Page 1

Multi-Homing Dual WAN
Firewall Router
User’s Manual
Doc. No.: 120602-04
- 1 -
Page 2

Contents
System
Admin
Setting
Date/Time
Multiple NAT
Hack Alert
Route Table
DHCP
DNS Proxy
Dynamic DNS
Logout
Software Update
Interface
5
7
12
19
20
25
27
31
33
37
41
42
43
LAN
WAN
Address
LAN
LAN Group
WAN
WAN Group
Service
Pre-defined
Custom
44
45
51
52
56
59
63
67
68
69
- 2 -
Page 3

Group
73
Schedule
Policy
Outgoing
Incoming
VPN
Autokey IKE
PPTP Server
PPTP Client
Content filtering
URL Blocking
General Blocking
Virtual Server
Mapped IP
77
81
82
89
93
94
98
103
107
108
112
113
114
Virtual Server
LOG
Traffic Log
Event Log
Log Backup
Alarm
Traffic Alarm
Event Alarm
Statistics
WAN Statistics
Policy Statistics
Status
118
125
126
129
132
135
136
139
143
144
145
147
- 3 -
Page 4

Interface Status
148
ARP Table
DHCP Clients
Setup Examples
149
150
151
- 4 -
Page 5

System
The device Multi-Homing Administration and monitoring control is set by the System Administrator.
The System Administrator can add or modify System settings and monitoring mode. The sub
Administrators can only read System settings but not modify them. In System, the System
Administrator can:
(1) Add and change the sub Administrator’s names and passwords;
(2) Back up all Multi-Homing settings into local files;
(3) Set up alerts for Hackers invasion.
What is System?
“System” is the managing of settings such as the privileges of packets that pass through the MultiHoming and monitoring controls. Administrators may manage, monitor, and configure Multi-Homing
settings. All configurations are “read-only” for all users other than the Administrator; those users are
not able to change any settings for the Multi-Homing.
The eleven sub functions under System are Admini, Setting, Date/Time, Multiple NAT, Hack Alert,
Route Table, DHCP, DNS Proxy, Dynamic DNS, Logout and Software Update.
Admin: has control of user access to the Multi-Homing. He/she can add/remove users and change
passwords.
Setting: The Administrator may use this function to backup Multi-Homing configurations and export
(save) them to an “Administrator” computer or anywhere on the network; or restore a configuration
file to the device; or restore the Multi-Homing back to default factory settings. Under Setting, the
Administrator may enable e-mail alert notification. This will alert Administrator(s) automatically
whenever the Multi-Homing has experienced unauthorized access or a network hit (hacking or
flooding). Once enabled, an IP address of a SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer protocol) Server is required.
Up to two e-mail addresses can be entered for the alert notifications.
Software Update: Administrators may visit distributor’s web site to download the latest firmware.
Administrators may update the device firmware to optimize its performance and keep up with the
latest fixes for intruding attacks.
Date/Time: This function enables the Multi-Homing to be synchronized either with an Internet Server
time or with the client computer’s clock.
Multiple NAT
Multiple NAT allows local port to set multiple subnetworks and connect with the
internet through different WAN 1 IP Addresses.
Hack Alert When abnormal conditions occur, the Multi-Homing will send an e-mail alert to notify the
Administrator, and also display warning messages in the Event window of Alarm.
Route Table Use this function to enable the Administrator to add static routes for the networks when
the dynamic route is not efficient enough.
DHCP Administrator can configure DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) settings for the LAN
(LAN) network.
- 5 -
Page 6

DNS Proxy The device’s Administrator may use the DNS Proxy function to make the 10/100M 2
WAN /4 LAN Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router act as a DNS Server for the LAN and WAN 1/2
network. All DNS requests to a specific Domain Name will be routed to the Multi-Homing’s IP
address. For example, let’s say an organization has their mail server (i.e., mail.dfl300.com) in the
WAN 1/2 network (i.e.192.168.10.10). The outside Internet world may access the mail server of the
organization easily by its domain name, providing that the Administrator has set up Virtual Server or
Mapped IP settings correctly. However, for the users in the LAN network, their WAN 1/2 DNS server
will assign them a public IP address for the mail server. So for the LAN network to access the mail
server (mail.dfl300.com), they would have to go out to the Internet, then come back through the MultiHoming to access the mail server. Essentially, the LAN network is accessing the mail server by a real
public IP address, while the mail server serves their request by a NAT address and not a real one.
This odd situation occurs when there are servers in the WAN 1/2 network and they are bounded to
real IP addresses. To avoid this, set up DNS Proxy so all the LAN network computers will use the
device as a DNS server, which acts as the DNS Proxy.
Dynamic DNS The Dynamic DNS (require Dynamic DNS Service) allows you to alias a dynamic IP
address to a static hostname, allowing your device to be more easily accessed by specific name. When
this function is enabled, the IP address in Dynamic DNS Server will be automatically updated with the
new IP address provided by ISP
Logout
Administrator logs out the Multi-Homing. This function protects your system while you are
away.
Software Update The administrator can update the device’s software with the latest version..
- 6 -
Page 7

Admin
On the left hand menu, click on Setup, and then select Admin below it. The current list of
Administrator(s) shows up.
- 7 -
Page 8

Settings of the Administration table
Administrator Name: The username of Administrators for the Multi-Homing. The user admin cannot
be removed.
Privilege:
The username of the main Administrator is Administrator with read / write privilege.
Sub Admins may be created by the Admin by clicking
only privilege.
Configure:
“Sub Administrator.”
The privileges of Administrators (Admin or Sub Admin)
New Sub Admin
Click Modify to change the “Sub Administrator’s” password and click Remove to delete a
. Sub Admins have read
- 8 -
Page 9
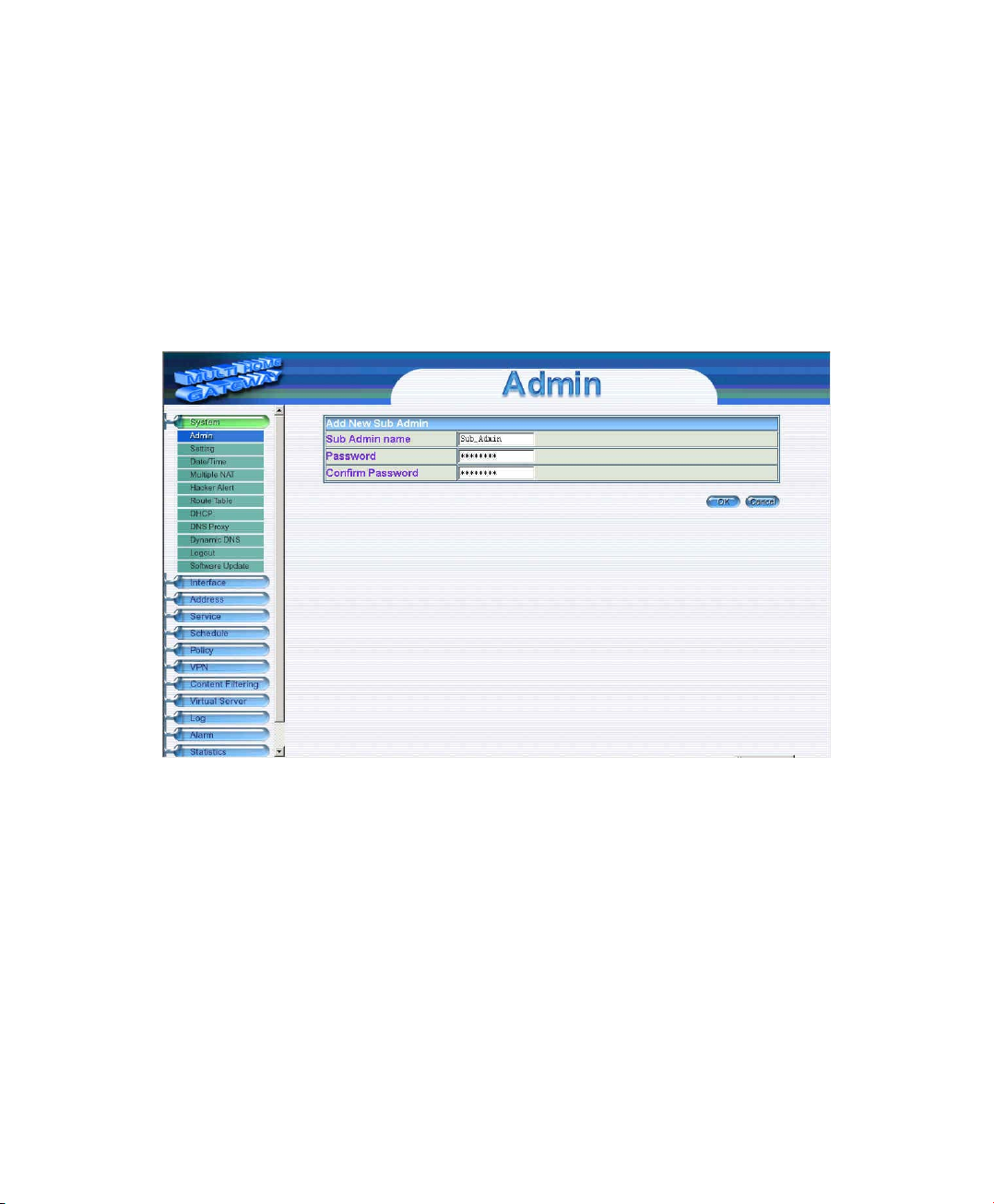
Adding a new Sub Administrator
Step 1. In the Admin window, click the New Sub Admin button to create a new Sub Administrator.
Step 2. In the Add New Sub Administrator window:
Sub Admin Name: enter the username of new Sub Admin.
Password: enter a password for the new Sub Admin.
Confirm Password: enter the password again.
Step 3. Click OK to add the user or click Cancel to cancel the addition.
- 9 -
Page 10

