Page 1
Safety classification
Protection against electric-shock:
Class I Equipment- type B application
by operation mode
Intermittent loading, continuous operation
The equipment cannot be used with flammable anesthetic gas mixed with air
or oxygen or nitrous oxide
Safety symbols
Symbol Content
Attention, consult accompanying documents.
Type B equipment.
Dangerous voltage.
X-ray radiate.
Ground.
Ionizing radiation.
Large spot.
i
Page 2
Small spot.
This symbol indicates that the waste of electrical and
electronic equipment must not be disposed as unsorted municipal
waste and must be collected separately. Please contact an
authorized representative of the manufacturer or an authorized
waste management company for information concerning the
decommissioning of your equipment.
Advisory Messages
Danger: Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will
result death or serious injury. This signal word is to be limited to the most
extreme situations.
Warning: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
could result death or serious injury.
Caution: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may
result in minor or moderate injury. It may also be used to alert against unsafe
practices.
Note: Indicates information or a company policy that relates directly or
indirectly to the safety of personnel or protection of property. This signal word
is associated directly with a hazard or hazardous situation.
ii
Page 3

Limited Condition For Transportation and Storage
Packed products may be stored up to 15 weeks in conditions as follows:
1. Environment temperature:-20~+45℃
2. Relative humidity range:20~80% no condensation
3. Range of atmospheric pressure :700~1060hPa
4. stored indoor without corrosive gas and with proper ventilation
iii
Page 4

Please contact your supplier of the manufacturer for repairs and maintenance if there is
any trouble of machine.
Manufacturer: Shenzhen Landwind Industry Co.,Ltd.
Address: 4F,Block E, Bijing Bldg.81, jingtian Road, Futian District, Shenzhen China
Call center: 400-700-3788
iv
Page 5

Content
Safety classification ............................................................................................................ i
Safety symbols ................................................................................................................... i
Advisory Messages ............................................................................................................ ii
Limited Condition For Transportation and Storage ............................................................ iii
1 Installation Condition ...................................................................................................... 5
1.1 Power Requirement ............................................................................................. 5
1.2 Room Requirement .............................................................................................. 5
1.3 Protection Requirement ....................................................................................... 5
2 Working principle of generator ....................................................................................... 6
2.1 Block diagram of circuit principle .......................................................................... 6
2.2 Principle of power and switch ............................................................................... 6
2.3 Generation and control principle .......................................................................... 7
2.4 X-ray tube filament heating principle .................................................................... 7
2.5 Start up and protection principles of rotary anode ................................................ 7
2.6 kV, mA and s interlock protection principle of capacity constraint ........................ 8
2.7 Control principle of radiography duration ............................................................. 8
2.8 Control principle of common radiography ............................................................. 8
2.9 Control principle of Bucky diaphragm radiography ............................................... 8
2.10 Fault detection principle ..................................................................................... 9
3 Installation .................................................................................................................... 10
3.1 Installation of Radiography Table ....................................................................... 10
3.2 Installation of column ......................................................................................... 10
3.3 X-ray Tube Installation ....................................................................................... 12
3.4 Operation Panel Installation ............................................................................... 13
3.5 Installation of Stand chest .................................................................................. 18
3.6 Generator Installation ......................................................................................... 18
3.6.1 Installation preparation ............................................................................. 18
1
Page 6

3.6.2 Connection between generator and tube ................................................. 19
3.6.3 Connection of generator mainframe and console .................................... 21
3.6.4 Connection of power cable ...................................................................... 22
4 Debugging and Calibration ........................................................................................... 24
4.1 X-ray debugging ................................................................................................. 24
4.1.1 Precautions in debugging ........................................................................ 24
4.1.2 Debug step by step .................................................................................. 24
4.1.3 Attentions during debugging .................................................................... 25
4.2 Collimator debugging ......................................................................................... 25
4.3 Generator debugging ......................................................................................... 25
4.3.1 Preparation before debugging.................................................................. 25
4.3.2 Rotating anode text .................................................................................. 26
4.3.3 Calibration of tube voltage ....................................................................... 26
4.3.4 Calibration of tube current ........................................................................ 27
4.3.5 Bucky text program .................................................................................. 29
4.3.6 Commissioning ........................................................................................ 29
5 Maintenance................................................................................................................. 30
5.1 Radiography Table ............................................................................................. 30
5.1.1 Regular maintenance ............................................................................... 30
5.1.2 Maintenance Record ................................................................................ 30
5.2 X-Ray Tube Assembly ........................................................................................ 31
5.2.1 Regular maintenance ............................................................................... 31
5.2.2 Year maintenance .................................................................................... 31
5.2.3 Maintenance Record ................................................................................ 31
5.3 Collimator ........................................................................................................... 32
5.3.1 Replacement of Lamp .............................................................................. 32
5.3.2 Recommended Maintenance Program .................................................... 32
5.3.3 Maintenance Record ................................................................................ 33
5.4 Generator ........................................................................................................... 33
2
Page 7

5.4.1 Regular maintenance ............................................................................... 33
5.4.2 Maintenance Record ................................................................................ 34
6 Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................ 35
6.1 Error Codes ........................................................................................................ 35
6.2 Key point in fault diagnosis ................................................................................ 36
6.2.1 Console .................................................................................................... 36
6.2.2 Interface unit ............................................................................................ 37
6.2.3 Mainframe control unit ............................................................................. 38
6.2.4 Pulse width modulation unit ..................................................................... 39
6.2.5 Auxiliary power ......................................................................................... 41
6.2.6 ±12V auxiliary power ................................................................................ 41
6.2.7 Sampling Unit .......................................................................................... 42
6.2.8 Protection Unit ......................................................................................... 43
6.2.9 Common troubleshooting judge ............................................................... 43
7 Attached figure ............................................................................................................. 45
3
Page 8

