Page 1

SENAO
Wireless LAN USB Adapter
User’s Manual
Page 2

Contents
1. Introduction 1
1.1 Package Contents 1
1.2 USB Adapter Description 1
1.3 System Requirements 1
1.4 Features and Benefits 1
1.5 Applications 2
1.6 Network Configurations 3
2. Installing Driver and Utility 7
2.1 Installation for Windows 98/ME/2000/XP 7
2.2 Checking after Installation 15
2.3 Wireless LAN Client Utility 18
2.4 Uninstalling Driver and Utility 31
3. Connecting to a Network 32
3.1 Checking and Adding Client for Microsoft Networks 32
3.2 Checking and Adding NetBEUI 33
3.3 Checking and Adding TCP/IP 34
3.4 Checking and Adding File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks 35
3.5 Checking and Adding Computer Name and Workgroup Name 35
4. Troubleshooting 36
Appendix A Product Specifications 39
Appendix B Regulatory Compliance Information 41
2
Page 3

Chapter 1 Introduction
This chapter describes the package contents, USB Adapter description,
system requirements, features & benefits, applications and network
configurations of our wireless LAN products.
1-1 Package Contents
The USB Adapter package contains the following items as shown in
1. One USB Adapter
2. One Installation CD
3. One Quick Installation Guide
1- 2 USB Adapter Descriptions
The USB Adapter is a st andard USB Adapter that fits into any USB
Interface. The USB Adapter has a LED indicator and an integrated
external diversity antenna.
1. Integrated, with external diversity Antennas. The adapter would switch
automatically to the antenna which receives single strongly .
2. Link LED
Peer to Peer – Solid GREEN, no matter the wireless is connected or not
Access Point – Solid GREEN when the wireless is connected and free
flickering when linking.
Off – No wireless activity.
1- 3 System Requirements
Installation of the USB Adapter requires:
1. PC compatible computer with USB Interface.
2. Windows 98//ME/2000/XP operating system environment.
3. Minimum 1.3M bytes free disk space for installing the USB Adapter
driver and utility program.
1- 4 Features and Benefits
11Mbps data rate High-speed data transmission
IEEE802.11b compliant
Fully interoperable with
IEEE802.11b compliant products
1
Page 4