Changing the Sub-Administrator’s Password
Step 1. In the Admin window, locate the Administrator name you want to edit, and click on
Modify in the Configure field.
Step 2. The Modify Administrator Password window will appear. Enter in the required
information:
Password: enter original password.
New Password: enter new password
Confirm Password: enter the new password again.
Step 3. Click OK to confirm password change or click Cancel to cancel it.
- 10 -
Page 11
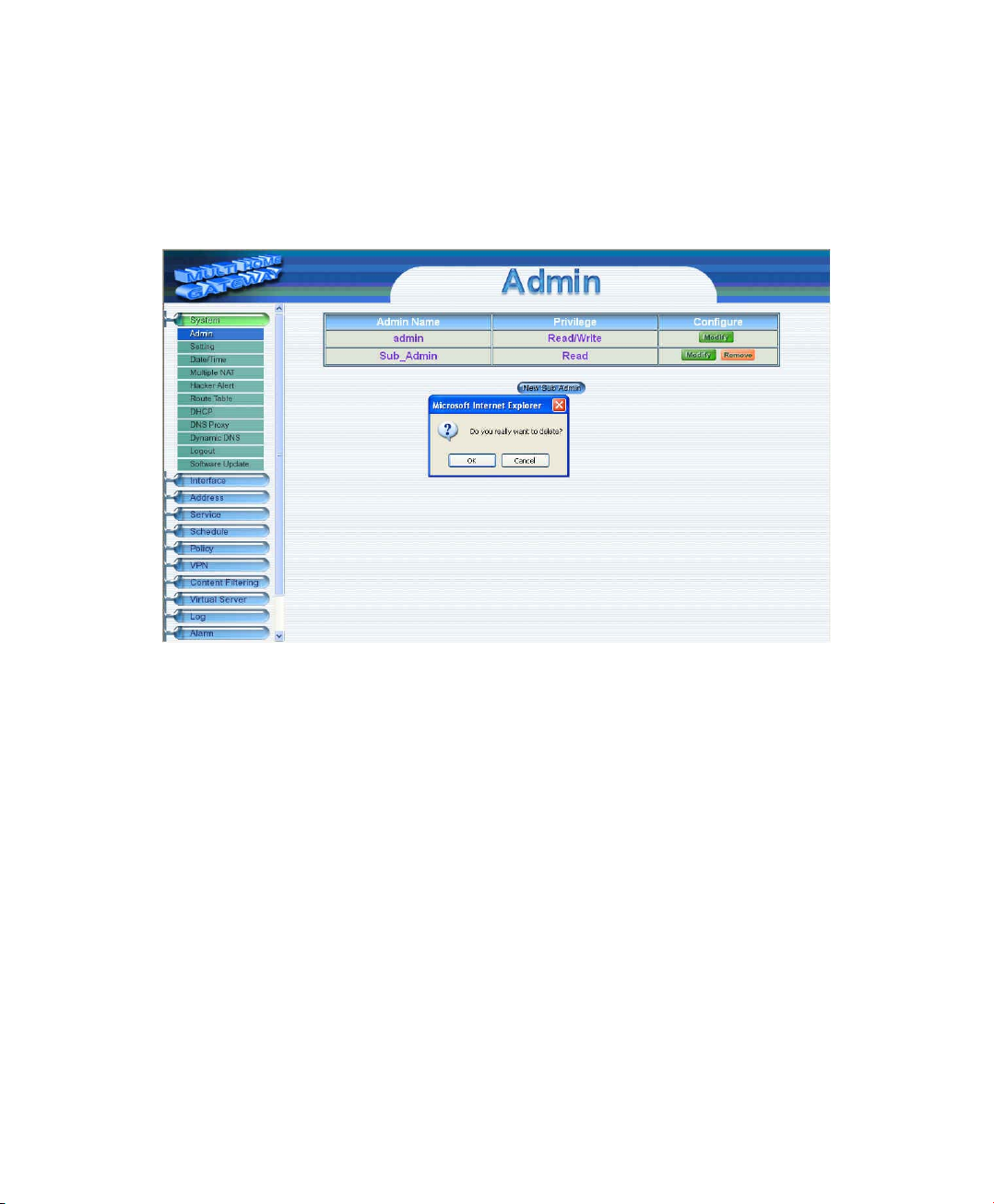
Removing a Sub Administrator
Step 1. In the Administration table, locate the Administrator name you want to edit, and click on the
Remove option in the Configure field.
Step 2. The Remove confirmation pop-up box will appear.
Step 3. Click OK to remove that Sub Admin or click Cancel to cancel.
- 11 -
Page 12

Settings
The Administrator may use this function to backup Multi-Homing configurations and export (save)
them to an “Administrator” computer or anywhere on the network; or restore a configuration file to
the device; or restore the Multi-Homing back to default factory settings.
Entering the Settings window
Click Setting in the System menu to enter the Settings window. The Multi-Homing Configuration
settings will be shown on the screen.
- 12 -
Page 13
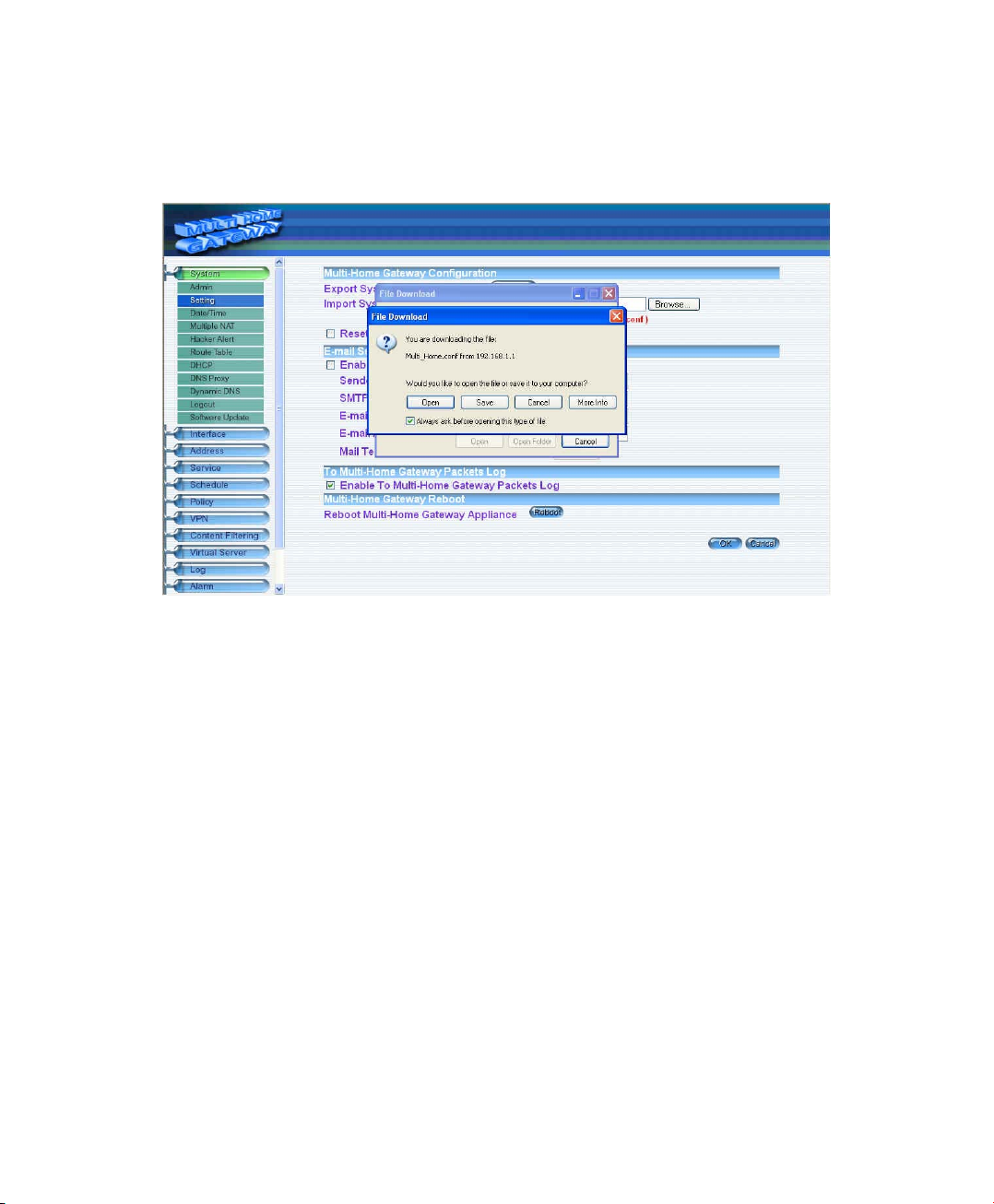
Exporting Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router settings
Step 1. Under Multi-Homing Configuration, click on the Download button next to Export System
Settings to Client.
Step 2. When the File Download pop-up window appears, choose the destination place in which to
save the exported file. The Administrator may choose to rename the file if preferred.
- 13 -
Page 14

Importing Multi-Homing settings
Step 1. Under Multi-Homing Configuration, click on the Browse button next to Import System
Settings. When the Choose File pop-up window appears, select the file to which contains
the saved Multi-Homing Settings, then click OK.
Step 2. Click OK to import the file into the Multi-Homing or click Cancel to cancel importing.
- 14 -
Page 15

