
■ Contents
Outdoor
Wireless Router/Bridge
User’s Manual
Before operating the unit, please read this manual thoroughly, and
retain it for future reference.
1. HARDWARE INSTALLATION........................................................1
1.1 BEFORE YOU START ........................................................................1
1.2 LOCATE THE ROUTER/BRIDGE AND INLINE POWER INJECTOR PORTS ..........3
1.3 PREPARING INSTALLATION .................................................................4
1.4 OUTDOOR INSTALLATION....................................................................7
1.4.1 Antenna Mast Requirements.....................................................8
1.4.2 Grounding................................................................................8
1.4.3 Antenna Alignment ...................................................................9
2. NETWORK TOPOLOGIES AND QUICK SETUP............................1
2.1 NETWORK TOPOLOGIES ..................................................................10
2.2 QUICK SETUP................................................................................15
2.2.1 Configure Requirements.........................................................15
2.2.2 Configure the RB....................................................................18
2.2.3 Configure the RB as bridge mode Root AP ..............................19
2.2.4 Configure the RB as Root AP with PPPoE Ethernet connection 25
2.2.5 Configure the RB as Root AP with dynamic IP address Ethernet
.............................................................................................27
2.2.6 Configure the RB as Root AP with static IP address Ethernet...29
2.2.7 Configure the RB as Remote Extension Bridge ........................31
3. INITIAL CONFIGURATION..........................................................33
3.1 CONFIGURE REQUIREMENTS ............................................................33
3.2 CONFIGURE THE RB .......................................................................35
3.2.1 Configure the RB as Central Wireless Bridge ..........................37
3.2.2 Configure the RB as Central Wireless Router with PPPoE
Ethernet connection...............................................................38
3.2.3 Configure the RB as Central Wireless Router with dynamic IP
address Ethernet ...................................................................44
3.2.4 Configure the RB as Central Wireless Router with static IP
address Ethernet ...................................................................45
3.2.5 Configure the RB as Remote Wireless Router.........................47
3.2.6 Configure the RB as Remote Wireless Bridge..........................52
3.3 CONFIGURE WIRELESS RELATED PARAMETERS ...................................53
3.3.1 Configure IEEE 802.11b WLAN parameters.............................53
A
i

4 5 6 8 9 10 12
3.3.2 Security.................................................................................54
3.3.3 IEEE 802.1x Access Control ..................................................55
3.3.4 MAC based Access Control....................................................57
3.4 CONFIGURE DHCP SERVER ............................................................58
3.5 CONFIGURE VIRTUAL SERVER..........................................................59
3.6 ADVANCED CONFIGURATION.............................................................61
3.6.1 Configure Routing Table.........................................................61
3.6.2 Configure Bridge ....................................................................63
3.6.3 Configure SNMP....................................................................64
3.6.4 Configuration Review and Apply the New Settings....................66
3.7 UTILITY ........................................................................................68
3.7.1 System Info...........................................................................68
3.7.2 Software Upgrade ..................................................................69
3.7.3 Wireless Link Info..................................................................70
4. TELNET CONFIGURATION ........................................................71
5. SPECIFICATIONS.......................................................................85
6. DEFAULT SETTINGS.................................................................86
6.1 BASIC CONFIGURATION ...................................................................86
6.1.1 System..................................................................................86
6.1.2 Interface................................................................................86
6.1.3 Telnet/Console.......................................................................88
6.1.4 ISP........................................................................................88
6.1.5 DHCP....................................................................................89
6.1.6 Virtual Server Mapping...........................................................91
6.1.7 NAT (Network Address Translation)........................................91
6.1.8 Wireless LAN........................................................................92
6.2 ADVANCE CONFIGURATION ..............................................................93
6.2.1 Bridging.................................................................................93
6.2.2 SNMP Community .................................................................94
6.2.3 SNMP Trap............................................................................94
6.3 UTILITY ........................................................................................95
6.3.1 Software Upgrade ..................................................................95
7. REGULATORY COMPLIANCE INFORMATION ............................96
Chapter 1. Hardware Installation
This chapter describes the procedures for installing the Outdoor
Router/Bridge.
Note: Before you mount the Router/Bridge to a mast or on the side of
a building, be sure to configure and test the device first.
1.1 Before You Start
After unpacking the system, make sure the following items are present and in
good condition.
1. Router/Bridge
2. Inline Power Injector
3. AC Power Cord
4. MIL-C-5015 style RS232 Console Port Cable
5. Grounding Wire
6. Cross over Ethernet Cable
7. Reverse Polarity-N Female RF Cable
8. 30M MIL-C-5015 style Ethernet Cable
9. Mast Mounting Kit
10. Wall Mounting Kit
11. User’s Manual Disk
12. Simple Spanner
ii
1
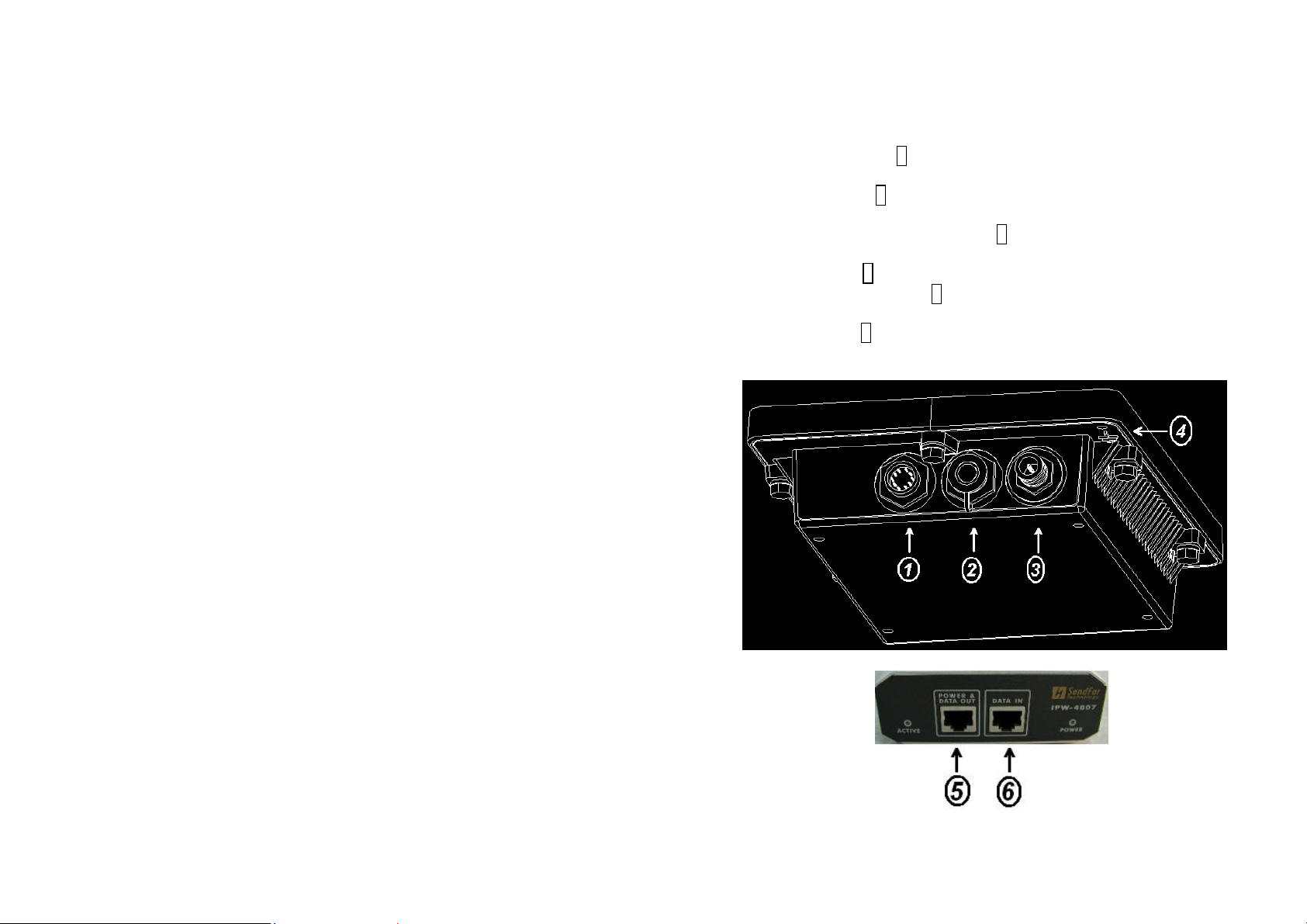
1.2 Locate the Router/Bridge and Inline Power
Injector Ports
l Special Ethernet port 1 for connecting the MIL-C-5015 style Ethernet
Cable
l Special serial port 2 for connecting the MIL-C-5015 style RS-232
console port cable
l Reverse Polarity-N Male connector 3 for connecting the antenna or RF
cable.
l Grounding port 4.
l Power & Data output port 5 for connecting the other of the MIL-C-5015
style Ethernet Cable
l Data input port 6 for connecting the Ethernet Cable to a Hub Switch
Router or a PC.
2
3
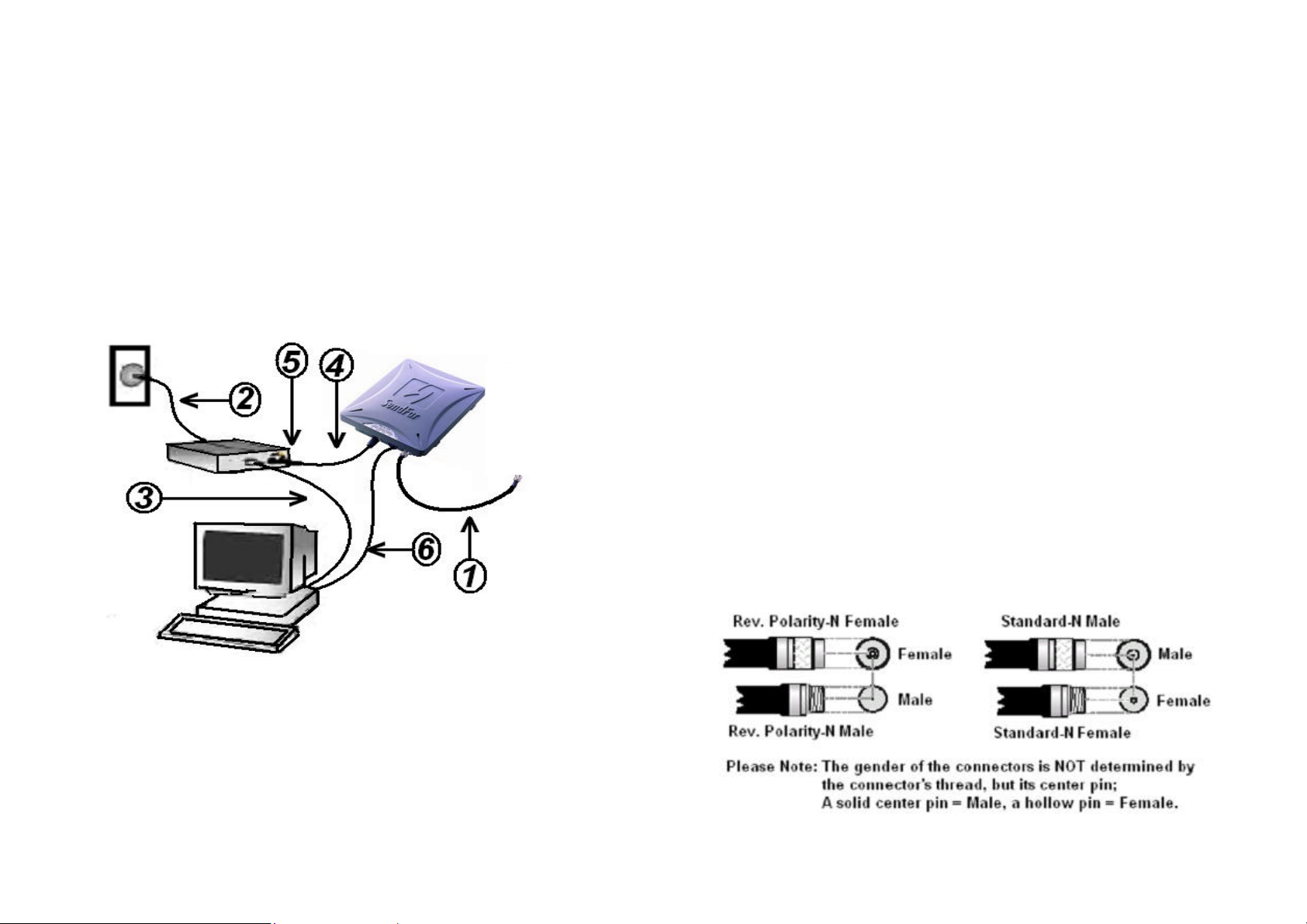
1.3 Preparing Installation
Before installing your Outdoor Wireless LAN system for your outdoor
application in a hard-to-reach location, we recommend that you configure
and test all the devices first.
For configuring the Outdoor Router/Bridge, you need follow the quick steps
below to power up your Router/Bridge:
Step 1: With the unit powered off, attach one end of the RF cable to the
antenna connector and then connect the antenna to the other end of the RF
cable as shown in following:
Step 2 Plug the female end of the power cord into the Inline Power Injector,
and then plug the male end of the power cord into a power outlet or power
strip. The Power LED on the front of the Inline Power Injector will light up.
Step 3 Run the cross over Ethernet cable (included in your package) from
Data Input Port (on the front of the Inline Power Injector) to the Ethernet Port
on a PC.
Antenna
NOTE: This connection is required for setting up initial configuration
information. After configuration is completed, this cable will be removed, and
then you should run an Ethernet cable from Data Input Port (on the front of
the Inline Power Injector) to the LAN connection (such as to a hub, bridge or
directly into a patch panel).
Step 4 Plug the MIL-C-5015 style Ethernet connector into the Special
Ethernet port on the back of the Router/Bridge.
Step 5 Plug the RJ-45 Ethernet connector (the other end of the Special
Ethernet cable) into the Power & Data Output Port on the front of the Inline
Power Injector.
Step 6 Attach the MIL-C-5015 style (RS-232) null modem cable to the Serial
Port Adapter. Connect the other cable end (DB9 female) to a terminal or a
PC running a terminal emulation program.
When the Router/Bridge receives power over the Ethernet cable, the
Router/Bridge will start its boot sequence and the Active LED on the front of
the Inline Power Injector will light up.
You can configure the Router/Bridge using the HTML browser, such as
Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator from a remote host or PC.
NOTE: The outdoor Router/Bridge antenna cabling systems be identified by
Reverse Polarity-N connectors (pictured in following)
4
5
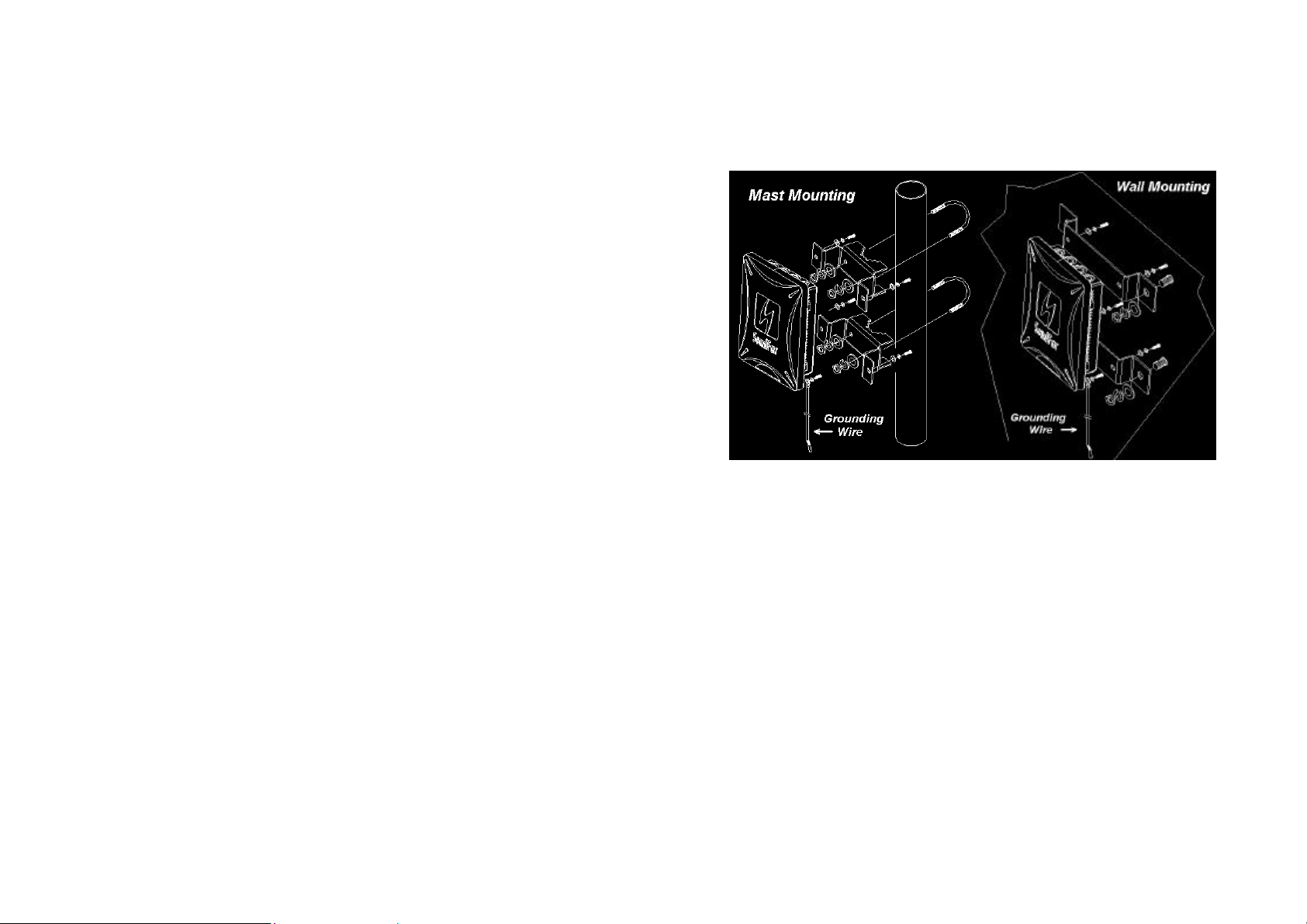
1.4 Outdoor Installation
Outdoor Router/Bridge device can be mounted on the side of a
building or mounted to an antenna mast as shown in following:
A wall (side) mount allows for mounting an antenna (mast) on the side
of a building or on the side of an elevator penthouse. This will provide
a convenient mounting location when the roof overhang is not
excessive and/or the location is high enough to provide a clear line of
sight.
In most situations mounting an antenna directly to the wall will not
allow you to properly align the antenna with the corresponding
antenna at the opposite end of your wireless link. As poor alignment
will typically result in poor performance, we advise you to always
mount the Outdoor Router/Bridge and antenna to a mast.
6
7

