Page 1
Wireless_N
PCI Adaptor
PC812Rn
User Guide
Page 2

Page 3

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION .............................................................................................1
Package Contents .............................................................................................................. 1
LEDs...................................................................................................................................1
Operation...........................................................................................................................1
CHAPTER 2 INITIAL INSTALLATION..............................................................................2
Requirements.....................................................................................................................2
Procedure...........................................................................................................................2
CHAPTER 3 USING THE WINDOWS UTILITY................................................................5
Overview ............................................................................................................................5
System Tray Icon...............................................................................................................5
Auto Profile Connect.........................................................................................................6
Site Survey Screen.............................................................................................................6
Profile Manager Screen .................................................................................................... 9
Network Status Screen....................................................................................................14
About Screen....................................................................................................................16
APPENDIX A SPECIFICATIONS .......................................................................................17
Wireless Adapter.............................................................................................................17
APPENDIX B ABOUT WIRELESS LANS..........................................................................18
Modes ...............................................................................................................................18
BSS/ESS............................................................................................................................18
Channels...........................................................................................................................19
WEP & WPA-PSK..........................................................................................................19
WPA2-PSK ......................................................................................................................19
Wireless LAN Configuration..........................................................................................20
P/N: 956YK80001
Copyright © 2008. All Rights Reserved.
Document Version: 1.0 (January, 2008)
All trademarks and trade names are the properties of their respective owners.
i
Page 4