Restoring Factory Default Settings
Step 1. Select Reset Factory Settings under Multi-Homing Configuration.
Step 2. Click OK at the bottom-right of the screen to restore the factory settings.
- 15 -
Page 16
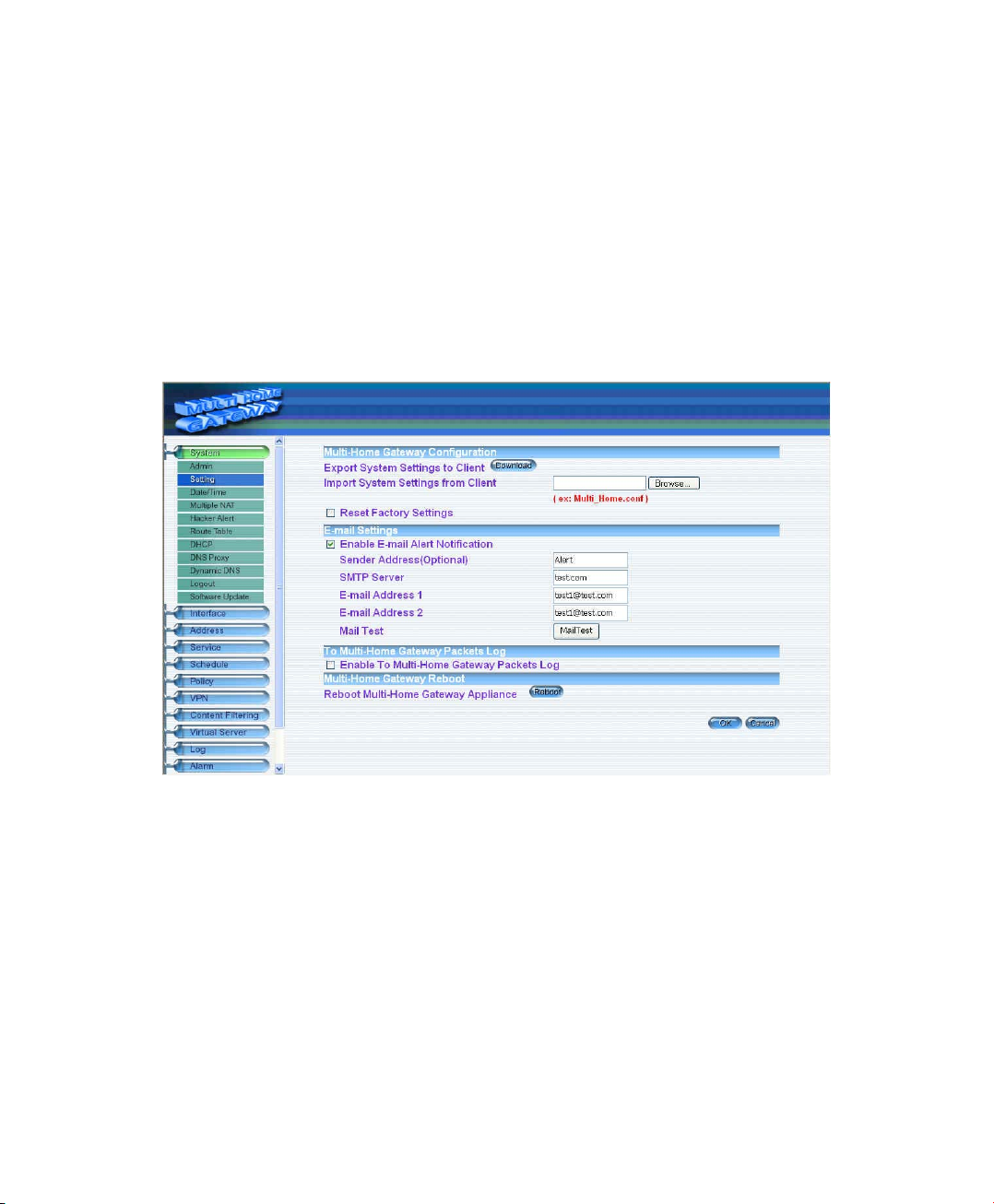
Enabling E-mail Alert Notification
Step 1. Select Enable E-mail Alert Notification under E-Mail Settings. This function will enable
the Multi-Homing to send e-mail alerts to the System Administrator when the network is
being attacked by hackers or when emergency conditions occur.
Step 2. SMTP Server IP: Enter SMTP server’s IP address.
Step 3. E-Mail Address 1: Enter the first e-mail address to receive the alarm notification.
Step 4. E-Mail Address 2: Enter the second e-mail address to receive the alarm notification.
(Optional)
Step 5. Click OK on the bottom-right of the screen to enable E-mail alert notification.
- 16 -
Page 17
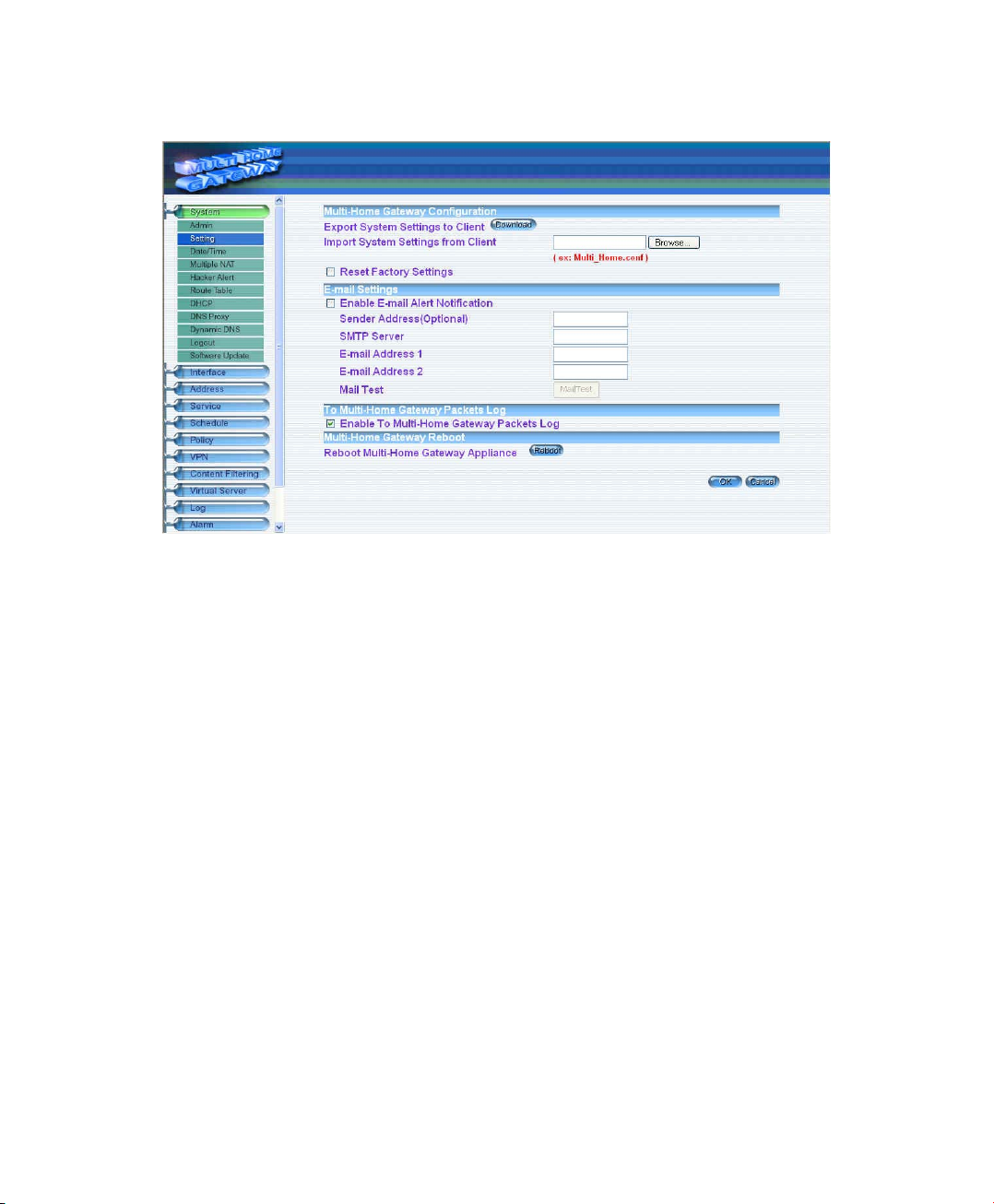
To-Multi-Homing Packets Log
Select this option to the device’s To-Multi-Homing Packets Log. Once this function is enabled,
every packet to this appliance will be recorded for system manager to trace.
- 17 -
Page 18
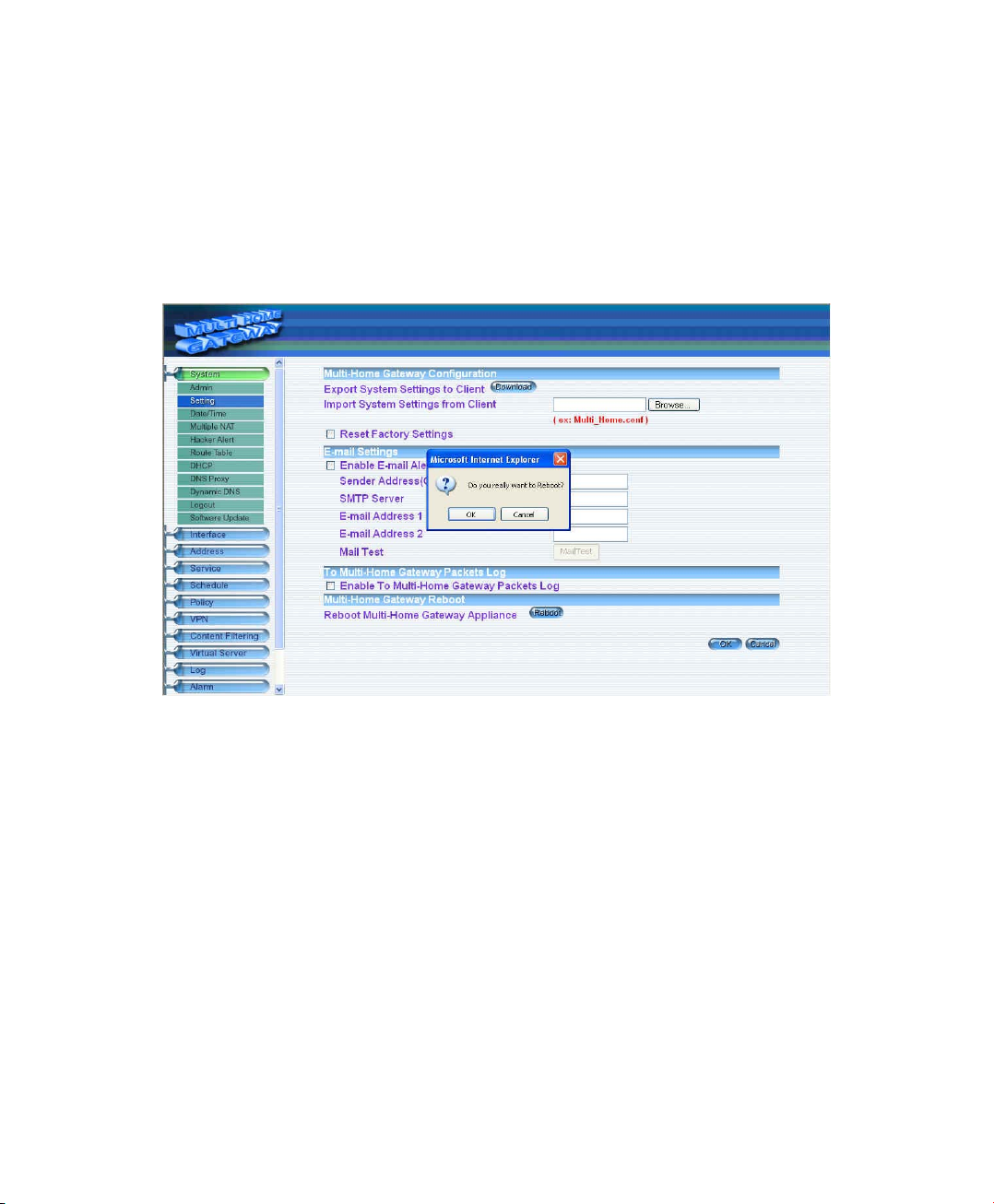
Multi-Homing Reboot
Select this option to the device’s Multi-Homing Reboot. Once this function is enabled, the MultiHoming will be reboot.
Step 1. Click Setting in the Administration menu to enter the settings window.
Step 2. Reboot Multi-Homing: Click Reboot.
Step 3. A confirmation pop-up box will appear.
Step 4. Follow the confirmation pop-up box, click OK to restart Multi-Homing or click Cancel to
discard changes.
- 18 -
Page 19

