Page 1

27
BlueSnapXP, BlueSnap-Standard, BlueSnap-9V Serial Adapters
BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 1 of
User Guide
For:
®
Serialio.com
Serial Module Command Set
As applied to
Bluetooth Modules:
Version 4.83SIO
January 20, 2016
Bluetooth
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 2

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 2 of
27
1 INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................................................ 3
2 MODES OF OPERATION ................................................................................................................................................. 4
3 CONFIGURATION ............................................................................................................................................................. 6
3.1 Configuration Locally over Serial port………………..….……………………………………6
3.2 Configuration Remotely over Bluetooth……………………………………………………….6
3.3 Using PIO/Dip switches for quick configuration………...……………………………………7
4 COMMAND SET REFERENCE ........................................................................................................................... 8
4.1.1 Using Low Power modes (inquiry and page timers)….……………………………………14
4.1.2 Using Low Power SNIFF mode……………………………………………………………14
4.2 Profile Selection………………………………………………………………………………16
4.3 Using PIO Pins to create Modem control signals………….…………………………………16
5 COMMAND QUICK REFERNCE TABLE..................................................................................................................... 17
6 FACTORY DEFAULT SETTINGS ................................................................................................................................. 19
7 COMMON PROBLEMS AND QUESTIONS: ............................................................................................................... 18
8 EXAMPLE OF A MASTER DISCOVERY/CONNECTION SEQUENCE .................................................................. 20
9 INSTANT CABLE REPLACEMENT EXAMPLE ................................................................................................22
10 BLUESNAP CONFIGURATION SWITCHES ....................................................................................................23
APPENDIX A - BLUESNAP EVALUATION BOARD CONNECTORS, SIGNALS..................................................24
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 3
BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 3 of
27
2. Introduction
Scope: This Command Set document is created to enable developers and integrators an
opportunity to create wireless networks using Bluetooth technology. The goal is to make the
transition to Bluetooth wireless networks as seamless and easy as possible. This document will
explain how to establish Bluetooth communications between Bluetooth enabled devices for
data applications.
Background: The BlueSnap evaluation board is designed to accommodate the Class1
Bluetooth radio modem serial modules with 2.4GHz RF ceramic chip antenna or external SMA
antenna Jack. The modules are Bluetooth ver. 2.0 compliant. The evaluation board enables
a stable platform environment to test serial RS-232 cable replacement over Bluetooth RF links
before going directly to an embedded printed circuit board design and layout.
Commands: This document describes the protocol used to control and configure Bluetooth
Serial Modules. The protocol is similar to the industry standard Hayes AT protocol used in
telephone modems due to the fact that both types of devices are connection oriented.
Appropriate commands have been provided to make the module perform the two core actions
of a Bluetooth device, which is make/break connections and Inquiry. Additional commands are
also provided to perform other functions. The serial radio modems can be configured,
commanded, and controlled through simple ASCII strings through the hardware serial UART or
over a remote Bluetooth RF connection .
Applications: The BlueSnap has RS-232, DB-9 and 0-3.3Vdc direct UART interfaces to the
module.
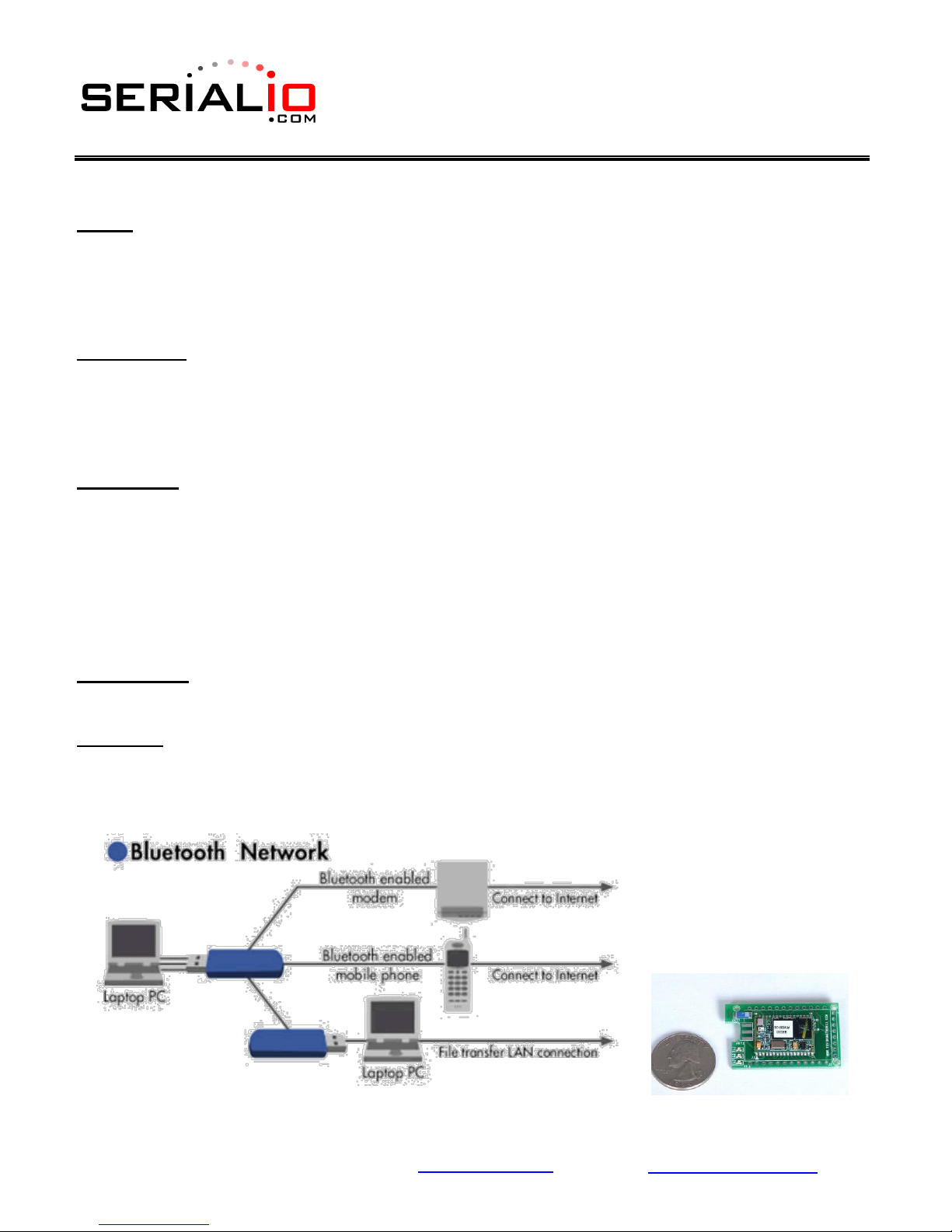
Pico-Nets: For applications that require more than point-to-point (2) devices communicating
simultaneously – this is called a pico-net. These applications require one of the Bluetooth
devices to manage all the network connections. The easiest implementation is using a
Personal Computer (PC) that manages this activity with MS Windows Bluetooth stack software
and USB Bluetooth Communicator plugged into the PC (see figure below).
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 4

