Seat Leon 5D 2010 Owner's Manual

LEON OWNER’S MANUAL


Foreword
This Instruction Manual and its corresponding supplements should be read carefully to familiarise yourself with
your vehicle.
Besides the regular care and maintenance of the vehicle, its correct handling will help preserve its value.
For safety reasons, note the information concerning accessories, modifications and part replacements.
If selling the vehicle, give all of the on-board documentation to the new owner, as it should be kept with the
vehicle.


Contents
Manual structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Safety First . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Safe driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brief introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Proper sitting position for occupants . . . . . . . . .
Pedal area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storing objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Seat belts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brief introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Why wear seat belts? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Seat belts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Seat belt tensioners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Airbag system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brief introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
front airbags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Side airbags* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Curtain airbags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Deactivating airbags* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Child safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brief introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Child seats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Securing child seats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5
Operating Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cockpit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6
Instruments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LPG system* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7
Digital instrument panel display . . . . . . . . . . . .
Instrument panel menus* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7
Warning lamps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7
Steering wheel controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
16
Audio system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
16
Radio navigation system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19
Unlocking and lo cking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19
Central locking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
21
Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
24
Radio frequency remote control . . . . . . . . . . . . .
28
Anti-theft alarm system* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
30
Tailgate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
30
Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
34
Sliding/tilting sunroof* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
37
Lights and visibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
41
Lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
44
Interior lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
46
Visibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
46
Windscreen wipers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
48
Rear-view mirrors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
51
Seats and storage compartments . . . . . . . . . .
The importance of correct seat adjustment . . . .
Head restraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front seats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear seats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage compartment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ashtrays*, cigarette lighter* and elec trical
55
sockets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
First-aid kit, warning triangle, fire extinguisher
55
Luggage compartment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
55
57
Air conditioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
60
Heating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
61
Climatic* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
68
2C-Climatronic* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
77
General notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
91
Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
91
Steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
92
Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
96
Ignition lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Starting and stopping the engine . . . . . . . . . . .
99
Driving with LPG* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
99
Start-Stop function* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
105
Manual gearbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
106
Automatic gearbox* / DSG automatic gearbox*
108
Handbrake . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
110
Acoustic parking aid system* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
112
Cruise control* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
114
117
117
Practical Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
125
Intelligent technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
127
127
Brakes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
131
Anti-lock brake system and traction control M-ABS
(ABS and TCS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
135
Electronic Stability Programme (ESP)* . . . . . . . .
135
Driving and the environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
136
Running-in . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
138
Exhaust gas purification system . . . . . . . . . . . . .
140
141
Contents 3
143
145
146
148
148
150
154
158
160
160
161
162
163
166
167
170
171
176
178
181
185
185
185
186
187
193
193
194

Contents4
Economical and environmentally friendly driving
Driving abroad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Trail er towin g . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Instructions to follow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ball coupling of towing bracket* . . . . . . . . . . . .
Driving tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fitting a towing bracket* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle maintenance and cleaning . . . . . . . .
General notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Care of the vehicle exterior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle interior maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accessories, parts replacement and
modifications
Accessories and spare parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical modifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Roof aerial* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mobile phones and two-way radios . . . . . . . . . .
Checking and ref illing levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Refuelling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LPG system* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Petrol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diesel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Working in the engine compartment . . . . . . . . .
Engine oil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Coolant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Washer fluid and windscreen wiper blades . . . .
Brake fluid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wheels and tyres . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wheels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
If and when . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tools, tyre repair kit and spare wheel . . . . . . . .
Changing a wheel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tyre repair kit (Tyre Mobility System)* . . . . . . . .
Fuses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Bulb change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
195
Jump-starting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
198
Towing and tow-starting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
199
199
200
Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . .
200
201
Description of specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Important information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
203
Information on fuel consumption . . . . . . . . . . . .
203
Towing a trailer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
204
Wheels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
209
Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Checking fluid levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
212
Petrol engine 1.4 63 kW (85 PS) . . . . . . . . . . . .
212
Petrol engine 1.6 75 kW (102 PS) . . . . . . . . . . .
212
Petrol engine 1.2 77 kW (105 PS) . . . . . . . . . . .
213
Petrol engine 1.4 92 kW (125 PS) . . . . . . . . . . .
213
Petrol engine 1.8 118 kW (160 PS) . . . . . . . . . .
214
Petrol engine 2.0 155 kW (211 PS) . . . . . . . . . .
214
Petrol engine 2.0 177 kW (240 PS) Cupra . . . . .
216
Petrol engine 2.0 195 kW (265 PS) Cupra R . . .
219
Diesel engine 1.6 TDI CR 77 kW (105 PS)
220
with/without DPF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
221
Diesel engine 1.6 TDI CR 77 kW (105 PS) DPF
224
Start&Stop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
228
Diesel engine 1.6 TDI CR 77 kW (105 PS) DPF
230
Ecomotive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
233
Diesel engine 2.0 TDI CR 103 kW (140 PS) DPF
234
Diesel engine 2.0 TDI PD 103 kW (140 PS) without
DPF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
237
Diesel engine 2.0 TDI CR 125 kW (170 PS) DPF
237
Dimensions and capacities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
245
245
247
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
252
254
259
267
270
273
273
273
275
275
276
277
277
278
279
280
282
283
284
286
287
288
289
291
292
293
294
296
297
Manual structure
What you should know before reading this manual
This manual contains a description of the equipment supplied with the
vehicle at the time of press. Some of the equipment hereunder described will
not be available until a later date, or is only available in certain markets.
Because this is a general manual for the LEON, some of the equipment and
functions that are described in this manual are not included in all types or
variants of the model or model year ; they may vary or be modified in accordance with technical or market requirements or model year; this can not be
interpreted as dishonest advertising .
The illustrations are intended as a general guide and may vary from the
equipment fitted in your vehicle in some details.
The direction indications (left, right, front, rear) appearing in this manual
refer to the normal forward working direction of the vehicle except when
otherwise indicated.
The equipment marked with an asterisk** is fit ted a s sta nda rd on ly i n cer tai n
versions, and is only supplied as optional extras for some versions, or are
only offered in certain countries.
® All registered marks are indicated with ®. Although the copyright symbol
does not appear, it is a copyrighted mark.
b The section is continued on the following page.
Marks the end of a section.
WARNING
Texts preceded by this symbol contain information on safety. They warn
you about possible dangers of accident or injury.
Manual structure 5
Cautio n
Texts with this symbol draw your attention to potential sources of damage to
your vehicle.
For the sake of the environment
Texts preceded by this symbol contain additional information on the protection of the environment.
Note
Texts preceded by this symbol contain additional information.

Content6
Content
This manual is structured to provide the information you need in an organised
way. The content of this Manual is divided into sections which belong to
chapters (e.g. “Air conditioning”). The entire manual is divided into five large
parts which are:
1. Safety First
Information on the vehicle equipment relating to passive safety such as seat
belts, airbags, seats, etc.
2. Operating instructions
Information about the distribution of controls in the driver position of your
vehicle, about the seat adjustment possibili ties, about how to create a suitable climate in the passenger compartment, etc.
3. Practical Tips
Advice relating to the driving, caring and maintenance of your vehicle and
certain pro blems you can solve yourself.
4. Technical Specifications
Figures, values and the dimensions of your vehicle.
5. Alphabetic index
At th e end of this man ual the re is a d etailed alphab etical i ndex, t his will help
you to rapidly find the information you require.
Safety First
Safe driving
Safe driving 7
Brief introduction
Dear SEAT Driver
Safety first!
This chapter contains important information, tips, suggestions and
warnings that you should read and consider for both your own safety
and for your passengers’ safety.