Page 9

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
1 Installation Condition
1.1 Power Requirement
1. External power requirement: single-phase 220V, diameter of connection line for
grid- cabinet, cabinet-generator phase line and diameter of earth line shall meet
requirement of electrical safety standard. Phase line, null line and earth line in the
distribution cabinet shall be equipped with terminals.
2. Installation shall conform to relevant specifications stipulated by power supply
authorities.
1.2 Room Requirement
1. Height of room shall be not less than 3m.
2. Protection of the room shall equal to 2.5mm lead equivalent, partition wall of
control room shall be brick or XF protective panel, the door is generally enclosed
Service
in sheet lead, radio protection shall meet national and local protection standards.
1.3 Protection Requirement
1. The brick wall of the examination room should has a thickness of 370mm
(equate with 2mm Al), the thickness of the concrete wall should be more than
200mm.
2. The lead glass thickness between examination room and operating room should
be more than 1.5mm lead equivalent, and field of vision should not less than 0.25
㎡,with height of 900mm from ground.
3. Roof is 1.0mm lead equivalent.
4. If the room is at the bottom of building, protection measure for the ceiling is
needed; the protection should not less than 2mm Al equivalent. If the room is not
at the bottom, there is not only the ceiling but ground is needed X-ray protection,
which also requires 2mmAl equivalent. While the room is at top, it just needed to
make a protection for ground.
5. If the room is at the bottom(either cottage or building), the glass of the
examination room should use lead glass with 1mmAl equivalent or 240mm brick
wall.
5
Page 10
Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
2 Working principle of generator
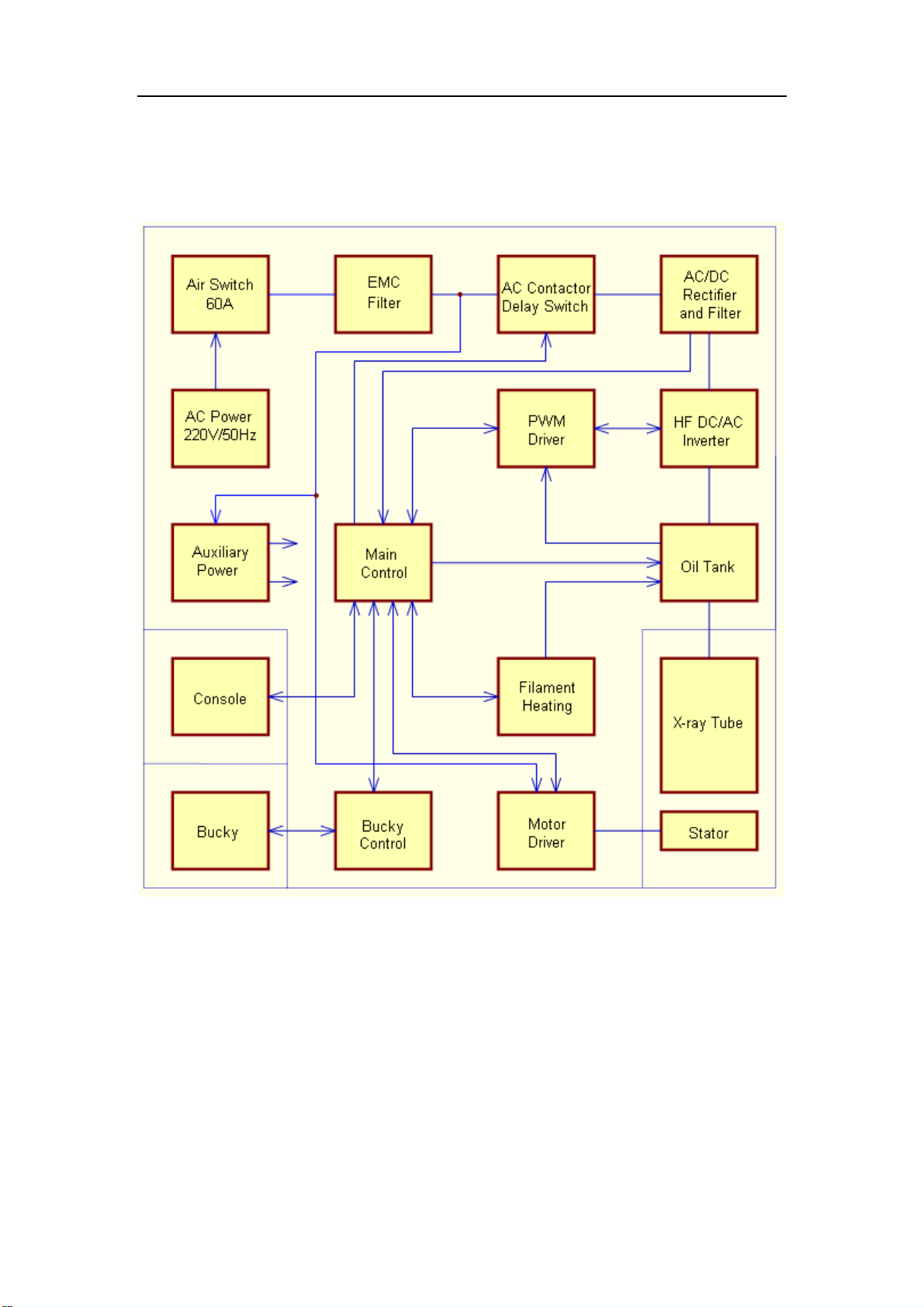
2.1 Block diagram of circuit principle
Figure 1 Block diagram of circuit principle
2.2 Principle of power and switch
The AC220V power connects to the mainframe via L1 and N of wiring terminal X1, and is
supplied to the inverter passing through air switch, filter, AC contact, rectifier module and
filter unit. Another line of L1 supply power to the auxiliary power supply, which outputs
+12V and -12V power to console and mainframe and auxiliary power to the driving circuit
for filament heating. After energization, the system is shutdown. When "Power On" key on
the console is pressed, the console send start orders to the mainframe which then
changes connector unit terminal X3-8 (power control terminal) to high level after receipt of
6
Page 11

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
the order, the soft charging relay K2 attracts, voltages from L1 perform soft charging to
filter unit capacitor through soft charging resistance R1and rectifier module. The charging
voltage is monitored and detected by connector unit X4-1 (“DC-”cold terminal),
X4-2(“DC+”hot terminal), , when the voltage exceeds 240Vdc, AC contact is pulled in,
voltages from L1 is sent to the inverter through AC contact, rectifier module V1 and filter
unit, and then the main power supply circuit is energized. The machine is ready for start,
X3-7 (“P_S”power status terminal) is at high level, the mainframe control unit sends
normal start signal to the console after receipt of ready-for-start signal, the whole machine
is standby.
2.3 Generation and control principle
After startup, AC 220V power is loaded on inverter after rectifying and wave-filtering; when
the console sends exposure order to the mainframe, the inverter acts, HF square wave
output is loaded on high voltage oil tank to generate high DC voltage. Voltage sampling
circuit of high voltage oil tank feedbacks sampling signals to pulse width modulation unit,
which generates real-control pulse width modulation signal to regulate high voltage and
consequently stabilizes high DC voltage.
Terminal “+kV FB” of generator oil tank top cover is feedback terminal of positive high
voltage, which outputs 1V equal to 10kV output at high voltage terminal; "“-kV FB”" is
feedback terminal of negative high voltage, which outputs -1V equal to -10kV output at
high voltage terminal.
2.4 X-ray tube filament heating principle
Generator heats the filament through pulse width modulation AC voltage. Under different
kV and mA combinations, the control procedure sends control signal of filament data
through digital analog converting circuit, this signal controls filament heating inverter to
generate pulse width modulation AC voltage on filament heating inverter. This HF voltage
excite heating of filament.
Note: Filament is in pre-heating status during standby status.
2.5 Start up and protection principles of rotary anode
Press the Prep. Key on the console key, the CPU issued a directive, rotating anode starter
terminal X5-5 is at low level, and rotating anode starter is energized to start. Rotating
anode of X-ray tube start, after 0.8-1.2 seconds, rotating anode starter automatically
switch to the running state, X-ray tube anode run normally, rotating anode starter terminal
X5-6 becomes low.
Until the exposure is finished the main control unit issued a directive, rotating anode
7
Page 12