Automatic data rate scaling at
11, 5.5, 2 and 1 Mbps
64/128-bit WEP data
encryption / decryption
Wide coverage range up to
400 meters in open space
Plug and Play USB interface Easy installation
Optimized throughput, range and
connectivity
Powerful data security
Wireless connectivity for all your
computers
1- 5 Applications
The wireless LAN products are easy to install and highly efficient. The
following list describes some of the many applications made possible
through the power and flexibility of wireless LANs:
1. Difficult-to-wire environments
There are many situations where wires can not or not easily be laid. Historic
buildings, older buildings, open areas and across busy streets make the
installation of LANs either impossible or very expensive.
2. Temporary workgroups
Consider situations in parks, athletic arenas, exhibitions, disaster-recovery,
temporary office and construction sites where one wants a temporary WLAN
established and removed.
3. The ability to access real-time information
Doctors/nurses, point-of-sale employees, and warehouse workers can access
real-time information while dealing with patients, serving customers and
processing information.
4. Frequently changed environments
Show rooms, meeting rooms, retail stores, and manufacturing sites where
frequently rearrange the workplace.
5. Small Office and Home Office (SOHO) networks
SOHO users need a cost-effective, easy and quick installation of a small
network.
6. Wireless extensions to Ethernet networks
Network managers in dynamic environments can minimize the overhead
caused by moves, extensions to networks, and other changes with wireless
LANs.
7. Wired LAN backup
Network managers implement wireless LANs to provide backup for
mission-critical applications running on wired networks.
8. Training/Educational Facilities
2
Page 5
Training sites at corporations and students at universities use wireless
connectivity to ease access to information, information exchanges, and
learning.
1- 6 Network Configurations
To better understand how the wireless LAN product s work together to
create a wireless network, it might be helpful to depict a few of the
possible wireless LAN USB Adapter network configurations. The wireless
LAN products can be configured as:
1. Ad-hoc (or peer-to-peer) for departmental or SOHO LANs.
2. Infrastructure for enterprise LANs.
3. IP Sharing for 56K/ISDN TA/Cable/DSL Modem – Connect Internet and your
SOHO network.
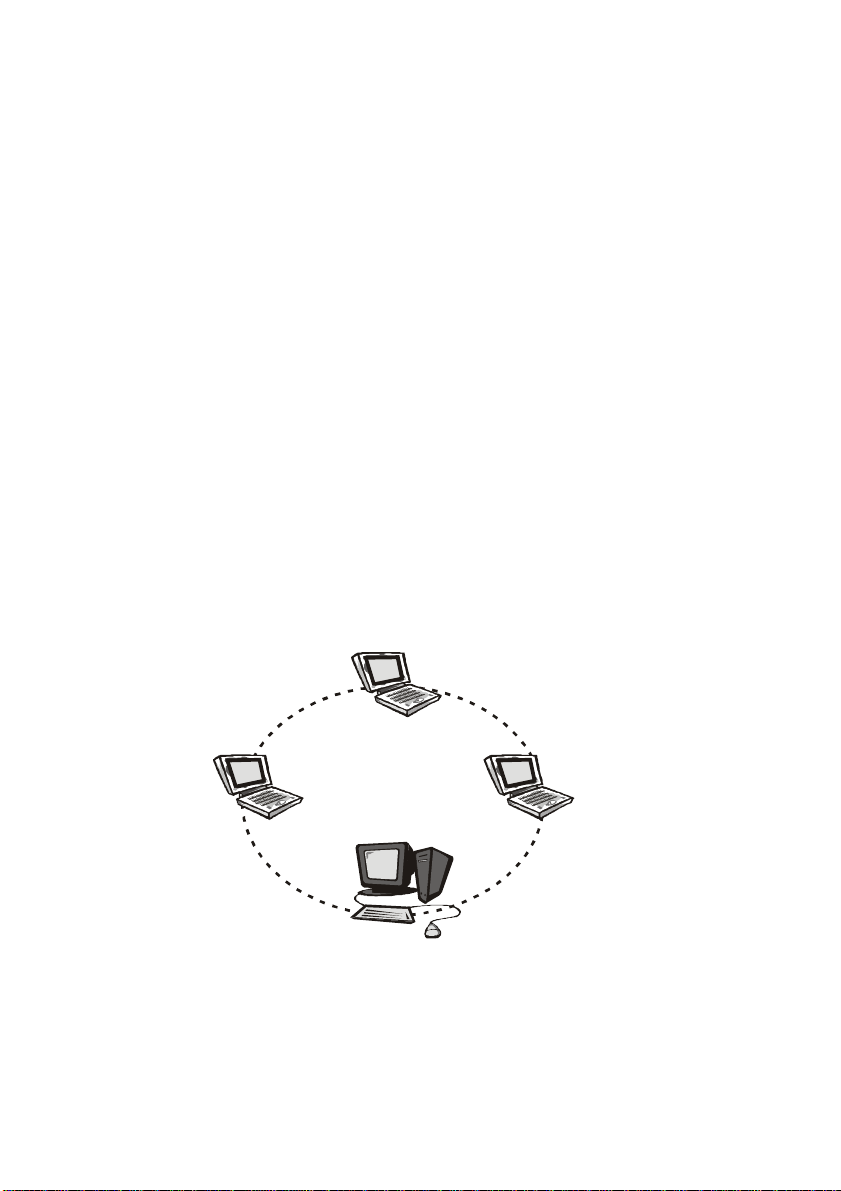
Ad-hoc (peer-to-peer) Mode
This is the simplest network configuration that several computers
equipped with the USB Adapters that form a wireless network whenever
they are within range of one another (Figure 1-3). In ad-hoc mode, each
client, is peer-to-peer, would only have access to the resources of the
other client and requires no the access point. This is the easiest and
least expensive way for the SOHO to set up a wireless network.
Peer to Peer
Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Wirel ess L AN US B Ad apte r
