
Wireless Concurrent AP
ENH700EXT
User Manual
Version : 1.0
1

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW..................................................................................................................................... 4
1.1 F
1.2 B
1.3
1.4
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................. 7
CHAPTER 3 CONFIGURING YOUR COMPUTER FOR TCP/IP...............................................................................................10
3.1 C
3.2 C
3.3 C
3.4 C
3.5 C
CHAPTER 4 INTRODUCING THE WEB CONFIGURATOR.....................................................................................................19
4.1 L
EATURES
................................................................................................................................................................. 4
ENEFITS
.................................................................................................................................................................. 5
PACKAGE CONTENTS
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
ONFIGURING MICROSOFT WINDOWS
ONFIGURING MICROSOFT WINDOWS VISTA
ONFIGURING MICROSOFT WINDOWS
ONFIGURING MICROSOFT WINDOWS
ONFIGURING AN APPLE MACINTOSH COMPUTER
OGGING IN TO THE WEB CONFIGURATOR
....................................................................................................................................................... 6
................................................................................................................................................. 6
7 ............................................................................................................................ 11
XP .......................................................................................................................... 15
2000 ...................................................................................................................... 16
........................................................................................................................... 19
....................................................................................................................... 13
................................................................................................................ 18
CHAPTER 5 WIRELESS CONFIGURATION..........................................................................................................................21
5.1 S
ELECTING OPERATING MODES
5.1.1 Selecting Separate Operating Modes for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Networks ......................................................... 21
5.1.2 Selecting Dual Mode for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Networks................................................................................... 22
5.2 W
IRELESS SETTINGS
5.2.1 Access Point Mode (Dual Mode) ..................................................................................................................... 24
5.2.2 Access Point Mode (5 GHz).............................................................................................................................. 27
5.2.3 Access Point Mode (2.4 GHz) .......................................................................................................................... 28
5.2.4 Client Bridge Mode/Client Router Mode (Dual Mode).................................................................................... 29
5.2.5 Client Bridge Mode/Client Router Mode (5 GHz) ............................................................................................ 30
5.2.6 Client Bridge Mode/Client Router Mode (2.4 GHz) ......................................................................................... 31
5.2.7 WDS Bridge Mode........................................................................................................................................... 32
5.4 5.3 S
AP S
5.5 W
ITE SURVEY
CAN LIST (5 GHZ /
IRELESS SECURITY SETTINGS
5.5.1 WEP (Access Point).......................................................................................................................................... 37
....................................................................................................................................................... 24
............................................................................................................................................................ 35
2.4 GHZ) .......................................................................................................................................... 36
......................................................................................................................................... 21
.......................................................................................................................................... 37
5.5.2 WEP (Client Bridge / Client Router)................................................................................................................. 38
5.5.3 WPA pre-shared Key (Access Point)................................................................................................................. 39
5.5.4 WPA pre-shared Key (Client Bridge / Client Router) ........................................................................................ 40
5.5.5 RADIUS (Access Point Mode Only)................................................................................................................... 41
5.6 W
IRELESS ADVANCED SETTINGS
5.6.1 Advanced Settings (Access Point) .................................................................................................................... 43
........................................................................................................................................ 43

5.6.2 Advanced Settings (Client Bridge / Client Router)........................................................................................... 44
5.7 W
IRELESS ACCESS CONTROL LIST
...................................................................................................................................... 45
CHAPTER 6 LAN SETUP....................................................................................................................................................47
6.1 LAN S
6.2 DHCP I
6.3 SNMP S
CHAPTER 7 INTERNET SETTINGS .....................................................................................................................................50
7.1 DHCP (D
7.2 S
7.3 PPPOE (P
7.4 PPTP (P
CHAPTER 8 INFORMATION STATUS..................................................................................................................................54
8.1 S
8.2 W
8.3 S
8.4 I
CHAPTER 9 MANAGEMENT SETTINGS .............................................................................................................................57
ETTINGS
.............................................................................................................................................................. 47
NFO
.................................................................................................................................................................. 48
ETTINGS
........................................................................................................................................................... 49
YNAMIC
IP) ..................................................................................................................................................... 50
TATIC
IP...................................................................................................................................................................... 50
OINT-TO-POINT PROTOCOL OVER ETHERNET
OINT-TO-POINT TUNNELING PROTOCOL
TATUS
......................................................................................................................................................................... 54
IRELESS CLIENT LIST
YSTEM LOG
NTERNET STATUS
................................................................................................................................................................. 55
..................................................................................................................................................... 55
........................................................................................................................................................... 56
)......................................................................................................... 51
)................................................................................................................. 52
9.1 P
ASSWORD SETTINGS
9.2 T
IME ZONE SETTINGS
9.3 D
IAGNOSIS
9.4 R
EMOTE CONTROL
9.5 U
PGRADE FIRMWARE
9.6 S
AVE/RELOAD SETTINGS
APPENDIX A – GLOSSARY................................................................................................................................................61
APPENDIX B – FCC INTERFERENCE STATEMENT ...............................................................................................................66
PROFESSIONAL INSTALLATION INSTRUCTION.................................................................................................................67
.................................................................................................................................................................... 58
...................................................................................................................................................... 57
...................................................................................................................................................... 57
......................................................................................................................................................... 59
...................................................................................................................................................... 59
.................................................................................................................................................. 59

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Thank you for choosing the ENH700EXT. The ENH700EXT is a dual-radio wireless outdoor Access
Point/Client/Bridge designed as an enterprise-scale product to deliver unparalleled range and
performance on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz wireless local-area networks (WLANs). With certified IP-68
protection, the ENH700EXT is designed to deliver high reliability whether installed indoors or
outdoors.
The ENH700EXT is actually three devices in one: an Access Point, a Client Bridge, and a Client Router.
Its wireless capabilities allow you to deliver Internet and intranet connectivity in locations where
wired connections are not possible or practical.
The ENH700EXT contains two radio-frequency (RF) interfaces, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, that support IEEE
802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n standards. Depending on the operating mode, the ENH700EXT can use
one or both RF interfaces at the same time. The ENH700EXT also supports Power over Ethernet and
is equipped with an external N-type antenna that delivers superior wireless signal quality, even in the
harshest environments. Best of all, the antenna is upgradeable.
In addition, the ENH700EXT can manage power level control, Wireless Access Control, and Wi-Fi
Multimedia (WMM), and show real-time received signal strength indicator (RSSI) status. For
security-conscious users, the ENH700EXT fully supports encryption, including Wi-Fi Protected Access
(WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK), 64/128/152-bit Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) Encryption, and IEEE 802.1x
RADIUS encryption.
1.1 Features
The following list summarizes the key features of the ENH700EXT.
- Operates as an Access Point, Client Bridge, or Client Router
- Works concurrently with 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks for optimum throughput
- Fully interoperable with IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11b/IEEE 802.11g and IEEE802.11n-compliant
devices
- Supports four independently configurable service set identifiers (SSIDs)
- Administrators can set up a VLAN for each SSID to isolate services among clients
- Exceptional extended range and coverage
- Easy Internet access using ISP service authentication
RSSI indicator shows the signal quality for each wireless client connected to the Access Point
-
- Fully supports the latest security capabilities
- Clients can access different networks through a single Access Point, and assign different policies

and functions to each SSID
- Collocates with any antenna in your environment
- Web-based Configurator lets administrators configure and manage the ENH700EXT remotely
- Watertight, weatherproof enclosure prevents interior damage from water and exterior damage
from weather corrosion
- Comes with a wall-mount and mast mounting kit support to simplify installation
1.2 Benefits
The ENH700EXT is the ideal product around which you can build your WLAN. The following list
summarizes a few key advantages that WLANs have over wired networks:
- Ideal for hard-to-wire environments
There are many scenarios where cables cannot be used to connect networking devices.
Historic and older buildings, open areas, and busy streets, for example, make wired LAN
installations difficult, expensive or impossible.
- Temporary workgroups
WLANs make it easy to provide connectivity to temporary workgroups that will later be
removed. Examples include parks, athletic arenas, exhibition centers, disaster-recovery
shelters, temporary offices, and construction sites.
- Ability to access real-time information
With a WLAN, workers who rely on access to real-time information, such as doctors and
nurses, point-of-sale employees, mobile workers, and warehouse personnel, can access
the data they need and increase productivity, without having to look for a place to plug
into the network.
- Frequently changed environments
WLANs are well suited for showrooms, meeting rooms, retail stores, and manufacturing
sites where workplaces are rearranged frequently.
- Wireless extensions to Ethernet networks
WLANs enable network managers in dynamic environments to minimize overhead caused
by moves, extensions to networks, and other changes.
- Wired LAN backup
Network managers can implement WLANs to provide backup for mission-critical
applications running on wired networks.
- Mobility within training/educational facilities
Training sites at corporations and students at universities are a few examples where
wireless connectivity can be used to facilitate access to information, information
exchanges, and learning.

1.3 Package Contents
Open the package carefully and make sure it contains all of the items listed below.
- One EnGenius Concurrent Dual Radio AP (ENH700EXT)
- One PoE injector 48V/0.8A Power Adapter
- One mounting kit
- One grounding cable
- One quick-installation guide
- One CD containing the user manual
- Two N-Type Dual Band Omni directional Antenna
If any item is missing or damaged, contact your place of purchase immediately.
Keep all packing materials in case you need to return the ENH700EXT. The ENH700EXT must be
returned in its original packing materials.
Note: Use only the power adapter supplied with your ENH700EXT. Using a different power adapter
can damage the ENH700EXT.
1.4 System Requirements
To install the ENH700EXT, you need an Ethernet cable and a computer equipped with:
- An Ethernet interface
- One of the following operating systems: Microsoft Windows XP, Vista, or 7; or Linux
- An Internet browser that supports HTTP and JavaScript.