Date/Time
Synchronizing the Multi-Homing with the System Clock
Select this option to synchronize this device’s System clock with the client computer’s clock. This will
allow the logs to be time stamped correctly according to the computer clock time.
Step 1. Click System →Date/Time.
Step 2. Click the down arrow b to select the offset time from GMT.
Step 3. Enter the Server IP Address or Server name with which you want to synchronize.
Step 4. Update system clock every minutes You can set the interval time to synchronize with
outside servers. If you set it to 0, it means the device will not synchronize automatically.
Step 5. Synchronize system clock with this client: You can synchronize this Homing Gateway with
this client computer by clicking the Sync button .
Step 6. Click the OK button below to change the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 19 -
Page 20

Multiple NAT
Multiple NAT allows local port to set multiple subnetworks and connect with the internet through
different WAN 1 IP Addresses.
For instance:The lease line of a company applies several real IP Addresses 168.85.88.0/24,and the
company is divided into R&D department, service, sales department, procurement department,
accounting department, the company can distinguish each department by different subneworks for
the purpose of convenient management. The settings are as the following:
1.R&D department subnetwork:192.168.1.11/24(Internal) 168.85.88.253(WAN 1)
2. Service department subnetwork: 192.168.2.11/24(Internal) 168.85.88.252(WAN 1)
3.Sales deparment subnetwork: 192.168.3.11/24(Internal) 168.85.88.251(WAN 1)
4.Procurement department subnetwork 192.168.4.11/24(Internal) 168.85.88.250(WAN 1)
5.Accounting department subnetwork 192.168.5.11/24(Internal) 168.85.88.249(WAN 1)
The first department(R&D department) was set while setting interface IP, the other four ones have
to be added in Multiple NAT,after completing the settings, each deparment use the different WAN
IP Address to connect to the internet. The settings of each department are as the following
Service IP Address:192.168.2.1
Subnet Mask:255.255.255.0
Default Gateway:192.168.2.11
The other departments are also set by groups, this is the function of Multiple NAT.
- 20 -
Page 21

Multiple NAT settings
Click Multiple NAT in the System menu to enter Multiple NAT window.
Multiple NAT
Global port interface IP Address:Global port IP Address.
Local port interface IP Address:Local port IP Address and subnet Mask.
Modify:Modify the settings of Multiple NAT. Click Modify to modify the parameters of
Multiple NAT or click Delete to delete settings.
- 21 -
Page 22
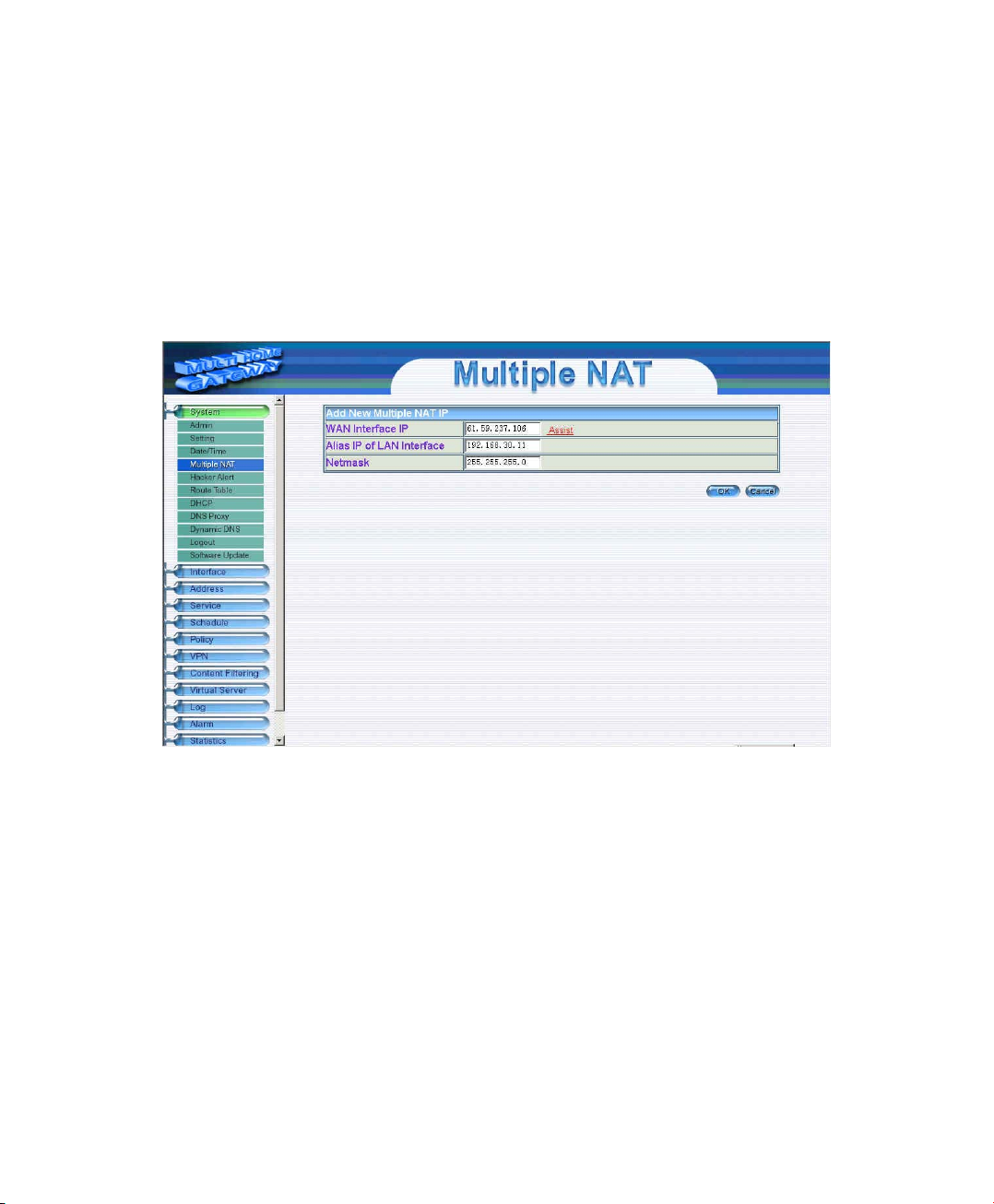
Add Multiple NAT
Step 1. Click Multiple NAT in the System menu to enter Multiple NAT window.
Step 2. Click the Add button below to add Multiple NAT.
Step 3. Enter the IP Address in the website name column of the new window.
1.1 Global port interface IP Address: Select Global port IP Address.
3.2 Local port interface IP Address: Enter Local port IP Address.
3.3 Subnet Mask:Enter Local port subnet Mask.
Step 4. Click OK to add Multiple NAT or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 22 -
Page 23

Modify Multiple NAT
Step 1.
Step 2. Find the IP Address you want to modify and click Modify
Step 3. Enter the new IP Address in Modify Multiple NAT window.
Click Multiple NAT in the System menu to enter Multiple NAT window.
Step 4.
Click the OK button below to change the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 23 -
Page 24

Delete Multiple NAT
Step 1.Click Multiple NAT in the System menu to enter Multiple NAT window.
Step 2.
Step 3.
changes.
Find the IP Address you want to delete and click Delete.
A confirmaion pop-up box will appear, click OK to delete the setting or click Cancel to discard
- 24 -
Page 25

Hacker Alert
The Administrator can enable the device’s auto detect functions in this section. When abnormal
conditions occur, the Multi-Homing will send an e-mail alert to notify the Administrator, and also
display warning messages in the Event window of Alarm.
Auto Detect functions
Detect SYN Attack: Select this option to detect TCP SYN attacks that hackers send to
server computers continuously to block or cut down all the connections of the servers. These
attacks will prevent valid users from connecting to the servers. After enabling this function,
the System Administrator can enter the number of SYN packets per second that is allow to
enter the network/Multi-Homing. Once the SYN packets exceed this limit, the activity will be
logged in Alarm and an email alert is sent to the Administrator. The default SYN flood
threshold is set to 200 Pkts/Sec
Detect ICMP Flood: Select this option to detect ICMP flood attacks. When hackers
continuously send PING packets to all the machines of theLAN networks or to the MultiHoming, your network is experiencing an ICMP flood attack. This can cause traffic
congestion on the network and slows the network down. After enabling this function, the
System Administrator can enter the number of ICMP packets per second that is allowed to
enter the network/Multi-Homing. Once the ICMP packets exceed this limit, the activity will
be logged in Alarm and an email alert is sent to the Administrator. The default ICMP flood
threshold is set to 1000 Pkts/Sec.
Detect UDP Flood: Select this option to detect UDP flood attacks. A UDP flood attack is
similar to an ICMP flood attack. After enabling this function, the System Administrator can
enter the number of UDP packets per second that is allow to enter the network/Multi-Homing.
Once the UDP packets exceed this limit, the activity will be logged in Alarm and an email
alert is sent to the Administrator. The default UDP flood threshold is set to 1000 Pkts/Sec .
.
- 25 -
Page 26

Detect Ping of Death Attack: Select this option to detect the attacks of tremendous trash
data in PING packets that hackers send to cause System malfunction This attack can cause
network speed to slow down, or even make it necessary to restart the computer to get a
normal operation.
Detect Tear Drop Attack: Select this option to detect tear drop attacks. These are packets
that are segmented to small packets with negative length. Some Systems treat the negative
value as a very large number, and copy enormous data into the System to cause System
damage, such as a shut down or a restart.
Detect IP Spoofing Attack: Select this option to detect spoof attacks. Hackers disguise
themselves as trusted users of the network in Spoof attacks. They use a fake identity to try
to pass through the Multi-Homing System and invade the network.
Filter IP Source Route Option: Each IP packet can carry an optional field that specifies the
replying address that can be different from the source address specified in packet’s header.
Hackers can use this address field on disguised packets to invadeLAN networks and
sendLAN networks’ data back to them.
Detect Port Scan Attack: Select this option to detect the port scans hackers use to
continuously scan networks on the Internet to detect computers and vulnerable ports that
are opened by those computers.
Detect Land Attack: Some Systems may shut down when receiving packets with the same
source and destination addresses, the same source port and destination port, and when
SYN on the TCP header is
marked. Enable this function to detect such abnormal packets.
Default Packet Deny: Denies all packets from passing the Multi-Homing. A packet can pass
only when there is a policy that allows it to pass.
After enabling the needed detect functions, click OK to activate the changes.
- 26 -
Page 27

Route Table
In this section, the Administrator can add static routes for the networks.
Entering the Route Table screen
Click System on the left side menu bar, then click Route Table below it. The Route Table window
appears, in which current route settings are shown.
Route Table functions
Interface: Destination network , LAN or WAN 1 networks.
Destination IP: IP address of destination network.
NetMask: Netmask of destination network.
Gateway: Gateway IP address for connecting to destination network.
Configure: Change settings in the route table.
- 27 -
Page 28

