Shenzhen Mindray Bio-medical Electronics Co BC-6800 Service Manual

BC-6800
Auto Hematology Analyzer
Service Manual

II

Copyright
© 2011-2012 Shenzhen Mindray Bio-medical Electronics Co., Ltd. All rights Reserved.
For this Service Manual, the issued Date is 2012-03 (Version: 2.0).
Intellectual Property Statement
SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO-MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO., LTD. (hereinafter called Mindray)
owns the intellectual property rights to this Mindray product and this manual. This manual may
refer to information protected by copyright or patents and does not convey any license under
the patent rights or copyright of Mindray, or of others.
Mindray intends to maintain the contents of this manual as confidential information. Disclosure
of the information in this manual in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of
Mindray is strictly forbidden.
Release, amendment, reproduction, distribution, rental, adaptation, translation or any other
derivative work of this manual in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of
Mindray is strictly forbidden.
. , are the trademarks, registered or otherwise, of Mindray in
China and other countries. All other trademarks that appear in this manual are used only for
informational or editorial purposes. They are the property of their respective owners.
Responsibility on the Manufacturer Party
Contents of this manual are subject to changes without prior notice.
All information contained in this manual is believed to be correct. Mindray shall not be liable for
errors contained herein nor for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the
furnishing, performance, or use of this manual.
Mindray is responsible for safety, reliability and performance of this product only in the
condition that:
I

all installation operations, expansions, changes, modifications and repairs of this
product are conducted by Mindray authorized personnel;
the electrical installation of the relevant room complies with the applicable national
and local requirements;
the product is used in accordance with the instructions for use.
zThis equipment must be operated by skilled/trained medical professionals.
zIt is important for the hospital or organization that employs this equipment to
carry out a reasonable service/maintenance plan. Neglect of this may result
in machine breakdown or injury of human health.
zBe sure to operate the analyzer under the situation specified in this manual;
otherwise, the analyzer will not work normally and the analysis results will
be unreliable, which would damage the analyzer components and cause
personal injury.
II

Warranty
THIS WARRANTY IS EXCLUSIVE AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES,
EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Exemptions
Mindray's obligation or liability under this warranty does not include any transportation or other
charges or liability for direct, indirect or consequential damages or delay resulting from the
improper use or application of the product or the use of parts or accessories not approved by
Mindray or repairs by people other than Mindray authorized personnel.
This warranty shall not extend to:
¾Malfunction or damage caused by improper use or man-made failure.
¾Malfunction or damage caused by unstable or out-of-range power input.
¾Malfunction or damage caused by force majeure such as fire and earthquake.
¾Malfunction or damage caused by improper operation or repair by unqualified or
unauthorized service people.
¾Malfunction of the instrument or part whose serial number is not legible enough.
¾Others not caused by instrument or part itself.
III
Customer Service Department
Manufacturer:
Address:
Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd.
Mindray Building,Keji 12th Road South,High-tech industrial
park,Nanshan,Shenzhen 518057,P.R.China
Website:
E-mail Address:
Tel:
Fax:
www.mindray.com
service@mindray.com
+86 755 81888998
+86 755 26582680
EC-Representative: Shanghai International Holding Corp. GmbH(Europe)
Address:
Fax:
Eiffestraβe 80, 20537 Hamburg, Germany
0049-40-2513175
Tel:
0049-40-255726
IV
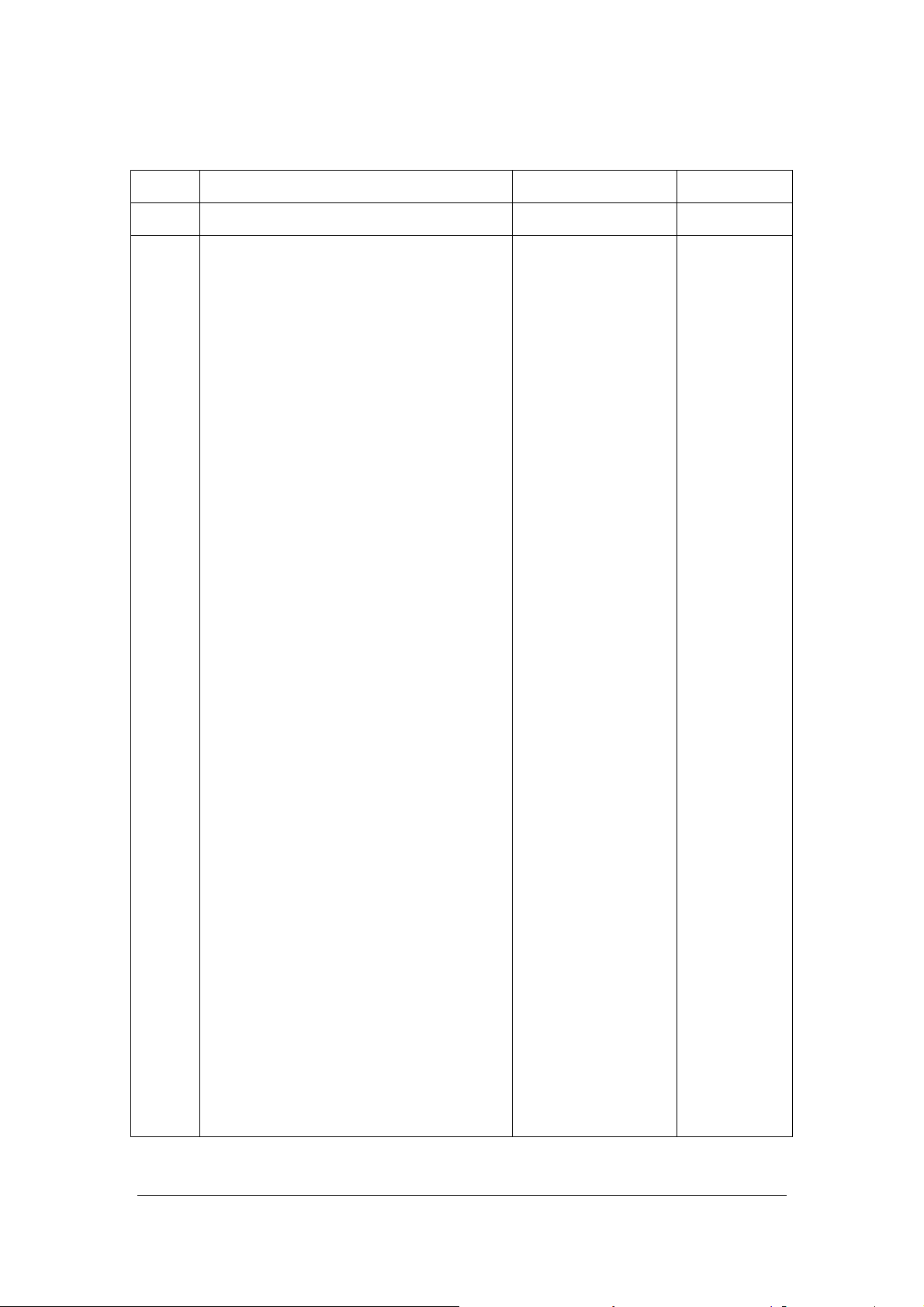
Version Record
Version Updated Contents Related T/N & S/N Updated Date
1.0 First version Released N/A
2.0
1:Update Error Code;
2:Added Preventive Maintenance
Chapter;
3:Updated FRU List;
4:Updated PC software name to DMU;
5:DMU IP connection screen changed
6:RUO parameters updated from12 items
to 14 items;
7 : Add ASTM protocol option in DMU
setup;
8:Correct some unclear pictures in
hardware;
9:Update partly materials name and part
number(like WC2 Waste Bath),Deleted
some wrong items;
10:Add part numbers of some cables in
FRU List;
TXQ-12009-BC-6800
TXQ-12013-BC-6800
TXQ-12022-BC-6800
SXQ-12001-BC-6800
TXQ-12027-BC-6800
2012.9
11:Vacuum Relieve Valve(Regulator)
updated the life time from 3-years to
4-years;
12:Add’801-3100-00208-00/Pneumatic
connecter kit into FRU List’;
130:Add‘801-3110-00114-00/reagents
connecter kit (6 colors) (FRU)’;
14:Correct DMU light status;
15: Add Scanner Rotation Function in
auxiliary Setup and update Rotation
scanner Debug screen in SPU;
16:Add floater setup option;
17:Add USB protection Open/close
function;
V

Table of Contents
Copyright................................................................................................................................... I
Version Record ........................................................................................................................ V
Table of Contents..................................................................................................................... 1
1 Using This Manual.............................................................................................................1-1
1.1 Scope ....................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.2 Introduction............................................................................................................... 1-1
1.3 General Operations.................................................................................................. 1-1
1.4 Symbol ..................................................................................................................... 1-2
2 Product Specification........................................................................................................ 2-1
2.1 Equipment Name ..................................................................................................... 2-1
2.2 Power Supply Requirement ..................................................................................... 2-1
2.3 Dimension and Weight ............................................................................................. 2-1
2.4 Measurement Mode ................................................................................................. 2-1
2.5 Sample Types........................................................................................................... 2-1
2.6 Minimum Sample Volume ........................................................................................ 2-2
2.7 Throughput............................................................................................................... 2-2
2.8 Capacity of the Autoloader....................................................................................... 2-2
2.9 Performance Specifications...................................................................................... 2-3
2.10 Conditions of Use ................................................................................................... 2-13
2.11 Sound ..................................................................................................................... 2-14
2.12 Functions of the Analyzer....................................................................................... 2-14
3 Software System................................................................................................................ 3-1
3.1 Overview .................................................................................................................. 3-1
3.2 Introduction of Startup and Shutdown...................................................................... 3-1
3.3 Menu Structure......................................................................................................... 3-1
3.4 Password.................................................................................................................. 3-6
3.5 Analyzer Software Update ..................................................................................... 3-20
3.6 DMU Software Installation...................................................................................... 3-26
3.7 DMU Software Update ........................................................................................... 3-33
1

Table of Contents
3.8 Backup and Restoration......................................................................................... 3-37
3.9 Connection device between the DMU and analyzer.............................................. 3-40
3.10 LIS Communication Setup ..................................................................................... 3-45
3.11 Uni-directional LIS Communication........................................................................ 3-48
3.12 Bi-Directional LIS Communication ......................................................................... 3-54
4 Operation Principles ......................................................................................................... 4-1
4.1 Measurement of the Optical Channel ...................................................................... 4-1
4.2 HGB Measurement .................................................................................................. 4-4
4.3 RBC/PLT Measurement ........................................................................................... 4-4
5 Fluidics ............................................................................................................................... 5-1
5.1 Parameter Measurement ......................................................................................... 5-2
5.2 Reagent System....................................................................................................... 5-3
5.3 Measurement Flow................................................................................................... 5-5
5.4 Sample Volume........................................................................................................ 5-6
5.5 Time of Preparation and Measurement.................................................................... 5-6
5.6 Temperature of Fluidics ............................................................................................ 5-6
5.7 Reagent Consumption Volume ................................................................................ 5-7
5.8 Sample Dilution Flow ............................................................................................... 5-8
5.9 Introduction to Fluidic Parts...................................................................................... 5-9
5.10 Pneumatic System ................................................................................................. 5-20
5.11 Detailed Introduction to Fluidic Channels .............................................................. 5-26
5.12 Introduction to Sequences ..................................................................................... 5-34
6 Optical System................................................................................................................... 6-1
6.1 Introduction of Optical Theories ............................................................................... 6-1
6.2 Optical System Structure.......................................................................................... 6-3
6.3 Troubleshooting of the Optical System .................................................................... 6-4
7 Hardware System...............................................................................................................7-1
7.1 Overview .................................................................................................................. 7-1
7.2 Data and COME Carrier Board ................................................................................ 7-1
7.3 Drive Control Board................................................................................................ 7-16
7.4 Motherboard........................................................................................................... 7-26
7.5 Network Board ....................................................................................................... 7-30