Chapter 2 Hardware Overview
The following figures show the key components on the ENH700EXT.
2.1 Bottom View
The bottom panel of the ENH700EXT contains an RJ-45 port and 4 N-type connectors.
- The RJ-45 port connects to an Ethernet adapter in a computer you use to configure the
ENH700EXT. For more information, see Chapter 4.
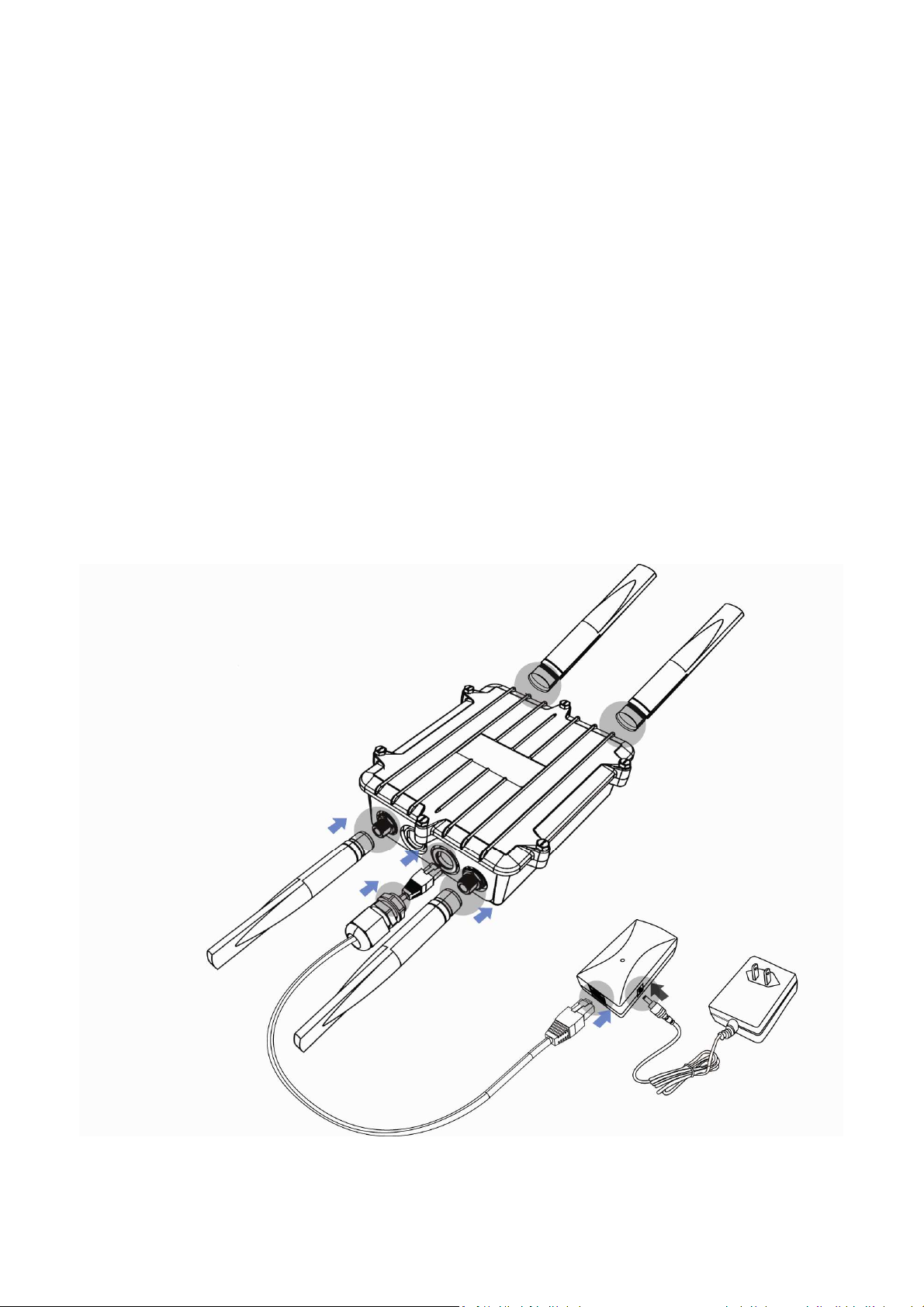
2.2 Installation
To install the ENH700EXT, use the following procedure and refer to the figure below.
1. Connect the 4 dipole antennas to the top and bottom of the ENH700EXT and tighten
them by hand.
2. Connect either end of an Ethernet cable to the ENH700EXT jack labeled RJ-45. Connect
the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 jack on the PoE adapter labeled AP/Bridge
Network.
3. Attach the round plug on the supplied power adapter to the DC48 V IN connector on the
Power on Ethernet adapter. Connect the other end to a working AC outlet. The red LED
on the PoE adapter goes ON to show it is receiving AC power.
WARNING: Only use the power adapter supplied with the ENH700EXT. Using a different power
adapter can damage the ENH700EXT.
2.3 Understanding the ENH700EXT LEDs
The ENH700EXT has LEDs that show the operating status of the device. The following table describes
the ENH700EXT LEDs.
LED Color Mode Status
Power Green OFF= ENH700EXT is not receiving power.
ON= ENH700EXT is receiving power.
LAN Green OFF = ENH700EXT is not connected to the network.
ON = ENH700EXT is connected to the network, but not sending or
receiving data.
Blink = ENH700EXT is sending or receiving data.
WLAN1
802.11a/n
WLAN2
802.11b/g/n
Green Access Point
or Client
Bridge Mode
Green Access Point
or Client
Bridge Mode
OFF = ENH700EXT radio is off and the device is not
sending or receiving data.
ON = ENH700EXT radio is on, and the device is not
sending or receiving data.
Blink = ENH700EXT radio is on, and the device is
sending or receiving data.
OFF = ENH700EXT radio is off and the device is not
sending or receiving data.
ON = ENH700EXT radio is on, and the device is not
sending or receiving data.
Blink = ENH700EXT radio is on, and the device is
sending or receiving data.