Safety equipment
The safety equipment is a part of the occupant protection
system and can reduce the risk of injury in the event of accident.
Never put your safety or the safety of your passengers in danger. In the event
of an accident, the safety equipment may reduce the risk of injury. The
following list includes most of the safety equipment in your SEAT:
• three-point seat belts,
• belt tension limiters for the front and rear side seats,
WARNING
• This manual contains important information about the operation of the
vehicle, both for the driver and the passengers. The other sections of the
owner’s manual also contain further information that you should be aware
of for your own safety and for the safety of your passengers.
• Ensure that the on-board documentation is kept in the vehicle at all
times. This is especially impor tant when lending or selling the vehicle to
another person.
• belt tensioners for the front seats,
• belt height adjustment for the front seats,
• front airbags,
• side airbags in the front seat backrests,
• side airbags in the rear seat backrests*,
• curtain airbags,
• active front head restraints*,
• ISOF IX anchor points for child seats in the rear side s eats with the ISOFIX
system,
• height-adjustable head restraints,
• head restraints with in-use position and non-use position
• adjustable steering column.
Safety First Operating Instructions Practical Tips Technical Speci fications

Safe driving8
The safety equipment mentioned above works together to provide you and
your passengers with the best possible protection in th e event of an accident.
However, these safety systems can only be effective if you and your passengers are sitting in a correct position and use this equipment properly.
Therefore, information is provided about why this equipment is so important,
ho w it pro tec ts you , wh at y ou h ave to cons id er w hen usi ng it a nd h ow y ou a nd
your passengers can achieve the greatest possible benefit from the safety
equipment fitted. This manual includes important warnings that you and your
passengers should note in order to reduce the risk of injury.
Safety is everyone’s business!
Before starting every trip
The driver is responsible for the safety of the passengers and
the safe operation of the vehicle.
For your own safety and the safety of your passengers, always note
the following points before every trip:
– Make sure that the vehicle’s lights and turn signals are working
properly.
– Check tyre pressure.
– Ensure that all windows provide a clear and good view of the
surroundings.
– Make sure all luggage is secured ⇒ page 16.
– Make sure that no objects can interfere with the pedals.
– Adjust front seat, head restraint and mirrors properly according
to your size.
– Ensure that the passengers in the rear seats always have the
head restraints in the in-use position ⇒ page 14.
– Instruct passengers to adjust the head restraints according to
their height.
– Protect children with appropriate child seats and properly
applied seat belts ⇒ page 46.
– Assume the correct sitting position. Instruct your passengers
also to assume a proper sitting position ⇒ page 10.
– Fasten your seat belt securely. Instruct your passengers also to
fasten their seat belts properly ⇒ page 19.
What affects driving safety?
Driving safety is largely determined by your driving style and
the personal behaviour of all occupants.
As a driver, you are responsible for yourself and your passengers.
When your concentration or driving safety is affected by any circumstance, you endanger yourself as well as others on the road ⇒ ,
for this reason:
– Always pay attention to traffic and do not get distracted by
passengers or telephone calls.
– Never drive when your driving ability is impaired (e.g. by medica-
tion, alcohol, drugs).
– Observe traffic laws and speed limits.
– Always reduce your speed as appropriate for road, traffic and
weather conditions.
– When travelling long distances, take breaks regularly - at least
every two hours.
– If possible, avoid driving when you are tired or stressed.
WARNING
When driving safety is impaired during a trip, the risk of injury and accidents increases.
Safe driving 9
Safety First Operating Instructions Practical Tips Technical Speci fications
Safe driving10
Proper sitting position for occupants
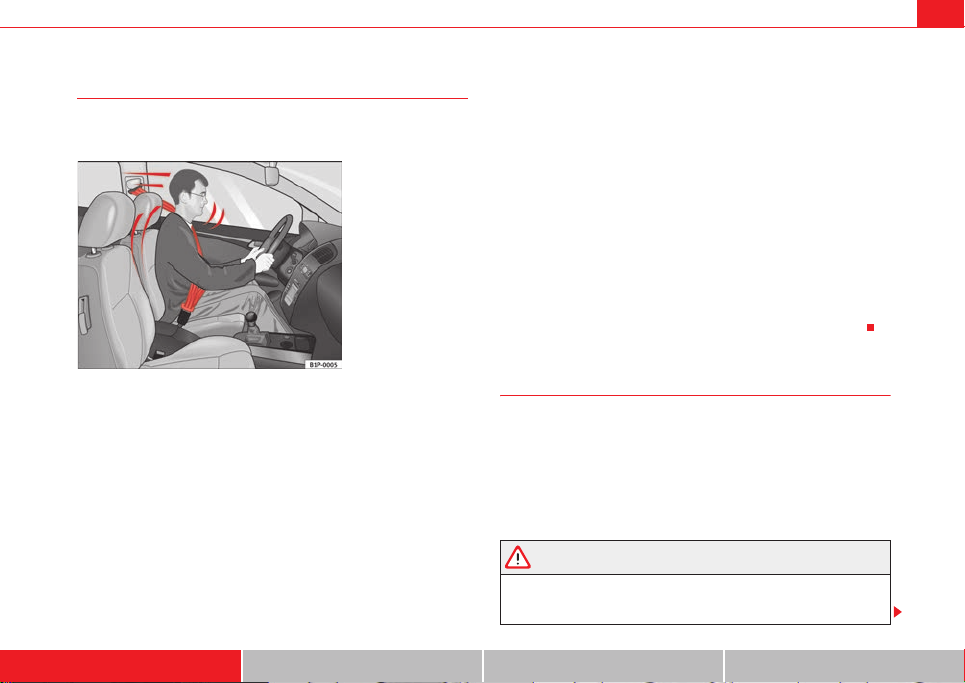
Proper sitting position for driver
The proper sitting position for the driver is important for a
safe and relaxed driving.
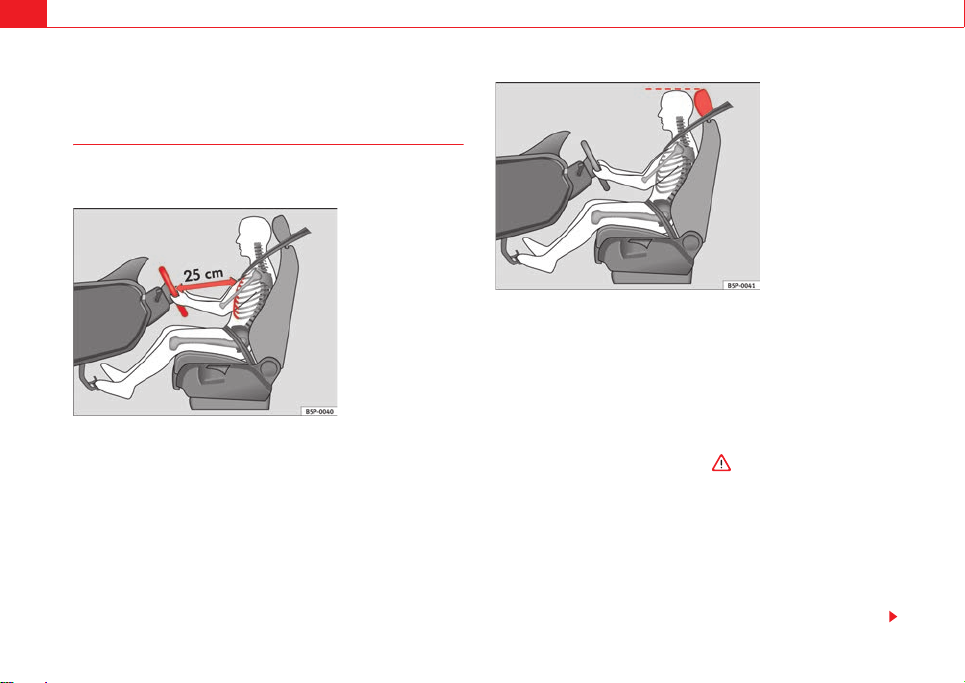
Fig. 1 The proper
distance between driver
and steering wheel
Fig. 2 Proper head
restraint p osition for
driver
For your own safety and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of an
accident, we recommend the following adjustments for the driver:
– Adjust the steering wheel so that there is a distance of at least 25
cm between the steering wheel and the centre of your chest
⇒ fig. 1.