7.6 Power Board........................................................................................................... 7-32
2

Table of Contents
7.7 Power Patching Board ........................................................................................... 7-36
7.8 Laser Drive Board .................................................................................................. 7-38
7.9 Scatter Pre-amplification Boards ........................................................................... 7-43
7.10 Fluorescence Pre-amplification Board ................................................................... 7-49
7.11 Pneumatic Pressure Detection Board.................................................................... 7-54
7.12 Heating Control Board............................................................................................ 7-56
7.13 Diluent Heating Board ............................................................................................ 7-60
7.14 Valve Drive Board................................................................................................... 7-64
7.15 Indicator Board ....................................................................................................... 7-74
7.16 Touchscreen Control Board.................................................................................... 7-75
7.17 Prefix List of Board Interfaces ................................................................................ 7-76
7.18 Motors, Photocouplers and Micro-switches ........................................................... 7-77
8 Mechanical System ........................................................................................................... 8-1
8.1 Analyzer Structure.................................................................................................... 8-1
8.2 Appearance.............................................................................................................. 8-1
8.3 Layout Introduction................................................................................................... 8-3
9 Replacing the FRU.............................................................................................................9-1
9.1 Overview .................................................................................................................. 9-1
9.2 Removal and Installation of the Board ..................................................................... 9-1
9.3 Sheath Fluid Impedance Bath................................................................................ 9-11
9.4 Aperture.................................................................................................................. 9-12
9.5 HGB Bath Assembly............................................................................................... 9-16
9.6 RBC Bath Assembly............................................................................................... 9-17
9.7 SRV Assembly........................................................................................................ 9-17
9.8 Sample Probe ........................................................................................................ 9-23
9.9 Pneumatic Unit....................................................................................................... 9-24
9.10 Barcode Scanner Assembly................................................................................... 9-26
9.11 Radiator Fan........................................................................................................... 9-27
9.12 Power Supply Assembly......................................................................................... 9-28
9.13 Diaphragm pump.................................................................................................... 9-30
9.14 WBC Mixing Assembly........................................................................................... 9-33
9.15 WBC Bath Assembly .............................................................................................. 9-35
9.16 Reagent Pre-Heating Bath Assembly .................................................................... 9-36
9.17 Sheath Fluid Pre-heating Bath Assembly .............................................................. 9-38
3

Table of Contents
9.18 Diluent Heating Bath Assembly.............................................................................. 9-39
9.19 Sheath Fluid Filter .................................................................................................. 9-40
9.20 Waste Filter ............................................................................................................ 9-40
9.21 START Switch Assembly........................................................................................ 9-41
9.22 Pressure Regulator ................................................................................................ 9-42
9.23 Vacuum Overflow Valve ......................................................................................... 9-43
9.24 Screen Assembly ................................................................................................... 9-45
9.25 Tube Clamp for Mixing ........................................................................................... 9-46
9.26 Autoloading Assembly............................................................................................ 9-47
9.27 Piercing Unit ........................................................................................................... 9-48
9.28 Autoloader .............................................................................................................. 9-50
9.29 Tube Sensor Assembly .......................................................................................... 9-52
9.30 Cistern and Waste Bath ......................................................................................... 9-53
9.31 Syringe Assembly................................................................................................... 9-56
9.32 Filter and Drying Assembly .................................................................................... 9-60
9.33 Replacing the Backwater Bath Assembly .............................................................. 9-61
9.34 USB Assembly ....................................................................................................... 9-62
9.35 Mindray Valve......................................................................................................... 9-63
9.36 Burkert Valve.......................................................................................................... 9-66
9.37 Waste Valve............................................................................................................ 9-67
9.38 Gas Valve............................................................................................................... 9-68
9.39 SMC 2-way Fluidic Valves...................................................................................... 9-69
9.40 Probe Wipe of the Open-Vial Module .................................................................... 9-70
9.41 Optical System ....................................................................................................... 9-71
9.42 Units in the Autoloader........................................................................................... 9-79
9.43 Power Board and Power Conversion Board .......................................................... 9-85
9.44 Pressure Detection Board ...................................................................................... 9-87
9.45 Indicator Board ....................................................................................................... 9-88
9.46 Valve Control Board ............................................................................................... 9-89
9.47 Heating Control Board............................................................................................ 9-91
9.48 Data Board and Power Drive Board....................................................................... 9-92
9.49 Mother Board ......................................................................................................... 9-93
9.50 Liquid Level Detection Board ................................................................................. 9-95
9.51 Network Port Patching Board................................................................................. 9-96
4

Table of Contents
9.52 Diluent Heating Control Board ............................................................................... 9-97
9.53 Touchscreen Control Board.................................................................................... 9-98
9.54 Pneumatic Unit Control Board................................................................................ 9-99
9.55 Boards inside the Optical System ........................................................................ 9-100
9.56 Cap Assembly ...................................................................................................... 9-101
9.57 Transformer.......................................................................................................... 9-102
9.58 Replacing the Wires ............................................................................................. 9-103
9.59 Replacing the Connectors.................................................................................... 9-104
9.60 Components inside the Assemblies ..................................................................... 9-106
9.61 Replacing the Photocoupler (PHC/Sensor) ..........................................................9-111
10 Error Code ...................................................................................................................... 10-1
10.1 Overview ................................................................................................................ 10-1
10.2 Message Area Error ............................................................................................... 10-3
10.3 Error Area Error ...................................................................................................... 10-6
11 Preventive Maintenance................................................................................................ 11-1
11.1 Tools and Consumables......................................................................................... 11-1
11.2 Service Plan ........................................................................................................... 11-2
11.3 Status Check ........................................................................................................ 11-23
11.4 Regular Replacement .......................................................................................... 11-26
12 FRU LIST......................................................................................................................... 12-1
12.1 Board list ................................................................................................................ 12-1
12.2 Valve list ................................................................................................................. 12-2
12.3 Tube and Connector list ......................................................................................... 12-2
12.4 Part list ................................................................................................................... 12-4
12.5 Cable list................................................................................................................. 12-9
12.6 Wearing parts list.................................................................................................. 12-10
A.1 Rubber Tubing Information ................................................................................... 12-13
A2. Connector Information .......................................................................................... 12-14
A3. Connecting Tubing Information ............................................................................. 12-16
A4. Other Material Information .................................................................................... 12-16
A5. Valve Information .................................................................................................. 12-17
A6. Table of All Tubes.................................................................................................. 12-21
5

Table of Contents
6
1 Using This Manual
zBe sure to operate and service the analyzer strictly as instructed in this manual
and the operator's manuals.