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 4 of
27
Making a Connection
BlueSnap shows up under Service discovery defaulted as Serial Port Profile (SPP) Service
“SPP on BlueSnap-5302”, where SPP is the service name and RN-5302 is the local device
name. The local device name can be changed, and defaults from the factory to the last 2 bytes
of the Bluetooth address.
To connect to BlueSnap, browse for services, you should see: “SPP” as the Profile. BlueSnap
and will be connected to a Virtual COM port on PCs, BlackBerrys, Palm Pilot’s, PocketPCs, or
other clients. Once connected, data will flow in both directions in regular data mode as if the
serial port were locally attached. Commands to the device can be sent by a remote RF
Bluetooth device or on the local UART hardware connection (if not connected over Bluetooth)
by typing “$$$” (three dollar signs) BlueSnap is a Class1 Bluetooth device with high power
transceiver (100meters/330 feet) actual range may vary due to environment or type of client
device used to connect to BlueSnap.
NOTE: Only one client can make connection to BlueSnap at a time, and there is a limit of 7 simultaneous
communicating devices in a Bluetooth pico-net network.
2. Modes of Operation
0- Slave mode – This is the default mode, whereby other Bluetooth devices can discover and
connect to the device. Outbound connections can also be made in this mode.
1- Master Mode - This mode is useful when the device only wants to initiate connections (not
receive them). In this mode the device will NOT be discoverable or connectable.
2- Trigger Master Mode - In this mode, the device will automatically connect to the pre
configured remote slave address when a character (or characters( are received on the local
UART. Connection will continue until a configurable idle timer (1 to 255 seconds) determines
that no more data is being received, or a configurable BREAK character is seen.
3-Auto-connect Master Mode- This mode can be set by command, or by sensing of Switch 3
during powerup on the BlueSnap.(PIO6 high on the module). If this mode is set, the device will
initiate a connection to the pre-stored remote address immediately upon power up. If no
address is stored, an inquiry process will be attempted and the first device found that matches
the COD will be stored. In this mode, data is passed without being interpreted by the
BlueSnap (high speed), hence the connection cannot be broken via command. If disconnect
occurs, the device will attempt to re-connect until successful.
4-Auto-connect DTR Mode- This mode must be set by command. This mode operates like
mode 3 Auto-Connect, except that the connection and disconnection are controlled by the DTR
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 5

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 5 of
27
line on the BlueSnap. Setting the DTR line high will initiate the auto-connect process, and
turning it off/low will cause a disconnect.
5-Auto-connect ANY Mode- This mode must be set by command. This mode operates like
mode 4 DTR mode, except that each time the Switch/PIO is set, an inquiry is performed and
the first device found is connected. The stored address is NOT used, and the found address is
never stored.
3. Configuration
Command Mode (vs Normal Data mode)- Upon powerup, the device will be in data mode. To enter
command mode, The characters “$$$” must be sent. The device will respond with “CMD”. To exit
command mode, send “---<cr>”. The device will respond with “END”.
Parameters, such as the Bluetooth Name, Class of Device and Serial Port settings can be viewed and
configured. This can be done locally through the serial port UART or from a remote Bluetooth RF link.
To access configuration, the device must be in command mode by issuing ($$$). While in command
mode, the device will accept ASCII bytes as commands.
3.1 LOCAL CONFIGURATION (via serial port)
Use a normal RS-232 pass through cable from PC passing ASCII characters through the terminal to the
BlueSnap. The communications settings should match the settings used when BlueSnap connects, for
example: the default is 115,200bps, 8 bits, No Parity, 1 stop bit, and hardware flow control disabled.
Local configuration works at any time when the device does NOT have a Bluetooth connection, and also
works under certain conditions when the device is connected (see the table below). If the device is in
configuration mode and a connection occurs, the device will exit configuration mode, and data will pass
back and forth from the remote device.
Run your favorite terminal emulator, HyperTerminal or other program. Type “$$$” on your screen. You
should see “CMD” returned to you. This will verify that your cable and comm. settings are correct. Valid
commands will return an “AOK”, response, and invalid ones will return “ERR “. Commands that are not
recognized will return a “?”.
To exit command mode, type “---“<cr>. (three minus signs).
NOTE1 : You can enter command mode locally over the serial port at any time when not connected.
Once a connection is made, you can only enter command mode if the config timer has not expired.
To enable continuous configuration, set the config timer to 255. Also, if the device is in Auto Master
mode 3, you will NOT be able to enter command mode when connected over Bluetooth.
3.2 REMOTE CONFIGURATION (via Bluetooth)
It is often useful to be able to perform configuration remotely over a Bluetooth connection. To do this,
connect to the device over Bluetooth, and using your terminal emulator, perform the same steps as you
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 6

