Seat Mii 2014 Owner's Manual

OWNER’S
MANUAL
Mii
About this manual
This manual contains a description of the
equipment supplied with the vehicle at the
time this manual was published. Some of the
units described herein will not be available
until a later date or are only available in certain markets.
Because this is a general manual for the MII,
some of the equipment and functions that are
described in this manual are not included in
all types or variants of the model; they may
vary or be modified depending on the technical requirements and on the market; this is in
no way deceptive advertising.
The illustrations are intended as a general
guide and may vary from the equipment fitted
in your vehicle in some details.
The steering indications (left, right, forward,
reverse) appearing in this manual refer to the
normal driving movements of the vehicle except when otherwise indicated.
The equipment marked with an aster-
*
isk* is fitted as standard only in certain
versions, and is only supplied as optional extras for some versions, or are
only offered in certain countries.
® All registered marks are indicated with
®. Although the copyright symbol does
not appear, it is a copyrighted mark.
>> The section is continued on the follow-
ing page.
WARNING
Texts preceded by this symbol contain information on safety. They warn you about possible dangers of accident or injury.
CAUTION
Texts with this symbol draw your attention to
potential sources of damage to your vehicle.
For the sake of the environment
Texts preceded by this symbol contain relevant information concerning environmental
protection.
Note
Texts preceded by this symbol contain additional information.
This manual is divided into five large parts,
which are:
1. Safety
2. Operation
3. Tips
4. Technical data
5. Alphabetical index
At the end of this manual, there is a detailed
alphabetical index that will help you quickly
find the information you require.

Foreword
This Instruction Manual and its corresponding supplements should be read carefully to
familiarise yourself with your vehicle.
Besides the regular care and maintenance of
the vehicle, its correct handling will help preserve its value.
For safety reasons, always note the information concerning accessories, modifications
and part replacements.
If selling the vehicle, give all of the on-board
documentation to the new owner, as it
should be kept with the vehicle.
You can access the information in this manual using:
●
Thematic table of contents that follows the
manual’s general chapter structure.
●
Alphabetical index with many terms and
synonyms to help you find information.
WARNING
Read and always observe safety information concerning the passenger's front airbag ››› page 25, Important information
regarding the front passenger's airbag.


Table of Contents
Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Safe driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Safety first! . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Tips for driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Correct sitting position for vehicle occupants . 6
Pedal area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Seat belts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Using seat belts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
How to properly adjust your seatbelt . . . . . . . . 15
Seat belt tensioners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Airbag system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Brief introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
General overview of the airbag . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Deactivating airbags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Transporting children safely . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Child safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Cockpit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Instruments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Control lamps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
SEAT information system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Opening and closing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Vehicle key set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Central locking* and locking system . . . . . . . . 45
Doors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Rear lid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Electric windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Sliding/tilting electric panoramic sunroof . . . . 53
Lights and visibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Visibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table of Contents
Windscreen wiper and rear window wiper
systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Rear vision mirror . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Seats and head restraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Adjusting the seat and head restraints . . . . . . 63
Seat functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Transport and practical equipment . . . . . . . . . 65
Transporting objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Practical equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Loading luggage compartment . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Roof carrier system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Air conditioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Heating, ventilation and air conditioning
system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Stopping and starting the engine . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Braking and parking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Changing gear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Run-in and economical driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Engine management and exhaust gas
purification system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Driving abroad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Driving along flooded roadways . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Driver assistance systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Braking and stability systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Parking sensor system* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Cruise control* (Cruise control system - CCS) . . 107
Safety Assist* (City Safety Assist function) . . . . 110
Hill driving assistant* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Start-Stop system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Towing bracket device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Trailer coupling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Advice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Care and maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Accessories, replacement of parts and
modifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Care and cleaning the vehicle exterior . . . . . . . 125
Caring for and cleaning the vehicle interior . . . 131
Notes for the user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Checking and refilling levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Fuel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Filling the tank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Bonnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Engine oil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Engine coolant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Brake fluid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Checking and topping up the windscreen
washer reservoir with water . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Vehicle battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Wheels and tyres . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Wheels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Emergencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
In case of emergency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Vehicle tool kit* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Changing a wheel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Tyre repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Starting assistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Towing and tow starting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Emergency locking and unlocking . . . . . . . . . . 186
Changing the windscreen wiper blades . . . . . . 188
Fuses and bulbs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Fuses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Changing bulbs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Technical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Technical features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Important information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Wheels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Engine specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
3

Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Capacities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Table of Contents
4
Safety
Safe driving
Safety first!
WARNING
●
This manual contains important information about the operation of the vehicle, both
for the driver and the passengers. The other
sections of the on-board documentation also
contain further information that you should
be aware of for your own safety and for the
safety of your passengers.
●
Ensure that the on-board documentation is
kept in the vehicle at all times. This is especially important when lending or selling the
vehicle to another person.
WARNING
Driving under the influence of alcohol, drugs,
medication or narcotics may result in severe
accidents and even loss of life.
●
Alcohol, drugs, medication and narcotics
may significantly alter perception, affect reaction times and safety while driving, which
could result in the loss of control of the vehicle.
Safe driving
Tips for driving
Before starting every trip
For your own safety and the safety of your
passengers, always note the following points
before every trip:
–
Make sure that the vehicle's lights and turn
signals are working properly.
–
Check tyre pressure.
–
Ensure that all windows provide a clear and
good view of the surroundings.
–
Make sure all luggage is secured
›››
page 65.
–
Make sure that no objects can interfere
with the pedals.
–
Adjust front seat, head restraint and rear vision mirrors properly according to your
size.
–
Ensure that the passengers in the rear
seats always have the head restraints in
the in-use position
–
Instruct passengers to adjust the head restraints according to their height.
–
Protect children with appropriate child
seats and properly applied seat belts
›››
page 25
›››
page 9.
.
–
s
ume the correct sitting position. Instruct
As
your passengers also to assume a proper
sitting position. ››› page 6.
–
Fasten your seat belt securely. Instruct your
passengers also to fasten their seat belts
properly. ››› page 11.
What affects driving safety?
As a driver, you are responsible for yourself
and your passengers. When your concentration or driving safety is affected by any circumstance, you endanger yourself as well as
others on the road ›››
–
Always pay attention to traffic and do not
get distracted by passengers or telephone
calls.
–
Never drive when your driving ability is impaired (e.g. by medication, alcohol, drugs).
–
Observe traffic laws and speed limits.
–
Always reduce your speed as appropriate
for road, traffic and weather conditions.
–
When travelling long distances, take
breaks regularly - at least every two hours.
–
If possible, avoid driving when you are tired
or stressed.
, for this reason:
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
»
5
Safety
WARNING
When driving safety is impaired during a trip,
the risk of injury and accidents increases.
Safety equipment
Never put your safety or the safety of your
passengers in danger. In the event of an accident, the safety equipment may reduce the
risk of injury. The following list includes most
of the safety equipment in your SEAT:
●
Three-point seat belts
●
belt tension limiters for the front and rear
side seats,
●
Belt tensioners for the front seats
●
Belt height adjustment for the front seats
●
Front airbags
●
Side airbags in the front seat backrests
●
Side airbags in the rear seat backrests*
●
Head-protection airbags
●
Active front head restraints*
●
“ISOFIX” anchor points for child seats in
the rear side seats with the “ISOFIX” system,
●
Height-adjustable front head restraints
●
Rear head restraints with in-use position
and non-use position
●
Adjustable steering column
6
The safety equipment mentioned above
works together to provide you and your passengers with the best possible protection in
the event of an accident. However, these
safety systems can only be effective if you
and your passengers are sitting in a correct
position and use this equipment properly.
Safety is everyone's business!
Correct sitting position for
vehicle occupants
Correct sitting position
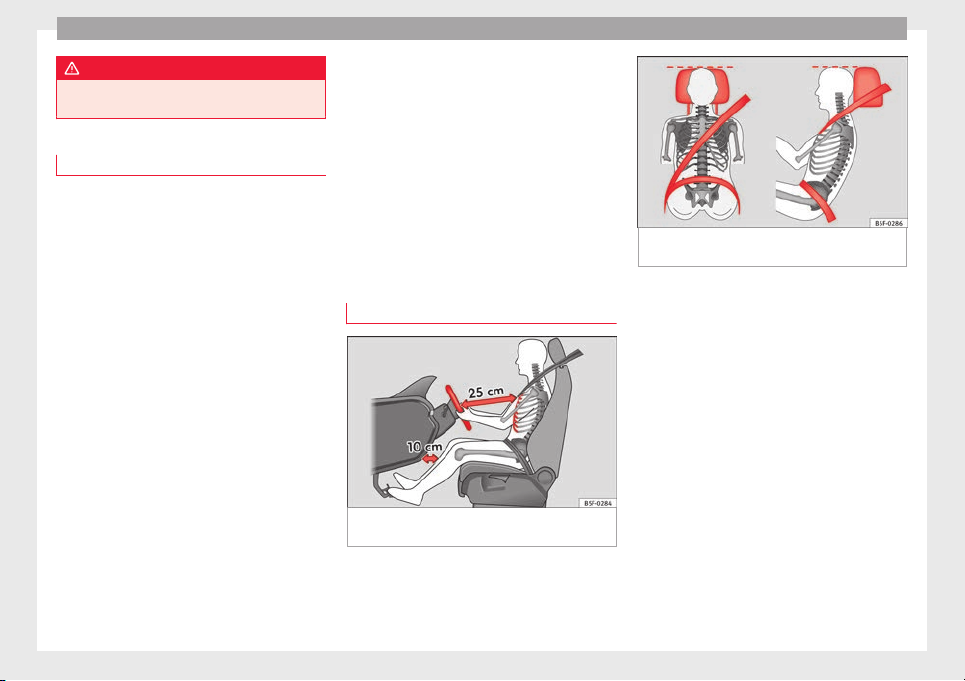
Fig. 1 The proper distance between driver
and steering wheel
Fig. 2 Correct belt web and head restraint po-
sitions
The correct sitting positions for the driver and
passengers are shown below.
