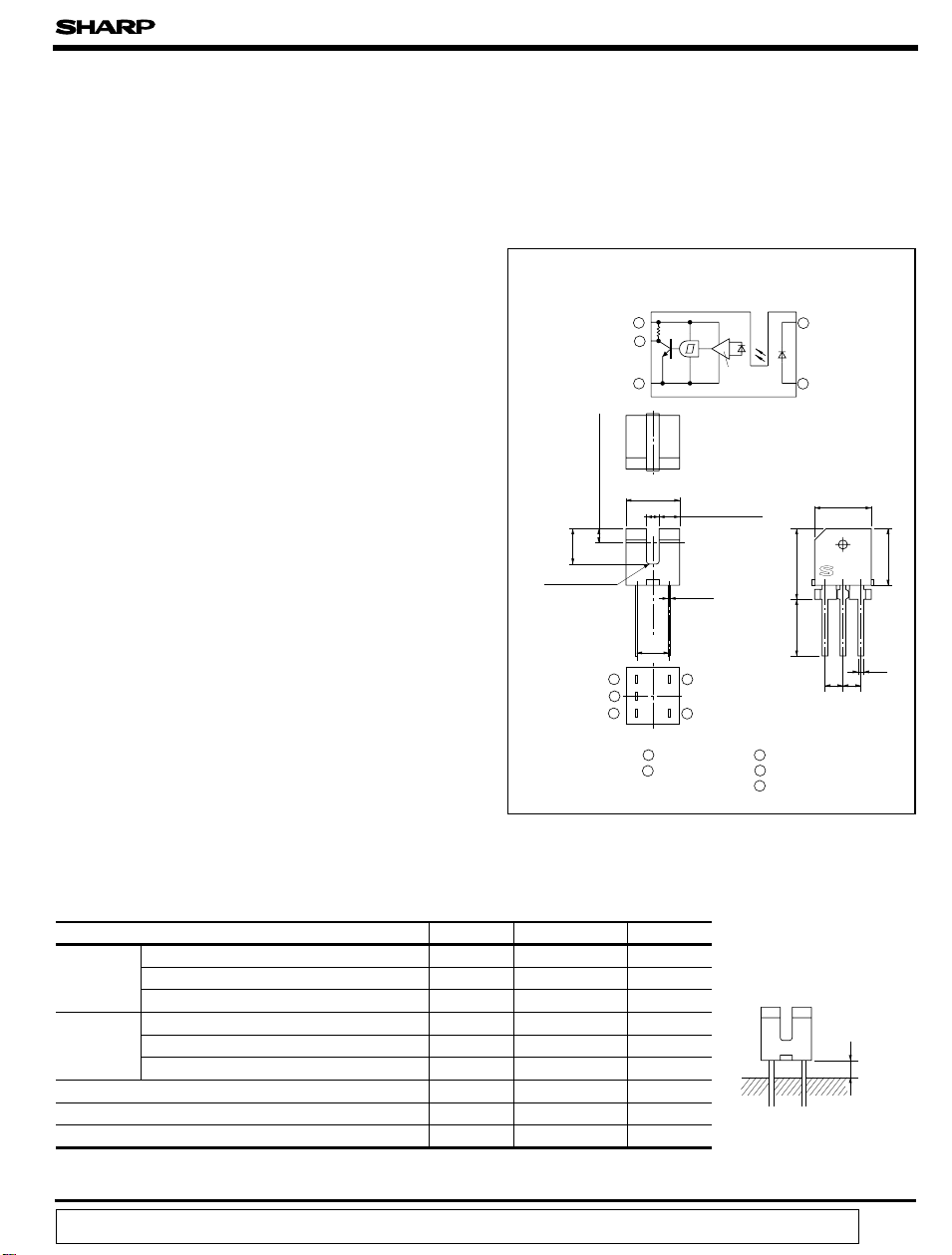
GP1A68L
GP1A68L
Low Voltage Driven Low Current
Consumption Type OPIC
Photointerrupter
■■
Features
1. Ultra-compact type (3.8 x 4.0 x 4.0 mm)
2. C-MOS and microcomputer compatible
3. Low voltage driven, low current consumption
(Operating supply voltage : 1.4 to 7.0V,
Standby current consumption : MAX. 0.5mA)
■
Applications
Outline Dimensions
Internal connection diagram
3
(
15kΩ
4
5
)
Amp.
(Unit : mm)
2
1
1. Cameras
2. Floppy disk drives
±
0.2
±
2.5
(
2- C0.3
(Sensor center)
)
1.0
(
)
5
4
3
0.2
3.8
±
0.2
0.9
❈
2.54
1 Anode
2 Cathode
±
0.2
1.45
Optical center
0.15
1
2
3 V
CC
4 V
out
5 GND
0.2
±
MIN.
5.0
4
±
4.0
1.27 1.27
0.2
0.2
±
4.0
0.4
* "OPIC" (Optical IC) is a trademark of the SHARP Corporation.
An OPIC consists of a light-detecting element and
signal-processing circuit integrated onto a single chip.
