SGS Thomson Microelectronics STPS20L25CG, STPS20L25CT Datasheet
®
LOW DROP POWER SCHOTTKY RECTIFIER
MAIN PRODUCT CHARACTERISTIC S
STPS20L25CT/CG
I
F(AV)
V
RRM
2 x 10 A
25 V
Tj (max) 150 °C
(max) 0.35 V
V
F
FEATURES AND BENEFITS
VERY LOW F O RW ARD VOLTAG E DROP FOR
LESS POWER DISSIPATION AND REDUCED
HEATSINK
OPTIMIZED CONDUCTION/REVERSE LOSSES
TRADE-OFF WHICH MEANS THE HIGHEST
EFFICIENCY IN THE APPLICATIONS
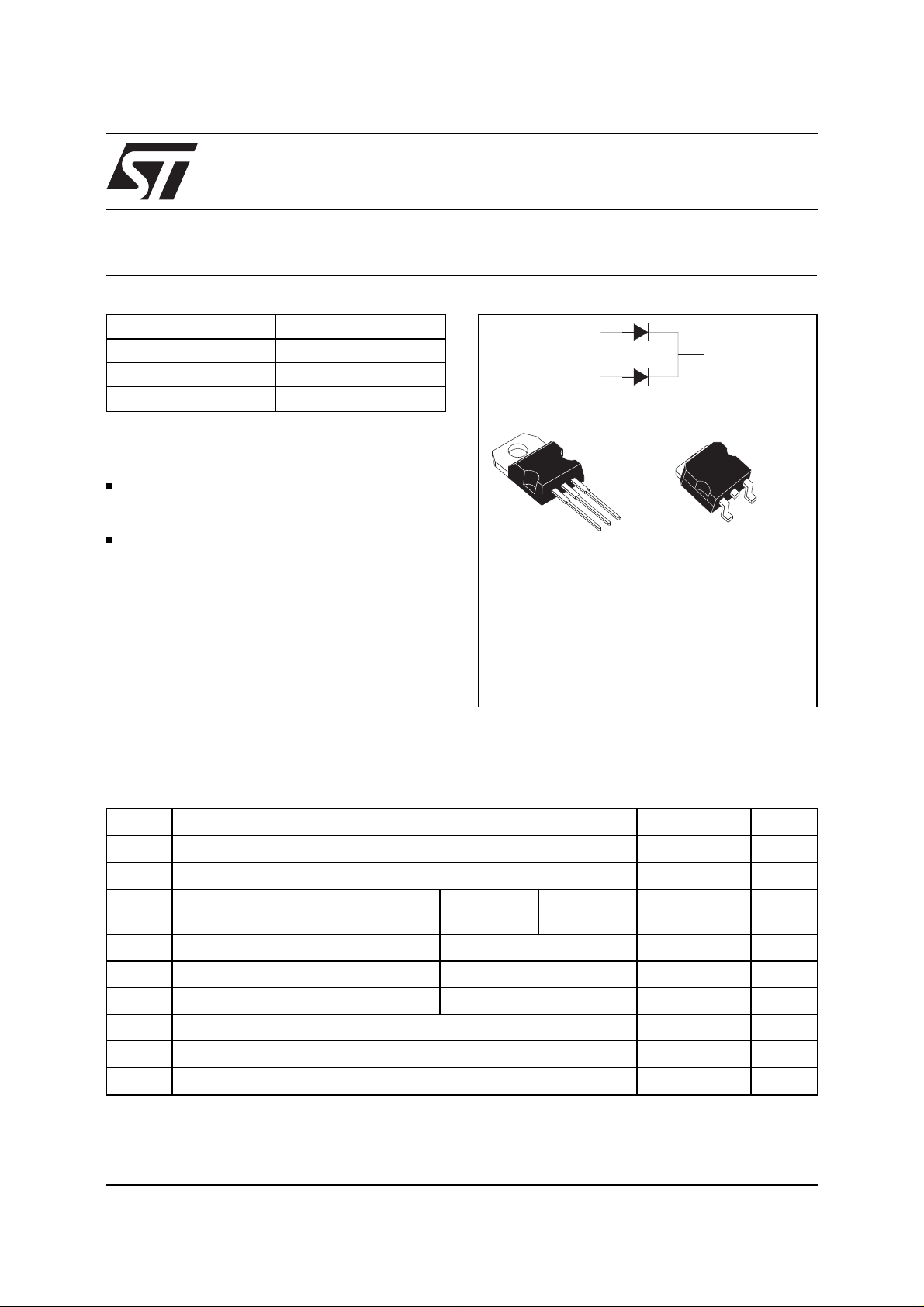
DESCR IPTION
Dual center tap Schottky rectifier suited to
Switched Mode Power Supplies and high
frequency DC to DC converters.
Packaged in TO-220AB and D
2
PAK, this device is
especially intended for use as a rectifier at the
secondary of 3.3V SMP S units.
