Page 1

Gaw9.5Z97-4
User Manual
Page 2

Contents
1 Introduction..................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Safety Precautions..............................................................................1
1.2 LEDs and Interfaces............................................................................2
1.3 System Requirements......................................................................... 4
1.4 Features..............................................................................................4
1.5 Supported Protocols............................................................................5
2 Hardware Installation...................................................................................... 6
3 About the Web Configuration..........................................................................9
3.1 How to Access the Router...................................................................9
3.2 Wizard...............................................................................................10
3.3 Status................................................................................................19
3.3.1 System ...................................................................................19
3.3.2 LAN........................................................................................20
3.3.3 WLAN.....................................................................................20
3.3.4 WAN.......................................................................................21
3.3.5 Port Mapping..........................................................................22
3.3.6 Statistics.................................................................................22
3.3.7 ARP Table...............................................................................24
3.4 Network.............................................................................................24
3.4.1 LAN........................................................................................25
3.4.2 WAN.......................................................................................30
3.4.3 WLAN.....................................................................................36
3.5 Service.............................................................................................. 45
3.5.1 DNS........................................................................................ 45
3.5.2 Firewall...................................................................................47
3.5.3 UPNP.....................................................................................53
3.5.4 IGMP Proxy............................................................................54
3.5.5 TR069.....................................................................................54
3.5.6 ACL........................................................................................57
3.6 Advance............................................................................................ 58
3.6.1 Bridge Setting......................................................................... 58
3.6.2 Routing...................................................................................59
3.6.3 Port Mapping..........................................................................62
i
Page 3

3.6.4 QoS........................................................................................64
3.6.5 SNMP.....................................................................................65
3.6.6 Others.....................................................................................66
3.7 Admin................................................................................................67
3.7.1 Commit/Reboot....................................................................... 67
3.7.2 Upgrade..................................................................................68
3.7.3 System Log............................................................................. 69
3.7.4 Password................................................................................70
3.7.5 Time Zone..............................................................................71
3.8 Diagnostic......................................................................................... 72
3.8.1 Ping........................................................................................72
3.8.2 ATM Loopback........................................................................ 73
3.8.3 ADSL......................................................................................73
4 Statement ..................................................................................................75
4.1 Europe - EU Declaration of Conformity Statement.............................75
4.2 Federal Communication Commission Intererence Statement............77
4.3 Part 68 statement.............................................................................. 79
ii
Page 4

1 Introduction
The ADSL Router supports multiple line modes. It provides four 10/100 base-T
Ethernet interfaces at the user end. The device provides high-speed ADSL
broadband connection to the Internet or Intranet for high-end users, such as net
bars and office users. The device provides high performance access to the
Internet, downlink up to 24 Mbps and uplink up to 1 Mbps.
The device supports WLAN access, as WLAN AP or WLAN router, to the Internet.
It complies with IEEE 802.11, 802.11b/g specifications, and WEP, WPA and
WPA2 security specifications.
1.1 Safety Precautions
Follow the following instructions to prevent the device from risks and damage
caused by fire or electric power:
Use volume labels to mark the type of power.
Use the power adapter packed within the device package.
Pay attention to the power load of the outlet or prolonged lines. An
overburden power outlet or damaged lines and plugs may cause electric
shock or fire accident. Check the power cords regularly. If you find any
damage, replace it at once.
Proper space left for heat dissipation is necessary to avoid damage caused
by overheating to the device. The long and thin holes on the device are
designed for heat dissipation to ensure that the device works normally. Do
not cover these heat dissipation holes.
Do not put this device close to a place where a heat source exits or high
temperature occurs. Avoid the device from direct sunshine.
Do not put this device close to a place where it is over damp or watery. Do
not spill any fluid on this device.
Do not connect this device to any PCs or electronic products, unless our
customer engineer or your broadband provider instructs you to do this,
because any wrong connection may cause power or fire risk.
Do not place this device on an unstable surface or support.
1
Page 5
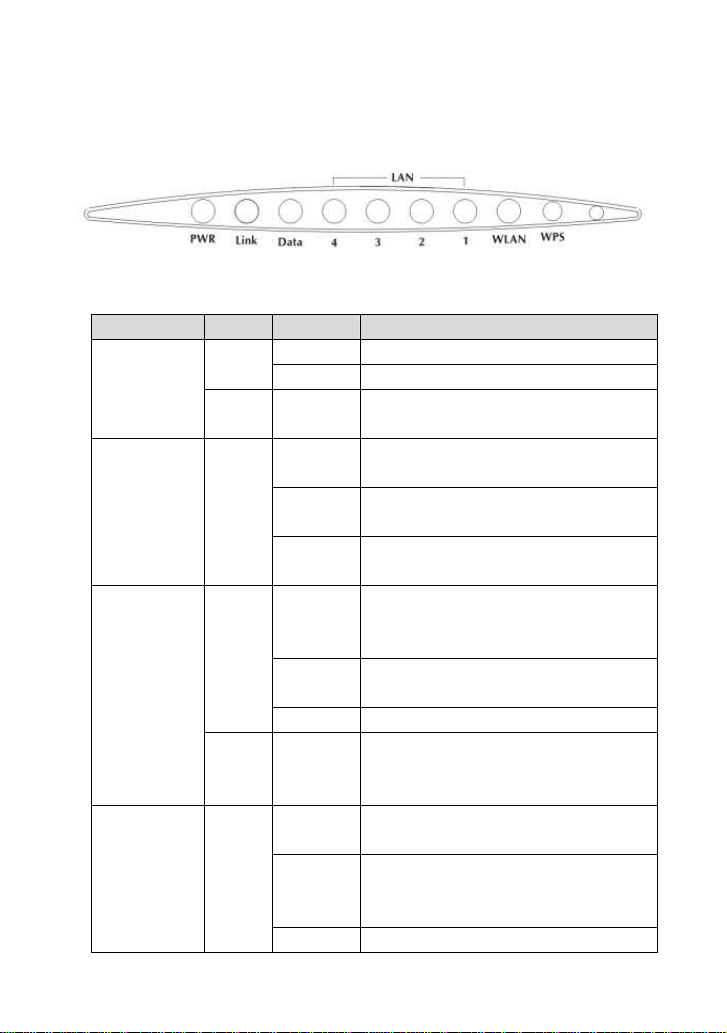
1.2 LEDs and Interfaces
Front Panel
The following table describes the LEDs of the device:
LEDs Color Status Description
Green
PWR
Red On
Link Green
Green
Data
Red On
LAN4-1 Green
On The device is powered on.
Off The device is powered off.
The device is self-testing or self-testing
is failed, or the software is upgrading.
On
Blinks
(fast)
Blinks
(slow)
On
Blinks
Off The device is in bridge mode.
On
Blinks
Off The LAN connection is failed.
The device has established connection
with the office physical layer.
The device is handshaking with the
office physical layer.
The device does not detect the signals.
The device has a successful Internet
connection in the routing mode, and no
data is being transmitted.
Data is being transmitted on the
Internet in the routing mode.
After the successful synchronous in
the routing mode, the Internet
connection is failed.
The device has successful LAN
connection.
Data is being transmitted on LAN or
data is being transmitted on the
Internet in the bridge mode.
2
Page 6
LEDs Color Status Description
The device has successful WLAN
connection.
WPS is enabled, and is waiting for
client to negotiate.
WLAN Green
WPS Green
On
Blinks Data is being transmitted on WLAN.
Off The WLAN connection is failed.
Off WPS is disabled.
Blinks
Rear Panel
The following table describes the interfaces of the device:
Interface
Line
LAN1/LAN2/
LAN3/LAN4
Power
Reset
WPS/WLAN
Wireless antenna.
RJ-11 interface, for connecting to the ADSL interface or a
splitter through a telephone cable.
RJ-45 interface, for connecting to the Ethernet interface of
the PC or the Ethernet devices through an Ethernet cable.
Power interface, for connecting to the power adapter of 12 V
DC, 1 A.
Reset to the factory defaults. To restore factory defaults, keep
the device powered on and push a paper clip into the hole.
Press down the button 3 seconds and then release.
Press the button silently less than 1 second to enable
WLAN function.
Press the button for more than 3 seconds (include 3
seconds) to enable to enable WPS function.
If you press the button between 1 second and 3
seconds, no function takes effective.
Description
3
Page 7

Interface
ON/OFF Power switch, power on or power off the router.
Description
1.3 System Requirements
Recommended system requirements are as follows:
A 10/100 base-T Ethernet card is installed on your PC
A hub or Switch. (attached to several PCs through one of Ethernet
interfaces on the device)
Operating system: Windows 98SE, Windows 2000, Windows ME,
Windows XP or Windows Vista
Internet Explorer V5.0 or higher, Netscape V4.0 or higher, or firefox 1.5 or
higher
1.4 Features
The device supports the following features:
Various line modes (line auto-negotiation)
External PPPoE dial-up access
Internal PPPoE/PPPoA dial-up access
Zero installation PPP bridge mode (ZIPB)
1483B/1483R/MER access
Multiple PVCs (eight at most)
A single PVC with multiple sessions
Multiple PVCs with multiple sessions
DHCP server
NAT/NAPT
Static route
Firmware upgrading through Web, TFTP, or FTP
Rsetting to the factory defaults through Reset button or Web
DNS relay
Virtual server
Web interface
Telnet CLI
System status display
4
Page 8

