Page 1

™
5400 RPM - SATA Product Manual
Standard models
ST2000LX001
ST1000LX015
ST500LX025
1007802299, Rev. C
August 2016
Page 2
Document Revision History
Revision Date Pages affected and Description of change
Rev. A 07/05/2016 Initial release.
Rev. B 08/18/2016
5, 13, 18 & 20: Re-Branded to FireCuda.
16: Added warning statement for Class B devices in Korean
Rev. C 08/31/2016 5-6: Added NAND flash text
a
© 2016 Seagate Technology LLC. All rights reserved.
Publication number: 1007802299, Rev. C August 2016
Seagate, Seagate Technology and the Spiral logo are registered trademarks of Seagate Technology LLC in the United States and/or other countries. SeaTools and 3D Defense System are
either a trademark or registered trademark of Seagate Technology LLC or one of its affiliated companies in the United States and/or other countries. The FIPS logo is a certification mark
of NIST, which does not imply product endorsement by NIST, the U.S., or Canadian governments. All other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective
owners.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without written permission of Seagate Technology LLC.
Call 877-PUB-TEK1(877-782-8351) to request permission.
When referring to drive capacity, one gigabyte, or GB, equals one billion bytes and one terabyte, or TB, equals one trillion bytes. Your computer’s operating system may use a different
standard of measurement and report a lower capacity. In addition, some of the listed capacity is used for formatting and other functions, and thus will not be available for data storage.
Actual quantities will vary based on various factors, including file size, file format, features and application software. Actual data rates may vary depending on operating environment
and other factors. The export or re-export of hardware or software containing encryption may be regulated by the U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (for
more information, visit www.bis.doc.gov), and controlled for import and use outside of the U.S. Seagate reserves the right to change, without notice, product offerings or specifications.
Page 3

Contents
Seagate® Technology Support Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
1.0 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
1.1 About the Serial ATA Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.0 Drive Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
2.1 Formatted Capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1.1 LBA mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2 Physical organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.3 Recording and Interface Technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.4 Physical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.5 Seek time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.6 Start/stop times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.7 Power Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.7.1 Power consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.7.2 Conducted noise. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.7.3 Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.7.4 Power management modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.8 Environmental Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.8.1 Shock. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.8.2 Vibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.9 Acoustics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.9.1 Test for prominent discrete tones (PDTs). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.10 Electromagnetic Immunity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.10.1 DC Magnetic Field Immunity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.11 Reliability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
2.12 Agency Certification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.12.1 Safety certification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.12.2 Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.12.3 FCC verification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
2.13 Environmental Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
2.13.1 European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
2.13.2 China Requirements — China RoHS 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.14 Corrosive Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.0 Configuring and Mounting the Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.1 Handling and Static-Discharge Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.2 Configuring the Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.2.1 Serial ATA Cables and Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.3 Drive Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.0 Serial ATA (SATA) Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.1 Hot-Plug Compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.2 Serial ATA Device Plug Connector Pin Definitions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.3 Supported ATA Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.3.1 Identify Device command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
4.3.2 Set Features command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.3.3 S.M.A.R.T. commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 2
Page 4

Figures
Figure 1 Typical 1D - 5V Startup and Operation Current Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 2 Typical 2D - 5V Startup and Operation Current Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 3 Attaching SATA Cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 4 Mounting Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 3
Page 5

Seagate® Technology Support Services
For information regarding online support and services, visit: http://www.seagate.com/contacts/
For information regarding Warranty Support, visit: http://www.seagate.com/support/warranty-and-replacements/
For information regarding data recovery services, visit: http://www.seagate.com/services-software/data-recovery-services/
For Seagate OEM, Distribution partner and reseller portals, visit: http://www.seagate.com/partners/
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 4
Page 6

1.0 Introduction
This manual describes the functional, mechanical and interface specifications for the following Seagate® FireCuda™ model drives:
Standard models
ST2000LX001
ST1000LX015
ST500LX025
These drives provide the following key features:
• 1000 Gs non-operating shock and 400 Gs of operating shock.
• 128MB buffer.
• 5400-RPM spindle speed.
• Flash-accelerated drives combining 8GB NAND technology with massive HDD storage capacity up to 2TB.
• Full-track multiple-sector transfer capability without local processor intervention.
• High instantaneous (burst) data-transfer rates (up to 6Gb/s).
• Native Command Queuing (NCQ) with command ordering.
• Perpendicular recording technology.
• Quiet operation. Fluid Dynamic Bearing (FDB) motor.
• SeaToolsTM diagnostic software performs a drive self-test that eliminates unnecessary drive returns.
• State-of-the-art cache and on-the-fly error-correction algorithms.
• Support for Read Multiple and Write Multiple commands.
• Support for S.M.A.R.T. drive monitoring and reporting.
• Worldwide Name (WWN) capability uniquely identifies the drive.
1.1 About the Serial ATA Interface
The Serial ATA interface provides several advantages over the traditional (parallel) ATA interface. The primary advantages include:
• Easy installation and configuration with true plug-and-play connectivity. It is not necessary to set any jumpers or other configuration options.
• Thinner and more flexible cabling for improved enclosure airflow and ease of installation.
• Scalability to higher performance levels.
In addition, Serial ATA makes the transition from parallel ATA easy by providing legacy software support. Serial ATA was designed to allow users to
install a Serial ATA host adapter and Serial ATA disk drive in the current system and expect all of the existing applications to work as normal.
The Serial ATA interface connects each disk drive in a point-to-point configuration with the Serial ATA host adapter. There is no master/slave
relationship with Serial ATA devices like there is with parallel ATA. If two drives are attached on one Serial ATA host adapter, the host operating
system views the two devices as if they were both “masters” on two separate ports. This essentially means both drives behave as if they are Device 0
(master) devices.
The host adapter may, optionally, emulate a master/slave environment to host software where two devices on separate Serial ATA ports
Note
The Serial ATA host adapter and drive share the function of emulating parallel ATA device behavior to provide backward compatibility with existing
host systems and software. The Command and Control Block registers, PIO and DMA data transfers, resets, and interrupts are all emulated.
The Serial ATA host adapter contains a set of registers that shadow the contents of the traditional device registers, referred to as the Shadow
Register Block. All Serial ATA devices behave like Device 0 devices. For additional information about how Serial ATA emulates parallel ATA, refer to
the Serial ATA International Organization: Serial ATA (Revision 2.6). The specification can be downloaded from www.serialata.or
are represented to host software as a Device 0 (master) and Device 1 (slave) accessed at the same set of host bus addresses. A host
adapter that emulates a master/slave environment manages two sets of shadow registers. This is not a typical Serial ATA environment.
g.
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 5
Page 7
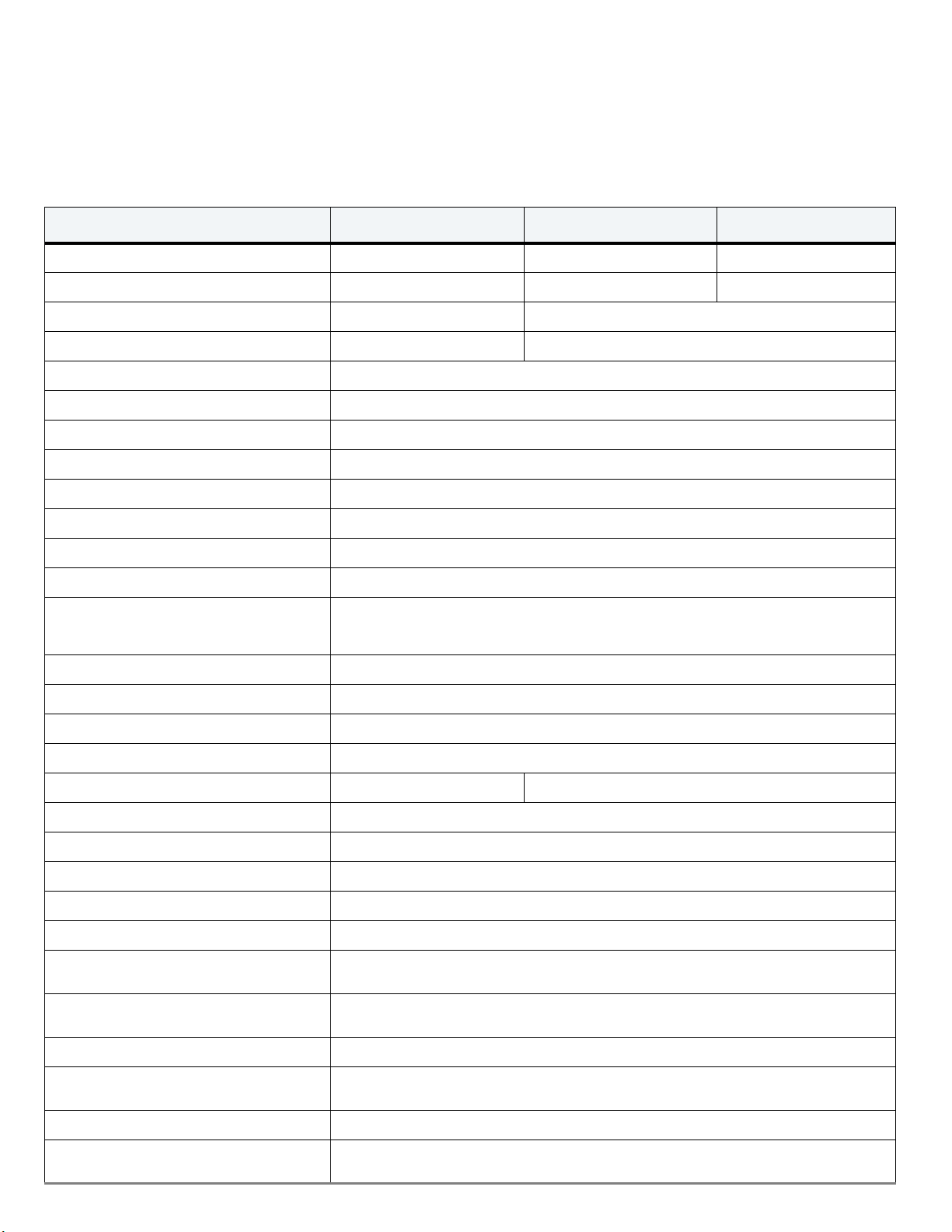
2.0 Drive Specifications
Unless otherwise noted, all specifications are measured under ambient conditions, at 25°C, and nominal power. For convenience, the phrases the
drive and this drive are used throughout this manual to indicate the following drive models:
The specification summaries listed in the following tables are for quick reference. For details on specification measurement or definition, refer to the
appropriate section of this manual.
Table 1 Drive Specifications Summary
Drive Specification ST2000LX001 ST1000LX015 ST500LX025
Formatted capacity
Guaranteed sectors 3,907,029,168 1,953,525,168 976,773,168
Heads 4 2
Disks 2 1
NAND flash Commercial Multilevel Cell (cMLC) 8GB
Bytes per sector 512 (logical) / 4096 (physical)
Recording density 2296 KFC/in
Track density 580 KTP/in avg
Areal density 1327 Mb/in
Spindle speed 5400 RPM
Data transfer rate (up to) 140 MB/s
Interface SATA 6Gb/s
ATA data-transfer modes supported
Cache buffer 128 MB
Height (mm/in) 7.0 (± 0.2) / 0.276 (± 008)
(1)
2TB 1TB 500GB
2
avg
PIO modes 0–4
Multiword DMA modes 0–2
Ultra DMA modes 0–6
Width (mm/in) 69.85 (± 0.25) / 2.750 (± 0.010)
Length (mm/in) 100.35 (+0.20/-0.25) / 3.951 (+0.008/-0.010)
Weight (g/lb) max 96 / 0.212 92 / 0.203
Average latency 5.6 ms
Startup current, Max (+5V ) 1.0 A
Voltage tolerance (including noise) 5V ± 5%
Operating temperature 0° to 60°C
Non-operating temperature (ambient) –40° to 70°C
Temperature gradient
Relative humidity
Relative humidity gradient (max) 30% per hour
Wet bulb temperature
Altitude, operating –304.8 m to 3048 m (–1000 ft to 10,000+ ft)
Altitude, non-operating
(below mean sea level, max)
20°C per hour max (operating)
35°C per hour max (non-operating)
5% to 95% (operating)
5% to 95% (non-operating)
37.7°C max (operating)
40.0°C max (non-operating)
–304.8 m to 12,192 m (–1000 ft to 40,000+ ft)
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 6
Page 8

