Page 1

Compact HD (11N) Wireless
Network Camera
User’s Guide
Page 2

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION..............................................................................................1
Overview.............................................................................................................................1
Physical Details - Network Camera..................................................................................4
Package Contents...............................................................................................................6
CHAPTER 2 BASIC SETUP....................................................................................................7
System Requirements........................................................................................................7
Installation - Network Camera.........................................................................................7
Setup using the Windows Wizard....................................................................................9
CHAPTER 3 VIEWING LIVE VIDEO ................................................................................14
Overview...........................................................................................................................14
Requirements...................................................................................................................14
Connecting to a Camera on your LAN..........................................................................14
Connecting to a Camera via the Internet.......................................................................16
Viewing Live Video..........................................................................................................18
CHAPTER 4 ADVANCED VIEWING SETUP....................................................................20
Introduction......................................................................................................................20
Adjusting the Video Image..............................................................................................20
Controlling User Access to the Video Stream................................................................22
Making Video available from the Internet....................................................................23
Viewing Live Video via the Internet...............................................................................26
Motion Detection Alerts ..................................................................................................27
CHAPTER 5 WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT.....................................................................28
Introduction......................................................................................................................28
Connecting to Network Camera.....................................................................................28
Welcome Screen...............................................................................................................29
Administration Menu......................................................................................................30
System Screen...................................................................................................................31
Network Screen................................................................................................................33
Wireless Screen................................................................................................................37
DDNS Screen....................................................................................................................40
IP Filter.............................................................................................................................42
I/O Port.............................................................................................................................43
Streamings........................................................................................................................44
Video & Audio Screen.....................................................................................................46
Video Access Screen.........................................................................................................48
User Database Screen......................................................................................................50
Motion Detection Screen.................................................................................................51
Audio Detection Screen...................................................................................................52
E-Mail Screen...................................................................................................................53
FTP Screen.......................................................................................................................55
HTTP Screen....................................................................................................................56
SD Card Screen................................................................................................................57
SMB/CIFS Client Screen.................................................................................................58
Event Trigger Screen.......................................................................................................59
Maintenance Screen.........................................................................................................61
Status Screen....................................................................................................................63
Log Screen........................................................................................................................65
i
Page 3

CHAPTER 6 WINDOWS VIEWING/RECORDING UTILITY........................................66
Overview...........................................................................................................................66
System Requirements......................................................................................................66
Installation........................................................................................................................ 66
System Tray Icon.............................................................................................................67
LiveView Screen...............................................................................................................68
Camera Setup...................................................................................................................69
LiveVew Program - for Streams Live Viewing.............................................................71
View Recordings Program - for Streams Recording....................................................73
Setup Program - for Streams Configuration.................................................................75
CHAPTER 7 TROUBLESHOOTING...................................................................................78
Overview...........................................................................................................................78
Problems...........................................................................................................................78
APPENDIX A SPECIFICATIONS........................................................................................81
Network Camera..............................................................................................................81
Regulatory Approvals......................................................................................................81
Copyright Notice..............................................................................................................82
APPENDIX B NETWORK CAMERA HTTP CGI..............................................................83
User-level CGI commands (user level privilege)...........................................................83
Admin-level CGI commands (administrator level privilege).......................................99
P/N: 956YWT0001
Copyright © 2010. All Rights Reserved.
Document Version: 1.0
All trademarks and trade names are the properties of their respective owners.
ii
Page 4
Chapter 1
Introduction
1
This Chapter provides details of the Network Camera's features,
components and capabilities.
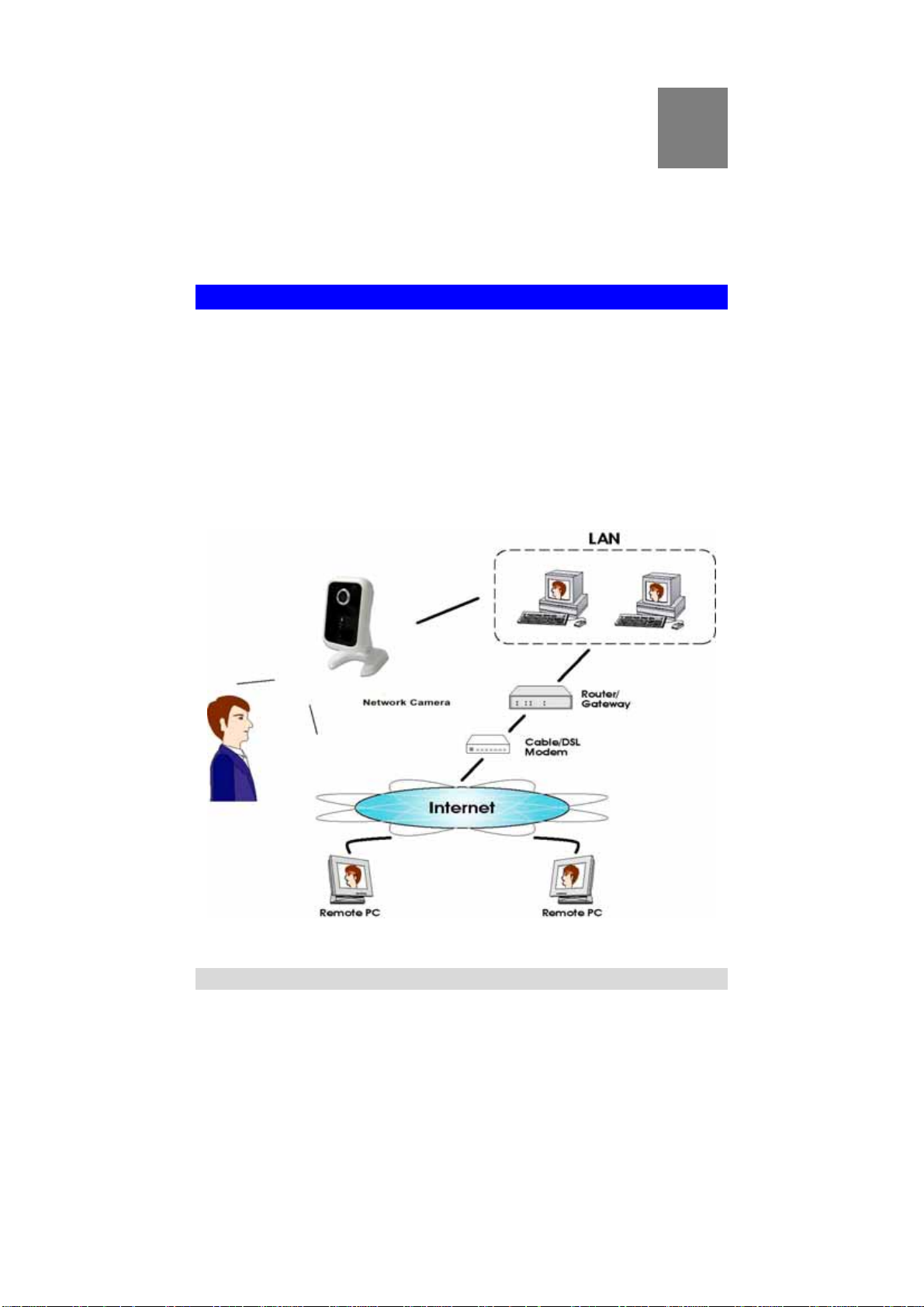
Overview
The Network Camera has an Integrated Microcomputer and a high quality Mega
Pixel Omni Vision CMOS Sensor, enabling it to display high quality live streaming
video over your wired LAN, the Internet, and for the Network Camera, an 802.11N
Wireless LAN.
Using enhanced H.264 technologies, the Network Camera is able to stream high
quality video and audio directly to your PC. The high compression capabilities of
H.264 reduce network bandwidth requirements to amazingly low levels.
A convenient and user-friendly Windows program is provided for both viewing and
recording video. If necessary, you can even view video using your Web Browser, on
a variety of software platforms.
Figure 1: Network Camera
Features
• Standalone Design. The Network Camera is a standalone system with built-
in CPU and Video encoder. It requires only a power source and a connection to
your LAN or Wireless LAN.
Triple Video Support. The Network Camera can support H.264, MPEG4 and
•
MJEPG video for different image compression.
1
Page 5

•
Stream Live Video to Multiple Users. The video encoder and
HTTP/HTTPS server built into the camera generate a ready-to-view video
stream. Just connect to the camera using your Web browser or the provided
Windows utility to view live video.
• Suitable for Home, Business or Public Facilities. Whether for Home,
Business or Public Facility surveillance, or just for entertainment and fun, the
Network Camera has the features you need.
Multi-Protocol Support. Supporting TCP/IP networking, SMTP (E-mail),
•
HTTP and other Internet related protocols, the Network Camera can be easily
integrated into your existing network.
• Easy Configuration. A Windows-based Wizard is provided for initial setup.
Subsequent administration and management can be performed using a standard
web browser. The administrator can configure and manage the Network Camera
via the LAN or Internet.
PIR (Passive Infrared Sensor) Support. The Network Camera is embedded
•
with a PIR Sensor, which senses infrared light radiating from human bodies in
its field of view. This feature is very helpful in enhancing home security
systems.
• Viewing/Recording Utility. A user-friendly Windows utility is provided for
viewing live video. For periods when you are absent, or for scheduled recording,
this application also allows you to export video to your PC. The recorded files
are in a standard Windows Media format, and thus usable by a wide variety of
programs if required.
• Motion Detection. This feature can detect motion in the field of view. The
Network Camera will compare consecutive frames to detect changes caused by
the movement of large objects. This function only works indoors due to the
sensitivity of the CMOS sensor. When motion is detection, an E-mail alert can
be sent, or some other action may be triggered.
•
Flexible Scheduling. You can limit access to the video stream to specified
times using a flexible scheduling system. The Motion Detection feature can also
have its own schedule, so it is active only when required.
Syslog Support. If you have a Syslog Server, the Network Camera can send
•
its log data to your Syslog Server.
Audio Support. You can listen as well as look! Audio is encoded with the
•
video if desired. You can use the built-in microphone.
Internet Features
• User-definable HTTP/HTTPS port number. This allows Internet
Gateways to use "port mapping" so the Network Camera and a Web Server can
share the same Internet IP address.
DDNS Support. In order to view video over the Internet, users must know the
•
Internet IP address of the gateway used by the Network Camera. But if the
Gateway has a dynamic IP address, DDNS (Dynamic DNS) is required. Since
many existing Gateways do not support DDNS, this function is incorporated
into the Network Camera.
•
NTP (Network-Time-Protocol) Support. NTP allows the Network Camera
to calibrate its internal clock from an Internet Time-Server. This ensures that the
time stamp on Video from the Network Camera will be correct.
2
Page 6