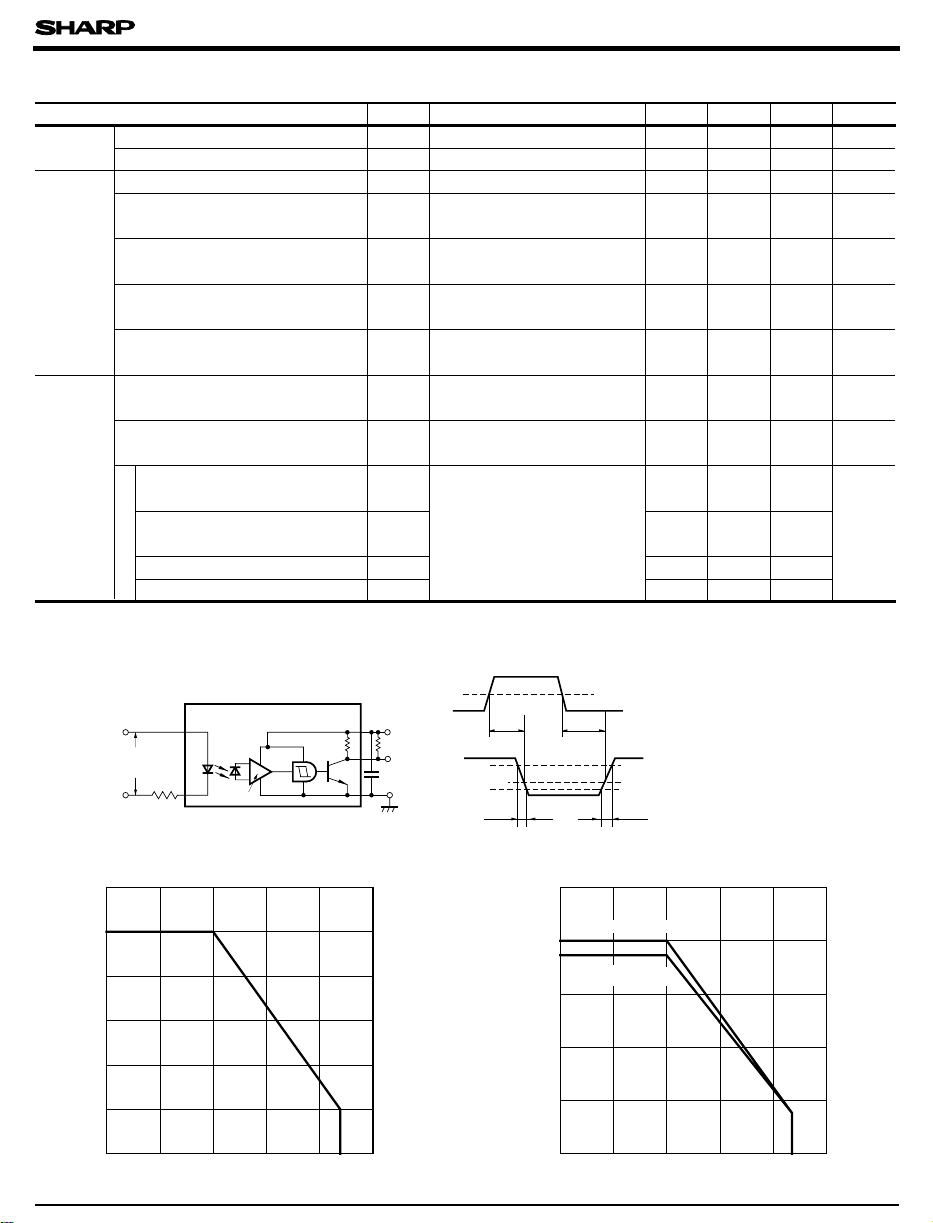
Absolute Maximum Ratings
■
(Ta=25˚C)
Parameter Symbol Rating Unit
Forward current
Input
Reverse voltage
Power dissipation
Supply voltage
Output
Low level output current
Power dissipation
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
*1
Soldering temperature
*1 For 5 seconds
“ In the absence of confirmation by device specification sheets, SHARP takes no responsibility for any defects that occur in equipment using any of SHARP's devices, shown in catalogs,
data books, etc. Contact SHARP in order to obtain the latest version of the device specification sheets before using any SHARP's device.”
I
F
V
R
P75mW
V
CC
ImA
OL
P
O
T
opr
T
stg
T
sol
50 mA
6V
7V
2
80 mW
-25to+85
- 40 to + 100
˚C
˚C
260 ˚C
MIN. 1mm
Soldering area
GP1A68L
■
Electro-optical Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Input
Forward voltage
Reverse current
Operating supply voltage
Low level
output voltage
High level
Output
output voltage
Low level
supply current
High level
supply current
*2
"High →Low"
threshold input current
*3
Hysteresis
Transfer
"Low →High"
propagation delay time
characteristics
"High→Low"
propagation delay time
Rise time
Response time
Fall time
*2 I represents forward current when output goes from "High" to "Low".
FHL
*3 Hysteresis stands for I /I .
