Page 1

Version:
0.9
Wireless Mini-PCI Card
User’s Manual
Page 2

Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for
a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of
the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by
the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to
operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated
with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter.
Page 3

This device is intended only for OEM integrators under the following
conditions:
1) The antenna must be installed such that 20 cm is maintained between the
antenna and users, and
2) The transmitter module may not be co-located with any other transmitter
or antenna.
As long as 2 conditions above are met, further transmitter test will not be
required. However, the OEM integrator is still responsible for testing their
end-product for any additional compliance requirements required with this
module installed (for example, digital device emissions, PC peripheral
requirements, etc.).
IMPORTANT NOTE: In the event that these conditions can not be met (for
example certain laptop configurations or co-location with another transmitter),
then the FCC authorization is no longer considered valid and the FCC ID can
not be used on the final product. In these circumstances, the OEM integrator
will be responsible for re-evaluating the end product (including the transmitter)
and obtaining a separate FCC authorization.
End Product Labeling
This transmitter module is authorized only for use in device where the
antenna may be installed such that 20 cm may be maintained between the
antenna and users (for example: AP, Notebook…etc.). The final end product
must be labeled in a visible area with the following: “Contains TX FCC ID:
QA5-MPI-04001”.
Manual Information That Must be Included
The OEM integrator has to be aware not to provide information to the end
user regarding how to install or remove this RF module in the users manual of
the end product which integrate this module.
The users manual for OEM integrators must include the following information
in a prominent location “ IMPORTANT NOTE: To comply with FCC RF
exposure compliance requirements, the antenna used for this transmitter
must be installed to provide a separation distance of at least 20 cm from all
persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
Page 4

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
Table of Contents
1 INTRODUCTION..........................................................................................................................3
1.1 FEATURES & BENEFITS..........................................................................................................3
1.2 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS .......................................................................................................3
1.3 APPLICATIONS........................................................................................................................3
1.4 NETWORK CONFIGURATION...................................................................................................4
2 INSTALL DRIVERS & CLIENT UTILITY ...................................................................................6
2.1 BEFORE YOU BEGIN ..............................................................................................................6
2.2 INSTALLING THE PC CARD DRIVERS ......................................................................................6
2.3 VERIFY THE INSTALLATION .....................................................................................................9
2.4 DISABLE WINDOWS SSID/WEP CONFIGURATION................................................................10
3 USING THE CLIENT UTILITY ..................................................................................................12
3.1 WIRELESS RADIO ON/OFF ...................................................................................................12
3.2 REMOVE STATUS ICON ........................................................................................................12
3.3 WIRELESS NETWORK STATUS..............................................................................................13
3.3.1 Status........................................................................................................................13
3.3.2 Configuration............................................................................................................14
3.3.3 Encryption.................................................................................................................15
3.3.4 Site Survey................................................................................................................15
3.3.5 IBSS..........................................................................................................................16
3.3.6 Rates.........................................................................................................................17
3.3.7 Domain......................................................................................................................18
3.3.8 About.........................................................................................................................19
4 CONFIGURE WPA.....................................................................................................................20
5 UNINSTALL THE CLIENT UTILITY.........................................................................................23
APPENDIX A – TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................................................24
APPENDIX B – SPECIFICATIONS...................................................................................................25
APPENDIX C – REGULATORY COMPLIANCE INFORMATION..................................................26
Page 2 of 26
Page 5

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
1 Introduction
This chapter describes the features & benefits, package contents, system
requirements, applications, and network configuration.
1.1 Features & Benefits
Feature Benefit
Up to 54Mbps high-speed data
rates
Up to 152-bit WEP Data
Encryption with TKIP
IEEE802.1x Client support
(Optional)
Multi-country Roaming
(802.11d) support
Advanced Power Management
1.2 System Requirements
The following are the minimum system requirements in order to use the Mini-PCI
card.
Desktop PC containing a 32-bit PCI slot.
Windows 98/ME/ /2000/XP operating system.
300 MHz or higher processor.
1.3 Applications
The wireless LAN products are easy to install and highly efficient. The following
list describes some of the many applications made possible through the power
and flexibility of wireless LANs:
a) Difficult-to-wire environments
There are many situations where wires cannot be laid easily. Historic
buildings, older buildings, open areas and across busy streets make the
installation of LANs either impossible or very expensive.
b) Temporary workgroups
Consider situations in parks, athletic arenas, exhibition centers, disasterrecovery, temporary offices and construction sites where one wants a
temporary WLAN established and removed.
c) The ability to access real-time information
Capable of handling heavy data payloads
such as MPEG video streaming.
Powerful data security.
Enhances authentication and security.
Automatically adjusts regulatory domain to
operate in different countries.
Low power consumption in power saving
mode.
Page 3 of 26
Page 6