Figure 1-3
3
Page 6
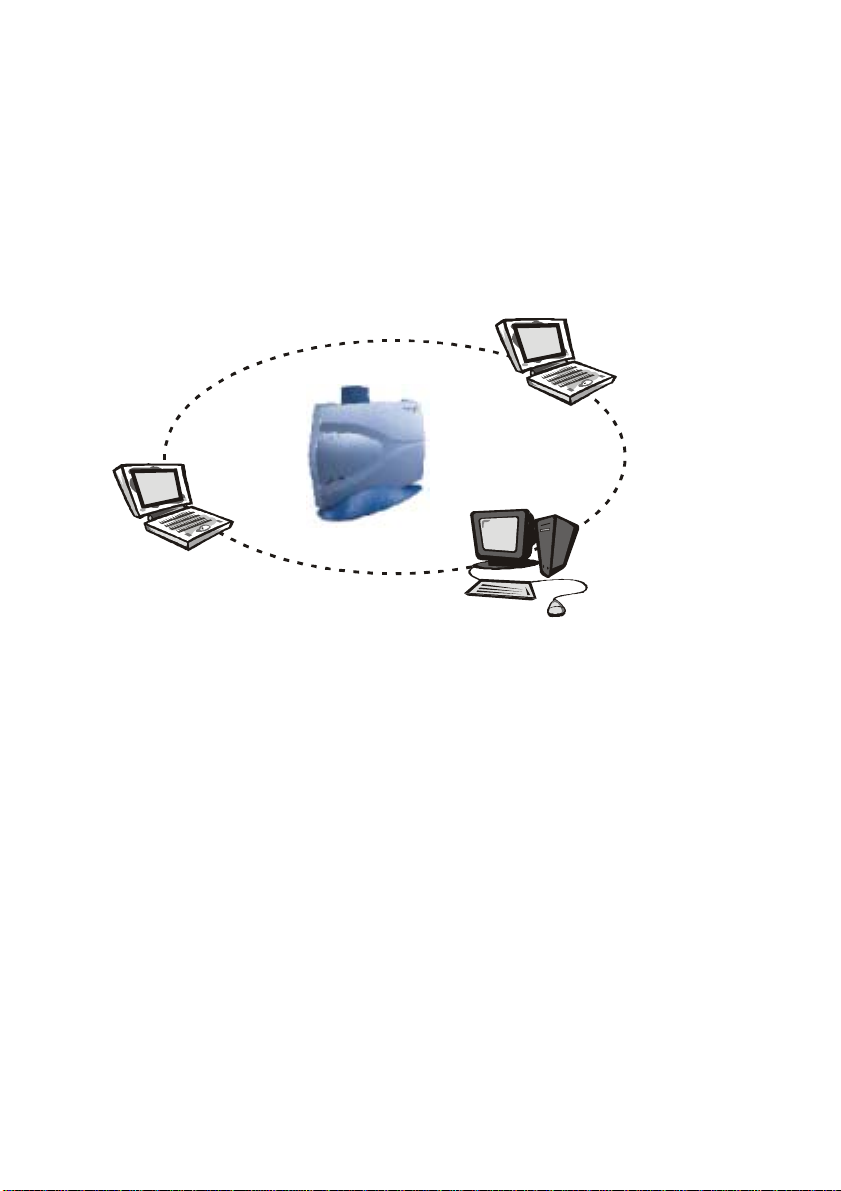
Infrastructure Mode
The infrastructure mode requires the use of an access point (AP). In this
mode, all wireless communications between two computers have to be
via the AP no matter the AP is wired to Ethernet network or stand-alone.
If used in stand-alone, the AP can extend the range of independent
wireless LANs by acting a repeater, which effectively doubling the
distance between wireless stations as shown in Figure 1-4.
Infrastructure
Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Wire les s LAN
Router/AP
Wireless LAN USB Adapter Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Figure 1-4
Extended-range independent WLAN using AP as repeater
If wired to an Ethernet network as shown in Figure 1-5, the AP serves as
a bridge and provides the link between the server and the wireless
clients. The wireless clients can move freely throughout the coverage
area of the AP while remaining connected to the server. Since the AP is
connected to the wired network, each client would have access to server
resources as well as to other clients
4
Page 7
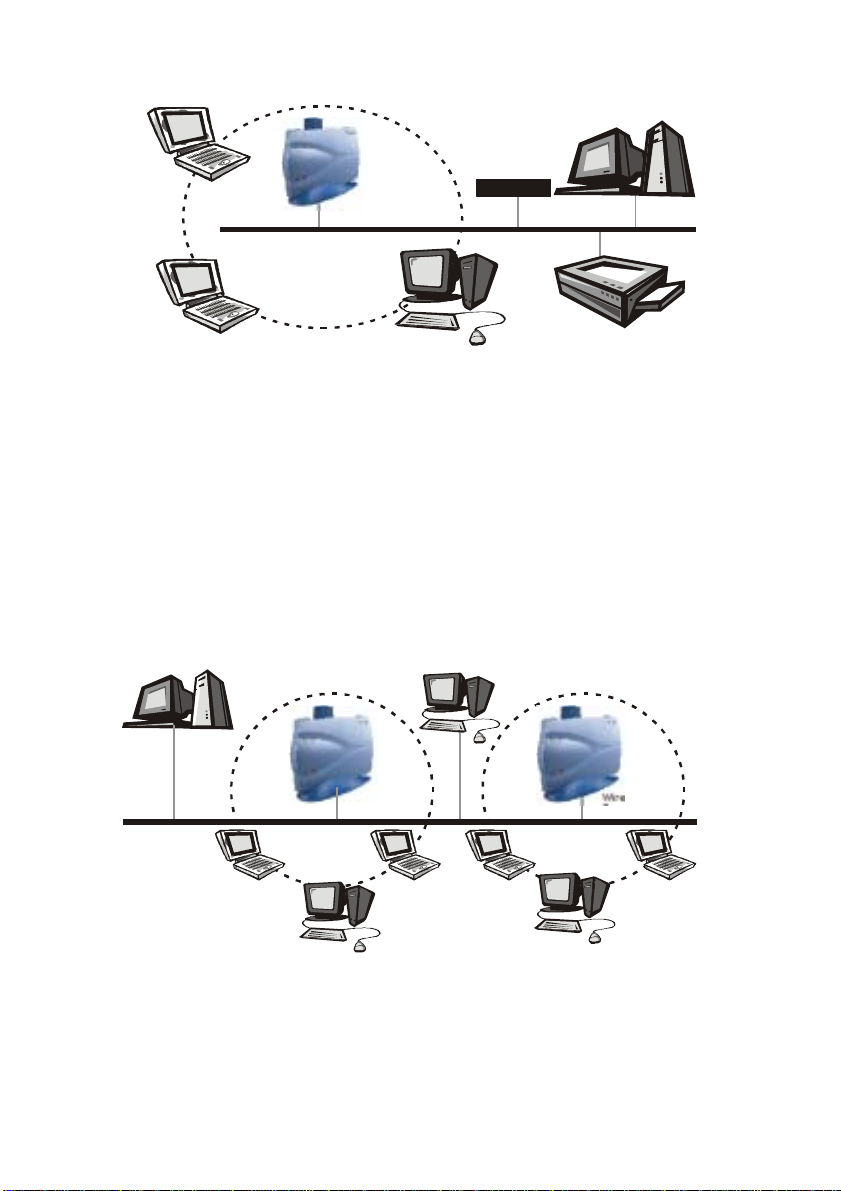
File server
Wireless LAN
ireless LAN USB Adapter
Wireless LAN USB Adapter Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Router/AP
Internet
Network Printer
Figure 1-5 Single AP bridge
Access points have a finite range, on the order of 50 meters indoor and
100 meters outdoors. In a very large facility such as an enterprise, a
warehouse, or on a college campus, it will probably be necessary to
install more than one access point to cover an entire building or campus,
as shown in Figure 1-6. In this scenario, access points hand the client off
from one to another in a way that is invisible to the client, ensuring
unbroken connectivity. Wireless clients can roam seamlessly between
different coverage areas and remain connected to the network.
Enterprise
File server
Ethernet
Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Wireless LAN
Router/AP
Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Wireless LAN USB Adapter Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Figure 1-6 Multiple-AP and roaming
5
Wireless LAN
Router/AP
Page 8
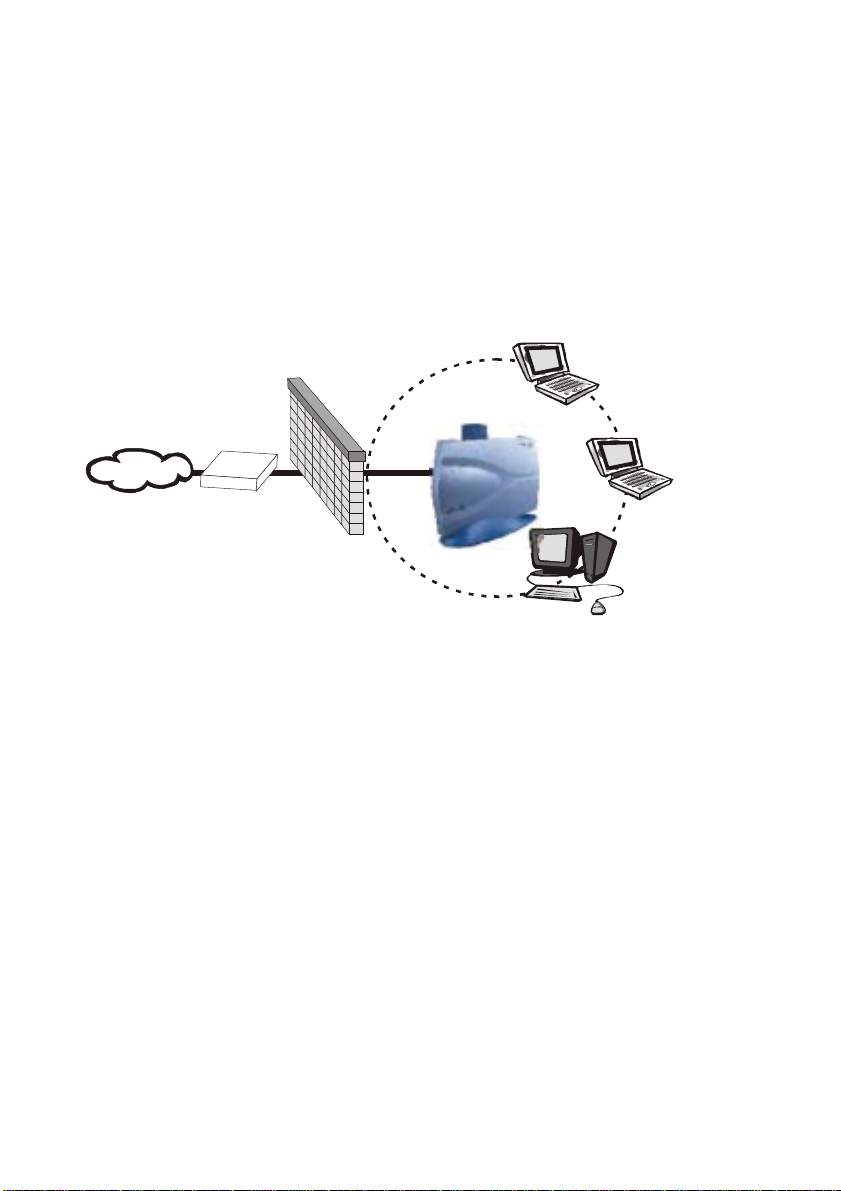
Wireless Router and IP Sharing
In infrastructure mode, in addition to acting as a bridge between an
Ethernet and wireless network, the AP can be configured as a wireless
router and IP sharing device for Internet access as shown in Figure 1-7.
You don’t have to buy an expensive router. Nor you have to buy several
modems and setup phone lines. Just share one AP, one Modem, single
dial-up account, and one phone line, dozens of network users can go
surfing the Internet concurrently.
SOHO
Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Firewall
Internet
Wireless LAN
Router/AP
56K/ISDN TA/
Cable/ADS L Modem
Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Wireless LAN USB Adapter
Figure 1-7 Wireless router and IP Sharing
6
Page 9

