Page 1
Also available from SECO-LARM:
Quad Photobeam
Detectors
4 Models available - up to
•
660ft (200m) range
Weatherproof
•
12~24 VAC/VDC
•
Laser-beam alignment
•
Reflective
Photobeam Sensor
Available with 45ft (14m) or
•
35ft (11m) range
Weatherproof
•
Mounting hardware included
•
Reflector included
•
Curtain Sensors Long-Range
Barrier Sensors
2, 4, 6, 8 or 10 Beams available
•
Up to 50ft (15m) range
•
Weatherproof
•
Slimline design
•
Laser-beam alignment
•
Hooded Reflective
Photobeam Sensor
Available with 50ft (15m) or
•
33ft (10m) range
Weatherproof
•
Polarized version available
•
Round reflector included
•
2, 4, 6, or 8 Beams available
•
Up to 393ft (120m) range
•
Weatherproof
•
Multi-frequency
•
Adjustable interruption time
•
Flush-Mount
Photobeam Sensors
Available with reflective beam and
•
16ft (5m) range or through-beam
and 33ft (10m) range
Adjustable alignment angle
•
Mounts to a single-gang box
•
Twin Photobeam Detectors
Manual
WARRANTY: This SECO-LARM product is warranted against defects in material and workmanship while used in normal
service for a period of one (1) year from the date of sale to the original consumer customer. SECO-LARM’s obligation is
limited to the repair or replacement of any defective part if the unit is returned, transportation prepaid, to SECO-LARM.
This Warranty is void if damage is caused by or attributed to acts of God, physical or electrical misuse or abuse, neglect,
repair, or alteration, improper or abnormal usage, or faulty installation, or if for any other reason SECO-LARM determines that
such equipment is not operating properly as a result of causes other than defects in material and workmanship.
The sole obligation of SECO-LARM, and the purchaser’s exclusive remedy, shall be limited to replacement or repair only, at
SECO-LARM’s option. In no event shall SECO-LARM be liable for any special, collateral, incidental, or consequential personal or
property damages of any kind to the purchaser or anyone else.
NOTICE: The information and specifications printed in this manual are current at the time of publication. However, the
SECO-LARM policy is one of continual development and improvement. For this reason, SECO-LARM reserves the right to
change specifications without notice. SECO-LARM is also not responsible for misprints or typographical errors.
Copyright © 2014 SECO-LARM U.S.A., Inc. All rights reserved. This material may not be reproduced or copied, in whole or in
part, without the written permission of SECO-LARM.
®
SECO-LARM
U.S.A., Inc. U.S.A., Inc.
U.S.A., Inc.
U.S.A., Inc. U.S.A., Inc.
16842 Millikan Avenue, Irvine, CA 92606
Tel: 800-662-0800 / 949-261-2999 Fax: 949-261-7326
file:DTP\Manual\MiE96x-DxxxQ_P1410.pmd
Website: www.seco-larm.com
@
E-mail: sales
seco-larm.com
PITSW3
12
Model # Outdoor Range Indoor Range
E-964-D390Q* 390 ft. (120m) 790 ft. (240m)
E-960-D290Q 290 ft. (90m) 590 ft. (180m)
E-960-D190Q 190 ft. (60m) 390 ft. (120m)
E-960-D90Q 90 ft. (30m) 190 ft. (60m)
* Multi-frequency version
SECO-LARM
®
®
Page 2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Important ................................................... 2
Choosing a Location ................................... 3
Typical Installations ....................................... 4
Running the Cable ........................................... 4
Wiring the Transmitter – Wall Mount ................ 4
Wiring the Transmitter – Pole Mount ................ 5
Wiring .............................................................. 5
Examples of Ways To Connect Sensors ............. 6
Selectable 4-channel Beam Frequency ............ 7
Beam Frequency Selection Chart...................... 7
(E-964-D390Q Model Only)
Multiple Sensors Sample Applications ........ 7-8
Adjusting the Alignment ................................. 9
Adjusting the Delay Time ............................... 10
Testing the Unit .............................................. 10
Specifications ................................................ 10
Dimensions ................................................... 11
Troubleshooting ............................................. 11
Fig. 12: Dimensions
43ST Pole Size
Top View
Side View
2.8” (72mm)
2.9” (74mm)
6.8” (173mm)
Front View
Rear View
Features:
●
Four selectable beam frequencies
(For E-964-D390Q model only).
