Page 1

IEEE 802.11a/b/g
Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter
User’s Manual
Version: 1.2
Page 2

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Table of Contents
1 INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................4
1.1 F
1.2 P
EATURES
ACKAGE CONTENTS ....................................................................................................5
1.3 USB A
1.4 S
1.5 A
1.6 N
YSTEM REQUIREMENTS ...............................................................................................5
PPLICATIONS ..............................................................................................................6
ETWORK CONFIGURATION ...........................................................................................7
DAPTER DESCRIPTION
& B
ENEFITS
.................................................................................................4
.........................................................................................5
2 INSTALL DRIVERS & CLIENT UTILITY .............................................................................9
2.1 B
2.2 I
EFORE YOU BEGIN ......................................................................................................9
NSTALLING THE DRIVERS
..............................................................................................9
3 USING THE CLIENT UTILITY ..........................................................................................15
3.1 C
3.2 P
URRENT STATUS
ROFILE MANAGEMENT ...............................................................................................16
......................................................................................................15
3.2.1 Scan for available networks..................................................................................17
3.2.2 Create a New Profile ............................................................................................18
3.2.3 Security................................................................................................................19
3.2.3.1 Security Disabled ......................................................................................... 19
3.2.3.2 WPA – TLS, TTLS........................................................................................ 19
3.2.3.3 WPA – PEAP (EAP-GTC) ............................................................................21
3.2.3.4 WPA – PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP-V2) ...............................................................23
3.2.3.5 WPA – LEAP ...............................................................................................25
3.2.3.6 WPA – Passphrase ......................................................................................27
3.2.3.7 802.1x – TLS, TTLS.....................................................................................28
3.2.3.8 802.1x – PEAP (EAP-GTC) ..........................................................................30
3.2.3.9 802.1x – PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP-V2).............................................................32
3.2.3.10 802.1x – LEAP .............................................................................................34
3.2.3.11 Pre-Shared Key (Static WEP).......................................................................36
3.2.4 Advanced Settings ...............................................................................................37
3.2.4.1 Infrastructure Settings ..................................................................................37
3.2.4.2 Ad Hoc Settings ...........................................................................................38
3.3 D
3.4 E
3.5 D
3.6 D
IAGNOSTICS ............................................................................................................. 39
NABLE
ISABLE TRAY ICON ....................................................................................................43
ISPLAY SETTINGS
ISABLE RADIO
/ D
............................................................................................ 41
.....................................................................................................43
4 UNINSTALL THE DRIVERS & CLIENT UTILITY .............................................................. 45
APPENDIX A – SPECIFICATIONS............................................................................................47
APPENDIX B – FCC INTERFERENCE STATEMENT ............................................................... 49
2
Page 3

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Revision History
Version Date Notes
1.0 June 20, 2005 Initial Version
1.1 Oct. 12, 2005 Utility Upgrading
1.2 Oct. 14, 2005 Spec Updating
3
Page 4
IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
1 Introduction
This is a wireless USB 2.0 adapter that supports dual-band 802.11a/b/g (2.4GHz &
5GHz) radio operation. It provides a high-speed wireless connection with data rate
up to 108Mbps.
To protect your wireless connectivity, the high-speed wireless USB adapter can
encrypt all wireless transmissions through 64/128/152-bit WEP data encryption and
also supports WPA. Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) puts your network on the
cleanest channel in your location. With the high-speed wireless USB adapter, you will
experience the best wireless connectivity available.
This chapter describes the features & benefits, package contents, applications, and
network configuration.
1.1 Features & Benefits
Features Benefits
High Speed Data Rate up to 108Mbps in
Super A/G mode
Capable of handling heavy data payloads
such as MPEG video streaming.
High Output Power up to 25 dBm
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES),
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and
Wired Equivalent Private (WEP)
IEEE802.1x Client Support
Support for draft IEEE 802.11h and j
standard
Support for 802.11e standard
Advanced Power Management
Support eXtended Range technology eXtended Range technology give Wi-Fi
More high power can advance the distance.
Powerful data security.
Enhances authentication and security.
Extended tuning range (2.300-2.500 &
4.900-5.850 GHz) for worldwide use
Dynamic Frequency Selection/Transmit
Power Control (DFS/TPC) for international
operation
Wireless Multimedia Enhancements Quality
of Service support (QoS)
Low power consumption in power saving
mode up to 98%.
products twice the range of existing
designs
4
Page 5

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
1.2 Package Contents
Open the package carefully, and make sure that none of the items listed below are
missing. Do not discard the packing materials, in case of return; the unit must be
shipped in its original package.
One Wireless LAN USB Adapter
One USB Cable
One CD-ROM with User’s Manual Included
1.3 USB Adapter Description
The USB adapter is a standard USB adapter that fits into any USB interface. The
USB adapter has a LED indicator and an external high-sensitivity dipole antenna.
High-sensitivity Dipole Antenna
USB port
LED Indicator:
Ad-hoc Mode: Solid Green, whether the
wireless is connected or not.
Infrastructure Mode: Solid green while
connected, and blinking during activity.
1.4 System Requirements
The following are the minimum system requirements in order to use the USB
adapter.
PC/AT compatible computer with a USB interface.
Windows 2000/XP operating system.
20 MB of free disk space for installing the USB adapter driver and utility
program.
5
Page 6

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
1.5 Applications
The wireless LAN products are easy to install and highly efficient. The following list
describes some of the many applications made possible through the power and
flexibility of wireless LANs:
a) Difficult-to-wire environments
There are many situations where wires cannot be laid easily. Historic
buildings, older buildings, open areas and across busy streets make the
installation of LANs either impossible or very expensive.
b) Temporary workgroups
Consider situations in parks, athletic arenas, exhibition centers, disasterrecovery, temporary offices and construction sites where one wants a
temporary WLAN established and removed.
c) The ability to access real-time information
Doctors/nurses, point-of-sale employees, and warehouse workers can
access real-time information while dealing with patients, serving
customers and processing information.
d) Frequently changed environments
Show rooms, meeting rooms, retail stores, and manufacturing sites where
frequently rearrange the workplace.
e) Small Office and Home Office (SOHO) networks
SOHO users need a cost-effective, easy and quick installation of a small
network.
f) Wireless extensions to Ethernet networks
Network managers in dynamic environments can minimize the overhead
caused by moves, extensions to networks, and other changes with
wireless LANs.
g) Wired LAN backup
Network managers implement wireless LANs to provide backup for
mission-critical applications running on wired networks.
h) Training/Educational facilities
Training sites at corporations and students at universities use wireless
connectivity to ease access to information, information exchanges, and
learning.
6
Page 7