7
Page 10

Figure 2-1-1
1. The setup program should start automatically as shown in Figure
2-1-1. If it does not start, you can run it manually by selecting RUN
from the Start menu and running Setup.htm from CD-ROM drive.
2. From Wireless LAN Installer, select Utility & Driver Install. The
driver and utility of Wireless LAN USB Adapter will be inst alled
automatically.
3. Insert the USB Adapter into the PCMCIA slot of your computer.
4. The Wireless LAN USB Adapter will be found and installed without
restart the computer .
5. Make sure that the network protocol parameters are set correctly for
your computer. These include the IP address, subnet mask, gateway
and DNS. If you are unfamiliar with how to set network protocol
parameters, refer to Chapter 3 Connection to Network for details.
8
Page 11

9
Page 12
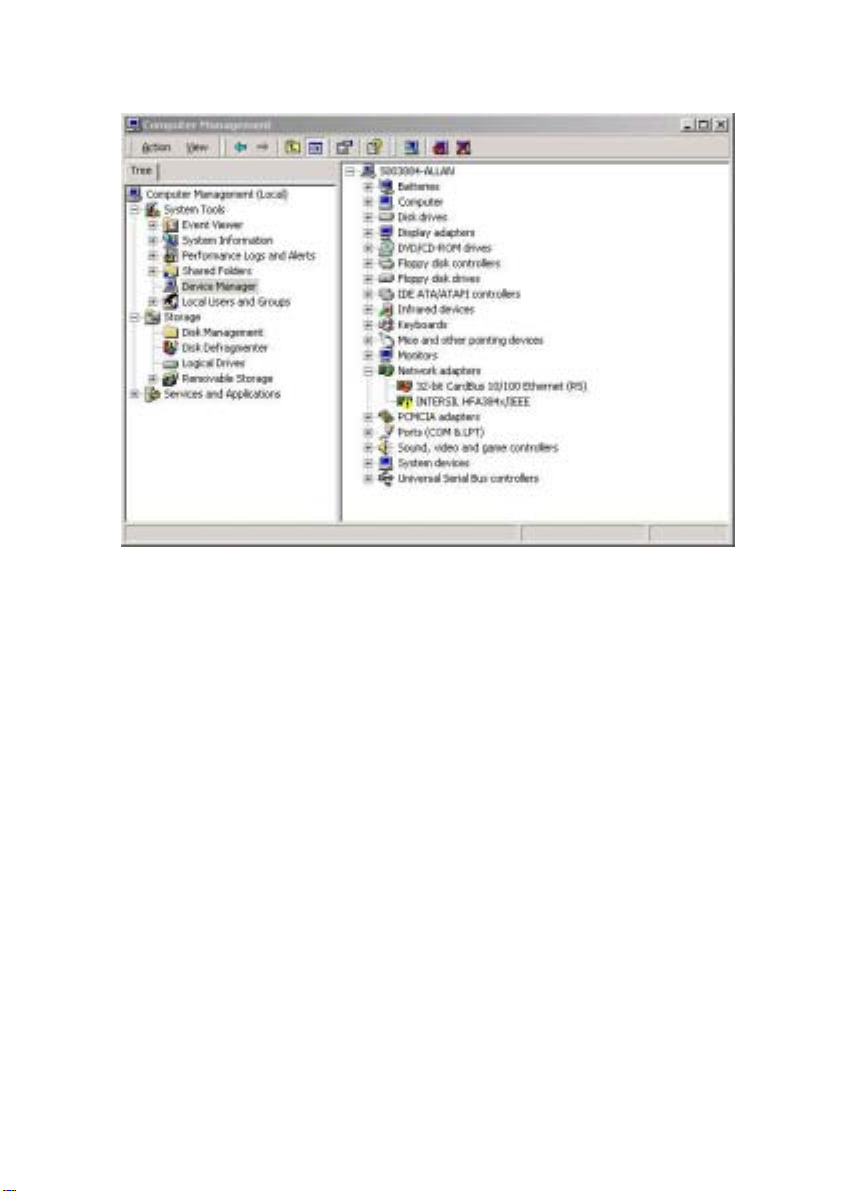
Figure 2-1-2
a. Click Update Driver button from the Driver tab as shown in
Figure 2-1-3.
10
Page 13
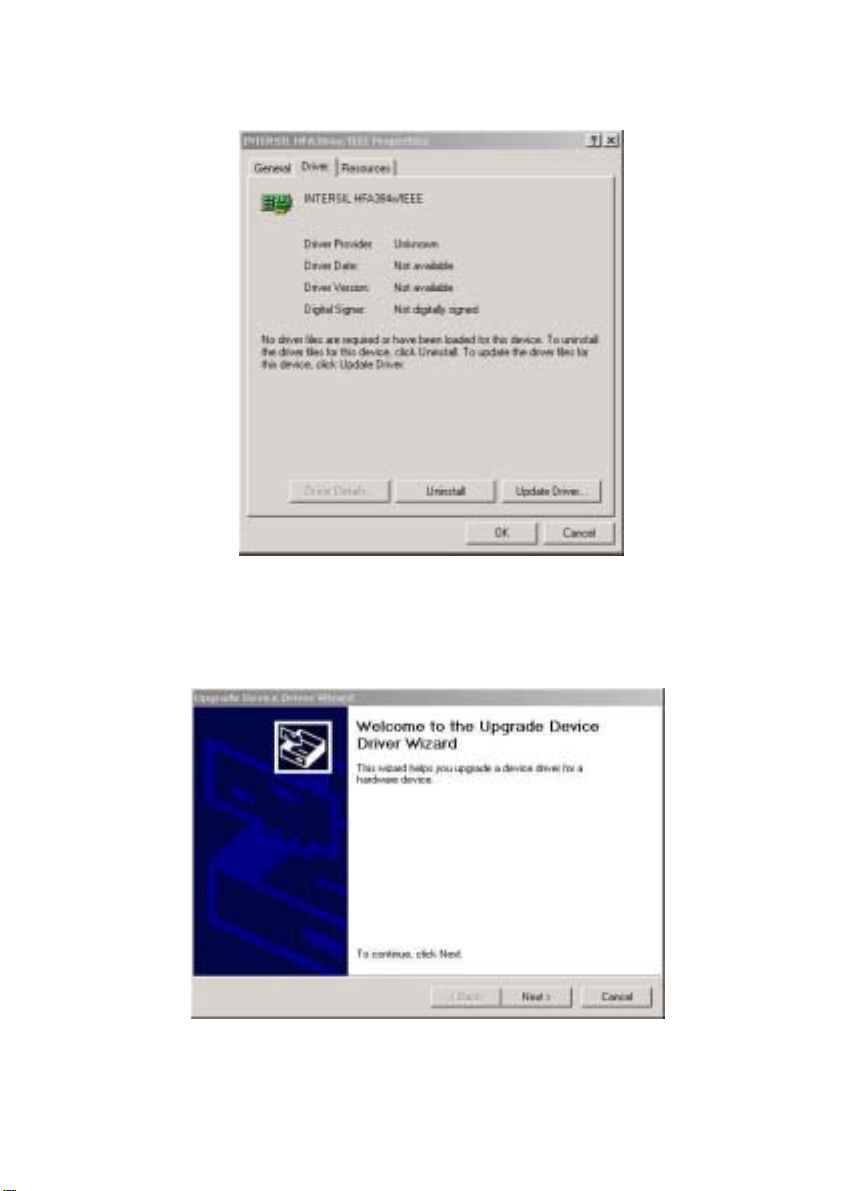
Figure 2-1-3
b. Click next of the Welcome to Upgrade the Device Driver
Wizard dialog box. The Install Hardware Device Driver dialog
window will be showed up as shown in Figure 2-1-4.
Figure 2-1-4
c. Choose Display a list of the known drivers for this device so
11
Page 14