If your physical constitution prevents you
from maintaining the correct sitting position,
contact a specialised workshop for help with
any special devices. The seat belt and airbag
can only provide optimum protection if a correct sitting position is adopted. SEAT recommends taking your car in for technical service.
For your own safety and to reduce the risk of
injury in the event of an accident or sudden
braking or manoeuvre, SEAT recommend the
following positions:
Valid for the driver:
●
Adjust the seat backrest to an upright position so that your back rests completely
against it.
●
Adjust the seat so that there is a distance
of at least 25 cm between the steering wheel
and your chest ››› Fig. 1
ho
d the steering wheel with both hands on
l
and so that you can
the outside of the ring at the 9 o'clock and 3
o'clock positions with your arms slightly
bent.
●
The adjusted steering wheel must face your
chest and not your face.
●
Adjust the driver seat forwards or backwards so that you are able to press the accelerator, brake and clutch pedals to the floor
with your knees slightly angled and the distance between your knees and the dash panel is at least 10 cm ››› Fig. 1.
●
Adjust the height of the driver seat so that
you can easily reach the top of the steering
wheel.
●
Keep both feet in the footwell so that you
have the vehicle under control at all times.
●
Adjust and fasten your seat belt correctly
››› page 11.
Valid for the passenger:
●
Adjust the seat backrest to an upright position so that your back rests completely
against it.
●
Move the front passenger seat back as far
as possible for optimum protection should
the airbag deploy.
●
Always keep your feet in the footwell while
the vehicle is in motion.
Safe driving
●
Adjust and fasten your seat belt correctly
››› page 11.
Valid for the passengers in the rear section:
●
Adjust the head restraint so that its upper
edge is at the same level as the top of your
head, or as close as possible to the same level as the top of your head and under no circumstances below eye level. Keep the back
of your neck as close as possible to the head
restraint ››› Fig. 1 and ››› Fig. 2.
●
Short people must lower the head restraint
to the first anchorage position, even if your
head is below its upper edge.
●
Tall people must raise the head restraint
completely.
●
Always keep your feet in the footwell while
the vehicle is in motion.
●
Adjust and fasten your seat belt correctly
››› page 11.
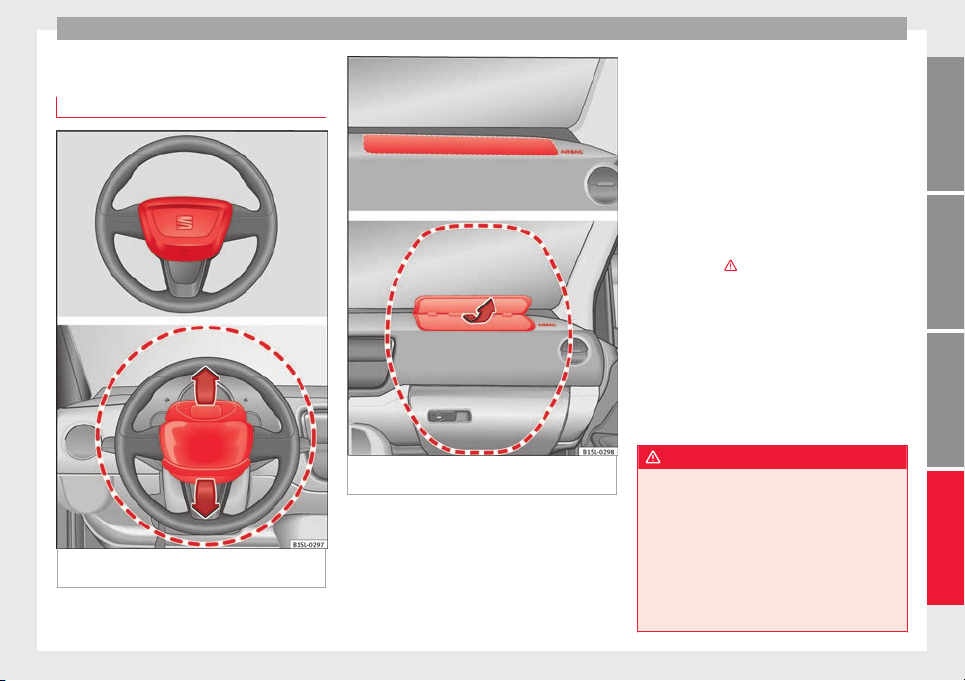
Adjusting the steering wheel position
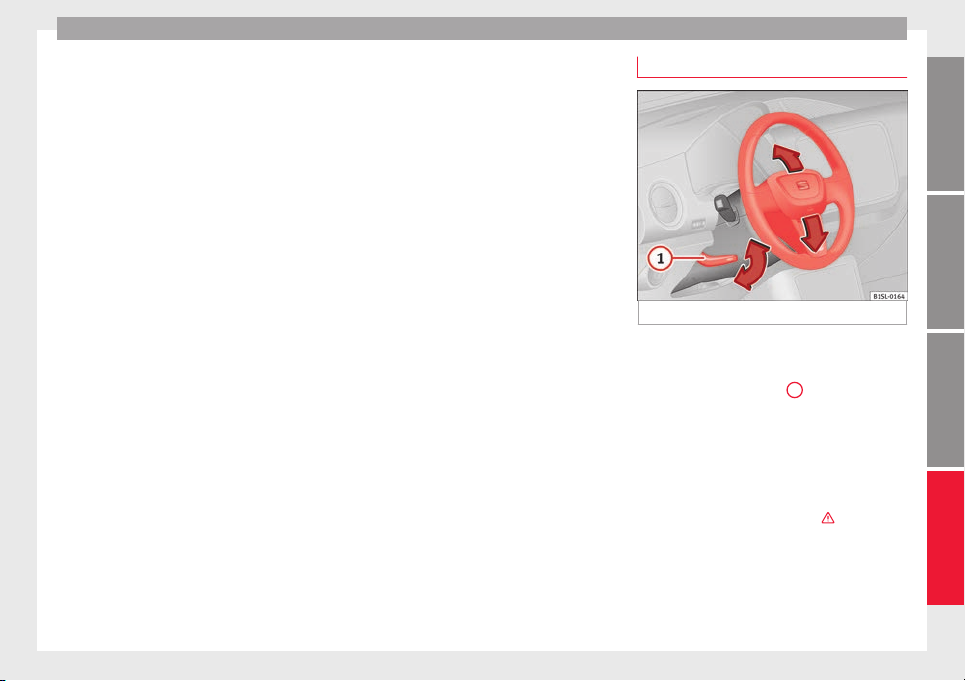
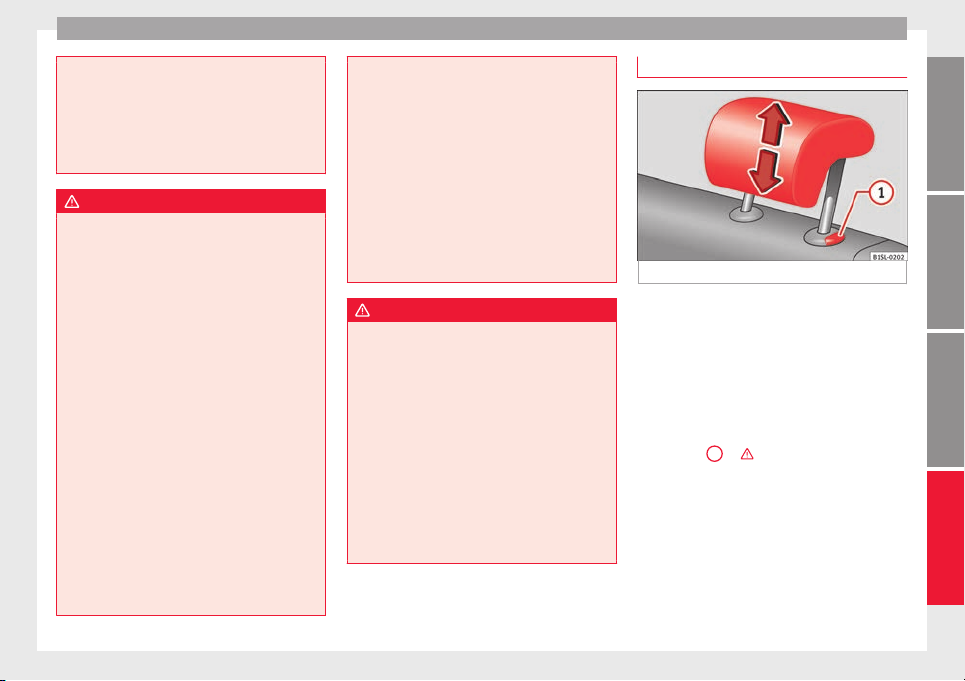
Fig. 3 Mechanical steering wheel adjustment
Adjust the steering wheel before your trip
and only when the vehicle is stationary.
●
Push the lever ››› Fig. 3 1 downwards.
●
Adjust the steering wheel so that you can
hold onto the steering wheel with both hands
on the outside of the ring at the 9 o'clock and
3 o'clock positions and your arms slightly
bent.
●
Push the lever firmly upwards until it is
flush to the steering column ››› .
Adjust the correct distance between the driver and the steering wheel ››› Fig. 1
c
ols on the driver seat ››› page 63.
ontr
using the
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
»
7
WARNING
Incorrect use of the steering wheel adjustment function and an incorrect adjustment of
the steering wheel can result in severe or fatal injury.
●
After adjusting the steering column, push
the lever ››› Fig. 3 1 firmly upwards to ensure the steering wheel does not accidentally
change position while driving.