●
Twin beams provide reliable perimeter
security,
minimizing false alarms from
falling leaves, birds, etc.
●
Lensed optics reinforce beam strength
and provide excellent immunity to false
alarms due to rain, snow, mist, etc.
●
Weatherproof, sunlight-filtering case for
indoor and outdoor use.
●
Non-polarized power inputs.
●
Automatically adjusts beam strength
to compensate for different weather
conditions
●
Automatic input power filtering with
special noise rejection circuitry.
●
N.C./N.O. alarm output.
●
N.C. tamper circuit included.
●
Quick, easy installation with built-in
laser beam alignment system.
●
Interruption time adjustable for nearly
all situations.
Included:
Mounting
hardware
also
included.
Pole mounting
Transmitter x 1 Receiver x 1 Mounting plates x 2
IMPORTANT –Do not connect to power until the sensor is completely installed and the
installation has been double-checked.
brackets (2 sets)
Fig. 13: Beam Spread
The beam spread (s) can be calculated as s=0.03xd.
Distance (d)
90ft (30m)
190 ft (60m)
290 ft (90m)
390 ft (120m)
Beam spread (s)
2.7 ft (0.8m)
5.7 ft (1.7m)
8.7 ft (2.7m)
11.7 ft (3.6m)
Table 6: Troubleshooting
Situation
Transmitter LED does not light.
Receiver LED never lights up
when the beam is interrupted.
Beams interrupted and LED
lights, but no alarm trigger.
Alarm LED continuously lit.
Alarm trigger becomes erratic
in bad weather.
Frequent false triggers from
leaves, birds, etc.
Possible Problem
Incorrectly wired and/or
insufficient voltage
a. Insufficient voltage
b. Beam reflected away from receiver
c. Beams not simultaneously interrupted.
Alarm trigger cable may be cut, or the
relay contact stuck due to overloading.
a. Lenses out of alignment.
b. Beams are blocked.
c. Cover is foggy or dirty.
Lenses out of alignment.
a. Too sensitive.
b. Bad location.
beam spread (s)
distance (d)
Solution
Ensure the power supply to the
transmitter is 12 to 24 VAC/VDC.
a. Double-check the voltage.
b. Clean the cover.
c. Check overall installation.
Check the continuity of the wiring
between the sensor and the alarm.
a. Realign the lenses.
b. Remove any obstacles.
c. Clean the cover.
Check overall system installation.
If still erratic, realign the lenses.
a. Reduce the response time.
b. Change the transmitter and/or
location.
2
11
Page 3

123
123
123
123
123
123
123
123
123
123
123
123
123
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
123
123
Adjusting the Delay Time
1. The delay time adjustment knob sets how long the beam can be interrupted
before triggering the alarm (see fig. 11):
a. A short interrupt time (high sensitivity) is suitable for catching fast moving
intruders, but more susceptible to false alarms.
b. A long interrupt time (low sensitivity) reduces false alarms, but fast
moving intruders may not trigger the sensor.
2. Adjust the knob to the site’s situation. You may need to make adjustments
later after the walk-through test.
Testing the Unit
1. Power up the transmitter and receiver.
2. If the yellow or red LED remains steady ON
even when the beam is not interrupted, readjust the alignment.
3. Walk between the transmitter and receiver to
interrupt the beams. Walk at various speeds, and
adjust the delay time adjustment knob as needed.
Table 5: Specifications
Model
Max. range (outdoor)
Max. range (indoor)
Max. current (Tx & Rx)
No. of beam channel
Voltage output (+/-10%)
Power
Detection method
Interrupt speed*
Alarm output
Tamper output (Tx & Rx)
Alarm LED
(receiver)
Signal LED
(receiver)
Power LED (Tx & Rx)
Laser wavelength
Laser output power
Alignment angle
Operating temperature
Weight
Case
*This is the minimum time interval between breaking of both beams which will trigger the output. Setting the interval
longer will reduce false alarms from birds or falling leaves, etc., while setting it shorter will detect faster moving objects.
