Page 1
Sharp EL-9900
Graphing Calculator
Basic Keyboard Activities
General Mathematics
Algebra
Programming
Advanced Keyboard Activities
Algebra
Calculus
Statistics
Trigonometry
Programming
Page 2

Sharp EL-9900
Graphing Calculator
Basic Keypad
EL-9900
SUB
SPLIT
TBLSET
DRAW
FORMAT
CALC
OPTION
LIST
CLIP
OFF
A-LOCK
STAT
PLOT
SLIDE
SHOW
2ndF
ALPHA
Y
=
GRAPH
TABLE
WINDOW
ZOOM
TRACE
ON
+
–
.
.
–
+
MATH
Simp
a
STAT
A
GH I J K
a
b
c
LMN
789
QRST
4
VW
1
0
PRGM
BCDEF
b
a
c
a
b
b
c
b
a
SET UP
INS
DEL BS
A.
xxx
RCL VARS
,
{}
(
5
2
SPACE ENTRY ANS
6
3
x
X
+
(–)
%
.
.
int
STO
O
CATALOG
Y
xp
QUIT
CL
–1
x
2
x
x
P
)
U
.
.
–
Z
–
ENTER
Page 3
1
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Press to access the calculation screen.
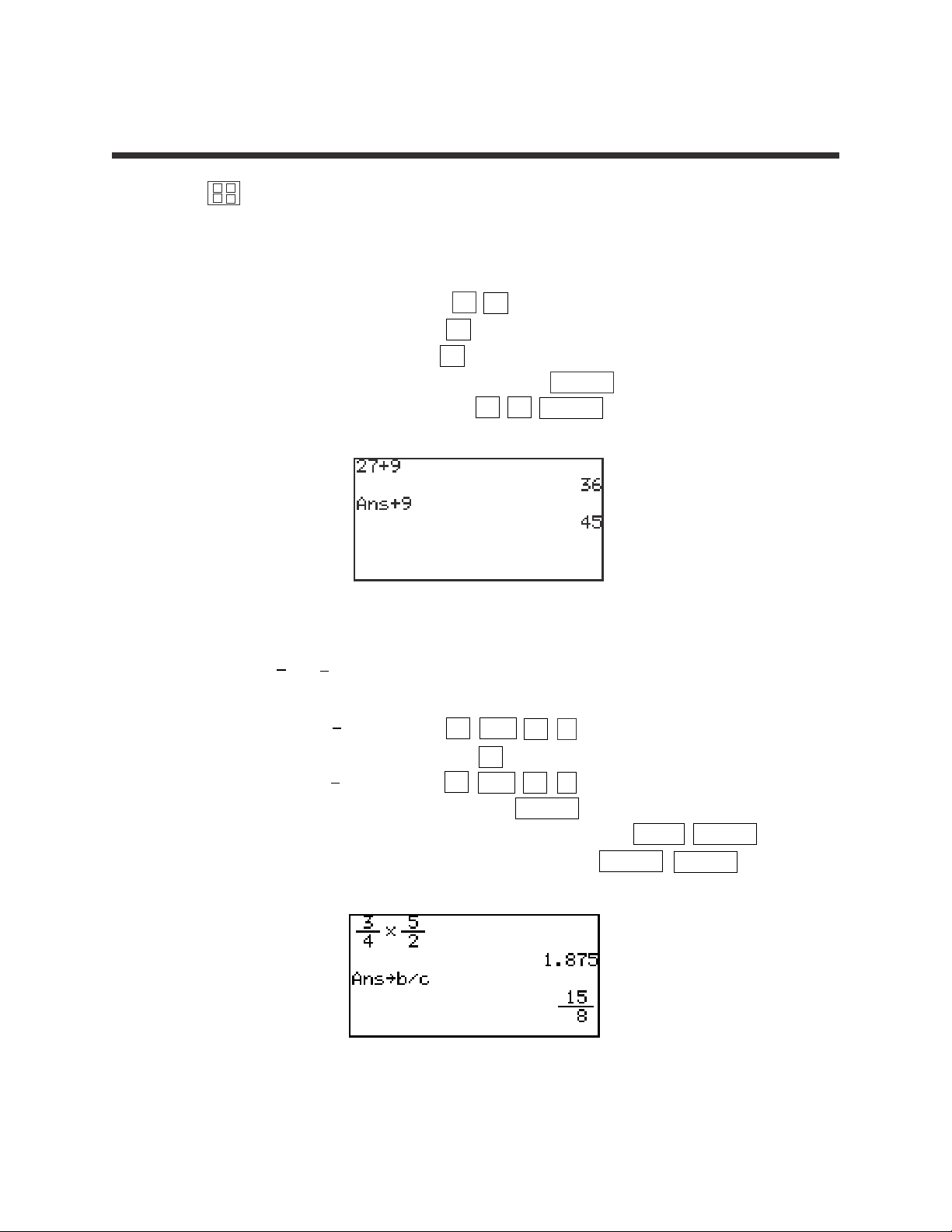
1. Add 9 to 27 twice.
STEP 1: Enter 27 by pressing 2 7 .
STEP 2: Add by pressing the + key.
STEP 3: Enter 9 by pressing 9 .
STEP 4: Find the first sum by pressing the ENTER key.
STEP 5: Add 9 again by pressing + 9 ENTER .
2. Multiply to . Then, convert to a decimal.
STEP 1: Enter by pressing 3 a/b 4 .
STEP 2: Multiply by pressing the × key.
STEP 3: Enter by pressing 5 a/b 2 .
STEP 4: Find the product by pressing ENTER .
STEP 5: Convert to an improper fraction by pressing ➞b/c ENTER .
STEP 6: Convert to a mixed number by pressing ➞ab/c ENTER .
BASIC ARITHMETIC
×
+
–
÷
▼
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
2
▼
Page 4
2
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Press to access the calculation screen.
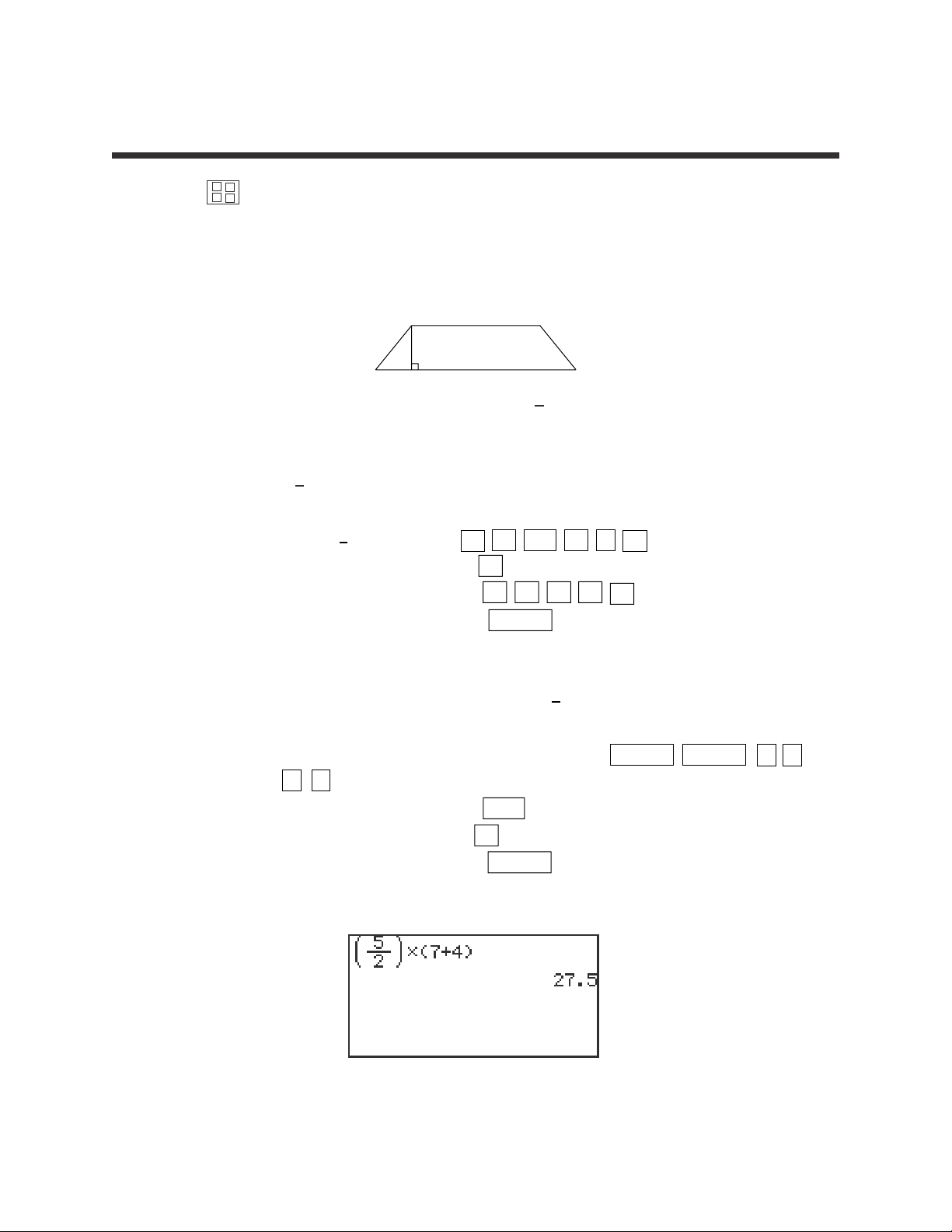
A trapezoid is a four-sided figure where two of the sides are parallel
and the other two sides are not parallel.
The area of a trapezoid is defined to be Area = ( )•(b
1
+ b2) where h
is the height or distance between the parallel sides b
1
and b2.
1. Calculate ( ) × (3 + 4).
STEP 1: Enter ( ) by pressing
(
5 a/b 2
)
.
STEP 2: Multiply by pressing the × key.
STEP 3: Enter (3 + 4) by pressing
(
3 + 4 ).
STEP 4: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is 17.5
2. Edit the previous calculation to find ( )•(7 + 4).
STEP 1: Edit the previous calculation by pressing 2ndF ENTRY
to move the blinking cursor to highlight the 3.
STEP 2: Delete the 3 by pressing DEL to backspace delete.
STEP 3: Insert the 7 by pressing 7 .
STEP 4: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is 27.5.
PARENTHESES AND EDITING
×
+
–
÷
h
2
5
2
5
2
5
2
▼
▼
▼
▼
h
b
1
b
2
▼
Page 5
3
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Press to access the calculation screen.
Mixtures contain two or more components. Percents are often used to
express the amount of a component in a mixture.
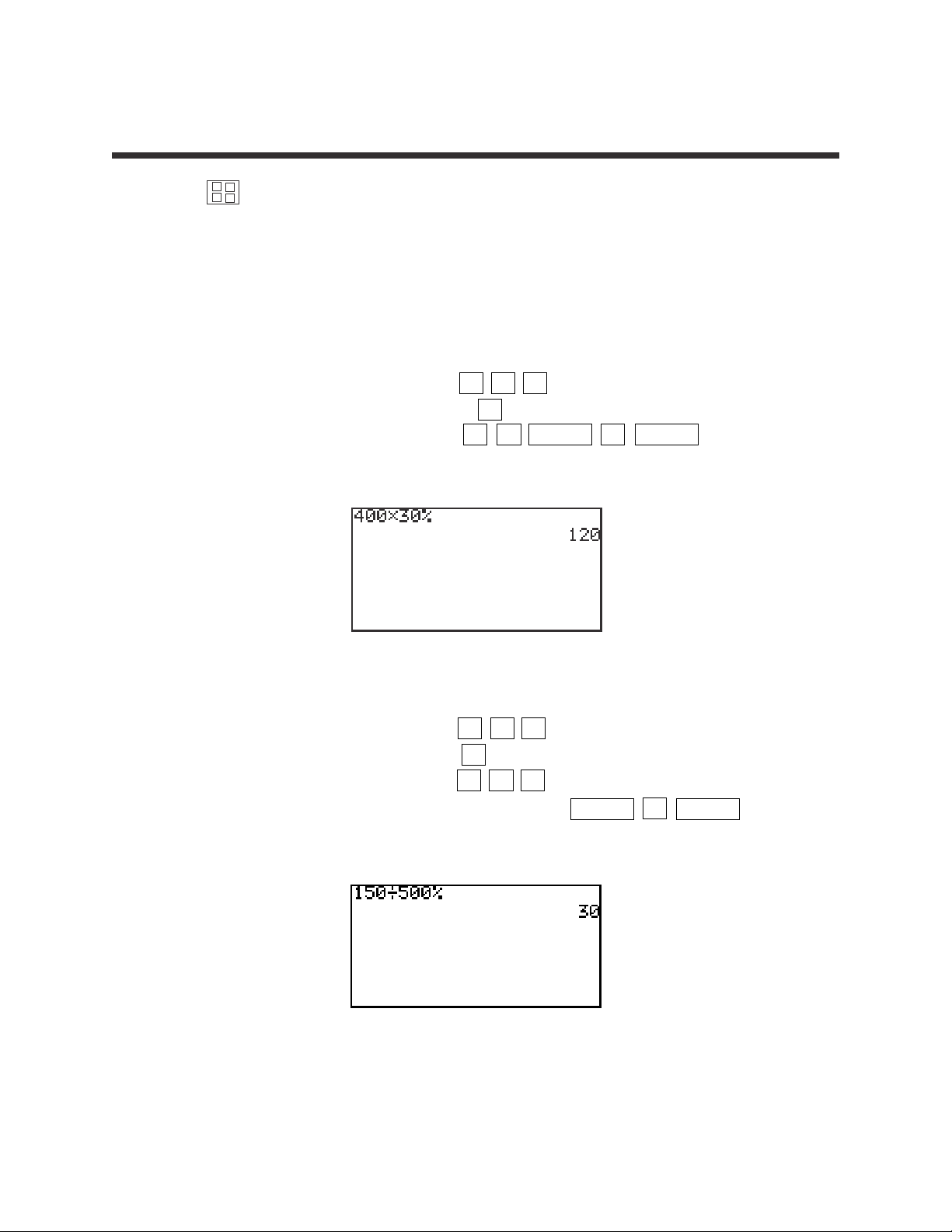
1. Find 30% of 400.
STEP 1: Enter 400 by pressing 4 0 0 .
STEP 2: Multiply by pressing the × key.
STEP 3: Enter 30% by pressing 3 0 2ndF % ENTER .
The answer is 120.
2. Find what percent of 500 is 150.
STEP 1: Enter 150 by pressing 1 5 0 .
STEP 2: Divide by pressing the ÷ key.
STEP 3: Enter 500 by pressing 5 0 0 .
STEP 4: Calculate by percentage by pressing 2ndF % ENTER .
The answer is 30%.
PERCENTS
×
+
–
÷
Page 6
4
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
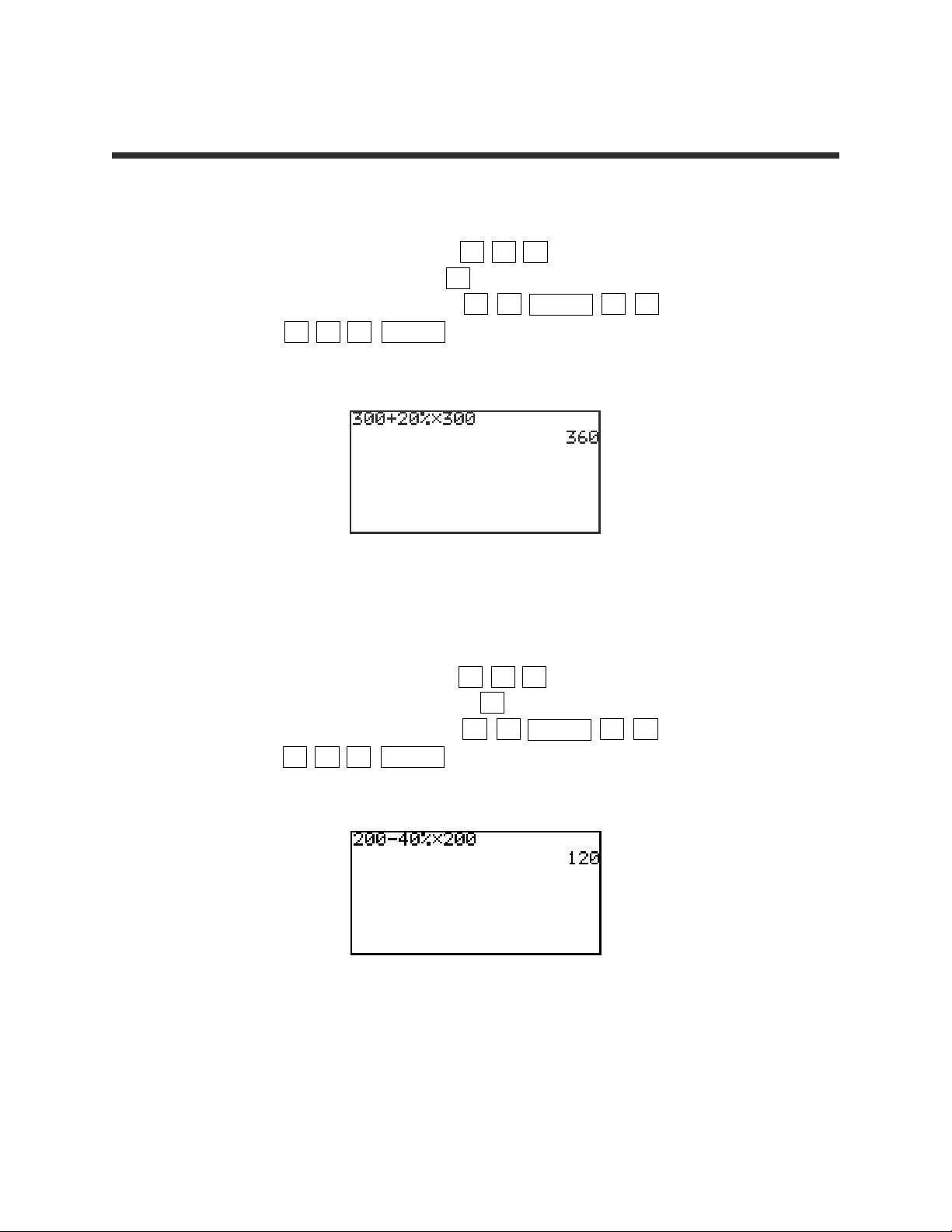
3. Add 20% to 300.
STEP 1: Enter 300 by pressing 3 0 0 .
STEP 2: Add by pressing the + key.
STEP 3: Enter 20% by pressing 2 0 2ndF % ×
3 0 0 ENTER .
The answer is 360.
4. Subtract 40% from 200.
STEP 1: Enter 200 by pressing 2 0 0 .
STEP 2: Subtract by pressing the – key.
STEP 3: Enter 40% by pressing 4 0 2ndF % ×
2 0 0 ENTER .
The answer is 120.
PERCENTS (continued)
Page 7