●
Never adjust the steering wheel while the
vehicle is in motion. If you need to adjust the
steering wheel while the vehicle is in motion,
stop safely and make the proper adjustment.
●
The adjusted steering wheel should be facing your chest and not your face so as not to
hinder the driver's front airbag protection in
the event of an accident.
●
When driving, always hold the steering
wheel with both hands on the outside of the
ring at the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock positions
to reduce injuries when the driver's front airbag deploys.
●
Never hold the steering wheel at the 12
o'clock position or in any other manner (e.g.
in the centre of the steering wheel). In such
cases, if the driver's airbag deploys, you may
sustain injuries to your arms, hands and
head.
8
Safety
Danger of injuries due to an incorrect
sitting position
Number of seats
The vehicle has a total of 4 seats: 2 front
seats
and 2 rear seats. Each seat is equipped
with a seat belt.
If the seat belts are worn incorrectly or not at
all, the risk of severe injuries increases. Seat
belts can provide optimal protection only if
the belt web is properly worn. Being seated
in an incorrect position means the seat belt
cannot offer its full protection. This could result in severe and even fatal injuries. The risk
of severe or fatal injuries is especially heightened when a deploying airbag strikes a vehicle occupant who has assumed an incorrect
sitting position. The driver is responsible for
all passengers in the vehicle, particularly
children.
The following list shows just some examples
of incorrect sitting positions which can be
dangerous to all vehicle occupants.
When the vehicle is in motion:
●
Never stand in the vehicle.
●
Never stand on the seats.
●
Never kneel on the seats.
●
Never tilt your seat backrest too far to the
rear.
●
Never lean against the dash panel.
●
Never lie on the rear seats.
●
Never sit on the front edge of a seat.
●
Never sit sideways.
●
Never lean out of a window.
●
Never put your feet out of a window.
●
Never put your feet on the dash panel.
●
Never put your feet on the surface of a seat
or seat backrest.
●
Never travel in a footwell.
●
Never travel on a seat without wearing the
seat belt.
●
Never carry any person in the luggage com-
partment.
WARNING
An incorrect sitting position in the vehicle
can lead to severe injuries or death in the
event of sudden braking or manoeuvres, collision or accidents or if the airbag deploys.
●
Before the vehicle moves, assume the proper sitting position and maintain it throughout
the trip. This also includes fastening the seat
belt.
●
Never transport more people than there are
seats with a seat belt available in the vehicle.
●
Children must always be protected with an
approved child restraint system suited to
their height and weight ››› page 25,
››› page 17.
Safe driving
●
Always keep your feet in the footwell while
the vehicle is in motion. Never, for example,
put your feet on the surface of a seat or on
the dash panel and never put them out of a
window. Otherwise the airbag and seat belt
offer insufficient protection and the risk of injury in the event of an accident is increased.
WARNING
Before every trip, adjust the seat, the seat
belt and the head restraints and instruct your
passengers to fasten their seat belts properly.
●
Move the front passenger seat back as far
as possible.
●
Adjust the driver seat so that there is at
least 25 cm distance between your chest and
the hub of the steering wheel. Adjust the
driver seat so that you are able to press the
accelerator, brake and clutch pedals to the
floor with your knees slightly angled and that
the distance between your knees and the
dash panel is at least 10 cm. If your physical
constitution prevents you from meeting these
requirements, contact a specialised workshop to make any modifications required.
●
Never drive with the seat backrest tilted far
back. The further the seat backrests are tilted
to the rear, the greater the risk of injury due
to incorrect positioning of the belt web or to
the incorrect sitting position!
●
Never drive with the seat backrest tilted
forwards. Should a front airbag deploy, it
could throw the seat backrest backwards and
injure the passengers of the rear seats.
●
Sit as far away as possible from the steer-
ing wheel and the dash panel.
●
Keep your back straight and resting completely against the seat backrest and the
front seats correctly adjusted. Never place
any part of your body in the area of the airbag
or very close to it.
●
If passengers on the rear seats are not sitting in an upright position, the risk of severe
injury due to incorrect positioning of the belt
web increases.
WARNING
Incorrect seat adjustment may lead to accidents and severe injuries.
●
Only adjust the seats when the vehicle is
stationary, as the seats could move unexpectedly while the vehicle is in motion and
you could lose control of the vehicle. Furthermore, an incorrect position is adopted when
adjusting the seat.
●
Only adjust the height, seat backrest and
forwards or backwards position of the seat
when there is nobody in the seat adjustment
area.
●
There must be no objects blocking the front
seat adjustment area.
Adjust the rear head restraints
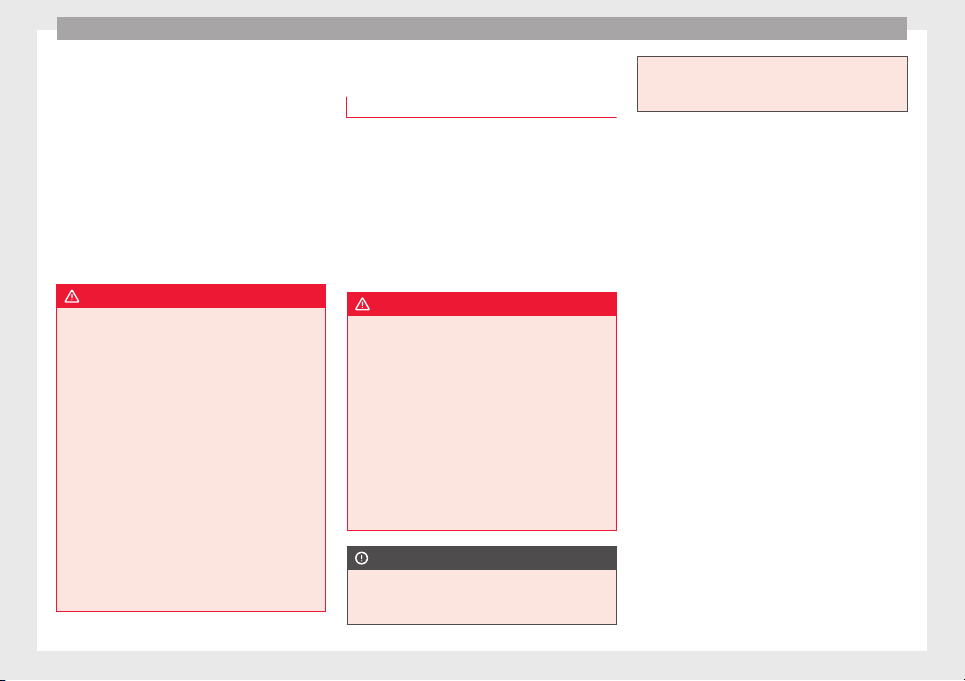
Fig. 4 Adjusting the rear head restraints
All seats are equipped with a head restraint.
The front seat head restraints are integrated
in the backrests and adjusting them is not
possible.
Adjusting height
●
Push the head restraint up or down in the
direction of the arrow with the button pressed ››› Fig. 4 1 ››› .
●
The head restraint must engage securely in
position.
Correct adjustment of head restraints
Adjust the head restraint so that its upper
edge is at the same level as the top of your
head, or as close as possible to the same level as the top of your head and under no circumstances below eye level. Keep the back
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
»
9
Safety
of your neck as close as possible to the head
restraint.
Adjusting the head restraint for short people
Set the head restraint in the first anchorage
position, even if your head is below its upper
edge. When the head restraint is at its lowest, it is possible that a small gap remains
between it and the seat backrest.
Adjusting the head restraint for tall people
Raise the head restraint completely.
WARNING
Travelling with the head restraints removed
or improperly adjusted increases the risk of
severe or fatal injuries in the event of accidents and sudden braking or manoeuvres.
●
Always fit and adjust the head restraint
properly whenever a person is occupying a
seat.
●
All vehicle occupants must correctly adjust
the head restraint according to their height to
reduce the risk of back injuries in the event of
an accident. The upper edge of the head restraint must be as close as possible to the
same level as the top of your head and under
no circumstances below eye level. Keep the
back of your neck as close as possible to the
head restraint.
●
Never adjust the head restraint while the
vehicle is in motion.
10
Pedal area
Pedals
Do not allow floor mats or other objects to
obstruct the free passage of the pedals.
Floor mats should leave the pedal area free
and unobstructed and be correctly secured in
the footwell zone.
In the event of failure of a brake circuit, the
brake pedal must be pressed harder than
normal to brake the vehicle.
WARNING
Objects falling into the driver's footwell could
prevent use of the pedals. This could lead the
driver to lose control of the vehicle, increasing the risk of a serious accident.
●
Make sure the pedals can be used at all
times, with no objects rolling underneath
them.
●
Always secure the mat in the footwell.
●
Never place other mats or rugs on top of
the original mat supplied by the factory.
●
Ensure that no objects can fall into the driver's footwell while the vehicle is in motion.
CAUTION
The pedals must always have free and unobstructed passage to the floor. For example, in
case of a fault in the brake circuit, the brake
pedal will need to be pressed further to stop
the vehicle. To press the brake pedal down
further will require more force than usual.
Seat belts
Seat belts
Using seat belts
Introduction
Check the condition of all the seat belts at
regular intervals. If you notice that the belt
webbing, fittings, retractor mechanism or
buckle of any of the belts is damaged, the
belt must be replaced immediately by a specialised workshop ›››
workshop must use the appropriate spare
parts corresponding to the vehicle, the
equipment and the model year. SEAT recommends taking your car in for technical service.
WARNING
Unbuckled or badly buckled seat belts increase the risk of severe or even fatal injuries. The seat belt cannot offer its full protection if it is not fastened and used correctly.
●
Seat belts are the most effective way of reducing the risk of sustaining severe or fatal
injuries in the event of an accident. Seat belts
must be correctly fastened when the vehicle
is in motion to protect the driver and all vehicle occupants.