Adding a new Static Route
Step 1. In the Route Table window, click the New Entry button.
Step 2. In the Add New Static Route window, enter new static route information.
Step 3. In the Interface field’s pull-down menu, choose the network to connect (Internal, WAN 1 or
WAN 2).
Step 4. Click OK to add the new static route or click Cancel to cancel.
- 28 -
Page 29

Modifying a Static Route:
Step 1. In the Route Table menu, find the route to edit and click the corresponding Modify option in
the Configure field.
Step 2. In the Modify Static Route window, modify the necessary routing addresses.
Step 3. Click OK to apply changes or click Cancel to cancel it.
- 29 -
Page 30

Removing a Static Route
Step 1. In the Route Table window, find the route to remove and click the corresponding Remove
option in the Configure field.
Step 2. In the Remove confirmation pop-up box, click OK to confirm removing or click Cancel to
cancel it.
- 30 -
Page 31

DHCP
In the section, the Administrator can configure DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) settings
for the LAN (LAN) network.
Entering the DHCP window
Step 1. Click System on the left hand side menu bar, then click DHCP below it. The DHCP window
appears in which current DHCP settings are shown on the screen.
Dynamic IP Address functions
Subnet :LAN network’s subnet
NetMask :LAN network’s netmask
Gateway:LAN network’s gateway IP address
Broadcast:LAN network’s broadcast IP address
- 31 -
Page 32

Enabling DHCP Support
Step 1. In the Dynamic IP Address window, click Enable DHCP Support.
Step 2. Domain Name: The Administrator may enter the name of theLAN network domain if
preferred.
Step 3. Domain Name Server: Enter in the IP address of the DNS Server to be assigned to theLAN
network.
Step 4. Client IP Address Range 1: Enter the starting and the ending IP address dynamically
assigning to DHCP clients.
Step 5. Client IP Address Range 2: Enter the starting and the ending IP address dynamically
assigning to DHCP clients. (Optional)
Step 6. Click OK to enable DHCP support.
- 32 -
Page 33

DNS-Proxy
The device’s Administrator may use the DNS Proxy function to make the 10/100M 2 WAN /4 LAN
Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router act as a DNS Server for the LAN and WAN 1/2 network. All
DNS requests to a specific Domain Name will be routed to the Multi-Homing’s IP address. For
example, let’s say an organization has their mail server (i.e., mail.dfl300.com) in the WAN 1/2 network
(i.e.192.168.10.10). The outside Internet world may access the mail server of the organization easily
by its domain name, providing that the Administrator has set up Virtual Server or Mapped IP settings
correctly. However, for the users in the LAN network, their WAN 1/2 DNS server will assign them a
public IP address for the mail server. So for the LAN network to access the mail server
(mail.dfl300.com), they would have to go out to the Internet, then come back through the MultiHoming to access the mail server. Essentially, the LAN network is accessing the mail server by a real
public IP address, while the mail server serves their request by a NAT address and not a real one.
This odd situation occurs when there are servers in the WAN 1/2 network and they are bounded to
real IP addresses. To avoid this, set up DNS Proxy so all the LAN network computers will use the
device as a DNS server, which acts as the DNS Proxy.
If you want to use the DNS Proxy function of the device, the end user’s main DNS server IP
address should be the same IP Address as the device.
Entering the DNS Proxy window
Click on System in the menu bar, then click on DNS Proxy below it. The DNS Proxy window will
appear.
Below is the information needed for setting up the DNS Proxy:
• Domain Name: The domain name of the server
• Virtual IP Address: The virtual IP address respective to DNS Proxy
• Configure: modify or remove each DNS Proxy policy
- 33 -
Page 34

Adding a new DNS Proxy
Step 1: Click on the New Entry button and the Add New DNS Proxy window will appear.
Step 2: Fill in the appropriate settings for the domain name and virtual IP address.
Step 3: Click OK to save the policy or Cancel to cancel.
- 34 -
Page 35

Modifying a DNS Proxy
Step 1: In the DNS Proxy window, find the policy to be modified and click the corresponding Modify
option in the Configure field.
Step 2: Make the necessary changes needed.
Step 3: Click OK to save changes or click on Cancel to cancel modifications.
- 35 -
Page 36

Removing a DNS Proxy
Step 1: In the DNS Proxy window, find the policy to be removed and click the corresponding
Remove option in the Configure field.
Step 2: A confirmation pop-up box will appear, click OK to remove the DNS Proxy or click Cancel.
- 36 -
Page 37

Dynamic DNS
The Dynamic DNS (require Dynamic DNS Service) allows you to alias a dynamic IP address to a
static hostname, allowing your device to be more easily accessed by specific name. When this
function is enabled, the IP address in Dynamic DNS Server will be automatically updated with the
new IP address provided by ISP.
Click Dynamic DNS in the System menu to enter Dynamic DNS window.
1. The nouns in Dynamic DNS window:
!:Update Status【
error】
Domain name:Enter the password provided by ISP.
WAN IP Address:IP Address of the WAN port.
Modify:Modify dynamic DNS settings. Click Modify to change the DNS parameters;
click Delete to delete the settings.
2. How to use dynamic DNS:
The Multi-Homing provides 3 service providers, users have to regidter first to use this
function. For the usage regulations, see the providers’ websites.
How to register:First, Click Dynamic DNS in the System menu to enter Dynamic DNS window,
then click Add button,on the right side of the service providers, click Register, the service
peroviders’ website will appear, please refer to the website for the way of registration.
Connecting; Update succeed; Update fail; Unidentified
- 37 -
Page 38

Dynamic DNS settings
Step 1: Click Dynamic DNS in the System menu to enter Dynamic DNS window.
Step 2: Click Add button.
Step 3: C
lick the information in the column of the new window.
Service providers:Select service providers.
Register:to the service providers’ website.
WAN IP Address:IP Address of the WAN port.
automatically fill in the WAN 1/2 IP:Check to automatically fill in the WAN
1/2 IP.。
User Name:Enter the registered user name.
Password:Enter the password provided by ISP(Internet Service Provider).
Domain name:Your host domain name provided by ISP.
Step 4: Click OK to add dynamic DNS or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 38 -
Page 39

Modify dynamic DNS
Step 1:
Step 2: Find the item you want to change and click Modify.
Step 3: Enter the new information in the Modify Dynamic DNS window.
Click Dynamic DNS in the System menu to enter Dynamic DNS window.
Step 4:
Click OK to change the settings or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 39 -
Page 40

Delete Dynamic DNS
Step 1:
Click Dynamic DNS in the System menu to enter Dynamic DNS window.
Step 2:
Step 3: A confirmation pop-up box will appear, click OK to delete the settings or click Cancel to
Find the item you want to change and click Delete.
discard changes.
- 40 -
Page 41

Logout
Select this option to the device’s Logout the Multi-Homing. This function protects your
system while you are away.
Step 1. Click Logout the Multi-Homing.
Step 2. Click OK to logout or click Cancel to discard the change.
- 41 -
Page 42

Software Update
Under Software Update, the admin may update the device’s software with a newer software.
- 42 -
Page 43

Interface
In this section, the Administrator can set up the IP addresses for the office network. The
Administrator may configure the IP addresses of the LAN network, the WAN 1 network, and the WAN
2 network. The netmask and gateway IP addresses are also configured in this section.
- 43 -
Page 44

LAN
Entering the Interface menu:
Click on Interface in the left menu bar. Then click on LAN below it. The current settings of the
interface addresses will appear on the screen.
Configuring the Interface Settings
Internal Interface
Using the LAN Interface, the Administrator sets up the LAN network. The LAN network will use a
private IP scheme. The private IP network will not be routable on the Internet.
IP Address: The private IP address of the Multi-Homing’s LAN network is the IP address of the LAN
port of the device. The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
If the new LAN IP Address is not 192.168.1.1, the Administrator needs to set the IP Address on the computer
to be on the same subnet as the Multi-Homing and restart the System to make the new IP address effective. For
example, if the Multi-Homing’s new LAN IP Address is 172.16.0.1, then enter the new LAN IP Address
172.16.0.1 in the URL field of browser to connect to Multi-Homing.
NetMask: This is the netmask of the LAN network. The default netmask of the device is
255.255.255.0.
Ping: Select this to allow the LAN network to ping the IP Address of the Multi-Homing. If set to
enable, the device will respond to ping packets from the LAN network.
WebUI: Select this to allow the device WEBUI to be accessed from the LAN network.
- 44 -
Page 45

WAN
Entering the Interface menu
Click on Interface in the left menu bar. Then click on WAN below it. The current settings of the
interface addresses will appear on the screen.
Balance Mode:
Auto: The Multi-Homing distributes the WAN 1/2 download by proportion automatically according to
the WAN download bandwidth. (For users who are using various download bandwidth.)
Round-Robin: The Multi-Homing distributes the WAN 1/2 download bandwidth 1:1, in other words,
it selects the agent by order. (For users who are using same download bandwidths.)
By Session: The Multi-Homing distributes the WAN 1/2 download bandwidth by session. (For users
who are connected to the Internet via a fixed WAN IP address.
WAN No: Set the WAN 1/2 order.
Connect Mode: Display the current connection mode: PPPoE,
or Static IP Address.
IP Address: Display the current WAN IP Address.
Saturated Connections: Set the number for saturation whenever session numbers reach it, the Multi-
Homing switches to the next agent on the list. This function is only applicable for By Session mode.
Enable: Display Ping/WebUI functions of WAN 1/2 to show if they are enabled or disabled.
Configure: Click Modify to modify WAN 1/2 settings.
Priority: Set priority of WAN 1/2 for Internet Access.
Dynamic IP Address (Cable Modem User)
- 45 -
Page 46