Security Features
• User Authentication. If desired, access to live video can be restricted to
known users. Users will have to enter their username and password before being
able to view the video stream.
Password-Protected Configuration. Configuration data can be password
•
protected, so that it only can be changed by the Network Camera Administrator.
Wireless Features
• Supports 11n Wireless Stations. The 802.11n Draft standard provides for
backward compatibility with the 802.11b standard, so 802.11n, 802.11b and
802.11g Wireless
stations can be used simultaneously.
• Wired and Wireless Network Support. The Network Camera supports
either wired or wireless transmission.
WEP Support. Full WEP support (64/128 Bit) on the Wireless interface is
•
provided.
WPA/WPA2 Support. The WPA Personal/WPA2 Personal standard is also
•
supported, allowing advanced encryption of wireless data.
WPS Support. WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) can simplify the process of
•
connecting any device to the wireless network by using the push button
configuration (PBC) on the Wireless Access Point, or entering a PIN code if
there's no button.
3
Page 7
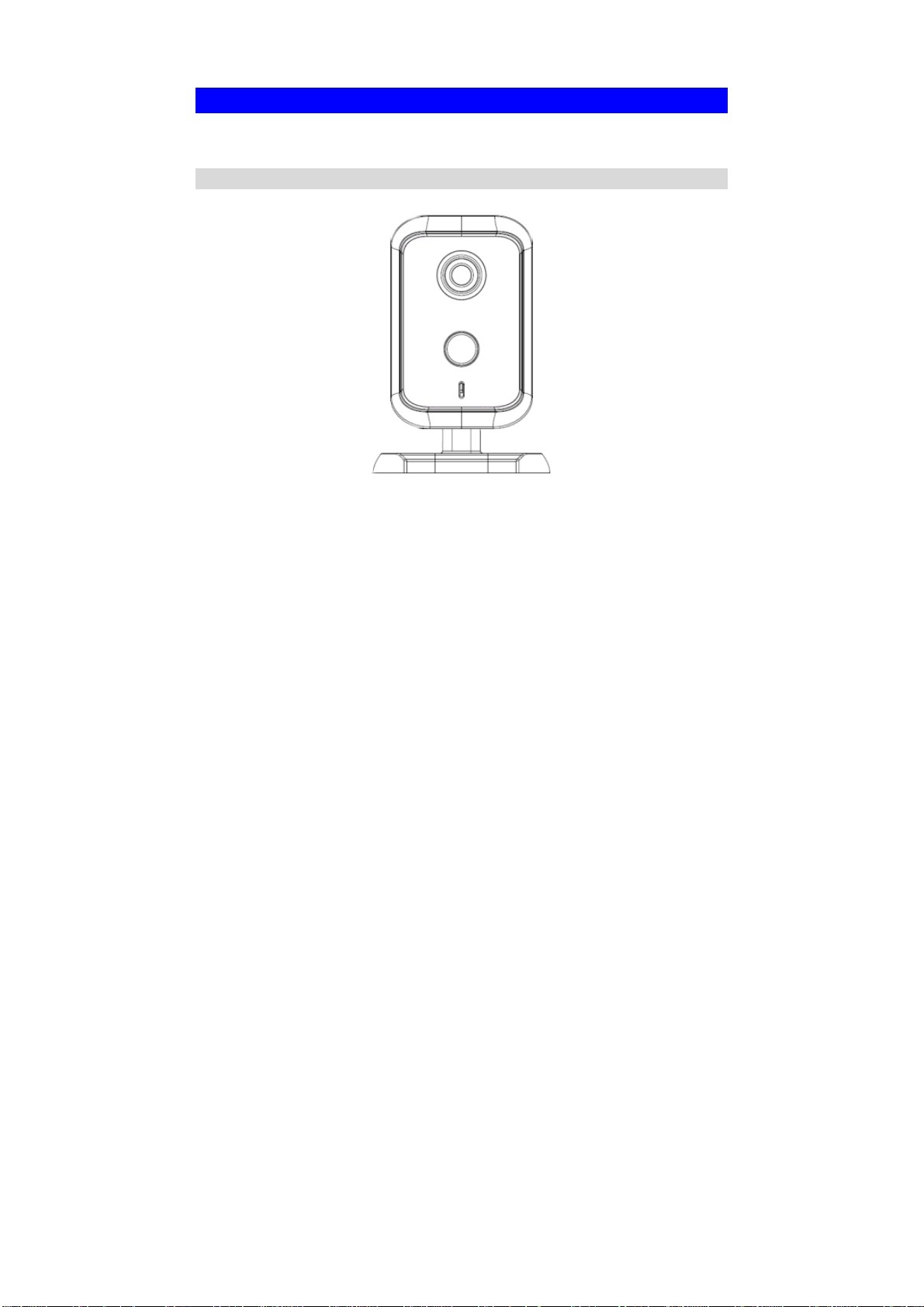
Physical Details - Network Camera
Front - Network Camera
Figure 2: Front Panel
Lens
PIR Sensor
Microphone
No physical adjustment is required or possible for the lens, but you
should ensure that the lens cover remain clean. The image quality is
degraded if the lens cover is dirty or smudged.
The PIR sensor is designed for human body detection.
The built-in microphone is mounted on the front.
4
Page 8
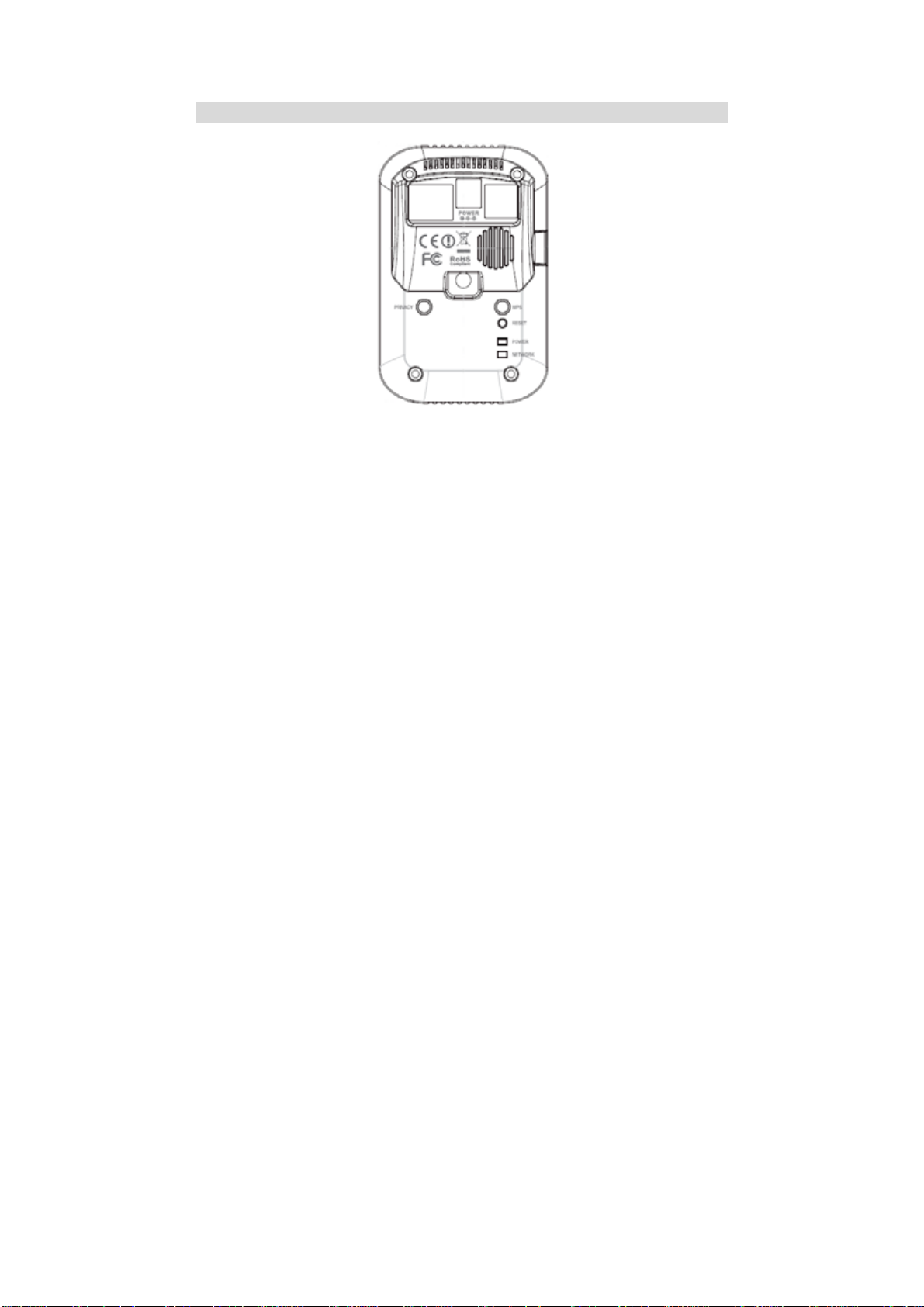
Rear - Network Camera
Figure 3: Rear Panel
LAN port
Power Input
Digital
Input/Output
Micro-SD Card slot
Privacy Button
WPS Button
Reset Button
Use a standard LAN cable to connect your Network Camera to a
10/100BaseT hub or switch.
Note:
• Plugging in the LAN cable will disable the Wireless interface.
Only 1 interface can be active at any time.
• The LAN cable should only be connected or disconnected when
the camera is powered OFF. Attaching or detaching the LAN
cable while the camera is powered on does NOT switch the
interface between wired and wireless.
Connect the supplied 12V power adapter here. Do not use other
power adapters; doing so may damage the camera.
The GPIO terminal block includes 1 input port and 1 output port.
Insert the SD card into the slot, if required.
On (Green) - The privacy mode is activated. User can not access to
the video/audio from the camera.
Off - The privacy mode is not in use. User can get access to the
video/audio from the camera.
Push the WPS button on the device and on your other wireless
device to perform WPS function that easily creates an encryptionsecured wireless connection automatically.
• WPS PBC Mode. When pressed and released (less then 3
seconds), the Network Camera will be in the WPS PBC mode
(Auto link mode).
• WPS Pin Code Mode. When pressed and held for over 3
seconds, the Network Camera will be in the WPS Pin Code.
mode.
This button is recessed; you need a pin or paper clip can be used to
depress it. It can be activated at any time the camera is in the
"ready" mode.
• Reset to manufacturer default valued and reboot. When
5
Page 9
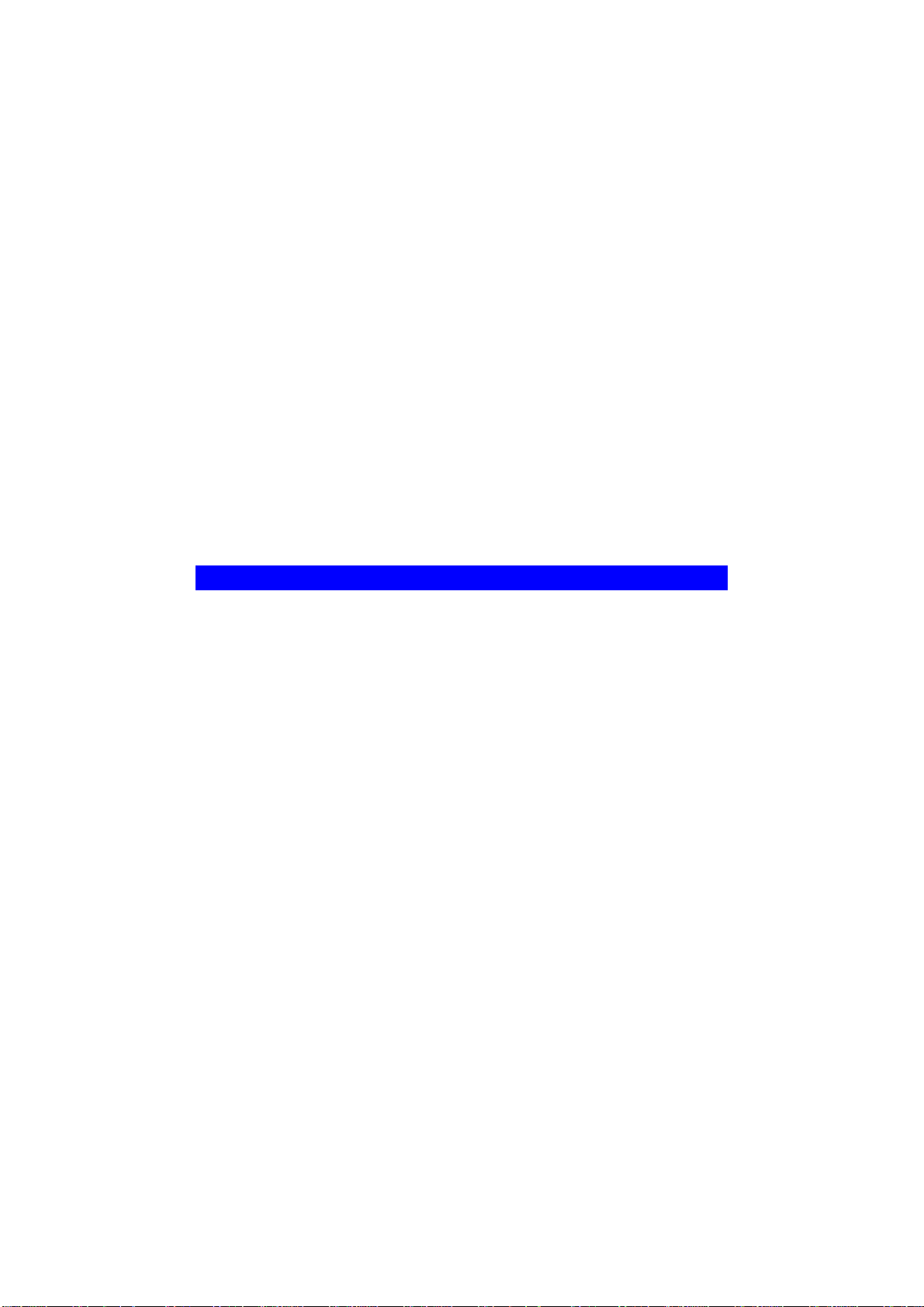
pressed and held over 10 seconds, the settings of Network
Camera will be set to their default values.
Note:
After this procedure is completed, the Power LED will blink three
times to confirm that the reset was completed successfully.
Power LED
(Green)
Network//WPS
LED
(Green, Amber)
On - Power on.
Off - No power.
Blinking - The Power LED will blink during start up. This will take
15 to 20 seconds.
On (Green) - Network (Wireless or LAN) connection is available.
Off - Wireless or LAN is not connected or camera is not
sending/receiving data.
Blinking (Green) - Data is being transmitted or received via the
LAN or Wireless connection.
On (Amber) - If the LED is on for 5 seconds, the WPS function is
failed.
Blinking (Amber) - WPS function is being processed.
Package Contents
The following items should be included: If any of these items are damaged or
missing, please contact your dealer immediately.
1. Network Camera
2. Camera Stand
3. Power adapter
4. Installation CD-ROM
5. Quick Installation Guide
6
Page 10
Chapter 2
Basic Setup
2
This Chapter provides details of installing and configuring the
Network Camera.
System Requirements
• To use the wired LAN interface, a standard 10/100BaseT hub or switch and
network cable is required.
• To use the Wireless interface on the wireless model, other Wireless devices
must be compliant with the IEEE802.11b, IEEE802.11g or IEEE 802.11n
specifications. All Wireless stations must use compatible settings.
The default Wireless settings are:
Mode: Infrastructure
SSID: ANY
Wireless Security: Disabled
Domain: USA
Channel No.: Auto
Installation - Network Camera
1. Assemble the Camera
On the Wireless Model, screw the supplied antenna to the mounting point on the
rear.
2. Connect the LAN Cable
Connect the Network Camera to a 10/100BaseT hub or switch, using a standard
LAN cable.
For this Model, it will disable the Wireless Interface. The
Wireless and LAN interfaces cannot be used simultaneously.
Using the LAN interface is recommended for initial
configuration. After the Wireless settings are correct, the
Wireless interface can be used.
The first time you connect to the camera, you should connect
the LAN cable and configure the Network Camera with
appropriate settings. Then you can unplug the LAN cable and
power off the camera. The Network Camera will be in wireless
interface when you power on the camera again.
7
Page 11

3. Power Up
Connect the supplied 12Vpower adapter to the Network Camera and power up.
Use only the power adapter provided. Using a different one may cause hardware
damage.
4. Check the LEDs
• The Power LED will turn on briefly, then start blinking. It will blink during
startup, which takes 15 to 20 seconds. After startup is completed, the Power
LED should remain ON.
• The Network LED should be ON.
For more information, refer to Physical Details - Network Camera in Chapter 1.
8
Page 12
Setup using the Windows Wizard
Initial setup should be performed using the supplied Windows-based setup Wizard.
This program can locate the Network Camera even if its IP address is invalid for
your network. You can then configure the Network Camera with appropriate TCP/IP
settings for your LAN.
Subsequent administration can be performed with your Web browser, as explained
in Chapter 5 - Web-based Management.
Setup Procedure
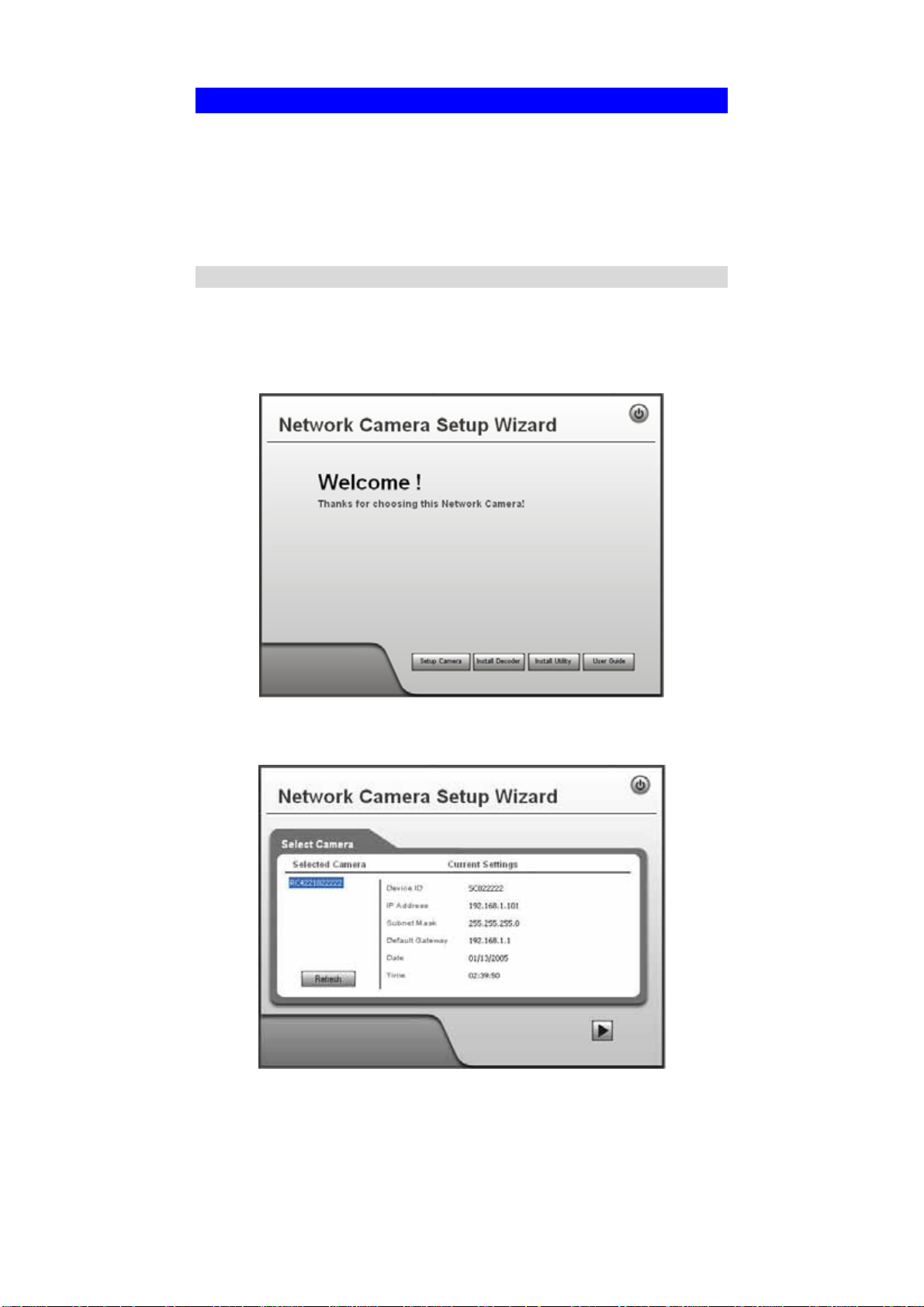
1. Insert the supplied CD-ROM into your drive. If the setup program does not start
automatically, run NetworkCamera.exe in the root folder.
• You will see the Welcome screen shown below.
• Click the Setup Camera button to start the setup Wizard
Figure 4: Welcome Screen
2. The next screen, shown below, will list all the Network Cameras on your LAN.
Figure 5: Camera List Screen
9
Page 13
• Select the desired Camera from the list on the left. The current settings for
the selected Camera will be displayed in the table on the right.
• Click Next to continue.
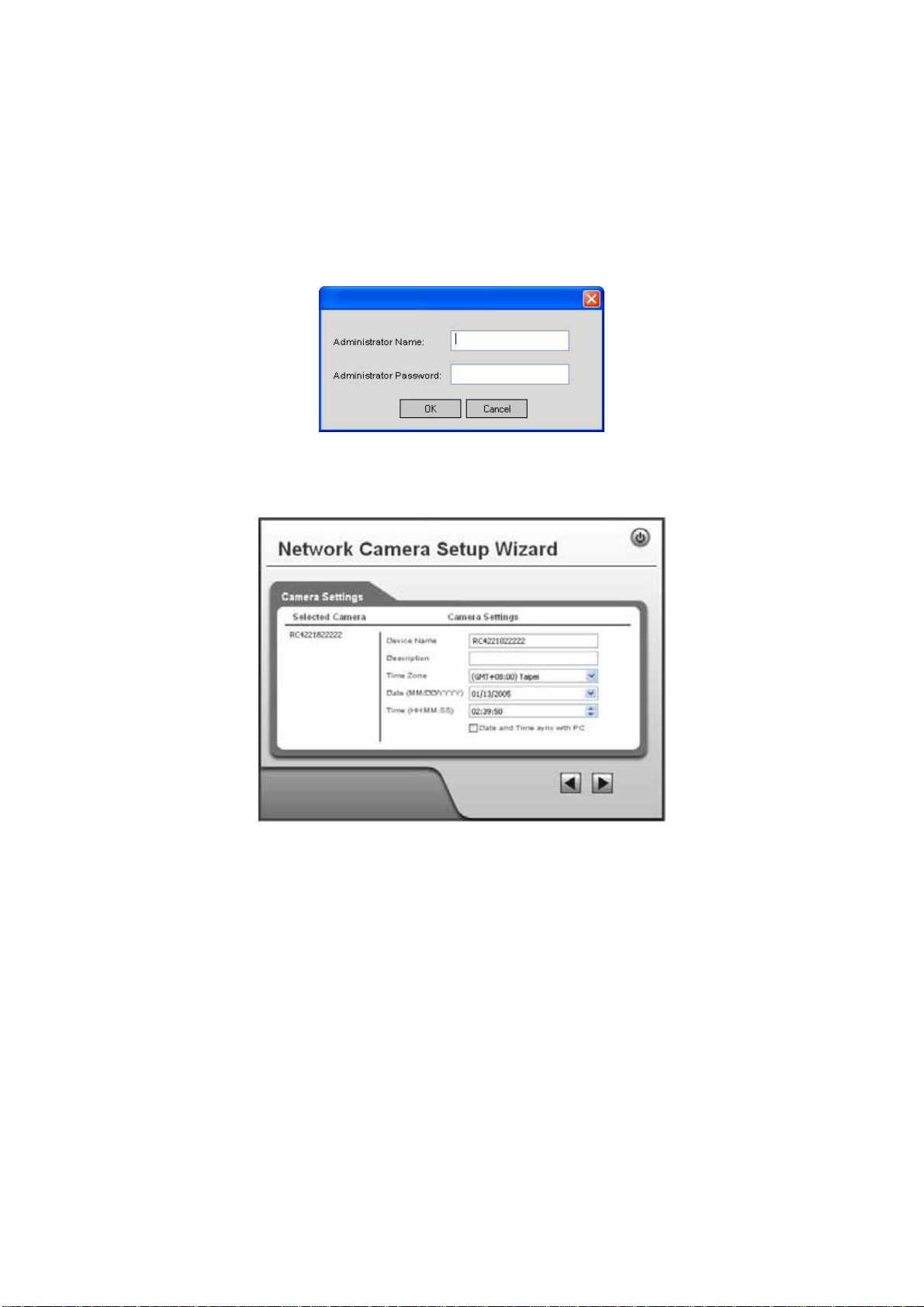
3. You will be prompted to enter the Administrator Nam e and Administrator
Password, as shown below.
• If using the default values, enter administrator for the name, and
leave the password blank.
• Otherwise, enter the Administrator Name and Administrator Password set
on the Maintenance screen.
Figure 6: Password Dialog
4. This screen allows you to enter a suitable Description, and set the correct Time
Zone, Date, and Time. Make any desired changes, then click Next to continue.
Figure 7: Camera Settings
5. On the following IP Address Settings screen, shown below, choose Fixed IP
Address, Dynamic IP Address or PPPoE.
10
Page 14