that I can choose the specific driver and click Next as shown
in Figure 2-1-5.
Figure 2-1-5
d. In the Network Type dialog window, choose Network
adapters and then click Next .
Figure 2-1-6
12
Page 15

e. Select the network adapter for 802.11b Wireless LAN USB
Adapter and then click Next. The Start Device Driver
Installation dialog window will show up, click Next to enter
the Digital Signature Notice window.
Figure 2-1-7
13
Page 16

f. Click Yes to continue the installation procedure.
Figure 2-1-8
g. Click Finish to complete the installation procedure.
14
Page 17

Figure 2-1-9
2- 2 Checking after Installation
After installing the driver and utility, follow the steps below to check
that the USB Adapter is operating correctly.
1. Click the Start button, select Settings, and then click Control
Panel.
2. In the Control Panel window, double-click the System icon, and
then select the Device Manager tab.
3. Double-click Network adapters, then select Wireless LAN USB
ADAPTER as shown in Figure 2-4.
15
Page 18

Figure 2-4
4. Click the Properties button, and then check the message. This
device is working properly is displayed for Device status as shown
in Figure 2-5.
5. If you find the Yellow (?) sign on the adapter or the above message
is not displayed, it shows the installation is not successful or the
wireless LAN USB Adapter is not operating properly. Uninst all and
re-install the driver, referring to Chapter 2-6 Uninstalling Driver and
Utility.
16
Page 19

Figure 2-5
17
Page 20

2- 3 Wireless LAN Client Utility
Wireless LAN Client Utility is used to display or change the USB Adapter
information about link, configuration, encryption, and
utility/driver/firmware version information. The client utility will also help
you with site selection. The client utility will be installed automatically
after installing the driver and utility. The USB Adapter Utility icon will
appear in the System Tray in the bottom right corner on your screen as
shown in the Figure 2-3-1 and Table 2-3-1.
Figure 2-3-1
Green indicates good or excellent link status
Yellow indicates fair link status
Red indicates no or poor link status
Table 2-3-1
After finishing installing the driver and utility, the client utility will
automatically be executed and show a small green radio icon at the right
corner of Taskbar whenever the USB Adapter is inserted into the USB
slot of your computer. Double-click the radio icon to open the Wireless
LAN Client Utility window as shown in Figure 2-3-2. You can click the
taps on the top of the windows to select various screen messages. Below
we explain the use and meanings of the various screen messages.
18
Page 21

Figure 2-3-2
1. Menu of System Icon
Right-click on the system tray icon, the icon menu will display as shown
in Figure 2-3-3. Below is the introduction to this icon menu.
Figure 2-3-3
Wireless Radio On/ Wireless Radio Off
19
Page 22

The first two items in the icon menu are used to turn on/off the wireless
radio. When the wireless radio is turned off, a red cross is placed on the
system tray icon as shown in Figure 2-3-4. When the wireless radio is
turned on, the icon will vary in colors depending on the link quality as
described in the Table 2-3-1.
Figure 2-3-4
Remove Status Icon
This item allows you to set the System Tray Icon to appear or disappear.
Once you choose this item, the system will display the dialog box to
confirm if you want to remove the System Tray Icon. You can also set the
System Tray Icon to disappear permanently by checking the box
Remove Status Icon Permanently as shown in the Figure 2-3-5. When
the computer is restarted, the System Tray Icon will come back if you
have removed the System Tray Icon before but not checked the box
Remove Status Icon Permanently.
Figure 2-3-5
Wireless Network St atus
This item launches the USB Adapter Utility with the t ab Status that
20
Page 23

displays the information about link status to users.
Advanced Configuration
This item launches the USB Adapter Utility with the t ab Configuration
that allows users to configure USB Adapters to suit their specific network
settings.
WEP Encryption
This item launches the USB Adapter Utility with the t ab WEP Encryption
that allows users to set up the Encryption Key which is used in their
network environment.
SITE Survey
This item launches the USB Adapter Utility with the t ab Site Survey that
allows users to browser the available active access points which users
can connect to by pressing the Connect button.
Version Information
This item launches the USB Adapter Utility with the t ab About that
displays the information about driver version, utility version, and firmware
version.
2. Status
State
Shows status information about the radio link, as shown in Figure
2-3-6
21
Page 24

Figure 2-3-6
Associated BSSID – means the wireless client is connected to an
access point. BSSID is shown in the form of six hex digits which is
the MAC address of the access point.
Scanning – means the wireless client is searching for an available
access point in infrastructure mode.
Disconnected – means there are no access points or other
wireless clients (if communicating in Ad-hoc mode), or the USB
Adapter is unplugged in your computer.
Current Tx Rate (Mbits/s)
The data speed that wireless client is transmitting.
Current Channel
The operation radio frequency channel that wireless client is using in
infrastructure mode. In infrastructure mode, wireless client will always
go the same channel as their Access Point.
22
Page 25

Throughput (Bytes/sec)
Tx: shows the outgoing (sent) data speed.
Rx: shows the incoming (received) data speed.
Link Quality
In infrastructure mode, this bar displays the transmission quality
between a WLAN station (Access Point) and Wireless LAN USB
Adapter. In Peer-to-Peer mode (Ad-Hoc), this bar displays the link
quality between two Wireless LAN USB Adapters.
Signal Strength
This bar displays the signal strength level. The higher bar is, the more
powerful radio signal is received by the USB Adapter.
Disable/Enable Radio
This button is used like a switch that allows users to turn off the
wireless radio by clicking this button and turn it on again.
Rescan
The radio will rescan all available channels by pressing this button.
You can push this button to rescan the channels for better link quality
when the link quality is poor.
3. Configuration
Make configuration changes by specifying the proper configuration
parameters on this configuration tab as shown in Figure 2-3-7.
Figure 2-3-7
23
Page 26