5
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Press to access the calculation screen.
1. Calculate 2 • 3 and store the value in A. Recall the A to
see the product stored in A.
STEP 1: Multiply 2 and 3 by pressing 2 × 3 ENTER .
The product is 6.
STEP 2: Store 6 into A by pressing STO ALPHA A ENTER .
STEP 3: Clear the screen by pressing CL .
STEP 4: Recall A by pressing ALPHA A ENTER .
2. Calculate 3 • 5 and store the value in M. Calculate 4 • 5
and add this product to M. Then, recall the M to see the
sum of the products.
STEP 1: Multiply 3 and 5 by pressing 3 × 5 ENTER .
The product is 15.
STEP 2: Store 15 into M by pressing STO ALPHA M ENTER .
STEP 3: Multiply 4 and 5 by pressing 4 × 5 ENTER .
The product is 20.
STEP 4: Add 20 to M by pressing + ALPHA M .
The sum of the products is 35.
3. Recall the previous answer.
STEP 1: With the display screen cleared, recall the previous answer
by pressing 2ndF ANS ENTER .
MEMORY USAGE
×
+
–
÷
Page 8
6
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Press to access the calculation screen.
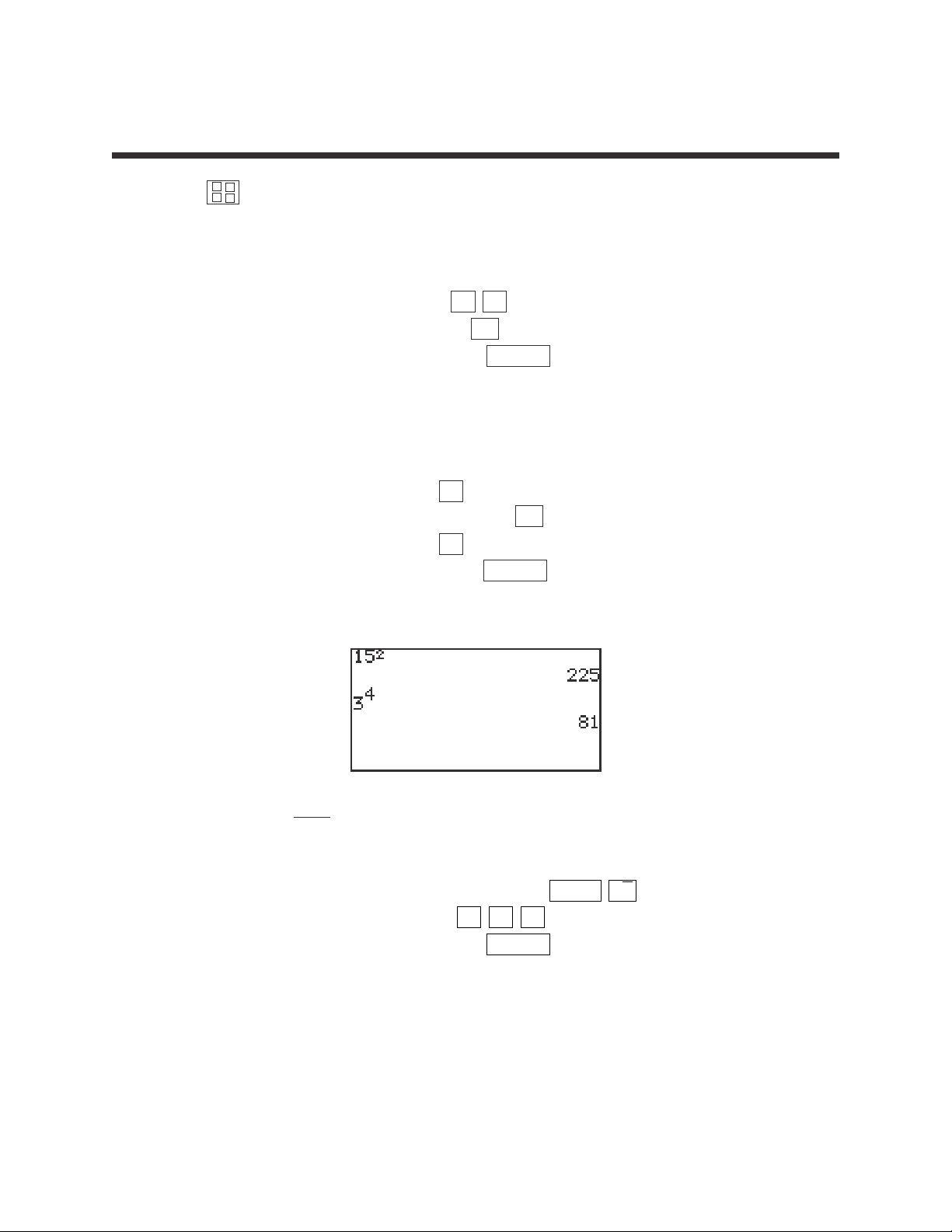
1. Calculate 152.
STEP 1: Enter 15 by pressing 1 5 .
STEP 2: Square by pressing the x
2
key.
STEP 3: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is 225.
2. Calculate 34.
STEP 1: Enter 3 by pressing 3 .
STEP 2: Exponentiate by pressing the a
b
key.
STEP 3: Enter 4 by pressing 4 .
STEP 4: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is 81.
3. Calculate √196.
STEP 1: Enter the square root by pressing 2ndF √ .
STEP 2: Enter 196 by pressing 1 9 6 .
STEP 3: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is 14.
POWERS AND ROOTS
×
+
–
÷
Page 9
7
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Press to access the calculation screen.
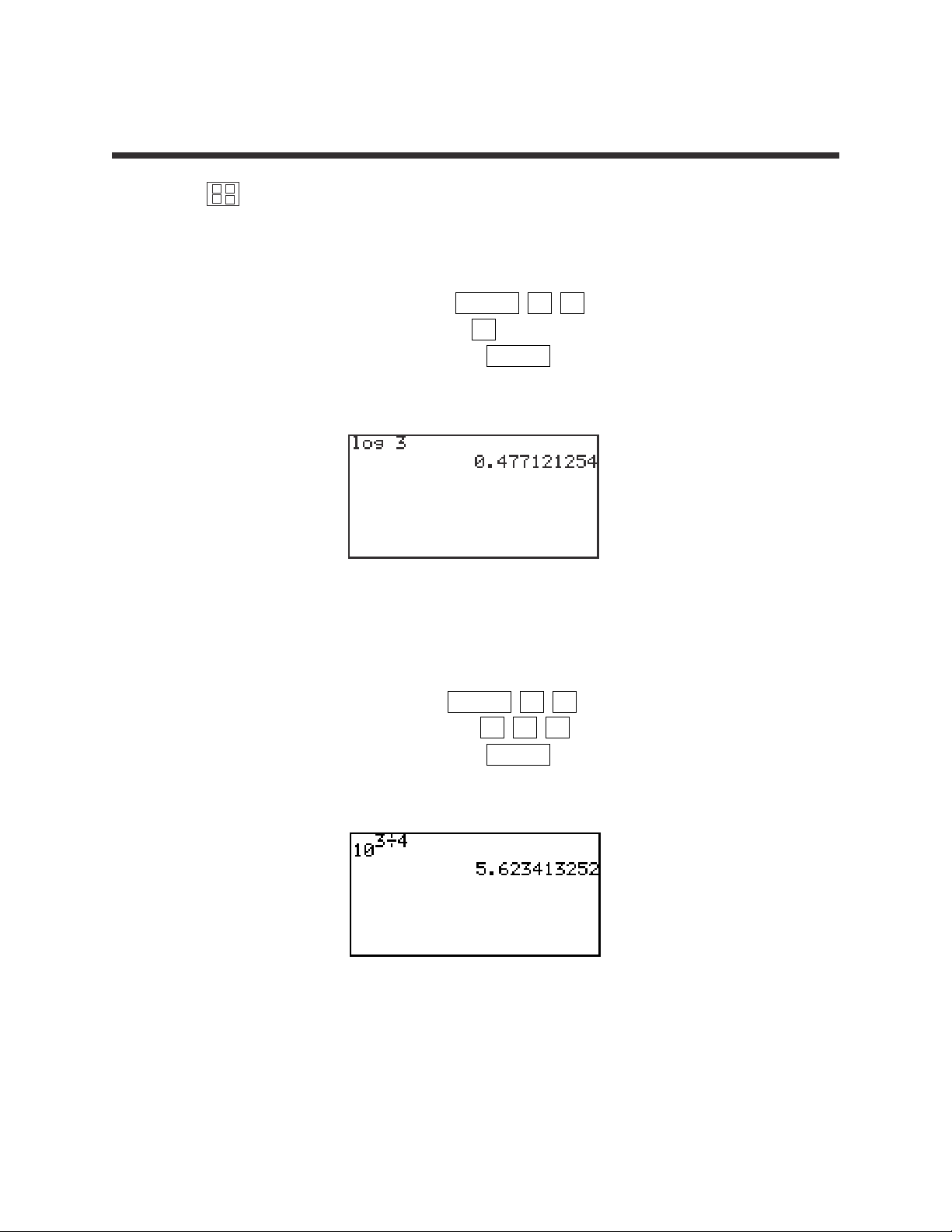
1. Find log 3.
STEP 1: Enter log by pressing MATH A 4 .
STEP 2: Enter 3 by pressing the 3 key.
STEP 3: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is 0.4771.
2. Find 10
(3÷4)
.
STEP 1: Enter 10 by pressing MATH A 5 .
STEP 2: Enter (3 ÷ 4) by pressing 3 ÷ 4 .
STEP 3: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is 5.6234.
LOGARITHMS AND EXPONENTIALS
×
+
–
÷
Page 10
8
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
The definitions of the trigonometric functions with regard to the right triangle
can be used to find distances between points. The sine function is defined to be
opposite side/hypotenuse, the cosine function is adjacent side/hypotenuse, and
the tangent function is opposite side/adjacent side.
Put the calclator in degree mode by pressing 2ndF SETUP B 1 .
1. Find sin 30°.
STEP 1: Press to access the calculation screen.
STEP 2: Enter sin 30 by pressing MATH Α 1 3 0 .
STEP 3: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is 0.5.
2. Find 3cos 20°.
STEP 1: Enter 3 cos 20 by pressing 3 MATH Α 2 2 0 .
STEP 2: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is 2.819
3. Find tan 50°.
STEP 1: Enter tan 50 by pressing MATH Α 3 5 0 .
STEP 2: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is 1.19.
Remember that cotangent = 1/tangent, secant = 1/cosine, and
cosecant = 1/sine.
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
×
+
–
÷
hypotenuse opposite side
adjacent side
θ
Page 11
9
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Put the calclator in radian mode by pressing 2ndF SETUP B 2 .
1. Find sin 2.1.
STEP 1: Press to access the calculation screen.
STEP 2: Enter sin 2.1 by pressing MATH Α 1 2
.
1.
STEP 3: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is .8632
2. Find cos (-1.7).
STEP 1: Enter 3 cos (-1.7) by pressing 3 MATH Α 2
(−)
1
.
7.
STEP 2: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is -.3865
3. Find tan 0.
STEP 1: Enter tan 0 by pressing MATH Α 3 0 .
STEP 2: Calculate by pressing the ENTER key.
The answer is zero.
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (continued)
×
+
–
÷
Page 12
10
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Angles can be expressed in degrees and radians. Degrees can be expressed in
either decimal degrees or degrees-minutes-seconds. The sum of the angles of a
triangle is 180° or π radians.
Press to access the calculation screen.
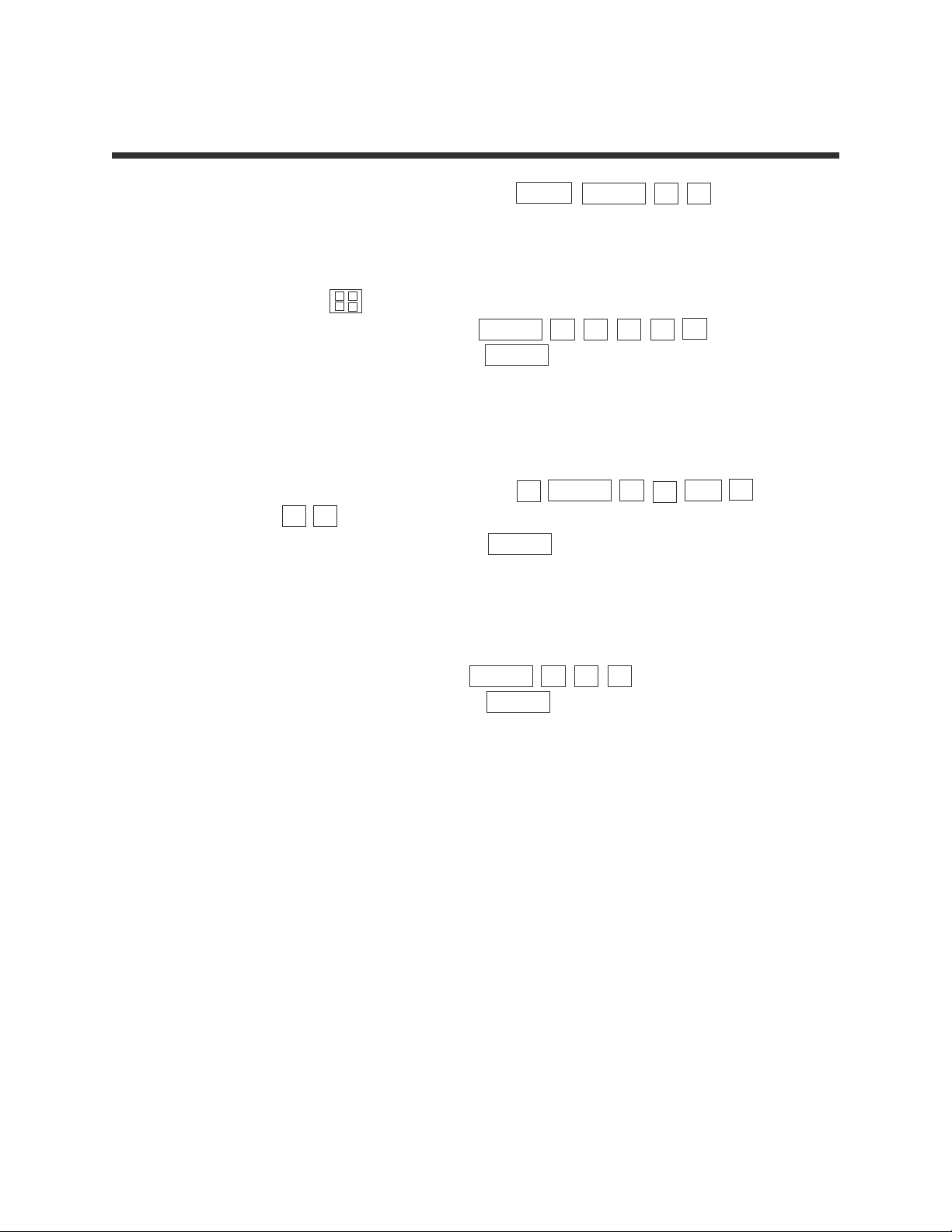
1. Convert 30° to radians.
Put the calclator in radian mode by pressing 2ndF SETUP B 2 .
STEP 1: Enter 30° by pressing 3 0 MATH Ε 1 .
STEP 2: Convert to radians by pressing ENTER .
The answer is 0.5236.
2. Convert 50°35’ to decimal degrees.
STEP 1: Enter 50°35’ by pressing 5 0 MATH E 1 3 5
MATH Ε 2 .
STEP 2: Calculate decimal degrees by pressing ENTER .
The answer is 50.5833.
ANGLE CONVERSIONS
×
+
–
÷
×
+
–
÷
Page 13
11
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
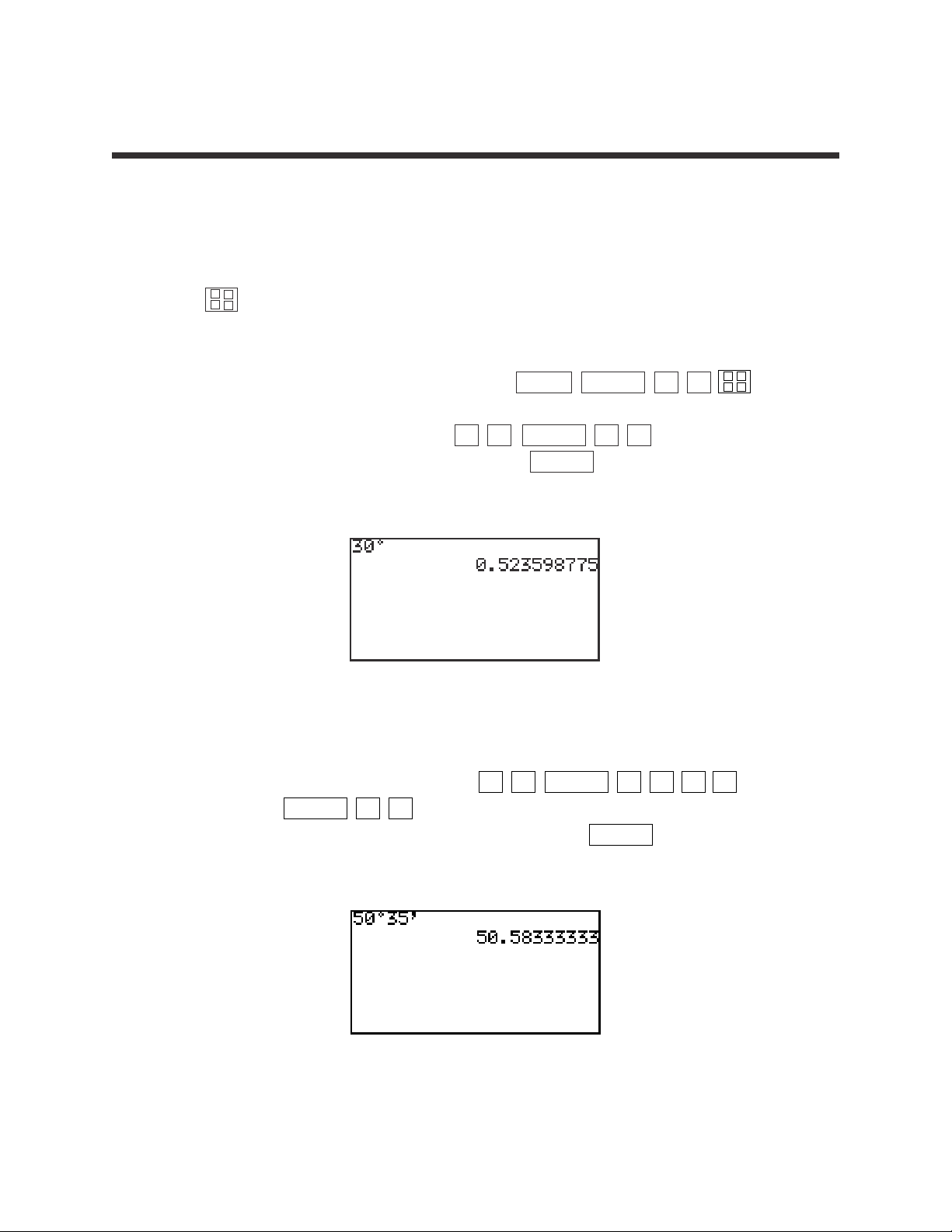
3. Convert 40.235° to degrees-minutes-seconds.
STEP 1: Enter 40.235° by pressing 4 0
.
23 5 .
STEP 2: Calculate degrees-minutes-seconds by pressing
MATH D 2 ENTER .
The answer is 40°14’06”.
4. Convert 1.25 radians to degrees.
Put the calclator in degree mode by pressing 2ndF SETUP B 1 .
STEP 1: Enter 1.25 radians by pressing 1
.
2 5 MATH
E4 .
STEP 2: Convert to degrees by pressing ENTER .
The answer is 71.6°.
ANGLE CONVERSIONS (continued)
×
+
–
÷
Page 14
12
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Press to access the calculation screen.
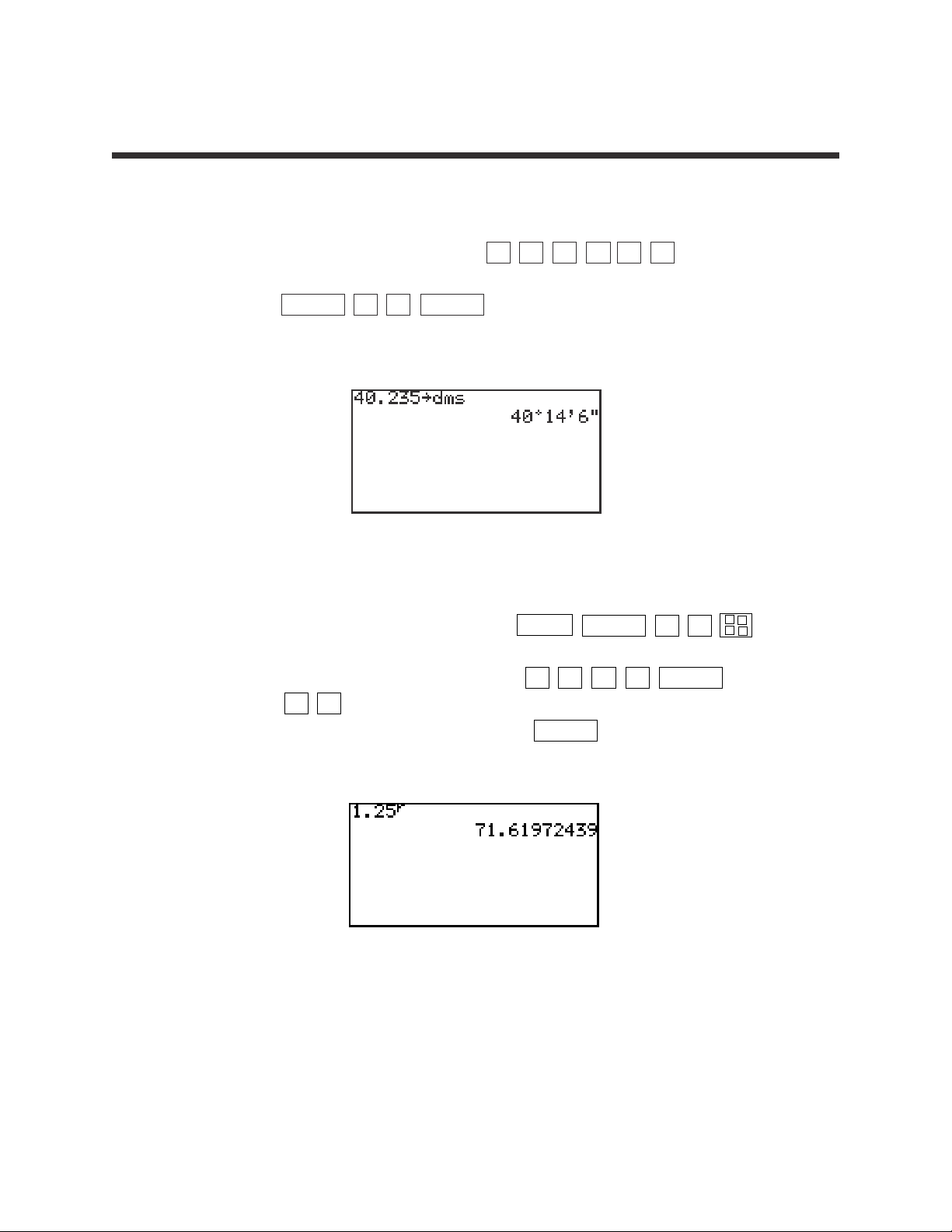
1. Find five factorial or 5!.
STEP 1: Enter 5! by pressing 5 MATH C 7 .
STEP 2: Calculate by pressing ENTER .
The answer is 120.
2. Find the number of combinations of 2 from a group of 5.
STEP 1: Enter the large number 5 by pressing 5 .
STEP 2: Enter the combination symbol by pressing MATH C 6 .
STEP 3: Enter the small number 2 and calculate by pressing
2 ENTER .
The answer is 10.
Permutations are found in the same manner.
3. Randomly select a person from an ordered group of 10.
STEP 1: Access the random integer command by pressing
MATH C 2 .
STEP 2: Enter the lower bound of 1 by pressing 1 ,.
STEP 3: Enter the upper bound of 10 by pressing 1 0 ).
STEP 4: Calculate the random person by pressing ENTER .
Answers will vary.
PROBABILITY
×
+
–
÷
Page 15

