Seagate ZP500GM300013, ZP500GM30023, ZP1000GM300013, ZP1000GM30023, ZP2000GM300013 Users Guide
...Page 1

Seagate® FireCuda® 530 SSD
200432500, Rev B
May 2021
Product Manual
Form Factor User Capacity Standard Models Heatsink Models
M.2 2280-S2
M.2 2280-D2
500 GB ZP500GM300013 ZP500GM30023
1000 GB ZP1000GM300013 ZP1000GM30023
2000 GB ZP2000GM300013 ZP2000GM30023
4000 GB ZP4000GM300013 ZP4000GM30023
Page 2

Revision History
Version and Date Description of Changes
Rev B, May 2021 Updated the document throughout to add models with heatsinks, different specifications, drawings, and
instructions.
Rev A, December 2020 First document release.
© 2021, Seagate Technology LLC All rights reserved. Publication number: 200432500, Rev B, May 202 1
Seagate Technology reserves the right to make changes to the product(s) or information disclosed herein at any time without notice.
Seagate, Seagate Technology and the Spiral logo are registered trademarks of Seagate Technology LLC in the United States and/or other countries. Nytro and SeaTools are either trademarks or registered trademarks of
Seagate Technology LLC or one of its affiliated companies in the United States and/or other countries. All other trademarks or registered trademarks are the propert y of their respective owners.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without written permission of Seagate Technology LLC. Call 877-PUB-TEK1(877-782-8351) to request permission.
The NVMe word mark and/or NVMExpress design mark are trademarks of NVMExpress, Inc. The PCIe word mark and/or PCIExpress desi gn mark are registered trademarks and/or service marks of PCI-SIG.
When referring to drive capacity, one gigabyte, or GB, equals one billion bytes and one terabyte, or TB, equals one trillion bytes. Your computer’s operating system may use a different standard of measurement and report
a lower capacity. In addition, some of the listed capacity is used for formatt ing and other func tions, and thus wil l not be available for data storage. Actual quantities will vary based on various factors, including file size, file
format, features and application software. Actual data rates may vary depending on operating environment and other factors. The export or re-export of hardware or software containing encryption may be regulated by
the U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (for more information, visit www.bis.doc.gov), and controlled for import and use outside of the U.S. Seagate reserves the right to change, without notice,
product offerings or specifications.
Page 3

Contents
Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.1 References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2. Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1 Models and Capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2 Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.3 Power Consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.4 Environmental Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.5 Reliability/Endurance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3. Mechanical Dimensions and Drawings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4. Pin and Signal Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5. NVMe Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6. SMART Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
6.1 SMART Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7. Feature Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
7.1 Flash Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
7.1.1 Error Correction Code (ECC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
7.1.2 Wear Leveling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
7.1.3 Bad Block Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
7.1.4 TRIM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
7.1.5 SMART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
7.1.6 Over Provisioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
7.1.7 Firmware Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
7.1.8 Thermal Throttling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
7.2 Advanced Device Security Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
7.2.1 NVMe format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
7.2.2 Sanitize Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
7.3 SSD Lifetime Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
7.3.1 Total Bytes Written (TBW) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
7.3.2 Media Wear Indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
7.3.3 Read Only Mode (End of Life) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
7.4 An Adaptive Approach to Performance Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
7.4.1 Throughput . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
7.4.2 Predict & Fetch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
7.4.3 SLC Caching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
8. Safety, Standards, and Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
8.1 Regulatory Model Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
9. FireCuda 530 Installation Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 3
Page 4

Contents
9.1 FireCuda 530 SSD Handling Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
9.2 FireCuda 530 SSD Installation Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
9.3 Heatsink Disclosures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 4
Page 5