Profile
You can give a name for this field to a setting of configuration
parameters, such as Network Name, Network Type, Transmit Rate,
Encryption (WEP Security), etc. It makes much easier for users to
change WLAN configuration settings who need to switch working
places frequently. Suppose that a user has to work between the two
different offices where there are different network settings. In this case,
this user just needs to setup two profiles for the two offices and simply
selects the proper profile when the user switches to the different office.
Network Name
For infrastructure mode, you need to type in the SSID of the access
point to which your computer connects. For Ad-Hoc (peer-to-peer)
mode, you need to type in the virtual SSID of the Ad-Hoc network to
which your computer attaches.
Network Type
There are two types of network modes in this drop-down list as shown
in Figure 2-3-8, Peer-to-Peer and Access Point (Infrastructure).
Figure 2-3-8
Peer to Peer: If two or more stations exchange data directly
24
Page 27

without an access point, you need to select Peer-to-Peer mode.
Each station in a Peer-to-Peer (Ad-Hoc) network must specify the
same network name (SSID) and peer-to-peer channel.
Access Point: If at least one access point involves in the
communications in a group of stations, you need to select
Infrastructure mode. Each station needs to specify the same
network name (SSID) as the access point. Please refer to the
section 1-6 for more details about peer-to-peer mode and Access
Point (infrastructure) mode.
Peer-to-Peer Channel
This option is just for Peer-to-Peer (Ad-Hoc) mode. You need to
specify a channel on which the communications are established. Each
station in a Peer-to-Peer (Ad-Hoc) network must specify the same
channel and network type (SSID).
Power Save Mode
Power Save function as shown in figure 2-3-9 .This function can
conserve more battery energy and extend the battery life. This function
has three options for power save mode. Below is detailed description.
1.On: Enable Power Save function.
2.Off: Disable Power Save function.
3.Auto: Utility will automatically detect what kind of power
supply a machine uses and then determine to enable
or disable Power Save function.
If device uses battery, Power Save Mode is set to on.
If device uses AC Power, Power Save Mode is set to
off.
25
Page 28

Figure 2-3-9
Transmit Rate
The transmission rate on which the data packets are transmitted by
the client can be specified in this drop-down list as shown in Figure
2-3-10. Below are the available transmission rates.
Full Automatic USB Adapter chooses the highest available
transmission rate
11 Mbps allows only 11 Mbps operation
5.5 Mbps allows only 5.5 Mbps operation
Auto 1 or 2 Mbp allows only 1 or 2 Mbps operation
Table 2-3-2
26
Page 29