E-960-D90Q
90’ (30m)
190’ (60m)
64mA
N/A N/A N/A 4
1~4V
10~30 VAC/VDC (non-polarized)
Simultaneous breaking of 2 beams
50msec~700msec (variable)
NO/NC relay, 1A @ 120VAC, min. 1 sec.
NC switch, 1A @ 120VAC
Red LED - ON: When transmitter and receiver are not
aligned or when beam is broken.
Yellow LED - ON: When receiver's signal is weak or when
beam is broken.
Green LED ON: Indicates connected to power
650nm
≤
5mW
Horizontal: ±900, Vertical: ±5
-130F (-250C) to +1310F (+550C)
2.5 lbs. (1.1kg)
PC Resin
NOTE – The alarm will be triggered only if both
the upper and lower beams are simultaneously
interrupted.
IMPORTANT – Test the detector periodically to
ensure the alignment and delay time settings are
suitable for the site.
E-960-D190Q
190’ (60m)
390’ (120m)
70mA
10
E-960-D290Q
290’ (90m)
590’ (180m)
74mA
0
Fig. 11:
Adjusting the
Delay Time
300ms
E-964-D390Q
390’ (120m)
790’ (240m)
88mA
Fig. 1: Identifying the Sensors
Receiver Transmitter Mounting Plate
Signal LED
Alarm LED
Frequency selection*
switch
700ms50ms
Power LED
Voltage output
probes
* For multi-frequency E-964-D390Q model only.
Terminals
Frequency selection*
switch
Delay time
adjustment knob
Power LED
Vertical adjustment
screw
Horizontal
adjustment
Lens
View finder
Alignment laser
Laser ON/OFF switch
Choose a Location
To prevent erratic operation and/or false alarms:
• Wind will not directly cause false alarms, but could cause leaves or similar objects to fly or wave
into the beams. Therefore, do not mount near trees, bushes, or other leafy vegetation.
• Do not mount where the transmitter or receiver could be splashed by water or mud.
• Do not mount where the unit could be suddenly exposed to a bright light, such as a floodlight or a
passing automobile’s headlight.
• Do not let sunlight or any direct beam of light enter the sensing spot of the transmitter. If needed,
mount so the receiver, not the transmitter, faces the sun.
• Do not mount where animals could break the beams.
Fig. 2: Vertical and Horizontal Adjustments Fig. 3:Typical Installations
Vertical adjustment
±5°
(10°)
adjustment
Horizontal adjustment
±90°(180°)
Vertical
screw
2
Side Views
32" to 39"
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
Top Views
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
Page 4

Typical Installations
The photoelectric beam lens can be adjusted horizontally ±90°, and vertically ±5° (see fig. 2). This
allows much flexibility in terms of how the transmitter and receiver can be mounted. See fig. 3.
Install at a distance of 32” to 39” (80 to 100 cm) above the ground for most situations. See fig. 3.
Running the Cable
Run a cable from the alarm control panel to the photobeam sensor. If burying the cable is required,
make sure to use electrical conduit. Shielded cable is strongly suggested. See Table 1 for maximum
cable length.
Table 1: Cable Length
Model E-964-D390Q
Wire Size
AWG22
0.33mm
0.0005in
AWG20
0.52mm
0.0008in
AWG18
0.83mm
0.0013in
AWG17
1.03mm
0.0016in
Note (1):
E-960-D90Q E-960-D190Q
12V 24V 12V 24V 12V 24V
320m
2
1,050 ft.
2
550m
2
1,800 ft.
2
800m
2
2,600 ft.
2
980m
2
3,190 ft.
2
2,800m
18,000 ft.
4,800m
15,750 ft.
7,200m
23,620 ft.
8,800m
28,870 ft.
280m
920 ft.
450m
1,480 ft.
700m
2,300 ft.
850m
2,790 ft.
2,400m
7,870 ft.
4,200m
13,780 ft.
6,200m
20,340 ft.
7,600m
24,930 ft.
Max. cable length when two or more sets are connected is the value shown in
Table 1 divided by the number of sets.
Note (2):
The power line can be wired to a distance of up to 3,300 ft. (1,000m) with
AWG22 (0.33mm2) telephone wire.
E-960-D290Q
200m
660 ft.
350m
1,150 ft.
500m
1,640 ft.
590m
1,940 ft.
1,600m
5,250 ft.