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 6 of
VALUE
(decimal)
DESCRIPTION
0
No remote config, No local config when connected
1-252
Time in seconds from powerup to allow config
253
Continous config LOCAL only
254
Contiuous config, REMOTE only
255
Continous config, both LOCAL and REMOTE
Function
DIP Switch
(adapters)
PIO (modules)
Settings
Factory Reset
1
PIO 4
OFF (0V) = disabled, ON (3V) = ARMED
Auto Discovery/Pairing
2
PIO 3
OFF (0V) = disabled, ON(3V) = enabled
Auto-Connect
3
PIO 6
OFF (0V) = disabled, ON(3V) = enabled
Baudrate
4
PIO 7
OFF (0V) = 115K, ON(3V) = 9600
27
would for local configuration above. When finished configuring, be sure to either reset the device, or
Send the “---“command, which will exit configuration mode and allow data to pass normally.
NOTE 2: You can only enter command mode remotely over Bluetooth if you have made a connection
and sent the $$$ within the “config timer” window after powerup. This can be modified, the default
config timer expires 60 seconds after powerup. Once the timer has expired, any data sent to the device
will pass unmodified and unrecognized by the command interpreter. The timer can be set to any value
from 0 (disable remote configuration) to 0xFF hex , which allows continuous (no timeout) configuration.
WARNING: Configuration (local or remote) is NEVER enabled when the device is in auto-mode and is
connected over Bluetooth.
CONFIG TIMER settings
3.3 Using the PIO pins/DIP switches to perform quick configuration
Factory Reset- Set this switch/PIO on powerup. This arms the reset function. Then toggle the
switch/PIO 3 times and all settings in the device (other than the Bluetooth name) will return to defaults.
Auto Discovery/Pairing Mode - Used with Switch3/PIO6. If Switch3/PIO6 also set,, the device will
perform a device Inquiry Scan, searching for a partner Device with a special matching class, (0x55AA)
and once found, store the address of such device into the remote address field, and then auto-connect
to the remote device. If Switch3/PIO6 is NOT set, the device will enter slave mode with the special
matching class, waiting to be found by the master. This mode is usually set once on both ends of a pair
of devices, for instant “cable replacement”, and then removed.
Auto Connect mode –This is equivalent to auto-master mode 3 in software. The device will connect to
the stored address. If Switch2/PIO3 is also set, new discovery/pairing can be made, see above.
Baud Rate select - used to configure 9600 or 115K default baudrate. If the baudrate is configured in
software, this switch is ignored.
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 7

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 7 of
27
NOTE: for the purpose of configuration above, the swithes/IO pins are sampled ONLY at power up
time, (during the first 500milliseconds) so they can be used for other functions once the device is in
operation. The exception is the factory reset switch/PIO, which once enabled, can be toggled at any
time after powerup, a total of 3 transitions will cause the factory reset to occur.
4. Command Reference
The commands are all single or 2 character, generally comma delimited. Commands and hex input data can be
upper or lower case. Text data, such as Bluetooth name, and pin code, are case sensitive. Commands fall into 4
general categories:
SET COMMANDS - Store information permanently and take effect after power cycle or software reset.
GET COMMANDS - Retrieve the permanently stored information for display to the user.
CHANGE COMMANDS – Temporarily change the value of serial baudrate, parity, etc.
ACTION COMMANDS – Perform action such as inquiry, connect, etc.
SET COMMANDS
S7,<1,0> 7 bit data mode. 1 to enable, 0 to disable. (setting can be seen with the “d” command).
SA,<1,0> Authentication. 1 to enable, 0 to disable. This will force authentication when any remote
device attempts to connect. Regardless of this setting, if a remote device forces
authentication, this device will respond with the stored pin code. Once a remote device
has exchanged pin codes with this device, a link key will be stored for future use. Up to 8
keys are automatically and permanently in flash on the device, in a first in, first out
fashion.
SB,<timer> Send BREAK. This is an immediate command, which can send a BREAK signal on the
TX . The timer is used to send a variable length BREAK signal.
Timer value Break length (in milliseconds)
1= 37ms, 2=18.5ms, 3=12ms, 4=9ms, 5= 7ms, 6=6ms.
Example : “SB,2” sends a 18.5 millisecond break signal.
SC,<hex word> Service Class ( 16 bits, 11 used, this is used with Device Class below to create the 24
bit class of device number.
Example : “SC,0002”
SD,<hex word> Device Class (major and minor in a 16bit word, used with service class above)
Example : “SD,8040”
SE,<1,0> Encryption 1 to enable, 0 to disable.
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 8

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 8 of
27
SF,1 Set Factory Defaults.
SI, <hex word> - Inquiry Scan Window. Sets amount of time device spends enabling inquiry scan
(discoverability) . Minimum value is 0x0012, corresponding to about 1% duty cycle.
Inquiry interval is fixed at 0x1000, so time spent in inquiry is 0x12/0x1000 by default.
Maximum value is 0x1000, set to 0x0000 to disable inquiry scan and make device nondiscoverable. Default value is 0x0200.
SJ, <hex word> - Page Scan Window. Sets amount of time device spends enabling page scan
(connectability) . Minimum value is 0x0012, corresponding to about 1% duty cycle.
Page Scan interval is fixed at 0x1000, so time spent in page scan mode is 0x12/0x1000 by
default. Maximum value is 0x1000, set to 0x0000 to disable page scan and make device
non-connectable. Default value is 0x0200.
SL,<E,O,N> Parity. Can be any of, Even, Odd, or None. Only the first character is needed
Example : “SL,E” sets the parity to Even.
SM,<3,2,1,0> Mode (0=slave, 1=master,2=trigger, 3=auto)
Example : “SM,1” sets the mode to Master
SN,<name> Friendly Name of the device, 16 characters maximum.
Example : “SN,MyDevice”
S-,<Name> This command automatically sets the Bluetooth Friendly Name to “Name-EC42”
where “EC42” is the last 4 digits of the Bluetooth address.
SO,<text> Extended Status String, 8 character maximum. Setting this string to from 1 to 8
characters will enable status messages to be sent to the local serial port. Two status
messages are sent, when a Bluetooth connection is established, the string
”<text>CONNECT” will be sent. Upon a Disconnect, the string <text>DISCONNECT
will be sent. This parameter is useful, for example, when connected to a printer, the
printer can examine an escape sequence, if the <text> is set to ESC%, the printer can parse
the ESC%CONNECT and ESC%DISCONNECT messages without interfering with
normal print jobs. In Trigger or Master modes, the first character of this string is used as
the BREAK connection character.
Example : “SO,ESC%”
SP,<text> Security Pin Code, 16 character maximum
Example : “SP,secretcode”
SR,<adr> Remote Address. 12 hex digits, (6 bytes) no spaces or chars between.
Example : “SR,00A053112233”
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 9