13
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Calculate statistics for a one-variable data set.
STEP 1: Turn the calculator on and press STAT to enter the statistics menu.
Press A (EDIT) ENTER to view the statistics data entry screen.
If there is a data set present within the lists on your calculator, use the
arrow keys to move to the list, if necessary, and press ▲ to highlight the
list label. Press DEL ENTER to delete the old data. Repeat for other lists
of data.
STEP 2: Move the highlighter to the cell directly below the L1 in the table.
Enter the following data set:
25 32 28 33 31 27 40 38 29 30
STEP 3: Check the data you have entered and correct any errors you may find.
Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the data entry screen. To calculate the numerical
descriptions of the data set, press STAT C (CALC) and 1 (1_Stats).
Press ENTER and the statistical results will appear.
2. The statistics displayed are:
1. the average or mean value of the data set, ;
2. the standard deviation assuming the data set is a sample from a
population, sx;
3. the standard deviation assuming the data set represents the entire
population, σx;
4. the sum of the data values, ∑x;
5. the sum of the squared data values, ∑x
2
;
Press ▼ five times to see more of the statistics.
6. the number of values in the data set, n;
7. the minimum value in the data set, xmin;
8. the first quartile (25th percentile), Q1;
9. the median (50th percentile), Med;
10. the third quartile (75th percentile), Q3; and
Press ▼ one more time to see the final statistic.
11. the maximum value in the data set, xmax.
ONE-VARIABLE STATISTICS
x
Page 16
14
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for creating a data set's histogram
STEP 1: Turn the calculator on, press STAT A (EDIT) ENTER to view the
statistics data entry screen. Delete old data sets.
STEP 2: Move the highlighter to the cell directly below the L1 in the table and enter
the following data set:
15 28 17 36 38 19 13 25 27 41
STEP 3: Check the data you have entered by pressing ▲ to move back through
the data.
STEP 4: To graph a histogram that represents the data set, you must first press
STAT PLOT A (PLOT1) and press ENTER . A PLOT1 setup screen
will appear. Turn the plot on by pressing ENTER . Select one-variable
data by pressing ▼ ENTER . Set the list to L1 by pressing ▼
2ndF L1 ENTER . A blank Freq: prompt indicates the data is non-weighted
and the frequencies are one. Choose the histogram graph by pressing ▼
STAT PLOT A (HIST) and 1 (Hist).
STEP 5: Set the calculator to rectangular graphing by pressing 2ndF SET UP
E (COORD) 1 (Rect) and press 2ndF QUIT .
STEP 6: Set the viewing window by pressing WINDOW . Set the horizontal axis to
10 < x < 50 with Xscl = 10 by pressing 1 0 ENTER 5 0 ENTER 1
0 ENTER . Set the vertical axis to 0 < y < 5 with Yscl = 1 by pressing 0
ENTER 5 ENTER 1 ENTER .
View the histogram by pressing GRAPH .
HISTOGRAM FOR A
ONE-VARIABLE DATA SET
Page 17
15
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for creating a data set's box-and-whisker chart
STEP 1: Press STAT to enter the statistics menu. Delete old data and enter the
following data set in L1:
1112222344
STEP 2: To construct a box-and-whisker chart, first press STAT PLOT A
ENTER . Press ENTER to turn PLOT1 on. Press ▼ ENTER to choose
one-variable data. Press ▼ 2ndF L1 ENTER to enter L1 as the data
list. Leave the Freq prompt blank. Set the graph to a box-and-whisker
chart by pressing ▼ STAT PLOT E (BOX) 1 Box.
STEP 3: In the example, the data is discrete with a smallest value of 1 and a largest
value of 4. Set the viewing window to 0 < x < 5 with Xscl = 1. Next, set the
vertical axis to 0 < y < 1 with Yscl = 1.
STEP 4: To view the box-and-whisker chart for the data, press GRAPH .
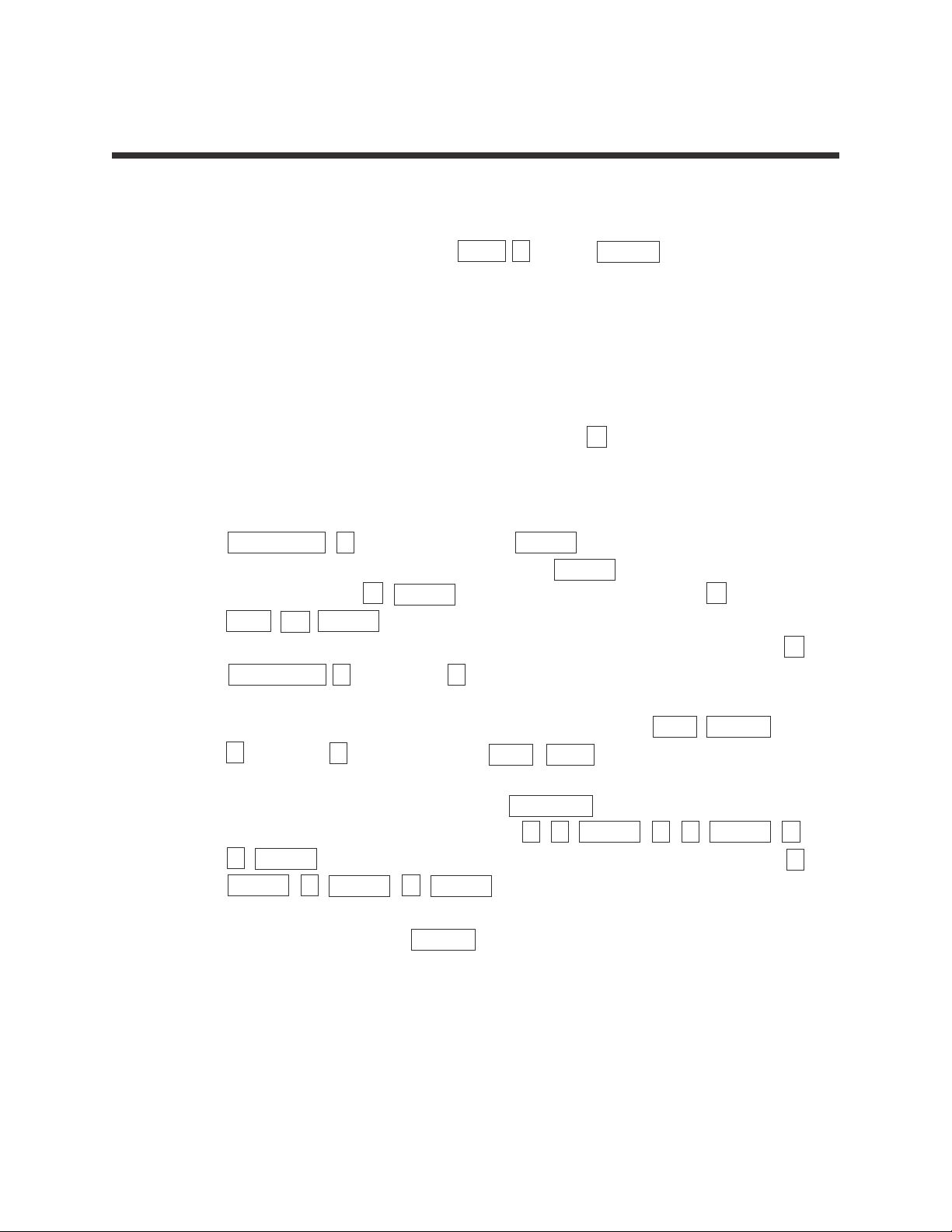
STEP 5: Press TRACE followed by and to view the five values making up the
box-and whisker chart.
STEP 6: Turn PLOT1 off by pressing STAT PLOT ENTER ENTER
2ndF QUIT .
BOX-AND-WHISKER CHART FOR A
ONE-VARIABLE DATA SET
▼
▼
▼
Page 18
16
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for creating a pie chart from count data
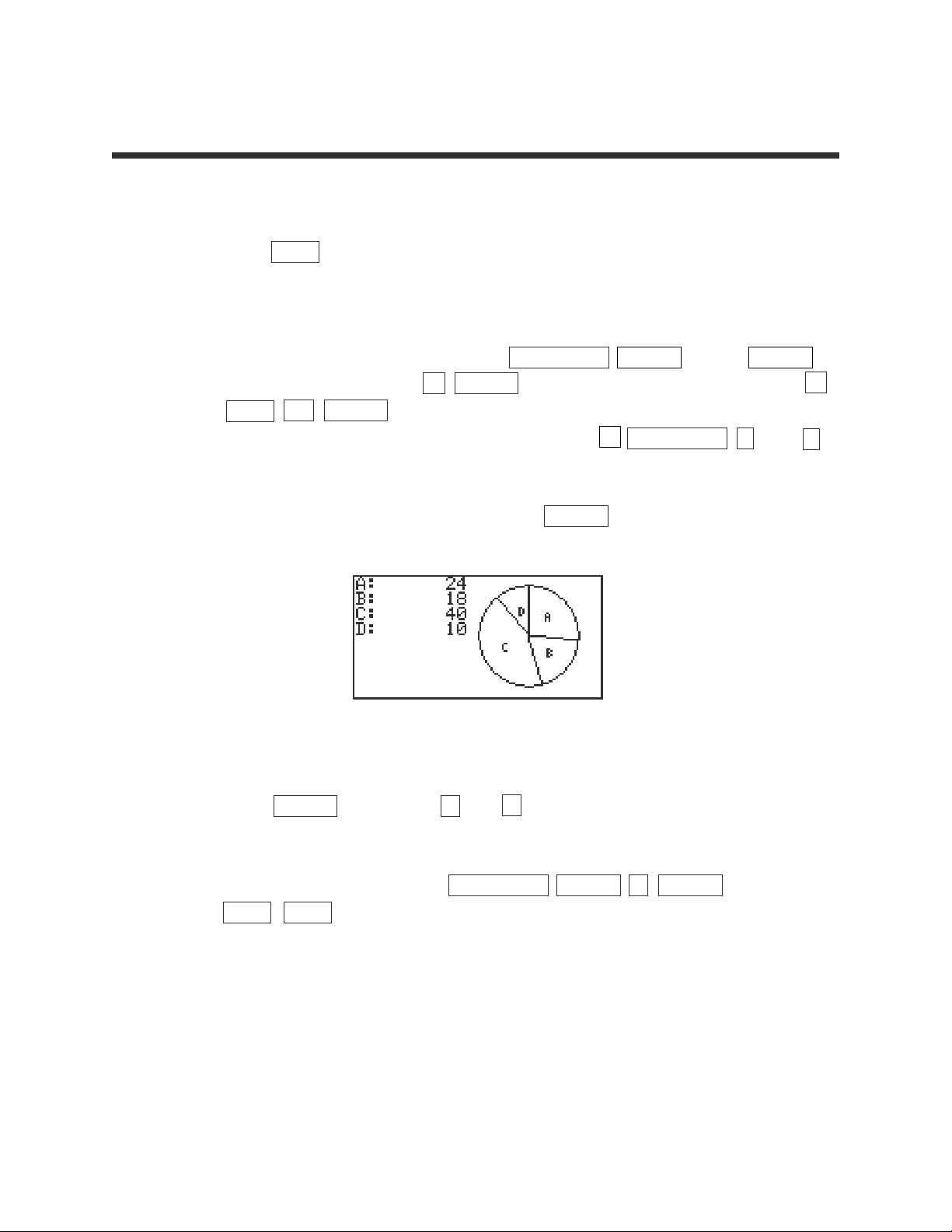
STEP 1: Press STAT to enter the statistics menu. Delete old data and enter the
following data set in L1 using weights in L2:
24 18 40 10
STEP 2: To construct a pie chart, first press STAT PLOT ENTER . Press ENTER
to turn PLOT1 on. Press ▼ ENTER to choose one-variable data. Press ▼
2ndF L1 ENTER to enter L1 as the data list. Leave the Freq prompt
blank. Set the graph to a pie chart by pressing ▼ STAT PLOT F (PIE) 1
(PIE) .
STEP 3: To view the pie chart for the data, press GRAPH .
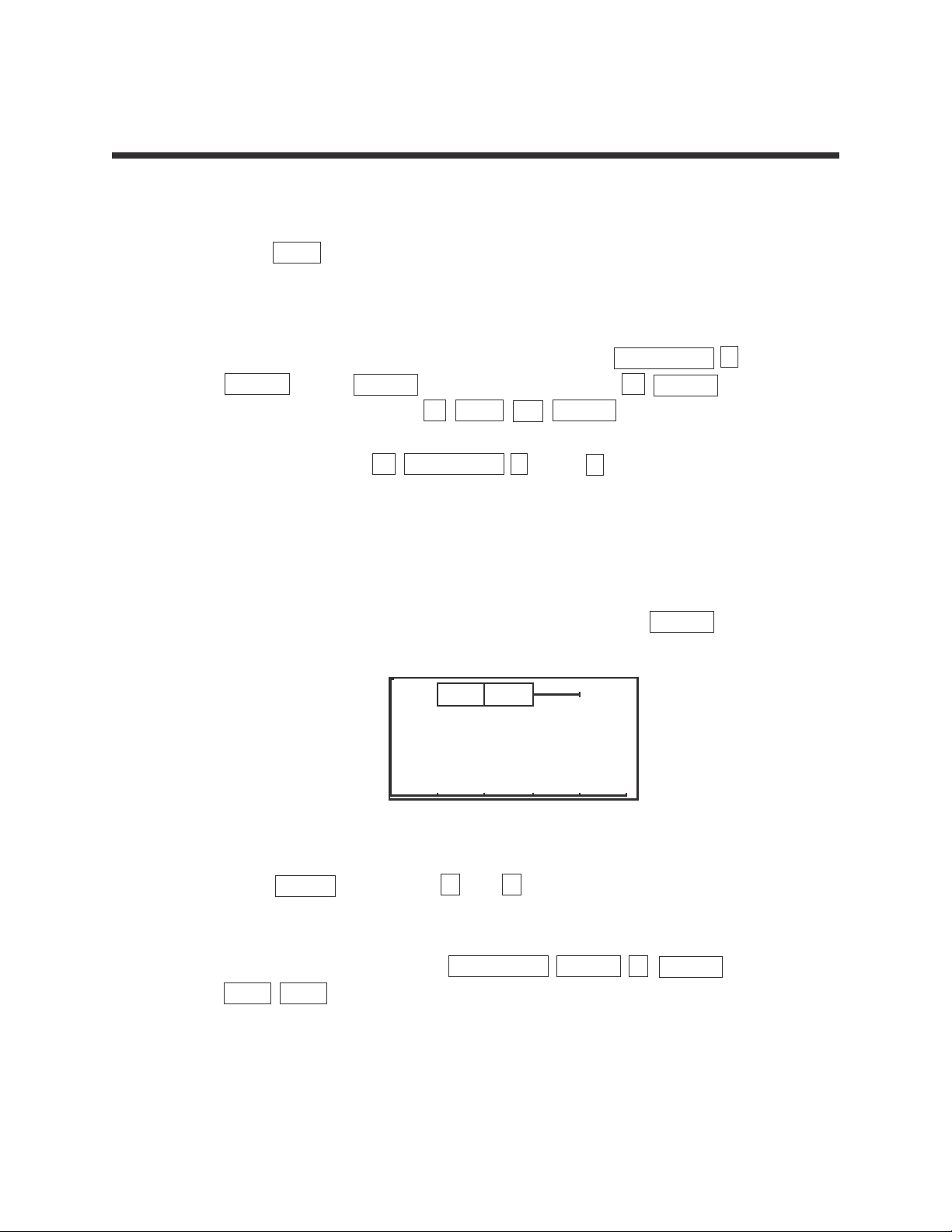
STEP 4: Press TRACE followed by and to highlight and mark the pieces
of the pie chart.
STEP 5: Turn PLOT1 off by pressing STAT PLOT ENTER ENTER
2ndF QUIT .
PIE CHART FOR A
ONE-VARIABLE DATA SET
▼
▼
▼
Page 19