Chapter 3 Configuring Your Computer for TCP/IP
To configure the ENH700EXT, use the instructions in the appropriate section of this chapter to
configure the TCP/IP settings on a computer that will be used to configure the ENH700EXT.
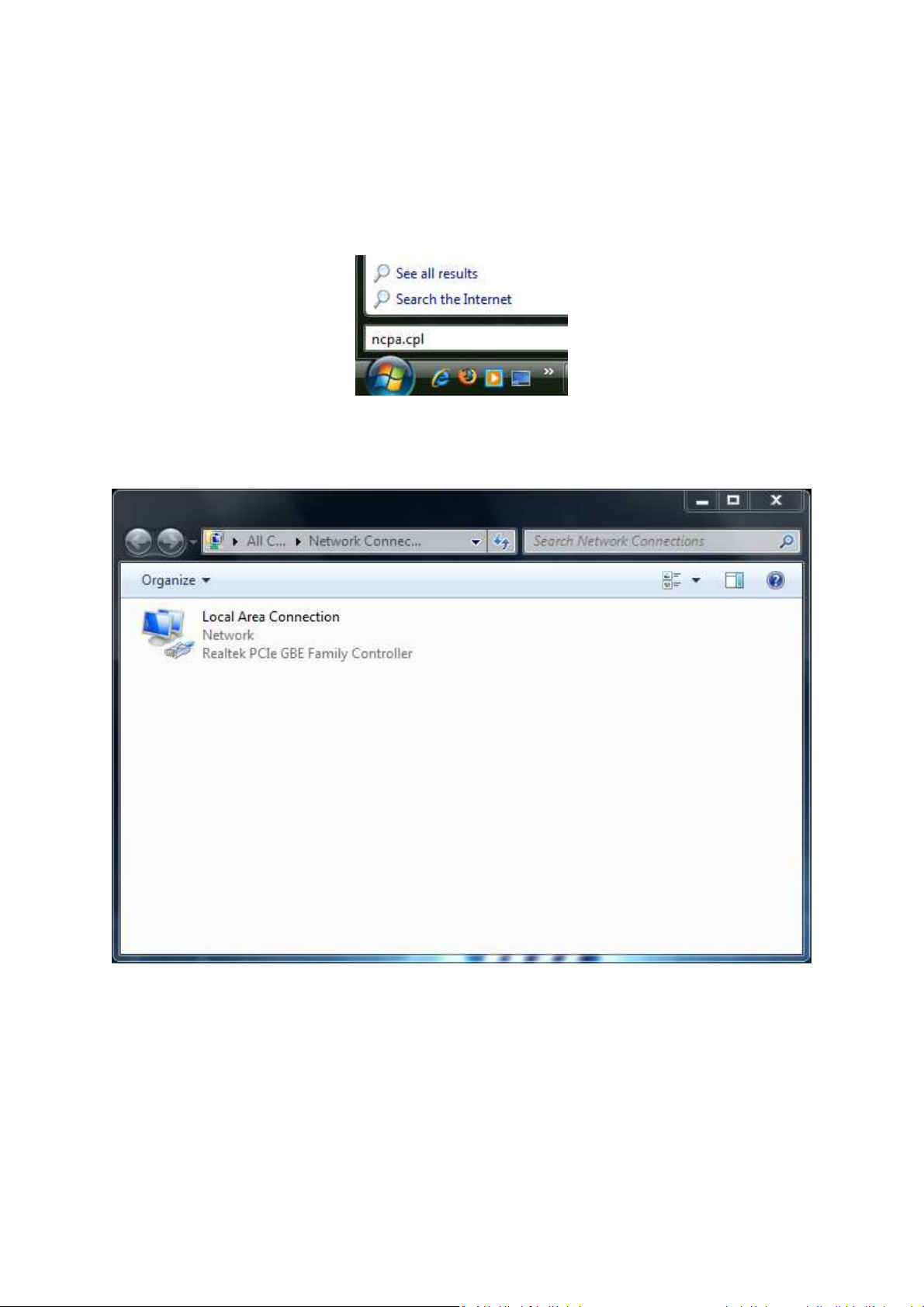
3.1 Configuring Microsoft Windows 7
Use the following procedure to configure a computer running Microsoft Windows 7.
1. In the Start menu search box, type: ncpa.cpl
2. When the Network Connections List appears, right-click the Local Area Connection icon
and click Properties.
3. In the Networking tab, click either Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) or Internet
Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6), and then click Properties.
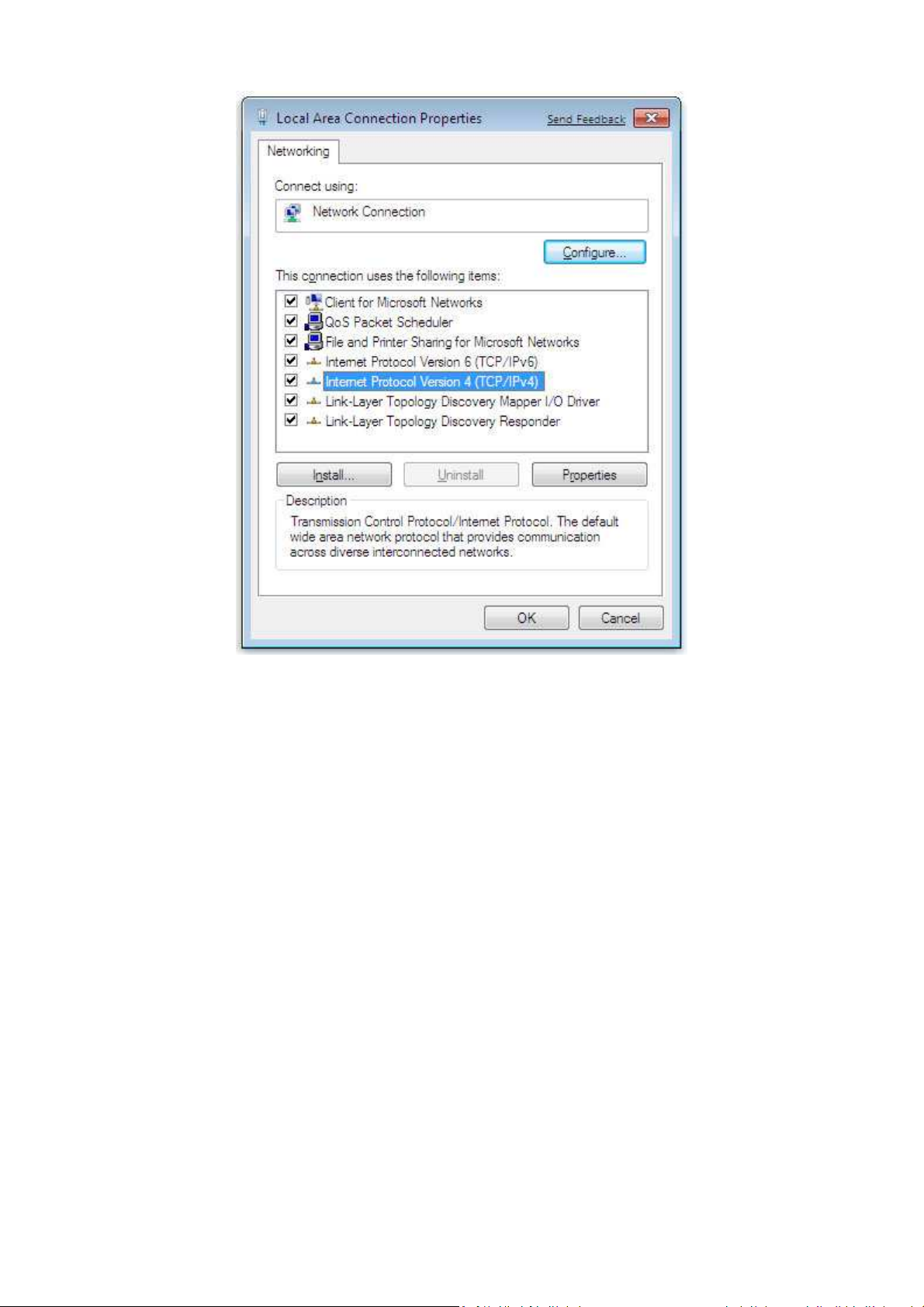
4. In the properties dialog box, click Obtain an IP address automatically to configure your
computer for DHCP.
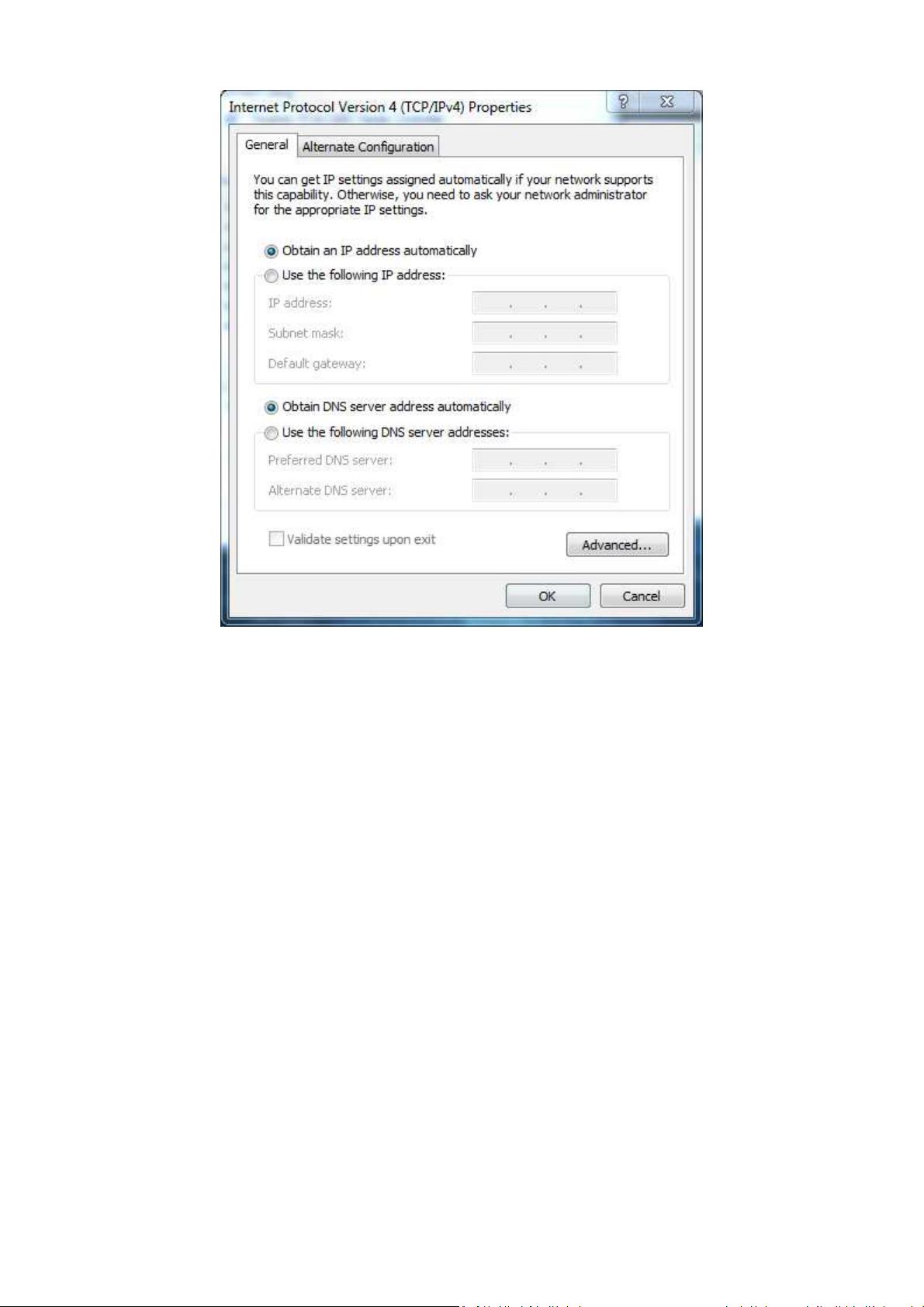
5. Click the OK button to save your changes and close the dialog box.
6. Click the OK button again to save your changes.
3.2 Configuring Microsoft Windows Vista
Use the following procedure to configure a computer running Microsoft Windows Vista with the
default interface. If you use the Classic interface, where the icons and menus resemble previous
Windows versions, perform the procedure in section 4.4.
1. On the Windows taskbar, click Start, click Control Panel, and then select the Network
and Internet icon.
2. Click View Networks Status and tasks and then click Management Networks
Connections.
3. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and click Properties.
4. Click Continue. The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box appears.
5. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, verify that Internet Protocol
(TCP/IPv4) is checked. Then select Internet Protocol (TCP/IPv4) and click the Properties
button. The Internet Protocol Version 4 Properties dialog box appears.
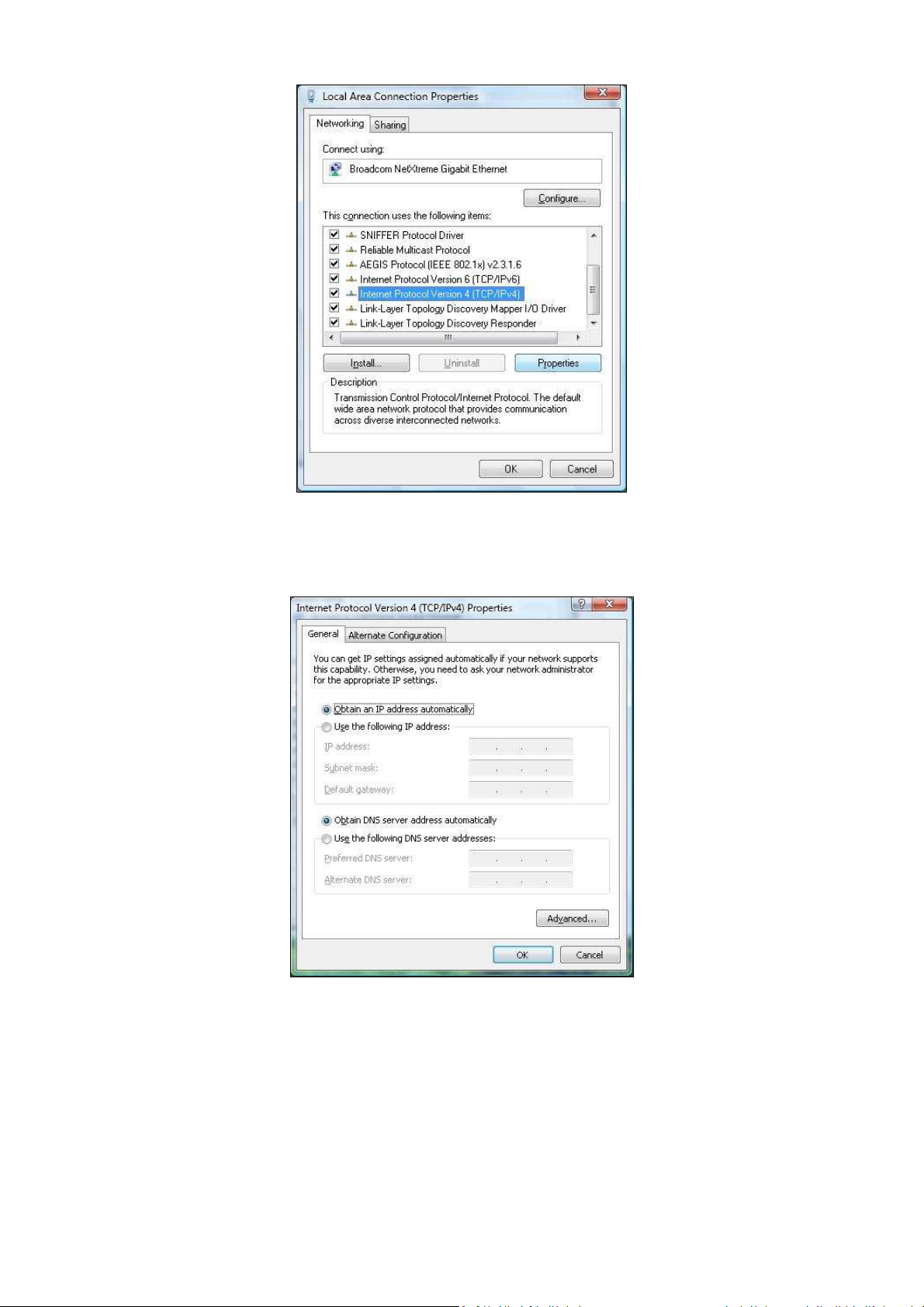
6. In the Internet Protocol Version 4 Properties dialog box, click Obtain an IP address
automatically to configure your computer for DHCP.
7. Click the OK button to save your changes and close the dialog box.
8. Click the OK button again to save your changes.
3.3 Configuring Microsoft Windows XP
Use the following procedure to configure a computer running Microsoft Windows XP with the default
interface. If you use the Classic interface, where the icons and menus resemble previous Windows
versions, perform the procedure in section 4.4.
1. On the Windows taskbar, click Start, click Control Panel, and then click Network and
Internet Connections.
2. Click the Network Connections icon.
3. Click Local Area Connection for the Ethernet adapter connected to the ENH700EXT. The
Local Area Connection Status dialog box appears.
4. In the Local Area Connection Status dialog box, click the Properties button. The Local
Area Connection Properties dialog box appears.
5. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, verify that Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
is checked. Then select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click the Properties button. The
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box appears.
6. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click Obtain an IP address
automatically to configure your computer for DHCP. Click the OK button to save this
change and close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box.
7. Click the OK button again to save your changes.
8. Restart your computer.
3.4 Configuring Microsoft Windows 2000
Use the following procedure to configure your computer if your computer has Microsoft Windows
2000 installed.
1. On the Windows taskbar, click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. In the Control Panel window, double-click the Network and Dial-up Connections icon. If
the Ethernet adapter in your computer is installed correctly, the Local Area Connection
icon appears.
3. Double-click the Local Area Connection icon for the Ethernet adapter connected to the
ENH700EXT. The Local Area Connection Status dialog box appears.
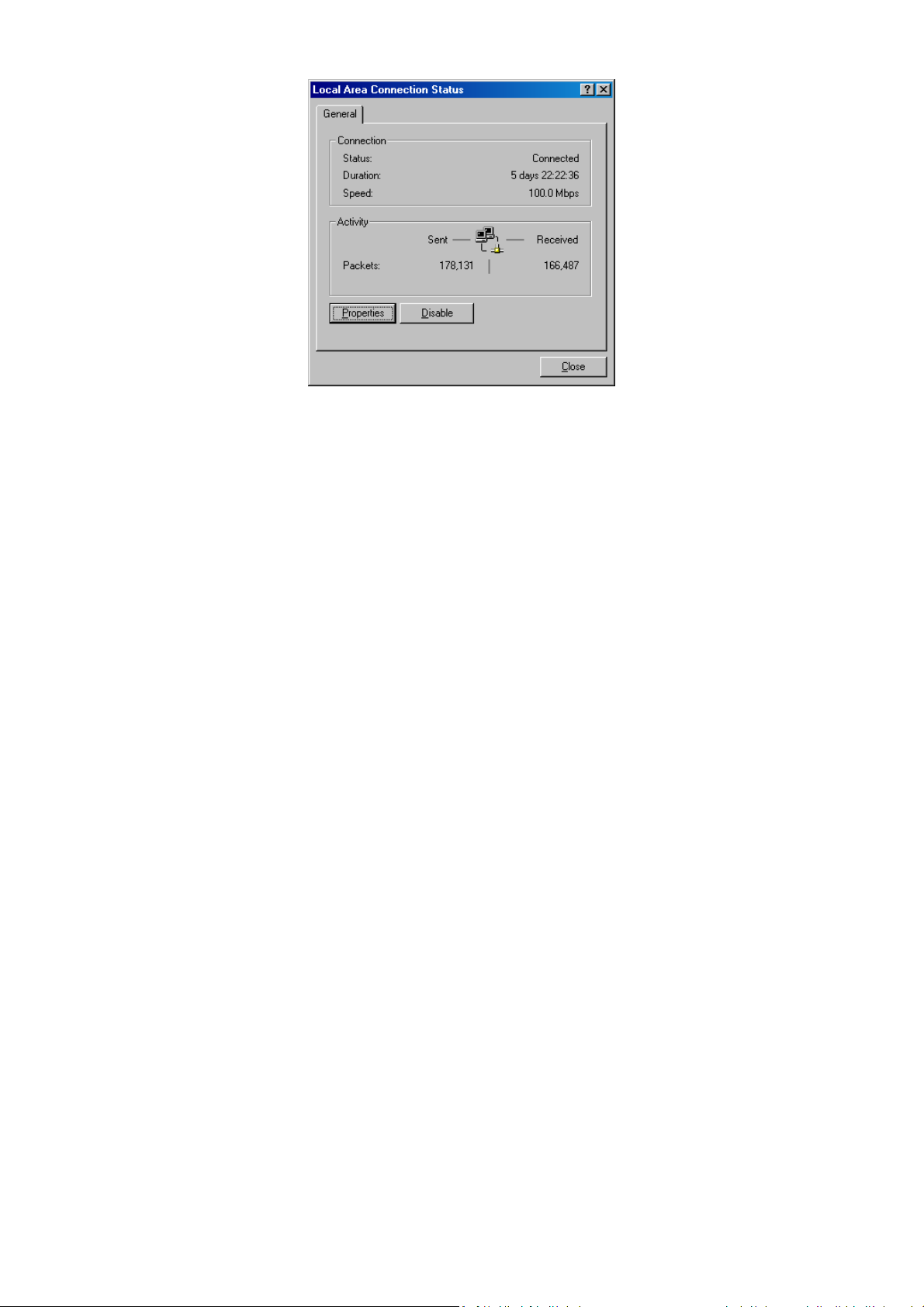
4. In the Local Area Connection Status dialog box, click the Properties button. The Local
Area Connection Properties dialog box appears.
5. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, verify that Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
is checked. Then select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click the Properties button.
6. Click Obtain an IP address automatically to configure your computer for DHCP.
7. Click the OK button to save this change and close the Local Area Connection Properties
dialog box.
8. Click OK button again to save these new changes.
9. Restart your computer.
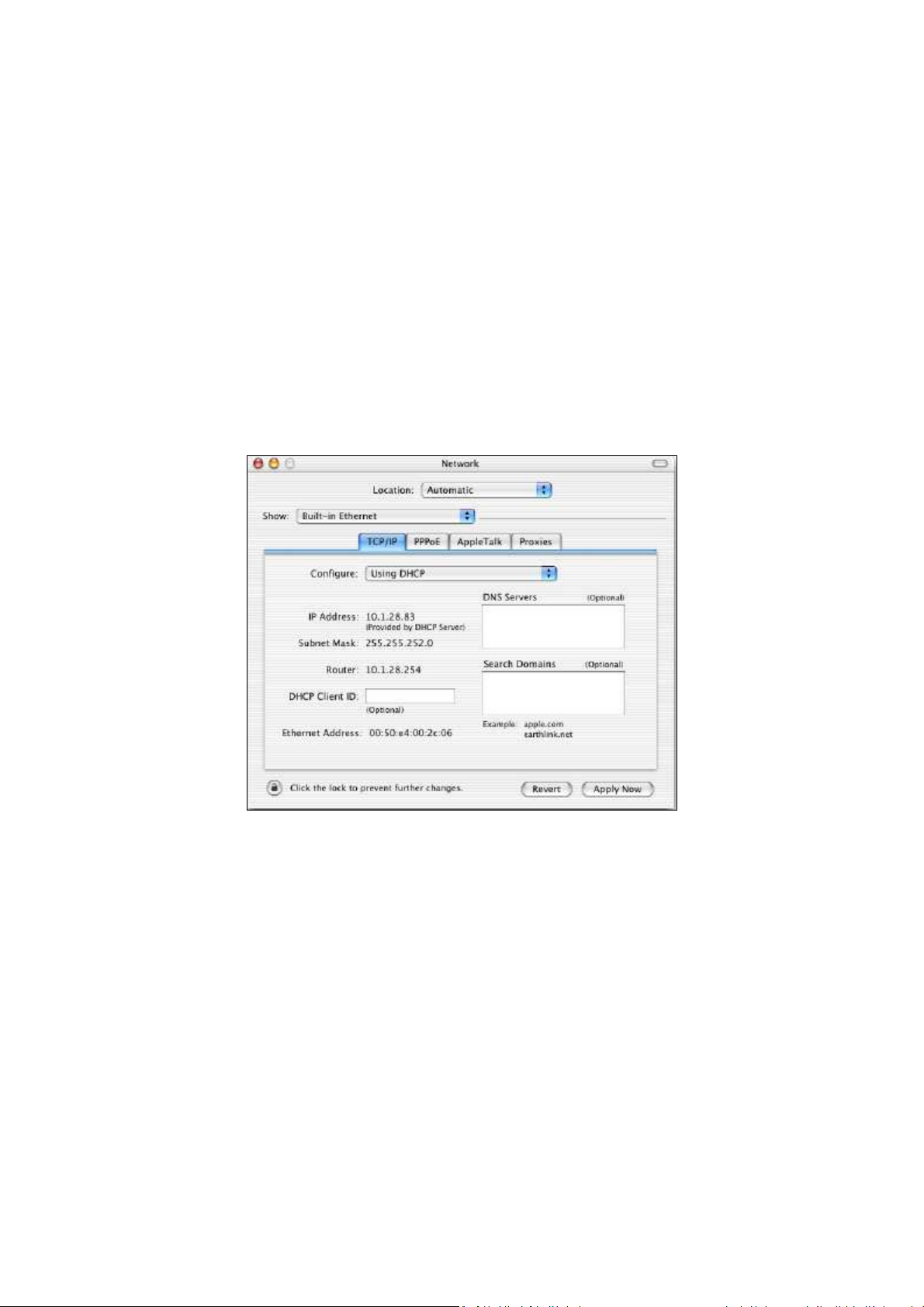
3.5 Configuring an Apple Macintosh Computer
The following procedure describes how to configure TCP/IP on an Apple Macintosh running Mac OS
10.2. If your Apple Macintosh is running Mac OS 7.x or later, the steps you perform and the screens
you see may differ slightly from the following. However, you should still be able to use this procedure
as a guide to configuring your Apple Macintosh for TCP/IP.
1. Pull down the Apple Menu, click System Preferences, and select Network.
2. Verify that the NIC connected to the ENH700EXT is selected in the Show field.
3. In the Configure field on the TCP/IP tab, select Using DHCP.
4. Click Apply Now to apply your settings and close the TCP/IP dialog box.
Chapter 4 Introducing the Web Configurator
The ENH700EXT has a built-in Web Configurator that lets you manage the unit from any location
using a Web browser that supports HTTP and has JavaScript installed.
4.1 Logging in to the Web Configurator
After configuring the computer for TCP/IP using the procedure appropriate for your operating system,
use that computer’s Web browser to log in to the ENH700EXT Web Configurator.
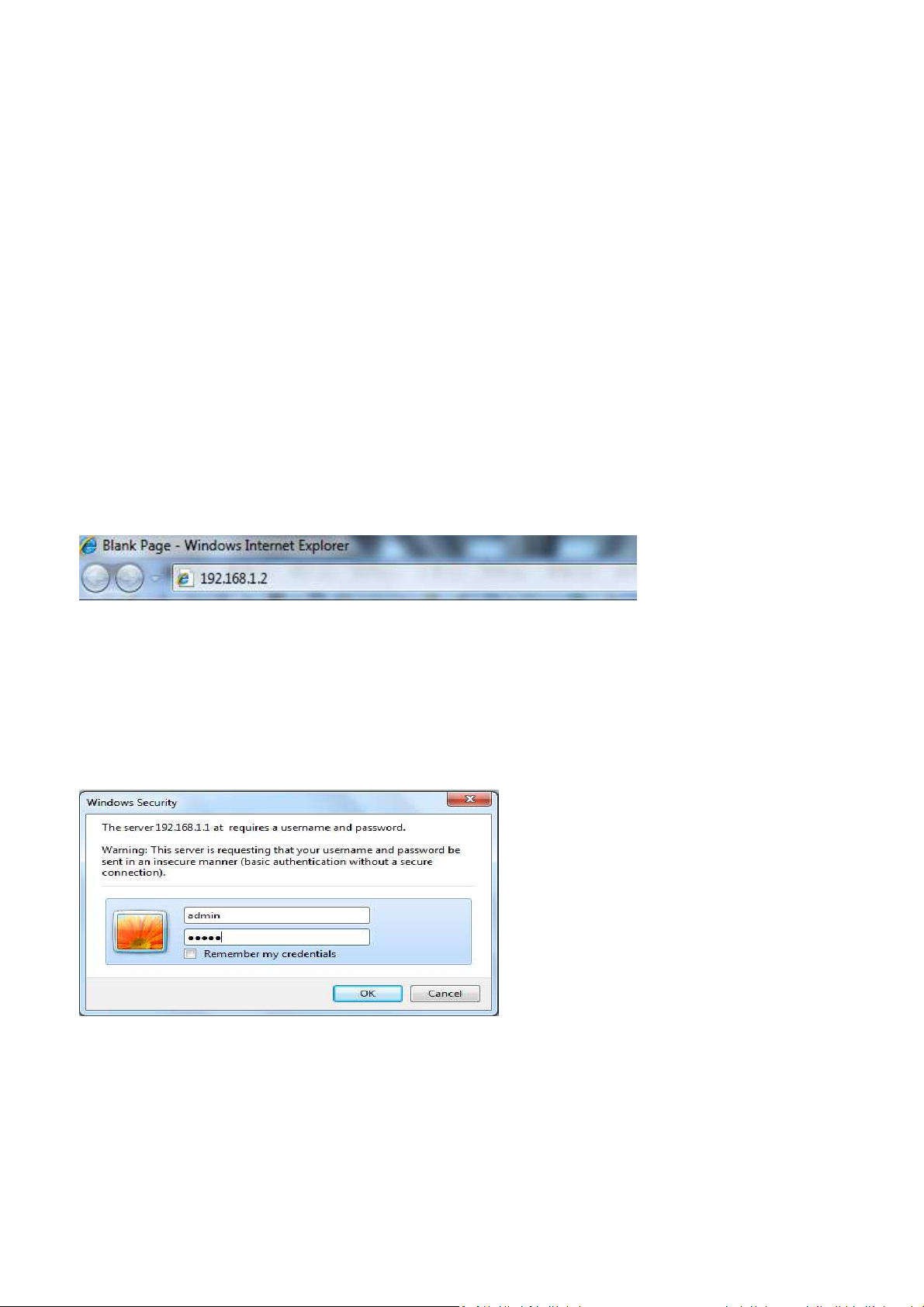
1. Launch your Web browser.
2. In the browser address bar, type 192.168.1.1 and press the Enter key.
Note: If you change the ENH700EXT’s IP address, enter the appropriate IP address.
3. When the Windows Security window appears, type admin as the username in the top field and
type admin as the password in the bottom field.
4. Click OK
You are now ready to use the instructions in the following chapters to configure the ENH700EXT.

