
TS616
DUAL WIDE BAND OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
WITH HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT
■ LOW NOISE : 2.5nV/√Hz
■ HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT : 420mA
■ VERY LOW HARMONIC AND INTERMODU-
LATION D I S TORTIO N
■ HIGH SLEW RA TE : 420V/µs
■ -3dB BANDWIDTH : 40MHz@gain=12dB on
25Ω load single ended.
■ 20.7Vp-p DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT SWING
on 50Ω load, 12V power supply
■ CURRENT FEEDBACK STRUCTURE
■ 5V to 12V POWER SUPPLY
■ SPECIFIED FOR 20Ω and 50Ω
DIFFERENTIAL LOAD
DESCRIPTION
The TS616 is a dual operational am plifier featuring a high output current o f 410m A. T he drivers
can be configured differentially for driving signals
in telecommunication systems using multiple carriers. The TS616 is ideally suited for xDSL (High
Speed Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line) applications. This circuit is c apable of driving a 10 Ω
or 25Ω load at ±2.5V, 5V, ±6V or +12V power
supply. The TS616 is able to reach a -3dB bandwidth of 40MHz on 25Ω load with a 12dB gain.
This device is designed for high slew rates supporting low harmonic distortion and intermodulation.
DW
SO8 Exposed-Pad
(Plastic Micro package)
ORDER CODE
Part Number Temperature Range Package
TS616IDW -40, +85°C DW
TS616IDWT -40, +85°C DW
DW = Small Outline Package with Exposed-Pad, T = Tape & Real
PIN CONNECTIONS (top view)
Output1
Output1
1
1
2
VCC -
VCC -
2
-
-
+
+
3
3
4
4
Inverting Input1 Output2
Inverting Input1 Output2
Non Inverting Input1
Non Inverting Input1
VCC +
VCC +
8
8
7
7
Inverting Input2
Inverting Input2
6
6
-
-
+
+
Non Inverting Input2
Non Inverting Input2
5
5
APPLICATION
■ Line driver for xDSL
■ Multiple Video Line Driver
December 2002
Cross Section View Showing Exposed-Pad
Cross Section View Showing Exposed-Pad
This pad can be connected to a (-Vcc) copper area on the PCB
This pad can be connected to a (-Vcc) copper area on the PCB
1/27
TS616
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
T
T
R
R
P
ESD
only pins
1, 4, 7, 8
ESD
only pins
2, 3, 5, 6
Supply voltage
CC
V
Differential Input Voltage
id
V
Input Voltage Range
in
Operating Free Air Temperature Range -40 to + 85 °C
oper
Storage Temperature -65 to +150 °C
std
T
Maximum Junction Temperature 150 °C
j
Thermal Resistance Junction to Case 16 °C/W
thjc
Thermal Resistance Junction to Ambient Area 60 °C/W
thja
Maximum Power Dissipation (@Ta=25°C) for Tj=150°C 2 W
max.
CDM : Charged Device Model
HBM : Human Body Model
MM : Machine Model
CDM : Charged Device Model
HBM : Human Body Model
MM : Machine Model
Output Short Circuit
1. All voltage values, except differential voltage are with respect to network terminal.
2. Differential voltage are non-inverting input terminal with respect to the inverting input terminal.
3. The magnitude of input and output voltage must never exceed V
4. An output current limitation protects the circuit from transient currents. Short-circuits can cause excessive heating.
Destructive dissipation can result from short circuit on amplifiers.
1)
2)
3)
±7 V
±2 V
±6 V
1.5
2
200
1.5
2
100
4)
+0.3V.
