Page 1

11n Wireless
Access Point
User's Guide
Page 2

Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................. 1
Features of your Wireless Access Point ........................................................................... 1
Package Contents .............................................................................................................. 3
Physical Details .................................................................................................................. 4
CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................... 6
Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 6
Procedure ........................................................................................................................... 6
CHAPTER 3 ACCESS POINT SETUP .................................................................................. 8
Overview ............................................................................................................................ 8
Setup using the Windows Utility ...................................................................................... 8
Setup using a Web Browser ............................................................................................ 11
System Basic Settings Screen .......................................................................................... 13
System Advanced Settings Screen .................................................................................. 15
Wireless Screens .............................................................................................................. 17
Basic Screen ..................................................................................................................... 17
Virtual AP Settings .......................................................................................................... 20
Virtual AP Screen ............................................................................................................ 22
Radius Server Settings .................................................................................................... 35
Access Control ................................................................................................................. 36
Advanced Settings ........................................................................................................... 39
Wi-Fi Protected Setup .................................................................................................... .40
CHAPTER 4 PC AND SERVER CONFIGURATION ....................................................... 41
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 41
Using WEP ....................................................................................................................... 40
Using WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK ........................................................................................ 42
Using WPA-Enterprise ................................................................................................... 43
802.1x Server Setup (Windows 2000 Server) ................................................................ 44
802.1x Client Setup on Windows XP ............................................................................. 54
Using 802.1x Mode (without WPA) ............................................................................... 60
CHAPTER 5 OPERATION AND STATUS ......................................................................... 61
Operation ......................................................................................................................... 61
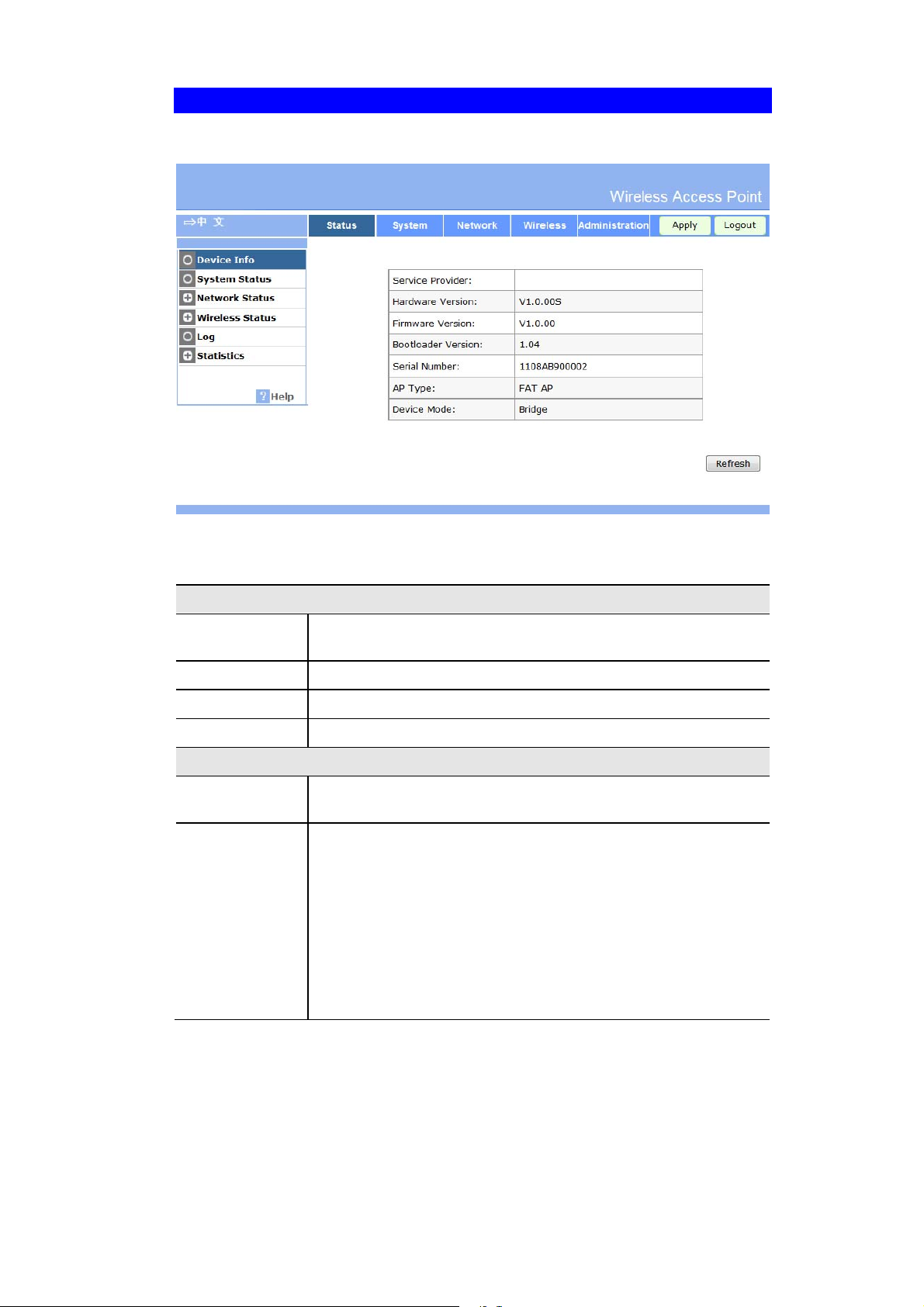
Status Screen .................................................................................................................... 61
CHAPTER 6 ACCESS POINT MANAGEMENT ............................................................... 68
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 68
Admin Login Screen ........................................................................................................ 68
Auto Config/Update ........................................................................................................ 73
Config File
SNMP ............................................................................................................................... 76
Log Settings ...................................................................................................................... 77
Firmware Upgrade .......................................................................................................... 78
APPENDIX A SPECIFICATIONS ....................................................................................... 79
Wireless Access Point ...................................................................................................... 79
APPENDIX B TROUBLESHOOTING ................................................................................ 82
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 82
General Problems ............................................................................................................ 82
APPENDIX C WINDOWS TCP/IP ....................................................................................... 84
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 84
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 9x/ME: ............................................................. 84
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows NT4.0 ............................................................... 86
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 2000 .................................................................. 88
........................................................................................................................ 74
i
Page 4

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows XP .................................................................... 90
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows Vista ................................................................. 92
APPENDIX D ABOUT WIRELESS LANS .......................................................................... 94
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 94
Wireless LAN Terminology ............................................................................................ 94
APPENDIX E COMMAND LINE INTERFACE ................................................................ 97
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 97
Command Reference ....................................................................................................... 97
ii
Page 5
Chapter 1
Introduction
1
This Chapter provides an overview of the Wireless Access Point's features
and capabilities.
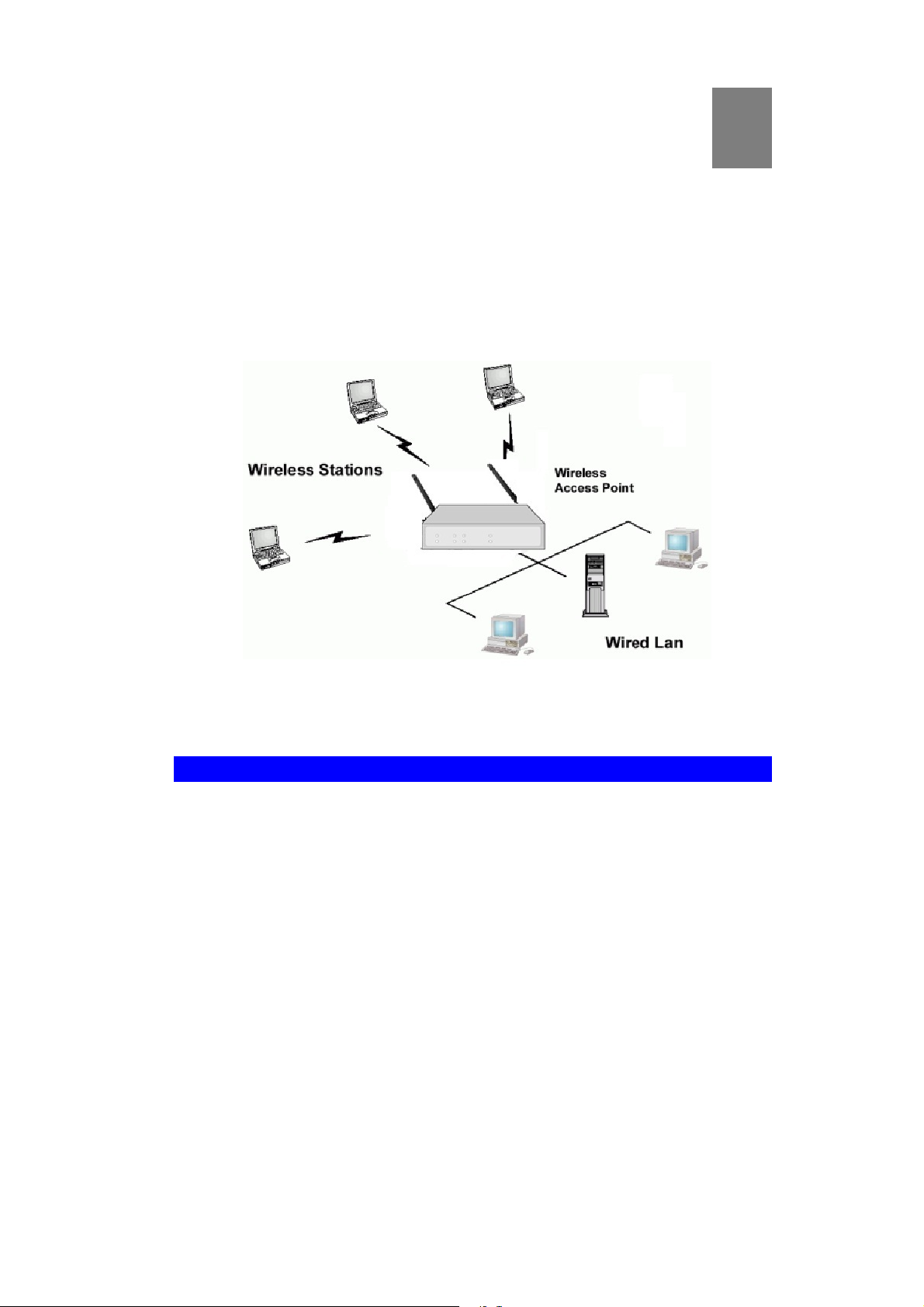
Congratulations on the purchase of your new Wireless Access Point. The Wireless Access
Point links your Wireless Stations to your wired LAN. The Wireless stations and devices on
the wired LAN are then on the same network, and can communicate with each other without
regard for whether they are connected to the network via a Wireless or wired connection.
Figure 1: Wireless Access Point
Features of your Wireless Access Point
The Wireless Access Point incorporates many advanced features, carefully designed to provide
sophisticated functions while being easy to use.
Standards Compliant. The Wireless Access Point complies with the IEEE802.11g and
IEEE802.11n draft 2.0 specifications for Wireless LANs.
Supports 11n Wireless Stations. The 802.11n Draft standard provides for backward
compatibility with the 802.11b standard, so 802.11n, 802.11b and 802.11g Wireless stations can be used simultaneously.
Bridge Mode Support. The Wireless Access Point can operate in Bridge Mode, con-
necting to another Access Point. Both PTP (Point to Point) and PTMP (Point to Mu ltiPoint) Bridge modes are supported.
And you can even use both Bridge Mode and Access Point Mode simultaneously!
DHCP Client Support. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol provides a dynamic IP
address to PCs and other devices upon request. The Wireless Access Point can act as a
DHCP Client, and obtain an IP address and related information from your existing DHPC
Server.
1
Page 6

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Thin AP. Support thin AP function.
Upgradeable Firmware. Firmware is stored in a flash memory and can be upgraded
easily, using only your Web Browser.
PoE Support. You can use PoE (Power over Ethernet) to provide power to the Wireless
Access Point, so only a single cable connection is required.
Security Features
Virtual APs. For maximum flexibility, wireless security settings are stored in Virtual AP.
Up to 8 Virtual APs can be defined and used as any time.
Multiple BSSIDs. Because each Virtual AP has it own SSID and beacon, and up to 4
Virtual APs can be active simultaneously, multiple SSIDs are supported. Different clients
can connect to the Wireless Access Point using different SSIDs, with different security
settings.
Virtual APs Isolation. If desired, PCs and devices connecting to different Virtual APs
can be isolated from each other.
VLAN Support. The 802.1Q VLAN standard is supported, allowing traffic from differ-
ent sources to be segmented. Combined with the multiple SSID feature, this provides a
powerful tool to control access to your LAN.
WEP support. Support for WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is included. Both 64 Bit
128 Bit, and 152 Bit keys are supported.
WPA support. Support for WPA is included. WPA is more secure than WEP, and
should be used if possible. Both TKIP and AES encryption methods are supported.
802.1x Support. Support for 802.1x mode is included, providing for the industrial-
strength wireless security of 802.1x authentication and authorization.
Radius Client Support. The Wireless Access Point can login to your existing Radius
Server (as a Radius client).
Radius MAC Authentication. You can centralize the checking of Wireless Station
MAC addresses by using a Radius Server.
Rogue AP Detection. The Wireless Access Point can detect unauthorized (Rouge)
Access Points on your LAN.
Access Control. The Access Control feature can check the MAC address of Wireless
clients to ensure that only trusted Wireless Stations can use the W ireless Access Po int to
gain access to your LAN.
Password - protected Configuration. Optional password protection is provided to
prevent unauthorized users from modifying the configuration data and settings.
Advanced Features
Command Line Interface. If desired, the command line interface (CLI) can be used for
configuration. This provides the possibility of creating scripts to perform common configuration changes.
Auto Configuration. The Wireless Access Point can perform self-configuration by
copying the configuration data from another Access Point. This feature is enabled by default.
Auto Update. The Wireless Access Point can automatically update its firmware, by
downloading and installing new firmware from your FTP server.
Radius Accounting Support. If you have a Radius Server, you can use it to provide
accounting data on Wireless clients.
2
Page 7