1.1 Scope
To use this manual effectively, you need the following capabilities:
Comprehensive knowledge of circuit and fluidics;
Comprehensive knowledge of reagents;
Comprehensive knowledge of controls;
Comprehensive knowledge of troubleshooting;
Mastering the way to operate this analyzer;
Using basic mechanical tools and understand related terminology;
Using a digital voltmeter (DVM) and an oscilloscope;
Reading pneumatic/hydraulic schematics and understand related terminology.
1.2 Introduction
This manual comprises 13 chapters and the fluidic diagrams in appendices.
1.3 General Operations
Name Operation
Click
Enter
press the desired item lightly with your finger; or to left-CLICK it
with the mouse.
to CLICK the desired edit box and use the external keyboard or
the pop-up keyboard to enter the desired characters or digits; or
to scan the number by using the bar-code scanner.
Delete
to move the cursor to the character or digit that you want to
delete by clicking the left button of the mouse or using
[←][→][Home][End], and then delete the character after the
cursor by pressing [Del], or delete the character before the cursor
by pressing [BackSpace] ([←] on the upper right part of the soft
keyboard).
1-1
Click the arrow buttons by the ends of the scroll bar, or move the
Drag Scroll Bar
SELECT from ××
pull-down list
(for pull-down list)
cursor to the slide bar and press the left key of the mouse; or
press the slide bar with your finger.
to CLICK the down arrow button of the desired box to display the
pull-down list, (and DRAG SCROLL BAR) to browse and then
CLICK the desired item; or to press the keys
([↑][↓][PageUp][PageDown]) to browse the current list and press
[ENTER] to select the desired item.
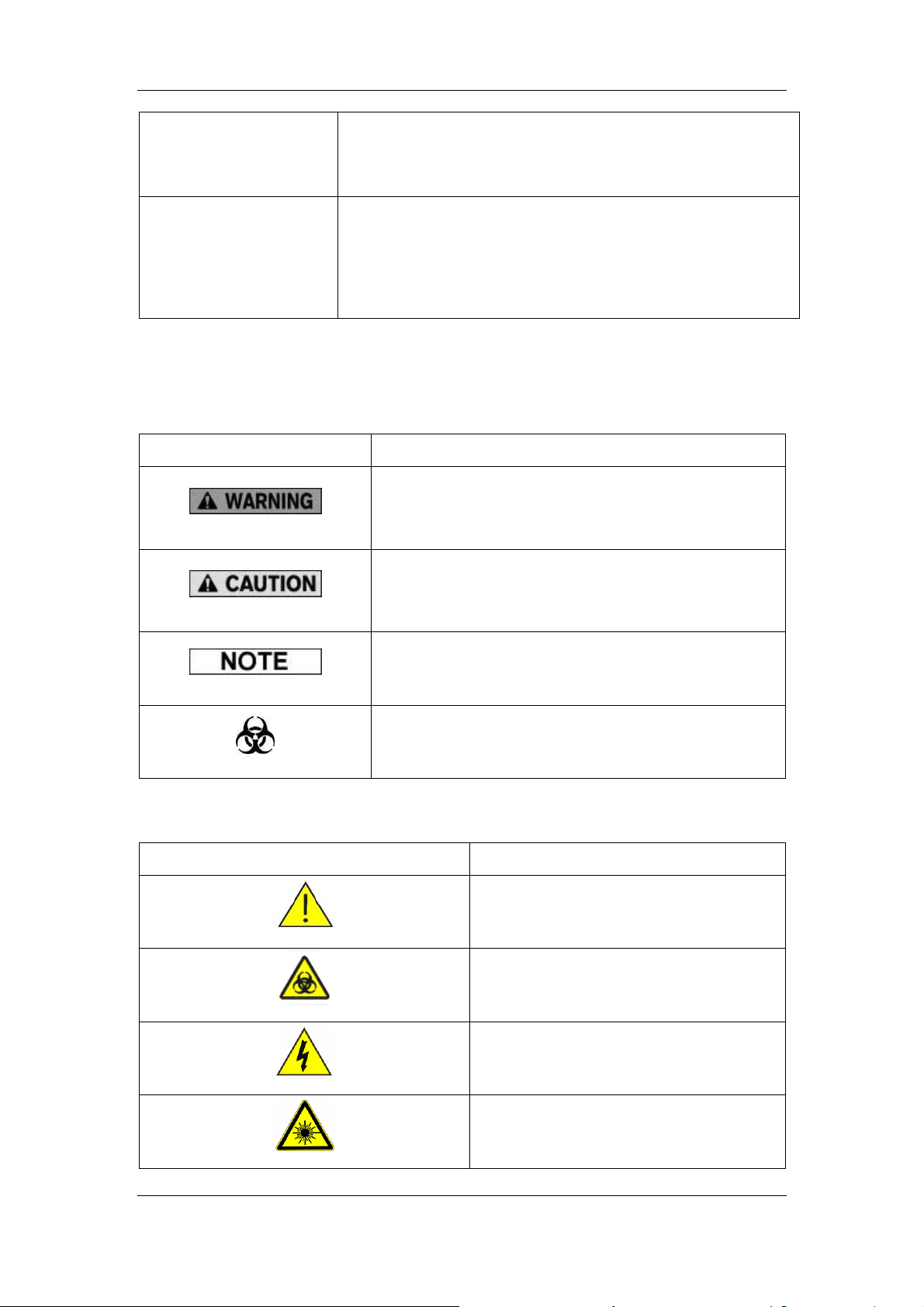
1.4 Symbol
You will find the following symbols in this manual.
Symbol It means...
read the statement below the symbol. The statement is
alerting you to an operating hazard that can cause
personnel injury.
read the statement below the symbol. The statement is
You may find the following symbols on the analyzer, reagents, controls or calibrators.
Symbol It means...
alerting you to a possibility of analyzer damage or
unreliable analysis results.
read the statement below the symbol. The statement is
alerting you to information that requires your attention.
read the statement below the symbol . The statement is
alerting you to a potentially biohazardous condition.
CAUTION, CONSULT ACCOMPANYING
DOCUMENTS.