– Move the driver seat forwards or backwards so that you are able
to press the accelerator, brake and clutch pedals to the floor with
your knees still slightly angled ⇒ .
– Ensure that you can reach the highest point of the steering
wheel.
– Adjust the head restraint so that its upper edge is at the same
level as the top of your head, or as close as possible to the same
level as the top of your head ⇒ fig. 2.
– Move the backrest to an upright position so that your backrests
completely against it.
Safe driving 11
– Fasten your seat belt securely ⇒ page 19.
– Keep both feet in the footwell so that you have the vehicle under
control at all times.
Adjustment of the driver seat ⇒ page 135.
WARNING
• An incorrect sitting position of the driver can lead to severe injuries.
• Adjust the driver seat so that there is at least 25 cm distance between
the centre of the chest and the centre of the steering wheel ⇒ page 10,
fig. 1. If you are sitting closer than 25 cm, the airbag system cannot protect
you properly.
• If you r physical constitution prevents you from maintaining the
minimum distance of 25 cm, contact a specialised workshop. The workshop will help you decide if special specific modifications are necessary.
• When driving, always hold the steering wheel with both hands on the
outside of the ring at the 9 o’clock and 3 o’clock positions. This reduces the
risk of injury when the driver airbag is triggered.
• Never hold the steering wheel at the 12 o’clock position, or in any other
manner (e.g. in the centre of the steering wheel). In such cases, if the
airbag is triggered, you may sustain injuries to the arms, hands and head.
• To reduce the risk of injury to the driver during sudden braking manoeu-
vres or an accident, never drive with the backrest tilted far back! The airbag
system and seat belts can only provide optimal protection when the backrest is in an upright position and the driver is wearing his or her seat belt
properly. The further the backrests are tilted to the rear, the greater the risk
of injury due to incorrect positioning of the belt web or to the incorrect
sitting position!
• Adjust the head restraint properly to achieve optimal protection.
Safety First Operating Instructions Practical Tips Technical Speci fications
Proper sitting position for front passenger
The front passenger must sit at least 25 cm away from the
dash panel so that the airbag can provide the greatest
possible protection in the event that it is triggered.
For your own safety and to reduce the risk of injur y in the event of an
accident, we recommend the following adjustments for the front
passenger:
– Move the front passenger seat back as far as possible ⇒ .
– Move the backrest to an upright position so that your backrests
completely against it.
– Adjust the head restraint so that its upper edge is at the same
level as the top of your head, or as close as possible to the same
level as the top of your head ⇒ page 13.
– Keep both feet in the footwell in front of the front passenger seat.
– Fasten your seat belt securely ⇒ page 19.
It is possible to deactivate the passenger airbag in exceptional circum-
stances ⇒ page 25.
Adjusting the front passenger seat ⇒ page 138.
WARNING
• An incorrect sitting position of the front passenger can lead to severe
injuries.
• Ad just the front pass enger sea t so that t here is at least 25 c m betwee n
your chest and the dash panel. If you are sitting closer than 25 cm, the
airbag system cannot protect you properly.
Safe driving12
WARNING (continued)
• If your physical constitution prevents you from maintaining the
minimum distance of 25 cm, contact a specialised workshop. The workshop will help you decide if special specific modifications are necessary.
• Al ways keep your feet in t he fo otwe ll wh en th e veh icle is m oving ; ne ver
rest them on the dash panel, out the window or on the seat. An incorrect
sitting position exposes you to an increased risk of injury in case of a
sudden braking or an accident. If the airbag is triggered, you could sustain
severe injuries due to an incorrect sitting position.
• To reduce the risk of injury to the front passenger in events such sudden
braking manoeuvres or an accident, never travel with the backrest tilted far
back! The airbag system and seat belts can only provide optimal protection
when the backrest is in an upright position and the front passenger is
wearing his or her seat belt properly. The further the backrests are tilted to
the rear, the greater the risk of injury due to incorrect positioning of the
belt web or to the incorrect sitting position!
• Adjust the head restraint properly in order to achieve maximum
protection.
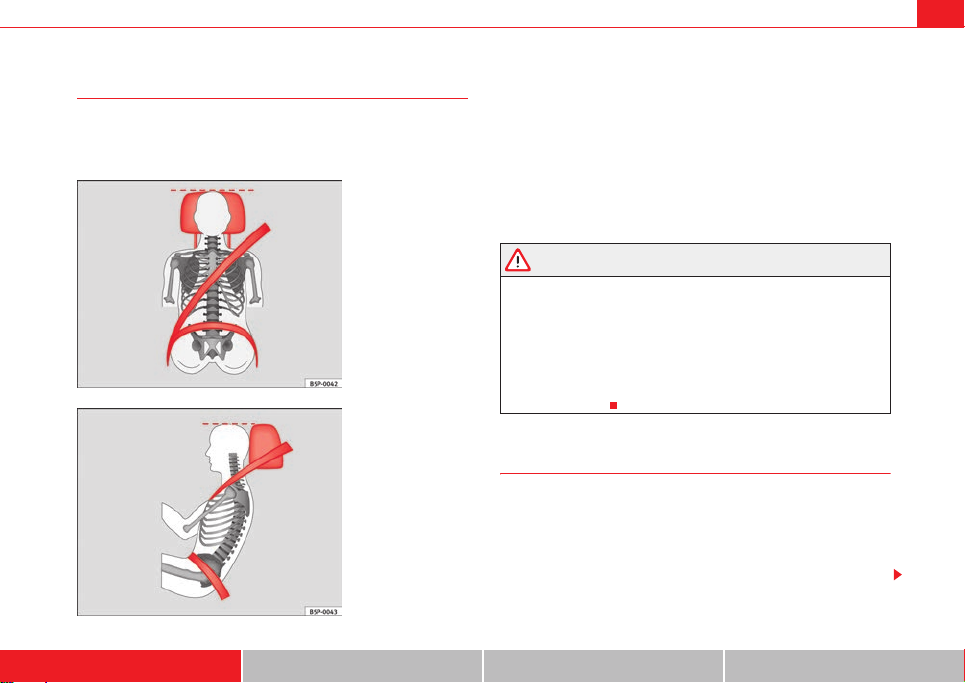
Correct sitting position for passengers in the rear seats
Passengers in the rear seats must sit up straight, keep their
feet on the footwells, have the head restraints positioned for
use and wear their seat belts properly.
To reduce the risk of injury in the event of a sudden braking
manoeuvre or an accident, passengers on the rear bench seat must
consider the following:
– Adjust the head restraint to the correct position ⇒ page 14.
– Keep both feet in the footwell in front of the rear seat.
–Fasten your seat belt securely ⇒ page 19.
– Use an appropriate child restraint system when you take children
in the vehicle ⇒ page 46.
WARNING
• If the passengers on the rear seat are not sitting properly, they could
sustain severe injuries.
• Adjust the head restraint properly in order to achieve maximum protec-
tion.