3,000m
9,840 ft.
4,200m
13,780 ft.
5,200m
17,060 ft.
12V 24V
110m
390 ft.
560 ft.
820 ft.
1,020 ft.
2,950 ft.
170m
4,590 ft.
250m
7,220 ft.
310m
8,530 ft.
900m
1,400m
2,200m
2,600m
Adjusting the Alignment
The transmitter and receiver sensor units can be adjusted ±5º
vertically and ±90º horizontally once the unit is mounted and
power is connected (see fig. 2 on page 3).
There are two ways to adjust alignment:
1. Laser adjustment (see fig. 1 on page 3):
Fig. 10:
Horizontal and Vertical
Sensor Adjustment
Vertical
Adjustment
Horizontal
Horizontal
Adjustment
Adjustment
a. Remove the transmitter cover, then turn the laser on with
the ON/OFF switch (see fig. 1 on page 3). A red dot will
show where the photoelectric beams are aimed.
b. Adjust the transmitter's sensor unit vertically and
horizontally until the red dot is centered on the receiver
and both the receiver’s LEDs turn off. See Table 3. It may
be necessary to adjust the horizontal and vertical angles
View
Finders
of the receiver's sensor unit as well.
c. Repeat steps a and b for the receiver.
d. Turn the lasers off, and then replace the covers.
WARNING: Do not look directly at the lasers.
2. Eyeball adjustment (see fig.10):
a. Remove the transmitter cover, and look into one of
the alignment viewfinders (one of the four holes
located between the two lenses) at a 45° angle.
b. Adjust the horizontal angle of the lens vertically
and horizontally until the receiver is clearly seen
in the viewfinder.
c. Repeat steps a and b for the receiver.
d. Replace the transmitter and receiver covers.
NOTE - If you cannot see the opposite unit in the viewfinder, put a sheet of white paper near the unit to
be seen, move your eyes about 2" (5cm) away from the viewfinder, and try again.
Table 3: Receiver LED Indicators
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
Signal (Yellow LED)
Single
frequency
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
frequency
Flash
Multi
OFF
ON
ON
Alarm
(Red LED)
Signal
strength
Best
Good
Fair
Re-adjust
Wiring the Transmitter – Wall Mount
1. Remove the cover. Remove the screw under
the lens unit in order to detach the mounting
plate. See fig. 4.
2. If the sensor wiring comes from inside the wall
– Break a hole in the mounting plate’s rubber
grommet, and pull the cable through the
grommet’s hole. Then run the cable through
the hole near the top of the sensor unit so it
comes out the front. Using two of the included
mounting screws, attach the mounting plate to
the wall. Then reattach the sensor unit to the
mounting plate, connect the wires, and snap
on the cover. See fig. 5.
3. If the sensor wiring is run along the surface of
the wall – There are two plastic knockouts on
the back of the sensor unit, one on top and one
on bottom. Break out the appropriate knockout,
and pull the wiring through the knockout. Then
run the wiring through the hole near the top of
the sensor unit so it comes out the front. Using
two of the included mounting screws, attach the
mounting plate to the wall. Then reattach the
sensor unit to the mounting plate, connect the
wires, and snap on the cover. See fig. 6.
4
Fine Tuning the Receiver
1. Once the sensor is mounted and aligned, the sensor
can be fine tuned using the voltage output jack.
a. Set the range of a volt-ohm meter (VOM) to
1~4VDC.
b. Insert the red (+) probe into the (+) terminal
and the black (-) probe into the (-) terminal.
c. Measure the voltage (see table 4).
d. Adjust the horizontal angle by hand until the
VOM indicates the highest voltage.
e. Adjust the vertical angle by turning the vertical
adjustment screw until the VOM indicates the
highest voltage.
NOTE -
Do not interrupt the beam while adjusting alignment.
9
Table 4:
Voltage output
Single
frequency
>2.8V
1.7~2.7V
1.1~1.6V
<1.0V
Note: 4VDC is maximum possible reading.
frequency
>2.8V
1.8~2.7V
1.1~1.7V
<1.0V
Multi
Alignment
quality
Best
Good
Fair
Re-adjust
Page 5

3. Two layer (double stacked) applications.
Sensor #1
Tx
Ch1
Sensor #4 Sensor #5 Sensor #6
Tx
Ch3
Rx
Ch1
Rx
Ch3
Sensor #2 Sensor #3
Rx
Ch1
Rx
Ch3
4. Perimeter security application.
Tx
Ch1
Ch3
Wiring the Transmitter – Pole Mount
(NOTE – Pole mounting bracket required.)