Introduction
Syslog Support. If you have a Syslog Server, the Wireless Access Point can send its log
data to your Syslog Server.
SNMP Support. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is supported, allowing
you to use a SNMP program to manage the Wireless Access Point.
Package Contents
The following items should be included:
Wireless Access Point
Power Adapter
2Pcs Antenna
If any of the above items are damaged or missing, please contact your dealer immediately.
3
Page 8
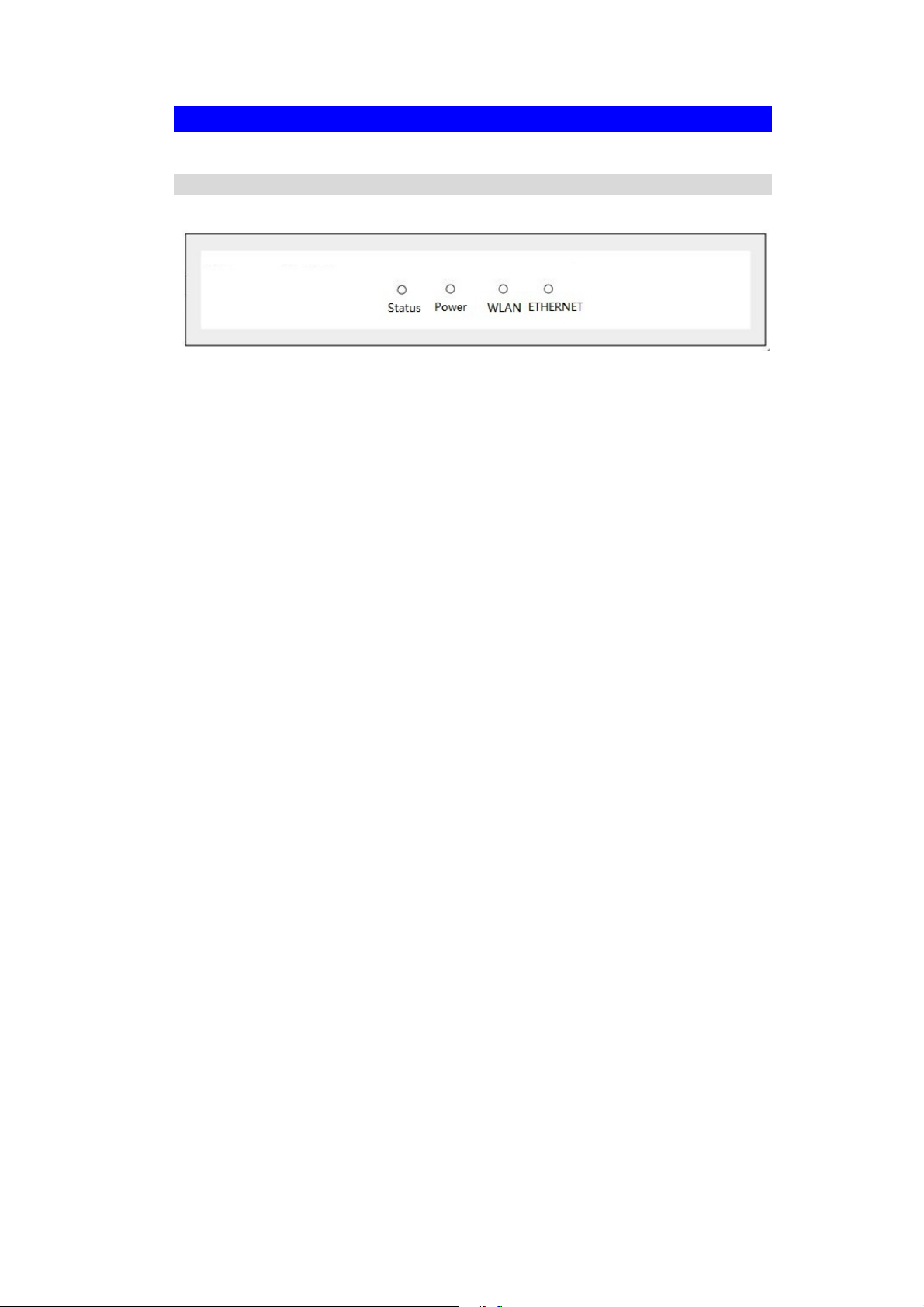
Wireless Access Point User Guide
Physical Details
Front Panel LEDs
Figure 2: Front Panel
Power On - Normal operation.
Off - No power
WLAN On -
Status On - Error condition.
Ethernet On - The LAN (Ethernet) port is active.
Idle
Off - Wireless connection is not available.
Flashing - Data is being transmitted or received via the Wireless access
point. Data includes "network traffic" as well as user data.
Off - Normal operation.
Blinking - During start up, and when the Firmware is being upgraded.
Off - No active connection on the LAN (Ethernet) port.
Flashing - Data is being transmitted or received via the corresponding
LAN (Ethernet) port.
4
Page 9

Rear Panel
Introduction
Figure 3: Rear Panel
Reset Button
ETHERNET
Power port
CONSOLE
This button has two (2) functions:
Reboot. When pressed and released, the Wireless Access Point
will reboot (restart).
Reset to Factory Defaults. This button can also be used to clear
ALL data and restore ALL settings to the factory default values.
To Clear All Data and restore the factory default values:
1. Hold the Reset Button until the Status (Red) LED blinks TWICE,
usually more than 5 seconds.
2. Release the Reset Button.
The factory default configuration has now been restored, and the
Access Point is ready for use.
Use a standard LAN cable (RJ45 connectors) to connect this port to a
10/100/1000BaseT hub/switch on your LAN.
Connect the supplied power adapter (12V@1A) here.
DB9 female RS232 port.
5
Page 10

Chapter 2
Installation
This Chapter covers the physical installation of the Wireless Access Point.
Requirements
Requirements:
TCP/IP network
Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connectors
Installed Wireless network adapter for each PC that will be wirelessly connected to the
network
Procedure
1. Select a suitable location for the installation of your Wireless Access Point. To maximize
reliability and performance, follow these guidelines:
Use an elevated location, such as wall mounted or on the top of a cubicle.
Place the Wireless Access Point near the center of your wireless coverage area.
If possible, ensure there are no thick walls or metal shielding between the Wireless
Access Point and Wireless stations. Under ideal conditions, the Wireless Access Point
has a range of around 150 meters (450 feet). The range is reduced, and transmission
speed is lower, if there are any obstructions between Wireless devices.
Figure 4: Installation Diagram
6
Page 11
Installation
2. Use a standard LAN cable to connect the "LAN" port on the Wireless Access Point to a
10/100/1000BaseT hub/switch on your LAN.
3. Connect the supplied power adapter to the Wireless Access Point and a convenient power
outlet, and power up.
4. Check the LEDs:
The Status LED should flash, then turn OFF.
The Power, Ethernet and WLAN LEDs should be ON.
For more information, refer to Front Panel LEDs in Chapter 1.
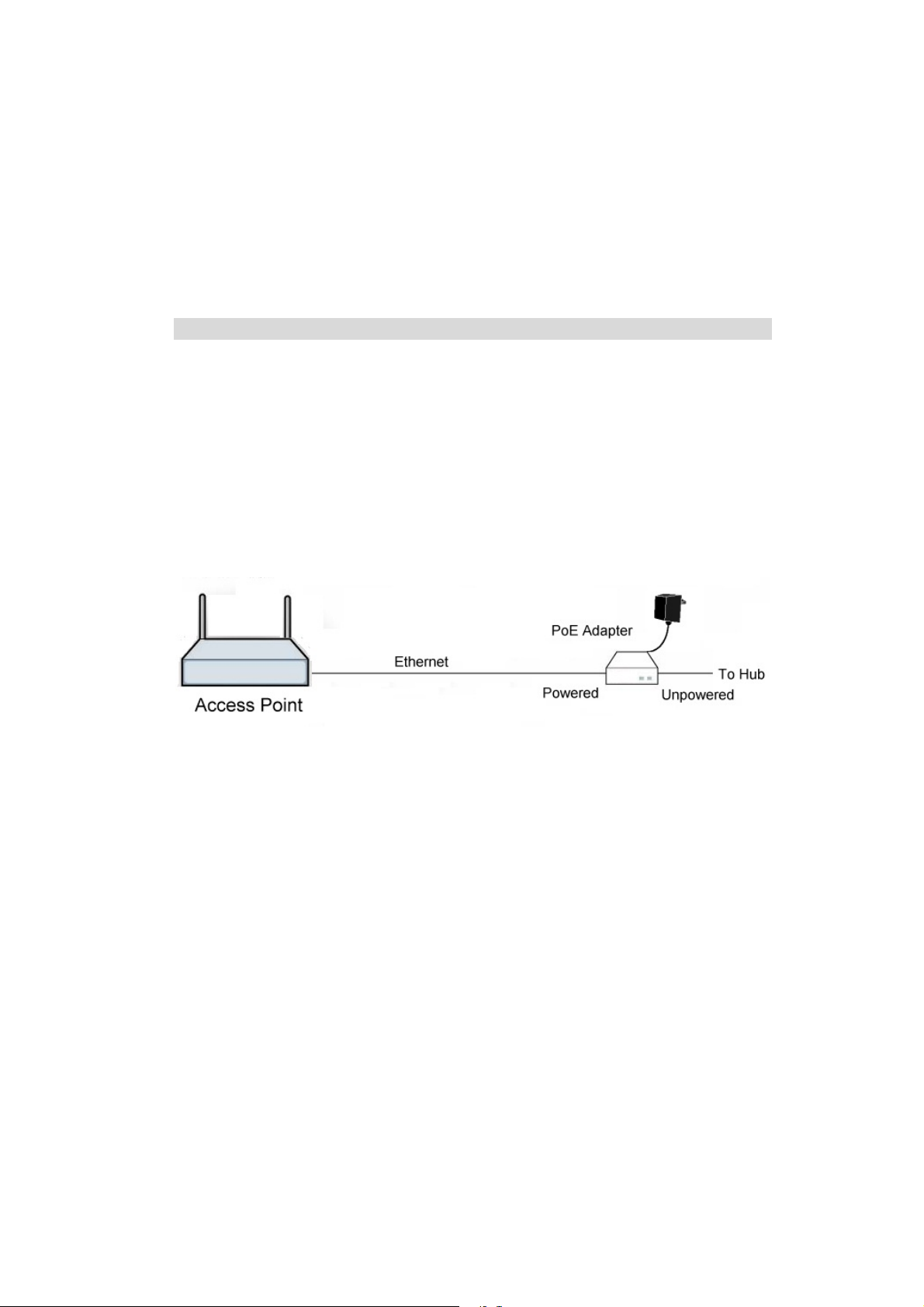
Using PoE (Power over Ethernet)
The Wireless Access Point supports PoE (Power over Ethernet). To use PoE:
1. Do not connect the supplied power adapter to the Wireless Access Point.
2. Connect one end of a standard (category 5) LAN cable to the Ethernet port on the Wire-
less Access Point.
3. Connect the other end of the LAN cable to the powered Ethernet port on a suitable PoE
Adapter. (48V DC)
4. Connect the unpowered Ethernet port on the PoE adapter to your Hub or switch.
5. Connect the power supply to the PoE adapter and power up.
6. Check the LEDs on the Wireless Access Point to see it is drawing power via the Ethernet
connection.
Figure 5: Using PoE (Power over Ethernet)
7
Page 12
Chapter 3
Access Point Setup
This Chapter provides details of the Setup process for Basic Operation of
your Wireless Access Point.
Overview
This chapter describes the setup procedure to make the Wireless Access Point a valid device
on your LAN, and to function as an Access Point for your Wireless Stations.
Wireless Stations may also require configuration. For details, see Chapter 4 - PC and Server
Configuration.
The Wireless Access Point can be configured using either the supplied Windows utility or your
Web Browser
Setup using the Windows Utility
A simple Windows setup utility is supplied on the CD-ROM. This utility can be used to assign
a suitable IP address to the Wireless Access Point. Using this utility is recommended, because
it can locate the Wireless Access Point even if it has an invalid IP address.
Installation
1. Insert the supplied CD-ROM in your drive.
2. If the utility does not start automatically, run the SETUP program in the root folder.
3. Follow the prompts to complete the installation.
Main Screen
Start the program by using the icon created by the setup program.
When run, the program searches the network for all active Wireless Access Points, then
lists them on screen, as shown by the example below.
8
Page 13

Access Point Setup
Figure 6: Management utility Screen
Wireless Access Points
The main panel displays a list of all Wireless Access Points found on the network. For each
Access Point, the following data is shown:
Name
IP address
MAC Address
IEEE Standard
The Name is shown on a sticker on the base of the device.
The IP address for the Wireless Access Point.
The hardware or physical address of the Wireless Access Point.
The wireless standard or standards used by the Wireless Access Point
(e.g. 802.11b, 802.11g)
FW Version
Description
The current Firmware version installed in the Wireless Access Point.
Any extra information for the Wireless Access Point, entered by the
administrator.
Note: If the desired Wireless Access Point is not listed, check that the device is installed and
ON, then update the list by clicking the Refresh button.
Buttons
Refresh
Detail Info
Web Management
Set IP Address
Click this button to update the Wireless Access Point device listing
after changing the name or IP Address.
When clicked, additional information about the selected Access
Point will be displayed.
Use this button to connect to the Wireless Access Point's Webbased management interface.
Click this button if you want to change the IP Address of the
Wireless Access Point.
Exit
Exit the Management utility program by clicking this button.
9
Page 14