●
Before each trip, every occupant in the vehicle occupants must sit properly, correctly
fasten the seat belt belonging to his or her
seat and keep it fastened throughout the trip.
. The specialised
This also applies to other vehicle occupants
when driving in town.
●
When travelling, children must be secured
in the vehicle with a child restraint system
suitable for their weight and height and with
the seat belts correctly fastened
››› page 25.
●
truct your passengers to fasten their
Ins
seat belts properly before driving off.
●
Insert the latch plate into the buckle for the
appropriate seat and ensure it is engaged.
Using the latch plate in the buckle of another
seat will not protect you properly and may
cause severe injuries.
●
Do not allow liquids or foreign bodies to enter the buckle fastenings. This could damage
the buckles and seat belts.
●
Never unbuckle your seat belt when the vehicle is moving.
●
Never allow more than one passenger to
share the same seat belt.
●
Never hold children or babies on your lap
sharing the same seat belt.
●
Loose, bulky clothing (such as a jacket) impairs the proper fit and function of the seat
belt.
WARNING
It is extremely dangerous to drive using damaged seat belts and could result in serious injury or loss of life.
●
Avoid damaging the seat belt by jamming it
in the door or the seat mechanism.
●
If the fabric or other parts of the seat belt
are damaged, the seat belts could break in
the event of an accident or sudden braking.
●
Always have damaged seatbelts replaced
immediately by seat belts approved for the
vehicle in question by SEAT. Seat belts which
have been worn in an accident and stretched
must be replaced by a specialised workshop.
Renewal may be necessary even if there is no
apparent damage. The belt anchorage should
also be checked.
●
Never attempt to repair, modify or remove a
seat belt yourself. All repairs to seat belts, retractors and buckles must be carried out by a
specialised workshop.
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
11
Safety
Warning lamp
Fig. 5 Warning lamp on the instrument panel
Fig. 6 Indication of seat belt status in the rear
seats on the instrument panel display
12
Lights
Possible cause Solution
up or
flashes
On the instrument panel:
Driver's seat belt not fastened or front passenger
seat belt not fastened if
the front passenger seat
is occupied.
On the instrument panel:
Objects on the front pas-
senger seat.
Instrument panel display: a passenger in the
rear seats has not fas-
tened their seat belt, if
the seat is occupied.*
On the instrument panel
display: a passenger in
the rear seats has fas-
tened their seat belt, if
the seat is occupied.*
Fasten seat
belts!
Remove any
objects from
the front passenger seat
and store them
safely.
Fasten seat
belts!
Several warning and control lamps light up
for a few seconds when the ignition is switched on, signalling that the function is being
verified. They will switch off after a few seconds.
An audible warning will be heard if the seat
belts are not fastened as the vehicle drives
off and reaches a speed of more then
25 km/h (15 mph) or if the seat belts are unfastened while the vehicle is in motion. The
seat belt warning lamp
The w
g lamp does not switch off until
arnin
will also flash.
the driver and front passenger fasten their
seat belts while the ignition is switched on.
Seat belt status display for rear seats
The seat belt status display on the instrument panel informs the driver, when the ignition is switched on, whether any passengers
in the rear seats have fastened their seat
belts. The symbol indicates that the passenger in this seat has fastened “his or her”
seat belt ››› Fig. 6.
The seat belt status is displayed for around
30 seconds when a seat belt in the rear seats
is fastened or unfastened. You can switch off
this display by pressing the
0.0 / SET
button.
The seat belt status flashes for a maximum of
30 seconds when a seat belt in the rear seats
is unfastened while the vehicle is in motion.
An audible warning will also be heard if the
vehicle is travelling at over 25 km/h
(15 mph).
Seat belt protection
Fig. 7 Drivers with properly worn seat belts
will not be thrown forward in the event of sudden braking
Properly worn seat belts hold the occupants
in the proper position. They also help prevent
uncontrolled movements that may result in
serious injury and reduce the risk of being
thrown out of the vehicle in case of an accident.
Vehicle occupants wearing their seat belts
correctly benefit greatly from the ability of the
belts to absorb kinetic energy. In addition,
the front part of your vehicle and other passive safety features (such as the airbag system) are designed to absorb the kinetic energy released in a collision. Taken together, all
these features reduce the releasing kinetic
energy and consequently, the risk of injury.
This is why it is so important to fasten seat
belts before every trip, even when "just driving around the corner".
Seat belts
Ensure that your passengers wear their seat
belts as well. Accident statistics have shown
that wearing seat belts is an effective means
of substantially reducing the risk of injury
and improving the chances of survival when
involved in a serious accident. Furthermore,
properly worn seat belts improve the protection provided by airbags in the event of an
accident. For this reason, wearing a seat belt
is required by law in most countries.
Although your vehicle is equipped with airbags, the seat belts must be fastened and
worn. The front airbags, for example, are only
triggered in some cases of head-on collision.
The front airbags will not be triggered during
minor frontal or side collisions, rear-end collisions, rollovers or accidents in which the airbag trigger threshold value in the control unit
is not exceeded.
Therefore, you should always wear your seat
belt and ensure that all vehicle occupants
have fastened their seat belts properly before
you drive off!
Using seat belts
Twisted seat belt
If it is difficult to remove the seat belt from
the guide, the seat belt may have become
twisted inside the side trim after being
wound too quickly on unfastening:
●
Pull out the seat belt completely, carefully
pulling on the latch plate.
●
Untwist the belt and guide it back, assist-
ing it by hand.
The seat belt must be fastened even if it is
impossible to untwist it. In this case, the
twisted area must not be in an area in direct
contact with your body. Have the seat belt
untwisted urgently by a specialised workshop.
WARNING
An improperly handled seat belt increases
the risk of sustaining severe or fatal injuries.
●
Regularly check that the seat belts and
their components are in perfect condition.
●
Always keep your seat belt clean.
●
Do not jam or damage the seat belt or rub it
with sharp edges.
●
Make sure there are no liquids or foreign
bodies on the latch plate and in the buckle.
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
13

Safety
Head-on collisions and the laws of
physics
Fig. 8 A driver not wearing a seat belt is
thrown forward violently
Fig. 9 The unbelted passenger in the rear
seat is thrown forward violently, hitting the
driver who is wearing a seat belt.
It is easy to explain how the laws of physics
work in the case of a head-on collision: when
a vehicle starts moving, a type of energy
14
called “kinetic energy” is created both in the
passengers and inside the vehicle.
The amount of “kinetic energy” depends on
the speed of the vehicle and the weight of
the vehicle and its passengers. The higher
the speed and the greater the weight, the
more energy there is to be “absorbed” in an
accident.
The most significant factor, however, is the
speed of the vehicle. If the speed doubles
from 25 km/h (15 mph) to 50 km/h
(30 mph), for example, the corresponding kinetic energy is multiplied by four.
Because the vehicle occupants in our example are not restrained by seat belts, in the
event of crashing against a wall, all of the occupants' kinetic energy will be absorbed
solely by said impact.
Even at speeds of 30 km/h (19 mph) to
50 km/h (30 mph), the forces acting on bodies in a collision can easily exceed one tonne
(1000 kg). At greater speed these forces are
even higher.
Vehicle occupants not wearing seat belts are
not “attached” to the vehicle. In a head-on
collision, they will move forward at the same
speed their vehicle was travelling just before
the impact. This example applies not only to
head-on collisions, but to all accidents and
collisions.
Even at low speeds the forces acting on the
body in a collision are so great that it is not
possible to brace oneself with one's hands.
In a frontal collision, unbelted passengers
are thrown forward and will make violent contact with the steering wheel, dash panel,
windscreen or whatever else is in the way
.
››› Fig. 8
It
s also important for rear passengers to
i
wear seat belts properly, as they could otherwise be thrown forward violently through the
vehicle interior in an accident. Passengers in
the rear seats who do not use seat belts endanger not only themselves but also the front
occupants ››› Fig. 9.
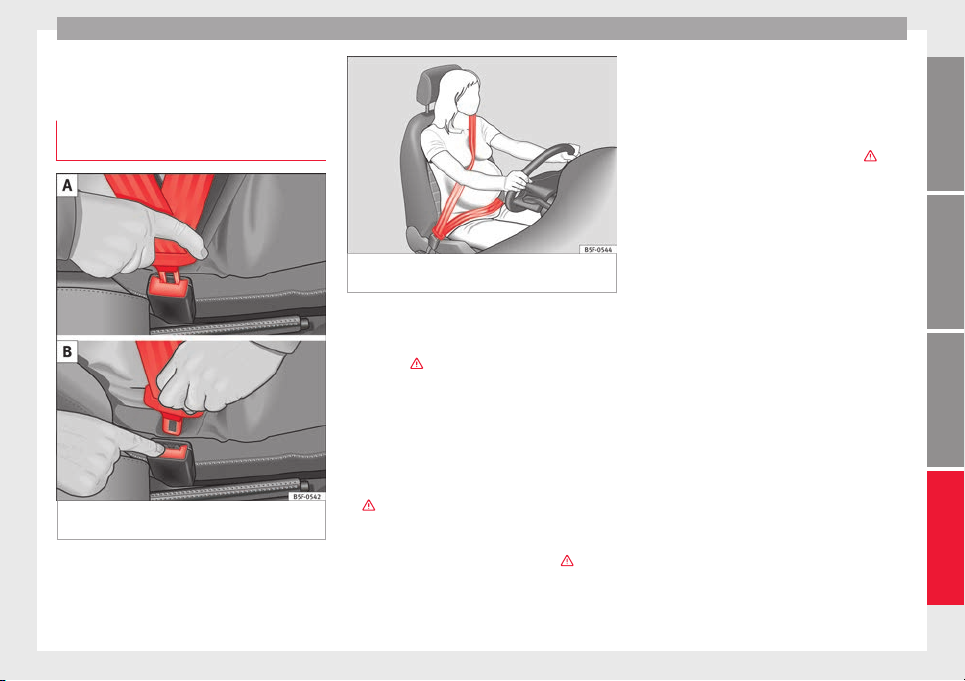
How to properly adjust your
seatbelt
Fastening and unfastening the seat
belt
Fig. 10 Positioning and removing the seat
belt buckle.