• Seat belts can only provide optimal protection when backrests are in an
upright position and the passengers are wearing their seat belts properly.
If passengers on the rear seat are not si tting in an upright position, the risk
of injury due to incorrect positioning of the seat belt increases.
Safe driving 13
Correct adjustment of front seat head restraints
Properly adjusted head restraints are an important part of
passenger protection and can reduce the risk of injuries in
most accident situations.
Adjust the head restraint properly in order to achieve maximum
protection.
– Adjust the head restraint so that its upper edge is at the same
level as the top of your head, or as close as possible to the same
level as the top of your head and, at the very least, at eye level
⇒ fig. 3 and ⇒ fig. 4.
Adjusting the head restraints ⇒ page 135.
WARNING
• Travelling with the head restraints removed or improperly adjusted
increases the risk of severe injuries.
• Incorrectly adjusted head restraints could result in death in the event of
a collision or accident.
Fig. 3 Properly adjusted
head restrai nt viewed
from the front
• Incorrectly adjusted head restraints also increase the risk of injury
during sudden or unexpected driving or braking manoeuvres.
• The head restraints must always be adjusted according to the
passenger’s height .
Active head restraints*
Vehicle occupants are pressed into their seats during a rear end collision. The
resulting body pressure on the backrest activates the active head restraint*
on the front seat, which moves rapidly forwards and upwards at the same
time. This movement reduces the distance between the occupant’s head and
the head restraint, thus reducing the risk of head injuries such as brain
Fig. 4 Properly adjusted
head restrai nt viewed
from the side
Safety First Operating Instructions Practical Tips Technical Speci fications
trauma.

Safe driving14
WARNING
Travelling with the head restraints removed or improperly adjusted
increases the risk of severe injuries.
• Incorrectly adjusted head restraints could result in death in the event of
a collision or accident.
• Incorrectly adjusted head restraints also increase the risk of injury
during sudden or unexpected driving or braking manoeuvres.
• The head restraints must always be adjusted according to the
passenger’s height.
Note
The active head restraints* could also be triggered if a vehicle occupant
ap pli es a hig h l eve l of pre ssu re on t he b ack res t (e .g. by “ fa lli ng” bac k in to t he
seat when entering the vehicle) or if pressure is applied to a front seat head
restraint from the rear. This accidental activatio n is, however, not dangerous,
as the active head restraints will return to the original position immediately
and are thus once again ready.
Correct adjustment of rear seat head restraints
Properly adjusted head restraints are an important part of the
passenger protection and can reduce the risk of injuries in
most accident situations
Fig. 5 Head restraints in
correct position
Rear outer seat head restraints
– The rear outer seat head restraints have 4 positions.
–Three positions for use ⇒ fig. 5. In these positions, the head
restraints are used normally, protecting passengers along with
the rear seat belts.
– And one position for non-use.
– To fit the head restraints in position for use, pull on the edges
with both hands in the direction of the arrow.
Safe driving 15
Centre rear head restraint
– The centre head restraint only has two positions, in-use (head
restraint up) and non-use (head restraint down).
WARNING
• Under no circumstances should the rear passengers travel while the
head restraints are in the non-use position.
• Do n ot swap the cen tre rear head restr aint with eith er of the outer seat
rear head restraints.
• Risk of injury in case of an accident!
Cautio n
Note the instructions on the adjustment of the head restraints. ⇒ page 136
The following list contains examples of sitting positions that could be
dangerous for all occupants. The list is not complete, but we would like to
make you aware of this issue.
Therefore, whenever the vehicle is in motion:
• Never stand in the vehicle,
• never stand on the seats,
• never kneel on the seats,
• never tilt your backrest far to the rear,
• never lean against the dash panel,
• never lie on the rear bench,
• never sit on the front edge of a seat,
• never sit sideways,
• never lean out of a window,
• never put your feet out of a window,
• never put your feet on the dash panel,
Examples of incorrect sitting positions
An incorrect sitting position can lead to severe injuries to
occupants.
Seat belts can provide optimal protection only when the belt webs
are properly positioned. Incorrect sitting positions substantially
reduce the protective function of seat belts and increase the risk of
injury due to incorrect seat belt position. As the driver, you are
responsible for all vehicle occupants, especially children.
– Never allow anyo ne to assume an incorrect sitting position in the
vehicle while travelling ⇒ .
Safety First Operating Instructions Practical Tips Technical Speci fications
• never put your feet on the surface of a seat,
• do not allow anyone to travel in the footwell,
• never travel without wearing the seat belt,
• do not allow anyone to travel in the luggage compartment.
WARNING
• Any incorrect sitting position increases the risk of severe injuries.
• Sitting in an incorrect position exposes the occupants to severe injuries
if airbags are triggered, by striking a passenger who has assumed an incorrect sitting position.
• Before the vehicle moves, assume the proper sitting position and main-
tain it throughout the trip. Before every trip, instruct your passengers to sit
properly and to stay in this position during the trip ⇒ page 10, “Proper
sitting position for occupants”.
Safe driving16
Pedal area
Pedals
The operation of all pedals must never be impaired by objects
or floor mats.
– Ensure that you can always press the accelerator, brake and
clutch pedals unimpaired to the floor.
– Ensure that the pedals can return unimpaired to their initial posi-
tions.
Use only floor mats which leave the pedal area free and can be securely
fastened on the footwell.
If a brake circuit fails, the brake pedal must be pressed down thoroughly in
order to stop the vehicle.
Wearing suitable shoes
Always wear shoes which support your feet properly and give you a good
feeling for the pedals.
WARNING
• Restricting pedal operation can lead to critical situations while driving.
• Never place objects on the driver footwell. An object could move into
the pedal area and impair pedal operation. In the event of a sudden driving
or braking manoeuvre, you will not be able to operate the brake, clutch or
accelerator pedal. Risk of accident!
Floor mats on the driver side
Only floor mats may be used which can be securely fastened
in the footwell and do not impair operation of the pedals.
– Ensure that the floor mats are securely fastened during the trip
and do not obstruct the pedals ⇒ .
Only use floor mats which leave the pedals clear and which are secured to
prevent them from slipping. You can obtain suitable floor mats from a specialised dealership. Fasteners* for floor mats are fitted in the footwells.
WARNING
• If the pedals are obstructed, an accident may occur. Risk of serious inju-
ries.
• Ensure that the floor mats are always securely attached.
• Never lay or fit floor mats or other floor coverings over the original floor
mats. This would reduce the pedal area and could obstruct the pedals. Risk
of accident.
Storing objects
Loading the luggage compartment
All luggage and other loose objects must be safely secured in
the luggage compartment.
Unsecured objects which shift back and forth could impair the
driving safety or driving characteristics of the vehicle by shifting the
centre of gravity.
Safe driving 17
– Distribute the load evenly in the luggage compartment.
– Place heavy objects as far forward as possible in the luggage
compartment.
–Place the heavy objects first.
– Secure heavy objects to the fastening rings ⇒ page 17.
WARNING
• Loose luggage and other objects in the luggage compartment could
cause serious injuries.
• Always stow objects in the luggage compartment and secure them on
the fastening rings.
WARNING (continued)
• Nev er allow children to play in or aro und the vehicle . Close and lock all
the doors and tailgate when you leave the vehicle. Before you lock the
vehicle, make sure that there are no adults or children in the vehicle.
• Never transpor t passengers in the luggage compartment. All passen-
gers must have their seat belt fastened ⇒ page 19 .
Note
• Air circulation in the vehicle helps reduce fogging of the windows. Used
air escapes through ventilation slits in the side trim of the luggage compartment. Ensure that the ventilation slits are never covered.
• Straps for securing the load to the fastening rings are commercially
available.