Figure 8: Fixed or Dynamic IP Selection
• Fixed IP Address is recommended, and can always be used.
• Dynamic IP Address can only be used if your LAN has a DCHP Server.
• PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) is the most common login method, widely
used with DSL modems.
Click Next to continue.
6. If you chose Fixed IP Address, the following TCP/IP Settings screen will be
displayed.
Figure 9: TCP/IP Settings
• Enter an unused IP Address from within the address range used on your
LAN.
• The Subnet Mask and Default Gateway fields must match the values used
by PCs on your LAN.
• The Primary DNS address is required in order to use the E-mail alert or
Dynamic DNS features. Enter the DNS (Domain Name Server) address
recommended by your ISP.
11
Page 15

• The Secondary DNS is optional. If provided, it will be used if the Primary
DNS is unavailable.
Click Next to continue.
7. If you chose PPPoE, the following PPPoE Settings screen will be displayed.
Figure 10: PPPoE Settings Screen
• Enter the User Name provided by your ISP.
• Enter the Password for the user name above.
Click Next.
8. The next screen, shown below, displays all details of the Network Camera.
• Click Next if the settings are correct
• Click Back to modify any incorrect values.
Figure 11: Save Settings
9. Click OK to confirm that you want to save the new settings. If you want to
cancel your changes, click Cancel.
12
Page 16
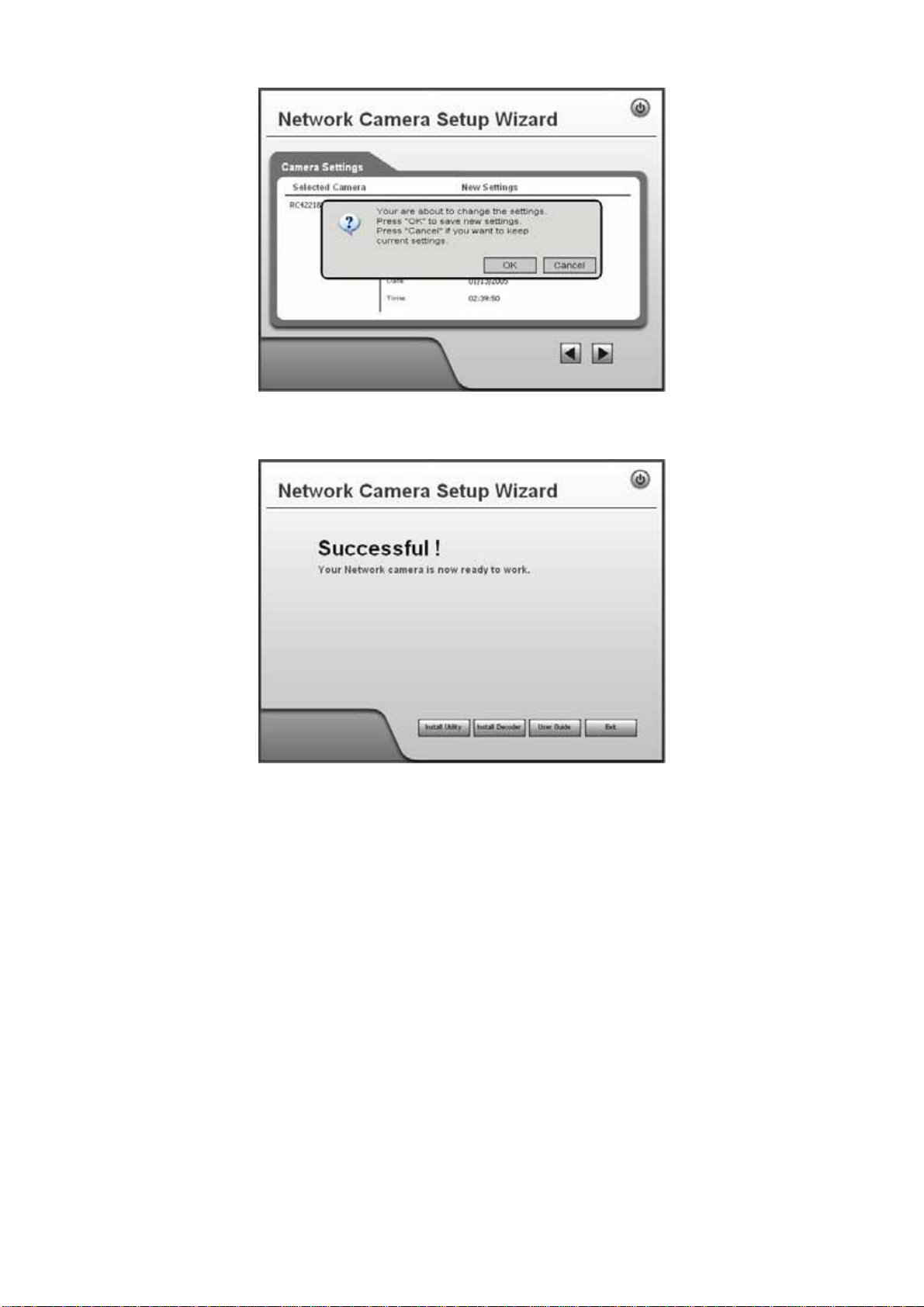
Figure 12: Confirm Screen
10. After clicking OK, you will see the screen below.
Figure 13: Final Screen
Clicking the Install Utility button will install the Viewing/Recording utility
described in Chapter 6 - Windows Viewing/Recording Utility.
11. Click Exit to end the Wizard.
Setup is now complete.
13
Page 17
Chapter 3
Viewing Live Video
3
This Chapter provides basic information about viewing live video.
Overview
After finishing setup via the Windows-based Wizard, all LAN users can view live
video using Internet Explorer on Windows.
This Chapter has details of viewing live video using Internet Explorer.
But many other powerful features and options are available:
• To view multiple cameras simultaneously, or record video (either interactively
or by schedule), you should install the Windows Viewing/Recording utility.
Refer to Chapter 6 - Windows Viewing/Recording Utility for details on
installing and using this program.
• The camera administrator can also adjust the Video Stream, and restrict access
to the video stream to known users by requiring viewers to supply a username
and password. See Chapter 4 - Advanced Viewing Setup for details.
• To make Live Video from the camera available via the Internet, your Internet
Gateway or Router must be configured correctly. See Making Video available
from the Internet in Chapter 4 - Advanced Viewing Setup for details.
Requirements
To view the live video stream generated by the Network Camera, you need to meet
the following requirements:
• Windows XP, 32-bit Windows Vista/Windows 7.
• Internet Explorer 6 or later, Firefox 3.0 or later.
Connecting to a Camera on your LAN
To establish a connection from your PC to the Network Camera:
1. Use the Windows utility to get the IP address of the Network Camera.
2. Start Internet Explorer.
3. In the Address box, enter "HTTP://" and the IP Address of the Network Camera.
4. When you connect, the following screen will be displayed.
14
Page 18
Figure 14: Home Screen
5. Click View Video.
6. If the Administrator has restricted access to known users, you will then be
prompted for a username and password.
Enter the name and password assigned to you by the Network Camera
administrator.
7. The first time you connect to the camera, you will be prompted to install an
ActiveX component (OCX or CAB file), as in the example below.
You must install this ActiveX component (OCX or CAB file) in order to
view the Video stream in Internet Explorer.
Click the "Yes" button to install the ActiveX component.
Figure 15: ActiveX OCX Prompt
8. Video will start playing automatically. There may be a delay of a few seconds
while the video stream is buffered.
15
Page 19

Connecting to a Camera via the Internet
You can NOT connect to a camera via the Internet unless the camera
Administrator has configured both the camera and the Internet
Gateway/Router used by the camera.
See Making Video available from the Internet in Chapter 4 - Advanced Viewing
Setup for details of the required configuration.
Also, you need a broadband Internet connection to view video effectively. Dial-up
connections are NOT supported.
To establish a connection from your PC to the Network Camera via the Internet:
1. Obtain the following information from the Administrator of the camera you
wish to connect to:
• Internet IP Address or Domain Name of the camera.
• Port number for HTTP connections.
• Login (username, password) if required.
2. Start Internet Explorer.
3. In the Address box, enter the following:
HTTP://Internet_Address:port_number
Where Internet_Address is the Internet IP address or Domain Name of
the camera, and port_number is the port number used for HTTP (Web)
connections to the camera.
Examples using an IP address:
HTTP://203.70.212.52:1024
Where the Internet IP address is 203.70.212.52 and the HTTP port number
is 1024.
Example using a Domain Name:
HTTP://mycamera.dyndns.tv:1024
Where the Domain name (using DDNS in this example) is
mycamera.dyndns.tv and the HTTP port number is 1024.
16
Page 20
4. When you connect, the following screen will be displayed.
Figure 16: Home Screen
5. Click View Video.
6. If the Administrator has restricted access to known users, you will then be
prompted for a username and password.
Enter the name and password assigned to you by the Network Camera
administrator.
7. The first time you connect to the camera, you will be prompted to install an
ActiveX component (OCX or CAB file), as in the example below.
You must install this ActiveX component (OCX or CAB file) in order to
view the Video stream in Internet Explorer.
Click the "Yes" button to install the ActiveX component.
Figure 17: ActiveX OCX Prompt
8. Video will start playing automatically. There may be a delay of a few seconds
while the video stream is buffered.
17
Page 21
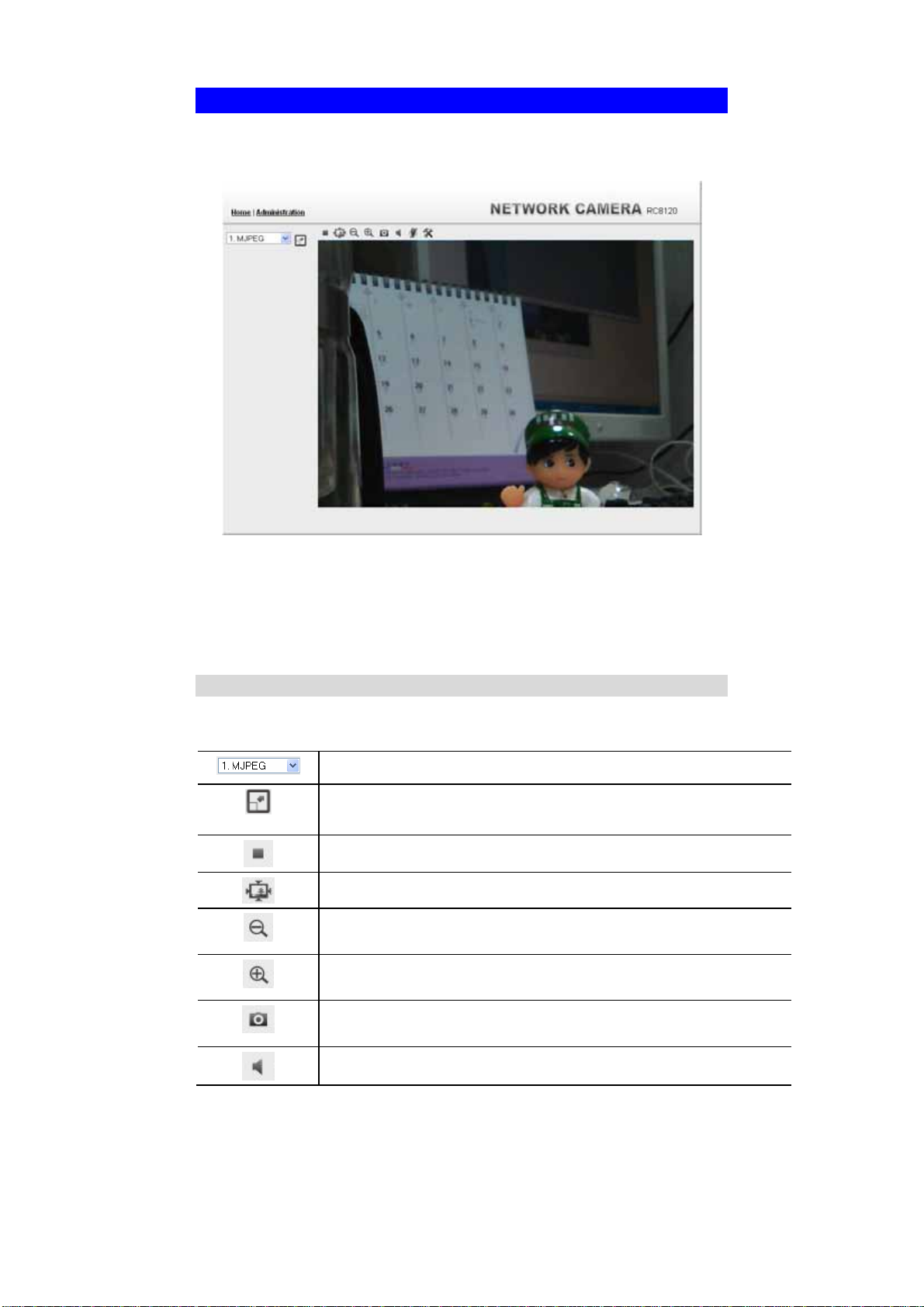
Viewing Live Video
After installing the ActiveX component, you will be able to view the live video
stream in its own window, as shown below.
Figure 18: View Video Screen
There are a number of options available on this screen, accessed by select list, button
or icon. See the table below for details.
Note: The options can only be configured while using IE browser. Other browsers
can just view the video rather than configuration.
General Options
These options are always available, regardless of the type of camera you are
connected to.
Streaming. Use this drop-down list to select the desired streaming.
Full Size. When using high-resolution mode (1280*960), click this
button to see the full size of the image.
Use this icon to start/stop viewing.
Use this icon to make the image back to original size.
Zoom Out. A digital zoom out feature is available. To zoom out the
window, click this icon.
Zoom In. A digital zoom in feature is available. To zoom in the
window, click this icon.
Snapshot. Click this to take a single JPEG "snapshot" image of the
current video.
Speaker On/Off. Use this button to turn the PC's speaker on or off.
18
Page 22

off.
Setup. Select the desired folder to save the file.
Microphone On/Off. Use this button to toggle the microphone on or
19
Page 23