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Setup Procedure
1. Select the desired Wireless Access Point.
2. Click the Set IP Address button.
3. If prompted, enter the user name and password. The default values are admin for the
User Name, and password for the Password.
4. Ensure the IP address, Network Mask, and Gateway are correct for your LAN. Save any
changes.
5. Click the Web Management button to connect to the selected Wireless Access Point using
your Web Browser. If prompted, enter the User Name and Password again.
6. Check the following screens, and configure as necessary for your environment. Use the
on-line help if necessary.
The later sections in this Chapter also provides more details about each of these screens.
7. You may also wish to set the admin password and administration connection options.
These are on the Admin Login screen accessed from the Management menu. See Chapter
6 for details of the screens and features available on the Management menu.
8. Use the Apply and Reboot buttons on the menu to apply your changes and restart the
Wireless Access Point.
Setup is now complete.
Wireless stations must now be set to match the Wireless Access Point. See Chapter 4 for
details.
10
Page 15
Access Point Setup
Setup using a Web Browser
Your Browser must support JavaScript. The configuration program has been tested on the
following browsers:
Netscape V4.08 or later
Internet Explorer V4 or later
Setup Procedure
Before commencing, install the Wireless Access Point in your LAN, as described previously.
1. Check the Wireless Access Point to determine its Default Name. This is shown on a label
on the base or rear, and is in the following format:
SCxxxxxx
Where xxxxxx is a set of 6 Hex characters (0 ~ 9, and A ~ F).
2. Use a PC which is already connected to your LAN, either by a wired connection or anoth-
er Access Point.
Until the Wireless Access Point is configured, establishing a Wireless connection to it
may be not possible.
If your LAN contains a Router or Routers, ensure the PC used for configuration is on
the same LAN segment as the Wireless Access Point.
3. Start your Web browser.
4. In the Address box, enter "HTTP://" and the IP Address of the 11N Wireless Access Point,
as in this example, which uses the Wireless Access Point's default IP Address:
HTTP://192.168.0.228
5. You should then see a login prompt, which will ask for a User Name and Password.
Enter admin for the User Name, and password for the Password.
These are the default values. The password can and should be changed. Always enter the
current user name and password, as set on the Admin Login screen.
Figure 7: Password Dialog
6. You will then see the Status screen, which displays the current settings and status. No data
input is possible on this screen. See Chapter 5 for details of the Status screen.
11
Page 16
Wireless Access Point User Guide
7. From the menu, check the following screens, and configure as necessary for your envi-
ronment. Details of these screens and settings are described in the following sections of
this chapter.
System - Basic and Advanced settings
Wireless - Basic, Advanced, Access Control, Radius Server, Virtual APs & WIFI
Protected Setup.
8. You may also wish to set the admin password and administration connection options.
These are on the Admin Login screen accessed from the Management menu. See Chapter
6 for details of the screens and features available on the Management menu.
9. Use the Apply and Reboot buttons on the menu to apply your changes and restart the
Wireless Access Point.
Setup is now complete.
Wireless stations must now be set to match the Wireless Access Point. See Chapter 4 for
details.
If you can't connect:
It is likely that your PC’s IP address is incompatible with the Wireless Access
Point’s IP address. This can happen if your LAN does not have a DHCP Server.
The default IP address of the Wireless Access Point is 192.168.0.228, with a
Network Mask of 255.255.255.0.
If your PC’s IP address is not compatible with this, you must change your PC’s IP
address to an unused value in the range 192.168.0.1 ~ 192.168.0.254, with a
Network Mask of 255.255.255.0. See Appendix C - Windows TCP/IP for details
for this procedure.
12
Page 17
System Basic Settings Screen
Click Basic Settings on the System menu to view a screen like the following.
Access Point Setup
Figure 8: System Basic Settings Screen
Data - System Basic Settings Screen
Identification
Access Point
Name
Description
Country Domain
MAC Address
IP Settings
DHCP Client
Fixed IP Address
Enter a suitable name for this Access Point.
If desired, you can enter a description for the Access Point.
The country or domain which is matching your current location.
The MAC address is displayed.
Select this option if you have a DHCP Server on your LAN, and you
wish the Access Point to obtain an IP address automatically.
If selected, the following data must be entered.
IP Address - The IP Address of this device. Enter an unused IP
address from the address range on your LAN.
Subnet Mask - The Network Mask associated with the IP Address
above. Enter the value used by other devices on your LAN.
Gateway - The IP Address of your Gateway or Router. Enter the
value used by other devices on your LAN.
DNS - Enter the DNS (Domain Name Server) used by PCs on
your LAN.
13
Page 18
Wireless Access Point User Guide
DHCP Server
Wins Server
Name/IP Address
TimeZone
TimeZone
NTP Server
Name/IP Address
If Enabled, the Access Point will allocate IP Addresses to PCs
(DHCP clients) on your LAN when they start up. The default (and
recommended) value is Enabled.
The Start IP Address and Finish IP Address fields set the values
used by the DHCP server when allocating IP Addresses to DHCP
clients. This range also determines the number of DHCP clients
supported.
Enter the server name or IP address of the Wins Server.
Choose the Time Zone for your location from the drop-down list. If
your location is currently using Daylight Saving, enable the Adjust for
Daylight Saving Time checkbox.
You must UNCHECK this checkbox when Daylight Saving Time
finishes.
Enter the server name or IP address of the NTP.
14
Page 19
Access Point Setup
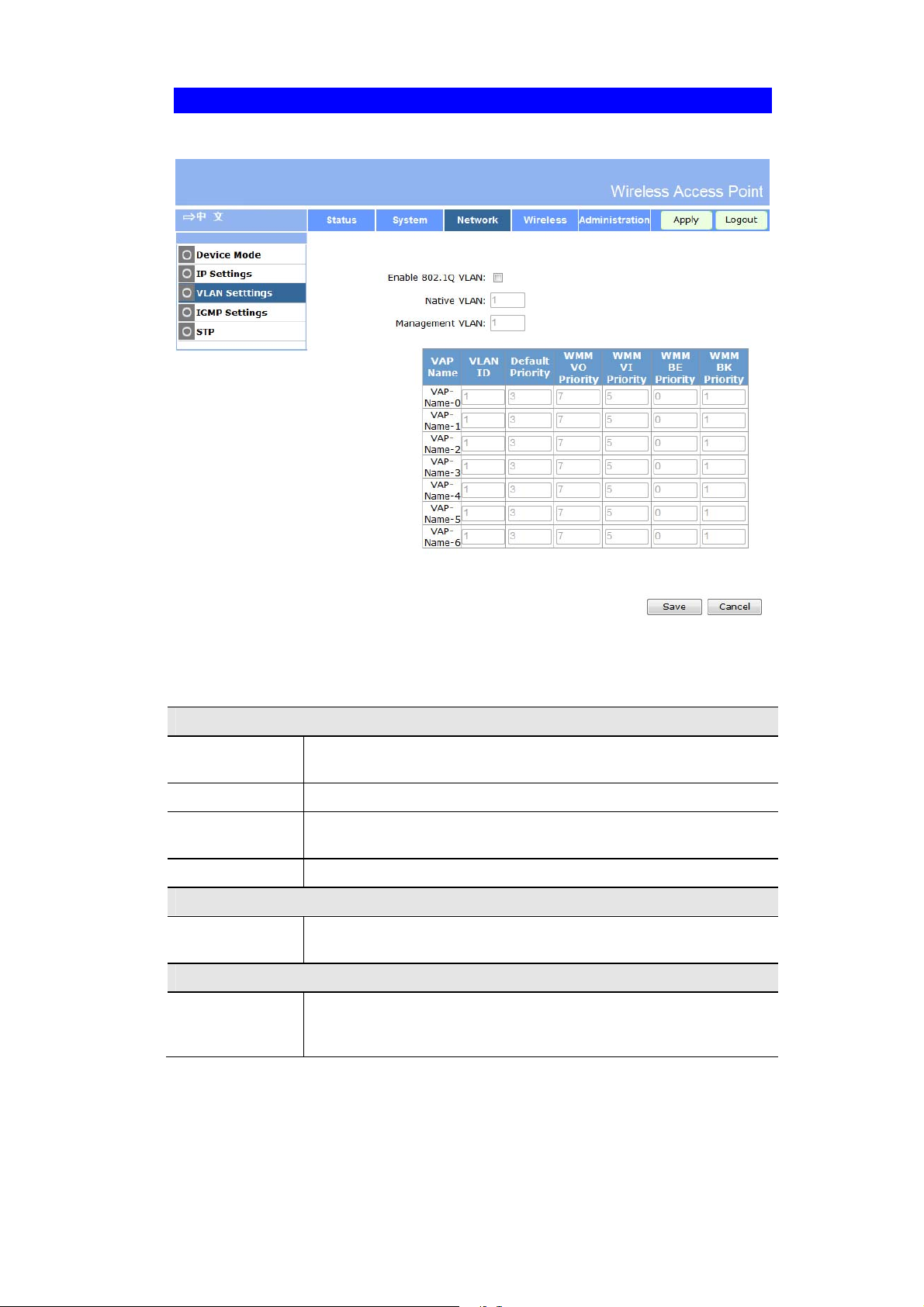
System Advanced Settings Screen
Click Advanced Settings on the System menu to view a screen like the following.
Figure 9: System Advanced Settings Screen
Data - System Advanced Settings Screen
VLAN
Enable 802.1Q
VLAN
Native VLAN
AP Management
VLAN
VLAN List
Network Integrality Check
Enable Network
Integrality Check
Enable Bonjour
Enable Bonjour
This option is only useful if the hubs/switches on your LAN support the
VLAN standard.
Enter the desired value for the Native VLAN. Default value is 1.
Define the VLAN ID used for management.
Define the unique ID value (1 - 4094) for each VAP.
If enabled, the AP will disable the wireless connection if the wired
connect of AP is invalid.
If checked, the Bonjour will enable applications to disco ver the devices
and the services on IP networks. Now, this AP only publish http and
https service.
15
Page 20
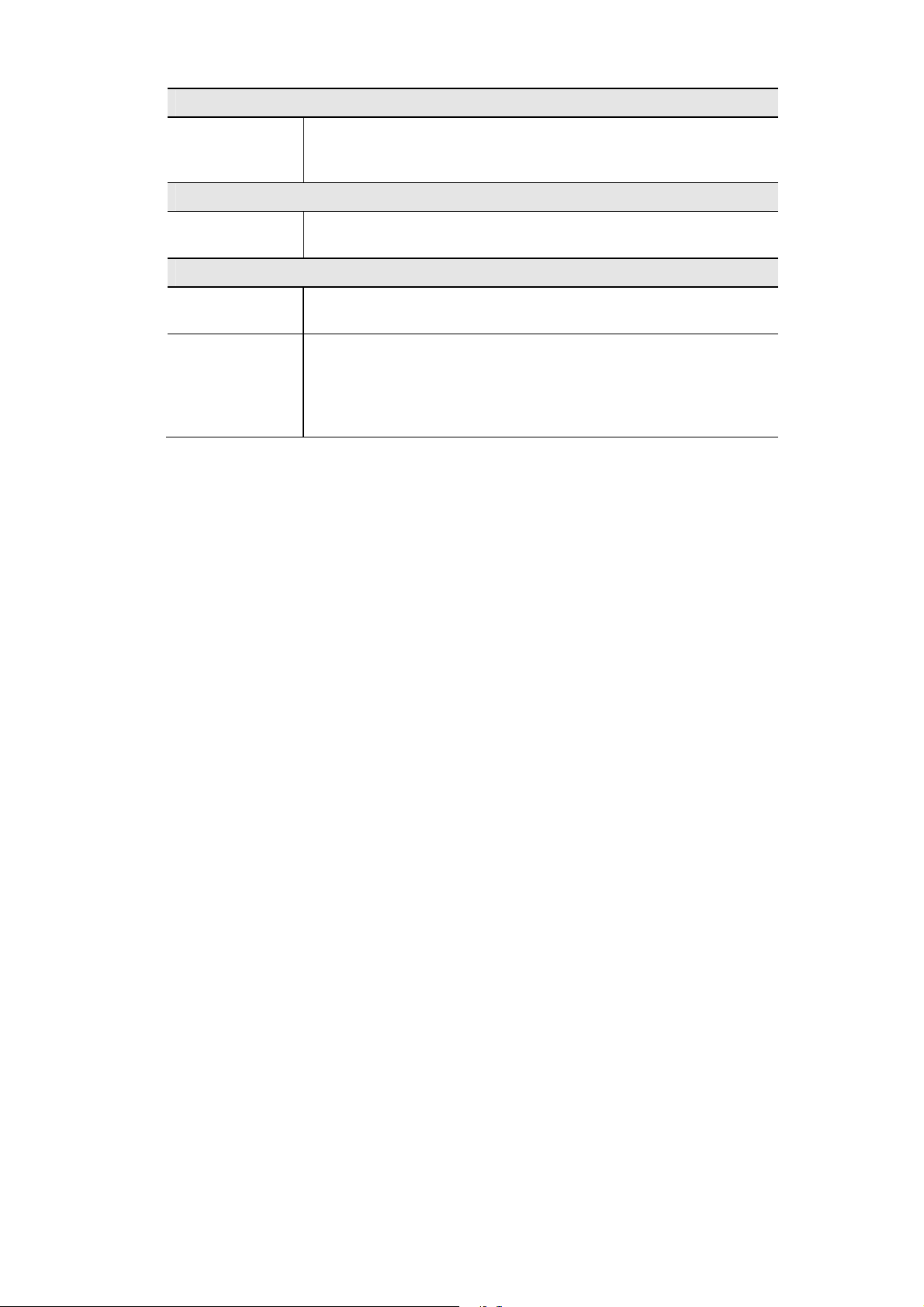
Wireless Access Point User Guide
LLTD
Enable Link
Layer Topology
Discovery
STP
Enable Spanning
tree Protocol
802.1x Supplicant
Enable 802.1x
Supplicant
Authentication
Enable this if you want to use Link Layer Topology Discovery protocol
(LLTD) feature.
Enable this if you want to use this feature.
Enable this if your network requires this AP to use 802.X authentication
in order to operate.
Authentication via MAC Address
Select this if you want to Use MAC Address for Authentication.
Authentication via Name and Password
Select this if you want to Use name and password for Authentication.
16
Page 21
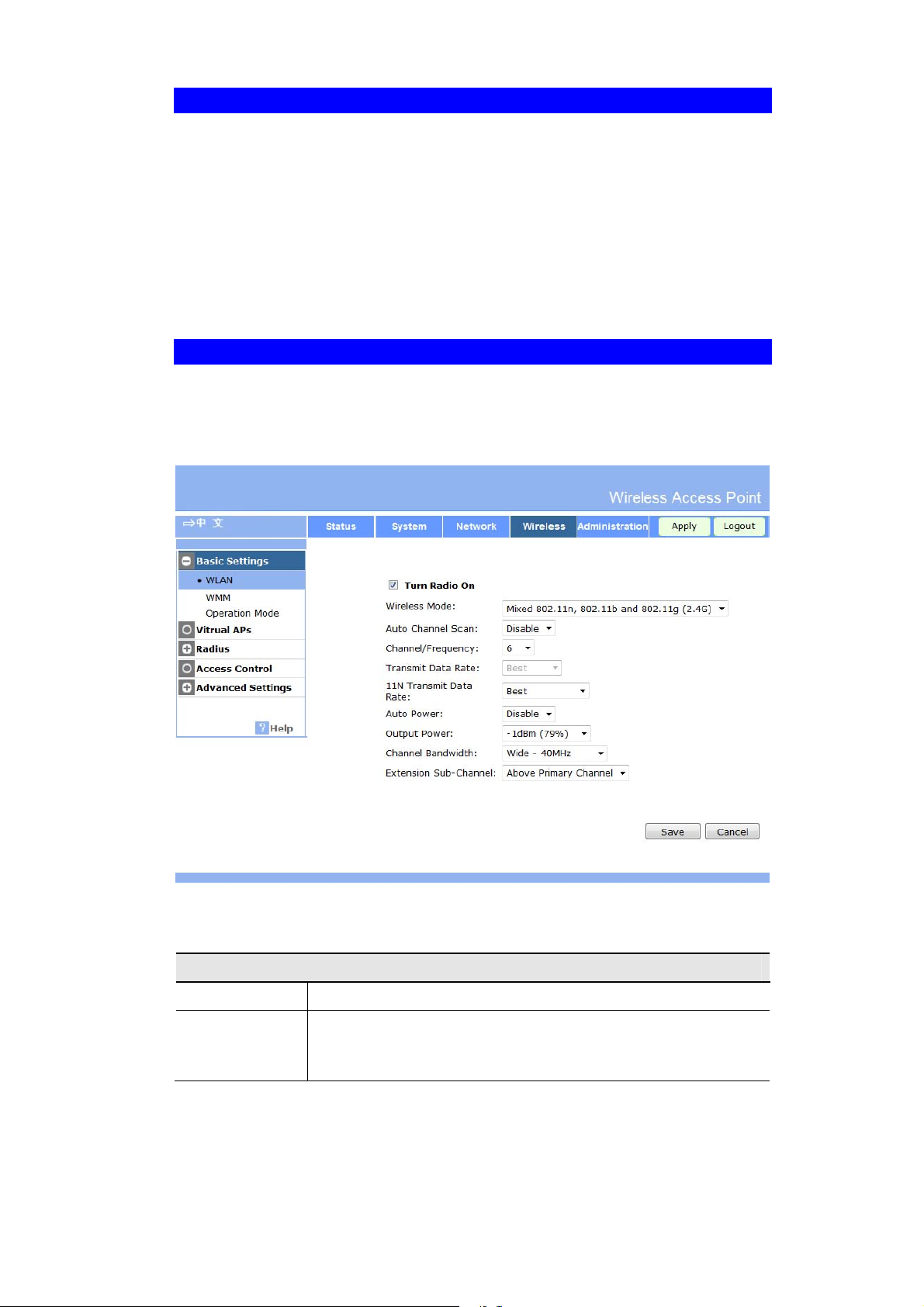
Wireless Screens
There are 6 configuration screens available:
Basic
Virtual APs
Radius Server Settings
Access Control
Advanced Settings
WIFI Protected Setup
Basic Screen
The settings on this screen must match the settings used by Wireless Stations.
Click Basic Settings on the Wireless menu to view a screen like the following.
Access Point Setup
Figure 10:Wireless Basic Screen
Data - Wireless Basic Settings Screen
Operation
Turn Radio On
Wireless Mode
Enable this to use the wireless feature.
Select the desired option:
Disable - select this if for some reason you do not this AP to
transmit or receive at all.
17
Page 22
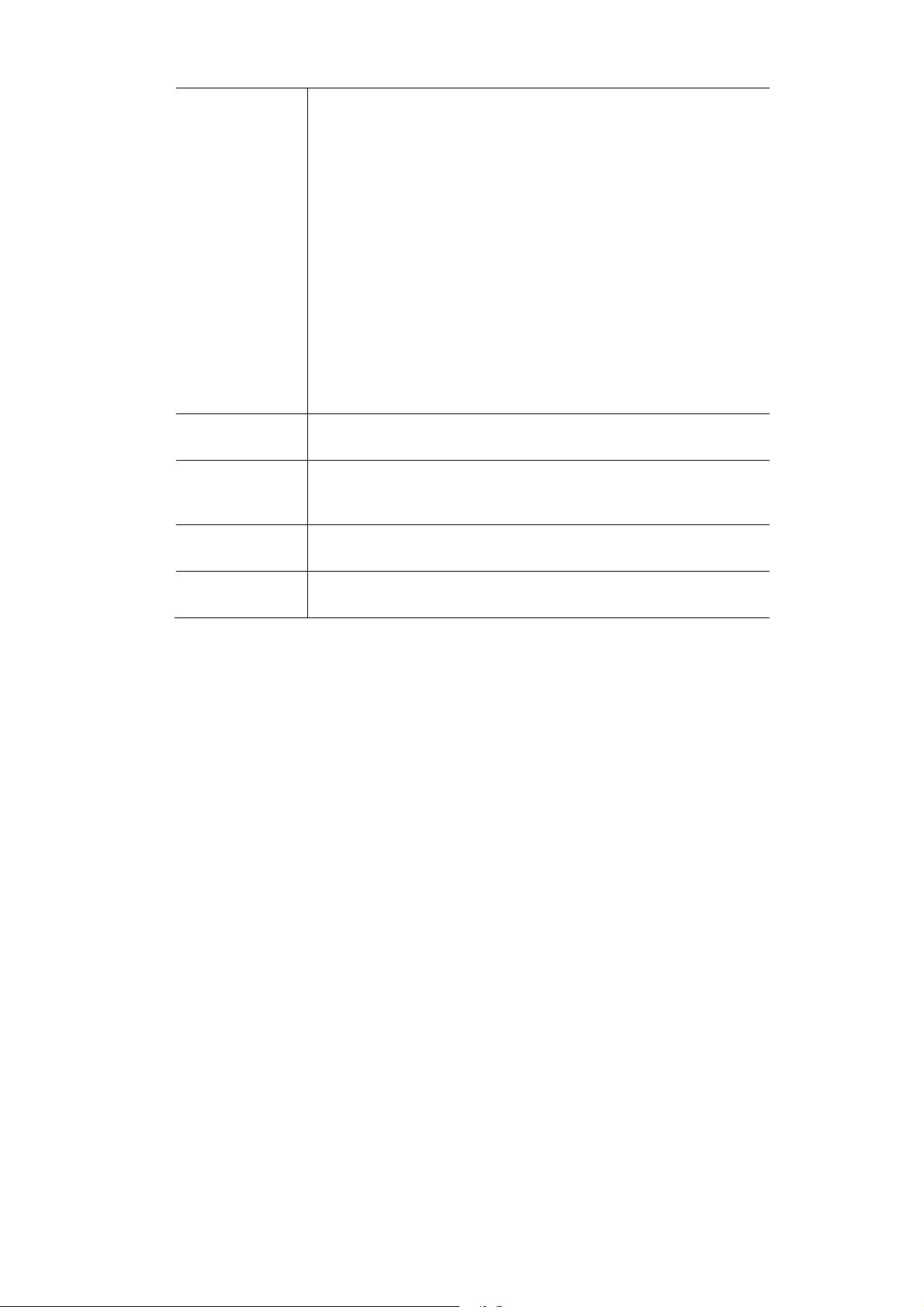
Wireless Access Point User Guide
802.11b - if selected, only 802.11b connections are allowed.
802.11g wireless stations will only be able to connect if they are
fully backward-compatible with the 802.11b standard.
802.11g - only 802.11g connections are allowed. If you only have
802.11g, selecting this option may provide a performance improvement over using the default setting.
802.11n - only 802.11n connections are allowed. If you only have
802.11n, selecting this option may provide a performance improvement over using the default setting.
802.11b and 802.11g - this will allow connections by both
802.11b and 802.11g wireless stations.
802.11n and 802.11g - this will allow connections by both
802.11n and 802.11g wireless stations.
Mixed 802.11n/802.11g/802.11b - this is the default, and will
allow connections by 802.11n, 802.11b and 802.11g wireless stations.
Auto Channel
Scan
Channel
/Frequency
Channel Bandwidth
Extension
Sub-Channel
If "Enable" is selected, the Access Point will select the best available
Channel.
If you experience interference (shown by lost connections and/or slow
data transfers) you may need to experiment with manually setting
different channels to see which is the best.
Select the desired bandwidth from the list.
Select Above or Below Primary Channel from the list.
18
Page 23
Access Point Setup
Operation Mode
Select the desired mode:
Access Point - operate as a normal Access Point
Bridge (Point-to-Point) - Bridge to a single AP. You must
provide the MAC address of the other AP in the PTP Bridge AP
MAC Address field.
Bridge (Multi-Point) - Select this only if this AP is the "Master"
for a group of Bridge-mode APs. The other Bridge-mode APs
must be set to Point-to-Point Bridge mode, using this AP's MAC
address. They then send all traffic to this "Master".
Wireless Client/Repeater - Act as a client or repeater for another
Access Point. If selected, you must provide Remote SSID and the
address (MAC address) of the other AP in the Remote AP MAC
Address field. In this mode, all traffic is sent to the specified AP.
Wireless Detection - This mode will turn the access point into a
wireless Monitor. A "Rouge AP" is an Access Point which should
not be in use, and so can be considered to be providing unauthorized access to your LAN.
No Security - If checked, then any AP operating with security
disabled is considered to be a Rogue AP.
Not in Legal AP List - If checked, then any AP not listed in
the "Legal AP List" is considered to be a Rogue AP. If
checked, you must maintain the Legal AP List.
Define Legal AP - Click this to open a sub-screen where you
can modify the "Legal AP List". This list must contain all
known APs, so must be kept up to date.
Remote MAC
Address
Select Remote
AP
You must enter the MAC address(es) of other AP(s) in the fields.
If the other AP is on-line, you can click the "Select Remote AP" button
and select from a list of available APs.
19
Page 24
Wireless Access Point User Guide
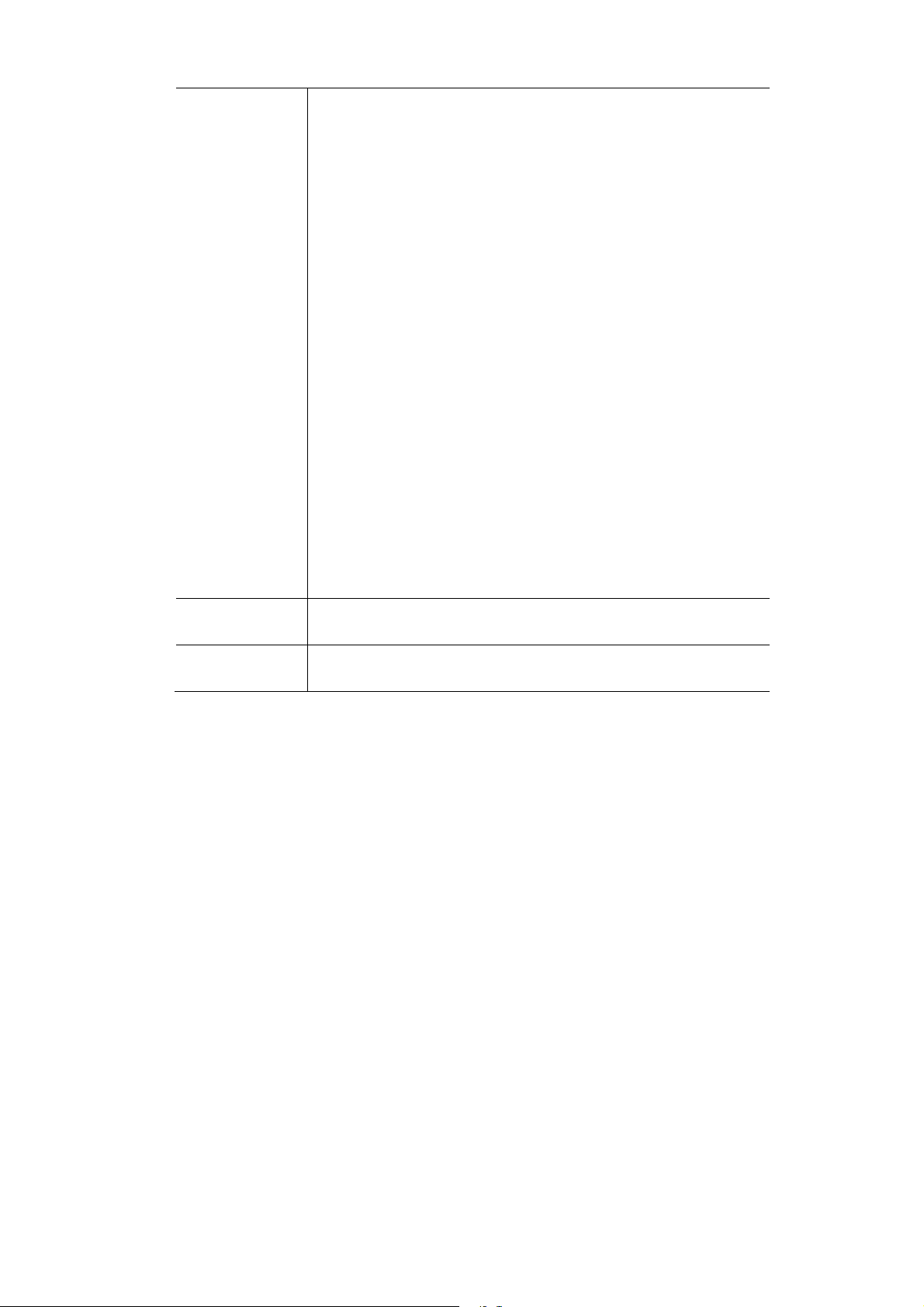
Virtual AP Settings
Clicking the Virtual APs link on the Wireless menu will result in a screen like the following.
Figure 11: Virtual AP Settings
20
Page 25
Data - Virtual AP Settings Screen
VAPs
Access Point Setup
VAP List
Enable Button
Configure Button
Disable Button
Isolation
Isolate all Virtual APs
from each other
All available VAPs are listed. For each VAP, the following data
is displayed:
*
If displayed before the name of the VAP, this indicates
the VAP is currently enabled. If not displayed, the
VAP is currently disabled.
VAP Name
The current VAP name is displayed.
[SSID]
The current SSID associated with this VAP.
Security System
The current security system (e.g. WPA-PSK) is dis-
played.
Enable the selected VAP.
Change the settings for the selected VAP.
Disable the selected VAP.
If this option is enabled, wireless clients using different VAPs
(different SSIDs) are isolated from each other, so they will
NOT be able to communicate with each other. They will still be
able to communicate with other clients using the same profile,
unless the "Wireless Separation" setting on the "Advanced"
screen has been enabled.
21
Page 26
Wireless Access Point User Guide
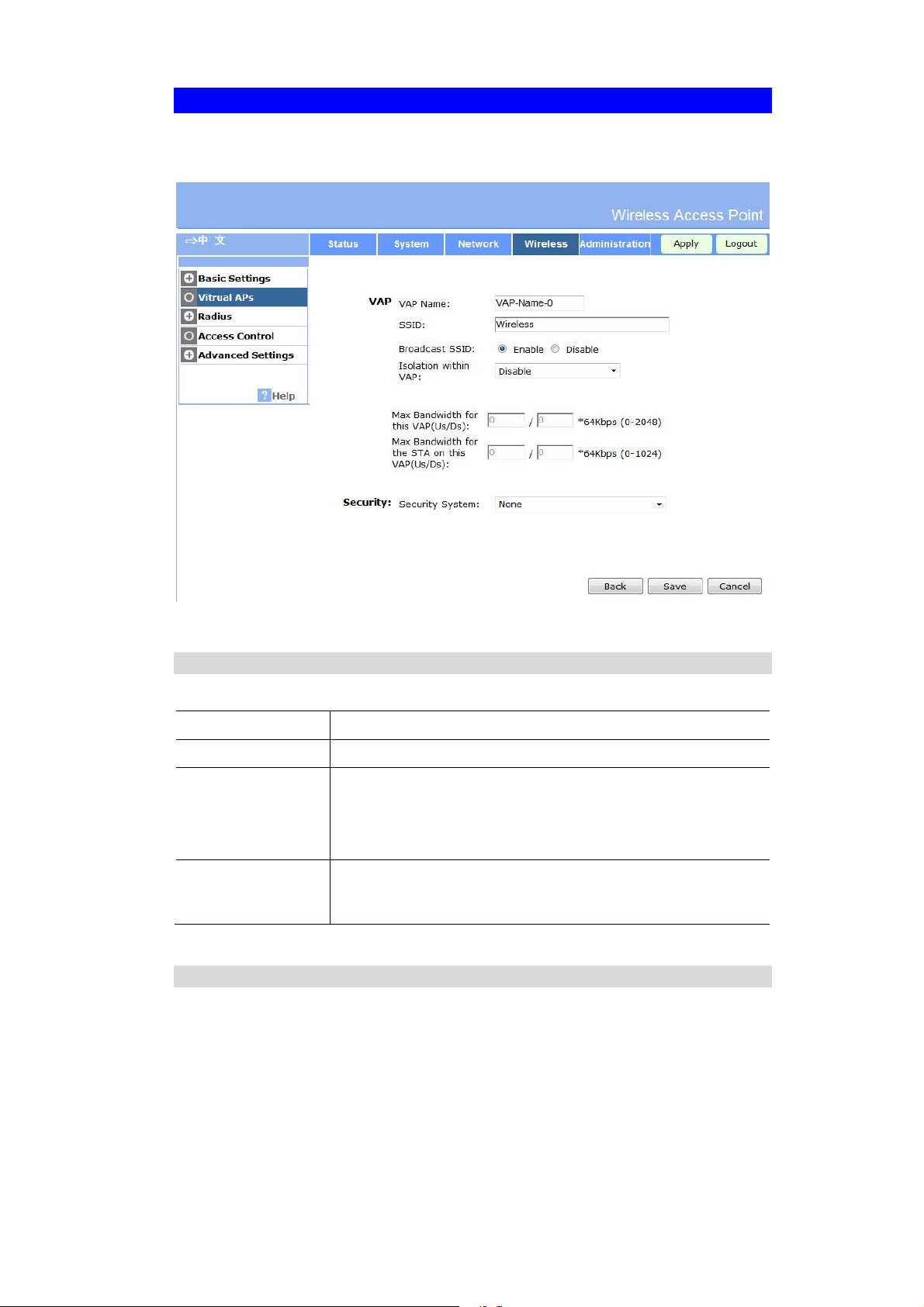
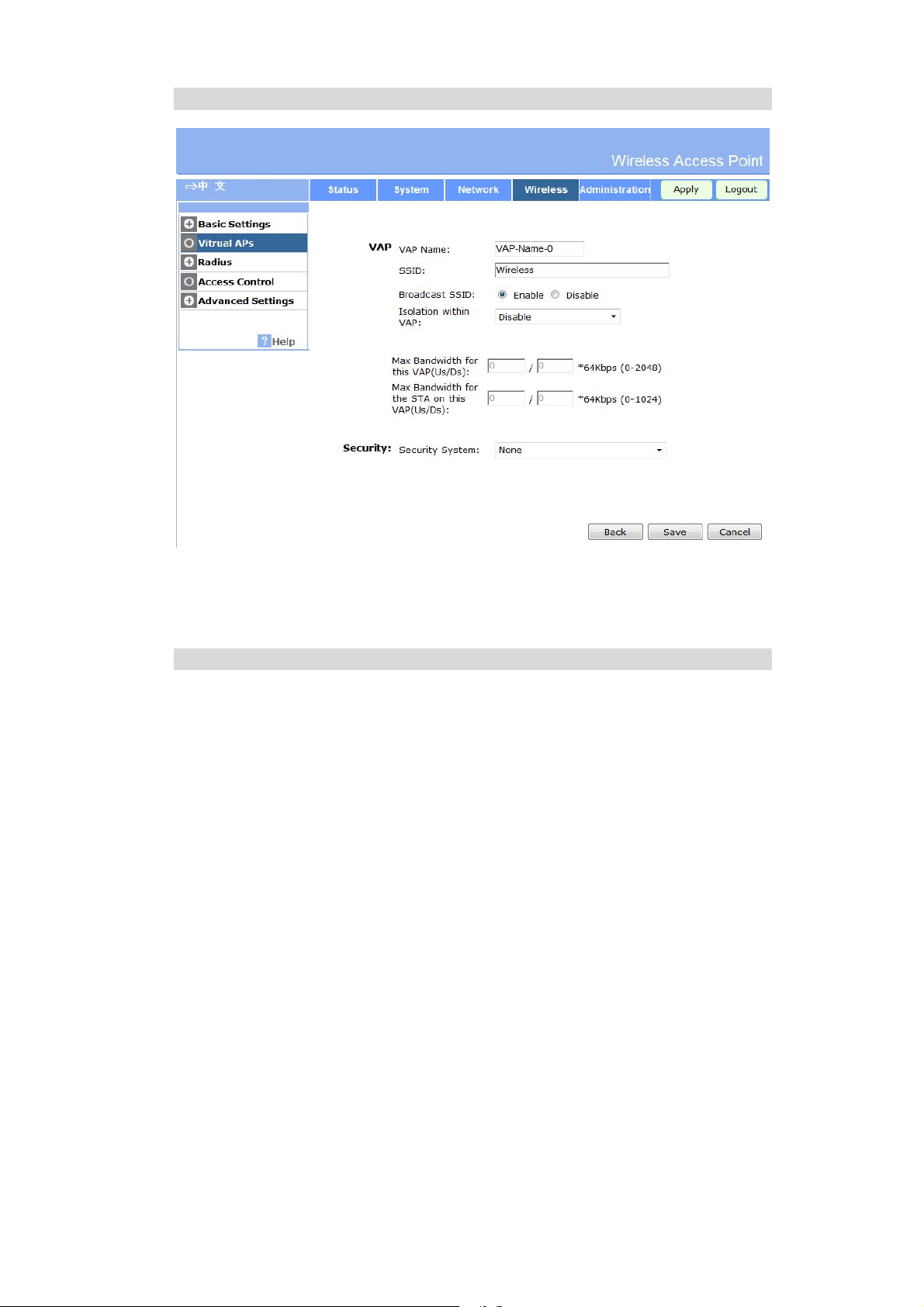
Virtual AP Screen
This screen is displayed when you select a VAP on the Virtual AP Settings screen, and click
the Configure button.
Figure 12: Virtual AP Screen
VAP Data
Enter the desired settings for each of the following:
VAP Name
SSID
Broadcast SSID
Isolation within
VAP
Enter a suitable name for this VAP.
Enter the desired SSID. Each VAP must have a unique SSID.
If Disabled, no SSID is broadcast.
If enabled, the SSID will then be broadcast to all Wireless Stations.
Stations which have no SSID (or a "null" value) can then adopt the
correct SSID for connections to this Access Point.
If enabled, then each Wireless station using the Access Point is
invisible to other Wireless stations. In most business stations, this
setting should be Disabled.
Security Settings
Select the desired option, and then enter the settings for the selected method.
The available options are:
None - No security is used. Anyone using the correct SSID can connect to your network.
22
Page 27

