SGS Thomson Microelectronics STPS20L60CR, STPS20L60CG Datasheet
®
STPS20L60CT/CG/CR
POWER SCHOTTKY RECTIFIER
MAIN PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
I
F(AV)
V
RRM
2x10A
60 V
Tj (max) 150 °C
V
(max) 0.56 V
F
FEATURES AND BENEFITS
LOW FORWARD VOLTAGE DROP
■
NEGLIGIBLE SWITCHING LOSSES
■
LOW THERMAL RESISTANCE
■
AVALANCHE CAPABILITY SPECIFIED
■
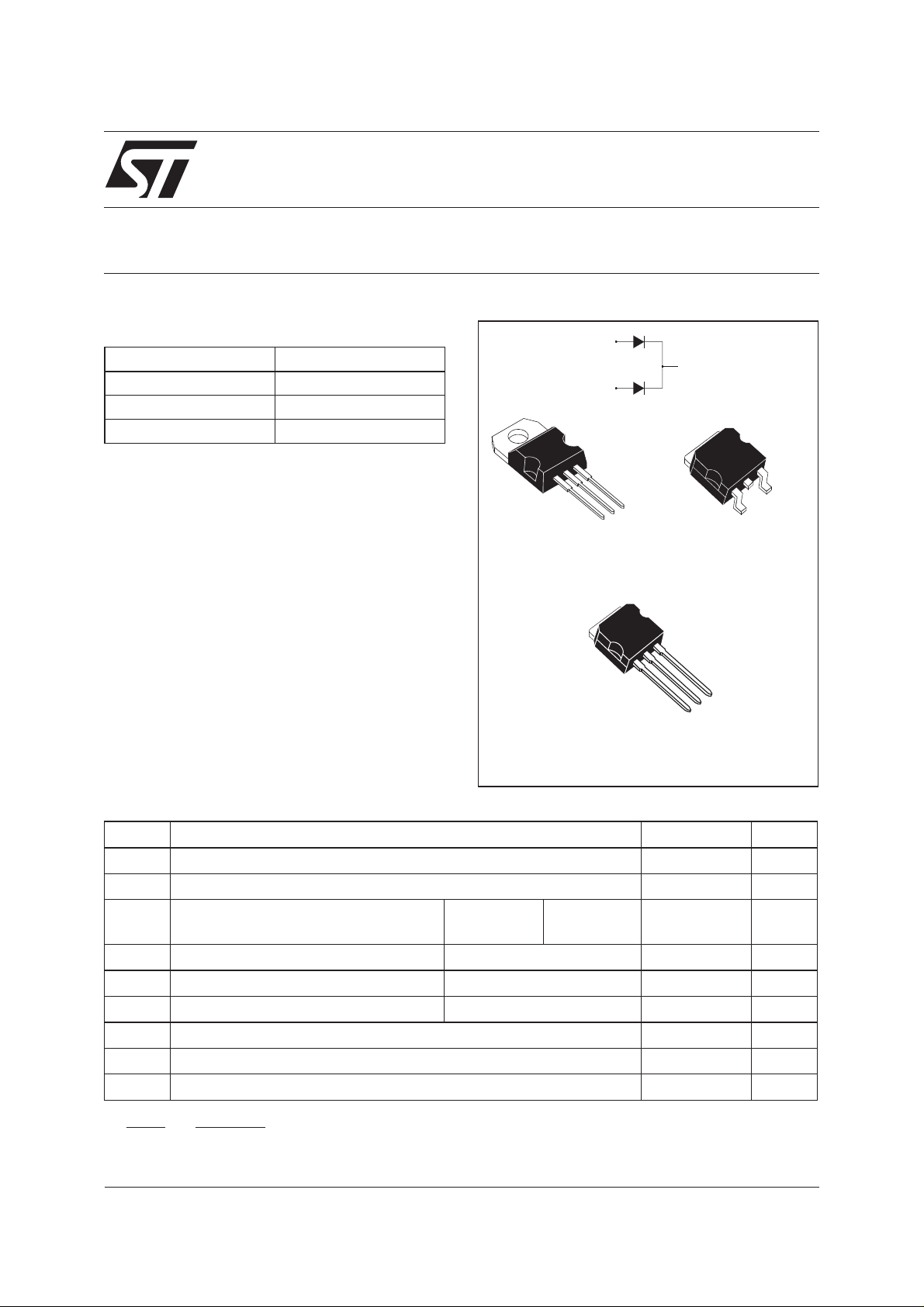
DESCRIPTION
Dual center tap Schottky rectifiers suited for
Switched Mode Power Supplies and high
frequency DC to DC converters.
2
Packaged in TO-220AB, I
PAK and D2PAK, this
device is intended for use in high frequency
inverters.