BIOLOGICAL RISK
HIGH VOLTAGE
WARNING, LASER BEAM
1-2
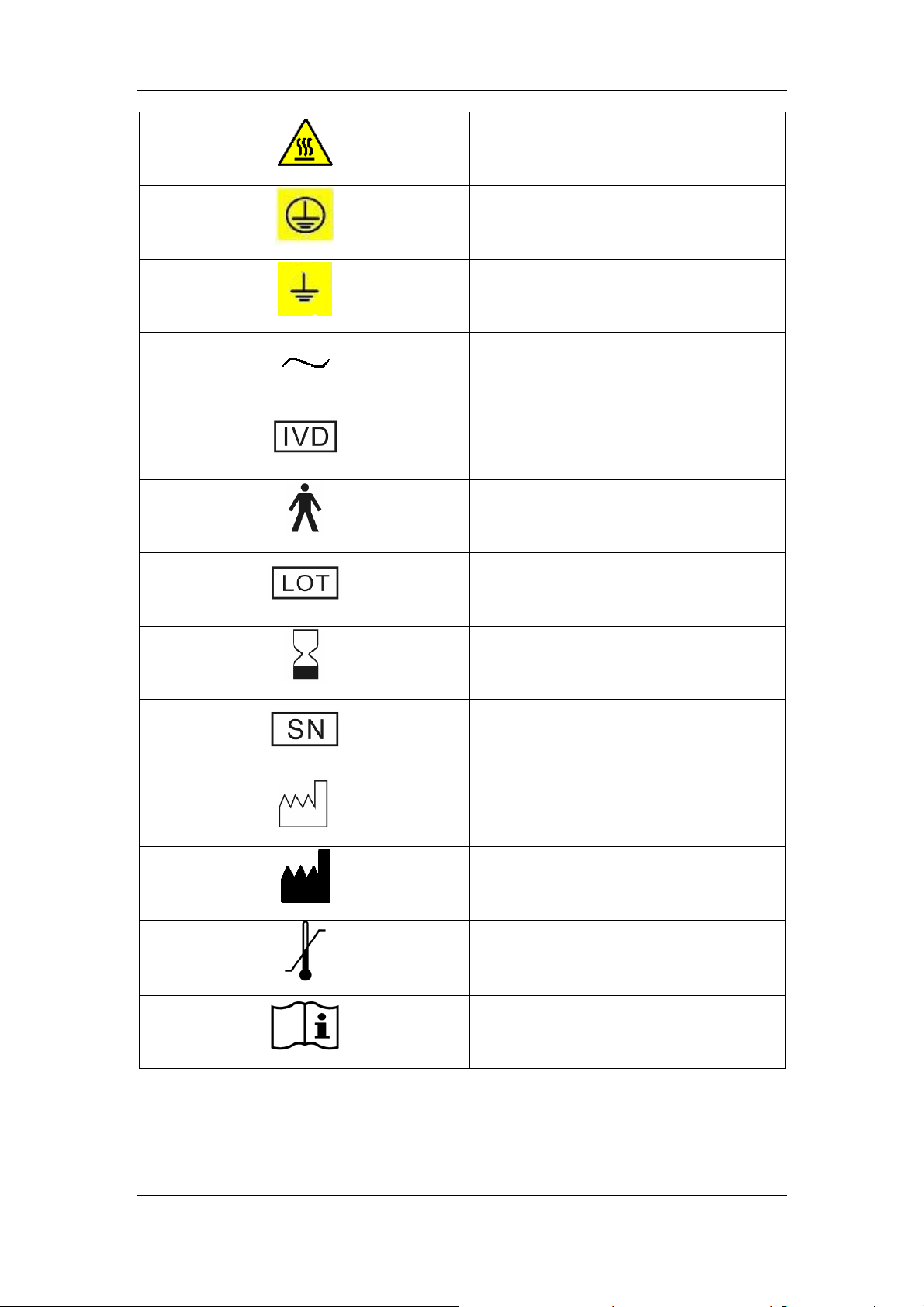
WARNING, HOT SURFACE
PROTECTIVE EARTH (GROUND)
EARTH (GROUND)
ALTERNATING CURRENT
FOR IN VITRO DIAGNOSTIC USE
TYPE B DEVICE
BATCH CODE
USE BY
SERIAL NUMBER
DATE OF MANUFACTURE
Manufacturer
TEMPERATURE LIMITATION
CONSULT INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Be sure to observe the following precautions when you are servicing the analyzer for the safety
of patients and operators.
1-3
zIt is important for the hospital or organization that employs this equipment to
carry out a reasonable installation plan. Neglect of this may result in
machine breakdown or injury of human health.
zNever use combustible gas (e.g. anesthetic) or combustible liquid (e.g. ethanol)
around the analyzer. Otherwise, the risk of explosion may exist.
zContacting exposed electronic components while the equipment is attached to
power can cause personal injury from electric shock or damage to electronic
components. Power down before removing covers to access electronic
components.
zConnect the analyzer to a socket having sole fuse and protective switch. Do
not use the same fuse and protective switch with other equipment (e.g. life
supporting equipment). Otherwise, the equipment failure, over current or
impulse current that occurs at the startup moment may lead to tripping.
zTo prevent personal injury during the maintenance, keep your clothes, hairs
and hands from the moving parts, such as sample probe, pincher and
piercer.
zPossible mechanical movement of the warned position may lead to personal
injury during normal operation, removal and maintenance.
zBe sure to dispose of reagents, waste, samples, consumables, etc. according
to government regulations.
zThe reagents are irritating to eyes, skin and diaphragm. Wear proper personal
protective equipment (e.g. gloves, lab coat, etc.) and follow safe laboratory
procedures when handling them in the laboratory.
zIf the reagents accidentally spill on your skin, wash them off with plenty of
water and if necessary, go see a doctor; if the reagents accidentally spill into
your eyes, wash them off with plenty of water and immediately go see a
doctor.
zImproper servicing may damage the analyzer. Improper maintenance may
damage the analyzer. Maintain the analyzer strictly as instructed by the
service manual and inspect the analyzer carefully after the maintenance.
zFor problems not mentioned in the service manual, contact Mindray customer
service department for maintenance advice.
zTo prevent personal injury or damage to equipment components, remove metal
1-4
jewelry before maintaining or servicing electronic components of the
equipment.
zElectrostatic discharge may damage electronic components. Electrostatic
discharge may damage electronic components. If there is a possibility of
ESD damage with a procedure, then do that procedure at an ESD
workstation, or wear an antistatic wrist strap.
zThis equipment must be operated by skilled/trained medical professionals.
zSamples, controls, calibrators and waste are potentially infectious. Wear
proper personal protective equipment (e.g. gloves, lab coat, etc.) and follow
safe laboratory procedures when handling them in the laboratory.
zAll the analyzer components and surfaces are potentially infectious, so take
proper protective measures for operation and maintenance.
zThe sample probe tip is sharp and may contain biohazardous materials.
Exercise caution to avoid contact with the probe when working around it.
1-5
2 Product Specification
2.1 Equipment Name
Auto Hematology Analyzer
Model: BC-6800/BC-6600
2.2 Power Supply Requirement
Table 2-1 Power Supply Requirement
Analyzer (outside China)
Analyzer (China)
Pneumatic unit (outside China)
Pneumatic unit (China)
Voltage Frequency Power
a.c. 110V/115V ±10% 50/60Hz ±2Hz 500VA
a.c. 220V/230V±10% 50/60Hz ±2Hz 500VA
(220V/230V)±10%~
a.c. 110V/115V±10% 60Hz ±2Hz 600VA
a.c. 220V/230V±10%
(220V)±10%~
2.3 Dimension and Weight
Table2-2 Analyzer Dimension and Weight
Analyzer
Pneumatic unit
Dimension (width x depth x height mm) Weight(Kg)
680×850×700 ≤125
310×480×430 ≤20
50Hz/60Hz±2Hz 500VA
50Hz ±2Hz 450VA
60Hz ±2Hz 300 VA
50Hz ±1Hz 400VA
2.4 Measurement Mode
There are 8 measurement modes altogether:
CBC, CBC+DIFF, CBC+DIFF+RET, CBC+RET, RET, CBC+DIFF+NRBC,
CBC+DIFF+RET+NRBC and CBC+NRBC.
2.5 Sample Types
The supported sample types are:
1) anticoagulated venous blood (use EDTAK2 or EDTAK3 as the anticoagulant, for whole
blood analysis)
2) capillary blood (for predilute analysis)
2-1
2.6 Minimum Sample Volume
To ensure the effective analysis of samples, the minimum sample volumes are specified as
follows:
1) Autoloading mode: ≥1ml
2) Open vial mode: ≥0.5ml (excluding predilute mode)
2.7 Throughput
1) Autoloading mode
Table 2-3 Throughput of auto-loading mode
Measurement
Mode
Throughput
(analyses/hour)
2) Open-vial mode
CBC CBC+
Whole blood mode
(continuous
analyses)
(analyses/hour)
Whole blood mode
(single analysis)
CBC CBC+
DIFF
125 125 90 90 125 125 90 90
DIFF
125 125 90 90 125 125 90 90
75 75 60 60 75 75 60 60
CBC+DIFF
+RET
Table 2-4 Throughput of open-vial mode
CBC+DIFF
+RET
CBC+
RET
CBC+
RET
CBC+
NRBC
CBC+
NRBC
CBC+DIFF+
NRBC
CBC+DIFF
+NRBC
CBC+DIFF+
RET+NRBC
CBC+DIFF+
RET+NRBC
RET
RET
(analyses/hour)
Predilute mode
(single analysis)
(analyses/hour)
2.8 Capacity of the Autoloader
Each tube rack can be loaded with 10 tubes.