1. Remove the cover. Remove the screw under
Tx
Ch2
Tx
Tx
Ch4
Rx
Ch2
Rx
Ch4
the lens unit in order to detach the mounting
plate. See fig. 4.
2. Break a hole in the mounting plate’s rubber
grommet, and pull the cable through the
grommet’s hole. Then run the cable through
the hole near the top of the sensor unit so it
comes out the front. Use the included
mounting bracket to mount to the pole. Then
reattach the sensor unit to the mounting plate,
connect the wires, and snap on the cover.
See fig. 7.
Wiring (fig. 8)
1. Screw the wires tightly to avoid slipping off the
terminals, but not so tight that they break.
2. Screws on terminals which are not used
should be tightened.
3. Grounding may be necessary, depending on
the location.
Rx
Ch2
Rx
Ch3
Tx
Ch1
Sensor #3
Sensor #1
Tx
Ch4
Sensor #2
Sensor #4
5. Two layer (double stacked) perimeter security application.
Tx
Ch2
Rx
Ch2
Ch4
Rx
Ch1
Ch3
Ch4
Tx
Ch1
Ch3
Rx
Ch1
Tx
Ch3
Fig. 5: Wall Mount, Wire from Inside WallFig. 4: Remove the Transmitter cover
Rx
Ch4
Tx
Ch2
Fig. 6: Wall Mount, Wire Runs Along Wall
Tx
Ch1
Ch3
Tx
Ch2
Ch4
Rx
Ch1
Ch3
Rx
Ch2
Ch4
Fig. 8: Wiring
Transmitter
12
10~30
AC/DC
{
Power
10~ 30 VAC/VDC
(non-polarized)
– or –
67
N.C.
{
Tamper output
N.C. switch 120V (AC/DC) 1A
(Triggers if cover detached)
Fig. 7: Pole Mount
Receiver
1234567
10~30
AC/DC
Power
10~ 30 VAC/VDC
(non-polarized)
COM. N.O.
{
Alarm output
120V (AC/DC) 1A
N.C.
{
N.C.
Tamper output
N.C. switch 120V (AC/DC) 1A
(Triggers if cover detached)
{
8
5
Page 6
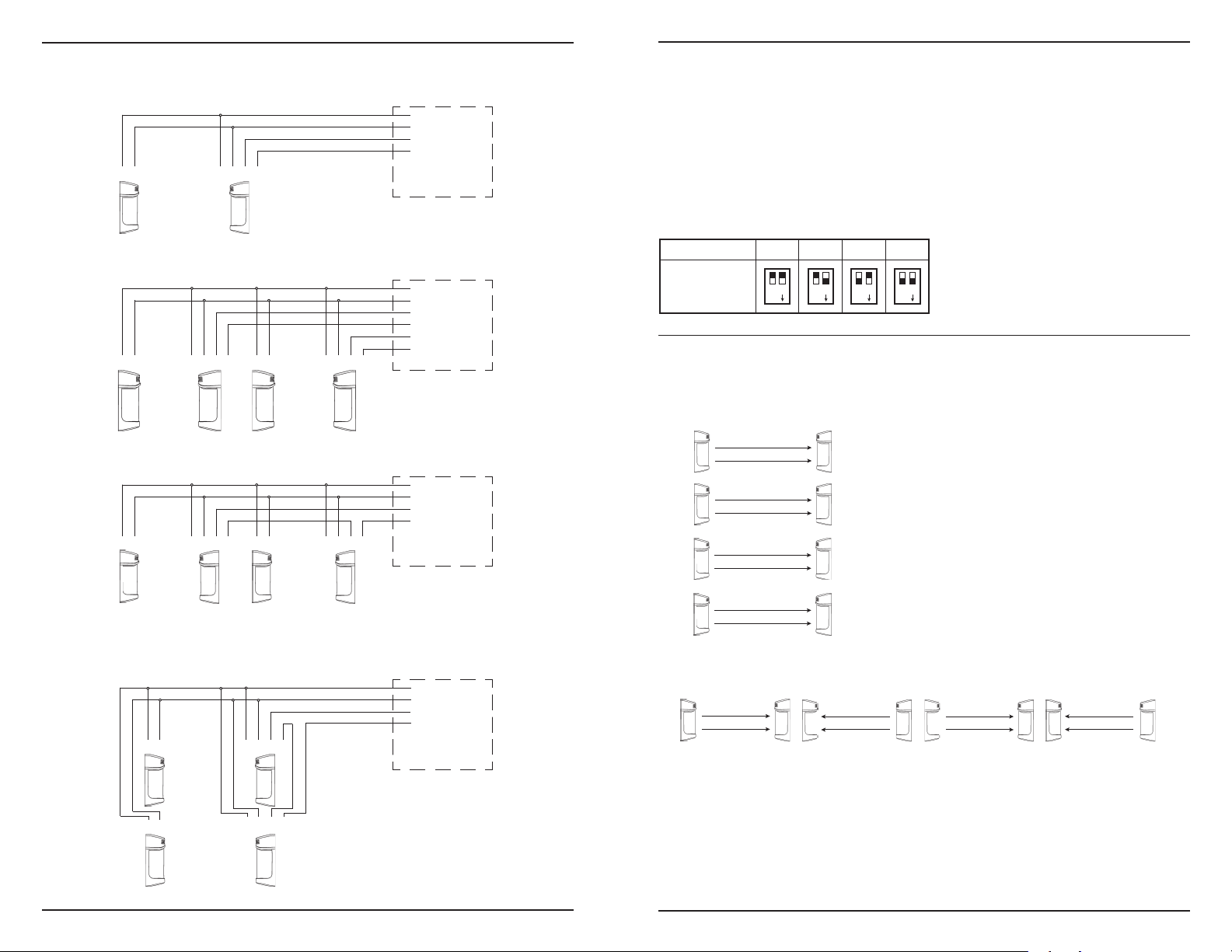
Fig. 9: Examples of Possible Ways To Connect One or More Sensors