Seat belts
Fig. 11 Position of seat belt during pregnan-
cy.
Properly worn seat belts hold the vehicle occupants in the position that most protects
them in the event of an accident or sudden
›››
braking
Fastening the seat belt
Fasten your seat belt before each trip.
●
Correctly adjust the front seat
●
Engage the seat backrest in the upright po-
sition and correctly adjust the hear restraint
›››
●
Pull the latch plate and place the belt web-
bing evenly across your chest and lap. Do not
twist the seat belt when doing so
●
Engage the latch plate in the buckle of the
corresponding seat
.
›››
page 6.
.
›››
.
›››
Fig. 10 A
.
●
Pull the belt to ensure that the latch plate is
securely engaged in the buckle.
Unfastening the seat belt
The seat belt must not be unfastened until
the vehicle has come to a standstill ›››
●
Press the red button on the buckle
››› Fig. 10
the buckle.
●
up easily and the trim will not be damaged.
Correct seat belt position
Seat belts offer their maximum protection in
the event of an accident and reduce the risk
of sustaining severe or fatal injuries only
when they are properly positioned. Furthermore, if the webbing is correctly positioned,
the seat belt will hold the vehicle occupants
in the optimum position to ensure the airbag
provides the maximum protection. The seat
belt must therefore always be worn and the
webbing correctly positioned.
Incorrectly worn seat belts can cause severe
or even fatal injuries ››› page 6, Correct sit-
ting position for vehicle occupants.
●
on the centre of the shoulder, never across
the neck or the arm, under the arm or behind
the shoulder.
. The latch plate is released from
B
Guide the belt back by hand so that it rolls
The shoulder part of the seat belt must lie
.
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
»
15
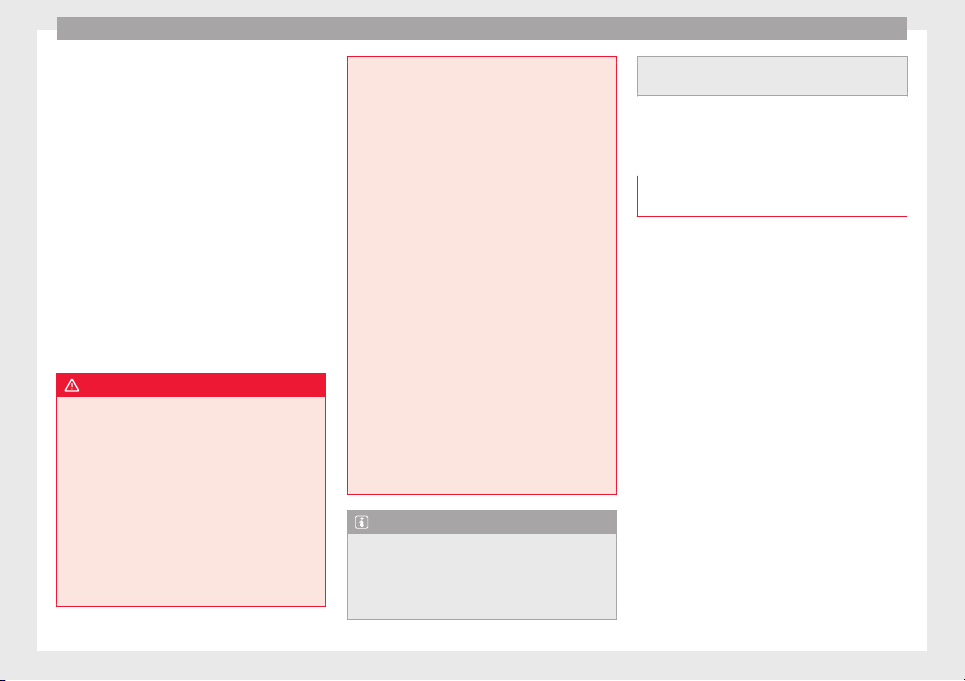
●
The lap part of the seat belt must lie across
the pelvis, never across the stomach.
●
The seat belt must lie flat and fit comfortably. Pull the belt tight if necessary to take up
any slack.
In the case of pregnant women, the seat belt
must lie evenly across the chest and as low
as possible over the pelvis, never across the
stomach and must be worn properly at all
times during the pregnancy ››› Fig. 11
Ad
g the position of the belt webbing to
aptin
your size
The seat belt can be adapted using the following equipment:
●
Front seat height adjustment.
WARNING
An incorrectly worn seat belt web can cause
severe or fatal injuries in the event of an accident.
●
The seat belt cannot offer its full protection
unless the seat backrest is in an upright position and the seat belt is worn correctly, according to your size.
●
Unbuckling your seat belt while the vehicle
is in motion can cause severe or fatal injuries
in the event of an accident or sudden braking.
●
The seat belt itself or a loose seat belt can
cause severe injuries if the belt moves from
16
Safety
hard areas of the body to soft areas (e.g. the
stomach).
●
The shoulder part of the seat belt must lie
on the centre of the shoulder, never across
the neck or the arm.
●
The seat belt must lie flat and fit comfortably on the torso
●
The lap part of the seat belt must lie across
the pelvis, never across the stomach. The
.
seat belt must lie flat and fit comfortably on
the pelvis Pull the belt tight if necessary to
take up any slack.
●
For pregnant women, the lap part of the
seat belt must lie as low as possible over the
pelvis and always lie flat, “surrounding” the
stomach.
●
Do not twist the seat belt while it is fastened.
●
Never pull the seat belt away from your
body using your hand.
●
Do not lie the seat belt across rigid or fragile objects, e.g. glasses, pens or keys.
●
Never use seat belt clips, retaining rings or
similar instruments to alter the position of
the belt webbing.
Note
If your physical constitution prevents you
from maintaining the correct position of the
belt webbing, contact a specialised workshop
for help with any special devices to ensure
the optimum protection of the seat belt and
airbag. SEAT recommends taking your car in
for technical service.
Seat belt tensioners
Automatic belt retainer, belt
tensioner, belt tension limiter
Seat belts are part of the vehicle safety concept ››› page 17 and consist of the follow-
tant functions:
ing impor
Automatic belt retainer
Every seat belt is equipped with an automatic
belt retainer on the shoulder belt. If the belt
is pulled slowly or during normal driving, the
system allows for total freedom of movement
on the shoulder belt. However, during sudden braking, during travel in mountains or
bends and during acceleration, the automatic belt retainer on the seat belt is locked is
pulled quickly.
Belt tensioners
The seat belts for the occupants in the front
seats are equipped with belt tensioners.
Sensors trigger the belt tensioners during severe head-on, lateral and rear collisions and
retract and tighten the seat belts. If the seat
belt is loose, it is retracted to reduce the forwards movement of occupants or movement
Airbag system
in the direction of the collision. The belt tensioner works in combination with the airbag
system. The belt tensioner will not be triggered in the event of the vehicle overturning
if the side airbags are not deployed.
If the belt tensioner is triggered, a fine dust is
produced. This is normal and it is not an indication of fire in the vehicle.
Belt tension limiter
The belt tension limiter reduces the force of
the seat belt on the body in the event of an
accident.
Note
The relevant safety requirements must be observed when the vehicle is dismantled or system components are removed. These requirements are known to specialised workshops
››› page 17.
Service and disposal of belt
tensioners
If you work on the belt tensioners or remove
and install other parts of the vehicle when
performing other repair work, the seat belt
may be damaged. The consequence may be
that, in the event of an accident, the belt tensioners function incorrectly or not at all.
So that the effectiveness of the belt tensioner
is not reduced and that removed parts do not
cause any injuries or environmental pollution, regulations must be observed. These requirements are known to specialised workshops.
WARNING
Improper handling and homemade repairs of
seat belts, automatic belt retainers and tension devices increase the risk of sustaining
severe or fatal injuries. The belt tensioner
may fail to trigger or may trigger in the wrong
circumstances.
●
Never attempt to repair, adjust or remove or
install parts of the belt tensioners or seat
belts. Any work must be performed by a specialised workshop only ››› page 118.
●
Belt tensioners and automatic belt retainers cannot be repaired and must be replaced.
For the sake of the environment
Airbag modules and belt tensioners may contain perchlorate. Observe the legal requirements for their disposal.
Airbag system
Brief introduction
Introduction
Front airbags have been installed for both
driver and passenger. The front airbags can
also protect the chest and head of driver and
passenger if the seats, seat belts head restraints and, for the driver, the steering
wheel are correctly adjusted and used. Airbags are considered as additional safety
equipment. An airbag cannot replace the
seat belt, which must be worn at all times,
even in front seats where front airbags have
been installed.
The airbag can protect vehicle occupants in
the event of an accidents, cushioning the
movement of the occupants in the direction
of the collision in frontal and side accidents.
Deployed airbags fill with a propellant gas.
This causes the airbag covers to break and
the airbags to deploy extremely quickly in
their entire deployment space within fractions of a second. When an occupant with the
seat belt properly fastened puts pressure on
the inflated airbag, the propellant gas escapes to absorb the force of the impact and
slow the movement. This reduces the risk of
severe or fatal injuries. Airbag deployment
does not mean that other types of injury such
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
»
17
Safety
as swelling, bruising and skin injuries can be
ruled out. Upon deployment of the airbag,
friction can cause the generation of heat.
Airbags do not protect the arms or the lower
part of the body.