Support
For Internal SSD Support, visit: https://www.seagate.com/support/products/
For Firmware Download and Tools Download for Secure Erase, visit: https://www.seagate.com/support/downloads/
For information regarding online support and services, visit: http://www.seagate.com/contacts/
For information regarding Warranty Support, visit: http://www.seagate.com/support/warranty-and-replacements/
For information regarding data recovery services, visit:
http://www.seagate.com/services-software/seagate-recovery-services/recover/
For Seagate OEM and Distribution partner and Seagate reseller portal, visit: http://www.seagate.com/partners
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 5
Page 6
www.seagate.com
1. Introduction
The Seagate® FireCuda® 530 SSD is a versatile NVMe SSD with PCIe Gen4 x4 interface. It is up to 12x faster than SATA
SSDs and delivers Ultra-fast performance and enhanced endurance for long term use.
Table 1 The FireCuda 530 SSD Features
Feature Description
Capacity
(User)
Certifications,
Eco-Compliance
Dimensions
Form Factor
Weight
Endurance
Interface
Compliance
500 GB, 1000 GB, 2000 GB, 4000 GB
CE, UL, FCC, BSMI, KCC, Microsoft WHQL, VCCI, CB
RoHS
500 GB, 1000 GB
Length, Max 80.15 mm
Width, Max 22.15 mm
Height, Max 2.23 mm
2000 GB, 4000 GB
Length, Max 80.15 mm
Width, Max 22.15 mm
Height, Max 3.58 mm
With heatsink
Length, Max 80.15 mm
Width, Max 24.20 mm
Height, Max 10.74 mm
M2 2280-S2-M
M2 2280-D2-M
500 GB: 7.7 g
1000 GB: 8.1 g
2000 GB: 10.0 g
4000 GB: 10.6 g
With heatsink
47 g
Total Bytes Written
500 GB: 640 TB
1000 GB: 1275 TB
2000 GB: 2550 TB
4000 GB: 5100 TB
NVMe 1.4
PCI Express Base 4.0, PCIe Gen 4 x 4 lane, and backward compatible to PCIe Gen3, Gen 2, and Gen 1
See Section 2.5, Reliability/Endurance.
NAND
Operating
Systems
Performance
Random
TLC
Windows 10 (64 bit)
Ubuntu 16.04, 18.04
CentOS 6, 7
Read: Up to 1,000,000 IOPS
Write: Up to 1,000,000 IOPS
Actual performance might vary depending on
use conditions and environment.
See Section 2.2, Performance.
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 6
Page 7
www.seagate.com
Table 1 The FireCuda 530 SSD Features (continued)
Performance
Sequential
Power
Consumption
Power
Management
Reliability
Shock and
Vibration
Temperature
Range
Volta ge
Warran ty
Feature Description
Read: Up to 7300MB/s
Write: Up to 6900MB/s
Actual performance might vary depending on
the capacity, use conditions and environment.
See Section 2.2, Performance.
Active Power, Average: <6.0 W
Idle Power PS3, Average: <25 mW
Low Power L1.2 mode: < 2 mW
Supports ActiveStatePower Management (ASPM)
Supports Autonomous Power StateTransition (APST)
Supports L1.2
End-to-end data path protection
MTBF: 1.9 million hours
UBER: 1 error in 10
16
bits read
See Section 2.3, Power Consumption.
Shock
Non-Operating: 1,500 G, at 0.5 ms
Vibration
Non-Operating: 1.52 G
, (20 to 80 Hz,
RMS
Frequency)
Operating: 0°C to 70°C
Non-operating: -40°C to 85°C
Min = 3.14V±5%
Max = 3.47V±5%
Five years, or when the device reaches Host TBW, whichever happens first. Endurance rating valid for SSD
Life Remaining > 1%.
See Section 2.4, Environmental
Conditions.
1.1 References
In case of conflict between this document and the following reference documents, this document takes precedence.
PCIe Specifications
— PCIe - PCI Express Electromechanical specification, revision 4.0
— NVMe - Non Volatile Memory Express specification 1.4
— PCIe CEM - PCI Express Card Electromechanical specification, revision 1.1
— PCI Express M.2 Specification, revision 1.1
Seagate Downloads are available on the Seagate Support page here:
https://www.seagate.com/support/
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 7
Page 8
www.seagate.com
2. Specifications
2.1 Models and Capacity
Table 2 Models and Capacity
User Capacity
500 GB ZP500GM300013 ZP500GM30023
1000 GB ZP1000GM300013 ZP1000GM30023
2000 GB ZP2000GM300013 ZP2000GM30023
4000 GB ZP4000GM300013 ZP4000GM30023
NOTE About capacity:
2.2 Performance
Table 3 Random and Sequential Read and Write Performance
Capacity
Standard
Models
Sector Size: 512 Bytes (default) and 4K
User-addressable LBA count = (97696368) + (1953504 x (Desired Capacity
Heatsink
Models
in Gb-50.0)) From International Disk Drive Equipment and Materials
Association (IDEMA) (LBA1-03_standard.doc)
CrystalDiskMark IOMeter
Read
(MB/s)
Write
(MB/s)
Read
(IOPS)
Write
(IOPS)
500 GB 7000 3000 400,000 700,000
1000 GB 7300 6000 800,000 1,000,000
2000 GB 7300 6900 1,000,000 1,000,000
4000 GB 7300 6900 1,000,000 1,000,000
NOTE About performance:
Fresh out of box (FOB) performance obtained on newly formatted drive.
Performance may vary based on the SSD’s firmware version, system
hardware, and configuration.
Performance is based on AMD Gen4 X570 + 8 Core CPU + 16 GB of DDR4
(3200mHz).
CrystalDiskMark 7.0.0, 1GB range, QD=16, Thread=1. IOMeter, 1GB range,
QD=32, 16 worker, 4k aligned.
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 8
Page 9
www.seagate.com
Sequential Read/Write is measured while testing 1000 MB five times by
CrystalDiskMark.
2.3 Power Consumption
Table 4 Power Consumption
Power Consumption
Capacity
Max Avg
Read
(W)
Max Avg
Write
(W)
Idle PS3
(mW)
L1.2
(mW)
500 GB 6.0 5.9 4.5 4.5
1000 GB 6.1 6.1 6.1 6.1
2000 GB 7.6 7.6 7.9 7.8
4000 GB 7.9 7.9 8.2 7.5
NOTE About power consumption:
The average value of power consumption is based on 100% conversion
efficiency.
Based on SU6SExxx-series under ambient temperature.
Use CrystalDiskMark 7.0.0, 1GB range, QD=8, Thread=1. Measuring power
consumption during sequential Read and sequential Write.
The measured power voltage is 3.3 V.
Measured under ambient temperature.
Power Consumption can differ with flash configuration and platform.
Power consumption during read and write operation is measured on
Gen4 X570 + 6 Core CPU.
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 9
Page 10
www.seagate.com
2.4 Environmental Conditions
Table 5 Temperature, Humidity, Shock
Specification Value
Temperature
Operating (case temperature at specific airflow)
Non-operating
Humidity
Operating
Non-operating (storage)
Shock
Non-operating
Vibration
Non-operating
NOTE Temperature is measured without condensation. Operating mode
temperature is measured by temperature sensor, SMART Attribute.
Airflow is suggested. Airflow allows the device to be operated at the
appropriate temperature for each component during heavy workloads
environments.
0°C to 70°C
-40°C to 85°C
1,500 G, duration 0.5 ms
1.52 G
(20Hz to 80Hz, Frequency)
RMS,
90%
93%
Shock and vibration results assume that the SSD is mounted securely with
the input vibration applied to the SSD mounting. These specifications do not
cover connection issues that may result from testing at this level. The
measured specification is in root mean square (RMS) form.
Non-operating Shock. The limits of non-operating shock applies to all
conditions of handling and transportation. This includes both isolated
SSD and integrated SSDs. Shock may be applied in the X, Y, or Z-axis.
Non-Operating Vibration. The limits of non-operating vibration shall
apply to all conditions of handling and transportation. This includes both
isolated SSD and integrated SSDs. Vibration may be applied in the X, Y, or
Z-axis.
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 10
Page 11