Drive Specifications
Table 1 Drive Specifications Summary (continued)
Drive Specification ST2000LX001 ST1000LX015 ST500LX025
Operational Shock 400 Gs at 2 ms max
Non-Operational Shock 1000 Gs at 1 ms max
Vibration, operating
Vibration, non-operating 5–500 Hz: 5.0 Gs
Nonrecoverable read errors 1 per 10
Average annualized workload rating: <55 TB/year.
Rated workload
Warranty
Load-unload cycles 600,000 at 25°C, 50% rel. humidity
Supports Hotplug operation per the
Serial ATA Revision 3.2 specification
1. One GB equals one billion bytes when referring to hard drive capacity. Accessible capacity may vary depending on operating environment and
formatting.
The AFR specification for the product assumes the I/O workload does not exceed the average
annualized workload rate limit of 55 TB/year. Workloads exceeding the annualized rate may
degrade the product AFR and impact reliability as experienced by the particular application.
The average annualized workload rate limit is in units of TB per calendar year.
To determine the warranty for a specific drive, use a web browser to access the following web
page: http://www.sea
From this page, click on the “Is my Drive under Warranty” link. The following are required to be
provided: the drive serial number, model number (or part number) and country of purchase.
The system will display the warranty information for the drive.
gate.com/support/warranty-and-replacements/.
5–200 Hz: 2.0 Gs
201–500 Hz: 1.0 Gs
14
bits read
Ye s
2.1 Formatted Capacity
Model
Formatted Capacity
(1)
Guaranteed Sectors Bytes per Sector
ST2000LX001 2000 GB 3,907,029,168
512 (logical) / 4096 (physical)ST1000LX015 1000 GB 1,953,525,168
ST500LX025 500 GB 976,773,168
1. One GB equals one billion bytes when referring to hard drive capacity. Accessible capacity may vary depending on operating
environment and formatting.
2.1.1 LBA mode
When addressing these drives in LBA mode, all blocks (sectors) are consecutively numbered from 0 to n–1, where n is the number of guaranteed
sectors as defined above.
Refer to Configuring and Mounting the Drive on page 18 (words 60-61 and 100-103) for additional information about 48-bit addressing support
of drives with capacities over 137 GB.
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 7
Page 9
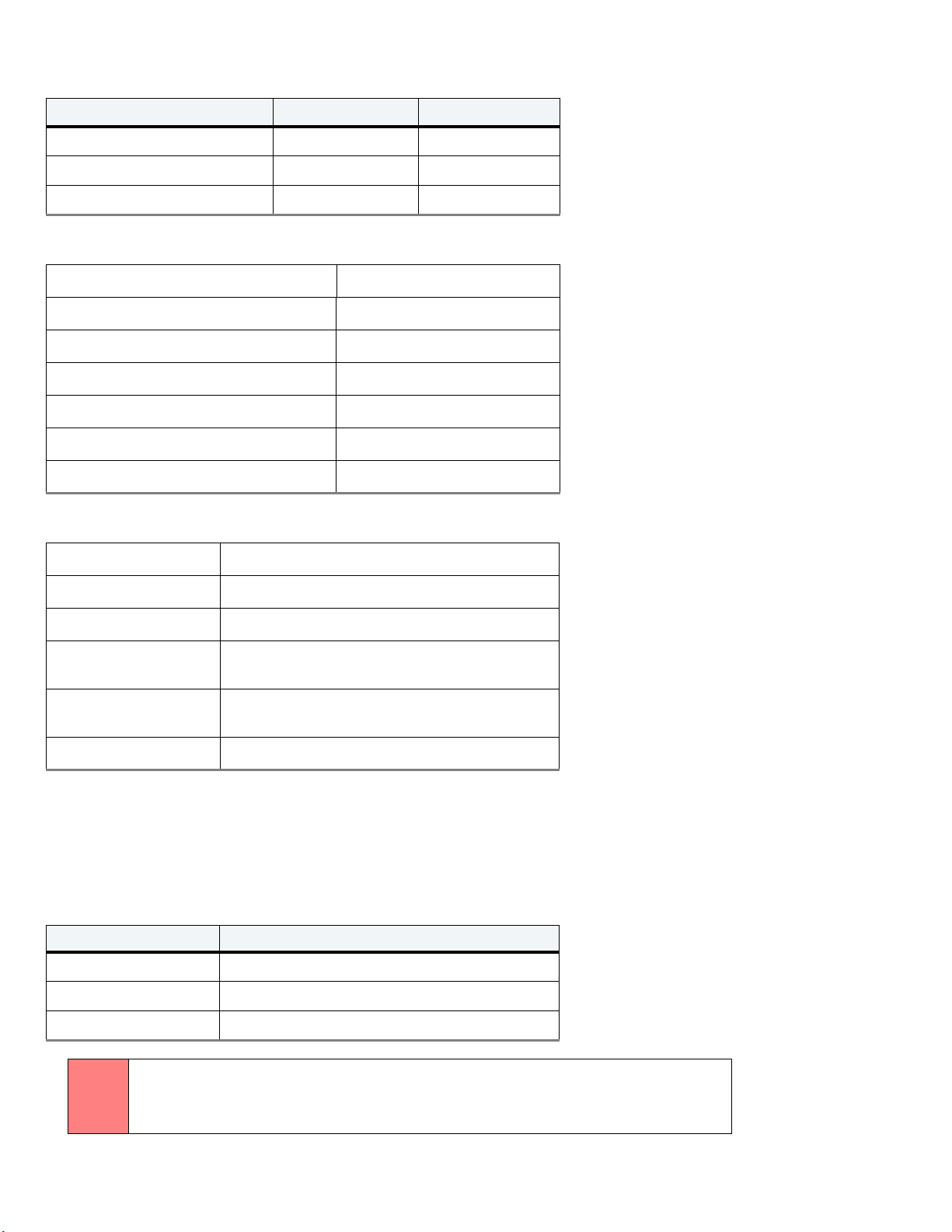
2.2 Physical organization
Drive model Read/write heads Number of discs
ST2000LX001 4 2
ST1000LX015 2 1
ST500LX025 2 1
2.3 Recording and Interface Technology
Interface SATA 6Gb/s
Recording method Perpendicular
Recording density 2276 Kb/in
Track density 580 ktracks/in avg
Areal density 1320 Gb/in2 avg
Spindle speed 5400 RPM
Drive Specifications
Data transfer rate (up to) 140 MB/s
2.4 Physical Characteristics
Height (mm/in) 7.0 (± 0.2) / 0.276 (± 008)
Width (mm/in) 69.85 (± 0.25) / 2.750 (± 0.010)
Length (mm/in) 100.35 (+0.20/-0.25) / 3.951 (+0.008/-0.010)
Typical weight (g/lb)
(2-Disk models)
Typical weight (g/lb)
(1-Disk models)
Cache buffer 128MB
96 / 0.212
92/ 0.203
2.5 Seek time
Seek measurements are taken with nominal power at 25°C ambient temperature. All times are measured using drive diagnostics. The specifications
in the table below are defined as follows:
• Track-to-track seek time is an average of all possible single-track seeks in both directions.
• Average seek time is a true statistical random average of at least 5000 measurements of seeks between random tracks, less overhead.
Table 2 Typical seek times
Typical seek times (ms) Read
Track -to-t rack 1.5
Average 13.0
Average latency 5.6
These drives are designed to consistently meet the seek times represented in this manual. Physical
Note
seeks, regardless of mode (such as track-to-track and average), are expected to meet the noted values.
However, due to the manner in which these drives are formatted, benchmark tests that include
command overhead or measure logical seeks may produce results that vary from these specifications.
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 8
Page 10
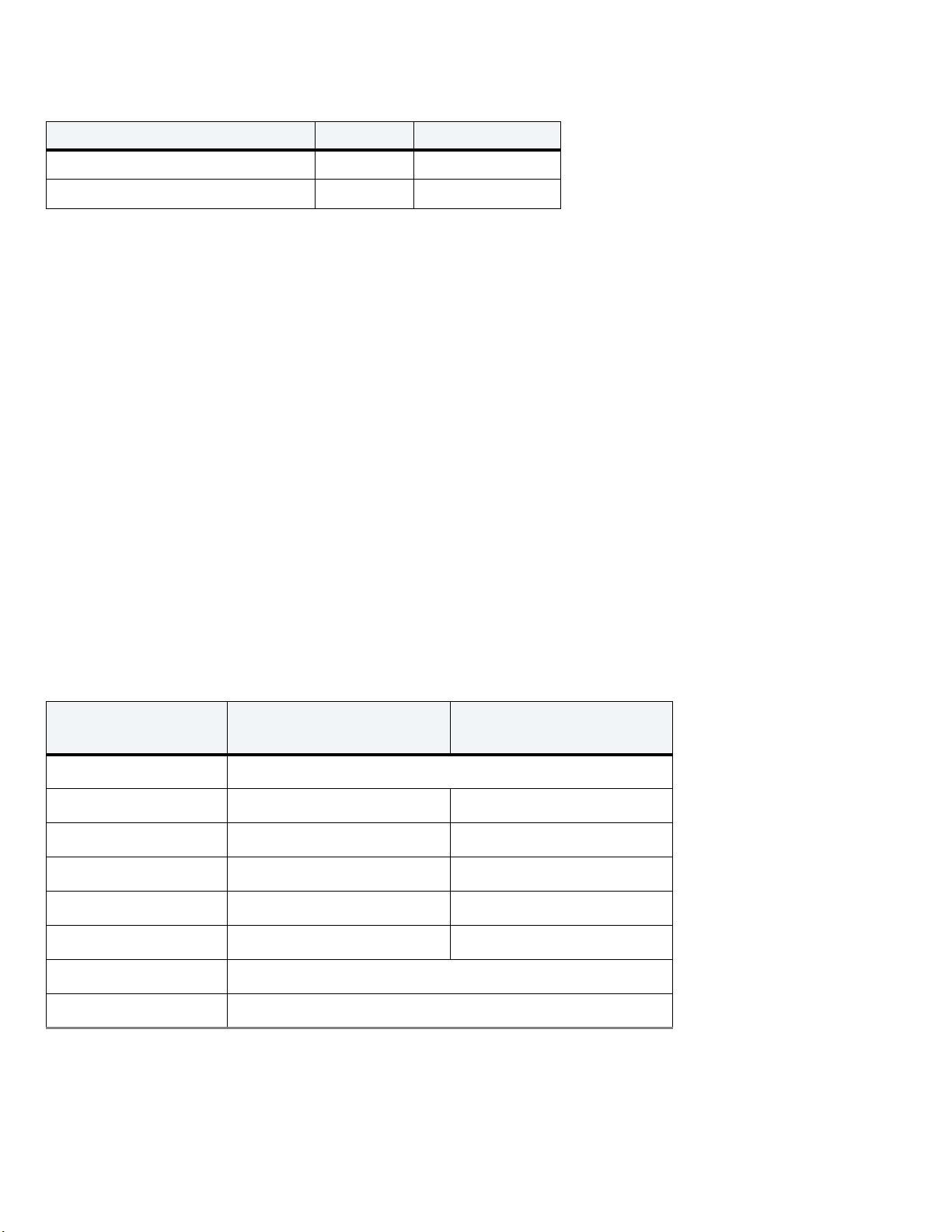
Drive Specifications
2.6 Start/stop times
Table 3 Start/stop times
Typical seek times (ms) Typ ica l Max @ 25°C
Power-on to ready (sec) 0.6 0.8
Standby to ready (sec) 2.5 3.0
2.7 Power Specifications
The drive receives DC power (+5V) through a native SATA power connector (refer to Figure 3).
2.7.1 Power consumption
Power requirements for the drives are listed in the table in Tab le 4 . Typical power measurements are based on an average of drives tested, under
nominal conditions, at 25°C ambient temperature. These power measurements are done with Interface Power Management modes like HIPM
and DIPM enabled.
• Spinup power
Spinup power is measured from the time of power-on to the time that the drive spindle reaches operating speed.
•Seek mode
During seek mode, the read/write actuator arm moves toward a specific position on the disk surface and does not execute a read or write
operation. Servo electronics are active. Seek mode power is measured based on three random seek operations every 100 ms. This mode is not
typical.
• Read/write power and current
Read/write power is measured with the heads on track, based on three 63 sector read or write operations every 100 ms.
•Idle mode power
Idle mode power is measured with the drive up to speed, with servo electronics active and with the heads in a random track location.
•Standby mode
During standby mode, the drive accepts commands, but the drive is not spinning, and the servo and read/write electronics are in
power-down mode.
Table 4 DC Power Requirements
Power Dissipation
2-Disk models
+5V input average (25° C)
1-Disk models
+5V input average (25° C)
Spinup (max) 1.00A
Write average 1.80W 1.70W
Read average 1.70W 1.60W
Idle, performance
(1)
1.50W 1.40W
Idle, active 0.85W 0.85W
Idle, low power mode 0.50W 0.45W
Standby
(2)
0.13W
Sleep 0.13W
1. During periods of drive idle, some offline activity may occur according to the S.M.A.R.T. specification, which
may increase acoustic and power to operational levels.
2. Standby power is measured at steady state (after 200ms from transition)
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 9
Page 11