CC
kV
kV
V
kV
kV
V
OPERATING CONDITIONS
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
V
Power Supply Voltage ±2.5 to ±6 V
CC
+1.5V to +VCC-1.5V
Common Mode Input Voltage
icm
-V
CC
TYPICAL APPLICATION:
Differential Line Driver for xDSL Applications
8
8
3
3
2
2
Vi
Vi
Vi
Vi
R1
R1
R4
R4
Vi Vo
Vi Vo
Vi Vo
Vi Vo
4
4
5
5
+
+
+
+
1/2TS615
1/2TS616
1/2TS615
1/2TS616
_
_
_
_
R2
R2
GND
GND
R3
R3
_
_
_
_
1/2TS615
1/2TS616
1/2TS615
1/2TS616
+
+
+
+
4
4
+Vcc
+Vcc
+Vcc
+Vcc
-Vcc
-Vcc
-Vcc
-Vcc
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
12.5
12.5
12.5
12.5
1
1
1
1
Vo
Vo
Vo
12.5
12.5
12.5
12.5
Vo
25
25
25
25
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
1:2
1:2
1:2
1:2
100
100
100
100
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
V
2/27

TS616
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
V
= ±6Volts, Rfb=910Ω,T
CC
Note: As described on page 24 (table 71), the TS616 requires a 620Ω feedback resistor for an optimized bandwidth with a gain of 12B for
a 12V power supply. Nevertheless, due to production test constraints, the TS616 is tested with the same feedback resistor for 12V and 5V
power su ppl i es (910Ω).
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
DC PERFORMANCE
V
Input Offset Voltage
io
V
∆
Z
C
CMR
SVR
Differential Input Offset Voltage
io
I
Positive Input Bias Current
ib+
I
Negative Input Bias Current
ib-
Input(+) Impedance 82 k
IN+
Z
Input(-) Impedance 54
IN-
Input(+) Capacitance 1 pF
IN+
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
20 log (∆V
/∆Vio)
ic
Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio
20 log (∆V
I
Total Supply Current per Operator No load 13.5 17 mA
CC
/∆Vio)
cc
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE and OUTPUT CHARACTERISTIC
R
Open Loop Transimpedance
OL
-3dB Bandwidth
Full Power Bandwidth
BW
Gain Flatness @ 0.1dB
Tr Rise Time
Tf Fall Time
Ts Settling Time
SR Slew Rate
V
High Level Output Voltage
OH
V
Low Level Output Voltage
OL
Output Sink Current
I
out
Output Source Current
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
T
amb
< T
T
min.
T
amb
T
amb
T
min.
T
amb
T
min.
V
∆
ic
T
min.
V
∆
cc
T
min.
V
out
T
min.
< T
amb
= 25°C
< T
< T
amb
< T
< T
amb
= ±4.5V
< T
< T
amb
=±2.5V to ±6V
< T
< T
amb
= 7Vp-p, RL = 25
< T
amb.
Small Signal V
A
= 12dB, RL = 25
V
Large Signal V
= 12dB, RL = 25
A
V
Small Signal V
= 12dB, RL = 25
A
V
V
= 6Vp-p, AV = 12dB, RL
out
= 25
Ω
= 6Vp-p, AV = 12dB, RL
V
out
= 25
Ω
= 6Vp-p, AV = 12dB, RL
V
out
= 25
Ω
= 6Vp-p, AV = 12dB, RL
V
out
= 25
Ω
R
=25Ω Connected to GND
L
R
=25Ω Connected to GND
L
V
= -4Vp
out
< T
T
min.
V
out
T
min.
amb
= +4Vp
< T
amb
< T
< T
< T
max.
max.
max.
max.
max.
max.
<20mVp
out
Ω
=3Vp
out
Ω
<20mVp
out
Ω
max.
max.
1 3.5
1.6
mV
2.5 mV
530
7.2
315
3.1
A
µ
A
µ
Ω
Ω
58 64
62
72 81
80
Ω
5 13.5
5.7
dB
dB
M
Ω
25 40
MHz
26
7 MHz
10.6 ns
12.2 ns
50 ns
330 420 V/µs
4.8 5.05 V
-5.3 -5.1 V
-320 -490
-395
330 420
mA
370
3/27

TS616
Note: As described on page 24 (table 71), the TS616 requires a 620Ω feedback resistor for an optimized bandwidth with a gain of 12B for
a 12V power supply. Nevertheless, due to production test constraints, the TS616 is tested with the same feedback resistor for 12V and 5V
power su ppl i es (910Ω).
