Page 1

Product Manual
Constellation® ES.3 SAS
Standard models
ST4000NM0023
ST3000NM0023
ST2000NM0023
ST1000NM0023
Self-Encrypting drive models
ST4000NM0043
ST3000NM0043
ST2000NM0043
ST1000NM0043
SED (FIPS 140-2) models
ST4000NM0063
ST3000NM0063
ST2000NM0063
ST1000NM0063
100671510
Rev. C
February 2014
Page 2
Document Revision History
Revision Date Description of changes
Rev. A 10/05/2011 Initial release.
Rev. B 10/31/2011 37.
Rev. C 02/13/2014 fc, 2, 9 & 53.
© 2014 Seagate Technology LLC. All rights reserved.
Publication number: 100671510, Rev. C February 2014
Seagate, Seagate Technology and the Wave logo are registered trademarks of Seagate Technology LLC in the United States and/or
other countries. Constellation ES and SeaTools are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Seagate Technology LLC or one of
its affiliated companies in the United States and/or other countries. The FIPS logo is a certification mark of NIST, which does not imply
product endorsement by NIST, the U.S., or Canadian governments.All other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of
their respective owners.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without written permission of Seagate Technology LLC.
Call 877-PUB-TEK1 (877-782-8351) to request permission.
When referring to drive capacity, one gigabyte, or GB, equals one billion bytes and one terabyte, or TB, equals one trillion bytes. Your
computer’s operating system may use a different standard of measurement and report a lower capacity. In addition, some of the listed
capacity is used for formatting and other functions, and thus will not be available for data storage. Actual quantities will vary based on
various factors, including file size, file format, features and application software. Actual data rates may vary depending on operating
environment and other factors. The export or re-export of hardware or software containing encryption may be regulated by the U.S.
Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (for more information, visit www.bis.doc.gov), and controlled for import
and use outside of the U.S. Seagate reserves the right to change, without notice, product offerings or specifications.
Page 3

Contents
Seagate® Technology Support Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.0 Scope. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2.0 Applicable standards and reference documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1 Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1.1 Electromagnetic compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1.2 Electromagnetic compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.1.3 European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.1.4 China Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.2 Reference documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
3.0 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.1 Standard features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.2 Media description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.3 Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.4 Reliability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.5 Formatted capacities. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.6 Programmable drive capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.7 Factory-installed options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
4.0 Performance characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.1 Internal drive characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.1.1 Format command execution time for 512-byte sectors (minutes) . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.1.2 General performance characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.2 Start/stop time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.3 Prefetch/multi-segmented cache control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.4 Cache operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.4.1 Caching write data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.4.2 Prefetch operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
5.0 Reliability specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.1 Error rates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.1.1 Recoverable Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.1.2 Unrecoverable Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.1.3 Seek errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.1.4 Interface errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.2 Reliability and service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.2.1 Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) and Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) . . . . . 13
5.2.2 Hot plugging the drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.2.3 S.M.A.R.T. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.2.4 Thermal monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.2.5 Drive Self Test (DST) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.2.6 Product warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
6.0 Physical/electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1 PowerChoiceTM power management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1.1 PowerChoice reporting methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.2 AC power requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.3 DC power requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.3.1 Conducted noise immunity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.3.2 Power sequencing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.3.3 Current profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Constellation ES.3 SAS Product Manual, Rev. C
Page 4

Contents
6.4 Power dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.5 Environmental limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
6.5.1 Temperature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
6.5.2 Relative humidity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
6.5.3 Effective altitude (sea level) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
6.5.4 Shock and vibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
6.5.5 Acoustics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
6.5.6 Air cleanliness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
6.5.7 Corrosive environment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
6.5.8 Electromagnetic susceptibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
6.6 Mechanical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
7.0 About FIPS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
8.0 About self-encrypting drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.1 Data encryption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.2 Controlled access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.2.1 Admin SP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.2.2 Locking SP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.2.3 Default password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.3 Random number generator (RNG). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.4 Drive locking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.5 Data bands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.6 Cryptographic erase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.7 Authenticated firmware download. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.8 Power requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.9 Supported commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.10 Sanitize - CRYPTOGRAPHIC ERASE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.11 RevertSP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
9.0 Defect and error management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
9.1 Drive internal defects/errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
9.2 Drive error recovery procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
9.3 SAS system errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
9.4 Background Media Scan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
9.5 Media Pre-Scan. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
9.6 Deferred Auto-Reallocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
9.7 Idle Read After Write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
9.8 Protection Information (PI). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
9.8.1 Levels of PI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.8.2 Setting and determining the current Type Level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.8.3 Identifying a Protection Information drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
10.0 Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
10.1 Drive orientation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
10.2 Cooling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
10.3 Drive mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
10.4 Grounding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
11.0 Interface requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
11.1 SAS features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
11.1.1 task management functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
11.1.2 task management responses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
11.2 Dual port support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Constellation ES.3 SAS Product Manual, Rev. C
Page 5

Contents
11.3 SCSI commands supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
11.3.1 Inquiry data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
11.3.2 Mode Sense data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
11.4 Miscellaneous operating features and conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
11.4.1 SAS physical interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
11.4.2 Physical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
11.4.3 Connector requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
11.4.4 Electrical description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
11.4.5 Pin descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
11.4.6 SAS transmitters and receivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
11.4.7 Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
11.5 Signal characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
11.5.1 Ready LED Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
11.5.2 Differential signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
11.6 SAS-2 Specification Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
11.7 Additional information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Constellation ES.3 SAS Product Manual, Rev. C
Page 6

Seagate® Technology Support Services
For information regarding online support and services, visit http://www.seagate.com/www/en-us/about/contact_us/
Available services include:
• Presales & Technical support
• Global Support Services telephone numbers & business hours
• Authorized Service Centers
For information regarding Warranty Support, visit http://www.seagate.com/support/warranty-and-returns/
For information regarding data recovery services, visit http://www.seagate.com/services-software/data-recovery-services/
For Seagate OEM and Distribution partner portal, visit https://direct.seagate.com/portal/system
For Seagate reseller portal, visit http://spp.seagate.com
Constellation ES.3 SAS Product Manual, Rev. C 1
Page 7
1.0 SCOPE
This manual describes Seagate Technology® LLC, Constellation® ES.3 SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) disk drives.
Constellation ES.3 drives support the SAS Protocol specifications to the extent described in this manual. The SAS Interface Manual (part
number 100293071) describes the general SAS characteristics of this and other Seagate SAS drives. The Self-Encrypting Drive
Reference Manual, part number 100515636, describes the interface, general operation, and security features available on Self-Encrypting
Drive models.
Product data communicated in this manual is specific only to the model numbers listed in this manual. The data listed in this manual may
not be predictive of future generation specifications or requirements. If you are designing a system which will use one of the models
listed or future generation products and need further assistance, please contact your Field Applications Engineer (FAE) or our global
support services group as shown in See “Seagate® Technology Support Services” on page 1.
Unless otherwise stated, the information in this manual applies to standard and Self-Encrypting Drive models.
Standard models
ST4000NM0023 ST4000NM0043 ST4000NM0063
ST3000NM0023 ST3000NM0043 ST3000NM0063
ST2000NM0023 ST2000NM0043 ST2000NM0063
ST1000NM0023 ST1000NM0043 ST1000NM0063
SELF-ENCRYPTING DRIVE
(SED)
FIPS 140-2 LEVEL 2
(REVIEW PENDING)
Previous generations of Seagate Self-Encrypting Drive models were called Full Disk
NOTE
Encryption (FDE) models before a differentiation between drive-based encryption and
other forms of encryption was necessary.
.
The Self-Encrypting Drive models indicated on the cover of this product manual have
NOTE
provisions for “Security of Data at Rest” based on the standards defined by the Trusted
Computing Group (see www.trustedcomputinggroup.org).
For more information on FIPS 140-2 Level 2 certification see Section 7.0 on page 38.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 2
Page 8

2.0 APPLICABLE STANDARDS AND REFERENCE DOCUMENTATION
The drives documented in this manual have been developed as system peripherals to the highest standards of design and construction.
The drives depends on host equipment to provide adequate power and environment for optimum performance and compliance with
applicable industry and governmental regulations. Special attention must be given in the areas of safety, power distribution, shielding,
audible noise control, and temperature regulation. In particular, the drive must be securely mounted to guarantee the specified
performance characteristics. Mounting by bottom holes must meet the requirements of Section 10.3.
2.1 STANDARDS
The Constellation ES.3 family complies with Seagate standards as noted in the appropriate sections of this manual and the Seagate SAS
Interface Manual, part number 100293071.
The drives are recognized in accordance with UL 60950-1 as tested by UL, CSA 60950-1 as tested by CSA, and EN60950-1 as tested by
TUV.
The security features of Self-Encrypting Drive models are based on the “TCG Storage Architecture Core Specification” and the “TCG
Storage Workgroup Security Subsystem Class: Enterprise_A” specification with additional vendor-unique features as noted in this
product manual.
2.1.1 Electromagnetic compatibility
The drive, as delivered, is designed for system integration and installation into a suitable enclosure prior to use. The drive is supplied as a
subassembly and is not subject to Subpart B of Part 15 of the FCC Rules and Regulations nor the Radio Interference Regulations of the
Canadian Department of Communications.
The design characteristics of the drive serve to minimize radiation when installed in an enclosure that provides reasonable shielding. The
drive is capable of meeting the Class B limits of the FCC Rules and Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications when
properly packaged; however, it is the user’s responsibility to assure that the drive meets the appropriate EMI requirements in their
system. Shielded I/O cables may be required if the enclosure does not provide adequate shielding. If the I/O cables are external to the
enclosure, shielded cables should be used, with the shields grounded to the enclosure and to the host controller.
2.1.1.1 Electromagnetic susceptibility
As a component assembly, the drive is not required to meet any susceptibility performance requirements. It is the responsibility of those
integrating the drive within their systems to perform those tests required and design their system to ensure that equipment operating in the
same system as the drive or external to the system does not adversely affect the performance of the drive. See Table 2, DC power
requirements.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 3
Page 9

2.1.2 Electromagnetic compliance
Seagate uses an independent laboratory to confirm compliance with the directives/standards for CE Marking and C-Tick Marking. The
drive was tested in a representative system for typical applications. The selected system represents the most popular characteristics for
test platforms. The system configurations include:
• Typical current use microprocessor
• Keyboard
• Monitor/display
• Printer
• Mouse
Although the test system with this Seagate model complies with the directives/standards, we cannot guarantee that all systems will
comply. The computer manufacturer or system integrator shall confirm EMC compliance and provide the appropriate marking for their
product.
Electromagnetic compliance for the European Union
If this model has the CE Marking it complies with the European Union requirements of the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive
2004/108/EC as put into place on 20 July 2007.
Australian C-Tick
If this model has the C-Tick Marking it complies with the Australia/New Zealand Standard AS/NZ CISPR22 and meets the
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Framework requirements of Australia’s Spectrum Management Agency (SMA).
Korean KCC
If these drives have the Korean Communications Commission (KCC) logo, they comply with paragraph 1 of Article 11 of the
Electromagnetic Compatibility control Regulation and meet the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Framework requirements of the
Radio Research Laboratory (RRL) Communications Commission, Republic of Korea.
These drives have been tested and comply with the Electromagnetic Interference/Electromagnetic Susceptibility (EMI/EMS) for Class B
products. Drives are tested in a representative, end-user system by a Korean-recognized lab.
• Family name: Constellation ES.3 SAS
• Certificate number: KCC-REM-STX-Constell-ES3
• Manufacturing date: (Date of Certification) 2012-July-16
• Manufacturer/nationality: USA, Singapore and China
Taiwanese BSMI
If this model has two Chinese words meaning “EMC certification” followed by an eight digit identification number, as a Marking, it
complies with Chinese National Standard (CNS) 13438 and meets the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Framework requirements of
the Taiwanese Bureau of Standards, Metrology, and Inspection (BSMI).
2.1.3 European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS)
The European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive, restricts the presence of chemical substances, including
Lead, Cadmium, Mercury, Hexavalent Chromium, PBB and PBDE, in electronic products, effective July 2006. This drive is
manufactured with components and materials that comply with the RoHS Directive.
A number of parts and materials in Seagate products are procured from external suppliers. We rely on the representations of our suppliers
regarding the presence of RoHS substances in these parts and materials. Our supplier contracts require compliance with our chemical
substance restrictions, and our suppliers document their compliance with our requirements by providing material content declarations for
all parts and materials for the disk drives documented in this publication. Current supplier declarations include disclosure of the inclusion
of any RoHS-regulated substance in such parts or materials.
Seagate also has internal systems in place to ensure ongoing compliance with the RoHS Directive and all laws and regulations which
restrict chemical content in electronic products. These systems include standard operating procedures that ensure that restricted
substances are not utilized in our manufacturing operations, laboratory analytical validation testing, and an internal auditing process to
ensure that all standard operating procedures are complied with.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 4
Page 10
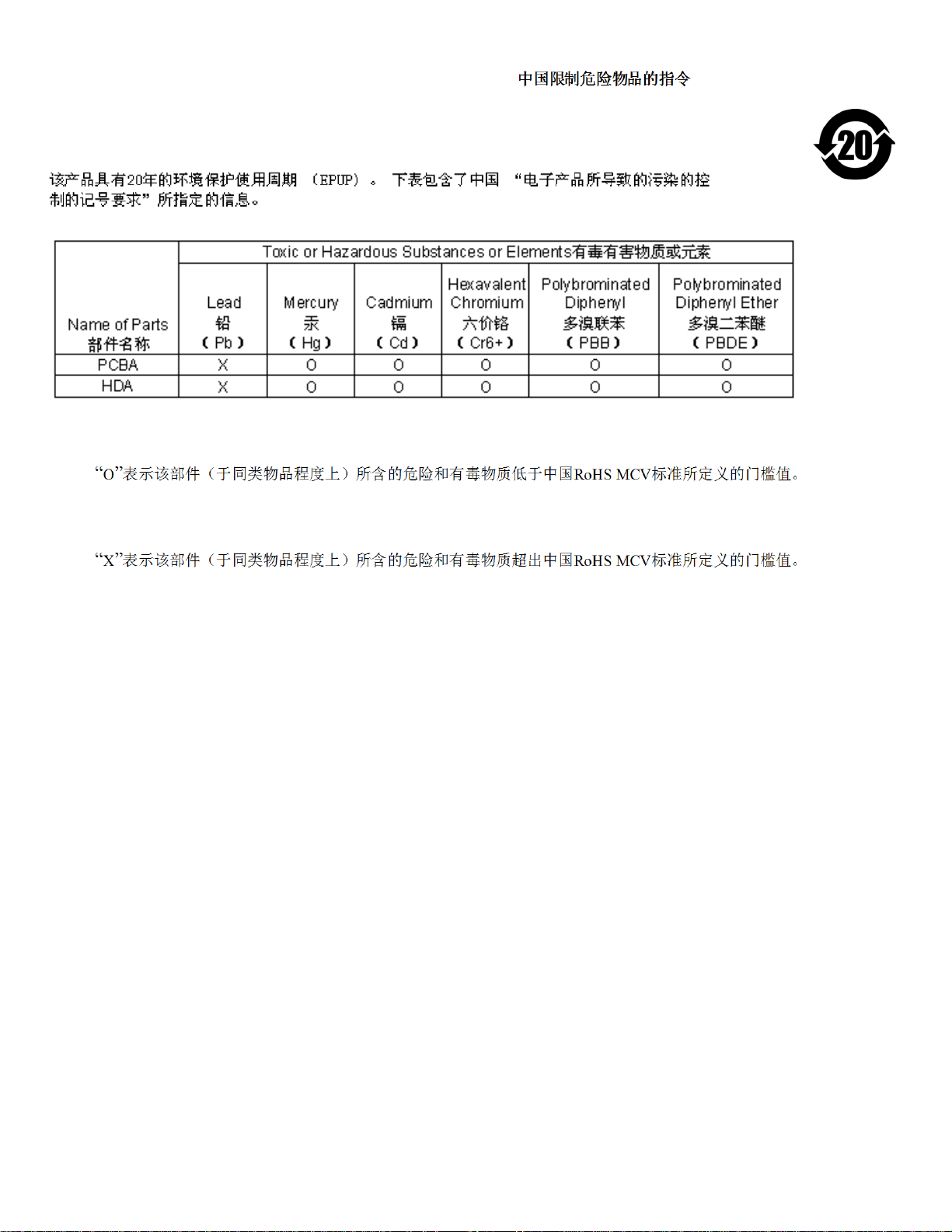
2.1.4 China Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive
This product has an Environmental Protection Use Period (EPUP) of 20 years. The following table contains information
mandated by China's "Marking Requirements for Control of Pollution Caused by Electronic Information Products" Standard.
"O" indicates the hazardous and toxic substance content of the part (at the homogenous material level) is lower than the threshold defined
by the China RoHS MCV Standard.
"X" indicates the hazardous and toxic substance content of the part (at the homogenous material level) is over the threshold defined by
the China RoHS MCV Standard.
2.2 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS
SAS Interface Manual
Seagate part number: 100293071
SCSI Commands Reference Manual
Seagate part number: 100293068
ANSI SAS Documents
SFF-8323 3.5” Drive Form Factor with Serial Connector
SFF-8460 HSS Backplane Design Guidelines
SFF-8470 Multi Lane Copper Connector
SFF-8482 SAS Plug Connector
ANSI INCITS.xxx Serial Attached SCSI (SAS-2) Standard (T10/1562-D)
ISO/IEC 14776-xxx SCSI Architecture Model-3 (SAM-4) Standard (T10/1561-D)
ISO/IEC 14776-xxx SCSI Primary Commands-3 (SPC-4) Standard (T10/1416-D)
ISO/IEC 14776-xxx SCSI Block Commands-2 (SBC-3) Standard (T10/1417-D)
ANSI Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) Documents
X3.270-1996 (SCSI-3) Architecture Model
Trusted Computing Group (TCG) Documents (apply to Self-Encrypting Drive models only)
TCG Storage Architecture Core Specification, Rev. 1.0
TCG Storage Security Subsystem Class Enterprise Specification, Rev. 1.0
Specification for Acoustic Test Requirement and Procedures
Seagate part number: 30553-001
In case of conflict between this document and any referenced document, this document takes precedence.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 5
Page 11