2.7.1.1 Typical current profiles
The typical 5V startup and operation current profile is shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
Figure 1 Typical 1D - 5V Startup and Operation Current Profile
Drive Specifications
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 10
Page 12
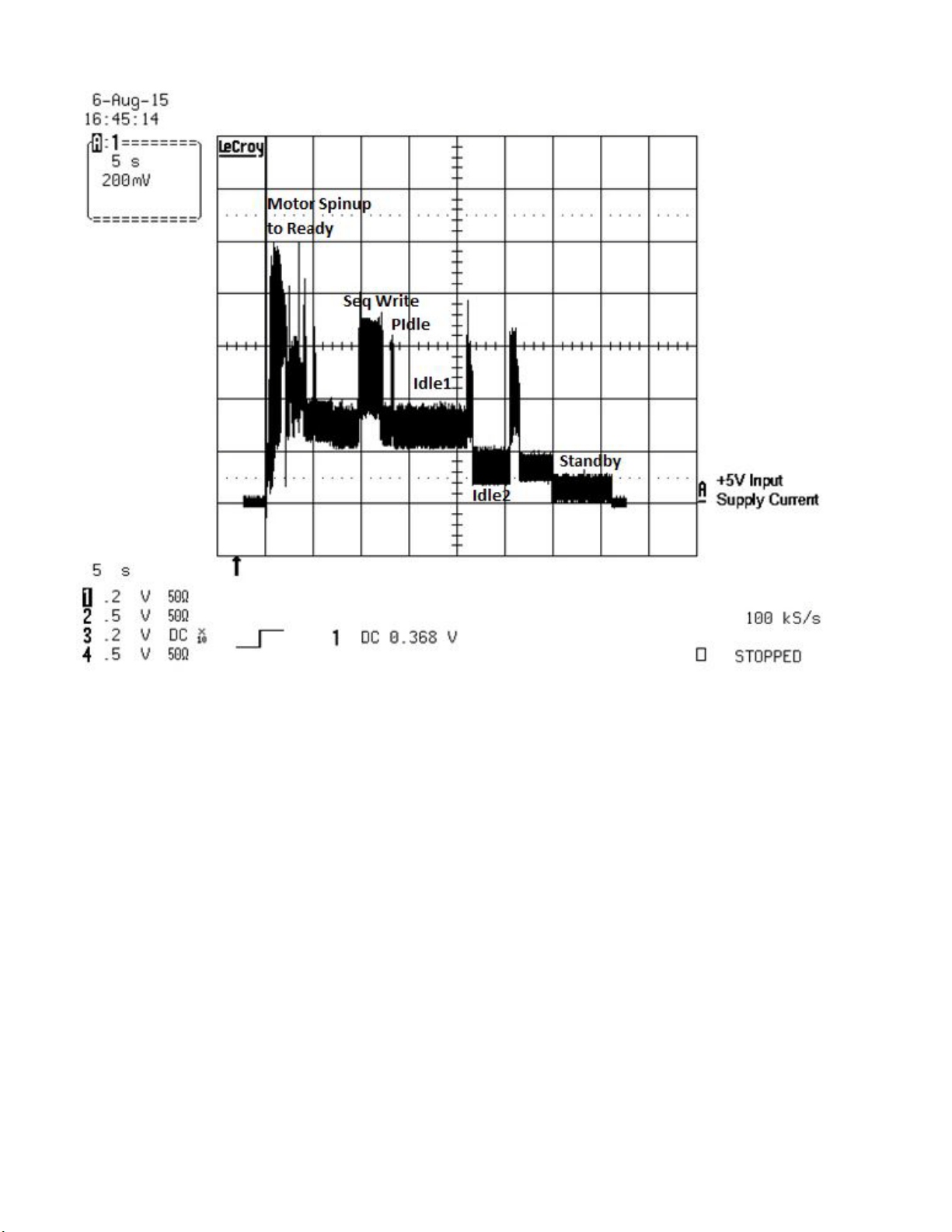
Figure 2 Typical 2D - 5V Startup and Operation Current Profile
Drive Specifications
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 11
Page 13