17
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for calculating statistics for a two-variable data set
STEP 1: Turn the calculator on and press STAT to enter the statistics menu. Press
A (EDIT) ENTER to access the data entry screen. Delete old data
by highlighting L1 and pressing DEL ENTER . Repeat for other lists.
STEP 2: Enter the following data set:
X
Y
25 32
28 33
31 27
40 38
29 30
STEP 3: Check the data you have entered and correct any errors you may find.
To calculate the numerical descriptions of the two variables, press 2ndF
QUIT STAT C (CALC) 2 2_Stats. Press ENTER and the statistical
results will appear.
STEP 4: Press ▼ to view the remaining statistics.
The statistics displayed are:
1. the average or mean value of the variable, or ;
2. the standard deviation assuming the data points are a sample from
a population, sx or sy;
3. the standard deviation assuming the data points represents the entire
population, σx or σy;
4. the sum of the values, ∑x or ∑y;
5. the sum of the squared values, ∑x
2
or ∑y2;
6. the number of data points, n;
7. the minimum variable value, xmin or ymin;
8. the maximum variable value, xmax or ymax; and
9. the sum of the x and y products, ∑xy.
STATISTICS FOR A
TWO-VARIABLE DATA SET
x
y
Page 20
18
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for drawing a scatter diagram for a two-variable data set
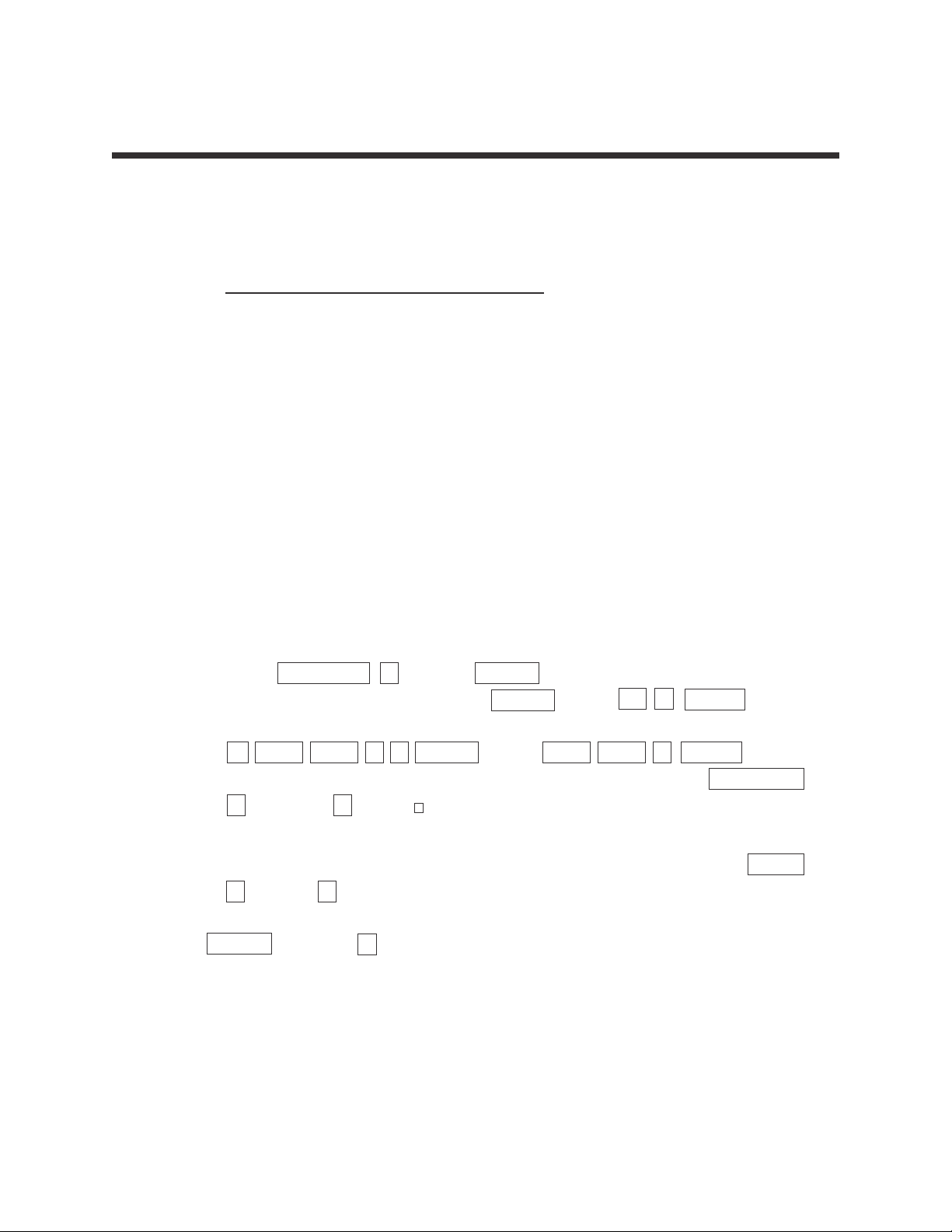
STEP 1: Consider the following table listing the revenue for a large corporation:
Y
ear Revenue (in millions of dollars)
1 48.63
2 48.86
3 48.91
4 49.69
5 51.10
6 52.00
7 52.03
STEP 2: Access the statistics data entry screen and delete old data.
STEP 3: Enter the data using L1 for the year and L2 for the revenue (in millions
of dollars). Check the data and correct any errors you may find.
STEP 4: Press STAT PLOT A (PLOT1) ENTER to access the PLOT1 set up
screen. To turn PLOT 1 on, press ENTER . Press ▼ ENTER
to set the data to two-variable. Set L1 for the x variable by pressing
▼ 2ndF LIST A 1 ENTER . Press 2ndF LIST 2 ENTER to set L2
for the y variable. To set the graph to scatter diagram, press STAT PLOT
G (S.D.) and 3 (Scattr ).
STEP 5: Construct an autoscaled scatter diagram of this data set by pressing ZOOM
A (ZOOM) 9 (Stat).
Press TRACE and press repeatedly to verify that Xmin= 1, Xmax= 7,
Ymin= 48.63, and Ymax= 52.03.
SCATTER DIAGRAM
FOR A TWO-VARIABLE DATA SET
▼
▼
Page 21
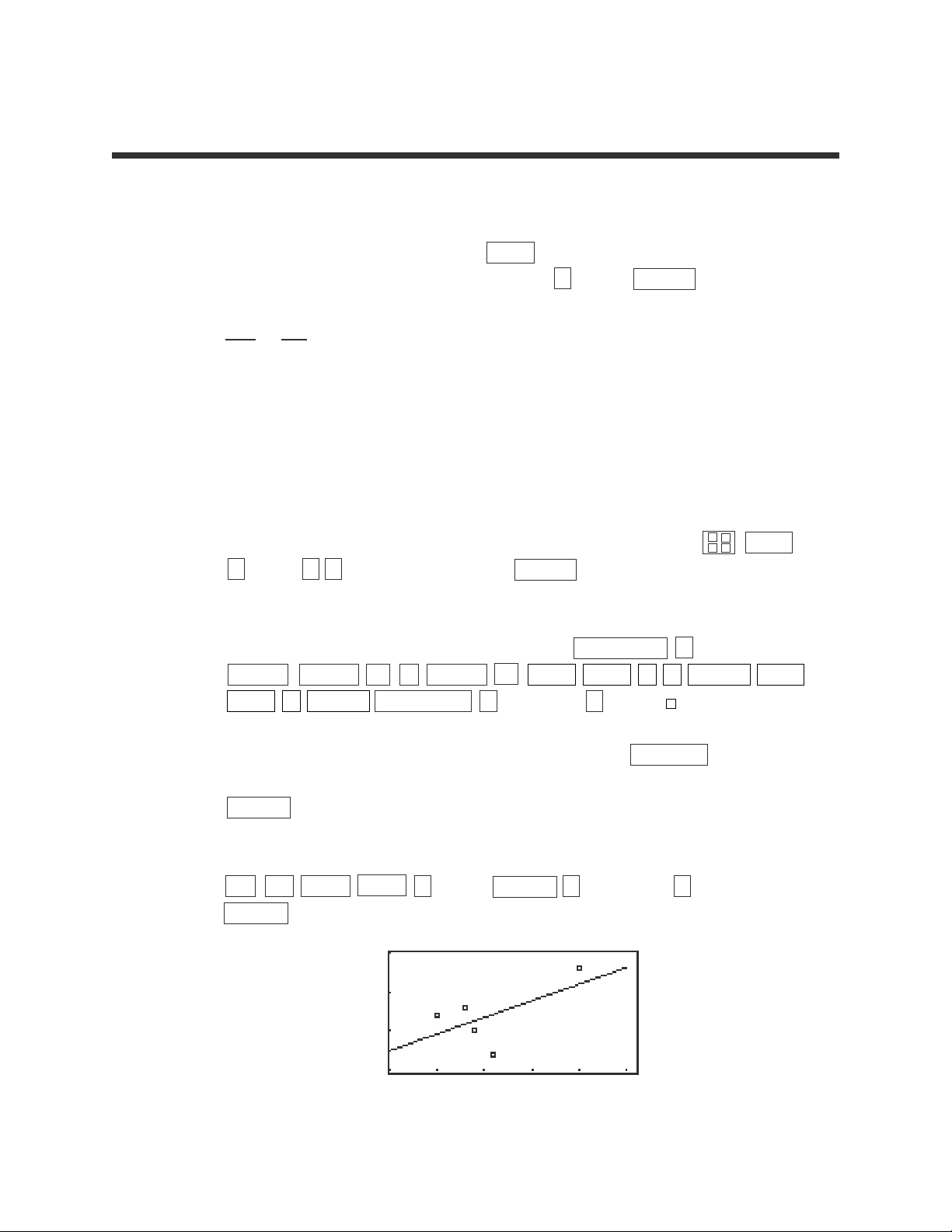
19
Basic Keyboard/GENERAL MATHEMATICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for calculating the best-fitting line
STEP 1: Turn the calculator on and press STAT to enter the statistics menu.
Access the data entry screen by pressing A (EDIT) ENTER .
Delete old data and enter the following data set:
X
Y
25 32
28 33
31 27
40 38
29 30
Check the data you have entered and correct any errors you may find.
STEP 2: To find the best-fitting line (regression line) for the data, press STAT
D (REG) 0 2 (Rg_ax+b) and press ENTER .
STEP 3: To overlay the regression line and the scatter diagram for the data, you must
first set up the scatter diagram by pressing STAT PLOT A (PLOT1)
ENTER ENTER ▼ ENTER ▼ 2ndF LIST A 1 ENTER 2ndF
LIST 2 ENTER STAT PLOT G (S.D.) and 3 (Scattr ).
STEP 4: Display the scatter diagram for the data by pressing WINDOW and setting
Xmin = 20, Xmax = 45, Xscl = 5, Ymin = 25, Ymax = 40, and Yscl = 5. Press
GRAPH to view the scatter diagram.
STEP 5: To view the overlay of the regression line and the scatter diagram, press
Y= CL 2ndF VARS H (STAT) ENTER B (REGEQN) 1 (RegEqn)
GRAPH .
LINEAR REGRESSIONS
×
+
–
÷
▼
Page 22
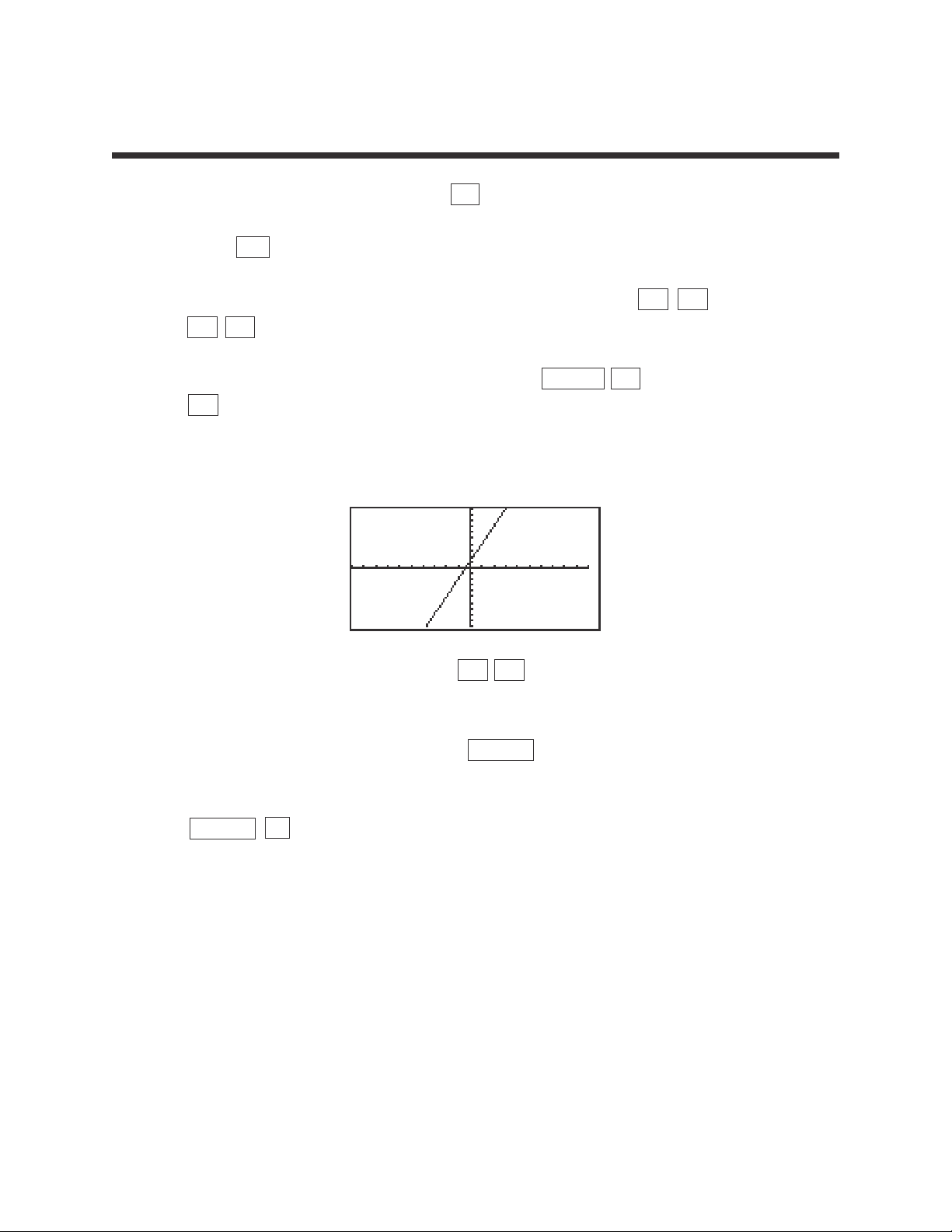
1
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Turn the calculator on and press Y= .
2. Press CL to remove an old Y1 expression.
3. Enter the linear equation ( y = 3x + 1 ) for Y1 by pressing 3 x
+ 1 .
4. Enter the viewing window range by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM)
5 (Default). This establishes the default viewing ranges for graphing
equations. These ranges are -10 < x < 10 and -10 < y < 10.
The scale for the x and y axes are 1.
5. To graph another equation, press Y= CL to access and clear the Y1=
prompt.
6. Enter the next equation, and press GRAPH to view the graph.
7. If the line does not appear in the default viewing window, press
ZOOM 4 (OUT) to enlarge the viewing window.
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS
Page 23
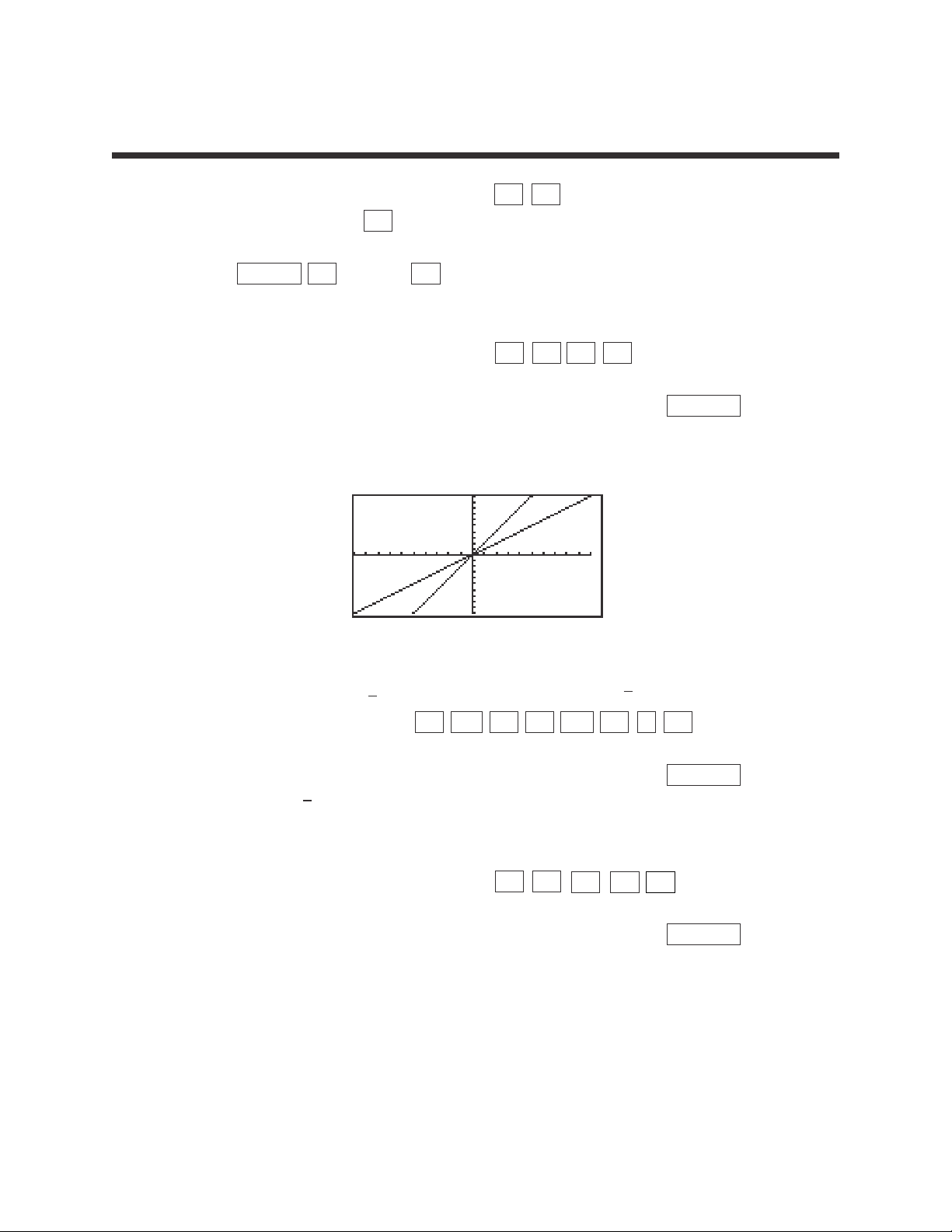
2
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Graph the equation y = 1x by pressing Y= CL to remove an old Y1
expression, and press x to enter the equation.
2. Press ZOOM A (ZOOM) 5 (Default) to view the graph.
3. Changing the slope to 2 will result in the equation y = 2x.
Enter this equation for Y2 by pressing Y= ▼ 2 x .
4. To view both the graphs on the same coordinate axes, press GRAPH .
The graph y = 2x has a greater slope than y = x.
5. Changing the slope to will result in the equation y = x. Enter this
equation for Y2 by pressing Y= ▼ CL 1 a/b 2 x .
6. To view both the graphs on the same coordinate axes, press GRAPH .
The graph y = x has less slope than y = x.
7. Changing the slope to -1 will result in the equation y =-x.
Enter this equation for Y2 by pressing Y= ▼ CL
(-)
x .
8. To view both the graphs on the same coordinate axes, press GRAPH .
The graph y =-x has the opposite slope of y = x.
CHARACTERISTICS OF SLOPE
1
2
1
2
▼
1
2
Page 24
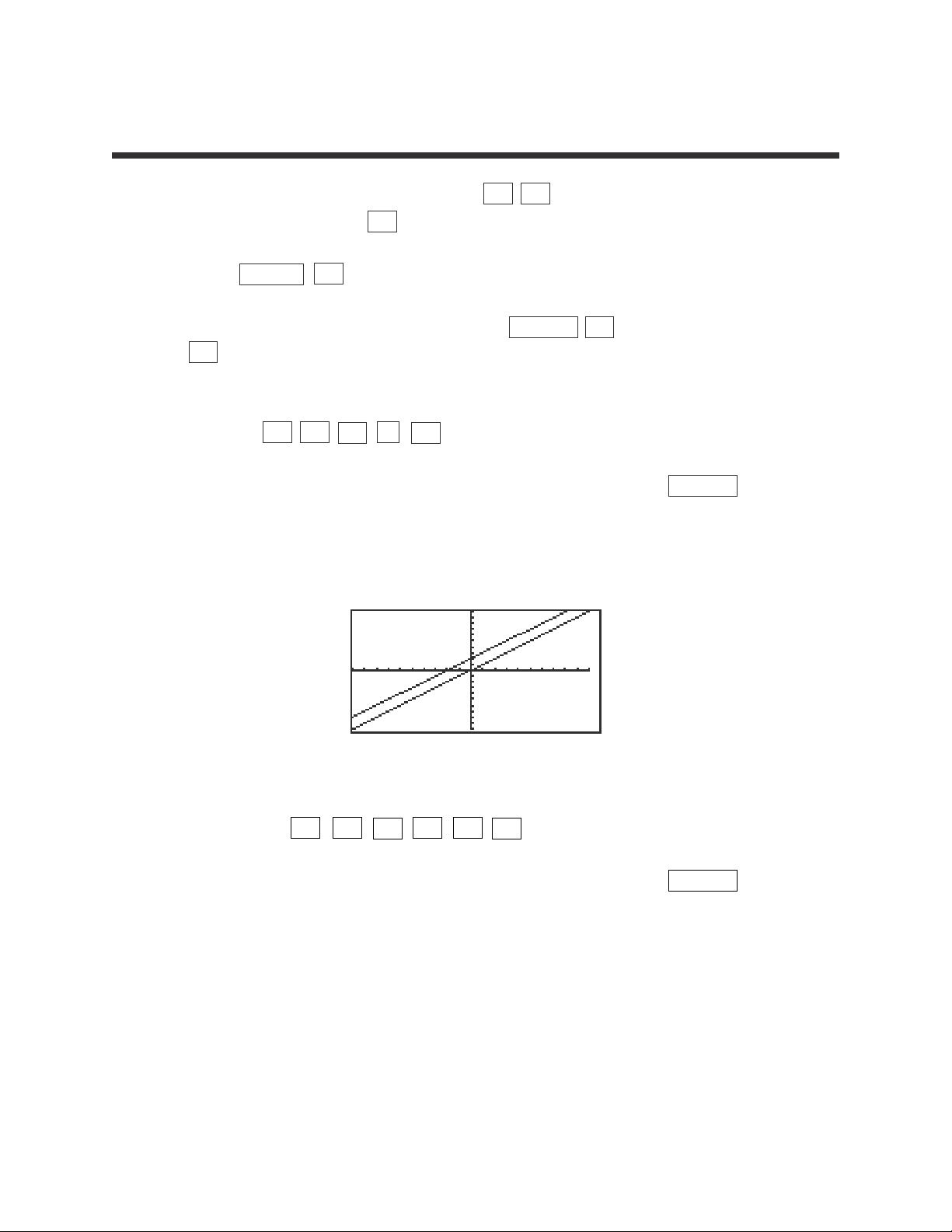
3
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Graph the equation y = x by pressing Y= CL to remove an old Y1
expression, and press x to enter the equation.
2. Press ENTER CL to clear Y2 or additional prompts.
3. Use the default viewing range, and press ZOOM A (ZOOM)
5 (Default) to view the graph.
4. Adding 2 will result in the equation y = x + 2. Enter this equation for Y2 by
pressing Y= ▼ x
+
2 .
5. To view both the graphs on the same coordinate axes, press GRAPH .
The graph y = x + 2 has shifted up from the graph of y = x . The y -
intercept is now y = 2.
6. Subtracting 2 will result in the equation y = x – 2. Enter this equation for Y2
by pressing Y= ▼ CL x – 2 .
7. To view both the graphs on the same coordinate axes, press GRAPH .
The graph y = x – 2 has shifted down from the graph of y = x . The y -
intercept is now y =-2.
CHARATERISTICS OF THE y-INTERCEPT
Page 25
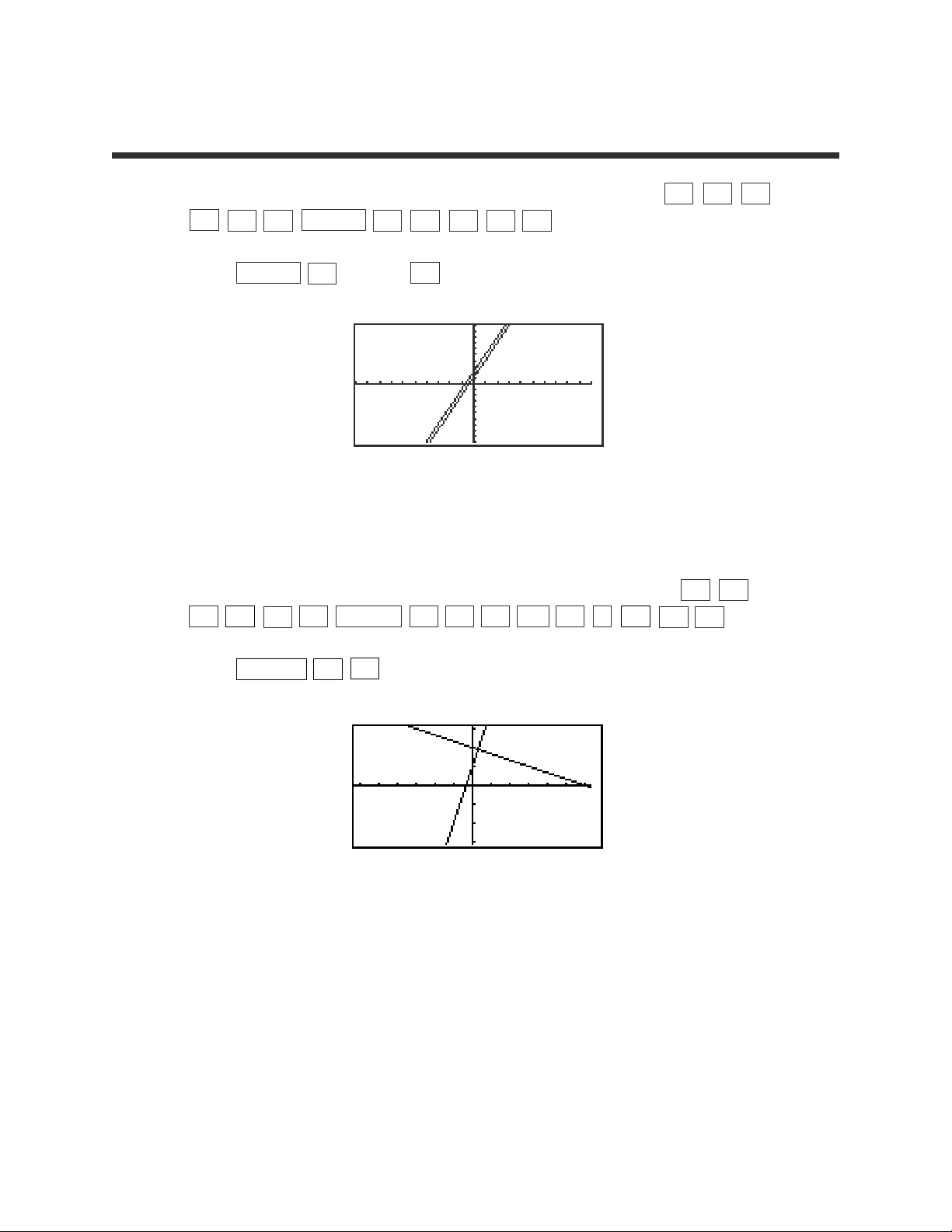
4
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Enter the equations Y1 = 3X + 1 and Y2 = 3X + 2 by pressing Y= CL 3
x
+ 1 ENTER CL 3 x + 2 .
2. Press ZOOM A (ZOOM) 5 (Default) to view the graphs.
3. These lines are called parallel since they have an equal slope but different
y-intercepts. These lines will not intersect.
4. Enter the equations Y1 = 3X - 1 and Y2 = -1/3 X + 1 by pressing Y= CL
3 x – 1 ENTER CL
(-)
1 a/b 3 x
+ 1 .
5. Press ZOOM A 7 to view the graphs.
6. These line are called perpendicular since they have slopes that are negative
reciprocals of each other (m
1
= -1/m2). Notice, these intersecting lines form
four equal angles.
7. Graph two lines with unequal slopes (not negative reciprocals). What do
you see? Are the lines parallel, perpendicular or neither?
PARALLEL AND
PERPENDICULAR LINES
▼
Page 26
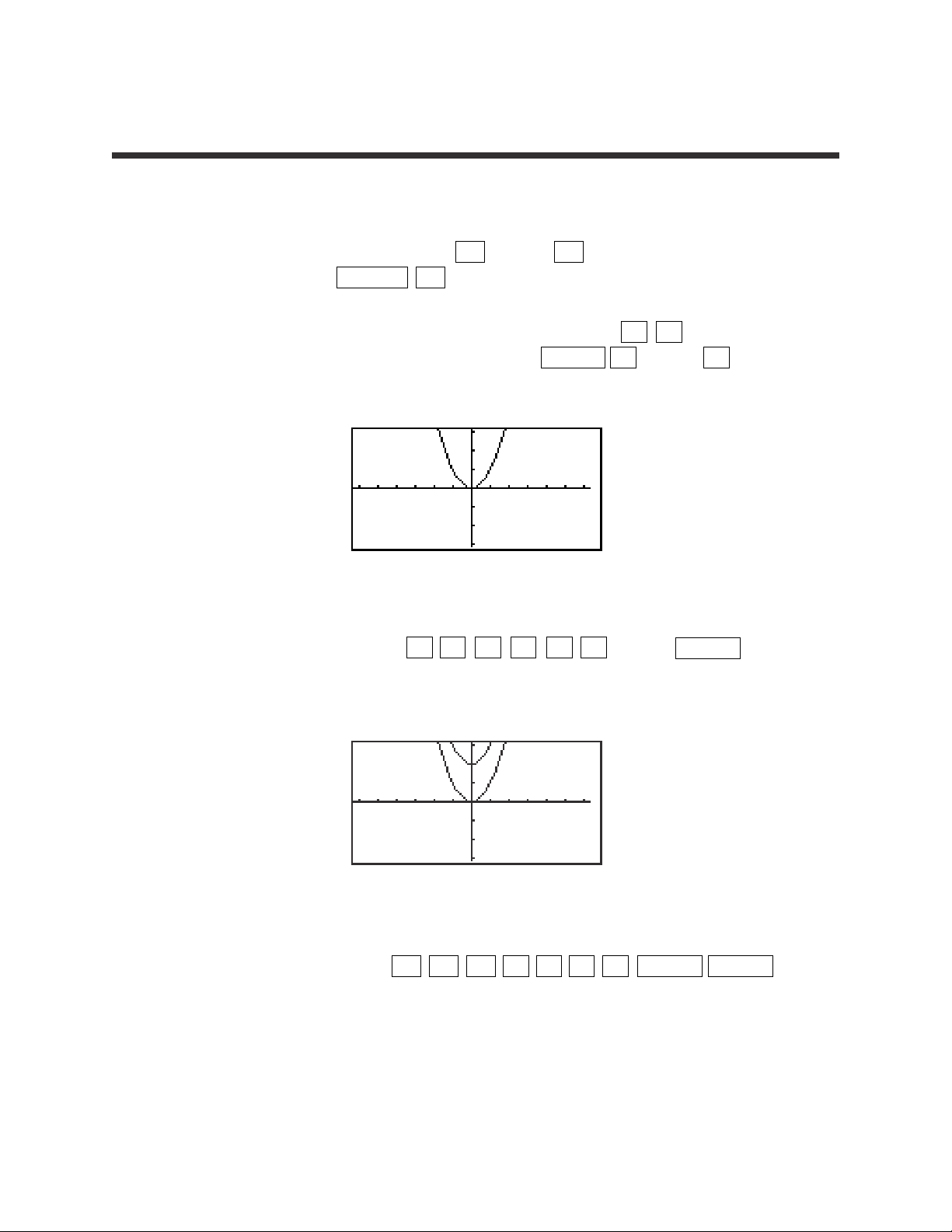
5
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Graphing and translations of quadratic equations
1. Turn the calculator on and press Y= . Press CL to remove an old Y1
expression. Press ENTER CL to remove an old Y2 expression.
2. To enter the quadratic equation ( y = x
2
) for Y1, press x x2.
Enter the viewing window range by pressing ZOOM A (Zoom) 7 (Dec).
3. When 2 is added to x2, the resulting equation is y = x2+ 2. Enter this
function for Y2 by pressing Y=
▼ x x
2
+ 2 . Press GRAPH .
What does the addition of 2 do?
4. When -2 is added to x2, the resulting equation is y = x2– 2. To change Y2
for this expression, press Y=
▼ CL x x
2
– 2 ENTER GRAPH .
What does the addition of -2 do?
QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
Page 27
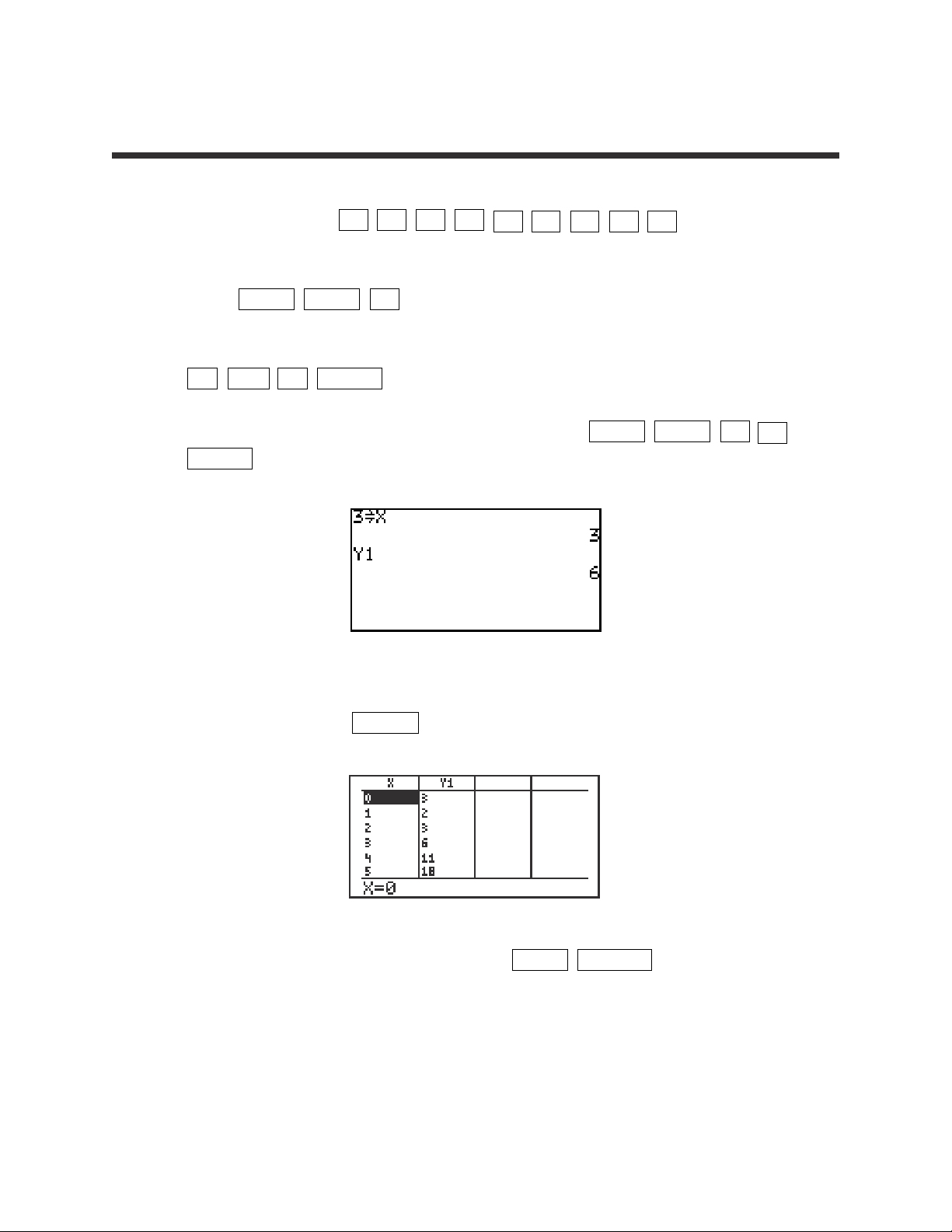
6
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. For example, to evaluate f(x)=x
2
-
2x + 3 for x=3, you will enter the function
for Y1 by pressing Y= CL x x
2
– 2 x + 3 . Be sure
to clear any other expressions.
2. Press 2ndF QUIT CL to return to and clear the calculation screen.
3. To evaluate the function at x = 3, first store 3 into the X variable by pressing
3 STO x ENTER .
4. Evaluate the function stored in Y1 at 3 by pressing 2ndF VARS A 1
ENTER .
5. Another way to evaluate a function for several values is using the Sharp’s
table feature. Press TABLE to view a table of values.
6. You can customize the table by pressing 2ndF TBLSET . You can set
the table’s minimum x value (TBLStrt) to another value than zero, and you
can change the table’s increment value (TBLStep) from 1 to another value.
EVALUATING A FUNCTION
Page 28
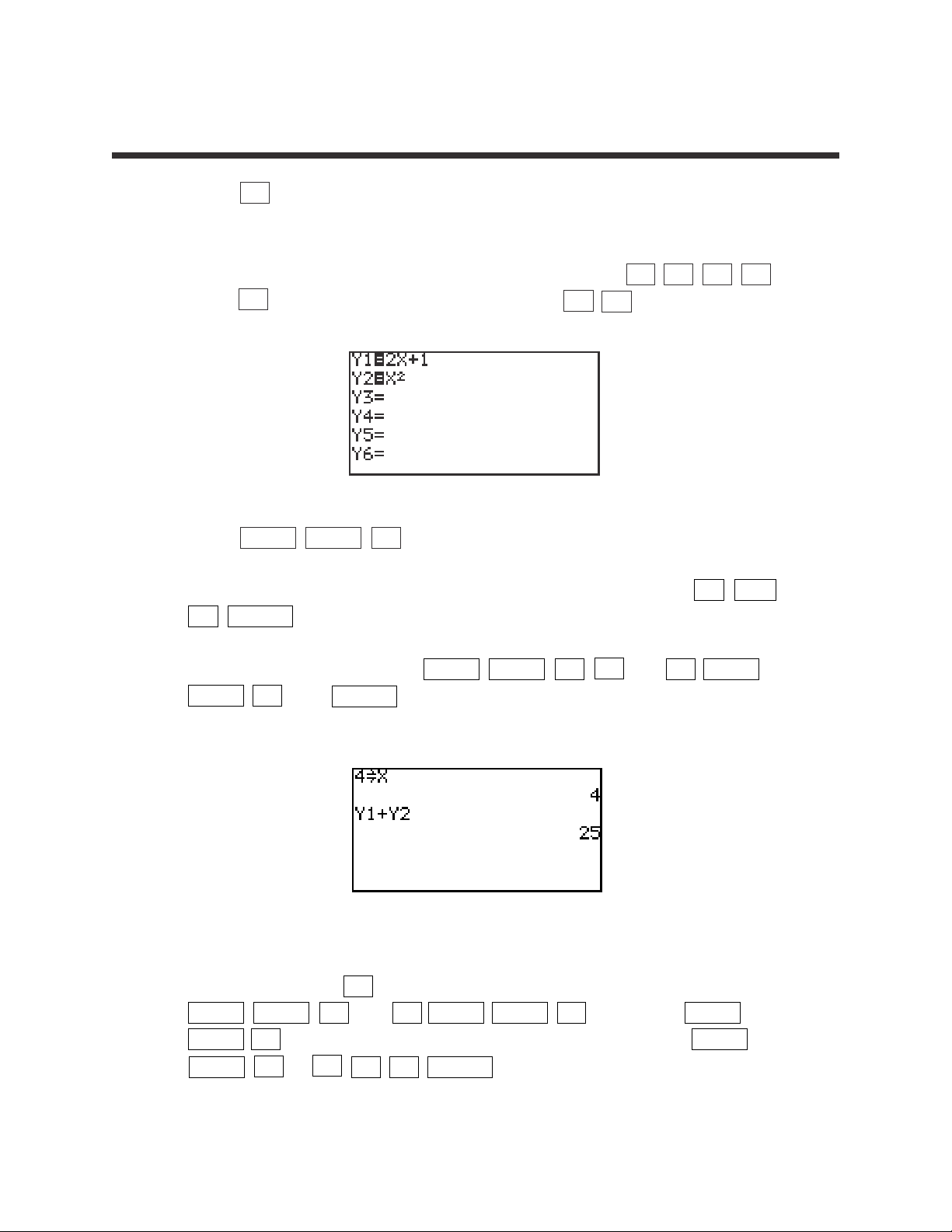
7
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Press Y= and clear old expressions.
2. Enter the functions for Y1 and Y2. For example, enter f(x)=2x + 1 for Y1 and
g(x)=x
2
for Y2 by moving the cursor to Y1 and pressing 2 x + 1 ,
press ▼ to move the cursor to Y2, and press x x
2
.
3. Press 2ndF QUIT CL to return to and clear the calculation screen.
4. To evaluate (f+g)(4), first store 4 into the X variable by pressing 4 STO
x ENTER .
5. Evaluate (f+g)(4) by pressing 2ndF VARS A 1 (Y1) + 2ndF
VARS 2 (Y2) ENTER . This can be repeated for (f-g)(x), (fg)(x), and
(f/g)(x).
6. Another way to conduct an operation on functions and evaluate it for a value
is to use Y3. Press Y= and enter the operation (f-g)(x) into Y3 by pressing
2ndF VARS 1 (Y1) – 2ndF VARS 2 (Y2). Press 2ndF
QUIT CL to return to and clear the calculation screen. Press 2ndF
VARS 3 Y3
(
4
)
ENTER .
OPERATIONS ON FUNCTIONS
Page 29
8
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Press Y= and clear old expressions.
2. Enter the two functions to be composed for Y1 and Y2. For example, enter
y=x
2
–1 for Y1 by pressing x x
2
– 1 ENTER and y=x+1 for Y2 by
pressing x
+
1 ENTER .
3. Enter the composition of Y2 into Y1 for Y3 by pressing 2ndF VARS A
1 (Y1)
(
2ndF VARS 2 (Y2)
)
ENTER .
4. Keep Y1 and Y2 graphs from appearing by deselecting Y1 and Y2. Do this by
pressing ENTER ENTER .
5. Press ZOOM A 7 (Dec) to view the composition of Y2 into Y1 in the
decimal window.
6. Change the Y3 composition to Y1 in Y2 by pressing Y= CL
2ndF VARS 2 (Y2)
(
2ndF VARS 1 (Y1) ).
7. Press ZOOM A 7 (Decimal) to view the composition of Y1 into Y2 in
the decimal window.
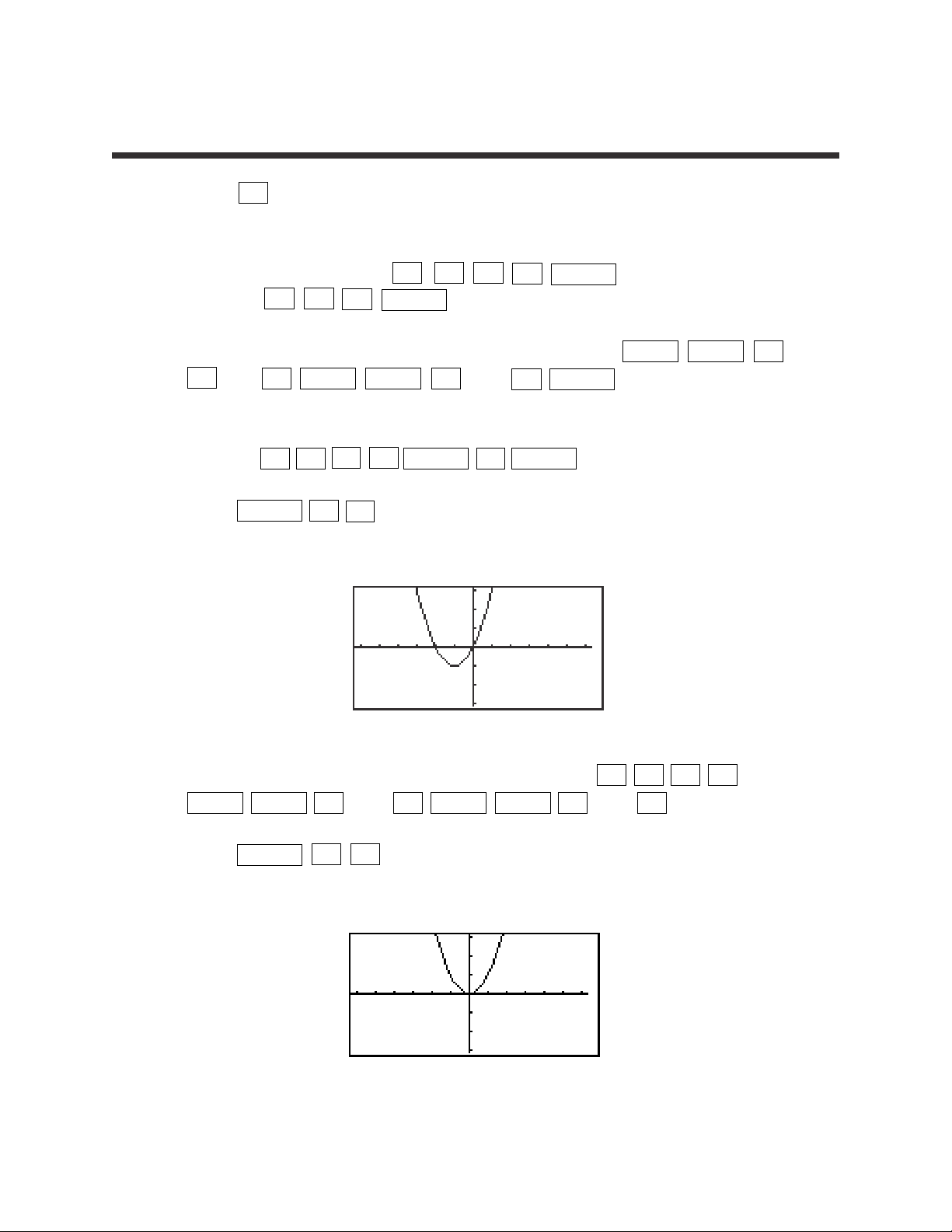
COMPOSITION OF FUNCTIONS
▼▼▼
▼
▼
▼ ▼
Page 30
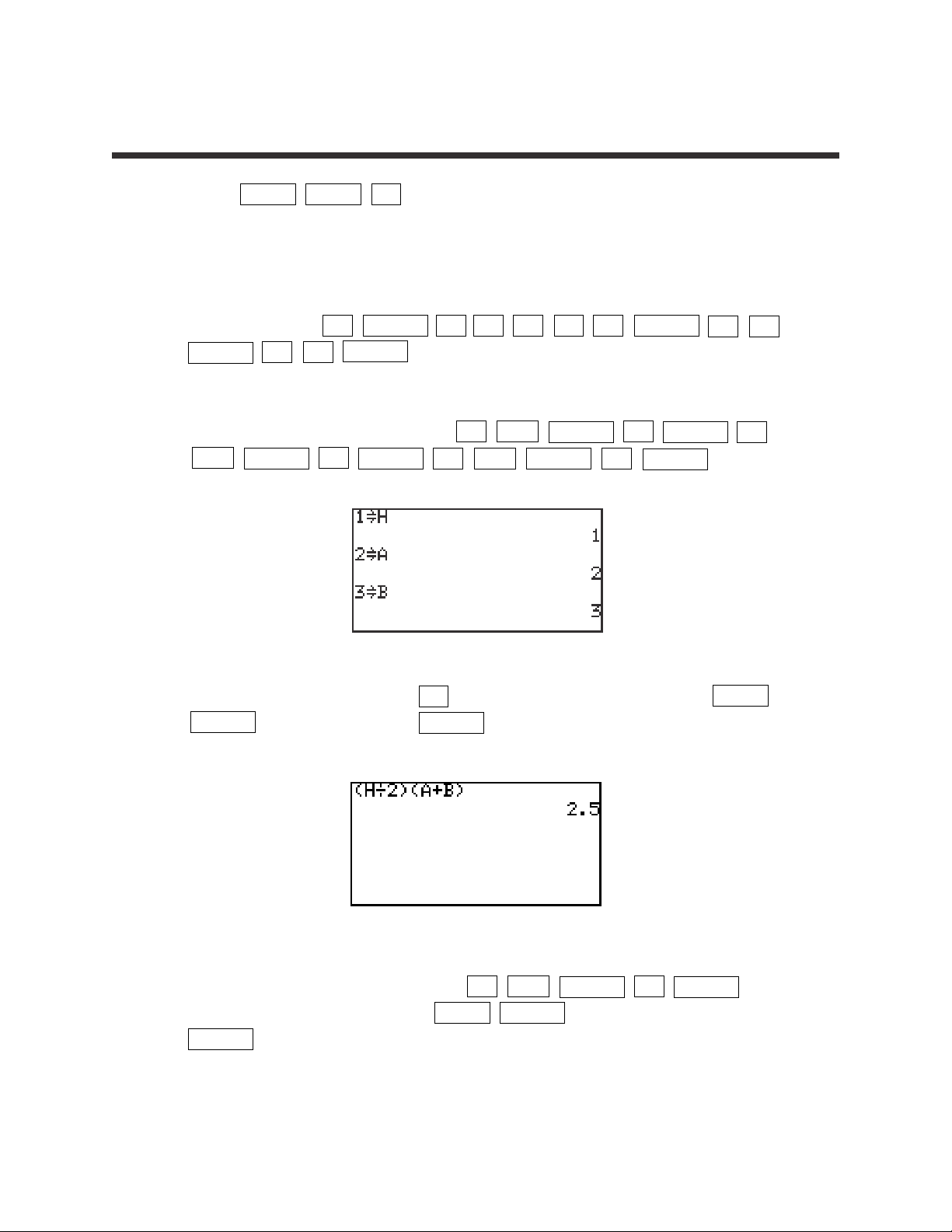
9
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Press 2ndF QUIT CL to return to and clear the calculation screen.
2. To evaluate the formula for the area of a trapezoid (Area=(h/2)(a+b), where
‘h’ is the height between the two bases (‘a’ and ‘b’) for different values, you
must first type in the formula. For example, to enter the area formula for a
trapezoid, press
(
ALPHA H ÷ 2
)(
ALPHA A +
ALPHA B
)
ENTER .
3. Now, store the values for ‘h,’ ‘a,’ and ‘b’ into the calculator. Use h=1, a=2,
and b=3. Store these by pressing 1 STO ALPHA H ENTER 2
STO ALPHA A ENTER 3 STO ALPHA B ENTER .
4. Clear the screen by pressing CL . Recall the formula by pressing 2ndF
ENTRY four times. Press ENTER to evaluate the formula for the stored
values.
5. Change the height to 4 by pressing 4 STO ALPHA H ENTER .
Recall the formula by pressing 2ndF ENTRY two times and press
ENTER to re-evaluate the formula for the new value.
FORMULAS
Page 31