1.4.1 Antenna Mast Requirements
To accommodate the outdoor antennas, the antenna mast must satisfy
the following requirements:
a. The construction of the mast must be of a sturdy, weatherproof and
no corrosive material like for example galvanized or stainless steel
construction pipe.
b. Typical diameter of the mast should be between 35 mm (1.4 in.) and
41 mm (1.625 in.). Subject to the type of antenna that you intend to
install other diameters may be possible as well.
c. The height of the antenna mast must be sufficient to allow the
antenna to be installed at least 1.5 m (5 ft.) above the peak of roof. If
the roof is metal, then the height of the antenna should be a minimum
of 3 m (10 ft) above the roof.
d. The mast or wall-bracket must be free from any substance that may
prevent
a good electrical connection with the antenna; for example, paint.
1.4.2 Grounding
A safety grounding system is necessary to protect your outdoor
installation from lightning strikes and the build-up of static electricity.
So direct grounding of the antenna mast, Outdoor Router/Bridge and
Surge Arrester is very important. The Outdoor Router/Bridge has built
in Surge Arrester. So Mounting the Outdoor Router/Bridge on the
antenna mast, you have to connect the Outdoor Router/Bridge to the
same grounding system with the AC wall outlet.
The grounding system must comply with the National Electrical Code
and safety standards that apply in your country. Always check with a
qualified electrician if you are in doubt as to whether your outdoor
installation is properly grounded.
1.4.3 Antenna Alignment
For optimal performance of your wireless link, make sure that the
antennas are properly aligned (facing one another “eye-to-eye”). To
align the antennas:
_ Use a pair of binoculars and/or a map of the area and compass to
point the antennas to one another.
_ Use the Utility- “Wireless Link Info” in the Web Configure as
described in the "Utility " section to analyze the radio link quality.
The “Wireless Link Info” will enable you to display the levels of signal
strength and link quality.
Looking at the Wireless Link Info screen, you can interactively optimize
antenna alignment if required, by making small modifications in the
antenna orientation.
_ Alternatively, consult a professional Antenna Installation Service to
optimize the antenna alignment.
Omni-directional antennas are characterized by a wide radiation
pattern. Therefore alignment of this type of antennas is less critical
than for directional antennas.
8
9
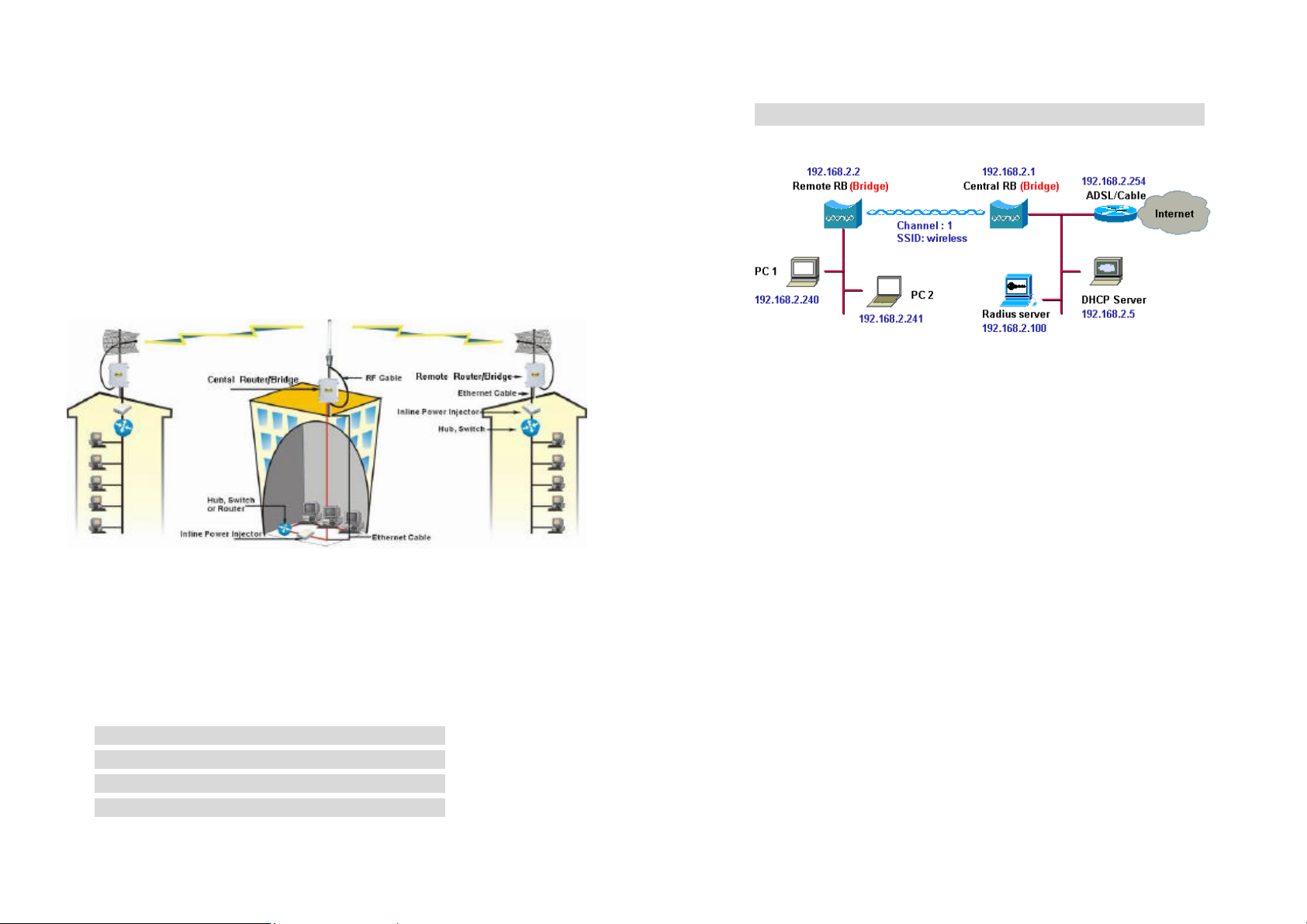
Chapter 2. Network Topologies and Quick Setup
2.1 Network Topologies
This section describes several main types of installations commonly
implemented using the Outdoor Wireless Router/Bridge System (RB). This is
by no means intended to be an exhaustive list of all possible configurations,
but rather shows examples of some of the more common implementations.
The RB can be configured into two roles: Central Router/Bridge (CRB) and
Remote Router/Bridge (RRB) to accomplish the broadband wireless point-tomultipoint systems (as shown in Figure 2-1).
Figure 2-1
Both the Central RB and the Remote RB can performed in router or bridge
modes. In a Point-to-Multipoint topology, all communication between network
systems is done through a centralized agent. In the Outdoor Wireless
Router/Bridge product, the centralized agent is Central Router or Central
Bridge and the individual network notes may be Remote Router or Remote
Bridge.
Configuration Examples
Remote Wireless Bridge-to-Central Wireless Bridge
1. Set the Central RB as a bridge (bridge IP address is 192.168.2.1).
2. Set Wireless parameters on Central RB: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless)
3. Set the Remote RB as a bridge (bridge IP address is 192.168.2.2).
4. Set Wireless parameters on Remote RB: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless), these parameters must same with Central RB.
5. Left side subnet is transparent to the right side.
6. DHCP server assign IP address to PC1 and PC2
To show some possibilities of Point-to-Multipoint topologies, the following
examples are provided:
1. Remote Wireless Bridge-to-Central Wireless Bridge
2. Remote Wireless Router-to-Central Wireless Bridge
3. Remote Wireless Bridge-to-Central Wireless Router
4. Remote Wireless Router-to-Central Wireless Router
10
11
Remote Wireless Router-to-Central Wireless Bridge
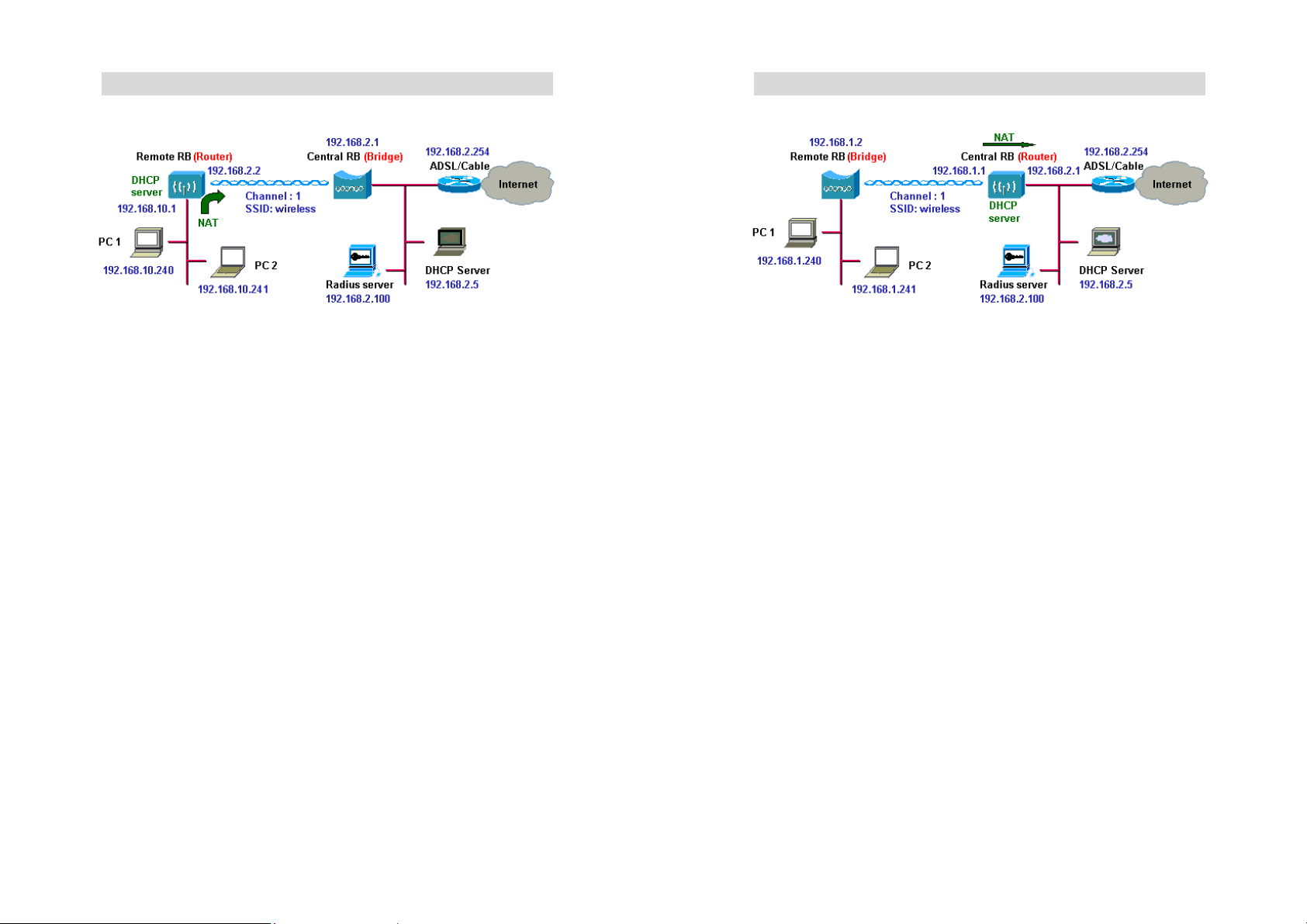
Remote Wireless Bridge-to-Central Wireless Router
1. Set the Central RB as a bridge (bridge IP address is 192.168.2.1).
2. Set Wireless parameters on Central RB: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless).
3. Set the Remote RB as a Router (Wireless Interface IP is
192.168.2.2, Ethernet Interface IP is 192.168.10.1, must turn on NAT
on Wireless Interface and turn off NAT on Ethernet interface, default
route is 192.168.2.254).
4. Set Wireless parameters on Remote RB: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless), these parameters must same with Central RB.
5. Set the DHCP server service on the Remote RB and apply it on
Ethernet Interface.
6. The Remote RB assign IP address to PC1 and PC2
1. Set the Central RB run as a Wireless Router (Wireless Interface IP
is 192.168.1.1, Ethernet Interface IP is 192.168.2.1, must turn off NAT
on Wireless Interface and turn on NAT on Ethernet interface, default
route is 192.168.2.254).
2. Set Wireless parameters on Central RB: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless)
3. Set the DHCP server service on the Central RB and apply it on
Wireless Interface.
4. Set the Remote RB as a Bridge (Bridge Interface IP is 192.168.1.2).
5. Set Wireless parameters on Remote RB: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless), these parameters must same with Central RB.
6. The Central RB assign IP address to PC1 and PC2
7. The operator can also turn off NAT behavior on Central RB and two
subnets are transparent.
12
13
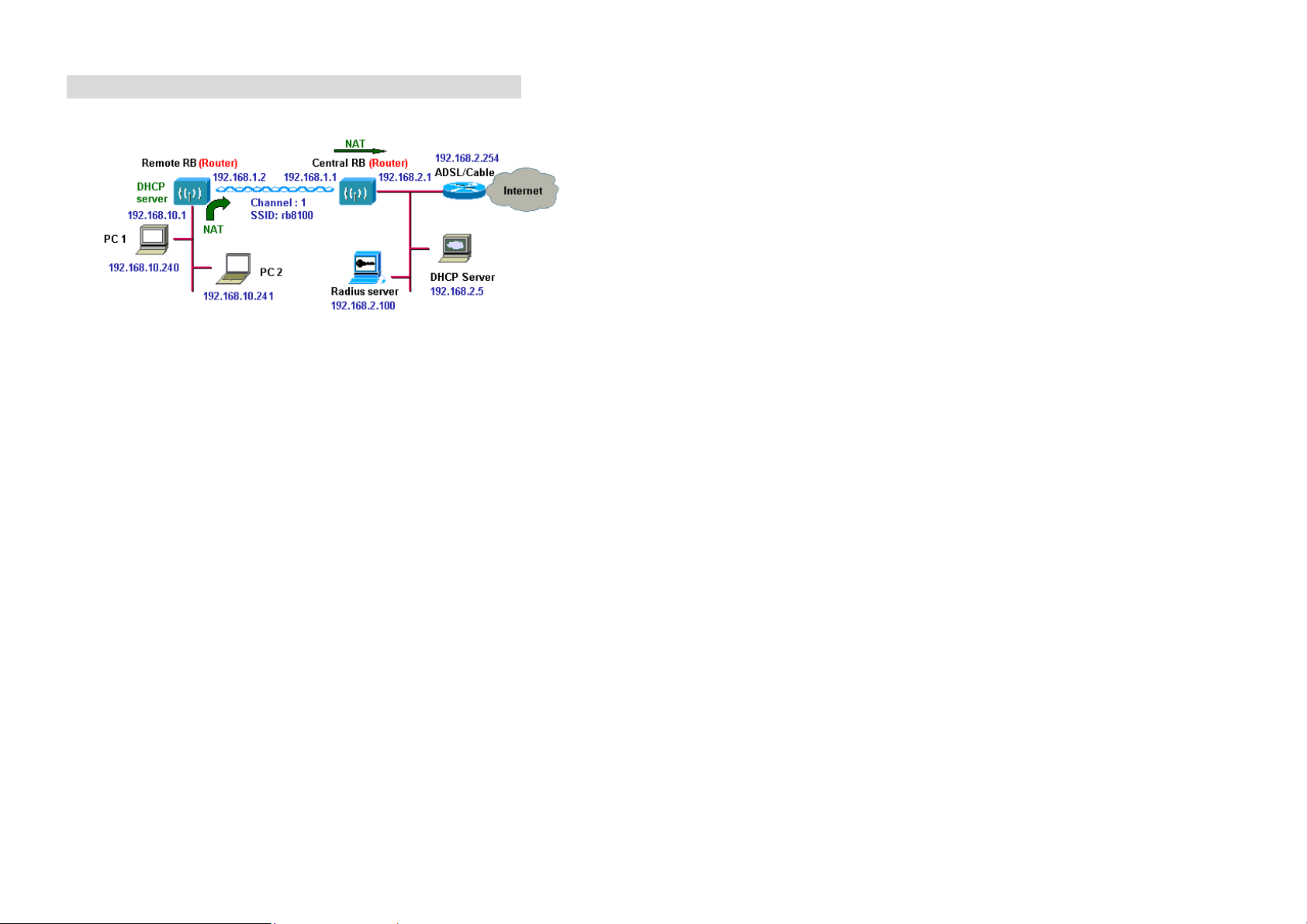
Remote Wireless Router-to-Central Wireless Router
1. Set the Central RB run as a Wireless Router (Wireless Interface IP
is 192.168.1.1, Ethernet Interface IP is 192.168.2.1, default route is
192.168.2.254).
2. Set Wireless parameters on Central RB: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless).
3. Set the Remote RB as a Wireless Router (Wireless Interface IP is
192.168.1.2, Ethernet Interface IP is 192.168.10.1, default route is
192.168.1.1).
4. Set Wireless parameters on Remote RB: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless), these parameters must same with Central RB.
5. Set the DHCP server service on the Remote RB and apply it on
Ethernet Interface.
6. The Remote RB assigns IP address to PC1 and PC2.
The operator can also turn off NAT behavior on Central RB and turn on
NAT behavior on Remote RB. Any outgoing packets will transfer to
192.168.1.2
l Central RB: turn off NAT on Wireless Interface and turn off NAT
on Ethernet interface.
l Remote RB: turn on NAT on Wireless Interface and turn off NAT
on Ethernet interface.
l Remote RB: turn on NAT on Wireless Interface and turn on NAT
on Ethernet interface.
2.2 Quick Setup
In this section, we only describe how to quickly configure the RB with
a web browser. For detailed descriptions of the many configuration
parameters and network configuration, refer to Chapter 3.
2.2.1 Configure Requirements
Before setup, we must install RB first
1. Connect power adaptor and power on the RB
2. Connect the Ethernet cable for connecting the RB to the network
3. Connect a computer to the same network with this RB
4. Start your Microsoft Internet Explorer web browser program from a LANattached computer. To access the web interface of the RB, you have to
disable Access the Internet using a proxy server function in View /
Internet Options / Connection as shown in Figure 2-2 or add the IP
address of the RB (default IP address is 192.168.2.1) to Bypass proxy
server for local addresses as shown in Figure 2-3.
5. Type the IP address and HTTP port of the RB (default IP address is
192.168.2.1) in the address field (http://192.168.2.1:2000/) and press
Enter. Make sure that the IP addresses of RB and your computer are in
the same subnet.
6. After the connection is established, you will see the User Identification
Window as shown in Figure 2-4 Enter the proper User Name and
Password to see the web user interface of the RB. The default user
name and password is root and root, respectively.
The operator can also turn on NAT behavior on Central RB and turn on
NAT behavior on Remote RB.
l Central RB: turn on NAT on Wireless Interface and turn on NAT
on Ethernet interface.
14
15
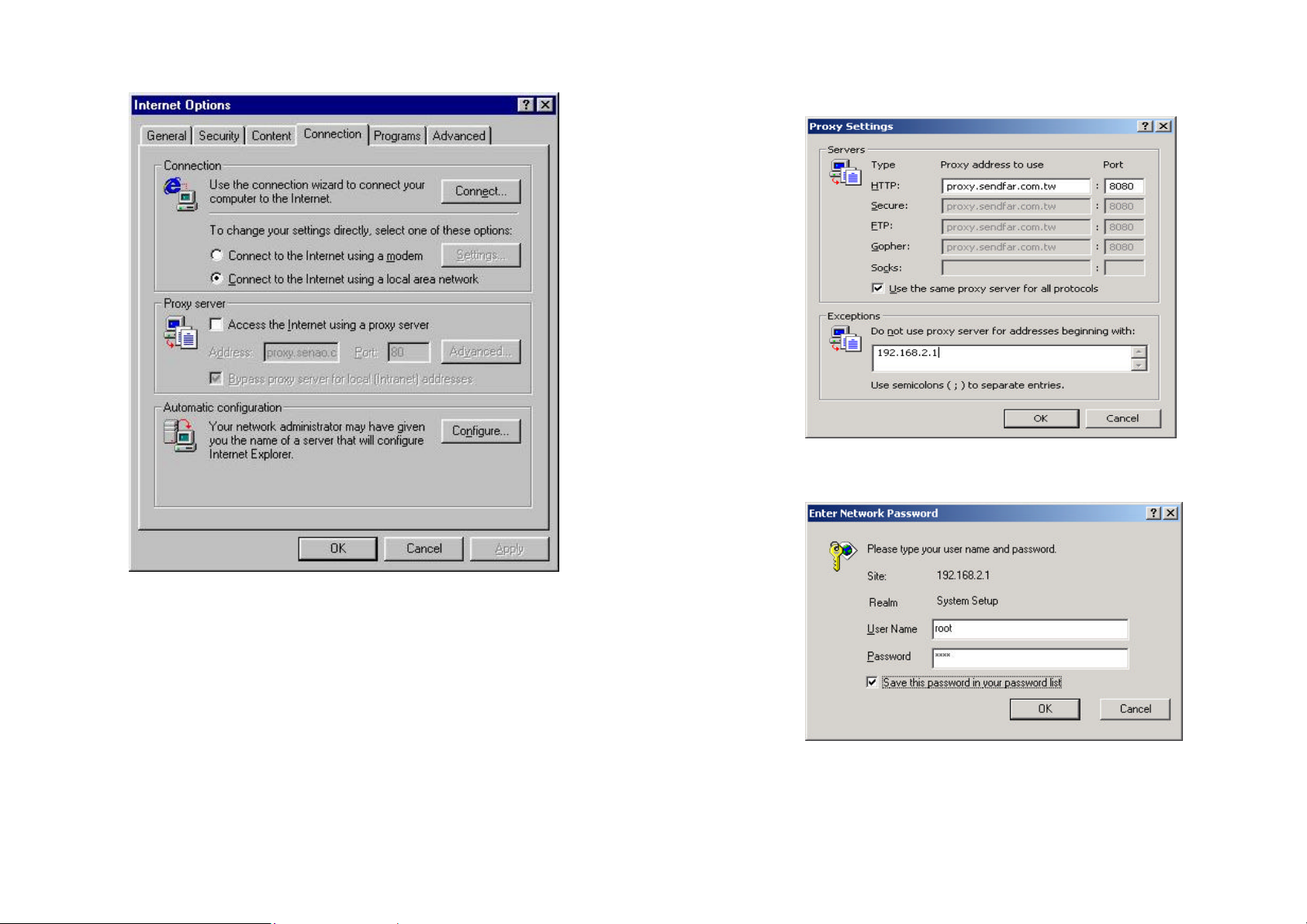
Figure 2-2
Figure 2-3
Figure 2-4
16
17
2.2.2 Configure the RB
The RB can be configured into two operation roles:
Central Wireless Router/Bridge (Central RB) and Remote Wireless
Router/Bridge (Remote RB).
Central RB can performed in four operation modes:
• Central Wireless Bridge
• Central Wireless Router with PPPoE Ethernet connection
• Central Wireless Router with dynamic IP address Ethernet
• Central Wireless Router with static IP address Ethernet
Remote RB can performed in two operation modes:
• Remote Wireless Bridge
• Remote Wireless Router
The RB is shipped with default configuration is as a bridge between an
Ethernet and wireless network. Users simply need to attach the RB to your
wired LAN. If users would like to configure the RB, please refer to the
following procedures.
The web user interface can be grouped into Quick setup, Basic
Configuration, Advanced Configuration and Utility as shown in Figure 2-5.
Figure 2-5
18
The left frame contains, in a tree structure, the contents of the RB web
configuration interface. Move through the tree by clicking on an icon to
expand or collapse the tree. The nodes on the tree represent web pages that
allow you to view and modify the parameters of the RB. In here, you can
click the Quick setup and following the setup wizard flow to configure this RB
step by step.
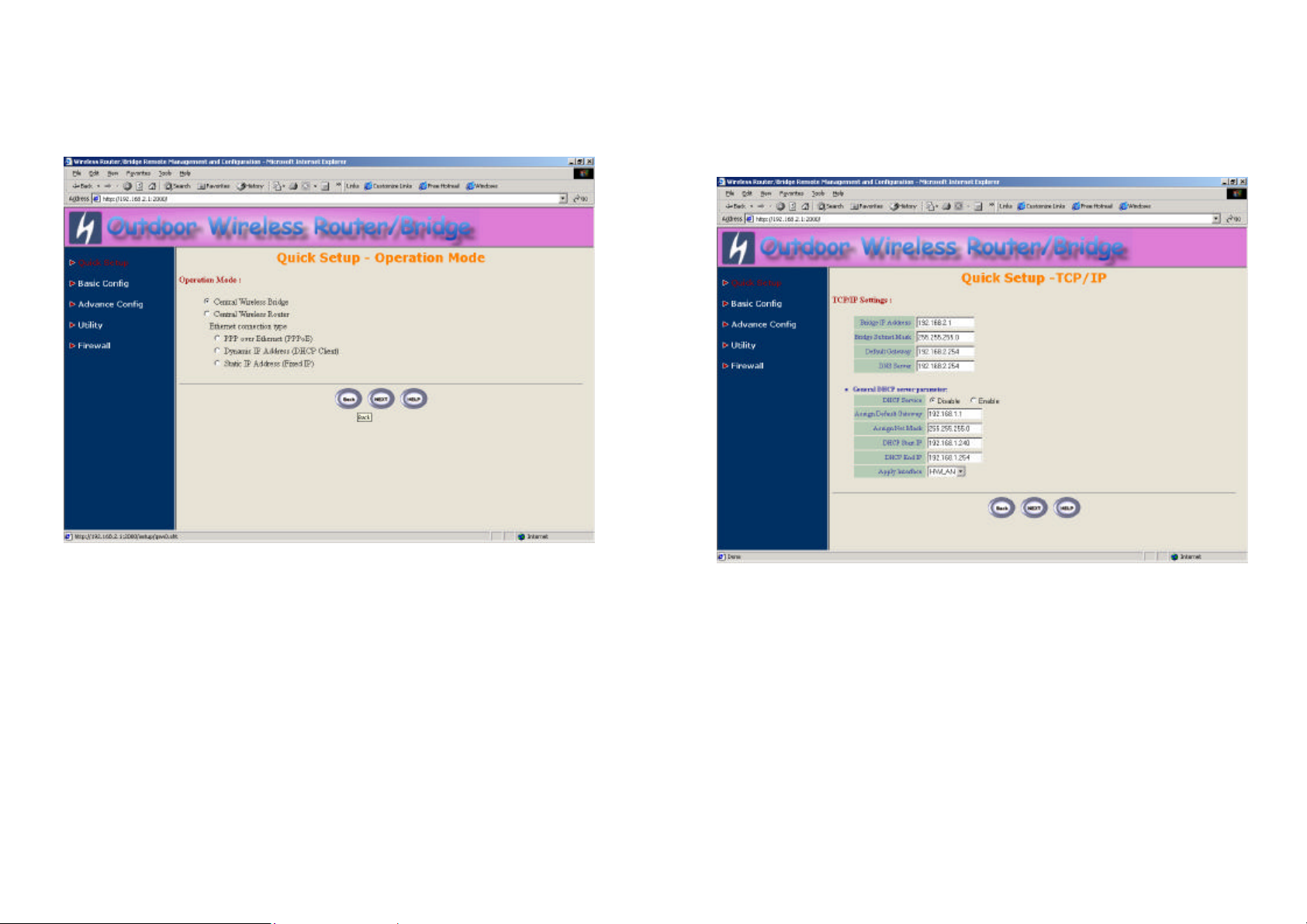
2.2.3 Configure the RB as a Central bridge
Step 1: Configure the operation role of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-6)
Click Quick Config, select Central Wireless Router/Bridge to setup this RB
that play with the Central RB role and then click NEXT at the bottom of this
page to complete the modification of this page.
Figure 2-6
19
Step 2: Configure the operation mode of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-7)
Click Quick Config, select central Wireless Bridge operation mode and
then click NEXT at the bottom of this page to complete the modification of
this page.
Figure 2-7
Step 3: Configure TCP/IP parameters (as shown in Figure 2-8)
In this page, enter the Bridge IP Address (default is 192.168.2.1) and
Bridge Subnet Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) that are suitable for your
network domain. After that, click NEXT at the bottom of this page to complete
the modification of this page.
Figure 2-8
20
21
Step 4: Configure IEEE 802.11b WLAN parameters (as shown in Figure 2-
9)
In this page, enter the Channel (default is 1), rts Threshold (default is 250),
frag Threshold (default is 1600), SSID (default is rb8100) and Station
Name (default is ap) that are suitable for your radio network and then you
can clicked radio button to disable WEP or enable 64/128 bit WEP services
(default is disable), if WEP is enabled, you must input corresponded Default
Key index and WEP Key. After that, click NEXT at the bottom of this page to
complete the modification of this page.
Figure 2-9
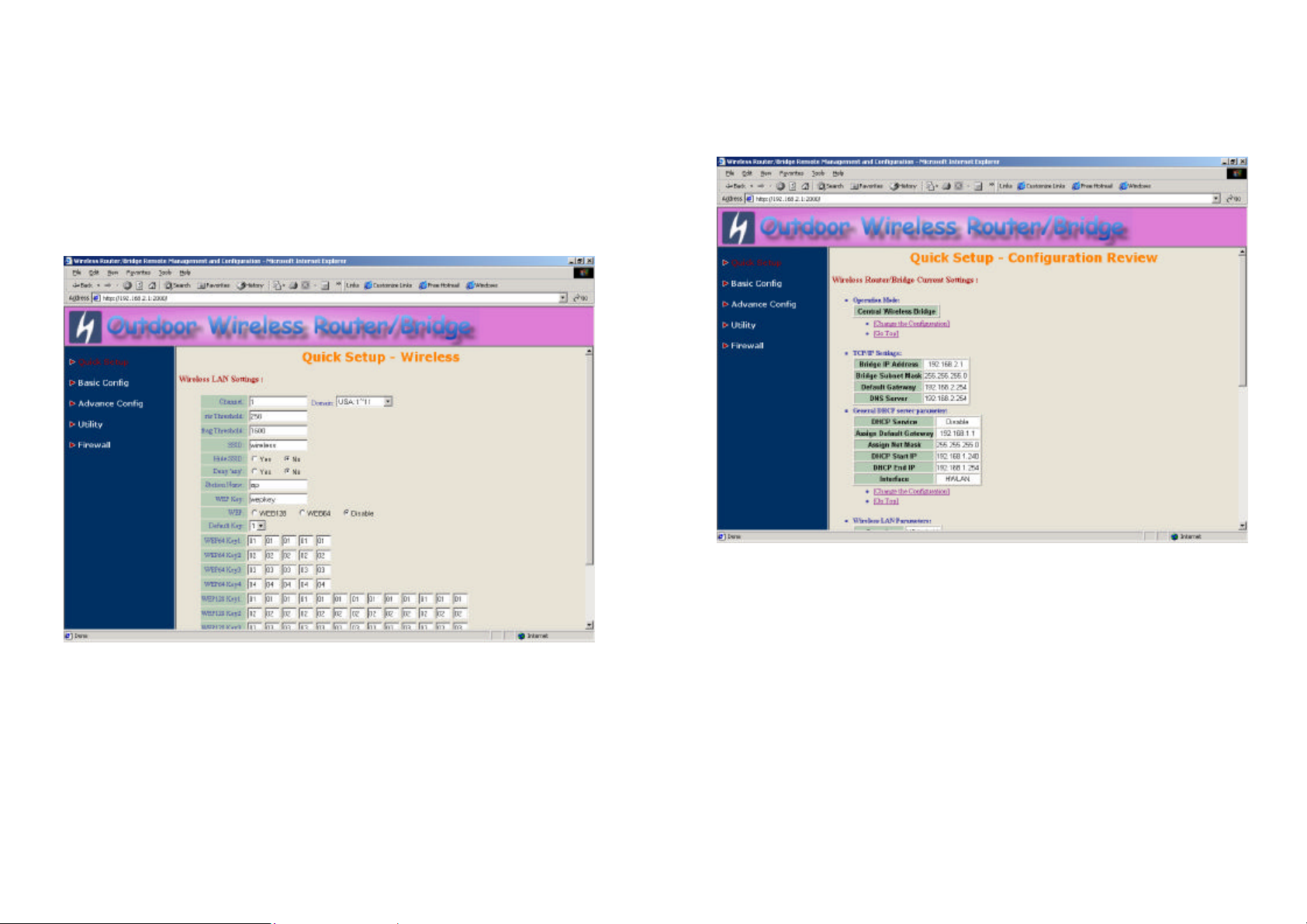
Step 5: Preview the configured setting of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-10)
This page will present the current settings of the RB to the system
administrator, the operator can easy to view all running configuration in here.
After that, click Save button to store the changes to the RB.
Figure 2-10
22
23
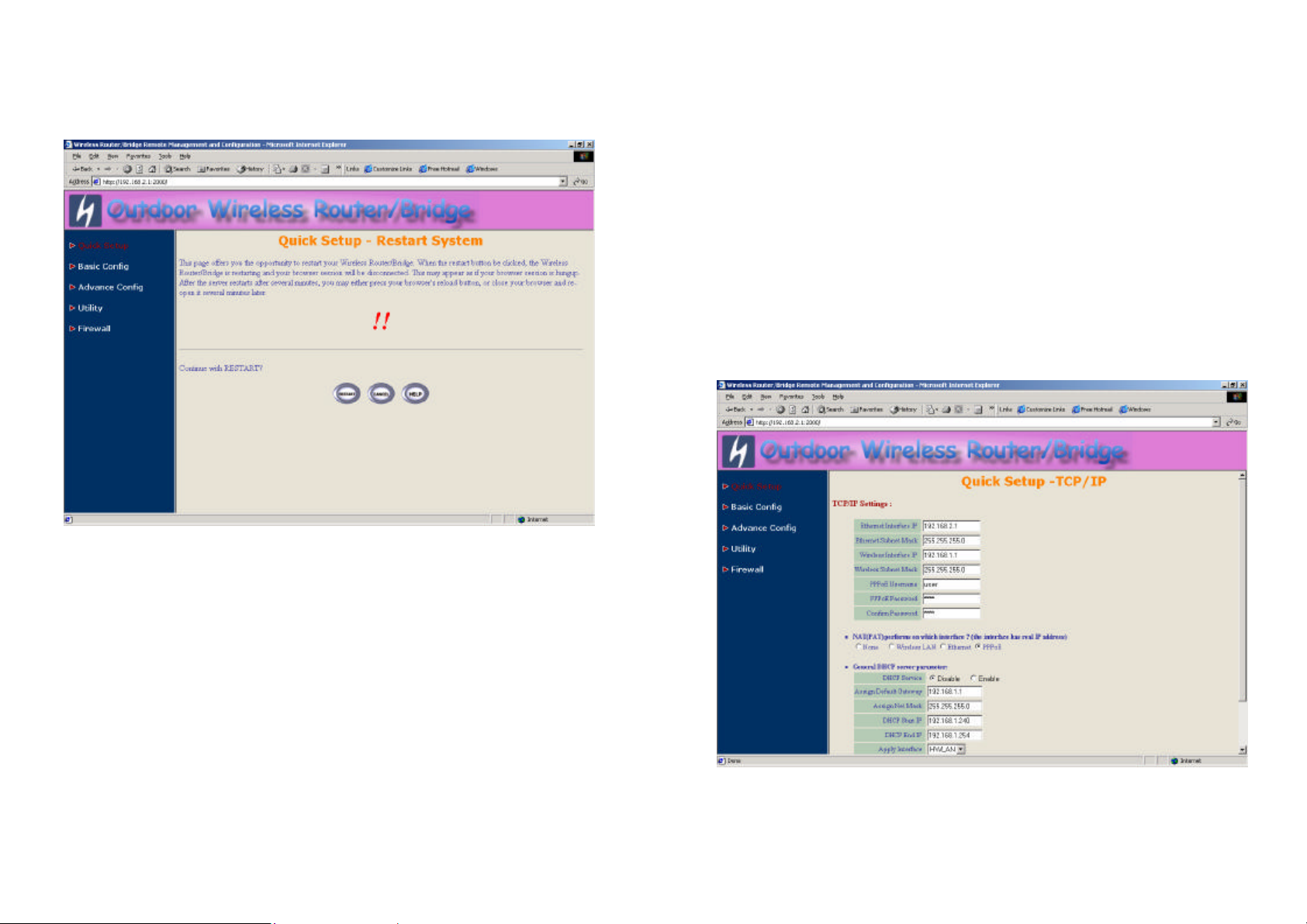
Step 6: Restart this RB (as shown in Figure 2-11)
In this page, you can click the RESTART button at the bottom of this page to
take effect the previous configuration changes.
Figure 2-11
2.2.4 Configure the RB as Central RB with PPPoE
Ethernet connection
Step 1: Configure the operation role of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-6)
Click Quick Config, select Central Wireless Router/Bridge to setup this RB
that play with the Central RB role and then click NEXT at the bottom of this
page to complete the modification of this page.
Step 2: Configure the operation mode of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-7)
Click Quick Config, select Central Wireless Router to setup this RB
operated in routing mode, you also need to select the Ethernet connection
type in PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE), and then click NEXT at the bottom of
this page to complete the modification of this page.
Step 3: Configure TCP/IP parameters (as shown in Figure 2-12)
Figure 2-12
24
25
In this page, enter the Wireless interface IP (default is 192.168.1.1) and
Wireless interface Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) that are suitable for
your wireless network, and specify the Ethernet IP address (default is
192.168.2.1) and Ethernet Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) of the
Ethernet interface. And then, if you are an ADSL subscriber, you may
specify that your personal ISP provided PPPoE Username and PPPoE
Password to enable ADSL broadband access.
Sometimes users have to conFigure 2-correct network settings in Gateway
and DNS tab of your wireless client computers to surf the Internet, or you
can enable DHCP server services for all wireless clients (default DHCP
server setting of the RB is disable in wireless network). In general DHCP
server parameters segment, input Assign Default Gateway (default is
192.168.2.254), Assign Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0), Assign Name
Server (default is 192.168.1.1), DHCP Start IP (default is 192.168.1.240),
DHCP End IP (default is 192.168.1.250) and choice Apply Interface on
HWLAN to made your DHCP server services available for wireless network,
at finally click NEXT at the bottom of this page to complete the modification
of this page.
Step 4: Configure IEEE 802.11b WLAN parameters (as shown in Figure 2-
9)
In this page, enter the Channel (default is 1), rts Threshold (default is 250),
frag Threshold (default is 1600), SSID (default is rb8100) and Station
Name (default is ap) that are suitable for your radio network and then you
can clicked radio button to disable WEP or enable 64/128 bit WEP services
(default is disable), if WEP is enabled, you must input corresponded Default
Key index and WEP Key. After that, click NEXT at the bottom of this page to
complete the modification of this page.
Step 5: Preview the configured setting of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-10)
This page will present the current settings of the RB to the system
administrator, the operator can easy to view all running configuration in here.
After that, click Save button to store the changes to the RB.
Step 6: Restart this RB (as shown in Figure 2-11)
In this page, you can click the RESTART button at the bottom of this page to
take effect the previous configuration changes.
2.2.5 Configure the RB as a Central RB with dynamic IP
address Ethernet
Step 1: Configure the operation role of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-6)
Click Quick Config, select Central Wireless Router/Bridge to setup this RB
that play with the Central RB role and then click NEXT at the bottom of this
page to complete the modification of this page.
Step 2: Configure the operation mode of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-7)
Click Quick Config, select Central Wireless Router to setup this RB
operated in routing mode, you also need to select the Ethernet connection
type in Dynamic IP address (DHCP Client), and then click NEXT at the
bottom of this page to complete the modification of this page.
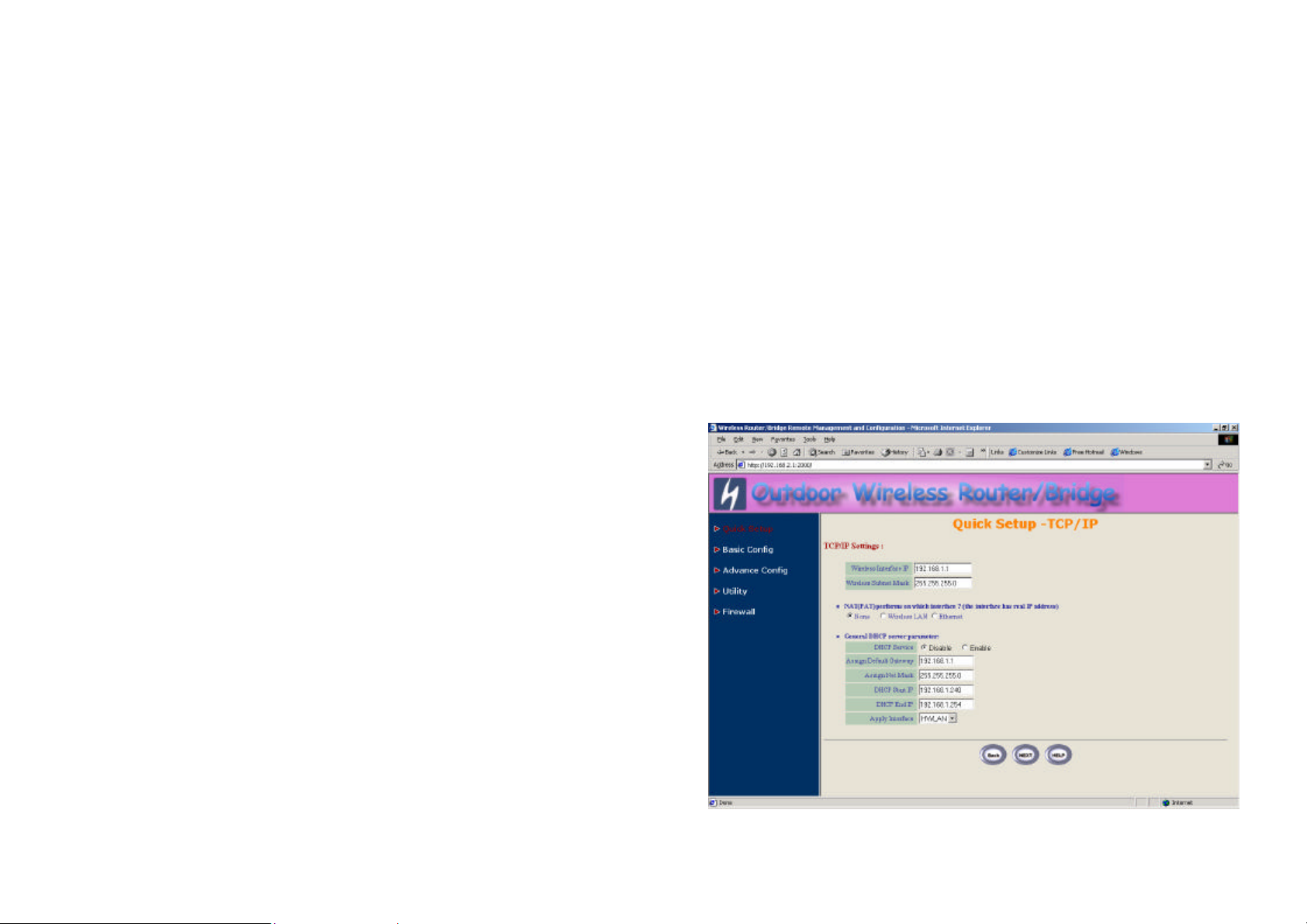
Step 3: Configure TCP/IP parameters (as shown in Figure 2-13)
In this page, enter the Wireless interface IP (default is 192.168.1.1) and
Wireless interface Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) that are suitable for
your wireless network.
Figure 2-13
26
27
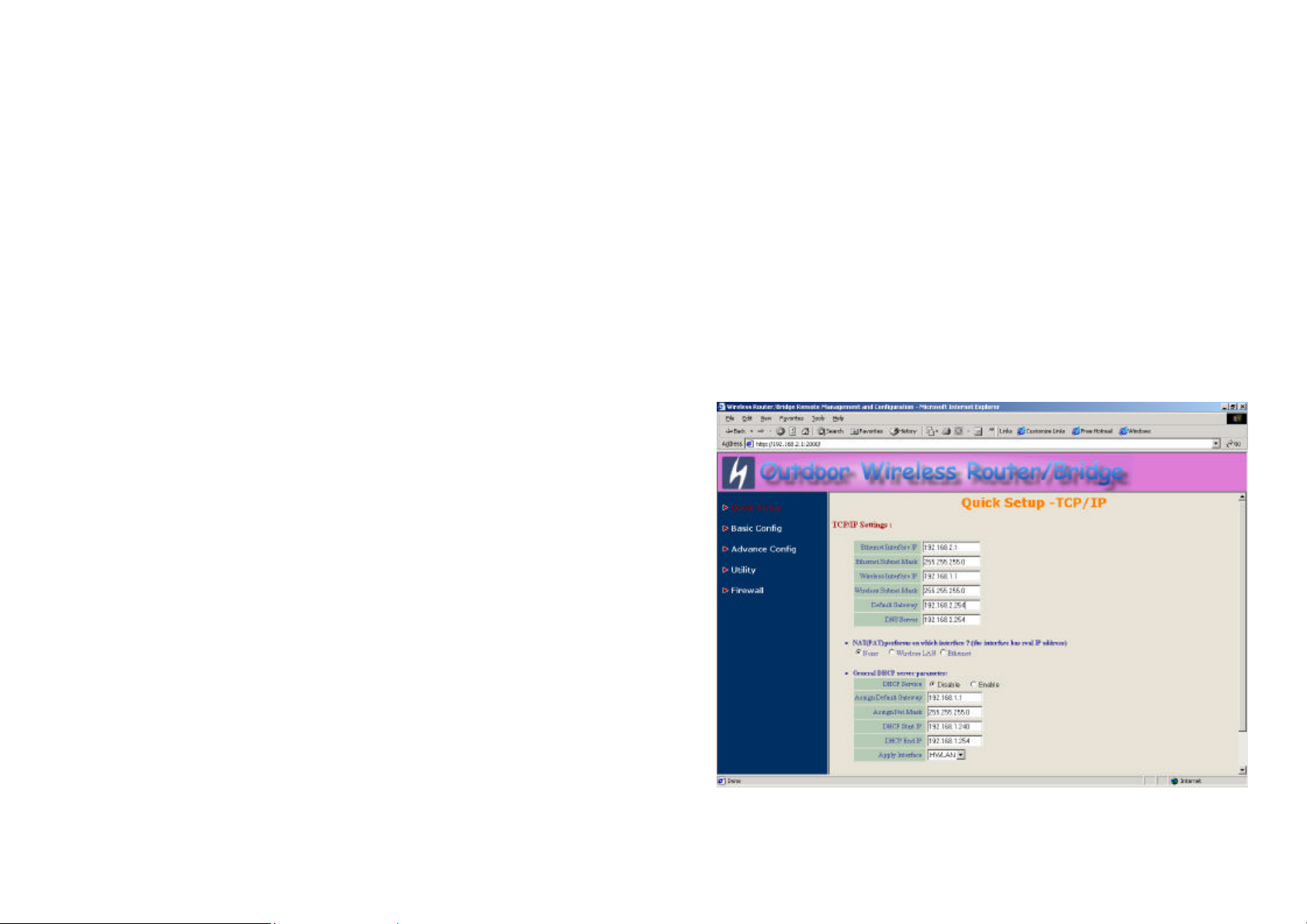
Sometimes users have to configure correct network settings in Gateway and
DNS tab of your wireless client computers to surf the Internet, or you can
enable DHCP server services for all wireless clients (default DHCP server
setting of the RB is disable in wireless network). In general DHCP server
parameters segment, input Assign Default Gateway (default is
192.168.1.1), Assign Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0), Assign Name
Server (default is 192.168.2.254), DHCP Start IP (default is
192.168.1.240), DHCP End IP (default is 192.168.1.250) and choice Apply
Interface on HWLAN to made your DHCP server services available for
wireless network, at finally click NEXT at the bottom of this page to complete
the modification of this page.
Step 4: Configure IEEE 802.11b WLAN parameters (as shown in Figure 2-
9)
In this page, enter the Channel (default is 1), rts Threshold (default is 250),
frag Threshold (default is 1600), SSID (default is rb8100) and Station
Name (default is ap) that are suitable for your radio network and then you
can clicked radio button to disable WEP or enable 64/128 bit WEP services
(default is disable), if WEP is enabled, you must input corresponded Default
Key index and WEP Key. After that, click NEXT at the bottom of this page to
complete the modification of this page.
Step 5: Preview the configured setting of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-10)
This page will present the current settings of the RB to the system
administrator, the operator can easy to view all running configuration in here.
After that, click Save button to store the changes to the RB.
Step 6: Restart this RB (as shown in Figure 2-11)
In this page, you can click the RESTART button at the bottom of this page to
take effect the previous configuration changes.
2.2.6 Configure the RB as a Central RB with static IP
address Ethernet
Step 1: Configure the operation role of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-6)
Click Quick Config, select Central Wireless Router/Bridge to setup this RB
that play with the Root AP role and then click NEXT at the bottom of this
page to complete the modification of this page.
Step 2: Configure the operation mode of this AP (as shown in Figure 2-7)
Click Quick Config, select Central Wireless Router to setup this RB
operated in routing mode, you also need to select the Ethernet connection
type in Static IP address (Fixed IP), and then click NEXT at the bottom of
this page to complete the modification of this page.
Step 3: Configure TCP/IP parameters (as shown in Figure 2-14)
Figure 2-14
28
29