Access Point Setup
WEP - The 802.11b standard. Data is encrypted before transmission, but the encryption
system is not very strong.
WPA-PSK - Like WEP, data is encrypted before transmission. WPA is more secure than
WEP, and should be used if possible. The PSK (Pre-shared Key) must be entered on each
Wireless station. The 256Bit encryption key is derived from the PSK, and changes frequently.
WPA2-PSK - This is a further development of WPA-PSK, and offers even greater securi-
ty, using the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) method of encryption.
WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK - This method, sometimes called "Mixed Mode", allows
clients to use EITHER WPA-PSK (with TKIP) OR WPA2-PSK (with AES).
WPA with Radius - This version of WPA requires a Radius Server on your LAN to
provide the client authentication according to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions are
encrypted using the WPA standard.
If this option is selected:
This Access Point must have a "client login" on the Radius Server.
Each user must have a "user login" on the Radius Server.
Each user's wireless client must support 802.1x and provide the login data when re-
quired.
All data transmission is encrypted using the WPA standard. Keys are au tomatically
generated, so no key input is required.
WPA2 with Radius - This version of WPA2 requires a Radius Server on your LAN to
provide the client authentication according to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions are
encrypted using the WPA2 standard.
If this option is selected:
This Access Point must have a "client login" on the Radius Server.
Each user must authenticate on the Radius Server. This is usually done using digital
certificates.
Each user's wireless client must support 802.1x and provide the Radius authentication
data when required.
All data transmission is encrypted using the WPA2 standard. Keys are automatically
generated, so no key input is required.
WPA and WPA2 with Radius - EITHER WPA or WPA2 require a Radius Server on
your LAN to provide the client authentication according to the 802.1x standard. Data
transmissions are encrypted using EITHER WPA or WPA2 standard.
If this option is selected:
This Access Point must have a "client login" on the Radius Server.
Each user must authenticate on the Radius Server. This is usually done using digital
certificates.
Each user's wireless client must support 802.1x and provide the Radius authentication
data when required.
All data transmission is encrypted using EITHER WPA or WPA2 standard. Keys are
automatically generated, so no key input is required.
802.1x - This uses the 802.1x standard for client authentication, and WEP for data encryp-
tion.
If this option is selected:
This Access Point must have a "client login" on the Radius Server.
Each user must have a "user login" on the Radius Server.
23
Page 28