Drive Specifications
2.7.2 Conducted noise
Input noise ripple is measured at the host system power supply across an equivalent 15-ohm resistive load on the +5 volt line.
• Using 5-volt power, the drive is expected to operate with a maximum of 100 mV peak-to-peak square-wave injected noise at up to 20 MHz.
Note
2.7.3 Supply Voltage
Equivalent resistance is calculated by dividing the nominal voltage by the typical RMS read/write current.
Allowable voltage 5V ± 5%
Allowable noise/ripple 100 p-p max, 0-20 MHz
Allowable supply rise time <100 ms
2.7.4 Power management modes
The drive provides programmable power management to provide greater energy efficiency. In most systems, power management is controlled
through the system setup program. The drive features the following power-management modes:
Power modes Heads Spindle Buffer
Active (operating) Tracking Rotating Full power
Idle, performance Tracking Rotating Self refresh—low power
Idle, active Floating Rotating Self refresh—low power
Idle, low power Parked Rotating Self refresh—low power
Standby Parked Stopped Self refresh—low power
Sleep Parked Stopped Self refresh—low power
• Active mode
The drive is in active mode during the read/write and seek operations.
n Idle mode
The buffer remains enabled, and the drive accepts all commands and returns to active mode any time disk access is necessary.
• Standby mode
The drive enters standby mode when the host sends a standby Immediate command. If the host has set the standby timer, the drive can also
enter standby mode automatically after the drive has been inactive for a specifiable length of time. The standby timer delay is established using
a standby or idle command. In standby mode, the drive buffer is enabled, the heads are parked and the spindle is at rest. The drive accepts all
commands and returns to active mode any time disk access is necessary.
n Sleep mode
The drive enters sleep mode after receiving a sleep command from the host. In sleep mode, the drive buffer is disabled, the heads are parked and
the spindle is at rest. The drive leaves sleep mode after it receives a hard reset or soft reset from the host. After receiving a reset, the drive exits
sleep mode and enters standby mode with all current translation parameters intact.
n Idle and standby timers
Each time the drive performs an active function (read, write or seek), the standby timer is reinitialized and begins counting down from its
specified delay times to zero. If the standby timer reaches zero before any drive activity is required, the drive makes a transition to standby mode.
In both Idle and standby mode, the drive accepts all commands and returns to active mode when disk access is necessary.
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 12
Page 14

2.8 Environmental Specifications
This section provides the temperature, humidity, shock, and vibration specifications for FireCuda drives.
Ambient temperature is defined as the temperature of the environment immediately surrounding the drive.
Above 1000 feet (305 meters), the maximum temperature is derated linearly by 1°C every 1000 feet.
Table 5: Environmental specifications
Parameters Operating Non-Operating
Ambient temperature 0° to 60°C (32° to 140°F) -40° to 70°C (-40° to 158°F)
Drive Specifications
Temperature gradient
Humidity
Wet bulb 37.7°C (99.8°F) max 40°C (104°F) max
Altitude
The recommended storage period:
Note
2.8.1 Shock
All shock specifications assume that the drive is mounted securely with the input shock applied at the drive mounting screws. Shock may be
applied in the X, Y, or Z axis.
2.8.1.1 Operating shock
These drives comply with the performance levels specified in this document when subjected to a maximum operating shock of 400 Gs based on
half-sine shock pulses of 2ms. Shocks should not be repeated more than one time per axis.
2.8.1.2 Non-operating shock
The non-operating shock level that the drive can experience without incurring physical damage or degradation in performance when subsequently
put into operation is 1000 Gs based on a nonrepetitive half-sine shock pulse of 1 ms duration.
• 1 year under controlled conditions of 34°C 90%RH or less
• 90 days in uncontrolled storage conditions
20°C per hour (68°F per hour) max,
without condensation
5% to 95% non-condensing
(30% per hour)
-304.8m to 3048m
(-1000ft to 10,000ft)
35°C per hour (95°F per hour) max,
without condensation
5% to 95% non-condensing
(30% per hour)
-304.8m to 12,192m
(-1000ft to 40,000ft)
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 13
Page 15

Drive Specifications
2.8.2 Vibration
All vibration specifications assume that the drive is mounted securely with the input vibration applied at the drive mounting screws. Vibration may
be applied in the X, Y, or Z axis.
2.8.2.1 Operating vibration
The maximum vibration levels that the drive may experience while meeting the performance standards specified in this document are specified
below.
5–200 Hz 2.0 Gs (0 to peak). Max displacement may apply below 10 Hz.
201–500 Hz 1.0 Gs (0 to peak).
2.8.2.2 Non-operating vibration
The maximum non-operating vibration levels that the drive may experience without incurring physical damage or degradation in performance
when subsequently put into operation are specified below.
5–500 Hz 5.0 Gs (0 to peak). Max displacement may apply below 22 Hz.
2.9 Acoustics
Drive emission of sound is measured consistent with the ECMA-74 and its referenced standards. Testing is conducted at room temperature
(approximately 25°C). Emission levels are reported as the total A-weighted sound power levers for steady state, idle, and active seeks modes of
operation.
Table 6 Drive A-weighted Sound Power Levels (SWL, BA)
Models 2-Disk 1-Disk
(1)
Idle
Performance Seek
2.2 bels (typ)
2.4 bels (max)
2.4 bels (typ)
2.6 bels (max)
2.0 bels (typ)
2.2 bels (max)
2.2 bels (typ)
2.4 bels (max)
1. During periods of drive idle, some offline activity may occur according to the
S.M.A.R.T. specification, which may increase acoustic and power to operational
levels.
2.9.1 Test for prominent discrete tones (PDTs)
Seagate follows the ECMA-74 standards for measurement and identification of PDTs. An exception to this process is the use of the absolute
threshold of hearing. Seagate uses the lower limit for the threshold curve* to discern tone audibility and to compensate for the inaudible
components of sound prior to computation of tone ratios according to Annex D of the ECMA-74 standards.
*Defined as the median curve given by ISO 389-7 (Tf curve) minus 10dB at all frequencies.
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 14
Page 16

Drive Specifications
2.10 Electromagnetic Immunity
When properly installed in a representative host system, the drive operates without errors or degradation in performance when subjected to the
radio frequency (RF) environment as defined in Tab le 7.
Table 7 Radio Frequency Environments
Te st Description
Performance
Level
Reference
Standard
Electrostatic discharge Contact, HCP, VCP: ± 4 kV; Air: ± 8 kV B EN 61000-4-2: 95
Radiated RF immunity
80 to 1GHz, 3 V/m, 80% AM with 1 kHz sine
900 MHz, 3 V/m, 50% pulse modulation @ 200 Hz
A
EN 61000-4-3: 96
ENV 50204: 95
Electrical fast transient ± 1 kV on AC mains, ± 0.5 kV on external I/O B EN 61000-4-4: 95
Surge immunity ± 1 kV differential, ± 2 kV common, AC mains B EN 61000-4-5: 95
Conducted RF immunity 150 kHz to 80 MHz, 3 Vrms, 80% AM with 1 kHz sine A EN 61000-4-6: 97
Power Frequency H-field immunity 1 A/m, 50Hz/60Hz, 3 axes A EN 61000-4-8: 97
Voltage dips, interrupts
30% Reduction for 25 cycles
>95% Reduction for 250 cycles
>95%, 0.5 cycles
C
C
B
EN 61000-4-11: 94
2.10.1 DC Magnetic Field Immunity
Table 8: DC Magnetic Field Immunity
Te st Product Spec (Standalone)
DC Magnetic Field Immunity
1
Field in Gauss at the drive envelope. Testing per procedures 20800109-349 and 20800109-350.
2
Passing Field in Gauss at the drive envelope. In practice, testing is conducted using a fixed distance from the bottom of the magnet to the top
of the drive. Calibration of the field vs. distance is done with a Hall probe with no magnetic materials present.
3
Testing to be done with magnet .375” dia. x 0.100” Ni-plated NdFeB; B,~11.5 kG, magnetized along its length; the magnet is oriented with the
length perpendicular to the drive cover/PCBA. Drive to be properly secured during test.
1, 2, 3
400 Gauss, RMS
2.11 Reliability
Nonrecoverable read errors 1 per 1014 bits read, max
Load/Unload (U/UL)
25°C, 50% relative humidity
Rated workload Average annualized workload rating: <55 TB/year.
Warranty To determine the warranty for a specific drive, use a web browser to access the following web
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 15
600,000 software-controlled power on/off cycles
20,000 hard power on/off cycles
The AFR specification for the product assumes the I/O workload does not exceed the average
annualized workload rate limit of 55 TB/year. Workloads exceeding the annualized rate may
degrade the product AFR and impact reliability as experienced by the particular application. The
average annualized workload rate limit is in units of TB per calendar year.
page: http://www.seagate.com/support/warranty-and-replacements/.
From this page, click on the “Is my Drive under Warranty” link. The following are required to be provided: the drive serial number, model number (or part number) and country of purchase. The system will display the warranty information for the drive.
Page 17