PPP session PAP/CHAP
IP/Port, MAC, URL filter
Remote access control
Line connection status test
Remote access control
Backup and restoration of configuration file
IP quality of service (QoS)
Universal plug and play (UPnP)
WLAN with high-speed data transmission rate, up to 54 Mbps, compatible
with IEEE 802.11b/g, 2.4 GHz compliant equipment
1.5 Supported Protocols
The device supports the following protocols:
ITU G.992.1 (G.DMT) Annex A
ITU G.992.2 (G.LITE)
ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
ITU G.992.3 (ADSL2)
ITU G.992.5 (ADSL2+)
Annex L
Annex M
5
Page 9

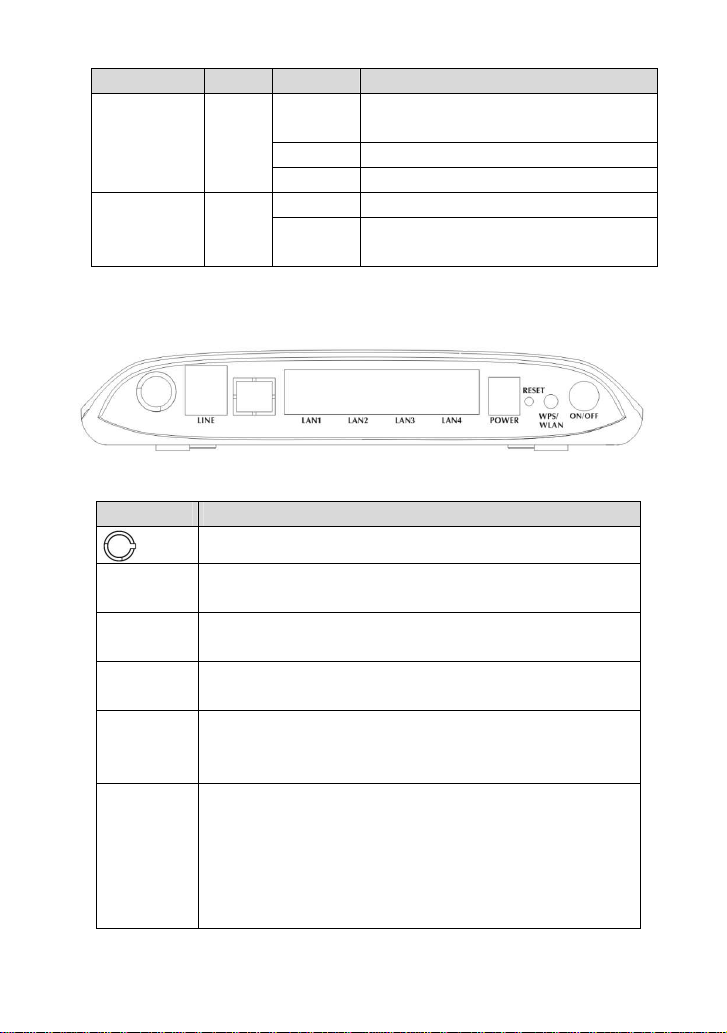
2 Hardware Installation
Step 1 Connect the Line interface of the device and the Modem interface of
the splitter through a telephone cable. Connect the phone to the
Phone interface of the splitter through a cable. Connect the incoming
line to the Line interface of the splitter.
The splitter has three interfaces:
Line: Connect to a wall phone jack (RJ-11 jack)
Modem: Connect to the ADSL jack of the device
Phone: Connect to a telephone set.
Step 2 Connect the Ethernet interface of the device to the network card of the
PC through an Ethernet cable (MDI/MDIX).
I Note:
Use twisted-pair cables to connect with the hub or switch.
Step 3 Plug one end of the power adapter to the wall outlet and connect the
other end to the Power interface of the device.
Connection 1
錯誤
錯誤! 找不到參照來源
找不到參照來源。
錯誤錯誤
找不到參照來源找不到參照來源
the router, PC, splitter and the telephone sets, when no telephone set is placed
before the splitter.
。 displays the application diagram for the connection of
。。
6
Page 10
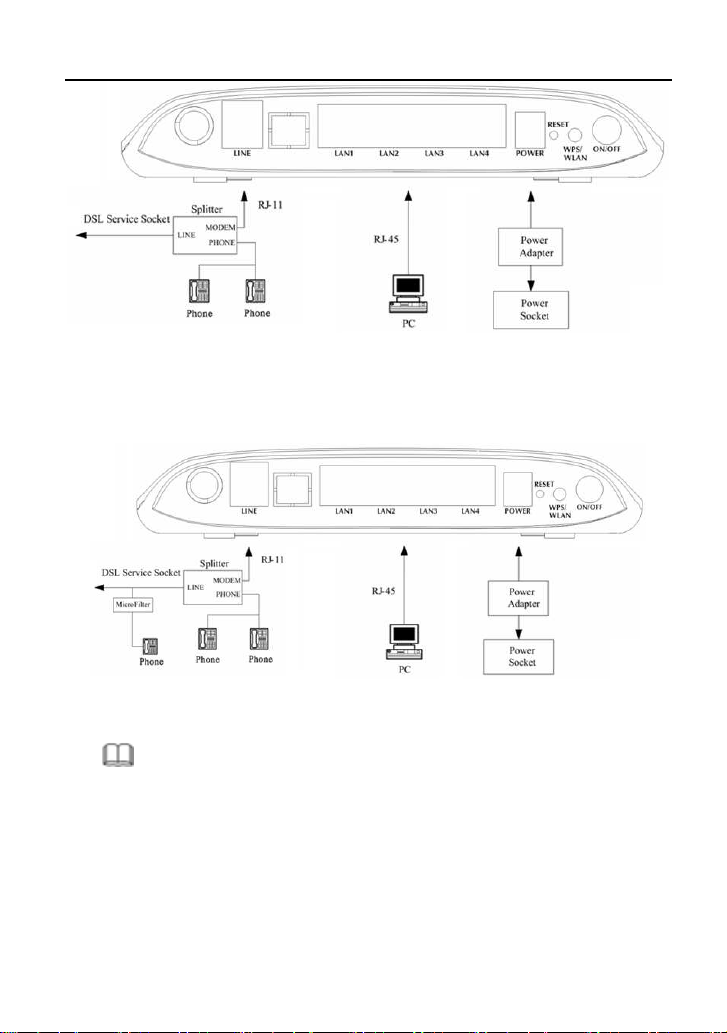
Figure 1 Connection diagram (Without connecting telephone sets before the splitter)
Connection 2
Figure 2 shows the connection when the splitter is installed close to the router.
Figure 2 Connection diagram (Connecting a telephone set before the splitter)
Note:
When connection 2 is used, the filter must be installed close to the telephone
cable. See Figure2. Do not use the splitter to replace the filter.
Installing a telephone directly before the splitter may lead to failure of connection
between the device and the central office, or failure of Internet access, or slow
connection speed. If you really need to add a telephone set before the splitter,
7
Page 11
you must add a microfilter before a telephone set. Do not connect several
telephones before the splitter or connect several telephones with the microfilter.
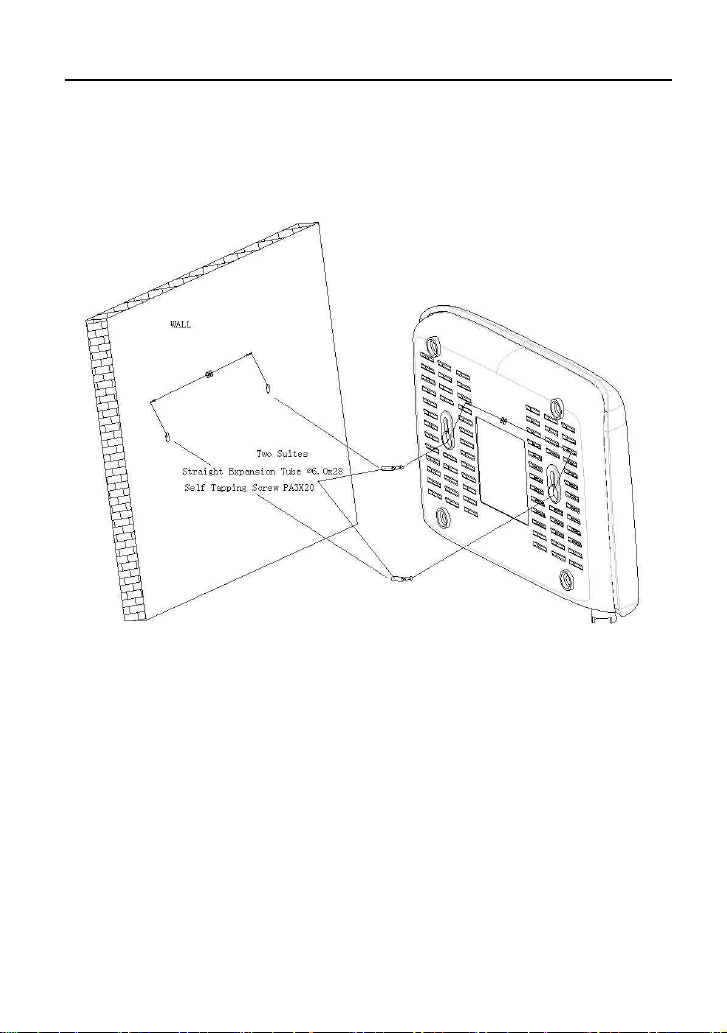
Wall Mount Diagram
The device can be mounted on the wall. Figure 3 shows the wall mount diagram.
Figure 3 Wall mount diagram
8
Page 12
3 About the Web Configuration
This chapter describes how to configure the router by using the Web-based
configuration utility.
3.1 How to Access the Router
The following is the detailed description of accesing the router for the first time.
Step 1 Open the Internet Explorer (IE) browser and enter http://192.168.1.1.
Step 2 In the LOGIN page that is displayed, enter the username and
password.
The username and password of the super user are admin and admin
respectively.
The user name and password of the common user are user and user
respectively.
If you log in as the super user, the page shown in the following figure appears.
9
Page 13
If you log in as a common user, you can check the status of the router, but can
not configure the most of the settings.
3.2 Wizard
When subscribing to a broadband service, you should be aware of the method by
which you are connected to the Internet. Your physical WAN device can be either
PPP, ADSL, or both. The technical information about the properties of your
Internet connection is provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). For
example, your ISP should inform you whether you are connected to the Internet
using a static or dynamic IP address, and the protocol that you use to
communicate on the Internet.
In the navigation bar, choose Wizard. The page shown in the following figure
appears. The Wizard page guides fast and accurate configuration of the Internet
connection and other important parameters. The following sections describe
these various configuration parameters. Whether you configure these
parameters or use the default ones, click NEXT to enable your Internet
connection.
10
Page 14
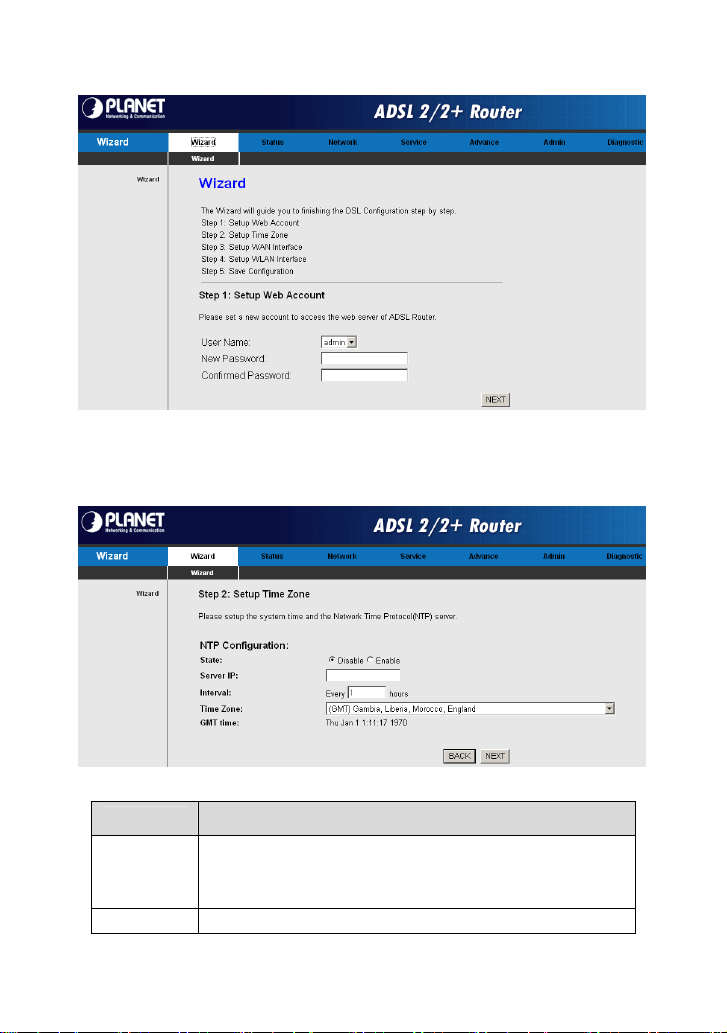
Enter the correct password and then click NEXT. The page shown in the
following figure appears. In this page, you can set the system time and Network
Time Protocol (NTP) server.
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field
You can disable or enable NTP function. You have to
State
Server IP Enter the IP address of the specified time server manually.
enable it if you want to configure the parameters in this
page.
Description
11
Page 15