The most important factors for triggering the
airbag are the type of accident, the angle of
impact, the vehicle speed and the characteristics of the object the vehicle hits. Therefore,
airbags are not triggered every time the vehicle is visibly damaged.
The activation of the airbag system depends
on the magnitude of the deceleration of the
vehicle caused by a collision, which registers
through an electronic control unit. If the deceleration magnitude value is below the reference value programmed in the control unit,
the airbags will not deploy even though serious damage might be caused to the vehicle
as the result of an accident. Damage suffered
by the vehicle, reparation costs or absence of
damage suffered from the accident are not
indications of whether an airbag should have
been deployed. Due to the varying nature of
collision situations, it is impossible to define
a speed range of the vehicle and reference
values. For this reason, it is not possible to
cover all types of collisions and collision angles resulting in the deployment of the airbag. Factors necessary for the airbag to be
deployed can be, the characteristics of the
object (hard or soft) against which the vehi-
18
cle collides, the collision angle and the vehicle speed.
Airbags act in conjunction with the threepoint seat belts in certain accident situations, when the vehicle deceleration rate is
severe enough to trigger the airbags. Airbags
only deploy once and only under certain circumstances. Seat belts remain present to offer protection in situations where airbags are
not triggered or where they have already deployed. For example, when a vehicle hits another after an initial collision or is hit by another vehicle.
The airbag system is an integral part of the
car's passive safety system. The airbag system can only work effectively when the vehicle occupants are wearing their seat belts
correctly and have adjusted the head restraints properly ››› page 6.
WARNING
Never exclusively trust the airbag system as a
means of protection.
●
Even when triggered, airbag protection is
only auxiliary.
●
The airbags provide the best protection
when the seat belts are properly fastened,
thus reducing the risk of sustaining injuries
››› page 11, Using seat belts.
●
Before each trip, every occupant must sit
properly, correctly fasten the seat belt belonging to his or her seat and keeping it fas-
tened throughout the trip. This rule is valid
for all vehicle occupants.
WARNING
Occupants sitting in the front of the vehicle
must never carry any objects in the deployment space between them and the airbags,
as this increases the risk of sustaining injuries if the airbag is triggered. This modifies
the airbag deployment space or the objects
may fly uncontrollably and hit your body.
●
Never carry objects in your hand or on your
lap while the vehicle is in motion.
●
Never transport objects on the front passenger seat. In the event of sudden braking
and manoeuvres, the objects may end up in
the airbag deployment space and fly uncontrollably around the interior if the airbag is
activated.
●
Occupants of the front and rear seats must
never carry any other people, pets or objects
in the deployment space between them and
the airbags. Make sure children and other
passengers also respect this recommendation.
WARNING
The airbag system provides protection for
one accident only. If they have been deployed, they must be replaced.
●
Ensure deployed airbags and the system
components involved are immediately replaced with new, SEAT-approved components
for the vehicle.
●
Have any repairs or modifications carried
out at a specialised workshop. Specialised
workshops have the necessary tools, diagnostics equipment, repair information and
qualified personnel.
●
Never fit recycled or reused airbag components in your vehicle.
●
Never modify the airbag system components.
WARNING
If the airbags are triggered, a fine dust is produced. This is normal and it is not an indication of fire in the vehicle.
●
This fine dust may irritate the skin and eyes
and cause breathing difficulties, particularly
in people suffering from or who have suffered
from asthma or other illnesses of the respiratory tract. To reduce breathing difficulties,
get out of the vehicle and open and doors and
windows to breath in fresh air.
●
Should you touch the dust, wash your
hands and face using a mild soap and water
before you eat.
●
Prevent the dust from affecting the eyes or
open wounds.
●
Rinse your eyes with water if you have dust
in them.
Airbag system
WARNING
Solvents cause the surfaces of the airbag
modules to become porous. If an airbag is accidentally triggered, the detachment of plastic parts could cause serious injury.
●
Never clean the dash panel and the surfaces of the airbag modules with cleaners containing solvents.
Description of airbag system
Vehicle safety components
The following safety equipment makes up the
vehicle safety design to reduce the risk of severe and fatal injuries. Depending on the vehicle equipment, some equipment may not
be fitted in the vehicle or may not be available in some markets.
●
Optimised seat belts for all seats.
●
Seat belt tension devices for driver and
passenger.
●
Seat belt force limiters for driver and pas-
senger.
●
Seat belt warning lamp
●
Front airbags for driver and passenger.
●
Side airbags for driver and passenger.
●
Airbag control lamp .
●
Control units and sensors.
●
Head restraints optimised for rear-end colli-
sion.
●
Adjustable steering column.
●
If necessary, anchor points for child seats
for the rear seats.
●
Where applicable, mountings for the child
seat upper retaining strap.
Situations in which the front and side
airbags do not deploy:
●
If the ignition is switched off during the col-
lision.
●
In frontal collisions, when the deceleration
measured by the control unit is too low.
●
In minor side collisions.
●
In rear collisions.
●
In the event of the vehicle overturning.
●
When the impact speed is lower than the
reference value set in the control unit.
There is a fault in the system if the control
lamp :
●
does not light up when the ignition is
switched on,
●
turns off after 4 seconds after the ignition
is switched on
●
turns off and then lights up again after the
ignition is switched on
●
illuminates or flashes while the vehicle is
moving.
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
»
19
WARNING
●
The seat belts and airbags can only provide
maximum protection if the occupants are
seated correctly ››› page 6.
●
If a f
ault has occurred in the airbag system,
have the system checked immediately by a
specialised workshop. Otherwise, during a
frontal collision the system might not trigger
correctly or may fail to trigger at all.
Airbag activation
The airbags deploy extremely rapidly, within
thousandths of a second, to provide additional protection in the event of an accident.
A fine dust may develop when the airbag deploys. This is normal and it is not an indication of fire in the vehicle.
The airbag system is only ready to function
when the ignition is on.
In special accidents instances, several airbags may activate at the same time.
In the event of minor head-on and side collisions, rear-end collisions, overturning or rollover of the vehicle, airbags do not activate.
Activation factors
The conditions that lead to the airbag system
activating in each situation cannot be generalised. Some factors play an important role,
such as the properties of the object the vehi-
20
Safety
cle hits (hard/soft), angle of impact, vehicle
speed, etc.
Deceleration trajectory is key for airbag activation.
The control unit analyses the collision trajectory and activates the respective restraint
system.
If the deceleration rate is below the predefined reference value in the control unit the
airbags will not be triggered, even though
the accident may cause extensive damage to
the car.
The following airbags are triggered in
serious head-on collisions
●
Driver airbag.
●
Front passenger front airbag
The following airbags are triggered in
serious side-on collisions
●
Front side airbag on the side of the acci-
dent.
●
Rear side airbag on the side of the acci-
dent.
In an accident with airbag activation:
●
the interior lights switch on (if the interior
light switch is in the courtesy light position);
●
the hazard warning lights switch on;
●
all doors are unlocked;
●
the fuel supply to the engine is cut.
Airbag system
General overview of the airbag
Front airbags
Fig. 12 Location and deployment area of the
front airbag for the driver.
Fig. 13 Location and deployment area of the
front airbag for the passenger.
In conjunction with the seat belts, the front
airbag system gives the driver and the front
passenger additional protection for the head
and chest in the event of a severe frontal collision. Always remain as far away as possible
from the front airbag ››› page 6. This way, in
the event of an accident, the front airbags
can deploy fully when triggered, providing
maximum protection.
The front airbag for the driver is located in
the steering wheel ››› Fig. 12
f
ont passenger is located in the dash
or the fr
and the airbag
panel ››› Fig. 13. Airbags are identified by the
word “AIRBAG”.
When the front airbags are triggered they fill
the zones marked in red ››› Fig. 12 and
››› Fig. 13 (radius of action). Therefore, ob-
jects should never be placed or mounted in
these areas ›››
are outside the range of the front airbag for
the driver and the front passenger, e.g. the
baseplate for the mobile phone support.
The airbag covers fold out of the steering
wheel ››› Fig. 12
when the driver and front passenger airbags
are triggered. The airbag covers remain connected to the steering wheel or the dash panel.
WARNING
The airbag is deployed at high speed in fractions of a second.
●
Always keep the deployment areas of the
front airbags vacant.
●
Never secure objects to the covers or in the
deployment area of the airbag modules, e.g.
drink holders or phone supports.
●
The deployment space between the front
passengers and the airbags must not in any
, Factory-fitted accessories
or dash panel ›
› Fig. 13
›
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
»
21

Safety
case be occupied by other passenger, pets
and objects.
●
Never fix any object to the windscreen
above the front airbag on the front passenger
side.
●
Do not alter, cover or stick anything to the
steering wheel hub or the surface of the airbag module on the passenger side of the
dash panel.
WARNING
Front airbags are deployed in front of the
steering wheel ››› Fig. 12
› Fig. 13.
››
●
When driving, always hold the steering
wheel on the outer edge of the ring with both
hands: 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock position.
●
Adjust the driver seat so that there is a distance of at least 25 cm (10 inches) between
the centre of your chest and the hub of the
steering wheel. If your physical constitution
prevents you from meeting these requirements, make sure you contact a specialised
workshop.
●
Adjust the front passenger seat so there is
as much distance as possible between the
front passenger and the dash panel.
22
and the dash panel
Types of front passenger front airbag
systems
There are two different SEAT front passenger
front airbag systems:
A
Characteristics of the passenger front airbag without
disabling.
– Control lamp on the instrument panel.*
– Front passenger front airbag on the dash panel.
Description: airbag system
B
Characteristics of the front passenger front airbag that
can be disabled manually ››› page 24.
– Control lamp on the instrument panel.
– Control lamp on the dash panel.
.
– Switch on the dash panel glove compartment, on the
passenger side.