4.2 Best Practices
Perform the following procedures regularly to make the ENH700EXT more secure and manage the
ENH700EXT more effectively.
- Change the default password. Use a password that is not easy to guess and that contains different
characters, such as numbers and letters. The ENH700EXT username cannot be changed. For more
information, see page 57.
- Back up the configuration and be sure you know how to restore it. Restoring an earlier working
configuration can be useful if the ENH700EXT becomes unstable or crashes. If you forget your
password, you will have to reset the ENH700EXT to its factory default settings and lose any
customized override settings you configured. However, if you back up an earlier configuration,
you will not have to completely reconfigure the ENH700EXT. You can simply restore your last
configuration. For more information, see page 59.

Chapter 5 Wireless Configuration
This chapter describes the ENH700EXT’s wireless settings.
5.1 Selecting Operating Modes
The ENH700EXT supports three operating modes: Access Point, Client Bridge, and Client Router.
Using the procedures in the following sections, you can configure the ENH700EXT to use one
operating mode for a 2.4 GHz network and another operating mode for 5 GHz networks (see section
5.1.1), or the same operating mode for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks (see section 5.1.2).
5.1.1 Selecting Separate Operating Modes for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Networks
To select a separate operating mode for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks, use the following procedure.
1. Under the Management section, click Operation Mode. The following page appears.
2. At the top of the page, click Separate Mode.

3. Under Please choose the Operation Mode. (5G), click the operating mode you want to use for the
5 GHz network.
4. Under Please choose the Operation Mode. (2.4G), click the operating mode you want to use for
the 2.4 GHz network.
Note: Client Bridge Mode and Client Router Mode cannot be used at the same time.
5. Click Apply.
5.1.2 Selecting Dual Mode for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Networks
The following procedure describes how to select the same operating mode for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
networks. If you select Client Bridge Mode or Client Router Mode, you must select the ENH700EXT
radio (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz radio) that will be used with that operating mode. If you select Access Point,
the operating mode is used with both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks automatically.
1. Under the Management section, click Operation Mode.
2. At the top of the page, click Dual Mode. The following page appears.

3. Under Please choose the Operation Mode, click the operating mode you want to use for the 5 GHz
network.
4. If you selected Client Bridge Mode or Client Router Mode in step 3, click a radio under Please
choose which Radio is Enabled. If you selected Access Point Mode in step 3, both radios are selected
automatically and cannot be changed because both bands can work at the same time.
5. Click Apply.

5.2 Wireless Settings
The ENH700EXT’s wireless settings are located in the Wireless section of the left pane.
5.2.1 Access Point Mode (Dual Mode)
The ENH700EXT contains both 2.4 GHz 802.11a and 5 GHz 802.11b/g radios, allowing it to support
simultaneous 2.4 GHz 11b/g/n and 5 GHz 11a/n wireless connections when configured for Access
Point Mode. In this mode, users with a wireless client device within range can connect to the
ENH700EXT to access the WLAN. Simultaneous transmission on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radios allows the
best throughput for bandwidth-intensive applications like voice, video, and gaming. The following
figure shows an example of an ENH700EXT operating in Access Point Dual Mode.
The sections that follow the figure below describe how to configure your ENH700EXT as a Dual Mode
Access Point.

Radio
Click the radio button to enable or disable wireless functions.
Enable SSID#
ESSID
5G Wireless Settings
Band
Channel
Data Rate
Auto Channel
The ENH700EXT supports four SSIDs. Each SSID can be configured to use a different
VLAN tag.
ESSID is the name of your wireless network (WLAN). In an area where more than one
WLAN is present, using a different ESSID allows you to separate the traffic. Any
device you want to participate in a particular WLAN must use the same ESSID. The
default ESSID is EnGenius. After specifying each ESSID, specify the VLAN ID for each
ESSID.
Select the IEEE 802.11 standard operating in your network environment.
You could select a channel you want.
Shows the available transmit data rate of the WLAN. The data rate affects
throughput. If you select a low data rate value, for example, the throughput is
reduced but the transmission distance increases.
By default, this option is disabled. If you click Enable, the ENH700EXT searches all
valid channels, then decides which channel is “cleanest” for transmissions and
change to that channel automatically.
2.4G Wireless Settings
Band
Channel
Select the IEEE 802.11 standard operating in your network environment.
You could select a channel you want.

Data Rate
Shows the available transmit data rate of the WLAN. The data rate affects
throughput. If you select a low data rate value, for example, the throughput is
reduced but the transmission distance increases.
Auto Channel
Apply / Cancel
By default, this option is disabled. If you click Enable, the ENH700EXT searches all
valid channels, then decides which channel is “cleanest” for transmissions and
change to that channel automatically.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
Note: Both 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz bands use the same SSID.

5.2.2 Access Point Mode (5 GHz)
Radio
Enable SSID#
ESSID
5G Wireless Settings
Band
Channel
Data Rate
Auto Channel
Select the appropriate radio button to enable or disable the ENH700EXT’s wireless
functions.
The ENH700EXT supports four SSIDs. Each SSID can be configured to use a different
VLAN tag.
ESSID is the name of your WLAN. In an area where more than one WLAN is present,
using a different ESSID allows you to separate the traffic. Any device you want to
participate in a particular WLAN must use the same ESSID. The default ESSID is
EnGenius. After specifying each ESSID, specify the VLAN ID for each ESSID.
Select the IEEE 802.11 standard operating in your network environment.
You could select a channel you want.
Shows the available transmit data rate of the WLAN. The data rate affects
throughput. If you select a low data rate value, for example, the throughput is
reduced but the transmission distance increases.
By default, this option is disabled. If you click Enable, the ENH700EXT searches all
valid channels, then decides which channel is “cleanest” for transmissions and
change to that channel automatically.
Apply / Cancel
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
Note: If you do not have experience setting data rates, do not change the default setting.

5.2.3 Access Point Mode (2.4 GHz)
Radio
Enable SSID#
ESSID
2.4G Wireless Settings
Band
Channel
Data Rate
Auto Channel
Select the appropriate radio button to enable or disable the ENH700EXT’s wireless
functions.
The ENH700EXT supports four SSIDs. Each SSID can be configured to use a different
VLAN tag.
ESSID is the name of your WLAN. In an area where more than one WLAN is present,
using a different ESSID allows you to separate the traffic. Any device you want to
participate in a particular WLAN must use the same ESSID. The default ESSID is
EnGenius. After specifying each E SSID, specify the VLAN ID for each ESSID.
Select the IEEE 802.11 standard operating in your network environment.
You could select a channel you want.
Shows the available transmit data rate of the WLAN. The data rate affects
throughput. If you select a low data rate value, for example, the throughput is
reduced but the transmission distance increases.
By default, this option is disabled. If you click Enable, the ENH700EXT searches all
valid channels, then decides which channel is “cleanest” for transmissions and
change to that channel automatically.
Apply / Cancel
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
Note: If you do not have experience setting data rates, do not change the default setting.

5.2.4 Client Bridge Mode/Client Router Mode (Dual Mode)
Client Bridge Mode/ Client Router Mode lets you connect two LAN segments via a wireless link as
though they are on the same physical network. Since the computers are on the same subnet,
broadcasts will reach all machines. As a result, DHCP information generated by the server will reach
all client computers as though the clients resided on one physical network.
The following figure shows an example of two ENH700EXT devices operating in Client Bridge Mode.
One ENH700EXT uses its 2.4 GHz radio to communicate with a 2.4 GHz Access Point, while the other
ENH700EXT uses its 5 GHz radio to communicate with a 5 GHz Access Point.
The sections that follow the figure below describe how to configure your ENH700EXT for Client
Bridge Mode.

ESSID
Preferred BSSID
5G Wireless Setting
2.4G Wireless Setting
Apply / Cancel
Specify the Access Point SSID if known. Otherwise, use Site Survey to scan for nearby
Access Points (see page 35).
Specify the MAC address of the Access Point with which you want to associate.
Click this radio button to use the 5 GHz network as your default WLAN.
Click this radio button to use the 2.4 GHz network as your default WLAN.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
Note: In Client Bridge Mode, the ENH700EXT cannot operate in 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz networks at the
same time.
5.2.5 Client Bridge Mode/Client Router Mode (5 GHz)

ESSID
Specify the Access Point SSID if known. Otherwise, use Site Survey to scan for nearby
Access Points (see page 35).
Preferred BSSID
5G Wireless Setting
Apply / Cancel
Specify the MAC address of the Access Point with which you want to associate.
Select a standard IEEE 802.11a wireless band you want to use on the 5 GHz network.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
5.2.6 Client Bridge Mode/Client Router Mode (2.4 GHz)
ESSID
Preferred BSSID
2.4G Wireless Setting
Apply / Cancel
Specify the Access Point SSID if known. Otherwise, use Site Survey to scan for nearby
Access Points (see page 35).
Specify the MAC address of the Access Point with which you want to associate.
Select a standard IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g wireless band.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.

5.2.7 WDS Bridge Mode
The Management > Operation Mode page has a 5G section that lets you configure the ENH700EXT
for WDS Bridge Mode.
Please Choose the
Operation Mode (5G)
Apply / Cancel
Select WDS Bridge Mode to configure the ENH200 for WDS Bridge Mode.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.

