service
3rd. line: 0123412345 = Data contents of the bar code
4th line: C39 = ID: Code type Code 39 along
100% = Identification quality (%)
ST = Read status (ST = 0: Good Read)
CL = Code length (number of characters)
CP = Code position
CD = Code distance (radial measured)(mm)
CS = Code reliability
CA = Scan effort
CK = Code continuity
DI = Decoding direction
(F = in scanning direction, R = against scanning direction)
5th line: PO = Exact code position (3-digit for tracking) (scale factor: 0.1°)
OW = Exact oscillating angle (3-digit for tracking) (scale factor: 0.1°)
FC = Current focus position (4-digit for tracking) (mm)
CX = X-coordinate of bar code (for OTS in transport direction)
CY = Y-coordinate of bar code (for OTS across to transport
direction)
CZ = Z-coordinate of bar code (for OTS from above directly)
6th line: MW = Modul width
VL = Velocity
CI = Special parameter for SICK-Service
Fig. 6-6: Reading result of the terminal interface: structure for Good Read
No Read:
TT=_ _ 360 ms MG=_51 % n=_0 AK=1
LS= _ _ _0 FL= _ _ _0 SB= _ _0 MB= _ _1 RM= _ _ _0
no code!
With:
1st. line : TT = Duration of the reading interval (ms)
MG = Temporal mean value of the identification quality (%)
n = Number of codes detected
AK = No. of the distance configuration used
2nd. line: LS = Special parameter for SICK-Service
FL = Special parameter for SICK-Service
SB = Special parameter for SICK-Service
MB = Special parameter for SICK-Service
RM = Special parameter for SICK-Service
3rd. line: no code! = No. bar codes found!
Fig. 6-7: Reading result of the terminal interface: structure for No Read
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-27
Page 98

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Triggering the reading pulse via the Terminal Emulator:
In the default setting the "Sensor" switching input is the (external) trigger source of the reading pulse. The reading pulse can also be triggered directly via the Terminal Emulator of CLVSetup for test purposes. To do so, a different trigger source must be selected temporarily
in the CLV.
1. Choose DEVICE CONFIGURATION tab.
2. In the READING TRIGGER SOURCE section click the SERIAL INTERFACE option.
3. Perform a download to the CLV.
To do so, click the SERIAL INTERFACE option again with the right mouse button and choose
D
OWNLOAD PARAMETER in the context menu.
CLV-Setup copies the parameter temporary to the CLV.
The serial interface has been activated as the trigger source of the reading pulse and
is ready to receive appropriate commands (until the CLV is switched off).
4. Click in the toolbar.
The Terminal Emulator window is then displayed.
The CLV is in the Reading mode.
5. Click the SW-TRIGGER ON button or press [F7].
CLV-Setup sends a start command to the CLV.
The "Sensor" LED lights up and the red scan line appears.
6. Present the bar code pattern from Fig. 6-1, Page 6-3 to the CLV.
7. Click the SW-TRIGGER OFF button or press [F8].
CLV-Setup sends a stop command to the CLV. The "Sensor" LED is extinguished. The
CLV switches off the laser diode. The CLV displays the reading result in the output win
dow of the Terminal Emulator. The "Read Result" LED lights up for a duration of 100 ms
(default setting).
-
6.5.2 Percentage evaluation
In the Percentage evaluation mode, the quality of the reading function is assessed (no conveyor movement).
The CLV performs 100 scans in the free running mode and evaluates the reading quality. It
outputs the reading result continuously every 2 s via the terminal interface. The reading
results can be displayed in the Terminal Emulator of CLV-Setup. The standard decoder has
to be set temporarily for the percentage evaluation.
The "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching
outputs do not become live in the Percentage evaluation mode.
The Percentage evaluation mode can be called up by choosing VIEW in the menu bar, as a
device function via CLV
Line scanner with oscillating mirror:
480 (interactively), or via the Terminal Emulator.
In the Percent Evaluation mode, the CLV behaves in the following manner:
– in "Oscillating" mode (basic setting: oscillating with a fixed amplitude), the CLV shuts off
oscillation and positions the scan line under the angle CW
deflection angle below 105
°). This position cannot be altered.
= 50 (corresponds to a
– in "One-Shot" mode, the CLV positions the scan line under the angle CW = 50 as well.
– in ”Fixed position” mode, however the scan line’s selected position remains unchanged.
1. Choose the CODE CONFIGURATION tab.
2. In the DECODER section, choose STANDARD.
3. Perform a download to the CLV.
6-28 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
Page 99