The autoloader can be loaded with 10 tube racks at the most.
The maximum capacity of a single loading is 100 tubes.
36 36 30 30 36 36 30 30
2-2
2.9 Performance Specifications
2.9.1 Sample Aspiration Volumes
OV-WB mode: 150ul
AL-WB mode: 200ul
OV-PD mode: 40 ul
2.9.2 General Performance Requirements
Table 2-5 General performance requirements
Items Temperature Design Requirement
Requirement of startup time
(the time taken from power-on
to ready-for-analysis)
Requirement of shutdown time
15℃~32℃
15℃~22℃
23℃~40℃
15℃~32℃
No more than 30 minutes
(normal and abnormal startup)
No more than 15 minutes
No more than 10 minutes
No more than 15 minutes
(normal shutdown)
2.9.3 Analysis Parameters
1) 33 reporting parameters
Table 2-6 Reporting parameters
Clone Name Abbreviation
White Blood Cell count WBC
Basophils number Bas#
Basophils percentage Bas%
Leukon (11 parameters)
Neutrophils number Neu#
Neutrophils percentage Neu%
Eosinophils number Eos#
Eosinophils percentage Eos%
Lymphocytes number Lym#
Lymphocytes percentage Lym%
meters)
(6para
clone
Monocytes number Mon#
Monocytes percentage Mon%
RET
Reticulocyte percentage RET%
Reticulocyte number RET#
2-3

Immature reticulocyte fraction IRF
Low fluorescent ratio LFR
Middle fluorescent ratio MFR
High fluorescent ratio HFR
Red Blood Cell count RBC
Hemoglobin Concentration HGB
(6 parameters)
RBC clone (10 parameters)
PLT clone
Mean Corpuscular Volume MCV
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin MCH
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
Concentration
Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Coefficient
of Variation
Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Standard
Deviation
Hematocrit HCT
Nucleated red blood cell number NRBC#
Nucleated red blood cell percentage NRBC%
Platelet count PLT
Mean Platelet Volume MPV
Platelet Distribution Width PDW
Plateletcrit PCT
Platelet-large cell ratio P-LCR
MCHC
RDW-CV
RDW-SD
Platelet-large cell count P-LCC
2) 14 RUO parameters
High fluorescent Cell number
High fluorescent Cell percentage
Immature Granulocyte
Immature Granulocyte percentage
Optical Red Blood Cell count
Optical Platelet count
Platelet count- Impedance
Optical white blood cell count
Table 2-7 RUO parameters
Name
Abbreviation
HFC#
HFC%
IMG#
IMG%
RBC-O
PLT-O
PLT-I
WBC-O
2-4
3) Graphs
Type Channel Name Three-dimensional
White blood cell count -DIFF
White blood cell count –BASO
White blood cell count-NRBC
Platelet Distribution Width Standard Deviation
Infected RBC number
Infected RBC ratio
Table 2-8 Graphs
DIFF optical
channel
BASO optical
channel
DIFF Scattergram
BASO
Scattergram
RET Scattergram
WBC-D
WBC-B
WBC-N
PDW-SD
INR#
INR‰
Scattergram
Yes
No
Yes
Scattergram
Histogram
RET optical
channel
NRBC optical
channel
RBC sheath fluid
impedance channel
2.9.4 Flag Messages
Clone Name
PLT-O
Scattergram
RET-EXT
Scattergram
NRBC
Scattergram
RBC Histogram
PLT Histogram
Table 2-9 Flag messages
No
No
Yes
/
/
WBC WBC Abn Scattergram
2-5
NRBC Abn Scattergram
Neutropenia
Neutrophilia
Lymphopenia
Lymphocytosis
Monocytosis
Eosinophilia
Basophilia
Leukocytopenia
Leukocytosis
NRBC present
Blasts?
Abn Lympho/ Blasts?
Immature Gran?
Left Shift?
Atypical Lympho?
NRBC?
RBC Lyse resistance?
RBC Abn Distribution
RET Abn Scattergram
Dimorphic Population
Reticulocytosis
Anisocytosis
Microcytosis
RBC
Macrocytosis
Hypochromia
Anemia
Erythrocytosis
RBC Aggulutination?
Turbudity/HGB Interference?
Iron Deficiency?
Fragments?
PLT Abn Scattergram
PLT Abn Distribution
PLT
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytosis
PLT Clumps?
Overall judgment Pancytopenia
2-6
2.9.5 Measurement and Display Range
1) Condition
WBC 0~500×109/L
RBC 0~8.00×1012/L
HGB 0~250g/L
PLT 0~5000×109/L
HCT
RET%
RET#
0~75%
0~30%
0~0.8×10
12
/L
2) Display range
WBC 0.00~999.99×109/L
Neu%/Lym%/ Mon%/ Eos%/ Bas%
0~100%
RBC 0.00~99.99×1012/L
HGB 0~300g/L
PLT 0~9999×109/L
HCT
0.0~100.0%
MCV (0.0-250.0)fL
RET%
RET#
0~100%
0.0000~9.9999×10
12
/L
NRBC%
0~9999.99%
NRBC# 0~9999.99×109/L
2.9.6 Background requirement
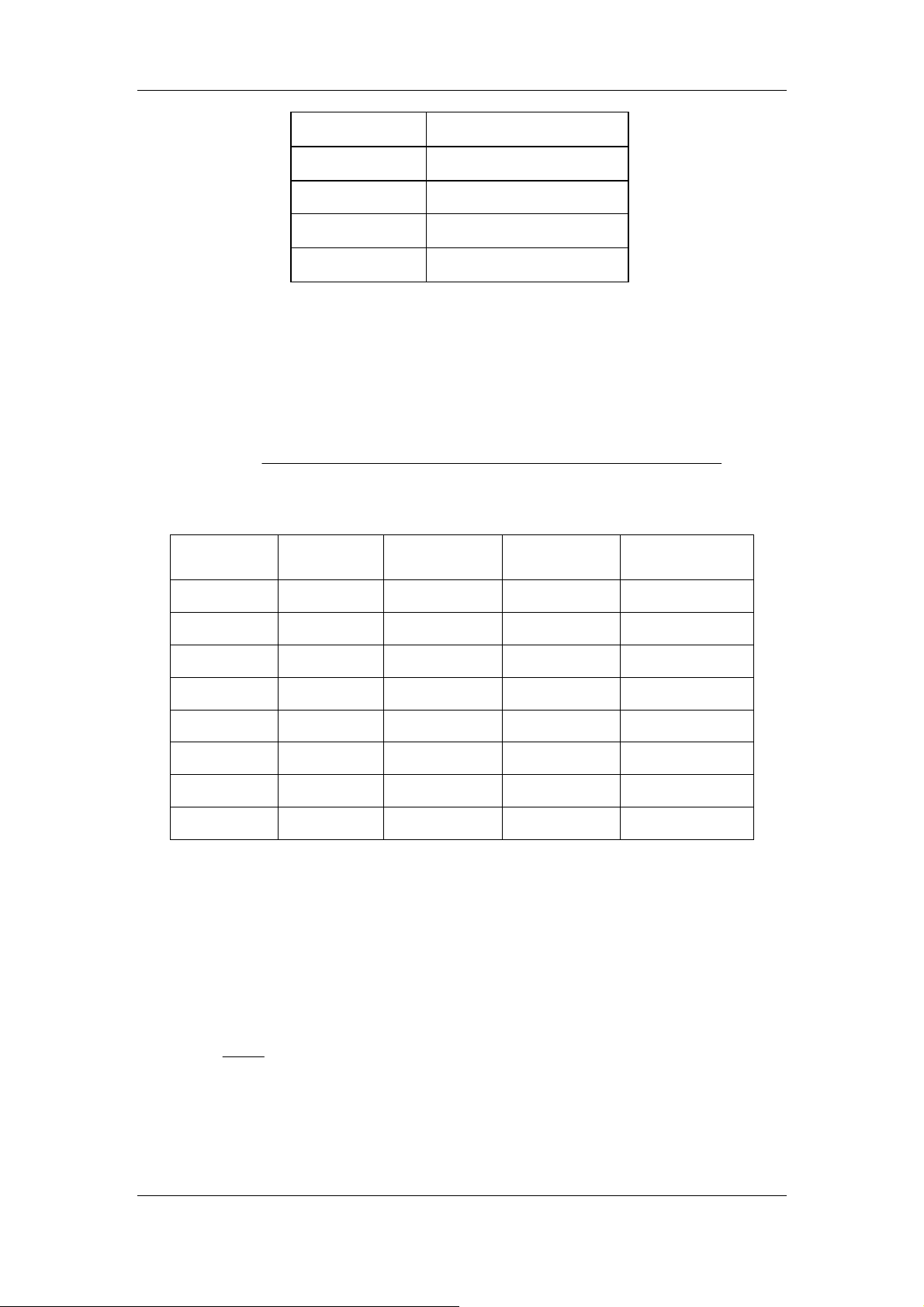
Background analysis method: run diluent sample and get the analysis result.