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
Doctors/nurses, point-of-sale employees, and warehouse workers can
access real-time information while dealing with patients, serving
customers and processing information.
d) Frequently changed environments
Show rooms, meeting rooms, retail stores, and manufacturing sites where
frequently rearrange the workplace.
e) Small Office and Home Office (SOHO) networks
SOHO users need a cost-effective, easy and quick installation of a small
network.
f) Wireless extensions to Ethernet networks
Network managers in dynamic environments can minimize the overhead
caused by moves, extensions to networks, and other changes with
wireless LANs.
g) Wired LAN backup
Network managers implement wireless LANs to provide backup for
mission-critical applications running on wired networks.
h) Training/Educational facilities
Training sites at corporations and students at universities use wireless
connectivity to ease access to information, information exchanges, and
learning.
1.4 Network Configuration
To better understand how the wireless LAN products work together to create a
wireless network, it might be helpful to depict a few of the possible wireless LAN
PC card network configurations. The wireless LAN products can be configured as:
a) Ad-hoc (or peer-to-peer) for departmental or SOHO LANs.
b) Infrastructure for enterprise LANs.
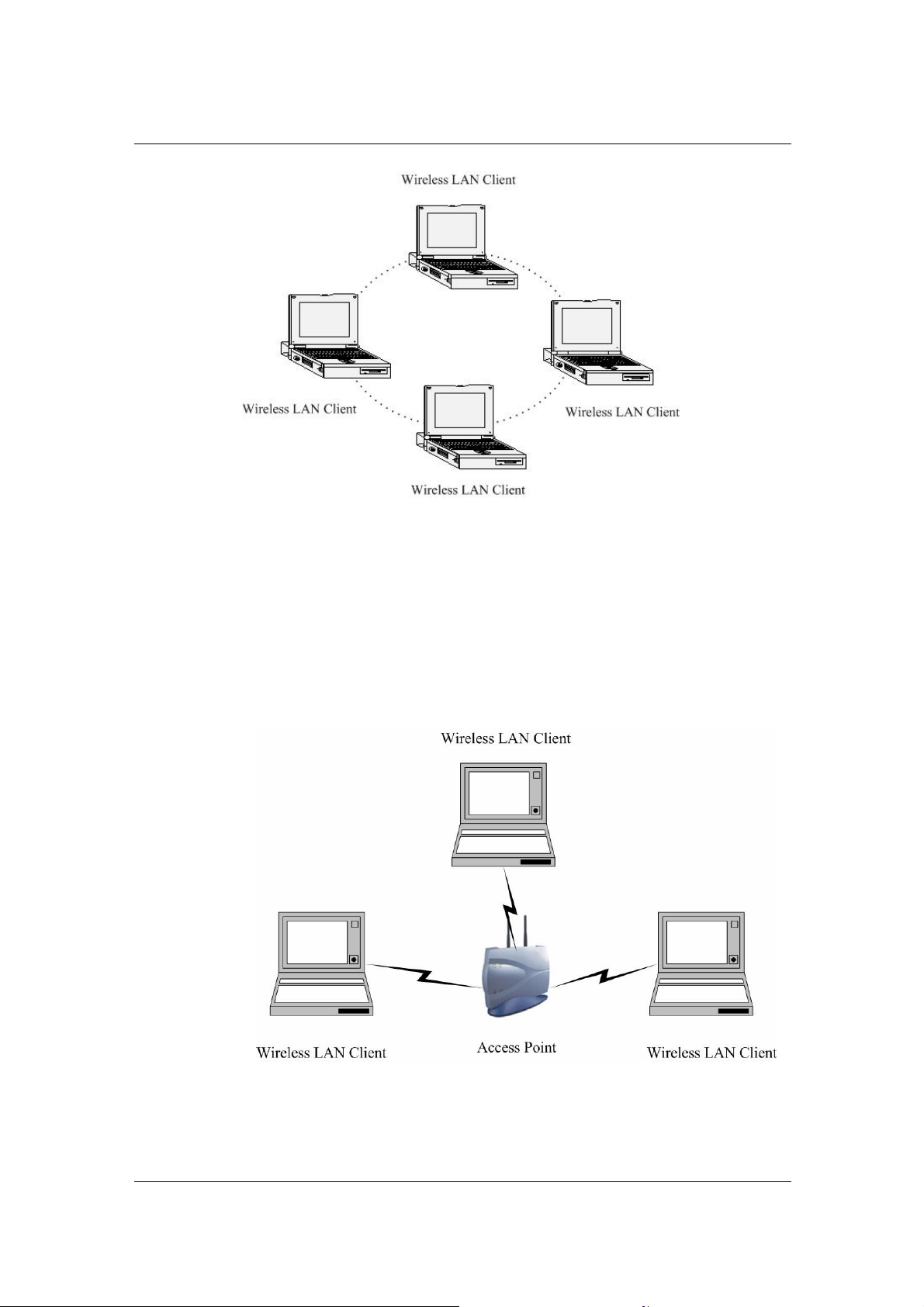