Drive Specifications
2.12 Agency Certification
2.12.1 Safety certification
These products are certified to meet the requirements of UL60950-1, CSA60950-1 and EN60950 and so marked as to the certify agency.
The following regulatory model number represent all features and configurations within the series:
Regulatory Model Numbers: SDC002/SDC004
2.12.2 Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Hard drives that display the CE mark comply with the European Union (EU) requirements specified in the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive
2004/108/EC (Until 19th April, 2016) and 2014/30/EU (From 20th April, 2016). Testing is performed to the levels specified by the product standards
for Information Technology Equipment (ITE). Emission levels are defined by EN 55022, Class B and the immunity levels are defined by EN 55024.
Drives are tested in representative end-user systems. Although CE-marked Seagate drives comply with the directives when used in the test systems,
we cannot guarantee that all systems will comply with the directives. The drive is designed for operation inside a properly designed enclosure, with
properly shielded I/O cable (if necessary) and terminators on all unused I/O ports. Computer manufacturers and system integrators should confirm
EMC compliance and provide CE marking for their products.
Korean RRA
If these drives have the Korean Communications Commission (KCC) logo, they comply with paragraph 1 of Article 11 of the Electromagnetic
Compatibility control Regulation and meet the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Framework requirements of the Radio Research Agency (RRA)
Communications Commission, Republic of Korea.
These drives have been tested and comply with the Electromagnetic Interference/Electromagnetic Susceptibility (EMI/EMS) for Class B products.
Drives are tested in a representative, end-user system by a Korean-recognized lab
Australian RCM Compliance Mark
Models displayed with the RCM compliance mark, comply with the mandatory standards as per the Australian Communications and Media
Authority (ACMA) Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) regulatory arrangement.
2.12.3 FCC verification
These drives are intended to be contained solely within a personal computer or similar enclosure (not attached as an external device). As such, each
drive is considered to be a subassembly even when it is individually marketed to the customer. As a subassembly, no Federal Communications
Commission verification or certification of the device is required.
Seagate has tested this device in enclosures as described above to ensure that the total assembly (enclosure, disk drive, motherboard, power
supply, etc.) does comply with the limits for a Class B computing device, pursuant to Subpart J, Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation with noncertified
assemblies is likely to result in interference to radio and television reception.
Radio and television interference.
with the manufacturer’s instructions, may cause interference to radio and television reception.
This equipment is designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference in a residential installation. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause interference to radio or television, which can be determined
by turning the equipment on and off, users are encouraged to try one or more of the following corrective measures:
• Reorient the receiving antenna.
• Move the device to one side or the other of the radio or TV.
• Move the device farther away from the radio or TV.
• Plug the computer into a different outlet so that the receiver and computer are on different branch outlets.
This equipment generates and uses radio frequency energy and if not installed and used in strict accordance
.
If necessary, users should consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for additional suggestions. Users may find helpful the
following booklet prepared by the Federal Communications Commission: How to Identify and Resolve Radio-Television Interference Problems. This
booklet is available from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC 20402. Refer to publication number
004-000-00345-4.
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 16
Page 18

Drive Specifications
20
2.13 Environmental Protection
Seagate designs its products to meet environmental protection requirements worldwide, including regulations restricting certain chemical
substances.
2.13.1 European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive
The European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive, restricts the presence of chemical substances, including Lead, Cadmium,
Mercury, Hexavalent Chromium, PBB and PBDE, in electronic products, effective July 2006. This drive is manufactured with components and
materials that comply with the RoHS Directive.
2.13.2 China Requirements — China RoHS 2
China RoHS 2 refers to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology Order No. 32, effective July 1, 2016, titled Management
Methods for the Restriction of the Use of Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Products. To comply with China RoHS 2,
we determined this product's Environmental Protection Use Period (EPUP) to be 20 years in accordance with the Marking for the
Restricted Use of Hazardous Substances in Electronic and Electrical Products, SJT 11364-2014.
中国电器电子产品有害物质限制使用管理办法
(Management Methods for the Restriction of the Use of Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic
Products _ China RoHS)
产品中有害物质的名称及含量
(Name and Content of the Hazardous Substances in Product)
Table 9 Hazardous Substances
有害物质
Hazardous Substances
部件名称
Part Name
印刷电路板组装
PCBA
机壳
Chassis
本表格依据 SJ/T 11364 的规定编制。
This table is prepared in accordance with the provisions of SJ/T 11364-2014
O:表示该有害物质在该部件所有均质材料中的含量均在 GB/T 26572 规定的限量要求以下。
O: Indicates that the hazardous substance contained in all of the homogeneous materials for this part is below the limit requirement of
GB/T26572.
X:表示该有害物质至少在该部件的某一均质材料中的含量超出 GB/T 26572 规定的限量要求。
X: Indicates that the hazardous substance contained in at least one of the homogeneous materials used for this part is above the limit
requirement of GB/T26572.
铅
Lead
(Pb)
XOOOOO
XOOOOO
汞
Mercury
(Hg)
镉
Cadmium
(Cd)
六价铬
Hexavalent
Chromium
(CF (VI))
多溴联苯
Polybrominated
biphenyls (PBB)
多溴二苯醚
Polybrominated
diphenyl ethers
(PBDE)
2.14 Corrosive Environment
Seagate electronic drive components pass accelerated corrosion testing equivalent to 10 years exposure to light industrial environments
containing sulfurous gases, chlorine and nitric oxide, classes G and H per ASTM B845. However, this accelerated testing cannot duplicate every
potential application environment.
Users should use caution exposing any electronic components to uncontrolled chemical pollutants and corrosive chemicals as electronic drive
component reliability can be affected by the installation environment. The silver, copper, nickel and gold films used in Seagate products are
especially sensitive to the presence of sulfide, chloride, and nitrate contaminants. Sulfur is found to be the most damaging. In addition, electronic
components should never be exposed to condensing water on the surface of the printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) or exposed to an ambient
relative humidity greater than 95%. Materials used in cabinet fabrication, such as vulcanized rubber, that can outgas corrosive compounds should
be minimized or eliminated. The useful life of any electronic equipment may be extended by replacing materials near circuitry with sulfide-free
alternatives.
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 17
Page 19