Field
Set the interval that the router obtains the time from the
Interval
Time Zone Choose the time zone of your country.
GMT time It displays the Greenwich mean time.
After finishing the configuration, click NEXT. The page shown in the following
figure appears.
time server. That is, the interval that the router verifies the
time with the server.
Description
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field
The virtual path between two points in an ATM
network, and its valid value is from 0 to 255.
PVC Settings
Encapsulation Select the method of encapsulation provided by your
The virtual channel between two points in an ATM
network, ranging from 32 to 65535 (0 to 31 is
reserved for local management of ATM traffic).
Description
12
Page 16
Field
ISP. You can select LLC/SNAP or VC-Mux.
Select the WAN connection type. You can select 1483
Channel Mode
PPP Settings
Default Route You can select Enable or Disable.
DNS Settings
After finishing the configuration, click NEXT. The page shown in the following
figure appears.
Bridged, 1483 MER, PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE),
PPP over ATM (PPPoA), or 1483 Routed.
The username and password apply to PPPoE and
PPPoA encapsulation only. Ensure that you enter the
correct username and password.
Obtain DNS Automatically: Obtain the DNS
server assigned by the uplink equipment, such as
BAS.
Use the following DNS server address: If you
want to enter the DNS server address by yourself,
select it and enter the related data.
Description
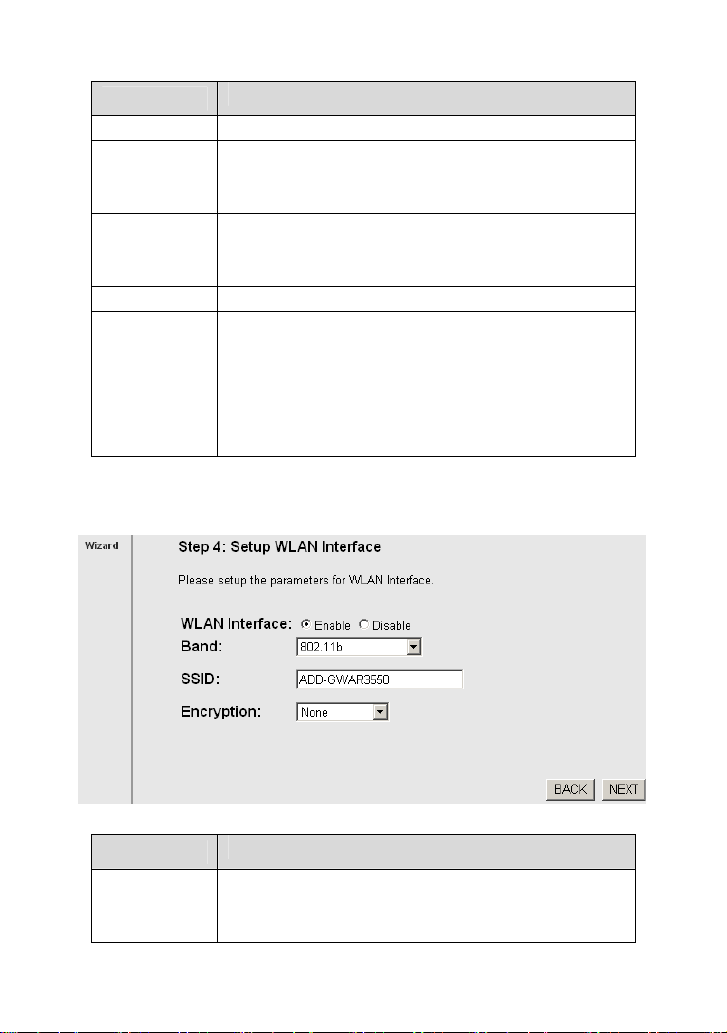
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field
WLAN
Interface
You can choose Enable or Disable. By default, WAN
interface is enabled.
You need to enable WAN interface, and then you can
Description
13
Page 17
Field
set the parameters in this page.
Choose the working mode of the router. You can choose
Band
SSID
Encryption
After finishing the configuration, click NEXT. The page shown in the following
figure appears.
2.4 GHz (B), 2.4 GHz (G), or 2.4 GHz (B + G). By
defaut, the band is 2.4 GHz (B + G).
The service set identification (SSID) is a unique name to
identify the router in the wireless LAN. Wireless stations
associating to the router must have the same SSID.
Enter a descriptive name that is used when the wireless
client connecting to the router.
Configure the wireless encryption mode. You can
choose None, WEP, WPA (TKIP), WPA (AES), WPA2
(AES), WPA2 (TKIP), or WPA2 Mixed.
Wired equivalent privacy (WEP) encrypts data
frames before transmitting over the wireless
network.
Wi-Fi protected access (WPA) is a subset of the
IEEE802.11i security specification draft.
WPA2 Mixed is the collection of WPA and WPA2
encryption modes. The wireless client establishes
the connection between the router through WPA or
WPA2.
Key differences between WPA and WEP are user
authentication and improved data encryption.
Description
14
Page 18

1483 Bridged
In the Setup WAN Interface page, set the channel mode to 1483 Bridged
1483 MER
15
Page 19

In the Setup WAN Interface page, set the channel mode to 1483 MER
PPPoE
16
Page 20