10
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Press Y= and clear old expressions. Press ZOOM A 7 to view a
clear viewing window.
2. To graph the circle in the form (x–h)
2
+ (y–k)2= r2, you will use the circle
drawing feature. For example, in the circle (x–3)
2
+ (y–2)2= 12, h=3, k=2
and r=1. Press 2ndF DRAW A 9 (Circle). Move the cursor right to
an ‘h’ of x=3 by pressing repeatedly until x=3. Move the cursor up to a
‘k’ of y=2 by pressing repeatedly until y=2. Press ENTER to set the
center point.
3. Move the cursor the length of the radius in one direction away from the
center. In the example use the arrow key. Move the cursor 1 unit away from
the center and press ENTER . The circle will be drawn with the cursor
appearing at the point in the circle to which you moved.
4. If the circle will not completely appear in the viewing window, zoom out on
the decimal window to a larger window, because any other windows may
distort the circle. Draw the circle again in the larger window.
GRAPHING CIRCLES
▼
▼
Page 32

11
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Turn the calculator on and press Y= . Y prompts will appear on the viewing
window. Press CL to remove old Y expressions. Setup the calculator with
rectangular coordinates and the equation editor mode by pressing 2ndF
SET UP E (COORD) 1 (Rect) G (EDITOR) and 1 (Equation). Press CL
to exit the menu and return to the Y prompts.
2. To enter the polynomial y = –3x
2
+ x + 1, press
(–)
3 x x
2
+
x
+
1 .
3. Press ZOOM A (Zoom) 7 (Dec) to establish the decimal viewing window
and view the graph. Press TRACE to engage the trace feature. Press to
move the cursor near the left-hand root.
4. Press ZOOM A (ZOOM) 3 (In) to zoom in on the left- hand root.
Press TRACE and move the tracer to approximate the root.
5. Press ZOOM G (RCL) 2 (PreWin) to return to the decimal viewing
window. Press TRACE and move the tracer to find the right-hand root.
6. Press ZOOM A (ZOOM) 3 (In) to zoom in. Press TRACE and move the
tracer to approximate the root.
ZOOMING TO FIND ROOTS
▼
Page 33

12
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Press Y= CL to return to and clear the Y1 prompt.
2. To enter the polynomial y = –5x
2
–3x + 1, press
(–)
5 xx2– 3
x + 1 .
3. View the graph in the decimal viewing window by pressing ZOOM
A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec).
4. Press TRACE and move cursor to the left of the left-hand root. Press 2ndF
CALC to view the calculate menu.
5. Press 5 (X_Incpt) to find the left-hand root.
6. Press 2ndF CALC 5 (X_Incpt) to find the next root.
JUMPING TO FIND ROOTS
Page 34

13
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. To solve 3(4 – 2x) ≥ 5 – x, rewrite it as 3(4 – 2x) – 5 + x ≥ 0 and determine the
values of x where the function y = 3(4 – 2x) – 5 + x is on or above the x-axis.
2. To do this, press Y= CL and enter 3(4 – 2x) – 5 + X in the Y1 location.
3. Set the viewing window of the graph by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM)
5 (Default). You should be able to clearly view the x-intercept.
4. Locate the x-intercept at the point (1.4, 0) by pressing 2ndF CALC and
5 (X_Incpt).
5. Since the graph is above the x-axis, to the left of the x-intercept, the solution
to the inequality 3(4 – 2x) – 5 + x ≥ 0 is all values of x such that x ≤ 1.4.
INEQUALITIES
Page 35

14
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. To solve the inequality 3(4 – 2x) ≥ 5 – x, press Y= CL , enter 3(4 – 2X) for
Y1 and 5 – X for Y2.
2. Set the viewing window by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM) 5 (Default).
3. Next, shade the set of points that make the inequality true by pressing 2ndF
DRAW G (SHADE) 1 (Set) to access the “Set Shade” screen. Since the
inequality you are solving is Y1 ≥ Y2 the solution is where the graph of Y1 is
“on the top” and Y2 is "on the bottom." Do this by pressing 2ndF VARS A
ENTER 2 2ndF VARS ENTER 1 . Press GRAPH to view the
shaded region.
4. Press 2ndF CALC 2 (Intsct) to find where the graphs intersect.
5. Since the shaded region is to the left of x = 1.4, the solution to the inequality
3(4 – 2x) ≥ 5 – x is all values of x such that x ≤ 1.4.
6. Turn off the shading by pressing 2ndF DRAW G (SHADE) 2 (INITIAL).
INEQUALITIES
▼
Page 36

15
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. The inequality -1 ≤ 2x – 5 ≤ 7 is commonly referred to as a “double” inequality.
2. Clear any previously entered functions by pressing Y= CL .
3. Enter Y1 = -1, Y2 = 2X – 5, and Y3 = 7.
4. Press ZOOM A (ZOOM) 5 (Default) to view the line y = 2x – 5 between
the lines y = -1 and y = 7.
5. Press 2ndF CALC 2 (Intsct) to find the point of intersection of the lines
y = 2x – 5 and y =-1 at (2, -1). Press ▲ to move the tracer to the y = 7 line.
Press 2ndF CALC 2 (Intsct) to find y = 2x – 5 and y = 7 at (6, 7).
6. The solution to the “double” inequality -1 ≤ 2x – 5 ≤ 7 consists of all values of
x in between, and including, 2 and 6 (i.e., x ≥ 2 and x ≤ 6). The solution is
2 ≤ x ≤ 6.
DOUBLE INEQUALITIES
Page 37