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
1.6 Network Configuration
To better understand how the wireless LAN products work together to create a
wireless network, it might be helpful to depict a few of the possible wireless LAN PC
card network configurations. The wireless LAN products can be configured as:
a) Ad-hoc (or peer-to-peer) for departmental or SOHO LANs.
b) Infrastructure for enterprise LANs.
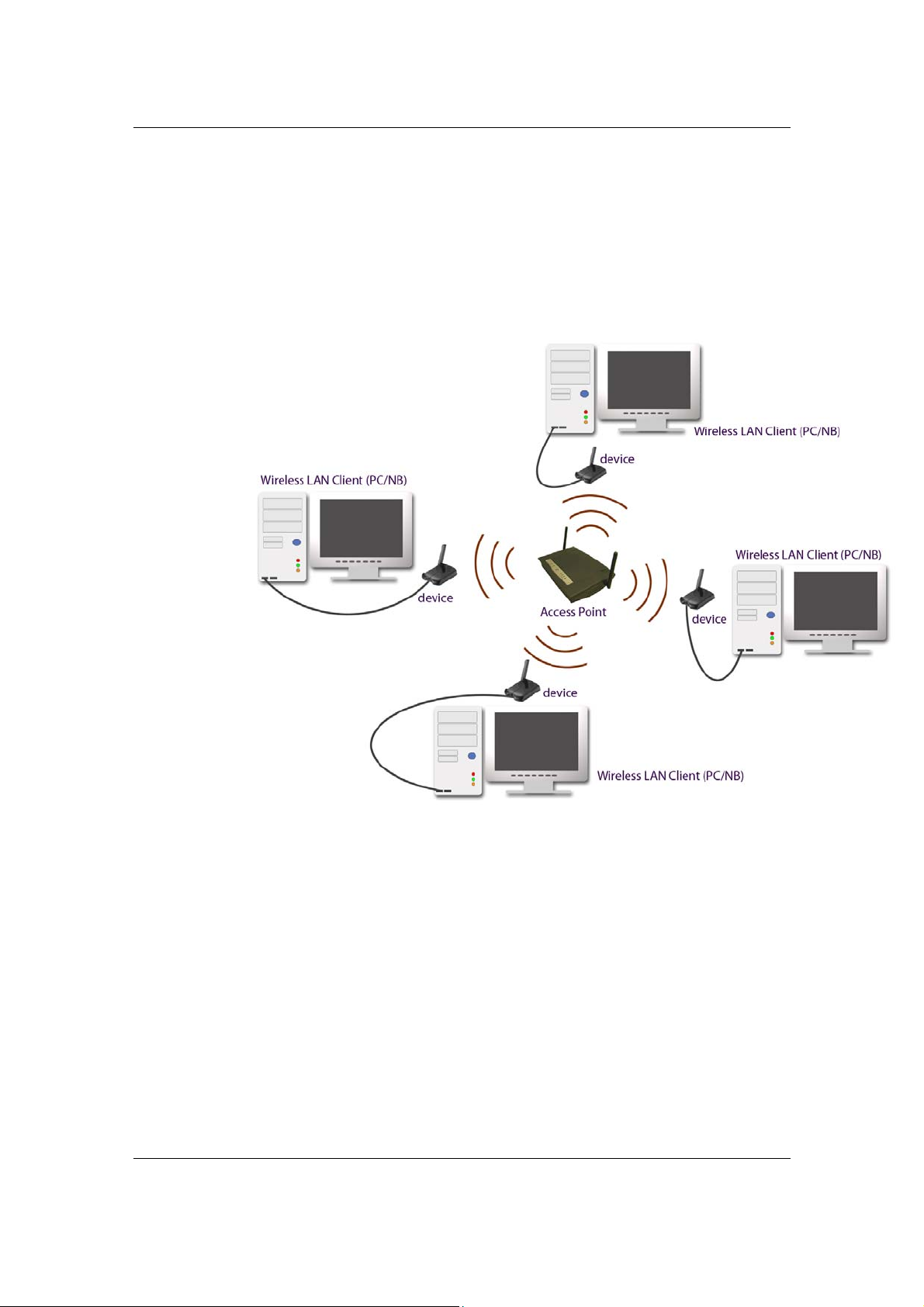
a) Ad-hoc (peer-to-peer) Mode
This is the simplest network configuration with several computers
equipped with the PC Cards that form a wireless network whenever they
are within range of one another. In ad-hoc mode, each client is peer-topeer, would only have access to the resources of the other client and
does not require an access point. This is the easiest and least expensive
way for the SOHO to set up a wireless network. The image below depicts
a network in ad-hoc mode.
7
Page 8
IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
b) Infrastructure Mode
The infrastructure mode requires the use of an access point (AP). In this
mode, all wireless communication between two computers has to be via
the AP. It doesn’t matter if the AP is stand-alone or wired to an Ethernet
network. If used in stand-alone, the AP can extend the range of
independent wireless LANs by acting as a repeater, which effectively
doubles the distance between wireless stations. The image below
depicts a network in infrastructure mode.
8
Page 9
IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
2 Install Drivers & Client Utility
2.1 Before You Begin
Before installing the new drivers of your USB adapter, you need to disable all of the
Wireless LAN drivers that you have installed.
During the installation, Windows 2000/XP may need to copy systems files from its
installation CD. Therefore, you may need a copy of the Windows installation CD at
hand before installing the drivers. On many systems, instead of a CD, the necessary