In the Setup WAN Interface page, set the channel mode to PPPoE
PPPoA
17
Page 21

In the Setup WAN Interface page, set the channel mode to PPPoA
1483 Routed
18
Page 22

In the Setup WAN Interface page, set the channel mode to 1483 Routed
3.3 Status
In the navigation bar, choose Status. In the Status page that is displayed
contains: System, LAN, WLAN, WAN, Port Mapping, Statistic, and ARP Table.
3.3.1 System
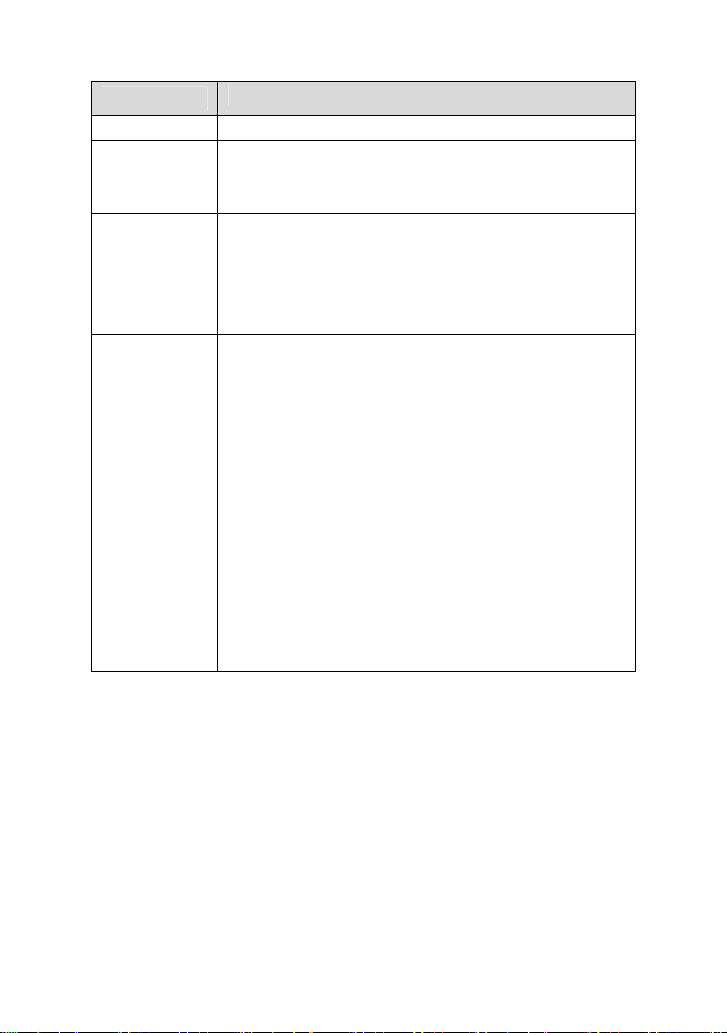
Choose Status > System. The page that is displayed shows the current status
and some basic settings of the router, such as software version, DSP version,
uptime, upstream speed, and downstream speed.
19
Page 23
3.3.2 LAN
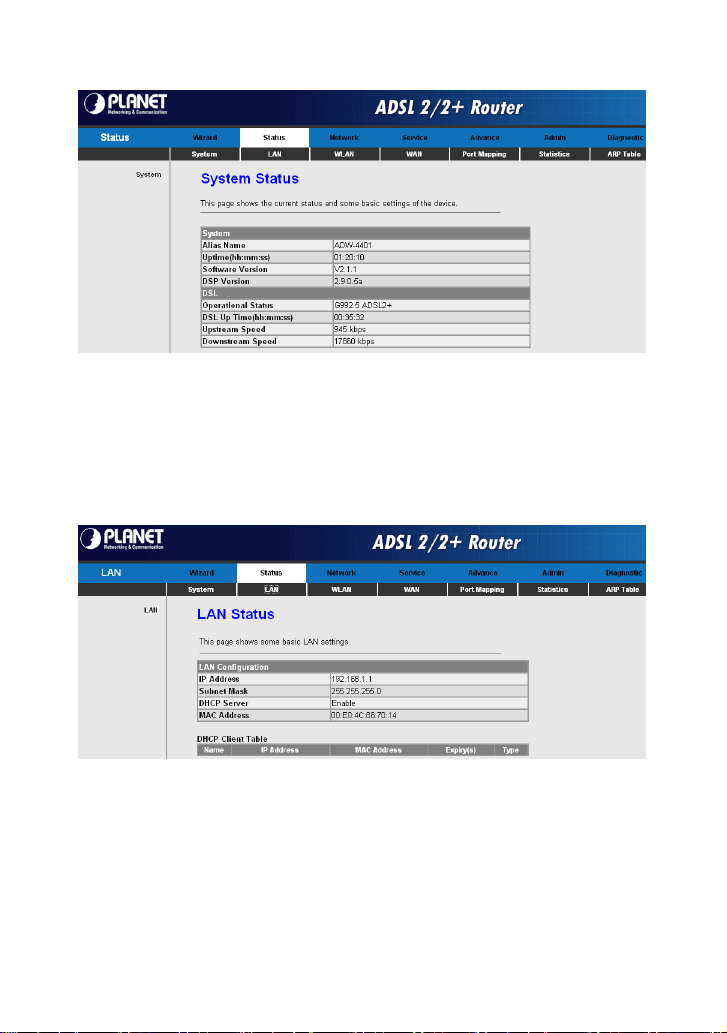
Choose Status > LAN. The page that is displayed shows some basic LAN
settings of the router. In this page, you can view the LAN IP address, DHCP
server status, MAC address, and DHCP client table. If you want to configure the
LAN network, refer to chapter 3.4.1.1 LAN IP.
3.3.3 WLAN
Choose Status > WLAN. The page that is displayed shows some basic WLAN
settings of the router. In this page, you can view basic status of WAN and DNS
server. If you want to configure the WAN network, refer to chapter 3.4.3 .
20
Page 24
3.3.4 WAN
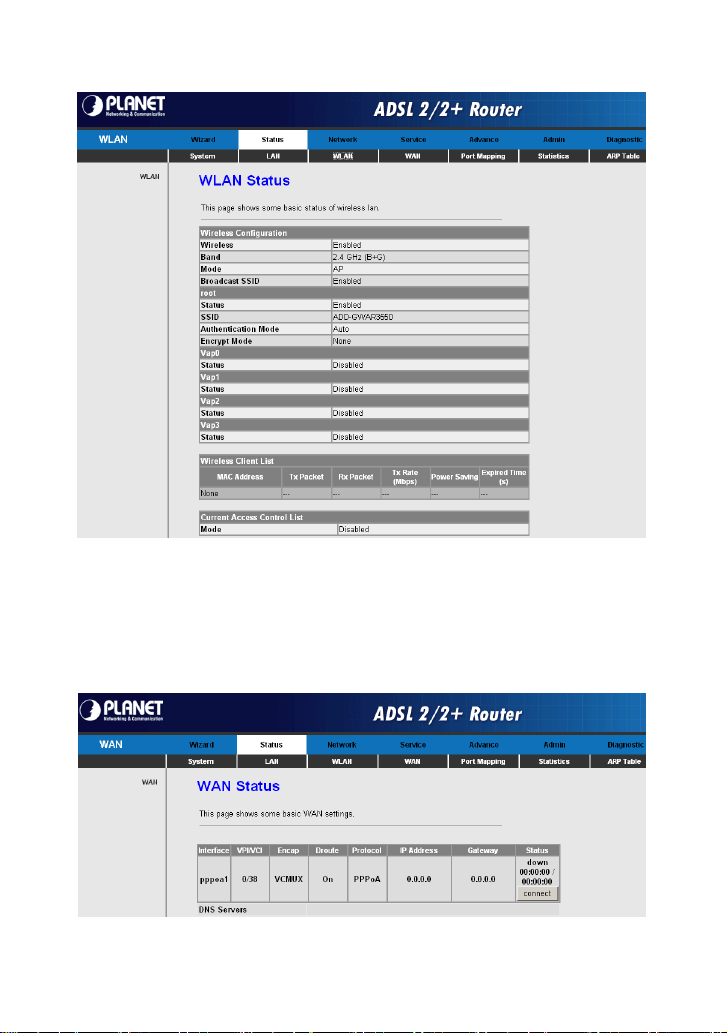
Choose Status > WAN. The page that is displayed shows some basic WAN
settings of the router. In this page, you can view basic status of WAN and DNS
server. If you want to configure the WAN network, refer to chapter 3.4.2.1 WAN.
21
Page 25
3.3.5 Port Mapping
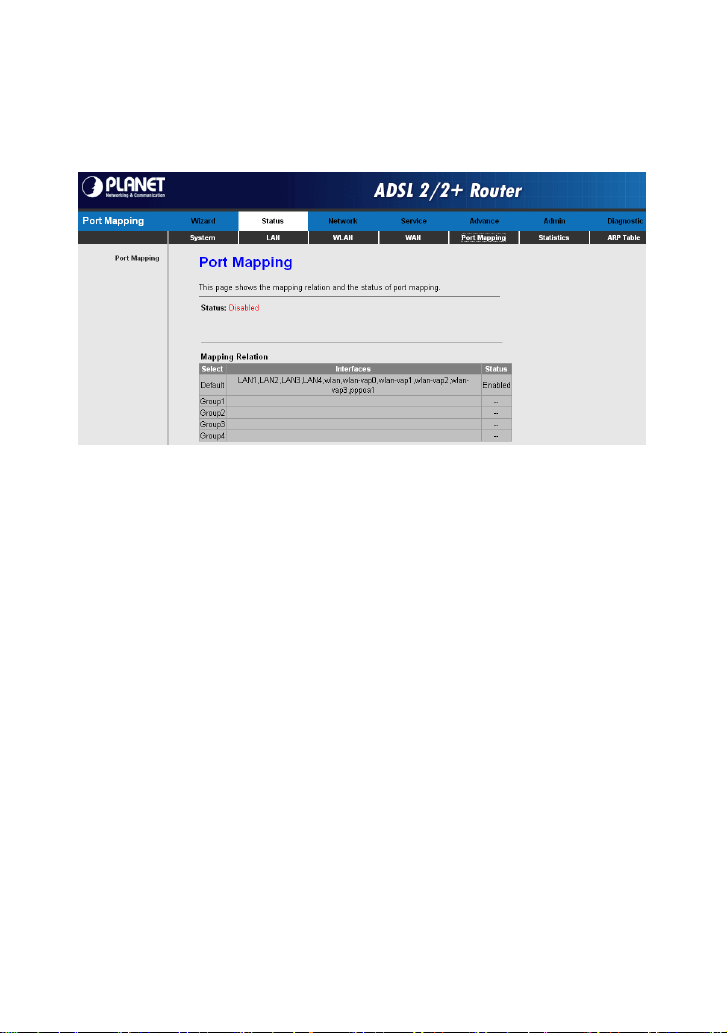
Choose Status > Port Mapping. In this page, you can view the mapping relation
and the status of port mapping.
3.3.6 Statistics
Choose Status > Statistics. The Statistics page that is displayed contains
Traffic Statistic and DSL Statistic.
3.3.6.1 Traffic Statistic
Click Traffic Statistic in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can view the statistics of each network port.
22
Page 26