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Each user's wireless client must support 802.1x and provide the login data when re-
quired.
All data transmission is encrypted using the WEP standard. You only have to select
the WEP key size; the WEP key is automatically generated.
24
Page 29
Security Settings - None
Access Point Setup
Figure 13: Wireless Security - None
No security is used. Anyone using the correct SSID can connect to your network.
Security Settings - WEP
This is the 802.11b standard. Data is encrypted before transmission, but the encryption system
is not very strong.
25
Page 30

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Figure 14: WEP Wireless Security Screen
Data - WEP Screen
WEP
Data
Encryption
Authentication
Key Input
Key Value
Passphrase
Select the desired option, and ensure your Wireless stations have the
same setting:
64 Bit Encryption - Keys are 10 Hex (5 ASCII) characters.
128 Bit Encryption - Keys are 26 Hex (13 ASCII) characters.
152 Bit Encryption - Keys are 32 Hex (16 ASCII) characters.
Normally, you can leave this at “Automatic”, so that Wireless Stations
can use either method ("Open System" or "Shared Key".).
If you wish to use a particular method, select the appropriate value "Open System" or "Shared Key". All Wireless stations must then be set
to use the same method.
Select "Hex" or "ASCII" depending on your input method. (All keys
are converted to Hex, ASCII input is only for convenience.)
Enter the key values you wish to use. The default key, selected by the
radio button, is required. The other keys are optional. Other stations
must have matching key values.
Use this to generate a key or keys, instead of entering them directly.
Enter a word or group of printable characters in the Passphrase box
and click the "Generate Key" button to automatically configure the
WEP Key(s).
26
Page 31

Access Point Setup
Security Settings - WPA-PSK
Like WEP, data is encrypted before transmission. WPA is more secure than WEP, and should
be used if possible. The PSK (Pre-shared Key) must be entered on each Wireless station. The
256Bit encryption key is derived from the PSK, and changes frequently.
Figure 15: WPA-PSK Wireless Security Screen
Data - WPA-PSK Screen
WPA-PSK
Network Key
WPA Encryption
Group Key Update
Key Lifetime
Update Group key
when any membership
terminates
Enter the key value. Data is encrypted using a 256Bit key derived
from this key. Other Wireless Stations must use the same key.
The encryption method is TKIP. Wireless Stations must also use
TKIP.
This refers to the key used for broadcast transmissions. Enable
this if you want the keys to be updated regularly.
This field determines how often the Group key is dynamically
updated. Enter the desired value.
If enabled, the Group key will be updated whenever any member
leaves the group or disassociates from the Access Point.
27
Page 32

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Security Settings - WPA2-PSK
This is a further development of WPA-PSK, and offers even greater security, using the AES
(Advanced Encryption Standard) method of encryption.
Figure 16: WPA2-PSK Wireless Security Screen
Data - WPA2-PSK Screen
WPA2-PSK
Network Key
WPA Encryption
Group Key Update
Key Lifetime
Update Group key
when any membership
terminates
Enter the key value. Data is encrypted using a 256Bit key derived
from this key. Other Wireless Stations must use the same key.
The encryption method is AES. Wireless Stations must also use
AES.
This refers to the key used for broadcast transmissions. Enable
this if you want the keys to be updated regularly.
This field determines how often the Group key is dynamically
updated. Enter the desired value.
If enabled, the Group key will be updated whenever any member
leaves the group or disassociates from the Access Point.
28
Page 33

Access Point Setup
Security Settings - WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK
This method, sometimes called "Mixed Mode", allows clients to use EITHER WPA-PSK (with
TKIP) OR WPA2-PSK (with AES).
Figure 17: WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK Wireless Security Screen
Data - WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK Screen
WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK
Network Key
WPA Encryption
Group Key Update
Key Lifetime
Update Group key
when any membership
terminates
Enter the key value. Data is encrypted using this key. Other
Wireless Stations must use the same key.
The encryption method is TKIP for WPA-PSK, and AES for
WPA2-PSK.
This refers to the key used for broadcast transmissions. Enable
this if you want the keys to be updated regularly.
This field determines how often the Group key is dynamically
updated. Enter the desired value.
If enabled, the Group key will be updated whenever any member
leaves the group or disassociates from the Access Point.
29
Page 34

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Security Settings - WPA with Radius
This version of WPA requires a Radius Server on your LAN to provide the client authentication according to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions are encrypted using the WPA
standard.
Figure 18: WPA with Radius Wireless Security Screen
Data - WPA with Radius Screen
WPA with Radius
WPA Encryption
Group Key Update
Key Lifetime
Update Group key
when any membership
terminates
The encryption method is TKIP. Wireless Stations must also use
TKIP.
This refers to the key used for broadcast transmissions. Enable
this if you want the keys to be updated regularly.
This field determines how often the Group key is dynamically
updated. Enter the desired value.
If enabled, the Group key will be updated whenever any member
leaves the group or disassociates from the Access Point.
30
Page 35