installation files are archived on the hard disk in C:\WINDOWS \OPTIONS\CABS
directory.
2.2 Installing the Drivers
Follow the steps below in order to install the USB adapter drivers:
1. Insert the CD-ROM that was provided to you in this package. The setup
should run automatically. If the setup does not run automatically, then you
must manually select the setup.exe file from the CD-ROM drive.
2. Once the setup begins you will see the Install Shield Wizard, as the image
depicts below.
9
Page 10
IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
3. Click on the Next button to continue.
4. The Setup Wizard will then allow you to install the driver & utility or just the
driver. Select the first option: Install Client Utilities and Driver.
5. Click on the Next button to continue.
6. This message informs you that the system must be restarted after the
installation is complete.
7. Click on the Yes button to continue.
10
Page 11
IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
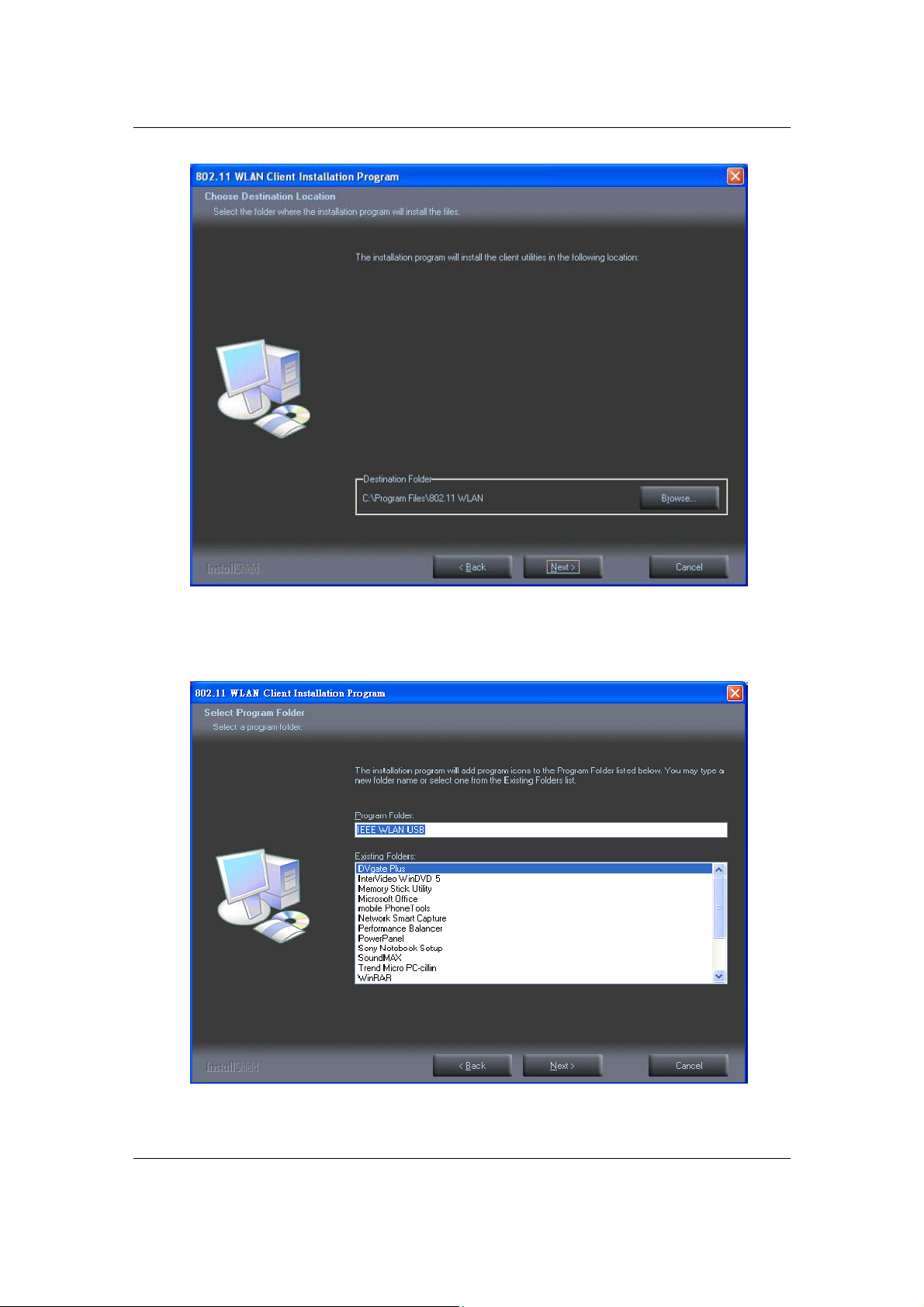
8. Click on the Browse button to select another drive or folder to install the
drivers, and then click on the Next button. If you would like to use the default
destination folder, click on the
Next
button.
9. Select a program folder for the Start menu, or use the default setting: 802.11
WLAN. Click on the Next button to continue.
11
Page 12
IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
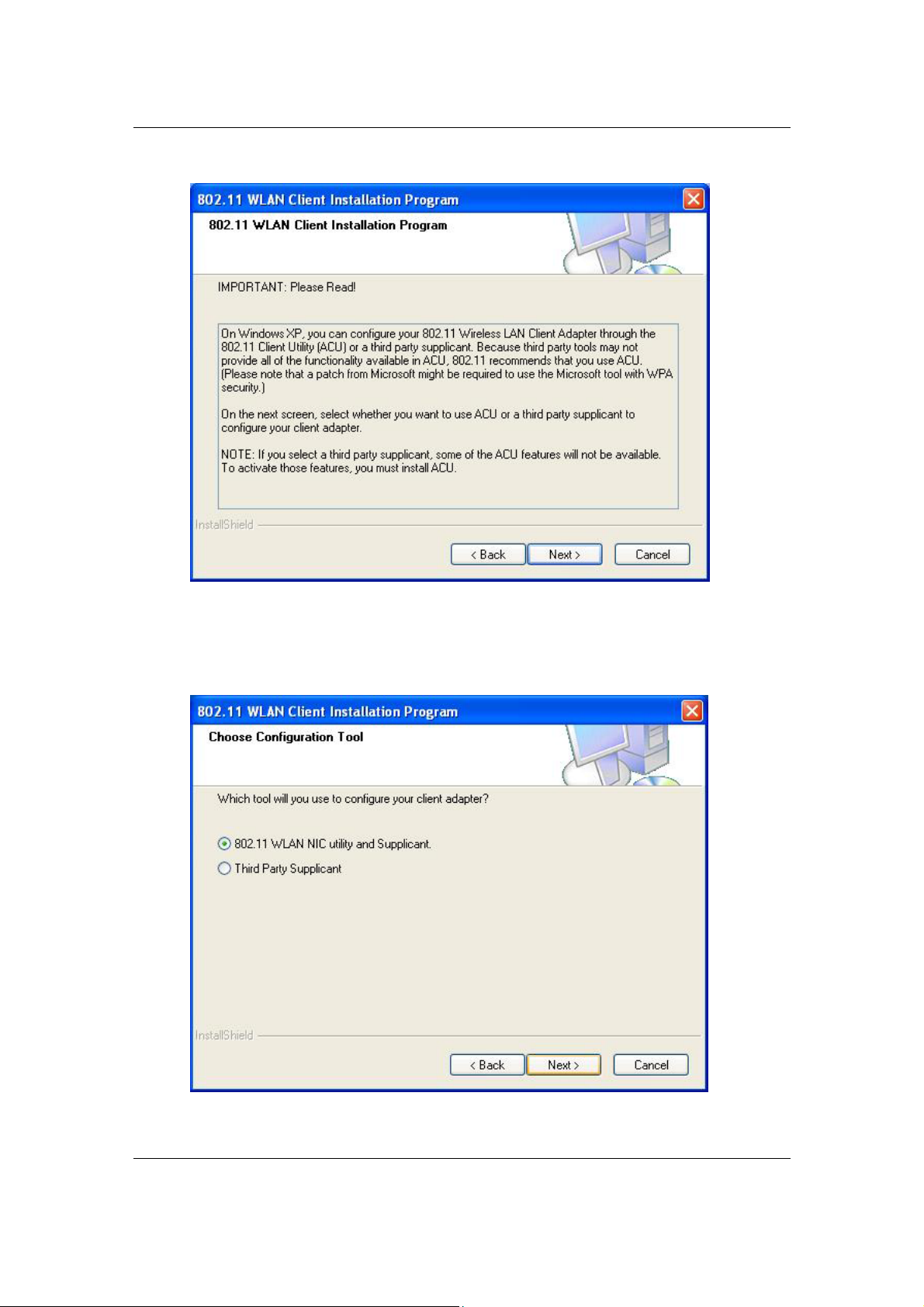
10. The message depicted above informs you about configuring this device
through the 802.11 Client Utility (ACU) or a third party supplicant. If you
choose to use a third party supplicant, some of the ACU features will not be
available. Click on the Next button to continue.
11. Select one of the options. However, it is recommended to select the first
12
Page 13
IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