Figure 2-3-10
Defaults
Once this button is pressed, all the settings will be set back to the
default settings.
4. Encryption
Encryption is designed to make the data transmission more secure. you
can select 64 or 128-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) key to encrypt
data (Default setting is Disable) as shown in Figure 2-3-11. WEP
encrypts each frame transmitted from the radio using one of the Keys
from this panel. When you use WEP to communicate with the other
wireless clients, all the wireless devices in this network must have the
same encryption key or passphrase.
Choose one of the encryption key (64 bit or 128bit) from the Encryption
(WEP Security) drop-down list to create encryption key. Click either on
Create Keys Manually radio button or on Create Keys with
Passphrase radio button. There are two ways, Alphanumeric and
Hexadecimal, to set the different characters as shown in Table 2-3-3.
Create Keys ManuallyAlphanumeric
Type 5/13 alphanumeric characters in the key field
27
Page 30
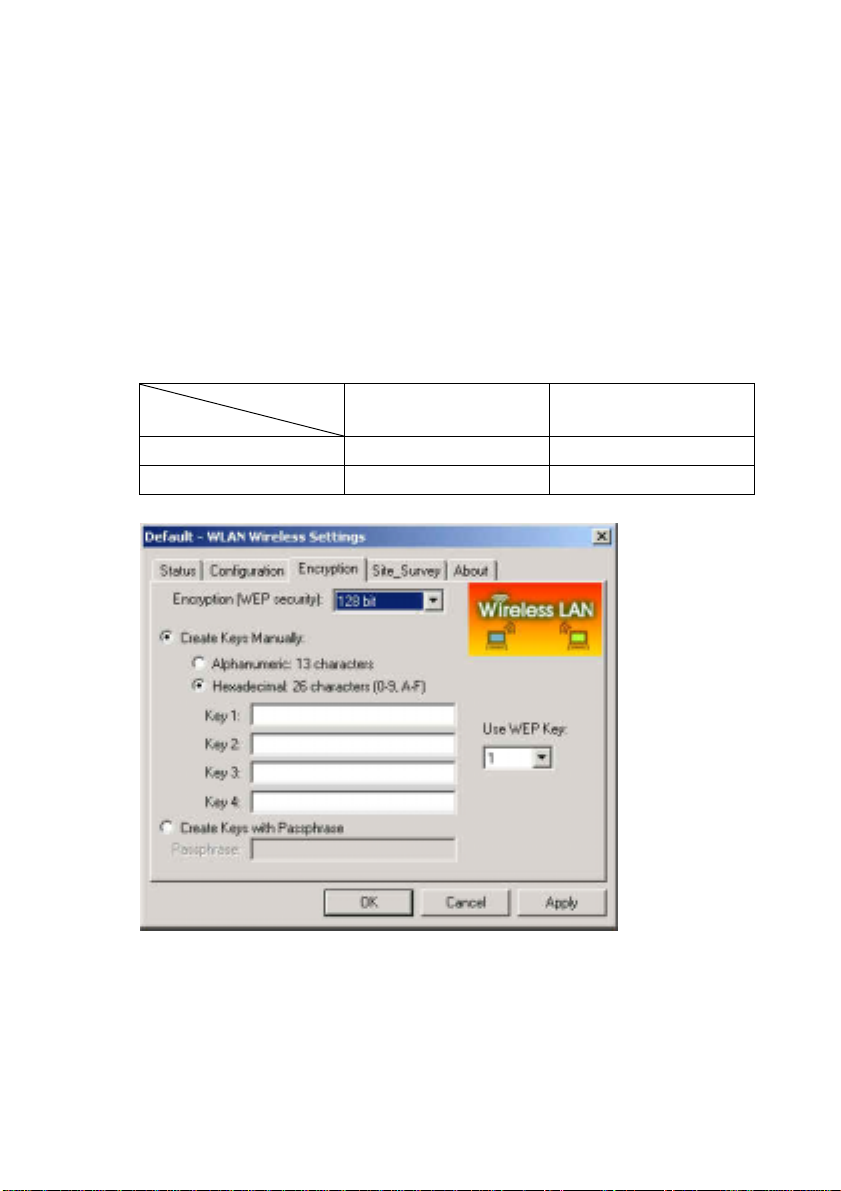
Create Keys ManuallyHexadecimal
Type a 10/26 hexadecimal numbers (1-9; A-F) in the key field
Use WEP Key
This drop-down list allows you to specify which of the four encryption
keys that you want to use.
Create Keys with Passphrase
Type a character string in the field Passphrase.
Disabled
Select Disabled item in the Encryption(WEP security) drop-down list
allows you to disable the encryption function.
Data
Mode
Alphanumeric Hexadecimal
64 bit 5 10
128 bit 13 26
Table 2-3-3
Figure 2-3-11
5. Site Survey
Browse the available access points in your network environment by
clicking the Rescan button and make a connection to one of them by
28
Page 31
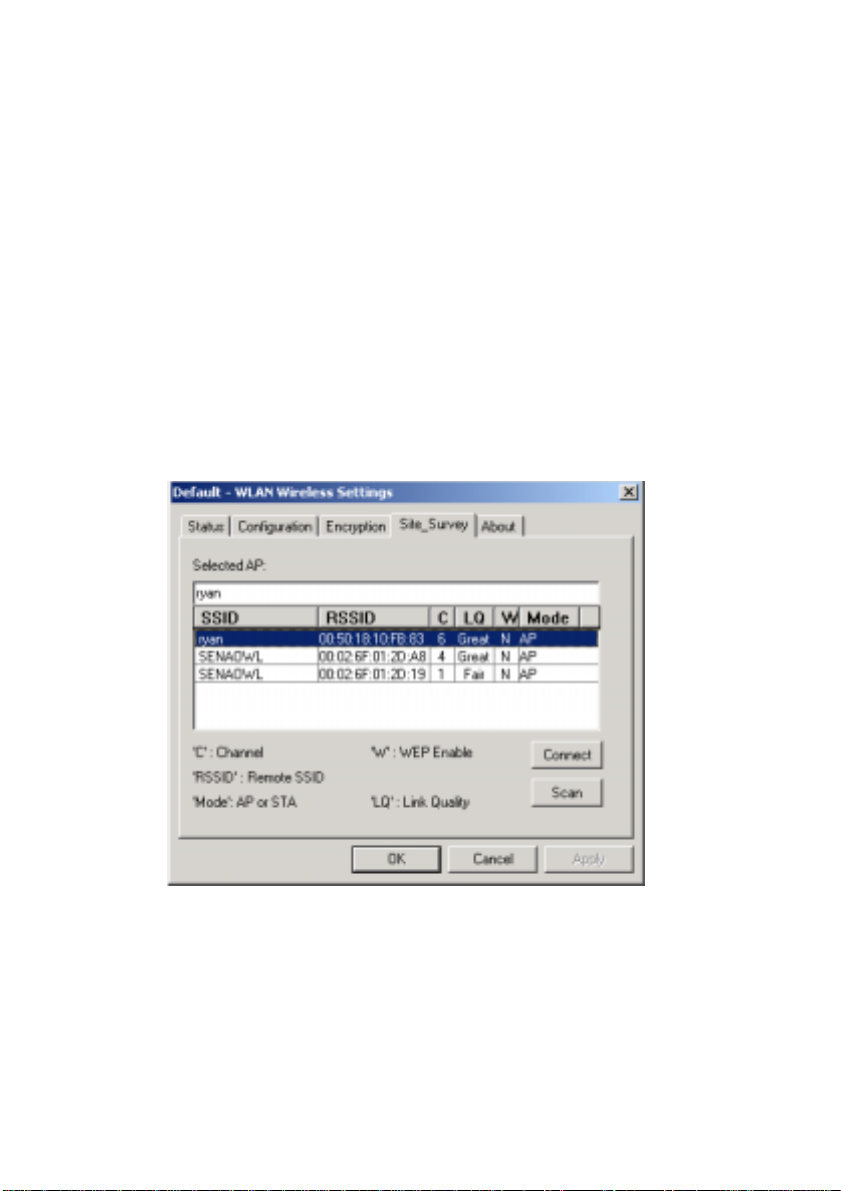
pushing the Connect button in the Site Survey tab as shown in Figure
2-3-12.
SSID The Network Type (SSID) of an access point
RSSID The MAC address of an access point
Channel
The operating channel number of an access
point
Link Quality The quality of link status
“Y” indicates the WEP function enabled in an
WEP
access poin
“N” indicates the WEP function disabled in an
access point
Mode
Indicates which mode does the access points
use (Infrastructure or Peer to Peer)
Figure
2-3-12
29
Page 32

6. About
About tab shows the product/driver/utility/USB Adapter firmware version
as shown in Figure 2-3-13. Users have to use this version number when
reporting their problems to technical support.
Figure 2-3-13
30
Page 33

2- 4 Uninstalling Driver and Utility
If the USB Adapter inst allation is unsuccessful for any reason, the best
way to solve the problem may be to completely uninstall the USB
Adapter and its software and repeat the installation procedure again.
1. Insert the Wireless LAN USB Adapter into the PCMCIA slot.
2. Right click My Computer--->Select Properties.
3. On the Hardware tab, choose Device Manager , and click
Network .Adapter.
4. Choose Wireless LAN USB Adapter and remove it.
5. After removing the Wireless LAN USB Adapter, restart your
computer.
6. Click the Start button, select Control Panel from Settings. Double
click the Add/Remove Programs icon on the Control Panel. In the
Change or Remove Programs dialog window, choose the 802.11b
Wireless LAN for Windows and click Change/Remove button to
uninstall this programs as shown in Figure 2-3-14.
Figure 2-3-14
31
Page 34

Chapter 3 Connecting to a Network
This chapter describes how to prepare for connection to network after
install the USB Adapter drivers and utility.
The following is required for all computers if you want to connect to a
network.
1. Check Client for Microsoft Networks is installed.
2. Check NetBEUI -> Wireless LAN USB Adapter installed.
3. Check TCP/IP -> Wireless LAN USB Adapter is installed.
4. Check file and printer sharing for Microsoft Networks.
5. Check computer name and workgroup name.
3-1 Checking and Adding Client for Microsoft Networks
The Client for Microsoft Networks enables you to connect to other
Microsoft Windows computers and servers and use the files and printers
shared on them. If you works on Microsoft network environment, you
need to set up Client for Microsoft Networks.
1. After finishing installing the driver & utility and rebooting the computer as
described in Chapter 2. The computer will show a dialog box titled Enter
Network Password dialog box. Enter your password if it had been set or just
click Cancel.
2. Click Start button, select Settings and then click Control Panel to open the
Control Panel window.
3. In the Control Panel window, double-click the Network icon to open the
Network dialog box.
4. Select Configuration tab to check Client for Microsoft Networks is installed
as shown in Figure 3-1. If no, click the Add button. Select Client and click the
Add button.
32
Page 35