Access Point Setup
Security Settings - WPA2 with Radius
This version of WPA2 requires a Radius Server on your LAN to provide the client authentication according to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions are encrypted using the WPA2
standard.
Figure 19: WPA2 with Radius Wireless Security Screen
Data - WPA2 with Radius Screen
WPA2 with Radius
WPA Encryption
Group Key Update
Key Lifetime
Update Group key
when any membership
terminates
The encryption method is AES. Wireless Stations must also use
AES.
This refers to the key used for broadcast transmissions. Enable
this if you want the keys to be updated regularly.
This field determines how often the Group key is dynamically
updated. Enter the desired value.
If enabled, the Group key will be updated whenever any member
leaves the group or disassociates from the Access Point.
31
Page 36

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Security Settings - WPA and WPA2 with Radius
EITHER WPA or WPA2 require a Radius Server on your LAN to provide the client authentication according to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions are encrypted using EITHER
WPA or WPA2 standard.
Figure 20: WPA and WPA2 with Radius Wireless Security Screen
Data - WPA and WPA2 with Radius Screen
WPA and WPA2 with Radius
WPA Encryption
Group Key Update
Key Lifetime
Update Group key
when any membership
terminates
The encryption method is TKIP for WPA, and AES for WPA2.
This refers to the key used for broadcast transmissions. Enable
this if you want the keys to be updated regularly.
This field determines how often the Group key is dynamically
updated. Enter the desired value.
If enabled, the Group key will be updated whenever any member
leaves the group or disassociates from the Access Point.
32
Page 37

Access Point Setup
Security Settings - 802.1x
This uses the 802.1x standard for client authentication, and WEP for data encryption. If this
option is selected:
This Access Point must have a "client login" on the Radius Server.
Each user must have a "user login" on the Radius Server. Normally, a Certificate is used to
authenticate each user. See Chapter4 for details of user configuration.
Each user's wireless client must support 802.1x.
All data transmission is encrypted using the WEP standard. You only have to select the
WEP key size; the WEP key is automatically generated.
Figure 21: 802.1x Wireless Security Screen
Data - 802.1x Screen
802.1x
WEP Key Size
Select the desired option:
64 Bit - Keys are 10 Hex (5 ASCII) characters.
128 Bit - Keys are 26 Hex (13 ASCII) characters.
152 Bit - Keys are 32 Hex (16 ASCII) characters.
33
Page 38

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Dynamic WEP Key
Click this if you want the WEP keys to be automatically generated.
The key exchange will be negotiated. The most widely
supported protocol is EAP-TLS.
The following Key Exchange setting determines how often
the keys are changed.
Both Dynamic and Static keys can be used simultaneously,
allowing clients using either method to use the Access
Point.
Key Exchange
This setting if only available if using Dynamic WEP Keys. If
you want the Dynamic WEP keys to be updated regularly,
enable this and enter the desired lifetime (in minutes).
Static WEP Key
(EAP-MD5)
Enable this if some wireless clients use a fixed (static) WEP
key, using EAP-MD5.
Note that both Dynamic and Static keys can be used simultaneously, allowing clients using either method to use the Access
Point.
WEP Key Enter the WEP key according to the WEP Key Size setting
above. Wireless stations must use the same key.
WEP Key Index
Select the desired index value. Wireless stations must use the
same key index.
34
Page 39

Access Point Setup
Radius Server Settings
Clicking the Radius Server Settings link on the Wireless menu will result in a screen like the
following.
Figure 22: Advanced Settings
Data - Radius Server Settings Screen
Authentication Server
Primary Authentication Server
Port Number
Shared Secret
Secondary Authentica-
tion Server
Accounting Server
Primary Accounting
Server
Port Number
Shared Secret
Secondary Accounting
Server
Enter the name or IP address of the Radius Server on your
network.
Enter the port number used for connections to the Radius
Server.
Enter the key value to match the Radius Server.
The Secondary Authentication Server will be used when the
Primary Authentication Server is not available.
Enter the IP address in the following fields if you want this
Access Point to send accounting data to the Radius Server.
The port used by your Radius Server must be entered in the
field.
Enter the key value to match the Radius Server.
The Secondary Accounting Server will be used when the
Primary Accounting Server is not available.
35
Page 40

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Access Control
This feature can be used to block access to your LAN by unknown or untrusted wireless
stations.
Click Access Control on the Wireless menu to view a screen like the following.
Figure 23: Access Control Screen
Data - Access Control Screen
Access Control
Local Trusted
Stations
Select the desired option, as required
Disabled - The Access Control feature is disabled.
Local - Select Allow only following MAC addresses or Deny
following MAC addresses.
Radius - The Access Point will use the MAC address table located
on the external Radius server on the LAN for Access Control.
Warning! Ensure your own PC is in the "Trusted Wireless Stations"
list before enabling this feature.
This table lists any Wireless Stations you have designated as "Trusted". If you have not added any stations, this table will be empty. For
each Wireless station, the following data is displayed:
Name - the name of the Wireless station.
MAC Address - the MAC or physical address of each Wireless
station.
Connected - this indicates whether or not the Wireless station is
currently associates with this Access Point.
36
Page 41

Buttons
Access Point Setup
Modify List
Read from File
Write to File
To change the list of Trusted Stations (Add, Edit, or Delete a Wireless
Station or Stations), click this button. You will then see the Trusted
Wireless Stations screen, described below.
To upload a list of Trusted Stations from a file on your PC, click this
button.
To download the current list of Trusted Stations from the Access Point
to a file on your PC, click this button.
Trusted Wireless Stations
To change the list of trusted wireless stations, use the Modify List button on the Access Control
screen. You will see a screen like the sample below.
Figure 24: Trusted Wireless Stations
Data - Trusted Wireless Stations
Trusted Wireless
Stations
Other Wireless
Stations
Name
Address
This lists any Wireless Stations which you have designated as
“Trusted”.
This list any Wireless Stations detected by the Access Point, which
you have not designated as "Trusted".
The name assigned to the Trusted Wireless Station. Use this when
adding or editing a Trusted Station.
The MAC (physical) address of the Trusted Wireless Station. Use
this when adding or editing a Trusted Station.
37
Page 42

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Buttons
<<
>>
Select All
Select None
Edit
Add a Trusted Wireless Station to the list (move from the "Other
Stations" list).
Select an entry (or entries) in the "Other Stations" list, and
click the " << " button.
Enter the Address (MAC or physical address) of the wireless
station, and click the "Add " button.
Delete a Trusted Wireless Station from the list (move to the "Other
Stations" list).
Select an entry (or entries) in the "Trusted Stations" list.
Click the " >> " button.
Select all of the Stations listed in the "Other Stations" list.
De-select any Stations currently selected in the "Other Stations"
list.
To change an existing entry in the "Trusted Stations" list, select it
and click this button.
1. Select the Station in the "Trusted Station" list.
2. Click the "Edit" button. The address will be copied to the
"Address" field, and the "Add" button will change to "Upd ate".
3. Edit the address (MAC or physical address) as required.
4. Click "Update" to save your changes.
Add
Clear
To add a Trusted Station which is not in the "Other Wireless
Stations" list, enter the required data and click this button.
Clear the Name and Address fields.
38
Page 43

Access Point Setup
Advanced Settings
Clicking the Advanced Settings link on the Wireless menu will result in a screen like the
following.
Figure 25: Advanced Settings
Data - Advanced Settings Screen
Options
Worldwide Mode
(802.11d)
WMM
Enable WMM Support
No Acknowledgement
Parameters
Disassociated Timeout
Fragmentation Length
Enable this setting if you wish to use this mode, and your
Wireless stations support this mode.
Check this to enable WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia) support in the
Access Point. If WMM is also supported by your wireless
clients, voice and multimedia traffic will be given a higher
priority than other traffic.
If enabled, then WMM acknowledgement is disabled. Depending on the environment, disabling acknowledgement may
increase throughput slightly.
This determines how quickly a Wireless Station will be considered "Disassociated" with this AP, when no traffic is received.
Enter the desired time period.
Enter the preferred setting between 256 and 2346. Normally,
this can be left at the default value.
Beacon Interval
Enter the preferred setting between 20 and 1000. Normally, this
can be left at the default value.
39
Page 44

Wireless Access Point User Guide
RTS/CTS Threshold
Preamble Type
802.11b Protection
Mode
Enter the preferred setting between 1 and 2347. Normally, this
can be left at the default value.
Select the desired option. The default is "Long". The "Short"
setting takes less time when used in a good environment.
The Protection system is intended to prevent older 802.11b
devices from interfering with 802.11g transmissions. (Older
802.11b devices may not be able to detect that a 802.11g
transmission is in progress.) Normally, this should be left at
"Auto".
40
Page 45

Chapter 4
PC and Server Configuration
4
This Chapter details the PC Configuration required for each PC on the local
LAN.
Overview
All Wireless Stations need to have settings which match the Wireless Access Point. These
settings depend on the mode in which the Access Point is being used.
If using WEP or WPA-PSK, it is only necessary to ensure that each Wireless station's
settings match those of the Wireless Access Point, as described below.
For 802.1x modes, configuration is much more complex. The Radius Server must be
configured correctly, and setup of each Wireless station is also more complex.
Using WEP
For each of the following items, each Wireless Station must have the same settings as the
Wireless Access Point.
Mode
SSID (ESSID)
Wireless
Security
On each PC, the mode must be set to Infrastructure.
This must match the value used on the Wireless Access Point.
The default value is wireless
Note! The SSID is case sensitive.
Each Wireless station must be set to use WEP data encryption.
The Key size (64 bit, 128 bit, 152 bit) must be set to match the
Access Point.
The keys values on the PC must match the key values on the Access
Point.
Note:
On some systems, the key sizes may be shown as 40bit, 104bit, and
128bit instead of 64 bit, 128 bit and 152bit. This difference arises because the key input by the user is 24 bits less than the key size used for
encryption.
41
Page 46

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Using WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
For each of the following items, each Wireless Station must have the same settings as the
Wireless Access Point.
Mode
SSID (ESSID)
Wireless
Security
On each PC, the mode must be set to Infrastructure.
This must match the value used on the Wireless Access Point.
The default value is wireless
Note! The SSID is case sensitive.
On each client, Wireless security must be set to WPA-PSK.
The Pre-shared Key entered on the Access Point must also be
entered on each Wireless client.
The Encryption method (e.g. TKIP, AES) must be set to match the
Access Point.
42
Page 47

PC and Server Configuration
Using WPA-Enterprise
This is the most secure and most complex system.
WPA-Enterprise mode provides greater security and centralized management, but it is more
complex to configure.
Wireless Station Configuration
For each of the following items, each Wireless Station must have the same settings as the
Wireless Access Point.
Mode
SSID (ESSID)
802.1x
Authentication
802.1x
Encryption
On each PC, the mode must be set to Infrastructure.
This must match the value used on the Wireless Access Point.
The default value is wireless
Note! The SSID is case sensitive.
Each client must obtain a Certificate which is used for authentication for
the Radius Server.
Typically, EAP-TLS is used. This is a dynamic key system, so keys do
NOT have to be entered on each Wireless station.
However, you can also use a static WEP key (EAP-MD5); the Wireless
Access Point supports both methods simultaneously.
Radius Server Configuration
If using WPA-Enterprise mode, the Radius Server on your network must be configured as
follow:
It must provide and accept Certificates for user authentication.
There must be a Client Login for the Wireless Access Point itself.
The Wireless Access Point will use its Default Name as its Client Login name. (How-
ever, your Radius server may ignore this and use the IP address instead.)
The Shared Key, set on the Security Screen of the Access Point, must match the
Shared Secret value on the Radius Server.
Encryption settings must be correct.
43
Page 48

Wireless Access Point User Guide
802.1x Server Setup (Windows 2000 Server)
This section describes using Microsoft Internet Authentication Server as the Radius Server,
since it is the most common Radius Server available that supports the EAP-TLS authentication
method.
The following services on the Windows 2000 Domain Controller (PDC) are also required:
dhcpd
dns
rras
webserver (IIS)
Radius Server (Internet Authentication Service)
Certificate Authority
Windows 2000 Domain Controller Setup
1. Run dcpromo.exe from the command prompt.
2. Follow all of the default prompts, ensure that DNS is installed and enabled d uring installa-
tion.
Services Installation
1. Select the Control Panel - Add/Remove Programs.
2. Click Add/Remove Windows Components from the left side.
3. Ensure that the following components are activated (selected):
Certificate Services. After enabling this, you will see a warning that the computer
cannot be renamed and joined after installing certificate services. Select Yes to select
certificate services and continue
World Wide Web Server. Select World Wide Web Server on the Internet Information
Services (IIS) component.
From the Networking Services category, select Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP), and Internet Authentication Service (DNS should already be selected and installed).
44
Page 49

Figure 26: Components Screen
4. Click Next.
5. Select the Enterprise root CA, and click Next.
PC and Server Configuration
Figure 27: Certification Screen
6. Enter the information for the Certificate Authority, and click Next.
45
Page 50

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Figure 28: CA Screen
7. Click Next if you don't want to change the CA's configuration data.
8. Installation will warn you that Internet Information Services are running, and must be
stopped before continuing. Click Ok, then Finish.
DHCP server configuration
1. Click on the Start - Programs - Administrative Tools - DHCP
2. Right-click on the server entry as shown, and select New Scope.
Figure 29: DHCP Screen
3. Click Next when the New Scope Wizard Begins.
4. Enter the name and description for the scope, click Next.
5. Define the IP address range. Change the subnet mask if necessary. Click Next.
46
Page 51

PC and Server Configuration
Figure 30:IP Address Screen
6. Add exclusions in the address fields if required. If no exclusions are required, leave it
blank. Click Next.
7. Change the Lease Duration time if preferred. Click Next.
8. Select Yes, I want to configure these options now, and click Next.
9. Enter the router address for the current subnet. The router address may be left blank if
there is no router. Click Next.
10. For the Parent domain, enter the domain you specified for the domain controller setup, and
enter the server's address for the IP address. Click Next.
Figure 31: DNS Screen
11. If you don't want a WINS server, just click Next.
12. Select Yes, I want to activate this scope now. Click Next, then Finish.
13. Right-click on the server, and select Authorize. It may take a few minutes to complete.
47
Page 52