• Use suitable straps to secure heavy objects.
• During sudden manoeuvres or accidents, loose objects can be thrown
forward, injuring vehicle occupants or passers-by. This increased risk of
injury will be further increased if a loose object is struck by an inflating
airbag. If this happens, objects can be transformed into “missiles”. Risk of
fatal inju ry.
• Please note that the centre of gravity may shift when transporting
heavy objects; this may affect the vehicle’s handling and lead to an accident. Therefore, it is essential to adjust your speed and dr iving style
accordingly, to avoid accidents.
• Never exceed the allowed axle weights or allowed maximum weight. If
the allowed axle load or the allowed total weight is exceeded, the driving
characteristics of the vehicle may change, leading to accidents, injuries
and damage to the vehicle.
• Never leave your vehicle unattended, especially when the tailgate is
open. Children could climb into the luggage compartment, closing the door
behind them; they will be trapped and run the risk of death.
Safety First Operating Instructions Practical Tips Technical Speci fications
Fastening rings*
There can be four fastening rings in the luggage compartment for fastening luggage and other objects.
– Always use suitable and undamaged straps to secure luggage
and other objects to the fastening rings ⇒ in “Loading the
luggage compartment” on page 16.
– Pull up the fastening rings to attach the straps.
During a collision or an accident, even small and light objects can build up so
much energy that they can cause very severe injuries. The amount of kinetic
energy depends on the speed of the vehicle and the weight of the object. The
most significant factor, however, is the speed of th e vehicle.

Safe driving18
Example: An object weighing 4.5 kg is lying unsecured in the vehicle. During
a frontal collision at a speed of 50 km/h, this object generates a force corresponding to 20 times its weight. That means that the effective weight of the
object increases to about 90 kg. You can imagine the severity of the injuries
which might be sustained if this object strikes an occupant as it flies through
the passenger compartment. This in creased risk of injury will be fur ther
increased if a loose object is struck by an inflating airbag.
WARNING
• If pieces of luggage or other objects are secured to the fastening rings
with inappropriate or damaged retaining cords, injuries could be sustained
in the event of braking manoeuvres or accidents.
• To prevent pieces of luggage or other objects from flying for ward,
always us e appropriate ret aining cords whi ch are secured to t he fastening
rings.
• Never secure a child seat on the fastening rings.
Seat belts
Seat belts 19
Brief introduction
Before driving: remember your seat belt!
Wearing a seat belt properly can save your life!
In this chapter you will learn the importance of wearing seat belts,
how they work and how to properly fasten, adjust and wear them.
– Read and consider all the information as well as the warnings in
this chapter.
WARNING
• If seat bel ts are wor n incorrec tly or n ot at all, the risk of severe injuries
increases.
• Properly worn seat belts can reduce severe injuries in case of sudden
braking manoeuvres or accidents. For safety reasons, you and your passengers must always wear the seat b elts properly while the vehicle is moving.
• P reg na nt w om en or p eo ple wi th phy sic al dis ab ili ti es mus t a lso us e se at
belts. Like all other passengers, these people can also sustain severe injuries if they are not wearing their seat belts properly.
Number of seats
Your vehicle has five seats, two in the front and three in the rear. Each seat is
equipped with a three-point seat belt.
Safety First Operating Instructions Practical Tips Technical Speci fications
In some versions, your vehicle is approved only for four seat s. Two front seats
and two rear seats.
WARNING
• More people than available seats must never be transported in your
vehicle.
• Every passenger in the vehicle must properly fasten and wear the seat
belt belonging to his or her seat. Children must be protected with an appropriate child restraint system.
Seat belt warning lamp*
The warning lamp acts as a reminder to the driver to fasten
the seat belt.
Before starting the vehicle:
– Fasten your seat belt securely.
– Instruct your passengers to fasten their seat belts properly before
driving off.
– Protect children by using a child seat according to the child’s
height and weight.

Seat belts20
After the ignition has been switched on, the warning lamp on the instrument panel lights up
acoustic signal is heard if the vehicle is driven at more than 30 km/h.
The warning lamp*
the ignition is switched on.
1)
Depending on the model version
1)
if the driver has not fastened his/her seat b elt, and an
is switched off if the driver seat belt is fastened while

Why wear seat belts?
Physical principles of frontal collisions
In the event of a frontal collision, a large amount of kinetic
energy must be absorbed.
Fig. 6 Vehicle about to hit
a wall: the occupants are
not wearing seat belts
Seat belts 21
Fig. 7 The ve hicle hits
the wall: the occupants
are not wearing seat belts
It is easy to explain how the laws of physics work in the case of a head-on
collision: When a vehicle starts moving ⇒ fig. 6, a certain amount of energy
known as kinetic energy is produced in the vehicle and its occupants.
The amount of kinetic energy depends on the speed of the vehicle and the
weight of the vehicle and its passengers. Th e higher the speed and the
greater the weight, the more energy there is to be released in an accident.
The most significant factor, however, is the speed of the vehicle. If the speed
doubles from 25 km/h to 50 km/h, for example, the kinetic energy is multiplied by four.
Because the passengers in our example are not restrained by seat belts, in
the case of a head-on collision all of their kinetic energy has to be absorbed
at the point of impact ⇒ fig. 7.
Even at spee ds of 30 km/h to 50 km /h, the forces acting on bodies in a collision can easily exceed one tonne (1000 kg). At greater spe ed these forces are
even higher.
Passengers not wearing seat belts are not “attached” to the vehicle. In a
head-on collision, they will move forward at the same speed their vehicle was
Safety First Operating Instructions Practical Tips Technical Speci fications
Seat belts22
travelling just before the impact. This example applies not only to head-on
collisions, but to all accidents and collisions.
The danger of not using the seat belt
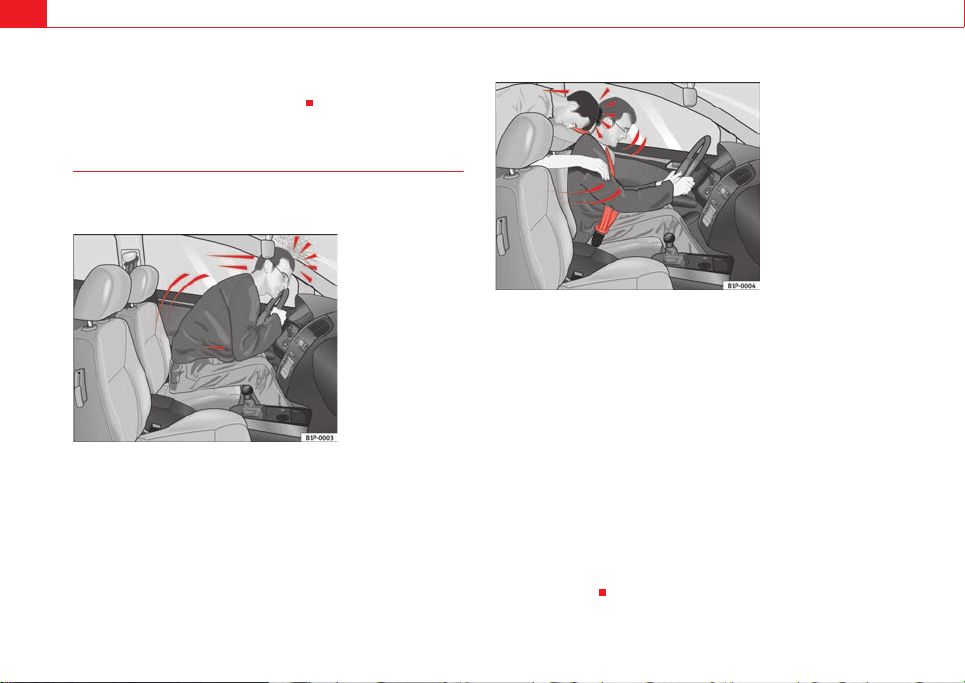
The general belief that the passengers can protect themselves with their hands in a minor collision is false.