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 9 of
27
NOTE: 2 special characters can be used here:
“SR,Z” will erase any stored address.
“SR,I” will write the last address seen by using the Inquiry command.
This can be helpful when you just have 1 other device in range and want to
quickly store and connect to it.
SS,<text> Service Name (1 to 16 characters ).
Example : “SS,SerialPort”
ST,<num> Config Timer, # of seconds ( range= 0 to 255 decimal,, default = 60 decimal) to allow
remote configuration over Bluetooth after power up in Slave Mode. In all Master modes,
the remote config timer is set to 0 (no remote configuration). In Trigger Master Mode,
this Timer is used as an Idle timer to Break the connection after the timer expires with no
characters being received.
Example : “ST,0” disables remote configuration
Example : “ST,255” enables remote configuration forever
SU,<rate> Baudrate, {1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2, 38.4, 57.6, 115K, 230K, 460K, 921K }, only
the first 2 characters are needed.
Example : “SU,96” sets the baudrate to 9600 buad.
SW,<hex word> Enable low power SNIFF mode. Default is 0000=disabled. SNIFF mode allows extreme
low power operation. Device goes into a deep sleep, and wakes up every
every 625us * <hex word> to send/receive chars.
Example: “SW,0050” enables Sniff mode and sets the interval time to 50 hex * .625 = 50
milliseconds. This will cause the module to enter low power sleep, and
wake once every 50 milliseconds to check for RF activity. See Section
4.1 for more details on Sniff.
SX,<1,0> Bonding enabled, which creates a single stored connection pair with a remote device.
SZ,<num> Raw Baudrate (decimal) allows entering of non-standard baudrates. Based on the
formula num = Baudrate * 0.004096.
S$,<char> Configuration detect character. This allows a change from the default $$$ to some other
character. Factory defaults returns the device to $$$.
S~,<0,1> Profile to use. 0=SPP (default), 1 = DUN DCE, 2 = DUN DTE, 3 = MDM.
See Section 4.2 for more details on Profiles.
S~,<6> Profile to use. 6=HID (Bluetooth keyboard), sets to HID mode when it has HID/SPP
firmware (version 6.10). Must reboot (r,1) after.
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 10

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 10 of
27
S?,<0,1> Role Switch. Enables and disables Role Switch. If set, when an incoming connection is
occurs to a slave mode device, an attempt will be made to force a role switch, allowing
the slave to become the master. This is useful in situations where high speed data is being
sent from the local device up to the remote host, and can result in better performance.
However this may create a situation whereby the connecting host will not be able to make
additional outbound connections (multipoint) while connected to this device. Disabled by
default.
S+,<num> Sleep timer settings. The default sleep time setting is set to 180, which is 3 minutes. In
Order to
Example : “S+,3600” To set the sleep time to one hour
S|,<hex> Low power connect mode. Disables the Bluetooth radio and LED timers while not
connected. When set, the module will cycle between active (discoverable and
connectable) and low power deep sleep. This can save considerable power when the
module is waiting for long periods of time without a connection. The trade off is
additional latency when connecting or pairing. The value is a four digit number made up
of two one byte intervals. The first interval is the OFF period and the
second the ON period. Both are in Hex seconds (not decimal). The maximum value
is 20 seconds for either of the periods. Default is 0000 always actively waiting for a
connection.
Example: S|,2001 // cycle ON for one second and OFF for 32 seconds (HEX
20=Decimal 32).
GET COMMANDS
D Display basic settings. Address, Name, Uart Settings, Security, Pin code, Bonding,
Remote Address. This command is an easy way to check the configuration.
E Display extended settings. Service Name, Service Class, Device Class, Config Timer.
M Display remote side modem signal status.
O Display other settings. Config character, IOport values, debug mode.
G<X> Display stored settings . These commands correspond to the SET commands above.
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 11

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 11 of
27
Example : “GS” will return 1 or 0 depending on the value of security.
In addition to the above, there are a few other useful commands available.
B Returns Battery Power information (See below)
GB Returns the Bluetooth Address of the device.
GK Returns the current connection status: 1=connected, 0 = not connected.
G& Return a hex byte containing the value of the PIO Pins
V Return the software release version
Example of result from “B” Battery Power command:
UP=62,PWR=1731,Batt=2FE,2298 mv
UP= seconds since being powered up.
PWR= charger reading. has to be > 1000 (this is hex) if < 1000 no charger running.
Batt= battery reading in HEX (this is the actually battery voltage / 3 referenced to 3.3V ).
2298 this is the actual battery voltage in millivolts.
CHANGE COMMANDS
U,<rate>,<E,O,N> Temporary Uart Change, will change the serial parameters immediately, but not
store them. Command will return “AOK” at current settings, then automatically exit
command mode, and switch to new baudrate until device is powered off.
Example : “U,9600,E” Sets baudrate to 9600, parity even.
ACTION COMMANDS
$$$ Enter command mode. Characters are PASSED until this exact sequence is seen. If any bytes are
seen before these chars, or after these chars, in a 1 second window, command mode will not be
entered and these bytes will be passed on to other side.
NOTE: this char is configurable, use the S$,<char> command to change the char.
--- Exit command mode. Exit command mode. “END” will be displayed. If connected
over BT, data will now pass in both directions.
+ Local echo. Toggle local echo of RX characters in command mode. (default is off)
C{,<address>} Connect to the remote stored BT address, or an optional address can be entered directly.
CF{,<address>} Connect and immediately go into FAST data mode. NOTE: You will not be able to enter
command mode while Connected. PIO6 can still be use to disconnect. Thus PIO6 should he held
HIGH before sending this command, as lowering PIO6 will cause a disconnect.
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 12