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
starter terminal X5_5 becomes high level, rotating anode starter automatically switch to
the brake status, X-ray tube rotating anode brakes, after 8 -- 10 seconds, the speed
drops to a low value, then the brake doesn’t work any more, rotating anode starter stop
working self-motion.
If the CPU to give directions to the rotating anode starter, but because X-ray tube rotating
anode can not be rotated or not meet the normal operating voltage, the level of the
rotating anode starter terminal X5_6 is low, the host CPU detect that X-ray tube rotation
anode is not working properly, the generator will not output voltage, that radiation is
stopped, and shows on the console.
2.6 kV, mA and s interlock protection principle of capacity constraint
kV, mA and s interlock protection principle of capacity constraint is controlled by
micro-computer control system intelligent module according to tube capacity
characteristics calculation.
2.7 Control principle of radiography duration
Control circuit of radiography duration is digital circuit with double time limit function.
2.8 Control principle of common radiography
When the console is in radiography status, parameters, such as kV, mA, s/mAs values
and Bucky diaphragm are selectable on the console according to radiation condition.
When the position 1 of hand switch or the Prep. Key on the console is pressed, CPU of
main control unit sends the order after detecting the information, and then the filament
heating circuit rapidly heats the cathode filament of the X-ray tube, rotary anode driver
starts up the rotary anode of X-ray tube for operation. When the position 2 of the hand
switch or the exposure key on the console is pressed, pulse width modulation circuit
generates pulse width modulation signal to drive the inverter, which then drives the high
voltage oil tank to generate high voltage which is loaded on the X-ray tube to generate
X-ray and to perform radiography. If the hand switch or the exposure key is loosed during
radiation, the exposure radiography will immediately stop.
2.9 Control principle of Bucky diaphragm radiography
Table or vertical chest radiography stand Bucky diaphragm is selectable on the console,
when the position 1 of the hand switch or the prep. Key on the console is pressed, the
rotary anode starts up to heat the filament, and when the position 2 of the hand switch or
the exposure key on the console is pressed, control relays of Bucky diaphragm and chest
radiography stand Bucky diaphragm are pulled in, the light-emitting diode V13 bright, the
Bucky diaphragm pickup winding is energized and starts to work, and pickup grid moves
8
Page 13

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
back and forth, after 0.5s latency, the radiography exposure begins, after pre-setting
exposure time, the control circuit is reset to the status as before.
2.10 Fault detection principle
Mainframe control system performs self-inspection during electrification and performs
monitoring to all units during operation of the mainframe, in case of abnormal condition,
the system may suspend in real-time, send fault information to the console and send fault
alert signal.
When the grid has phase voltage lower than 170Vac or loses phase, terminal X3-7”P_S” is
at low level, the control system may generate power fault information code "E00" after
detecting this low level, the mainframe cut off main power supply.
When the position 1 of hand brake switch or the prep. Key is pressed, the control system
will monitor filament heating circuit and anode driving circuit. The filament is heated and
temperature will be increased, if the heating current is over-low or the heating voltage is
over-high, the control system will generate default information of filament unit as "E03".
Level of X3_12“FIL CON” of filament heating inverter which on the 21003C increases,
filament heating inverter cut off, at the same time, the main power supply disconnects.
When the rotary anode is driven abnormally, level of X5_6“M_S” of interface unit
decreases, the system detects the signal and generates anode default information "E04",
the main power supply is cut off.
During exposure, if the inverter components fail due to over-current or poor connection of
power components caused by discharge in the high voltage circuit, voltage of inverter
X1_6“OC_A” or X2_6“OC_B” will decrease below 4V. The protection circuit of the
pulse-width modulation unit begins working and cuts off the PWM signal; at the same time
the inverter stop working. At this moment, the LED indicator lamp on 21003C circuit board
lit, main control unit generates an interrupt signal to terminate the exposure operation,
close the power loop power, and send the wrong message "E01" or "E02"to the console.
9
Page 14

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
3 Installation
3.1 Installation of Radiography Table
Radiography table shall be placed horizontally on the floor of room, distance between
sliding seat of column and wall shall be not less than 1m for installation of column, and
then all guide rails on the machine shall be calibrated with leveler (horizontal and vertical
directions).
Note: After lay the radiography table horizontally, the table shall be firmly
attached to the ground with four expansion bolts.
3.2 Installation of column
1. Carried out the column from the box and moved to radiography table installation
location;
Note: For the column is heavy, it is needed at least four people to perform this
step; and the installers must be careful to avoid personal injury or damage of
the equipment.
2. Loose screw at the end-plate of the column guild with a screwdriver and remove the
end-plate;
End-plate
Limited block
Figure 2 End-plate
3. Raise the column upright slowly, slide the column sliding seat into the guild rail.
10
Page 15
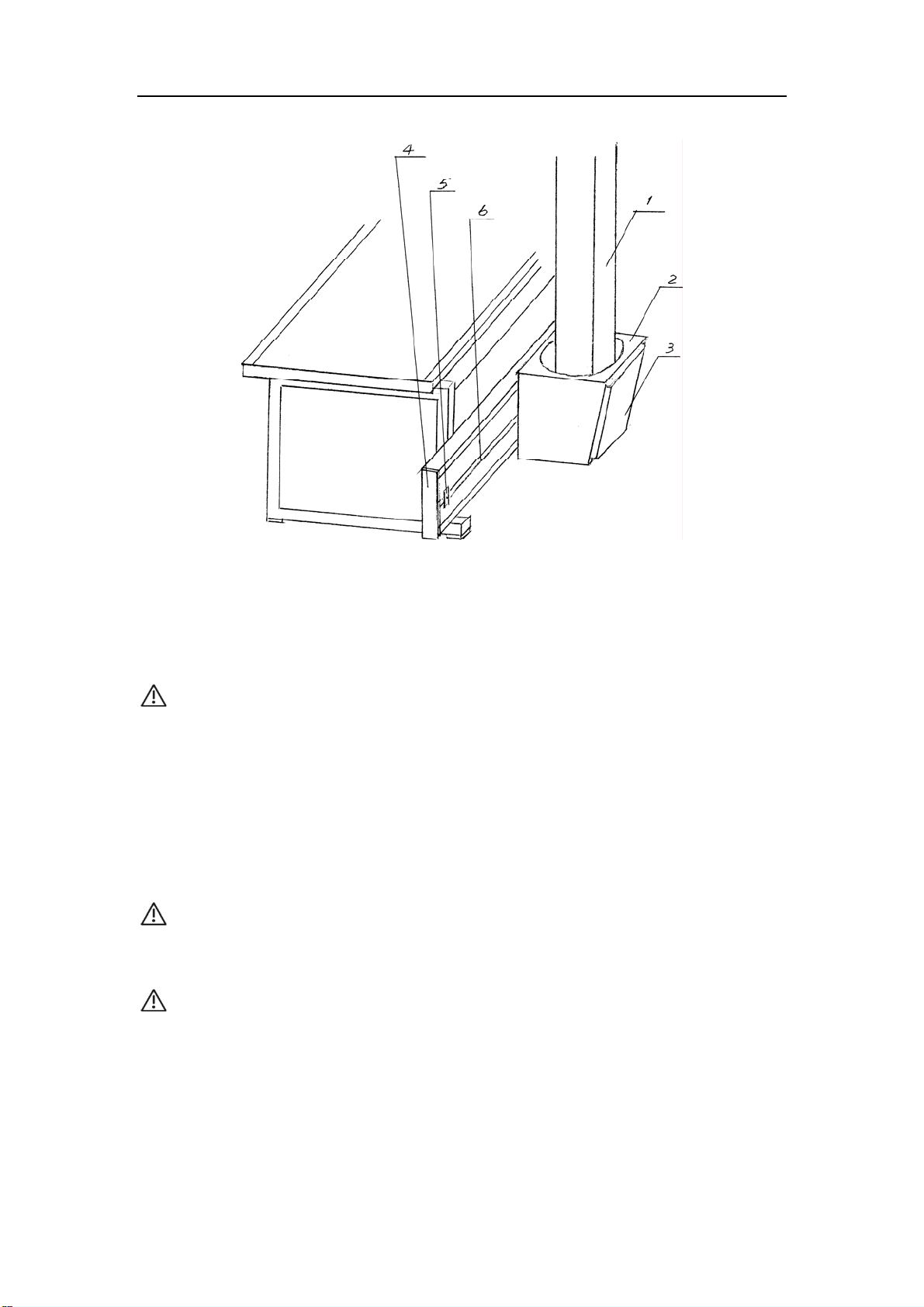
Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
1 Column 2 Column sliding seat 3 Back cover of column sliding seat
4 End-plate of guide rail 5 Limited block of guide rail 6 Column guide rail
Figure 3 Diagram of column installation
Warning: It is needed at least four people to perform to avoid personal injury or
damage of the equipment.
4. In this case, care shall be taken to avoid impaction of electromagnet, and then limited
block shall be installed, the column shall slide easily on the guide rail without clearance.
5. Set the end-plate back onto the guild rail and fixup it with installation screws.
Warning: For the column is heavy, care shall be taken to avoid impaction of
electromagnet.
Warning: When install columns, the weight inside the column will cause the
tube support frame automatically rise to the top of column; in order to avoid
personal injury or equipment damage, it is required that one person hold on the
support frame, and then slowly released until it rise to the top.
11
Page 16