Fig. 8 A driver not
wearing a seat belt is
thrown forward violently.
Fig. 9 The unbelted rear
passenger is thrown
forward violently, hitting
the driver wearing a seat
belt.
Even at low speeds the forces acting on the bo dy in a collision are so great
that it is not possible to brace oneself with one’s hands. In a frontal collision,
unbelted passengers are thrown forward and will make violent contact with
the steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen or whatever else is in the way
⇒ fig. 8.
The airbag system is not a substitute for seat belts. When triggered, airbags
provide only additional protection. All occupants (including the driver) must
wear seat belts properly during the trip. This will reduce the risk of severe
inju ries in the eve nt of an accident – regardless of whether an airbag is fitted
for the seat or not.
Note that airbags can be triggered only once. To achieve the best possible
protection, the seat belt must always be worn properly so that you will be
protected in accidents in which no airbag is deployed.
It is a lso imp or tan t f or t he r ear pas sen ger s t o we ar s eat be lts pro per ly, as t he y
could otherwise be thrown forward violently in a n accident. Rear passengers
who do not use seat belts endanger not only themselves but also the front
occupants ⇒ fig. 9.
Seat belts 23
Seat belt protection
Passengers not wearing seat belts risk severe injuries in the
event of an accident.
Fig. 10 A driver wearing
the seat belt properly is
secured by the belt in
sharp braking
Properly worn seat belts hold the veh icle occupants in the correct sitting positions and substantially reduce the kinetic energy in the event of an accident.
Seat belts also help to prevent uncontrolled movements that could lead to
severe injuries. In addition, properly worn seat belts reduce the danger of
being thrown from the vehicle.
Passengers wearing their seat belts correctly benefit greatly from the ability
of the belts to absorb kinetic e nergy. The front part of your vehicle and other
passive safety features (such as the airbag system) are also designed to
absorb the kinetic energy released in a collision. Taken together, all these
features reduce the releasing kinetic energy and consequently, the risk of
injury.
Our examples d escribe frontal collisions . Of course, properly wo rn seat belts
substantially reduce the risk of injury in all other types of accidents. This is
Safety First Operating Instructions Practical Tips Technical Speci fications
why it is so important to fasten seat belts before every trip, even when "just
driving around the corner".
Ensure that your passengers wear their seat belts as well. Accident statistics
have shown that wearing seat belts is an effective means of substantially
reducing the risk of injury and improving the chances of survival in a serious
accident. Furthermore, properly worn seat belts improve the protection
provided by airbags in the event of an accident. For this reason, wearing a
seat belt is required by law in most countries.
Although your vehicle is equipped with airbags, the seat belts must be
fastened and worn. The front airbags, for example, are only triggered in some
frontal accid ents. The front airb ags will not be triggered during minor frontal
collisions, mi nor side collisions, rear coll isions, overturns or acci dents in
which the airbag trigger threshold value in the control unit is not exceeded.
Therefore, you should always wear your seat belt and ensure that your
passengers have fastened their seat belts properly before you drive off!
Safety instructions on using seat belts
If seat belts are used correctly, they can reduce the risk of
injury in an accident.
– Always wear the seat belt as described in this section.
– Ensure that the seat belts can be fastened at all times and are not
damaged.
WARNING
• If the seat belts are worn incorrectly or not at all, the risk of severe inju-
ries increases. The optimal protection from seat belts can be achieved only
if you use them properly.
Seat belts24
WARNING (continued) WARNING (continued)
• Fasten your seat belt before every trip - even when driving in town. The
oth er pass eng ers mus t al so w ear the sea t be lts at al l ti mes , ot her wis e th ey
run the risk of being injured.
• The seat belt cannot offer its full protection if the seat belt is not posi-
tioned correctly.
• Do not attempt to repair a damaged seat belt yourself. The seat belts
must not be removed or modified in any way.
• The belts must be kept clean, otherwise the retractors may not work
properly ⇒ page 211.
• Never allow two passengers (even children) to share the same seat belt.
• Ke ep b oth fe et i n th e fo otw ell in f ron t of you r se at a s lo ng a s th e ve hic le
is in motion.
• Never unbuckle a seat belt while the vehicle is in motion. Risk of fatal
injury.
• The seat belt must never be twisted while it is being worn.
• The seat belt should never lie on hard or fragile objects (such as glasses
or pens, etc.) because this can cause injuries.
• Do not allow the seat belt to be damaged or jammed, or to rub on any
sharp edges.
• Never wear the seat belt under the arm or in any other incorrect posi-
tion.
• Loose, bulky clothing (such as an overcoat over a jacket) impairs the
proper fit and function of the belts, reducing their capacity to protect.
• Th e slot in the seat be lt buc kle mus t not b e blocke d with paper or oth er
objects, as this can prevent the latch plate from engaging securely.
• Never use seat belt clips, retaining rings or similar instruments to alter
the position of the belt webbing.
• Frayed or torn seat be lts or damage to the connections, belt retractors
or parts of the buckle could cause severe injuries in the event of an accident. Therefore, you must check the condition of all seat belts at regular
intervals.
• Seat belts which have been worn in an accident and stretched must be
replaced by a specialised workshop. Renewal may be necessary even if
there is no apparent damage. The belt anchorage should also be checked.
Seat belts
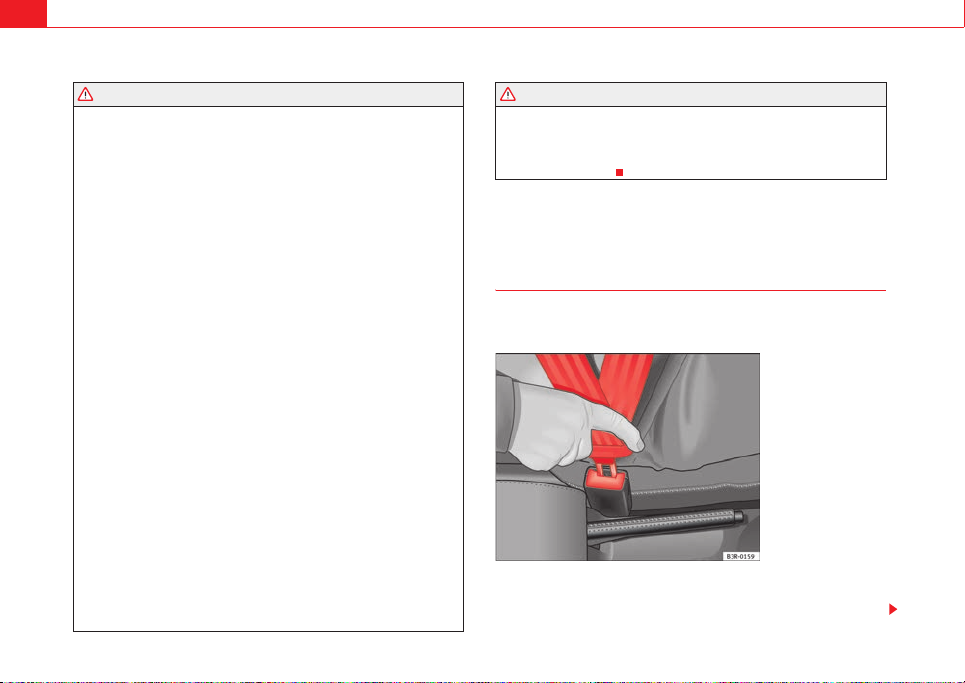
Seat belt adjustment
The seat belts for the front and rear occupants are locked into
position by a latch.