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 12 of
27
CFI- Connect and immediately go into FAST data mode using the LAST address found from the
Inquiry command. NOTE: You will not be able to enter command mode while Connected. PIO6
can still be use to disconnect.
CFR- Connect and immediately go into FAST data mode using the REMOTE address. Similar to the C
command but bypasses the configuration timer.
CT<address>,<timer> Connect with TIMER. The device will NOT use or store the remote address, rather will
make a connection to the <address> (REQUIRED). The device will automatically disconnect after
7 seconds if no data is seen from the UART or BT. An optional timer value can be entered to
change the timer. This value is in ¼ seconds. So for a 30 second timer, use 120 as the value. The
maximum value is 255 (64 seconds).
F,1 Go to FAST data mode, ends configuration immediately.
I<,time>,<cod> performs an inquiry scan. Default time is 10 seconds, maximum is 48. Cod
is optional class of device, 0 or no entry looks for all device classes. A maximum of 9 devices
will be returned. As devices are found, they are displayed in the format below:
<bt address> , <bt name> ,<cod>
00A053000123,MySerialPort,72010C
IN<time>,<cod> Performs an inquiry scan, does not return the Bluetooth NAME (returns much
faster, since name requires a remote lookup for each device found).
IR<time> Performs an inquiry scan, with a COD of 0x001F00, which is the default COD for
SerialIO.com Serial adapters and modules.
IS<time> Performs an inquiry scan, with a COD of 0x0055AA, which is the special COD used
by SerialIO.com Serial adapters and modules to enable “instant cable replacement.”
H Help, will print out a list of commands and their basic syntax
K, Kill (disconnect) from the current connection. The characters KILL<CR><LF> will be echoed to
the local UART once the connection is broken.
L Link quality. Returns real-time streaming link quality values at 5Hz. Value returned as 2 bytes
separated by a comma. A value of “ff” is the highest value. The first byte is the current reading
and the second byte is the low water mark. Example output: RSSI =ff,e6
P,<char> Pass thru, sends any chars along up to a CR or LF while in command mode.
Q Causes device to be non-discoverable and non-connectable (temporarily). Does not survive a
power cycle or reset. Used with the Z command below.
R,1 Forces a complete reboot of the device (similar to a power cycle)
T,<0,1> Pass receive data (from uart or BT) while in command mode. Returns (T=0 , T=1 based on input).
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 13

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 13 of
CMD
VALUE
DESCRIPTION
@
<hexword>
Set direction bits for GPIO
&
<hexword>
Set values for GPIO
%
<hexword>
Store powerup direction bits for GPIO
^
<hexword>
Store powerup values for GPIO
*
<hexword>
Set values for PIO8,9,10,11
27
& Returns the value of the switches on BlueSnap.
W Re-enables discovery and connection. This command reloads the stored value of the Inquiry and
Page Window to re-enable. For example, to turn off Discovery but still allow connections, send an
“SI,0000” command, and follow it with a “W” command. This command returns “Wake” as a
response.
Z Enters low power deep sleep mode (<2ma) when NOT connected. Can only be exited by toggling
the RESET pin on the module (causing a HARD reset) , or power cycling the device. To get the
lowest power mode, first issue a Q, then a Z. Use the SNIFF settings to get lowest power while
connected.
Limitations of using 7 Bit data mode
SerialIO.com firmware now supports (from version 4.22 and on) selectable 7 bit data mode, using the “S7,1” command.
Unfortunately the Bluetooth hardware does not support 7 bit data, so this function is accomplished in the firmware application.
While completely functional, the performance in 7 bit mode is less than ideal, because software emulation is required to make
this work. Hence, there is a noticeable latency and character per second processing limit in this mode. Therefore it is not
recommended that this mode be used if the desired serial baudrate is greater than 9600 baud.
COMMANDS to MANIPULATE GPIO
The GPIO command interface uses combination
of 2bytes, a mask, and value, packed into a hex
word for each command. The first byte, the
mask, determines which GPIO are to be
affected, and the second byte is the value to set.
15 --------- 8 7 -------- 0
<hexword> = MASK[7...0] VALUE[7..0]
There are 2 registers used to control the GPIO, the first is a direction register. This controls whether the GPIO is an input or
an output. The second register is the value to apply to the GPIO if set to an output, or is the value of the built-in weak pull-up
resistor if the GPIO is set to an input. These settings are immediate, and do not survive a power cycle.
Examples: S@,8080 sets GPIO-7 to an output
S&,8080 drives GPIO-7 high
S&,8000 drives GPIO-7 low
Power-up values: These 2 registers will apply the direction and values upon each subsequent power-up:
Examples: S%,0101 sets GPIO-0 to an output on power-up
S^,0303 drives GPIO-0 high, and pulls up GPIO-1.
Multiple bits can be set, any bits with a mask of 0 are left unaffected for the command.
Some GPIO are checked at power-up time to perform certain functions, so care must be taken when manipulating them.
GPIO3, 6, are used to automatically set master mode, and auto discovery. If it is desired to use these GPIO for other purposes
at power-up, a special command must be used to disable their being sensed at power-up time. This command is “SQ,4<cr>”
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 14

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 14 of
27
this will set a flag in a stored register that is read at power-up. The Power-up settings for the GPIO can also be viewed using
the “O” (other settings) command.
WARNING:
GPIO-4 is used by the system to reset stored parameters to factory defaults. If GPIO4 is pulled high on power-up, and then
toggled 3 times, all user settings will return to default values. Therefore this pin should not be used as an output, and should
not be driven high at power-up time (first 1 second of operation).
NOTE:
GPIO2 and 5 are driven by the embedded software as outputs, they can be disabled using the direction command, (to save
power, for example) and used as inputs. If set to outputs the software will override any user values.
SETTING GPIO 8-9-10-11
S*,<hexword> = MASK[11..8] VALUE[11..8]
For the upper 4 GPIO, a single word controls the mask and values, and only the lower 4 bits of each byte are used. The first
time this command is used, all 4 GPIO are driven as outputs and remain so until a power cycle. There is no powerup
command for these bits, only the interactive one. Some modules do not offer these GPIO.
Examples:
S*,0101 GPIO-8 driven HIGH.
S*,0100 GPIO-8 driven LOW.
S*,0202 GPIO-9 driven HIGH.
4. 1 Using Low Power Modes
4.1.1 Inquiry(Discovery) and Page(Connection) Windows
There are 2 timers that can be used to lower the idle Slave mode power of the radio. When not connected, the
Radio is active for a percentage of time listening to see if any other device wants to Discovery (inquire) or
Connect (page). The amount of time the radio is on is called the window, and the rate at which the process cycles
is called the interval. The interval is fixed at 0x800 (1.28seconds) with Sniff disabled, and 2.56 seconds with Sniff
enabled. The window can be adjusted. The default window is 0x200 (320 ms) or 25% duty cycle.
By lowering the window value, power can be saved at the expense of possibly missing an inquiry or page. Since
the host usually retries automatically many times, the only downside is a delay in discovery or connection time.
The minimum window for inquiry or page is 0x0012 (11.25ms). corresponding to about a 1% duty cycle.
Thus, average power can be reduced from >20ma to <5ma in standard mode, and <3ma in Sniff mode.
It is also possible (and desirable for security reasons) to completely disable inquiry. Once a host has found and
installed a device, inquiry is not needed, only page is used to make a connection.
To disable inquiry and still allow connections, set the Inquiry timer to 0 with “SI,0000”.
4.1.2 SNIFF mode
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 15