Chapter 4
Advanced Viewing Setup
4
This Chapter provides information about the optional settings and
features for viewing video via the Network Camera. This Chapter is
for the Camera Administrator only.
Introduction
This chapter describes some additional settings and options for viewing live Video:
• Adjusting the video image
• Controlling user access to the live video stream
• Making video available from the Internet
• Using the Motion Detection feature
Adjusting the Video Image
If necessary, the Network Camera Administrator can adjust the Video image.
To Adjust the Video Image:
1. Connect to the Web-based interface of the Network Camera. (See Chapter 5 -
Web-based Management for details.)
2. Select Administration, then Streamings. You will see a screen like the example
below.
Figure 19: Streamings Screen
20
Page 24
3. Make the required adjustments, as explained below, and save your changes.
Video Mode
Select either "High Resolution Mode" or "High Frame Rate Mode".
Options
Default Streaming
Select the default channel for streaming from the drop-down list.
Channel
Streaming 1 Settings (MJPEG)
Video Format
Resolution
This displays the default format.
Select the desired video resolution format. The default resolution is
set to 1280*960.
Fixed Video
Select the desired option. The default fix quality is set to Normal.
Quality
Max. Frame Rate
Select the desired Maximum frame rate for the video stream.
The default value is 15.
Streaming 2/3 Settings
Video Format
Resolution
Video Quality
Control
GOV Length
Max. Frame Rate
Select the desired format from the list.
Select the desired video resolution format.
• Constant Bit Rate: Select the desired bit rate.
• Fixed Quality: Select the desired option.
Enter the desired value between 1 and 150.
Select the desired Maximum frame rate for the video stream.
The default value is 15.
User Defined URI
You may enter the URI up to 32 characters long for accessing the
live video from camera through cell phone connection.
21
Page 25
Controlling User Access to the Video Stream
By default, anyone can connect to the Network Camera and view live Video at any
time.
If desired, you can limit access to scheduled times, and also restrict access to known
users.
To Control User Access to Live Video:
1. Connect to the Web-based interface of the Network Camera. (See Chapter 5 -
Web-based Management for details.)
2. Select Administration, then Video Access.
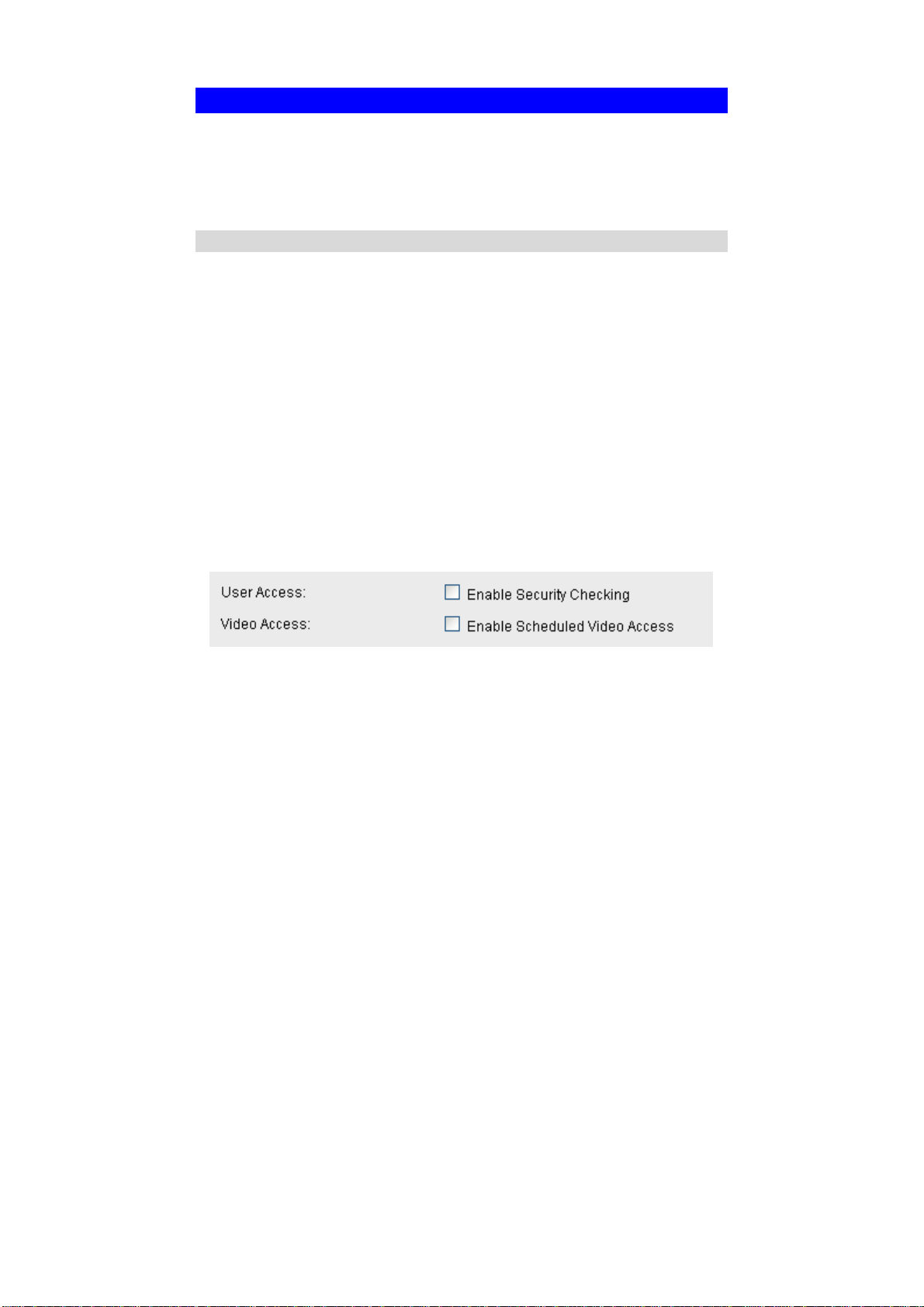
3. Set the desired options for Access.
Access
Select the desired option as required:
• If the User Access is enabled, users will be prompted for a username and
password when they connect to the camera for viewing video.
• When Video Access is enabled, viewing video is only available during the
scheduled periods, and unavailable at other times. If this option is selected, you
need to define a schedule; otherwise it is always disabled.
However, viewing video is still possible by logging in as the Administrator.
Figure 20: Controlling User Access
See Chapter 5 - Web-based Management for further details about using the Video
Access and User Database screens.
22
Page 26
Making Video available from the Internet
If your LAN is connected to the Internet, typically by a Broadband Gateway/Router
and Broadband modem, you can make the Network Camera available via the
Internet. You will need to configure your Router or Gateway to allow connections
from the Internet to the camera.
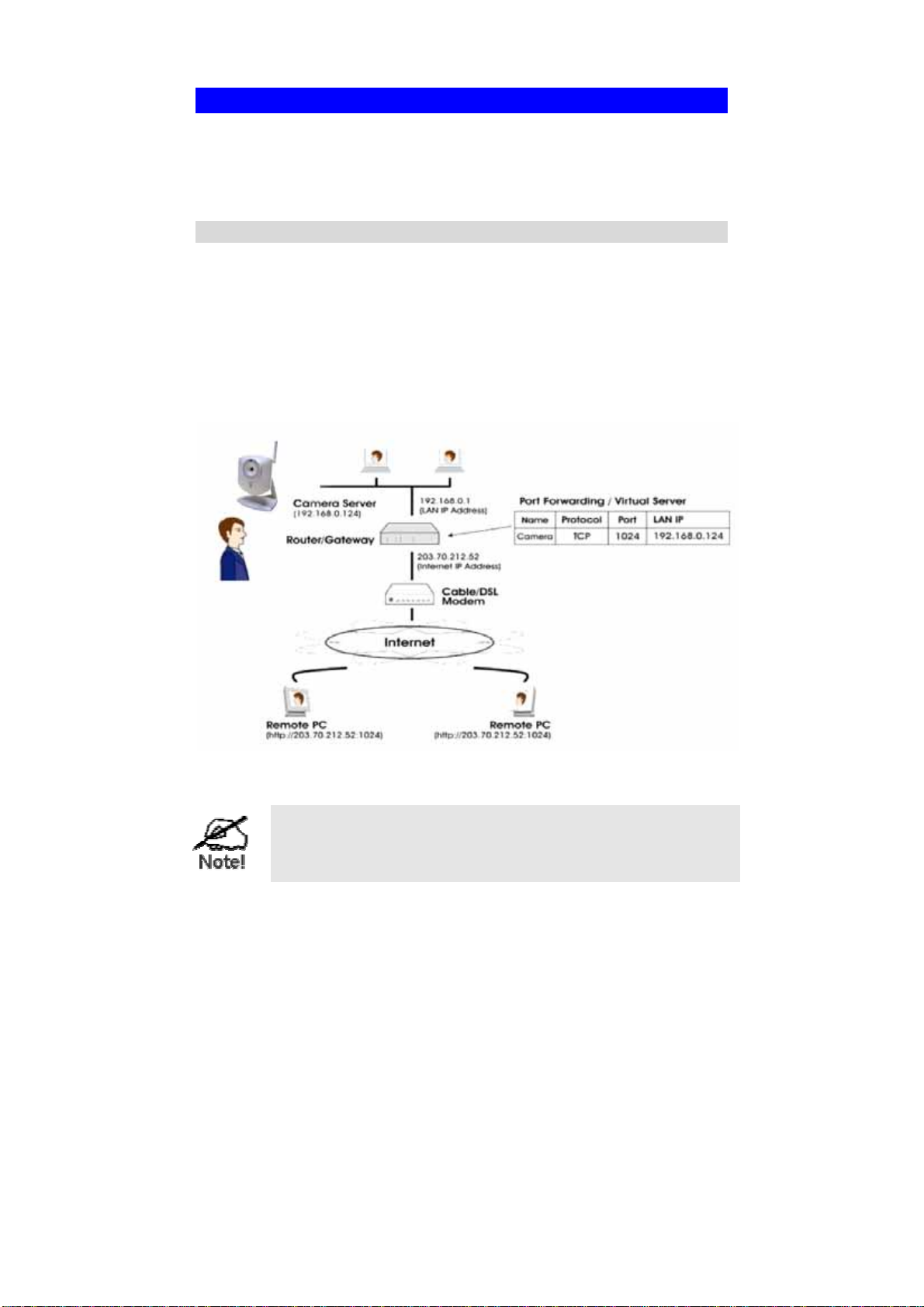
Router/Gateway Setup
Your Router or Gateway must be configured to pass incoming TCP (HTTP)
connections (from Internet Viewers) to the Network Camera. The Router/Gateway
uses the Port Number to determine which incoming connections are intended for the
Network Camera.
This feature is normally called Port Forwarding or Virtual Servers, and is illustrated
below. The Port Forwarding/Virtual Server entry tells the Router/Gateway that
incoming TCP connections on port 1024 should be passed to the Network Camera.
If necessary, check the user manual for your Router/Gateway for further details.
Figure 21: Connecting via the Internet
The "Port" for the Port Forwarding / Virtual Server entry
above is the " Secondary Port" number specified on the
Network screen of the Network Camera.
23
Page 27
Network Camera Setup
The Network Camera configuration does NOT have be changed, unless:
• You wish to change the port number from the default value.
• You wish to use the DDNS (Dynamic DNS) feature of the Network Camera.
HTTPS Port Configuration
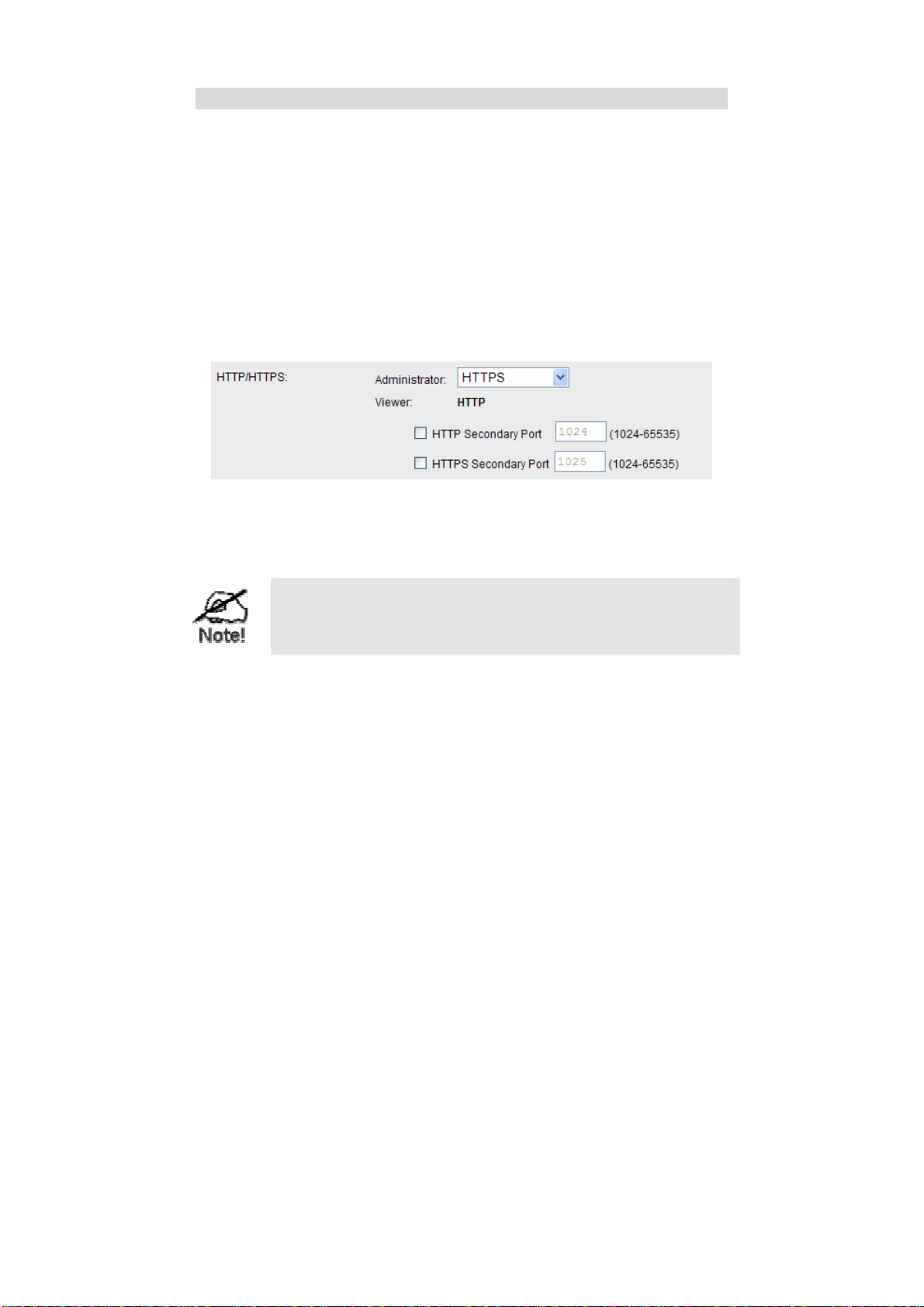
Normally, HTTP (Web) connections use port 80. Since the Network Camera uses
HTTP, but port 80 is likely to be used by a Web Server, you can use a different port
for the Network Camera. This port is called the Secondary Port.
The default HTTP/HTTPS Secondary Port is 1024/1025. If you prefer to use a
different port number, you can specify the port number on the Network Camera's
Network screen, as shown below.
Figure 22: Network Screen
See Chapter 5 - Web-based Management for further details on using the Network
screen.
Viewers need to know this port number in order to connect
and view live Video, so you must inform viewers of the
correct port number.
DDNS (Dynamic DNS)
Many internet connections use a "Dynamic IP address", where the Internet IP
address is allocated whenever the Internet connection is established.
This means that other Internet users don't know the IP address, so can't establish a
connection.
DDNS is designed to solve this problem, by allowing users to connect to your LAN
using a domain name, rather than an IP address.
To use DDNS:
1. Register for the DDNS service with a supported DDNS service provider. You
can then apply for, and be allocated, a Domain Name.
2. Enter and save the correct DDNS settings on the DDNS screen of the Network
Camera.
3. Both Router and Camera should use the same port number for DDNS service.
24
Page 28
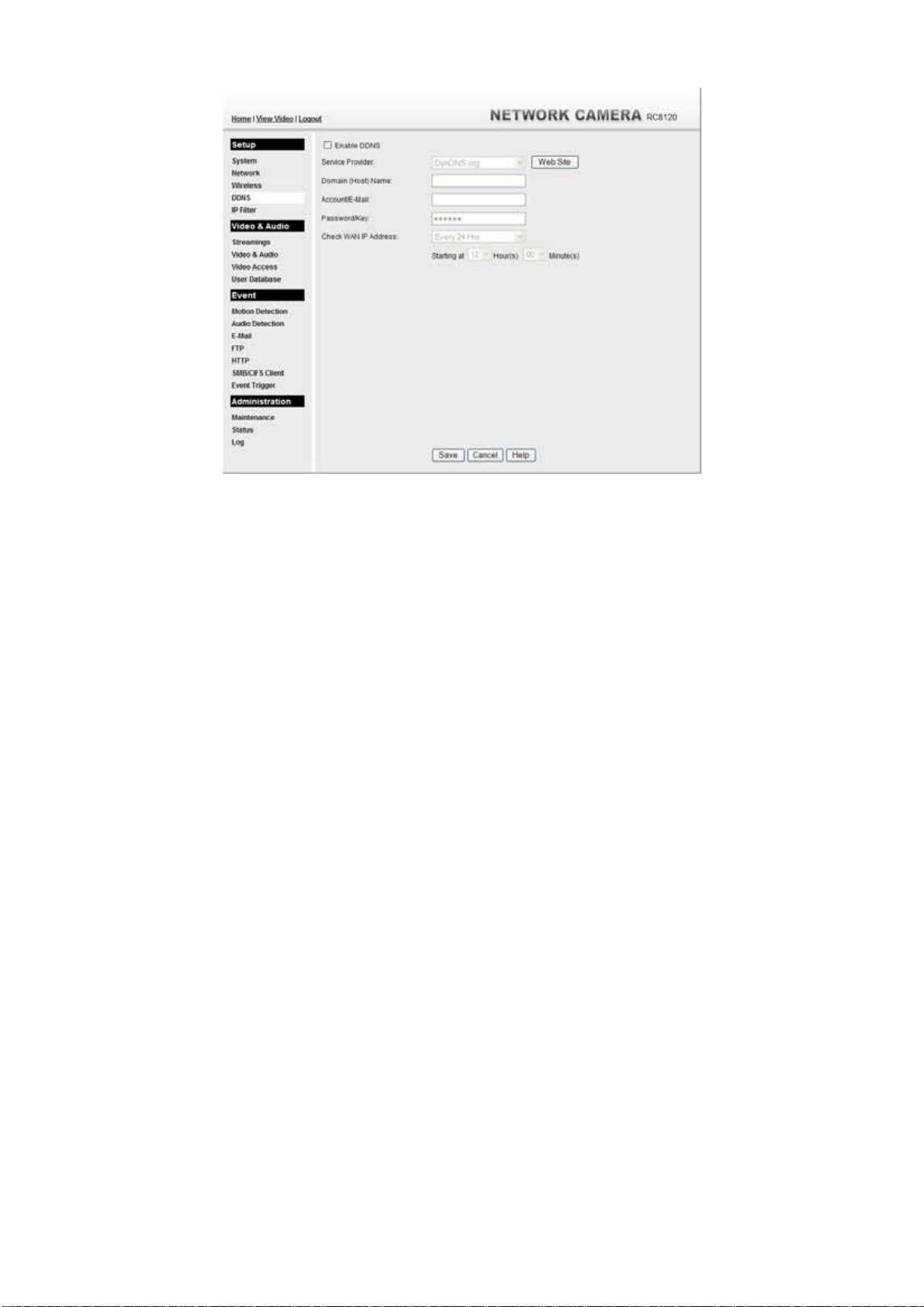
Figure 23: DDNS Screen
4. Operation is then automatic:
• The Network Camera will automatically contact the DDNS server
whenever it detects that the Internet IP address has changed, and inform the
DDNS server of the new IP address.
• Internet users can then connect to the camera using the Domain Name
allocated by the DDNS service provider.
Example: HTTP://mycamera.dyndns.tv:1024
mycamera.dyndns.tv is domain host name. 1024 is the port number.
25
Page 29
Viewing Live Video via the Internet
Clients (viewers) will also need a broadband connection; dial-up connections are
NOT recommended.
Viewing Live Video Using your Web Browser
If using your Web browser, you need to know the Internet IP address (or the Domain
name) of the camera's Router/Gateway, and the correct port number.
Enter the Internet address of the Router/Gateway, and its port number, in the
Address (or Location) field of your Browser.
Example - IP address:
HTTP://203.70.212.52:1024
Where the Router/Gateway's Internet IP address is 203.70.212.52 and the
"Secondary Port" number on the Network Camera is 1024.
Example - Domain Name:
HTTP://mycamera.dyndns.tv:1024
Where the Router/Gateway's Domain name is mycamera.dyndns.tv and the
"Secondary Port" number on the Network Camera is 1024.
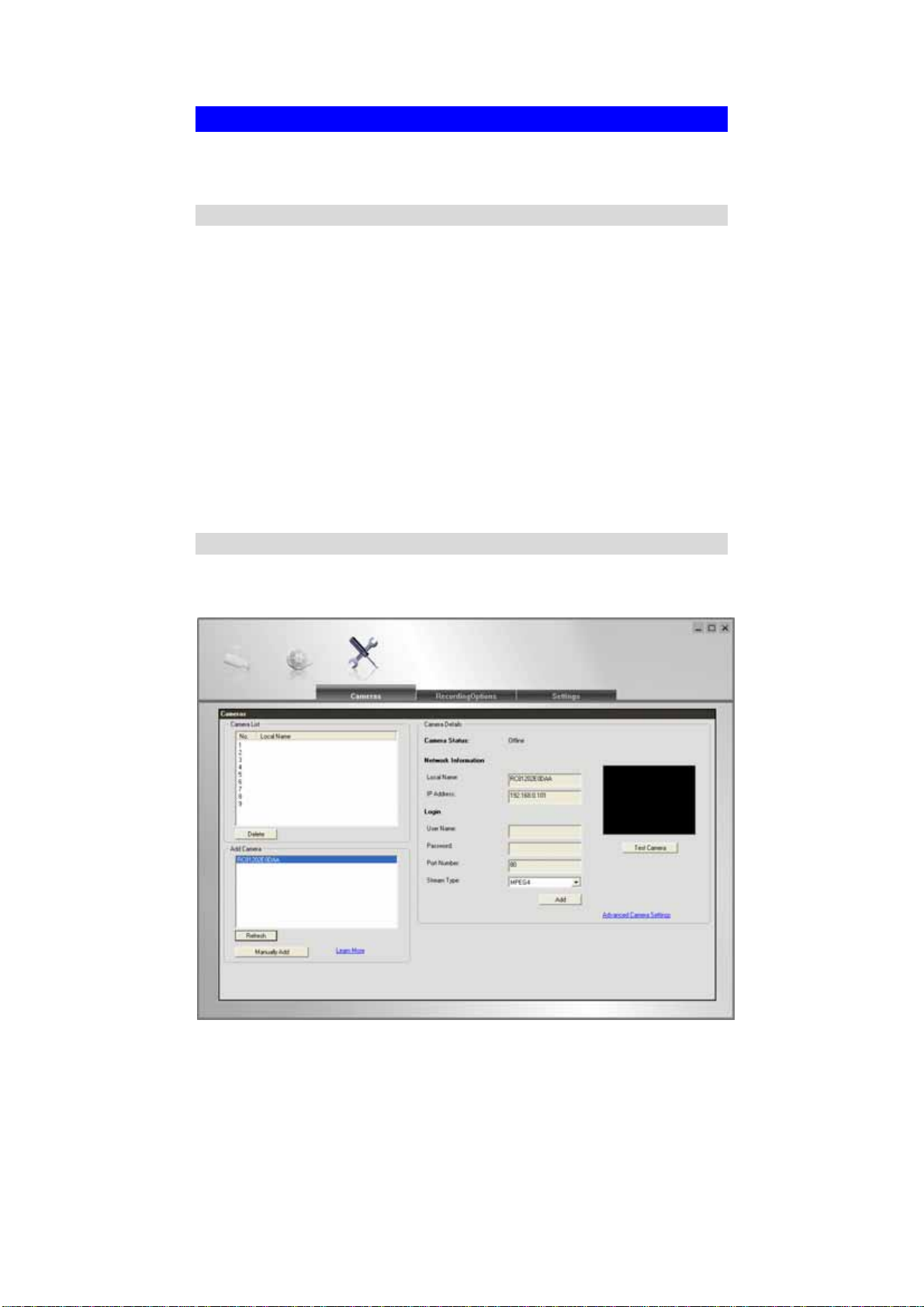
Viewing Live Video with the Viewing/Recording Utility
If using the Windows Viewing/Recording Utility, the details of the Network Camera
must be entered on the Setup screen.
Figure 24: Add Camera from LAN
See Chapter 6 - Window Viewing/Recording Utility for full details on using the
Windows Viewing/Recording utility.
26
Page 30
Motion Detection Alerts
The Motion Detection feature can generate an Alert when motion is detected.
The Network Camera will compare consecutive frames to detect changes caused by
the movement of large objects.
But the motion detector can also be triggered by:
• Sudden changes in the level of available light
• Movement of the camera itself.
Try to avoid these situations. The motion detection feature works best in locations
where there is good steady illumination, and the camera is mounted securely. It
cannot be used outdoors due to the sensitivity of the CMOS sensor.
Note: The Motion Detection settings can only be configured while using IE browser.
To Use Motion Detection Alerts
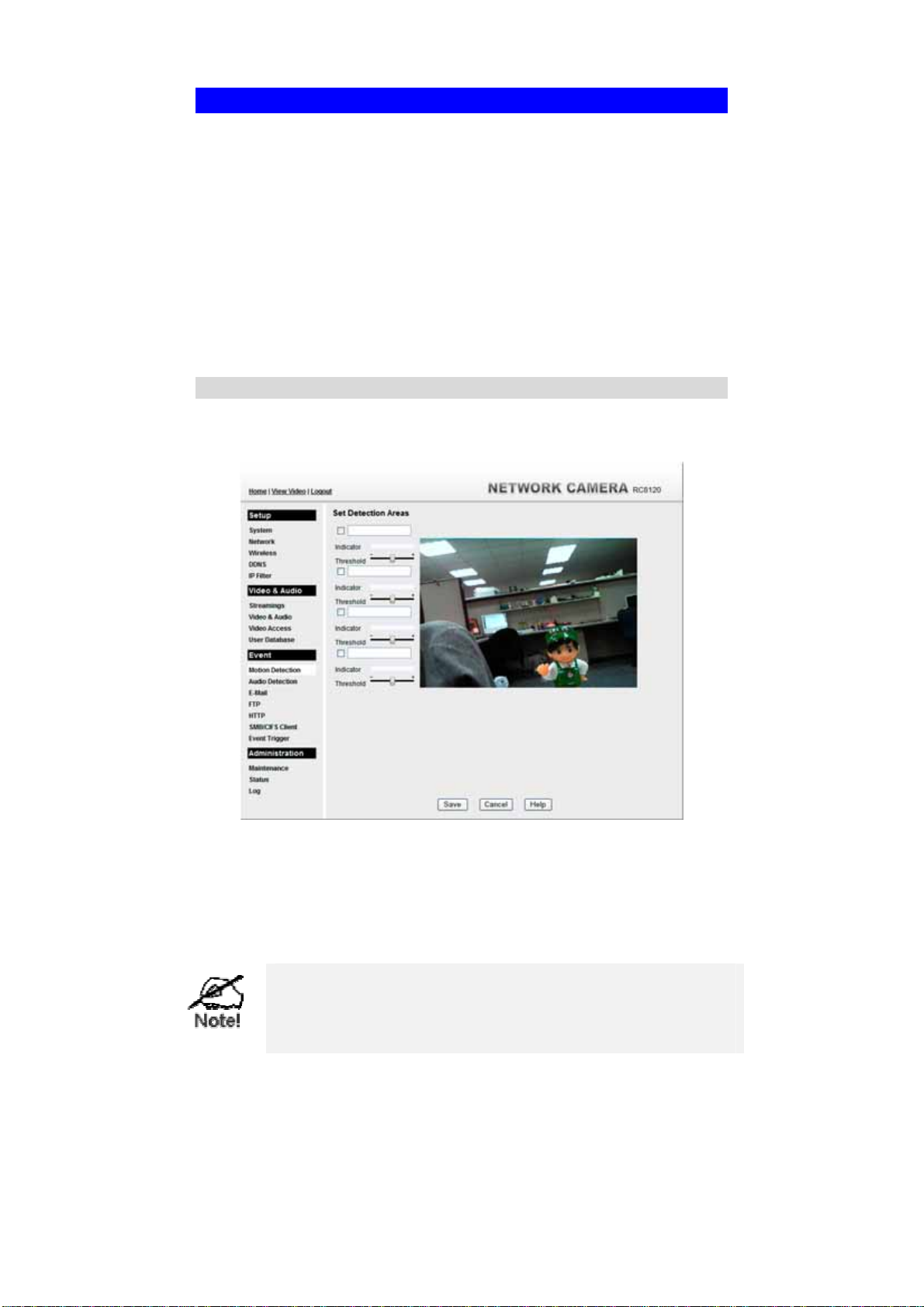
Using the Web-based interface on the Network Camera, select the Motion Detection
screen, then configure this screen as described below.
Figure 25: Motion Detection
1. Enable the Motion Detection feature.
2. Set the area or areas of the video image to be examined for movement. You can
define up to 4 areas, and set the motion threshold individually for each area.
3. If using a schedule, define the desired schedule in Event Trigger screen.
4. Save your changes.
If the Motion Detection feature is enabled, but the related
options in the Event Trigger screen are not enabled, then the
only action when motion is detected is to log this event in the
system log.
27
Page 31