3.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Constellation ES.3 drives provide high performance, high capacity data storage for a variety of systems including engineering
workstations, network servers, mainframes, and supercomputers. The Serial Attached SCSI interface is designed to meet next-generation
computing demands for performance, scalability, flexibility and high-density storage requirements.
Constellation ES.3 drives are random access storage devices designed to support the Serial Attached SCSI Protocol as described in the
ANSI specifications, this document, and the SAS Interface Manual (part number 100293071) which describes the general interface
characteristics of this drive. Constellation ES.3 drives are classified as intelligent peripherals and provide level 2 conformance (highest
level) with the ANSI SCSI-1 standard. The SAS connectors, cables and electrical interface are compatible with Serial ATA (SATA),
giving future users the choice of populating their systems with either SAS or SATA hard disk drives. This allows you to continue to
leverage your existing investment in SCSI while gaining a 6Gb/s serial data transfer rate.
The Self-Encrypting Drive models indicated on the cover of this product manual have provisions for “Security of Data at Rest” based on
the standards defined by the Trusted Computing Group
(see www.trustedcomputinggroup.org).
The head and disk assembly (HDA) is sealed at the factory. Air recirculates within the HDA through a non-replaceable filter to maintain
a contamination-free HDA environment.
Never disassemble the HDA and do not attempt to service items in the sealed
NOTE
enclosure (heads, media, actuator, etc.) as this requires special facilities. The drive
does not contain user-replaceable parts. Opening the HDA for any reason voids your
warranty.
Constellation ES.3 drives use a dedicated load/unload zone at the outermost radius of the media to eliminate the possibility of destroying
or degrading data by landing in the data zone. The heads automatically go to the ramp load/unload when power is removed from the
drive.
An automatic shipping lock prevents potential damage to the heads and discs that results from movement during shipping and handling.
The shipping lock disengages and the head load process begins when power is applied to the drive.
Constellation ES.3 drives decode track 0 location data from the servo data embedded on each surface to eliminate mechanical transducer
adjustments and related reliability concerns.
The drives also use a high-performance actuator assembly with a low-inertia, balanced, patented, straight arm design that provides
excellent performance with minimal power dissipation.
NOTE
Seagate recommends validating your configuration with the selected HBA/RAID
controller manufacturer to ensure full 3TB and 4TB capacity capabilities.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 6
Page 12

3.1 STANDARD FEATURES
Constellation ES.3 drives have the following standard features:
• Perpendicular recording technology
• 1.5 / 3.0 / 6.0 Gb Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) interface
• Integrated dual port SAS controller supporting the SCSI protocol
• Support for SAS expanders and fanout adapters
• Firmware downloadable using the SAS interface
• 128 - deep task set (queue)
• Supports up to 32 initiators
• Jumperless configuration.
• User-selectable logical block size (512, 520 or 528 bytes per logical block).
• Industry standard 3.5-in dimensions
• Programmable logical block reallocation scheme
• Flawed logical block reallocation at format time
• Programmable auto write and read reallocation
• Reallocation of defects on command (Post Format)
• ECC maximum burst correction length of 400 bits
• No preventive maintenance or adjustments required
• Embedded servo design
• Dedicated head load/unload zone
• Self diagnostics performed when power is applied to the drive
• Vertical, horizontal, or top down mounting
• 128 MB data buffer (see Section 4.4).
• Drive Self Test (DST)
• Background Media Scan (BMS)
• Seagate RAID Rebuild
• Idle Read After Write (IRAW)
• Power Save
TM
Constellation® ES.3 SAS Self-Encrypting Drive models have the following additional features:
• Automatic data encryption/decryption
• Controlled access
• Random number generator
• Drive locking
• 16 independent data bands
• Cryptographic erase of user data for a drive that will be repurposed or scrapped
• Authenticated firmware download
3.2 MEDIA DESCRIPTION
The media used on the drive has a aluminum substrate coated with a thin film magnetic material, overcoated with a proprietary protective
layer for improved durability and environmental protection.
3.3 PERFORMANCE
• Programmable multi-segmentable cache buffer
• 600MB/s maximum instantaneous data transfers.
• 7200 RPM spindle. Average latency = 4.16ms
• Background processing of queue
• Supports start and stop commands (spindle stops spinning)
• Adaptive seek velocity; improved seek performance
.
NOTE
There is no significant performance difference between Self-Encrypting Drive and
standard (non-Self-Encrypting Drive) models.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 7
Page 13
3.4 RELIABILITY
• Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) of 0.63%
• Mean time between failures (MTBF) of 1,400,000 hours
• Balanced low mass rotary voice coil actuator
• Incorporates industry-standard Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.)
• 5-year warranty
3.5 FORMATTED CAPACITIES
Standard OEM models are formatted to 512 bytes per block. The block size is selectable at format time and must be a multiple of 4 bytes.
Users having the necessary equipment may modify the data block size before issuing a format command and obtain different formatted
capacities than those listed.
To provide a stable target capacity environment and at the same time provide users with flexibility if they choose, Seagate recommends
product planning in one of two modes:
1. Seagate designs specify capacity points at certain block sizes that Seagate guarantees current and future products will meet. We recommend customers use this capacity in their project planning, as it ensures a stable operating point with backward and forward compatibility from generation to generation. The current guaranteed operating points for this product are
SECTOR
SIZE
512
520
528
7,814,037,168 1D1C0BEB0 5,860,533,168 15D50A3B0 3,907,029,168 E8E088B0 1,953,525,168 74706DB0
7,648,717,976 1C7E62C98 5,736,538,480 155ECA170 3,824,358,992 E3F31650 1,923,076,936 729FD348
7,438,330,376 1BB5BEA08 5,578,747,784 14C84EF88 3,719,165,192 DDADF508 1,876,331,336 6FD68B48
4TB models 3TB models 2TB models 1TB models
Decimal Hex Decimal Hex Decimal Hex Decimal Hex
3.6 PROGRAMMABLE DRIVE CAPACITY
Using the Mode Select command, the drive can change its capacity to something less than maximum. See the Mode Select (6) parameter
list table in the SAS Interface Manual, part number 100293071. A value of zero in the Number of Blocks field indicates that the drive will
not change the capacity it is currently formatted to have. A number other than zero and less than the maximum number of LBAs in the
Number of Blocks field changes the total drive capacity to the value in the Number of Blocks field. A value greater than the maximum
number of LBAs is rounded down to the maximum capacity.
3.7 FACTORY-INSTALLED OPTIONS
You may order the following items which are incorporated at the manufacturing facility during production or packaged before shipping.
Some of the options available are (not an exhaustive list of possible options):
• Other capacities can be ordered depending on sparing scheme and sector size requested.
• Single-unit shipping pack. The drive is normally shipped in bulk packaging to provide maximum protection against transit damage.
Units shipped individually require additional protection as provided by the single unit shipping pack. Users planning single unit distribution should specify this option.
• The Safety and Regulatory Agency Specifications, part number 75789512, is usually included with each standard OEM drive shipped,
but extra copies may be ordered.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 8
Page 14

4.0 PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
This section provides detailed information concerning performance-related characteristics and features of Constellation ES.3 drives.
4.1 INTERNAL DRIVE CHARACTERISTICS
ST4000NM0023 ST3000NM0023 ST2000NM0023 ST1000NM0023
ST4000NM0043 ST3000NM0043 ST2000NM0043 ST1000NM0043
ST4000NM0063 ST3000NM0063 ST2000NM0063 ST1000NM0063
Drive capacity 4TB 3TB 2TB 1TB (fomatted, rounded off value)
Read/write data heads 10 8 5 3
Bytes/track 1,668,096 Bytes (average, rounded off values)
Bytes/surface 400,000 MB (unfomatted, rounded off values)
Tracks/surface (total) 320,800 Tracks (user accessible)
Tracks/in 305,000 TPI (average)
Peak bits/in 1,904,000 BPI
Areal density 578 Gb/in2
Internal data rate 2210 Mb/s (max)
Disk rotation speed 7200 RPM
Avg rotational latency 4.16 ms
4.1.1 Format command execution time for 512-byte sectors (minutes)
4TB models 3TB models 2TB models 1TB models
Maximum (with verify)
Maximum (without verify)
917 693 456 263
455 347 228 132
Execution time measured from receipt of the last byte of the Command Descriptor Block (CDB) to the request for a Status Byte Transfer
to the Initiator (excluding connect/disconnect).
When changing sector sizes, the format times shown above may need to be increased by 30 minutes.
4.1.2 General performance characteristics
Minimum sector interleave 1 to 1
Maximum Internal data rate* 2.21 Gb/s
Sustained transfer rate 83 to 175 MB/s **
SAS Interface maximum instantaneous transfer rate 600MB/s* per port
Logical block sizes
512 (default), 520 or 528.
Read/write consecutive sectors on a track Yes
Flaw reallocation performance impact (for flaws reallocated at format time using the
spare sectors per sparing zone reallocation scheme.)
(dual port = 1200MB/s*)
Negligible
Average rotational latency 4.16ms
*Assumes no errors and no relocated logical blocks. Rate measured from the start of the first logical block transfer to or
from the host.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 9
Page 15

4.2 START/STOP TIME
The drive accepts the commands listed in the SAS Interface Manual less than 3 seconds after DC power has been applied.
If the drive receives a NOTIFY (ENABLE SPINUP) primitive through either port and has not received a START STOP UNIT command
with the START bit equal to 0, the drive becomes ready for normal operations within 30 seconds (excluding the error recovery
procedure).
If the drive receives a START STOP UNIT command with the START bit equal to 0 before receiving a NOTIFY (ENABLE SPINUP)
primitive, the drive waits for a START STOP UNIT command with the START bit equal to 1. After receiving a START STOP UNIT
command with the START bit equal to 1, the drive waits for a NOTIFY (ENABLE SPINUP) primitive. After receiving a NOTIFY
(ENABLE SPINUP) primitive through either port, the drive becomes ready for normal operations within 30 seconds (excluding the error
recovery procedure).
If the drive receives a START STOP UNIT command with the START bit and IMMED bit equal to 1 and does not receive a NOTIFY
(ENABLE SPINUP) primitive within 5 seconds, the drive fails the START STOP UNIT command.
The START STOP UNIT command may be used to command the drive to stop the spindle. Stop time is 23 seconds (maximum) from
removal of DC power. SCSI stop time is 23 seconds. There is no power control switch on the drive.
4.3 PREFETCH/MULTI-SEGMENTED CACHE CONTROL
The drive provides a prefetch (read look-ahead) and multi-segmented cache control algorithms that in many cases can enhance system
performance. Cache refers to the drive buffer storage space when it is used in cache operations. To select this feature, the host sends the
Mode Select command with the proper values in the applicable bytes in page 08h. Prefetch and cache operations are independent features
from the standpoint that each is enabled and disabled independently using the Mode Select command; however, in actual operation, the
prefetch feature overlaps cache operation somewhat as described in sections 4.4.1 and 4.4.2.
All default cache and prefetch mode parameter values (Mode Page 08h) for standard OEM versions of this drive family are given in Table
11.
4.4 CACHE OPERATION
.
NOTE
Refer to the SAS Interface Manual for more detail concerning the cache bits.
Of the 128MB physical buffer space in the drive, approximately (60,000) KB can be used as a cache. The buffer is divided into logical
segments from which data is read and to which data is written.
The drive keeps track of the logical block addresses of the data stored in each segment of the buffer. If the cache is enabled (see RCD bit
in the SAS Interface Manual ), data requested by the host with a read command is retrieved from the buffer, if possible, before any disk
access is initiated. If cache operation is not enabled, the buffer is still used, but only as circular buffer segments during disk medium read
operations (disregarding Prefetch operation for the moment). That is, the drive does not check in the buffer segments for the requested
read data, but goes directly to the medium to retrieve it. The retrieved data merely passes through some buffer segment on the way to the
host. All data transfers to the host are in accordance with buffer-full ratio rules. See the explanation provided with the information about
Mode Page 02h (disconnect/reconnect control) in the SAS Interface Manual.
The following is a simplified description of the prefetch/cache operation:
Case A—read command is received and all of the requested logical blocks are already in the cache:
1. Drive transfers the requested logical blocks to the initiator.
Case B—A Read command requests data, and at least one requested logical block is not in any segment of the cache:
1. The drive fetches the requested logical blocks from the disk and transfers them into a segment, and then from there to the host in
accordance with the Mode Select Disconnect/Reconnect parameters, page 02h.
2. If the prefetch feature is enabled, refer to section 4.4.2 for operation from this point.
Each cache segment is actually a self-contained circular buffer whose length is an integer number of logical blocks. The drive
dynamically creates and removes segments based on the workload. The wrap-around capability of the individual segments greatly
enhances the cache’s overall performance.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 10
Page 16

The size of each segment is not reported by Mode Sense command page 08h, bytes 14 and 15. The value 0XFFFF is always reported
regardless of the actual size of the segment. Sending a size specification using the Mode Select command (bytes 14 and 15) does not set
up a new segment size. If the STRICT bit in Mode page 00h (byte 2, bit 1) is set to one, the drive responds as it does for any attempt to
change an unchangeable parameter.
4.4.1 Caching write data
Write caching is a write operation by the drive that makes use of a drive buffer storage area where the data to be written to the medium is
stored while the drive performs the Write command.
If read caching is enabled (RCD=0), then data written to the medium is retained in the cache to be made available for future read cache
hits. The same buffer space and segmentation is used as set up for read functions. The buffer segmentation scheme is set up or changed
independently, having nothing to do with the state of RCD. When a write command is issued, if RCD=0, the cache is first checked to see
if any logical blocks that are to be written are already stored in the cache from a previous read or write command. If there are, the
respective cache segments are cleared. The new data is cached for subsequent Read commands.
If the number of write data logical blocks exceed the size of the segment being written into, when the end of the segment is reached, the
data is written into the beginning of the same cache segment, overwriting the data that was written there at the beginning of the operation;
however, the drive does not overwrite data that has not yet been written to the medium.
If write caching is enabled (WCE=1), then the drive may return Good status on a write command after the data has been transferred into
the cache, but before the data has been written to the medium. If an error occurs while writing the data to the medium, and Good status
has already been returned, a deferred error will be generated.
The Synchronize Cache command may be used to force the drive to write all cached write data to the medium. Upon completion of a
Synchronize Cache command, all data received from previous write commands will have been written to the medium. Table 11 shows the
mode default settings for the drive.
4.4.2 Prefetch operation
If the Prefetch feature is enabled, data in contiguous logical blocks on the disk immediately beyond that which was requested by a Read
command are retrieved and stored in the buffer for immediate transfer from the buffer to the host on subsequent Read commands that
request those logical blocks (this is true even if cache operation is disabled). Though the prefetch operation uses the buffer as a cache,
finding the requested data in the buffer is a prefetch hit, not a cache operation hit.
To enable Prefetch, use Mode Select page 08h, byte 12, bit 5 (Disable Read Ahead - DRA bit). DRA bit = 0 enables prefetch.
The drive does not use the Max Prefetch field (bytes 8 and 9) or the Prefetch Ceiling field (bytes 10 and 11).
When prefetch (read look-ahead) is enabled (enabled by DRA = 0), the drive enables prefetch of contiguous blocks from the disk when it
senses that a prefetch hit will likely occur. The drive disables prefetch when it decides that a prefetch hit is not likely to occur.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 11
Page 17