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 15 of
27
Sniff mode is another power conservation method utilized by Bluetooth. By default, Sniff mode is disabled, and
the radio is active continuously when connected (about 25-30ma) . In Sniff mode, the radio wakes up at specific
intervals, and sleeps in very low power mode (around 2ma) otherwise. The power savings can be quite dramatic.
To enable it, use the “SW,<hex word>“ command.
Example interval timers:
0x0020 = 20ms. (32 decimal * .625 = 20).
0x0050 = 50ms, 0x00A0 = 100ms, 0x0190 = ¼ second, 0x0320 = ½ second, 0x0640 = 1 second.
Sniff mode only pertains to an active connection. When a connection is made, both master and slave must
support Sniff mode, and agree to the Sniff window, otherwise the radio will stay in full active on mode.
Note: the maximum allowed Sniff interval is about 20 seconds = 0x7FFF sniff word setting.
Enabling DEEP SLEEP.
Deep Sleep mode can be used to obtain extremely low power operation. The device totally shuts down and only
draws about 300uA of current in this mode. To enable Deep Sleep, set the high order bit of the Sniff word =
0x8000. This bit is NOT used to determine the sleep interval, it is only used as a flag to enable deep sleep. For
example, If you want ½ second sleep 0x0320, with Deep sleep, you would set the sniff word to 0x8320.
In normal low power sleep (not deep sleep) the firmware is still running in idle mode, and wakes up about 20
times per second to check ports, update Leds etc. During Deep sleep, the firmware actually stops running some
tasks. For example, the LEDs only update about once per second.
There are 3 ways to wake the radio from sleep mode. The first is to send a character to the UART. Transitions on
the RX pin will wake the device from sleep. Wake time is worst case 5ms. Because of this, the first character
sent is generally lost by the radio. A better way to wake the radio is to toggle the CTS line from LOW to HIGH,
Wait 5ms, and then send data. The third way is automatic, the radio will wake every <hex word> slot times (1 slot
time = 625us) as defined above. The radio wakes and listens to see if the other side of the connection has
anything to send. This wake time is typically about 5ms (8 slots) even if no data is to be transferred.
Once the radio is awake it will stay active for exactly 1 second of inactivity, and then sleep again.
NOTE: setting this mode can cause latency issues, and dropped bytes/loss of performance in cases where large
amounts of data are being transferred. The nuances of Bluetooth Sniff can be complex, contact SerialIO.com if
necessary for more details on how to utilize Sniff mode.
4.1.3 Disabling Output drivers
Use the command “ S%,1000” to set all PIO0-11 to inputs.
This will also turn off the LED (PIO5) on the BlueSnap adapter.
4.2 Profile Selection
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 16

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 16 of
27
The default profile is Serial Port Profile (SPP). The firmware also supports the DUN profile in both master and
slave modes. To change the profile, use the “S~,<num>” command.
Profile:
0 - Default SPP. (no modem control)
1 - DUN DCE (slave or gateway).
2 - DUN DTE ( master or client).
3 - MDM SPP with modem control signals.
The most common use of DUN profile is to enable a BT client to connecti to a dialup modem. For this mode, use
profile 1 (DUN DCE) via command “S~,1” . You may also want to set the Class Of Device so that clients can
recognize the device as a Bluetooth modem. The correct COD for a Bluetooth modem is 0x040210. This can be
set using the commands below:
“SC,0004”
“SD,0210”
A number of modem control signals are supported when in DUN or MDM modes and their use is described below.
4.2 PIOs used as modem control signals
The BlueSnap modules have the ability to replicate the required modem control hardware signals automatically
once a connection is made. These signals are transferred outside the data channel (using RFCOMM control
channels) and are automatically updated. The default SPP profile (profile=0) does NOT drive these signals or
report back inputs. If DUN or MDM profiles are enabled (pofile =1,2, or 3), the following signals are
automatically driven and received.
Inputs: (read and sent back over Bluetooth to the remote host).
PIO3 = DCD ( switch 2)
PIO6 = DSR (switch 3)
PIO7 = CTS (switch 4)
Outputs: (sent from the remote Bluetooth host, and driven out )
PIO10 = DTR
PIO11 = RTS
Inputs and outputs are ACTIVE LOW.
On the BlueSnap, the DIP switches can also be used to set/clear the DCD, CTS, and DSR signals. DTR and RTS
are available on the 9 pin header as well.
5. Command Quick Reference
SET COMMANDS FACTORY SETTING
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 17

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 17 of
27
S7,<1,0> - 7 bit data mode enable/disable 0= disabled
SA,<1,0> - Authentication enable/disable 0= disabled
SB,<timer> - Send BREAK Not Applicable
SC,<hex word> - Service Class 0x0000= unknown
SD,<hex word> - Device Class 0x1F00= undefined
SE,<1,0> - Encryption enable/disable 0=disabled
SF,1 - Factory Defaults
SI,<hex word> - Inquiry Scan window 0x0200
SJ,<hex word> - Page Scan window 0x0200
SL,<E,O,N> - Parity N=None
SM,<0,1,2,3> - Mode (0=Slave, 1=mstr,2=trig, 3=auto) 0=Slave
SN,<text> - Name BlueSnap
SO,<text> - Connect/Disconnect Status String NULL= no status string
SP,<text> - Pin Code 1234
SR,<adr> - Remote Address (SR,Z to remove) NONE SET
SS,<text> - Service Name SPP
ST,<num> - Config Timer 60 seconds
SU,<rate> - Baudrate 115K
SW,<hex> - SNIFF rate 0x0000=disabled
SX,<1,0> - Bonding 0=disabled
SZ,<num> - Raw Baudrate
S-,<name> - Serialized Name BlueSnap-xxxx
S?,<1,0> - Role Switch 0=disabled
S~,<1,0> - Profile setting 0=SPP, 1=DCE, 2=DTE, 3=MDM 0 = SPP
S~,<6> - Profile setting 6=HID 6 = HID
S+,<num> - Sleep timer 180 seconds
GET, DISPLAY COMMANDS
D - Basic Settings
E - Extended Settings
O - Other Settings
G<X> - Stored setting
H - Help
GB - BT Address
GK - Connection Status
G& - I/O Ports
V - Firmware version
ACTION COMMANDS
$$$ - Enter Command Mode
--- - Exit Command Mode
+ - Local echo. Toggle local echo of RX characters in command mode. (default is off)
C,<address> - Connect, optional address, if no address, use stored remote address.
CT - Connect Timer,
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 18