Example connection 1 - Standard
Control panel
(12VDC)
}
Power
}
Alarm signal
Selectable 4-channel beam frequency (For E-964-D390Q model only)
The sensor beam frequency can be set at different levels on-site to avoid interference from other twin
photobeam sensors nearby. Useful during mutliple sensor applications as shown below. To select
between four different beam frequencies, adjust the beam channel switch of the transmitter side and
receiver side. See fig. 1 for switch location and table 2 for switch position.
➀➁
Transmitter
➀➁➂➃
Receiver
Example connection 2 - Dual Sensors, Separate Channels
➀➁ ➀➁➂➃
Transmitter
Receiver
➀➁ ➀➁➂➃
Transmitter
Receiver
Example connection 3 - In-line Single Channel
➀➁
Transmitter
➀➁➂➃
Receiver
➀➁
Transmitter
➀➁➂➃
Receiver
Control panel
(12VDC)
}
Power
}
Alarm (ch. 1)
}
Alarm (ch. 2)
Control panel
(12VDC)
}
Power
}
Alarm signal
Important –
The transmitter and receiver sensor pair must be set with the same frequency.
Table 2: Beam Frequency Selection Chart (For E-964-D390Q model only)
CH4
12
NO
CH3
12NO12
NO
Frequency channel CH1 CH2
Switch position
12
NO
Multiple sensor sample applications ( For E-964-D390Q model only)
1. Single pair multiple layer application.
Tx
Ch1
Tx
Ch2
Tx
Ch3
Tx
Ch4
Sensor #1
Sensor #2
Sensor #3
Sensor #4
Rx
Ch1
Rx
Ch2
Rx
Ch3
Rx
Ch4
Example connection 4 - Two stacked
➀➁ ➀➁➂➃
Tx
➀➁
Tx
Rx
➀➁➂➃
Rx
2. Long distance series application.
}
Power
}
Alarm signal
6
Tx
Ch1
Sensor #1
Rx
Ch1
Sensor #2 Sensor #3 Sensor #4
Rx
Ch2
Tx
Ch2
Tx
Ch3
Rx
Ch3
Rx
Ch4
7
Tx
Ch4
 Loading...
Loading...