The seat belt cannot offer its full protection if the seat belt is not
positioned correctly.
Fig. 11 Belt buckle and
latch plate of seat belt
Seat belts 25
– Adjust the seat and head restraint correctly.
– To fasten the belt, take hold of the latch plate and pull it slowly
across your chest and lap.
Seat belt position
Seat belts offer their maximum protection only when they are
properly positioned.
– Insert the latch plate i nto the buckle for the appropriate seat and
push it down until it is securely locked with an audible click
⇒ page 24, fig. 11.
– Pull the belt to ensure that the latch plate is securely engaged in
the buckle.
The seat belts are equipped with an automatic retractor on the shoulder
strap. Full freedom of movement is permitted when the s houlder belt is pulled
slowly. However, during sudden braking, during travel in steep areas or
bends and during acceleration, the automatic retractor on the shoulder belt
is locked.
The automatic belt retractors on the front seats are fitted with seat belt
tensioners ⇒ page 28.
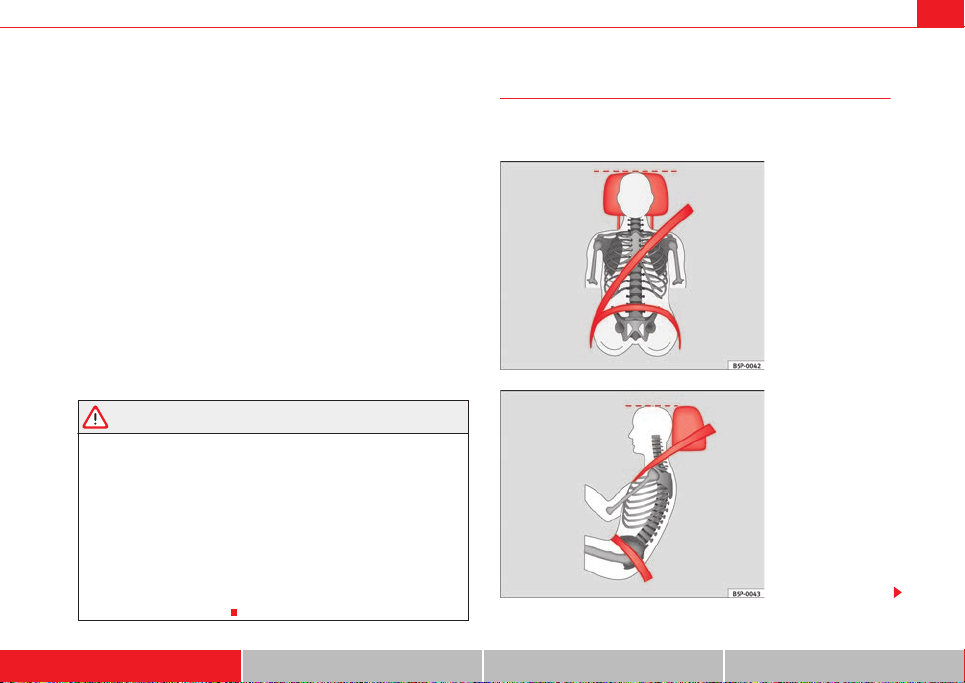
Fig. 12 Correct seat belt
and head restraint positions, viewed from front
WARNING
• An incorrectly worn seat belt can cause severe injuries in the event of
an accident.
• The seat belts offer best protection only when the backrests are in an
upright position and the seat belts have been fastened properly.
• Never put the latch plate in the buckle of another seat. If you do this, the
seat belt will not protect you properly and the risk of injury is increased.
• I f an occu pan t is inc orr ect ly b elt ed i n, t he b elt can not pro tect him or h er
properly. An incorrectly positioned seat belt can cause extremely severe
injuries.
• Always engage the retractor lock when you are securing a child seat in
group 0, 0+ or 1 ⇒ page 46.
Safety First Operating Instructions Practical Tips Technical Speci fications
Fig. 13 Correct seat belt
and head restraint positions, viewed from side
Seat belts26
The following features are available to adjust the seat belt in the shoulder
region:
• belt height adjustment for the front seats.
• front seat height adjustment*.
WARNING
• An incorrectly worn seat belt can caus e severe injuries in the event of
an accident.
• The shoulder part of the seat belt must lie on the centre of the shoulder,
never across the neck. The seat belt must lie flat and snugly on the torso
⇒ page 25, fig. 12.
• Th e lap p art of the se at bel t must lie acr oss the pelvi s, nev er acro ss the
stomach. The seat belt must lie flat and snugly on the pelvis ⇒ page 25,
fig. 13. Pull the belt tight if necessary to take up any slack.
• Read and observe the warnings ⇒ page 23.
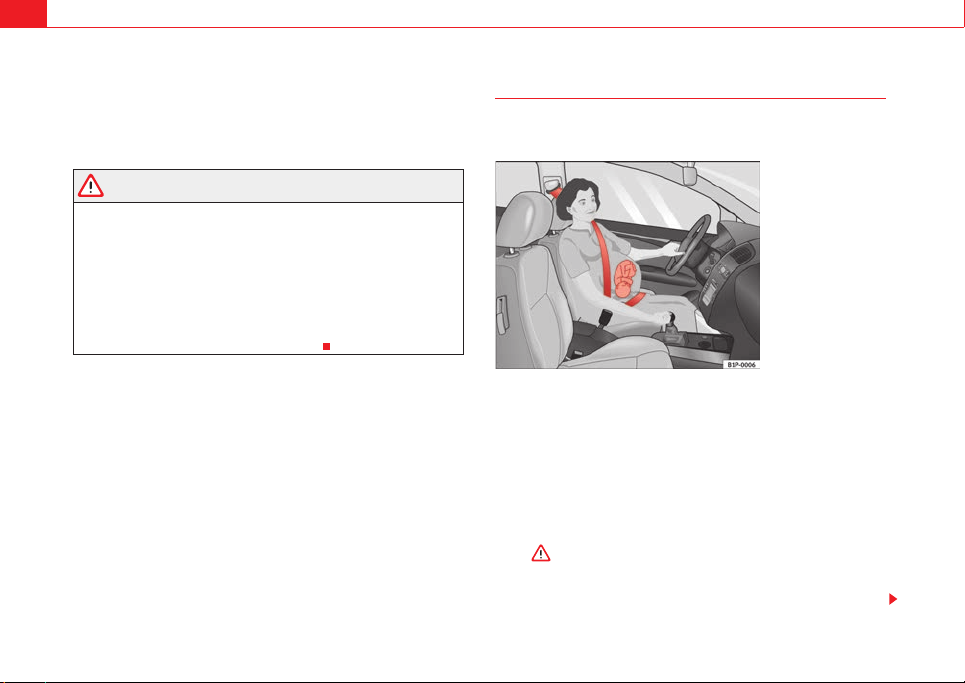
Pregnant women must also fasten their seat belts properly
The best protection for the unborn child is for the mother to
wear the seat belt properly at all times during the pregnancy.
Fig. 14 Positioning seat
belts during pregnancy
The seat belt provides maximum protection only when the seat belt
is properly positioned ⇒ page 25.
– Adjust the front seat and head restraint correctly ⇒ page 10.
– Holding the latch plate, pull t he belt evenly across your chest and
as low as possible over the pelvis ⇒ fig. 14.