3.3.6.2 DSL Statistic
Click DSL Statistic in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can view the ADSL line status, upstream rate,
downstream rate, and other information.
23
Page 27

3.3.7 ARP Table
Choose Status > ARP Table. In the ARP Table page, you can view the table that
shows a list of learned MAC addresses.
3.4 Network
In the navigation bar, choose Network. The Network page that is displayed
contains LAN, WAN, and WLAN.
24
Page 28

3.4.1 LAN
Choose Network > LAN. The LAN page that is displayed contains LAN IP,
DHCP, and DHCP Static IP.
3.4.1.1 LAN IP
Click LAN IP in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure appears.
In this page, you can change IP address of the router. The default IP address is
192.168.1.1. This is the private IP address of the router. This is the address
under which the router can be reached in the local network. It can be freely
assigned from the block of available addresses.
The following table describes the parameters and button of this page:
Field Description
Enter the IP of LAN interface. It is recommended to
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Secondary IP
IGMP Snooping You can disable or enable IGMP Snooping.
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
use an address from a block that is reserved for
private use. This address block is 192.168.1.1-
192.168.255.254.
Enter the subnet mask of LAN interface. The range
of subnet mask is from
255.255.0.0-255.255.255.254.
Select it to enable the secondary LAN IP. The two
LAN IP addresses must be in the different network.
25
Page 29

3.4.1.2 DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows the individual PC to obain
the TCP/IP configuration from the centralized DHCP server. You can configure
this router as a DHCP server or disable it. The DHCP server can assign IP
address, IP default gateway, and DNS server to DHCP clients. This router can
also act as a surrogate DHCP server (DHCP proxy) where it relays IP address
assignment from an actual real DHCP server to clients. You can enable or
disable DHCP server or DHCP proxy.
Click DHCP in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure appears.
The following table describes the parameters in this page:
Field Description
If set to DHCP Server, the router can assign IP
DHCP Mode
IP Pool Range
addresses, IP default gateway and DNS Servers to
Windows95, Windows NT and other systems that
support the DHCP client.
It specifies the first and the last of contiguous IP
address of the IP address pool.
26
Page 30

Field Description
Show Client
Default
Gateway
Max Lease
Time
Domain Name
Set
VendorClass IP
Range
Click Show Client in the DHCP Settings page. The page shown in the following
figure appears. You can view the IP address assigned to each DHCP client.
Click it, the Active DHCP Client Table page appears.
It shows the assigned IP address of the clients.
Enter the IP default gateway of the IP address pool.
The lease time determines the period that the PCs
retain the assigned IP addresses before the IP
addresses change.
Enter the domain name if you know. If you leave this
blank, the domain name obtained by DHCP from the
ISP is used. You must enter host name (system name)
on each individual PC. The domain name can be
assigned from the router through the DHCP server.
Click it, the Device IP Range Table page appears. You
can configure the IP address range based on device
type.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons in this page:
Field
IP Address
MAC Address
Description
It displays the IP address relative to the MAC
address.
It displays the MAC address of the PC.
Each Ethernet device has a unique MAC address.
The MAC address is assigned at the factory and it
consists of six pairs of hexadecimal character, for
27
Page 31

Field
Expired (s)
Refresh Click it to refresh this page.
Close Click it to close this page.
Click Set VendorClass IP Range in the DHCP Settings page. The page shown
in the following figure appears. You can configure the IP address range based on
device type.
Description
example, 00-A0-C5-00-02-12.
It displays the lease time. The lease time determines
the period that the PCs retain the assigned IP
addresses before the IP addresses change.
Choose None in the DHCP Settings page. The page shown in the following
figure appears.
28
Page 32

Choose DHCP Relay in the DHCP Mode page. The page shown in the following
figure appears.
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
If set to DHCP Relay, the router acts a surrogate DHCP
DHCP Mode
Relay Server Enter the DHCP server address provided by your ISP.
Server and relays the DHCP requests and reponses
between the remote server and the client.
29
Page 33

3.4.1.3 DHCP Static IP
Click DHCP Static IP in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears. You can assign the IP addresses on the LAN to the specific individual
PCs based on their MAC address.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
IP Address It specifies the IP address of the IP address pool.
Mac Address Enter the MAC address of a PC on the LAN.
Add After entering the IP address and MAC address,
click it. A row will be added in the DHCP Static IP
Table.
Delete Selected Select a row in the DHCP Static IP Table, then
click it, this row is deleted.
Undo Click it to refresh this page.
DHCP Static IP Table It shows the assigned IP address based on the
MAC address.
3.4.2 WAN
Choose Network > WAN. The WAN page that is displayed contains WAN, ATM
Setting, and ADSL Setting.
3.4.2.1 WAN
Click WAN in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure appears.
30
Page 34

In this page, you can configure WAN interface of your router.
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
Default Route Selection You can choose Auto or Specified.
VPI
VCI
Encapsulation You can choose LLC and VC-Mux.
Channel Mode
Enable NAPT
Enabel IGMP You can enable or disable IGMP function.
The virtual path between two points in an
ATM network, ranging from 0 to 255.
The virtual channel between two points in an
ATM network, ranging from 32 to 65535 (1 to
31 are reserved for known protocols)
You can choose 1483 Bridged, 1483 MER,
PPPoE, PPPoA, or 1483 Routed.
Select it to enable the NAPT function of the
router. If you do not select it and you want to
access the Internet normally, you must add a
route on the uplink equipment. Otherwise, the
access to the Internet fails. Normally, it is
required to enable NAPT.
31
Page 35

Field Description
PPP Settings
User Name
Password
Type
Idle Time (min)
WAN IP Settings
Type
Local IP Address
Remote IP Address
Netmask It is the subnet mask of the local IP address.
Unnumbered
Add
Modify
The correct user name that your ISP has
provided to you.
The correct password that your ISP has
provided to you.
You can choose Continuous, Connect on
Demand, or Manual.
If select connect on demand, you need to
enter the idle timeout time. Within the preset
minutes, if the router does not detect the flow
of the user continuously, the router
automatically disconnects the PPPoE
connection.
You can choose Fixed IP or DHCP. If select
fixed IP, you should enter the local IP
address, remote IP address and subnet
mask. If set to use DHCP, the router is a
DHCP client, the WAN IP address is
assigned by the remote DHCP server.
It is the IP address of WAN interface that is
provided by your ISP.
This is the gateway IP address that is
provided by your ISP.
Select this checkbox to enable IP
Unnumbered function.
After configuring the parameters of this page,
click it to add a new PVC into the current ATM
VC table.
Select a PVC in the current ATM VC table,
then modify the parameters of this PVC. After
finishing, click it to apply the change of this
PVC.
32
Page 36

Field Description
This table shows the existed PVCs. It shows
the Interface name, channel mode, VPI/VCI,
Current ATM VC Table
Click in the PPPoE mode. The page shown in the following figure appears.
In this page, you can configure parameters of this PPPoE PVC.
encapsulation mode, local IP address,
remote IP address and other information. The
maximum item of this table is eight.
Click it, the PPP Interface-Modify page
appears. You can modify the PVCs’
parameters.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Protocol The protocol type used for this WAN
connection.
ATM VCC The ATM virtual circuit connection assigned for
33
Page 37