FLH FHL
(Ta=25 ˚C)
V
I
= 5mA 1.15 1.25
F
F
V
I
R
V
CC
V
OL
V
OH
I
CCL
I
CCH
I
FHL
I
/I
FLH
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
r
t-
f
=3V - - 10 µA
R
-
V
= 3V,I
CC OL F
= 3V,I
V
CC F
= 3V,I
V
CC F
= 3V,I
V
CC F
=3V
V
CC
=3V
V
CC
FHL
=3V
V
CC
= 1mA,I
=0
= 5mA
=0
= 5mA
IF= 5mA
=3kΩ
R
L
-V
1.4
- 0.4 V
2.9
-mA
-mA
- 7.0 V
0.1
--V
0.7
0.3
1.2
0.5
- 0.9 2.5 mA
0.55 0.8 0.95 -
10
-30
- 3.0 15
0.6
-
0.2
1.0
3
µs
Test Circuit for Response Time
Input
GND
3kΩ
0.1µF
100755025
+ 3V
Output
Input
= t
= 0.01µs
t
r
f
ZO= 50Ω
47Ω
Amp.
15kΩ
Fig. 1 Forward Current vs. Ambient
Temperature
60
50
)
mA
40
(
F
30
20
Forward current I
10
0
-25 -25
0
Ambient temperature Ta (˚C)
50%
Output
90 %
10 %
t
PHL
t
r
t
PLH
Output
V
OH
1.5V
V
OL
t
f
Fig. 2 Power Dissipation vs. Ambient
Temperature
100
Output side power dissipation
80
Input side power dissipation
60
40
Power dissipation P (mW)
20
0
0
25 50 75 100
Ambient temperature Ta (˚C)

GP1A68L
Fig. 3 Low Level Output Current vs.
Ambient Temperature
2.5
)
2.0
mA
(
OL
1.5
1.0
0.5
Low level output current I
0
-25 85
0
25 50 75 100
Ambient temperature Ta (˚C) Forward voltage VF (V
Fig. 5 Relative Threshold Input Current
vs. Supply Voltage
1.2
I
FLH
1.0
, I
FHL
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
Relative threshold input current I
0
0
2.5 5.0 7.5 10.0
Supply voltage V
FHL
IFLH
Ta=25˚C
I
FHL
at Vcc=3V
(V
CC
=1
)
Fig. 7 Low Level Output Voltage vs.
Low Level Output Current
1.00
)
V
(
OL
Ta=25˚C
CC=3V
V
F=5mA
I
Fig. 4 Forward Current vs. Forward Voltage
500
T
= 75˚C
200
)
100
mA
(
50
F
20
10
5
Forward current I
2
1
a
50˚C
-
25˚C
0˚C
25˚C
3.50 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
)
Fig. 6 Relative Threshold Input Current
vs. Ambient Temperature
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
Relative threshold input current
0.4
0.2
-25 0
FHL
I
IFLH
VCC=3V
=1
I
FHL
at Ta=25
˚C
25 50 75 100
Ambient temperature Ta (˚C)
Fig. 8 Low Level Output Voltage vs.
Ambient Temperature
0.4
)
V
(
0.3
OL
CC=3V
V
I
F=5mA
0.10
Low level output voltage V
0.01
0.1 0.2
0.5 1 2 5 10
Low level output current IOL (mA
0.2
OL=2mA
I
OL=1mA
0.1
Low level output voltage V
0.0
-25 0
)
25 50 75 100
Ambient temperature Ta (˚C)
I
OL=0mA
I

GP1A68L
Fig. 9 Low Level Supply Current vs.
Supply Voltage
1.4
F = 5mA
I
)
1.2
mA
(
1.0
CCL
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
Low level supply current I
0.0
246810
0
Supply voltage VCC (V
Ta=- 25˚C
Ta= 25˚C
Ta= 85˚C
)
Fig. 11 Propagation Delay Time vs.
Forward Current
12
CC=3V
V
R
L=3kΩ
)
Ta= 25˚C
10
µ s
(
PLH
,t
8
PHL
6
4
2
Propagation delay time t
0
10 20 30 40 50
0
Forward current I
tPLH
tPHL
)
(mA
F
Fig. 10 High Level Supply Current vs.
Supply Voltage
0.6
F= 0mA
I
)
mA
(
CCH
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
Ta=- 25˚C
Ta= 25˚C
Ta= 85˚C
High level supply current I
0.0
246810
0
Supply voltage VCC (V
)
Fig. 12 Rise, Fall Time vs. Load Resistance
0.4
0.3
)
µ s
(
f
,t
r
0.2
Rise, fall time t
0.1
0
0.1
1 10 100
Load resistance R
L
t
(kΩ
r
tr
CC=5V
V
F= 5mA
I
Ta= 25˚C
)
(Precautions for Operation)
1) It is recommended that a by-pass capacitor of 0.1 µF or more between Vcc and GND near
the device in order to stabilize power supply line.
2) As for other general precautions, refer to the the chapter "Precautions for Use".
 Loading...
Loading...