Chapter 5
Web-based
5
Management
This Chapter provides Setup details of the Network Camera’s Webbased Interface. This Chapter is for the Camera Administrator only.
Introduction
The Network Camera can be configured using your Web Browser. The Network
Camera must have an IP address which is compatible with your PC.
The recommended method to ensure this is to use the supplied Windows-based
Wizard, as described in Chapter 2 - Basic Setup.
Connecting to Network Camera
• If using only your Web Browser, use the following procedure to establish a
connection from your PC to the Network Camera:
• Once connected, you can add the Network Camera to your Browser's Favorites
or Bookmarks.
Connecting using your Web Browser
1. Use the Windows utility to get the IP address of the Network Camera.
2. Start your WEB browser.
3. In the Address box, enter "HTTP://" and the IP Address of the Network Camera.
4. You will then be prompted for a username and password.
• If using the default values, enter administrator for the name, and
leave the password blank.
• Otherwise, enter the Administrator ID and Administrator Password set on
the Maintenance screen.
28
Page 32

Welcome Screen
When you connect, the following screen will be displayed.
Figure 26: Welcome Screen
The menu options available from this screen are:
• View Video - View live Video using your Web Browser. See Chapter 3 -
Viewing Live Video for details.
• Administration - Access the Administration menu.
29
Page 33

Administration Menu
Clicking on Administration on the menu provides access to all the settings for the
Network Camera.
The Administration menu contains the following options:
Setup
• System
• Network
• Wireless
• DDNS
• IP Filter
• I/O Port
Video & Audio
• Streaming
• Video & Audio
• Video Access
• User Database
Event
• Motion Detection
• Audio Detection
• E-Mail
• FTP
• HTTP
• SD Card
• SMB/CIFS Client
• Event Trigger
Administration
• Maintenance
• Status
• Log
30
Page 34

System Screen
After clicking Administration on the main menu, or selecting System on the
Administration menu, you will see a screen like the example below.
Data - System Screen
System Settings
Device ID
Camera Name
Description
Date & Time
Date Format
Current
Date & Time
This displays the ID for the Network Camera.
Enter the desired name for the Network Camera.
This field is used for entering a description, such as the location of the
Network Camera.
Select the desired date format, it will also be used to display the date
and time as an overlay on the video image.
The abbreviations used to predefine the date formats are list as follows:
This displays the current date and time on the camera.
If it's not correct, click the Change button to modify the date/time
settings. This button will open a sub-screen where you have 2 options:
• Set the camera's date and time to match your PC.
• Enter the correct date and time.
Figure 27: System Screen
• YYYY-MM-DD = Year-Month-Day, e.g. 2006-01-31
• MM/DD/YYYY = Month/Day/Year, e.g. 01/31/2006
• DD/MM/YYYY = Day/Month/Year, e.g. 31/01/2006
31
Page 35

Time Zone
Network Time
Protocol
NTP Server
Address
Update
LED Operation
Privacy Button
Choose the Time Zone for your location from the drop-down list.
If your location is currently using Daylight Saving, please enable the
Adjust for daylight saving checkbox.
Enable or disable the Time Server feature as required.
If Enabled, the Network Camera will contact a Network Time Server at
regular intervals and update its internal timer.
Enter the address for the desired NTP server.
The Schedule determines how often the Network Camera contacts the
NTP Server.
Select the desired options.
Enable this if you want to use this function.
If Enabled, click the Privacy button will stop uploading the stream
without turning the camera off. Click the button one more time to
continue uploading. The default is Enabled.
32
Page 36

Network Screen
This screen is displayed when the Network option is clicked.
Figure 28: Network Screen
33
Page 37

Data - Network Screen
Network
Internet Connection
Type
Obtain DNS server
address
automatically
There are 3 connection types:
• Obtain Address Automatically (DHCP): If selected, the
Network Camera will obtain its IP address and related
information from a DHCP Server. Only select this option if
your LAN has a DHCP Server.
• Static IP Address: If selected, you must assign the following
data to the Network Camera.
• IP Address - Enter an unused IP address from the address
range used on your LAN.
• Subnet Mask - Use the same value as PCs on your LAN.
• Default Gateway - Use the same value as PCs on your
LAN.
• PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet): This is the most common login
method, widely used with DSL modems. Normally, your ISP
will have provided some software to connect and login. This
software is no longer required, and should not be used.
• Username - The user name (or account name) provided by
your ISP.
• Password - Enter the password for the login name above.
If selected, the Network Camera will use the DNS address or
addresses provided by the DHPC server.
This option is only available if the IP address setting is Obtain an
IP address Automatically.
Use the following
DNS server address
WINS Address
Primary DNS server - Use the same value as PCs on your LAN.
Normally, your ISP will provide this address.
Secondary DNS server - This is optional. If entered, this DNS will
be used if the Primary DNS does not respond.
There are 2 options:
• Obtain WINS address automatically - If selected, the
Network Camera will obtain its IP address from DHCP server.
• Use the following WINS address - Enter the IP address of
your WINS server.
34
Page 38

HTTP/HTTPS
RTP/RTSP
This sets the port number for HTTP/HTTPS connections to the
Camera, whether for administration or viewing video.
The HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) is used for the standard
of transferring files (text, graphic images and other multimedia
files) on the World Wide Web. The default HTTP port is 1024.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) can provide more
secure communication with the SSL/TLS protocol, which support
data encryption to HTTP clients and servers. The default HTTPS
port is 1025.
The Secondary port can be used for DDNS, other service and when
more than 2 cameras are in use.
If enabled, you can connect using either port 80 or the Secondary
port. You must enter the Secondary port number (between 1024 to
65535) in the field provided.
Note that when using a port number which is not 80, you must
specify the port number in the URL. For example, if the Camera's
IP address was 192.168.1.100 and the Secondary port was 1024,
you would specify the URL for the Camera as follows:
http://192.168.1.100:1024
The RTSP (Real Time Streaming Protocol), a standard for
connected client(s) to control streaming data (MPEG-4) over the
World Wide Web. Enter the RTSP Port number (between 1024 and
65535) in the field provided. The default RTSP Port is 554.
Multicast RTP/RTSP
Enable Multicast
Video Address
Video Port
Audio Address
Audio Port
Time to Live
UPnP
Enable Discovery
The RTP (Real Time Transport Protocol), an Internet protocol for
transmitting real-time data such as audio and video.
Max RTP Data Packet field will let users limit the size of the file.
Enter the desired value between 400 and 1400.
Note: RTSP and RTP settings are for cell phone only.
Enable the feature as required.
Enter the address of video.
Enter the desired value (between 1024 to 65534) in the field
provided. The number you entered must be even values.
Enter the address of the audio.
Enter the desired value (between 1024 to 65534) in the field
provided. The number you entered must be even values.
Enter the desired length of time, if the packets fail to be delivered
to their destination within. The Time to Live you entered must be
in-between 1 to 255.
If enabled, the Network Camera will broadcast its availability
through UPnP. UPnP compatible systems such as Windows XP will
then be able to detect the presence of the Network Camera.
35
Page 39

Enable Traversal
Bonjour
Enable Bonjour
Service
QoS
Enable QoS Mode
DSCP
If enabled, HTTP connections (from your Web Browser or the
Viewer and Recorder utility) can use secondary port instead of port
80 (the standard HTTP port) to access the camera.
If enabled, the Network Camera can be accessed through a
"Bonjour" enabled browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer
(with a Bonjour plug-in) or Safari browser. You can also find other
Bonjour-enabled devices on your network.
If enabled, the throughput level (for Video and Audio) is
guaranteed through QoS (Quality of Service).
Enter the desired value of Differentiated Services Code Point
(DSCP). The value must be between 0 and 63.
36
Page 40