Page 5
Chapter 1
Introduction
1
This Chapter provides an overview of the Wireless Adapter's features and capabilities.
Congratulations on the purchase of your new Wireless Adapter. The Wireless Adapter provides a wireless network interface for your Notebook or PC.
Package Contents
The following items should be included:
• The Wireless Adapter Unit
• 2 Antennas
• Quick Start Guide
• CD-ROM containing the on-line manual.
If any of the above items are damaged or missing, please contact your dealer immediately.
LEDs
Wireless Adapter
The Wireless Adapter has a single Link/Activity LED.
Link/Act LED
Operation
You should install the supplied software on the CD-ROM before inserting the Wireless
adapter.
• On - Associated with the network.
• Off - Not associated with the network.
• Blinking - Data being transferred.
1
Page 6
Chapter 2
Initial Installation
2
This Chapter covers the software installation of the Wireless Adapter.
Requirements
• Windows 2000/XP/Vista.
• CD-ROM drive.
• IEEE802.11n, IEEE802.11b or IEEE802.11g wireless LAN.
Procedure
You should install the supplied software BEFORE inserting the Wireless Adapter.
1. Insert the CD-ROM into the drive on your PC.
2. The installation program should start automatically. If it does not, run the SETUP.EXE
program.
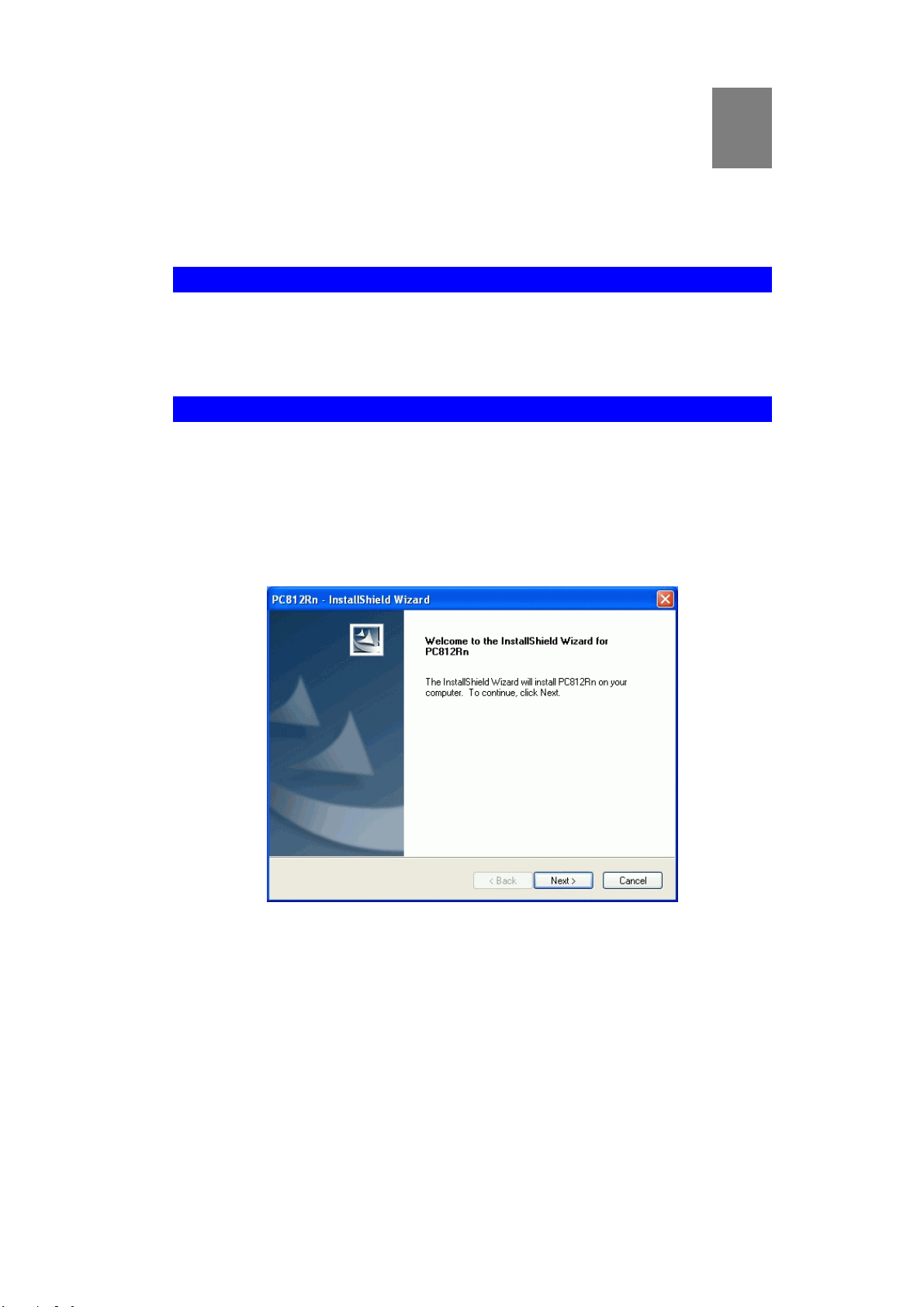
3. Select the desired installation language on the screen.
Figure 1: Start Installation
4. On the screen above, click "Next" to start the installation.
5. Select the location on the screen.
2
Page 7
Initial Installation
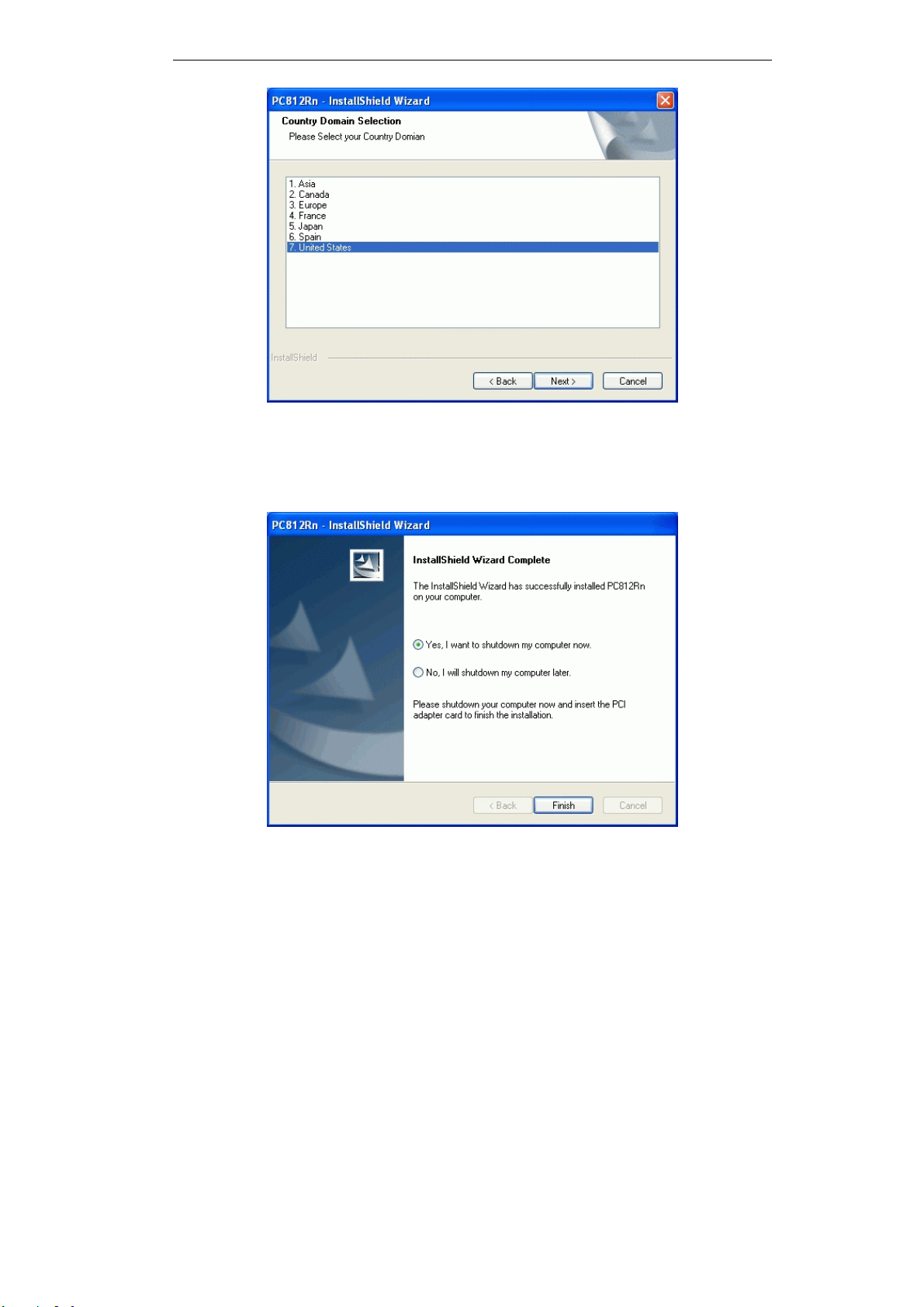
Figure 2: Country Domain Screen
6. Step though the procedure.
7. After the installation is complete, select Yes, I want to shutdown my computer now and then
click "Finish".
Figure 3: Installation Screen
8. Insert the Card into your computer.
• Remove the cover on one side of the computer.
• Find an empty PCI expansion slot inside the computer.
• Press the Card firmly into the slot.
• Connect the supplied antenna cable to the port on the Card.
• Replace the computer’s cover and power it on.
9. The Windows "New Hardware" wizard will then start.
• Select Install the software automatically to allow it to complete the installation of the
Windows driver
3
Page 8