Operating Instructions Chapter 6
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
Operation
To do so, click the STANDARD option again with the right mouse button and choose
D
OWNLOAD PARAMETER in the context menu.
CLV-Setup copies the parameter temporary to the CLV.
The CLV then uses the standard decoder (until the CLV is switched off).
4. Click in the toolbar.
The Terminal Emulator window is displayed. The CLV is in the Reading mode.
5. In the DEVICE MODE section, choose PERCENTAGE EVALUATION
The dialog box for choosing the distance configuration is then displayed.
6. Choose the appropriate distance configuration that corresponds to the reading
distance of the object (default setting: no. 1, focus position F1 = 1,200 mm (47.3 in)).
7. Confirm the dialog box with OK.
The ”Device Ready” LED is extinguished. The CLV initiates the percentage evaluation
and outputs the reading results continuously.
8. Present the bar code pattern from Fig. 6-1, Page 6-3 and monitor the reading results
in the Terminal Emulator window. An example of this can be seen in Fig. 6-8.
The ”Read Result” LED also provides information on the reading quality:
– The LED is extinguished if reading quality is < 30 %
– The LED blinks twice per second if the reading quality is 30 % to 70 %
– The LED blinks five times per second if the reading quality is 70 % to 90 %
– The LED is lit continuously if the reading quality is > 90 %
Fig. 6-8: CLV-Setup: Displaying the percentage evaluation in the Terminal Emulator
The output format of the reading result is the same as that of the Reading mode. Fig. 6-6,
Page 6-27 explains the structure and function of the reading diagnosis data.
8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 6-29
Page 100

Chapter 6 Operating Instructions
Operation
CLV 480 Bar Code Scanner
6.5.3 Adjusting mode
The Adjusting mode enables the center of the scan line to be optimally positioned on the
bar code.
Chapter 4.3.3 Help functions for adjusting the CLV, Page 4-9 describes the pro-
cedure for going about this after the Adjusting mode has been called up. The CLV does not
output a reading result in this mode.
The "Result 1" to "Result 4" switching outputs do not
become live.
The Adjusting mode can be called up by choosing VIEW in the menu bar, as a device
function via CLV 480 (interactively), or via the Terminal Emulator.
Line scanner with oscillating mirror:
In the "Adjusting" mode, the CLV behaves in the following manner:
– In "Oscillating" mode (default setting: oscillating with a fixed amplitude), the CLV shuts
of oscillation and positions the scan line under the angle CW
angle of deflection below 105
°). This position cannot be altered.
= 50 (corresponds to an
– In "One-Shot" mode, the CLV positions the scan line under the angle CW = 50
– In "Fixed Position" mode, the scan line’s selected position remains unchanged.
1. Click in the toolbar.
The Terminal Emulator window is then displayed. The CLV is in the Reading mode.
2. In the DEVICE MODE section, choose ADJUSTING MODE.
The "Device Ready" LED is extinguished. The CLV cancels the Reading mode and
blanks the red scan line as of position CP
= 50 to position CP = 100.
3. Choose READING MODE to exit the Adjusting mode.
The CLV returns to the Reading mode and the "Device Ready" LED lights up.
6.5.4 Show CP-limits
In this mode, the CLV blanks certain parts of the red scan line so that any limit values defined
for the active evaluation range of the scan line can be checked directly during parameteri
zation. The restricted active evaluation range shortens the evaluation time for fast applications, for example, because the evaluation routine only has to take account of unblanked
parts of the scan line. The range is restricted by entering appropriate values for M
C
ODE POSITION and MAXIMUM CODE POSITION in the DISTANCE CONFIGURATIONS tab of the READING
C
ONFIGURATION tab. The CLV does not output a reading result in this mode.
INIMUM
Show CP-limits enables you to check whether the restriction has been adapted for each active distance configuration ("Christmas tree" effect)
Show CP-limits can be called up via VIEW in the menu bar, as a device function via CLV 480
(interactively), or via the Terminal Emulator.
Line scanner with oscillating mirror:
In "Show CP-limits" mode, the CLV behaves in the following manner:
– in "Oscillating" mode (default setting: oscillating with a fixed amplitude), the CLV shuts
off oscillation and positions the scan line under the angle CW
angle of deflection below 105
°). This position cannot be altered.
= 50 (corresponds to an
– in "One-Shot" mode, the CLV positions the scan line under the angle CW = 50.
– in "Fixed Position" mode, the scan line’s selected position remains unchanged.
The CLV blanks the scan line alternately as of the set value for CP
for CP
. Fig. 6-9 shows an example of this. The switchover is made continuously at inter-
max
and as of the set value
min
vals of 1 second. The part of the scan line that remains active for the reading procedure is
the section between CP
and CP
min
max
.
-
6-30 © SICK AG · Division Auto Ident · Germany · All rights reserved 8 010 080/O824/10-02-2005
 Loading...
Loading...