a) Ad-Hoc (peer-to-peer) Mode
This is the simplest network configuration with several computers
equipped with the PC Cards that form a wireless network whenever they
are within range of one another. In ad-hoc mode, each client is peer-topeer, would only have access to the resources of the other client and
does not require an access point. This is the easiest and least expensive
way for the SOHO to set up a wireless network. The image below depicts
a network in ad-hoc mode.
Page 4 of 26
Page 7
Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
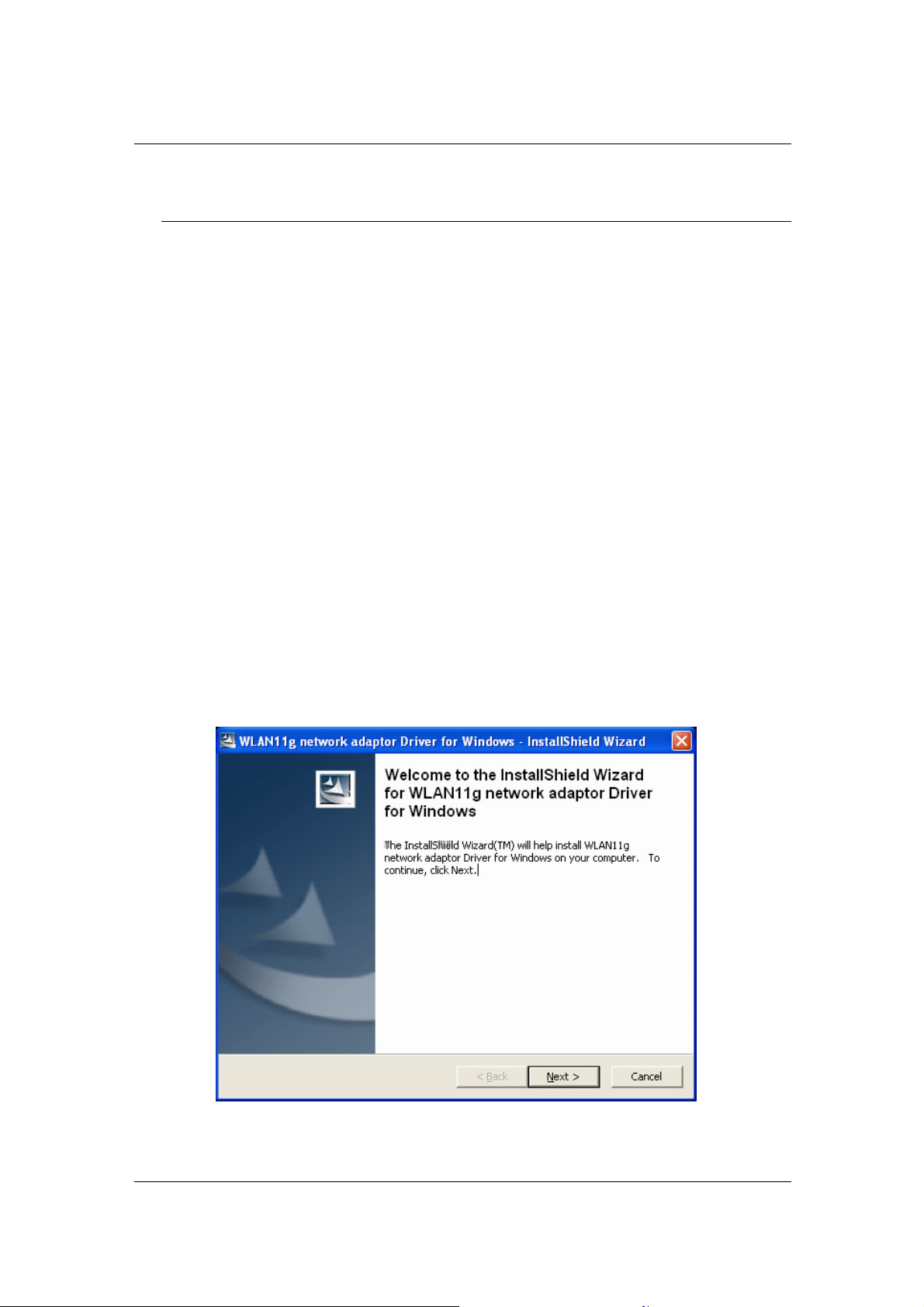
b) Infrastructure Mode
The infrastructure mode requires the use of an access point (AP). In this
mode, all wireless communication between two computers has to be via
the AP. It doesn’t matter if the AP is stand-alone or wired to an Ethernet
network. If used in stand-alone, the AP can extend the range of
independent wireless LANs by acting as a repeater, which effectively
doubles the distance between wireless stations. The image below
depicts a network in infrastructure mode.
Page 5 of 26
Page 8
Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
2 Install Drivers & Client Utility
This chapter describes how to install the drivers and client utility in Windows
98/ME/2000/XP.
2.1 Before You Begin
Before installing the new drivers into your PC, you need to remove all of the Wireless
LAN PC card drivers that you have installed.
During the installation, Windows 98/ME/2000/XP may need to copy systems files
from its installation CD. Therefore, you may need a copy of the Windows installation
CD at hand before installing the drivers. On many systems, instead of a CD, the
necessary installation files are archived on the hard disk in C:\WINDOWS
\OPTIONS\CABS directory.
2.2 Installing the PC Card Drivers
Follow the steps below in order to install the PC card drivers:
1. Insert the CD-ROM that was provided to you in this package. The setup
should run automatically. If the setup does not run automatically, then you
must manually select the setup.exe file from the CD-ROM drive.
2. Once the setup begins you will see the Install Shield Wizard, as the image
depicts below.
Page 6 of 26
Page 9
Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
3. Click on the Next button to continue. The Install Wizard will then copy a few
files that are necessary to install the PC card. You will then see the Welcome
screen, as the image depicts below.
4. Click on the Next button to continue. The setup will then bring you to the
Software License Agreement screen, as the image depicts below.
5. After reading the license agreement click on the Yes button to continue. The
setup will then copy the drivers into your PC. You will then see the Setup
Complete screen, as the image depicts below.
Page 7 of 26
Page 10