A1
A2
A1
TO-220AB
STPS20L60CT
K
K
A2
K
STPS20L60CG
A1
I2PAK
STPS20L60CR
A2
A1
D2PAK
A2
K
ABSOLUTE RATINGS (limiting values, per diode)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
RRM
I
F(RMS)
I
F(AV)
I
FSM
I
RRM
P
ARM
T
stg
Tj
dV/dt
dPtot
*:
Repetitive peak reverse voltage
RMS forward current
Average forward current Tc = 140°C
Surge non repetitive forward current tp = 10 ms Sinusoidal
Repetitive peak reverse current tp=2µssquare F = 1kHz
Repetitive peak avalanche power tp = 1µs Tj = 25°C
Storage temperature range
Maximum operating junction temperature *
Critical rate of rise of reverse voltage
<
dTj Rth j a
July 2003 - Ed: 3C
Per diode
δ = 0.5
Per device
thermal runaway condition for a diode on its own heatsink
−1()
60 V
30 A
10
20
220 A
1A
5800 W
-65 to+175 °C
150 °C
10000 V/µs
A
1/6
STPS20L60CT/CG/CR
THERMAL RESISTANCE
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
th (j-c)
R
th (c)
Junction to case TO-220AB / I2PAK/D2PAK
TO-220AB / I2PAK/D2PAK
When the diodes 1 and 2 are used simultaneously :
∆ Tj(diode 1) = P(diode1) x R
(Per diode) + P(diode 2) x R
th(j-c)
STATIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (per diode)
Symbol Parameter Tests conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Per diode
Total
1.6
0.85
Coupling 0.1 °C/W
th(c)
°C/W
*
I
R
Reverse leakage current Tj = 25°C V
R=VRRM
Tj = 125°C
V
*
F
Forward voltage drop Tj = 25°CI
Tj = 125°C I
Tj=25°CI
Tj = 125°C I
=10A
F
=10A
F
=20A
F
=20A
F
Pulse test : * tp = 380 µs, δ <2%
To evaluate the conduction losses use the following equation :
P = 0.42x I
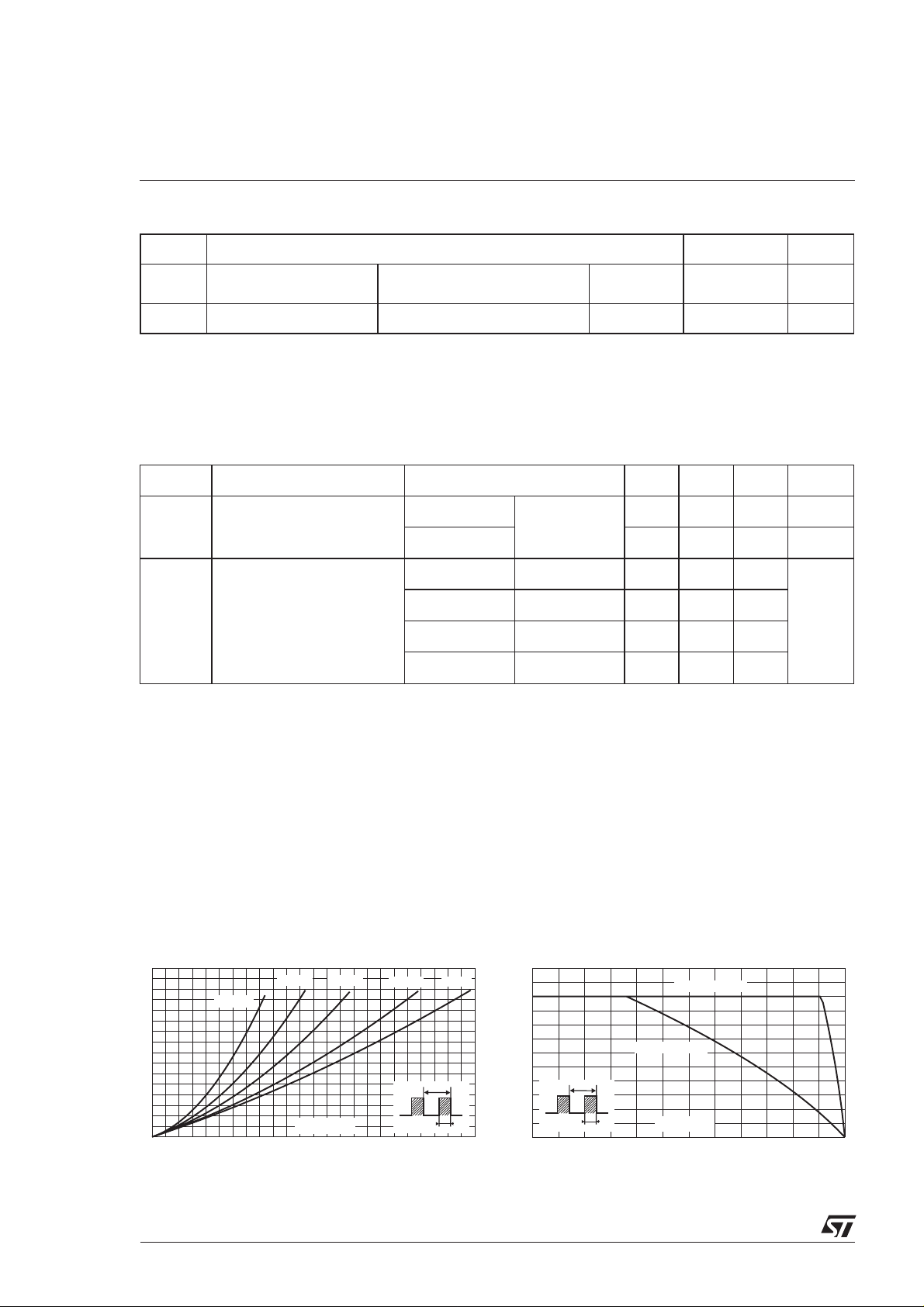
Fig. 1: Average forward power dissipation versus
average forward current (per diode).
PF(av)(W)
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0123456789101112
F(AV)
δ = 0.05
+ 0.014 I
δ = 0.1
F2(RMS)
δ = 0.2
IF(av) (A)
δ = 0.5
δ
=tp/T
Fig. 2: Average current versus ambient
temperature (δ=0.5) (per diode).
IF(av)(A)
δ = 1
T
tp
12
10
8
6
4
2
δ
0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150
=tp/T
350 µA
65 95 mA
0.6 V
0.48 0.56
0.74
0.62 0.7
Rth(j-a)=Rth(j-c)
Rth(j-a)=15°C/W
T
tp
Tamb(°C)
2/6
 Loading...
Loading...