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
NOISE AND DISTORTION
eN Equivalent Input Noise Voltage F = 100kHz 2.5 nV/√Hz
iNp Equivalent Input Noise Current (+) F = 100kHz 15 pA/√Hz
iNn Equivalent Input Noise Current (-) F = 100kHz 21 pA/√Hz
= 14Vp-p, AV = 12dB
HD2
HD3
IM2
IM3
2nd Harmonic Distortion
(differential configuration)
3rd Harmonic Distortion
(differential configuration)
2nd Order Intermodulation Product
(differential configuration)
3rd Order Intermodulation Produ ct
(differential configuration)
V
out
F= 110kHz, R
= 14Vp-p, AV = 12dB
V
out
F= 110kHz, R
= 50Ω diff.
L
= 50Ω diff.
L
F1= 100kHz, F2 = 110kHz
= 16Vp-p, AV = 12dB
V
out
= 50Ω diff.
R
L
F1= 370kHz, F2 = 400kHz
= 16Vp-p, AV = 12dB
V
out
R
= 50Ω diff.
L
F1 = 100kHz, F2 = 110kHz
= 16Vp-p, AV = 12dB
V
out
= 50Ω diff.
R
L
F1 = 370kHz, F2 = 400kHz
= 16Vp-p, AV = 12dB
V
out
= 50Ω diff.
R
L
-87 dBc
-83 dBc
-76
dBc
-75
-88
dBc
-87
4/27

TS616
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
V
= ±2.5Volts, Rfb=910Ω,T
CC
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
DC PERFORMANCE
V
Input Offset Voltage
io
V
∆
Z
C
CMR
SVR
Differential Input Offset Voltage
io
I
Positive Input Bias Current
ib+
I
Negative Input Bias Current
ib-
Input(+) Impedance 71 k
IN+
Z
Input(-) Impedance 62
IN-
Input(+) Capacitance 1.5 pF
IN+
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
20 log (∆V
/∆Vio)
ic
Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio
20 log (∆V
I
Total Supply Current per Operator No load 11.5 15 mA
CC
/∆Vio)
cc
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE and OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
R
Open Loop Transimpedance
OL
-3dB Bandwidth
BW
Full Power Bandwidth
Gain Flatness @ 0.1dB
Tr Rise Time
Tf Fall Time
Ts Settling Time
SR Slew Rate
V
High Level Output Voltage
OH
V
Low Level Output Voltage
OL
Output Sink Current
I
out
Output Source Current
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
T
amb
< T
T
min.
T
amb
T
amb
T
min.
T
amb
T
min.
V
∆
ic
T
min.
V
∆
cc
T
min.
V
out
T
min.
< T
amb
= 25°C
< T
< T
amb
< T
< T
amb
= ±1V
< T
< T
amb.
=±2V to ±2.5V
< T
< T
amb.
= 2Vp-p, RL = 10
< T
< T
amb.
Small Signal V
= 12dB, RL = 10
A
V
Large Signal V
= 12dB, RL = 10
A
V
Small Signal V
A
= 12dB, RL = 10
V
V
= 2.8Vp-p, AV = 12dB
out
= 10
R
Ω
L
V
= 2.8Vp-p, AV = 12dB
out
= 10
R
Ω
L
= 2.2Vp-p, AV = 12dB
V
out
= 10
R
Ω
L
= 2.2Vp-p, AV = 12dB
V
out
R
= 10
Ω
L
R
=10Ω Connected to GND
L
R
=10Ω Connected to GND
L
= -1.25Vp
V
out
< T
T
min.
V
out
T
min.
< T
amb
= +1.25Vp
< T
< T
amb
max.
max.
max.
max.
max.
Ω
max.
<20mVp
out
Ω
= 1.4Vp
out
Ω
<20mVp
out
Ω
max.
max.