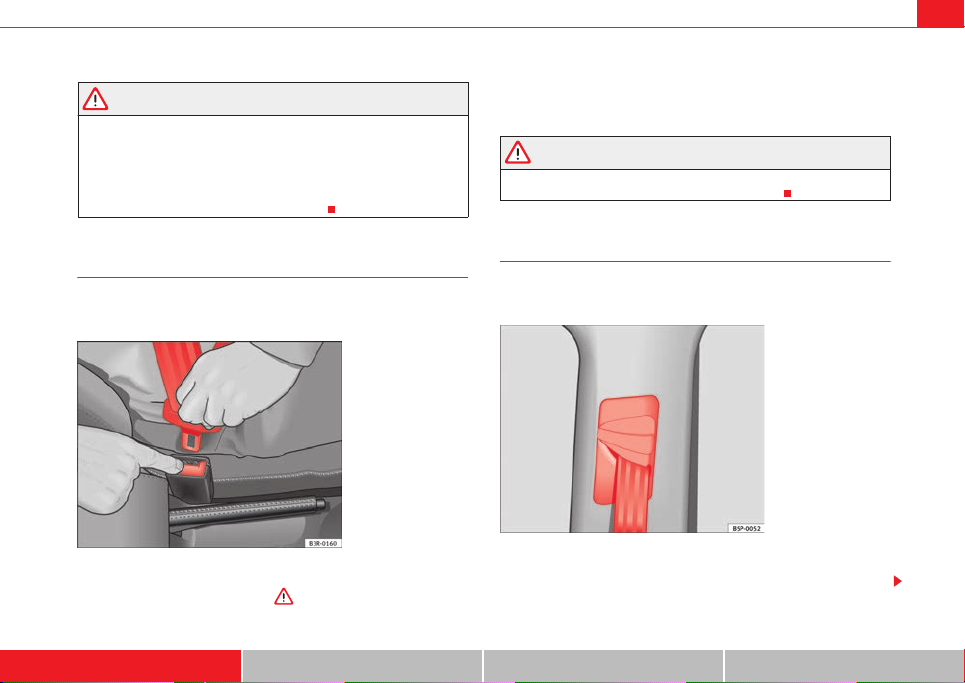
– Insert the latch plate into the buckle for the corresponding seat
and push it down until it is securely locked with an audible click
⇒ .
– Pull the belt to ensure that the latch plate is securely engaged in
the buckle.
Seat belts 27
WARNING
• An incorrectly worn seat belt can cause severe injuries in the event of
an accident.
• For pregnant women, the lap part of the seat belt must lie as low as
possible over the pelvis, never across the stomach, and always lie flat so
that no pressure is exerted on the abdomen.
– G uide the belt bac k by hand so tha t it rolls up ea sily and the trim
is not damaged
WARNING
Never unbuckle a seat belt while the vehicle is in motion. If you do, you
increase the risk of sustaining severe or fatal injuries.
• Read and observe the warnings ⇒ page 23.
Seat belt release
The seat belt must not be unfastened until the vehicle has
come to a standstill.
Fig. 15 Removing latch
plate from buckle
– Press the red button on the belt buckle ⇒ fig. 15. The latch plate
is released and springs out ⇒ .
Safety First Operating Instructions Practical Tips Technical Speci fications
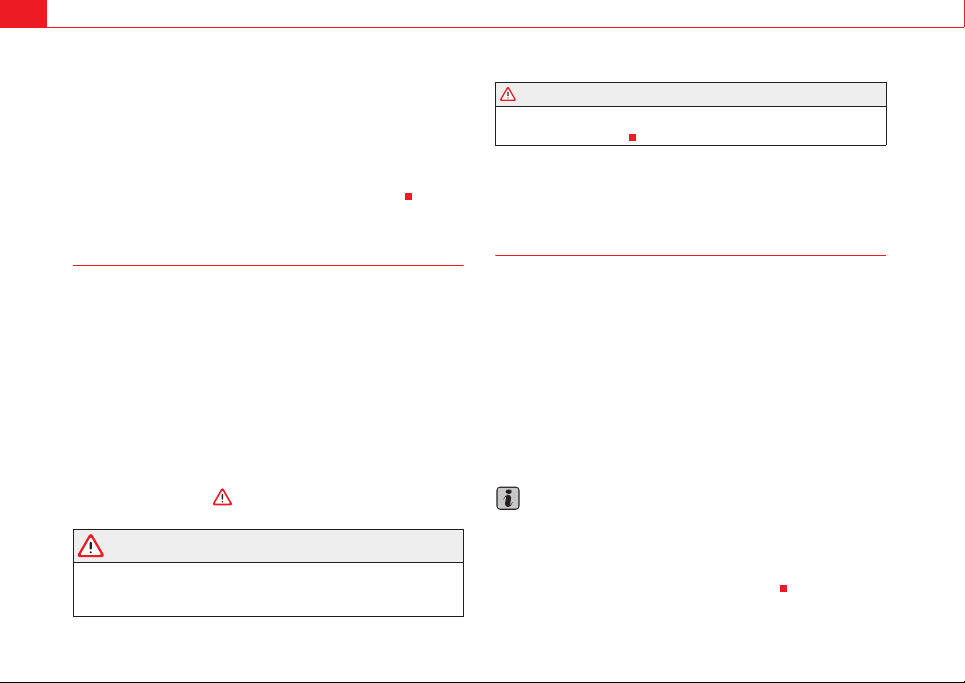
Adjusting the seat belt height
Seat belt height adjusters can be used to adjust the position
of the seat belt at the shoulder.
Fig. 16 Loca tion of the
belt height adjuster
The seat belt adjuster for the front seats can be used to adjust the
proper belt position at the shoulder.
Seat belts28
– Press the upper part of the shoulder belt guide and hold it in this
position ⇒ page 27, fig. 16.
– Move the shoulder belt guide up or down until you have adjusted
the seat belt ⇒ page 25.
– After adjusting, pull the shoulder belt sharply to check that the
catch on the shoulder belt guide is engaged securely.
Incorrectly fastened seat belts
Incorrectly worn seat belts can cause severe or even mortal
injuries.
Seat belts can provide optimal protection only if the belt web is
properly worn. The seat belts must be fastened exactly in the order
described in this chapter. An incorrect sitting position impairs
substantially the protection a seat belt offers and can lead to severe
or fatal injuries. The risk of severe or fatal injuries is especially
increased when a deploying airbag strikes an occupant who has
assumed an incorrect sitting position. As the driver, you are responsible for all vehicle occupants, especially children. Therefore:
– Never allow anyone to wear the seat belt incorrectly while the
vehicle is moving ⇒ .
WARNING
• An incorrectly worn seat belt increases the risk of severe injuries.
• Before every trip, instruct your passengers to adjust their seat belts
properly and to wear them for the whole journey.
WARNING (continued)
• Read and always obs erve information and warnings concerning the use
of seat belts ⇒ page 23.
Seat belt tensioners
Function of the seat belt tensioner
During a frontal collision, the seat belts on the front seats are
retracted automatically.
The seat belts for the front occupants are equipped with belt tensioners.
Sensors will only trigger the belt tensioners during severe head-on, lateral
and rear collisions, and only if the seat belt is ac tually being worn. This
retracts and tightens the seat belts, red ucing the forward motion of the occupants.
The seat belt tensioner can be triggered only once.
The seat belt tensioners will not be triggered in the event of a light frontal,
side or rear collision, if the vehicle overturns or in situat ions where no large
forces act on the front, side or rear of the vehicle.
Note
• If the seat belt tensioners are triggered, a fine dust is produced. This is
normal and it is not an indication of fi re in the vehicle.
• The relevant safety requirements must be observed when the vehicle or
components of the system are scrapped. Specialised workshops are familiar
with these regulations, which are also available to you.
 Loading...
Loading...