3.0 Configuring and Mounting the Drive
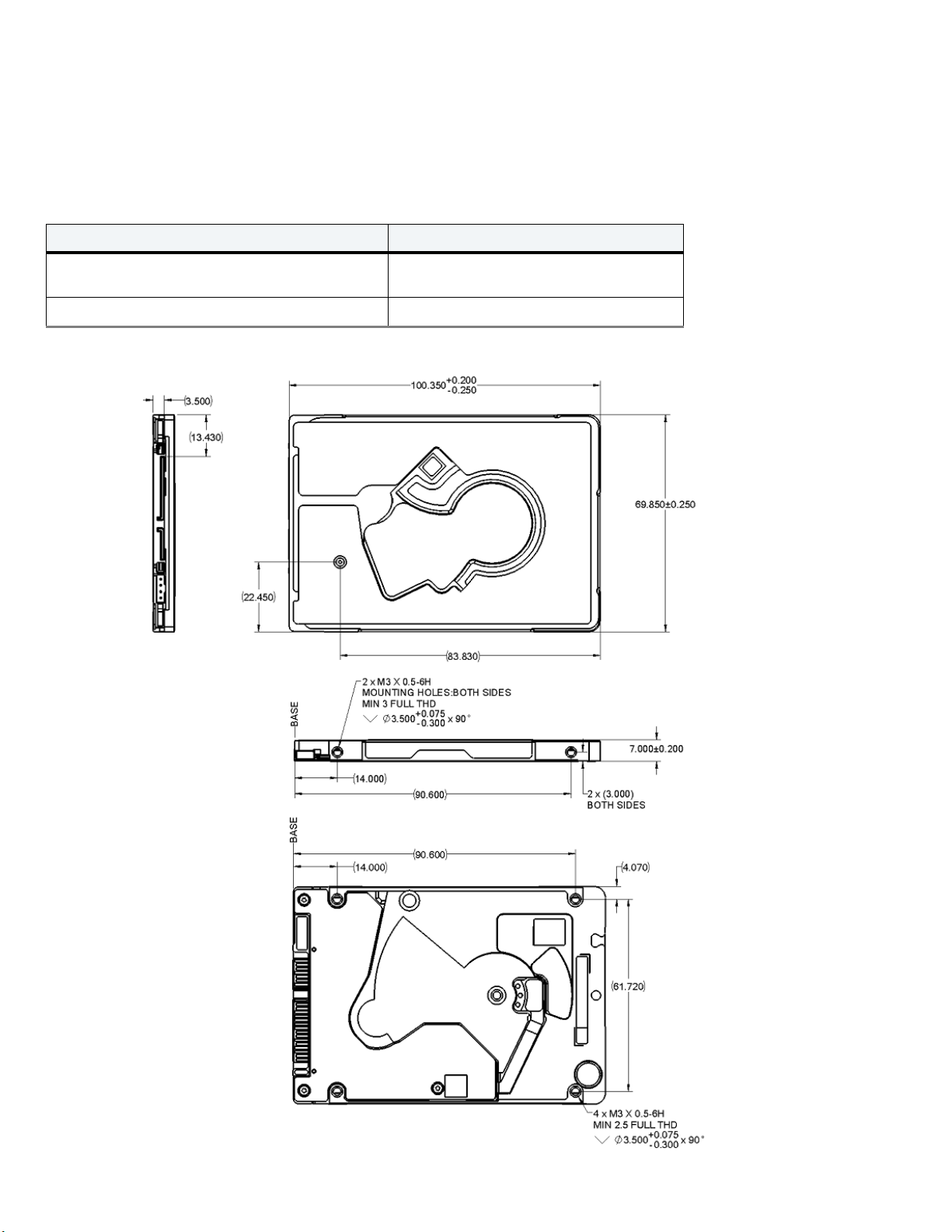
Power cable
Signal cable
Signal connector
Power connector
This section contains the specifications and instructions for configuring and mounting the drive.
3.1 Handling and Static-Discharge Precautions
After unpacking, and before installation, the drive may be exposed to potential handling and electrostatic discharge (ESD) hazards. Observe the
following standard handling and static-discharge precautions.
• Keep the drive in the electrostatic discharge (ESD) bag until ready for installation to limit the
drive’s exposure to ESD.
• Before handling the drive, put on a grounded wrist strap, or ground yourself frequently by
touching the metal chassis of a computer that is plugged into a grounded outlet. Wear a
grounded wrist strap throughout the entire installation procedure.
CAUTION
3.2 Configuring the Drive
Each drive on the Serial ATA interface connects in a point-to-point configuration with the Serial ATA host adapter. There is no master/slave
relationship because each drive is considered a master in a point-to-point relationships. If two drives are attached on one Serial ATA host adapter,
the host operating system views the two devices as if they were both “masters” on two separate ports. Both drives behave as if they are Device 0
(master) devices.
• Handle the drive by its edges or frame only.
• The drive is extremely fragile—handle it with care. Do not press down on the drive top cover.
• Always rest the drive on a padded, antistatic surface until mounting it in the computer.
• Do not touch the connector pins or the printed circuit board.
• Do not remove the factory-installed labels from the drive or cover them with additional
labels. Removal voids the warranty. Some factory-installed labels contain information
needed to service the drive. Other labels are used to seal out dirt and contamination.
3.2.1 Serial ATA Cables and Connectors
The Serial ATA interface cable consists of four conductors in two differential pairs, plus three ground connections. The cable size may be 30 to 26
AWG with a maximum length of one meter (39.37 in). Refer to Tabl e 10 for connector pin definitions. Either end of the SATA signal cable can be
attached to the drive or host.
For direct backplane connection, the drive connectors are inserted directly into the host receptacle. The drive and the host receptacle incorporate
features that enable the direct connection to be hot pluggable and blind mateable. For installations which require cables, users can connect the
drive as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Attaching SATA Cabling
Each cable is keyed to ensure correct orientation. FireCuda drives support latching SATA connectors.
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 18
Page 20
Configuring and Mounting
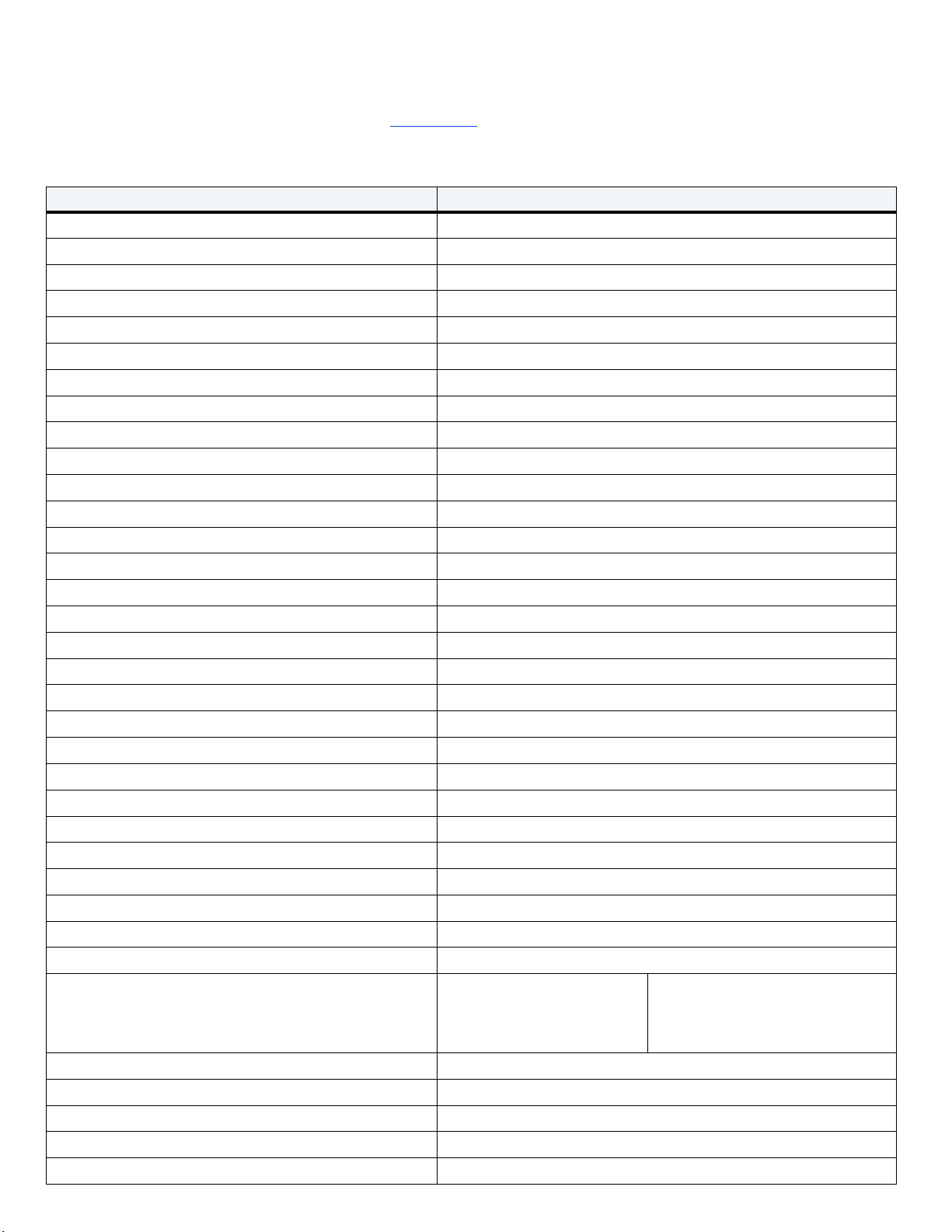
3.3 Drive Mounting
Users can mount the drive in any orientation using four screws in the side-mounting holes or four screws in the bottom-mounting holes. Refer to
Figure 4 for drive mounting dimensions. Follow these important mounting precautions when mounting the drive:
• Allow a minimum clearance of 0.030 in (0.76 mm) around the entire perimeter of the drive for cooling.
• Use only M3 x 0.5 mounting screws.
• Do not overtighten the mounting screws. Maximum torque: 4.0 in-lb (0.4519 N-m).
• Four (4) threads (0.080 in, 2.032 mm) minimum screw engagement recommended.
• Avoid excessive drive distortion when mounting. Refer to the following specifications for stiffness/deflection information:
Top cover stiffness/deflection
Operating: no performance degradation, emitted noise,
mechanical damage, or hard errors
Non-operating: no hard errors 10 mm probe: maximum 2.0kgf (instantaneous)
Figure 4 Mounting Dimensions
10 mm probe: 2.0kgf (typical)
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 19
Page 21