www.seagate.com
2.5 Reliability/Endurance
Table 6 Reliability/Endurance
Specification Value
Mean time between failures (MTBF) 1.9 million hours
Bit Error Rate
Endurance Total Bytes Written
NOTE About endurance:
The SSD achieves the specified MTBF in an operational environment that
complies with the operational temperature range specified in this manual.
Operating temperatures are measured by temperature sensor.
Endurance rating valid for SSD Life Remaining > 1%.
1 error in 10
500 GB: 640 TB
1000 GB: 1275 TB
2000 GB: 2550 TB
4000 GB: 5100 TB
16
bits read
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 11
Page 12
www.seagate.com
3. Mechanical Dimensions and Drawings
This section includes, weight, dimensions, and mechanical drawings.
Table 7 Weight and Dimensions
Capacity Weight (g)
500 GB 7.7
1000 GB 8.1
2000 GB 10.0
4000 GB 10.6
With heatsink 47g 80.15 mm 24.20 mm 10.74 mm
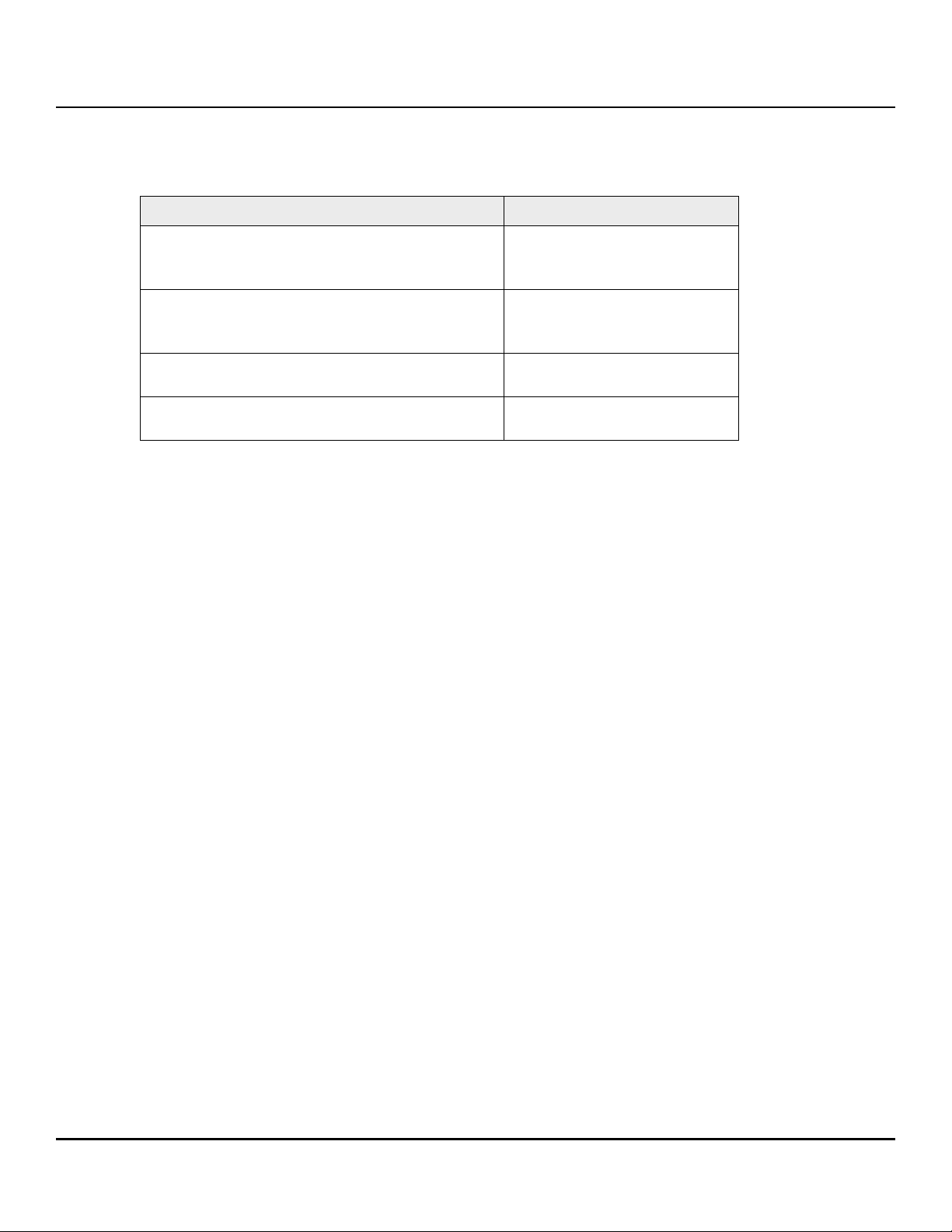
Figure 1 FireCuda 530 SSD M2 2280-D2-M Top View
Length
(Max)
80.15 mm 22.15 mm
Width
(Max)
Height
2.23 mm
3.58 mm
(Max)
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 12
Page 13