– Front passenger front airbag in the dash panel.
Description: airbag system with front passenger front
airbag disabling.
Side airbags
Fig. 14 On the side of the front seat: location
of the side airbag
Fig. 15 On the left side of the vehicle: deploy-
ment area of side airbag
The side airbags are located in the outer
cushion of the driver and front passenger
seat backrests ››› Fig. 14
dic
ed by the word “AIRBAG”. The area
at
marked in red ››› Fig. 15 indicates the side
airbag deployment zone.
. Their position is in-
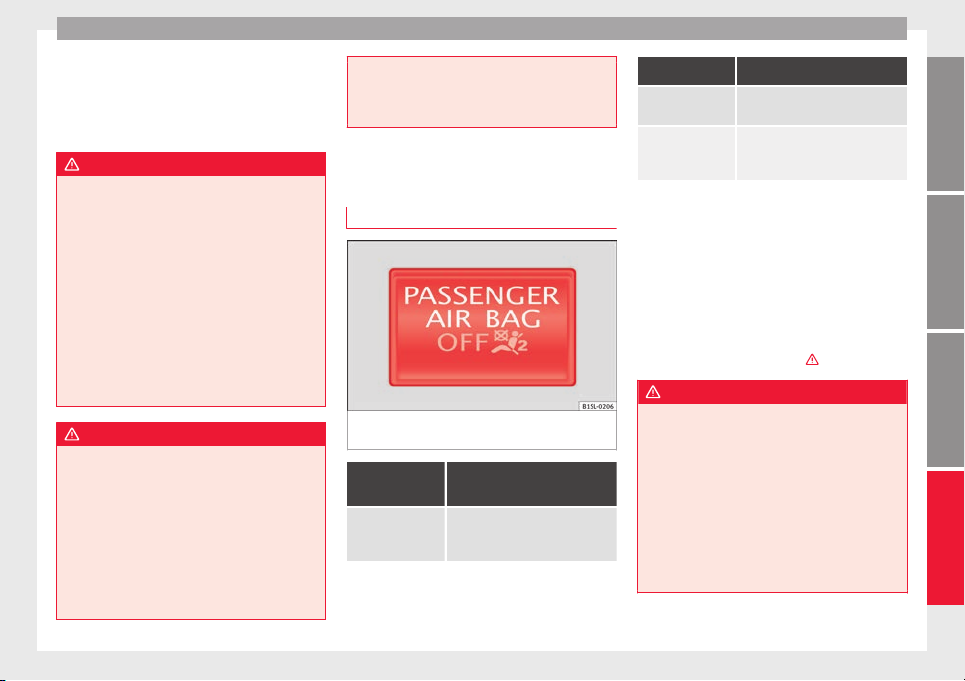
Airbag system
In the event of a side-on collision, the side
airbag will deploy in the side of the vehicle
affected ››› Fig. 15
injurie
to passengers on the side of the
s
, thus reducing the risk of
body and the head facing the accident side.
WARNING
The airbag is deployed at high speed in fractions of a second.
●
Always keep the deployment areas of the
side airbags vacant.
●
The deployment space between the front
passengers and the airbags must not in any
case be occupied by other passenger, pets
and objects.
●
Do not mount accessories on the doors.
●
Only used protective covers for the seats
that are approved for the vehicle. Otherwise,
the side airbag would be obstructed when deployed.
WARNING
Incorrect handling of the driver's and front
passenger seat could prevent the side airbag
from deploying properly and cause severe injuries.
●
Never remove the front seats of the vehicle
or modify any of their components.
●
Great forces must not be exerted on the
seat backrest bolsters because the side airbags might not deploy correctly, might not
deploy at all or might deploy unexpectedly.
●
Any damage to the original seat upholstery
or around the seams of the side airbag units
must be repaired immediately by a specialised workshop.
Deactivating airbags
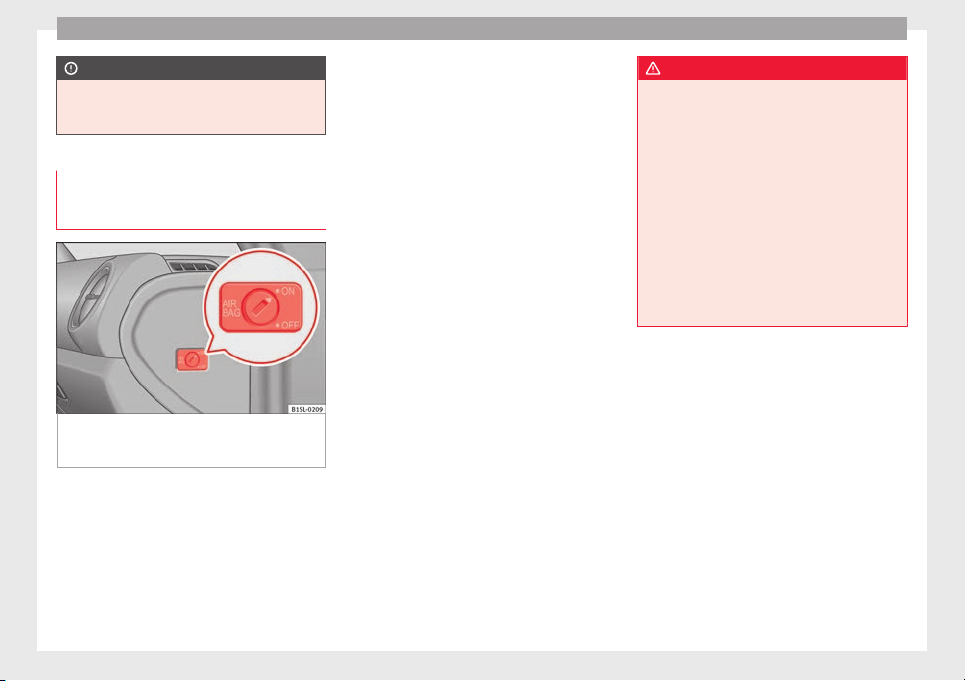
Control lamps
Fig. 16 Control lamp for disabling the front
passenger front airbag on the dash panel
Fault in airbag system and seat belt
tensioners.
It lights up on the combi-in-
strument
Have the system checked immediately by a specialised workshop.
Fault in the airbag
system.
Front passenger
front airbag disabled.
It lights up on the dash panel
Have the system checked immediately by a specialised workshop.
Check whether the airbag should
remain disabled.
Several warning and control lamps light up
for a few seconds when the ignition is switched on, signalling that the function is being
verified. They will switch off after a few seconds.
If the front passenger airbag is deactivated,
the lamp
ain lit
, or if it is lit together with the control
m
does not re-
lamp on the dash panel, there may be a
fault in the airbag system
WARNING
In the event of a fault in the airbag system,
the airbag may not trigger correctly, may fail
to trigger or may even trigger unexpectedly,
leading to severe or fatal injuries.
●
Have the airbag system checked immedi-
ately by a specialised workshop.
●
Never mount a child seat in the front passenger seat or remove the mounted child
seat! The front passenger front airbag may
deploy during an accident in spite of the
fault.
›››
.
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
»
23
CAUTION
Always pay attention to any lit control lamps
and to the corresponding descriptions and instructions to avoid damage to the vehicle.
Deactivating and activating the front
passenger front airbag using the key
switch
Safety
●
Using the vehicle key, turn the key switch to
›
›› Fig. 17
.
OFF
●
Close the door on the front passenger side.
●
The control lamp on
the dash panel will remain lit while the ignition is switched on ››› page 23.
Activating the front passenger front airbag
●
Switch the ignition off.
●
Open the door on the front passenger side.
●
Unfold the vehicle key shaft ››› page 43.
●
Using the vehicle key, turn the key switch to
ON ››› Fig. 17.
●
Close the door on the front passenger side.
●
Check that, with the ignition switched on,
the control lamp on the
dash panel is not lit ››› page 23.
WARNING
The front passenger front airbag must only be
disabled in special cases.
●
Disable and activate the front passenger
front airbag when the ignition is switched off
to avoid damage to the airbag system.
●
It is the driver's responsibility to ensure
that the key operated switch is set to the correct position.
●
Only disable the front passenger front airbag when a child seat is to be mounted under
exceptional circumstances.
●
As soon as the child seat is no longer needed on the front passenger seat, reconnect
the front passenger front airbag.
Fig. 17 On front passenger side: Key switch
for enabling and disabling the front passenger front airbag.
The front passenger front airbag must be disabled when a rear-facing child seat is mounted.
Disabling the front passenger front airbag
●
Switch the ignition off.
●
Open the door on the front passenger side.
●
Unfold the vehicle key shaft ››› page 43.
24
How to know whether the front passenger
front airbag is disabled
The only indication of the front passenger airbag being disabled is that the
control lamp on the dash panel re-
mains lit ( stays yellow) ››› page 23.
If the control lamp on the dash panel
does not remain lit or is lit in combination
with the control lamp on the instrument
panel, a child restraint system cannot be
mounted on the front passenger seat for
safety reasons. The front passenger front airbag may deploy during an accident.
Transporting children safely
Transporting children safely
Child safety
Introduction
Before transporting babies and children in a
child seat placed in the front passenger seat,
first completely read the information regarding the airbag system.
This information is extremely important for
driver and passenger safety, particularly that
of babies and children.
SEAT recommends the use of child seats from
the SEAT accessory programme. These child
seats have been designed and tested for use
in SEAT vehicles. You can purchase child
seats with different mountings from a SEAT
dealership.
WARNING
Make sure children are properly belted in and
correctly secured to avoid severe or fatal injuries while the vehicle is in motion.
●
Never use a rear-facing child seat in the
front passenger seat if the front passenger
front airbag is enabled.
●
Children up to 12 years old should always
travel on the rear seat.
●
Children must always be protected with an
approved child restraint system suited to
their height and weight.