Wireless Adapter User Guide
10. When the Windows wizard is complete, you will now have a new icon in your system tray,
as shown below.
Figure 4: System Tray Icon
Wireless Adapter Icon Table
Connection to the Wireless Adapter is established. The length of green
color indicates the signal strength.
No connection to the Wireless Adapter.
The Wireless Adapter is unplugged.
11. You can double- click this icon to configure the Wireless interface. See the following
chapter for details.
4
Page 9

Chapter 3
Using the Windows Utility
3
This Chapter provides Setup details for the AP mode of the Wireless Adapter.
Overview
If using Windows, you can use the supplied utility to configure the Wireless interface.
To Use the supplied Windows utility for Configuration
• Double-click the PC812Rn WLan Application icon in the desktop.
• Click Start - Programs - SerComm - PC812Rn - WLan Application.
This Chapter assumes you are using the supplied WLan Application utility.
System Tray Icon
If the WLan Application program is running, you can double-click the icon in the System Tray
or right-click the icon and select "Restore" to open the application.
Status Information
The menu options available from the System Tray icon are:
• Restore - This will display the main screen.
• Radio Off - The wireless adapter is not associated with the network when the radio is off.
• WZC On - Click this to turn the Wireless Zero Configuration on.
• Exit - Terminate the connection to the Wireless Adapter.
Figure 5: Wireless Adapter menu
5
Page 10