Field Description
this PPP interface (VPI/VCI).
Login Name The login name provided by your ISP.
Password The password provided by your ISP.
Authentication Method You can choose AUTO, CHAP, or PAP.
Connection Type You can choose Continuous, Connect on
Demand, or Manual.
Idle Time (s) If choose Connect on Demand, you need to
enter the idle timeout time. Within the preset
minutes, if the router does not detect the flow of
the user continuously, the router automatically
disconnects the PPPoE connection.
Bridge You can choose Bridged Ethernet, Bridged
PPPoE, or Disable Bridge.
AC-Name The accessed equipment type.
Service-Name The service name.
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
Return Click it to return to the WAN Interface page.
Undo Click it to refresh this page.
3.4.2.2 ATM Setting
Click ATM Setting in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears.
In this page, you can configure the parameters of the ATM, including QoS, PCR,
CDVT, SCR, and MBS
34
Page 38

The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
VPI The virtual path identifier of the ATM PVC.
VCI The virtual channel identifier of the ATM PVC.
QoS The QoS category of the PVC. You can choose
UBR, CBR, rt-VBR, or nrt-VBR.
PCR The maximum rate at which cells can be
transported along a connection in the ATM
network.
CDVT The amount of delay permitted between ATM
cells (expressed in microseconds).
SCR The maximum rate that traffic can pass over a
PVC without the risk of cell loss.
MBS The maximum number of cells that can be
transmitted at the PCR.
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
Undo Click it to refresh this page.
3.4.2.3 ADSL Setting
Click ADSL Setting in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears.
35
Page 39

In this pae, you can select the DSL modulation. Mostly, you need to remain this
factory default settings. The router supports these modulations: G.lite, G.Dmt,
T1.413, ADSL2, ADSL2+, AnnexL, and AnnexM. The router negotiates the
modulation modes with the DSLAM.
3.4.3 WLAN
Choose Network > WLAN. In the WLAN page that is displayed contains Basic
Setting, Security, Access Control, multi-SSID, Advance Setting, and WPS.
3.4.3.1 Basic Setting
Click Basic Setting in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can configure the parameters for wireless LAN clients
that may connect to the router.
36
Page 40

The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Choose the working mode of the router. You can
Band
Mode
SSID
Channel Number
choose 2.4 GHz (B), 2.4 GHz (G), or 2.4 GHz (B
+ G). By defaut, the band is 2.4 GHz (B + G).
Choose the network modle of the router, which is
varied according to the software. By defaut, the
network model of the router is AP.
The service set identification (SSID) is a unique
name to identify the router in the wireless LAN.
Wireless stations associating to the router must
have the same SSID. Enter a descriptive name
that is used when the wireless client connecting to
the router.
A channel is the radio frequency used by
802.11b/g wireless devices. You may have a
choice of channels (for your region) and you
should use a different channel from an adjacent
AP to reduce the interference. Interference and
degrading performance occurs when radio signal
from different APs overlap.
37
Page 41

Field Description
Choose a channel from the drop-down list box.
Radio Power
(Percent)
Show Active Clients
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
3.4.3.2 Security
Click Security in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure appears.
You can choose the transmission power of the
radio signal. It is recommended to choose the
default value 100%.
Click it to view the information of the wireless
clients that are connected to the router.
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
Encryption Configure the wireless encryption mode. You can
38
Page 42

Field Description
choose None, WEP, WPA (TKIP), WPA (AES),
WPA2 (AES), WPA2 (TKIP), or WPA2 Mixed.
Wired equivalent privacy (WEP) encrypts
data frames before transmitting over the
wireless network.
Wi-Fi protected access (WPA) is a subset of
the IEEE802.11i security specification draft.
WPA2 Mixed is the collection of WPA and
WPA2 encryption modes. The wireless client
establishes the connection between the
router through WPA or WPA2.
Key differences between WPA and WEP are user
authentication and improved data encryption.
It is available when you set the encryption mode
Set WEP Key
WPA Authentication
Mode
Click Set WEP Key, and the following page appears.
to WEP. Click it, the Wireless WEP Key Setup
page appears.
Select Personal (Pre-Shared Key), enter the
pre-shared key in the Pre-Shared Key field.
Select Enterprise (RADIUS), enter the port,
IP address, and password of the Radius
server. You need to enter the username and
password provided by the Radius server
when the wireless client connects the router.
If the encrypton is set to WEP, the router uses
802.1 X authentication, which is Radius
authentication.
39
Page 43

The following describes the parameters and button of this page:
Field Description
Key Length
Key Format
Default Tx Key
Encryption Key 1
to 4
Choose the WEP key lenth. You can Choose 64-bit
or 128-bit.
If you choose 64-bit, you can choose ASCII (5
characters) or Hex (10 characters).
If you choose 128-bit, you can choose ASCII
(13 characters) or Hex (26 characters).
Choose the index of WEP Key. You can choose Key
1, Key 2, Key 3, or Key 4.
The Encryption keys are used to encrypt the data.
Both the router and wireless stations must use the
same encryption key for data transmission.
If you choose 64-bit and ASCII (5 characters),
enter any 5 ASCII characters.
If you choose 64-bit and Hex (10 characters),
enter any 10 hexadecimal characters.
40
Page 44

Field Description
If you choose 128-bit and ASCII (13
characters), enter any 13 ASCII characters.
If you choose 128-bit and Hex (26 characters),
enter any 26 hexadecimal characters.
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
3.4.3.3 Access Control
Click Advanced Setting in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can configure the access control of the wireless
clients.
Choose Allow Listed in the Wireless Access Control Mode field to enable
white list function. Only the devices whose MAC addresses are listed in the
Current Access Control List can access the router.
Choose Deny Listed in the Wireless Access Control Mode field to enable
black list function. The devices whose MAC addresses are listed in the Current
Access Control List are denied to access the router.
41
Page 45

3.4.3.4 multi-SSID
Click multi-SSID in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears.
The following table describes parameterand button of this page:
Field Description
SSID The service set identification (SSID) is a unique name
to identify the router in the wireless LAN.
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
42
Page 46

3.4.3.5 Advance Setting
Click Advance Setting in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can configure the wireless advanced parameters. It is
recommended to use the default parameters.
Note:
The parameters in the Wireless Advanced Settings page are modified by
the professional personnel, it is recommended to keep the default values.
The following table describes the parameters and button of this page:
Field Description
Select the router operating in the open system or
encryption authentication. You can choose Open
Authentication
System, Shared Key, or Auto.
In the open system, the wireless client can
directly connect to the device
43
Page 47

Field Description
In the encryption authentication, the wireless
client connects to the router through the
shared key.
Choose the transmission rate of the wireless data.
Data Rate
Broadcast SSID
Relay Blocking
Ethernet to
Wireless Blocking
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
3.4.3.6 WPS
Click WPS in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure appears.
You can choose Auto, 1 M, 2 M, 5.5 M, 11 M, 6 M,
9 M, 12 M, 18 M, 24 M, 36 M, 48 M, or 54 M.
Select whether the router broadcasts SSID or not.
You can select Enable or Disable.
Select Enable, the wireless client searchs the
router through broadcasting SSID.
Select Disable to hide SSID, the wireless
clients can not search the SSID.
Wireless isolation. Select Enable, the wireless
clients that are connected to the router can not
intercommunication.
Wheteher the wireless network can communicate
with the Ethernent network or not.
44
Page 48

WPS Authentication: The WPS service is enabled by default.
There are there methods used in the Wi-Fi Protected Setup. In order to use wps
authentication, you can select one method from the following there methods.
Press the WPS button on the rear panel for more than 3 seconds.
The router generates PIN, see the above figure. Click Regenerate PIN to
generate a new PIN, then click Start PCB, press WPS button on the
wireless client simultaneously. The wireless client automatically establishes
the connection with the router through the encryption mode, and you need
not to enter the key.
The wireless client generates PIN. In the above figure, enter PIN of the
wireless client in the Client PIN Number field, then click Start PIN to
establish the connection.
Note:
The wireless client establishes the connection with the router through WPS
negotiation.The wireless client must support WPS.
3.5 Service
In the navigation bar, choose Service. The Service page that is displayed
contains DNS, Firewall, UPNP, IGMP Proxy, TR069, and ACL.
3.5.1 DNS
Choose Service > DNS. The DNS page that is displayed contains DNS and
DDNS.
3.5.1.1 DNS
Click DNS in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure appears.
Domain name system (DNS) is an Internet service that translates the domain
name into IP address. Because the domain name is alphabetic, it is easier to
remember. The Internet, however, is based on IP addresses. Every time you use
a domain name, a DNS service translates the name into the corresponding IP
address. For example, the domain name www.example.com might translate to
198.105.232.4. The DNS system has its own network. If one DNS server does
45
Page 49

not know how to translate a particular domain name, it asks another one, and so
on, until the correct IP address is returned.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Attain DNS
Automatically
Set DNS
Manually
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
Reset Selected Click it to refresh this page.
Select it, the router accepts the first received DNS
assignment from one of the PPPoA, PPPoE or MER
enabled PVC(s) during the connection establishment.
Select it, enter the primary and optional secondary
DNS server IP addresses.
3.5.1.2 DDNS
Click DDNS in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure appears.
46
Page 50

The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
DDNS provider Choose the DDNS provider name.
Hostname The DDNS identifier.
Interface The WAN interface of the router.
Enable Enable or disable DDNS function.
Username The name provided by DDNS provider.
Password The password provided by DDNS provider.
Email The email provided by DDNS provider.
Key The key provided by DDNS provider.
3.5.2 Firewall
Choose Service > Firewall. The Firewall page that is displayed contains IPPort
Fileter, MAC Filter, URL Blocking, Virtual Server, DMZ Setting, ALG Setting,
and DoS Setting.
47
Page 51