Wireless Screen
This screen is displayed when the Wireless menu option is clicked.
Figure 29: Wireless Screen
Data - Wireless Screen
Wireless Network
Site Survey
WSC PIN Code
Network Type
SSID
Domain
Click the "Site Survey" button and select from a list of available
APs.
It displays the WSC PIN code number for the camera.
This determines the type of wireless communication used by the
Network Camera.
• If you have an Access Point, select Infrastructure.
• Otherwise, select Ad-hoc.
This must match the value used by other devices on your wireless
LAN. The Default is ANY.
Note! The SSID is case sensitive.
Select your region from the drop-down list.
37
Page 41

Channel No.
Security
Security System
WEP
Authentication Type
• In Infrastructure mode, this setting is ignored. The Network
Camera will use the Channel set on the Access Point.
• For Ad-hoc mode, select the Channel you wish to use on your
Network Camera. Other Wireless stations should use the same
setting.
• If you experience interference (shown by lost connections
and/or slow data transfers) you may need to experiment with
different channels to see which one is the best.
Select the desired option, and then enter the settings for the selected
method:
• Disabled - No security is used. Anyone using the correct SSID
can connect to your network. This is default.
• WEP - The 802.11b standard. Data is encrypted before
transmission, but the encryption system is not very strong.
• WPA/WPA2 Personal - Like WEP, data is encrypted before
transmission. WPA is more secure than WEP, and should be
used if possible. WPA Personal is the version of WPA which
does NOT require a Radius Server on your LAN.
Normally this can be left at the default value of "Automatic." If that
fails, select the appropriate value - "Open System" or "Shared
Key." Check your wireless card's documentation to see what
method to use.
Note: In Infrastructure mode, either setting will normally work,
since most Access Points can use both methods.
WEP Encryption
Passphrase
WEP Keys
Select the WEP Encryption level:
• 64 Bit Keys (10 Hex chars)
• 128 Bit Keys (26 Hex chars)
• 64 Bit Keys (5 ASCII chars)
• 128 Bit Keys (13 ASCII chars)
Enter a word or group of printable characters in the Passphrase box
and click the "Generate Key" button to automatically configure the
WEP Key(s). If encryption strength is set to 64-bit, then each of the
four key fields will be populated with key values. If encryption
strength is set to 128-bit, then only the selected WEP key field will
be given a key value.
• Use the radio buttons to select the default key.
• Enter the key value you wish to use. Other stations must have
the same key values.
• Keys must be entered in Hex. Hex characters are the digits (0 ~
9) and the letters A ~ F.
• Click Clear Keys to set the Keys to be blank.
38
Page 42

WPA/WPA2 Personal
Shared Key
Enter the key value. Data is encrypted using a key derived from the
network key. Other Wireless Stations must use the same network
key. The PSK must be from 8 to 63 characters or 64 hex characters
in length.
39
Page 43

DDNS Screen
Many Internet connections use a "Dynamic IP address", where the Internet IP
address is allocated whenever the Internet connection is established.
This means that other Internet users don't know the IP address, so can't establish a
connection.
DDNS is designed to solve this problem, as follows:
• You must register for the DDNS service with a DDNS service provider. The
DDNS Service provider will allocate a Domain Name to you upon request.
• The DDNS settings on the DDNS screen above must be correct.
• The Network Camera will then contact the DDNS server whenever it detects
that the Internet IP address has changed, and inform the DDNS server of the
new IP address. (The Check WAN IP Address determines how often the
Network Camera checks if the Internet IP address has changed.)
This system allows other internet users to connect to you using the Domain Name
allocated by the DDNS service provider.
This screen is displayed when the DDNS menu option is clicked.
Data - DDNS Screen
DDNS
Enable DDNS
Service Provider
Web Site Button
Figure 30: DDNS Screen
Enable or disable the DDNS function, as required.
Only enable this feature if you have registered for the DDNS
Service with a DDNS Server provider.
Choose a service provider from the list.
Click this button to open a new window and connect to the Web
site for the selected DDNS service provider.
40
Page 44

Domain (Host)
Name
Account/E-Mail
Password/Key
Check WAN IP
Address
Enter the Domain Name (Host Name) allocated to you by the
DDNS Server provider.
Enter the login name for the DDNS account.
Enter the password for the DDNS account.
Set the schedule for checking if the Internet IP address has
changed. If the IP address has changed, the DDNS Server will be
notified.
NOTE: If the DDNS Service provided some software to perform
this IP address update or notification, you should NOT use this
software. The update is performed by the camera.
41
Page 45

IP Filter
The IP Filter feature allows administrator to control network camera access by
filtering IP addresses. This screen is displayed when the IP Filter menu option is
clicked.
Data - IP Filter Screen
IP Filter
IP Filter
Single/Range
IP Address
Select the desired method to perform the IP address (or addresses)
filtering function.
Select to perform either single IP address or a range of IP addresses
that you desired.
Enter an IP address or a range of IP addresses you would like to
allow or deny.
Figure 31: IP Filter Screen
42
Page 46

I/O Port
The Network Camera supports 1 input port and 1 output port. This screen is
displayed when the I/O Port menu option is clicked.
Data - I/O Port Screen
Input Ports
Current State
Triggered When…
Output Ports
Current State
Default State
Manual Trigger
Action When
Triggered
It indicates the current state of the input port. Once the configured
state is happened, it will trigger the event actions.
Select the desired State:
• High
• Low
• Rising
• Falling
It indicates the current state of the output port.
Select the desired option from the drop-down list.
Select the option to control the output state.
If an event is happened, it will trigger the event alerting.
Figure 32: I/O Port Screen
43
Page 47

Streamings
This screen is displayed when the Streamings menu option is clicked.
If you want to view streaming via the cell phone:
1. Cell phone should be supported by 3GPP protocol.
2. Enter 554 for RTSP port number in the Network screen.
3. Both MPEG-4 and H.264 format support cell phone option.
4. Enter the following address in the URI:
RTSP:// Router IP address / User Defined URI
5. Select 15 fps for Max Frame Rate.
Note! Due to the bandwidth limitation for the cell phone usage, please set the
resolution, quality and frame rate to lower values.
Figure 33: Streamings Screen
44
Page 48

Data - Streamings Screen
Video Mode
Options
Select either "High Resolution Mode" or "High Frame Rate Mode".
The resolution of the streaming will be different according to the
video mode you choose.
Default Streaming
Select the default channel for streaming from the drop-down list.
Channel
Streaming 1 Settings (MJPEG)
Video Format
Resolution
Fixed Video
This displays the default format.
Select the desired video resolution format.
Select the desired option. The default fix quality is set to Normal.
Quality
Max. Frame Rate
Select the desired Maximum frame rate for the video stream.
The default value is 15.
Streaming 2/3 Settings
Video Format
Resolution
Video Quality
Control
Select the desired format from the list.
Select the desired video resolution format.
• Constant Bit Rate: Select the desired bit rate. The default is set
to 1.0 Mbps.
• Fixed Quality: Select the desired option. The default fix quality
is set to Normal.
GOV Length
Max. Frame Rate
User Defined URI
Adjust the GOV interval in frame base. 1 means all frames are Iframe. Enter the desired value between 1 and 150.
Select the desired Maximum frame rate for the video stream.
The default value is 15.
You may enter the URI up to 32 characters long for accessing the
live video from camera through cell phone connection.
45
Page 49

Video & Audio Screen
This screen is displayed when the Video & Audio menu option is clicked.
Figure 34: Video & Audio Screen
Data - Video & Audio Screen
Video Adjustment
Power Line
Frequency
White Balance
Brightness
Sharpness
Options
Enable Microphone
Audio Type
Enable Speaker
Select the power line frequency (50Hz or 60Hz) used in your region,
to improve the picture quality under florescent lighting.
Select the desired option to match the current environment and
lighting.
If necessary, you can adjust the brightness to obtain a better image.
For example, if the camera is facing a bright light, the image may be
too dark. In this case, you can increase the brightness.
Select the desired option for the sharpness. You can select a
Sharpness value between -3 and 3.
Enable audio by checking this checkbox. Using Audio will increase
the bandwidth requirements slightly.
Select the desired audio type.
Enable speaker sound by checking this checkbox.
Flip
Mirror
Enable Time Stamp
This setting will have the image swapped top-to-bottom.
This setting will have the image swapped left-to-right.
If enabled, the current time will be displayed on the Video image.
46
Page 50

Enable Text
Display
Enable Privacy
Mask
Enable this setting if you want text to be displayed on the Video
image, and enter the desired text - up to 20 characters. This feature
is often used to identify each camera when multiple cameras are
installed.
Enable this to place the grey square on the area of the current image
that you want to hide from others. The grey square can be enlarged
or shrunk as required.
47
Page 51

Video Access Screen
This screen is displayed when the Video Access option is clicked.
Figure 35: Video Access Screen
Data - Video Access Screen
User Access
Enable Security
Checking
Video Access
Enable Scheduled
Video Access
Access Schedule
• If disabled (default) - No login required. Users do not have to
provide a username and password when they connect to the
camera for viewing video.
• If enabled - Require login. Users will be prompted for a
username and password when they connect to the camera for
viewing video. The camera administrator must use the "User
Database" menu option to create the desired users.
• If enabled - Viewing video is available during the scheduled
periods, and unavailable at other times. If this option is selected,
you need to define a schedule. If no schedule is defined, this
option is always disabled.
• If disabled - The option will remain disabled until you enable it.
Note that regardless of which setting is chosen, the Administrator
can ALWAYS access the camera and view live video.
Scheduled Periods
Delete
This displays all periods you have entered into the database. If you
have not entered any periods, this list will be empty.
Use the Delete button to delete the selected item in the list.
48
Page 52

Add New Schedule
Day
Start Time
End Time
Add
Clear
Choose the desired option for the period.
Enter the start time using a 24 hr clock.
Enter the end time using a 24 hr clock.
Click this button to add a new period.
Use this button to clear the input fields.
49
Page 53

User Database Screen
This screen is displayed when the User Database option is clicked.
Figure 36: User Database Screen
Data - User Database Screen
Existing Users
User List
Edit, Delete, Delete
All
User Properties
User Name
User Password
Confirm Password
Add Button
This displays all users you have entered into the User database. If
you have not entered any users, this list will be empty.
The maximum number of users is 20.
Use these buttons to manage the user database.
Enter the name for the user here.
• Spaces, punctuation, and special characters must NOT be used
in the name.
• The name is case insensitive (case is ignored), so you can not
have 2 names which differ only by case.
The password for this user.
Re-enter the password for the user, to ensure it is correct.
Click this button to add a new user, using the data shown on screen.
Clear Button
Use this button to clear the input fields, ready to add a new user.
50
Page 54

Motion Detection Screen
This screen is displayed when the Motion Detection option on the Event menu is
clicked.
.
Figure 37: Motion Detection Screen
Data - Motion Detection Screen
Motion Detection
Set Detection
Areas
Indicator/
Threshold
You can set the full screen or selected areas of the video image to be
examined.
Note: Motion detection can be triggered by rapid changes in lighting
condition, as well as by moving objects. For this reason, it should only
be used indoors.
Administrator needs to adjust the relation between indicator and
threshold for each area.
51
Page 55

Audio Detection Screen
This screen is displayed when the Audio Detection option on the Event menu is
clicked.
.
Figure 38: Audio Detection Screen
Data - Audio Detection Screen
Audio Detection
Current
Volume
Triggered
Volume
Triggered
When
It displays the current volume of the environment.
Drag the bar to set the volume for triggering.
Choose the desired situation for triggering the audio detection.
52
Page 56

E-Mail Screen
This screen is displayed when the E-Mail option on the Event menu is clicked.
.
Figure 39: E-Mail Screen
Data - E-Mail Screen
Primary/Secondary SMTP Server
SMTP Server
Address
Authentication
SMTP Login name
SMTP Password
POP server name
Show "From" as
Test the Server
Secondary SMTP
E-Mail Setup
E-mail Address
Enter the address of the SMTP (Simple Mail Transport Protocol)
Server to be used to send E-Mail.
Select the desired Authentication type for the SMTP Server.
Enter your login name for the SMTP Server.
Enter your password for the SMTP Server.
Enter the name for the POP Server.
Enter the E-Mail address to be shown in the "From" field when the
E-Mail is received.
Click this button to test the server connection.
Check the box to upload to the Secondary SMTP if the camera can
not connect to the primary SMTP.
Enter at least one (1) E-Mail address; the 2nd and 3rd addresses are
optional. The E-Mail alert will be sent to the E-Mail address or
addresses specified here.
With Attachment
Enable the checkbox if you want to attaché files to the E-mail.
53
Page 57

Subject
Enter the desired text to be shown as the "Subject" for the E-Mail
when it is received. Subject can not exceed 48 alphanumeric
characters.
54
Page 58

FTP Screen
This screen is displayed when the FTP option on the Event menu is clicked.
Data - FTP Screen
Primary/Secondary FTP
FTP Server
Port
Login name
Password
Enable Passive
Mode
File Path Name
Test the Server
Secondary FTP
Enter the address of the FTP Server.
Enter the Port of the FTP Server to be connected.
Enter your login name for the FTP Server.
Enter your password for the FTP Server.
Check the box to enable the Passive mode feature of the FTP.
Enter the file path/name of the FTP.
Click this button to test the server connection.
Check the box to upload to the Secondary FTP if the camera can not
connect to the primary FTP.
Figure 40: FTP Screen
55
Page 59

HTTP Screen
This screen is displayed when the HTTP option on the Event menu is clicked.
Data - HTTP Screen
HTTP Notification
URL
User Name
Password
Proxy Server
Name
Proxy User Name
Proxy Password
Proxy Port
Number
Method
Figure 41: HTTP Screen
Enter the URL of your HTTP notification server.
Enter the user name of your HTTP server.
Enter the password to match the user name above.
Specify the proxy server name in the provided field if the camera
needs to pass through a Proxy Server to do the HTTP notification.
Enter the user name for the proxy server.
Enter the password for the proxy server.
Enter the port number for the proxy server.
Select the desired method of form data encoding.
• Get - It should be used if and only if the form processing is
independent, which typically means a pure query form.
Generally it is advisable to do so.
• Post - If there are problems related to long URLs and non-ASCII
character repertoires, which can make it necessary to use
"POST" even for independent processing.
56
Page 60

SD Card Screen
Data - SD Card Screen
HTTP Notification
URL
User Name
Password
Proxy Server
Name
Enter the URL of your HTTP notification server.
Enter the user name of your HTTP server.
Enter the password to match the user name above.
Specify the proxy server name in the provided field if the camera
needs to pass through a Proxy Server to do the HTTP notification.
Figure 42: SD Card Screen
57
Page 61

SMB/CIFS Client Screen
This screen is displayed when the SMB/CIFS Client option on the Event menu is
clicked.
Figure 43: SMB/CIFS Client Screen
Data - SMB/CIFS Client Screen
SMB/CIFS Client
Browse SMB/CIFS
Server
Server Name
File Path
User Name
Password
Test the Server
Click Browse button to select the desired SMB/CIFS server.
Enter the name of your SMB/CIFS server.
Enter the file path of your SMB/CIFS server.
Enter the user name for the SMB/CIFS client account.
Enter the password for the SMB/CIFS client account.
Click this button to test the server connection.
58
Page 62

Event Trigger Screen
This screen is displayed when the Event Trigger option on the Event menu is clicked.
Figure 44: Event Trigger Screen
Data - Event Trigger Screen
Event Schedule
Schedule List
New Schedule
Effective Time
Frame
Start Time
End Time
The Event Schedule shows all of the event types currently
configured in the Network Camera, along with various information
about their configuration, as listed below:
• Name - the descriptive event name set by the user.
• Effective Time Frame - shows when the event at a set time will
be triggered.
• Trigger by - shows what kind trigger activate the event.
• Action - shows what kind of the actions will be issued when the
event been triggered
Choose the desired option for the period.
Choose the desired start time using a 24 hr clock.
Choose the desired end time using a 24 hr clock.
59
Page 63

Trigger Event
Enable
Interval
Trigger by
Actions
Attachment Type
Check to perform all of the event(s) that were configured and
scheduled.
Select the desired option for the events interval. (* "0" = No Delay)
• Audio Detection - The sound detection can be used to trigger
events.
• Motion Detection - Movement in a motion detection window
can be used to trigger events.
• E-Mail - If checked, an E-Mail (with "Attachment") will be
delivered to the SMTP server. (SMTP Server must be
configured on the E-Mail page.)
• FTP - If checked, an FTP upload will be activated to the FTP
server. (FTP servers must be configured on the FTP page.)
• HTTP - If checked, a HTTP CGI command will be delivered to
the HTTP server.
• SMB/CIFS - If checked, JPEG image(s) or video files will be
uploaded to the SMB server. (SMB must first be enabled and
configured on the SMB Client page.)
• Streaming Channel - Select the desired type for the video file.
• Pre/Post Capture - Select the desired length. The size of the
file depends on this setting, and also the Video size and degree
of compression.
60
Page 64

Maintenance Screen
.
Figure 45: Maintenance Screen
Data - Maintenance Screen
Administrator Login
Administrator
ID
Administrator
Password
Verify Password
Firmware Upgrade
Upgrade File
Start
Clear File Name
Enter the name for the Administrator here.
Spaces, punctuation, and special characters must NOT be used in the
name.
The password for the Administrator.
Re-enter the password for the Administrator, to ensure it is correct.
Click the "Browse" button and browse to the location on your PC
where you stored the Firmware file. Select this file.
Click this button to start the Firmware. When the upgrade is finished,
the Network
Camera will restart, and this management connection will be
unavailable during the restart.
This does NOT stop the Upgrade process if it has started. It only clears
the input for the "Upgrade File" field.
61
Page 65

Backup & Restore
Backup
Configuration
File
Restore
Configuration
File
Clear File Name
Restore Factory
Defaults
Restart Camera
Click Backup button to save the current configuration information to a
text file.
It is suggested to backup the configuration file, in order to restore the
camera easily.
Click Restore button to reinitialize the camera to load the new updated
software. Do this after loading the upgrade file.
This does NOT stop the Restore process if it has started. It only clears
the input for the "Restore Configuration File" field.
Click Defaults button to reloads all default settings on the camera.
Click Restart button to restarts the camera.
62
Page 66