5.0 RELIABILITY SPECIFICATIONS
The following reliability specifications assume correct host and drive operational interface, including all interface timings, power supply
voltages, environmental requirements and drive mounting constraints.
Seek error rate: Less than 10 errors in 10
Read Error Rates
1
Recovered Data Less than 10 errors in 1012 bits transferred (OEM default settings)
Unrecovered Data Less than 1 sector in 1015 bits transferred
Miscorrected Data Less than 1 sector in 10
Interface error rate: Less than 1 error in 10
Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF): 1,400,000 hours
Annualized Failure Rate (AFR): 0.63%
Preventive maintenance: None required
1. Error rate specified with automatic retries and data correction with ECC enabled and all flaws reallocated.
5.1 ERROR RATES
The error rates stated in this manual assume the following:
• The drive is operated in accordance with this manual using DC power as defined in paragraph 6.3, "DC power requirements."
• Errors caused by host system failures are excluded from error rate computations.
• Assume random data.
• Default OEM error recovery settings are applied. This includes AWRE, ARRE, full read retries, full write retries and full retry time.
8 seeks
21
bits transferred
12
bits transferred
5.1.1 Recoverable Errors
Recoverable errors are those detected and corrected by the drive, and do not require user intervention.
Recoverable Data errors will use correction, although ECC on-the-fly is not considered for purposes of recovered error specifications.
Recovered Data error rate is determined using read bits transferred for recoverable errors occurring during a read, and using write bits
transferred for recoverable errors occurring during a write.
5.1.2 Unrecoverable Errors
An unrecoverable data error is defined as a failure of the drive to recover data from the media. These errors occur due to head/media or
write problems. Unrecoverable data errors are only detected during read operations, but not caused by the read. If an unrecoverable data
error is detected, a MEDIUM ERROR (03h) in the Sense Key will be reported. Multiple unrecoverable data errors resulting from the
same cause are treated as 1 error.
5.1.3 Seek errors
A seek error is defined as a failure of the drive to position the heads to the addressed track. After detecting an initial seek error, the drive
automatically performs an error recovery process. If the error recovery process fails, a seek positioning error (Error code = 15h or 02h)
will be reported with a Hardware error (04h) in the Sense Key. Recoverable seek errors are specified at Less than 10 errors in 108 seeks.
Unrecoverable seek errors (Sense Key = 04h) are classified as drive failures.
5.1.4 Interface errors
An interface error is defined as a failure of the receiver on a port to recover the data as transmitted by the device port connected to the
receiver. The error may be detected as a running disparity error, illegal code, loss of word sync, or CRC error.
5.2 RELIABILITY AND SERVICE
You can enhance the reliability of Constellation ES.3 disk drives by ensuring that the drive receives adequate cooling. Section 6.0
provides temperature measurements and other information that may be used to enhance the service life of the drive. Section 10.2 provides
recommended air-flow information.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 12
Page 18
5.2.1 Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) and Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF)
The product shall achieve an AFR of 0.63% (MTBF of 1,400,000 hours) when operated at nominal power and typical case temperatures
of 40°C. Operation at temperatures outside the specifications in Section 6.5 may increase the product AFR (decrease MTBF). AFR and
MTBF are population statistics that are not relevant to individual units.
The AFR and MTBF specifications are based on the following assumptions for business critical storage system environments:
• 8760 power-on hours per year.
• Operations at nominal voltages
• Temperatures outside the specifications in Section 6.5 may reduce the product reliability.
• A workload rate below the average annualized specified limits. Operation at excessive I/O duty cycle may degrade product reliability.
The enterprise application nearline environment of power-on-hours, temperature, and I/O duty cycle affect the product AFR and MTBF.
Nonrecoverable read errors 1 per 1015 bits read, max
Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) 0.63% (nominal power, 40°C case temperature)
Load unload cycles 600,000 cycles
Rated Workload Average rate of <550TB/year
The MTBF specification for the drive assumes the I/O workload does not exceed the
Average Annualized Workload Rate Limit of <550TB/year. Workloads exceeding the
annualized rate may degrade the drive MTBF and impact product reliability. The Average Annualized Workload Rate Limit is in units of TB per year, or TB per 8760 power
on hours. Workload Rate Limit = TB transferred * ( 8760 / recorded power on hours).
Warranty To determine the warranty for a specific drive, use a web browser to access the
Preventive maintenance None required.
following web page:
From this page, click on the "Verify Your Warranty" link. You will be asked to provide
the drive serial number, model number (or part number) and country of purchase.The
system will display the warranty information for your drive.
http://www.seagate.com/support/warranty-and-returns/
5.2.2 Hot plugging the drive
When a disk is powered on by switching the power or hot plugged, the drive ru ns a self test before att empting to commun icate on its’
interfaces. When the self test completes successfully, the drive initiates a Link Reset starting with OOB. An attached device should
respond to the link reset. If the link reset attempt fails, or any time the drive looses sync, the drive initiated link reset. The drive will
initiate link reset once per second but alternates between port A and B. Therefore each port will attempt a link reset once per 2 seconds
assuming both ports are out of sync.
If the self-test fails, the drive does not respond to link reset on the failing port.
It is the responsibility of the systems integrator to assure that no temperature, energy, voltage hazard, or ESD potential hazard is
presented during the hot connect/disconnect operation. Discharge the static electricity from the drive carrier prior to inserting it into the
system.
CAUTION
The drive motor must come to a complete stop prior to changing the
plane of operation. This time is required to insure data integrity.
5.2.3 S.M.A.R.T.
S.M.A.R.T. is an acronym for Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology. This technology is intended to recognize conditions
that indicate imminent drive failure and is designed to provide sufficient warning of a failure to allow you to back up the data before an
actual failure occurs.
.
NOTE
The drive’s firmware monitors specific attributes for degradation
over time but can’t predict instantaneous drive failures.
Each monitored attribute has been selected to monitor a specific set of failure conditions in the operating performance of the drive and the
thresholds are optimized to minimize “false” and “failed” predictions.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 13
Page 19

Controlling S.M.A.R.T.
The operating mode of S.M.A.R.T. is controlled by the DEXCPT and PERF bits on the Informational Exceptions Control mode page
(1Ch). Use the DEXCPT bit to enable or disable the S.M.A.R.T. feature. Setting the DEXCPT bit disables all S.M.A.R.T. functions.
When enabled, S.M.A.R.T. collects on-line data as the drive performs normal read and write operations. When the PERF bit is set, the
drive is considered to be in “On-line Mode Only” and will not perform off-line functions.
You can measure off-line attributes and force the drive to save the data by using the Rezero Unit command. Forcing S.M.A.R.T. resets the
timer so that the next scheduled interrupt is in one hour.
You can interrogate the drive through the host to determine the time remaining before the next scheduled measurement and data logging
process occurs. To accomplish this, issue a Log Sense command to log page 0x3E. This allows you to control when S.M.A.R.T.
interruptions occur. Forcing S.M.A.R.T. with the RTZ command resets the timer.
Performance impact
S.M.A.R.T. attribute data is saved to the disk so that the events that caused a predictive failure can be recreated. The drive measures and
saves parameters once every one hour subject to an idle period on the drive interfaces. The process of measuring off-line attribute data
and saving data to the disk is interruptable. The maximum on-line only processing delay is summarized below:
Maximum processing delay
Fully-enabled delay
DEXCPT = 0
S.M.A.R.T. delay times 75 ms
Reporting control
Reporting is controlled by the MRIE bits in the Informational Exceptions Control mode page (1Ch). An example, if the MRIE is set to
one, the firmware will issue to the host an 01-5D00 sense code. The FRU field contains the type of predictive failure that occurred. The
error code is preserved through bus resets and power cycles.
Determining rate
S.M.A.R.T. monitors the rate at which errors occur and signals a predictive failure if the rate of degraded errors increases to an
unacceptable level. To determine rate, error events are logged and compared to the number of total operations for a given attribute. The
interval defines the number of operations over which to measure the rate. The counter that keeps track of the current number of
operations is referred to as the Interval Counter.
S.M.A.R.T. measures error rates. All errors for each monitored attribute are recorded. A counter keeps track of the number of errors for
the current interval. This counter is referred to as the Failure Counter.
Error rate is the number of errors per operation. The algorithm that S.M.A.R.T. uses to record rates of error is to set thresholds for the
number of errors and their interval. If the number of errors exceeds the threshold before the interval expires, the error rate is considered to
be unacceptable. If the number of errors does not exceed the threshold before the interval expires, the error rate is considered to be
acceptable. In either case, the interval and failure counters are reset and the process starts over.
Predictive failures
S.M.A.R.T. signals predictive failures when the drive is performing unacceptably for a period of time. The firmware keeps a running
count of the number of times the error rate for each attribute is unacceptable. To accomplish this, a counter is incremented each time the
error rate is unacceptable and decremented (not to exceed zero) whenever the error rate is acceptable. If the counter continually
increments such that it reaches the predictive threshold, a predictive failure is signaled. This counter is referred to as the Failure History
Counter. There is a separate Failure History Counter for each attribute.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 14
Page 20

5.2.4 Thermal monitor
Constellation ES.3 drives implement a temperature warning system which:
1. Signals the host if the temperature exceeds a value which would threaten the drive.
2. Signals the host if the temperature exceeds a user-specified value.
3. Saves a S.M.A.R.T. data frame on the drive which exceeds the threatening temperature value.
A temperature sensor monitors the drive temperature and issues a warning over the interface when the temperature exceeds a set
threshold. The temperature is measured at power-up and then at ten-minute intervals after power-up.
The thermal monitor system generates a warning code of 01-0B01 when the temperature exceeds the specified limit in compliance with
the SCSI standard. The drive temperature is reported in the FRU code field of mode sense data. You can use this information to determine
if the warning is due to the temperature exceeding the drive threatening temperature or the user-specified temperature.
This feature is controlled by the Enable Warning (EWasc) bit, and the reporting mechanism is controlled by the Method of Reporting
Informational Exceptions field (MRIE) on the Informational Exceptions Control (IEC) mode page (1Ch).
The current algorithm implements two temperature trip points. The first trip point is set at 65°C which is the maximum temperature limit
according to the drive specification. The second trip point is user-selectable using the Log Select command. The reference temperature
parameter in the temperature log page (see Table 1) can be used to set this trip point. The default value for this drive is 65°C, however,
you can set it to any value in the range of 0 to 65°C. If you specify a temperature greater than 65°C in this field, the temperature is
rounded down to 65°C. A sense code is sent to the host to indicate the rounding of the parameter field.
Table 1: Temperature Log Page (0Dh)
Parameter Code Description
0000h
0001h
Primary Temperature
Reference Temperature
5.2.5 Drive Self Test (DST)
Drive Self Test (DST) is a technology designed to recognize drive fault conditions that qualify the drive as a failed unit. DST validates
the functionality of the drive at a system level.
There are two test coverage options implemented in DST:
1. Extended test
2. Short test
The most thorough option is the extended test that performs various tests on the drive and scans every logical block address (LBA) of the
drive. The short test is time-restricted and limited in length—it does not scan the entire media surface, but does some fundamental tests
and scans portions of the media.
If DST encounters an error during either of these tests, it reports a fault condition. If the drive fails the test, remove it from service and
return it to Seagate for service.
5.2.5.1 DST failure definition
The drive will present a “diagnostic failed” condition through the self-tests results value of the diagnostic log page if a functional failure
is encountered during DST. The channel and servo parameters are not modified to test the drive more stringently, and the number of
retries are not reduced. All retries and recovery processes are enabled during the test. If data is recoverable, no failure condition will be
reported regardless of the number of retries required to recover the data.
The following conditions are considered DST failure conditions:
• Seek error after retries are exhausted
• Track-follow error after retries are exhausted
• Read error after retries are exhausted
• Write error after retries are exhausted
Recovered errors will not be reported as diagnostic failures.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 15
Page 21

5.2.5.2 Implementation
This section provides all of the information necessary to implement the DST function on this drive.
5.2.5.2.1 State of the drive prior to testing
The drive must be in a ready state before issuing the Send Diagnostic command. There are multiple reasons why a drive may not be
ready, some of which are valid conditions, and not errors. For example, a drive may be in process of doing a format, or another DST. It is
the responsibility of the host application to determine the “not ready” cause.
While not technically part of DST, a Not Ready condition also qualifies the drive to be returned to Seagate as a failed drive.
A Drive Not Ready condition is reported by the drive under the following conditions:
• Motor will not spin
• Motor will not lock to speed
• Servo will not lock on track
• Drive cannot read configuration tables from the disk
In these conditions, the drive responds to a Test Unit Ready command with an 02/04/00 or 02/04/03 code.
5.2.5.2.2 Invoking DST
To invoke DST, submit the Send Diagnostic command with the appropriate Function Code (001b for the short test or 010b for the
extended test) in bytes 1, bits 5, 6, and 7.
5.2.5.2.3 Short and extended tests
DST has two testing options:
1. short
2. extended
These testing options are described in the following two subsections.
Each test consists of three segments: an electrical test segment, a servo test segment, and a read/verify scan segment.
Short test (Function Code: 001b)
The purpose of the short test is to provide a time-limited test that tests as much of the drive as possible within 120 seconds. The short test
does not scan the entire media surface, but does some fundamental tests and scans portions of the media. A complete read/verify scan is
not performed and only factual failures will report a fault condition. This option provides a quick confidence test of the drive.
Extended test (Function Code: 010b)
The objective of the extended test option is to empirically test critical drive components. For example, the seek tests and on-track
operations test the positioning mechanism. The read operation tests the read head element and the media surface. The write element is
tested through read/write/read operations. The integrity of the media is checked through a read/verify scan of the media. Motor
functionality is tested by default as a part of these tests.
The anticipated length of the Extended test is reported through the Control Mode page.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 16
Page 22

5.2.5.2.4 Log page entries
When the drive begins DST, it creates a new entry in the Self-test Results Log page. The new entry is created by inserting a new self-test
parameter block at the beginning of the self-test results log parameter section of the log page. Existing data will be moved to make room
for the new parameter block. The drive reports 20 parameter blocks in the log page. If there are more than 20 parameter blocks, the least
recent parameter block will be deleted. The new parameter block will be initialized as follows:
1. The Function Code field is set to the same value as sent in the DST command
2. The Self-Test Results Value field is set to Fh
3. The drive will store the log page to non-volatile memory
After a self-test is complete or has been aborted, the drive updates the Self-Test Results Value field in its Self-Test Results Log page in
non-volatile memory. The host may use Log Sense to read the results from up to the last 20 self-tests performed by the drive. The self-test
results value is a 4-bit field that reports the results of the test. If the field is set to zero, the drive passed with no errors detected by the
DST. If the field is not set to zero, the test failed for the reason reported in the field.
The drive will report the failure condition and LBA (if applicable) in the Self-test Results Log parameter. The Sense key, ASC, ASCQ,
and FRU are used to report the failure condition.
5.2.5.2.5 Abort
There are several ways to abort a diagnostic. You can use a SCSI Bus Reset or a Bus Device Reset message to abort the diagnostic.
You can abort a DST executing in background mode by using the abort code in the DST Function Code field. This will cause a 01 (self-
test aborted by the application client) code to appear in the self-test results values log. All other abort mechanisms will be reported as a 02
(self-test routine was interrupted by a reset condition).
5.2.6 Product warranty
See “Seagate® Technology Support Services” on page 1 for warranty contact information.
Shipping
When transporting or shipping a drive, use only a Seagate-approved container. Keep your original box. Seagate approved containers are
easily identified by the Seagate Approved Package label. Shipping a drive in a non-approved container voids the drive warranty.
Seagate repair centers may refuse receipt of components improperly packaged or obviously damaged in transit. Contact your authorized
Seagate distributor to purchase additional boxes. Seagate recommends shipping by an air-ride carrier experienced in handling computer
equipment.
Storage
The maximum recommended storage period for the drive in a non-operational environment is 90 days. Drives should be stored in the
original unopened Seagate shipping packaging whenever possible. Once the drive is removed from the Seagate original packaging the
recommended maximum period between drive operation cycles is 30 days. During any storage period the drive non-operational temperature, humidity, wet bulb, atmospheric conditions, shock, vibration, magnetic and electrical field specifications should be followed.
Product repair and return information
Seagate customer service centers are the only facilities authorized to service Seagate drives. Seagate does not sanction any third-party
repair facilities. Any unauthorized repair or tampering with the factory seal voids the warranty.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 17
Page 23
6.0 PHYSICAL/ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
This section provides information relating to the physical and electrical characteristics of the drive.
6.1 POWERCHOICETM POWER MANAGEMENT
Drives using the load/unload architecture provide programmable power management to tailor systems for performance and greater
energy efficiency.
The table below lists the supported PowerChoice modes. The further you go down in the table, the more power savings you get. For
example, Idle_B mode results in greater power savings than Idle_A mode. Standby_Z mode results in the greatest power savings.
PowerChoice modes
M
ODE DESCRIPTION
Idle_A Reduced electronics
Idle_B Heads unloaded. Disks spinning at full RPM
Idle_C Heads unloaded. Disks spinning at reduced RPM
Standby_Y Heads unloaded. Disks spinning at reduced RPM.
Standby_Z Heads unloaded. Motor stopped (disks not spinning)
PowerChoice
TM
can be invoked using one of these two methods:
Recovery requires the NOTIFY (Enable Spinup) command.
Recovery requires the NOTIFY (Enable Spinup) command.
• Power Condition mode page method—Enable and initialize the idle condition timers and/or the standby condition timers. The timer
values are based on the values set in the Power Condition mode page.
• START STOP UNIT command method—Use the START STOP UNIT command (OPERATION CODE 1Bh). This allows the host to
directly transition the drive to any supported PowerChoice mode.
If both the Power Condition mode page and START STOP UNIT command methods are used, the START STOP UNIT command request
takes precedence over the Power Condition mode page power control and may disable the idle condition and standby condition timers.
The REQUEST SENSE command reports the current PowerChoice state if active and also the method by which the drive entered the
PowerChoice state.
When the drive receives a command, all power condition timers are suspended if they were enabled via the Power Condition mode page.
Once all outstanding commands are processed, the power condition timers are reinitialized to the values defined in the Power Condition
mode page
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 18
Page 24