The background specification of BC-6800 is as follows:
Table 2-10 Background requirements
Parameter Background requirement
WBC
WBC-D
WBC-N
≤ 0.1 × 10
≤ 0.2 × 10
≤ 0.2 × 10
2-7
9
/ L
9
/ L
9
/ L
X
X
X
RBC
RBC-O
≤ 0.02× 10
≤ 0.02× 10
12
/ L
12
/ L
HGB ≤1 g/L
PLT
PLT-O
≤ 5 × 10
≤ 5 × 10
9
/ L
9
/ L
2.9.7 Carryover
Carryover analysis method: analyze 3 high value samples consecutively when the
analyzer is under stable conditions, and then analyze 3 low value samples immediately,
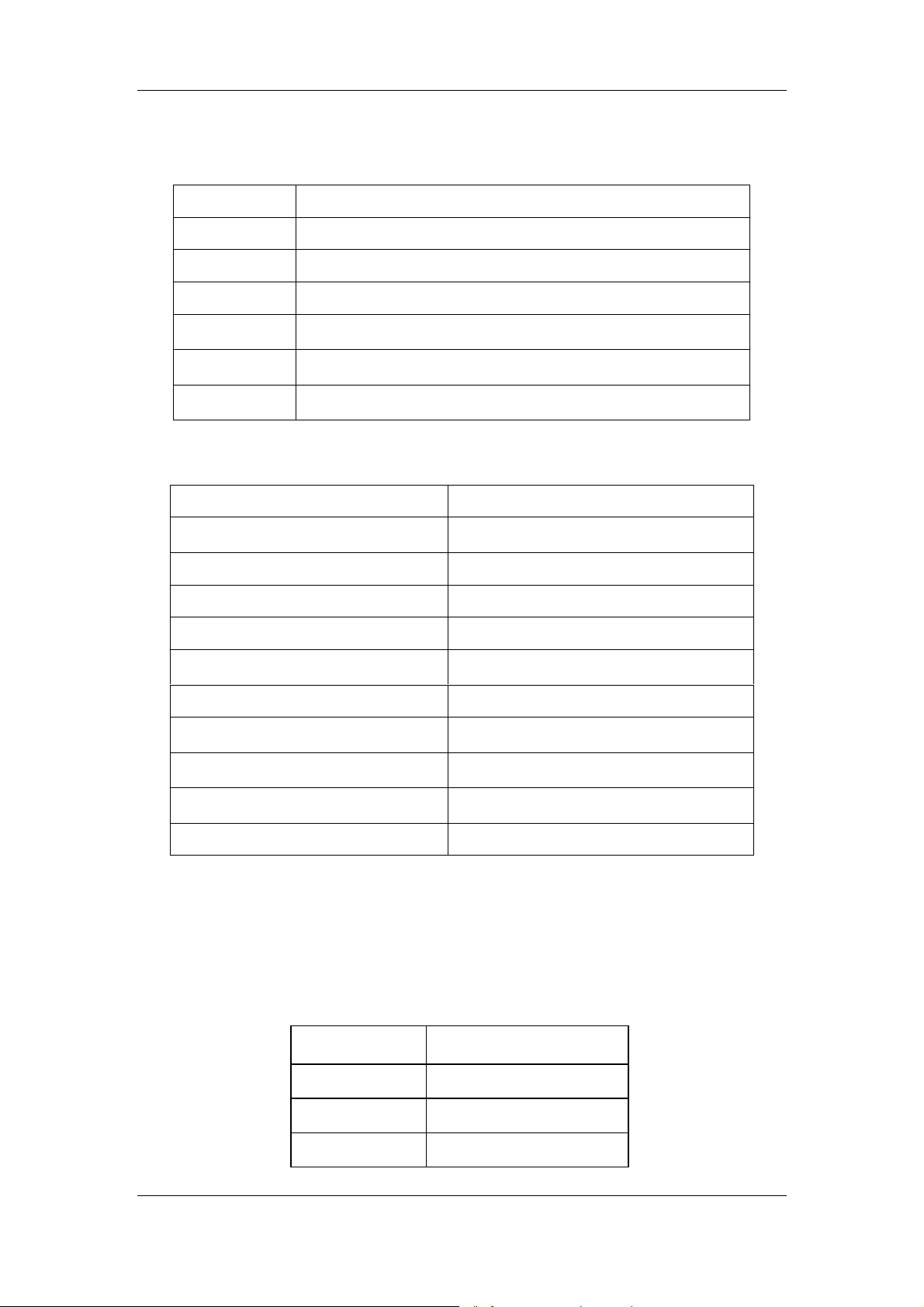
then calculate the carryover rate per the following equation.
(%)Carryover ×=
-
-
Table 2-11 Carryover requirements
Parameter Unit High value
sample
WBC ×109/L > 15.0 < 3.0 ≤1.0%
Low value
sample
result sample level-low hirdTresult sample level-lowFirst
result sample level-low hirdTresult sample level-high hirdT
Carryover
100
%
RBC ×1012/L > 6.0 < 2.00 ≤1.0%
HGB g/L > 200 < 40 ≤1.0%
HCT % >54.0 <18.0 ≤1.0%
PLT ×109/L > 300 < 100 ≤1.0%
RBC-O ×1012/L > 6.0 < 2.00 ≤1.5%
WBC-D ×109/L > 15.0 < 3.0 ≤1.0%
WBC-N ×109/L > 15.0 < 3.0 ≤1.5%
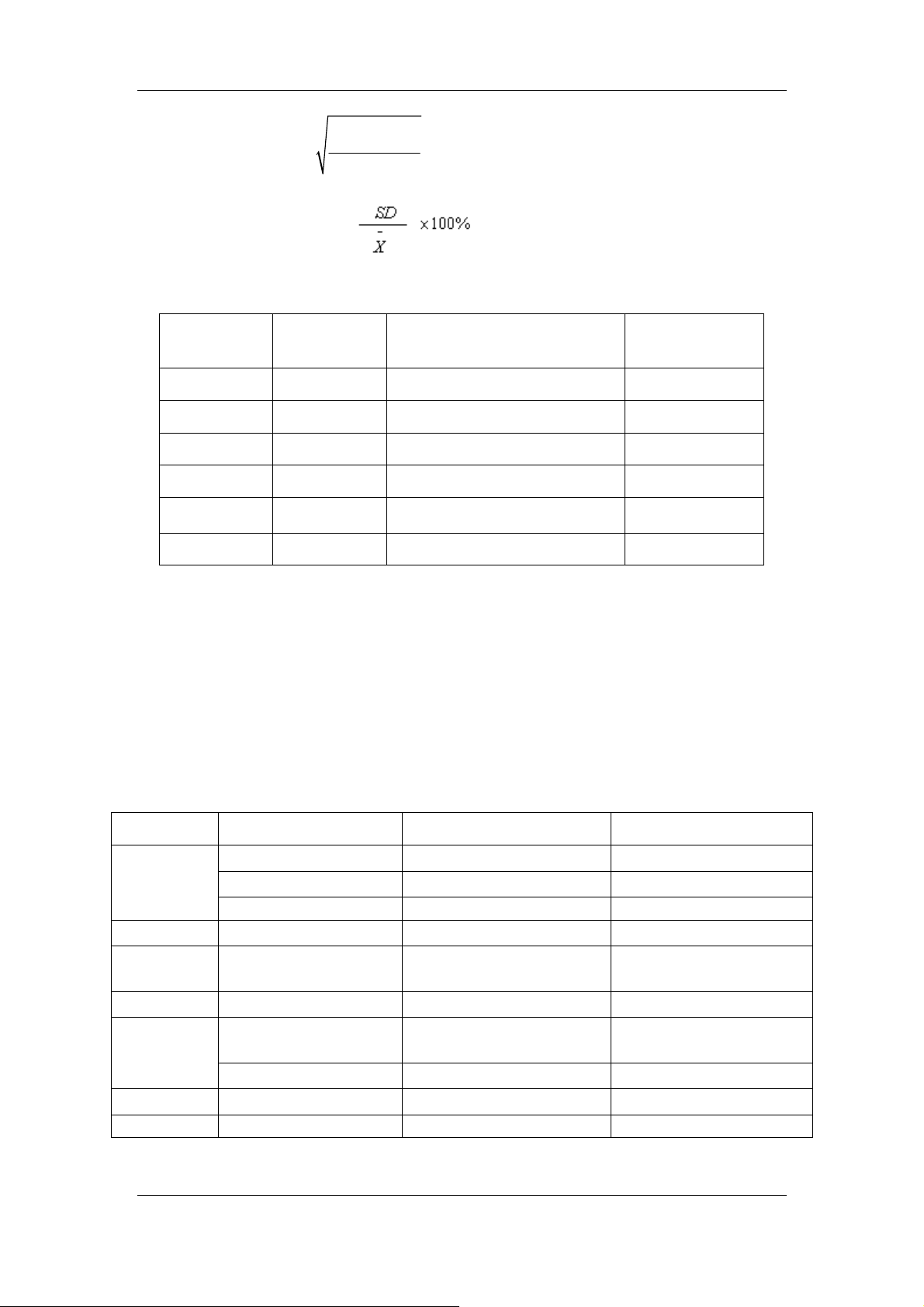
2.9.8 Reproducibility
Reproducibility analysis method: select a qualified sample and analyze it for 10
consecutive times, and then calculate the CV (%) and absolute deviation D of each
parameter. Calculation method:
n
∑
i
1
i
=
; n: analysis times
n
Mean(
−
)=
−
Absolute deviation di =xi -
2-8
X
−
2
X
−
i
−
; i: the parameter result of the ith analysis
1
Standard deviation (SD)=
()
∑
n
Coefficient variation (CV)%=
Table 2-12 Reproducibility requirements
Parameter Range
9
WBC
RBC
HGB
MCV
HCT
PLT
≥4×10
≥3.5×10
(110-180)g/L
(80-100)fL
(30~50)%
≥100×10
/L
12
/L
9
/L
Whole blood (CV/Absolute
deviation d*)
≤2.5% ≤4.0%
≤1.5% ≤2.0%
≤1.0% ≤2.0%
≤1.0% ≤3.0%
≤1.5% ≤3.0%
≤4.0% ≤8.0%
Predilute (CV)
*Note: absolute deviation d= measured value- mean of measured value.