www.seagate.com
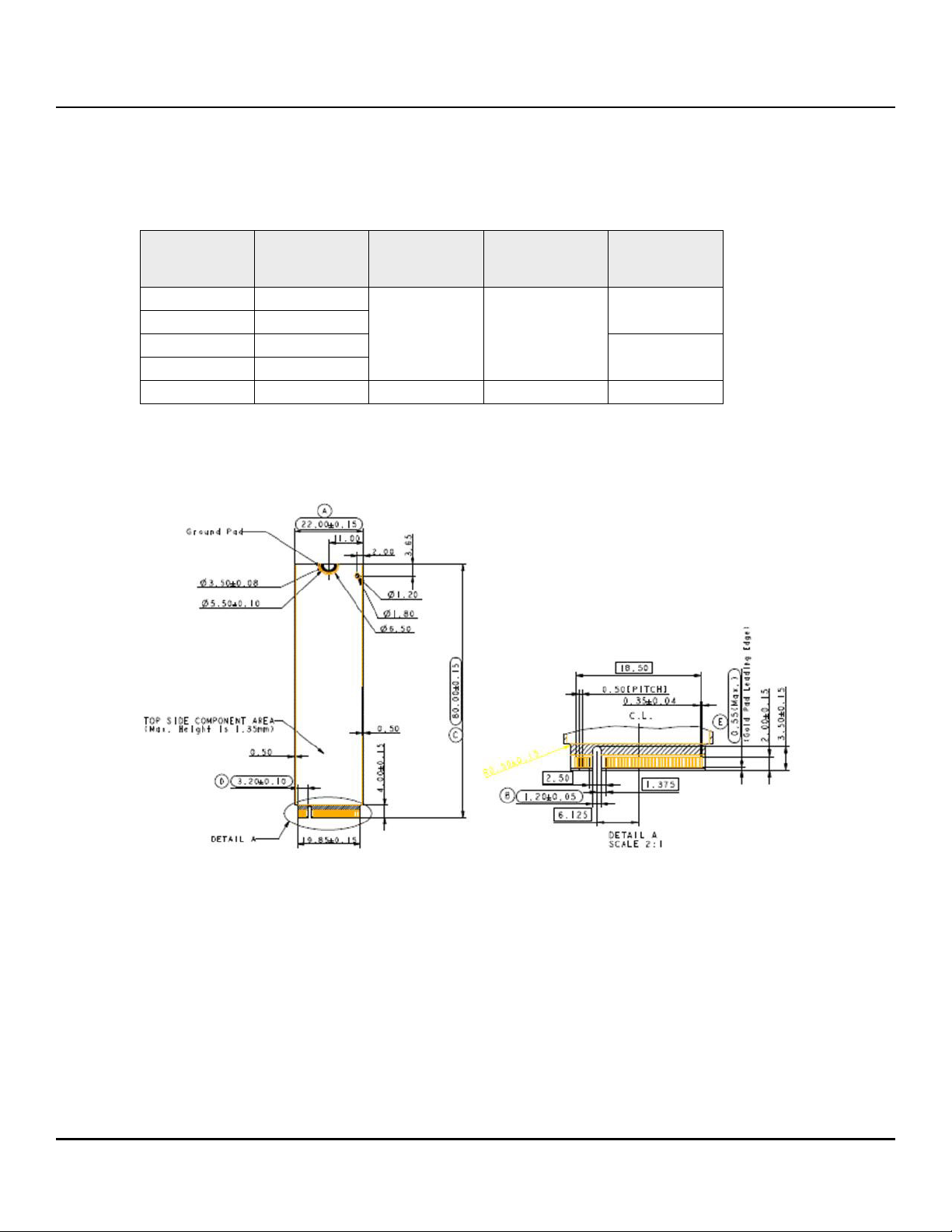
Figure 2 FireCuda 530 SSD M2 2280-D2-M Side View
Figure 3 FireCuda 530 SSD M2 2280-D2-M Bottom View
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 13
Page 14
www.seagate.com
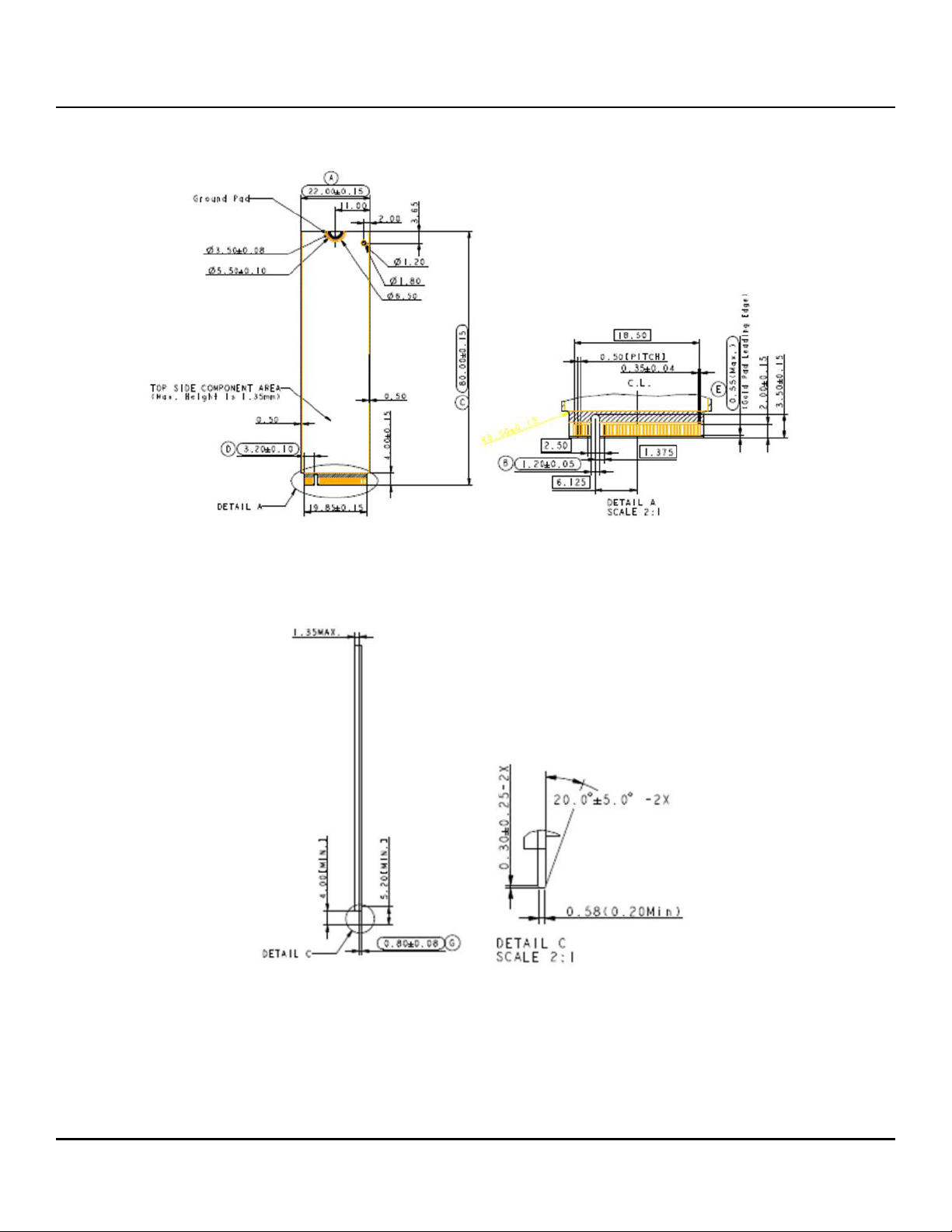
Figure 4 FireCuda 530 SSD M2 2280-S2-M Top View
Figure 5 FireCuda 530 SSD M2 2280-S2-M Side View
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 14
Page 15
www.seagate.com
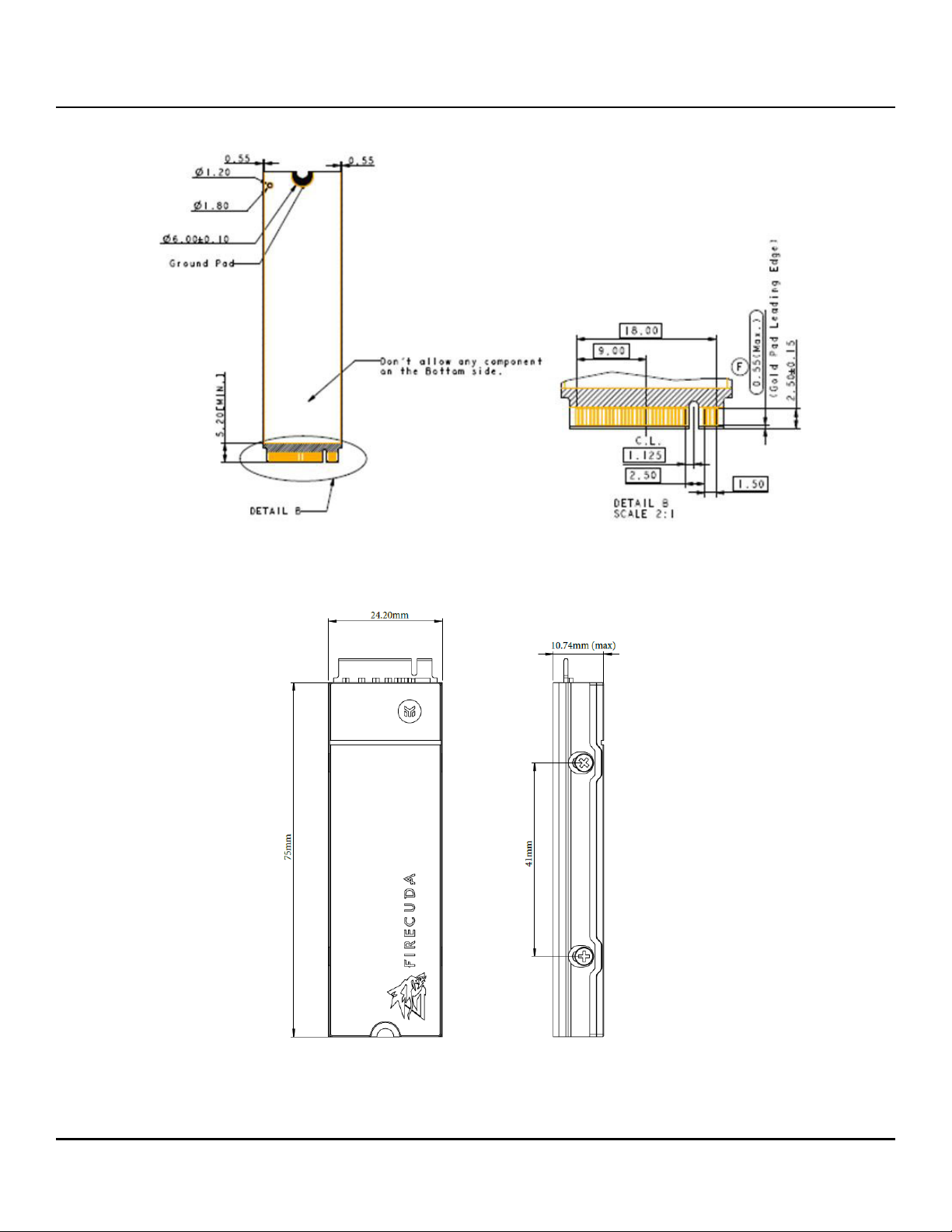
Figure 6 FireCuda 530 SSD M2 2280-S2-M Bottom View
Table 8 FireCuda 530 SSD with Heatsink
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 15
Page 16
www.seagate.com
4. Pin and Signal Descriptions
Table 9 Pin Descriptions
Pin No. PCIe Pin Description
1GND
23.3V
3GND
43.3V
5PETn3
6N/C
7PETp3
8N/C
9GND
10 LED1#
CONFIG_3 = GND
3.3V source
Ground
3.3V source
PCIe TX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
No connect
PCIe TX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
No connect
Ground
Open drain, active low signal. These signals are used to allow the add- in card to provide status
indicators via LED devices that will be provided by the system.
11 PERn3
12 3.3V
13 PERp3
14 3.3V
15 GND
16 3.3V
17 PETn2
18 3.3V
19 PETp2
20 N/C
21 GND
22 N/C
23 PERn2
24 N/C
25 PERp2
26 N/C
27 GND
28 N/C
29 PETn1
30 N/C
PCIe RX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
3.3V source
PCIe RX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
3.3V source
Ground
3.3V source
PCIe TX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
3.3V source
PCIe TX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
No connect
Ground
No connect
PCIe RX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
No connect
PCIe RX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
No connect
Ground
No connect
PCIe TX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
No connect
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 16
Page 17