3.5.2.1 IPPort Filter
Click IPPort Filter in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears. Entries in this table are used to restrict certain types of data packets
through the gateway. These filters are helpful in securing or restricting your local
network.
Click Apply Changes to save the settings of this page.
Click Add to add a new rule of the IP/Port filter.
3.5.2.2 MAC Filter
Click MAC Filter in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure appears.
Entries in this table are used to restrict certain types of data packets from your
local network to Internet through the gateway. These filters are helpful in securing
or restricting your local network.
48
Page 52

Click Apply Changes to save the settings of this page.
Click Add to add a new rule of the MAC filter.
3.5.2.3 URL Blocking
Click URL Blocking in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears. This page is used to block a fully qualified domain name (FQDN), such
as tw.yahoo.comand and filtered keyword. You can add or delete FQDN and
filtered keyword.
49
Page 53

The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
URL Blocking
Capability
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
Keyword The keyword to block.
Add Keyword Click it to add the keyword to the keyword filtering
Delete Selected
Keyword
URL Blocking
Table
You can choose Disable or Enable.
Choose Disabled to turn off URL blocking and
keyword filtering.
Choose Enable to block access to the URLs and
keywords specified in the URL Blocking Table
and Keyword Filtering Table.
table.
Select a row in the Keyword Filtering Table and click it
to delete the row.
A list of the URL (s) to which access is blocked.
3.5.2.4 Virtual Server
Click Virtual Server in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears.
50
Page 54

The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
You can choose the common service type, such as
AUTH, DNS, or FTP. You can also define a service
name.
If you choose the common service type, the
Service Type
Protocol
WAN Setting You can choose Interface or Ip Address.
WAN Interface Choose the router port that uses virtual server.
WAN Port Enter the access port on the WAN.
LAN Open Port Enter the port number of the specified service type.
LAN Ip Address
corresponding WAN communication
port/service host communication port has the
default settings.
If you define service type, you need to enter the
corresponding port.
Choose the transport layer protocol that the service
type uses. You can choose TCP or UDP.
Enter the IP address of the virtual server. It is in the
same network segment with LAN IP address of the
router.
51
Page 55

3.5.2.5 DMZ Setting
Click DMZ Setting in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears. A demilitarized zone is used to provide Internet services without
sacrificing unauthorized access to its local private network. Typically, the DMZ
host contains services accessible to Internet traffic, such as web (HTTP) servers,
FTP servers, SMTP (e-mail) servers and DNS servers.
Step 1 Select Enable DMZ to enable this function.
Step 2 Enter an IP address of the DMZ host.
Step 3 Click Apply Changes to save the settings of this page.
3.5.2.6 DoS Setting
Click DoS Setting in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears. Denial-of-service attack (DoS Attack) is a type of attack on a network
that is designed to bring the network to its knees by flooding it with useless traffic.
In this page, you can prevent DoS attacks.
52
Page 56

3.5.3 UPNP
Choose Service > UPNP. The page shown in the following figure appears. This
page is used to configure UPnP. The system acts as a daemon after you enable
it.
53
Page 57

3.5.4 IGMP Proxy
Choose Service > IGMP Proxy in the left pane. The page shown in the following
figure appears. IGMP proxy enables the system to issue IGMP host messages
on behalf of hosts that the system discovered through standard IGMP interfaces.
The system acts as a proxy for its hosts after you enable it.
3.5.5 TR069
Choose Service > TR069. The page shown in the following page appears. In this
page, you can configure the TR-069 of the router.
54
Page 58

The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page.
Field Description
ACS
55
Page 59

Field Description
URL The URL of the auto-configuration server
to connect to.
User Name The user name for logging in to the ACS.
Password The password for logging in to the ACS.
Periodic Inform Enable Select Enable to periodically connect to
the ACS to check for configuration
updates.
Periodic Inform Interval Specify the amount of time between
connections to ACS.
Connection Request
User Name The username to connect the router from
the ACS.
Password The password to connect the router from
the ACS.
Debug
ACS Certificates CPE Specify whether to check the ACS
certification of the router.
Show Message Select Enable to display ACS SOAP
messages on the serial console.
CPE Sends GetRPC Select Enbale, the CPE contact the ACS
to obtain configuration updates.
Skip MReboot Specify whether to send an MReboot event
code in the inform message.
Delay Specify whether to start the TR-069
program after a short delay.
Auto-Execution Specify whether to automatically start the
TR-069 after the router is powered on.
CT Inform Extension Specify whether to support China Telecom
extension inform type.
Apply Changes Save the settings in this page.
Undo Refresh this page.
Certificate Management
CPE Certificate Password The certificate password of the router
Apply Save the settings of this page.
56
Page 60

Field Description
CPE Certificate Click it to browse and upload the certificate
for the router.
CA Certificate Click it to browse and upload the CA
certificate for the router.
3.5.6 ACL
Choose Service > ACL. The page shown in the following figure appears.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Direction Select
LAN ACL Switch Enable or disable ACL.
IP Address
Select the router interface. You can select LAN or
WAN.
Enter the IP address of the specified interface. Only
the IP address that is in the same network segment
with the IP address of the specified interface can
access the router.
57
Page 61

Field Description
You can choose the following services from LAN or
Services Allowed
Add
Reset Click it to refresh this page.
WAN: web, telnet, ftp, tftp, snmp, or ping. You can
also choose all the services.
After setting the parameters, click it to add the
Current ACL Table.
3.6 Advance
In the navigation bar, choose Advance. The Advance page that is displayed
contains Bridge Setting, Routing, Port Mapping, QoS, SNMP, and Others.
3.6.1 Bridge Setting
Choose Advance > Bridge Setting. The page shown in the following figure
appears. This page is used to configure the bridge parameters. In this page, you
can change the settings or view some information in the bridge mode and its
attached ports.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Aging Time If the host is idle for 300 seconds (default value), its
entry is deleted from the bridge table.
802.1d Spanning
Tree
You can select Disable or Enable.
Select Enable to provide path redundancy while
58
Page 62

Field Description
preventing undesirable loops in your network.
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
Undo Click it to refresh this page.
Show MACs Click it to show a listing of the learned MAC
addresses for the bridge.
Click Show MACs. The page shown in the following figure appears. This table
shows a list of learned MAC addresses for this bridge.
3.6.2 Routing
Choose Advance > Routing. The Routing page that is displayed contains
Static Route and RIP.
3.6.2.1 Static Route
Click Static Route in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can configure the routing information. You can add or
delete IP routes.
59
Page 63

The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Enable Select it to use static IP routes.
Destination Enter the IP address of the destination device.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask of the destination device.
Next Hop Enter the IP address of the next hop in the IP route to the
destination device.
Metric The metric cost for the destination.
Interface The interface for the specified route.
Add Route Click it to add the new static route to the table.
Update Select a row in the table to populate the configuration
fields with that row’s values. Make any necessary
changes to those values and click it to save those
changes.
Delete
Selected
Show
Routes
Static Route
Table
Select a row in the table and click it to delete the row.
Click it, the IP Route Table appears. You can view a list
of destination routes commonly accessed by your
network.
A list of the previously configured static IP routes.
60
Page 64

Click Show Routes. The table shown in the following figure appears. The table
shows a list of destination routes commonly accessed by your network.
3.6.2.2 RIP
Click RIP in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure appears. If you
are using this device as a RIP-enabled router to communicate with others who is
using the Routing Information Protocol (RIP), enable the RIP. This page is used
to select the interfaces on your devices that use RIP, and the version of the
protocol used.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
RIP Select On, the router communicates with other
RIP-enabled devices.
61
Page 65

Field Description
Apply Click it to save the settings of this page.
Interface The router interface that uses RIP.
Recv Version The interface type to accept RIP messages. You can
choose RIP1, RIP2, or Both.
Choose RIP1 indicates the router receives RIP v1
messages.
Choose RIP2 indicates the router receives RIP v2
messages.
Choose Both indicates the router receives RIP v1
and RIP v2 messages.
Send Version The working mode for sending RIP messages. You can
choose RIP1 or RIP2.
Choose RIP1 indicates the router broadcasts RIP1
messages only.
Choose RIP2 indicates the router multicasts RIP2
messages only.
Add Click it to add the RIP interface to the Rip Config Table.
Delete Select a row in the Rip Config Table and click it to
delete the row.
Rip Config Table A list of the router interfaces that enble RIP.
3.6.3 Port Mapping
Choose Advance > Port Mapping. The page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can bind the WAN interface and the LAN interface to
the same group.
62
Page 66

The procedure for manipulating a mapping group is as follows:
Step 1 Select Enable to enable this function.
Step 2 Select a group from the table.
Step 3 Select interfaces from the WAN and LAN interface list and add them to
the grouped interface list using the arrow buttons to manipulate the
required mapping of the ports.
63
Page 67

Step 4 Click Apply to save the changes.
3.6.4 QoS
Choose Advance > QoS. The page shown in the following figure appears.
Entries in this table are used to assign the precedence for each incoming packet
based on physical LAN port, TCP/UDP port number, and source/destination IP
address/subnet masks.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
IP QoS You can choose disable or enable. By default, IP QoS
64
Page 68