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Certificate Authority Setup
1. Select Start - Programs - Administrative Tools - Certification Authority.
2. Right-click Policy Settings, and select New - Certificate to Issue.
Figure 32: Certificate Authority Screen
3. Select Authenticated Session and Smartcard Logon (select more than one by holding down
the Ctrl key). Click OK.
Figure 33: Template Screen
4. Select Start - Programs - Administrative Tools - Active Directory Users and Computers.
5. Right-click on your active directory domain, and select Properties.
48
Page 53

Figure 34: Active Directory Screen
PC and Server Configuration
6. Select the Group Policy tab, choose Default Domain Policy then click Edit.
Figure 35: Group Policy Tab
7. Select Computer Configuration - Windows Settings - Security Settings - Public Key
Policies, right-click Automatic Certificate Request Settings - New - Automatic Certificate
Request.
49
Page 54

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Figure 36: Group Policy Screen
8. When the Certificate Request Wizard appears, click Next.
9. Select Computer, then click Next.
Figure 37: Certificate Template Screen
10. Ensure that your certificate authority is checked, then click Next.
11. Review the policy change information and click Finish.
12. Click Start - Run, type cmd and press enter.
Enter secedit /refreshpolicy machine_policy
This command may take a few minutes to take effect.
50
Page 55

PC and Server Configuration
Internet Authentication Service (Radius) Setup
1. Select Start - Programs - Administrative Tools - Internet Authentication Service
2. Right-click on Clients, and select New Client.
Figure 38: Service Screen
3. Enter a name for the access point, click Next.
4. Enter the address or name of the Wireless Access Point, and set the shared secret, as
entered on the Security Settings of the Wireless Access Point.
5. Click Finish.
6. Right-click on Remote Access Policies, select New Remote Access Policy.
7. Assuming you are using EAP-TLS, name the policy eap-tls, and click Next.
8. Click Add...
If you don't want to set any restrictions and a condition is required, select Day-And-Time-
Restrictions, and click Add...
Figure 39: Attribute Screen
9. Click Permitted, then OK. Select Next.
10. Select Grant remote access permission. Click Next.
51
Page 56

Wireless Access Point User Guide
11. Click Edit Profile... and select the Authentication tab. Enable Extensible Authentication
Protocol, and select Smart Card or other Certificate. Deselect other authentication meth-
ods listed. Click OK.
Figure 40: Authentication Screen
12. Select No if you don't want to view the help for EAP. Click Finish.
52
Page 57

PC and Server Configuration
Remote Access Login for Users
1. Select Start - Programs - Administrative Tools- Active Directory Users and Computers.
2. Double click on the user who you want to enable.
3. Select the Dial-in tab, and enable Allow access. Click OK.
Figure 41: Dial-in Screen
53
Page 58

Wireless Access Point User Guide
802.1x Client Setup on Windows XP
Windows XP ships with a complete 802.1x client implementation. If using Windows 2000,
you can install SP3 (Service Pack 3) to gain the same functionality.
If you don't have either of these systems, you must use the 802.1x client software provided
with your wireless adapter. Refer to your vendor's documentation for setup instructions.
The following instructions assume that:
You are using Windows XP
You are connecting to a Windows 2000 server for authentication.
You already have a login (User name and password) on the Windows 2000 server.
Client Certificate Setup
1. Connect to a network which doesn't require port authentication.
2. Start your Web Browser. In the Address box, enter the IP address of the Windows 2000
Server, followed by /certsrv
e.g
http://192.168.0.2/certsrv
3. You will be prompted for a user name and password. Enter the User name and Password
assigned to you by your network administrator, and click OK.
Figure 42: Connect Screen
4. On the first screen (below), select Request a certificate, click Next.
54
Page 59

PC and Server Configuration
Figure 43: Wireless CA Screen
5. Select User certificate request and select User Certificate, the click Next.
6. Click Submit.
Figure 44: Request Type Screen
55
Page 60

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Figure 45: Identifying Information Screen
7. A message will be displayed, then the certificate will be returned to you.
Click Install this certificate.
Figure 46:Certificate Issued Screen
8. . You will receive a confirmation message. Click Yes.
56
Page 61

PC and Server Configuration
Figure 47: Root Certificate Screen
9. Certificate setup is now complete.
802.1x Authentication Setup
1. Open the properties for the wireless connection, by selecting Start - Control Panel Network Connections.
2. Right Click on the Wireless Network Connection, and select Properties.
3. Select the Authentication Tab, and ensure that Enable network access control using IEEE
802.1X is selected, and Smart Card or other Certificate is selected from the EAP type.
Figure 48: Authentication Tab
Encryption Settings
The Encryption settings must match the APs (Access Points) on the Wireless network you
wish to join.
Windows XP will detect any available Wireless networks, and allow you to configure
each network independently.
57
Page 62

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Your network administrator can advise you of the correct settings for each network.
802.1x networks typically use EAP-TLS. This is a dynamic key system, so there is no
need to enter key values.
Enabling Encryption
To enable encryption for a wireless network, follow this procedure:
1. Click on the Wireless Networks tab.
Figure 49: Wireless Networks Screen
2. Select the wireless network from the Available Networks list, and click Configure.
3. Select and enter the correct values, as advised by your Network Administrator.
For example, to use EAP-TLS, you would enable Data encryption, and click the checkbox
for the setting The key is provided for me automatically, as shown below.
58
Page 63

Figure 50: Properties Screen
PC and Server Configuration
Setup for Windows XP and 802.1x client is now complete.
59
Page 64

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Using 802.1x Mode (without WPA)
This is very similar to using WPA-Enterprise.
The only difference is that on your client, you must NOT enable the setting The key is provid-
ed for me automatically.
Instead, you must enter the WEP key manually, ensuring it matches the WEP key used on the
Access Point.
Figure 51: Properties Screen
Note:
On some systems, the "64 bit" WEP key is shown as "40 bit" and the "128 bit" WEP key is
shown as "104 bit". This difference arises because the key input by the user is 24 bits less than
the key size used for encryption.
60
Page 65

Chapter 5
Operation and Status
5
This Chapter details the operation of the Wireless Access Point and the status
screens.
Operation
Once both the Wireless Access Point and the PCs are configured, operation is automatic.
However, you may need to perform the following operations on a regular basis.
If using the Access Control feature, update the Trusted PC database as required. (See
Access Control in Chapter 3 for details.)
If using 802.1x mode, update the User Login data on the Windows 2000 Server, and
configure the client PCs, as required.
Status Screen
Use the Status link on the main menu to view this screen.
Figure 52: Status Screen
61
Page 66

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Data - Status Screen
Access Point
Access Point Name
MAC Address
Country/Domain
Hardware Version
Firmware Version
TCP/IP
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Gateway
DHCP Client
DHCP Server
Ethernet Status
Wireless
The current name will be displayed.
The MAC (physical) address of the Wireless Access Point.
The region or domain, as selected on the System screen.
The version of the hardware currently used.
The version of the firmware currently installed.
The IP Address of the Wireless Access Point.
The Network Mask (Subnet Mask) for the IP Address above.
Enter the Gateway for the LAN segment to which the Wireless
Access Point is attached (the same value as the PCs on that LAN
segment).
This indicates whether the current IP address was obtained from a
DHCP Server on your network.
It will display "Enabled" or "Disabled".
"Enabled" or "Disabled" is displayed for the DHCP server status.
The current Ethernet status is displayed.
Channel/Frequency
Wireless Mode
AP Mode
Buttons
Virtual AP Status
Statistics
Log
Stations
The Channel currently in use is displayed.
The current mode (e.g. 802.11g) is displayed.
The current Access Point mode is displayed.
Click this to open a sub-window displaying Virtual AP Status
about the information of Name, SSID, Broadcast SSID, Security,
Status and Clients.
Click this to open a sub-window where you can view Statistics on
data transmitted or received by the Access Point.
Click this to open a sub-window where you can view the activity
log.
Click this to open a sub-window where you can view the list of
all current Wireless Stations using the Access Point.
62
Page 67

Operation and Status
Statistics Screen
This screen is displayed when the Statistics button on the Status screen is clicked. It shows
details of the traffic flowing through the Wireless Access Point.
Figure 53: Statistics Screen
63
Page 68

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Data - Statistics Screen
System Up Time
Up Time
VAP
Authentication
Deauthentication
Association
Disassociation
Reassociation
Wireless
Data
Management
This indicates how long the system has been running since the last
restart or reboot.
The number of "Authentication" packets received. Authentication
is the process of identification between the AP and the client.
The number of "Deauthentication" packets received. Deauthentication is the process of ending an existing authentication relationship.
The number of "Association" packets received. Association creates
a connection between the AP and the client. Usually, clients associate with only one (1) AP at any time.
The number of "Disassociation" packets received. Disassociation
breaks the existing connection between the AP and the client.
The number of "Reassociation" packets received. Reassociation is
the service that enables an established association (between AP and
client) to be transferred from one AP to another (or the same) AP.
Number of valid Data packets transmitted to or received from
Wireless Stations, at driver level.
Number of Management packets transmitted to or received from
Wireless Stations.
Control
Number of Control packets transmitted to or received from Wireless Stations.
64
Page 69

Operation and Status
Virtual AP Status
This screen is displayed when the Virtual AP Status button on the Status screen is clicked.
Figure 54: Virtual AP Status Screen
For each VAP, the following data is displayed:
Name
The name you gave to this VAP; if you didn't change the name, the
default name is used.
BSSIS
SSID
Broadcast SSID
Security
Status
Clients
The MAC address of the VAP.
The SSID assigned to this VAP.
Indicates whether or not the SSID is broadcast.
The security method used by this VAP.
Indicates whether or not this VAP is enabled or currently used.
The number of wireless stations currently using accessing this Access
Point using this VAP.
If the VAP is disabled, this will always be zero.
65
Page 70

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Activity Log
This screen is displayed when the Log button on the Status screen is clicked.
Figure 55: Activity Log Screen
Data - Activity Log
Data
Current Time
Log
Buttons
Refresh
Save to File
Clear Log
The system date and time is displayed.
The Log shows details of the connections to the Wireless Access
Point.
Update the data on screen.
Save the log to a file on your pc.
This will delete all data currently in the Log. This will make it
easier to read new messages.
66
Page 71

Operation and Status
Station List
This screen is displayed when the Stations button on the Status screen is clicked.
Figure 56 Station List Screen
Data - Station List Screen
Station List
MAC Address
Mode
SSID
Refresh Button
The MAC (physical) address of each Wireless Station is displayed.
The mode of each Wireless Station.
This displays the SSID used the Wireless station. Because the Wire-
less Access Point supports multiple SSIDs, different PCs could
connect using different SSIDs.
Update the data on screen.
67
Page 72

Chapter 6
Access Point Management
6
This Chapter explains when and how to use the Wireless Access Point's "Administration" Features.
Overview
This Chapter covers the following features, available on the Wireless Access Point’s Management menu.
AP Type
Management
Auto Config
Config File
Ping Test
Auto Reboot
Firmware Upgrade
AP Type Screen
The AP Type screen allows you to assign Fat AP mode or Fit AP mode. The Wireless Access
Point will work as general AP in Fat AP mode. The Wireless Access Point must work with AC
in Fit AP mode.
Figure 57: AP Type Screen
68
Page 73

Data – AP Type Screen
FAT AP
Access Point Management
FAT AP
FIT AP
FIT AP
Select the mode. The AP will work as general AP. All of
function on the AP need User to configure it everyone.
Select the mode. The AP will work as thin AP mode. The IP
Address will change to DHCP Client. It will ask one IP
Address from DHCP Server on the LAN. So User can configure it by Web or AC.
69
Page 74

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Management
To reach this screen, select Management in the Administrtion section of the menu.
70
Page 75

Access Point Management
Figure 58: Management Screen
Data - Management Screen
Account
Admin User Name
Change Admin
Password
New Password
Re-enter to Confirm
Method
Enable Wireless Web
Access
Enable HTTP Admin
Connections.
HTTP Port Number
The name for login the Device Web.
If checked, You can change the login password. The default
password is “password”.
Input the new password.
Avoid the error. Re-enter the new password.
If enabled, the device will allow wireless client access the Device
Web by wireless.
If disabled, the device will only allow Ethernet client access the
Device Web.
If enabled. The device will allow user via it by HTTP method.
If disabled. The device will refuse user via it by HTTP method.
Input the desired HTTP port. The default port is 80.
71
Page 76

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Enable HTTPS
(secure HTTP) Admin connections
HTTPS Port Number
Enable Management
via SSH
Control
Turn IP Management
Control On
Allow Following IP
Addresses to Manage
the Device
Deny Following IP
Addresses to Manage
the Device
PCs List
If enabled. The device will allow user via it by HTTPS method.
If disabled. The device will refuse user via it by HTTPS method.
Input the desired HTTPS port. The default port is 443.
If enabled. The device will allow via it by SSH method.
If enabled, the device will limit user access it. Not all of user can
manger it so improve safety.
If enabled. The device only allow the follows PCs access it. The
PC not in the list will not access it.
If enabled. The device will refuse the follows PCs access it. The
PC not in the list will allow access it.
You can define the desired network subnet. You need input the
subnet and subnet mask.
For example. 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0.
It include 8 group subnet.
72
Page 77

Access Point Management
Auto Config
Auto Config is only useful if you have a FTP Server on your LAN. So the d evice will auto
load the config file from the FTP Server. To reach this screen, select Auto Config in the Ad-
ministration section of the menu.
Data – Auto Config Screen
Auto Config
FTP Server
User Name
Password
Config file
Interval
Check now
If enable. The device will auto load config file from server.
If disable. The function is invalid.
Input the FTP Server IP address.
Input the user names for login FTP Server.
Input the password for login FTP Server.
Input the config file path on the FTP Server.
The device will as the interval time to check new config file on FTP
Server. If find new config file will auto load it. The unit is hours.
Press the button. The device will check new config file on FTP
Server immediately.
Figure 59: SNMP Screen
73
Page 78

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Config File
This screen allows you to Backup (download) the configuration file, and to restore (upload) a
previously-saved configuration file.
You can also set the Wireless Access Point back to its factory default settings.
To reach this screen, select Config File in the Administration section of the menu.
Data - Config File Screen
Backup
Save a copy of current settings to a file
Restore
Restore saved settings
from a file
Once you have the Access Point working properly, you should
back up the settings to a file on your computer. You can later
restore the Access Point's settings from this file, if necessary.
To create a backup file of the current settings:
Click Backup.
If you don't have your browser set up to save downloaded
To restore settings from a backup file:
1. Click Browse.
2. Locate and select the previously saved backup file.
3. Click Restore
Figure 60: Config File Screen
files automatically, locate where you want to save the file,
rename it if you like, and click Save.
74
Page 79