option: 802.11 WLAN Client Utility and 802.1x Supplicant. Click on the
Next button to continue.
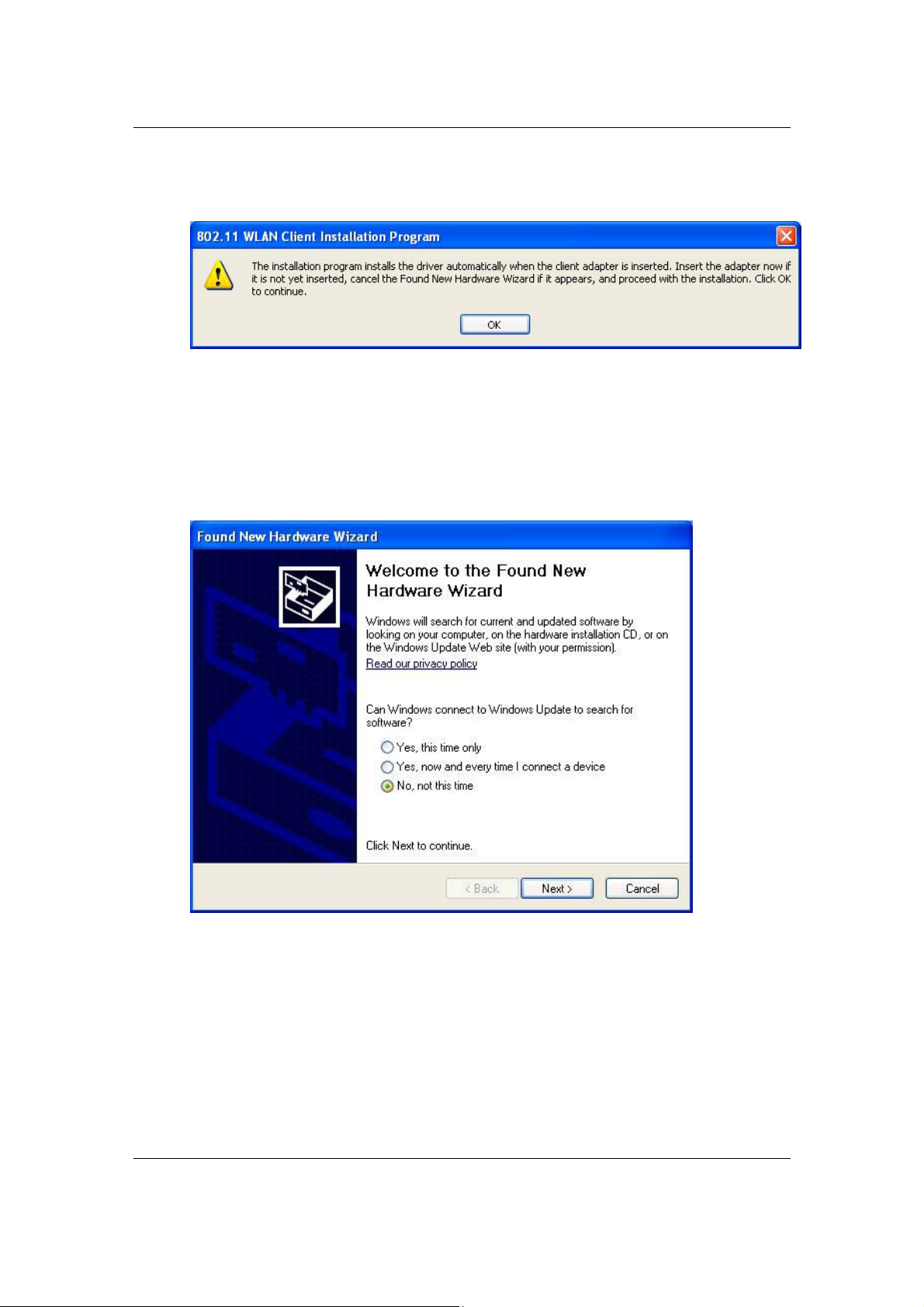
12. At this point, carefully insert the device into the USB port of your computer,
and click on the OK button.
13. Windows will automatically detect the device and display the Found New
Hardware Wizard, as the image depicts below. It will ask you to connect to
the Windows Update website, to search for software. Select No, not this
time, and click on the Next button.
14. Once again the Found New Hardware Wizard will ask you to install software.
Click on the Cancel button to continue.
15. If you are using Windows XP, you will see a message regarding Windows
Logo Testing, click on the Continue Anyway button to continue.
13
Page 14
IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
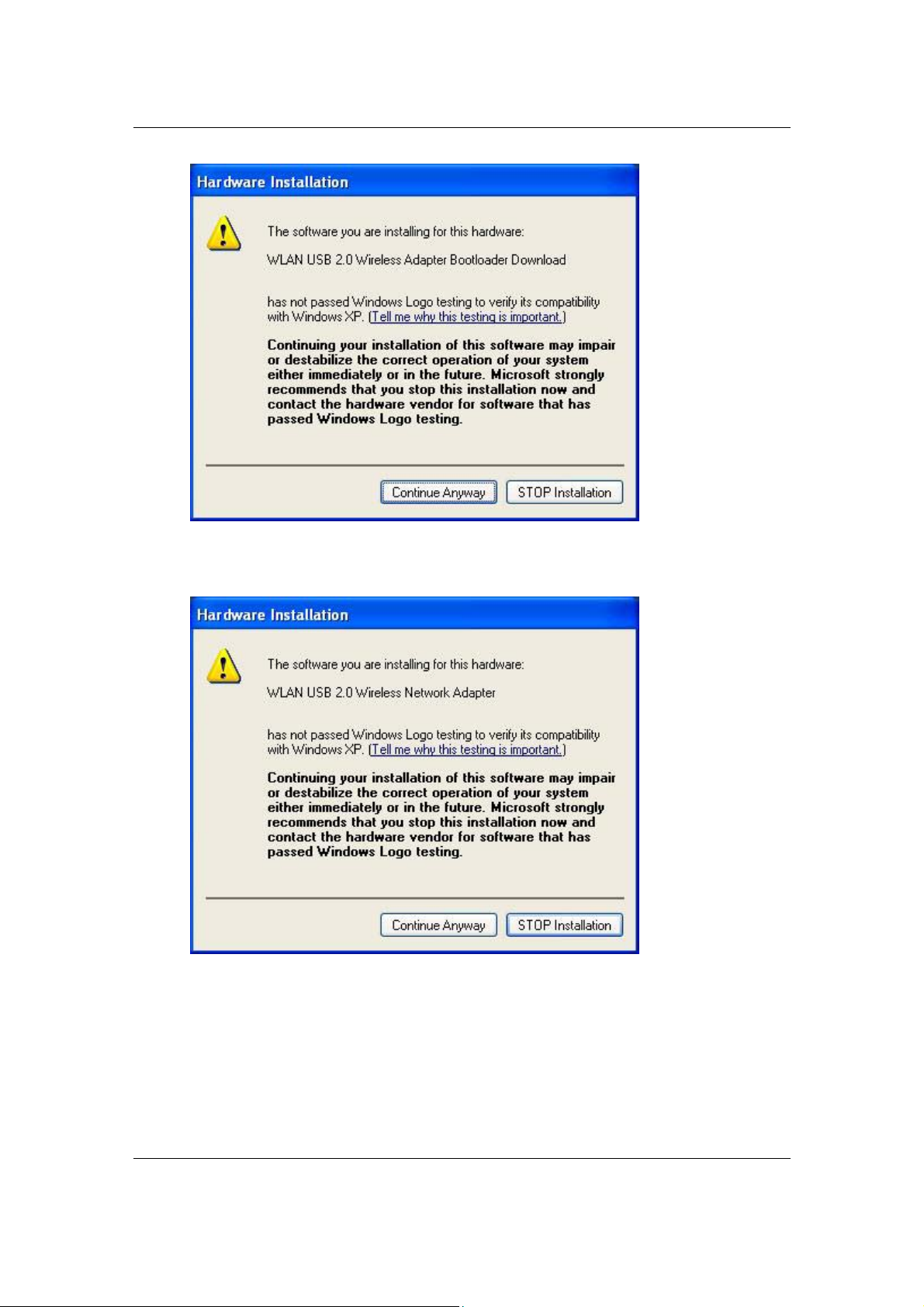
16. Once again, you will see a message regarding Windows Logo Testing, click
on the Continue Anyway button to continue.
17. A message will then appear indicating that the installation process is
complete Click on the OK button to reboot the system.
14
Page 15
IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
3 Using the Client Utility
After a successful installation you will see the USB adapter Client Utility in the
Windows Program group called 802.11 WLAN.
To run the Client Utility click Start > Programs > WLAN DUAL
. You will then see the Client Utility icon in the system tray
USB
of your computer.
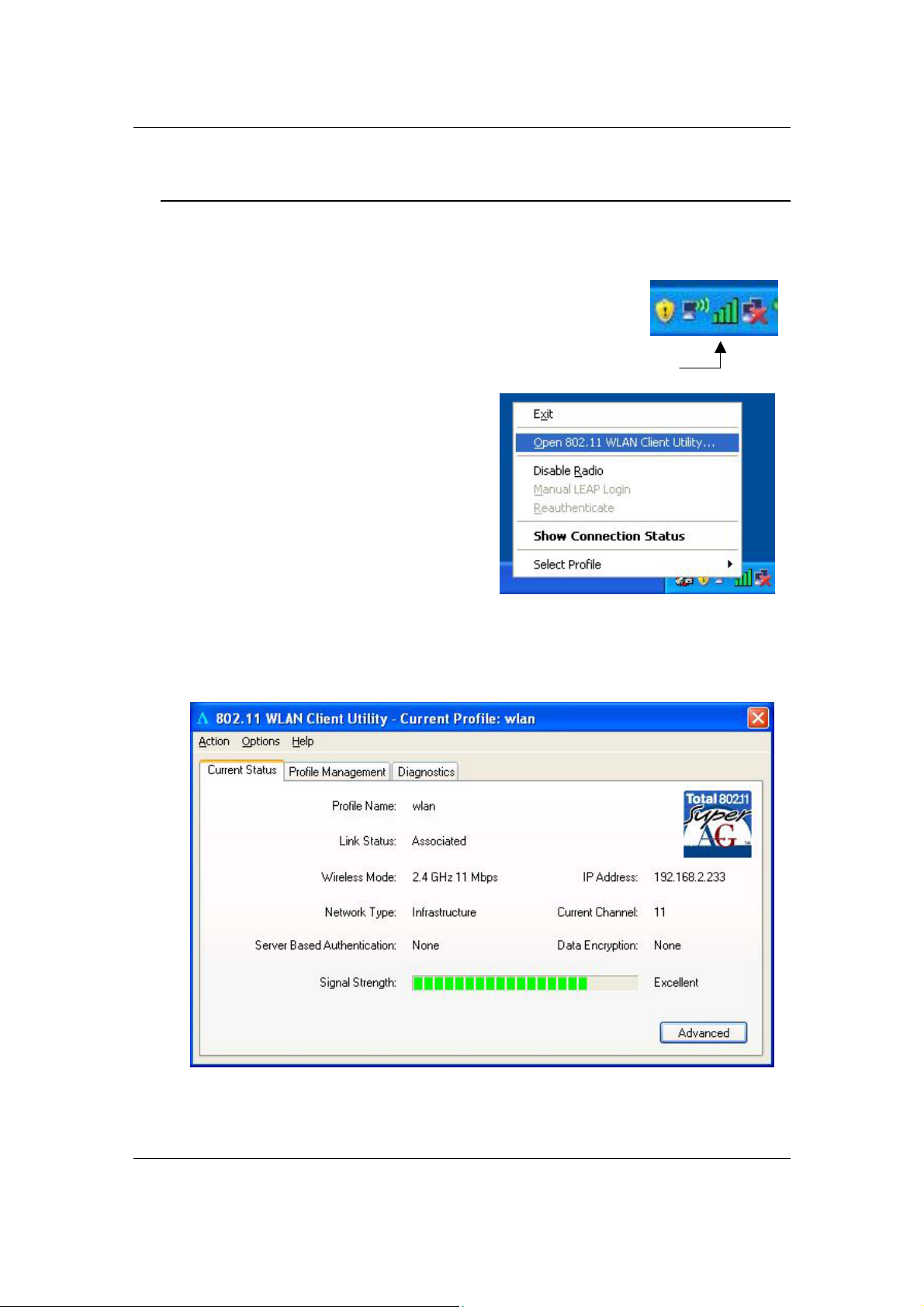
To open the Client Utility, right click on the
icon in the system tray, and then select
Open 802.11 WLAN Client Utility.
3.1 Current Status
Client Utility
The Current Status tab displays the current status of the wireless radio. The
following information is included in this tab, as the image depicts below.
Profile Name: Displays the name of this profile. One device can have
many profiles, but only one profile can be loaded at a time.
15
Page 16