In this page, enter the Wireless interface IP (default is 192.168.1.1) and
Wireless interface Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) that are suitable for
your wireless network, and specify the Ethernet IP address (default is
192.168.2.1) and Ethernet Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) of the
Ethernet interface. Specify the Default Gateway (Default is 192.168.2.254)
as the IP Address of the ADSL/Cable modem connected to the RB or the IP
Address of the Gateway in your Ethernet environment and the IP address of
the DNS servers provided by your ISP in the DNS server (Default is
192.168.2.254) parameter.
Sometimes users have to configure correct network settings in Gateway and
DNS tab of your wireless client computers to surf the Internet, or you can
enable DHCP server services for all wireless clients (default DHCP server
setting of the RB is disable in wireless network). In general DHCP server
parameters segment, input Assign Default Gateway (default is
192.168.1.1), Assign Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0), Assign Name
Server (default is 192.168.2.254), DHCP Start IP (default is
192.168.1.240), DHCP End IP (default is 192.168.1.250) and choice Apply
Interface on HWLAN to made your DHCP server services available for
wireless network, at finally click NEXT at the bottom of this page to complete
the modification of this page.
Step 4: Configure IEEE 802.11b WLAN parameters (as shown in Figure 2-
9)
In this page, enter the Channel (default is 1), rts Threshold (default is 250),
frag Threshold (default is 1600), SSID (default is rb8100) and Station
Name (default is ap) that are suitable for your radio network and then you
can clicked radio button to disable WEP or enable 64/128 bit WEP services
(default is disable), if WEP is enabled, you must input corresponded Default
Key index and WEP Key. After that, click NEXT at the bottom of this page to
complete the modification of this page.
Step 5: Preview the configured setting of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-10)
This page will present the current settings of the RB to the system
administrator, the operator can easy to view all running configuration in here.
After that, click Save button to store the changes to the RB.
Step 6: Restart this RB (as shown in Figure 2-11)
In this page, you can click the RESTART button at the bottom of this page to
take effect the previous configuration changes.
30
2.2.7 Configure the RB as Remote Wireless Bridge
Step 1: Configure the operation role of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-6)
Click Quick Config, select Remote Wireless Bridge to setup this RB that
play with the Remote Bridge role and then click NEXT at the bottom of this
page to complete the modification of this page.
Step 2: Configure TCP/IP parameters (as shown in Figure 2-14)
In this page, enter the Wireless interface IP (default is 192.168.1.1) and
Wireless interface Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) that are suitable for
your wireless network, and specify the Ethernet IP address (default is
192.168.2.1) and Ethernet Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) of the
Ethernet interface. Specify the Default Gateway (Default is 192.168.2.254)
as the Wireless IP Address of the Root RB and the IP address of the DNS
servers provided by your ISP in the DNS server (Default is 192.168.2.254)
parameter.
Sometimes users have to configure correct network settings in Gateway and
DNS tab of your wireless client computers to surf the Internet, or you can
enable DHCP server services for all wireless clients (default DHCP server
setting of the RB is disable in wireless network). In general DHCP server
parameters segment, input Assign Default Gateway (default is
192.168.1.1), Assign Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0), Assign Name
Server (default is 192.168.2.254), DHCP Start IP (default is
192.168.1.240), DHCP End IP (default is 192.168.1.250) and choice Apply
Interface on HWLAN to made your DHCP server services available for
wireless network, at finally click NEXT at the bottom of this page to complete
the modification of this page.
Step 3: Configure IEEE 802.11b WLAN parameters (as shown in Figure 2-
9)
Make sure the SSID parameter is same with the configuration of the Root
RB.
In this page, enter the Channel (default is 1), rts Threshold (default is 250),
frag Threshold (default is 1600), SSID (default is rb8100) and Station
Name (default is ap) that are suitable for your radio network and then you
can clicked radio button to disable WEP or enable 64/128 bit WEP
services (default is disable), if WEP is enabled, you must input
corresponded Default Key index and WEP Key. After that, click NEXT at
the bottom of this page to complete the modification of this page.
31