**Note: Range=maximum measured value- minimum measured value.
2.9.9 Linearity
Prepare samples of different concentrations, analyze the samples, and calculate slope
coefficient and intercept in the linearity regression equation. Then calculate the theoretical
value and the deviation between the theoretical value and the test value.
Table 2-13 Linearity requirements
Parameter Condition Whole blood mode Predilute mode
(0 ~ 100.00)×109/L
WBC
(100.01 ~ 350.00)×109/L
(350.01 ~ 500)×10
9
/L ±11% ±11%
RBC (0 ~ 8.00)×1012/L
HGB (0-250)g/L
HCT
PLT*
RET%
(0~75)% ±1.0%(HCT value) or ±2% ±2.0%(HCT value) or ±4%
(0 ~ 1000)×109/L
(1001 ~ 5000)×10
9
/L
(0~30)% ±0.3%(RET value) or ±20%
±0.20×10
±6% ±6%
±0.03×10
±2g/L or ±2%
±10×10
±6%
9
/L or ±2%
12
/L or ±2%
9
/L or ±5% ±10×109/L or ±10%
±0.50×10
±0.05×10
±20×10
9
/L or ±5%
12
/L or ±5%
±2g/L or ±3%
±4g/L or ±4%
9
/L or ±10%
±10%
/
RET# (0 ~ 0.8)×1012/L ±0.015×1012/L or ±20% /
* Note: PLT linearity may not meet the requirement, it is mainly determined by RBC
concentration.
2-9
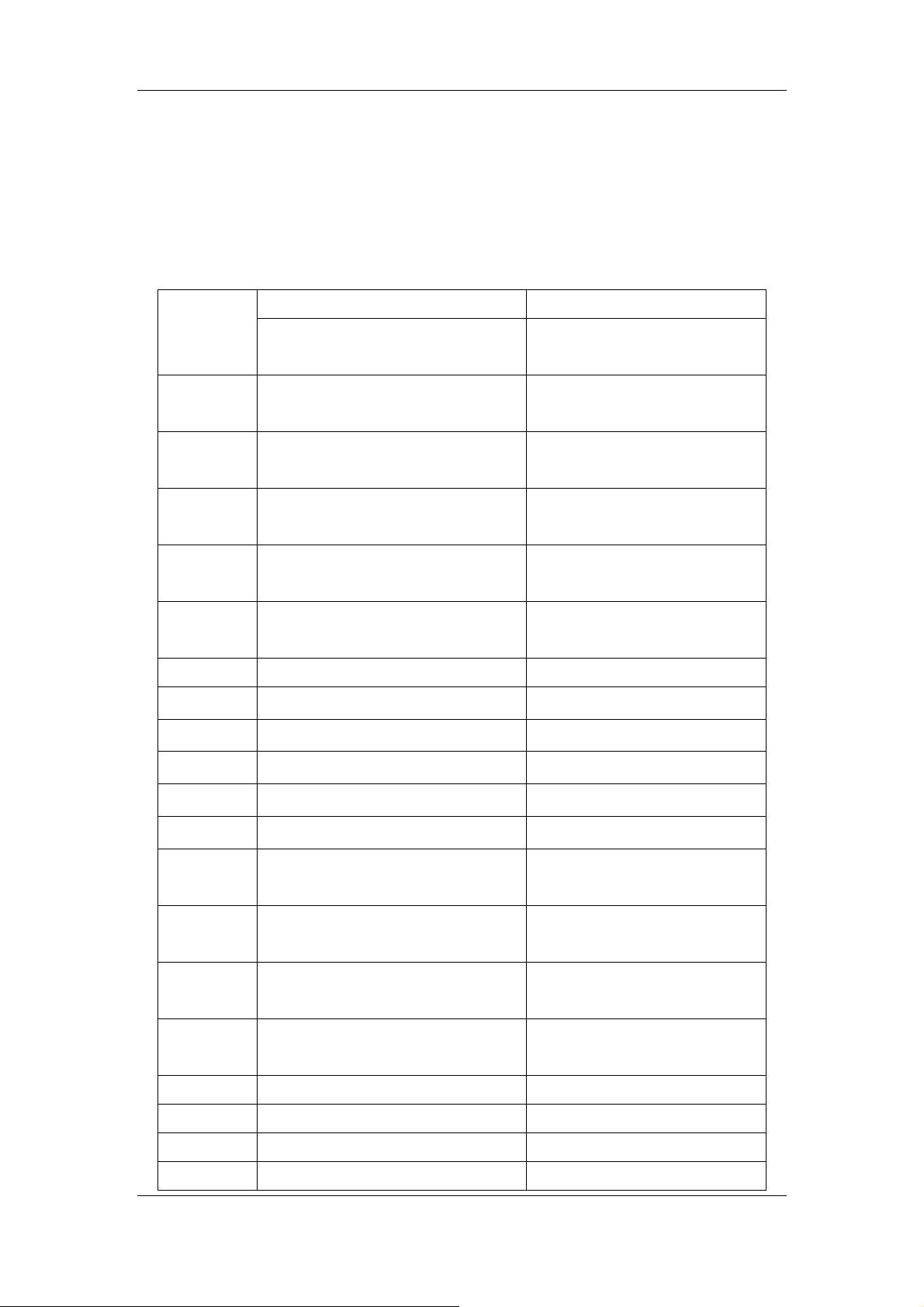
2.9.10 Deviation between Different Modes
The way to measure deviation between different modes: perform calibration under each
mode using fresh blood or calibrator, then analyze a normal fresh blood sample for 5 times
under the autoloading mode, open vial whole blood mode and open vial predilute mode
respectively, and calculate the deviations of the parameters between the modes.