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Note: The profile name and network name (SSID) are not the same.
State: This indicates the state of the client, associated or not associated.
Wireless Mode: Displays the 802.11 mode such as: 2.4GHz 11 Mbps,
2.4GHz 54 Mbps, 2.4GHz 108Mbps, 5GHz 54Mbps or 5GHz 108Mbps.
Network Type: Displays the type of network, such as: Infrastructure or
Ad-hoc.
Server Based Authentication
: Displays information about the
authentication method.
IP address: Displays the IP address of this device.
Current Channel: Displays the channel at which this device is
connected.
Current Channel: Displays the type of encryption used.
Signal Strength: Displays the strength of the signal.
Click on the Advanced button to view more details about the current status. This
window includes information such as: network name (SSID), AP MAC address,
power save mode, power levels, signal strength, noise level, channel, frequency,
and channel set (country). Click on the OK button to close the window.
3.2 Profile Management
The second tab displayed is the Profile Management tab. This tab is used to
create a new profile, modify an existing profile, remove an existing profile, and
activate an existing profile.
16
Page 17

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
3.2.1 Scan for available networks
Click on the Scan button to view a list of available infrastructure and ad-hoc
networks. This table lists the network name, encryption key if required, signal
strength, channel, and wireless mode.
If you would like to associate with a specific network, select the network name
(SSID) and then click on the Activate button. You will then get connected to the
network if you have the correct permission keys.
17
Page 18