WAN 1 Interface
Using the WAN 1 Interface, the Administrator sets up the WAN 1 network. These IP Addresses are
real public IP Addresses, and are routable on the Internet.
For PPPoE (ADSL User):
password in order to connect, such as ADSL users.
Current Status: Displays the current line status of the PPPoE connection.
IP Address: Displays the IP Address of the PPPoE connection
Username: Enter the PPPoE username provided by the ISP.
Password: Enter the PPPoE password provided by the ISP.
IP Address provided by ISP:
Dynamic: Select this if the IP address is automatically assigned by the ISP.
Fixed: Select this if you were given a static IP address. Enter the IP address that is given to
you by your ISP.
Service-On-Demand:
Auto Disconnect: The PPPoE connection will automatically disconnect after a length of idle
time (no activities). Enter in the amount of idle minutes before disconnection. Enter ‘0’ if you
do not want the PPPoE connection to disconnect at all.
Ping: Select this to allow the WAN 1 network to ping the IP Address of the Multi-Homing. This
will allow people from the Internet to be able to ping the Multi-Homing. If set to enable, the
device will respond to echo request packets from the WAN 1 network.
WebUI: Select this to allow the device WEBUI to be accessed from the WAN 1 network. This
will allow the WebUI to be configured from a user on the Internet. Keep in mind that the
device always requires a username and password to enter the WebUI.
This option is for PPPoE users who are required to enter a username and
For Dynamic IP Address (Cable Modem User):
assigned an IP address by their ISP, such as cable modem users. The following fields apply:
IP Address: The dynamic IP address obtained by the Multi-Homing from the ISP will be
displayed here. This is the IP address of the WAN 1 (WAN) port of the device.
MAC Address: This is the MAC Address of the device.
Hostname: This will be the name assign to the device. Some cable modem ISP assign a
specific hostname in order to connect to their network. Please enter the hostname here. If
not required by your ISP, you do not have to enter a hostname.
Ping: Select this to allow the WAN 1 network to ping the IP Address of the Multi-Homing. This
will allow people from the Internet to be able to ping the Multi-Homing. If set to enable, the
device will respond to echo request packets from the WAN 1 network.
WebUI: Select this to allow the device WEBUI to be accessed from the WAN 1 network. This
will allow the WebUI to be configured from a user on the Internet. Keep in mind that the
device always requires a username and password to enter the WebUI.
This option is for users who are automatically
- 46 -
Page 47

For Static IP Address: This option is for users who are assigned a static IP Address from their ISP.
Your ISP will provide all the information needed for this section such as IP Address, Netmask,
Gateway, and DNS. Use this option also if you have more than one public IP Address assigned to
you.
IP Address: Enter the static IP address assigned to you by your ISP. This will be the public
IP address of the WAN 1 port of the device.
Netmask: This will be the Netmask of the WAN 1 network. (i.e. 255.255.255.0)
Default Gateway: This will be the Gateway IP address.
Domain Name Server (DNS): This is the IP Address of the DNS server.
Ping: Select this to allow the WAN 1 network to ping the IP Address of the Multi-Homing.
This will allow people from the Internet to be able to ping the Multi-Homing. If set to enable,
the device will respond to echo request packets from the WAN 1 network.
WebUI: Select this to allow the device WEBUI to be accessed from the WAN 1 network. This
will allow the WebUI to be configured from a user on the Internet. Keep in mind that the
device always requires a username and password to enter the WebUI.
- 47 -
Page 48

WAN 2 Interface
Using the WAN 2 Interface, the Administrator sets up the WAN 2 network. These IP Addresses are
real public IP Addresses, and are routable on the Internet.
For PPPoE (ADSL User):
password in order to connect, such as ADSL users.
Current Status: Displays the current line status of the PPPoE connection.
IP Address: Displays the IP Address of the PPPoE connection
Username: Enter the PPPoE username provided by the ISP.
Password: Enter the PPPoE password provided by the ISP.
IP Address provided by ISP:
Dynamic: Select this if the IP address is automatically assigned by the ISP.
Fixed: Select this if you were given a static IP address. Enter the IP address that is given to
you by your ISP.
Service-On-Demand:
Auto Disconnect: The PPPoE connection will automatically disconnect after a length of idle
time (no activities). Enter in the amount of idle minutes before disconnection. Enter ‘0’ if you
do not want the PPPoE connection to disconnect at all.
Ping: Select this to allow the WAN 2 network to ping the IP Address of the Multi-Homing. This
will allow people from the Internet to be able to ping the Multi-Homing. If set to enable, the
device will respond to echo request packets from the WAN 2 network.
WebUI: Select this to allow the device WEBUI to be accessed from the WAN 2 network. This
will allow the WebUI to be configured from a user on the Internet. Keep in mind that the
device always requires a username and password to enter the WebUI.
This option is for PPPoE users who are required to enter a username and
For Dynamic IP Address (Cable Modem User):
assigned an IP address by their ISP, such as cable modem users. The following fields apply:
IP Address: The dynamic IP address obtained by the Multi-Homing from the ISP will be
displayed here. This is the IP address of the WAN 2 port of the device.
MAC Address: This is the MAC Address of the device.
Hostname: This will be the name assign to the device. Some cable modem ISP assign a
specific hostname in order to connect to their network. Please enter the hostname here. If
not required by your ISP, you do not have to enter a hostname.
Ping: Select this to allow the WAN 2 network to ping the IP Address of the Multi-Homing. This
will allow people from the Internet to be able to ping the Multi-Homing. If set to enable, the
device will respond to echo request packets from the WAN 2 network.
WebUI: Select this to allow the device WEBUI to be accessed from the WAN 2 network. This
will allow the WebUI to be configured from a user on the Internet. Keep in mind that the
device always requires a username and password to enter the WebUI.
This option is for users who are automatically
- 48 -
Page 49

For Static IP Address: This option is for users who are assigned a static IP Address from their ISP.
Your ISP will provide all the information needed for this section such as IP Address, Netmask,
Gateway, and DNS. Use this option also if you have more than one public IP Address assigned to
you.
IP Address: Enter the static IP address assigned to you by your ISP. This will be the public
IP address of the WAN 2 port of the device.
Netmask: This will be the Netmask of the WAN 2 network. (i.e. 255.255.255.0)
Default Gateway: This will be the Gateway IP address.
Domain Name Server (DNS): This is the IP Address of the DNS server.
Ping: Select this to allow the WAN 2 network to ping the IP Address of the Multi-Homing.
This will allow people from the Internet to be able to ping the Multi-Homing. If set to enable,
the device will respond to echo request packets from the WAN 2 network.
WebUI: Select this to allow the device WEBUI to be accessed from the WAN 2 network. This
will allow the WebUI to be configured from a user on the Internet. Keep in mind that the
device always requires a username and password to enter the WebUI.
- 49 -
Page 50

- 50 -
Page 51

Address
The 10/100M 2 WAN /4 LAN Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router allows the Administrator to set
Interface addresses of the LAN network, LAN network group, WAN 1/2 network, WAN 1/2 group.
What is the Address Table?
An IP address in the Address Table can be an address of a computer or a sub network. The
Administrator can assign an easily recognized name to an IP address. Based on the network it
belongs to, an IP address can be an LAN IP address, WAN1/2 IP address . If the Administrator needs
to create a control policy for packets of different IP addresses, he can first add a new group in the
LAN Network Group or the WAN 1/2 Network Group and assign those IP addresses into the newly
created group. Using group addresses can greatly simplify the process of building control policies.
With easily recognized names of IP addresses and names of address groups shown in the address
table, the Administrator can use these names as the source address or destination address of control
policies. The address table should be built before creating control policies, so that the Administrator
can pick the names of correct IP addresses from the address table when setting up control policies.
- 51 -
Page 52

LAN
Entering the LAN window
Step 1. Click LAN under the Address menu to enter the LAN window. The current setting
information such as the name of the LAN network, IP and Netmask addresses will show on
the screen.
- 52 -
Page 53

Adding a new LAN Address
Step 1. In the LAN window, click the New Entry button.
Step 2. In the Add New Address window, enter the settings of a new LAN network address.
Step 3. Click OK to add the specified LAN network or click Cancel to cancel the changes.
- 53 -
Page 54

Modifying an LAN Address
Step 1. In the LAN window, locate the name of the network to be modified. Click the Modify option
in its corresponding Configure field. The Modify Address window appears on the screen
immediately.
Step 2. In the Modify Address window, fill in the new addresses.
Step 3. Click OK to save changes or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 54 -
Page 55

Removing an LAN Address
Step 1. In the LAN window, locate the name of the network to be removed. Click the Remove option
in its corresponding Configure field.
Step 2. In the Remove confirmation pop-up box, click OK to remove the address or click Cancel to
discard changes.
- 55 -
Page 56

LAN Group
Entering the LAN Group window
The LAN Addresses may be combined together to become a group.
Click LAN Group under the Address menu to enter the LAN Group window. The current setting
information for the LAN network group appears on the screen.
Adding an LAN Group
Step 1. In the LAN Group window, click the New Entry button to enter the Add New Address
Group window.
Step 2. In the Add New Address Group window:
Available Address: list the names of all the members of the LAN network.
Selected Address: list the names to be assigned to the new group.
Name: enter the name of the new group in the open field.
Step 3. Add members: Select names to be added in Available Address list, and click the Add>>
button to add them to the Selected Address list.
Step 4. Remove members: Select names to be removed in the Selected Address list, and click the
<<Remove button to remove these members from Selected Address list.
Step 5. Click OK to add the new group or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 56 -
Page 57

Modifying an LAN Group
Step 1. In the LAN Group window, locate the network group desired to be modified and click its
corresponding Modify option in the Configure field.
Step 2. A window displaying the information of the selected group appears:
Available Address: list names of all members of the LAN network.
Selected Address: list names of members which have been assigned to this group.
Step 3. Add members: Select names in Available Address list, and click the Add>> button to add
them to the Selected Address list.
Step 4. Remove members: Select names in the Selected Address list, and click the <<Remove
button to remove these members from the Selected Address list.
Step 5. Click OK to save changes or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 57 -
Page 58

Removing an LAN Group
Step 1. In the LAN Group window, locate the group to be removed and click its corresponding
Remove option in the Configure field.
Step 2. In the Remove confirmation pop-up box, click OK to remove the group or click Cancel to
discard changes.
- 58 -
Page 59

WAN
Entering the WAN window
Click WAN under the Address menu to enter the WAN window. The current setting information, such
as the name of the WAN network, IP and Netmask addresses will show on the screen.
- 59 -
Page 60

Adding a new WAN Address
Step 1. In the WAN window, click the New Entry button.
Step 2. In the Add New Address window, enter the settings for a new WAN network address.
Step 3. Click OK to add the specified WAN network or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 60 -
Page 61

Modifying an WAN Address
Step 1. In the WAN table, locate the name of the network to be modified and click the Modify
option in its corresponding Configure field.
Step 2. The Modify Address window will appear on the screen immediately. In the Modify
Address window, fill in new addresses.
Step 3. Click OK to save changes or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 61 -
Page 62

Removing an WAN Address
Step 1. In the WAN table, locate the name of the network to be removed and click the Remove
option in its corresponding Configure field.
Step 2. In the Remove confirmation pop-up box, click OK to remove the address or click Cancel to
discard changes.
- 62 -
Page 63

WAN Group
Entering the WAN Group window
Click the WAN Group under the Address menu bar to enter the WAN window. The current settings
for the WAN network group(s) will appear on the screen.
- 63 -
Page 64

Adding an WAN Group
Step 1. In the WAN Group window, click the New Entry button and the Add New Address Group
window will appear.
Step 2. In the Add New Address Group window the following fields will appear:
Name: enter the name of the new group.
Available Address: List the names of all the members of the WAN network.
Selected Address: List the names to assign to the new group.
Step 3. Add members: Select the names to be added in the Available Address list, and click the
Add>> button to add them to the Selected Address list.
Step 4. Remove members: Select the names to be removed in the Selected Address list, and
click the <<Remove button to remove them from the Selected Address list.
Step 5. Click OK to add the new group or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 64 -
Page 65