Defaults
Access Point Management
Revert to factory
default settings
To erase the current settings and restore the original factory
default settings, click Set to Defaults button.
Note!
This will terminate the current connection. The Access Point
will be unavailable until it has restarted.
By default, the Access Point will act as a DHCP client, and
automatically obtain an IP address. You will need to determine its new IP address in order to re-connect.
75
Page 80

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Ping Test
Ping Test is one useful function for test the Ethernet integrality. If the device can PING the IP
address so the device will work normal. If the device can’t PING the IP address so the device
will disable the wireless function. To reach this screen, select Ping Test in the Administration
section of the menu.
Data – Ping Test Screen
Ping Test
Ping Test Mode
Ping IP Address
Select enable or disable.
If enable the function. You must input one IP address and it is valid.
If the IP address is invalid that the device will disable wireless
function.
Figure 61: SNMP Screen
76
Page 81

Auto Reboot
Access Point Management
Figure 62: Auto Reboot Screen
Data – Auto Reboot Screen
Auto Reboot Mode
Reboot Interval
Select enable or disable.
If enable the function. Please input the desired time. The unit
is hours. The device will auto reboot as the time interval.
77
Page 82

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Firmware Upgrade
The firmware (software) in the Wireless Access Point can be upgraded using your Web
Browser.
You must first download the upgrade file, and then select Upgrade Firmware in the Admin-
istration section of the menu. You will see a screen like the following.
Figure 63: Firmware Upgrade Screen
To perform the Firmware Upgrade:
1. Click the Browse button and navigate to the location of the upgrade file.
2. Select the upgrade file. Its name will appear in the Upgrade File field.
3. Click the Upgrade button to commence the firmware upgrade.
The Wireless Access Point is unavailable during the
upgrade process, and must restart when the upgrade is completed. Any connections to or through
the Wireless Access Point will be lost.
78
Page 83

Appendix A
Specifications
Wireless Access Point
Hardware Specifications
LAN port
11b Embedded Atheros solution
1 x Auto-MDIX RJ 45 for 10/100/1000Mbps PoE port
IEEE 802.3af compliance
Network Standard IEEE 802.11b (Wi-Fi™) and IEEE
802.11g compliance
OFDM; 802.11b: CCK (11 Mbps, 5.5 Mbps), DQPSK (2
Mbps), DBPSK (1 Mbps)
Operating Frequencies 2.412.2.497 GHz
Operating Channels 802.11g: 11 for North America, 13
for Europe (ETSI), 14 for Japan
802.11b: 11 for North America, 14 for Japan, 13 for
Europe (ETSI)
A
IEEE802.11n draft 2.0 compliant
11n
Antennae 2 x 2dbi detachable antenna
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Power Adapter 12VDC 1A External
Dimensions 235mm(W) * 145mm(D) * 40mm(H)
Rx Sensitivity: 11.n: 300Mbps@ -69dBm, 11.g:
54Mbps@ -73dBm, 11.b: 11Mbps@ -88dBm
0 C to 40 C
-20 C to 70 C
79
Page 84

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Software Specifications
Feature Details
Wireless
Operation Mode
Security
Management
Access point support
Roaming supported
IEEE 802.11n/11g/11b compliance
Auto Sensing Open System / Share Key authentication
Wireless Channels Support
Automatic Wireless Channel Selection
Country Selection
Preamble Type: long or short support
RTS Threshold Adjustment
Fragmentation Threshold Adjustment
Beacon Interval Adjustment
8x Multi-BSSID assignment
802.11i pre-authentication
Short Slot time support
IEEE 802.11d
CTS-only & CTS/RTS protect mechanism support
WMM support
WPS support
Wireless isolations
Common AP+PTMP/PTP
Thin AP mode
Wireless Router mode
Rogue AP Detection
Open, shared, WPA, WPA-PSK, and WPA2-PSK authentication
64bit/128bit WEP, TKIP, AES-CCMP support
802.1x support
EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, PEAP
RADIUS based MAC authentication
Block inter-wireless station communication (wireless separation)
Block SSID broadcast
Web based configuration
Configurable Web port
RADIUS Accounting
RADIUS-On feature
RADIUS Accounting update
Telnet/CLI
Syslog/internal Log
Access Control list
Editable Configuration file backup/Restore
80
Page 85

Other Features
Firmware Upgrade
Appendix A - Specifications
Statistics support
SNMP v1 & v2c & v3
LLTD
Only wired users to be able to control
Auto configuration
DHCP client
WINS client
Radius client
Enable/Disable wireless
Network Integrality Check
FTP client
HTTP/FTP network protocol download
81
Page 86

Appendix B
Troubleshooting
B
Overview
This chapter covers some common problems that may be encountered while using the Wireless
Access Point and some possible solutions to them. If you follow the suggested steps and the
Wireless Access Point still does not function properly, contact your dealer for further advice.
General Problems
Problem 1:
Solution 1:
Can't connect to the Wireless Access Point to configure it.
Check the following:
The Wireless Access Point is properly installed, LAN connections are
OK, and it is powered ON. Check the LEDs for port status.
Ensure that your PC and the Wireless Access Point are on the same
network segment. (If you don't have a router, this must be the case.)
If your PC is set to "Obtain an IP Address automatically" (DHCP
client), restart it.
You can use the following method to determine the IP address of the
Wireless Access Point, and then try to connect using the IP address, instead of the name.
To Find the Access Point's IP Address
1. Open a MS-DOS Prompt or Command Prompt Window.
2. Use the Ping command to “ping” the Wireless Access Point. Enter
ping followed by the Default Name of the Wireless Access Point.
e.g.
ping SC003318
3. Check the output of the ping command to determine the IP address of
the Wireless Access Point, as shown below.
Figure 64: Ping
If your PC uses a Fixed (Static) IP address, ensure that it is using an IP
Address which is compatible with the Wireless Access Point. (If no DHCP
Server is found, the Wireless Access Point will default to an IP Address and
Mask of 192.168.0.228 and 255.255.255.0.) On Windows PCs, you can use
Control Panel-Network to check the Properties for the TCP/IP protocol.
82
Page 87

Appendix B - Troubleshooting
Problem 2:
Solution 2
My PC can't connect to the LAN via the Wireless Access Point.
Check the following:
The SSID and WEP settings on the PC match the settings on the Wire-
less Access Point.
On the PC, the wireless mode is set to "Infrastructure"
If using the Access Control feature, the PC's name and address is in the
Trusted Stations list.
If using 802.1x mode, ensure the PC's 802.1x software is configured
correctly. See Chapter 4 for details of setup for the Windows XP 802.1x
client. If using a different client, refer to the vendor's documentation.
83
Page 88

Appendix C
Windows TCP/IP
C
Overview
Normally, no changes need to be made.
By default, the Wireless Access Point will act as a DHCP client, automatically obtaining a
suitable IP Address (and related information) from your DHCP Server.
If using Fixed (specified) IP addresses on your LAN (instead of a DHCP Server), there is
no need to change the TCP/IP of each PC. Just configure the Wireless Access Point to
match your existing LAN.
The following sections provide details about checking the TCP/IP settings for various types of
Windows, should that be necessary.
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 9x/ME:
1. Select Control Panel - Network. You should see a screen like the following:
Figure 65: Network Configuration
2. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
3. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following.
84
Page 89

Appendix C - Windows TCP/IP
Figure 66: IP Address (Win 95)
Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct, as follows:
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the default
Windows settings. To work correctly, you need a DHCP server on your LAN.
Using "Specify an IP Address"
If your PC is already configured for a fixed (specified) IP address, no changes are required.
(The Administrator should configure the Wireless Access Point with a fixed IP address from
the same address range used on the PCs.)
85
Page 90

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows NT4.0
1. Select Control Panel - Network, and, on the Protocols tab, select the TCP/IP protocol, as
shown below.
Figure 67: Windows NT4.0 - TCP/IP
2. Click the Properties button to see a screen like the one below.
Figure 68: Windows NT4.0 - IP Address
86
Page 91

Appendix C - Windows TCP/IP
3. Select the network card for your LAN.
4. Select the appropriate radio button - Obtain an IP address from a DHCP Server or Specify
an IP Address, as explained below.
Obtain an IP address from a DHCP Server
This is the default Windows setting. This is the default Windows settings. To work correctly,
you need a DHCP server on your LAN.
Using "Specify an IP Address"
If your PC is already configured for a fixed (specified) IP address, no changes are required.
(The Administrator should configure the Wireless Access Point with a fixed IP address from
the same address range used on the PCs.)
87
Page 92

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 2000
1. Select Control Panel - Network and Dial-up Connection.
2. Right click the Local Area Connection icon and select Properties. You should see a screen
like the following:
Figure 69: Network Configuration (Win 2000)
3. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
4. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following.
Figure 70: TCP/IP Properties (Win 2000)
88
Page 93

Appendix C - Windows TCP/IP
5. Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct:
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the default
Windows setting. This is the default Windows settings. To work correctly, you need a DHCP
server on your LAN.
Using a fixed IP Address ("Use the following IP Address")
If your PC is already configured for a fixed (specified) IP address, no changes are required.
(The Administrator should configure the Wireless Access Point with a fixed IP address from
the same address range used on the PCs.)
89
Page 94

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows XP
1. Select Control Panel - Network Connection.
2. Right click the Local Area Connection and choose Properties. You should see a screen
like the following:
Figure 71: Network Configuration (Windows XP)
3. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
4. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following.
Figure 72: TCP/IP Properties (Windows XP)
90
Page 95

Appendix C - Windows TCP/IP
5. Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct.
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the default
Windows setting. To work correctly, you need a DHCP server on your LAN.
Using a fixed IP Address ("Use the following IP Address")
If your PC is already configured for a fixed (specified) IP address, no changes are required.
(The Administrator should configure the Wireless Access Point with a fixed IP address from
the same address range used on the PCs.)
91
Page 96

Wireless Access Point User Guide
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows Vista
1. Select Control Panel - Network Connections.
2. Right click the Local Area Connection Status and choose Properties. Click Continue to
the User Account Control dialog box, then you should see a screen like the following:
Figure 73: Network Configuration (Windows Vista)
3. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
4. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following.
92
Page 97

Appendix C - Windows TCP/IP
Figure 74: TCP/IP Properties (Windows Vista)
5. Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct.
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the default
Windows setting. To work correctly, you need a DHCP server on your LAN.
Using a fixed IP Address ("Use the following IP Address")
If your PC is already configured for a fixed (specified) IP address, no changes are required.
(The Administrator should configure the Wireless Access Point with a fixed IP address from
the same address range used on the PCs.)
93
Page 98

Appendix D
About Wireless LANs
D
Overview
Wireless networks have their own terms and jargon. It is necessary to understand many of
these terms in order to configure and operate a Wireless LAN.
Wireless LAN Terminology
Modes
Wireless LANs can work in either of two (2) modes:
Ad-hoc
Infrastructure
Ad-hoc Mode
Ad-hoc mode does not require an Access Point or a wired (Ethernet) LAN. Wireless Stations (e.g. notebook PCs with wireless cards) communicate directly with each other.
Infrastructure Mode
In Infrastructure Mode, one or more Access Points are used to connect Wireless Stations
(e.g. Notebook PCs with wireless cards) to a wired (Ethernet) LAN. The Wireless Stations
can then access all LAN resources.
Access Points can only function in "Infrastructure" mode,
and can communicate only with Wireless Stations which are
set to "Infrastructure" mode.
SSID/ESSID
BSS/SSID
A group of Wireless Stations and a single Access Point, all using the same ID (SSID),
form a Basic Service Set (BSS).
Using the same SSID is essential. Devices with different SSIDs are unable to communicate with each other. However, some Access Points allow connections from Wireless
Stations which have their SSID set to “any” or whose SSID is blank (null).
ESS/ESSID
A group of Wireless Stations, and multiple Access Points, all using the same ID (ESSID),
form an Extended Service Set (ESS).
94
Page 99

Appendix D - About Wireless LANs
Different Access Points within an ESS can use different Channels. To reduce interference,
it is recommended that adjacent Access Points SHOULD use different channels.
As Wireless Stations are physically moved through the area covered by an ESS, they will
automatically change to the Access Point which has the least interference or best performance. This capability is called Roaming. (Access Points do not have or require Roaming
capabilities.)
Channels
The Wireless Channel sets the radio frequency used for communication.
Access Points use a fixed Channel. You can select the Channel used. This allows you to
choose a Channel which provides the least interference and best performance. For 802.11g,
13 channels are available in the USA and Canada, but 11channels are available in North
America if using 802.11b.
If using multiple Access Points, it is better if adjacent Access Points use different Chan-
nels to reduce interference. The recommended Channel spacing between adjacent Access
Points is 5 Channels (e.g. use Channels 1 and 6, or 6 and 11).
In "Infrastructure" mode, Wireless Stations normally scan all Channels, looking for an
Access Point. If more than one Access Point can be used, the one with the strongest signal
is used. (This can only happen within an ESS.)
If using "Ad-hoc" mode (no Access Point), all Wireless stations should be set to use the
same Channel. However, most Wireless stations will still scan all Channels to see if there
is an existing "Ad-hoc" group they can join.
WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a standard for encrypting data before it is transmitted. This
is desirable because it is impossible to prevent snoopers from receiving any data which is
transmitted by your Wireless Stations. But if the data is encrypted, then it is meaningless
unless the receiver can decrypt it.
If WEP is used, the Wireless Stations and the Wireless Access Point must have the same
settings.
WPA-PSK
Like WEP, data is encrypted before transmission. WPA is more secure than WEP, and should
be used if possible. The PSK (Pre-shared Key) must be entered on each Wireless station. The
256Bit encryption key is derived from the PSK, and changes frequently.
WPA2-PSK
This is a further development of WPA-PSK, and offers even greater security, using the AES
(Advanced Encryption Standard) method of encryption.
WPA-Enterprise
This version of WPA requires a Radius Server on your LAN to provide the client authentication according to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions are encrypted using the WPA
standard.
95
Page 100

Wireless Access Point User Guide
If this option is used:
The Access Point must have a "client login" on the Radius Server.
Each user must have a "user login" on the Radius Server.
Each user's wireless client must support 802.1x and provide the login data when required.
All data transmission is encrypted using the WPA standard. Keys are automatically generated,
so no key input is required.
802.1x
This uses the 802.1x standard for client authentication, and WEP for data encryption. If possible, you should use WPA-Enterprise instead, because WPA encryption is much stronger than
WEP encryption.
If this option is used:
The Access Point must have a "client login" on the Radius Server.
Each user must have a "user login" on the Radius Server.
Each user's wireless client must support 802.1x and provide the login data when required.
All data transmission is encrypted using the WEP standard. You only have to select the
WEP key size; the WEP key is automatically generated.
96
 Loading...
Loading...