0.2 2.5
1
2.5 mV
430
7
1.1 11
1.2
55 61
60
63 79
78
24.2
1.5
20 28
MHz
20
5.7 MHz
11 ns
11.5 ns
39 ns
100 130 V/µs
1.5 1.7 V
-1.9 -1.7 V
-300 -400
-360
200 270
240
mV
A
µ
A
µ
Ω
Ω
dB
dB
M
Ω
mA
5/27
TS616
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
NOISE AND DISTORTION
eN Equivalent Input Noise Voltage F = 100kHz 2.5 nV/√Hz
iNp Equivalent Input Noise Current (+) F = 100kHz 15 pA/√Hz
iNn Equivalent Input Noise Current (-) F = 100kHz 21 pA/√Hz
= 6Vp-p, AV = 12dB
HD2
HD3
IM2
IM3
2nd Harmonic Distortion
(differential configuration)
3rd Harmonic Distortion
(differential configuration)
2nd Order Intermodulation Product
(differential configuration)
3rd Order Intermodulation Produ ct
(differential configuration)
V
out
F= 110kHz, R
= 6Vp-p, AV = 12dB
V
out
F= 110kHz, R
= 20Ω diff.
L
= 20Ω diff.
L
F1= 100kHz, F2 = 110kHz
= 6Vp-p, AV = 12dB
V
out
R
= 20Ω diff.
L
F1= 370kHz, F2 = 400kHz
V
= 6Vp-p, AV = 12dB
out
= 20Ω diff.
R
L
F1 = 100kHz, F2 = 110kHz
= 6Vp-p, AV = 12dB
V
out
= 20Ω diff.
R
L
F1 = 370kHz, F2 = 400kHz
V
= 6Vp-p, AV = 12dB
out
R
= 20Ω diff.
L
-97 dBc
-98 dBc
-86
-88
-90
-85
dBc
dBc
6/27
TS616
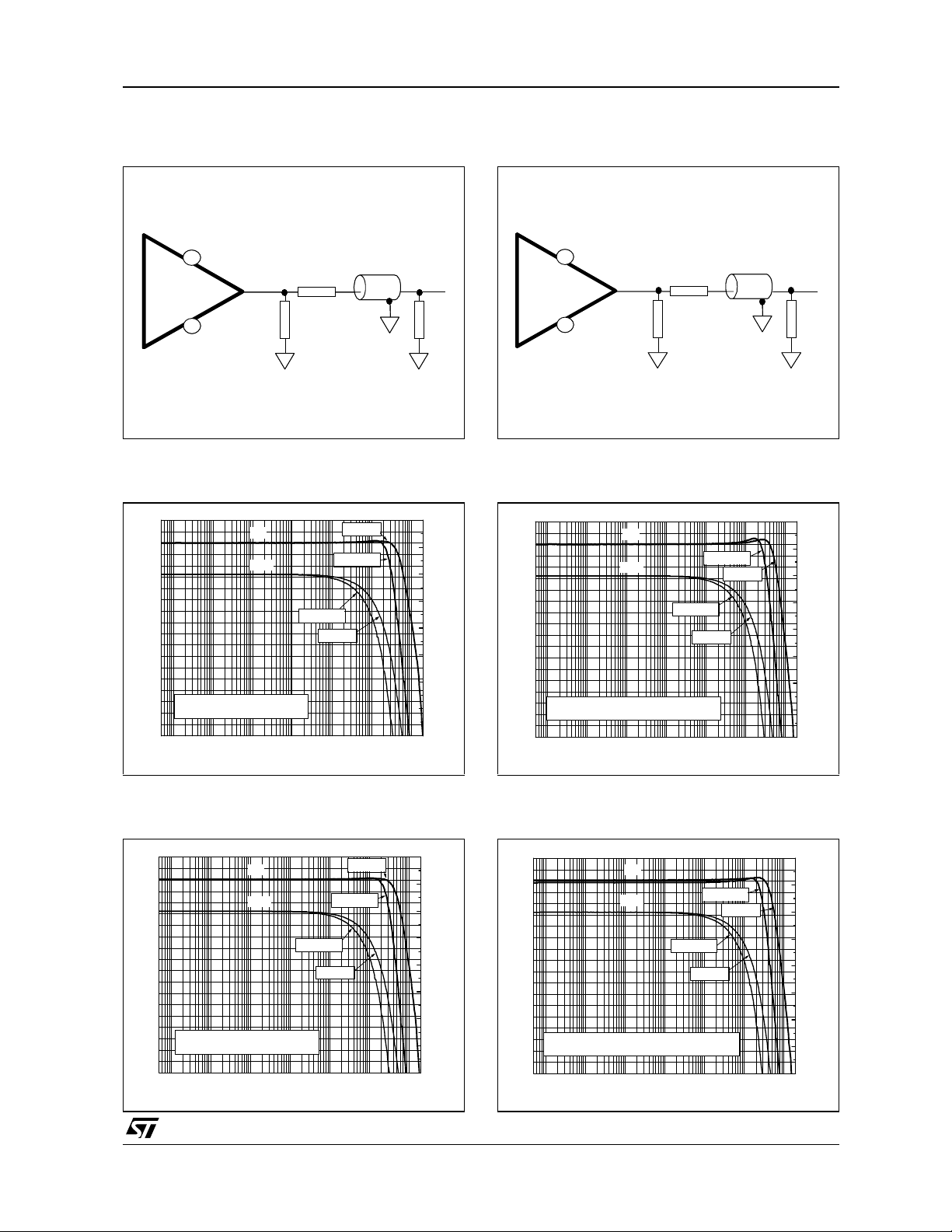
Figure 1: Load Configuration
Load: RL=25Ω, VCC=±6V
+6V
TS616
TS616
+6V
-6V
-6V
+
+
_
_
25Ω
25Ω
50Ω
50Ω
cable
49.9Ω
49.9Ω
33Ω
33Ω
1W
1W
cable
Figure 2: Closed Loop Gain vs. Frequency
AV=+1
2
0
-2
-4
-6
-8
(gain (dB)
-10
-12
-14
(Vcc=±2.5V, Rfb=1.1kΩ, Rload=10Ω)
(Vcc=±6V, Rfb=750
-16
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