Wireless Adapter User Guide
Connecting to a Wireless Network
Double-click the Icon to open the Site Survey screen, when you can select the Wireless network you wish to join.
Auto Profile Connect
Normally, this option should be enabled. The adapter will then connect to an available network
which was connected successfully last time.
There are various methods to specify the required network.
• On the Profile Manager tab, select the desired profile in the list, an d click the Apply
Profile button.
• On the Site Survey tab, either double-click the network in the list, or select the network
and click the Connect button.
Site Survey Screen
This screen is displayed when you double-click the system tray icon. You can also click the
Site Survey Tab in the screen.
Data - Site Survey Screen
Display PC To PC
(Ad-Hoc)
Select this check box to display ad-hoc (computer-to-computer)
networks.
Figure 6: Site Survey Screen
6
Page 11

Using the Windows Utility
Display 802.11b
Access Points
Display 802.11a
Access Points
Display 802.11g
Access Points
Network Name
MAC Address
Security
WPS
CH.
Signal
Network Type
Frequency
Status
Select this check box to display 802.11b (infrastructure) networks.
Select this check box to display 802.11a (infrastructure) networks.
Select this check box to display 802.11g (infrastructure) networks.
Available wireless networks are listed.
This is the MAC address of the Access Point (or Wireless station, if
the network is an Ad-hoc network).
Data encryption and authentication methods used on the wireless
network
It will display "Y" if the Access Point has WPS function.
The channel used by the Wireless network.
This is displayed as percentage (0 ~ 100%).
This will indicate "Infrastructure" (displayed device is an Access
Point) or "Ad-hoc". (displayed device is a Wireless station)
The Wireless band used by this Wireless network.
The area to the left of the "Rescan" button shows the current status. In
the example above, it shows "Connected".
Rescan
Disconnect
Connect
Click this button to rescan for all Wireless networks.
Click this button to exit the current Wireless network.
Click this button to connect the Wireless network .
Wireless Network Sequence (order)
You can click the headings (ex. Network Name, MAC Address, Security…) of the Wireless
network table to arrange the Wireless network in the desired order.
To Connect to a Wireless Network
• Double-click on the desired network.
• Click the name of the wireless network to which you want to connect, and then click
Connect.
Note that once you are connected to a Wireless network, the Site Survey screen will identify
the current wireless network with a blue icon, as shown below.
7
Page 12

Wireless Adapter User Guide
Figure 7: Site Survey Screen - Connected
8
Page 13

Using the Windows Utility
Profile Manager Screen
This screen is accessed by clicking the Profile Manager tab on the main screen.
Figure 10: Profile Manager Screen
Data - Profile Manager Screen
Profile Name
Network Name
(SSID)
Advanced Settings
WPS Function
Network Type
Wireless Mode
Prefer Channel
Enter or select a suitable name for this profile. Each profile must
have a unique name.
If the desired wireless network is currently available, you can
select its SSID. Otherwise, type in the SSID of the desired wireless network.
On the resulting sub-screen, enter the required data for the advanced settings.
Click this button to configure the WPS settin gs in the sub-screen.
Select the desired option:
• Infrastructure - Select this to connect to an Access point.
• Ad-Hoc - Select this if you are connecting directly to another
computer.
Select the desired wireless mode to which you want to connect.
Select the channel you would like to use.
9
Page 14