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
6. Click on the Finish button. The first part of the installation is complete.
7. Gently insert the PC card into the PCMCIA Type II slot of your PC. Windows
will automatically detect the PC card and display the Found New Hardware
Wizard, as the image depicts below.
8. Select the Install the software automatically (Recommended) radio button,
and then click on the Next button to continue. The setup will then begin to
copy the necessary files. After the copying is completed you will see the final
screen of the installation procedure, as the image depicts below.
Page 8 of 26
Page 11

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
9. The installation of the PC card is now complete. Click on the Finish button.
2.3 Verify the installation
Follow the steps below in order to verify that the PC card has been installed and is
functioning properly:
1. Click on Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double click on the System icon.
3. Click on the Hardware tab, and then click on the Device Manger button.
4. Select Network adapters to view a list of network adapters on your PC. You
will then see a window similar to the image below.
Page 9 of 26
Page 12

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
5. Make sure that you do not see a yellow (?) or a red (X) next to the PC card
(IEEE 802.1g WLAN 11g network adaptor 802.11g Adapter). If you do see a
(?) or (X) you would need to uninstall the drivers, and reinstall them again. In
order to uninstall the drivers refer to section 2.6 Uninstall Client Utility.
2.4 Disable Windows SSID/WEP Configuration
In order to configure SSID and WEP settings from the Client Utility, you must first
disable the Windows based SSID and WEP configuration from the Network
Configuration in the Control Panel. Follow the steps below in order to disable the
SSID and WEP on Windows.
1. Click on Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double click on the Network Connections icon.
3. Right-click on the wireless network connection for the PC card, and then
select Properties. The icon may look similar to the image below.
After you click on Properties, the Wireless Network Connection Properties
window will appear, as the image depicts below:
Page 10 of 26
Page 13

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
4. Click on the Wireless Networks tab, you will then see the following screen.
5. Make sure that there isn’t any check placed in the Use Windows to
configure my wireless network settings check box.
6. Click on the OK button.
Page 11 of 26
Page 14

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
3 Using the Client Utility
After a successful installation you will see the PC card Client Utility radio icon in the
system tray.
PC Card Client Utility radio
The client utility will automatically be executed and show a small green radio
icon at the bottom right corner of your screen in the system tray whenever the PC
card is inserted into the PC card slot of your computer. Right-click the radio icon
to view the list of options available. Each item is described below.
3.1 Wireless Radio On/Off
The first two items in the icon menu are used to
turn on/off the wireless radio (image right).
When the wireless radio is turned off, a red
cross is placed over the radio icon in the
system tray as shown below. When the
wireless radio is turned on, the icon will vary in
colors depending on the link quality.
Wireless Radio Off
3.2 Remove Status Icon
This item allows you to set the system tray radio icon to appear or disappear.
Once you choose this item, the system will display the dialog box to confirm if
you want to remove the system tray icon as shown below.
Link Quality
Green indicates good or excellent link status.
Yellow indicates fair link status.
Red indicates poor or no link status.
Green indicates good or excellent link status.
Yellow indicates fair link status.
Red indicates poor or no link status.
Page 12 of 26
Page 15

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
You can also set the system tray radio icon to disappear permanently by placing
a check in the box Remove Status Icon Permanently as shown above. When
the computer is restarted, the system tray radio icon will reappear unless the
Remove Status Icon Permanently box was checked.
3.3 Wireless Network Status
This item allows you to view the status, configure IBSS, Rates, Domain, and view
information about the client utility.
3.3.1 Status
The Status tab displays the current status of the wireless radio. The following
information is included in this tab, as the image depicts below.
State: this displays the MAC address of the AP that the radio is associated
with.
Current Tx Rate: this displays the current transfer rate.
Page 13 of 26
Page 16

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
Disable Radio: click on this button to turn the radio off.
Rescan: click on this button if you would like the radio to scan for a
different channel.
Current Channel: this displays the current channel that the radio is using.
Throughput (bytes/sec): this displays the transmitting (Tx) and receiving
(Rx) bytes per second.
Link Quality: this displays the quality of the link from the radio to the AP.
Signal Strength: this displays the strength of the signal from the radio to
the AP.
Click on the Apply or OK button if you have made any changes.
3.3.2 Configuration
The Configuration tab allows you to configure the SSID and type of network.
The following information is included in this tab, as the image depicts below.
Profile Name: enter a name for this profile; this can be any name that you
may associate with your network.
Network Name: enter the SSID of the network. The SSID is a unique
name shared among all points in your wireless network. The SSID must be
identical for all points in the network, and is case-sensitive.
Network Type: select Peer-to-Peer or Access Point from the drop-down
list.
Click on the Apply or OK button if you have made any changes.
Page 14 of 26
Page 17