16
Basic Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Graphing a system of equations and using the calculate feature to
find the solutions
1. Turn the calculator on and press Y= .
2. Press CL to clear an old Y1 expression. Press ENTER CL to clear
additional Y prompts.
3. To enter the system of equations: y = x
2
– 1
y = 2x
press xx
2
– 1 ENTER 2 x . View the graphs by pressing ZOOM
A (Zoom) 5 (Default).
4. Press 2ndF CALC to access the calculate feature. Press 2 (Intsct).
The left-hand intersection will appear on the screen.
5. Press 2ndF CALC to access the calculate feature again. Press 2
(Intsct). The right-hand intersection will appear on the screen.
SOLVING A
SYSTEM OF EQUATIONS
Page 38

1
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. The Basic keyboard can only execute a program. Use the Advanced
Keyboard to enter and check the program.
2. Turn the calculator on and press PRGM to enter the programming menu.
The menu consists of commands to execute, edit, and create new programs.
3. Press C (NEW) and ENTER to open a new program. The calculator is
now locked in ALPHA mode and is prepared to accept a name for the new
program. Enter the program name.
4. You can now enter the program. All program commands are obtained in the
program menu. You cannot type program commands using the ALPHA
key. To reach this menu, press PRGM . All the program commands begin
with an uppercase letter.
5. Press CL to exit the program commands. When entering a new
program, you must press ENTER at the end of each line.
6. If you make a mistake entering a program, use the calculator's editing
feature to correct the error. First, you can press the arrow keys to move
around the program. Second, you can use the DEL key which deletes a
highlighted item, the BS key which backspace deletes an item, and the
2ndF INS keys which allow you to insert new items. Third, the
calculator operates in typeover mode which allows you to simply type over
a mistake. You must press ENTER after correcting a mistake for the
correction to be saved for future use.
CREATING A NEW PROGRAM
Page 39

2
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. After entering the program with the Advanced Keyboard, press 2ndF
QUIT to save the program and exit the editing mode.
2. Execute a program by pressing PRGM A (EXEC) and select the program
using the arrow keys and press ENTER .
3. If you receive an error statement, press to go to the line within the
program in which the error occurs. Compare your line with the correct one
above to find the error. Correct the error using the editing features of the
calculator and press ENTER to save the correction. Press 2ndF QUIT
and try to execute the program again.
4. Once the program is working, you can execute the program from the Basic
Keyboard.
EXECUTING A PROGRAM
▼
▼
Page 40

3
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Program the calculator to find the prime factorization of a whole number
greater than 2. This method decomposes a number into the prime factors
2, 3, 5, etc.
2. Create a new program with the name DECOMP. Enter the following program
and remember to press ENTER at the end of each line. If you make a
mistake, use the calculator’s editing features to correct the error.
3. Enter the following program using the Advanced Keyboard:
Input N PRGM A 3 ALPHA N ENTER
2⇒D 2 STO ALPHA D ENTER
Label A PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA A ENTER
If (N
÷D) = int PRGM B 0 3
(
ALPHA N ÷
(N÷D) Goto B ALPHA D
)
ALPHA = MATH B 0 5
(
ALPHA N ÷ ALPHA D
)
PRGM B 0 2 ALPHA B ENTER
D+1⇒D ALPHA D
+
1 STO ALPHA D
ENTER
If D ≤√N Goto A PRGM B 0 3 ALPHA D MATH
F 6 2ndF √ ALPHA N PRGM
B 0 2 ALPHA A ENTER
Goto C PRGM B 0 2 ALPHA C ENTER
Label B PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA B ENTER
N
÷D⇒N ALPHA N ÷ ALPHA D STO ALPHA
N ENTER
Print D PRGM A 1 ALPHA D ENTER
Goto A PRGM B 0 2 ALPHA A ENTER
Label C PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA C ENTER
Print N PRGM A 1 ALPHA N ENTER
End PRGM A 6 ENTER
Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the editor.
PRIME FACTORIZATION
Page 41

4
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
4. Execute the DECOMP program from the Basic Keyboard by pressing
PRGM and selecting DECOMP. Enter the number for which you want to
find the prime factorization. Try 56. Press 5 6 ENTER to find the
prime factorization of 56. You should then see the following prime
factorization.
You can repeat this program for other numbers by pressing ENTER
to execute the program over and over again. Press CL to clear the
screen.
PRIME FACTORIZATION (continued)
Page 42

5
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Program the calculator to find the common factors and the greatest common
factor of any pair of whole numbers.
2. Create a new program with the name FACTORS. Enter the following program
and remember to press ENTER at the end of each line. If you make a
mistake, use the calculator’s editing features to correct the error.
3. Enter the following program using the Advanced Keyboard:
Input A PRGM A 3 ALPHA A ENTER
Input B PRGM A 3 ALPHA B ENTER
2⇒D 2 STO ALPHA D ENTER
Label A PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA A ENTER
If fpart (A÷D)π0 PRGM B 0 3 MATH B 4
(
Goto B ALPHA A ÷ ALPHA D
)
MATH F
2 0 PRGM B 0 2 ALPHA B
ENTER
If fpart (B÷D)π0 PRGM B 0 3 MATH B 4
(
Goto B ALPHA B ÷ ALPHA D
)
MATH F
2 0 PRGM B 0 2 ALPHA B
ENTER
Print D PRGM A 1 ALPHA D ENTER
Label B PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA B ENTER
D+1⇒D ALPHA D + 1 STO ALPHA D
ENTER
If D≤min(A,B) PRGM B 0 3 ALPHA D MATH
Goto A F 6 MATH B 6 ALPHA A ,
ALPHA B
)
PRGM B 0 2
ALPHA A ENTER
End PRGM A 6 ENTER
COMMON FACTORS
Page 43

6
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
4. Execute the FACTORS program from the Basic Keyboard by pressing
PRGM and selecting FACTORS. Enter the numbers for which you
want to find the common factors. Try 60 and 48. Press 6 0 ENTER
4 8 ENTER to find the common factors of 60 and 48. You should
then see the following common factors.
You can repeat this program for other numbers by pressing ENTER to
execute the program over and over again. Press CL to clear the screen.
COMMON FACTORS (continued)
Page 44

7
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Program the calculator to perform synthetic division of a polynomial
by a linear divisor.
2. Create a new program with the name SYNTHETI. Enter the following
program and remember to press ENTER at the end of each line. If you
make a mistake, use the calculator’s editing features to correct the error.
3. Enter the following program using the Advanced Keyboard:
Input D PRGM A 3 ALPHA D ENTER
0⇒P 0 STO ALPHA P ENTER
{D+1,1}⇒ 2ndF
{
ALPHA D + 1 , 1 2ndF
dim(mat A) } STO 2ndF MATRIX C 0 1 2ndF
MATRIX A 1
)
ENTER
Print “COEFFIC PRGM A 1 PRGM 2
IENTS P(X) 2ndF A-LOCK C O E F F I
C I E N T S SPACE P ALPHA
( X/θ/T/n ) ENTER
Label A PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA A ENTER
P+1⇒P ALPHA P + 1 STO ALPHA P
ENTER
Input C PRGM A 3 ALPHA C ENTER
C⇒mat A(P,1) ALPHA C STO 2ndF MATRIX A 1
(
ALPHA P , 1
)
ENTER
If P<D+1 PRGM B 0 3 ALPHA P MATH
Goto A F 5 ALPHA D + 1 PRGM
B 0 2 ALPHA A ENTER
Label B PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA B ENTER
Input R PRGM A 3 ALPHA R ENTER
Label C PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA C ENTER
1⇒P 1 STO ALPHA P ENTER
0⇒S 0 STO ALPHA S ENTER
SYNTHETIC DIVISION
Page 45

8
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Print “COEFFIC PRGM A 1 PRGM 2
IENTS Q(X) 2ndF A-LOCK C O E F F I C
I E N T S SPACE Q ALPHA
(
X/θ/T/n
)
ENTER
Label D PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA D ENTER
mat A(P,1)⇒F 2ndF MATRIX A 1
(
ALPHA P , 1
)
STO ALPHA F ENTER
F+S⇒Q ALPHA F + ALPHA S STO ALPHA
Q ENTER
Print Q PRGM A 1 ALPHA Q ENTER
Wait PRGM A 4 ENTER
R×Q⇒S ALPHA R × ALPHA Q STO ALPHA
S ENTER
P+1⇒P ALPHA P + 1 STO ALPHA P
ENTER
If P<D+1 PRGM B 0 3 ALPHA P MATH
Goto D F 5 ALPHA D + 1 PRGM B 0
2 ALPHA D ENTER
mat A(P,1)⇒F 2ndF MATRIX A 1
(
ALPHA P , 1
)
STO ALPHA F ENTER
F+S⇒Q ALPHA F + ALPHA S STO ALPHA
Q ENTER
Print PRGM A 1 PRGM 2 2ndF
“REMAINDER A-LOCK R E M A I N D E R
ALPHA ENTER
Print Q PRGM A 1 ALPHA Q ENTER
End PRGM A 6 ENTER
Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the editor.
SYNTHETIC DIVISION (continued)
Page 46

9
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
4. Execute the SYNTHETI program from the Basic Keyboard by pressing
PRGM and selecting SYNTHETI. Use synthetic division to divide
P(x) = 2x
3
+ 3x2+ 4x + 5 by x – 1. Enter the degree for P(x) by pressing
3 ENTER . Next enter the coefficients and constant for P(x) by pressing
2 ENTER 3 ENTER 4 ENTER 5 ENTER . Enter the r
value of 1 by pressing 1 ENTER . The first coefficient of Q(x) will
appear. Press ENTER to see additional coefficients. The remainder will
be shown to end the program. You should then see the following
coefficients, constant and remainder (Q(x) = 2x
2
+ 5x + 9, remainder = 14).
You can repeat this program for other numbers by pressing ENTER to
execute the program over and over again. Press CL to clear the screen.
SYNTHETIC DIVISION (continued)
Page 47

10
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Program the calculator to graph a random walk. A random walk can go in
any direction for a random distance. This program stops when the graph
tries to go outside the calculator display.
2. Create a new program with the name WALK. Enter the following program
and remember to press ENTER at the end of each line. If you make a
mistake, use the calculator’s editing features to correct the error.
3. Enter the following program using the Advanced Keyboard:
ClrDraw 2ndF DRAW A 1 ENTER
0⇒D 0 STO ALPHA D ENTER
.5⇒X . 5 STO X/θ/T/n ENTER
.5⇒Y . 5 STO ALPHA Y ENTER
Label A PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA A ENTER
.2(random–.5)⇒H . 2
(
MATH C 1 – . 5 )STO
ALPHA H ENTER
.2(random–.5)⇒K . 2
(
MATH C 1 – . 5
)
STO
ALPHA K ENTER
Line(X,Y,X+H, 2ndF DRAW A 2 X/θ/T/n , ALPHA
Y+K) Y , X/θ/T/n + ALPHA H , ALPHA
Y + ALPHA K
)
ENTER
X+H⇒XX/θ/T/n + ALPHA H STO X/θ/T/n ENTER
Y+K⇒Y ALPHA Y + ALPHA K STO ALPHA
Y ENTER
If X<0 Goto B PRGM B 0 3 X/θ/T/n MATH F
5 0 PRGM B 0 2 ALPHA B ENTER
If X>1 Goto B PRGM B 0 3 X/θ/T/n MATH F 3 1
PRGM B 0 2 ALPHA B ENTER
If Y<0 Goto B PRGM B 0 3 ALPHA Y MATH F 5 0
PRGM B 0 2 ALPHA B ENTER
RANDOM WALKS
Page 48

11
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
If Y>1 Goto B PRGM B 0 3 ALPHA Y MATH F 3
1 PRGM B 0 2 ALPHA B ENTER
D+√(H
2+K2
)⇒D ALPHA D + 2ndF √
(
ALPHA H
x
2
+ ALPHA K x
2
)
STO ALPHA
D ENTER
Goto A PRGM B 0 2 ALPHA A ENTER
Label B PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA B ENTER
Print D PRGM A 1 ALPHA D ENTER
End PRGM A 6 ENTER
4. First, press Y= and CL to clear the Y1 prompt. Press CL to clear
additional prompts if necessary. Set the viewing window for the graphing by
pressing WINDOW 0 ENTER 1 ENTER 1 ENTER 0
ENTER 1 ENTER 1 ENTER . Execute the WALK program by
pressing PRGM and selecting WALK. The program will show you the
random walk and then display the distance traveled in the walk. If your walk
is short, then press ENTER to execute the program again. When you
have a long walk, press GRAPH to view the graph. A long walk is greater
than 10.
RANDOM WALKS (continued)
▼
Page 49

12
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Program the calculator to roll a set of dice.
2. Create a new program with the name ROLLING. Enter the following program
and remember to press ENTER at the end of each line. If you make a
mistake, use the calculator’s editing features to correct the error.
3. Enter the following program using the Advanced Keyboard:
Print “NUMBER PRGM A 1 PRGM A 2 2ndF
OF DICE A-LOCK N U M B E R
SPACE O F SPACE D I C E ENTER
Input N PRGM A 3 ALPHA N ENTER
0⇒K 0 STO ALPHA K ENTER
Label A PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA A ENTER
Print int ( PRGM A 1 MATH B 5
(
random × 6)+1 MATH C 1 × 6
)
+ 1 ENTER
K+1⇒K ALPHA K + 1 STO ALPHA K
ENTER
If K<N PRGM B 0 3 ALPHA K MATH
Goto A F 5 ALPHA N PRGM B 0 2
ALPHA A ENTER
End PRGM A 6 ENTER
ROLLING DICE
Page 50

13
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
4. Execute the ROLLING program by pressing PRGM and selecting
ROLLING. Enter the number of dice, up to eight, that you wish the calculator
to roll for you. Roll five dice by pressing 5 ENTER . The program will
show the five values for the dice on the screen. You should see a screen
similar to the following (the values for the dice should be different).
ROLLING DICE (continued)
Page 51

14
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Program the calculator to find Pythagorean triples. Pythagorean triples are
three numbers x, y, and z that satisfy x
2
+ y2= z2.
2. Create a new program with the name PYTHAG. Enter the following program
and remember to press ENTER at the end of each line. If you make a
mistake, use the calculator’s editing features to correct the error.
3. Enter the following program using the Advanced Keyboard:
Input N PRGM A 3 ALPHA N ENTER
2⇒J 2 STO ALPHA J ENTER
1⇒K 1 STO ALPHA K ENTER
Label A PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA A ENTER
If √(J
2+K2
)≠ipart PRGM B 0 3 2ndF √
(
ALPHA J
(√(J
2+K2
)) Goto B x2+ ALPHA K x
2
)
MATH F 2
MATH B 3
(
2ndF √
(
ALPHA
J x
2
+ ALPHA K x
2
))
PRGM B
0 2 ALPHA B ENTER
Print J PRGM A 1 ALPHA J ENTER
Print K PRGM A 1 ALPHA K ENTER
Print √(J
2+K2
) PRGM A 1 2ndF √
(
ALPHA
J x
2
+ ALPHA K x
2
)
ENTER
Print “ PRGM A 1 PRGM A 2 ENTER
Wait PRGM A 4 ENTER
Label B PRGM B 0 1 ALPHA B ENTER
K+1⇒K ALPHA K + 1 STO ALPHA K ENTER
If K≤(J–1) PRGM B 0 3 ALPHA K MATH
Goto A F 6 ( ALPHA J – 1
)
PRGM B 0
2 ALPHA A ENTER
J+1⇒J ALPHA J + 1 STO ALPHA J ENTER
1⇒K 1 STO ALPHA K ENTER
If J≤N PRGM B 0 3 ALPHA J MATH
PYTHAGOREAN TRIPLES
Page 52

15
Basic Keyboard/PROGRAMMING USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Goto A F 6 ALPHA N PRGM B 0 2
ALPHA A ENTER
End PRGM A 6 ENTER
4. Execute the PYTHAG program by pressing PRGM and selecting
PYTHAG. Enter the upper bound for the Pythagorean triples. Set the upper
bound to 15 by pressing 1 5 ENTER . The program will show the first
Pythagorean triple. Press ENTER to view additional triples. You should
see screens similar to the following ones.
PYTHAGOREAN TRIPLES (continued)
Page 53

Sharp EL-9900
Graphing Calculator
Advanced Keypad
EL-9900
SUB
SPLIT
TBLSET
DRAW
FORMAT
CALC
OPTION
LIST
CLIP
OFF
A-LOCK
STAT
PLOT
SLIDE
SHOW
2ndF
ALPHA
Y
=
GRAPH
TABLE
WINDOW
ZOOM
TRACE
ON
sin cos
+
–
.
.
–
+
TOOL
MATRIX
MATH
sin
a
uvw
STAT
–1
A
cos
GH I J K
b
c
L
789
QRST
L4 L5 L6
4
VW
L1 L2 L3
1
0
<
0
SOLVER
PRGM
–1
BCDEF
tan
a
a
b
MN
–1
tan
a
INS
DEL BSInCL
x
10
log
b
,
{}
SET UP
RCL VARS
(
X
=
x
FINANCE
+
ENTRY
5
2
i
SPACE
6
3
(–)
x
e
STO
O
CATALOG
Y Z
EXE
.
.
xp
ENTER
QUIT
–1
x
2
x
X/0/T/n
P
)
U
.
.
–
–
ANS
Page 54

1
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Graphing and translations of quadratic equations
1. Turn the calculator on and press Y= . Press CL to remove an old Y1
expression. Press ENTER CL to remove an old Y2 expression.
2. To enter the quadratic equation ( y = x
2
) for Y1, press X/θ/T/n x2.
Enter the viewing window range by pressing ZOOM A (Zoom) 7 (Dec).
3. When 2 is added to x2, the resulting equation is y = x2+ 2. Enter this
function for Y2 by pressing Y=
▼ X/θ/T/n x
2
+ 2 . Press GRAPH .
What does the addition of 2 do?
4. When -2 is added to x2, the resulting equation is y = x2– 2. To change Y2
for this expression, press Y=
▼ CL X/θ/T/n x
2
– 2 .
ENTER GRAPH . What does the addition of -2 do?
5. Summarize the effect of k within the standard equation y = a(x – h)
2
+ k.
QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
Page 55

2
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for solving an equation using the equation method
1. Turn the calculator on and press 2ndF SOLVER to access the solver
feature. A blank screen should appear. If the screen is not blank, then press
CL to clear the screen.
2. Select the Equation method for solving by pressing 2ndF SOLVER ,
A (METHOD) 1 (Equation).
3. Enter the formula P = L 1 – ( 1 + I÷12)
–
N
-
1
I÷12
Press ALPHA P ALPHA = ALPHA L
(
a/b 1 –
(
1
+ ALPHA I ÷ 1 2
)
a
b
(-)
ALPHA N
ALPHA I ÷ 1 2
)
a
b
(-)
1 .
This equation is referred to as the amortization formula, with a loan (L) with
a fixed rate of interest (I).
4. Press ENTER to view the variable list. To find the monthly payment on
a $15,000 car loan made at 9% interest over four years (48 months), enter
the values by pressing ▼ 1 5 0 0 0 ENTER • 0 9
ENTER 4 8 ENTER . Press and notice the payment ( P)
is now highlighted by the cursor, press 2ndF EXE to solve for the
payment.
5. Pressing CL will return you to the variable screen. You can now change
or solve for any of the values. Save this formula by pressing 2ndF
SOLVER C (SAVE) ENTER and entering the formula name. Give the
formula the name AMORT by pressing A M O R T ENTER .
FORMULAS OR LITERAL EQUATIONS
▼
▼
▼
▼
▼
▼
[
]
Page 56

3
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for solving an equation using the graphic method
1. Turn the calculator on and press 2ndF SOLVER to access the solver
feature. Press CL to clear the formula entry screen.
Select the Graphic method for solving by pressing 2ndF SOLVER A
(METHOD) 3 (Graphic).
2. Enter the formula V = π r
2
h by pressing ALPHA V ALPHA = 2ndF
π ALPHA R a
b
2 ALPHA H .
3. This equation is the formula for calculating the volume of a cylinder ( V) in
terms of the cylinder's height ( H) and radius ( R). Press ENTER to view the
variable list.
4. To find the radius of a cylinder with a volume of 30 cubic inches, and a
height of 10 inches, enter the values by pressing 3 0 ENTER ▼ 1
0 ENTER . Press ▲ and notice the radius ( R) is now highlighted by
the cursor.
5. Press 2ndF EXE to solve for the radius. The graphic solver will prompt
you for a variable range to solve within. Set the variable range to 0 and 2 by
pressing 0 ENTER 2 ENTER .
6. Press 2ndF EXE to solve.
7. Pressing CL will return you to the variable screen. You can now change or
solve for any of the values. Save this formula by pressing 2ndF SOLVER ,
C (SAVE) pressing ENTER , and entering the formula name. Give
the formula the name VCYL by pressing V C Y L ENTER .
FORMULAS OR LITERAL EQUATIONS
▼
Page 57

4
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Solving an equation using Newton's method
1. Press 2ndF SOLVER to enter the solver feature. Press CL to clear the
formula entry screen.
2. Select the Newton's method for solving by pressing 2ndF SOLVER ,
A (METHOD) 2 (Newton). Enter the formula A = H(B + C) by pressing
ALPHA A ALPHA = 1 a/b 2 ALPHA H
(
ALPHA B +
ALPHA C ).
3. Press ENTER to view the variable list. To find the height of a trapezoid with
an area of 25 in
2
, and bases of length 5 and 7 inches, enter the values by
pressing 2 5 ENTER ▼ 5 ENTER 7 ENTER ▲▲.
Notice the height (H) is now highlighted by the cursor.
4. Press 2ndF EXE to continue. Newton's method will prompt you for a
guess or starting point. Enter a starting point of 1 by pressing 1 ENTER .
5. Press 2ndF EXE to solve. A height of 4.1667 will appear on the screen.
6. Pressing CL will return you to the variable screen. You can now change or
solve for any of the values. Save this formula by pressing 2ndF SOLVER ,
C (SAVE) ENTER and entering the formula name. Give the formula the
name "ATRAP," by pressing A T R A P ENTER .
FORMULAS OR LITERAL EQUATIONS
1
2
▼
Page 58

5
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Graphing a polynomial and zooming to find the roots
1. Turn the calculator on and press Y= . Y prompts will appear on the viewing
window. Press CL to remove old Y expressions. Setup the calculator with
rectangular coordinates and the equation editor mode by pressing 2ndF
SET UP E (COORD) 1 (Rect) G (EDITOR) and 1 (Equation). Press CL
to exit the menu and return to the Y prompts.
2. To enter the polynomial y = x
3
– 3x2+ x + 1, press X/θ/T/n ab3
– 3 X/θ/T/n x
2
+
X/θ/T/n
+
1 .
3. Press ZOOM A (Zoom) 7 (Dec) to establish the decimal viewing window
and view the graph. Press TRACE to engage the trace feature. Press to
move the cursor near the left-hand root.
4. Set the zoom factors to 5 by pressing ZOOM B (FACTOR) press
ENTER 5 ENTER 5 ENTER . Press ZOOM A (ZOOM) 3 (In)
to zoom in on the left- hand root. Press TRACE and move the tracer to
approximate the root.
5. Press ZOOM H (RCL) 2 (PreWin) to return to the decimal viewing
window. Press TRACE and move the tracer to find the middle root.
6. Press repeatedly to move the tracer near the right-hand root. Press
ZOOM A (ZOOM) 3 (In) to zoom in. Press TRACE and move the tracer
to approximate the root.
GRAPHING POLYNOMIALS AND
FINDING THE ROOTS
▼
▼
▼
Page 59