A1
A2
A1
TO-220AB
STPS20L25CT
K
K
A2
K
A2
A1
D2PAK
STPS20L25CG
ABSOLUTE RATINGS
(limiting values, per diode)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
RRM
I
F(RMS)
I
F(AV)
I
FSM
I
RRM
I
RSM
T
stg
Repetitive peak reverse voltage 25 V
RMS forward current 30 A
Average forward current Tc = 145°C
δ
= 0.5
Per diode
Per device
10
20
Surge non repetitive forward current tp = 10 ms S inusoidal 220 A
Repetitive peak reverse current tp=2 µs square F=1kHz 1 A
Non repetitive peak reverse current tp = 100 µs square 3 A
Storage temperature range - 65 to + 150
Tj Maximum operating junction temperature * 150 °C
dV/dt Critical rate of rise of reverse voltage 10000 V/µs
dPtot
* :
June 1999 - Ed : 3A
dTj
<
1
Rth(j−a
thermal runaway condition for a diode on its own heatsink
)
A
°
C
1/5
STPS20L25CT/CG
THERMAL RE SISTA NC ES
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
th (j-c)
Junction to case Per diode 1.5
Total 0.8
R
th (c)
Coupling
0.1
When the diodes 1 and 2 are used simultaneously :
∆
Tj(diode 1) = P(diode1) x R
(Per diode) + P(diode 2) x R
th(j-c)
th(c)
STATIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTE RISTICS (per diode)
Symbol Tests conditions Tests conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
I
* Reverse leakage current Tj = 25°CV
R
= V
R
RRM
800
Tj = 125°C 125 250 m A
V
* Forward voltage drop Tj = 25°CI
F
Tj = 125°CI
Tj = 25°CI
Tj = 125°CI
= 10 A 0.46 V
F
= 10 A 0.30 0.35
F
= 20 A 0.56
F
= 20 A 0.41 0.48
F
°
C/W
µ
A
Pulse test : * tp = 380 µs, δ < 2%
To evaluate the maximum conduction losses use the following equation :
P = 0.22 x I
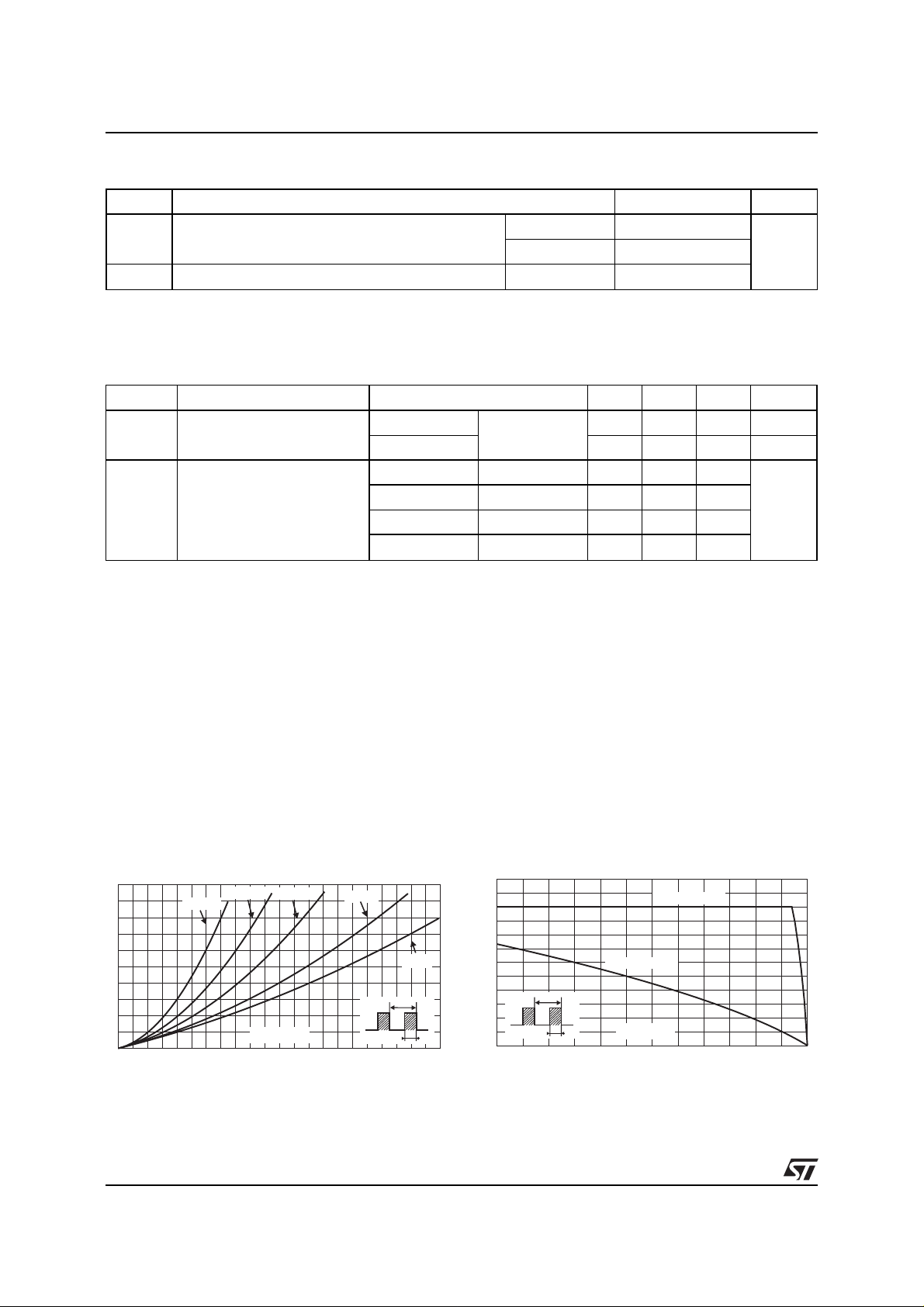
Fig.1 :
Average forward power dissipation versus
average forward current.
PF(av)(W)
5
4
3
2
1
0
01234567891011
F(AV)
δ = 0.05
+ 0.013 I
δ = 0.1
IF(av) (A)
F2(RMS )
δ = 0.2
δ = 0.5
δ
=tp/T
T
δ = 1
Fig.2 :
Average forward current versus ambient
temperature ( δ = 0.5).
IF(av)(A)
12
10
8
6
4
2
tp
0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150
δ
=tp/T
T
tp
Rth(j-a)=Rth(j-c)
Rth(j-a)=50°C/W
Tamb(°C)
2/5
 Loading...
Loading...