Step 4: Preview the configured setting of this RB (as shown in Figure 2-10)
This page will present the current settings of the RB to the system
administrator, the operator can easy to view all running configuration in here.
After that, click Save button to store the changes to the RB.
Step 5: Restart this RB (as shown in Figure 2-11)
In this page, you can click the RESTART button at the bottom of this page to
take effect the previous configuration changes.
Hint: Users may to configure correct network settings as following sample
Remote
Extension
Bridge 2
Root AP
Remote
Extension
Bridge 1
Wireless link
Wireless IP: 192.168.1.3
SSID : rb8100
Channel : 1
Station Name: ext2
Ethernet IP: 192.168.20.1
Default Route: 192.168.1.1
Wireless IP: 192.168.1.1
SSID : rb8100
Channel : 1
Ethernet IP: 192.168.2.1
Default Route: 192.168.2.254
Static Route:
192.168.10.0 / 24 / 192.168.1.2
192.168.20.0 / 24 / 192.168.1.3
Wireless IP: 192.168.1.2
SSID : rb8100
Channel : 1
Station Name: ext1
Ethernet IP: 192.168.10.1
Default Route: 192.168.1.1
Chapter 3. Initial Configuration
This chapter describes how to easy setup and configure the Outdoor
Wireless Broadband Router / Bridge System (RB). The RB can be
configured into two roles: Central Wireless Router/Bridge (Central RB) and
Remote Wireless Router/Bridge (Remote RB) to accomplish the broadband
wireless point-to-point and multipoint systems (as shown in Figure 3-1).
Users can use a LAN-attached (wired or wireless) computer to configure the
RB through a web browser or a telnet session on a LAN computer.
Figure 3-1
In this chapter, we only describe how to quickly configure the RB with a web
browser. For detailed descriptions of the many configuration parameters and
network configuration, refer to Chapter 4.
3.1 Configure Requirements
The RB is shipped with configuration that can be utilized right out of the box.
Default configuration is as a bridge between an Ethernet and wireless
network. Users simply need to attach the RB to your wired LAN. If users
would like to configure the RB, please refer to the following procedures.
Before setup, we must install RB first
1. Connect power adaptor and power on the RB
32
33
2. Connect the Ethernet cable for connecting the RB to the network
3. Connect a computer to the same network with this RB
4. Start your Microsoft Internet Explorer web browser program from a
LAN-attached computer. To access the web interface of the RB, you
have to disable Access the Internet using a proxy server function in
Windows 2000 [Control Panel / Internet Options / Connections/LAN
Settings] as shown in Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2
7. Type the IP address and HTTP port of the RB (default port is 2000, IP
is 192.168.2.1) in the address field (http://192.168.2.1:2000/) and press
Enter. Make sure that the IP addresses of RB and your computer are in
the same subnet.
Figure 3-3
3.2 Configure the RB
The RB can be configured into two operation roles:
Central Wireless Router/Bridge(Central RB) and Remote Wireless
Router/Bridge(Remote RB), the Central RB can performed in four operation
modes and the Remote RB can performed in two operation modes
Central RB:
1. Central Wireless Bridge
2. Central Wireless Router with PPPoE Ethernet connection
3. Central Wireless Router with dynamic IP address Ethernet
4. Central Wireless Router with static IP address Ethernet
8. After the connection is established, you will see the User Identification
Window as shown in Figure3-3 Enter the proper User Name and
Password to see the web user interface of the RB. The default user
name and password is root and root, respectively
34
Remote RB:
1. Remote Wireless Bridge
2. Remote Wireless Router
The RB is shipped with default configuration is as a bridge between an
Ethernet and wireless network. Users simply need to attach the RB to your
wired LAN. If users would like to configure the RB, please refer to the
35