Status Screen
.
Figure 46: Status Screen
Data - Status Screen
System
Device Name
Description
F/W version
Network
MAC Address
IP Address
Network Mask
Gateway
WINS Address
Wireless
WSC PIN Dode
This shows the name of the Network Camera.
This shows the description of the Network Camera, such as location.
The version of the current firmware installed.
The current IP address of the Network Camera.
The IP Address of the Network Camera.
The network mask associated with the IP address above.
The IP Address of the remote Gateway associated with the IP Address
above.
The IP Address of the WINS server.
It displays the current WSC PIN code.
Network Type
This shows the Network Type currently in use (Ad-hoc or
Infrastructure).
63
Page 67

SSID
Channel
Security
Signal Strength
Streaming (1~3)
Video Format
Resolution
Video Quality
Frame Rate
Buttons
Refresh
This displays the wireless SSID.
This shows the wireless channel currently used.
The current security setting for Wireless connections.
This shows the strength of the signal.
It displays the current format of video.
The image size of the video stream.
This displays the image quality of the video stream.
This displays the frame rate of the video stream.
Update the log and any other data on screen.
64
Page 68

Log Screen
This screen displays a log of system activity.
.
Data - Log Screen
Log
System Log
Refresh
Button
Clear Log
Enable Syslog
Service
Syslog Server
Address
Figure 47: Log Screen
This is a log of system activity.
Click this to update the data shown on screen.
Click this button to restart the log.
Check the box to enable the System Log Server feature.
Enter the address of the Syslog Server.
65
Page 69

Chapter 6
Windows
6
Viewing/Recording Utility
This Chapter describes how to use the supplied Utilities package to
view and listen the live streams generated by the Network Camera.
Overview
The Utilities package includes following three functions:
• LiveView - to view/listen the live streams.
• View Recordings - to record the live streams.
• Setup - to configure the Utilities such as adding camera, making recording
schedules and setting required parameters, etc..
The Utilities must be installed in the Windows before they can be configured.
System Requirements
In order to use the utility of Network Camera, you need to meet the following
requirements:
• Windows XP SP3, 32-bit Windows Vista/Windows 7.
• Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5 Service Pack 1 (it should be installed on
Windows XP/VISTA via "Windows Update").
• Internet Explorer 6 or later, Firefox 3.0 or later
• 2GB RAM
• Individual Graphic Card
Installation
1. Insert the supplied CD-ROM into your drive. If the setup program does not start
automatically, run NetworkCamera.exe in the root folder. You will see the
Welcome screen shown below.
66
Page 70

Figure 48: Welcome Screen
2. Click the Install Utility button to start the installation of the Utilities package.
3. Follow the prompts to complete the installation.
4. After the installation, double click the Monitor icon on the desktop or click
Monitor menu item in the Windows main program menu to launch the Utilities.
System Tray Icon
When started, the program will create an icon in the Windows system tray on the
taskbar, as shown below.
Figure 49: System Tray Icon
You can right click the icon and it will provides a menu which allows you to launch
utility program, view the utility details or even exit the utility package.
67
Page 71

LiveView Screen
When Utility launched, the Camera Utility screen like the example below will be
displayed.
Figure 50: Main Screen
If no cameras have been defined and added to the Utilities, no video will be
displayed. Utilities should be configured first to view the camera streams. See the
following section for information on defining a camera. Note that each Camera is
given a number (Channel Number).
68
Page 72

Camera Setup
To define a camera and associate it with a Channel Number:
1. Click the Setup icon on the main screen. You will see a screen like the example
below.
Figure 51: Cameras Setup Screen
2. Add desired Network Camera to the Camera List:
• To associate a camera automatically with the current Channel:
• The Utilities will search and display all available Network Cameras
found on your LAN in the Add Camera list automatically. The Add
Camera list can be updated by clicking the Refresh button.
• The Camera Details panel, on the right, displays the data for the
selected camera.
• Check that the Camera Details shown on the right is correct. Enter
associated User Name and Password.
Note: The Port Number, User Name, Password and Stream Type
can only be modified in the WEB UI instead of Camera Setup screen.
• Click the Test Camera button to check that a connection and login can
be performed successfully.
• Click Add button. The camera will now appear in the Camera List.
• To associate a camera manually with the current Channel:
• Click Manually Add button.
• Enter the Local Name, IP Address, User Name, Password, Port
Number and Stream Type in the Camera Details section.
69
Page 73

Note: The Port Number, User Name, Password and Stream Type
can only be modified in the WEB UI instead of Camera Setup screen.
• Click the Test Camera button to check that a connection and login can
be performed successfully.
• Click Add button. The camera will now appear in the Camera List.
Cameras Data
Camera list
Add cameras
Address
Camera Status
Local Name
IP Address
Login
Port Number
Stream Type
This displays the cameras you've added, if any. Use the Delete button to
delete the selected camera in the list.
This list displays all available Network Cameras found on your LAN.
If you cannot find the desired camera in the above list, you can add it
manually by entering the IP address in this field.
This displays the current status of the selected camera.
This is the default name for the Wireless Network Camera, and can be
changed.
The current IP address of the Wireless Network Camera. Or enter the
Domain Name or Internet IP address of the desired Wireless Network
Camera.
The camera Administrator can require that users provide a username and
password before being allowed to view the live video.
• If the Administrator has not enabled this option, the Login fields can
be left blank.
• Otherwise, you must enter the User Name and Password allocated
to your by Administrator.
This will normally display "80". Only change this if requested to do so
by the Wireless Network Camera Administrator.
Select the desired type from the drop-down list.
Delete Button
Refresh Button
Add Button
Test Camera
Advanced
Camera
Settings
Click this button to delete the selected camera in My camera list.
The Add cameras list can be updated by clicking the Refresh button.
Click the button to add the selected camera to the list.
Check the connection of the selected camera by clicking this button.
Click this link to connect to the Web UI of the Network Camera
immediately.
70
Page 74

LiveVew Program - for Streams Live Viewing
You can view live video in the Monitor screen. The built-in software can let you
view up to 9 cameras on a single computer screen at one central location.
The following table lists the icons displayed on the Monitor screen:
View Layout. Use this to select the number of Channels (Cameras) to be
displayed on screen. Up to 9 cameras can be displayed.
View. This indicates if the camera stream is being viewed.
Red indicates the configured camera is being viewed.
Gray indicates that no camera is configured or the configured camera is not
connected to the Monitor.
Instant Record. Click this to start recording the current stream. While
recording, this button will be red. To stop recording, click this button again.
Gray indicates no recording.
Red indicates recording is in progress.
Snapshot. Click this to take a still image of the current video stream. The
image format is BMP.
Mirror. Click this to have the image swapped left-to-right.
Flip Video. Click this to have the image swapped top-to-bottom.
Speaker On/Off. To turn On/Off the speaker volume for the camera in
focused viewport.
Microphone On/Off. To turn On/Off the audio upload function for the
camera in the focused viewport.
Volume. If Speaker/Microphone is enabled, you can click the icon, then
drag and drop to raise or lower the volume.
Zoom Camera. A digital zoom-in feature is available. Drag the slider bar
to the desired magnified rate in a viewport.
Day/Night Mode. The Network Camera supports Day/Night mode switch
for getting better quality of the low light condition. This function is
available depending on the model of Network Camera.
IO Port 1/2. It indicates if there is any I/O type triggered event detected in
the port 1/2.
Patrol. Move through the Preset positions in the sequence defined by the
Camera Administrator.
Camera Auto Pan. Click this to have the camera moved from left to right
automatically.
Motion Detection. Click this button to have the camera moved to the
Motion Detection Preset position.
Direct P/T. Use this to move the camera to the Pan/Tilt position directly.
Preset Points. Select the desired Preset points.
71
Page 75

Move Control. Use this to move the camera to the desired position. There
may a short delay after clicking the desired icon. You should wait a couple
of seconds rather than click again.
Or you can drag the vertical or horizontal slider bar to have quicker
movement of the Network Camera to the desired position.
Setup. Click this button to open the Utilities configuration program.
View Recordings. Click this button to launch the recording program, which
allows you to browse through the previously saved recordings. Please see
the " View Recordings Program - for Streams Recording " section for
details.
Channel Indicator. This indicates the current channel (camera).
72
Page 76

View Recordings Program - for Streams Recording
To access the saved recordings of the Cameras, click View Recordings icon on the
top of the screen, then you will see a screen like following.
Figure 52: View Recordings Screen
Searching Recorded Streams Files
Skip to Next Record. Use this to view the next available record.
Play. Use this to re-start viewing, after using the Pause button.
Playing speed. Use the
speed.
Pause. Use this to temporarily stop playing.
Skip to Previous Record. Use this to view the previous record.
Zoom In. To zoom in on a section of the window, drag the slider bar to the desired
magnified rate of a viewport.
Snapshot. Click this to take a still image of the current video.
Print. Click this to print the current frame which is showing in the screen.
Speaker. To play a recorded file, select the desired volume.
Hour Left. It displays the possible available time for recording.
Space Left. It displays the current available space of the memory.
All recordings. Click this button to select the type (All recordings or Event
recordings) of the recorded files.
to accelerate (right) or decelerate (left) the playing
Select Camera. Click the desired camera to find the recordings.
73
Page 77

Recording Bar. It displays the recordings that match your requests.
Calendar. Choose the date of the calendar for finding desired recordings.
74
Page 78

Setup Program - for Streams Configuration
There are 3 tabs of the Setup program:
• Cameras
• Recording Options
• Settings
For the Cameras configuration, please refer to the Camera Setup for details.
You can record the streams from camera by pressing the Instant Record button in
the Monitor program as mentioned in the " LiveVew Program - for Streams Live
viewing" section or by making schedules to let the recording happen on the arranged
time period.
All the recorded streams are stored in files with a proprietary format and can be
viewed via Playback program in the Utilities package.
If you want to change the default settings of recording parameters before doing any
recording, please see the "Settings" section for details.
Recording Options
To make recording schedules, click the Recording Options tab on the Setup screen.
You will see a screen like the example below.
Figure 53: Recording Options
If necessary, change these settings to suit your environment. Please follow the steps
below to make a schedule for recording:
1. Select a camera from the available camera list.
2. Select either Always Record or Record in a Scheduled Time Range for recording
type.
75
Page 79

3. If Record in a Scheduled Time Range is selected, set the recording time range
from Start Date, Start Time and End Time boxes.
4. Press Add button to add the schedule.
You will see all the schedules in the recording list.
Settings
Clicking the Settings tab on the Configuration program to make change of default
Utilities parameter settings.
Figure 54: Settings Screen
Data - Settings
Recording Path
Recording
Instant Recording Time Limit
Maximum Time Limit
for Instant Recording
This is the Drive and Folder on your PC/Notebook where
recorded files will be placed. You need a drive which has large
amounts (Gigabytes) of free space. Click the Browse button to
select the drive and folder if you want to change the default
path. Note that file names for the recordings are automatically
assigned, using an internal date-time coding rule.
This sets the maximum time period of a recording which is
started by clicking the Record button on the Monitor main
screen. If the recording is not stopped manually before the
arranged time period elapsed, it will be terminated automatically
when the end time hit.
76
Page 80

Motion Detection
Record Before and
after motion begins
Set the time so that the Recorder will make a pre-recording and
post-recording for at most the specified time range while a
motion begins and ends.
Disk Space for Each Camera Recording
Total Disk Space
Available Disk Space
This displays the total size of the selected disk.
This displays the available space of the selected disk for storing
recordings.
Enable Disk space
limitation
Maximum Allowed
Space per Camera
When allowed space
is full.
Enable this if you wish to limit the disk space used by video
recordings.
Enter the maximum amount of disk space assigned to each
camera for stream recordings.
Select the desired option for the behavior when the disk space
limit is reached.
• Overwrite earliest file. The Recorder will overwrite the
oldest file if the space is not enough for further recording.
• Stop Recording. If the disk space limit is reached, no
further recording is done.
Initial Settings
Launch this utility
Check this to have this utility start when Windows starts.
when Windows starts
77
Page 81

Chapter 7
Troubleshooting
7
This chapter covers the most likely problems and their solutions.
Overview
This chapter covers some common problems that may be encountered while using
the Network Camera and some possible solutions to them. If you follow the
suggested steps and the Network Camera still does not function properly, contact
your dealer for further advice.
Problems
Problem 1: I can't connect to the Network Camera with my Web Browser to
configure it.
Solution 1:
Problem 2: The Windows utility doesn't list any Network Camera.
It is possible that your PC's IP address is not compatible with the IP
address of the Network Camera.
Use the Windows utility to configure the Network Camera with a valid IP
address.
Solution 2:
Problem 3 When I try to connect to the Network Camera, I get prompted for a
Solution 3
Check the following:
• The Network Camera is installed, LAN connections are OK, it is
powered ON and startup is complete.
• Ensure that your PC and the Network Camera are on the same network
segment. (If you don't have a router, this must be the case.)
• Ensure that your PC has the TCP/IP network protocol loaded. In
Windows, this is done by using Control Panel-Network.
• If an entry for TCP/IP -> Network card is not listed, use Add -
Protocol - Microsoft - TCP/IP to add it.
• You then need to select the new entry (TCP/IP -> Network card),
click Properties, and configure the IP Address tab.
• If your LAN has a DHCP Server, you can select "Obtain an IP
Address automatically". Otherwise, you must select "Specify an
IP Address", and enter values for IP Address, Su bnet Mask , and
Gateway. All devices on your LAN must use compatible values.
Remember that each device needs a unique IP Address, and the
same Subnet Mask.
user name and password.
You SHOULD be prompted for a user name and password if trying to
access the Administration menu.
Enter the Administrator ID and Administrator Password set on the
Maintenance screen.
78
Page 82

If you are just trying to view Video, the User Name/Password prompt
indicates that the Administrator has restricted access to specified users.
Ask the Administrator for your User Name and Password.
Problem 4 I can't connect to the Network Camera using a Wireless connection.
Solution 4
1) If a LAN cable is connected to the LAN port, the Wireless interface is
disabled. Only one interface can be active.
2) Check that your PC and the Network Camera have compatible Wireless
settings.
• Mode (Infrastructure or Ad-hoc) must be correct.
• ESSID must match.
• WEP settings must match.
• In Ad-hoc mode, the Channel should match, although this is often not
required.
Problem 5 Video quality may suddenly deteriorate.
Solution 5
This can happen when an additional viewer connects to the Network
Camera, overloading the camera or the available bandwidth. The image
size and quality can be adjusted to cater for the required number of viewers
and the available bandwidth.
Problem 6
Solution 6
The motion detection feature doesn't send me any E-mail.
It may be that the SMTP (Simple Mail Transport Protocol) server used by
the camera to send the E-Mail will not accept mail. (This is to prevent span
being sent from the server.). Try using a different SMTP server, or contact
your ISP to see if SMTP access is being blocked.
Problem 7
Using the motion detection feature, I receive E-Mails which don't show
any moving objects.
Solution 7
Problem 8
Solution 8
Problem 9
Solution 9
Problem 10
The motion detection feature doesn't actually detect motion. It compares
frames to see if they are different. Major differences between frames are
assumed to be caused by moving objects.
But the motion detector can also be triggered by:
• Sudden changes in the level of available light
• Movement of the camera itself.
Try to avoid these situations. The motion detection feature works best in
locations where there is good steady illumination, and the camera is
mounted securely. This feature can NOT be used if the camera is outdoors.
The image is blurry.
Try cleaning the lens, or adjusting the Video Quality Control setting on the
Streamings screen. Video created by the lower settings will contain less
detail; this is the trade-off for using less bandwidth.
When is the best time to press WPS button?
If there is no cable connected, you can press the WPS button after the
Power LED starts blinking.
In some older Window XP systems, it may not be able to see
H.264/MPEG4 video streaming.
79
Page 83

Solution 10
Problem 11
Solution 11
In order to view H.264/MPEG4 video streaming in the older Window XP
systems, please install the Microsoft .net framework 2.0 or later version, so
the system will be able to deploy the built-in H.264/MPEG4 decoder of the
camera.
I use the camera via IE browser in protected mode of Windows
Vista/7, there is no local recording/setup feature to be used.
Even if I run it with IE browser in non-protected mode of Windows 7,
the folder like "Windows" still can not be accessed. (There is no
recording files found in this folder as well)
There will be no local recording files and the setup service of associated
folder if the IE browser is in protected mode.
To use the local recording feature, please operate IE browser in
non-protected mode.
Note! Some folders (ex. ″Windows″ folder) with high integrity level can
not be accessed via non-protected mode of IE in Window 7.
80
Page 84

Appendix A
Specifications
Compact HD(11N) Wireless Network Camera
Model RC8221
Dimensions 63mm (W) x 95mm (H) x 35mm (D)
A
Operating Temperature
Video compression H.264, MPEG4 and MJPEG
Image resolution 1280x 720, 640x480 (VGA, system default ), 320x 240 (QVGA),
Storage Temperature
Network Protocols TCP/IP, HTTP, HTTPS, DHCP, NTP, SMTP, UPnP, FTP,
Network Interface 1 Ethernet 10/100BaseT (RJ45) LAN connection
Wireless interface IEEE 802.11n/802.11b/802.11g compatible, Infrastructure/Ad-
LEDs 3
Power Adapter 12V/1A, 100~240 VAC
0° C to 50° C
160 x 120 (QQVGA)
-20° C to 70° C
RTP/RTSP
hoc mode, WEP 64/128 bit, WPA/WPA2 personal security
support
Regulatory Approvals
CE Approvals
The Network Camera and the Ethernet Network Camera meet the guidelines of the
European Union and comply with the 99/5/EEC and RTTE 99/5EG directives,
including the following standards:
• EN60950
• EN300 328
• EN301 489-1
• EN301 489-17
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio
interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
81
Page 85