6.1.1 PowerChoice reporting methods
PowerChoiceTM provides these reporting methods for tracking purposes:
Request Sense command reports
• Current power condition
• Method of entry
.
NOTE
Processing the Request Sense command does not impact the drive’s power save state.
Mode Sense command reports (mode page 0x1A)
• Idle conditions enabled / disabled
• Idle condition timer values (100ms increments) (default, saved, current, changeable)
Power Condition Vital Product Data (VPD) Page (VPD page 0x8A)
• Supported power conditions
• Typical recovery time from power conditions (1ms increments)
Start/Stop Cycle Counter Log Page reports (log page 0x0E)
• Specified and accumulated Start/Stops and Load/Unload cycles
Power Condition Transitions Log Page reports (log page 0x1A, subpage 0x00)
• Accumulated transitions to Active, Idle_A, Idle_B, Idle_C, Standby_Y, Standby_Z
6.2 AC POWER REQUIREMENTS
None.
6.3 DC POWER REQUIREMENTS
The voltage and current requirements for a single drive are shown below. Values indicated apply at the drive connector.
The standard drive models and the SED drive models have identical hardware, however the security and encryption portion of the drive
controller ASIC is enabled and functional in the SED models. This represents a small additional drain on the 5V supply of about 30mA
and a commensurate increase of about 150mW in power consumption. There is no additional drain on the 12V supply.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 19
Page 25

Table 2 4TB drive DC power requirements
NOTES
Voltage +5V +12V [2] +5V +12V [2]
Regulation [5] ± 5% [2] ± 5% [2]
Avg idle current DCX [1] [7] 0.40 0.51 0.37 0.51
Advanced idle current
Idle A
Idle B
Idle C
Standby
Maximum starting current
(peak DC) DC
(peak AC) AC
Delayed motor start (max) DC
Peak operating current (random read):
Typical DCX [1] [6] 0.50 0.78 0.50 0.78
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
3s
3s
3s
3s
3s [3]
3s [3]
3s [1] [4]
3s
[1] 0.75 0.79 0.72 0.80
3s
3.0GB MODE 6.0GB MODE
(AMPS)(AMPS)(AMPS)(AMPS)
0.35 0.51 0.36 0.50
0.25 0.44 0.28 0.43
0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25
0.24 0.01 0.24 0.00
0.63 2.16 0.63 2.16
0.81 2.74 0.83 2.69
0.28 0.01 0.26 0.01
1.75 2.37 1.78 2.36
Peak operating current (random write)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
Peak operating current (sequential read)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
Peak operating current (sequential write)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
[1]
3s [1]
3s
[1]
3s [1]
3s
[1]
3s [1]
3s
0.51 0.69 0.52 0.68
0.76 0.71 0.80 0.71
1.13 2.29 1.13 2.50
0.83 0.55 0.82 0.55
1.03 0.58 1.07 0.58
1.27 0.96 1.30 0.93
0.66 0.60 0.67 0.59
0.69 0.62 0.69 0.63
0.80 2.20 0.84 2.40
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 20
Page 26

Table 3 3TB drive DC power requirements
NOTES
Voltage +5V +12V [2] +5V +12V [2]
Regulation [5] ± 5% [2] ± 5% [2]
Avg idle current DCX [1] [7] 0.33 0.43 0.36 0.43
Advanced idle current
Idle A
Idle B
Idle C
Standby
Maximum starting current
(peak DC) DC
(peak AC) AC
Delayed motor start (max) DC
Peak operating current (random read):
Typical DCX [1] [6] 0.49 0.71 0.44 0.71
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
3s
3s
3s
3s
3s [3]
3s [3]
3s [1] [4]
3s
[1] 0.72 0.77 0.63 0.76
3s
3.0GB MODE 6.0GB MODE
(AMPS)(AMPS)(AMPS)(AMPS)
0.33 0.42 0.34 0.42
0.25 0.37 0.28 0.37
0.24 0.22 0.27 0.22
0.26 0.00 0.24 0.00
0.62 2.20 0.65 2.19
0.85 2.71 0.79 2.75
0.29 0.01 0.29 0.01
1.58 2.24 1.71 2.28
Peak operating current (random write)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
Peak operating current (sequential read)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
Peak operating current (sequential write)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
[1]
3s [1]
3s
[1]
3s [1]
3s
[1]
3s [1]
3s
0.47 0.61 0.48 0.62
0.72 0.64 0.74 0.65
0.95 2.24 1.63 2.31
0.71 0.47 0.77 0.47
0.75 0.49 0.99 0.50
0.97 0.84 1.21 0.83
0.56 0.50 0.61 0.50
0.59 0.53 0.87 0.53
0.74 0.89 1.00 2.19
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 21
Page 27

Table 4 2TB drive DC power requirements
NOTES
Voltage +5V +12V [2] +5V +12V [2]
Regulation [5] ± 5% [2] ± 5% [2]
Avg idle current DCX [1] [7] 0.33 0.34 0.33 0.34
Advanced idle current
Idle A
Idle B
Idle C
Standby
Maximum starting current
(peak DC) DC
(peak AC) AC
Delayed motor start (max) DC
Peak operating current (random read):
Typical DCX [1] [6] 0.46 0.62 0.43 0.62
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
3s
3s
3s
3s
3s [3]
3s [3]
3s [1] [4]
3s
[1] 0.81 0.64 0.70 0.66
3s
3.0GB MODE 6.0GB MODE
(AMPS)(AMPS)(AMPS)(AMPS)
0.33 0.34 0.34 0.34
0.24 0.31 0.25 0.31
0.24 0.19 0.24 0.19
0.23 0.01 0.23 0.00
0.62 2.16 0.64 2.15
0.76 2.84 0.78 2.79
0.27 0.02 0.27 0.02
1.54 2.18 1.64 2.23
Peak operating current (random write)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
Peak operating current (sequential read)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
Peak operating current (sequential write)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
[1]
3s [1]
3s
[1]
3s [1]
3s
[1]
3s [1]
3s
0.45 0.53 0.42 0.53
0.81 0.54 0.69 0.56
0.99 2.18 1.24 2.22
0.70 0.39 0.70 0.39
0.77 0.42 0.77 0.42
1.24 0.81 1.16 0.80
0.56 0.42 0.56 0.42
0.60 0.45 0.62 0.46
0.72 2.50 0.76 2.02
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 22
Page 28

Table 5 1TB drive DC power requirements
NOTES
Voltage +5V +12V [2] +5V +12V [2]
Regulation [5] ± 5% [2] ± 5% [2]
Avg idle current DCX [1] [7] 0.34 0.27 0.32 0.27
Advanced idle current
Idle A
Idle B
Idle C
Standby
Maximum starting current
(peak DC) DC
(peak AC) AC
Delayed motor start (max) DC
Peak operating current (random read):
Typical DCX [1] [6] 0.46 0.54 0.49 0.54
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
3s
3s
3s
3s
3s [3]
3s [3]
3s [1] [4]
3s
[1] 0.77 0.59 0.83 0.59
3s
3.0GB MODE 6.0GB MODE
(AMPS)(AMPS)(AMPS)(AMPS)
0.31 0.27 0.32 0.27
0.23 0.24 0.23 0.24
0.23 0.16 0.24 0.16
0.22 0.01 0.22 0.00
0.59 2.19 0.58 2.18
0.77 2.73 0.75 2.70
0.55 0.01 0.25 0.01
1.66 2.17 1.75 2.11
Peak operating current (random write)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
Peak operating current (sequential read)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
Peak operating current (sequential write)
Typical DCX
Maximum DC
Maximum (peak) DC
[1]
3s [1]
3s
[1]
3s [1]
3s
[1]
3s [1]
3s
0.51 0.44 0.49 0.44
0.83 0.48 0.83 0.48
1.04 2.07 1.05 2.10
0.72 0.31 0.69 0.31
0.97 0.33 0.73 0.33
1.32 0.64 1.47 0.69
0.56 0.34 0.56 0.34
0.58 0.36 0.58 0.36
0.94 1.89 0.74 1.21
[1] Measured with average reading DC ammeter. Instantaneous +12V current peaks will exceed these values. Power supply at nominal voltage. N
(number of drives tested) = 6, 35 Degrees C ambient.
[2] For +12 V, a –10% tolerance is allowed during initial spindle start but must return to ± 5% before reaching 7200 RPM. The ± 5% must be main-
tained after the drive signifies that its power-up sequence has been completed and that the drive is able to accept selection by the host initiator.
[3] See +12V current profile in Figure 1. (for 4TB models)
[4] This condition occurs after OOB and Speed Negotiation completes but before the drive has received the Notify Spinup primitive.
[5] See paragraph 6.3.1, "Conducted noise immunity." Specified voltage tolerance includes ripple, noise, and transient response.
[6] Operating condition is defined as random 8 block reads.
[7] During idle, the drive heads are relocated every 60 seconds to a random location within the band from three-quarters to maximum track.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 23
Page 29

General DC power requirement notes.
1. Minimum current loading for each supply voltage is not less than 1.7% of the maximum operating current shown.
2. The +5V and +12V supplies should employ separate ground returns.
3. Where power is provided to multiple drives from a common supply, careful consideration for individual drive power requirements
should be noted. Where multiple units are powered on simultaneously, the peak starting current must be available to each device.
4. Parameters, other than spindle start, are measured after a 10-minute warm up.
5. No terminator power.
6.3.1 Conducted noise immunity
Noise is specified as a periodic and random distribution of frequencies covering a band from DC to 10 MHz. Maximum allowed noise
values given below are peak-to-peak measurements and apply at the drive power connector.
+5v = 250 mV pp from 100 Hz to 20 MHz.
+12v = 800 mV pp from 100 Hz to 8 KHz.
450 mV pp from 8 KHz to 20 KHz.
250 mV pp from 20 KHz to 5 MHz.
6.3.2 Power sequencing
The drive does not require power sequencing. The drive protects against inadvertent writing during power-up and down.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 24
Page 30

6.3.3 Current profiles
The +12V (top) and +5V (bottom) current profiles for the Constellation ES drives are shown below.
Figure 1. 4TB model current profiles
Note: All times and currents are typical. See Table 2 for maximum current requirements.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 25
Page 31

The +12V (top) and +5V (bottom) current profiles for the Constellation ES drives are shown below.
Figure 2. 3TB model current profiles
Note: All times and currents are typical. See Table 3 for maximum current requirements.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 26
Page 32

The +12V (top) and +5V (bottom) current profiles for the Constellation ES drives are shown below.
Figure 3. 2TB model current profiles
Note: All times and currents are typical. See Table 4 for maximum current requirements.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 27
Page 33

The +12V (top) and +5V (bottom) current profiles for the Constellation ES drives are shown below.
Figure 4. 1TB model current profiles
Note: All times and currents are typical. See Table 5 for maximum current requirements.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 28
Page 34

6.4 POWER DISSIPATION
4TB models in 3Gb operation
Please refer to Table 2 for power dissipation numbers.
To obtain operating power for typical random read operations, refer to the following I/O rate curve (see Figure 5). Locate the typical I/O
rate for a drive in your system on the horizontal axis and read the corresponding +5 volt current, +12 volt current, and total watts on the
vertical axis. To calculate BTUs per hour, multiply watts by 3.4123.
Figure 5. 4TB models (3Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second
4TB models in 6Gb operation
Please refer to Table 2 for power dissipation numbers.
To obtain operating power for typical random read operations, refer to the following I/O rate curve (see Figure 6.). Locate the typical I/O
rate for a drive in your system on the horizontal axis and read the corresponding +5 volt current, +12 volt current, and total watts on the
vertical axis. To calculate BTUs per hour, multiply watts by 3.4123.
Figure 6. 4TB models (6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 29
Page 35

3TB models in 3Gb operation
Please refer to Table 3 for power dissipation numbers.
To obtain operating power for typical random read operations, refer to the following I/O rate curve (see Figure 5). Locate the typical I/O
rate for a drive in your system on the horizontal axis and read the corresponding +5 volt current, +12 volt current, and total watts on the
vertical axis. To calculate BTUs per hour, multiply watts by 3.4123.
Figure 7. 3TB models (3Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second
3TB models in 6Gb operation
Please refer to Table 3 for power dissipation numbers.
To obtain operating power for typical random read operations, refer to the following I/O rate curve (see Figure 6.). Locate the typical I/O
rate for a drive in your system on the horizontal axis and read the corresponding +5 volt current, +12 volt current, and total watts on the
vertical axis. To calculate BTUs per hour, multiply watts by 3.4123.
Figure 8. 3TB models (6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 30
Page 36

2TB models in 3Gb operation
Please refer to Table 4 for power dissipation numbers.
To obtain operating power for typical random read operations, refer to the following I/O rate curve (see Figure 5). Locate the typical I/O
rate for a drive in your system on the horizontal axis and read the corresponding +5 volt current, +12 volt current, and total watts on the
vertical axis. To calculate BTUs per hour, multiply watts by 3.4123.
Figure 9. 2TB models (3Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second
2TB models in 6Gb operation
Please refer to Table 4 for power dissipation numbers.
To obtain operating power for typical random read operations, refer to the following I/O rate curve (see Figure 6.). Locate the typical I/O
rate for a drive in your system on the horizontal axis and read the corresponding +5 volt current, +12 volt current, and total watts on the
vertical axis. To calculate BTUs per hour, multiply watts by 3.4123.
Figure 10. 2TB models (6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 31
Page 37

1TB models in 3Gb operation
Please refer to Table 5 for power dissipation numbers.
To obtain operating power for typical random read operations, refer to the following I/O rate curve (see Figure 5). Locate the typical I/O
rate for a drive in your system on the horizontal axis and read the corresponding +5 volt current, +12 volt current, and total watts on the
vertical axis. To calculate BTUs per hour, multiply watts by 3.4123.
Figure 11. 1TB models (3Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second
1TB models in 6Gb operation
Please refer to Table 5 for power dissipation numbers.
To obtain operating power for typical random read operations, refer to the following I/O rate curve (see Figure 6.). Locate the typical I/O
rate for a drive in your system on the horizontal axis and read the corresponding +5 volt current, +12 volt current, and total watts on the
vertical axis. To calculate BTUs per hour, multiply watts by 3.4123.
Figure 12. 1TB models (6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 32
Page 38

6.5 ENVIRONMENTAL LIMITS
Temperature and humidity values experienced by the drive must be such that condensation does not occur on any drive part. Altitude and
atmospheric pressure specifications are referenced to a standard day at 58.7°F (14.8°C). Maximum wet bulb temperature is 82°F (28°C).
6.5.1 Temperature
a. Operating
The drive meets the operating specifications over a 41°F to 140°F (5°C to 60°C) drive case temperature range with a maximum
temperature gradient of 36°F (20°C) per hour.
The maximum allowable drive case temperature is 60°C. See Figure 13 for HDA case temperature measurement location.
The MTBF specification for the drive assumes the operating environment is designed to maintain nominal case temperature. The
rated MTBF is based upon a sustained case temperature of 104°F (40°C). Occasional excursions in operating temperature between the
rated MTBF temperature and the maximum drive operating case temperature may occur without impact to the rated MTBF
temperature.
drive MTBF and reduce product reliability.
Air flow may be required to achieve consistent nominal case temperature values (see Section 10.2). To confirm that the required
cooling is provided for the electronics and HDA, place the drive in its final mechanical configuration, and perform random write/read
operations. After the temperatures stabilize, measure the case temperature of the drive.
b. Non-operating
–40° to 158°F (–40° to 70°C) package ambient with a maximum gradient of 36°F (20°C) per hour. This specification assumes that the
drive is packaged in the shipping container designed by Seagate for use with drive.
However, continual or sustained operation at case temperatures beyond the rated MTBF temperature will degrade the
HDA Temp.
Check Point
Figure 13. Location of the HDA temperature check point
NOTE
Image is for reference only, may not represent actual drive.
6.5.2 Relative humidity
The values below assume that no condensation on the drive occurs.
a. Operating
5% to 95% non-condensing relative humidity with a maximum gradient of 20% per hour.
b. Non-operating
5% to 95% non-condensing relative humidity.
6.5.3 Effective altitude (sea level)
a. Operating
–1000 to +10,000 feet (–304.8 to +3048 meters)
b. Non-operating
–1000 to +40,000 feet (–304.8 to +12,192 meters)
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 33
Page 39