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
3.3.3 Encryption
The Encryption tab allows you to configure WEP security. The following
information is included in this tab, as the image depicts below.
Encryption (WEP security): WEP is an acronym for Wired Equivalent
Privacy, which is a security protocol for Wireless Local Area Networks
(WLANs) defined in the 802.11 standard. WEP is designed to provide the
same level of security as a wired LAN. Select disabled, 64-bit, or 128-bit
from the drop-down list.
Alphanumeric characters: select this radio button if you would like to use
characters/numbers for the WEP key.
Hexadecimal digits (0-9, A-F): select this radio button if you would like to
use hexadecimal digits for the WEP key.
Key 1 – Key 4: enter the WEP key here.
Create Keys with Pass phrase: enter a string of characters to be used as
a WEP key.
Use WEP key: select a key number from the drop down list.
Click on the Apply or OK button if you have made any changes.
3.3.4 Site Survey
The Site Survey tab displays a list of Access Points in the area, and allows you
to connect to a specific Access Point. The following information is included in
this tab, as the image depicts below.
Page 15 of 26
Page 18

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
SSID: displays the SSID of the Access Point.
LQ: displays the link quality of the Access Point.
C: displays the channel number of the Access Point.
BSSID: displays the MAC address of the Access Point.
W: indicates whether WEP is enabled.
Mode: indicates whether the SSID is a Station (STA) or Access Point (AP).
WPA: indicates whether WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) is enabled.
Connect: to connect with a specific Access Point, select the Access Point
from the drop-down list, and then click on the Connect button.
Scan: to view a list of Access Points in the area click on the Scan button.
Click on the Apply or OK button if you have made any changes.
3.3.5 IBSS
The IBSS tab displays IBSS Channel Selection. You may select a channel from
the list, or click on the Default button, for a default channel. The image below
depicts the IBSS tab.
Page 16 of 26
Page 19

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
Click on the Apply or OK button if you have made any changes.
3.3.6 Rates
The Rates tab displays the data rate. You may select a data rate from the list, or
click on the Default button, for a default data rate (Fully Automatic). The image
below depicts the Rates tab.
Click on the Apply or OK button if you have made any changes.
Page 17 of 26
Page 20

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
3.3.7 Domain
The Domain tab displays the 802.11d support and current countries/domains, as
the image depicts below.
802.11d Support: by default 802.11d support is set to flexible. You may
change this by selecting None or Strict.
Countries/Domains: you may select your country from the drop-down list.
You will then see country specific information in the text box.
Click on the Apply or OK button if you have made any changes.
Page 18 of 26
Page 21

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
3.3.8 About
The About tab displays information about the PC card. This includes the network
driver version and date, configuration utility version and date, and the NIC
(Network Interface Card) firmware version and date.
Page 19 of 26
Page 22

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
4 Configure WPA
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) was designed to improve upon the security features
of WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy). The technology is designed to work with
existing Wi-FI products that have been enabled with WEP. WPA provides improved
data encryption through the Temporal Integrity Protocol (TKIP), which scrambles the
keys using a hashing algorithm and by adding an integrity-checking feature which
makes sure that keys haven’t been tampered with.
Note: WPA can only be used in Windows XP and must have the WPA patch
installed. If you do not have the patch installed, you may download and install
Q815485 (WPA Patch) from www.microsoft.com/security.
In order to configure WPA settings for the Client Utility, you must first enable the
Windows based wireless network configuration in the Control Panel by following the
steps below:
1. Click on Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double click on the Network Connections icon.
3. Right-click on the wireless network connection for the PC card, and then
select Properties. The icon may look similar to the image below.
4. After you click on Properties, the Wireless Network Connection
Properties window will appear, as the image depicts below:
Page 20 of 26
Page 23

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
5. Click on the Wireless Networks tab, you will then see the following screen.
6. Select the available network, and then click on the Configure button; you will
then see the Association screen.
Page 21 of 26
Page 24

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
7. Select a Network Authentication type: WPA or WPA-PSK (Pre-shared key)
from the drop-down list.
8. Select a Data Encryption type: WEP or TKIP from the drop-down list, as the
image depicts below.
9. Enter the Network Key; this key must match the key in the Access Point.
Retype the key in the Confirm network key, and then click on the OK button.
Page 22 of 26
Page 25