4.0 Ser ia l ATA (SATA) I nter face
These drives use the industry-standard Serial ATA interface that supports FIS data transfers. It supports ATA programmed input/output (PIO) modes
0–4; multiword DMA modes 0–2, and Ultra DMA modes 0–6. The drive also supports the use of the IORDY signal to provide reliable high-speed data
transfers.
For detailed information about the Serial ATA interface, refer to the Serial ATA: High Speed Serialized AT Attachment specification.
4.1 Hot-Plug Compatibility
FireCuda drives incorporate connectors which enable users to hot plug these drives in accordance with the Serial ATA: High Speed Serialized AT
Attachment specification revision 2.0. This specification can be downloaded from www.serialata.org. This device requires a COMRESET from the host
after a hotplug event.
4.2 Serial ATA Device Plug Connector Pin Definitions
Tab le 1 0 summarizes the signals on the Serial ATA interface and power connectors. Refer to the Notes below.
Table 10 Serial ATA Connector Pin Definitions
Segment Pin Function Definition
S1 Ground 2nd mate
S2 A+
S3 A-
Signal
Key and spacing separate signal and power segments
Power
S4 Ground 2nd mate
S5 B-
S6 B+
S7 Ground 2nd mate
P1 V33 3.3V power
P2 V33 3.3V power
P3 V33 3.3V power, pre-charge, 2nd mate
P4 Ground 1st mate
P5 Ground 2nd mate
P6 Ground 2nd mate
P7 V5 5V power, pre-charge, 2nd mate
P8 V5 5V power
P9 V5 5V power
P10 Ground 2nd mate
P11 Ground or LED signal If grounded, drive does not use deferred spin
P12 Ground 1st mate
P13 V12 12V power, pre-charge, 2nd mate
P14 V12 12V power
P15 V12 12V power
Differential signal pair A from Phy
Differential signal pair B from Phy
Notes
1 All pins are in a single row, with a 1.27 mm (0.050 in) pitch.
2 The comments on the mating sequence apply to the case of backplane blindmate connector only. In this case, the mating sequences are:
• the ground pins P4 and P12.
• the pre-charge power pins and the other ground pins.
• the signal pins and the rest of the power pins.
3 There are three power pins for each voltage. One pin from each voltage is used for pre-charge when installed in a blind-mate backplane
configuration.
4 All used voltage pins (V
) must be terminated.
x
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 20
Page 22
Serial ATA (SATA) Interface
4.3 Supported ATA Commands
Tab l e 1 1 lists Serial ATA standard commands that the drive supports. For a detailed description of the ATA commands, refer to the Serial ATA
International Organization: Serial ATA (Revision 2.6). Refer to www.sata-io.org.
Refer to S.M.A.R.T. commands on page 28 for details and subcommands used in the S.M.A.R.T. implementation.
Table 11 Supported ATA commands
ATA-standard commands names Command code (in hex)
Device Configuration Restore B1h/C0h
Device Configuration Freeze Lock B1h/C1h
Device Configuration Identify B1h/C2h
Device Configuration Set B1h/C3h
Download Microcode 92h
Execute Device Diagnostics 90h
Flush Cache E7h
Flush Cache Extended EAh
Identify Device ECh
Initialize Device Parameters 91h
Read Buffer E4h
Read DMA C8h
Read DMA Extended 25h
Read DMA without Retries C9h
Read Long with Retries 22h
Read Long without Retries 23h
Read Multiple C4h
Read Multiple Extended 29h
Read Native Max Address F8h
Read Native Max Address Extended 27h
Read Sectors 20h
Read Sectors Extended 24h
Read Sectors without Retries 21h
Read Verify Sectors 40h
Read Verify Sectors Extended 42h
Read Verify Sectors without Retries 41h
Seek 70h
Set Features EFh
Set Max Address F9h
Note: Individual Set Max commands are identified by the value
placed in the Set Max Features register as defined to the right.
Set Max Address Ext 37h
Set Multiple Mode C6h
S.M.A.R.T. Disable Operations B0h/D9h
S.M.A.R.T. Enable/Disable Autosave B0h/D2h
S.M.A.R.T. Enable Operations B0h/D8h
Address:
Password:
Lock:
Unlock:
Freeze Lock:
00
01
02
03
04
H
H
H
H
H
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 21
Page 23

Table 11 Supported ATA commands
ATA-standard commands names Command code (in hex)
S.M.A.R.T. Enable/Disable Auto Offline B0h/DBh
S.M.A.R.T. Enable One Attribute Modification B0h/E0h
S.M.A.R.T. Execute Offline B0h/D4h
S.M.A.R.T. Free Fall Protection Host Interface FEh
S.M.A.R.T. Read Attribute Thresholds B0h/D1h
S.M.A.R.T. Read Data B0h/D0h
S.M.A.R.T. Read Log Sector B0h/D5h
S.M.A.R.T. Return Status B0h/DAh
S.M.A.R.T. Save Attribute Values B0h/D3h
S.M.A.R.T. Write Attribute Thresholds B0h/D7h
S.M.A.R.T. Write Attribute Values B0h/E1h
S.M.A.R.T. Write Log Sector B0h/D6h
Trusted Receive 5Ch (SED only)
Trusted Receive DMA 5Dh (SED only)
Trusted Send 5Eh (SED only )
Trusted Send DMA 5Fh (S ED only)
Write Buffer E8h
Write DMA CAh
Write DMA Extended 35h
Write DMA without Retries CBh
Write Long with Retries 32h
Write Long without Retries 33h
Write Multiple C5h
Write Multiple Extended 39h
Write Sectors 30h
Write Sectors Extended 34h
ATA-standard power-management commands
Check Power Mode E5h
Idle E3h
Idle Immediate E1h
Sleep E6h
Standby E2h
Standby Immediate E0h
ATA-standard security commands
Security Set Password F1h
Security Unlock F2h
Security Erase Prepare F3h
Security Erase Unit F4h
Security Freeze Lock F5h
Security Disable Password F6h
,
31h
Serial ATA (SATA) Interface
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 22
Page 24

Serial ATA (SATA) Interface
4.3.1 Identify Device command
The Identify Device command (command code ECH) transfers information about the drive to the host following power up. The data is organized as
a single 512-byte block of data, whose contents are shown in Tab le 1 2. All reserved bits or words should be set to zero. Parameters listed with an “x”
are drive-specific or vary with the state of the drive. Refer to Drive Specifications on page 6 for default parameter settings.
The following commands contain drive-specific features that may not be included in the Serial ATA specification.
Table 12 Identify Device command
Wor d Description Value
Configuration information:
0
1 Number of logical cylinders 16,383
2 Specific configuration C837H
3 Number of logical heads 16
• Bit 15: 0 = ATA; 1 = ATAPI
• Bit 7: removable media
• Bit 6: removable controller
• Bit 0: reserved
0C5A
H
4 Retired 0000
5 Retired 0000
6 Number of logical sectors per logical track: 63 003F
7–9 Retired 0000
10–19 Serial number: (20 ASCII characters, 0000H = none) ASCII
20 Retired 0000
21 Retired 8000
22 Obsolete 0004
23–26
27–46
47
Firmware revision:
(8 ASCII character string, padded with blanks to end of string)
Drive model number:
(40 ASCII characters, padded with blanks to end of string)
(Bits 7–0)
Maximum sectors per interrupt on Read multiple and Write multiple (16)
x.xx
ST2000LX001
ST1000LX015
ST500LX025
8010
48 Trusted Computing Feature set options 4001
49 Standard Standby timer, IORDY supported and may be disabled 2F00
50 Capabilities 4000
51 PIO data-transfer cycle timing mode 0200
52 Retired 0200
53 Words 54–58, 64–70 and 88 are valid 0007
54 Number of current logical cylinders xxxx
55 Number of current logical heads xxxx
56 Number of current logical sectors per logical track xxxx
57–58 Current capacity in sectors xxxx
59
Number of sectors transferred during a
Read Multiple or Write Multiple command
xxxx
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
Total number of user-addressable sectors
60–61
This field contains a value that is one greater than the total number of
user-addressable sectors. The maximum value that shall be placed in this field is
0FFFFFFFh. The 0FFFFFFFh value applies to all capacities over 137GB
ST2000LX001 = 0FFFFFFFh
ST1000LX015 = 0FFFFFFFh
ST500LX025 = 0FFFFFFFh
(see Section 2.1, Formatted Capacity for related information).
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 23
Page 25
Table 12 Identify Device command
Wor d Description Value
Serial ATA (SATA) Interface
62 Retired 0000
63
Multiword DMA active and modes supported
(see note following this table)
xx07
64 Advanced PIO modes supported (modes 3 and 4 supported) 0003
65 Minimum multiword DMA transfer cycle time per word (120 ns) 0078
66 Recommended multiword DMA transfer cycle time per word (120 ns) 0078
67 Minimum PIO cycle time without IORDY flow control (240 ns) 0078
68 Minimum PIO cycle time with IORDY flow control (120 ns) 0078
xx1x
or
xx9x
69
Additional Supported bits
Bit 4 means Device Encrypts All User Data on the device.
Bit 7 means IEEE1667 protocol is supported.
70–74 ATA-reserved 0000
75 Queue depth 001F
76 Serial ATA capabilities 0D06
77 ATA-reserved 0000
78 Serial ATA features supported 0048
79 Serial ATA features enabled 0048
80 Major version number 01F0
81 Minor version number 0029
82 Command sets supported 746B
83 Command sets supported 7D69
84 Command sets support extension 61E3
85 Command sets enabled 7469
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
86 Command sets enabled BC49
87 Command sets enable extension 61E3
88 Ultra DMA support and current mode (see note following this table) xx7F
89 Security erase time xxxx
90 Enhanced security erase time xxxx
91 Current APM values 8080
92 Master password revision code FFFE
93 Hardware reset value (see description following this table) xxxx
94 Auto acoustic management setting xxxx
95 Stream Min. Request Size 0000
96 Streaming Transfer Time - DMA 0000
97 Streaming Access Latency - DMA and PIO 0000
98-99 Streaming Performance Granularity 0000
100–103
Total number of user-addressable LBA sectors available
(see Section 3.2, Configuring the Drive for related information)
These words are required for drives that support the 48-bit addressing
feature. Maximum value: 0000FFFFFFFFFFFFh.
ST2000LX001 = 3,907,029,168
ST1000LX015 = 1,953,525,168
ST500LX025 = 1,953,525,168
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 24
Page 26
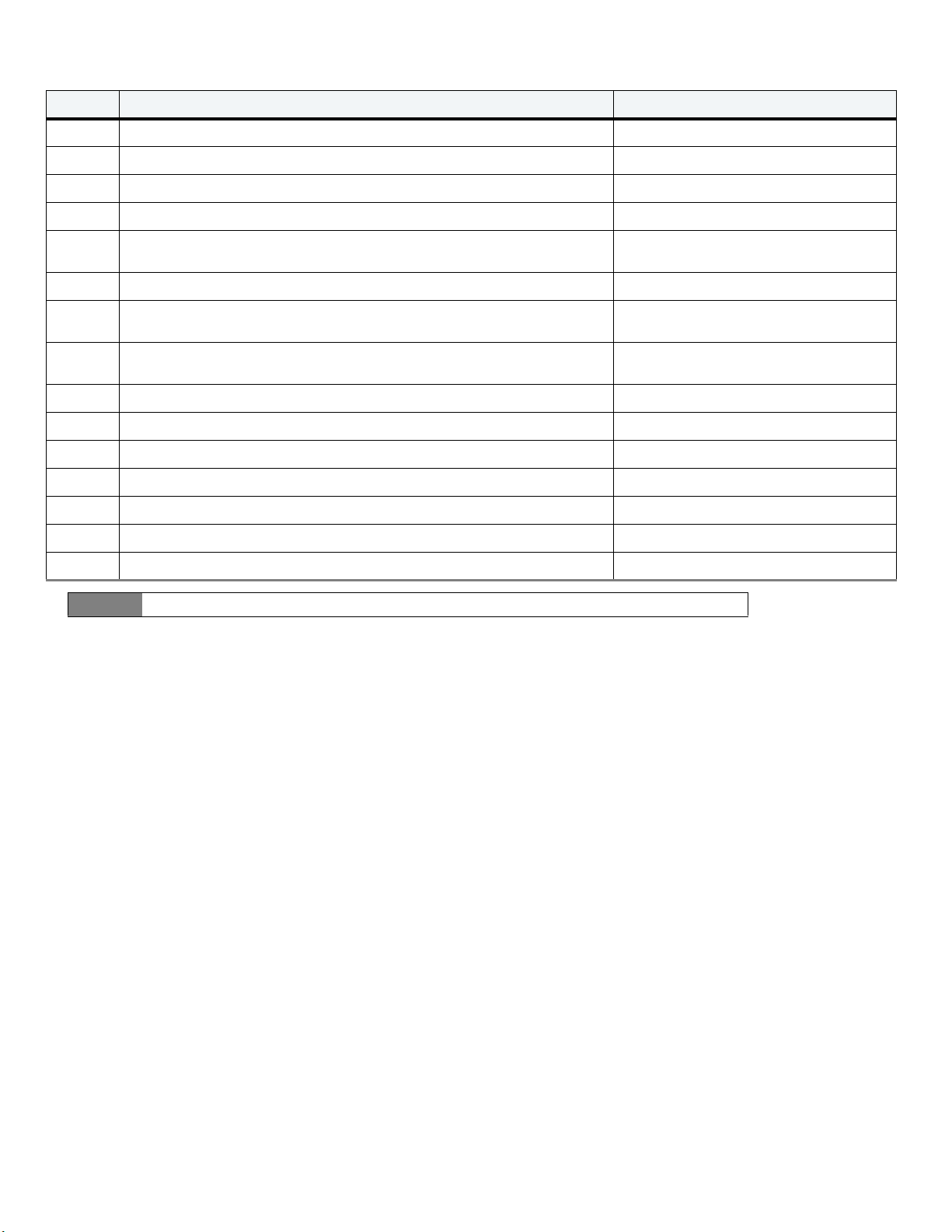
Table 12 Identify Device command
Wor d Description Value
Serial ATA (SATA) Interface
104 Streaming Transfer Time - PIO 0000
105 Reserved 0000
106 Physical sector size / Logical sector size 6003
107 Seagate reserved 0000
108-111
The mandatory value of the world wide name (WWN) for the drive. NOTE: This field
is valid if word 84, bit 8 is set to 1 indicating 64-bit WWN support.
Each drive will have a unique value.
112-118 ATA-reserved 0000
119 Free Fall Protection support (bit 5)
120 Free Fall Protection enable/disable (bit 5)
1 = Free Fall Protection supported
0 = Free Fall Protection not supported
1 = Free Fall Protection feature is enabled
0 = Free Fall Protection feature is disabled
121–127 ATA-reserved 0000
128 Security status 0021
129–159 Seagate-reserved xxxx
160–221 ATA-reserved 0000
222 Transport major version number 101F
223–254 ATA-reserved 0000
255 Integrity word xxA5
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
Note
See the bit descriptions below for words 63, 88 and 93 of the Identify Drive data. (on next page)
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 25
Page 27