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 18 of
27
F,1 - Enter Fast data mode, end configuration immediate.
I,<time>,<cod> - Device Scan Inquiry, time in seconds, optional cod = class of device filter, 0=all
IN<time>,<cod>- Device Scan Inquiry, returns NAMEs.
IR<time> - Device Scan Inquiry, fixed cod=0x001F00 to find SerialIO.com devices.
IS<time> - Device Scan Inquiry, fixed cod =0x0055AA to find instant cable pairs.
K, - Kill (disconnect) from current connection
Q - Turn off Discovery and Connectability
R,1 - Reboot
T,<0,1> - Pass receive data (from uart or BT) while in command mode.
U,<rate>,<E,O,N> - Temporary UART change of baud rate and parity (Even, Odd, None)
& - return the value of the DIP Switches
Z - Enter low power Sleep mode
6. Factory Default Power up Settings
Bluetooth Service Profile = Serial Port Profile (SPP)
Device Mode = 0 (Slave)
Baud Rate = 115200bps,Parity=None, Data bits = 8 bits(fixed), Stop bits 1 (fixed).
Power Mode = Auto low power discoverable mode
Name of Device (local name) = BlueSnap-XXXX last 2 bytes of BT address
Service Name = SPP
Service Class=0000 (undefined service type)
Major & Minor Class Of Device (COD) = 0x1F00 (unknown device type)
Authentication Disabled
Encryption Disabled
Discovery Enabled (0x0200 = windowl, fixed interval of 0x800= 1.28 Seconds )
Connection Enabled (0x0200=window, fixed interval of 0x800 = 1.28Seconds)
Bonding Disabled
Config Timer=60 seconds
SNIFF mode disabled
Default PIN = “1234”
Note: PIO(4) Switch 1, Set ON at power up time, and then toggled 3 times will change all
settings above back to their factory values. (except the Device name). Device will reboot
immediately upon detection of this mode.
7. COMMON PROBLEMS and QUESTIONS:
My Bluetooth client can see the BlueSnap and its serial service, but I can’t connect: This
is most likely caused by a security setting on your client. BlueSnap does support
authentication by default if the client requires it (using default pincode of “1234”,) but for
ease of use, you may want to turn security off on your client. Some clients have these setting
off by default, others have them on. To check and disable security:
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 19

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 19 of
27
From your PC desktop, click My Bluetooth Places, go to the Bluetooth Device configuration (or
Advanced Configuration) drop down menu, click on the client applications tab, Select the
Bluetooth serial port application name, and click on the properties button, if “secure
connection”, or “authentication”, or “encryption” is checked, un check it.
Changing the clients COM port: Widcomm stack, the most common stack out there allows
you to connect to BlueSnap using a “Virtual COM” port mapper. The software installs with a
default COM port, usually COM3, COM4, or COM5. To change this setting:
From your PC desktop, click My Bluetooth Places, go to the Bluetooth Device configuration (or
Advanced Configuration) drop down menu, click on the client applications tab, Select the
Bluetooth serial port application name, and click on the properties button, then you can change
the com port.
Connecting to more than one BlueSnap from the same client at the same time: Bluetooth
allows 7 devices at a time in a piconet. The Widcomm stack allows you to create multiple
instances of serial port profile and connect to multiple BlueSnaps at the same time. To do
this: From your PC desktop, click My Bluetooth Places, go to the Bluetooth Device configuration
(or Advanced Configuration) drop down menu, click on the client applications tab, Select the
Bluetooth serial port application name, and click on the ADD COM port button, then you can
add another Bluetooth serial port and assign it to another virtual com port (such as COM9).
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 20

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 20 of
27
8 Example of a Master Discovery/Connection Sequence
From power up and no connection:
1) Perform an Inquiry to obtain BT_Address (unless it is already known).
Sent : $$$ // Places Radio in Command Mode
Reply:CMD<cr>
Sent : I,30<cr> // Looks forBluetooth devices
Reply:00A096112233,1F00<cr>Inquiry Done<cr
2) Store the remote address just found.
Sent : SR,00A096112233 <cr> (or just SR,I if this was the only device found ).
Reply:AOK<cr>
3) Connect.
Sent : C <cr> // Places Radio in Connect
Reply:AOK<cr>
Device will attempt connection to remote slave. “TRYING” will be displayed.
Reply:<text>CONNECT<cr> // this will be displayed once connection is made, if <text>
string is defined in the stored parameters.
4) Send /Receive data.
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 21

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 21 of
NAME
DB-9 male
IO DIR
DCE(PC)*
DTE
3-WIRE-DCE
1-DCD
NC
2-RX
2-RX
IN
|
--
|
3-TX
3-TX
OUT
|
--
|
4-DTR
NC
5-GND
5-GND
<—>
6-DSR
NC
7-RTS
7 -RTS
OUT
|
--
|
8 - CTS
8 -CTS
IN
|
--
X
9 - RING
V+
IN
27
9 BlueSnap Configuration: BlueSnap Serial Jumpers
Below are Internal Jumper options for BlueSnap XP
DTE 3 Wire Factory Default (CTS shorted to RTS), DTE RX=2, TX=3, RTS=7, CTS=8
remove 3rd , 4th jumpers and one jumper in position 5
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
DCE , RX=3, TX=2, RTS=8, CTS=7
Page 22

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 22 of
27
Below are Internal Jumper options for BlueSnap Standard (Male) and BlueSnap 9V (Male)
(internal jumpers for Female DB9 versions are different, see the following page)
DCE 3 Wire Factory Default (CTS shorted to RTS), DTE (Like a PC) RX=2, TX=3, RTS=7, CTS=8
Remove 3rd, 4th jumpers and one jumper in position 5
DCE (Like a Modem), RX=3, TX=2, RTS=8, CTS=7
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 23

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 23 of
27
Below are Internal Jumper options for BlueSnap Standard (Female) and BlueSnap 9V (Female)
(internal jumpers for Male DB9 versions are different, see prior page)
DCE 3 Wire Factory Default (CTS shorted to RTS),
Remove 3rd, 4th jumpers and one jumper in position 5
DTE (Like a PC) RX=2, TX=3, RTS=7, CTS=8
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 24