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
5 Uninstall the Client Utility
If the PC card installation is unsuccessful for any reason, the best way to solve
the problem may be to completely uninstall the PC card and its software and
repeat the installation procedure again.
Follow the steps below in order to uninstall the Client Utility:
1. Click on Start > Settings > Control Panel, and then click on the Add or
Remove Programs icon. A window will then appear listing all the programs
on your PC. From the list click on the PC card item, as the image depicts
below.
2. Click on the Change/Remove button. You will then be asked to confirm the
file deletion, as the image depicts below.
3. Click on the Yes button. The uninstall shield will then begin to uninstall the
files from you computer, as the image depicts below.
4. Click on the OK button, the uninstallation is successful.
Page 23 of 26
Page 26

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
Appendix A – Troubleshooting
The following table describes the solutions for the problems that may occur when
installing the PC card.
Problem Solution
Windows does not detect the PC card
when installed
Driver fails to load A resource conflict could exit. Use the Device Manger
Device conflict on Windows system A device conflict may be related to PC card. Use the
No resource conflicts were detected,
but the wireless station does not attach
to the network
Non functioning card LED The PC card is not powered on: The cause may be:
Verity that the PC card is properly inserted into the PC
card slot.
Check whether the computer has a Plug and Play
BIOS.
Windows 98/ME/2000/XP might not detect the PC card
if a previous installation of the PC card was cancelled
before it was completed. Remove the driver and
reinstall it again.
to resolve the resource conflict.
computer properties to identify the Port Address and
IRQ values. If there is a device conflict, select
alternative settings for I/O Base Address or IRQ values.
If you know which device is conflicting with the PC
card, you have the option of changing the device’s I/O
address or IRQ instead of the PC card.
Verify that the SSID of the PC card matches that of the
Access Point. Use the Network Configuration
properties in the control panel to modify the SSID.
No driver loaded or installed.
Card – Driver mismatch, which prevented the
driver from loading.
Device conflict, which prevented the driver
from loading.
Actions:
Verify that the driver has been installed.
Determine if there is a conflict with another
device.
Page 24 of 26
Page 27

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
Appendix B – Specifications
General
Data Rates 1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 Mbps
Network Standards IEEE 802.11, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g
Compliance FCC Part 15/UL
Drivers Windows 98/ME/2000/XP
Operational Voltage 3.3+-10%
Current Consumption Continue Tx: < 850mA
Continue Rx: < 550mA
Security IEEE802.1x Client Support—Work with Windows XP Utility
WPA -- Wi-Fi Protected Access (64,128-bit WEP with TKIP, PreShare Key) —Work with Windows XP Utility
RF Information
Frequency Band 2412 – 2483.5 MHz
Channels 11 for North America, 14 for Japan, 13 for Europe,
2 for Spain, 4 for France
Media Access Protocol Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance
(CSMA/CA)
Modulation Technology Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
DBPSK @ 1Mbps
DQPSK @ 2 Mbps
CCK @ 5.5 & 1 Mbps
BPSK @ 6 & 9 Mpbs
QPSK @ 12 & 18 Mbps
16-QAM @ 24 & 36 Mbps
64-QAM @ 48 and 54 Mbps
Receive Sensitivity
(Typical)
Available transmit power
(Depend on Different
Countries’ Regulation)
Physical
LED RF link activity
Interface Mini-PCI
Antenna diversity external antenna connector
Dimensions 60 (L)mm x 51(W)mm x 4(H)mm
Environmental
Temperature Range -0°C to 55°C - Operating
Humidity (non-condensing) 5%~95% Typical
-89dBm @ 1Mbps -88dBm @ 6Mbps -79dBm @ 24Mbps
-86dBm @ 2Mbps -87dBm @ 9Mbps -75dBm @ 36Mbps
-85dBm @ 5.5Mbps -84dBm @ 12Mbps -68dBm @ 48Mbps
-82dBm @ 11Mbps -82dBm @ 18Mbps -68dBm @ 54Mbps
20 ± 2dBm @1, 2, 5.5 and 11Mbps
20 ± 2dBm @6, 9, 12, 18Mbps
17 ± 2dBm @24, 36Mbps
16 ± 2dBm @48, 54Mbps
-40°Cto 70°C - Storage
Page 25 of 26
Page 28

Wireless Mini-PCI Card Version: 0.9
Appendix C – Regulatory Compliance
Information
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment.
This device complies with FCC RF Exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment, under 47
CFR 2.1093 paragraph (d)(2).
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
Page 26 of 26
 Loading...
Loading...