following procedures.
The web user interface can be grouped into Quick setup, Basic
Configuration, Advanced Configuration, Utility and Firewall as shown in
Figure 3-4. The left frame contains, in a tree structure, the contents of the
RB web configuration interface. Move through the tree by clicking on an icon
to expand or collapse the tree. The nodes on the tree represent web pages
that allow you to view and modify the parameters of the RB.
Figure 3-4
If users want to connect multiple wireless computers to a broadband (ADSL
or Cable) modem or an Ethernet switch to surf the Internet, you need to
configure the RB as a broadband wireless router to share a single IP
address with the multiple wireless computers as described as follows.
3.2.1 Configure the RB as Central Wireless Bridge
Configure TCP/IP parameters
1. Click Advanced Config, select Bridging, and then click Enable for
Bridge Function as shown in Figure 3-5. In the Bridging Parameter
window, enter the IP Address (default is 192.168.2.1) and Subnet
Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) that are suitable for your network
domain. After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete
the modification of this page.
Figure 3-5
36
37

3.2.2 Configure the RB as Central Wireless Router with
PPPoE Ethernet connection
Configure TCP/IP parameters
1. Click Advanced Config, select Bridging, and then click Disable for
Bridge Function as shown in Figure 3-5. After that, click FINISH at the
bottom of this page to complete the modification of this page.
2. If you are an ADSL subscriber, you need specify that your personal ISP
PPPoE username and password to enable ADSL broadband access, in
here, click Basic Config, select ISP (as shown in Figure 3-6), In this
page, enter MODIFY button to setup the correct ISP parameters: ISP
Name, ISP Phone, PPPoE Username and PPPoE Password to (as
shown in Figure 3-7).
Hint: Ask your ISP for the correct settings.
Figure 3-6
Figure 3-7
3. Click Basic Config, select Interface (as shown in Figure 3-8) and in
this page, you can click radio button and enter MODIFY to choice which
one that you want to change it (as shown in Figure 3-9).
In interface 1, Make sure this wireless interface status is Active, enter
the Wireless interface IP (default is 192.168.1.1) and Wireless
interface Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) that are suitable for your
wireless network.
In interface 2, Make sure this Ethernet interface status is Active, and
specify the Ethernet IP address (default is 192.168.2.1) and Ethernet
Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) of the Ethernet interface.
In interface 3, Make sure this PPPoE interface status is Active, and
specify the Ethernet IP address (default is 192.168.3.1) and Ethernet
Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0), choice the ISP index that your are
38
39
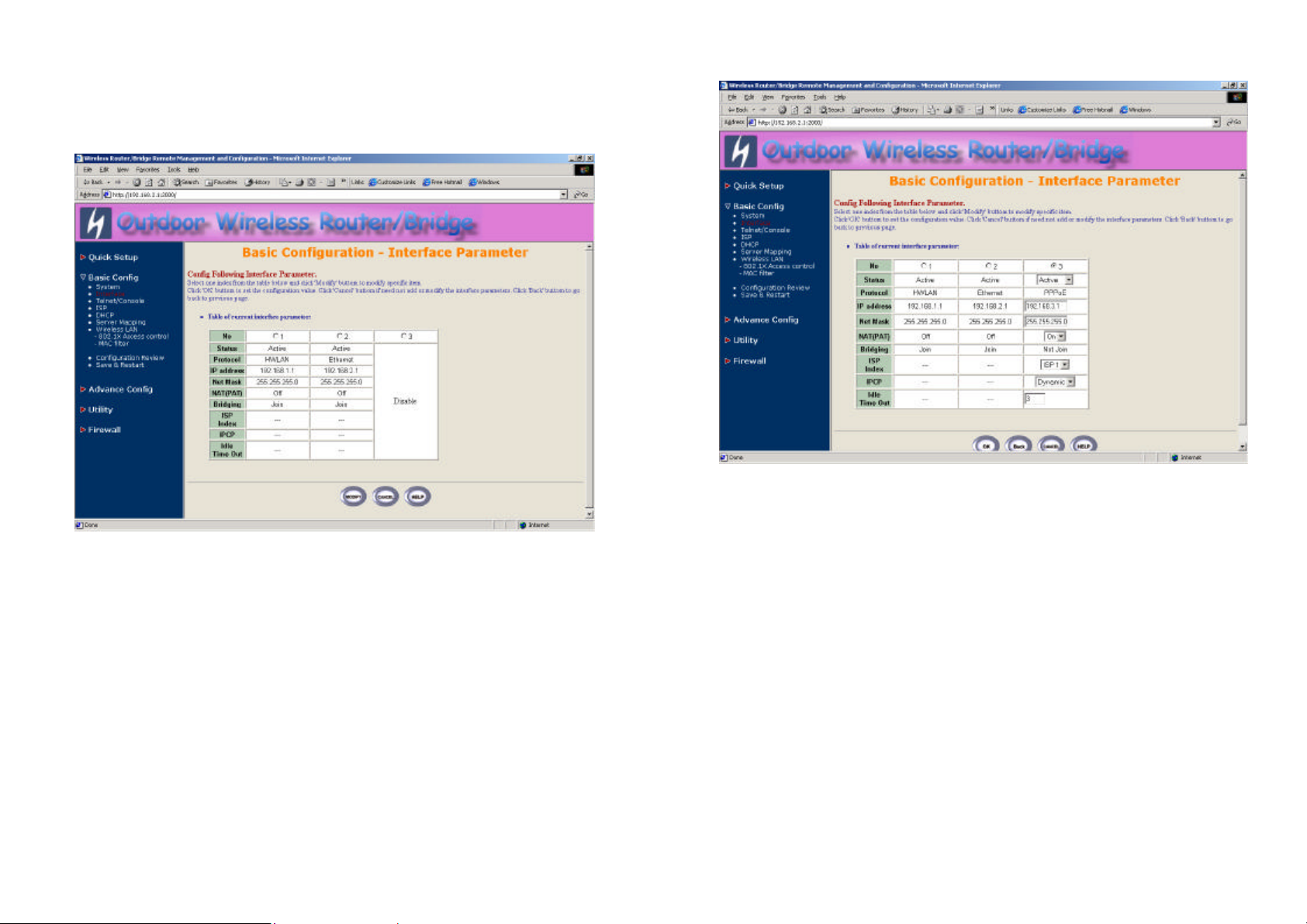
configured in step 1. After that, follow the default setting and Click the OK
button to return to the Interface Parameter window. Finally, you need to
click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the modification of
this page.
Figure 3-8
Figure 3-9
Hint1: Make sure interface 4 within status Disable.
Hint2: Choice the NAT(PAT) in every interfaces to enable NAT
service. For example, make sure PPPoE interface within
NAT(PAT) On and others are Off, it means that every
communications through the PPPoE interface needs NAT
transfer.
40
41