www.seagate.com
Table 9 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Pin No. PCIe Pin Description
31 PETp1
32 N/C
33 GND
34 N/C
35 PERn1
36 N/C
37 PERp1
38 N/C
39 GND
40 SMB_CLK (I/O)(0/1.8V)
41 PETn0
42 SMB_DATA (I/O)(0/1.8V)
43 PETp0
44 ALERT#(O) (0/1.8V)
PCIe TX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
No connect
Ground
No connect
PCIe RX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
No connect
PCIe RX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
No connect
Ground
SMBus Clock; Open Drain with pull-up on platform
PCIe TX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
SMBus Data; Open Drain with pull-up on platform.
PCIe TX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
Alert notification to master; Open Drain with pull-up on platform;
Active low.
45 GND
46 N/C
47 PERn0
48 N/C
49 PERp0
50 PERST#(I)(0/3.3V)
51 GND
52 CLKREQ#(I/O)(0/3.3V)
53 REFCLKn
54 PEWAKE#(I/O)(0/3.3V )
55 REFCLKp
56 Reserved for MFG DATA
Ground
No connect
PCIe RX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
No connect
PCIe RX Differential signal defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec
PE-Reset is a functional reset to the card as defined by the PCIe Mini
CEM specification.
Ground
Clock Request is a reference clock request signal as defined by the
PCIe Mini CEM specification; Also used by L1 PM Sub-states.
PCIe Reference Clock signals (100 MHz)
defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec.
PCIe PME Wake.
Open Drain with pull up on platform; Active Low.
PCIe Reference Clock signals (100 MHz)
defined by the PCI Express M.2 spec.
Manufacturing Data line. Used for SSD manufacturing only.
Not used in normal operation.
Pins should be left N/C in platform Socket.
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 17
Page 18