6
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Graphing a polynomial and jumping to find the roots
1. Press Y= CL to return to and clear the Y1 prompt.
2. To enter the polynomial y = x
4
+ x3–5x2–3x + 1, press X/θ/T/n ab4
+ X/θ/T/n a
b
3
–
5 X/θ/T/nx2– 3 X/θ/T/n + 1 .
3. View the graph in the decimal viewing window by pressing ZOOM
A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec).
4. Press TRACE and move cursor to the left of the left-hand root. Press 2ndF
CALC to view the calculate menu.
5. Press 5 (X_Incpt) to find the left-hand root.
6. Press 2ndF CALC 5 (X_Incpt) to find the next root.
7. Press 2ndF CALC 5 (X_Incpt) to find the next root.
8. Press 2ndF CALC 5 (X_Incpt) to find the next root.
GRAPHING POLYNOMIALS AND
FINDING THE ROOTS
▼
▼
Page 60

7
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Graphing a system of equations and using the calculate feature to
find the solutions
1. Turn the calculator on and press Y= .
2. Press CL to clear an old Y1 expression. Press ENTER CL to clear
additional Y prompts.
3. To enter the system of equations: y = x
2
– 1
y = 2x
press X/θ/T/nx
2
– 1 ENTER 2 X/θ/T/n . View the graphs
by pressing ZOOM A (Zoom) 5 (Default).
4. Press 2ndF CALC to access the calculate feature. Press 2 (Intsct).
The left-hand intersection will appear on the screen.
5. Press 2ndF CALC to access the calculate feature again. Press 2
(Intsct). The right-hand intersection will appear on the screen.
SOLVING A SYSTEM OF EQUATIONS
Page 61

8
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Solving a system of linear equations using the tool feature
1. Press 2ndF TOOL to access the tool menu.
2. Press B (SYSTEM) 2 (2) to view the entry screen for solving a
linear-system of equations. Systems up to six variables and six equations
can be solved.
3. To enter the system of equations: 5x + y = 1
-
3x + y =-5
Press 5 ENTER 1 ENTER 1 ENTER
(–)
3 ENTER 1
ENTER
(–)
5 ENTER .
4. Press 2ndF EXE to solve the system.
SOLVING A SYSTEM OF EQUATIONS
Page 62

9
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Press 2ndF MATRIX to access the matrix menu.
2. Press B (EDIT) 1 (mat A) to select matrix A.
3. Now, enter the size or dimension of the matrix. We will enter
the 3
× 3 matrix. 1 2 1
2 1 -1
1 1 -2
Press 3 ENTER 3 ENTER to set the dimension of the matrix at
three rows by three columns.
4. The calculator will now prompt you for the matrix. Enter the elements of
the matrix by pressing 1 ENTER 2 ENTER 1 ENTER 2 ENTER
1 ENTER
(–)
1 ENTER 1 ENTER 1 ENTER
(–)
2 ENTER .
5. Press 2nd QUIT to exit the display of matrix A.
6. Repeat the process to enter a 3
× 3 matrix B = 1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9 .
7. Matrix multiplication can be performed if the number of columns of the first
matrix is equal to the number of rows of the second matrix. In the matrix
multiplication A
× B, the elements in the first row of A are multiplied to the
corresponding elements in the first column of B. The sum of these
multiplications is placed in the 1,1(first row, first column) position of the
resulting matrix. This process is repeated until each row of A has been
multiplied to each column of B. Press 2nd QUIT to leave matirx entry
mode.
8. To multiply the matrices A and B together, press 2ndF MATRIX A (NAME)
1 (mat A)
× 2ndF MATRIX 2 (mat B) and ENTER .
MATRIC SOLUTIONS TO
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
[
]
[
]
Page 63

10
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. The calculator will directly establish an identity matrix of a given size by
pressing 2ndF MATRIX C (OPE) 0 5 (identity) and pressing 3
ENTER . To save the identity matrix in matrix C, press STO 2ndF
MATRIX A (NAME) 3 (mat C) ENTER . Confirm that the identity matrix
is stored in matrix C by pressing 2ndF MATRIX B (EDIT) 3 (mat C).
Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the matrix editor and press CL to clear
the screen.
2. Find the inverse of the square matrix A by pressing 2ndF MATRIX
A (NAME) 1 (mat A) 2ndF x
-
1
ENTER . Press to see more of
the matrix.
3. To solve the system of equations x + 2y + z = 8
2x + y – z = 1
x + y – 2z =-3
using matrices, use the matrix A entered previously as the coefficient matrix,
and enter the constants on the right side of the equal sign into matrix B,
where B = 8
1
-
3 .
Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the display of the B matrix. The solution matrix
X is found by multiplying mat A
-1
B • mat B.
4. This multiplication is derived from the equation AX= B,
A
-1
• A • X = A-1• B (multiply both sides by A-1)
I • X = A
-1
•B (A-1• A = I, identity matrix)
X = A
-1
• B (I • X = X )
Multiply A
-1
• B by pressing 2ndF MATRIX A (NAME) 1 (mat A)
2ndF x
-
1
× 2ndF MATRIX A (NAME) 2 (mat B) and ENTER .
The solution matrix will appear.
MATRIC SOLUTIONS TO
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
▼
[
]
Page 64

11
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. To solve 3(4 – 2x) ≥ 5 – x, rewrite it as 3(4 – 2x) – 5 + x ≥ 0 and determine the
values of x where the function y = 3(4 – 2x) – 5 + x is on or above the x-axis.
2. To do this, press Y= CL and enter 3(4 – 2x) – 5 + X in the Y1 location.
3. Set the viewing window of the graph by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM)
5 (Default). You should be able to clearly view the x-intercept.
4. Locate the x-intercept at the point (1.4, 0) by pressing 2ndF CALC and
5 (X_Incpt).
5. Since the graph is above the x-axis, to the left of the x-intercept, the solution
to the inequality 3(4 – 2x) – 5 + x ≥ 0 is all values of x such that x ≤ 1.4.
INEQUALITIES
Page 65

12
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. To solve the inequality 3(4 – 2x) ≥ 5 – x, press Y= CL , enter 3(4 – 2X) for
Y1 and 5 – X for Y2.
2. Set the viewing window by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM) 5 (Default).
3. Next, shade the set of points that make the inequality true by pressing 2ndF
DRAW G (SHADE) 1 (Set) to access the “Set Shade” screen. Since the
inequality you are solving is Y1 ≥ Y2 the solution is where the graph of Y1 is
“on the top” and Y2 is "on the bottom." Do this by pressing 2ndF VARS A
ENTER 2 2ndF VARS ENTER 1 . Press GRAPH to view the
shaded region.
4. Press 2ndF CALC 2 (Intsct) to find where the graphs intersect.
5. Since the shaded region is to the left of x = 1.4, the solution to the inequality
3(4 – 2x) ≥ 5 – x is all values of x such that x ≤ 1.4.
6. Turn off the shading by pressing 2ndF DRAW G (SHADE) 2 (INITIAL).
INEQUALITIES
▼
Page 66

13
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. The inequality -1 ≤ 2x – 5 ≤ 7 is commonly referred to as a “double” inequality.
2. Clear any previously entered functions by pressing Y= CL .
3. Enter Y1 = -1, Y2 = 2X – 5, and Y3 = 7.
4. Press ZOOM A (ZOOM) 5 (Default) to view the line y = 2x – 5 between
the lines y = -1 and y = 7.
5. Press 2ndF CALC 2 (Intsct) to find the point of intersection of the lines
y = 2x – 5 and y =-1 at (2, -1). Press ▲ to move the tracer to the y = 7 line.
Press 2ndF CALC 2 (Intsct) to find y = 2x – 5 and y = 7 at (6, 7).
6. The solution to the “double” inequality -1 ≤ 2x – 5 ≤ 7 consists of all values of
x in between, and including, 2 and 6 (i.e., x ≥ 2 and x ≤ 6). The solution is
2 ≤ x ≤ 6.
DOUBLE INEQUALITIES
Page 67

14
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. The solution region of a system of inequalities consists of all points (a, b)
such that when x = a and y = b, all inequalities in the system are true.
2. For example, to graph the solution region for the system
2x + y ≥ 1
x
2
+ y ≤ 1,
first rewrite each inequality in the system so that the left-hand-side is y:
y ≥ 1 – 2x
y ≤ 1 – x
2
3. Press Y= CL and enter 1 – 2X in Y1 and 1 – X2in Y2.
4. Next, shade the points that have a y-value less than Y2 and greater than Y1.
Do this by pressing 2ndF DRAW G (SHADE) 1 (Set) 2ndF VARS A
ENTER 1 2ndF VARS ENTER 2 .
5. Graph the system by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec).
6. Turn off the shading by pressing 2ndF DRAW G (SHADE) 2 (INITIAL).
SYSTEMS OF INEQUALITIES
▼
Page 68

15
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Evaluate |-2(5 – 1)| by pressing to access the home or computation
screen. Enter the absolute value symbol by pressing MATH B (NUM)
1 (abs). You should see | | on the screen. Enter -2(5-1) inside the
absolute value symbols and evaluate by pressing
(–)
2
(
5 – 1
)
ENTER .
2. Graph y = |x| by pressing Y= CL to clear the Y1 prompt. Press ENTER
CL to clear the remaining prompts if necessary. Enter |x| in Y1 by pressing
MATH B (NUM) 1 (abs) and pressing X/θ/T/n . Press ZOOM A
(ZOOM) 5 (Default) to draw the graph.
ABSOLUTE VALUE
×
+
–
÷
Page 69

16
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Solve |5 – 4x| = 6 by first pressing Y= CL to clear the Y1 prompt.
2. Enter |5 – 4x| in Y1 with the keystrokes MATH B (NUM) 1 (abs)
5 – 4 X/θ/T/n .
3. Next, press ENTER CL 6 to enter 6 in Y2.
4. Press ZOOM A (ZOOM) 5 (Default) to view the two points of
intersection of the absolute value and the horizontal line y = 6.
5. Press 2ndF CALC 2 (Intsct) to find one point of intersection of the
two graphs. Press 2ndF CALC 2 (Intsct) again to find the other point
of intersection.
6. The solution to the equation |5 – 4x| = 6 consists of the two
values-0.25 and 2.75.
ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATIONS
Page 70

17
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. To solve < 8 , rewrite the inequality so that the right-hand side
of the inequality is zero: – 8 < 0.
2. Press Y= and clear all the Y prompts.
3. Enter the left-hand side of the inequality – 8 in Y1 by pressing
MATH B (NUM) 1 (abs) a/b 2 0 – 6 X/θ/T/n 5
–
8 .
4. Graph the expression by pressing ZOOM A (Zoom) 5 (Default).
The x-intercepts of the graph are clearly visible.
5. Press 2ndF CALC 5 (X_Incpt) to find the first x-intercept. Press 2ndF
CALC 5 (X_Incpt) to find the second x-intercept.
6. Since the graph is below the x-axis for x in between the two x-intercepts,
the solution is -3.33 < x < 10.
ABSOLUTE VALUE INEQUALITIES
20 – 6x
5
20 – 6x
5
20 – 6x
5
▼
▼
▼
Page 71

18
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. To solve the inequality |3.5x + 4| ≥ 10, press Y= CL to clear the Y1
prompt. Press ENTER CL to clear additional prompts.
2. Enter the function |3.5x + 4| in Y1 by pressing MATH B (NUM)
1 (abs) 3 • 5 X/θ/T/n + 4 ENTER . Enter 10 in Y2 by pressing
1 0 .
3. Access the Set Shade screen by pressing 2ndF DRAW G (SHADE) 1
(SET). Since Y2 is the function "on the bottom," press 2ndF VARS A
ENTER 2 (Y2) and since Y1 is the function "on the top," press 2ndF
VARS ENTER 1 (Y1).
4. Set the viewing window by pressing ZOOM A (Zoom) 5 (Default). Press
ZOOM 4 (out) to see the intersection.
5. Press 2ndF CALC 2 (Intsct) to locate a point of intersection. Repeat to
find the other. The intersections are (-4, 10) and (1.714, 10). The solution of
the inequality |3.5x + 4| > 10 is all values of x such that x ≤-4 or x ≥ 1.714.
6. Turn off the shading by pressing 2ndF DRAW G (SHADE) 2 (INITIAL).
ABSOLUTE VALUE INEQUALITIES
▼
Page 72

19
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Graph the rational function f(x) = by first pressing Y= CL to clear
the Y1 prompt. Press ENTER CL to clear additional Y prompts.
2. Enter Y1 = by pressing a/b X/θ/T/n – 1 X/θ/T/nx
2
– 1 .
3. Graph in the decimal window by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec).
4. The function consists of two branches separated by the vertical asymptote
(the line x =-1). Look closely at the graph and observe the “hole” in it at
x = 1. Press TRACE and investigate the "hole." Note that the hole will be
seen only when the window is a "friendly" or decimal window.
5. Notice that there are no x-intercepts for the graph. The y-intercept can
easily be found at x = 0, y = 1 by pressing 2ndF CALC and 6 (Y_Incpt).
6. Observe that the line y = 0 is very likely a horizontal asymptote of f(x).
RATIONAL FUNCTIONS
(x – 1)
(x
2
– 1)
(x – 1)
(x
2
– 1)
▼
Page 73

20
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Solve the inequality ≤ 2 using the intersection method with shading,
by first pressing Y= CL to clear the Y1 prompt.
2. Enter the left-hand side of the inequality in Y1 by pressing MATH B (NUM)
1 (abs) pressing a/b X/θ/T/n 1 – X/θ/T/nx
2
ENTER . Enter 2
in Y2 by pressing 2 ENTER .
3. Press 2ndF DRAW G (SHADE) 1 (SET) 2ndF VARS A ENTER 1 (Y1)
2ndF VARS ENTER 2 (Y2).
4. View the graph by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec).
5. Press 2ndF CALC 2 (Intsct) repeatedly, to locate the x-values of the
points of intersection, x =-1.281,-0.781, 0.781, and 1.281. The solution is all
values of x such that x ≤-1.281 or -0.781 ≤ x ≤ 0.781 or x ≥ 1.281.
6. Turn off the shading by pressing 2ndF DRAW G (SHADE) 2 (INITIAL).
RATIONAL INEQUALITIES
x
(1 – x
2
)
▼
▼
Page 74

21
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for graphing a parabola in rectangular mode
1. Graph the parabola x = y2– 2 by first rewriting as y = ± (x + 2).
2. Press Y= CL to clear the Y1 prompt. Press ENTER CL to clear
additional prompts. Enter (x + 2) in Y1 with the keystrokes 2ndF
X/θ/T/n + 2 .
3. Press ENTER and enter -Y1 = -(x + 2) in Y2 with the key strokes
(–)
2ndF
VARS A (EQVARS) ENTER 1 (Y1).
4. View the graph by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec).
Steps for graphing a parabola in parametric mode
1. Change to parametric mode by pressing 2ndF SET UP E (COORD)
2 (Param). Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the set-up screen.
2. Press Y= CL to clear the X1T prompt. To rewrite x = y
2
– 2 in parametric
form, simply let y = T and substitute in x = y
2
– 2 to obtain x = T2– 2. Enter
X1T = T
2
– 2 in the calculator by pressing X/θ/T/nx2– 2 ENTER .
Enter Y1T = T by pressing X/θ/T/n .
3. View the graph by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec).
4. Notice that only a half of the parabola is drawn. To see the rest of the
parabola, press WINDOW and adjust the Tmin. Set Tmin to -6 by pressing
(–)
6 ENTER . Press GRAPH to view the complete parabola.
5. Change the calculator back to rectangular mode by pressing 2ndF SET UP
E (COORD) 1 (Rect).
CONIC SECTIONS
√
√
√
√
Page 75

22
Advanced Keyboard/ALGEBRA USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for graphing a circle in rectangular mode
1. To graph the circle x2+ y2= 4, solve for y in terms of x . The result is
y =±4 – x
2
.
2. Press Y= CL to clear the Y1 prompt. Enter Y1 = (4 – X
2
) by pressing
2ndF 4 – X/θ/T/nx
2
ENTER and then enter Y2 = -(4 – X2) by
pressing CL
(–)
2ndF VARS A (EQVARS) ENTER A (XY) 1 (Y1).
View the graph by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec).
Steps for graphing a circle not in standard form
1. First solve the equation for y by completing the square on the y-term and
solving for y. For example, draw the graph of the circle x
2
– 2x + y2+ 4y = 2
by rewriting as y = ± (6 – x
2
+ 2x) – 2.
2. Enter Y1 = (6 – x
2
+ 2x), Y2 = Y1 – 2 and Y3 = -Y1 – 2. “Turn off” Y1 so that
it will not graph by pressing ▲ to move the blinking cursor to the Y1
expression. Press to position the blinking cursor over the = sign, and
press ENTER so that “=” is no longer darkened.
3. To view the graph, press ZOOM 7 (Dec).
4. Adjust the screen to see the bottom part of the circle by pressing ZOOM
A (ZOOM) 4 (OUT).
CONIC SECTIONS (continued)
√
√
√
√
√
√
▼
Page 76

1
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Set the calculator to floating point decimal display by pressing 2ndF
SET UP C (FSE) and 1 (Float Pt). Set the calculator to rectangular
coordinates E (COORD) and 1 (Rect). Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the
set up menu.
2. Consider the function f(x) = . Press Y= CL to access and clear the
Y1 prompt. Press ENTER CL to clear the remaining prompts.
3. Construct a graph of f(x) in the Decimal viewing window by first entering
Y1= with the keystrokes a/b 2 X/θ/T/n + 2 X/θ/T/n
x
2
– 1 , and then press ZOOM A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec) to see
the graph.
4. Notice that even though is not defined at x =-1 (as evidenced by the
hole in the graph at that point), the functional values appear to be getting
closer and closer to -1. A careful observation of the graph leads to the
following estimates:
lim f(x) = 0,
x → -∞
lim f(x) = -1,
x →-1
lim f(x) does not exist,
x → 1
and lim f(x) = 0.
x →∞
5. It also appears that the line y = 0 is a horizontal asymptote and the line x = 1
is a vertical asymptote for this function.
EVALUATING LIMITS
(2x + 2)
(x
2
– 1)
(2x + 2)
(x
2
– 1)
(2x + 2)
(x
2
– 1)
▼
Page 77

2
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
6. Tables of functional values sometimes provide more detailed information
than a graph when investigating limits. The TABLE feature will assist
you in constructing a numerical table of values. Press TABLE to access the
TABLE feature.
7. Notice the table provides the x-values and their corresponding y-values
according to Y1. You can change the table settings by pressing 2ndF
TBLSET . You can change the table start value and the table step value.
Verify the following values using the the TABLE feature.
x gets smaller and smaller→
x-10
-
50
-
100
-
250
-
500
-
1000
-
10,000
y-.18182-.03922-.01980 .00797
-
.00399
-
.00200
-
.00020
y = f(x) appears to get closer and closer to 0
This provides evidence that lim f(x) = 0.
x →∞
x approaches -1 from the left x approaches -1 from the right
x-1.05
-
1.01
-
1.001
-
1.0001
-
.9999
-
.999
-
.99
-
.90
y-.9756-.99502
-
.9995
-
.9999
-
1.0001-1.0005-1.0051-1.0526
y = f(x) gets closer and closer to -1 from above y = f(x) gets closer and closer to -1 from below
This provides evidence that lim f(x) = -1.
x →-1
EVALUATING LIMITS (continued)
Page 78

3
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. The calculator has a built-in function denoted by d/dx that uses numerical
methods to estimate the derivative of a function at a given value. The entry
form of the derivative function is d/dx (f(x), a).
2. Estimate f’(2) for f(x) = x
2
using the derivative function. Press MATH
A (CALC) 05(d/dx() X/θ/T/nx
2
,
2 )to input: d/dx (X
2
, 2).
Press ENTER to compute.
3. The calculator also has a derivative trace.
Activate the derivative trace by pressing 2ndF FORMAT C (Y') and
1 (ON). Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the FORMAT menu.
4. Press Y= CL and enter the function for Y1 by pressing X/θ/T/nx
2
.
5. Draw the graph by pressing ZOOM A (Zoom) 7 (Dec).
6. Press TRACE to activate the trace and press to the values for the derivative.
7. Be sure to turn off the derivative trace.
DERIVATIVES
×
+
–
÷
▼
Page 79

4
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Enter and execute a program for finding a tangent line to a curve
at a given point.
1. Turn the calculator on and press PRGM to enter the programming
menu.
2. Press C (NEW) and ENTER to open a new program.
3. Name the new program TANGENT by pressing T A N G E N T
ENTER .
4. Press ENTER at the end of each line. If you make a mistake, use the
calculator's editing features to correct the error. Enter the following program:
PROGRAM KEYSTROKES
Input X PRGM A 3 X/θ/T/n ENTER
(Y1,X)⇒M MATH A 0 5 2ndF VARS A ENTER A 1
,
X/θ/T/n )
STO ALPHA M ENTER
Y1(X)⇒Y 2ndF VARS A ENTER 1 ( X/θ/T/n ) STO ALPHA
Y ENTER
-
M
xX+Y⇒B (–) ALPHA M × X/θ/T/n + ALPHA Y STO ALPHA
B ENTER
ClrT PRGM C 1 ENTER
Print PRGM A 1 PRGM 2 2ndF A-LOCK T A N G
"TANGENT E N T SPACE L I N E = ALPHA ENTER
LINE= PRGM 1 PRGM 2 ALPHA Y ALPHA = ALPHA
Print M X/θ/T/n + ALPHA B ENTER
"Y=MX+B
TANGENT LINES
d
dx
Page 80

5
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Continue to enter the TANGENT program.
Print "M= PRGM 1 PRGM 2 ALPHA M ALPHA = ENTER
Print M PRGM 1 ALPHA M ENTER
Print "B= PRGM 1 PRGM 2 ALPHA B ALPHA = ENTER
Print B PRGM 1 ALPHA B ENTER
End PRGM 6 ENTER
5. Press 2ndF QUIT to save the program and exit the editing mode.
6. Enter f(x) =x
3
– x2+1 for Y1 by pressing Y= CL X/θ/T/n ab3
–
X/θ/T/nx
2
+ 1 ENTER .
7. Execute the TANGENT program by pressing PRGM A (EXEC) and
selecting TANGENT.
8. Enter an X of 1 by pressing 1 ENTER . You should then see the equation
for the tangent line to the curve at x = 1.
9. You can repeat this process for other x values. Press ENTER to execute the
program over and over again.
10. If you receive an error statement, press or to go to the line within the
program in which the error occurs. Compare your line with the correct one
above to find the error. Correct the error using the editing features
of the calculator and save the corrections by pressing ENTER .
Press 2ndF QUIT and try executing the program again.
TANGENT LINES (continued)
▼
▼
▼
Page 81

6
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Draw the tangent line to a function at a given point.
1. To draw the tangent line on a displayed graph, you must first enter the
graph for Y1. Enter the function f(x) = x
3
– x2+ 1 for Y1 by pressing Y=
CL X/θ/T/n a
b
3 – X/θ/T/nx2+ 1 ENTER .
2. Graph the function by pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec).
3. Draw the tangent line at x = 1 by pressing 2ndF DRAW A (DRAW)
5 (T_line
(), move the tracer right to x =1 by pressing repeatedly,
and then press ENTER .
TANGENT LINES
▼
▼
Page 82