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
3.3 X-ray Tube Installation
1. Installation of tube hoop. This step takes at least two people to work at the same time.
While one pull the tube supporting frame to a suitable height and keep it, the other align
mounting holes of support frame and tube hoop, and fix up with screws.
Fixed screws
Tube rotation lock screw
Figure 4 Installation of tube hoop
2. X-ray tube installation. Pull down the tube supporting frame to a suitable height and
keep it, then lay the tube on the hoop. Gently rotate the tube back and forth, so that the
outlet port of tube vertically upward and then screw for fixing up the hoop;
Caution: In order to avoid unnecessary personal injury and equipment damage,
this step requires at least three people to work at the same time.
Caution: The installer must be careful to avoid equipment damage caused by
dropping of the tube.
12
Page 17

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
Outlet port
Cable interface
Figure 5 Tube installation
3. Fasten the other half of hoop and fix it with screws incidental with the equipment.
4. Buck-up the two tube rotation lock screws on the hoop as show in following figure:
Figure 6 Fix up the tube
3.4 Operation Panel Installation
1. Uprightness spin the tube supporting frames, so that the installation interface of tube
and collimator is upward to facilitate the installation of collimator.
2. This step needs at least two people to perform simultaneity. One of them pulls the tube
support frame and keeps it, another person will gently placed the panel backstop on the
tube installation interface, and align the mounting holes.
3. Placed the flange which remove from collimator beforehand on the panel backstop, and
align the mounting holes, then fix up it with four installation screws. It is shown as follow:
13
Page 18

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
p
Service
Installation
Screws
Flange
Panel
backsto
Figure 7 Flange installation
4. Cover the collimator into the flange gently as show in the figure, and gently rotate until
they are completely anastomose.
Figure 8 Collimator installation
14
Page 19

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
Note: The face of the collimator should be forward as same as the panel, it is
shown as follow:
Figure 9 Direction of collimator
5. Fix up four screws of the collimator as follow:
Fixup screws
Figure 10 Fix up collimator
6. Loosen the fixup screws of the glass baffle at the light exit of the collimator, and take
down the baffle, then cut the belt for fixing internal components of the collimator and
remove it.
15
Page 20

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
Figure 11 Fixing belt of collimator
7. Connect the data/power line between column and operation panel.
Figure 12 Data/power line interface(at the back of the operation panel)
8. Power line of collimator connection. Connect the collimator power line which leads from
16
Page 21

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
radiography table into the interface at the upper left corner of the collimator.
Figure 13 Collimator power line connector
Service
Figure 14 Collimator power line interface
9. Connect the panel control line into the interface at bottom of column.
Figure 15 Panel control line connection
17
Page 22

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
3.5 Installation of Stand chest
Carried out the stand chest from the box and moved to the installation location, Raise the
stand chest upright slowly;
Rotate the tube to 90°, and measure the distance of focus and film box of stand
chest(two vertices), the subtraction should less than 2mm.
Positioning the stand chest and fix it at ground.
3.6 Generator Installation
3.6.1 Installation preparation
Power interface terminal X1 is indicated in following figure:
1. Before installation, the user shall and have to supply the following information:
1) Number of power phases and capacities meet requirement of this machine.
2) Information of installation place.
2. Installation tools and articles are as follows:
1) Standard engineering tool kits
2) Electrical tape
3) Clean cotton cloth
4) Silicon insulation grease
5) Alcohol cleaning agent
Note: Transportation and package opening may cause loss of screws and nuts
on port terminals, in this case, used screw drivers, wrenches or other tools to
tighten all fixed wiring terminals.
18
Page 23

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
1 Power line connection (L1) 3 PE terminal
2 Power neutral line (N)
Figure 16 Power port terminal XP1
Service
1 Power output running winding port of
rotating anode(2)
2 Power output starting winding port of
rotating anode(1)
3 Driving power output common port of
rotating anode (0)
4 Power neutral line (N)
5 NC
6 input port of running power supply
(RUN)
7 input port of starting power supply
(ST)
8 input port of brake power supply
(BRAKE)
Figure 17 interface terminal X6
3.6.2 Connection between generator and tube
Anode and cathode cables shall be arranged according to space arrangement (length of
cable).
19
Page 24

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
1. Connection of high voltage cable
Note:
Terminal plug of high voltage cable is subject to damage and shall be
careful during use.
These terminal plugs shall be kept straight, and dowels shall be open (in
parallel edge to edge.
1) Accessories of each terminal plug shall be installed in accordance with instruction
of cable manufacturer.
2) High voltage port of X-ray tube shall be kept clean. The whole surface of high
voltage plug to be connected to X-ray tube including metal pin shall be coated a
layer of silicon grease. Anode cable and cathode cable shall be carefully
connected to corresponding X-ray tube input terminal. All connections shall be
correct, anode and cathode directions shall be correct, Cable nuts shall be
tightened.
3) The high voltage cable plug to be connected to the generator shall be coated a
layer of silicone grease. The anode and cathode cable which have been
connected with the X-ray tube shall be connected to corresponding generator
plug. All connections shall be correct, anode and cathode directions are correct.
Cable nuts shall be tightened.
2. Wiring of rotating anode motor cable
Interface terminal X6 which on the interface unit is indicated in figure 17; connect rotating
anode cable to X6 terminal of generator. The connection is shown at following figure.
The machine may drive middle speed tube.
20
Page 25

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
Figure 18 Installation diagram of terminal X6
3.6.3 Connection of generator mainframe and console
1. The pin plug of accessory communication cable shall be inserted in port X2 of
mainframe control unit circuit board (PCB 21002C), plug screws shall be tightened, as
indicated in figure 20, and communication cable shall be properly laid.
2. Another end of communication cable shall be plugged into pin bed of console, as
indicated in figure 19. Plug screw shall be tightened.
Main control unit X2 and X3
Communication cable
Figure 19 Communication cable wiring diagram
21
Page 26