Copyright Notice
Many software components are covered by the GNU GPL (General Public License).
Some are covered by other Licenses.
You can check more details of each applicable license by clicking the License button
in the Maintenance screen.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy
and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
-Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
-Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
-Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
-Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
You are cautioned that changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void your authority to operate the equipment.
82
Page 86

Appendix B
B
Network Camera HTTP
CGI
User-level CGI commands (user level privilege)
Notes: If camera is in privacy mode, it will reject the streaming/snapshot
request with “406 Not Acceptable” and stop video post for event.
Video and Image commands
Stream M-JPEG video
HTML page for the end user
Method: GET
URL: http://<ip>/img/mjpeg.htm
Return:
HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n
…
content-type: text/html\r\n
…
http://<ip>/img/video.mjpeg
…
83
Page 87

Server Push page for the programmer
Method: GET
SerComm
URL: http://<ip>/img/video.mjpeg
(utility)
The camera will check the request User-Agent parameter in HTTP header to
identify the client type. The camera will regard the client as MSIE if there is the
string “MSIE”, regard the client as SerComm OCX if there are the strings
“CameraActiveX” or “Viewer” or “AlertCfg”, and regard others as PushServer.
Return (OK situation):
If the client is MSIE
HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n
…
content-type: image/jpeg\r\n
…
<MJPEG data>
If the client is SerComm OCX
HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n
…
<MJPEG video or AUDIO data>
The format of motion JPEG for OCX, to support the audio stream feature, we
add an extra header at begin of the stream data (mjpeg/audio) to describe the
frame information and sending status. The extra header contains 48 bytes in
little-endian, the fields are shown as following:
Location Parameter Value and description
0-3 Magic
String
The string to identify the header.
It must be "MJPG".
4-7 Frame Size The frame size. (bytes)
8-9 Width The JPEG width.
10-11 Height The JPEG height.
12-15 Sent Size The size of the sent frame. (bytes)
16-17 Slice Size The size of the slice. (bytes)
18-21 Timestamp The time stamp of the frame.
The time stamp of the first frame is always 0.
22 Frame
Type
The frame type.
0x01 (01): JPEG
0x02 (02): G.726 Audio|
0x03 (03): G.711 a law Audio
0x04 (04): G.711 u law Audio
0x05 (05): AMR Audio
0x10 (16): LPCM mono Audio at 8KHz Sample Rate
84
Page 88

23-24 Bit Rate The audio bit rate.
0x02 (02): 2 KbytesPerSecond
0x04 (04): 4 KbytesPerSecond
0x08 (08): 8 KbytesPerSecond
25 Version The version number.
It is 0x02 (02).
SerComm
26-45 Time
String
46 Padding
flag
The ASCII string to present the current camera time. (Not
used)
The padding flag
0x00: No padding data
0x01: There is the padding data at the end of the frame,
please refer to chapter “Padding data format” for details
47 Reserved Reserved
Example, A normal JPEG frame:
Image size is 5930, width is 320, height is 240, sent data size is 2000, slice size is
2000, timestamp is 0, frame type is 1 (JPEG), version number is 1. The header will
look like as follows:
4D 4A 50 47 2A 17 00 00 40 01 F0 00 D0 07 00 00
D0 07 00 00 00 00 01 02 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
(2000 bytes JPEG data)
We will regard others client as the PushServer.
HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n
…
content-type: multipart/x-mixed-released;boundary=<xxx>\r\n
--<xxx>
content-type:image/jpeg\r\n
content-length: <image-size>\r\n\r\n
<jpeg image date>
--<xxx>
content-type:image/jpeg\r\n
content-length: <image-size>\r\n\r\n
<jpeg image date>
...
--<boundary>--
Return (ERROR situation):
85
Page 89

HTTP/1.0 400 Bad Request\r\n
…
content-type: text/plain\r\n
\r\n
current_ resolution=A\r\n
current_framerate=B\r\n
The A and B are in the following format.
Parameter Value and description
A
B
Image resolution
1: 160x120 (or 160x128, 176x120 (NTSC)/
176x144(PAL), depends on models)
2: 320x240 (or 352x240(NTSC)/ 352x288(PAL), depends
on models)
3: 640x480 (or 704x480(NTSC)/ 704x576(PAL), depends
on models)
4: 1280x960 (depends on models)
Frame rate 1 ~ 30fps
SerComm
Snapshot
Method: GET
URL: http://<ip>/img/snapshot.cgi?[size=<value>][&quality=<value>]
Parameter Value and description
size
quality
Example 1: To sanshot a 640x480 (or 704x480(NTSC)/ 704x576(PAL), depends on
models) very high qulity JPEG image from network camera 192.168.0.99.
http://192.168.0.99/img/snapshot.cgi?size=3&quality=1
Image resolution
1: 160x120 (or 160x128, 176x120 (NTSC)/ 176x144(PAL),
depends on models)
2: 320x240 (or 352x240(NTSC)/ 352x288(PAL), depends on
models)
3: 640x480 (or 704x480(NTSC)/ 704x576(PAL), depends on
models)
4: 1280x960 (depends on models)
Quality level
1: Very high
2: High
3: Normal
4: Low
5: Very low
Example 2: To snapshot a JPEG image from network camera 192.168.0.99 (with
current resolution and quality)
http://192.168.0.99/img/snapshot.cgi
Example 3: To snapshot a low quality JPEG image with current resolution from the
network camera 192.168.0.99.
86
Page 90

SerComm
http://192.168.0.99/img/snapshot.cgi?quality=4
Return: A JPEG image will be returned to client with user specified resolution and
quality.
HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n
…
content-type: image/jpeg\r\n
…
<JPEG image data>
SDP (MPEG-4/H.264 video, not for MJPEG video)
Method: GET
URL: http://<ip>/img/media.sdp
Return: A SDP file will be returned.
HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n
…
<SDP data>
Audio Upload (uploading audio streaming to the camera)
Method: POST
URL: http://<ip>/img/g726.cgi
32Kbps, depends on models)
URL: http://<ip>/img/g711a.cgi
URL: http://<ip>/img/g711u.cgi
Example (client side):
POST http://192.168.0.99/img726.cgi HTTP/1.0\r\n
Authrization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4= \r\n
\r\n
Return:
OK
HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n
Client starts to upload the audio stream.
Unauthorized (Bad username, password)
G.726 audio stream (16Kbps or
G.711 a-law audio stream (64Kbps)
G.711 u-law audio stream (64Kbps)
HTTP/1.0 401 Unauthorized\r\n
RTP/RTSP
User can stream video and audio through the following URLs.
Video and audio: rtsp://<ip>/img/media.sav
Video only: rtsp://<ip>/img/video.sav
87
Page 91

SerComm
Audio only: rtsp://<ip>/img/audio.sav
If the client player is QuickTime player, there are always around 3 seconds
latency. If there is not audio content in the streaming, you can use the extension
parameter “[?|&]latency=no” to push QuickTime player to play the streaming
without any latency, but this method causes the frame rate is not stable.
Example: rtsp://<ip>/img/video.sav?latency=no
Note that camera is able to support the following four RTP protocols. But user
needs to specify the desired RTP protocol in the player.
1. Unicast RTP
2. Multicast RTP
3. RTP over RTSP (RTP over TCP)
4. RTP over RTSP over HTTP (HTTP tunnel)
Return: Video and/or audio will be returned.
88
Page 92

SWF/FLV
Method: GET
SerComm
URL: http://<ip>/img/media.swf
Return: Action script content to trigger the player to get the media content.
HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n
…
<data>
Method: GET
URL: http://<ip>/img/media.flv
Return: media content.
HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n
…
<data>
Extension to the streaming URL defines
We extend some parameters for some products which support the multiple
streamings simulatenously.
Related URLs:
video.asf, video.mjpeg, mjpeg.cgi, snapshot.cgi, media.sdp, media.sav,
video.sav
Extension syntax:
89
Page 93

SerComm
Parameter Description
channel If the product supports multiple streaming channels
simultaneously, we will append the parameter
“[?|&]channel=[1|2|...]” to identify, example:
To view the 1st channel streaming: video.sav or
video.sav?channel=1
To view the 2nd channel streaming:
video.sav?channel=2
video If the product supports multiple video codec simultaneously,
we will append the parameter
“[?|&]video=[MPEG4|MJPEG|H264]” at the end of original
URL to identify, example:
To view streaming with MPEG4 video:
video.sav?video=MPEG4
To view streaming with H264 video:
video.sav?video=H264
Mix the
parameters
channel and
video
If the product supports multiple streaming channels and
multiple video codec at one video channel simultaneously, we
will append both channel and video parameters to identify, the
parameter “channel” is the main key with priority.
Response error if parameters are not correct.
If only “channel” parameter provided, stream the
default video, priority is: MPEG4, MJPEG, H264.
If none parameter provide, use the default channel
number, and then stream the video by priority channel 1,2,3…
If only “video” parameter provided, stream the video
from the channel supports, use the default channel number, and
then priority is: 1,2,3,…
Example#1:
Total is 3 channels, the 1
and the 2
nd
channel has MPEG4 video, the 3rd channel has
MJPEG video, default viewer channel is 1
To view the H264 (or to view the 1
st
channel has H264 video
st
, then:
st
channel video):
video.sav?channel=1 or
video.sav?video=H264 or
video.sav?channel=1&video=H264
To view the MPEG4 (or to view the 2
nd
channel
video):
video.sav?channel=2 or
video.sav?video=MPEG4 or
video.sav?channel=2&video=MPEG4
To view the MJPEG (or to view the 3
rd
channel
video):
video.mjpeg
90
Page 94

SerComm
Example#2:
Total is 3 channels, the 1
and the 2
nd
channel has H264 video, the 3rd channel has
MJPEG video, default viewer channel is 1
To view the H264 at 1
st
channel has H264 video
st
st
channel:
, then:
video.sav?channel=1&video=H264 or
video.sav?video=H264
To view the H264 at 2
nd
channel:
video.sav?channel=2&video=H264
Have not MPEG4 video for viewing.
To view the MJPEG:
video.mjpeg
Example#3 (not supported in product spec yet):
Total is 2 channels, the 1
nd
and the 2
channel is 1
channel has H264 & MPEG4 videos, default viewer
st
, then:
To view the H264 at 1
st
channel has H264 video
st
channel:
video.sav?channel=1&video=H264
To view the H264 at 2
nd
channel:
video.sav?channel=2&video=H264
To view the MPEG4 at 2
nd
channel:
video.sav?channel=2&video= MPEG4 or
video.sav?video=MPEG4
padding If the product supports padding data over the streaming, such
as motion information, we will append the parameter
“[?|&]padding=[no|yes]” to identify, default (no this parameter)
depends on products and streaming types. Example:
To view the streaming without padding data:
video.sav?padding=no
To view the streaming with padding data:
video.sav?padding=yes
* You can refer to the section 2.11 for more
details.
Player commands
Query
Method: GET
URL: http://<ip>/util/query.cgi[?extension=value]
This CGI indicates the H/W capability, component setting. Ex: The camera got
I/O port (or not). The camera got Speaker (or not), etc.
91
Page 95

SerComm
Parameter Value and description
extension
Extension value
yes: extension is enabled, the extended data as below will be
extended to generic response.
fw_ver=V1.0.0R44\r\n
ip_addr=192.168.1.12\r\n
netmask=255.255.255.0\r\n
gateway=192.168.1.1\r\n
current_time=07/02/200
24-Hour format
timezone=4\r\n
http_port=80\r\n -> The value is -1 or none this parameter
indicate the HTTP disabled.
https_port=443\r\n -> The value is -1 or none this parameter
indicate the HTTPS disabled.
rtsp_port=554\r\n
8 10:12:10\r\n -> MM/DD/YYYY HH:MM:SS
Return:
HTTP/1.0 200 OK \r\n
…
content-type: text/plain\r\n
\r\n
<parameter pair>\r\n
<parameter pair>\r\n
......
Here are the details of parameter pairs:
Parameter Value and description
hostname
description
defname
mac
company_name
model_number
resolutions
Camera name, example: sc123456
Camera description, example: Hello camera
Camrea default name, example: default name
Camera's MAC address, example: 00C002123456
Camera's comany name, example: SerComm
Camera's model number, example: RC8020
Phase out in new projects. The resolutions camera support, depends
on models, valid values:
[1280*960,640*480,320*240,160*120|704*480,352*240,176*120|7
04*576,352*288,176*144]
92
Page 96

SerComm
mpeg4_resolutio
n
mjpeg_resolutio
n
h264_resolution
mic_in
Current MPEG-4 resolution setting, depends on models, valid values:
[1280|640|320|160|704|352|176]
For multiple streaming channels, use the keys: mpeg4_resolution,
mpeg4_resolution2, …
Won't provide this paramter if there is not such video format enabled
or supportted.
Current JPEG resolution setting, depends on models, valid values:
[1280|640|320|160|704|352|176]
For multiple streaming channels, use the keys: mjpeg_resolution,
mjpeg_resolution2, …
Won't provide this paramter if there is not such video format enabled
or supportted.
Current H.264 resolution setting, depends on models, valid values:
[1280|640|320|160|704|352|176]
For multiple streaming channels, use the keys: h264_resolution,
h264_resolution2, …
Won't provide this paramter if there is not such video format enabled
or supportted.
Current MIC in setting, valid values: [on|off]
speaker_out
audio_duplex_
mode
ptctrl
ioctrl
serial
privacy_button
pir_sensor
Current Speaker out setting, valid values: [on|off]
Only valid for the products have such setting feature in Web UI.
Current audio duplex mode setting, only “off” is valid, example:
Talk only:
mic_in=off, speaker_out=on
Listen only:
mic_in=on, speaker_out=off
Talk & Listen duplex:
mic_in=on, speaker_out=on
Talk & Listen half:
mic_in=on, speaker_out=on,
audio_duplex_mode=off
PT HW capability, valid values: [on|off]
IO HW capability, valid values: [on|off]
RS485 capability, valid values: [pelco|off]
Privacy button HW capability, valid values: [on|off]
PIR sensor HW capability, valid values: [on|off]
wlled
White light LED HW capability, valid values: [on|off]
93
Page 97

SerComm
irled
wps_pin_code
wireless
sw_pppoe
IR LED HW capability, valid values: [on|off]
WPS PIN code value, example: 00000048
Wireless HW capability, example: [on|off]
PPPoE software feature capability/supported, valid values: [yes|no]
URL: http://<ip>/img/query.cgi
This CGI indicates the accessed user's privilege with some H/W features. Ex.
The user could use Speaker Out, but couldn't control the I/O ports, etc.
Return:
HTTP/1.0 200 OK \r\n
…
content-type: text/plain\r\n
\r\n
mic_in=[on|off]r\n
speaker_out=[on|off]\r\n
ptctrl=[on|off]\r\n
ioctrl=[on|off]\r\n
interlace=[0|1]\r\n(only for analog CCTV input)
94
Page 98

Query/Control the peripheral components status (Operator,
combination CGI)
Notes: This combination CGI command will replace the separated
peripheral control CGIs.
Query the peripheral components status
Method: GET
URL: http://<ip>/io/query_pc.cgi[?<parameter>[&<parameter>...]]
Input parameters:
None parameter provided, CGI responds all supported peripherals' status.
The peripheral parameter provided, CGI just responds the specific
peripherals' status. Please refer to the “Parameter Pairs Table” for specific
input paramters.
Return:
HTTP/1.0 200 OK \r\n
…
content-type: text/plain\r\n
\r\n
<parameter pair>\r\n
<parameter pair>\r\n
......
Here are the details of parameter pairs, parameters depend on product
models.
“error” value response indicate that “Failed to query/control the
peripheral equipments”
Parameter Pairs Table
Parameter Get/Set Value and description
95
Page 99

SerComm
privacy_button
pir
light_sensor
pt_position
input_1
input_2
output_1
output_2
Query
Query
Query
Query
Query
Get &
Set
Privacy button status, valid values: [disabled|off|on]
only
PIR status, valid values: [disabled|actionless|active]
only
Light sensor status, valid values: [disabled|night|day]
only
Query current Pan & Tilt position, because the MCU can’t get
only
response from PT, so the values maybe wrong under some
conditions. Format is “X,Y”
“X” is the Pan position; “Y” is the Tilt position.
Input #1,#2 status, valid values: [high|low]
only
Onput #1,#2 status,
Query format is “A,B”.
“A” valid values: [high|low]
“B” valid values: [pulse|static]
Control format is “A”.
“A” valid values: [high|low]
dn_mode
Get &
Set
Day/Night mode status, valid values: [day|night]
Day mode, IR LED off, IR cut switch close the window to
filter the IR lights.
Night mode, IR LED on, IR cut switch open the window not
to filter the IR lights.
ir_cut
Get &
IR cut switch status, valid values: [close|open]
Set
ir_leds
wl_leds
Get &
Set
Get &
Set
IR LEDs status, valid values: [disabled|off|on], disabled is
only valid for query CGI
White light LEDs status, valid values: [disabled|off|on],
disabled is only valid for query CGI
Control the peripheral components status
Method: GET
URL: http://<ip>/io/control_pc.cgi?<parameter>=<value>[&<parameter
pair>…]
Parameter Value and description
Please refer to the “Parameter Pairs Table”
Return:
Successful request returns all group parameters or the specified parameters
as below.
HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n
…
content-type: text/plain\r\n
96
Page 100

SerComm
...
\r\n
OK\r\n
97
 Loading...
Loading...