www.seagate.com
Table 9 Pin Descriptions (continued)
Pin No. PCIe Pin Description
57 GND
Ground
58 Reserved for MFG
CLOCK
59 Module Key M
60 Module Key M
61 Module Key M
62 Module Key M
63 Module Key M
64 Module Key M
65 Module Key M
66 Module Key M
67 N/C
68
69 N/C
70 3.3V
71 GND
72 3.3V
73 GND
74 3.3V
75 GND
SUSCLK(32KHz)
(I)(0/3.3V)
Manufacturing Clock line. Used for SSD manufacturing only.
Not used in normal operation.
Pins should be left N/C in platform Socket.
Module Key
No connect
32.768 kHz clock supply input that is provided by the platform chipset to reduce power and cost
for the module.
PEDET (NC-PCIe)
3.3V source
Ground
3.3V source
Ground
3.3V source
Ground
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 18
Page 19

www.seagate.com
5. NVMe Commands
Table 10 Admin Commands
Identifier O/M Command Description Supported
00h M Delete I/O Submission Queue Supported
01h M Create I/O Submission Queue Supported
02h M Get Log Page Supported
04h M Delete I/O Completion Queue Supported
05h M Create I/O Completion Queue Supported
06h M Identify Supported
08h M Abort Supported
09h M Set Feature Supported
0Ah M Get Feature Supported
0Ch M Asynchronous Event Request Supported
10h O Firmware Commit Supported
11h O Firmware Image Download Supported
14h O Device Self-test Supported
80h O Format NVM Supported
81h O Security Send Supported
82h O Security Receive Supported
84h O Sanitize Supported
Table 11 I/O Commands
Identifier O/M Command Description Supported
00h O Flush Supported
01h O Write Supported
02h O Read Supported
04h O Write Uncorrectable Not Supported
05h O Compare Supported
08h O Write Zeroes Supported
09h O Dataset Management Supported
Table 12 Set Feature Commands
Identifier O/M Command Description Supported
00h Reserved
01h M Arbitration Supported
02h M Power Management Supported
03h O LBA Range Type Not Supported
04h M Temperature Threshold Supported
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 19
Page 20

www.seagate.com
Table 12 Set Feature Commands
05h M Error Recovery Supported
06h O Volatile Write Cache Supported
07h M Number Of Queues Supported
08h M Interrupt Coalescing Supported
09h M Interrupt Vector Configuration Supported
0Ah M Write Atomicity Normal Supported
0Bh M Asynchronous Event Configuration Supported
0Ch O Autonomous Power State Transition Supported
0Dh O Host Memory Buffer Not Supported
0Eh O Timestamp Supported
10h O Host Controlled Thermal Management Supported
11h O Non-Operational Power State Config Supported
0Eh - 7Dh Reserved
80h O Software Progress Marker Supported
Table 13 Get Log Page Commands
Identifier O/M Command Description Supported
00h Reserved
01h M Error Information Supported
02h M SMART / Health Information Supported
03h M Firmware Slot Information Supported
04h O Changed Namespace List Supported
06h O Device Self-test Supported
09h - 7Fh Reserved
81h O Sanitize Status Supported
82h - FFh Reserved
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 20
Page 21

www.seagate.com
6. SMART Support
The FireCuda 530 SSD supports the SMART command set.
6.1 SMART Attributes
The following table lists SMART Attributes and Descriptions.
Table 14 SMART Attributes (Log Identifier 02h)
Bytes Index Bytes Description
[0] 1
[2:1] 2
[3] 1
[4] 1
[5] 1
[31:6] 26
[47:32] 16
[63:48] 16
[79:64] 16
[95:80] 16
[111:96] 16
[127:112] 16
[143:128] 16
[159:144] 16
[175:160] 16
[191:176] 16
[195:192] 4
[199:196] 4
[201:200] 2
[203:202] 2 Temperature Sensor 2 (N/A)
[205:204] 2 Temperature Sensor 3 (N/A)
[207:206] 2 Temperature Sensor 4 (N/A)
[209:208] 2 Temperature Sensor 5 (N/A)
[211:210] 2 Temperature Sensor 6 (N/A)
[213:212] 2 Temperature Sensor 7 (N/A)
[215:214] 2 Temperature Sensor 8 (N/A)
[511:216] 296 Reserved
Critical Warning
Composite Temperature
Available Spare
Available Spare Threshold
Percentage Used
Reserved
Data Units Read
Data Units Written
Host Read Commands
Host Write Commands
Controller Busy Time
Power Cycles
Power On Hours
Unsafe Shutdowns
Media and Data Integrity Errors
Number of Error Information Log Entries
Warning Composite Temperature Time
Critical Composite Temperature Time
Temperature Sensor 1 (Current Temperature)
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 21
Page 22

www.seagate.com
NOTES For (Log Identifier 02h:
"Critical Warning [Byte 0]"
This field indicates critical warnings for the state of the controller.
• Bit#0: Available spare is below threshold
• Bit#1: Temperature exceeded threshold or below an under temperature threshold
• Bit#2: Reliability is degraded due to excessive media or internal errors
• Bit#3: Media is placed in read only mode
• BIt#4: Volatile memory backup device has failed.
• Bit#5 - Bit#7: Reserved
"Available Spare [Byte 3]" Value (percentage) = 100* [(total reserved VB -
consumed VB caused by early, later bad)/ total reserved VB]
"Percentage Used [Byte 5]"
Value (percentage) = 100* (total VB erase count/ PE cycle for total VB)
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 22
Page 23