gain
phase
Ω, Rload=25Ω)
Frequency (Hz)
(Vcc=±6V)
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc=±6V)
50Ω
50Ω
40
20
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
-120
Figure 4: Load Configuration
Load: RL=10Ω, VCC=±2.5V
+2.5V
TS616
TS616
+2.5V
-2.5V
-2.5V
10Ω
10Ω
+
+
_
_
11Ω
11Ω
0.5W
0.5W
49.9Ω
49.9Ω
Figure 5: Closed Loop Gain vs. Frequency
AV=-1
2
0
-2
)
°
Phase (
-4
-6
-8
(gain (dB))
-10
-12
-14
(Vcc=±2.5V, Rfb=1kΩ, Rin=1kΩ , Rload=10Ω)
(Vcc=±6V, Rfb=680
-16
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
gain
phase
(Vcc=±2.5V)
Ω, Rin=680Ω, Rload=25Ω)
Frequency (Hz)
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc=±6V)
50Ω
50Ω
cable
cable
(Vcc=±6V)
50Ω
50Ω
-140
-160
-180
-200
-220
-240
-260
-280
-300
)
°
Phase (
Figure 3: Closed Loop Gain vs. Frequency
AV=+2
8
6
4
2
0
-2
(gain (dB))
-4
-6
(Vcc=±2.5V, Rfb=1kΩ, Rload=10Ω)
-8
(Vcc=±6V, Rfb=680
-10
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
gain
phase
(Vcc=±2.5V)
Ω, Rload=25Ω)
Frequency (Hz)
(Vcc=±6V)
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc=±6V)
40
20
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
-120
Figure 6: Closed Loop Gain vs. Frequency
AV=-2
8
6
4
)
°
Phase (
2
0
-2
(gain (dB))
-4
-6
(Vcc=±2.5V, Rfb=1kΩ, Rin=510Ω, Rload=10Ω)
-8
(Vcc=±6V, Rfb=680
-10
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
gain
phase
(Vcc=±2.5V)
Ω, Rin=750//620Ω, Rload=25Ω)
Frequen c y (Hz)
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc=±6V)
(Vcc=±6V)