Table 2-14 Requirements of deviations under different modes
Autoloading and open vial mode Open vial and predilute mode
Parameter
Relative deviation or absolute
deviation requirement
WBC ±5% or ±0.4×109/L
RBC ±2% or ±0.1×1012/L
HGB ±2% or ±4g/L
HCT ±2% or ±0.3HCT%
PLT ±7% or ±20×109/L
Neu%
Lym%
Mon%
Eos%
±5.0% ±9.0%
±4.0% ±9.0%
±3.0% ±6.0%
±2.0% ±3.0%
Relative deviation or absolute
deviation requirement
9
±5% or ±0.4×10
±10% or ±0.8×10
±2% or ±0.1×10
±4% or ±0.2×10
/L
9
/L
12
/L
9
/L
±2% or ±4g/L
±4% or ±6g/L
±2% or ±0.3HCT%
±4% or ±0.6HCT%
9
9
/L
/L
±7% or ±20×10
±14% or ±30×10
Bas%
NRBC%
RET#
±20% or ±2.0NRBC% /
±1.0% ±3.0%
±20% or ±0.015×10
12
/L
±20% or ±0.015×10
±30% or ±0.02×10
RET%
±20% or ±0.3 RET%
±20% or ±0.3 RET%
±30% or ±0.45 RET%
RBC-O ±20%
PLT-O ±20%
LFR
MFR
HFR
IRF
±30% or ±10 LFR%
±30% or ±10 MFR%
±30% or ±5 HFR%
±30% or ±10 IRF%
2-10
±20%
±30%
±20%
±30%
12
/L
12
/L

2.9.11 Correlation Requirements of the Analyzer and
Comparator
1. Requirements of Deviation of the Analyzer and Comparator
Analyzer a fresh blood sample or calibrator with traceability for 5 consecutive times on a
comparator of good conditions and calculate the mean of each parameter. Take the means as
targets, and calibrate the analyzer to be tested with the sample or calibrator mentioned above.
When the calibration finishes, test another fresh blood samples for 5 times on the two
analyzers respectively and calculate the deviation rate of the means of each parameter.
Deviation requirements: WBC - ≤ ±3%, RBC - ≤ ±2%, HGB- ≤ ±2%, PLT - ≤ ±5%, HCT or MCV
- ≤ ±2%.
2. Correlation Requirements of the Analyzer and Comparator
Test at least 100 fresh anticoagulated venous blood samples (able to cover the reportable
range as much as possible, with at least 50 abnormal samples) for 2 times on the comparator
and the analyzer respectively, calculate the mean and the correlation coefficient R.
Table 2-15 Requirements on the Comparative Index of the Analyzer and Comparator
Parameter
WBC ≥0.99
RBC ≥0.99
HGB ≥0.98
MCV ≥0.98
PLT ≥0.95
NRBC ≥0.90
RET#/RET% ≥0.90
Comparative Correlation Coefficient of
the Analyzer and Comparator
2.9.12 Correlation and Accuracy Requirements of WBC
Differential and Manual Differential
1. Correlation
Prepare 100 normal samples and 100 abnormal samples, test the samples with the analyzer
and the reference method (manual differential) respectively. Test each sample on the analyzer
twice. Manual differential shall be conducted per the requirement of CLSI H20, 400 cells from
each sample are analyzed, and the mean is calculated. Conduct correlation analysis for
Neu%, Lym%, Mon%, Eos%, Bas% and IG.
2-11
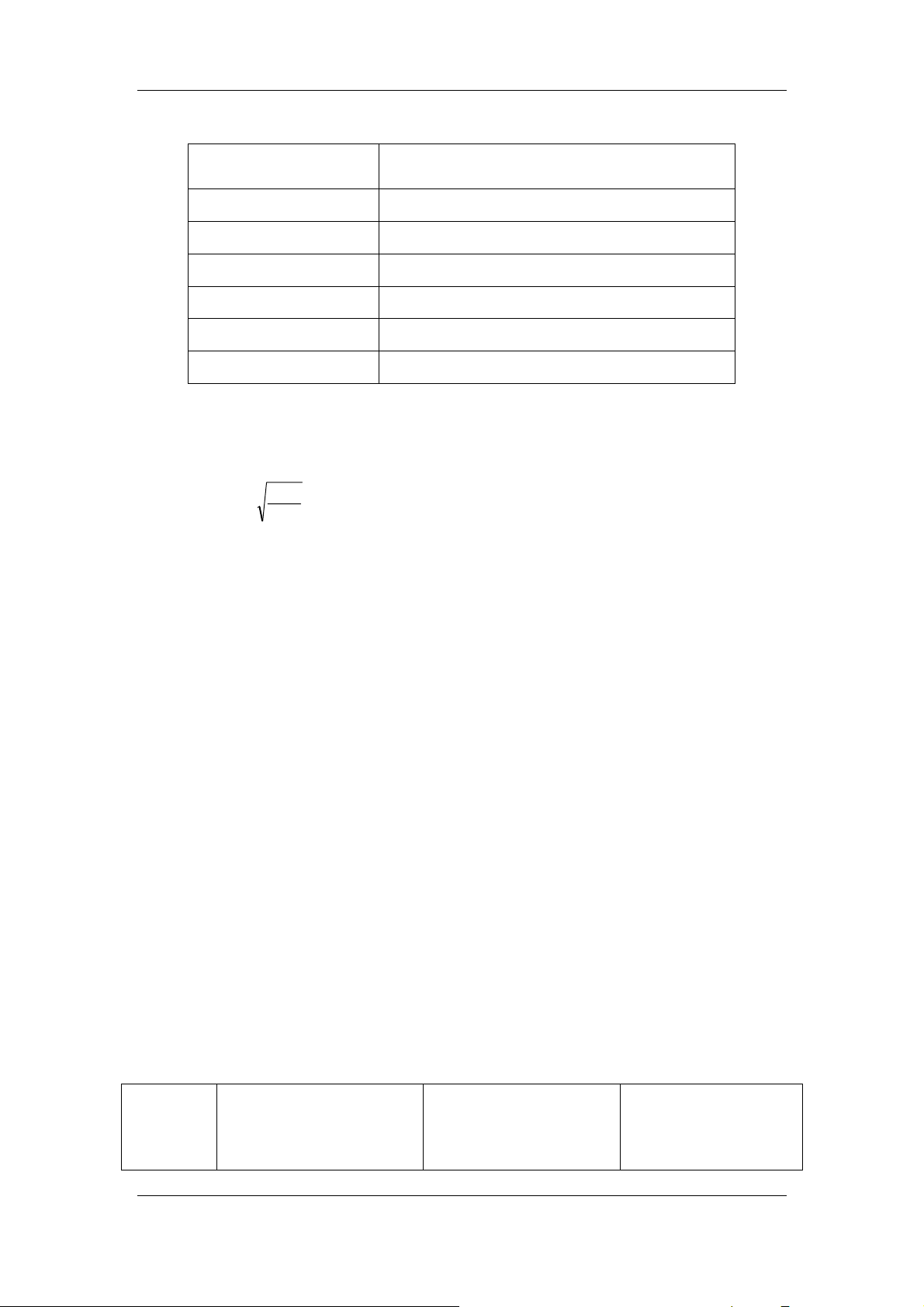
Table 2-16 Correlation Requirements of Differential Parameters
Parameter Correlation Coefficient of WBC Differential of
the Analyzer and Manual Differential
Neu% ≥0.90
Lym% ≥0.90
Mon% ≥0.75
Eos% ≥0.80
Bas% ≥0.50
IG% ≥0.80
2. Accuracy
Run calculation over results of the 200 samples tested for correlation analysis.
qp×
Equation: SEp=
n
In the equation, n=200; p= mean obtained with the reference method; q=100-p; when freedom
is 199, the t distribution factor of 99% credibility limit =2.57.
Calculating credibility range
The 99% credibility range of a parameter rate: p±2.57×SEp.
Requirement: The Lym%, Neu%, Mon%, Eos% and Bas% results tested by the analyzer
must be within the 99% credibility range of the results tested by the reference method.
2.9.13 Sample Stability
Prepare 5 normal anticoagulated fresh venous blood samples, separate each sample into 17
shares. Test 1 share for twice after it has been prepared for 0.5 hour. Group the other 16
shares into 2 groups, store 1 group in room temperature and the other in the environment of 4
℃. Test 1 share from each group at hour 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48 and 72 after they have been
prepared (the samples stored in the environment of 4℃ must be warmed to room temperature
and then mixed). Record the parameter results of each sample and observe the change of
parameter results, histogram and scattergram over time. Calculate the change of parameter
results of each sample over time against the results of the test done at hour 0.5, and
representing the change in absolute or relative deviation.
Parameter
Table 2-17 Sample Stability Requirements
Relative deviation or
absolute deviation
Acceptance Range
Long Term Stability in
Room Temperature
(18℃-26 )℃
2-12
Long Term Stability in
Refrigerated
Temperature (2℃-8 )℃
 Loading...
Loading...