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
3.2.2 Create a New Profile
Multiple profiles can be created for different Network Names (SSIDs). This allows
a user to quickly associate with another network, instead of entering the
credentials each time.
Click on the New button to create a new profile. You will then see the General
tab of the profile management window.
Profile Name: Enter a name for this profile; this can be any name that
18
Page 19

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
you may associate with your network. This feature comes in handy when
you need to work at several locations where there are different network
settings. Using this you can configure a different profile for each of your
networks.
Client Name: Enter any name to describe the profile.
SSID1: Enter the SSID of the network. The SSID is a unique name
shared among all points in your wireless network. The SSID must be
identical for all points in the network, and is case-sensitive.
Click on the OK button to continue.
3.2.3 Security
The next tab displayed is the Security tab. Here you can configure the
authentication and encryption method that is used on your network. There are
five types of security methods available: none, WPA, WPA-PSK, 802.1x, Preshared WEP key. The configuration steps for each method are described below.
3.2.3.1 Security Disabled
If your network does not require any security methods, then select None in the
security tab, and then click on the OK button.
3.2.3.2 WPA – TLS, TTLS
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) was designed to improve upon the security
features of WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy). The technology is designed to work
with existing Wi-Fi products that have been enabled with WEP. WPA provides
improved data encryption through the Temporal Integrity Protocol (TKIP), which
scrambles the keys using a hashing algorithm and by adding an integrity-
19
Page 20

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
checking feature which makes sure that keys haven’t been tampered with.
Select the WPA radio button, and then select EAP – TLS or EAP – TTLS from
the drop-down list. TLS (Transport Layer Security) is an IETF standardized
authentication protocol that uses PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) certificate-based
authentication of both the client and authentication server.
Click on the Configure button to configure the TTLS settings.
Trusted Root Certification Authorities:
Select the appropriate
certificate authority from the drop-down list.
20
Page 21

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
User Name: Enter the user name for the certificate authority.
Password: Enter the password that corresponds with the user name for
the certificate authority.
Confirm Password: Re-type the password.
Click on the Advanced button.
Specific Server or Domain: Leave the server name blank for the client
to accept a certificate from any server with a certificate signed by the
authority listed in the Network Certificate Authority drop-down list.
(Recommended). You can also enter the domain name of the server
from which the client will accept a certificate.
Login Name: Enter the login name if required.
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window. Once again, click on
the OK button to return to the Profile Management window.
3.2.3.3 WPA – PEAP (EAP-GTC)
PEAP (EAP-GTC) was standardized along with EAP in RFC 2284. EAP-GTC
allows the exchange of clear text authentication credentials across the network.
The GTC method does provide a way to move a simple username and password
from client to server using an EAP method, so it can be used to provide an
authentication method. Naturally, if EAP-GTC is used to transport reusable
passwords, it must be used inside a tunnel for protection and server
authentication. EAP-GTC can be used with both TTLS and PEAP.
Select the WPA radio button, and then select PEAP (EAP-GTC) from the drop-
down list.
21
Page 22

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Click on the Configure button to configure the PEAP (EAP-GTC) settings.
Trusted Root Certification Authorities: Select the appropriate
certificate authority from the drop-down list.
User Name: Enter the user name for the certificate authority.
Set Password: Select Tok en or Static Password radio button. The
default setting is Static Password.
Click on the Advanced button.
22
Page 23

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Specific Server or Domain: Leave the server name blank for the client
to accept a certificate from any server with a certificate signed by the
authority listed in the Network Certificate Authority drop-down list.
(Recommended). You can also enter the domain name of the server
from which the client will accept a certificate.
Login Name: Enter the login name if required.
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window. Once again, click on
the OK button to return to the Profile Management window.
3.2.3.4 WPA – PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP-V2)
The PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP V2) authentication type is based on EAPTLS
authentication, but uses a password instead of a client certificate for
authentication. PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP V2) uses a dynamic session-based WEP
key, which is derived from the device and RADIUS server, to encrypt data.
Select the
the drop-down list.
radio button, and then select
WPA
PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP-V2)
from
23
Page 24

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Click on the Configure button to configure the PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP-V2)
settings.
Trusted Root Certification Authorities:
certificate authority from the drop-down list.
User Name: Enter the user name for the certificate authority.
Password: Enter the password that corresponds with the user name for
the certificate authority.
Confirm Password: Re-type the password.
Select the appropriate
24
Page 25

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Click on the Advanced button.
Specific Server or Domain: Leave the server name blank for the client
to accept a certificate from any server with a certificate signed by the
authority listed in the Network Certificate Authority drop-down list.
(Recommended). You can also enter the domain name of the server
from which the client will accept a certificate.
Login Name: Enter the login name if required.
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window. Once again, click on
the OK button to return to the Profile Management window.
3.2.3.5 WPA – LEAP
LEAP (Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol) also known as CiscoWireless EAP provides username/password-based authentication between a
wireless client and a RADIUS server. LEAP is one of several protocols used with
the IEEE 802.1X standard for LAN port access control. LEAP also delivers a
session key to the authenticated station, so that future frames can be encrypted
with a key that is different than keys used by others sessions. Dynamic key
delivery eliminates one big vulnerability; static encryption keys that are shared by
all stations in the WLAN.
Select the
radio button, and then select
WPA
from the drop-down list.
LEAP
25
Page 26

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Click on the
Configure
button to configure the LEAP settings.
Use Temporary User Name and Password: Select this radio button for
26
Page 27