-140
-160
-180
-200
-220
-240
-260
-280
-300
)
°
Phase (
7/27

TS616
Figure 7: Closed Loop Gain vs. Frequency
AV=+4
14
12
10
8
6
4
(gain (dB))
2
0
-2
(Vcc=±2.5V, Rfb=910Ω, Rg=300Ω, Rload=10Ω)
(Vcc=±6V, Rfb=620
-4
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
gain
phase
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc=±6V)
Ω, R g =560//330Ω, Rload=25Ω)
Frequency (Hz)
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc=±6V)
Figure 8: Closed Loop Gain vs. Frequency
AV=+8
20
18
16
14
12
10
(gain (dB))
8
6
4
(Vcc=±2.5V, Rfb=680Ω, Rg=240//160Ω, Rload=10Ω)
(Vcc=±6V, Rfb=510
2
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
gain
phase
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc=±6V)
Ω, Rg=270//100Ω, Rload=25Ω)
Frequency (Hz)
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc=±6V)
40
20
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
-120
40
20
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
-120
)
°
Phase (
Figure 10: Closed Loop Gain vs. Frequency
AV=-4
14
12
10
8
)
°
Phase (
6
4
(gain (dB))
2
0
(Vcc=±2.5V, Rfb=1kΩ, Rin=320//360Ω, Rload=10Ω)
-2
(Vcc=±6V, Rfb=620
-4
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
gain
phase
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc=±6V)
Ω, Rin=360//270Ω, Rload=25Ω)
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 11: Closed Loop Gain vs. Frequency
AV=-8
20
18
16
14
12
10
(gain (dB))
8
6
4
(Vcc=±2.5V, Rfb=680Ω, Rin=160//180Ω, Rload=10Ω)
(Vcc=±6V, Rfb=510
2