Wireless Adapter User Guide
Authentication Mode
You MUST select the option to match the Wireless LAN you
wish to join. The available options are:
• Open System - Broadcast signals are not encrypted. This
method can be used only with no encryption or with WEP.
• Shared Key - Broadcast signals are encrypted using WEP.
This method can only be used with WEP.
• Auto Switch - This is another WEP system; it will select
either Open System or Shared Key as required.
• WPA-PSK - PSK means "Pre-shared Key". You must enter
this Passphrase value; it is used for both authentication and
encryption.
• WPA2-PSK - This is a further development of WPA-PSK,
and offers even greater security. You must enter this
Passphrase value; it is used for both authentication and en-
cryption.
• WPA Radius - This version of WPA requires a Radius
Server on your LAN to provide the client authentication ac-
cording to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions are
encrypted using the WPA standard.
• WPA2 Radius - This version of WPA2 requires a Radius
Server on your LAN to provide the client authentication
according to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions are
encrypted using the WPA2 standard.
Encryption Method
Create with
Passphrase
Enter Key Manually
Enter ASCII Key
Manually
Passphrase
The available options depend on the Authentication method
selected above. The possible options are:
• Security Off - No data encryption is used.
• WEP - If selected, you must enter the WEP data shown
below. This WEP data must match the Access Point or other
Wireless stations.
• AES, TKIP - These options are available with WPA-PSK,
WPA2-PSK, WPA-Radius and WPA2-Radius. Select the
correct option.
Enable this check box and enter a word or group of printable
characters in the Passphrase box, select the desired encryption to
automatically configure the WEP Key.
Enable this check box and select the desired key in the dropdown list. Then enter the key values you wish to use and select
the desired encryption. Other stations must have matching key
values.
Enable this check box and select the desired key in the dropdown list. Then enter the key values you wish to use and select
the desired encryption. Other stations must have matching key
values.
For WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK modes, you need to enter the
desired value (8~63 characters). Data is encrypted using a 256Bit
key derived from this key. Other Wireless Stations must use the
same key.
10
Page 15

Using the Windows Utility
Confirm
802.1x Authentication
Protocol
Configure WPA
Radius
For WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK modes, re-enter the value in this
field.
For WPA Radius and WPA2 Radius modes, select the desired
option in the drop-down list.
For WPA Radius and WPA2 Radius modes, click this button to
open a sub-window where you can enter details of the Radius
Server.
To add a profile
1. On the Profile Manager tab, complete the settings on this screen.
2. Verify that the settings you configured are correct.
3. Click Save Profile.
To export profiles
1. On the Profile Manager tab, click Export Profiles. The Save As dialog box appears.
2. Type a name for the profile that you are saving, and then verify that the file name extension is set to .cfg.
3. Click Save.
To import profiles
1. On the Profile Manager tab, click Import Profiles. The open dialog box appears.
2. Select the profile set that you want to import.
3. Click Open.
To delete a profile
1. On the Profile Manager tab, select the profile that you want to delete.
2. Click Delete Profile.
To edit a profile
1. On the Profile Manager tab, select the profile that you want to edit.
2. Change the profile settings as necessary.
3. Click Save Profile.
To enable a profile
1. In the list of available profiles, click the profile th at you want to enable.
2. Click Apply Profile.
11
Page 16

Wireless Adapter User Guide
Advanced Settings Screen
Once you have created a profile, as described above, the Advanced Settings tab will be
available on the Profile Manager screen.
Figure 8: Advanced Settings Screen
Data - Advanced Settings Screen
Do not change
settings
Preamble (2.4GHz)
Transmit Rate
Fragment Thresh-
old
RTS/CTS Threshold
802.11n
Enable 802.11n
Network
Channel Width
Guard Interval
Extension Channel
Enable this check box if you don’t want to modify the settings in
this screen.
Normally, this should be left at "Auto".
Use this to manually set the speed, if desired. The default is "Auto".
The default value is 2346. In some cases, you may be able to
improve performance by adjusting this value.
The default value is 2346. In some cases, you may be able to
improve performance by adjusting this value.
Enable this if you want to use the 802.11n network.
Select the desired channel width.
Use this to manually set the interval, if desired. The default is
"Auto".
Select the desired channel.
Antenna Selection
Select the desired option. The default is set to "Auto".
12
Page 17

Using the Windows Utility
WPS Screen
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) can simplify the process of connecting any device to the wireless network by using the push button configuration (PBC) on the Wireless Access Point, or
entering a PIN code.
You will see the WPS screen when you try to connect the wireless network with the WPS
function.
Figure 9: Wi-Fi Protected Setup Screen
Data - Wi-Fi Protected Setup Screen
WPS Status
Join a Wireless Network
Network Name
Push the Button on
my access point
Enter a PIN into my
access point
Enter a PIN from
my access point
Start
The image indicates the status of WPS.
Select the desired network name from the list.
Push the WPS button of the access point and enable this button.
Enable this and enter the PIN code displayed in the following field
to the WPS screen of the access point.
Enable this and enter the PIN code of the access point in the following field.
Click this button to start the WPS process.
13
Page 18