In the next screen, manually enter static IP addresses for the two devices. This mode requires the
ENH700EXT’s DHCP server to be turned off, as noted in the table below. This is the default setting. If
you change it, please turn off DHCP Server for WDS Bridge Mode.
IP Address
IP Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
802.1d Spanning Tree
DHCP Server
DHCP Server
Lease Time
Start IP
End IP
Specify the IP address of the ENH700EXT LAN port.
Specify the subnet mask of the ENH700EXT LAN port.
Specify the default gateway of the ENH700EXT LAN port.
Enable or disable Spanning Tree. It is disabled by default
Disable the DHCP server to prevent automatic allocation of IP addresses to LAN
client PCs. Then configure your PC’s local IP address to access the Web Configurator.
Specify the amount of time a DHCP network user is allowed connection to the
ENH700EXT with their current dynamic IP address.
Specify the starting IP address range for the pool of allocated for private IP
addresses. The starting IP address must be on the same subnet as the ending IP
address; that is the first three octets specified here must be the same as the first
three octets in End IP.
Specify the ending IP address range for the pool of allocated for private IP addresses.
The ending IP address must be on the same subnet as the starting IP address; that is
the first three octets specified here must be the same as the first three octets in
Start IP.
Domain Name
Apply / Cancel
Specify the domain name of the ENH700EXT’s private LAN settings.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.

Go to the Management > Status page. Under 5GHz WDS, find the Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID)
or MAC address of the devices you want to bridge together.
BSSID (WLAN MAC
address)
MAC address of the devices you want to bridge together. Record the value below:
Record BSSID here: ___________________________________________
Go to the 5GHz Wireless > WDS Link page and configure desired 5GHz wireless channel/frequency.
Channels
Data rates
Select the desired 5 GHz channel/frequency. All devices on the WDS network has to
has matching channels.
Accept the Auto default to have the bridged devices connect and exchange data at
an automatically agreed-to data rate. Or you can select a specific speed, so long as
the other bridged device(s) can communicate at that speed.
WDS Bridges
Apply / Cancel
Enter the WDS link partner’s 5GHz BSSID (MAC address) that you recorded on above.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.

5.4 5.3 Site Survey
Use this feature to scan nearby Access Points.
No
Select
Channel
SSID
BSSID
Encryption
Signal(dBm)
Refresh
Connect
Numbers of Access Points that the site survey has discovered.
Click the radio button that corresponds to the Access Point with which you want to
associate.
Channel that the Access Point is using.
SSID that the Access Point is broadcasting.
Access Point’s wireless MAC address.
Encryption method that the Access Point is using to secure data over the WLAN.
Signal strength from the Access Point to your station.
Click Refresh to rescan nearby Access Points.
Click Connect to process the connection.
Note: If you select 5 GHz as your default WLAN, you cannot scan Access Points operating in the 2.4
GHz band.

AP Scan List (5 GHz / 2.4 GHz)
This feature can help you select an Access Point channel by scanning nearby Access Points.
Refresh
Click Refresh to rescan nearby Access Points.

5.5 Wireless Security Settings
The Wireless Security Settings section lets you configure the ENH700EXT’s security settings. We
strongly recommend you use WPA2-PSK AES for your security settings.
5.5.1 WEP (Access Point)
ESSID Selection
Hidden SSID
WMM
Encryption
Authentication Type
The ENH700EXT supports four SSIDs. Each SSID can be configured to use a different
type of authentication.
Select Enable or Disable to broadcast or not broadcast the ENH700EXT’s SSID. Users
cannot reconnect automatically or manually to a WLAN that uses a hidden SSID. A
WLAN that uses a hidden SSID does not appear in the Microsoft Windows Wireless
Network Connection window.
Select Enable or Disable to enable or disable the ENH700EXT’s WMM functions.
WMM is based on the four access categories: voice, video, best effort, and
background, which are used to prioritize traffic so these applications have access to
the necessary network resources. WMM does not guarantee transmission speed.
Select WEP from the drop-down list to display the configuration options.
Select Open System or Shared Key as your authentication type.
•
Open System = no authentication. Any client, regardless of its WEP keys, can

authenticate itself with the Access Point and then try to associate with it.
•
Shared Key = all wireless stations share the same secret key.
Key Length
Key Type
Default Key
Key1
Key2
Key3
Key4
Apply / Cancel
Level of WEP encryption applied to all WEP keys. Choices are 64-bit and 128-bit.
Select an input type of either Hex or ASCII.
Specify which of the four WEP keys the ENH700EXT uses as its default.
Specify a password for security key index number 1. For security, each typed
character is masked by a dot (●).
Specify a password for security key index number 2. For security, each typed
character is masked by a dot (●).
Specify a password for security key index number 3. For security, each typed
character is masked by a dot (●).
Specify a password for security key index number 4. For security, each typed
character is masked by a dot (●).
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
5.5.2 WEP (Client Bridge / Client Router)
Network Name (SSID)
Encryption
Authentication Type
Specify the Access Point SSID with which you want to associate.
Select WEP from the drop-down list to display the configuration options.
Select Open System or Shared Key as your authentication type.
•
Open System = no authentication. Any client, regardless of its WEP keys, can

authenticate itself with the Access Point and then try to associate with it.
•
Shared Key = all wireless stations share the same secret key.
Key Length
Key Type
Default Key
Key1
Key2
Key3
Key4
Apply
Level of WEP encryption applied to all WEP keys. Choices are 64-bit and 128-bit.
Select an input type of either Hex or ASCII.
Specify which of the four WEP keys the ENH700EXT uses as its default.
Specify a password for security key index number 1.
Specify a password for security key index number 2.
Specify a password for security key index number 3.
Specify a password for security key index number 4.
Click Apply to apply the changes.
5.5.3 WPA pre-shared Key (Access Point)
ESSID Selection
Hidden SSID
WMM
Encryption
WPA Type
The ENH700EXT supports four SSIDs. Each SSID can be configured to use a different
type of authentication.
Select Enable or Disable to broadcast or not broadcast the ENH700EXT’s SSID. Users
cannot reconnect automatically or manually to a WLAN that uses a hidden SSID. A
WLAN that uses a hidden SSID does not appear in the Microsoft Windows Wireless
Network Connection window.
Select Enable or Disable to enable or disable the ENH700EXT’s WMM functions.
WMM is based on the four access categories: voice, video, best effort, and
background, which are used to prioritize traffic so these applications have access to
the necessary network resources. WMM does not guarantee transmission speed.
Select WPA pre-shared Key from the drop-down list to display the configuration
options.
Select WPA(TKIP), WPA2(AES), or WPA2 Mixed as your authentication type.

•
TKIP = automatic encryption with WPA-PSK; requires pre-shared key.
•
AES = automatic encryption with WPA2-PSK; requires pre-shared key.
•
WPA2 Mixed = uses both TKIP and AES cipher types; requires a pre-shared key.
Pre-shared Key Type
Pre-shared Key
Apply / Cancel
Select Passphrase or Hex (64 characters) that can be used to automatically generate
security keys.
Shared secret between the ENH700EXT and Access Points and wireless clients. You
cannot type special characters in the pre-shared key.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
5.5.4 WPA pre-shared Key (Client Bridge / Client Router)
Network Name (SSID)
Encryption
WPA Type
Pre-shared Key Type
Pre-shared Key
Apply
Specify the Access Point’s SSID which you want to associate.
Select WPA pre-shared key from the drop-down list to display the configuration
options.
Select WPA(TKIP) or WPA2(AES) as your authentication type.
•
TKIP = automatic encryption with WPA-PSK; requires pre-shared key.
•
AES = automatic encryption with WPA2-PSK; requires pre-shared key.
Select Passphrase or Hex (64 characters) that can be used to automatically generate
security keys.
Shared secret between the ENH700EXT and Access Points and wireless clients. You
cannot type special characters in the pre-shared key.
Press Apply to save the changes.

5.5.5 RADIUS (Access Point Mode Only)
Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) authentication is only available when the
ENH700EXT is configured for Access Point Mode. Use this feature if you have a RADIUS server.
WPA(TKIP), WPA2(AES), and WPA2 Mixed encryption types are also supported.
The following figure shows an example of a RADIUS configuration, where two ENH700EXT devices
installed at different locations communicate with each other wirelessly. In this configuration, one
ENH700EXT is configured for Access Point Mode and connected to a RADIUS server via a switch,
while the other ENH700EXT is configured for Client Bridge Mode. The RADIUS server uses an
authentication scheme such as PAP or CHAP to verify a user's identification, along with, optionally,
other information related to the request, such as the user's network address or phone number,
account status and specific network service access privileges. The RADIUS server then returns one of
three responses to the ENH700EXT : Access Reject (user is denied access to all requested network
resources), Access Challenge (requests additional information from the user such as a secondary
password), PIN, token or card), or Access Accept (user is granted access).
The sections that follow the figure below describe how to configure your ENH700EXT for use in a
RADIUS environment.

ESSID Selection
Hidden SSID
WMM
Encryption
WPA Type
The ENH700EXT supports four SSIDs. Each SSID can be configured to use a different
type of authentication.
Select Enable or Disable to broadcast or not broadcast the ENH700EXT’s SSID. Users
cannot reconnect automatically or manually to a WLAN that uses a hidden SSID. A
WLAN that uses a hidden SSID does not appear in the Microsoft Windows Wireless
Network Connection window.
Select Enable or Disable to enable or disable the ENH700EXT’s WMM functions.
WMM is based on the four access categories: voice, video, best effort, and
background, which are used to prioritize traffic so these applications have access to
the necessary network resources. WMM does not guarantee transmission speed.
Select WPA RADIUS from the drop-down list to display the configuration options.
Select WPA(TKIP), WPA2(AES), or WPA2 Mixed as your authentication type.
•
TKIP = automatic encryption with WPA-PSK; requires pre-shared key.
•
AES = automatic encryption with WPA2-PSK; requires pre-shared key.
•
WPA2 Mixed = uses both TKIP and AES cipher types; requires a pre-shared key.
RADIUS Server IP Address
RADIUS Server Port
RADIUS Server Password
Apply / Cancel
Specify your RADIUS server’s IP address.
Specify the port number that your RADIUS server uses for authentication.
Specify the password used to negotiate the authentication between the ENH700EXT
and the RADIUS server. For security, each typed character is masked by a dot (●).
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.