●
Children must assume the proper sitting
position and be properly belted in while travelling.
●
Ensure the seat backrest is upright when a
child seat is being used on it.
●
Do not allow the child's head or other part
of his or her body to enter the deployment
area of the side airbags.
●
Make sure the belt webbing is correctly
positioned.
●
Never hold children or babies on your lap or
in your arms.
●
Only one child may occupy a child seat.
●
Please read and observe the child seat
manufacturer's handling instructions.
WARNING
An empty or loose child seat could fly uncontrollably around the vehicle interior and
cause injuries in the event of an accident or
sudden braking.
●
When not in use while the vehicle is in motion, always safely secure the child seat or
store it in the luggage compartment.
Note
Replace the child seat after an accident, as it
may have invisible damage.
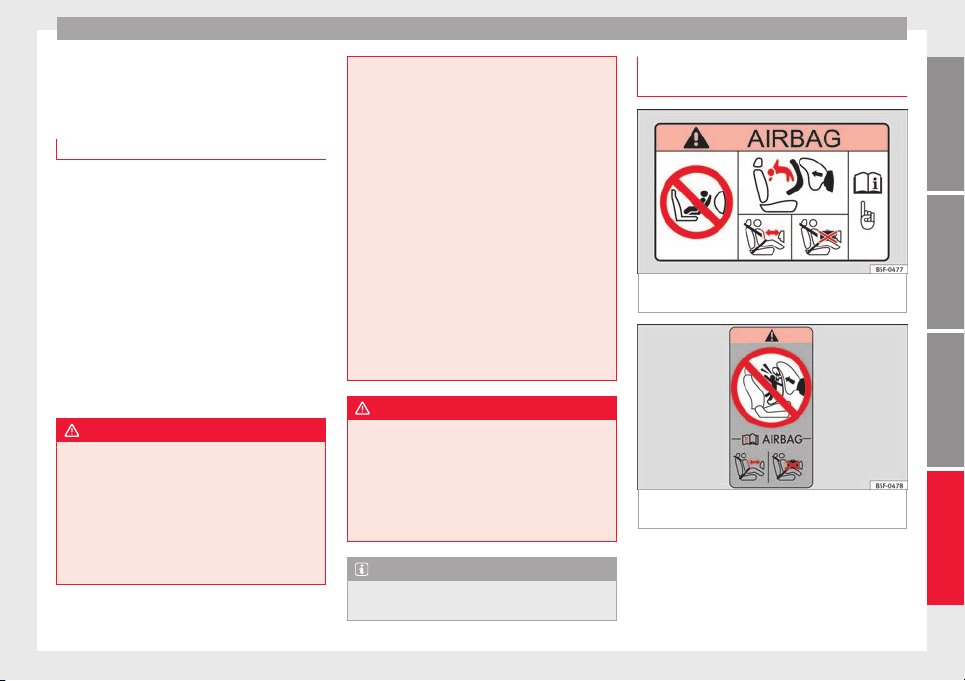
Important information regarding the
front passenger's airbag
Fig. 18 Passenger's side sun visor: airbag
sticker
Fig. 19 On the rear frame of the passenger
side door: airbag sticker.
A sticker with important information about
the passenger airbag is located on the passenger's sun visor and/or on the passenger
side door frame. Read and always observe
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
»
25

the safety information included in the
following chapters:
●
Child seats and passenger side airbag
››› page 28, Use of the child seat on the
front passenger seat.
●
Safety distance with respect to the passen-
ger airbag ››› in Introduction on page 18.
●
Objects between the passenger and the
passenger side airbag ››› in Front airbags
on page 21
.
Safety
26
Transporting children safely
General information on transporting
children in the vehicle
Legal regulations and provisions will always
take priority over the descriptions of this instruction manual. There are different regulations and provisions for the use of child seats
and their mountings (››› table on page 27).
In some countries, for example, the use of
child seats on certain seats in the vehicle
may be forbidden.
The physical principles and the forces acting
on the vehicle in the event of a collision or
other type of accidents also apply to children
››› page 11
y
oped muscle and bone structures. In the
event of an accident, children are subject to a
greater risk than adults of sustaining severe
injuries.
Given that children's bodies are not yet fully
developed, child restraint systems must be
used that are especially adapted to their
height, weight and constitution. There are
laws in force in many countries that indicate
1)
. However, unlike adults and
ou
ngsters, children do not have fully devel-
ECE-R: Economic C
omission for Europe Regulation.
the use of approved seat systems for transporting babies and children.
Only used authorised, approved child seats
that are suitable for the vehicle. Always consult with a SEAT dealership or a Specialised
workshop should you have any doubts.
Specific child seat regulations for each
country (selection)
Child seats must comply with the ECE-R 44
regulation. You can consult additional information at your SEAT dealership at the internet address www.seat.es.
Categorisation of child seats according to
ECE-R 44
Weight cat-
egory
Group 0 up to 10 kg
Group 0+ up to 13 kg
Group 1 9 to 18 kg
Group 2 15 to 25 kg approx. 3 to 7 years
Group 3 22 to 36 kg approx. 6 to 12 years
Weight of
the child
Age
up to approximately.
9 months
up to approximately.
18 months
approx. 8 months to
31/2 years
Not all children fit in the seat of their weight
group. Nor do all seats adapt to the vehicle.
Therefore, always check whether the child fits
properly in the child seat and whether the
seat can be installed safely in the vehicle.
Child seats approved under the ECE-R 44 regulation are fitted with the corresponding approval symbol. The sign is an upper-case E in
a circle with the identification number below
it.
1)
WARNING
In general, the rear seat is always the safest
place for children, who are belted correctly, in
the event of an accident.
●
A suitable child seat that is correctly installed and used on one of the rear seats offer
the most protection possible for babies and
children up to 12 years in most accidents.
Technical specifications
AdviceOperationSafety
27
Different mounting systems
Always secure child seats properly and safely
in the vehicle according to the child seat
manufacturer's installation instructions.
Mounted child seats must rest correctly on
the vehicle's seat and must not move or rock
more than 2.5 cm.
Child seats equipped for a Top Tether strap
must also be secured using the Top Tether retaining strap in the vehicle ››› page 32. At-
tach the retaining strap to the corresponding
retaining rings only. Not all rings can be used
with the Top Tether system. Always tighten
the Top Tether retaining strap so that the
child seat fits snugly against the corresponding seat in the vehicle.
Specific mounting systems for each country
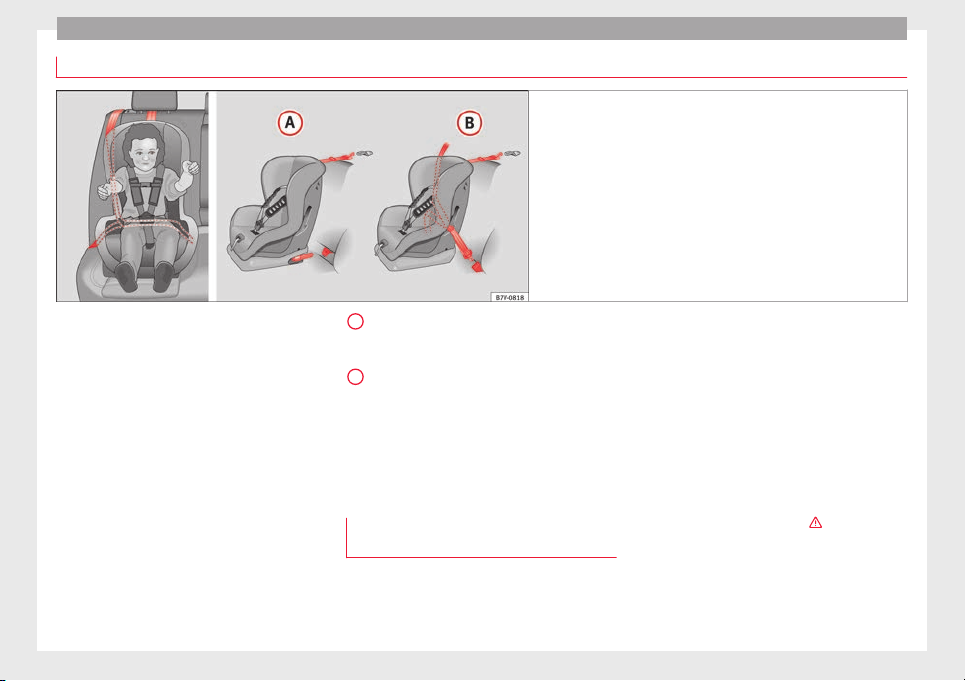
Attachment variants ››› Fig. 20
28
Safety
Fig. 20 On the rear seats: Possible installations for the child seat.
A
E
ope: ISOFIX retaining rings and upper
ur
retaining strap ››› page 31 and
››› page 32.
B
Three-point seat belt and upper retaining
strap ››› page 30.
The systems include the child restraint system mounting with an upper retaining strap
(Top Tether) and lower anchoring points on
the seat.
Use of the child seat on the front
passenger seat
Transporting children on the front passenger
seat is not permitted in all countries. Furthermore, not all child seats are approved for use
:
on the front passenger seat. Your SEAT deal-
ership has an updated list of all approved
child seats. Only used child seats that are approved for each vehicle.
The front airbag on the front passenger side
is highly dangerous for a child. The front passenger seat is life-threatening to a child if he
or she is transported in a rear-facing child
seat.
If a rear-facing child seat is secured to the
front passenger seat, an inflating front airbag
can strike it with such great force that severe
or fatal injuries may result ››› . Therefore,
rear-facing child seats must never
on the fr
passenger front airbag is enabled.
Only use a rear-facing child seat on the front
passenger seat if the front passenger front
airbag is disabled. When it is disabled, the
passenger seat when the front
ont
be placed
 Loading...
Loading...