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
N
N
r
Service
3.6.4 Connection of power cable
L1
PE
Electrical cabinet
QS
SB2
KM
KM
SB1
KM
L L
SB3 SBn
Emergency switch
L1
PE
To generato
Figure 20 Arrangement diagram of X-ray room power
Before power cable connection, user should properly prepare electrical cabinet as
indicated in figure 21 or electrical cabinet with equivalent function and emergency switch.
Power cable should be high quality multi-strand copper core insulation cable. When the
power cable is shorter than 5m, cross section of multi-strand conductors should not less
than 6mm
conductors should not less than 8mm
2.
When the power cable is between 5m and 10m, cross section of multi-strand
2
. Protective earthing cable shall be yellow-green
double color insulation high quality copper core multi-strand cable with cross section not
less than 6mm
2
.
Followings shall be noted during connection:
a) It is proposed to install an emergency switch beside the console.
b) Circuit breaker power of electrical cabinet is off.
c) The cable shall be cut off a proper length, and insulations on both ends of the cable
shall be removed, and wire lug shall be connected through pressure welding.
d) Power phase lines of L1 and neutral line (N) shall be connected to corresponding
port of X1 terminal, and protective earth shall be connected to PE terminal of X1
terminal. See the following figure.
e) Power line shall be laid properly and connected to corresponding interface of
electrical cabinet.
f) Make sure that the emergency switch has been correctly connected to the electrical
cabinet; when the emergency switch is pressed, generator power can be cut off.
22
Page 27

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
g) Text and make sure that the power cable has connected correctly. Suggest that
disconnect the air-switch of generator mainframe, and then directly measured by
multimeter on X1 of four power ends.
Note: contact resistance of protective earth line shall meet standard.
Service
Figure 21 wiring diagram of power cable
Warning: the generator keeps connection with the power line, unless the circuit
breaker installed on the electrical cabinet is closed, or the safety switch on the
generator is closed, otherwise the power will keep on.
Note:
Although the console is closed, the internal auxiliary power supply and
control circuit of the generator still connects with the po wer line. Make sure
that the system shall have been fully disconnected with the grid before
repair and maintenance.
X1-PE is protective earth port. Protective earth connector shall be copper
line with cross section not less than 6mm
2
;The earth line shall be properly
connected with special earth line.
23
Page 28

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
4 Debugging and Calibration
4.1 X-ray debugging
X-ray tube has been debugged; however, it shall be re-debugged after installation and
before operation to eliminate errors caused by improper installation. Debugging method is
as follows:
4.1.1 Precautions in debugging
1) To prevent body injury caused by X-ray radiation generated during debugging, the
collimator shall be closed or effective obstacles shall be placed at ray window of the
assembly.
2) Power for filament and stators shall meet parameters of the same filament and stators.
3) Time relay, instrument and other measuring tools shall be checked for their accuracy.
4) Cold high voltage (without tube current) shall not be loaded.
5) Filament current shall be carefully adjusted to suitable tube current to prevent burning
of filament.
4.1.2 Debug step by step
In first use or reuse after more than one-month storage, operation shall be in accordance
with following steps:
1) The tube current of assembly shall be maintained at 2mA. Tube voltage o shall be
gradually increased from 50kV to rating value at rate not more than 1-kv/min, and rating
voltage shall be maintained for 3 minutes.
2) The assembly shall be left for 5 minutes after unloading.
3) Tube voltage and current shall be selected according to load characteristics, exposure
shall be at 0.1s position, 1—2 exposure shall be made at each position from 60kV, then
tube voltage shall be increased by10kV and the tube shall continuously expose at this
level to rating value (note: X-ray tube shall be checked for normal rotation prior to the first
exposure), interval of exposures shall be not less than 1 min to cool down the assembly.
4) If tube current is instable during loading, the tube voltage shall be reduced by 10kV till it
becomes stable, and then the tube shall be maintained at this level for 2 min, then tube
voltage of the assembly shall be continuously increased to rating value.
5) X-ray source assembly shall be started from step 3) in the complete machine. Under
radiography status, tube current shall be adjusted among 50mA, 100mA, 200mA and
24
Page 29

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
300mA, time shall be 0.1s, tube voltage shall be gradually increased from 50kV to 80kV,
100kVand 120kV till rating value.
4.1.3 Attentions during debugging
Temperature of assembly shall be maintained normal. If temperature of external wall of
tube sleeve is over-high, loading shall be stopped till complete cool-down of the assembly.
4.2 Collimator debugging
Prior to ex-factory, the collimator has been debugged, after installation and before use, the
collimator shall be rechecked to eliminate errors caused by improper installation,
debugging method is as follows:
1) After connection of collimator with X-ray tube assembly, the collimator lighting lamp
shall be illuminated to align vertical axis of prediction field cross line with center line of
radiography machine tabletop.
2) Adjust cross center lines of radiation field and prediction field to coincide them.
3) If it is used in common X-ray unit, place an X-ray film in center of a cassette.
4) Place cassette on radiography machine, focus-film distance is set in 1000mm, place
metal line (diameter is larger than 1mm) on center of film and two
analog center line and radiography scope; After exposure and development, check the
center cross line for position in the center of radiation field (i.e. exposure area).
4. One end of collimator lighting lamp power line shall be connected to internal terminal of
collimator with another end connected to wiring terminal of radiography table component
assembly.
opposite angles to
4.3 Generator debugging
4.3.1 Preparation before debugging
1. Debugging or detection instrument is as follows:
1)Storage oscillograph Tektronix TDS210 or similar products
2)Multimeter
3)Digital milliammeter (optional)
4)Digital milliampere-second meter(optional)
5)Voltage box(optional)
6)X-ray dose tester (optional)
25
Page 30

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
2. Before energization, all power terminals and connectors shall be scrutinized to
eliminate short-circuit or open-circuit and etc, to ensure correct and firm connection.
1) Protective earth shall be specially checked for reliable connection, and shield of
high voltage cable shall be specially checked for reliable connection to the ground.
2) High voltage socket of oil tank shall be checked for reliable connection to tube
anode and cathode.
3) If tube current is directly tested, two ends of mA text point on the oil tank shall be
check to make sure reliable connection with mA testing instrument. If tube current
is indirectly tested, the resistance of the two ends shall be check to make sure is
10Ω.
4.3.2 Rotating anode text
This test requires two operators, one operates console, the other operator observes
rotating speed of anode of X-ray tube. When the first-class of hand-switch is pressed,
checked of rotating speed of anode and if the start up of anode is normal.
Note: during test, exposure shall be avoided; otherwise, operators approaching
to the X ray tube may suffer X-ray radiation.
4.3.3 Calibration of tube voltage
Before ex-factory, KV value of the machine has been correctly calibrated, in general,
recalibration is not necessary, however, if necessary, following steps shall be followed for
recalibration:
1. Protective unit (PCB 2100108)TP1 is test point of +kV value, TP3 is test point of -kV
value and text point of TP15 is earth end.
2. At test point of kV value, ratio of voltage value to kV is 1V:10kV, hot end of digital
storage oscilloscope probe 1 is clamped to test point of +kV value, cold end is clamped to
measuring earth, hot end of probe 2 is clamped to test point of -kV value and cold end is
clamped to measuring earth. (or apply volt box or other measuring instrument) .
3. Voltage of 21002C panel TP2 shall be 3.20V (±0.05V) measured, otherwise lightly
adjust potentiometer RW3 of 21002; Voltage of 21002 panel TP3 shall be 0.57V(±0.05V)
measured, otherwise lightly adjust potentiometer RW2 ;
4. Parameter selection of calibration point: small focus, 50mA,100ms,40kV (note: voltage
on one side is half of this kV value.)
5. Exposure (the output voltage waveform texted by oscilloscope is shown as figure 8
adjusted pulse width modulator 21003 potentiometer RW1 (adjustment + kV value), RW2
26
Page 31