Editing an WAN Group
Step 1. In the WAN Group window, locate the network group to be modified and click its
corresponding Modify button in the Configure field.
Step 2. A window displaying the information of the selected group appears:
Available Address: list the names of all the members of the WAN network.
Selected Address: list the names of the members that have been assigned to this group.
Step 3. Add members: Select the names to be added in the Available Address list, and click the
Add>> button to add them to the Selected Address list.
Step 4. Remove members: Select the names to be removed in the Selected Address list, and
click the <<Remove button to remove them from the Selected Address list.
Step 5. Click OK to save changes or click Cancel to discard changes.
- 65 -
Page 66

Removing an WAN Group
Step 1. In the WAN Group window, locate the group to be removed and click its corresponding
Modify option in the Configure field.
Step 2. In the Remove confirmation pop-up box, click OK to remove the group or click Cancel to
discard changes.
- 66 -
Page 67

Service
In this section, network services are defined and new network services can be added. There are
three sub menus under Service which are: Pre-defined, Custom, and Group. The Administrator
can simply follow the instructions below to define the protocols and port numbers for network
communication applications. Users then can connect to servers and other computers through these
available network services.
What is Service?
TCP and UDP protocols support varieties of services, and each service consists of a TCP Port or
UDP port number, such as TELNET(23), SMTP(21), POP3(110),etc. The 10/100M 2 WAN /4 LAN
Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router defines two services: pre-defined service and custom
service. The common-use services like TCP and UDP are defined in the pre-defined service and
cannot be modified or removed. In the custom menu, users can define other TCP port and UDP port
numbers that are not in the pre-defined menu according to their needs. When defining custom
services, the client port ranges from 1024 to 65535 and the server port ranges from 0 to 1023.
How do I use Service?
The Administrator can add new service group names in the Group option under Service menu, and
assign desired services into that new group. Using service group the Administrator can simplify the
processes of setting up control policies. For example, there are 10 different computers that want to
access 5 different services on a server, such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP, POP3, and TELNET. Without the
help of service groups, the Administrator needs to set up 50 (10x5) control policies, but by applying
all 5 services to a single group name in the service field, it takes only one control policy to achieve
the same effect as the 50 control policies.
- 67 -
Page 68

Pre-defined
Entering a Pre-defined window
Click Service on the menu bar on the left side of the window. Click Pre-defined under it. A window
will appear with a list of services and their associated IP addresses. This list cannot be modified.
- 68 -
Page 69

Custom
Entering the Custom window
Click Service on the menu bar on the left side of the window. Click Custom under it. A window will
appear with a table showing all services currently defined by the Administrator.
- 69 -
Page 70

Adding a new Service
Step 1 In the Custom window, click the New Entry button and a new service table appears.
Step 2 In the new service table:
New Service Name: This will be the name referencing the new service.
Protocol: Enter the network protocol type to be used, such as TCP, UDP, or Other (please
enter the number for the protocol type).
Client Port: enter the range of port number of new clients.
Server Port: enter the range of port number of new servers.
The client port ranges from 1024 to 65535 and the server port ranges from 0 to 1023.
Step 3 Click OK to add new services, or click Cancel to cancel.
- 70 -
Page 71

Modifying Custom Services
Step 1. In the Custom table, locate the name of the service to be modified. Click its corresponding
Modify option in the Configure field.
Step 2. A table showing the current settings of the selected service appears on the screen
Step 3. Enter the new values.
Step 4. Click OK to accept editing; or click Cancel.
- 71 -
Page 72

Removing Custom Services
Step 1. In the Custom window, locate the service to be removed. Click its corresponding Remove
option in the Configure field.
Step 2. In the Remove confirmation pop-up box, click OK to remove the selected service or click
Cancel to cancel action.
- 72 -
Page 73

Group
Accessing the Group window
Click Service in the menu bar on the left hand side of the window. Click Group under it. A window
will appear with a table displaying current service group settings set by the Administrator.
- 73 -
Page 74

Adding Service Groups
Step 1. In the Group window, click the New Entry button.
In the Add Service Group window, the following fields will appear:
Available Services: list all the available services.
Selected Services: list services to be assigned to the new group.
Step 2. Enter the new group name in the group Name field. This will be the name referencing the
created group.
Step 4. To add new services: Select the services desired to be added in the Available Services
list and then click the Add>> button to add them to the group.
Step 5. To remove services: Select services desired to be removed in the Available Services, and
then click the <<Remove button to remove them from the group.
Step 6. Click OK to add the new group.
- 74 -
Page 75

Modifying Service Groups
Step 1. In the Group window, locate the service group to be edited. Click its corresponding Modify
option in the Configure field.
Step 2. In the Mod (modify) group window the following fields are displayed::
Available Services: lists all the available services.
Selected Services: list services that have been assigned to the selected group.
Step 3. Add new services: Select services in the Available Services list, and then click the Add>>
button to add them to the group.
Step 4. Remove services: Select services to be removed in the Selected Services list, and then
click the <<Remove button to remove theses services from the group.
Step 5. Click OK to save editing changes.
- 75 -
Page 76

Removing Service Groups
Step 1. In the Group window, locate the service group to be removed and click its corresponding
Remove option in the Configure field.
Step 2. In the Remove confirmation pop-up box, click OK to remove the selected service group or
click Cancel to cancel removing.
- 76 -
Page 77

Schedule
The 10/100M 2 WAN /4 LAN Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router allows the Administrator to
configure a schedule for policies to take affect. By creating a schedule, the Administrator is allowing
the Multi-Homing policies to be used at those designated times only. Any activities outside of the
scheduled time slot will not follow the Multi-Homing policies therefore will likely not be permitted to
pass through the Multi-Homing. The Administrator can configure the start time and stop time, as well
as creating 2 different time periods in a day. For example, an organization may only want the MultiHoming to allow the LAN network users to access the Internet during work hours. Therefore, the
Administrator may create a schedule to allow the Multi-Homing to work Monday-Friday, 8AM-5PM
only. During the non-work hours, the Multi-Homing will not allow Internet access.
Accessing the Schedule window
Click on Schedule on the menu bar and the schedule window will appear displaying the active
schedules.
The following items are displayed in this window:
Name: the name assigned to the schedule
Comment: a short comment describing the schedule
Configure: modify or remove
- 77 -
Page 78

Adding a new Schedule
Step 1: Click on the New Entry button and the Add New Schedule window will appear.
Step 2:
Schedule Name: Fill in a name for the new schedule.
Period 1: Configure the start and stop time for the days of the week that the schedule will be
active.
Step 3: Click Ok to save the new schedule or click Cancel to cancel adding the new schedule.
- 78 -
Page 79

Modifying a Schedule
Step 1: In the Schedule window, find the policy to be modified and click the corresponding Modify
option in the Configure field.
Step 2: Make needed changes.
Step 3: Click OK to save changes.
- 79 -
Page 80

Removing a Schedule
Step 1: In the Schedule window, find the policy to be removed and click the corresponding Remove
option in the Configure field.
Step 2: A confirmation pop-up box will appear, click on OK to remove the schedule.
- 80 -
Page 81

Policy
This section provides the Administrator with facilities to sent control policies for packets with different
source IP addresses, source ports, destination IP addresses, and destination ports. Control policies
decide whether packets from different network objects, network services, and applications are able to
pass through the Multi-Homing.
What is Policy?
The device uses policies to filter packets. The policy settings are: source address, destination
address, services, permission, packet log, packet statistics, and flow alarm. Based on its source
addresses, a packet can be categorized into:
(1). Outgoing: a client is in the LAN networks while a server is in the WAN 1/2 networks.
(2) Incoming, a client is in the WAN 1/2 networks, while a server is in the LAN networks.
How do I use Policy?
The policy settings are source addresses, destination addresses, services, permission, log, statistics,
and flow alarm. Among them, source addresses, destination addresses and IP mapping addresses
have to be defined in the Address menu in advance. Services can be used directly in setting up
policies, if they are in the Pre-defined Service menu. Custom services need to be defined in the
Custom menu before they can be used in the policy settings.
If the destination address of an incoming policy is a Mapped IP address or a Virtual Server address,
then the address has to be defined in the Virtual Server section instead of the Address section.
Policy Directions:
Step 1. In Address, set names and addresses of
source networks and destination networks.
Step 2. In Service, set services.
Step 3. In Virtual Server, set names and addresses
of mapped IP or virtual server (only applied to
Incoming policies).
Step 4. Set control policies in Policy
- 81 -
Page 82

Outgoing
This section describes steps to create policies for packets and services from the LAN network to the
WAN 1/2 network.
Entering the Outgoing window:
Click Policy on the left hand side menu bar, then click Outgoing under it. A window will appear with
a table displaying currently defined Outgoing policies.
The fields in the Outgoing window are:
Source: source network addresses that are specified in the LAN section of Address menu,
or all the LAN network addresses.
Destination: destination network addresses that are specified in the WAN section of the
Address menu, or all of the WAN network addresses.
Service: specify services provided by WAN network servers.
Action: control actions to permit or reject/deny packets from LAN networks to WAN 1/2
network travelling through the Multi-Homing.
Option: specify the monitoring functions on packets from LAN networks to WAN 1/2
networks travelling through the Multi-Homing.
Configure: modify settings.
Move: this sets the priority of the policies, number 1 being the highest priority.
- 82 -
Page 83

Adding a new Outgoing Policy
Step 1: Click on the New Entry button and the Add New Policy window will appear.
Step 2:
Source Address: Select the name of the LAN network from the drop down list. The drop down list
contains the names of all LAN networks defined in the LAN section of the Address menu. To create a
new source address, please go to the LAN section under the Address menu.
Destination Address: Select the name of the WAN 1/2 network from the drop down list. The drop
down list contains the names of all WAN 1/2 networks defined in the WAN 1/2 section of the Address
window. To create a new destination address, please go to the WAN 1/2 section under the Address
menu.
Service: Specified services provided by WAN 1/2 network servers. These are services/application
that are allowed to pass from the LAN network to the WAN 1/2 network. Choose ANY for all services.
Action: Select Permit,Permit WAN 1,Permit WAN 2 or Deny from the drop down list to allow or
reject the packets travelling between the source network and the destination network.
Logging: Select Enable to enable flow monitoring.
Statistics: Select Enable to enable flow statistics.
Alarm Threshold: set a maximum flow rate (in Kbytes/Sec). An alarm will be sent if flow rates are
higher than the specified value.
Step 3: Click OK to add a new outgoing policy; or click Cancel to cancel adding a new outgoing
policy.
- 83 -
Page 84