Wireless Adapter User Guide
Network Status Screen
This screen displays the status of the current wireless link. Clicking the Network Status tab
will display a screen like the following.
Figure 10: Network Status Screen
You may have to wait a few seconds for the screen to be populated.
Data - Network Status Screen
Link Information
Current Status
Network SSID
Network BSSID
Network Type
Authentication Mode
Encryption Method
Tx/Rx Speed
Internet Protocol
DHCP Option
IP Address
It will indicate the current link status.
It shows the SSID or network name of the selected wireless
network.
It shows the MAC address of the access point.
This will indicate "Infrastructure" or "Ad-hoc".
It will indicate the current authentication mode in use.
It shows the wireless security that the wireless network is using.
It shows the current wireless connection speed.
It shows if the IP address was automatically obtained from a
DHCP server.
It shows the current IP address on the wireless interface.
14
Page 19

Using the Windows Utility
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
DHCP Server
Channel Performance
Channel Performance
Signal
Signal
Subnet mask for the current IP address.
Gateway IP address associated with the current IP address.
It shows the IP address of the DHCP Server.
It graphically presents the Transmission (Tx) rate and Receiving
(Rx) rate over time.
It graphically presents the Signal strength.
15
Page 20

Wireless Adapter User Guide
About Screen
This screen displays details of the traffic sent or received on the current Wireless network.
Figure 11: About Screen
This tab shows the following information:
• Regional Domain
• Firmware Version
• Driver Version
• MAC Address
• SerComm DLL Version
• SerComm Utility Version
16
Page 21

Appendix A
Specifications
Wireless Adapter
Model:
Standards:
Computer Slot Type:
Data Rates:
Operating Channels:
Operating Frequency:
Modulation Technique:
Draft 802.11n: OFDM
802.11g: DBPSK, DQPSK, CCK, BPSK, QPSK, QAM
802.11b: CCK, DQPSK, DBPSK
PC812Rn
IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g, Draft 802.11n compliant
PCI Card
20 MHz BW: 145, 130, 117, 104, 78
40 MHz BW: 300, 270, 243, 240, 216, 180, 162, 120,108
Receive PHY Rate: 300Mbps
Transmit PHY Rate: 150Mbps
(802.11n)
54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9, and 6 Mbps (802.11g)
11, 5.5, 2, 1 Mbps (802.11b)
USA: channel 1-11
USA: 2.412 ~ 2.462 GHz
A
Media Access Protocol:
Operating Voltage:
Antenna Type
Security:
OS Requirements
CSMA/CA
3.3V±5%
Detachable antenna*2
64/128/152-bit WEP Shared-key encryption
WPA-PSK(Personal)/WPA2-PSK(Personal)
WPA-EAP(Enterprise)/WPA2-EAP(Enterprise)
802.1x WEP
TKIP/AES encryption
Windows Vista/XP/2000
17
Page 22

Appendix B
About Wireless LANs
B
This Appendix provides some background information about using Wireless
LANs (WLANs).
Modes
Wireless LANs can work in either of two (2) modes:
• Ad-hoc
• Infrastructure
Ad-hoc Mode
Ad-hoc mode does not require an Access Point or a wired (Ethernet) LAN. Wireless Stations (e.g. notebook PCs with wireless cards) communicate directly with each other.
Infrastructure Mode
In Infrastructure Mode, one or more Access Points are used to connect Wireless Stations
(e.g. Notebook PCs with wireless cards) to a wired (Ethernet) LAN. The Wireless Stations
can then access all LAN resources.
Access Points can only function in "Infrastructure" mode,
and can communicate only with Wireless Stations which are
set to "Infrastructure" mode.
BSS/ESS
BSS
A group of Wireless Stations and a single Access Point, all using the same ID (SSID), form a
Basic Service Set (BSS).
Using the same SSID is essential. Devices with different SSIDs are unable to communicate
with each other.
ESS
A group of Wireless Stations, and multiple Access Points, all using the same ID (ESSID), form
an Extended Service Set (ESS).
Different Access Points within an ESS can use different Channels. In fact, to reduce interference, it is recommended that adjacent Access Points SHOULD use different channels.
As Wireless Stations are physically moved through the area covered by an ESS, they will
automatically change to the Access Point which has the least interference or best performance.
This capability is called Roaming. (Access Points do not have or require Roaming capabilities.)
18
Page 23