4. The RB supports PPPoE auto dial-up, please make sure your default
route is zero. In here, click Basic Config, and then select System as
shown in Figure 3-10. In the System Setup page, specify the Default
Route (Default is 192.168.2.254) is 0.0.0.0 and then click FINISH
button at the bottom of this page to complete the modification of this
page.
Figure 3-10
5. Click Basic Config, select DHCP (as shown in Figure 3-11) and make
sure the DHCP client service is Disable. After that, click FINISH at the
bottom of this page to complete the modification of this page.
Figure 3-11
42
43

3.2.3 Configure the RB as Central Wireless Router with
dynamic IP address Ethernet
Configure TCP/IP parameters
1. Click Advanced Config, select Bridging, and then click Disable for
Bridge Function as shown in Figure 3-5. After that, click FINISH at the
bottom of this page to complete the modification of this page.
2. Click Basic Config, select Interface (as shown in Figure 3-8), in this
page, you can click radio button and enter MODIFY to choice which
interface that you want to change it (as shown in Figure 3-9).
In interface 1, Make sure this wireless interface status is Active, enter
the Wireless interface IP (default is 192.168.1.1) and Wireless
interface Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) that are suitable for your
wireless network.
In interface 2, Make sure this Ethernet interface status is Active, and
other parameters will obtain automatically by DHCP from your network
environment.
Click the OK button to return to the Interface Parameter window.
Finally, you need to click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete
the modification of this page.
Hint1: Make sure interface 3 and 4 within status Disable.
Hint2: In order to enable NAT service, choice the NAT(PAT) in the
interface Wireless and Ethernet. For example, make sure
Ethernet interface within NAT(PAT) On and Wireless interface
is NAT(PAT) Off, it means that every communication through
the Ethernet interface needs to do NAT transfer.
3. Click Basic Config, select DHCP (as shown in Figure 3-11) and apply
the DHCP client service running on interface 2 (Ethernet interface),
After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the
modification of this page.
3.2.4 Configure the RB as Central Wireless Router with
static IP address Ethernet
Configure TCP/IP parameters
1. Click Advanced Config, select Bridging, and then click Disable for
Bridge Function as shown in Figure 3-5. After that, click FINISH at the
bottom of this page to complete the modification of this page.
2. Click Basic Config, select DHCP (as shown in Figure 3-11) and make
sure the DHCP client service is Disable. After that, click FINISH at the
bottom of this page to complete the modification of this page.
3. Click Basic Config, select Interface (as shown in Figure 3-8), In this
page, you can click radio button and enter MODIFY to choice which
interface that you want to change it(as shown in Figure 3-9).
In interface 1, Make sure this wireless interface status is Active, enter
the Wireless interface IP (default is 192.168.1.1) and Wireless
interface Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) that are suitable for your
wireless network.
In interface 2, Make sure this Ethernet interface status is Active, and
specify the Ethernet IP address (default is 192.168.2.1) and Ethernet
Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) of the Ethernet interface.
Click the OK button to return to the Interface Parameter window.
Finally, you need to click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete
the modification of this page.
Hint1: Make sure interface 3 and 4 within status Disable.
Hint2: In order to enable NAT service, choice the NAT(PAT) in the
interface Wireless and Ethernet. For example, make sure
Ethernet interface within NAT(PAT) On and Wireless interface
is NAT(PAT) Off, it means that every communication through
the Ethernet interface needs to do NAT transfer.
4. Click Basic Config, and then select System as shown in Figure 3-10. In
the System Setup page, specify the Default Route (Default is
192.168.2.254) as the IP Address of the ADSL/Cable modem connected
to the AP or the IP Address of the Gateway in your LAN environment,
and Specify at least one IP address of the DNS parameter (Default
DNS server 1 is 192.168.2.254) provided by your ISP in the DNS
44
45

server parameter and then click FINISH button at the bottom of this page
to complete the modification of this page.
3.2.5 Configure the RB as Remote Wireless Router
The RB series can easy build out Point-to-Point, Point-to-Multipoint wireless
backbone infrastructure, you can configure your RB as the Remote Wireless
Router that connect to the Central RB.
1. Configure the operation role of this RB (as shown in Figure 3-12)
Click Quick Config, select Remote Wireless Router/Bridge to setup this
RB that play the Remote RB role and then click NEXT at the bottom of
this page to complete the modification of this page.
Figure 3-12
2. Configure the operation mode of this Remote RB (as shown in Figure 3-
13). Click Quick Config, select Remote Wireless Router to setup this
Remote RB that in the Routing mode and then click NEXT at the bottom
of this page to complete the modification of this page.
46
47
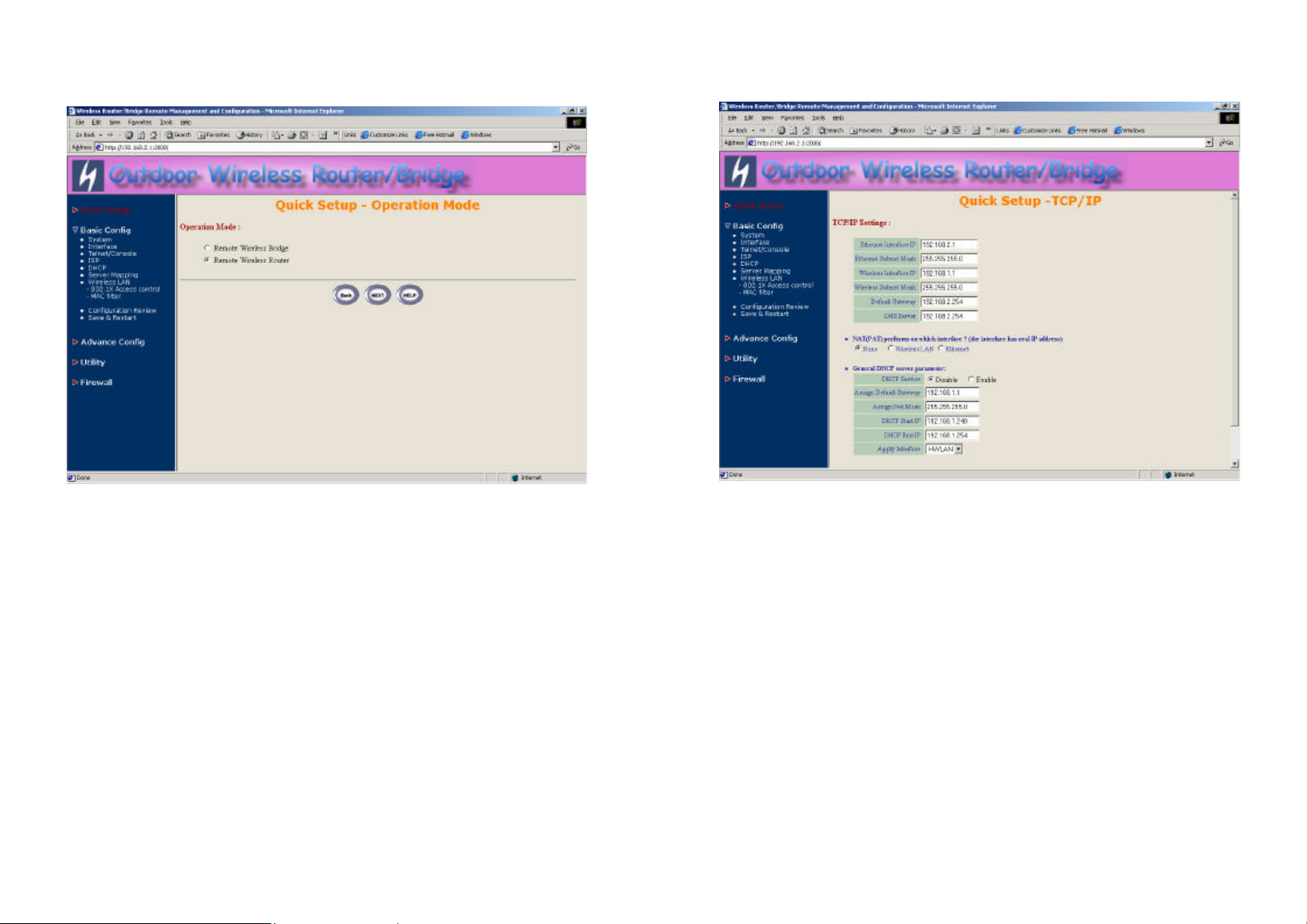
Figure 3-13
3. Configure TCP/IP parameters on Wireless (as shown in Figure 3-14)
In this page, enter the Wireless interface IP (default is 192.168.1.1)
and Wireless interface Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) that are
suitable for your wireless network, and specify the Default Gateway
(Default is 192.168.2.254) as the Wireless IP Address of the Central RB.
After that, specify the IP address of the DNS servers provided by your
ISP in the DNS server (Default is 192.168.2.254) parameter.
Hint: Designed your network infrastructure and assigned the
correct IP address for the Central RB and the Remote RB.
4. Configure TCP/IP parameters on Ethernet
Specify the Ethernet IP address (default is 192.168.2.1) and Ethernet
Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) of the Ethernet interface that is
suitable for your Ethernet network. At finally, click NEXT at the bottom of
this page to complete the modification of this page.
Figure 3-14
5. Configure Wireless parameters (as shown in Figure 3-15)
In this page, enter the Channel (default is 1), rts Threshold (default is
250), frag Threshold (default is 1600), SSID (default is wireless) and
Station Name (default is ap) that are suitable for your radio network and
then you can clicked radio button to disable WEP or enable 64/128 bit
WEP services (default is disable), if WEP is enabled, you must input
corresponded Default Key index and WEP Key. After that, click NEXT
at the bottom of this page to complete the modification of this page.
Hint: Make sure the SSID parameter is same with the configuration
of the Central RB.
48
49

Figure 3-15
6. Preview the configured setting of this RB (as shown in Figure 3-16)
This page will present the current settings of the RB to system
administrator, the operator can easy to view all running configuration in
here. After that, click Save button to store the changes to the RB.
Figure 3-16
7. Enable NAT
Sometimes, the operator may implement NAT on the network. In here,
you can click Basic Config, select Interface (as shown in Figure 3-9),
in this page, you can click radio button and enter MODIFY to choice
which interface that you want to change it (as shown in Figure 3-10).
In order to enable NAT service, choice the NAT(PAT) in the interface
Wireless and Ethernet. For example, make sure Ethernet interface within
NAT(PAT) Off and Wireless interface is NAT(PAT) On, it means that
every communication through the Wireless interface needs to do NAT
transfer.
50
51

3.2.6 Configure the RB as Remote Wireless Bridge
The RB series can easy build out Point-to-Point, Point-to-Multipoint wireless
backbone infrastructure, you can configure your RB as the Remote Wireless
Bridge that connect to the Central RB.
Configure the operation role of this RB (as shown in Figure 3-12)
1. Click Quick Config, select Remote Wireless Router/Bridge to setup
this RB that play the Remote RB role and then click NEXT at the bottom
of this page to complete the modification of this page.
2. Configure the operation mode of this Remote RB (as shown in Figure 3-
13). Click Quick Config, select Remote Wireless Bridge to setup this
Remote RB that in the Bridge mode and then click NEXT at the bottom of
this page to complete the modification of this page.
3. Configure TCP/IP parameters (as shown in Figure 3-14)
In this page, enter the Bridge interface IP (default is 192.168.2.1) and
Bridge interface Net Mask (default is 255.255.255.0) that are suitable
for your network, and then click NEXT at the bottom of this page to
complete the modification of this page.
4. Configure Wireless parameters (as shown in Figure 3-15)
In this page, enter the Channel (default is 1), rts Threshold (default is
250), frag Threshold (default is 1600), SSID (default is wireless) and
Station Name (default is ap) that are suitable for your radio network and
then you can clicked radio button to disable WEP or enable 64/128 bit
WEP services (default is disable), if WEP is enabled, you must input
corresponded Default Key index and WEP Key. After that, click NEXT
at the bottom of this page to complete the modification of this page.
Hint: Make sure the SSID parameter is same with the configuration
of the Central RB.
5. Preview the configured setting of this RB (as shown in Figure 3-16)
This page will present the current settings of the RB to system
administrator, the operator can easy to view all running configuration in
here. After that, click Save button to store the changes to the RB.
3.3 Configure Wireless related parameters
3.3.1 Configure IEEE 802.11b WLAN parameters
Click Basic Config, select Wireless LAN page (as shown in Figure 3-17).
In here, enter the Channel (default is 1), rts Threshold (default is 250), frag
Threshold (default is 1600), SSID (default is wireless) and Station Name
(default is ap) that are suitable for your radio network and then you can
clicked radio button to disable WEP or enable 64/128 bit WEP services
(default is disable), if WEP is enabled, you must input corresponded Default
Key index and WEP Key. After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page
to complete the modification of this page.
Figure 3-17
52
53

3.3.2 Security
3.3.2.1 WEP encryption
1. Click Basic Config, select Wireless LAN page, and configure it to
disable or enable 64/128 bit WEP services (default is Disable) as
shown in Figure 3-17.
2. Key-in the WEP Key and specify which WEP Key id you want to use it.
After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page to generate the real
WEP key complete the modification of this page.
Hint: If you enable WEP services on RB, all of the communication
between stations to RB will be encrypted. You must make sure all
wireless client and RB with the same WEP key.
3.3.2.2 Hide the SSID
This function is only workable on the Central RB.
Click Basic Config, select Wireless LAN page, and click Yes or No to
choose enable/disable the Hide SSID function on this wireless page (default
is No), as shown in Figure 3-17.
Hint: If you enable Hide SSID on CRB, all of the client stations or RRB
must to specify the SSID of this RB, otherwise your client stations or
RRB can’t see (survey) this RB if using any Site Survey tools.
3.3.3 IEEE 802.1x Access Control
You can configure Authenticator on RB:
1. Click Basic Config, select 802.1x Access Control page, and choice
the IEEE 802.1x services is Enable or Disable (as shown in Figure 3-
18).
2. The RB supporting authentication which based on two kinds of user
information base, Local User Database or Remote Radius Servers.
You can specify which user database you want to use.
3. You can specify the username/password of an accessible 802.1x user.
All user information entries in the Local User Database are permitted to
connect to the RB. You can also click ADD, DELETE, MODIFY button
to maintain this User Information table.
4. Some Radius server implements EAP authentication, like Microsoft
Windows 2000 server or Cisco ACS. To set up the Radius server and
RB for authentication, you must specify the Radius server IP address,
Share key between RB and Radius server, authentication port and
accounting port on this Radius server.
5. Click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the modification of
this page.
3.3.2.3 Deny ‘ANY’ client station
This function is only workable on the Central RB.
Click Basic Config, select Wireless LAN page, and click Yes or No to
choose enable/disable the Deny ‘ANY’ function on this wireless page
(default is No), as shown in Figure 3-17.
Hint: If you enable Deny ANY on CRB, all of the client stations or RRB
can’t use the well define SSID keyword ‘ANY’ or ‘any’.
54
55
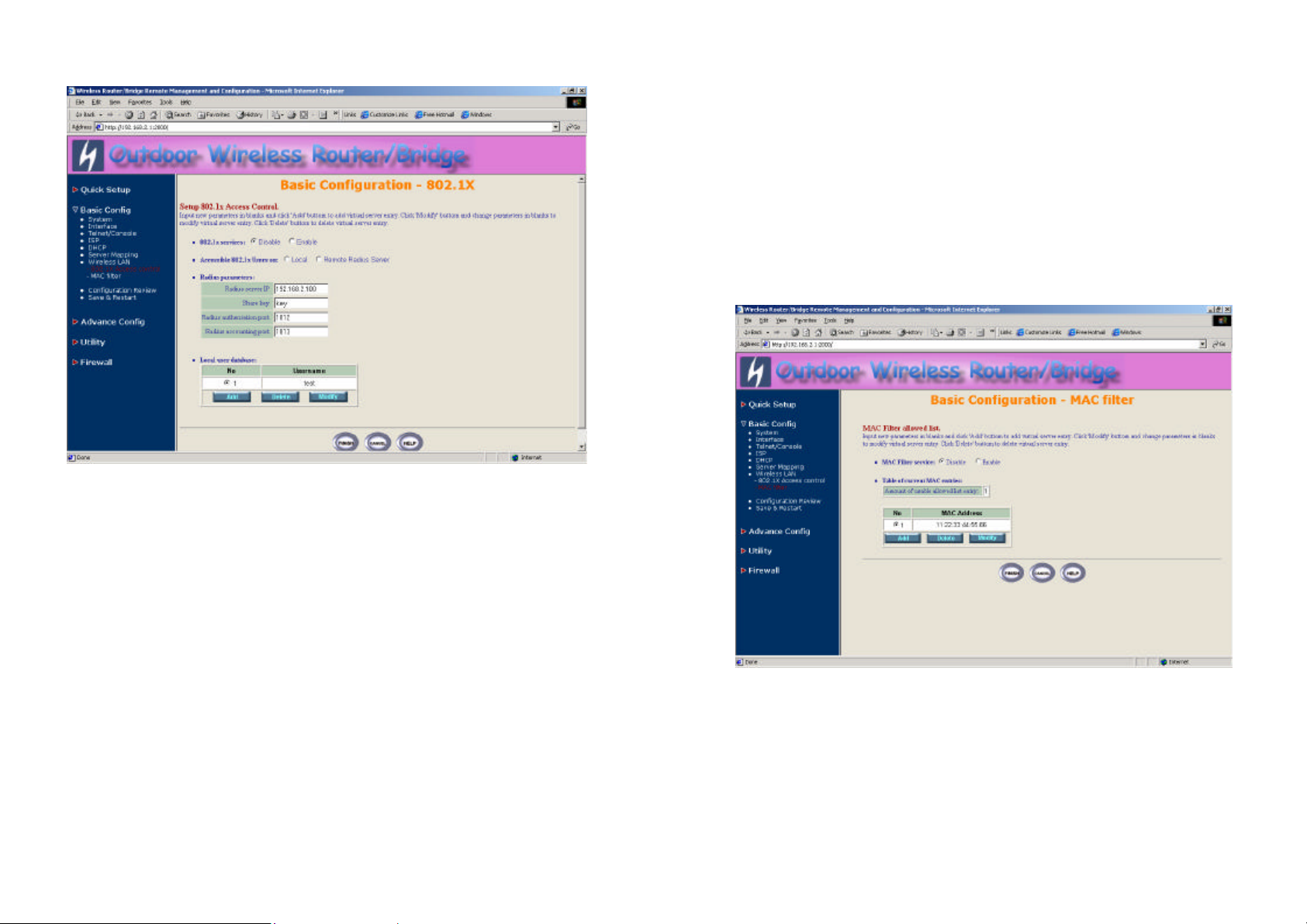
Figure 3-18
3.3.4 MAC based Access Control
1. Click Basic Config, select MAC Filter page, and choice the MAC Filter
services is Enable or Disable (as shown in Figure 3-19).
2. You can specify the MAC address of a wireless client station. All MAC
entries in the MAC address table are permitted to connect to the RB.
You can also click ADD, DELETE, MODIFY button to maintain this MAC
address table. After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page to
complete the modification of this page.
Figure 3-19
56
57