Field Description
is disabled.
You need to enable IP QoS, and then you can set the
parameters in this page.
QoS Policy You can choose stream based, 802.1p based, or
DSCP based.
Schedule Mode You can choose strict prior or WFQ (4:3:2:1).
Src IP The IP address of the source data packet.
Src Mask The subnet mask of the source IP address.
Src Port The port of the source data packet.
Dest IP The IP address of the destination data packet.
Dest Mask The subnet mask of the destination IP address.
Dest Port The port of the destination data packet.
Protocol The protocol responds to the IP QoS rules. You can
choose TCP, UDP, or ICMP.
Phy Port The LAN interface responds to the IP QoS rules,
including four LAN interfaces, one AP interface, and
four virtual AP interfaces.
Set priority The priority of the IP QoS rules. P0 is the highest
priority and P3 is the lowest.
IP Precedence You can choose from 0 to 7 define the priority in the
ToS of the IP data packet.
IP ToS The type of IP ToS for classifying the data package
You can choose Normal Service, Minimize Cost,
Maximize Reliability, Maximize Throughput, or
Minimize Delay.
802.1p You can choose from 0 to 7.
delete Select a row in the table and click it to delete the row.
delete all Select all the rows in the table and click it to delete the
rows.
3.6.5 SNMP
Choose Advance > SNMP. The page shown in the following figure appears.
65
Page 69

The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Trap IP Address
Community name
(read-only)
Community name
(read-write)
Enter the IP address of trap host. The trap
information is sent to the host.
The common character string that is used for
obtaining the device information. It is like
password, through which SNMP application
entry obtains the device information directly.
Modify the common character string that is
configured by the device. It is like password,
through which SNMP application entry
modifies the device information directly.
3.6.6 Others
Choose Advance > Others. The page shown in the following figure appears.
66
Page 70

3.7 Admin
In the navigation bar, choose Admin. The Admin page that is displayed contains
Commit/Reboot, Upgrade, System Log, Password, and Time Zone.
3.7.1 Commit/Reboot
Choose Admin > Commit/Reboot. The page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can set the router reset to the default settings or set
the router to commit the current settings.
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
Factory Default
Configuration
Save Current
Configuration
Select it to reset the router to the default
settings.
Select it to save the current settings and reboot
the router.
67
Page 71

Field Description
Reboot Click it to reboot the router.
3.7.2 Upgrade
Choose Admin > Upgrade. The Upgrade page that is displayed contains
Upgrade Firmware and Backup/Restore.
3.7.2.1 Upgrade Firmware
Click Upgrade Firmware in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure
appears.In this page, you can upgrade the firmware of the router.
I Note:
Do not turn off your router or press the Reset button while this procedure is in
progress.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Select File Click Browse to select the firmware file.
Upload
Reset Click it to begin selecting the firmware file.
Select the firmware file and click Upload to begin
upgrading the firmware.
68
Page 72

3.7.2.2 Backup/Restore
Click Backup/Restore. The page shown in the following figure appears. In this
page, you can backup the current settings to a file and restore the settings from
the file which was saved previously.
Note:
Do not turn off your router or press the Reset button while these procedures
are in progress.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Save Settings to
File
Load Settings from
File
Upload
Click it and select the path. Then you can save the
configuration file of the router.
Click Browse to select the configuration file.
Select the configuration file of the router. Click
Upload to begin restoring the router configuration.
3.7.3 System Log
Choose Admin > System Log. The page shown in the following figure appears.
In this page, you can view the log information.
69
Page 73

3.7.4 Password
Choose Admin > Password. The page shown in the following figure appears. In
this page, you can change the password of the user, including admin and user.
By default, the super user name and password are admin and admin. The
common user name and password are user and user.
70
Page 74

The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
User Name You can choose admin or user.
New Password
Confirmed Password Enter the new password again.
Set to Default
Password
Enter the password to which you want to change
the old password.
After selecting it, the password you set does not
take effect. It keeps the default password.
3.7.5 Time Zone
Choose Admin > Time Zone. The page shown in the following figure appears. In
this page, you can set the system time manually or get the system time from the
time server.
71
Page 75

3.8 Diagnostic
In the navigation bar, choose Diagnostic. The Diagnostic page that is displayed
contains Ping, ATM Loopback, ADSL and Diagnostic.
3.8.1 Ping
Choose Diagnostic > Ping. The page shown in the following figure appears.
72
Page 76

The following table describes the parameters and buttons in this page:
Field Description
Host Enter the IP address.
PING Click it to begin to Ping the host address.
3.8.2 ATM Loopback
Choose Diagnostic > ATM Loopback. The page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can use VCC loopback function to check the
connectivity of the VCC.
3.8.3 ADSL
Choose Diagnostic > ADSL. The page shown in the following figure appears. It
is used for ADSL tone diagnostics.
73
Page 77

Click Start to begin ADSL tone diagnostics.
3.8.4 Diagnostic Test
Choose Diagnostic > Diagnostic Test. The page shown in the following figure
appears. In this page, you can test the DSL connection.
Click Run Diagnostic Test to begin testing.
74
Page 78

4 Statement
4.1 Europe – EU Declaration of Conformity
This device complies with the essential requirements of the R&TTE Directive
1999/5/EC. The following test methods have been applied in order to prove
presumption of conformity with the essential requirements of the R&TTE Directive
1999/5/EC:
- EN 60950-1: 2001
Safety of Information Technology Equipment
- EN50385 : 2002
Product standard to demonstrate the compliance of radio base stations and
fixed terminal stations for wireless telecommunication systems with the basic
restrictions or the reference levels related to human exposure to radio
frequency electromagnetic fields (110MHz - 40 GHz) - General public
- EN 300 328 V1.7.1: (2006-10)
Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Wideband
Transmission systems; Data transmission equipment operating in the 2,4 GHz
ISM band and using spread spectrum modulation techniques; Harmonized EN
covering essential requirements under article 3.2 of the R&TTE Directive
- EN 301 489-1 V1.8.1: (2008-04)
Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM);
ElectroMagnetic Compatibility (EMC) standard for radio equipment and
services; Part 1: Common technical requirements
- EN 301 489-17 V1.2.1 (2002-08)
Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM);
ElectroMagnetic Compatibility (EMC) standard for radio equipment and
services; Part 17: Specific conditions for 2,4 GHz wideband transmission
75
Page 79

systems, 5 GHz high performance RLAN equipment and 5,8 GHz Broadband
Data Transmitting Systems.
This device is a 2.4 GHz wideband transmission system (transceiver),
intended for use in all EU member states and EFTA countries, except in
France and Italy where restrictive use applies.
In Italy the end-user should apply for a license at the national spectrum
authorities in order to obtain authorization to use the device for setting up
outdoor radio links and/or for supplying public access to telecommunications
and/or network services.
This device may not be used for setting up outdoor radio links in France and in
some areas the RF output power may be limited to 10 mW EIRP in the
frequency range of 2454-2483.5 MHz. For detailed information the end-user
should contact the national spectrum authority in France.
76
Page 80

4.2 Federal Communication Commission Interference
Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
77
Page 81

equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which
can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to
try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by
the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to
operate this equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject
to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with
minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
The availability of some specific channels and/or operational frequency bands are
78
Page 82

country dependent and are firmware programmed at the factory to match the
intended destination. The firmware setting is not accessible by the end user.
4.3 Part 68 statements
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the FCC rules and the requirements
adopted by the ACTA. On the bass unit of this equipment is a label that contains,
among other information, a product identifier in the format
US: SGEDL01BGAW95Z97. If requested, this number must be provided to the
telephone company.
The REN is used to determine the number of devices that may be connected to a
telephone line. Excessive RENs on a telephone line may result in the devices not
ringing in response to an incoming call. In most but not all areas, the sum of RENs
should not exceed five (5.0). To be certain of the number of devices that may be
connected to a line, as determined by the total RENs, contact the local telephone
company. For products approved after July 23, 2001, the REN for this product is
part of the product identifier that has the format US: SGEDL01BGAW95Z97. The
digits represented by 01 are the REN without a decimal point (e.g., 03 is a REN of
0.3). For earlier products, the REN is separately shown on the label.
If your equipment causes harm to the telephone network, the telephone company
may discontinue your service temporarily. If possible, they will notify you in
advance. But if advance notice is not practical, you will be notified as soon as
possible. You will be informed of your right to file a complaint with the FCC. Your
telephone company may make changes in its facilities, equipment, operations or
procedures that could affect the proper functioning of your equipment. If they do,
you will be notified in advance to give you an opportunity to maintain uninterrupted
telephone service.
79
Page 83

If you experience trouble with this telephone equipment, please contact the
following address and phone number for information on obtaining service or
repairs.
The telephone company may ask that you disconnect this equipment from the
network until the problem has been corrected or until you are sure that the
equipment is not malfunctioning.
This equipment may not be used on coin service provided by the telephone
company. Connection to party lines is subject to state tariffs.
Company: Encore Electronics, Inc.
Address: 16483 Old Valley Blvd, La Puente, CA 91745
Tel no.: 626-336-4567
A plug and jack used to connect this equipment to the premises wiring and
telephone network must comply with the applicable FCC Part 68 rules and
requirements adopted by the ACTA. A compliant telephone cord and modular plug
is provided with this product. It is designed to be connected to a compatible
modular jack that is also compliant. See installation instructions for details.
80
 Loading...
Loading...