www.seagate.com
Table 15 SMART Attributes (Log Identifier C0h)
Bytes Index Bytes Description
[7:0] 8 Device Capacity
[15:8] 8 User Capacity
[23:16] 8 NAND Read
[31:24] 8 NAND Write
[39:32] 8 NAND Erase Sector
[47:40] 8 SSD Life Remaining Percent D3
[55:48] 8 SSD Life Used Percent D3
[56] 1 WP Water Mark
[58:57] 2 Highest temperature
[62:59] 4 Flash UNC Error Count
[67:63] 5 Data E3D Error
[70:67] 4 PHY Error Count
[74:71] 4 Total Bad Block Count
[78:75] 4 Total Early Bad Block Count
[82:79] 4 Total Later Bad Block Count
[86:83] 4 Read Fail Count
[90:87] 4 Program Fail Count
[94:91] 4 Erase Failure Count
[102:95] 8 System Table Copy Count
[110:103] 8 Read Move Table Count
[114:111] 4 Data read retry count
[118:115] 4 RAID ECC retry count
[122:119] 4 RAID ECC failed count
[130:123] 8 Total Erase Count
[134:131] 4 Max Erase Count
[138:135] 4 Average Erase Count
[142:139] 4 Min Erase Count
[150:143] 8 Background read count
[154:151] 4 Host Write Uncorrectable Sector Count
[158:155] 4 PS3 Enter Success
[162:159] 4 PS4 Enter Success
[166:163] 4 Wear Leveling Count
[167] 1 Chip internal temperature
[169:168] 2 Thermal throttling
[171:170] 2 Thermal throttling time
[179:172] 8 FW Code Update Count
[511:181] 331 RSV
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 23
Page 24

www.seagate.com
NOTES For Log Identifier C0h:
"SSD Life Remaining Percent D3 [Byte 47:40]"
• Value (percentage) = 100 *[1 - (Average of the Flash's block erase count / NAND EOL
erase count)]
"SSD Life Used Percent [Byte 55:48]"
• Value (percentage) = 100 *(Average of the Flash's block erase count / NAND EOL erase
count)
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 24
Page 25

www.seagate.com
7. Feature Details
7.1 Flash Management
7.1.1 Error Correction Code (ECC)
Flash memory cells will deteriorate with use, which might generate random bit errors in the stored data. Thus,
FireCuda 530 SSD applies the fourth generation LDPC(Low Density Parity Check) of ECC algorithm, which can detect
and correct errors that occur during read process, ensure data has been read correctly, as well as protect data from
corruption.
7.1.2 Wear Leveling
NAND flash devices can only undergo a limited number of program/erase cycles, and in most cases, the flash media
are not used evenly. If some areas get updated more frequently than others, the lifetime of the device would be
reduced significantly. Thus, Wear Leveling is applied to extend the lifespan of NAND Flash by evenly distributing write
and erase cycles across the media.
Seagate provides advanced Wear Leveling algorithm, which can efficiently spread out the flash usage through the
whole flash media area. Moreover, by implementing both dynamic and static Wear Leveling algorithms, the life
expectancy of the NAND flash is greatly improved.
7.1.3 Bad Block Management
Bad blocks are blocks that do not function properly or contain more invalid bits causing stored data to become
unstable, and their reliability is not guaranteed. Blocks that are identified and marked as bad by the manufacturer are
referred to as “Early Bad Blocks”. Bad blocks that are developed during the lifespan of the flash are named “Later Bad
Blocks”. Seagate implements an efficient bad block management algorithm to detect the factory- produced bad
blocks and manages bad blocks that appear with use. This practice prevents data being stored into bad blocks and
further improves the data reliability.
7.1.4 TRIM
TRIM is a feature which helps improve the read/write performance and speed of solid-state drives (SSD). Unlike hard
disk drives (HDD), SSDs are not able to overwrite existing data, so the available space gradually becomes smaller with
each use. With the TRIM command, the operating system can inform the SSD which blocks of data are no longer in use
and can be removed permanently. Thus, the SSD will perform the erase action, which prevents unused data from
occupying blocks all the time.
7.1.5 SMART
SMART, an acronym for Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology, is an open standard that allows a hard
disk drive to automatically detect its health and report potential failures. When a failure is recorded by SMART, users
can choose to replace the drive to prevent unexpected outage or data loss. Moreover, SMART can inform users of
impending failures while there is still time to perform proactive actions, such as copy data to another device.
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 25
Page 26

www.seagate.com
7.1.6 Over Provisioning
Over Provisioning refers to the inclusion of extra NAND capacity in a SSD, which is not visible and cannot be used by
users. With Over Provisioning, the performance and IOPS (Input/output Operations per Second) are improved by
providing the controller additional space to manage P/E cycles, which enhances the reliability and endurance as well.
Moreover, the write amplification of the SSD becomes lower when the controller writes data to the flash.
7.1.7 Firmware Upgrade
Firmware can be considered as a set of instructions on how the device communicates with the host. Firmware will be
upgraded when new features are added, compatibility issues are fixed, or read/write performance gets improved.
7.1.8 Thermal Throttling
The purpose of thermal throttling is to prevent any components in a SSD from over-heating during read and write
operations. The device is designed with an on-die and an on-board thermal sensor, and with its accuracy, firmware can
apply different levels of throttling to achieve the purpose of protection efficiently and proactively via SMART reading.
Table 16 Current version: Thermal Throttling 2.0
Item Content
Reference of temp. reading On-board thermal sensor, Controller on-die thermal sensor
tmt1 threshold (PE < 500) 82°C per Smart reported
tmt2 threshold (PE < 500) 85°C per Smart reported
tmt1 threshold (PE > 500) 68°C per Smart reported
tmt2 threshold (PE > 500) 70°C per Smart reported
Protect controller threshold 115°C from on-die thermal sensor
Fatal threshold 120°C from on-die thermal sensor
Resume performance threshold
(PE < 500)
Resume performance threshold
(PE > 500)
Temperature polling frequency Every 1 sec
TMT1_state impact ±10% CE
TMT2_state impact -20% CE
78°C per Smart reported
64°C per Smart reported
NOTE For optimal performance:
Provide sufficient airflow and cooling.
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 26
Page 27