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
(adjustment -kV value) (kV value increases in clockwise adjustment and reduces in
counterclockwise adjustment), and then exposure and adjustment repeat untill correct
calibration is achieved (error less than 5%).
6. Voltage calibration of the tube has been completed.
Figure 22 Output voltage waveform(40kV waveform)
4.3.4 Calibration of tube current
4.3.4.1 Principle
Calibration of tube current is realized by setting the tube current through changing
corresponding byte in filament current data ROM. Data corresponding to each setting
value varies with different parameters of tube and high voltage cable. Even in a same tube,
after a period of time, the setting current may deviate from the actual tube current,
therefore, the tube current shall be subject to preliminary calibration after installation;
during use, regular calibration shall be performed at 6 months or shorter interval.
Calibrated data are stored in nonvolatile memory chip, which locates on PCB of
mainframe control unit.
When tube current is directly measured, current measurer has special requirement to
shortest sampling time for measurement, such as continuous measurement sampling time
of milliampere-second meter is longer than 70ms, continuous measurement sampling time
of current position of common digital multi-meter is longer than 500ms, to shorten time for
27
Page 32

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
calibration and reduce X-ray radiation hazard to calibrators, it is proposed to adopt current
resistance sampling for indirect measurement, which adopts storage oscillograph to
measure voltages on both ends of sampling resistance.
During tube current calibration, the storage oscillograph is used as measuring tool,
Tektronix TDS210 storage oscillograph is recommended to use. Test point of tube current
is at TP13 of protective panel (PCB 200108). At this point, ratio of voltage to tube current
is 1V:100mA.
4.3.4.2 Radiography tube current shall be calibrated as per following steps:
1)Press “?/CLR” key untill two "Di" sound, and then release the key, then the system
is enter into maintenance status.
2)Press kV increase/decrease selective key to display "2" in kV display screen, at
this moment, modification of password unit is selectable.
3)Press mA increase/decrease selective key to display modification password "88"
on mA display screen.
4)Press "M" key to store this value
5)Press “?/CLR” key to return to standby status.
6)Select focus. such as small focus.
7)Press mA increase/decrease key to select pre-set value, such as 100mA.
8)Press kV increase/decrease key to select kV value, such as 70kV.
9) Press “?/CLR” key till four "Di" sound, release the key.
10) Press S/mAs increase/decrease key to display data to be input in S/mAs display
screen, such as " 80".
11) Press "M" key to store this value.
12) Press “?/CLR” key to return to standby status.
13) Perform exposure action under this condition.
14) Read recorded value of storage oscillograph. If recorded value is higher than
setting value, value in ROM shall be reduced, on the contrary, the value shall be
increased.
15) Repeat 9)--12) steps till record value of oscillograph is in line with the setting
value, and then the calibration of combined parameter of kV value and mA value
28
Page 33

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
has completed.
4.3.5 Bucky text program
Under safety assurance condition, press prepare button. If the filter is electric it will
running. If the filter is vibrator filter, press exposure button, the filter will vibrate. When
exposure is finished, filter stop vibrator. This device can configure with two kinds of filter:
vibrating and electrical. The filter shall be calibrated as per following steps:
1)Press “?/CLR” key until four "Di" sound, and then release the key,
2)Press kV increase/decrease selective key to display "2" in kV display screen, at
this moment, modification of password unit is selectable.
3)Press mA increase/decrease selective key to display modification password "88"
on mA display screen.
4)Press "M" key to store this value
5)Press kV increase/decrease selective key to display "9" in kV display screen,
6)If is vibrating filter, press mA increase/decrease selective key to display "0" on mA
display screen. If is electrical filter, press mA increase/decrease selective key to
display "1" on mA display screen
7) Press "M" key to store this value.
8) The driving model of filter is setting over, click “?/CLR” return standby status..
Note: Setting the driving model of filter must based on the actual work,
otherwise will cause damage to filter.
4.3.6 Commissioning
After debugging and in normal operation condition, test card or water bag maybe used as
test piece for radiography to determine normality of the machine.
29
Page 34

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
5 Maintenance
5.1 Radiography Table
5.1.1 Regular maintenance
Routine maintenance of the machine may be performed by professional service crew or
by user.
The machine shall operate in dry and clean environment. Machine unused in
long term shall be covered by dustproof film.
During operation, proper surface cleaning and protection shall be performed;
after use by patient with infective disease, the machine, in particular to the
tabletop shall be disinfected and sterilized (wiping with clean gauze dipping with
70%--80% alcohol).
All bearings and moving parts shall be checked regularly; friction surface shall be
cleaned and lubricated.
During normal operation, steel wire shall be checked regularly. Any breakage of
wire shall be promptly notified to the professional technicians approved by the
company for replacement.
Protective yellow/green ground wire shall be checked frequently for good connection.
5.1.2 Maintenance Record
1. Consumable:
Consumable Quantity
Suds skit
Absolute alcohol skit
Soft fabric skit
2. Maintenance record
Item Level A Level B Description Record
1 √ Cleaning the tabletop with suds
2 √
3 √ √
4 √
30
Cleaning and disinfection the tabletop
with Absolute alcohol
Examine and clean the axletree and
lubricate with lubricant
Examine the wire rope, and replace it if
necessary
Page 35

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
5 √ Grand wires connecting examination
6 √ Radiography table function examination
5.2 X-Ray Tube Assembly
5.2.1 Regular maintenance
Assembly surface shall be cleaned with absolute alcohol and the assembly shall be
regularly maintained.
Following items shall be checked periodically:
1)Leakage of lubricant of tube assembly.
2)Temperature control switch of tube assembly.
3 ) Connection of high voltage line: loose of line plug and clamp, leakage of
insulation silicone grease and coating.
4)Coarseness and stains on X-ray tube target.
5)Abnormal noise or vibration of X-ray tube anode during rotation.
6)Ground line and earth resistance. r
5.2.2 Year maintenance
On yearly basis, insulation grease in the high voltage cable connector shall be replaced,
grounding and temperature switch of the assembly shall be checked for normality and
external case of the assembly shall be checked for leakage.
5.2.3 Maintenance Record
1. Consumable:
Consumable Quantity
Absolute alcohol skit
Soft fabric skit
2. Maintenance record
Item Level A Level B Description Record
1 √
Cleaning the cover with Absolute
31
Page 36