Modifying an Outgoing policy
Step 1: In the Outgoing policy section, locate the name of the policy desired to be modified and click
its corresponding Modify option under the Configure field.
Step 2: In the Modify Policy window, fill in new settings.
Note: To change or add selections in the drop-down list for source or destination address, go to the
section where the selections are setup. (Source Address→LAN of Address menu;
Destination Address → WAN 1 of Address menu; Service→[Pre-defined],[Custom] or
Group under Service).
Step 3: Click OK to do confirm modification or click Cancel to cancel it.
- 84 -
Page 85

Removing the Outgoing Policy
Step 1. In the Outgoing policy section, locate the name of the policy desired to be removed and click
its corresponding Remove option in the Configure field.
Step 2. In the Remove confirmation dialogue box, click OK to remove the policy or click Cancel to
cancel removing.
- 85 -
Page 86

Enabled Monitoring function:
Log: If Logging is enabled in the outgoing policy, the MULTI-HOMING DUAL WAN FIREWALL
ROUTER will log the traffic and event passing through the Multi-Homing. The Administrator can click
Log on the left menu bar to get the flow and event logs of the specified policy.
Note: System Administrator can back up and clear logs in this window. Check the chapter entitled “Log”
to get details about the log and ways to back up and clear logs.
- 86 -
Page 87

Alarm: If Logging is enabled in the outgoing policy, the MULTI-HOMING DUAL WAN FIREWALL
ROUTER will log the traffic alarms and event alarms passing through the Multi-Homing. The
Administrator can click Alarm on the left menu to get the logs of flow and event alarms of the
specified policy.
Note: The Administrator can also get information on alarm logs from the Alarm window. Please refer to the
section entitled “Alarm” for more information.
- 87 -
Page 88

Statistics: If Statistics is enabled in the outgoing policy, the MULTI-HOMING DUAL WAN FIREWALL
ROUTER will display the flow statistics passing through the Multi-Homing.
Note: The Administrator can also get flow statistics in Statistics. Please refer to Statistics in Chapter 11
for more details.
- 88 -
Page 89

Incoming
This chapter describes steps to create policies for packets and services from the WAN 1/2 network to
the LAN network including Mapped IP and Virtual Server.
Enter Incoming window
Step 1: Click Incoming under the Policy menu to enter the Incoming window. The Incoming table
will display current defined policies from the WAN 1/2 network to assigned Mapped IP or
Virtual Server.
Step 2: The fields of the Incoming window are:
Source: source networks which are specified in the WAN section of the Address menu, or
all the WAN network addresses.
Destination: destination networks, which are IP Mapping addresses or Virtual server
network addresses created in Virtual Server menu.
Service: services supported by Virtual Servers (or Mapped IP).
Action: control actions to permit or deny packets from WAN networks to Virtual
Server/Mapped IP travelling through the device.
Option: specify the monitoring functions on packets from WAN networks to Virtual
Server/Mapped IP travelling through the Multi-Homing.
Configure: modify settings or remove incoming policy.
Move: this sets the priority of the policies, number 1 being the highest priority.
- 89 -
Page 90

Adding an Incoming Policy
Step 1: Under Incoming of the Policy menu, click the New Entry button.
Step 2:
Source Address: Select names of the WAN networks from the drop down list. The drop down list
contains the names of all WAN networks defined in the WAN section of the Address menu. To
create a new source address, please go to the LAN section under the Address menu.
Destination Address: Select names of the LAN networks from the drop down list. The drop down list
contains the names of IP mapping addresses specified in the Mapped IP or the Virtual Server
sections of Virtual Server menu. To create a new destination address, please go to the Virtual
Server menu.
Service: Specified services provided by LAN network servers. These are services/application that
are allowed to pass from the network to the LAN network. Choose ANY for all services.
Action: Select Permit or Deny from the drop down list to allow or reject the packets travelling
between the specified WAN network and Virtual Server/Mapped IP.
Logging: select Enable to enable flow monitoring.
Statistics: select Enable to enable flow statistics.
Alarm Threshold: set a maximum flow rate (in Kbytes/Sec). An alarm will be sent if flow rates are
higher than the specified value.
Step 3: Click OK to add new policy or click Cancel to cancel adding new incoming policy.
- 90 -
Page 91

Modifying Incoming Policy
Step 1: In the Incoming window, locate the name of policy desired to be modified and click its
corresponding Modify option in the Configure field.
Step 2: In the Modify Policy window, fill in new settings.
Step 3: Click OK to save modifications or click Cancel to cancel modifications.
- 91 -
Page 92

Removing an Incoming Policy
Step 1: In the Incoming window, locate the name of policy desired to be removed and click its
corresponding [Remove] in the Configure field.
Step 2: In the Remove confirmation window, click Ok to remove the policy or click Cancel to cancel
removing.
- 92 -
Page 93

VPN
The 10/100M 2 WAN /4 LAN Multi-Homing Dual WAN Firewall Router’s VPN (Virtual Private Network)
is set by the System Administrator. The System Administrator can add, modify or remove VPN
settings.
What is VPN?
To set up a Virtual Private Network (VPN), you don’t need to configure an Access Policy to enable
encryption. Just fill in the following settings: VPN Name, Source Subnet, Destination Gateway,
Destination Subnet, Authentication Method, Preshare key, Encapsulation and IPSec lifetime. The
Multi-Homings on both ends must use the same Preshare key and IPSec lifetime to make a VPN
connection.
- 93 -
Page 94

Autokey IKE
This chapter describes steps to create a VPN connection using Autokey IKE. Autokey IKE (Internet
Key Exchange) provides a standard method to negotiate keys between two security gateways. For
example, with two Multi-Homing devices, IKE allows new keys to be generated after a set amount of
time has passed or a certain threshold of traffic has been exchanged.
Accessing the Autokey IKE window
Click Autokey IKE under the VPN menu to enter the Autokey IKE window. The Autokey IKE table
displays current configured VPNs.
The fields in the Autokey IKE window are:
Name: The VPN name to identify the VPN tunnel definition. The name must be different for the two
sites creating the tunnel.
Gateway IP: The WAN 1 interface IP address of the remote Multi-Homing.
Destination Subnet: Destination network subnet.
PSK/RSA: The IKE VPN must be defined with a Preshared Key. The Key may be up to 128 bytes
long.
Status: Connect/Disconnect or Connecting/Disconnecting.
Configure: Connect, Disconnect, Modify and Delete.
- 94 -
Page 95

Adding the Autokey IKE
Step 1. Click the New Entry button and the VPN Auto Keyed Tunnel window will appear.
Step 2:
Preshare Key: The IKE VPN must be defined with a Preshared Key. The Key may be up to 128
bytes long.
ESP/AH: The IP level security headers, AH and ESP, were originally proposed by the Networking
Group focused on IP security mechanisms, IPSec. The term IPSec is used loosely here to
refer to packets, keys, and routes that are associated with these headers. The IP
Authentication Header (AH) is used to provide authentication. The IP Encapsulating Security
Header (ESP) is used to provide confidentially to IP datagrams.
ESP-Encryption Algorithm: The device auto-selects 56 bit DES-CBC or 168-bit Triple DES-CBC
encryption algorithm. The default algorithm is 168-bit Triple DES-CBC.
ESP-Authentication Method: The device auto-selects MD5 or SHA-1 authentication algorithm.
The default algorithm is MD5.
IPSec Lifetime: New keys will be generated whenever the lifetime of the old keys is exceeded. The
Administrator may enable this feature if needed and enter the lifetime in seconds to re-key.
The default is 28800 seconds (eight hours). Selection of small values could lead to frequent
re-keying, which could affect performance.
- 95 -
Page 96

Modifying an Autokey IKE
Step 1: In the Autokey IKE window, locate the name of policy desired to be modified and click its
corresponding Modify option in the Configure field.
Step 2: In the Modify Policy window, fill in new settings.
Step 3: Click OK to save modifications.
Connecting the VPN connection:
Once all the policy is created with the correct settings, click on the Connect option in the Configure
field. The Status field will change to indicate Connecting. If the remote Multi-Homing is set up
correctly with the VPN active, the VPN connection will be made between the two Multi-Homings and
the Status field will change to Connect.
- 96 -
Page 97

Removing Autokey IKE
Step 1. Locate the name of the Autokey IKE desired to be removed and click its corresponding
Delete option in the Configure field.
Step 2. In the Remove confirmation pop-up box, click OK to remove the Autokey IKE or click Cancel
to cancel deleting.
- 97 -
Page 98

PPTP Server
Entering the PPTP Server window
Step 1. Select VPN→PPTP Server.
PPTP Server:Click Modify to select Enable or Disable.
Client IP Range: 192.26.145.1-254:Display the IP addresses range for PPTP
Client connection.
User Name:Displays the PPTP Client user’s name for authentication.
Client IP:Displays the PPTP Client’s IP address for authentication.。
Uptime:Displays the connection time between PPTP Server and Client.
Status:Displays current connection status between PPTP Server and PPTP client.
Configure:Click 【Modify】to modify the PPTP Client settings or click
【Remove】to remove the item.
- 98 -
Page 99

Modifying PPTP Server Design
Step 1.
Select VPN→PPTP Server.
。
Step 2.
Click【Modify】after the Client IP Range.
Step 3. In the【Modify Server Design 】Window, enter appropriate settings.
Modify Server Design
Disable PPTP:Check to disable PPTP Server.
Enable PPTP:Check to enable PPTPServer.
1.Encyption: the default is set to disabled.
2.Client IP Range:Enter the IP range allocated for PPTP Client to connect to the
PPTP server.
Auto-Disconnect if idle
minutes: Configure this device to disconnect to the PPTP
Server when there is no activity for a predetermined period of time. To keep the line
always connected, set the number to 0.
Schedule:Click the down arrow to select the schedule, which was pre-determined in
Schedule. Refer to the corresponding section for details.
Step 4. Click OK to save modifications or click Cancel to cancel modifications
- 99 -
Page 100

Adding PPTP Server
Step 1. Select VPN→PPTP Server. Click NewEntry.
Step 2. Enter appropriate settings in the following window.
User name: Specify the PPTP client. This should be unique.
Password: Specify the PPTP client password.
Remote Client:
Single Machine: Check to connect to single computer.
Multi-Machine: Check to allow multiple computers connected to the PPTP server.
IP Address:Enter the PPTP Client IP address.
Netmask: Enter the PPTP Client Sub net mask.
Client IP assigned by:
1. IP Range: check to enable auto-allocating IP for PPTP client to connect.
2. Fixed IP: check and enter a fixed IP for PPTP client to connect.
Step 3. Click OK to save modifications or click Cancel to cancel modifications
- 100 -
 Loading...
Loading...