3.4 Configure DHCP server
Sometimes, the operator want to managing a large TCP/IP network requires
maintaining accurate and up-to-date IP address and domain name
information. In this situation, it needs manually configure and enable the
DHCP server service.
1. Click Basic Config, select DHCP (as shown in Figure 3-11) and Enable
the DHCP server service (Default is Disable).
2. Specify the DHCP server parameters (Assign Gateway, Assign
Subnet Mask, Assign DNS server, DHCP Start IP address, DHCP
End IP address and Apply Interface) to allow any DHCP client to
acquire the IP information.
Assign Gateway: Configure the default router for the client.
Assign Subnet Mask: Configure the subnet for the client.
Assign DNS Server: Configure the DNS servers IP for the client.
DHCP Start IP address, DHCP End IP address: Configure the DHCP
IP address pool for the client.
Apply Interface: Enable DHCP server service on Wireless or Ethernet
interface.
3. After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the
modification of this page.
Hint: The operator must to configure correct network settings in
Gateway and DNS server of your wireless stations / Remote RBs /
Ethernet clients to surf the Internet.
3.5 Configure Virtual Server
Sometimes, the operator can expose the internal servers on the local intranet
to the public Internet. For this, you must create the Virtual Server Mapping
for these invisible internal servers.
1. Click Basic Config, select Server Mapping (as shown in Figure 3-20)
and click ADD, DELETE or MODIFY button to change to configure
Virtual Server Mapping page (as shown in Figure 3-21). In this page,
you can maintain this Virtual Server Mapping pool (Default Virtual
Server Mapping pool is empty) to enable the internal servers.
2. In configure Virtual Server Mapping page, you must specify some
parameters (Service Name, Protocol, Public Access Interface, Public
Access Port number, Virtual Server IP address and Virtual Server
Port Number) to allow Internet user to access the Internal servers.
Service Name: Alias name of this internal server, such as FTP.
Access Interface: Indicate the translation occurs on which interface
(Wireless interface, NO. 1/Ethernet interface, NO. 2), such as NO. 2.
Protocol: Indicate which protocol (TCP/UDP) you want to translate from
outside to internal server, such as TCP.
Public Access Port number: Indicate which socket port (1 ~ 65535)
you want to translate from outside to internal server, such as 21.
Virtual Server IP address: Specify the private IP address of the internal
server, such as 192.168.1.100.
Virtual Server Port number: Specify the socket port (1 ~ 65535) of the
internal server, such as 21.
3. After that, click FINISH at the bottom of PAT page to complete the
modification for the Virtual Server Mapping.
58
59

Figure 3-20
Figure 3-21
3.6 Advanced Configuration
3.6.1 Configure Routing Table
1. Click Advence Config and select the Static Route page. This page (as
shown in Figure 3-22) will present the current configuration for the
routing table. You can also click ADD, DELETE or MODIFY button to
maintain the Static Routing table (Default Routing table only contain
single routing entry: Default Route entry).
2. Every Route entry contains three parameters: Network Address,
Subnet Mask and Gateway.
Network Address and Subnet Mask: Specify the destination network.
Gateway: Indicate the forward gateway.
3. After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the
modification of this page.
Hint: The operator must to configure correct routing settings following
the network infrastructure.
60
61

Figure 3-22
3.6.2 Configure Bridge
1. Click Advence Config and select the Bridging, and then click Enable
for Bridge Function as shown in Figure 3-5. In the Bridging Parameter
window, enter the IP Address (default is 192.168.2.1) and Subnet Mask
(default is 255.255.255.0) that are suitable for your network domain.
2. You can specify the MAC address of a Wireless/Ethernet client. All MAC
entries in the MAC address table are Permitted/Blocked/Learning to
connect to the RB. In here, you can also click ADD, DELETE, MODIFY
button to maintain this MAC address table.
3. After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the
modification of this page.
62
63

3.6.3 Configure SNMP
1. Click Advence Config and select the SNMP Community page. This
page (as shown in Figure 3-23) will present the current accessible snmp
communities and correspond Read/Write privilege. After that, click
FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the modification of this
page.
Figure 3-23
2. Click Advence Config and select the SNMP Trap page (as shown in
Figure 3-24). In this page, you can specify the SNMP Trap host and
correspond SNMP Trap Community in this page. After that, click
FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the modification of this
page.
Figure 3-24
64
65
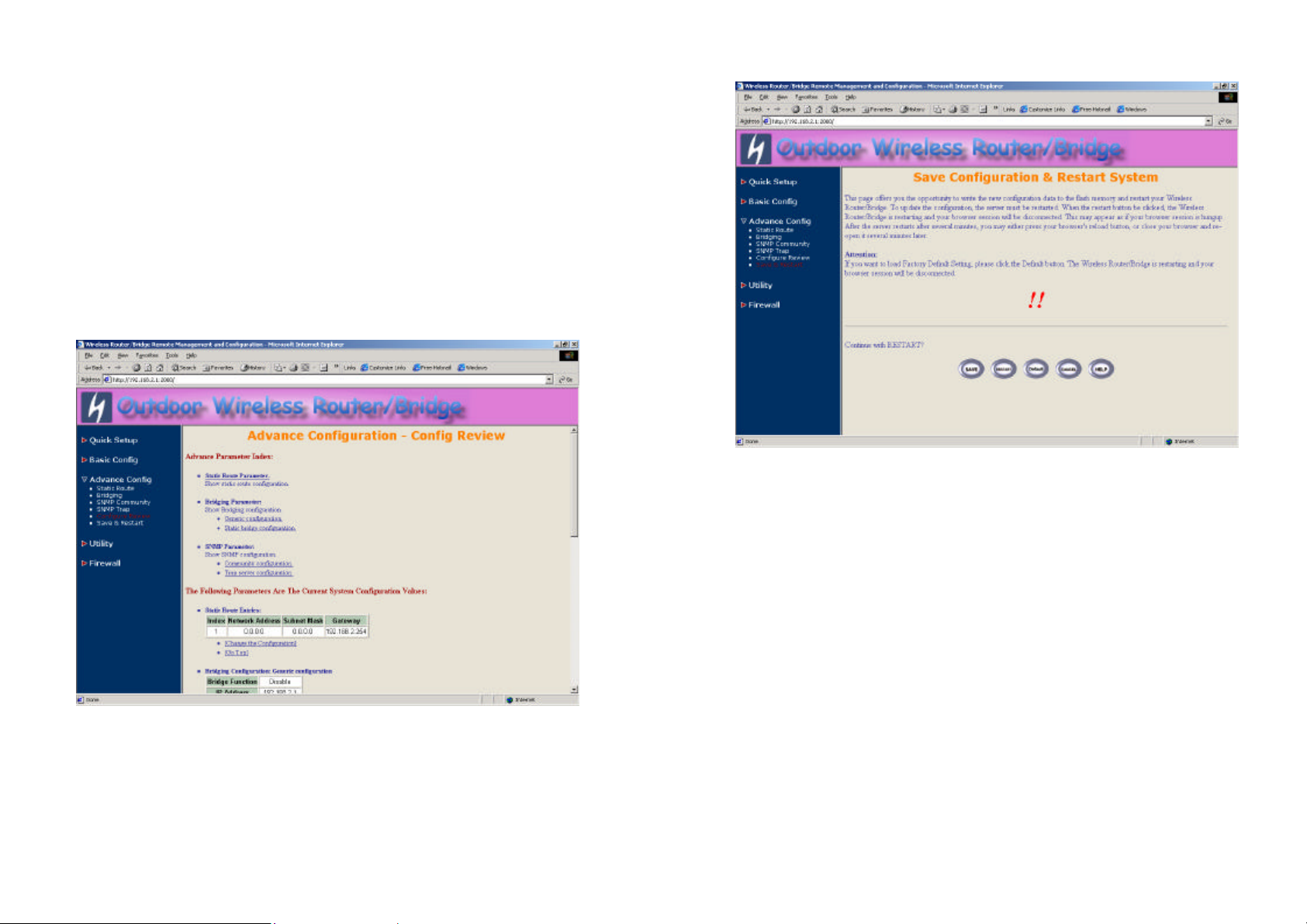
3.6.4 Configuration Review and Apply the New Settings
1. Click Basic Config or Advence Config and select the Configuration
Review page. This page (as shown in Figure 3-25) will present the
current configuration settings the operator has made.
2. Click Basic Config or Advence Config and select the Save & Restart
page. In this page (as shown in Figure 3-26), you can click the SAVE
button to apply the new configuration settings and click the Restart
button to take effect the previous configuration changes.
Hint: It needs to take about 10 seconds for the RB to complete the
restart process.
Figure 3-25
Figure 3-26
66
67
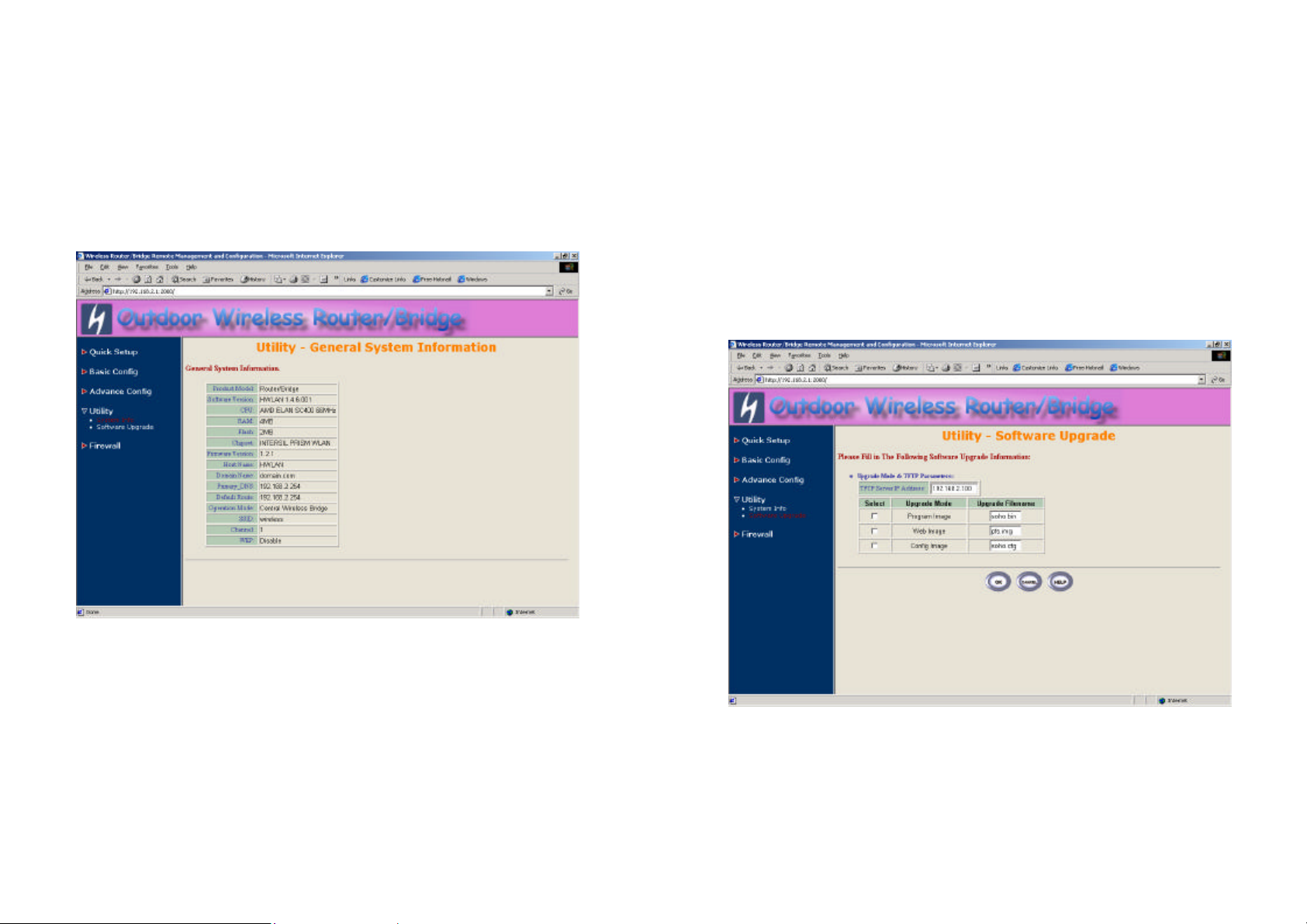
3.7 Utility
3.7.1 System Info
Click Utility, select System Info page (as shown in Figure 3-27), you can
view some system information on this, such as Model Name, Software
Version, CPU and RAM, …etc.
Figure 3-27
3.7.2 Software Upgrade
1. Click Utility, select Software Upgrade page (as shown in Figure 3-28),
and then you can use TFTP to upgrade your RB. In here, you must
specify the TFTP server IP and select which file you want to upgrade it
(Program image, Web image and Config file), then click OK button to
start the TFTP upgrade process.
2. If the upgrade process is success, the RB will apply the new settings and
start rebooting right away.
Hint: You must set up a TFTP server and this server must contain one
newest image.
Figure 3-28
68
69

3.7.3 Wireless Link Info
1. Click Utility, select Wireless Link Info page (as shown in Figure 3-29),
and then you can view the Link Quality and the Signal Strength of this
wireless connection.
2. The Link Quality and the Signal Strength are valid only in the role of
Remote RB. In here, you can also see the quality level for this wireless
connection.
Figure 3-29
Chapter 4. Telnet configuration
The RB is designed to operate as shipped from the factory without any special setup. However, it has many options and parameters that can be changed if users
have special requirements. Most of the management functions can be accessed
using TCP/IP protocol, it also configured by Telnet/Console.
The user can use a LAN attached (wired or wireless) computer to
configure the RB through using a Telnet session on a LAN attached
computer. To use the Telnet session simply open a Telnet window
using the IP address which has been assigned to the RB.
1. Click Start button, select Run to open the Run dialog box. Enter telnet
192.168.2. 1(default terminal type of Telnet is VT100, default IP address
of the RB is 192.168.2.1). Then click OK as shown in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1.
2. In the Telnet window, enter the User Name and User Password as
shown in Figure 4-2 (default User Name and User Password is user1
and test) to see the main screen of Telnet user interface as shown in
Figure 4-3.
70
71