Figure 3-1
5. Select Microsoft for Manufacturer and Client for Microsoft Networks for
Network Client, and then click OK.
3-2 Checking and Adding NetBEUI
NetBEUI is a protocol you can use to connect to Windows NT, Windows
for Workgroups, or LAN Manager servers. If you work on Microsoft
network environment, you need to set up NetBEUI protocol.
1. Repeat the step 2 and 3 of Chapter 3-1 Checking and Adding Client for
Microsoft Networks.
2. Select Configuration tab to check NetBEUI -> Wireless LAN USB Adapter
is installed. If no, click the Add button. Select Protocol and click the Add
button.
3. Select Microsoft for Manufacturer and NetBEUI for Network Protocol, and
then click OK.
33
Page 36

3-3 Checking and Adding TCP/IP
TCP/IP is the protocol you use to connect to the Internet and wide-area
networks. If you want to connect to Internet, you need to set up TCP/IP
protocol.
1. Repeat the step 2 and 3 of Chapter 3-1 Checking and Adding Client for
Microsoft Networks.
2. Select Configuration tab to check TCP/IP -> Wireless LAN USB Adapter is
installed. If no, click the Add button. Select Protocol and click the Add button.
3. Select Microsoft for Manufacturer and TCP/IP for Network Protocol, and then
click OK.
4. If yes, double-click TCP/IP -> Wireless LAN USB Adapter to open TCP/IP
properties as shown in Figure 3-2. Due to different network applications
there are many different settings here. You can select either Obtain an IP
address automatically or Specify an IP address. If you use the Specify
and IP address, then you need to enter an IP address, Subnet Mask,
Gateway IP address, and DNS Server IP address for connecting to Internet.
Figure 3-2
34
Page 37

3-4 Checking and Adding File and Printer Sharing for
Microsoft Networks
File and printer sharing for Microsoft networks gives you the ability to
share your files or printers with Windows NT and Windows for
Workgroups computers. If you want to share your files or printers with
Microsoft networks, you need to set up this service.
1. Repeat the step 2 and 3 of Chapter 3-1 Checking and Adding Client for
Microsoft Networks.
2. Select Configuration tab to check File and printer sharing for Microsoft
Networks is installed. If no, click the File and Printer Sharing button.
3. In the File and Print Sharing window, select what you need, and click OK.
File and printer sharing for Microsoft Networks, and then click OK.
3-5 Checking and Adding Computer Name & Workgroup
Name
Windows uses the computer name and workgroup name to identify your
computer on the network. Please enter a unique name for your computer,
the workgroup it will appear in, and a short description of the computer.
1. Repeat the step 2 and 3 of Chapter 3-1 Checking and Adding Client for
Microsoft Networks.
2. Select Identification tab (Windows 98) or User Information tab to check the
computer name, workgroup and computer description are entered. If no, enter
a computer name, a workgroup name and then click OK. The description field
may be left blank. If you want to share data with other persons, make sure you
have the same workgroup name.
35
Page 38

Chapter 4 Troubleshooting
This chapter describes the problems and corresponding solutions that
may occur when installing a USB Adapter.
Symptom Solution
Verify that the USB Adapter is properly
inserted into the USB Interface.
Windows does not
detect the USB Adapter
when installed.
Driver fails to load
Check whether the computer has a
Plug and Play BIOS.
Windows 98/ME/2000/XP might not
detect the USB Adapter if a previous
installation of the USB Adapter was
cancelled before it was finished.
Remove the previous driver, and redo
the installation again.
A resource conflict could exist.
For Windows 98/ME/2000/XP, use the
Device Manager to resolve resource
conflicts.
Select System from the Control Panel,
then click on the Device Manager tab.
36
Page 39

Device conflict on a
Windows system
No resource conflicts were
detected, but the wireless
station does not attach to
the network
A device conflict under Windows
98/ME/2000/XP may be related to
the USB Adapter.
For Windows 98/ME/2000/XP, use the
Computer properties to identify the
used I/O port addresses and IRQ
values.
If there is a device conflict, select
alternative settings for I/O Base Address
or IRQ values. If you know which device
is conflicting with the USB Adapter, you
have the option of changing that device’s
I/O address or IRQ instead of changing the
USB Adapter.
Verify that the SSID of the USB Adapter
matches that of the access point. Use
the Network Configuration Properties
Application in the Control Panel to
modify the SSID.
Verify that the Network Mode of the
USB Adapter is configured correctly.
37
Page 40

Nonfunctioning card LED
Weak signal or
intermittent connection.
The USB Adapter is not powered on. The
cause may be:
No Driver loaded or installed.
Adapter – Driver mismatch which
prevented the driver from loading.
Device conflicts which prevented the
driver from loading.
Actions:
Verify that a driver has been installed.
Determine if there is a conflict with
another device.
Try reorienting the antenna. The USB
Adapter antenna is attached to the two
sides of the USB Adapter. For best use of
the antenna:
Keep the area around the antenna
clear from materials that could block
radio transmission, such as metal
objects, electronic devices, and
cordless telephones.
If your signal is weak, change the
direction of the antenna slightly.
If necessary, move your notebook
computer a few inches to find a better
signal.
Use the Link Quality and Signal Strength
display in the Monitor Utility to determine
the best location and orientation for a
network connection.
38
Page 41
Appendix A – Specifications
General
Data Rates
Network Standards
Compliance
Drivers
Operational Voltage
Security
RF Information
Frequency Band 2412 – 2483.5 MHz
Channels 11 for North America, 14 for Japan, 13 for Europe,
Media Access Protocol Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA)
1,2,5.5,6,9,11 Mbps
IEEE 802.11b
FCC Part 15/UL, ETSI 300/328/CE
Windows 98/ME/2000/XP
5± 0.15V
IEEE802.1x Client Support
WPA -- Wi-Fi Protected Access (64,128-bit WEP with TKIP,
Pre-Share Key)
2 for Spain, 4 for France
Modulation Technology Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
DBPSK @ 1Mbps
DQPSK @2Mbps
CCK @ 5.5 & 11Mbps
Receive Sensitivity (Typical) -92dBm @ 1Mbps
-89dBm @ 2Mbps
-88dBm @ 5.5Mbps
-85dBm @ 11Mbps
Available transmit power 15 dBm
Physical
LED RF link activity
Interface USB 2.0
Antenna Dipole antenna
Dimensions 75 (L)mm x 54(W)mm x14(H)mm
Environmental
Temperature Range 0°C to 55°C - Operating
-20°Cto 70°C - Storage
Humidity (non-condensing) 5%~95% Typical
Page 42

Appendix B Regulatory Compliance Information
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for
a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of
the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by
the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to
operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth
for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed
and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your
body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with
any other antenna or transmitter.
 Loading...
Loading...