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
gain
phase
(Vcc= ± 2. 5V)
(Vcc=±6V)
Ω, Rin=150//110Ω, Rload=25Ω)
Frequency (Hz)
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc=±6V)
(Vcc=±2.5V)
(Vcc= ± 6V )
-140
-160
-180
-200
-220
-240
-260
-280
-300
-140
-160
-180
-200
-220
-240
-260
-280
-300
)
°
Phase (
)
°
Phase (
Figure 9: Bandwidth vs. Temperature
AV=+4, Rfb=910
50
45
40
35
Bw (MHz)
30
25
20
-40-200 20406080
8/27
Ω
Vcc=±6V
Load=25
Vcc=±2.5V
Load=10
Ω
Ω
Temperature (°C)
Figure 12: Positive Slew Rate
AV=+4, Rfb=620
4
2
(V)
0
OUT
V
-2
-4
0.0 10.0n 20.0n 30.0n 40.0n 50.0n
, V
Ω
=±6V, RL=25
CC
Time (s)
Ω
TS616
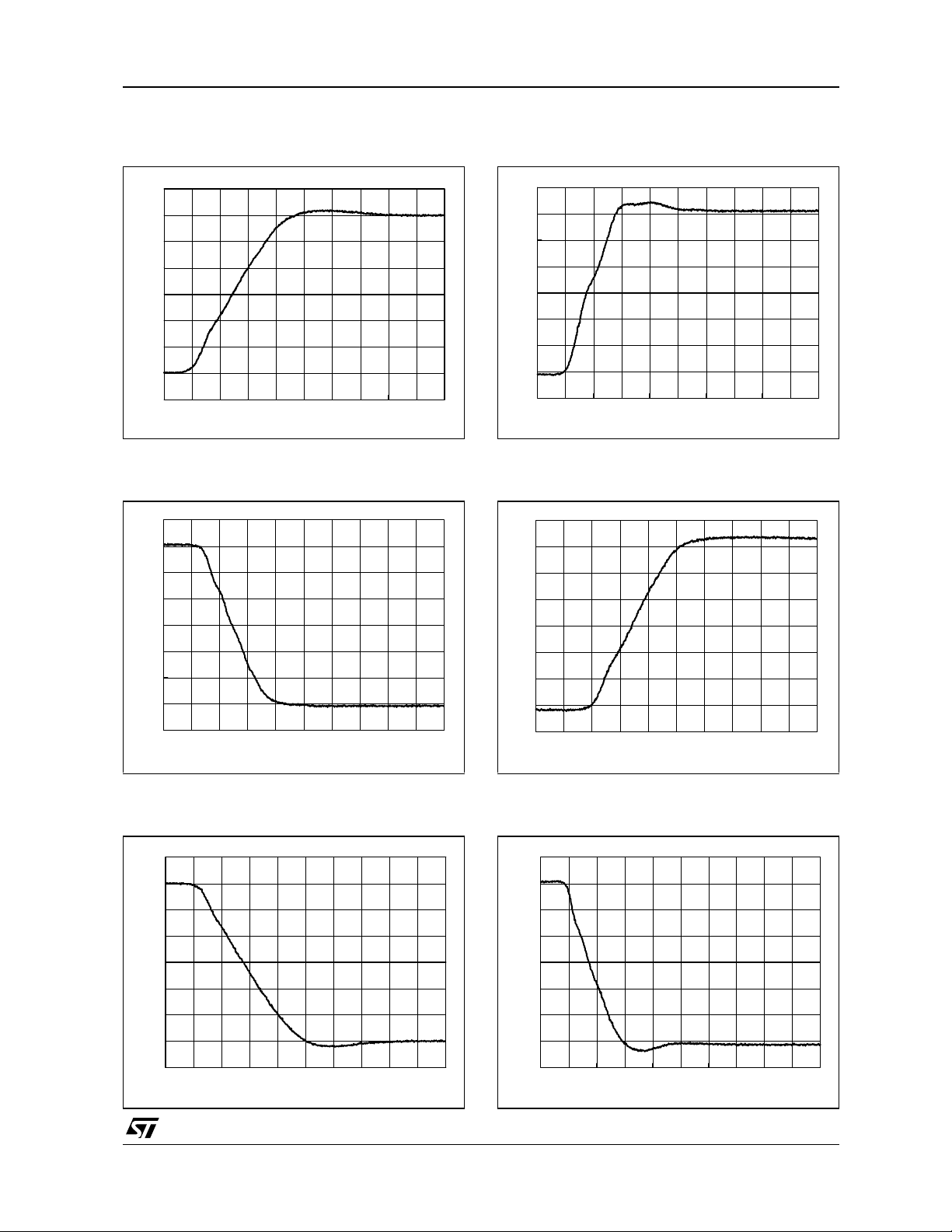
Figure 13: Positive Slew Rate
AV=+4, Rfb=910
2
1
(V)
0
OUT
V
-1
-2
0.0 10.0n 20.0n 30.0n 40.0n 50.0n
, V
Ω
CC
=±2.5V, RL=10
Time (s)
Ω
Figure 14: Negative Slew Rate
AV=+4, Rfb=620Ω, VCC=±6V, RL=25
4
2
Ω
Figure 16: Positive Slew Rate
AV= - 4, Rfb=620
4
2
(V)
0
OUT
V
-2
-4
0.0 10.0n 20.0n 30.0n 40.0n 50.0n
, V
Ω
=±6V, RL=25
CC
Time (s)
Ω
Figure 17: Positive Slew Rate
AV= - 4, Rfb=910
2
1
, V
Ω
CC
=±2.5V, RL=10
Ω
(V)
0
OUT
V
-2
-4
0.0 10.0n 20.0n 30.0n 40.0n 50.0n
Time (s)
Figure 15: Negative Slew Rate
AV=+4, Rfb=910
2
1
(V)
0
OUT
V
-1
-2
0.0 10.0n 20.0n 30.0n 40.0n 50.0n
, V
Ω
CC
=±2.5V, RL=10
Time (s)
Ω
(V)
0
OUT
V
-1
-2
0.0 10.0n 20.0n 30.0n 40.0n 50.0n
Time (s)
Figure 18: Negative Slew Rate
AV= - 4, Rfb=620Ω, VCC=±6V, RL=25
4
2
(V)
0
OUT
V
-2
-4
0.0 10.0n 20.0n 30.0n 40.0n 50.0n
Time (s)
Ω
9/27
 Loading...
Loading...