5.6 Wireless Advanced Settings
If you do not have experience with configuring advanced wireless settings, leave these options at
their default settings. Otherwise, any changes you make can affect performance adversely.
5.6.1 Advanced Settings (Access Point)
Fragment Threshold
RTS Threshold
Beacon Interval
Specify the maximum packet size during transmission. If a large number of clients are
accessing the WLAN, specify a small value to avoid collisions.
RTS threshold is a trigger to engage the exchange of RTS and CTS messages between
the Access Point and client. The trigger is a type of “handshaking” approach that
provides an additional layer of control over the use of the shared medium by
indicating the amount of time a wireless device, attempting to send, will wait for a
recipient to acknowledge that it is ready. If the packet size is smaller than the RTS
threshold, the wireless router will not use the RTS/CTS mechanism to send the
packet. To ensure communication, use the maximum value. Decreasing this value
causes the sending device to discard the current packet and move on to the next.
Specify the duration between beacon packets. Access Points broadcast Beacons or
Traffic Indication Messages (TIM) to synchronize WLANs. The default setting of 100
should be fine for most situations. In a "noisy" environment with much interference,
decreasing this value can improve network performance. In very remote locations
(with few wireless nodes), you can increase this value.
DTIM Period
Specify a value between 1 and 255 for the Delivery Traffic Indication Message

(DTIM). A DTIM is a countdown that informs clients about the next window for
listening to broadcast and multicast messages. The default value is 1.
Note: The DTIM is a multiple of the Beacon (TIM), so if the DTIM is set to 3, a DTIM
message is sent with every third Beacon.
Preamble Type
Tx Power
Distance
Layer 2 Isolation
Tells the receiver that data is on the way. The preamble allows the receiver to
acquire the wireless signal and synchronize itself with the transmitter. Select Long
Preamble or Short Preamble. Long Preamble can provide better wireless LAN
compatibility with legacy devices, while Short Preamble can provide better WLAN
performance.
Auto Transmitted Power
Specify the distance between Access Points and clients. Longer distances may drop
high-speed connections.
Enable or disable Layer 2 Isolation. Layer 2 isolation prevents communication and
data sharing between wireless stations associated with different Access Points.
5.6.2 Advanced Settings (Client Bridge / Client Router)
Fragment Threshold
RTS Threshold
Specify the maximum packet size during transmission. If a large number of clients are
accessing the WLAN, specify a small value to avoid collisions.
RTS threshold is a trigger to engage the exchange of RTS and CTS messages between
the Access Point and client. The trigger is a type of “handshaking” approach that
provides an additional layer of control over the use of the shared medium by
indicating the amount of time a wireless device, attempting to send, will wait for a
recipient to acknowledge that it is ready. If the packet size is smaller than the RTS
threshold, the wireless router will not use the RTS/CTS mechanism to send the
packet. To ensure communication, use the maximum value. Decreasing this value

causes the sending device to discard the current packet and move on to the next.
Preamble Type
802.11g Protection
Tx Power
Distance
Tells the receiver that data is on the way. The preamble allows the receiver to
acquire the wireless signal and synchronize itself with the transmitter. Select Long
Preamble or Short Preamble. Long Preamble can provide better wireless LAN
compatibility with legacy devices, while Short Preamble can provide better WLAN
performance.
If you enable protection mode, every transmitted packet must wait until CTS is
received before it can be sent. Protection mode can prevent collision, but slows
wireless transmission speeds.
Auto Transmitted Power
Specify the distance between Access Points and clients. Longer distances may drop
high-speed connections.
5.7 Wireless Access Control List
Use the Wireless Access Control List provide or deny network access to wireless clients according to
their MAC addresses.
Enable Wireless Access
Control
Description
Place a Check to enable Wireless Access Control.
Enter a description for the MAC address you want to add.
MAC Address
Add
Reset
MAC Address Filtering
Table
Delete Selected
Specify the MAC address.
Click Add to add the MAC address.
Click Reset to discard your entries.
Check all the conditions you added.
Check an option below the Select column and click Delete Selected to delete the

option.
Delete All
Reset
Apply / Cancel
Click Delete All to erase all options in the table.
Click Reset to discard your selection.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.

Chapter 6 LAN Setup
This chapter describes the ENH700EXT Local Area Network (LAN) settings.
6.1 LAN Settings
Note: Changing LAN IP address changes the LAN Interface IP address. When you click Apply, the Web
Configurator automatically redirects you to the new IP address .
LAN IP
IP Address
IP Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
802.1d Spanning Tree
DHCP Server
DHCP Server
Lease Time
Start IP
Specify the IP address of the ENH700EXT LAN port.
Specify the subnet mask of the ENH700EXT LAN port.
Specify the default gateway of the ENH700EXT LAN port.
Enable or disable Spanning Tree.
Enable or disable the DHCP server to allow automatic allocation of IP addresses to
LAN client PCs. If you disable DHCP Server, you must configure your PC’s local IP
address to access the Web Configurator.
Specify the amount of time a DHCP network user is allowed connection to the
ENH700EXT with their current dynamic IP address.
Specify the starting IP address range for the pool of allocated for private IP
addresses. The starting IP address must be on the same subnet as the ending IP

address; that is the first three octets specified here must be the same as the first
three octets in End IP.
End IP
Domain Name
Apply / Cancel
Specify the ending IP address range for the pool of allocated for private IP addresses.
The ending IP address must be on the same subnet as the starting IP address; that is
the first three octets specified here must be the same as the first three octets in
Start IP.
Specify the domain name of the ENH700EXT’s private LAN settings.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
6.2 DHCP Info
Click on DHCP Info under the TCP/IP section to view clients associated with the ENH700EXT via DHCP.
You can also assign an IP address for certain MAC addresses. The IP Address, MAC Address, and
Expiration Time for each IP address are displayed. Click the Refresh button to update the client list.
Enable Static DHCP IP
IP Address
MAC Address
Add
Reset
Current Static DHCP Table
Check Enable Static DHCP IP.
Specify the IP address of the MAC address you want to add.
Specify the MAC address.
Click Add to add the MAC address.
Click Reset to discard your changes.
View your selections.

Delete Selected
Check an option below the Select column and click Delete Selected to delete the
option.
Delete All
Reset
Apply / Cancel
6.3 SNMP Settings
Click Delete All to erase all options in the table.
Click Reset to discard your selection.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
SNMP Enable
SNMP Disable
Apply / Cancel
Click this radio button to enable the ENH700EXT’s SNMP feature.
Click this radio button to disable the ENH700EXT’s SNMP feature.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.

Chapter 7 Internet Settings
This chapter describes the ENH700EXT’s Internet settings.
7.1 DHCP (Dynamic IP)
To obtain an IP address for the ENH700EXT automatically, select Dynamic IP for your WAN connection.
As part of this procedure, you will need to enter a host name
Hostname
Apply / Cancel
Specify the host name furnished by your Internet Service Provider.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
7.2 Static IP
If your ISP provided you with an IP address, subnet mask, default ENH700EXT, and primary DNS and
secondary DNS to use, select Static IP for your WAN connection.
IP Address
IP Subnet Mask
ENH700EXT IP Address
Primary DNS
Secondary DNS
Specify the IP address of the ENH700EXT’s WAN settings.
Specify the subnet mask of the ENH700EXT’s WAN settings.
Specify the ENH700EXT’s WAN IP address.
Specify the static IP address of the primary DNS server.
Specify the static IP address of the secondary DNS server.

Apply / Cancel
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
7.3 PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet)
Select Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) if your ISP uses a PPPoE connection. Your ISP
will provide you with a username and password. This option is typically used for DSL services.
Remove your PPPoE software from your computer, as it is not needed and will not work with your
ENH700EXT.
Login
Password
Service Name
MTU
Authentication Type
Type
Specify the user name supplied by your ISP.
Specify the password supplied by your ISP.
Specify the service name supplied by your ISP.
Specify the Maximum Transmit Unit size. It is recommended you accept the default
setting of Auto. Otherwise, packets will be fragmented downstream if the MTU is set
too high or too low, which impacts network performance. In extreme cases, an MTU
setting that is too low can prevent the ENH700EXT from establishing some
connections.
Select the algorithm used for authentication. Choices are PAP, CHAP, or Auto.
Default is Auto.
Select a connection type from the drop-down menu. Choices are:
•
Keep Connection = device connects to the Internet automatically.
•
Automatic Connection = device connects to the Internet automatically when the
traffic goes through the Internet and disconnects after a period of idle time
elapses.
Idle Timeout
•
Manual Connection = device connects to the Internet manually.
If the ENH700EXT is configured for Automatic Connection, specify the maximum

amount of time the device can remain idle before disconnecting.
Apply / Cancel
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
7.4 PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
Select PPTP as your WAN connection type if your ISP uses a Point-to-Point-Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
connection. There are two WAN interface types you can select: Dynamic IP Address and Static IP
address. Select Static if your ISP assigned you the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS server
addresses. In most cases, select Dynamic.
Dynamic IP Address
WAN Interface Type
Hostname
Static IP Address
WAN Interface Type
IP Address
IP Subnet Mask
ENH700EXT IP Address
Select Dynamic IP Address as your WAN Interface.
Specify the Hostname is given by your Internet Service Provider.
Select Static IP Address as your WAN Interface.
Specify the static IP address for the ENH700EXT WAN Interface.
Specify the WAN subnet mask.
Specify the ENH700EXT WAN IP address.

Login
Password
Service IP Address
Connection ID
MTU
Type
Specify the user name supplied by your ISP.
Specify the password supplied by your ISP.
Specify the service IP address supplied by your ISP.
Specify the connection ID supplied by your ISP.
Specify the Maximum Transmit Unit size. It is recommended you accept the default
setting of Auto. Otherwise, packets will be fragmented downstream if the MTU is set
too high or too low, which impacts network performance. In extreme cases, an MTU
setting that is too low can prevent the ENH700EXT from establishing some
connections.
Select a connection type from the drop-down menu. Choices are:
•
Keep Connection = device connects to the Internet automatically.
•
Automatic Connection = device connects to the Internet automatically when the
traffic goes through the Internet and disconnects after a period of idle time
elapses.
•
Manual Connection = device connects to the Internet manually.
Idle Timeout
Enable PPTP pass through
on VPN Connection
Enable IPSec pass through
on VPN Connection
Enable L2TP pass through
on VPN Connection
Apply / Cancel
If the ENH700EXT is configured for Automatic Connection, specify the maximum
amount of time the device can remain idle before disconnecting.
Check PPTP pass through on VPN Connection. Otherwise, the ENH700EXT will not
be able to connect to the Internet via PPTP.
Check IPSec pass through on VPN Connection. Otherwise, the ENH700EXT will not
be able to transmit data using the IPSec protocol.
Check L2TP pass through on VPN Connection. Otherwise, the ENH700EXT will not be
able to connect to the Internet using L2TP.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the

previous settings.
Chapter 8 Information Status
Use the Status section to check device information such as system up time, firmware version,
wireless client list, and Internet status.
8.1 Status
Click Status under the Management section to display sections that show various information about
the device. For example, the:
- System section shows current time, hardware version, kernel version, and application version.
- LAN Settings section shows the LAN IP address, subnet mask, DHCP status, and MAC address.
- Wireless Information section shows basic Access Point, client bridge, and client router settings.

8.2 Wireless Client List
Click Client List under the 5G/2.4G Wireless section to view a list of clients associated with the
ENH700EXT. The MAC addresses, signal strength, and Idle Time for each client are displayed. Click
the Refresh button to update the client list.
8.3 System Log
The ENH700EXT automatically logs (records) events of possible interest in memory. To view the log
entries, click Log under the Management section. If there is not enough internal memory for all
events, logs of older events are deleted, but logs of the latest events are retained. Buttons below the
log entries let you save your current system operation information to a text file, clear all logs, or
refresh the information shown.

8.4 Internet Status
Click Status under the Internet section to view the status of the current network connection.
Information shown includes the network type, SSID, BSSID, connection status, wireless mode,
current channel, security, data rate, noise level, and signal strength.
Note: If your internet connection type is PPPoE or PPTP with Manual Connection, you can connect to
he Internet from this page.