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
a temporary user name and password. This will manually prompt for the
user name and password.
Use Saved User Name Password: Select this radio button if the user
name and password will be saved in this profile.
User Name: Enter the user name for the certificate authority.
Password:
Enter the password that corresponds with the user name for
the certificate authority.
Confirm Password: Re-type the password.
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window
3.2.3.6 WPA – Passphrase
Select the WPA Passphrase radio button and then click on the Configure button.
27
Page 28

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Enter a WPA passphrase. For ASCII text, enter 8-63 characters, for
hexadecimal enter 64 characters).
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window. Once again, click on
the OK button to return to the Profile Management window.
3.2.3.7 802.1x – TLS, TTLS
802.1X provides an authentication framework for wireless LANs allowing a user
to be authenticated by a central authority. 802.1X uses an existing protocol
called EAP. EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) is an extension to the PPP
protocol that enables a variety of authentication protocols to be used. It passes
through the exchange of authentication messages, allowing the authentication
software stored in a server to interact with its counterpart in the client.
Select the 802.1x radio button, and then select EAP – TLS or EAP – TTLS from
the drop-down list. TLS (Transport Layer Security) is an IETF standardized
authentication protocol that uses PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) certificatebased authentication of both the client and authentication server.
Click on the Configure button to configure the TTLS settings.
28
Page 29

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Trusted Root Certification Authorities: Select the appropriate
certificate authority from the drop-down list.
User Name: Enter the user name for the certificate authority.
Password: Enter the password that corresponds with the user name for
the certificate authority.
Confirm Password: Re-type the password.
Click on the Advanced button.
Specific Server or Domain: Leave the server name blank for the client
to accept a certificate from any server with a certificate signed by the
authority listed in the Network Certificate Authority drop-down list.
(Recommended). You can also enter the domain name of the server
from which the client will accept a certificate.
Login Name: Enter the login name if required.
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window. Once again, click on
29
Page 30

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
the OK button to return to the Profile Management window.
3.2.3.8 802.1x – PEAP (EAP-GTC)
PEAP (EAP-GTC) was standardized along with EAP in RFC 2284. EAP-GTC
allows the exchange of clear text authentication credentials across the network.
The GTC method does provide a way to move a simple username and password
from client to server using an EAP method, so it can be used to provide an
authentication method. Naturally, if EAP-GTC is used to transport reusable
passwords, it must be used inside a tunnel for protection and server
authentication. EAP-GTC can be used with both TTLS and PEAP.
Select the 802.1x radio button, and then select PEAP (EAP-GTC) from the dropdown list.
Click on the Configure button to configure the PEAP (EAP-GTC) settings.
30
Page 31

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Trusted Root Certification Authorities: Select the appropriate
certificate authority from the drop-down list.
User Name: Enter the user name for the certificate authority.
Set Password: Select Tok en or Static Password radio button. The
default setting is Static Password.
Click on the Advanced button.
Specific Server or Domain: Leave the server name blank for the client
to accept a certificate from any server with a certificate signed by the
authority listed in the Network Certificate Authority drop-down list.
(Recommended). You can also enter the domain name of the server
from which the client will accept a certificate.
Login Name: Enter the login name if required.
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window. Once again, click on
the OK button to return to the Profile Management window.
31
Page 32

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
3.2.3.9 802.1x – PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP-V2)
The PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP V2) authentication type is based on EAPTLS
authentication, but uses a password instead of a client certificate for
authentication. PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP V2) uses a dynamic session-based WEP
key, which is derived from the device and RADIUS server, to encrypt data.
Select the 802.1x radio button, and then select PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP-V2) from
the drop-down list.
Click on the Configure button to configure the PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP-V2)
settings.
32
Page 33

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Trusted Root Certification Authorities: Select the appropriate
certificate authority from the drop-down list.
User Name: Enter the user name for the certificate authority.
Password: Enter the password that corresponds with the user name for
the certificate authority.
Confirm Password: Re-type the password.
Click on the Advanced button.
Specific Server or Domain: Leave the server name blank for the client
to accept a certificate from any server with a certificate signed by the
authority listed in the Network Certificate Authority drop-down list.
(Recommended). You can also enter the domain name of the server
from which the client will accept a certificate.
Login Name: Enter the login name if required.
33
Page 34

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window. Once again, click on
the OK button to return to the Profile Management window.
3.2.3.10 802.1x – LEAP
LEAP (Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol) also known as CiscoWireless EAP provides username/password-based authentication between a
wireless client and a RADIUS server. LEAP is one of several protocols used with
the IEEE 802.1X standard for LAN port access control. LEAP also delivers a
session key to the authenticated station, so that future frames can be encrypted
with a key that is different than keys used by others sessions. Dynamic key
delivery eliminates one big vulnerability; static encryption keys that are shared by
all stations in the WLAN.
Select the 802.1x radio button, and then select LEAP from the drop-down list.
Click on the
Configure
button to configure the LEAP settings.
34
Page 35

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Use Temporary User Name and Password: Select this radio button for
a temporary user name and password. This will manually prompt for the
user name and password.
Use Saved User Name Password: Select this radio button if the user
name and password will be saved in this profile.
User Name: Enter the user name for the certificate authority.
Password: Enter the password that corresponds with the user name for
the certificate authority.
Confirm Password: Re-type the password.
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window
35
Page 36

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
3.2.3.11 Pre-Shared Key (Static WEP)
You may select 64, 128 or 152 bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) key to encrypt
data (Default setting is Disable). WEP encrypts each frame transmitted from the
radio using one of the Keys from a panel. When you use WEP to communicate
with the other wireless clients, all the wireless devices in this network must have
the same encryption key or pass phrase.
Select the Pre-Shared Key (Static WEP) radio button and click on the
Configure button.
36
Page 37

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Key Entry: Select Hexadecimal or ASCII depending on the WEP key
that is used.
WEP Key Size: Select 64, 128, or 152 bit WEP key size.
Transmit Key: Enter the WEP key in the four WEP key text boxes.
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window
3.2.4 Advanced Settings
Click on the Advanced tab in the Profile Management section. Here you can
configure the transmit power level, wireless mode, power save mode, and
network type.
3.2.4.1 Infrastructure Settings
Wireless Mode: Place a check in the preferred frequency and data
rates.
Power Save Mode:
Select
Maximum, Normal
, or
from the drop-
Off
down list. Selecting Maximum will save the most power; this is
recommended if using a laptop running on battery. For other instances,
use the Normal or Off setting.
Network Type: Select Infrastructure from the drop-down list.
802.11 Preamble: This setting should be the same as the access point.
If you are not sure of that setting, select Short & Long.
Preferred APs: Click on this button to add specific access points to this
profile. Then enter the MAC addresses of the specific access points and
then click on the OK button to return to the previous window.
37
Page 38