6.5.4 Shock and vibration
Shock and vibration limits specified in this document are measured directly on the drive chassis. If the drive is installed in an enclosure to
which the stated shock and/or vibration criteria is applied, resonances may occur internally to the enclosure resulting in drive movement
in excess of the stated limits. If this situation is apparent, it may be necessary to modify the enclosure to minimize drive movement.
The limits of shock and vibration defined within this document are specified with the drive mounted by any of the four methods shown in
Figure 14, and in accordance with the restrictions of Section 10.3.
6.5.4.1 Shock
a. Operating—normal
The drive, as installed for normal operation, shall operate error free while subjected to intermittent shock not exceeding 70 Gs (read)
and 40 Gs (write) at a maximum duration of 2ms (half sinewave). Shock may be applied in the X, Y, or Z axis. Shock is not to be
repeated more than once every 2 seconds.
b. Operating—abnormal
Equipment, as installed for normal operation, does not incur physical damage while subjected to intermittent shock not exceeding 40
Gs at a maximum duration of 11ms (half sinewave). Shock occurring at abnormal levels may promote degraded operational
performance during the abnormal shock period. Specified operational performance will continue when normal operating shock levels
resume. Shock may be applied in the X, Y, or Z axis. Shock is not to be repeated more than once every 2 seconds.
c. Non-operating
The limits of non-operating shock shall apply to all conditions of handling and transportation. This includes both isolated drives and
integrated drives.
The drive subjected to nonrepetitive shock not exceeding 80 Gs at a maximum duration of 11ms (half sinewave) shall not exhibit
device damage or performance degradation. Shock may be applied in the X, Y, or Z axis.
The drive subjected to nonrepetitive shock not exceeding 300 Gs at a maximum duration of 2ms (half sinewave) does not exhibit
device damage or performance degradation. Shock may be applied in the X, Y, or Z axis.
The drive subjected to nonrepetitive shock not exceeding 200 Gs at a maximum duration of 0.5ms (half sinewave) does not exhibit
device damage or performance degradation. Shock may be applied in the X, Y, or Z axis.
d. Packaged
Disk drives shipped as loose load (not palletized) general freight will be packaged to withstand drops from heights as defined in the
table below. For additional details refer to Seagate specifications 30190-001 (under 100 lbs/45 kg) or 30191-001 (over 100 lbs/45
Kg).
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 34
Page 40

PACKAGE SIZE PACKAGED/PRODUCT WEIGHT DROP HEIGHT
<600 cu in (<9,800 cu cm) Any 60 in (1524 mm)
600-1800 cu in (9,800-19,700 cu cm) 0-20 lb (0 to 9.1 kg) 48 in (1219 mm)
>1800 cu in (>19,700 cu cm) 0-20 lb (0 to 9.1 kg) 42 in (1067 mm)
>600 cu in (>9,800 cu cm) 20-40 lb (9.1 to 18.1 kg) 36 in (914 mm)
Drives packaged in single or multipacks with a gross weight of 20 pounds (8.95 kg) or less by Seagate for general freight shipment
shall withstand a drop test from 48 in (1070 mm) against a concrete floor or equivalent.
Z
Y
X
Figure 14. Recommended mounting
NOTE
Image is for reference only, may not represent actual drive.
X
Y
Z
C
ONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 35
Page 41

6.5.4.2 Vibration
a. Operating—normal
The drive as installed for normal operation, shall comply with the complete specified performance while subjected to continuous
vibration not exceeding
5 - 22 Hz 0.25 Gs, limited displacement
22 - 350 Hz 0.5 Gs
350 - 500 Hz 0.25 Gs
Vibration may be applied in the X, Y, or Z axis.
b. Operating—abnormal
Equipment as installed for normal operation shall not incur physical damage while subjected to periodic vibration not exceeding:
15 minutes of duration at major resonant frequency
Vibration occurring at these levels may degrade operational performance during the abnormal vibration period. Specified operational
performance will continue when normal operating vibration levels are resumed. This assumes system recovery routines are available.
Operating abnormal translational random flat profile
5-500 Hz @ 0.75 G (X, Y, or Z axis)
c. Non-operating
The limits of non-operating vibration shall apply to all conditions of handling and transportation. This includes both isolated drives
and integrated drives.
The drive shall not incur physical damage or degraded performance as a result of continuous vibration not exceeding
5 - 22 Hz 2 Gs (0 to peak, linear, swept sine, 0.5 octave/min)
22 - 350 Hz 5 Gs (0 to peak, linear, swept sine, 0.5 octave/min)
350 - 500 Hz 2 Gs (0 to peak, linear, swept sine, 0.5 octave/min)
Vibration may be applied in the X, Y, or Z axis.
6.5.5 Acoustics
Sound power during idle mode shall be 2.8 bels typical when measured to ISO 7779 specification.
Sound power while operating shall be 3.0 bels typical when measured to ISO 7779 specification.
There will not be any discrete tones more than 9 dB above the masking noise when measured according to
Seagate specification 30553-001.
6.5.6 Air cleanliness
The drive is designed to operate in a typical office environment with minimal environmental control.
6.5.7 Corrosive environment
Seagate electronic drive components pass accelerated corrosion testing equivalent to 10 years exposure to light industrial environments
containing sulfurous gases, chlorine and nitric oxide, classes G and H per ASTM B845. However, this accelerated testing cannot
duplicate every potential application environment.
Users should use caution exposing any electronic components to uncontrolled chemical pollutants and corrosive chemicals as electronic
drive component reliability can be affected by the installation environment. The silver, copper, nickel and gold films used in Seagate
products are especially sensitive to the presence of sulfide, chloride, and nitrate contaminants. Sulfur is found to be the most damaging.
In addition, electronic components should never be exposed to condensing water on the surface of the printed circuit board assembly
(PCBA) or exposed to an ambient relative humidity greater than 95%. Materials used in cabinet fabrication, such as vulcanized rubber,
that can outgas corrosive compounds should be minimized or eliminated. The useful life of any electronic equipment may be extended by
replacing materials near circuitry with sulfide-free alternatives.
6.5.8 Electromagnetic susceptibility
See Section 2.1.1.1.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 36
Page 42

6.6 MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Refer to Figure 15 for detailed mounting configuration dimensions. See Section 10.3, “Drive mounting.”
4TB 1.543 lb 700 g
Weight:
3TB 1.444 lb 655 g
2TB 1.400 lb 635 g
1TB 1.334 lb 605 g
NOTE
These dimensions conform to the Small Form Factor Standard documented
in SFF-8301 and SFF-8323, found at www.sffcommittee.org.
in
mm
Figure 15. Mounting configuration dimensions
in
mm
in
mm
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 37
Page 43

7.0 ABOUT FIPS
The Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) Publication 140-2 is a U.S. Government Computer Security Standard used to
accredit cryptographic modules. It is titled 'Security Requirements for Cryptographic Modules (FIPS PUB 140-2)' and is issued by the
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Purpose
This standard specifies the security requirements that will be satisfied by a cryptographic module utilized within a security system pro-
sensitive but unclassified information. The standard provides four increasing, qualitative levels of security: Level 1, Level 2,
tecting
Level 3 and Level 4. These levels are intended to cover the wide range of potential applications and environments in which cryptographic
modules may be employed.
Validation Program
Products that claim conformance to this standard are validated by the Cryptographic Module Validation Program (CMVP) which is a
joint effort between National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Communications Security Establishment (CSE) of
the Government of Canada. Products validated as conforming to FIPS 140-2 are accepted by the Federal agencies of both countries for
the protection of sensitive information (United States) or Designated Information (Canada).
In the CMVP, vendors of cryptographic modules use independent, accredited testing laborites to have their modules tested. National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP) accredited laboratories perform cryptographic module compliance/conformance
testing.
Seagate Enterprise SED
The SEDs referenced in this Product Manual have been validated by CMVP and have been thoroughly tested by a NVLAP accredited lab
to satisfy FIPS 140-2 Level 2 requirements. In order to operate in FIPS Approved Mode of Operation, these SEDs require security initialization. For more information, refer to 'Security Rules' section in the 'Security Policy' document uploaded on the NIST website. To reference the product certification visit - http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/STM/cmvp/documents/140-1/1401vend.htm, and search for “Seagate”.
Security Level 2
Security Level 2 enhances the physical security mechanisms of a Security Level 1 cryptographic module by adding the requirement for
tamper-evidence, which includes the use of tamper-evident coatings or seals on removable covers of the module. Tamper-evident coatings or seals are placed on a cryptographic module so that the coating or seal must be broken to attain physical access to the critical
security parameters (CSP) within the module. Tamper-evident seals (example shown in Figure 16, page 38) are placed on covers to
protect against unauthorized physical access. In addition Security Level 2 requires, at a minimum, role-based authentication in which a
cryptographic module authenticates the authorization of an operator to assume a specific role and perform a corresponding set of services.
Figure 16. Example of FIPS tamper evidence labels.
NOTE
Image is for reference only, may not represent actual drive.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 38
Page 44

8.0 ABOUT SELF-ENCRYPTING DRIVES
Self-encrypting drives (SEDs) offer encryption and security services for the protection of stored data, commonly known as “protection of
data at rest.” These drives are compliant with the Trusted Computing Group (TCG) Enterprise Storage Specifications as detailed in
Section 2.2.
The Trusted Computing Group (TCG) is an organization sponsored and operated by companies in the computer, storage and digital
communications industry. Seagate’s SED models comply with the standards published by the TCG.
To use the security features in the drive, the host must be capable of constructing and issuing the following two SCSI commands:
• Security Protocol Out
• Security Protocol In
These commands are used to convey the TCG protocol to and from the drive in their command payloads.
8.1 DATA ENCRYPTION
Encrypting drives use one inline encryption engine for each port, employing AES-256 data encryption in Cipher Block Chaining (CBC)
mode to encrypt all data prior to being written on the media and to decrypt all data as it is read from the media. The encryption engines
are always in operation and cannot be disabled.
The 32-byte Data Encryption Key (DEK) is a random number which is generated by the drive, never leaves the drive, and is inaccessible
to the host system. The DEK is itself encrypted when it is stored on the media and when it is in volatile temporary storage (DRAM)
external to the encryption engine. A unique data encryption key is used for each of the drive's possible16 data bands (see Section 8.5).
8.2 CONTROLLED ACCESS
The drive has two security providers (SPs) called the "Admin SP" and the "Locking SP." These act as gatekeepers to the drive security
services. Security-related commands will not be accepted unless they also supply the correct credentials to prove the requester is
authorized to perform the command.
8.2.1 Admin SP
The Admin SP allows the drive's owner to enable or disable firmware download operations (see Section 8.4). Access to the Admin SP is
available using the SID (Secure ID) password or the MSID (Manufacturers Secure ID) password.
8.2.2 Locking SP
The Locking SP controls read/write access to the media and the cryptographic erase feature. Access to the Locking SP is available using
the BandMasterX or EraseMaster passwords. Since the drive owner can define up to 16 data bands on the drive, each data band has its
own password called BandMasterX where X is the number of the data band (0 through 15).
8.2.3 Default password
When the drive is shipped from the factory, all passwords are set to the value of MSID. This 32-byte random value can only be read by
the host electronically over the interface. After receipt of the drive, it is the responsibility of the owner to use the default MSID password
as the authority to change all other passwords to unique owner-specified values.
8.3 RANDOM NUMBER GENERATOR (RNG)
The drive has a 32-byte hardware RNG that it is uses to derive encryption keys or, if requested to do so, to provide random numbers to the
host for system use, including using these numbers as Authentication Keys (passwords) for the drive’s Admin and Locking SPs.
8.4 DRIVE LOCKING
In addition to changing the passwords, as described in Section 8.2.3, the owner should also set the data access controls for the individual
bands.
The variable "LockOnReset" should be set to "PowerCycle" to ensure that the data bands will be locked if power is lost. In addition
"ReadLockEnabled" and "WriteLockEnabled" must be set to true in the locking table in order for the bands "LockOnReset" setting of
"PowerCycle" to actually lock access to the band when a "PowerCycle" event occurs. This scenario occurs if the drive is removed from
its cabinet. The drive will not honor any data read or write requests until the bands have been unlocked. This prevents the user data from
being accessed without the appropriate credentials when the drive has been removed from its cabinet and installed in another system.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 39
Page 45

When the drive is shipped from the factory, the firmware download port is unlocked.
8.5 DATA BANDS
When shipped from the factory, the drive is configured with a single data band called Band 0 (also known as the Global Data Band)
which comprises LBA 0 through LBA max. The host may allocate Band1 by specifying a start LBA and an LBA range. The real estate
for this band is taken from the Global Band. An additional 14 Data Bands may be defined in a similar way (Band2 through Band15) but
before these bands can be allocated LBA space, they must first be individually enabled using the EraseMaster password.
Data bands cannot overlap but they can be sequential with one band ending at LBA (x) and the next beginning at LBA (x+1).
Each data band has its own drive-generated encryption key and its own user-supplied password. The host may change the Encryption
Key (see Section 8.6) or the password when required. The bands should be aligned to 4K LBA boundaries.
8.6 CRYPTOGRAPHIC ERASE
A significant feature of SEDs is the ability to perform a cryptographic erase. This involves the host telling the drive to change the data
encryption key for a particular band. Once changed, the data is no longer recoverable since it was written with one key and will be read
using a different key. Since the drive overwrites the old key with the new one, and keeps no history of key changes, the user data can
never be recovered. This is tantamount to an instantaneous data erase and is very useful if the drive is to be scrapped or redispositioned.
8.7 AUTHENTICATED FIRMWARE DOWNLOAD
In addition to providing a locking mechanism to prevent unwanted firmware download attempts, the drive also only accepts download
files which have been cryptographically signed by the appropriate Seagate Design Center.
Three conditions must be met before the drive will allow the download operation:
1. The download must be an SED file. A standard (base) drive (non-SED) file will be rejected.
2. The download file must be signed and authenticated.
3. As with a non-SED drive, the download file must pass the acceptance criteria for the drive. For example it must be applicable to the
correct drive model, and have compatible revision and customer status.
8.8 POWER REQUIREMENTS
The standard drive models and the SED drive models have identical hardware, however the security and encryption portion of the drive
controller ASIC is enabled and functional in the SED models. This represents a small additional drain on the 5V supply of about 30mA
and a commensurate increase of about 150mW in power consumption. There is no additional drain on the 12V supply. See the tables in
Section 6.3 for power requirements on the standard (non-SED) drive models.
8.9 SUPPORTED COMMANDS
The SED models support the following two commands in addition to the commands supported by the standard (non-SED) models as
listed in Table 9:
• Security Protocol Out (B5h)
• Security Protocol In (A2h)
8.10 SANITIZE - CRYPTOGRAPHIC ERASE
This command cryptographically erases all user data on the drive by destroying the current data encryption key and replacing it with a
new data encryption key randomly generated by the drive. Sanitize CRYPTOGRAPHIC ERASE is a SCSI CDB Op code 48h and selecting the service action code 3 (CRYPTOGRAPHIC ERASE)
8.11 REVERTSP
SED mo del s wil l sup port t he Re ver tSP f eat ure wh ich e ras es al l dat a in al l band s on th e dev ice a nd re turn s the c ont ent s of al l SPs
(Security Providers) on the device to their original factory state. In order to execute the RevertSP method the unique PSID (Physical
Secure ID) printed on the drive label must be provided. PSID is not electronically accessible and can only be manually read from the
drive label or scanned in via the 2D barcode.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 40
Page 46