Chapter 9 Management Settings
The Management section on the navigation drop-down menu can help you manage your device and
adjust system settings such as password, time zone, diagnosis, remote control, upgrade firmware,
and save/load settings. Each option is described below.
9.1 Password Settings
Click Password under the Management section to change the password you specify to access the
ENH700EXT Web Configurator. The default password is admin. For security reasons it is highly
recommended that you create a new password.
Old Password
New Password
Repeat New Password
Apply / Cancel
Enter the current password.
Specify a new password for login.
Re-enter the new password for confirmation.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
9.2 Time Zone Settings
Click Time Zone under the Management menu to configure the ENH700EXT system time. Using
these settings, you can synchronize the ENH700EXT system time with a Network Time Protocol (NTP)
server.

Time Zone
Select your country or region from the drop-down list.
NTP Time Server
Daylight Saving
Apply / Cancel
Specify the domain name or IP address of a NTP server.
Check Enable if your area observes daylight savings time . Then specify the starting
(From) and ending (To) range when daylight savings time is observed.
Click Apply to apply the changes or Cancel to discard your changes and return to the
previous settings.
9.3 Diagnosis
If you encounter connectivity problems, click Diagnostics under the Management menu to
troubleshoot the connection and trace the routing to a target.
Address to Ping
Start
Count
Ping Result
Enter the IP address you would like to Ping.
Click Start to begin.
Specify numbers of times the IP address is to be pinged.
Displays ping results.

9.4 Remote Control
Host Address
Specify the IP address you want to use as your remote controller.
Port
Enable
Apply/Reset
Specify the port number.
Check Enable to enable remote management.
Click Apply to save the changes or Reset to discard your changes.
9.5 Upgrade Firmware
Click Upgrade Firmware under the Management menu to upgrade the ENH700EXT firmware. To
perform this procedure, downloaded the appropriate firmware from your vendor.
Note: The firmware upgrade procedure can take few minutes. Do not power off the ENH700EXT
during the firmware upgrade, as it can cause the device to crash or become unusable. The
ENH700EXT restarts automatically after the upgrade completes.
9.6 Save/Reload Settings
Click Save/Reload Setting under the Management menu to save the current settings of the device in
a file to your local disk or load settings to the device from your local disk. This feature is handy for
administrators who have several devices that need to be configured with the same settings.

Restore to Factory
Default Settings
Click the Reset button to reset all the settings to the default values.
Backup Settings
Restore Settings
Restart
Click Save to save current configured settings.
The ENH700EXT can store a previous setting that has been saved. Click Browse to
select the file and Upload.
Click Restart to reboot the ENH700EXT.
Note: If you choose to Restore to Factory Default, all custom settings that override the default
settings will be erased. We recommend you save your current settings before your proceed.

Appendix A – Glossary
Access Point
A base station in a WLAN that act as a central transmitter and receiver of WLAN radio signals.
Ad Hoc Network
Ad hoc network refers to a short-term WLAN framework created between two or more WLAN
adapters, without going through an Access Point. An ad hoc network allows computers to "talk"
(send data) directly to and from one another. For an ad hoc network to work, each computer on the
network needs a WLAN card installed configured for Ad Hoc mode.
Antenna
A device that transmits and receives radio-frequency (RF) signals. Often camouflaged on existing
buildings, trees, water towers or other tall structures, the size and shape of antennas are generally
determined by the frequency of the signal they manage.
Authentication
A process that verifies the identity of a wireless device or end-user. One of the most common
forms of authentication is to verify identities by checking a user name and password to allow
network access.
Backbone
A high-speed line or series of connections forming a major pathway within a network.
Bandwidth
The portion of the frequency spectrum required to transmit desired information. Each radio
channel has a center frequency and additional frequencies above and below this carrier
frequency which is used to carry the transmitted information. The range of frequencies from the
lowest to the highest used is called the bandwidth.
Bridge
A wireless device that connects multiple networks that are physically separate or use different
media, but which use similar standards.
Bridge Mode
An Access Pointy in bridge mode can operate as a WLAN bridge that connects two wired network
segments. The peer device also must be in bridge mode. This wireless bridge connection is
equivalent to a Wireless Distribution System (WDS).
CHAP
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol is an alternative protocol that avoids sending
passwords over the wire by using a challenge/response technique.
Collision
Interference that occurs when two network devices transmit data at the same time. The network
detects the collision of the two transmitted packets and discards both of them.

Coverage
The region within which a paging receiver can receive reliably the transmission of the paging
signals.
Coverage Area
The geographical reach of a mobile communications network or system.
Coverage Hole
An area within the radio coverage footprint of a wireless system in which the RF signal level is
below the design threshold. Coverage holes are usually caused by physical obstructions such as
buildings, foliage, hills, tunnels, and indoor parking garages.
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
A common technique for detecting data transmission errors.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
A protocol that automatically assigns temporary IP addresses to client stations logging onto an IP
network, so users do not have to configure the IP addresses manually. The ENH700EXT contains
an internal DHCP server that automatically allocates IP address using a user-defined address
range.
Dead Spot
An area within the coverage area of a WLAN in which there is no coverage or transmission falling
off. Dead spots are often caused by electronic interference or physical barriers such as hills,
tunnels, and indoor parking garages. See also coverage area.
802.11
A category of WLAN standards defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
(IEEE).
802.11a
An IEEE standard for WLANs that operate at 5 GHz, with rates up to 54 Mbps.
802.11b
An IEEE standard for WLANs that operate at 2.4 GHz, with rates up to 11 Mbps.
802.11g
An IEEE standard for WLANs that operates at 2.4 GHz with rates up to 54 Mbps.
Encryption
The translation of data into a secret code. Encryption is the most effective way to achieve data
security. To read an encrypted file, you must have access to a secret key or password that enables
you to decrypt it. Unencrypted data is called plain text ; encrypted data is referred to as cipher text
ESS ID
An ESSID is the unique identifier for an ESS. All Access Points and their associated wireless
stations in the same group must have the same ESSID.
Footprint
Geographical areas in which an entity is licensed to broadcast its signal.
Gateway
A computer system or other device that acts as a translator between two systems that do not use
the same communication protocols, data formatting structures, languages and/or architecture.

Keys
Keys are used like passwords to open and close (encrypt and decrypt) messages. While many
encryption algorithms are commonly known and public, the key must be kept secret.
Local-Area Network (LAN)
A small data network covering a limited area, such as a building or group of buildings. Most LANs
connect workstations or personal computers. This allows many users to share devices, such as
printers, as well as data. The LAN also allows easy communication, by facilitating e-mail or
supporting chat sessions.
Media Access Control (MAC) Address
The address associated with every hardware device on the network. Every 802.11 wireless device
has its own specific MAC address hard-coded into it. This unique identifier can be used to provide
security for WLANs. When a network uses a MAC table, only the 802.11 radios that have had
their MAC addresses added to that network's MAC table are able to get onto the network.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
An Internet standard that enables a LAN to use one set of IP addresses for internal traffic and a
second set of addresses for external traffic.
Network Time Protocol (NTP)
A protocol that allows devices to synchronize their time with a time server. It uses TCP or UDP
port 123 by default
Passphrase
A text string used to automatically generate WEP keys on wireless client adapters.
Power Over Ethernet (PoE)
The ability to provide power to a PoE-enabled device via an 8-pin CAT 5 Ethernet cable,
eliminating the need for a nearby power source.
Preamble
Used to synchronize transmissions in a WLAN. The preamble type defines the length of the Cyclic
Redundancy Check block for communication between the device and roaming wireless stations.
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP)
An authentication protocol of IEEE 802.1x used to transmit authentication data, including
passwords, over 802.11 WLANs.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Refers to a network’s ability to deliver data with minimum delay, and to the networking methods
used to provide bandwidth for real-time multimedia applications.
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS)
A networking protocol that provides centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting
management for computers to connect and use a network service. Because of the broad support
and the ubiquitous nature of the RADIUS protocol, it is often used by ISPs and enterprises to
manage access to the Internet or internal networks, WLANs, and integrated e-mail services.
Service Set Identifier (SSID)
The name of a WLAN. All wireless devices on a WLAN must use the same SSID in order to
communicate with each other.

Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
SNMP is an Internet-standard protocol for managing devices on IP networks.
Snooping
Passively watching a network for data that can be used to benefit a hacker, such as passwords.
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
An encryption protocol that uses 128-bit keys that are dynamically generated and distributed by
the authentication server. TKIP regularly changes and rotates the encryption keys so that the
same encryption key is never used twice.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
A protocol permitting communications over and between networks. The TCP/IP protocol is the
basis for Internet communications.
Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ)
WFQ services queues based on their priority and queue weight. Queues with larger weights get
more service than queues with smaller weights. This queuing mechanism is highly efficient in that
it divides any available bandwidth across the different traffic queues. See also Queuing
Algorithms.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
A security protocol that provides a WLAN with a level of security and privacy comparable to what
is usually expected of a wired LAN. WEP encrypts data transmitted between wired and WLANs to
keep the transmission private.
Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN)
WLANs use RF technology to transmit and receive data wirelessly in a certain area. This allows
users in a small zone to transmit data and share resources, such as printers, without physically
connecting each computer with cables.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA )
A subset of the IEEE 802.11i standard. WPA applies IEEE 802.1x and Extensible Authentication
Protocol (EAP) to authenticate wireless clients using an external RADIUS database. WPA encrypts
data by using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), Message Integrity Check (MIC) and IEEE
802.1x. See also WPA-PSK (WPA -Pre-Shared Key).
Wi-Fi MultiMedia (WMM)
Part of the IEEE 802.11e QoS enhancement to the Wi-Fi standard that ensures quality of service
for multimedia applications in WLANs.
Wireless Client Supplicants
A wireless client supplicant is the software that runs on an operating system instructing the
wireless client how to use WPA.
WPA -Pre-Shared Key (WPA-PSK)
WPA-PSK requires a single (identical) password entered into each access point, wireless gateway
and wireless client. As long as the passwords match, a client will be granted access to a WLAN.
See also WPA.
WPA2
A wireless security standard that defines stronger encryption, authentication and key

management than WPA. It includes two data encryption algorithms, Temporal Key Integrity
Protocol (TKIP) and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in the Counter mode with Cipher block
chaining Message authentication Code Protocol (CCMP). See also WPA.
Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
A technology that enables access points to communicate with one another in order to extend the
range of a WLAN. WDS is appearing in 802.11g-based Access Points.

Appendix B – FCC Interference Statement
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the following
measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
For operation within 5.15 ~ 5.25GHz frequency range, it is restricted to indoor environment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 25cm
between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.

Professional installation instruction
1. Installation personal
This product is designed for specific application and needs to be installed by a
qualified personal who has RF and related rule knowledge. The general user shall
not attempt to install or change the setting.
2. Installation location
The product shall be installed at a location where the radiating antenna can be kept
25 cm from nearby person in normal operation condition to meet regulatory RF
exposure requirement.
3. External antenna,
Use only the antennas which have been approved by Seano. The non-approved
antenna(s) may produce unwanted spurious or excessive RF transmitting power
which may lead to the violation of FCC limit and is prohibited.
4. Installation procedure
Please refer to user’s manual for the detail.
5. Warning
Please carefully select the installation position and make sure that the final output
power does not exceed the limit set force in US Rule CFR 47 part 15 section 15.247 & 15.407. The
violation of the rule could lead to serious federal penalty.
 Loading...
Loading...