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 24 of
27
Below are Internal Jumper options for BlueSnap AAA (Male)
DCE 3 Wire Factory Default (CTS shorted to RTS),
Remove 3rd, 4th jumpers and one jumper in position 5
DTE (Like a PC) RX=2, TX=3, RTS=7, CTS=8
Use these settings for devices like Sylvac Digital Caliper
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 25

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 25 of
BOTTOM SIDE
4- Default baud(9600/ 115k)
3- AUTO MASTER
2 - AUTO DISCOVER
1 – FACTORY DEFAULTS
ON - OFF
BOTTOM SIDE
4- Default baud(9600/ 115k)
3- AUTO MASTER
2 - AUTO DISCOVER
1 – FACTORY DEFAULTS
ON - OFF
BOTTOM SIDE
4- Default baud(9600/ 115k)
3- AUTO MASTER
2 - AUTO DISCOVER
1 – FACTORY DEFAULTS
ON - OFF
27
10 BlueSnap Configuration Switches
1- FACTORY DEFAULTS- Set this switch ON, power up unit, and toggle the switch from ON to OFF 3 times to return the unit
to factory settings.
2-AUTO DISCOVER MODE – In Slave mode, sets a special class of device which is used by a remote Master to auto connect.
IF Switch 3 also SET, the device performs a search, stores, and connects to a remote slave which has this switch 2 set .
3- AUTO MASTER MODE- BlueSnap acts as master, auto-connect to a stored remote address. First set the BT address of the
device to connect to using the SR command. or, have BlueSnap auto discover and connect by via Switch 3 AND Switch 2.
4- DEFAULT BAUD RATE - OFF = 115K (factory setting), ON = 9600. Overridden by software configuration.
Instant Cable Replacement Example
MASTER
SLAVE
1. Set switches as shown above.
2. Power up both devices
3. Master finds and store slave address, and auto connects.
4. Set Switch 2 on both Master and Slave back to OFF.
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 26

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 26 of
Signal Name
CONNECTOR
PIN #
IO DIR
Board PWR
P1 1 Power IN (5.0 -8.0 Vdc)
Board GND
P1 2 <—>
RS-232 SERIAL-CN1
Modem control options
Pin 1 - DCD
DB9
Not used
Connect to PIO2
Pin 2 - TX
DB9
2
OUT
Pin 3 - RX
DB9
3
IN
Pin 4 - DTR
DB9
4
Not used
Connect to PIO10
Pin 5 - GND
DB9
5
<—>
Pin 6 - DSR
DB9
6
Not used
Pin 7 - RTS
DB9
7
OUT→ * (active low)
Pin 8 - CTS
DB9
8
IN← * (active low)
Pin 9 - RING
DB9
9
Pwr →IN (4.5 -11Vdc)
SERIAL 3.3V (J1)
PWR
J3-1
1
Optional 5VDC in
GND
J3-2
2
GROUND
CTS
J3-3
3
IN
RTS
J3-4
4
OUT→ 0 - 3.3Vdc
TX
J3-5
5
OUT→ 0 - 3.3Vdc
RX
J3-6
6
IN
PIO#2
J3-7
7
BT Connection (high state)
PIO#10
J3-8
8
GPIO
DTR output
PIO#11
J3-9
9
GPIO
RTS output
PIO-SWITCH-LEDS
PIO#4
SWITCH-1
1
Reset Default Settings
PIO#3
SWITCH-2
2
Auto Discover and Pairing
DCD input
PIO#6
SWITCH-3
3
Auto Connect as Master
DSR input
PIO#7
SWITCH-4
4
Def Baud Rt (115K - 9600)
CTS input
PIO#5
LED-DL1
GREEN
Pulses for status 0-3.3Vdc
LED-DL2
YELLOW
RX, TX data low to high
PIO#8
LED-DL3
RED
Software controlled
RX char low speed mode
6-Pin SPI (J2)
MISO
J2-1
Reserved programming)
MOSI
J2-2
Reserved programming)
SPICK
J2-3
Reserved programming)
SPICS
J2-4
Reserved programming)
PWR
J2-5
Optional 3.3VDC Power
GND
J2-6
Optional Ground
27
Appendix A BlueSnap Evaluation Board Physical Ports
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
Page 27

BlueSnap Commands Version 4.81SIO, 1/20/2016 Page 27 of
MODE
GREEN LED blink rate
Configuring
10 times per second
Startup/Config Timer
2 times per second
Discoverable/Inquiring/Idle
Once per second
Connected
Solid ON
27
Important Notes:
Placing 3.3Vdc into the PIO’s while they are set as outputs will permanently damage the
radio modules. The failure mode is short across GND and VCC. Use a 10KΩ resistor in
series or a 10KΩ pull up resistor for input and output PIO’s respectively.
Make sure to connect a common ground when using the external TX, RX inputs on the
0 – 3.3Vdc.
For a 3 wire DB-9 interface (tx, rx, gnd only) connect/short CTS to RTS, Factory default
is hardware flow control enabled CTS and RTS connected.
When using a 5.0Vdc Input, PIO’s require a 10K ohm series resistor. PIO’s are 0-3.3Vdc
not 5 volt tolerant.
A null modem adapter is required to make a direct connection to a PC serial port.
Power Terminals for Evaluation Board
Inputs on P1 power connector can be 4.5VDC to 11.0VDC. There is internal regulation down
to 3.3VDC for all circuitry. Worst case power draw for the board is 80ma when the Bluetooth
radio/modem connection is established and transmitting. Power can be as low as 1ma to 25ma
average when the Bluetooth radio/modem is not connected depending on parameter settings.
Hardware Communications Connections for Modules and Eval Board
Radio TX RX of the application Micro Controller Unit (MCU)
Radio RX TX of the application Micro Controller Unit (MCU)
Radio RTS CTS of the application Micro Controller Unit (MCU)
Radio CTS RTS of the application Micro Controller Unit (MCU)
LEDs
The YELLOW LED should blink whenever data is transferred on either the RX or TX pins of the
DB9 serial port. It is a physical monitor of the actual voltage on the pins, and is not driven by
software from the module.
Cedar Park, TX, USA • (512) 994-3630 • sales@serialio.com www.serialio.com
 Loading...
Loading...