9.0 DEFECT AND ERROR MANAGEMENT
Seagate continues to use innovative technologies to manage defects and errors. These technologies are designed to increase data integrity,
perform drive self-maintenance, and validate proper drive operation.
SCSI defect and error management involves drive internal defect/error management and SAS system error considerations (errors in
communications between the initiator and the drive). In addition, Seagate provides the following technologies used to increase data
integrity and drive reliability:
• Background Media Scan (see Section 9.4)
• Media Pre-Scan (see Section 9.5)
• Deferred Auto-Reallocation (see Section 9.6)
• Idle Read After Write (see Section 9.7)
The read error rates and specified storage capacities are not dependent on host (initiator) defect management routines.
9.1 DRIVE INTERNAL DEFECTS/ERRORS
During the initial drive format operation at the factory, media defects are identified, tagged as being unusable, and their locations
recorded on the drive primary defects list (referred to as the “P’ list and also as the ETF defect list). At factory format time, these known
defects are also reallocated, that is, reassigned to a new place on the medium and the location listed in the defects reallocation table. The
“P” list is not altered after factory formatting. Locations of defects found and reallocated during error recovery procedures after drive
shipment are listed in the “G” list (defects growth list). The “P” and “G” lists may be referenced by the initiator using the Read Defect
Data command.
Details of the SCSI commands supported by the drive are described in the SAS Interface Manual. Also, more information on the drive
Error Recovery philosophy is presented in the SAS Interface Manual.
9.2 DRIVE ERROR RECOVERY PROCEDURES
When an error occurs during drive operation, the drive, if programmed to do so, performs error recovery procedures to attempt to recover
the data. The error recovery procedures used depend on the options previously set in the Error Recovery Parameters mode page. Error
recovery and defect management may involve using several SCSI commands described in the SAS Interface Manual. The drive
implements selectable error recovery time limits required in video applications.
The error recovery scheme supported by the drive provides a way to control the total error recovery time for the entire command in
addition to controlling the recovery level for a single LBA. The total amount of time spent in error recovery for a command can be
limited using the Recovery Time Limit bytes in the Error Recovery mode page. The total amount of time spent in error recovery for a
single LBA can be limited using the Read Retry Count or Write Retry Count bytes in the Error Recovery mode page.
The drive firmware error recovery algorithms consist of 12 levels for read recoveries and five levels for write. Each level may consist of
multiple steps, where a step is defined as a recovery function involving a single re-read or re-write attempt. The maximum level used by
the drive in LBA recovery is determined by the read and write retry counts.
Table 6 equates the read and write retry count with the maximum possible recovery time for read and write recovery of individual LBAs.
The times given do not include time taken to perform reallocations. Reallocations are performed when the ARRE bit (for reads) or
AWRE bit (for writes) is one, the RC bit is zero, and the recovery time limit for the command has not yet been met. Time needed to
perform reallocation is not counted against the recovery time limit.
When the RC bit is one, reallocations are disabled even if the ARRE or AWRE bits are one. The drive will still perform data recovery
actions within the limits defined by the Read Retry Count, Write Retry Count, and Recovery Time Limit parameters. However, the drive
does not report any unrecovered errors.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 41
Page 47

Table 6 Read and write retry count maximum recovery times
Maximum recovery time per
Read retry count*
1 124.32 1 53.91
5 621.62 2 79.89
10 1243.23 3 97.86
15 1864.85 4 175.85
20 (default) 2486.47 5 (default) 421.79
LBA (cumulative, ms) Write retry count
0 35.94
Maximum recovery time per
LBA (cumulative, ms)
* For read retry count, every tick ~ 5% of total error recovery. Valid range setting is 1-20.
e.g. 1 ~ 5%
5 ~ 25%
20 ~ 100%
Setting these retry counts to a value below the default setting could result in degradation of the unrecovered error rate. For example,
suppose the read/write recovery page has the RC bit = 0 and if the read retry count is set to 5, this means ~ 25% of error recovery will be
executed which consumes 621.62 ms (please refer to the table above). If the limit is reached and a LBA has not yet been recovered (i.e.
requires retries beyond 621.62 ms), the command will end with Check Condition status report and unrecoverable read error will be
reported.
9.3 SAS SYSTEM ERRORS
Information on the reporting of operational errors or faults across the interface is given in the SAS Interface Manual. The SSP Response
returns information to the host about numerous kinds of errors or faults. The Receive Diagnostic Results reports the results of diagnostic
operations performed by the drive.
Status returned by the drive to the initiator is described in the SAS Interface Manual. Status reporting plays a role in systems error
management and its use in that respect is described in sections where the various commands are discussed.
9.4 BACKGROUND MEDIA SCAN
Backg rou nd Med ia Sc an (BM S) is a s elf- ini tiat ed me dia sc an. B MS is d efin ed in t he T10 d ocu ment S PC- 4 avai lab le fro m the T 10
committee. BMS performs sequential reads across the entire pack of the media while the drive is idle. In RAID arrays, BMS allows hot
spare drives to be scanned for defects prior to being put into service by the host system. On regular duty drives, if the host system makes
use of the BMS Log Page, it can avoid placing data in suspect locations on the media. Unreadable and recovered error sites will be logged
or reallocated per ARRE/AWRE settings.
With BMS, the host system can consume less power and system overhead by only checking BMS status and results rather than tying up
the bus and consuming power in the process of host-initiated media scanning activity.
Since the background scan functions are only done during idle periods, BMS causes a negligible impact to system performance. The first
BMS scan for a newly manufactured drive is performed as quickly as possible to verify the media and protect data by setting the “Start
time after idle” to 5ms, all subsequent scans begin after 500ms of idle time. Other features that normally use idle time to function will
function normally because BMS functions for bursts of 800ms and then suspends activity for 100ms to allow other background functions
to operate.
BMS interrupts immediately to service host commands from the interface bus while performing reads. BMS will complete any BMSinitiated error recovery prior to returning to service host-initiated commands. Overhead associated with a return to host-servicing activity
from BMS only impacts the first command that interrupted BMS, this results in a typical delay of about 1 ms.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 42
Page 48

9.5 MEDIA PRE-SCAN
Media Pre-Scan is a feature that allows the drive to repair media errors that would otherwise have been found by the host system during
critical data accesses early in the drive’s life. The default setting for Media Pre-Scan is enabled on standard products. Media Pre-Scan
checks each write command to determine if the destination LBAs have been scanned by BMS. If the LBAs have been verified, the drive
proceeds with the normal write command. If the LBAs have not been verified by BMS, Pre-Scan will convert the write to a write verify
to certify that the data was properly written to the disk.
NOTE
To expedite the scan of the full pack and subsequently exit from the Pre-Scan period, BMS will begin scanning immediately when the
drive goes to idle during the Pre-Scan period. In the event that the drive is in a high transaction traffic environment and is unable to
complete a BMS scan within 24 power on hours BMS will disable Pre-Scan to restore full performance to the system.
During Pre-Scan write verify commands, write performance may decrease by 50% until Pre-Scan completes. Write
performance testing should be performed after Pre-Scan is complete. This may be checked by reading the BMS status.
9.6 DEFERRED AUTO-REALLOCATION
Deferred Auto-Reallocation (DAR) simplifies reallocation algorithms at the system level by allowing the drive to reallocate unreadable
locations on a subsequent write command. Sites are marked for DAR during read operations performed by the drive. When a write
command is received for an LBA marked for DAR, the auto-reallocation process is invoked and attempts to rewrite the data to the
original location. If a verification of this rewrite fails, the sector is re-mapped to a spare location.
This is in contrast to the system having to use the Reassign Command to reassign a location that was unreadable and then generate a write
command to rewrite the data. DAR is most effective when AWRE and ARRE are enabled—this is the default setting from the Seagate
factory. With AWRE and ARRE disabled DAR is unable to reallocate the failing location and will report an error sense code indicating
that a write command is being attempted to a previously failing location.
9.7 IDLE READ AFTER WRITE
Idle Read After Write (IRAW) utilizes idle time to verify the integrity of recently written data. During idle periods, no active system
requests, the drive reads recently written data from the media and compares it to valid write command data resident in the drives data
buffer. Any sectors that fail the comparison result in the invocation of a rewrite and auto-reallocation process. The process attempts to
rewrite the data to the original location. If a verification of this rewrite fails, the sector is re-mapped to a spare location.
9.8 PROTECTION INFORMATION (PI)
Protection Information is intended as a standardized approach to system level LRC traditionally provided by systems using 520 byte formatted LBAs. Drives formatted with PI information provide the same, common LBA count (i.e. same capacity point) as non-PI formatted drives. Sequential performance of a PI drive will be reduced by approximately 1.56% due to the extra overhead of PI being
transferred from the media that is not calculated as part of the data transferred to the host. To determine the full transfer rate of a PI drive,
transfers should be calculated by adding the 8 extra bytes of PI to the transferred LBA length, i.e. 512 + 8 = 520. PI formatted drives are
physically formatted to 520 byte sectors that store 512 bytes of customer data with 8 bytes of Protection Information appended to it. The
advantage of PI is that the Protection Information bits can be managed at the HBA and HBA driver level. Allowing a system that typically does not support 520 LBA formats to integrate this level of protection.
Protection Information is valid with any supported LBA size. 512 LBA size is used here as common example.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 43
Page 49

9.8.1 Levels of PI
There are 4 types of Protection Information.
Type 0 - Describes a drive that is not formatted with PI information bytes. This allows for legacy support in non-PI systems.
Type 1 - Provides support of PI protection using 10 and 16 byte commands. The RDPROTECT and WRTPROTECT bits allow for
checking control through the CDB. Eight bytes of Protection Information are transmitted at LBA boundaries across the interface if
RDPROTECT and WRTPROTECT bits are nonzero values. Type 1 does not allow the use of 32 byte commands.
Type 2 - Provides checking control and additional expected fields within the 32 byte CDBs. Eight bytes of Protection Information are
transmitted at LBA boundaries across the interface if RDPROTECT and WRTPROTECT bits are nonzero values. Type 2 does allow the
use of 10 and 16 byte commands with zero values in the RDPROTECT and WRTPROTECT fields. The drive will generate 8 bytes
(e.g.0xFFFF) 8 bytes of Protection Information to be stored on the media, but the 8 bytes will not be transferred to the host during a read
command.
Type 3 - Seagate products do not support Type 3.
9.8.2 Setting and determining the current Type Level
A drive is initialized to a type of PI by using the format command on a PI capable drive. Once a drive is formatted to a PI Type, it may be
queried by a Read Capacity (16) command to report the PI type which it is currently formatted to. PI Types cannot coexist on a single
drive. A drive can only be formatted to a single PI Type. It can be changed at anytime to a new Type but requires a low level format which
destroys all existing data on the drive. No other vehicle for changing the PI type is provided by the T10 SBC3 specification.
Type 1 PI format CDB command: 04 90 00 00 00 00, Write Buffer: 00 A0 00 00
Type 2 PI format CDB command: 04 D0 00 00 00 00, Write Buffer: 00 A0 00 00
9.8.3 Identifying a Protection Information drive
The Standard Inquiry provides a bit to indicate if PI is support by the drive. Vital Product Descriptor (VPD) page 0x86 provides bits to
indicate the PI Types supported and which PI fields the drive supports checking.
NOTE
For further details with respect to PI, please refer to SCSI Block
Commands - 3 (SBC-3) Draft Standard documentation.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 44
Page 50

10.0 INSTALLATION
Constellation ES.3 disk drive installation is a plug-and-play process. There are no jumpers, switches, or terminators on the drive.
SAS drives are designed to be used in a host system that provides a SAS-compatible backplane with bays designed to accommodate the
drive. In such systems, the host system typically provides a carrier or tray into which you need to mount the drive. Mount the drive to the
carrier or tray provided by the host system using four M3 x 0.5 metric screws. When tightening the screws, use a maximum torque of 4.5
in-lb +/- 0.45 in-lb. Do not over-tighten or force the screws. You can mount the drive in any orientation.
SAS drives are designed to be attached to the host system without I/O or power cables. If you
NOTE
Slide the carrier or tray into the appropriate bay in your host system using the instructions provided by the host system. This connects the
drive directly to your system’s SAS connector. The SAS connector is normally located on a SAS backpanel. See Section 11.4.1 for
additional information about these connectors.
Power is supplied through the SAS connector.
The drive is shipped from the factory low-level formatted in 512-byte logical blocks. You need to reformat the drive only if you want to
select a different logical block size.
intend the use the drive in a non-backplane host system, connecting the drive using high-quality
cables is acceptable as long as the I/O cable length does not exceed 4 meters (13.1 feet).
Figure 17. Physical interface
NOTE
Image is for reference only, may not represent actual drive.
10.1 DRIVE ORIENTATION
The drive may be mounted in any orientation. All drive performance characterizations, however, have been done with the drive in
horizontal (discs level) and vertical (drive on its side) orientations, which are the two preferred mounting orientations.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 45
Page 51

10.2 COOLING
Cabinet cooling must be designed by the customer so that the ambient temperature immediately surrounding the drive will not exceed
temperature conditions specified in Section 6.5.1, "Temperature."
The rack, cabinet, or drawer environment for the drive must provide heat removal from the electronics and head and disk assembly
(HDA). You should confirm that adequate heat removal is provided using the temperature measurement guidelines described in Section
6.5.1.
Forced air flow may be required to keep temperatures at or below the temperatures specified in Section 6.5.1 in which case the drive
should be oriented, or air flow directed, so that the least amount of air flow resistance is created while providing air flow to the
electronics and HDA. Also, the shortest possible path between the air inlet and exit should be chosen to minimize the travel length of air
heated by the drive and other heat sources within the rack, cabinet, or drawer environment.
If forced air is determined to be necessary, possible air-flow patterns are shown in Figure 18. The air-flow patterns are created by one or
more fans, either forcing or drawing air as shown in the illustrations. Conduction, convection, or other forced air-flow patterns are
acceptable as long as the temperature measurement guidelines of Section 6.5.1 are met.
ote Air flo s in the direction sho n (back to front)
or in reverse direction (front to back)
ote Airflosinthedirectionshonor
in reverse direction (side to side)
Figure 18. Air flow
NOTE
Image is for reference only, may not represent actual drive.
Above unit
nder unit
Above unit
nder unit
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 46
Page 52

10.3 DRIVE MOUNTING
Mount the drive using the bottom or side mounting holes. If you mount the drive using the bottom holes, ensure that you do not
physically distort the drive by attempting to mount it on a stiff, non-flat surface.
The allowable mounting surface stiffness is 80 lb/in (14.0 N/mm). The following equation and paragraph define the allowable mounting
surface stiffness:
KxX=F< 15lb = 67N
where K is the mounting surface stiffness (units in lb/in or N/mm) and X is the out-of-plane surface distortion (units in inches or
millimeters). The out-of-plane distortion (X) is determined by defining a plane with three of the four mounting points fixed and
evaluating the out-of-plane deflection of the fourth mounting point when a known force (F) is applied to the fourth point.
NOTE
Breather hole location - top cover
Do not cover breather hole on top cover.
Breather Hole
Do Not
Cover
10.4 GROUNDING
Signal ground (PCBA) and HDA ground are connected together in the drive and cannot be separated by the user. The equipment in which
the drive is mounted is connected directly to the HDA and PCBA with no electrically isolating shock mounts. If it is desired for the
system chassis to not be connected to the HDA/PCBA ground, the systems integrator or user must provide a nonconductive (electrically
isolating) method of mounting the drive in the host equipment.
Increased radiated emissions may result if you do not provide the maximum surface area ground connection between system ground and
drive ground. This is the system designer’s and integrator’s responsibility.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 47
Page 53

11.0 INTERFACE REQUIREMENTS
This section partially describes the interface requirements as implemented on Constellation ES.3 drives. Additional information is
provided in the SAS Interface Manual (part number 100293071).
11.1 SAS FEATURES
This section lists the SAS-specific features supported by Constellation ES.3 drives.
11.1.1 task management functions
Table 7 lists the SAS task management functions supported.
Table 7 SAS task management functions supported
TASK NAME SUPPORTED
Abort Task Yes
Clear ACA Yes
Clear task set Yes
Abort task set Yes
Logical Unit Reset Yes
Query Task Yes
11.1.2 task management responses
Table 8 lists the SAS response codes returned for task management functions supported.
Table 8 Task management response codes
FUNCTION NAME RESPONSE CODE
Function complete 00
Invalid frame 02
Function not supported 04
Function failed 05
Function succeeded 08
Invalid logical unit 09
11.2 DUAL PORT SUPPORT
Constellation ES.3 SAS drives have two independent ports. These ports may be connected in the same or different SCSI domains. Each
drive port has a unique SAS address.
The two ports have the capability of independent port clocking (e.g. both ports can run at 6Gb/s or the first port can run at 6Gb/s while the
second port runs at 3Gb/s. The supported link rates are 1.5, 3.0, or 6.0 Gb/s.
Subject to buffer availability, the Constellation ES.3 drives support:
• Concurrent port transfers—The drive supports receiving COMMAND, TASK management transfers on both ports at the same time.
• Full duplex—The drive supports sending XFER_RDY, DATA and RESPONSE transfers while receiving frames on both ports.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 48
Page 54

11.3 SCSI COMMANDS SUPPORTED
Table 9 lists the SCSI commands supported by Constellation ES.3 drives.
Table 9 Supported commands
COMMAND NAME COMMAND CODE SUPPORTED
Change Definition 40h N
Compare 39h N
Copy 18h N
Copy and Verify 3Ah N
Format Unit [1] [5] 04h Y
DCRT bit supported Y
DPRY bit supported N
DSP bit supported Y
IMMED bit supported Y
IP bit supported Y
SI (Security Initialize) bit supported N
STPF bit supported Y
VS (vendor specific) N
Inquiry 12h Y
Date Code page (C1h) Y
Device Behavior page (C3h) Y
Firmware Numbers page (C0h) Y
Implemented Operating Def page (81h) Y
Jumper Settings page (C2h) Y
Supported Vital Product Data page (00h) Y
Unit Serial Number page (80h) Y
Lock-unlock cache 36h N
Log Select 4Ch Y
PCR bit Y
DU bit N
DS bit Y
TSD bit Y
ETC bit N
TMC bit N
LP bit N
Protocol-specific Log Page for SAS (18h) Y
Log Sense 4Dh Y
Application Client Log page (0Fh) N
Buffer Over-run/Under-run page (01h) N
Cache Statistics page (37h) Y
Factory Log page (3Eh) Y
Information Exceptions Log page (2Fh) N
Last n Deferred Errors or Asynchronous Events page (0Bh) N
Last n Error Events page (07h) N
Non-medium Error page (06h) Y
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 49
Page 55