Appendix B - About Wireless LANs
Channels
The Wireless Channel sets the radio frequency used for communication.
• Access Points use a fixed Channel. You can select the Channel used. This allows you to
choose a Channel which provides the least interference and best performance. In the USA
and Canada, 11 channels are available. If using multiple Access Points, it is better if adjacent Access Points use different Channels to reduce interference.
• In "Infrastructure" mode, Wireless Stations normally scan all Channels, looking for an
Access Point. If more than one Access Point can be used, the one with the strongest signal
is used. (This can only happen within an ESS.)
• If using "Ad-hoc" mode (no Access Point), all Wireless stations should be set to use the
same Channel. However, most Wireless stations will still scan all Channels to see if there
is an existing "Ad-hoc" group they can join.
WEP & WPA-PSK
Both WEP and WPA-PSK are standards for encrypting data before it is transmitted.
This is desirable because it is impossible to prevent snoopers from receiving any data which is
transmitted by your Wireless Stations. But if the data is encrypted, then it is meaningless
unless the receiver can decrypt it.
WPA-PSK is a later standard than WEP, and is more secure.
WPA2-PSK
This is a later version of WPA (WPA-PSK). The major change is the use of AES (Advanced
Encryption System) for protecting data. AES is very secure, considered to be unbreakable. The
PSK (Pre-shared Key) must be entered on each Wireless station.
If WPA2-PSK is used, the Wireless Stations and the Access Point must have the same
settings for each of the following:
WPA2 PSK
(Pre-shared Key)
Encryption
Enter the same value on every station and the AP. The PSK
must be from 8 to 63 characters in length. The 256Bit key
used for the actual encryption is derived from this key.
The same encryption method must be used. The most
common encryption method is TKIP. Another widelysupported method is AES.
19
Page 24

Wireless Adapter User Guide
Wireless LAN Configuration
To allow Wireless Stations to use the Access Point, the Wireless Stations and the Access Point
must use the same settings, as follows:
Mode
SSID (ESSID)
Security
On client Wireless Stations, the mode must be set to "Infrastructure".
(The Access Point is always in "Infrastructure" mode.)
Wireless Stations should use the same SSID (ESSID) as the Access
Point they wish to connect to. Alternatively, the SSID can be set to "any"
or null (blank) to allow connection to any Access Point.
The Wireless Stations and the Access Point must use the same settings
for Wireless security (Disabled, WEP, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA
Radius, WPA2 Radius)
• If Wireless security remains disabled on the Access Point, all
stations must have wireless security disabled.
• If Wireless security is enabled on the Access Point, each station
must use the same settings.
20
Page 25

Regulatory Approvals
FCC Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
To assure continued compliance, any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
(Example - use only shielded interface cables when connecting to computer or peripheral
devices).
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with a minimum distance of 20
centimeters between the radiator and your body.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
The antennas used for this transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance of at
least 20 cm from all persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter.
Channel
The Wireless Channel sets the radio frequency used for communication.
•Access Points use a fixed Channel. You can select the Channel used. This allows you to
choose a Channel which provides the least interference and best performance. In the USA
and Canada, 11 channel are available. If using multiple Access Points, it is better if adjacent
Access Points use different Channels to reduce interference.
• In "Infrastructure" mode, Wireless Stations normally scan all Channels, looking for an
Access Point. If more than one Access Point can be used, the one with the strongest
signal is used. (This can only happen within an ESS.)
• If using "Ad-hoc" mode (no Access Point), all Wireless stations should be set to use the
same Channel. However, most Wireless stations will still scan all Channels to see if there
is an existing "Ad-hoc" group they can join.
Note:This equipment marketed in USA is restricted by firmware to only operate on 2.4G channel 1-11
.
 Loading...
Loading...