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
3.2.4.2 Ad Hoc Settings
Wireless Mode: Place a check in the preferred frequency and data
rates.
Network Type: Select Ad hoc from the drop-down list.
802.11 Preamble: This setting should be the same as the access point.
If you are not sure of that setting, select Short & Long.
38
Page 39

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window
3.3 Diagnostics
The third tab displayed is the Diagnostics tab. This tab displays the number of
transmitted and received packets.
Click on the Adapter Information button to view information about the Cardbus
adapter such as: card name, MAC address, driver name, driver version, and
driver date.
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window
39
Page 40

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Click on the Advanced Statistics button to view detailed statistics about transmit
and receive frames.
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window
40
Page 41

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
3.4 Enable / Disable Radio
To disable the radio, click on Action in the menu bar, and then click on Disable
Radio.
You will then see a confirmation message “The RF signals for the following
network card(s) have been successfully disabled”.
Click on the OK button to continue.
41
Page 42

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
To enable the radio, click on Action in the menu bar, and then click on Enable
Radio.
You will then see a confirmation message “The RF signals for the following
network card(s) have been successfully enabled”.
Click on the OK button to continue.
42
Page 43

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
3.5 Disable Tray Icon
To disable the tray icon, click on Action in the menu bar, and then click on
Disable Tray Icon.
You will then notice that the tray icon has disappeared from the system tray.
3.6 Display Settings
To change the display settings, click on Options in the menu bar, and then click
on Display Settings.
In this window you can change the Signal Strength Display Units from dBm to %,
43
Page 44

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
and increase or decrease the refresh interval rate, as well as displaying the data
in a cumulative or relative fashion.
Click on the OK button to return to the previous window.
44
Page 45

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
4 Uninstall the Drivers & Client Utility
If the device installation is unsuccessful for any reason, the best way to solve the
problem may be to completely uninstall the device and its utility and repeat the
installation procedure again.
Follow the steps below in order to uninstall the Drivers and Client Utility:
1. Click on Start > Settings > Control Panel > Add or Remove Programs
2. You will then see the following window. Select the Atheros Utility and then
click on Change/Remove.
3. Click on Uninstall the previous installation radio button.
45
Page 46

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
4. Click on the Next button to continue. You will then see the following message
informing you that you must restart the system after installation. .
5. Click on the Yes button to continue. You will then see the following message
asking you if you would like to remove the application.
6. Click on the OK button to continue. You will then see the following message
asking you if you would like to remove the driver and all the existing profiles.
7. Click on the Ye s button to continue. You must then restart your system to
complete the Uninstallation.
8. Remove the device form your computer and then click on the OK button. The
Uninstallation process is complete.
46
Page 47

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Appendix A – Specifications
Data Rates
802.11a: 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54, 72, 96 &
108 (Super A) Mbps
802.11g: 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54, 72, 96
& 108 (Super G) Mbps
802.11b: 1, 2, 5.5, 11Mbps
Standards / Compliance
IEEE802.11, IEEE802.11a, IEEE802.11g,
IEEE802.11b, draft IEEE 802.11e, f, h, and i
standards, IEEE802.1x
Regulation Certifications
FCC Part 15/UL, ETSI 300/328/CE
Operating Voltage
5 V ± 0.25V
Status LEDs
RF link activity
Drivers
Windows 2000/XP
RF Information
Frequency Band
802.11a: 5.15~5.25GHz,
5.25~5.35GHz, 5.725~5.850GHz
802.11b/g: U.S., Europe and Japan product
covering 2.4 to 2.484 GHz, programmable for
different country regulations
Media Access Protocol
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision
Avoidance (CSMA/CA)
Modulation Technology
802.11a/g: OFDM (64-QAM, 16-QAM, QPSK,
BPSK)
802.11b: DSSS (DBPSK, DQPSK, CCK)
Operating Channels
11 for North America, 14 for Japan, 13 for
Europe, 2 for Spain, 4 for France
Receive Sensitivity (Typical)
5.15~5.35GHz
6Mbps@ -90dBm;
54Mbps@ -74dBm
5.47~5.725GHz
6Mbps@ -90dBm;
54Mbps@ -73dBm
5.75~5.85GHz
6Mbps@ -89dBm;
54Mbps@ -72dBm
2.412~2.472G(IEEE802.11g)
6Mbps@ -91dBm;
Antenna
54Mbps@ -76dBm
2.412~2.472G(IEEE802.11b)
11Mbps@ -91dBm;
1Mbps@ -96dBm
Available transmit power (Typical)
FCC (Typical)
5.15~5.24 GHz
17 dBm @6Mbps
17 dBm @54Mbps
5.26~5.35 GHz
20 dBm @6Mbps
17 dBm @54Mbps
5.725 ~ 5.850GHz
19 dBm @6Mbps
15 dBm @54Mbps
2.412~2.462GHz(IEEE802.11g)
24 dBm @ 6 ~ 24 Mbps
21 dBm @ 36 Mbps
20 dBm @ 48 Mbps
19 dBm @ 54 Mbps
2.412~2.462GHz(IEEE802.11b)
25 dBm @1~11Mbps
ETSI (Typical)
5.15~5.35 GHz
20 dBm @6Mbps
17 dBm @54Mbps
5.47 ~ 5.725GHz
19 dBm @6Mbps
16 dBm @54Mbps
5.725 ~ 5.825GHz
18
dBm @6Mbps
15 dBm @54Mbps
2.412~2.472G(IEEE802.11g)
20 dBm @ 6 ~ 24 Mbps
20 dBm @ 36 Mbps
20 dBm @ 48 Mbps
19 dBm @ 54 Mbps
2.412~2.472G(IEEE802.11b)
20 dBm @1~11Mbps
Dipole antenna
Networking
Topology
Ad-Hoc, Infrastructure
Security
47
Page 48

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
IEEE802.1x support for LEAP/PEAP
WEP 64,128,152bit
WPA (PSK,TKIP)
WPA2 (AES)
Physical
Form Factor
USB 2.0/1.1
Dimensions
75.2(L) mm x 53.9(W) mm x 14(H) mm
Weight
40 g/ 1.5oz
Environmental
Temperature Range
Operating: -0°C to 55°C
Storage: -20°Cto 75°C
Humidity (non-condensing)
5%~95% Typical
Package Contents
One USB Adapter
One USB Cable
One CD-ROM with User’s Manual and
Drivers
48
Page 49

IEEE 802.11a/b/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter Version 1.2
Appendix B – FCC Interference Statement
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, includi ng interference that may cause undesired operat ion.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment.
This device complies with FCC RF Exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment, under 47
CFR 2.1093 paragraph (d)(2). This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with
any other antenna or transmitter.
This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator &
your body.
If this device is going to be operated in 5.15 ~ 5.25GHz frequency range, then it is restricted in indoor
environment only.
48
 Loading...
Loading...