Table 9 Supported commands
COMMAND NAME COMMAND CODE SUPPORTED
Pages Supported list (00h) Y
Read Error Counter page (03h) Y
Read Reverse Error Counter page (04h) N
Self-test Results page (10h) Y
Start-stop Cycle Counter page (0Eh) Y
Temperature page (0Dh) Y
Verify Error Counter page (05h) Y
Write error counter page (02h) Y
Mode Select (same pages as Mode Sense 1Ah) 15h Y [2]
Mode Select (10) (same pages as Mode Sense 1Ah) 55h Y
Mode Sense 1Ah Y [2]
Caching Parameters page (08h) Y
Control Mode page (0Ah) Y
Disconnect/Reconnect (02h) Y
Error Recovery page (01h) Y
Format page (03h) Y
Information Exceptions Control page (1Ch) Y
Notch and Partition Page (0Ch) N
Protocol-Specific Port page (19h) Y
Power Condition page (1Ah) Y
Rigid disk Drive Geometry page (04h) Y
Unit Attention page (00h) Y
Verify Error Recovery page (07h) Y
Xor Control page (10h) N
Mode Sense (10) (same pages as Mode Sense 1Ah) 5Ah Y
Persistent Reserve In 5Eh Y
Persistent Reserve Out 5Fh Y
Prefetch 34h N
Read (6) 08h Y
Read (10) 28h Y
DPO bit supported Y
FUA bit supported Y
Read (12) A8h N
Read (16) 88h Y
Read (32) 7Fh/0009h N
Read Buffer (modes 0, 2, 3, Ah and Bh supported) 3Ch Y (non-SED drives only)
Read Capacity (10) 25h Y
Read Capacity (16) 9Eh/10h Y
Read Defect Data (10) 37h Y
Read Defect Data (12) B7h Y
Read Long 3Eh Y (non-SED drives only)
Read Long (16) 9Eh/11h Y
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 50
Page 56

Table 9 Supported commands
COMMAND NAME COMMAND CODE SUPPORTED
Reassign Blocks 07h Y
Receive Diagnostic Results 1Ch Y
Supported Diagnostics pages (00h) Y
Translate page (40h) Y
Release 17h Y
Release (10) 57h Y
Report LUNs A0h Y
Request Sense 03h Y
Actual Retry Count bytes Y
Extended Sense Y
Field Pointer bytes Y
Reserve 16h Y
3rd Party Reserve Y
Extent Reservation N
Reserve (10) 56h Y
3rd Party Reserve Y
Extent Reservation N
Rezero Unit 01h Y
Sanitize (CRYPTOGRAPHIC ERASE) 48h Y (SED drives only)
Search Data Equal 31h N
Search Data High 30h N
Search Data Low 32h N
Security Protocol In A2h Y (SED models only)
Security Protocol Out B5h Y (SED models only)
Seek (6) 0Bh Y
Seek (10) 2Bh Y
Send Diagnostics 1Dh Y
Supported Diagnostics pages (00h) Y
Translate page (40h) Y
Set Limits 33h N
Start Unit/Stop Unit (spindle ceases rotating) 1Bh Y
Synchronize Cache 35h Y
Synchronize Cache (16) 91h Y
Test Unit Ready 00h Y
Verify (10) 2Fh Y
BYTCHK bit Y
Verify (12) AFh N
Verify (16) AFh Y
Verify (32) 7Fh/000Ah N
Write (6) 0Ah Y
Write (10) 2Ah Y
DPO bit Y
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 51
Page 57

Table 9 Supported commands
COMMAND NAME COMMAND CODE SUPPORTED
FUA bit Y
Write (12) AAh N
Write (16) 8Ah Y
Write (32) 7Fh/000Bh N
Write and Verify (10) 2Eh Y
DPO bit Y
Write and Verify (12) AEh N
Write and Verify (16) 8Eh Y
Write and Verify (32) 7Fh/000Ch N
Write Buffer (modes 0, 2, supported) 3Bh Y (non-SED drives only)
Write Buffer 3Bh
Firmware Download option (modes 5, 7, Ah and Bh) [3] Y (non-SED drives only)
Firmware Download option (modes 4, 5, 7) Y (SED drives only)
Write Long (10) 3Fh Y
Write Long (16) 9Fh/11h Y
Write Same (10) [5] 41h Y
PBdata N
LBdata N
Write Same (16) [5] 93h Y
Write Same (32) 7Fh/000Dh N
XDRead 52h N
XDWrite 50h N
XPWrite 51h N
[1] Constellation ES.3 drives can format to 512, 520 or 528 bytes per logical block.
[2] Warning. Power loss during flash programming can result in firmware corruption. This usually makes the drive inoperable.
[3] Reference Mode Sense command 1Ah for mode pages supported.
[4] Y = Yes. Command is supported.
N = No. Command is not supported.
A = Support is available on special request.
[5] Approximately 1.5 increase in time to complete this command for a SED drive versus a non-SED drive of the same capacity.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 52
Page 58

11.3.1 Inquiry data
Table 10 lists the Inquiry command data that the drive should return to the initiator per the format given in the SAS Interface Manual.
Table 10 Constellation ES.3 inquiry data
BYTES DATA (HEX)
0-15 00 00 xx** 12 8B 00 30 02 53 45 41 47 41 54 45 20 Vendor ID
16-31 [53 54 34 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 32 33} 20 20 20 20 Product ID
32-47 R# R# R# R# S# S# S# S# S# S# S# S# 00 00 00 00
48-63 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
64-79 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
80-95 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
96-111 00 43 6F 70 79 72 69 67 68 74 20 28 63 29 20 32* *Copyright
112-127 30* 30* 39* 20 53 65 61 67 61 74 65 20 41 6C 6C 20 notice
128-143 72 69 67 68 74 73 20 72 65 73 65 72 76 65 64 20
* Copyright year (changes with actual year).
** SCSI Revision support. See the appropriate SPC release documentation for definitions.
PP 10 = Inquiry data for an Inquiry command received on Port A.
30 = Inquiry data for an Inquiry command received on Port B.
R# Four ASCII digits representing the last four digits of the product firmware release number.
S# Eight ASCII digits representing the eight digits of the product serial number.
[ ] Bytes 16 through 26 reflect model of drive. The table above shows the hex values for Model ST4000NM0023.
Refer to the values below for the values of bytes 16 through 26 of your particular model:
ST4000NM0043 53 54 34 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 34 33
ST4000NM0063 53 54 34 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 36 33
ST3000NM0023 53 54 33 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 32 33
ST3000NM0043 53 54 33 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 34 33
ST3000NM0063 53 54 33 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 36 33
ST2000NM0023 53 54 32 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 32 33
ST2000NM0043 53 54 32 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 34 33
ST2000NM0063 53 54 32 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 36 33
ST1000NM0023 53 54 31 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 32 33
ST1000NM0043 53 54 31 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 34 33
ST1000NM0063 53 54 31 30 30 30 4E 4D 30 30 36 33
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 53
Page 59

11.3.2 Mode Sense data
The Mode Sense command provides a way for the drive to report its operating parameters to the initiator. The drive maintains four sets of
mode parameters:
1. Default values
Default values are hard-coded in the drive firmware stored in flash E-PROM (nonvolatile memory) on the drive’s PCB. These
default values can be changed only by downloading a complete set of new firmware into the flash E-PROM. An initiator can request
and receive from the drive a list of default values and use those in a Mode Select command to set up new current and saved values,
where the values are changeable.
2. Saved values
Saved values are stored on the drive’s media using a Mode Select command. Only parameter values that are allowed to be changed
can be changed by this method. Parameters in the saved values list that are not changeable by the Mode Select command get their
values from default values storage.
When power is applied to the drive, it takes saved values from the media and stores them as current values in volatile memory. It is
not possible to change the current values (or the saved values) with a Mode Select command before the drive achieves operating
speed and is “ready.” An attempt to do so results in a “Check Condition” status.
On drives requiring unique saved values, the required unique saved values are stored into the saved values storage location on the
media prior to shipping the drive. Some drives may have unique firmware with unique default values also.
On standard OEM drives, the saved values are taken from the default values list and stored into the saved values storage location on
the media prior to shipping.
3. Current values
Current values are volatile values being used by the drive to control its operation. A Mode Select command can be used to change
the values identified as changeable values. Originally, current values are installed from saved or default values after a power on reset,
hard reset, or Bus Device Reset message.
4. Changeable values
Changeable values form a bit mask, stored in nonvolatile memory, that dictates which of the current values and saved values can be
changed by a Mode Select command. A one (1) indicates the value can be changed. A zero (0) indicates the value is not changeable.
For example, in Table 11, refer to Mode page 81, in the row entitled “CHG.” These are hex numbers representing the changeable values for Mode page 81. Note in columns 5 and 6 (bytes 04 and 05), there is 00h which indicates that in bytes 04 and 05 none of the
bits are changeable. Note also that bytes 06, 07, 09, 10, and 11 are not changeable, because those fields are all zeros. In byte 02, hex
value FF equates to the binary pattern 11111111. If there is a zero in any bit position in the field, it means that bit is not changeable.
Since all of the bits in byte 02 are ones, all of these bits are changeable.
The changeable values list can only be changed by downloading new firmware into the flash E-PROM.
NOTE
Because there are often several different versions of drive control firmware in the total population of drives in
the field, the Mode Sense values given in the following tables may not exactly match those of some drives.
The following tables list the values of the data bytes returned by the drive in response to the Mode Sense command pages for SCSI
implementation (see the SAS Interface Manual ).
DEF = Default value. Standard OEM drives are shipped configured this way.
CHG = Changeable bits; indicates if default value is changeable.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 54
Page 60

Table 11 Mode Sense data changeable and default values for 4TB drives
MODE DATA HEADER:
01 9a 00 10 01 00 00 10
BLOCK DESCRIPTOR:
00 00 00 01 5d 50 a3 b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 02 00
MODE PAGES:
DEF 81 0a c0 14 ff 00 00 00 05 00 ff ff
CHG 81 0a ff ff 00 00 00 00 ff 00 ff ff
DEF 82 0e 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 a0 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 82 0e 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff ff ff ff 00 00 00 00
DEF 83 16 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 02 04 c4 02 00 00 01 00 dc 00 1c 40 00 00 00
CHG 83 16 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 84 16 00 00 04 0a 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 1c 20 00 00
CHG 84 16 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 87 0a 00 14 ff 00 00 00 00 00 ff ff
CHG 87 0a 0f ff 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff ff
DEF 88 12 14 00 ff ff 00 00 ff ff ff ff 80 20 00 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 88 12 a5 00 00 00 ff ff ff ff 00 00 20 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 8a 0a 06 00 00 80 00 00 00 00 7f bc
CHG 8a 0a 0f f6 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 98 06 06 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 98 06 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 99 0e 46 00 07 d0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 99 0e 50 00 ff ff ff ff ff ff 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 9a 26 00 06 00 00 04 b0 00 00 8c a0 00 00 17 70 00 00 46 50 00 00 46 50 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 58
CHG 9a 26 01 0f ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 fc
DEF 9c 0a 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 01
CHG 9c 0a 9d 0f ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
DEF 80 06 00 80 0f 00 00 00
CHG 80 06 b7 c0 8f 00 00 00
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 55
Page 61

Table 12 Mode Sense data changeable and default values for 3TB drives
MODE DATA HEADER:
01 9a 00 10 01 00 00 10
BLOCK DESCRIPTOR:
00 00 00 01 5d 50 a3 b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 02 00
MODE PAGES:
DEF 81 0A C0 14 FF 00 00 00 05 00 FF FF
CHG 81 0A FF FF 00 00 00 00 FF 00 FF FF
DEF 82 0E 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 A0 00 00 00 00
CHG 82 0E 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF FF FF 00 00 00 00
DEF 83 16 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 02 04 C4 02 00 00 01 00 DC 00 1C 40 00 00 00
CHG 83 16 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 84 16 00 00 04 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 1C 20 00 00
CHG 84 16 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 87 0A 00 14 FF 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF
CHG 87 0A 0F FF 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF
DEF 88 12 14<00 FF FF 00 00 FF FF FF FF 80 20 00 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 88 12 A5 00 00 00 FF FF FF FF 00 00 20 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 8A 0A 06 00 00 80 00 00 00 00 65 90
CHG 8A 0A 0F F6 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 98 06 06 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 98 06 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 99 0E 46 00 07 D0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 99 0E 50 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 9A 26 00 06 00 00 04 B0 00 00 8C A0 00 00 17 70 00 00 46 50 00 00 46 50 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 58
CHG 9A 26 01 0F FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 FC
DEF 9C 0A 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 01
CHG 9C 0A 9D 0F FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
DEF 80 06 00 80 0F 00 00 00
CHG 80 06 B7 C0 8F 00 00 00
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 56
Page 62

Table 13 Mode Sense data changeable and default values for 2TB drives
MODE DATA HEADER:
01 9a 00 10 01 00 00 10
BLOCK DESCRIPTOR:
00 00 00 01 5d 50 a3 b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 02 00
MODE PAGES:
DEF 81 0A C0 14 FF 00 00 00 05 00 FF FF
CHG 81 0A FF FF 00 00 00 00 FF 00 FF FF
DEF 82 0E 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 A0 00 00 00 00
CHG 82 0E 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF FF FF 00 00 00 00
DEF 83 16 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 02 04 C4 02 00 00 01 00 DC 00 1C 40 00 00 00
CHG 83 16 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 84 16 00 00 04 05 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 1C 20 00 00
CHG 84 16 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 87 0A 00 14 FF 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF
CHG 87 0A 0F FF 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF
DEF 88 12 14 00 FF FF 00 00 FF FF FF FF 80 20 00 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 88 12 A5 00 00 00 FF FF FF FF 00 00 20 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 8A 0A 02 00 00 80 00 00 00 00 47 7C
CHG 8A 0A 0F F6 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 98 06 06 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 98 06 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 99 0E 46 00 07 D0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 99 0E 50 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 9A 26 00 06 00 00 04 B0 00 00 8C A0 00 00 17 70 00 00 46 50 00 00 46 50 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 58
CHG 9A 26 01 0F FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 FC
DEF 9C 0A 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 01
CHG 9C 0A 9D 0F FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
DEF 80 06 00 80 0F 00 00 00
CHG 80 06 B7 C0 8F 00 00 00
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 57
Page 63

Table 14 Mode Sense data changeable and default values for 1TB drives
MODE DATA HEADER:
01 9a 00 10 01 00 00 10
BLOCK DESCRIPTOR:
00 00 00 01 5d 50 a3 b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 02 00
MODE PAGES:
DEF 81 0A C0 14 FF 00 00 00 05 00 FF FF
CHG 81 0A FF FF 00 00 00 00 FF 00 FF FF
DEF 82 0E 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 A0 00 00 00 00
CHG 82 0E 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF FF FF 00 00 00 00
DEF 83 16 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 02 04 C4 02 00 00 01 00 DC 00 1C 40 00 00 00
CHG 83 16 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 84 16 00 00 04 03 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 1C 20 00 00
CHG 84 16 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 87 0A 00 14 FF 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF
CHG 87 0A 0F FF 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF
DEF 88 12 14<00 FF FF 00 00 FF FF FF FF 80 20 00 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 88 12 A5 00 00 00 FF FF FF FF 00 00 20 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 8A 0A 02 00 00 80 00 00 00 00 2A 30
CHG 8A 0A 0F F6 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 98 06 06 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 98 06 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 99 0E 46 00 07 D0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
CHG 99 0E 50 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 00 00 00 00 00
DEF 9A 26 00 06 00 00 04 B0 00 00 8C A0 00 00 17 70 00 00 46 50 00 00 46 50 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 58
CHG 9A 26 01 0F FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 FC
DEF 9C 0A 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 01
CHG 9C 0A 9D 0F FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
DEF 80 06 00 80 0F 00 00 00
CHG 80 06 B7 C0 8F 00 00 00
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 58
Page 64