Table 13 Bit Descriptions
Description (if bit is set to 1)
Bit Word 63
0 Multiword DMA mode 0 is supported.
1 Multiword DMA mode 1 is supported.
2 Multiword DMA mode 2 is supported.
8 Multiword DMA mode 0 is currently active.
9 Multiword DMA mode 1 is currently active.
10 Multiword DMA mode 2 is currently active.
Bit Word 88
0 Ultra DMA mode 0 is supported.
1 Ultra DMA mode 1 is supported.
2 Ultra DMA mode 2 is supported.
3 Ultra DMA mode 3 is supported.
Serial ATA (SATA) Interface
4 Ultra DMA mode 4 is supported.
5 Ultra DMA mode 5 is supported.
6 Ultra DMA mode 6 is supported.
8 Ultra DMA mode 0 is currently active.
9 Ultra DMA mode 1 is currently active.
10 Ultra DMA mode 2 is currently active.
11 Ultra DMA mode 3 is currently active.
12 Ultra DMA mode 4 is currently active.
13 Ultra DMA mode 5 is currently active.
14 Ultra DMA mode 6 is currently active.
Bit Word 93
13 1 = 80-conductor cable detected, CBLID above VIH
0 = 40-conductor cable detected, CBLID below VIL
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 26
Page 28

Serial ATA (SATA) Interface
4.3.2 Set Features command
This command controls the implementation of various features that the drive supports. When the drive receives this command, it sets BSY, checks
the contents of the Features register, clears BSY and generates an interrupt. If the value in the register does not represent a feature that the drive
supports, the command is aborted. Power-on default has the read look-ahead and write caching features enabled.
The acceptable values for the Features register are defined as follows:
Table 14 Set Features command values
02
03
Enable write cache (default).
H
Set transfer mode (based on value in Sector Count register).
H
Sector Count register values:
00
Set PIO mode to default (PIO mode 2).
H
01
Set PIO mode to default and disable IORDY (PIO mode 2).
H
08
PIO mode 0
H
09
PIO mode 1
H
0A
PIO mode 2
H
0B
PIO mode 3
H
0C
PIO mode 4 (default)
H
20
Multiword DMA mode 0
H
21
Multiword DMA mode 1
H
22
Multiword DMA mode 2
H
40
Ultra DMA mode 0
H
41
Ultra DMA mode 1
H
55
82
AA
C1
F1
42
Ultra DMA mode 2
H
43
Ultra DMA mode 3
H
44
Ultra DMA mode 4
H
45
Ultra DMA mode 5
H
46
Ultra DMA mode 6
H
Disable read look-ahead (read cache) feature.
H
Disable write cache
H
Enable read look-ahead (read cache) feature (default).
H
Disable the Free Fall Protection feature (41H above enables the Free Fall Protection feature)
H
Report full capacity available
H
Note
At power-on, or after a hardware or software reset, the default values of the features are as indicated above
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 27
Page 29

Serial ATA (SATA) Interface
4.3.3 S.M.A.R.T. commands
S.M.A.R.T. provides near-term failure prediction for disk drives. When S.M.A.R.T. is enabled, the drive monitors predetermined drive attributes that
are susceptible to degradation over time. If self-monitoring determines that a failure is likely, S.M.A.R.T. makes a status report available to the host.
Not all failures are predictable. S.M.A.R.T. predictability is limited to the attributes the drive can monitor. For more information on S.M.A.R.T.
commands and implementation, see the Draft ATA- 5 St and ard.
SeaTools diagnostic software activates a built-in drive self-test (DST S.M.A.R.T. command for D4
diagnostic software ships with all new drives and is also available at: http://www.seagate.com/support/downloads/seatools/.
This drive is shipped with S.M.A.R.T. features disabled. Users must have a recent BIOS or software package that supports S.M.A.R.T. to enable this
feature. The table below shows the S.M.A.R.T. command codes that the drive uses.
Table 15 S.M.A.R.T. Commands
) that eliminates unnecessary drive returns. The
H
Code in features register S.M.A.R.T. command
D0
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D8
D9
DA
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
S.M.A.R.T. Read Data
S.M.A.R.T. Enable/Disable Attribute Autosave
S.M.A.R.T. Save Attribute Values
S.M.A.R.T. Execute Off-line Immediate (runs DST)
S.M.A.R.T. Read Log Sector
S.M.A.R.T. Write Log Sector
S.M.A.R.T. Enable Operations
S.M.A.R.T. Disable Operations
S.M.A.R.T. Return Status
Note
If an appropriate code is not written to the Features Register, the
command is aborted and 0x 04 (abort) is written to the Error register.
Seagate FireCuda Product Manual, Rev. C 28
Page 30

Seagate Technology LLC
AMERICAS Seagate Technology LLC 10200 South De Anza Boulevard, Cupertino, California 95014, United States, 408-658-1000
ASIA/PACIFIC Seagate Singapore International Headquarters Pte. Ltd. 7000 Ang Mo Kio Avenue 5, Singapore 569877, 65-6485-3888
EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Seagate Technology SAS 16-18 rue du Dôme, 92100 Boulogne-Billancourt, France, 33 1-4186 10 00
Publication Number: 1007802299, Rev. C
August 2016
 Loading...
Loading...