Figure 4-2
3. The structure of menu tree is shown in Figure 4-4. Users can use the
following keys to select the parameter you want to change or add. The
definition of the parameters is described in Table 4-1 to Table 4-14.
l Up/Down or i/k key: move the cursor up/down to the specific
item.
l Right or l or Enter key: select the item or enter to sub-menu.
l Left or j key: return to previous menu page.
l Home or Ctrl-A: move the cursor to the first item of the menu
page.
l End or Ctrl-E: move the cursor to the last item of the menu page.
l Ctrl-Q or F1: Show the help page.
Hint 1 : * denote the function is displayed after enable configuration
mode is enabled.
Hint 2 : In item su, type default password root to enter the supervisor
configuration mode.
Figure 4-3
72
73

Su
Attrib <Enable | Disable> <Global | Virtual>
ISP <ISP Index> <idle disconnect time> <Dial priority>
image
bootstrap 2
Wan
Config_access [Generic| Profile | Pool]
Passwd <
Setup
System
Ian
Address <ip> <netmask>
Bridge <Enable | Disable>
Wan
Address <ip> <netmask>
link - Type <Disable | Ethernet | PPP >
Attrib <
Enable | Disable> <Global | Virtual>
ether_interface <interface>
Bridge <Enable | Disable>
| PPPoE
PPP
Peer_address <ip>
User_profile <name> <pass_set0>
ISP
*ISP_ profile <ISP name> <ISP destination>
*account - profile <Access account> <Passwd>
Configuration
<name> <pass_conf> <ip>
Upgrade
*Enable
Monitor
<ip> <file>
webimage
(CR)
<ip> <file>
<ip> <file>
*System
pass_conf>
OP _ mode <Router | Bridge | Host>
hostname <name>
default _ route <ip>
Figure 4-4
74
75

*Interface
address <ip> <netmask>
link type <Disable | Ethernet>
attrib <Disable | Enable> <Global | Virtual>
attrib <Disable | Enable> <Global | Virtual>
link type <Disable | Ethernet | PPP | PPPoE>
attrib <Disable | Enable> <Global | Virtual>
ISP <ISP Index> <dialup timeout> <Dial priority>
ISP <ISP Index> <Idle disconnect time> <Dial priority>
*PPP
modify (5)
Figure 4-4
lan
1
bridge <Disable | Enable>
2
address <ip> <netmask>
link type <Disable | Ethernet>
wan
bridge <Disable | Enable>
1
address <ip> <netmask>
bridge <Disable | Enable>
ether_interface <interface>
2
address <ip> <netmask>
link type <Disable | Ethernet | PPP | PPPoE>
attrib <Disable | Enable> <Global | Virtual>
bridge <Disable | Enable>
ether_interface <interface>
User_edit
profile <name> <pass_set0>
delete
address_pool
authenticate
assign_address
ip_pool <ip> <1~127>
<Userpool | RADIUS> <Userpool | RADIUS>
<Address_Pool | RADIUS> <Address_Pool | RADIUS>
76
77

<TCPIUDP>
port <1~65534>
interface <1~2>
protocol <TCPIUDP>
range <1~5> <ip> <1~253>
global
range <1~5> <ip> <1~253>
modify <1~128> <ip> <ip>
isp - profile (ISP name) (destination string)
isp - profile (ISP name) (destination string)
isp - profile (ISP name) (destination string)
isp - profile (ISP name) (destination string)
*ISP
1
2
3
4
*IP _ share
pat
nat
account - profile (name) (pass - set 1)
account - profile (name) (pass - set 1)
account - profile (name) (pass - set 1)
account - profile (name) (pass - set 1)
add
protocol
server <ip> <1~65534>
name <name>
dalete
<1~10>
modify (10)
port <1~65534>
interface <1~2>
server <ip> <1~65534>
name <name>
local
delete <1~5>
interface <1~5> <1~5>
delete <1~5>
fixed
interface <1~128> <1~5>
delete <1~128>
Figure 4-4
78
79

service <Disable | Enable>
edit <Disable | Enable> <string> <Read_Only | Read_Write | Denied>
generic
static
*dhcp
*snmp
*tftp
<ip> <file>
*bridge
generic
interface <1~2>
gateway <ip>
netmask <netmask>
ip range <ip> <number>
name server 1 <ip>
name server 2 <ip>
name server 3 <ip>
fixed
add <mac> <ip>
delete
community (5)
delete
trap (5)
edit <Disble | 1 | 2> <ip> <string>
delete
<Disable | Enable> <ip> <netmask>
add
mac _ address <mac>
lan1_ port <Filter | Forward | Dynamic>
lan2 _ port <Filter | Forward | Dynamic>
wan 1 _ port <Filter | Forward | Dynamic>
wan 2 _ port <Filter | Forward | Dynamic>
delete (1~20)
Figure 4-4
80
81

lan2 _ port <Filter | Forward | Dynamic>
lan _ port <1~2> <Disable | Enable> <number>
channel <1~14>
modify (20)
mac _ address <mac>
lan1_ port <Filter | Forward | Dynamic>
wan 1 _ port <Filter | Forward | Dynamic>
wan 2 _ port <Filter | Forward | Dynamic>
stp
module <Disable | Enable>
bridge <number>
wan _ port <1~2> <Disable | Enable> <number>
activate _ stp
<CR>
WLAN
weprequired <Disable | Enable>
rts Threshold <0~3000>
frag Threshold <256^2346>
SSID <string>
station Name <string>
defaultkeyId <1~4>
defaultkeys <1~4> <hex>
Figure 4-4
82
83

ip _ share
*reset - default
reboot
su
sys info
exit
profile <name> <pass _ conf> <Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Unlimited>
modify <1~10> <ip>
profile <name> <pass _ conf> <Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Unlimited>
48 VDC/0.7A (power over
configuration
max _ user <1~5>
telnet_port <1~65534>
console _ port <com 1 | com 2 >
user _ profile
add
attrib <13~30><command | Menu><VT100 | ANSI | LINUX | XTerm>
source <-1~10>
profile <name> <pass _ conf> <Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Unlimited>
delete (1~5)
attrib <13~30><command | Menu><VT100 | ANSI | LINUX | XTerm>
source <-1~10>
modify
attrib <13~30><command | Menu><VT100 | ANSI | LINUX | XTerm>
source <-1~10>
legal - address
delete <1~10>
*Show: Show the current configuration values
interface
PPP
dhcp
snmp
bridge
isp
run
write
Ping <ip> [1~65534| - t] [1~1999]
Figure 4-4
Chapter 5. Specifications
General
Compatibility Fully interoperable with IEEE802.11b
compliant products
Regulation Certifications FCC Part 15, ETSI 300/328
Output: –
Power Supply
Temperature Range -20 to 70 ℃ (operating)
Humidity (non-condensing) 5% to 95% typical
Surge Arrester
Radio
Frequency Band 2.4 – 2.484 GHz
Radio Type Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
Modulation CCK (11, 5.5Mbps)
Operation Channels 11 for North America, 14 for Japan,
RF Output Power (without
ANT)
RF Connector Proprietary N-type (Reverse Polarity)
Network Information
Ethernet Interface 10-Base T (RJ45)
IP Sharing Supports NAT
Roaming Seamless roaming (IEEE802.11b
Security 64/128-bit WEP data encryption
Management
Local Configuration RS-232 serial port
Remote Configuration HTTP, Telnet, SNMP
Firmware Upgrade Upgrade via Serial Interface or TFTP
IP Auto-configuration Supports DHCP server
Physical Specifications
Dimensions 245(L) mm x 200(W) mm x 70(H) mm
Weight 2100 g
Ethernet)
Input: 100/240 VAC; 50/60 Hz
-40 to 80 ℃ (storage)
20KA Surge Current
(DSSS)
DQPSK (2Mbps)
DBPSK (1Mbps)
13 for Europe, 2 for Spain, 4 for France
28dBm typically
compliant)
84
85
No.3 is effective
Chapter 6. Default Settings
6.1 Basic Configuration
6.1.1 System
Parameter Description Default Value
Supervisor ID Supervisor’s identity code root
Supervisor Password Supervisor’s password root
Password Confirm Confirm the password again root
Host Name Host name for the AP HWLAN
Domain Name Domain name for the AP domain.com
Default Route IP
Address
DNS Server Parameter
DNS Server 1 Address
DNS Server 2 Address
DNS Server 3 Address
6.1.2 Interface
Parameter Description Default Value
Interface No.
IP address of the gateway for
default route when TCP/IP
filtering
IP addresses of the DNS Servers
of your Local ISP
No.1 Wireless Interface
No.2 Ethernet Interface
No.3 PPPoE Interface
No.4 PPP Interface
192.168.2.254
192.168.2.254
Note:
1.
only when No.2 is
Active.
2. Default No.3 &
No. 4 is Disable
Status
IP address
Net Mask
NAT(PAT)
Bridging
ISP Index
IPCP
Idle Time Out (min)
Dial Priority
Dial-in
Enable or disable the
Corresponding interface
IP address of the corresponding
interface. The user can use a
LAN attached (wired or wireless)
computer to configure the AP
through using a web browser
or telnet program on a LAN
attached computer.
Consists of four sets of digits
that help divide a network into
sub-networks and simplify
routing and data transmission
Select the network type for NAT
function.
OFF <-> ON: NAT enable
ON <-> ON: NAT disable
OFF <-> OFF: NAT disable
Shows the corresponding
interface that joins to form a
bridge
Select the ISP index given in
the ISP pool
Select IP Control Protocol
(Static or dynamic) for
PPP/PPPoE interface
Cancel the dial if not connected
within this period
Set the dial-up priority of the
corresponding interface
Enable or disable the dial-in
function of the corresponding
interface
Active
No.1: 192.168.1.1
No.2: 192.168.2.1
No.3: 192.168.3.1
No.4: 192.168.4.1
No.1:255.255.255.0
No.2:255.255.255.0
No.3:255.255.255.0
No.4:255.255.255.0
No.1: OFF
No.2: OFF
No.3: ON
No.4: OFF
No.1: Not Join
No.2: Not Join
No.3: Not Join
No.4: Not Join
ISP1
Dynamic
3min
PPPoE: 3
PPP: 2
Disable
86
87

Selects the authentication protocol
Dial-in Authentication
for the corresponding dial-in
interface
6.1.3 Telnet/Console
Parameter Description
Set the maximum number of the
Maximum User
Telnet Port
Console Port
ID Number Index for Telnet users
User Name User name for Telnet session
Privilege
Max. Screen Line
Show Mode
Keyboard Type
users that can login the AP
through Telnet session at the
same time
The port number for Telnet
Program
The communication port that is
used to login the AP
Select the user’s privilege level
for Telnet session
Set the maximum number of
lines displayed on the screen
Select the type of display for
Telnet session
(Command/Menu mode)
Select the type of the keyboard
for Telnet session
6.1.4 ISP
Parameter Description
ISP Name
Name of Internet Service
Provider
None
Default Value
2
23
COM1
1
user1
Unlimited
24
Menu
VT100
Default Value
ISP-1
The phone number that is used
Phone Number
Username The user name used to login ISP
Password The password used to login ISP pass
to dial up your ISP
Note: The phone number must
enter direct line phone number
12345678
user
6.1.5 DHCP
Parameter Description
Enable or disable the specified
DHCP Client Setting
Trigger DHCP Service
Default Gateway
Net Mask
Name Server IP address of the DNS host 192.168.2.254
DHCP Start IP IP starting address 192.168.1.240
DHCP End IP IP ending address 192.168.1.254
Interface
Fixed Host Entry
interface to obtain an IP address
automatically
Enable or disable automatic IP
address assignment to wireless
stations
IP address of the gateway for
default route when TCP/IP
filtering
Consists of four sets of digits
that help divide a network into
sub-networks and simplify
routing and data transmission
Select the interface to provide
DHCP service
Define a fixed Ethernet-to-IP
address mapping to limit the
client station with the Ethernet
address to get the IP address
Default Value
Disable
Disable
192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0
HWLAN
88
89
6.1.6 Virtual Server Mapping
Parameter Description
Service Name
Protocol Select a protocol for public access
Public Access – Interface
Public Access – Port
Number
Virtual Server – IP
Address
Virtual Server – Port
Number
Specify the service for public
access
Select an interface for public
access
Specify the port number of the
interface for public access
Specify the IP address of the
virtual server
Specify the port number of internal
virtual server
Default Value
NULL
NULL
NULL
NULL
NULL
NULL
6.1.7 NAT (Network Address Translation)
Parameter Description
Default Value
Local IP Address Pool –
Base IP Address
Local IP Address Pool –
Count
Global IP Address Pool –
Base IP Address
Global IP Address Pool –
Count
Global IP Address Pool –
Interface
Fixed IP Address
Mapping – Local/Global
IP Address
Fixed IP Address
Mapping – Interface
90
IP starting address of local IP
address
Number of local IP address NULL
IP starting address of global IP
address
Number of global IP address NULL
Specify the interface as global IP
address
Define a local and global IP
address pair for network address
translation
Specify the interface for network
address translation
NULL
NULL
NULL
NULL
NULL
91

Define the regulatory domain to
6.1.8 Wireless LAN
Parameter Description
Regulatory Domain
Channel
RTS Threshold
Fragmentation
Threshold
SSID
Station Name Shows the name of the AP ap
WEP
Default Key
Key Panel
which this NIC may be deployed
The operating radio frequency
channel for the AP
Set RTS (Request To Send)
threshold value
Set fragmentation threshold
value
Wireless LAN service area
identifier of the AP (case sensitive)
Enable or disable 64-bit WEP
(Wired Equivalent Privacy) key to
encrypt data
Select a WEP key to encrypt
each frame transmitted from the
radio using one the of the Keys
from the Key Panel
When you use WEP to
communicate with the other
wireless clients, all the wireless
devices in this network must have
the same encryption key or pass
phrase.
Note: each key must consist of
hex digits, it means that only
digit 0 -9 and letters A-F are
valid entries. If entered
incorrectly, program will not
write keys to a driver.
Default Value
11
250
1600
wireless
Disable
6.2 Advance Configuration
6.2.1 Bridging
1
1
Parameter Description
Bridging Function
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Operation mode
MAC Address
Interface
Enable or disable bridging
Function
IP Address of the AP when in
Bridging mode. The user can
use a LAN attached (wired or
wireless) computer to configure
the AP through using a web
browser or telnet program on a
LAN attached computer.
Consists of four sets of digits
that help divide a network into
sub-networks and simplify
routing and data transmission
Enable or disable the operation
mode
MAC address to be considered
in forward/filter policy
Select Filter(always block the
frames), Forward(always
forward the frames) or
Dynamic(forward the frames if
the MAC address exists) to the
corresponding interface
Default Value
Enable
192.168.2.1
255.255.255.0
Enable
Enable
Disable
Disable
00-00-00-00-00-00
1. Filter
2. Filter
3. ---
4. ---
92
93
6.2.2 SNMP Community
Parameter Description Default Value
Enable or disable the function of
Validity
Access Right
Community
the corresponding community
index
Select the access right
(Deny/Read/Write/Create) for
SNMP Manager
Specify the type of community
(public or private) for SNMP
Manager
6.2.3 SNMP Trap
Parameter Description Default Value
Index
Version
IP Address
Community
Enable or disable the activity of
the corresponding community
Select or disable the SNMP
Version
Version 1: MIB1
Version 2: MIB2
Specify the IP address of the
SNMP Manager for SNMP Trap
Report
Specify the type of community
(public or private) for SNMP
Manager
Enable
Version1
192.168.2.100
Public
Enable
Read
Public
6.3 Utility
6.3.1 Software Upgrade
Parameter Description
TFTP Server IP
Address
Upgrade Filename
Specify the IP address of the
TFTP server to upgrade the
firmware of the AP
Specify the filename of
requested firmware
stored in TFTP server
Default Value
192.168.2.100
Soho.bin
94
95

Chapter 7. Regulatory Compliance Information
Radio Frequency Interference Requirements
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC Rules and Canada RSS-210.
Operation is subject to the following conditions:
This device may not cause harmful interference.
This device must accept any interference received, including interference
that may cause undesired operation.
Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated
with minimum distance 20 cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna of transmitter.
Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules and Regulation.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to
nearby TV’s, VCR’s, radio, computers, or other electronic devices. To
minimize or prevent such interference, this equipment should not be placed
or operated near these devices. If interference is experienced, moving the
equipment away from them will often reduce or eliminate the interference.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If the equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
Re-orient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that which the
receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
96
Information to User
The user manual or instruction manual for an intentional or unintentional
radiator shall caution the user that changes or modifications not expressly
approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s
authority to operate the equipment.
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in
a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of
the following measures:
甲、 Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
乙、 Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
丙、 Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
丁、 Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to
the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate
this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE: FCC Radiation Exposure Statement: This equipment
complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum
distance 20cm between the radiator & your body. This transmitter must not
be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
97

98
 Loading...
Loading...