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
alcohol
2 √
3 √
4 √ √
5 √ √ Exposure
check that if there is any leakage of
insulating oil of the cover
Check the function of the temperature
control switch
Replace the insulating oil in high voltage
cable interface
5.3 Collimator
5.3.1 Replacement of Lamp
Replace the lamp: lamp should same as original
1) Disconnect supply
2) Remove the back panel
3) Remove the lamp protection dissipater
4) Carefully remove the faulty lamp
5) Substitute the lamp with an identical lamp
6) Make sure that the lamp pins are completely inserted in the lamp holder
7) Check on light field/x-ray field correspondence
5.3.2 Recommended Maintenance Program
A yearly servicing program is recommended. However shorter intervals are advisable
when the collimator is subject to heavy workloads.
Re-calibration of the collimator will be necessary whenever the x-ray tube is changed or at
each substitution of the lamp used to simulate the light field.
1) Check that the screws and tabs which serve to secure the collimator to the
flange/tube adapter are correctly tightened.
2) Remove the covers and panels from collimator. Inspect the moving parts for signs of
wear or damage.
3) Check the electric system and substitute parts that show wear.
4) Check the PVC (: Material is Lexan) panel and substitute if necessary.
32
Page 37

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
5) Clean the collimator with a soft cloth paying particular attention to the Lexan window.
Do not use abrasive or inflammable cleaning products.
6) Sparingly lubricate the moving parts using graphite oil.
7) Wipe away all excess oil.
8) Remount the cover.
5.3.3 Maintenance Record
1. Consumable:
Consumable Quantity
suds skit
Soft fabric skit
2. Maintenance record
Item Level A Level B Description Record
1 √
2 √
3 √ √
4 √ √
5 √ √ Indicator lamp replacement
6 √ √ Collimator Calibration
Cleaning the cover of the collimator with
suds
Examine the function of lead leaf control
knobs
Examine that if the lead leaf is start and
fix up it if necessary
Check on the internal mechanical parts
and add lubricants
5.4 Generator
5.4.1 Regular maintenance
For the lasting and safe operation of the X-ray generator, periodic maintenance is
necessary. Do the initial maintenance six month later after the machine is installed, and
then keep the maintenance once every other year.
1. When the x-ray generator is working, do not clean any part of it. Do cleaning after the
33
Page 38

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
generator is shut down and the power is turned off.
2. Clean the machine, esp. when there is corrosive matter. Spray inorganic detergent on a
piece of rag and use the rag to clean the machine casing. Do not use vacuums or organic
solvents for cleaning.
3. Keep the machine room tidy, dry and airy. The machine shuns heat and the sun.
4. Replace the dewatering filler vaseline in HT connectors periodically. for connectors
used for HT generator components the replacement is done once less than a year; for
connectors used for x-ray tube components, the replacement is done once less than half
year. Intensify examination and updating during the summer or when there is heavy work.
5. Pay attention to the condition of power supply. Check if its internal resistance (or
voltage drop) has changed. Make efforts to realize the requirements for the power supply
of the machine.
6. Check the grounding device frequently to make sure all parts are safely and reliably
grounded.
5.4.2 Maintenance Record
1. Consumable:
Consumable Quantity
Soft fabric skit
Soft fabric skit
2. Maintenance record
Item Level A Level B Description Record
1 √ Cleaning the cover of the equipment
2 √
3 √
Examine the connection of the
high-voltage cable
Examine the shield of the high-voltage
cable
4 √ Examine the ground wires connection
5 √ Examine the function of the console
6 √ Analysis of the error code
7 √ √ Configuration and calibration
34
Page 39

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
6 Troubleshooting
6.1 Error Codes
In case of system error, fault causes can be diagnosed rapidly through checking test point
and signal indicator of corresponding parts, and trouble-shooting may be performed
quickly to recover normal operation of the system.
Note: When the system needs replacement as X-ray tube, HV transformer, or
the main control board that which calibration data is stored in, their owned
configuration and calibration procedures are needed. After pre-calibration,
record the new values.
Error code display
Error code Where and what is the problem?
E00 Abnormal power or fault of input circuit
E01
E02
E03 Failure of cathode heating or the fault of heating driver circuit
E04 Failure of anode heating or the fault of anode heating driver circuit
E05 The machine fails to start.
E06 The machine fails to shutdown.
E07 Self-diagnosis fails.
E08 Resetting fail.
E09 The internal radiating port fails.
E10 The protective circuit of the inverter fails.
E11 The focus switching fails.
Overcurrent or fault of inverter discharge of BR1. X-ray tubes or
HT parts and lead to over-loading.
Overcurrent or fault of the inverter discharge of BR2. X-ray tubes
or HT parts and lead to over-loading.
E12 The Bucky diaphragm fails
E13 Positive deviation of tube voltage.
E14 Negative deviation of tube voltage.
E15 Positive deviation of tube current
35
Page 40

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
E16 Negative deviation of tube current
E17 Positive deviation of voltage reference.
E18 Negative deviation of voltage reference.
E19 Positive deviation of current reference
E20 Negative deviation of current reference
E21 Invalid parameters
E22 Invalid orders
E23 Automatic reset of main system
E24 EEPROM is not initialized
6.2 Key point in fault diagnosis
6.2.1 Console
After switching the power supply on, the control system is energized and begins to self
inspection. Console luminescent indicators flashes to help repairman to perform
inspection. After self inspection, kV screen displays "OFF" or "E"; "E" indication is normal
since last operation shuts down and losses power abnormally.
If the console has no reaction after switching-on, or "E00" is displayed, this may be
caused by abnormal power supply system, and following inspection steps shall be
followed:
a)Is the power supply normal?
b)Is the mainframe cabinet air switch normal?
c)Is L1 phase powers are normal ?
d)Is auxiliary power +9V is normal?
e)Is communication cable connected correctly?
f)That is a fault of console.
When "ON" key of the console is pressed, the system begins soft-start; kV display screen
displays initialization accounting. After soft-start, main power source is connected, the
console shall display normal X-ray radiography parameters.
36
Page 41

6.2.2 Interface unit
Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
Figure 23 Interface unit
The interface unit is equipped with LED status indicator and reference voltage precision
potentiometer. Item code and information of LED indicator is as follows:
1. V42--filter unit stored energy status indicator lamp. Illumination of V42 indicates
electrification of capacitor. When charge voltage remained in the capacitor is less than
10V, V42 blacks out. Note! Power shall be off at least 3minutes prior to complete
discharging of the capacitor! Black V42 does not mean complete discharge.
2. V19---On indicator. When "ON" key is pressed, the lamp shall illuminate. If black, the
machine will not start, port X3-7 shall be checked for level. If level is low, connection line
with main control unit (PCB 21002) shall be checked; if level is high, this unit (PCB21001)
or null line and the phase shall be checked.
3. V20---Bucky diaphragm 1 Working status indicator. If Bucky diaphragm 1 is selected,
the indicator illuminates during exposure preparation and at the moment of exposure.
4. V20---Bucky diaphragm 2 Working status indicator. If Bucky diaphragm 1 is selected,
the indicator illuminates during exposure preparation and at the moment of exposure.
5. V22----Ready-start status indicator. When the machine is ready for start, the indicator
illuminates, X3-7 is at high level. If black, the machine cannot start up, and the console
displays "E00", in this case, check shall be performed according to potentiometer RW3,
which is pre-charging voltage regulation potentiometer, TP4 point beside is level test
point.
(1)If pre-charging voltage exceeds 260VDC and V22 is black, the console displays
37
Page 42