11.4 MISCELLANEOUS OPERATING FEATURES AND CONDITIONS
Table 15 lists various features and conditions. A “Y” in the support column indicates the feature or condition is supported. An “N” in the
support column indicates the feature or condition is not supported.
Table 15 Miscellaneous features
Supported Feature or condition
N Automatic contingent allegiance
N Asynchronous event notification
N Synchronized (locked) spindle operation
Y Segmented caching
N Zero latency read
Y Queue tagging (up to 64 queue tags supported)
Y Deferred error handling
Y Parameter rounding (controlled by Round bit in Mode Select page 0)
Y Reporting actual retry count in Extended Sense bytes 15, 16, and 17
N Adaptive caching
Y SMP=1inModeSelect command needed to save RPL and rotational offset bytes
Table 16 Miscellaneous status
Supported Status
Y Good
Y Check condition
Y Condition met/good
Y Busy
Y Intermediate/good
Y Intermediate/condition met/good
Y Reservation conflict
Y Task set full
N ACA active
N ACA active, faulted initiator
11.4.1 SAS physical interface
Figure 19 shows the location of the SAS device connector J1. Figures 20 and 21 provide the dimensions of the SAS connector.
Details of the physical, electrical, and logical characteristics are provided within this section. The operational aspects of Seagate’s SAS
drives are provided in the SAS Interface Manual.
Figure 19. Physical interface
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 59
Page 65

0.80 (6X)
0.30 0.05 (2X)
2.00 (3X)
7.625.92
5.08
42.73 REF.
41.13 0.15
0.20 B
C
A
4.65
0.52 0.08 x 45
0.45 0.03 (7X)
0.10 M E
B
1.10
4.00 0.08
0.15 D
0.30 0.05 (4X)
0.35MIN
C OF DATUM D
L
A
B
15.875
1.27 (14X)
P15
C
33.43 0.05
5.08
C OF DATUM B
L
15.875
1.27 (6X)
P1
SEE Detail1
B
0.84 0.05 (22X)
S1
S7
R0.30 0.08 (4X)
0.15 B
4.90 0.08
Figure 20. SAS device plug dimensions
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 60
Page 66

Detail A
SEE Detail 2
2.25 0.05
4.85 0.05
0.10
E
B
S14
6.10
CORING ALLOWED
IN THIS AREA.
4.40 0.15
S8
0.30 0.05 x 45 (5X)
0.40 0.05 X 45 (3X)
R0.30 0.08
A
45
C
1.95 0.08
3.90 0.15
1.23 0.05
0.08 0.05
SECTION A - A
0.08 0.05
Detail 2
0.35 0.05
CONTACT SURFACE FLUSH
TO DATUM A 0.03
30
2.40 0.08
0.10 A
D
SECTION C - C
65
SECTION B - B
1.90 0.08
Figure 21. SAS device plug dimensions (detail)
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 61
Page 67

11.4.2 Physical characteristics
This section defines physical interface connector.
11.4.3 Connector requirements
Contact your preferred connector manufacturer for mating part information. Part numbers for SAS connectors will be provided in a future
revision of this publication when production parts are available from major connector manufacturers.
The SAS device connector is illustrated in Figures 20 and 21.
11.4.4 Electrical description
SAS drives use the device connector for:
• DC power
• SAS interface
• Activity LED
This connector is designed to either plug directly into a backpanel or accept cables.
11.4.5 Pin descriptions
This section provides a pin-out of the SAS device and a description of the functions provided by the pins.
Table 17 SAS pin descriptions
PIN SIGNAL NAME SIGNAL TYPE PIN SIGNAL NAME SIGNAL TYPE
S1 Port A Ground P1* NC (reserved 3.3Volts)
S2* +Port A_in Diff. input pair P2* NC (reserved 3.3Volts)
S3* -Port A_in P3 NC (reserved 3.3Volts)
S4 Port A Ground P4 Ground
S5* -Port A_out Diff output pair P5 Ground
S6* +Port A_out P6 Ground
S7 Port A Ground P7 5 Volts charge
S8 Port B Ground P8* 5 Volts
S9* +Port B_in Diff. input pair P9* 5 Volts
S10* -Port B_in P10 Ground
S11 Port A Ground P11* Ready LED Open collector out
S12* -Port B_out Diff output pair P12 Ground
S13* +Port B_out P13 12 Volts charge
S14 Port B Ground P14* 12 Volts
P15* 12 Volts
* - Short pin to support hot plugging
NC - No connection in the drive.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 62
Page 68

11.4.6 SAS transmitters and receivers
A typical SAS differential copper transmitter and receiver pair is shown in Figure 22. The receiver is AC coupling to eliminate ground
shift noise.
01
01
RX
Receiver
100100
RY
TX
Transmitter
TY
Figure 22. SAS transmitters and receivers
Transfer Medium
Differential
11.4.7 Power
The drive receives power (+5 volts and +12 volts) through the SAS device connector.
Three + 12 vol t pin s prov ide po wer to t he dr ive, 2 s hort a nd 1 lo ng. Th e curr ent re tur n for th e +12 vo lt po wer su pply i s thr ough the
common ground pins. The supply current and return current must be distributed as evenly as possible among the pins.
Three +5 volt pins provide power to the drive, 2 short and 1 long. The current return for the +5 volt power supply is through the common
ground pins. The supply current and return current must be distributed as evenly as possible among the pins.
Current to the drive through the long power pins may be limited by the system to reduce inrush current to the drive during hot plugging.
11.5 SIGNAL CHARACTERISTICS
This section describes the electrical signal characteristics of the drive’s input and output signals. See Table 17 for signal type and signal
name information.
11.5.1 Ready LED Out
The Ready LED Out signal is driven by the drive as indicated in Table 18.
Table 18 Ready LED Out conditions
NORMAL COMMAND ACTIVITY LED STATUS
Ready LED Meaning bit mode page 19h
Spun down and no activity Off Off
Spun down and activity (command executing) On On
Spun up and no activity On Off
Spun up and activity (command executing) Off On
01
Spinning up or down Blinks steadily
Format in progress, each cylinder change Toggles on/off
(50% on and 50% off, 0.5 seconds on and off for 0.5 seconds)
The Ready LED Out signal is designed to pull down the cathode of an LED. The anode is attached to the proper +3.3 volt supply through
an appropriate current limiting resistor. The LED and the current limiting resistor are external to the drive. See Table 19 for the output
characteristics of the LED drive signals.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 63
Page 69

Table 19 LED drive signal
STATE TEST CONDITION OUTPUT VOLTAGE
LED off, high 0 V ≤ VOH ≤ 3.6 V -100 μA < IOH < 100 μA
LED on, low I
= 15 mA 0 ≤ VOL ≤ 0.225 V
OL
11.5.2 Differential signals
The drive SAS differential signals comply with the intra-enclosure (internal connector) requirements of the SAS standard.
Table 20 defines the general interface characteristics.
Table 20 General interface characteristics
CHARACTERISTIC UNITS 1.5GB/S 3.0GB/S 6.0GB/S
Bit rate (nominal) Mbaud 1,500 3,000 6,000
Unit interval (UI)(nominal) ps 666.6 333.3 166.6
Impedance (nominal, differential ) ohm 100 100 100
Transmitter transients, maximum V ± 1.2 ± 1.2 ± 1.2
Receiver transients, maximum V ± 1.2 ± 1.2 ± 1.2
11.6 SAS-2 SPECIFICATION COMPLIANCE
Seagate SAS-2 drives are entirely compatible with the latest SAS-2 Specification (T10/1760-D) Revision 16.
The most important characteristic of the SAS-2 drive at 6Gb/s is that the receiver is capable of adapting the equalizer to optimize the
receive margins. The SAS-2 drive has two types of equalizers:
1. A Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) which utilizes the standard SAS-2 training pattern transmitted during the SNW-3 training
gap. The DFE circuit can derive an optimal equalization characteristic to compensate for many of the receive losses in the system.
2. A Feed Forward Equalizer (FFE) optimized to provide balanced receive margins over a range of channels bounded by the best and
worst case channels as defined by the relevant ANSI standard.
11.7 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Please contact your Seagate representative for SAS electrical details, if required.
For more information about the Phy, Link, Transport, and Applications layers of the SAS interface, refer to the Seagate SAS Interface
Manual, part number 100293071.
For more information about the SCSI commands used by Seagate SAS drives, refer to the Seagate SCSI Commands Reference Manual,
part number 100293068.
CONSTELLATION ES.3 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 64
Page 70

Index
Numerics
12 volt
pins 63
5 volt pins 63
6 Gbps 64
A
abort task set function 48
AC coupling 63
AC power requirements 19
ACA active status 59
ACA active, faulted initiator status 59
acoustics 36
active LED Out signal 63
actuator 8
assembly design 6
adaptive caching 59
Admin SP 39
AES-128 data encryption 39
air cleanliness 36
air flow 46
illustrated 46
air inlet 46
altitude 33
ambient 33
ambient temperature 46
Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) 13
ANSI documents
SCSI 5
Serial Attached SCSI 5
asynchronous event notification 59
audible noise 3
Australian C-Tick 4
auto write and read reallocation
programmable 7
automatic contingent allegiance 59
average idle current 20, 21, 22, 23
average rotational latency 9
B
Background Media Scan 42
backpanel 62
Band 0 40
BandMasterX 39
BMS 42
BSMI 4
buffer
data 7
space 10
busy status 59
bytes per surface 9
bytes per track 9
C
cache operation 10
cache segments 10
caching write data 11
Canadian Department of Communications 3
capacity
unformatted 9
CBC 39
CE Marking 4
check condition status 59
China RoHS directive 5
Cipher Block Chaining 39
class B limit 3
clear ACA function 48
clear task set function 48
commands supported 49
condensation 33
condition met/good status 59
connector
illustrated 62
requirements 62
continuous vibration 36
cooling 46
CRC
error 12
Cryptographic erase 40
cryptographic erase 40
C-Tick 4
Current profiles 25
customer service 17
D
DAR 43
Data Bands 40
data bands 39
data block size
modifing the 8
data buffer to/from disk media 9
Data encryption 39
Data Encryption Key 39
data heads
read/write 9
data rate
internal 9
data transfer rate 9
DC power 62
requirements 19
Decision Feedback Equalizer 64
decrypt 39
default MSID password 39
defect and error management 41
defects 41
Constellation ES.3 SAS Product Manual, Rev. C 65
Page 71

Deferred Auto-Reallocation 43
deferred error handling 59
DEK 39
description 6
DFE 64
dimensions 37
disk rotation speed 9
drive 36
drive characteristics 9
Drive Locking 39
drive mounting 37, 47
drive select 62
dual port support 48
E
electrical
description of connector 62
signal characteristics 63
specifications 18
electromagnetic compatibility 3
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) 4
Electromagnetic Compatibility control Regulation 4
Electromagnetic compliance for the European Union
4
electromagnetic susceptibility 36
EMI requirements 3
encryption engine 39
encryption key 40
environment 46
environmental
limits 33
requirements 12
environmental control 36
EraseMaster 39
error
management 41
rates 12
errors 13, 41
European Union 4
F
FCC rules and regulations 3
features 7
interface 48
Federal Information Processing Standard 38
feed forward equalizer 64
FFE 64
FIPS 38
firmware 7
corruption 52
firmware download port 40
flawed sector reallocation 7
Format command execution time 9
function
complete, code 00 48
not supported, code 05 48
reject, code 04 48
G
Global Data Band 40
Good status 59
gradient 33
ground shift noise 63
grounding 47
H
HDA 46, 47
head and disk assembly (HDA) 6
head and disk assembly. See HDA
heads
read/write data 9
heat removal 46
heat source 46
host equipment 47
hot plugging the drive 13
humidity 33
humidity limits 33
I
Identifying a PI drive 44
Idle Read After Write 43
Idle1 18
Idle2 18
Idle3 18
inquiry data 53
installation 45
guide 5
interface
commands supported 49
error rate 12
errors 12
illustrated 59
physical 59
requirements 48
interleave
minimum 9
intermediate/condition met/good status 59
intermediate/good status 59
internal data rate 9
internal defects/errors 41
internal drive characteristics 9
IRAW 43
J
jumpers 45
Constellation ES.3 SAS Product Manual, Rev. C 66
Page 72

K
KCC 4
Korean Communications Commission 4
Korean KCC 4
L
latency
average rotational 9
Locking SP 39
LockOnReset 39
logical block address 10
logical block reallocation scheme 7
logical block size 7, 9
logical segments 10
M
maintenance 12, 13
Manufacturers Secure ID 39
maximum delayed motor start 20, 21, 22, 23
maximum start current 20, 21, 22, 23
mean time between failure. See MTBF
media description 7
Media Pre-Scan 43
minimum sector interleave 9
miscellaneous feature support
Adaptive caching 59
Asynchronous event notification 59
Automatic contingent allegiance 59
Deferred error handling 59
Parameter rounding 59
Queue tagging 59
Reporting actual retry count 59
Segmented caching 59
SMP = 1 in Mode Select command 59
Synchronized (locked) spindle operation 59
Zero latency read 59
miscellaneous status support
ACA active 59
ACA active, faulted initiator 59
Busy 59
Check condition 59
Condition met/good 59
Good 59
Intermediate/condition met/good 59
Intermediate/good 59
Reservation conflict 59
Task set full 59
miscorrected media data 12
Mode sense
data, table 54, 55, 56, 57, 58
mounting 47
holes 47
orientations 45
mounting configuration 37
mounting configuration dimensions 37
MSID 39
MTBF 12, 13
N
noise
audible 3
noise immunity 24
non-operating 33, 34, 36
temperature 33
non-operating vibration 36
Nonrecoverable read errors 13
O
office environment 36
operating 33, 34, 36
option selection 62
options 8
out-of-plane distortion 47
P
package size 35
packaged 34
parameter rounding 59
password 39
passwords 39
PCBA 47
peak bits per inch 9
peak operating current 20, 21, 22, 23
peak-to-peak measurements 24
performance characteristics
detailed 9
general 9
performance degradation 34
performance highlights 7
physical damage 36
physical interface 59
physical specifications 18
PI level - Type 0 44
PI level - Type I 44
PI level - Type II 44
PI level - Type III 44
PI Levels 44
pin descriptions 62
power 63
dissipation 29
requirements, AC 19
requirements, DC 19
sequencing 24
Power Condition mode page 18
power distribution 3
power management 18
PowerChoice 18
PowerChoice reports 19
Constellation ES.3 SAS Product Manual, Rev. C 67
Page 73

PowerCycle 39
prefetch/multi-segmented cache control 10
preventive maintenance 12
protection information 43
protection of data at rest 39
Q
queue tagging 59
R
radio interference regulations 3
RAID Rebuild 7
Random number generator 39
RCD bit 10
read error rates 12, 41
read errors 13
read/write data heads 9
ReadLockEnabled 39
receivers 63
recommended mounting 35
Recoverable Errors 12
recovered media data 12
reference
documents 5
relative humidity 33
reliability 8
specifications 12
reliability and service 12
repair and return information 17
reporting actual retry count 59
reservation conflict status 59
resonance 34
return information 17
RevertSP 40
RNG 39
RoHS 4, 5
rotation speed 9
S
safety 3
Sanitize 40
SAS
interface 62
physical interface 59
task management functions 48
SAS documents 5
SAS Interface Manual 3, 5
SAS-2 specification compliance 64
SCSI interface
commands supported 49
Seagate Technology Support Services 1
Secure ID 39
Security Protocol In 39
Security Protocol Out 39
security providers 39
seek error
defined 12
rate 12
segmented caching 59
self-encrypting drives 39
Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology
8, 13
Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) Interface Manual 2
shielding 3
shipping container 33
shock 34
and vibration 34
shock mount 47
SID 39
signal
characteristics 63
single-unit shipping pack kit 8
SMART 8, 13
SMP = 1 in Mode Select command 59
SNW-3 training gap 64
standards 3
Standby1 18
Standby2 18
START STOP UNIT command 18
start/stop time 10
surface stiffness
allowable for non-flat surface 47
switches 45
synchronized spindle
operation 59
system chassis 47
T
Taiwanese BSMI 4
task management functions 48
Abort task set 48
Clear ACA 48
Clear task set 48
terminate task 48
task management response codes 48
Function complete 00 48
Function not supported 05 48
Function reject 04 48
task set full status 59
TCG 39
temperature 33, 46
limits 33
non-operating 33
regulation 3
See also cooling
terminate task function 48
terminators 45
tracks per inch 9
tracks per surface 9
Constellation ES.3 SAS Product Manual, Rev. C 68
Page 74

transmitters 63
transporting the drive 17
Trusted Computing Group 39
Type 1 PI format 44
Type 2 PI format 44
U
unformatted 8
Unrecoverable Errors 12
unrecovered media data 12
V
vibration 34, 36
W
warranty 17
WriteLockEnabled 39
Z
zero latency read 59
Constellation ES.3 SAS Product Manual, Rev. C 69
Page 75

Seagate Technology LLC
AMERICAS Seagate Technology LLC 10200 South De Anza Boulevard, Cupertino, California 95014, United States, 408-658-1000
ASIA/PACIFIC Seagate Singapore International Headquarters Pte. Ltd. 7000 Ang Mo Kio Avenue 5, Singapore 569877, 65-6485-3888
EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Seagate Technology SAS 16-18 rue du Dôme, 92100 Boulogne-Billancourt, France, 33 1-4186 10 00
Publication Number: 100671510, Rev. C
February 2014
 Loading...
Loading...