www.seagate.com
7.2 Advanced Device Security Features
7.2.1 NVMe format
Secure Erase is a standard NVMe format command and it writes all “0xFF” to fully wipe all the data on the SSDs. When
this command is issued, the SSD controller erases its storage blocks and returns the drive to its factory default settings.
7.2.2 Sanitize Operation
The Sanitize feature is an alternative to the existing secure erase capabilities through the Format NVM command and
makes a robust data security by ensuring the user data from the drive's media, caches and the Controller Memory
Buffer are all wiped by the block erase operations, overwriting or destroying the encryption key. The following table
illustrates the types of Sanitize Operations supported.
Table 17 Supported Sanitize Operations
Sanitize Operation
Drive Security Type
Overwrite Block Erase
Non-SED Yes Yes No
Crypto
Erase
NOTE Sanitize Overwrite command completion takes at least one hour per terabyte
per pass. The number of passes is drive-selectable. The NVMe spec default is 16
passes. Contact Seagate Support for more detailed information.
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 27
Page 28

www.seagate.com
7.3 SSD Lifetime Management
7.3.1 Total Bytes Written (TBW)
TBW (total bytes written) is a measurement of the SSDs’ expected lifespan, which represents the amount of data
written to the device. To calculate the TBW of a SSD, the following equation is applied:
TBW = [(NAND Endurance) x (SSD Capacity)] / WAF
NAND Endurance: NAND endurance refers to the P/E (Program/Erase) cycle of a NAND flash. SSD Capacity: The SSD
capacity is the specific capacity in total of a SSD.
WAF: Write Amplification Factor (WAF) is a numerical value representing the ratio between the amount of data that a
SSD controller needs to write and the amount of data that the host’s flash controller writes. A better WAF, which is near
1, guarantees better endurance and lower frequency of data written to flash memory.
7.3.2 Media Wear Indicator
Actual life indicator reported by SMART Attribute byte index [5], Percentage Used, recommends User to replace drive
when reaching to 100%.
7.3.3 Read Only Mode (End of Life)
When drive is aged by cumulated program/erase cycles, media worn- out may cause increasing numbers of later bad
block. When the number of available spare is less the threshold(5%, SMART attribute log ID 02h Byte4), the drive will
notify Host through AER event and Critical Warning to enter Read Only Mode to prevent further data corruption. User
should start to replace the drive with another one immediately.
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 28
Page 29

www.seagate.com
7.4 An Adaptive Approach to Performance Tuning
7.4.1 Throughput
Based on the available space of the disk, the drive will regulate the read/write speed and manage the performance of
throughput. When there still remains a lot of space, the firmware will continuously perform read/write action. There is
still no need to implement garbage collection to allocate and release memory, which will accelerate the read/write
processing to improve the performance. Contrarily, when the space is being used up, the drive will slow down the
read/write processing, and implement garbage collection to release memory. Hence, read/write performance will
become slower.
7.4.2 Predict & Fetch
Normally, when the Host tries to read data from the PCIe SSD, the PCIe SSD will only perform one read action after
receiving one command. However, the drive applies Predict & Fetch to improve the read speed. When the host issues
sequential read commands to the PCIe SSD, the PCIe SSD will automatically expect that the following will also be read
commands. Thus, before receiving the next command, flash has already prepared the data. Accordingly, this
accelerates the data processing time, and the host does not need to wait so long to receive data.
7.4.3 SLC Caching
The firmware design of the device currently adopts dynamic caching to deliver better performance for better
endurance and consumer user experience. The SLC caching size is up to 1/3 of free capacity of the SSD.
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 29
Page 30

www.seagate.com
8. Safety, Standards, and Compliance
Each Hard Drive and Solid State Drive ("device") has a product label that includes certifications that apply to that
specific drive. The following information provides an overview of requirements that may apply to the drive.
NOTE The most up to date information on Safety, Standards, and Compliance for
this product is available in the Seagate HDD and SSD Regulatory Compliance
and Safety document. You can find this document on the Seagate Support
page here:
https://www.seagate.com/support/
8.1 Regulatory Model Numbers
The following regulatory model number represents all features and configurations in the series:
STA025
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 30
Page 31

www.seagate.com
9. FireCuda 530 Installation Precautions
9.1 FireCuda 530 SSD Handling Instructions
There are a lot of components assembled on a single SSD device. Handle the drive with care especially when it has any
WLCSP (Wafer Level Chip Scale Packaging) components such as PMIC, thermal sensor or load switch. WLCSP is a
packaging technology widely used for making smaller footprints. However, any bumps or scratches may damage
those ultrasmall parts so you must handle with gentle care. See Figure 9.2, FireCuda 530 SSD Installation Instructions
CAUTION! DO NOT DROP SSD
CAUTION! INSTALL SSD WITH CARE
CAUTION! STORE SSD IN A PROPER PACKAGE
9.2 FireCuda 530 SSD Installation Instructions
FireCuda 530 features the PCIe connector with M-key, which is compatible only with the M-key socket. See Use Case 1
in Figure 7, M-Key M.2 Assembly Precautions. As shown in Use Case 2, misuse may cause severe damage to an SSD
including burn-out.
Figure 7 M-Key M.2 Assembly Precautions
9.3 Heatsink Disclosures
NOTE About Heatsink SSDs.
Heatsinks are pre-installed. Do not remove the heatsink; you can damage
the SSD.
Dimensions exceed standard size specifications for the M.2 without a
heatsink. Please verify that your system has enough space for installation.
SSDs with heatsinks are recommended for M.2 with connectors H3.2 and
above.
Seagate FireCuda 530 SSD Product Manual, Rev B 31
Page 32

Seagate Technology LLC
AMERICAS Seagate Technology LLC 47488 Kato Road, Fremont, California 94538, United States, 510-661-1000
ASIA/PACIFIC Seagate Singapore International Headquarters Pte. Ltd. 90 Woodlands Avenue 7, Singapore 737911, 65-6412-3666
EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Seagate Technology (Netherlands) B.V. Koolhovenlaan 1, 1119 NB Schiphol-Rijk, Netherlands, 31-20-316-7300
Publication Number: 200432500, Rev B
May 2021
 Loading...
Loading...