7
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Set the graphing calculator to rectangular graphing by pressing 2ndF
SET UP E (COORD) 1 (Rect). Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the SET UP
menu.
2. Consider f(x) = 2x
3
– 7x2– 70x + 75. Press Y= CL to access and clear Y1.
Press ENTER CL to clear additional Y prompts. Enter f(x) for Y1 by
pressing 2 X/θ/T/n a
b
3 – 7 X/θ/T/nx2– 7 0 X/θ/T/n
+ 7 5 .
3. Graph the function by pressing WINDOW
(–)
1 0 ENTER 1 0 ENTER
1 ENTER ZOOM A (Zoom) 1 (Auto).
4. To determine the point at which the relative maximum occurs, press
2ndF CALC 4 (Maximum). The maximum occurs at x =-2.44.
5. Find the point at which the relative minimum occurs by pressing 2ndF
CALC 3 (Minimum). The minimum occurs at x = 4.776.
6. Combining this information with a view of the graph, we see that f(x) is
increasing for x = -∞ to-2.4427 and from 4.776 to ∞ while f(x) is decreasing
for x between-2.4427 and 4.776.
RELATIVE EXTREMA
▼
Page 83

8
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Graph f ’(x) by pressing Y= ENTER entering f(x)= 2x3– 7x2– 70x + 75 for
Y1, and entering (Y1) for Y2. Enter Y2 by pressing MATH A (CALC)
0 5 (d/dx
() 2ndF VARS ENTER A (XY) 1 (Y1) and press ) ENTER .
2. Press WINDOW
(–)
1 0 ENTER 1 0 ENTER 1 ENTER ZOOM A
(Zoom) 1 (Auto) to obtain the graphs of f(x) and f ’(x).
3. We now want to find the two x-intercepts of f’(x). Press TRACE ▼ to
place the tracer on the graph of the derivative. Then, press 2ndF CALC
and 5 (X_Incpt). Press 2ndF CALC 5 (X_Incpt) again to obtain the
other x-intercept.
4. Comparing these values to the x-coordinates of the points at which the
maxima and minima of f(x) occur, we see they are the same.
5. Where is f’(x) positive? Notice this is where the graph of f(x) is increasing.
Where is f’(x) negative? Notice this is where f(x) is decreasing.
6. Next, find the minimum point of f ’(x) by first making sure the trace cursor is
on the graph of the derivative, pressing 2ndF CALC 3 (Minimum).
7. Look at f(x) and observe that this appears to be the point at which the
function “bends a different way.”
8. Find the point of inflection directly by moving the cursor to the original
function and pressing 2ndF CALC 7 (Inflec).
GRAPHS OF DERIVATIVES
d
dx
Page 84

9
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
9. Graph the second derivative by pressing Y= ENTER ENTER , and input
d/dx (Y2) in the Y3 location with the keystrokes MATH A (CALC)
0 5 (d/dx
() 2ndF VARS ENTER A (XY) 2 (Y2) and press )
ENTER .
10. Press GRAPH to obtain the graphs of f(x), f ’(x), and f’’(x). Where is f’’(x).
zero? After pressing TRACE ▼▼to place the tracer on the second
derivative, press 2ndF CALC 5 (X_Incpt) to find that f’’(x) = 0 at
X= 1.167.
11. Find the y-value of this point of inflection by pressing ▲▲to move the
cursor to the original function. Press 2ndF CALC 1 (Value) and enter
1.167 and press ENTER .
12. The connections we have discovered between the graphs of f(x), f ’(x), and
f’’(x) are summarized in the tables below.
GRAPHS OF DERIVATIVES (continued)
x <-2.4427
-
2.4427 < x < 1.1656
1.1656 < x < 4.776
x > 4.776
x – value
x =-2.4427
x = 1.16567
x = 4.776
Page 85

10
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Set the calculator to rectangular graphing by pressing 2ndF SETUP E
(Coord) 1 (Rect). Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the setup menu.
2. A new product was introduced through a television advertisement appearing
during the Super Bowl. Suppose that the proportion of people that
purchased the product x days after the advertisement appeared is given by
f(x) = . When did maximum sales occur and what proportion of
people purchased the product at that time?
3. Press Y= CL to clear the Y1 prompt. Press ENTER CL to clear
additional prompts. Enter f(x) in the Y1 location with the keystrokes a/b
5
•
3 X/θ/T/n X/θ/T/nx2+ 1 5 .
4. Let’s examine the graph for the first 25 days after the advertisement
appeared. Press WINDOW , enter Xmin = 0, Xmax = 25, Xscl = 5, Ymin = 0,
Ymax = 1, Yscl = 1.
5. Press GRAPH to view the graph.
6. When did maximum sales occur and what proportion of people
purchased the product at that time? Press 2ndF CALC and
4 (Maximum) to find a maximum sales at x = 3.87 days with a 68%
proportion.
OPTIMIZATION
(5.3x)
(x2+ 15)
▼
Page 86

11
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Find an estimate of 2xdx.
2. Integrate a function by pressing MATH A (CALC) 0 6
( ∫ ).
3. Enter 0 for the lower limit. Press ▲ , input 1 for the upper limit, and press
. Next, press 2 X/θ/T/n to input the integrand. Enter the “dx” by
pressing MATH 0 7 (dx). Press ENTER to compute.
4. Shade the region by first pressing Y= CL to access and clear the Y1
prompt. Clear additional prompts by pressing ENTER CL .
5. Enter f(x) in Y1 with the keystrokes 2 X/θ/T/n . Press WINDOW and
enter Xmin = 0 and Xmax = 1. Draw the graph by pressing ZOOM
A (ZOOM) 1 (Auto).
6. Shade the region by pressing 2ndF DRAW G (SHADE) and 1 (Set)
to access the shading screen.
7. Since Y1= 2X is the function “on the top,” press 2ndF VARS ENTER
A (XY) 1 . Leave the lower bound location empty. Press GRAPH
to view the shaded region.
8. Turn off the shading by pressing 2ndF DRAW G (SHADE) 2 (INITIAL).
SHADING AND CALCULATING AREAS
REPRESENTED BY AN INTEGRAL
×
+
–
÷
▼
∫
0
1
▼
Page 87

12
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Calculate and draw a graph of the area of the region between
f(x) = 5x – x
2
+ 12 and g(x) = ex+ 5.
2. Return to and clear the Y prompts by pressing Y= CL . Clear additional
prompts if necessary.
3. Input f(x) in Y1 with the keystrokes 5 X/θ/T/n – X/θ/T/nx
2
+ 1
2 ENTER . Input g(x) in Y2 with the keystrokes 2ndF e
x
X/θ/T/n
+ 5 .
4. Enter the viewing window -5 < x < 5 and-5 < y < 20. Your viewing window
should clearly show the region between f(x) and g(x) and, if applicable,
display the intersections of the functions. Press GRAPH to view the graphs.
5. Shade the region between the two curves by pressing 2ndF DRAW
G (SHADE) 1 (SET). Since Y2 is the function "on the bottom," press
2ndF VARS ENTER A (EQVARS) ENTER 2 (Y2) and since Y1 is the
function “on the top," press 2ndF VARS ENTER 1 (Y1). Press GRAPH
to view the shaded region.
6. Next, find the limits of integration. Press 2ndF CALC 2 (Intsct). Do this
twice to obtain the x-coordinates of the two points of intersection. The
points of intersection are x =-1.09 and x = 2.58.
7. Find the approximate area by pressing CL MATH A (CALC) 06
( ∫) enter-1.09, press ▲ , enter 2.58, press , enter the function
“on the top,” 5x – x
2
+ 12, press – ( , enter the function “on the bottom,”
e
x
+ 5, press )MATH 0 7 (dx). Press ENTER to obtain the approximate
area of 20.34.
AREA BETWEEN CURVES
▼
▼
×
+
–
÷
Page 88

13
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Enter and execute a program for finding the rectangular
approximation for an area,
1. Press 2ndF PRGM to enter programming mode. Press C (NEW) to enter a
new program, followed by ENTER . Name the new program RECTAPP by
pressing R E C T A P P followed by ENTER .
2. You can now enter in the RECTAPP program. Remember to press ENTER at
the end of each line. If you make a mistake, use the calculator's editing
features to make corrections. Enter the following program:
PROGRAM KEYSTROKES
Input N PRGM A 3 ALPHA N ENTER
Input A PRGM 3 ALPHA A ENTER
Y1(A)⇒L 2ndF VARS A ENTER A 1 (ALPHA A )STO
ALPHA L ENTER
Input B PRGM 3 ALPHA B ENTER
Y1(B)⇒R 2ndF VARS ENTER 1 (ALPHA B )STO ALPHA
R ENTER
(B–A)÷N⇒W
(
ALPHA B – ALPHA A )÷ ALPHA N STO
ALPHA W ENTER
A+W÷2⇒X ALPHA A + ALPHA W ÷ 2 STO X/θ/T/n
ENTER
Y1(X)⇒M 2ndF VARS ENTER 1 (X/θ/T/n
)
STO ALPHA
M ENTER
A+W⇒X ALPHA A + ALPHA W STO X/θ/T/n ENTER
Label LOOP PRGM B 0 1 2ndF A-LOCK L O O P
ALPHA ENTER
Y1(X)+L⇒L 2ndF VARS ENTER 1 (X/θ/T/n
)
+ ALPHA L STO
ALPHA L ENTER
PROGRAM FOR RECTANGULAR
APPROXIMATION OF AREA
Page 89

14
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Y1(X)+R⇒R 2ndF VARS ENTER 1
(
X/θ/T/n
)
+ ALPHA R STO
ALPHA R ENTER
X+W÷2⇒XX/θ/T/n + ALPHA W ÷ 2 STO X/θ/T/n ENTER
Y1(X)+M⇒M 2ndF VARS ENTER 1
(
X/θ/T/n
)
+ ALPHA M STO
ALPHA M ENTER
X+W÷2⇒XX/θ/T/n + ALPHA W ÷ 2 STO X/θ/T/n ENTER
If X<BGoto PRGM B 0 3 X/θ/T/n MATH F 5 ALPHA
LOOP B PRGM B 0 2 2ndF A-LOCK L O O P
ALPHA ENTER
ClrT PRGM C 1 ENTER
Print "LEFT= PRGM A 1 PRGM 2 2ndF A-LOCK L E F T =
ALPHA ENTER
Print W×L PRGM 1 ALPHA W × ALPHA L ENTER
Print "MID= PRGM 1 PRGM 2 2ndF A-LOCK M I D
= ALPHA ENTER
Print W×M PRGM 1 ALPHA W × ALPHA M ENTER
Print "RIGHT= PRGM 1 PRGM 2 2ndF A-LOCK R I G H T
= ALPHA ENTER
Print W× R PRGM 1 ALPHA W × ALPHA R ENTER
End PRGM 6 ENTER
Press 2ndF QUIT to save the program and exit the editing mode.
PROGRAM FOR RECTANGULAR
APPROXIMATION OF AREA (continued)
Page 90

15
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Executing a program
3. Enter the function f(x) = cos x, by pressing Y= CL cos X/θ/T/n .
Press ENTER CL to clear additional prompts.
4. Execute the RECTAPP program, press PRGM A , highlight the
'RECTAPP' program, and press ENTER . Enter 'N' of 5 by pressing 5
ENTER , followed by 'A' of 0 and 'B' of 1. You will see a display of left,
midpoint and right rectangular approximations for the area under the
cosine function between 0 and 1 with 5 intervals in the partition.
5. You can repeat this process for a different number of partitions, different
limits, or another function. Press ENTER to execute the program over and
over again. Press CL to exit the program.
6. If you receive an error statement, press or to go to the line within the
program in which the error occurs. Compare your line with the correct one
above to find the error. Correct the error using the editing features of the
calculator and save the program by pressing 2ndF QUIT . Try executing
the program again.
PROGRAM FOR RECTANGULAR
APPROXIMATION OF AREA (continued)
▼
▼
Page 91

16
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
A program for finding the trapezoidal approximation for an area.
Input N PRGM A 3 ALPHA N ENTER
Input A PRGM 3 ALPHA A ENTER
Y1(A)⇒L 2ndF VARS A ENTER A 1 (ALPHA A )STO
ALPHA L ENTER
Input B PRGM 3 ALPHA B ENTER
Y1(B)⇒R 2ndF VARS ENTER 1 (ALPHA B )STO ALPHA R
ENTER
0⇒Z 0 STO ALPHA Z ENTER
(B–A)÷N⇒W
(
ALPHA B – ALPHA A )÷ ALPHA N STO
ALPHA W ENTER
A+W⇒X ALPHA A + ALPHA W STO X/θ/T/n ENTER
Label LOOP PRGM B 0 1 2ndF A-LOCK L O O P
ALPHA ENTER
2Y1(X)+Z⇒Z 2 2ndF VARS ENTER 1 (X/θ/T/n
)
+ ALPHA Z STO
ALPHA Z ENTER
X+W⇒XX/θ/T/n + ALPHA W STO X/θ/T/n ENTER
If X<BGoto PRGM B 0 3 X/θ/T/n MATH F 5 ALPHA B
LOOP PRGM 0 2 2ndF A-LOCK L O O P ENTER
ClrT PRGM C 1 ENTER
Print "TRAP= PRGM A 1 PRGM 2 2ndF A-LOCK T R A P =
PRGM 2 ENTER
Print (W÷2) PRGM 1 (ALPHA W ÷ 2
)(
ALPHA
(L+Z+R) L + ALPHA Z + ALPHA R )ENTER
End PRGM 6 ENTER
Execute like the rectangular program to find an approximate area of .83866.
TRAPEZOIDAL
APPROXIMATION OF AREA
Page 92

17
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for graphing the hyperbolic sine function.
1. Turn the calculator on and press Y= CL to access and clear the Y1
prompt. Press ENTER CL to remove additional expressions.
2. To enter the hyperbolic sine function ( y = sinh x ) for Y1, press MATH ,
A (CALC) 15(sinh) and press X/θ/T/n .
3. Enter the viewing window by pressing ZOOM F (HYP) 1 (sinh x).
Steps for graphing the hyperbolic cosine function.
4. Press Y= CL to remove the hyperbolic sine function.
5. To enter the hyperbolic cosine function ( y = cosh x ) for Y1, press MATH
1 6 (cosh x) press X/θ/T/n .
6. Press GRAPH to view the graph.
HYPERBOLIC FUNCTIONS
Page 93

18
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Turn the calculator on and set the calculator to sequence mode by pressing
2ndF SET UP E (COORD) 4 (Seq).
2. Press 2ndF QUIT Y= to access the sequence prompts. Clear
any sequences by presing CL .
3. Enter the sequence generator a
n
= n2– n for u(n) by pressing X/θ/T/n
x
2
– X/θ/T/n ENTER . Enter n1= 1 for u(nMin) by pressing
1 ENTER .
4. View a table of sequence values by pressing TABLE .
5. Graph the sequence by first setting the format to time and drawing to dot
mode. Do this by pressing 2ndF FORMAT G (TYPE) 2 (Time).
Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the FORMAT menu. Change to dot mode by
pressing 2ndF DRAW D (LINE) ENTER ENTER . Enter the viewing
window by pressing WINDOW 1 ENTER 1 0 ENTER 1 ENTER
1 ENTER
(–)
1 ENTER 1 1 ENTER 1 ENTER
(–)
1 0
ENTER 1 0 0 ENTER 1 0 ENTER . View the sequence by
pressing GRAPH .
6. Turn off sequence mode and dot mode.
SEQUENCES
▼
Page 94

19
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
1. Change to sequence mode, time format, and dot mode.
2. Enter the recursive sequence generator a
n
= a
n – 1
+ 2n for u(n) by pressing
Y= CL 2ndF u
(
X/θ/T/n – 1
)
+ 2 X/θ/T/n ENTER .
Enter a
1
= 1 by pressing 1 ENTER .
3. View a table of sequence values by pressing TABLE .
4. Graph the sequence in the window as -1< x < 11, -10 < y < 100 by pressing
GRAPH .
5. Turn off sequence mode and dot mode.
RECURSIVE SEQUENCES
Page 95

20
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Find the partial sum of a series, ∑ 1/X, for the first 10 terms.
1. Make sure the SET UP to rectangular mode by pressing 2ndF SET UP ,
E (COORD) 1 (Rect). Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the SET UP menu.
2. First find the sequence of the first 10 terms of series ∑ 1/X by first pressing
CL 2ndF LIST A (OPE) 5 (seq
( ). Enter the generator 1/X by
pressing 1
÷ X/θ/T/n
,
. Enter the lower and upper bounds for the
sequence by pressing 1
,
1 0
)
. Find the sequence by pressing
ENTER . Press to see more of the sequence.
3. Find the partial sum of the first 10 terms by pressing 2ndF LIST
6 (cumul) and pressing 2ndF ANS ENTER . Press to move right
in the sequence of partial sums until the last term is seen. The partial sum
of the first 10 terms is 2.9289.
PARTIAL SUM OF A SERIES
▼
▼
×
+
–
÷
Page 96

21
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for graphing a polar function:
1. Turn the calculator on and press 2ndF SET UP E (COORD)
3 (Polar) to change to polar mode. While in the SET UP menu, the
calculator should be setup in radian mode. To complete this setup, press
B (DRG) 2 (Rad). Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the SET UP menu.
2. Make sure calculator is in connected mode by pressing 2ndF DRAW D
(LINE) ENTER . The first option should be reflected for R1. Set the
calculator to display polar coordinates when tracing, by pressing 2ndF
FORMAT F (CURSOR) and 2 (PolarCoord). Also, set the calculator to
display the expression during tracing by pressing B (EXPRESS) 1 (ON).
Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the FORMAT menu.
3. Press Y= to access the R1 prompt. Press CL to remove an old R1
expression. Press ENTER CL to clear additional R prompts.
4. Enter the polar function r = 2(1 – cos θ) for R1, by pressing 2 (1 –
cos X/θ/T/n
)
. Notice, when in polar mode the X/θ/T/n key
provides a θ for equation entry.
5. Now, graph the polar function in the Decimal viewing window by pressing
ZOOM A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec).
6. This particular shape of curve is called a cardoid. Trace the curve by
pressing TRACE . Notice the expression is displayed at the top of the
screen.
GRAPHING POLAR EQUATIONS
Page 97

22
Advanced Keyboard/CALCULUS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for graphing a parametric function:
1. Turn the calculator on and press 2ndF SET UP E (COORD)
2 (Param) to change to parametric mode. Press 2ndF QUIT
to exit the SET UP menu.
2. Make sure calculator is set to display rectangular coordinates when tracing
by pressing 2ndF FORMAT F (CURSOR) 1 (RectCoord)
. Press 2ndF
QUIT to exit the FORMAT menu.
3. To enter the parametric function X1T = 2(cos T)
3
, Y1T = 2(sin T)3, press
Y= CL 2
(
cos X/θ/T/n
)
a
b
3 ENTER CL 2
(
sin
X/θ/T/n
)
a
b
3 ENTER . Notice, when in parametric mode the
X/θ/T/n key provides a T for equation entry.
4. Now, graph the parametric function in the Decimal viewing window by
pressing ZOOM A (ZOOM) 7 (Dec).
5. Press TRACE and notice the expression and T values now appear on the
range screen.
GRAPHING PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS
Page 98

1
Advanced Keyboard/STATISTICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for creating a non-weighted one-variable data set
1. Turn the calculator on and press STAT to enter the statistics menu.
2. Touch A (EDIT) ENTER , to view the statistics data entry screen.
If there is a data set present within the lists on your calculator, use the
arrow keys to move to the list, if necessary, and press ▲ to highlight the
list label.
3. Press DEL ENTER to delete the old data. Repeat for other lists of data.
4. Move the highlighter to the cell directly below the L1 in the table. Enter the
following data set:
58768935
by pressing 5 ENTER 8 ENTER 7 ENTER 6 ENTER 8 ENTER
9 ENTER 3 ENTER 5 ENTER .
5. To check the data you have entered, press ▲ to move back through the
data values.
6. To sort your data set in an ascending manner, press STAT B
(OPE) 1 (sortA) 2ndF L1 ) ENTER . Press STAT A (EDIT)
ENTER . Notice this first cell now contains the smallest value 3.
7. To save this data set, press 2ndF LIST C (L_DATA) 1
(StoLD) 1 ENTER . You can store up to ten sets of six lists.
8. To retrieve a data set matrix into a statistical data set, press 2ndF
LIST C (L_DATA) 2 (RclLD) 1 ENTER .
CREATION OF A ONE-VARIABLE DATA SET
×
+
–
÷
×
+
–
÷
×
+
–
÷
Page 99

2
Advanced Keyboard/STATISTICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for creating a weighted one-variable data set
1. Turn the calculator on and press STAT to enter the statistics menu.
2. Press A (EDIT) ENTER , to view the statistics data entry screen.
Remove old data by using the arrow keys to move to the list of data, and
press ▲ to highlight the list label. Press DEL ENTER to delete the old
data. Repeat for other lists of data.
3. Move the highlighter to the cell directly below the L1 in the table. Enter the
following data set into L1 with the frequencies entered into L2. If a value
appears three times within a data set, its weight or frequency is 3. Enter the
following data set using the weights:
5557777899
by pressing 5 ENTER 7 ENTER 8 ENTER 9 ENTER 3
ENTER 4 ENTER 1 ENTER 2 ENTER .
4. To save this data set, press 2ndF LIST C (L_DATA)
1 (StoLD) 2 ENTER .
CREATION OF A ONE-VARIABLE DATA SET
▼
×
+
–
÷
Page 100

3
Advanced Keyboard/STATISTICS USING THE SHARP EL-9900
Copyright © 2002, Sharp Electronics Corporation. Permission is granted to photocopy for educational use only.
Steps for calculating numerical descriptions of a one-variable
non-weighted data set
1. Turn the calculator on and press STAT to enter the statistics menu.
Press A (EDIT) ENTER to view the statistics data entry screen.
If there is a data set present within the lists on your calculator, use the
arrow keys to move to the list, if necessary, and press ▲ to highlight the
list label. Press DEL ENTER to delete the old data. Repeat for other lists
of data.
2. Move the highlighter to the cell directly below the L1 in the table.
Enter the following data set:
25 32 28 33 31 27 40 38 29 30
3. Check the data you have entered and correct any errors you may find.
Press 2ndF QUIT to exit the data entry screen. To calculate the numerical
descriptions of the data set, press STAT C (CALC) and 1 (1_Stats).
Press ENTER and the statistical results will appear.
4. The statistics displayed are:
1. the average or mean value of the data set, ;
2. the standard deviation assuming the data set is a sample from a
population, sx;
3. the standard deviation assuming the data set represents the entire
population, σx;
4. the sum of the data values, ∑x;
5. the sum of the squared data values, ∑x
2
;
Press ▼ five times to see more of the statistics.
6. the number of values in the data set, n;
7. the minimum value in the data set, xmin;
8. the first quartile (25th percentile), Q1;
9. the median (50th percentile), Med;
10. the third quartile (75th percentile), Q3; and
Press ▼ one more time to see the final statistic.
11. the maximum value in the data set, xmax.
NUMERICAL DESCRIPTION OF A
ONE-VARIABLE DATA SET
x
 Loading...
Loading...