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
"E00" or continuous counting, this may be caused by modified feature of components of
pre-charging voltage monitoring circuit. Press "OFF" key till LED V42 blacks out, finely
adjust RW3 (level at TP4 point decrease) to set low pre-charging voltage, repeat start-up,
fine adjustment and detection till pre-charging voltage reaches to 240VDC and AC contact
K1 attracts.
(2)If pre-charging voltage is lower than 200VDC, V22 illuminates, AC contact K1 of main
power supply line attracts, the mainframe starts up, after long run operation in this status,
service life of energy storage filtration capacitor (PCB 21007B) will be shorten. Finely
adjust RW3 (level at TP4 point increase) in counter clockwise to increase pre-charging
voltage to 240VDC.
6. V45……Rotary anode working signal lamp. During standby, the lamp blacks out.
When the Ready key is pressed, the indicator lamp shall illuminates, otherwise, it
indicates that exposure ready check is not passed, the console displays "E04", in this
case, voltage at port X6_6、X6_7、X6_8 (against X 6-4) shall be checked for normality. If
abnormal, corresponding connection wire and fuse and power transformer T1 on terminal
block shall be checked; if normal, voltage at X5-5 port shall be checked for low level after
pressing the exposure Ready button, if low, this connection wire and main control unit
(PCB21002E) shall be checked, otherwise, the unit (PCB 21001) shall be replaced.
6.2.3 Mainframe control unit
Figure 24 Mainframe control unit
Normal start-up indicates that mainframe micro processer's function and communication
interface are normal. Normality of other I/O interface maybe traced and checked through
38
Page 43

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
observing normality of other units. If it is required to replace mainframe control unit circuit
board, the non- volatile store D1 for storing calibration data on original circuit board shall
be shift to newly replaced circuit board.
6.2.4 Pulse width modulation unit
Figure 25 Pulse width modulation unit
The pulse width modulation unit is equipped with 8 LED status indicators and two kV
calibration precision potentiometers.
1. V7----Fluoroscopy/radiography status indicator. The indicator illuminates during
fluoroscopy and blacks out during radiography.
2. V23----inverter BR1 protection test indicator. The indicator illuminates during standby
status, when "Power ON" key is pressed to reset the machine, the indicator blacks out.
3. V24----inverter BR2 protection test indicator. The indicator illuminates during standby.
When "Power ON" key is pressed to reset the machine, the indicator blacks out.
4. V35---Inverter BR1 fault indicator. The indicator illuminates during standby. When
"Power ON" key is pressed to reset the machine, the indicator blacks out. During
exposure, if this indicator is black and exposure is abnormally interrupted, this indicates
that inverter BR1 is in overcurrent protection status, the console displays "E01” and
repair shall be performed according to steps as follows:
1) Press Maintenance/Clear key or restart machine, select lowest value of 40kv,
lowest mA, 250ms and perform exposure with this parameter.
39
Page 44

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
2) If exposure is normal, select 80kV and maintain other parameters unchanged,
and re-exposure.
3) If exposure is normal, select 120kV and maintain other parameters unchanged,
and re-exposure.
4) If normal, preliminary judgment may deny the existence of discharge fault in high
voltage circuit.
5) If a same fault (fault "E01") occurs during these three exposures, this indicates
that the machine is subject to serious interference or indicates existence of
discharge fault in high voltage circuit or fault in power circuit, in this case,
communication cable, earthing, high voltage connection (high voltage plug,
socket and cable) , tube, inverter, high voltage oil tank, main control penal and
consol shall be checked for normality.
5. V32----Inverter BR2 fault indicator. Ditto perform check.
6. V31--inverter working status signal lamp. The lamp illuminates during standby or
protection; during exposure, the lamp blacks out.
7. V38----filament heating status indicator. The indicator blacks out during standby or
abnormal status; press Ready key, filament is heated, and this indicator illuminates, if this
indicator is black, this indicates abnormal heating, the console displays error code "E03",
and repair shall be performed as follows:
1) Is filament heating data normal ?
2) Is communication flat cable connection among pulse width modulation plate and
main control panel are normal?
3) Is filament heating auxiliary power normal?
4) Is filament transformer driving circuit normal?
5) Is filament normal?
6) Replace this unit circuit board.
8. V67----focus working indicator. The indicator illuminates during large focus and blacks
out during small focus. When focus selection key is pressed, V67 is in corresponding
working status.
9. Potentiometer functions are as follows:
1 ) RW1----+kV adjust potentiometer, turn clockwise to increase +kV, turn
40
Page 45

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
counter-clockwise to reduce +kV.
2 ) RW2------kV adjust potentiometer, turn clockwise to increase -kV, turn
counter-clockwise to reduce -kV.
6.2.5 Auxiliary power
In case of fault of filament heating auxiliary power +48V, press of Prep. Key may display
error code "E03".
6.2.6 ±12V auxiliary power
Fault of ±12V auxiliary power may cause no reaction of console or continuous counting
after switch-on, the main power cannot connect.
Figure 26 ±12V auxiliary power
41
Page 46

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
6.2.7 Sampling Unit
Figure 27 Sampling Unit
The board has an LED light V5 and six test points as show, which use for sampling
collection of the current and voltage of high-voltage generator. In the exposure process,
the board detected feedback signal then lights V5. The factory set is + MA sample, the
-MA samples is earthing.
42
Page 47

6.2.8 Protection Unit
Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
Figure 28 Protection Unit
The protection board can detect the feedback current and voltage for the high-voltage
generator protection control.
TP1 of protection unit(PCB 2100108) is the +kV test point, while TP3 is the –kV test point,
cathode V4 is earthing. The ratio of the test point voltage and actual kV value is 1V:10kV.
Hot end of digital storage oscilloscope probe 1 is clamped to test point of +kV value, cold
end is clamped to measuring earth, hot end of probe 2 is clamped to test point of -kV value
and cold end is clamped to measuring earth. (Or apply volt box or other measuring
instrument) .
Test point of tube current is at TP13 of protection board (PCB 200108C). At this point, ratio
of voltage to tube current is 1V:100mA. Hot end of digital storage oscilloscope probe is
clamped to test point TP13, cold end is clamped to cathode V4.
6.2.9 Common troubleshooting judge
a) E00: indicate failure of start-up. A possible damaged part is interface unit or tube
overheating protection.
b) E01/E02: indicate overcurrent protection of generator. A possible damaged part
is inverter or tube discharge or grid voltage exceeds power requirement.
43
Page 48

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
c) E03: indicate failure of filament heating. Possible damaged part is pulse width
unit or poor contact of 48V power or high voltage cable cathode or burn out of
tube filament.
d) E04: indicate start failure of tube rotary anode. A possible damaged part is burn
out of interface unit or tube rotary anode power fuse or abnormal rotation of tube
rotary anode.
44
Page 49

7 Attached figure
Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
(For reference only)
Figure 1 Layout of machine room
45
Page 50

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
46
Figure 2 Maximum Rating Charts
Page 51

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
Figure 3 Emission & Filament Characteristics
47
Page 52

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
48
Figure 4 Housing Thermal Characteristics
Page 53

Medical X-Ray Radiography System
Service
Figure 5 Anode Thermal Characteristics
49
 Loading...
Loading...