Seagate ST500NM0041, ST2000NM0001, ST2000NM0021, ST500NM0001, ST1000NM0041 User Manual
...
Product Manual
Constellation® ES.1 Series SAS
Standard Models
ST2000NM0001
ST1000NM0001
ST500NM0001
Self-Encrypting Drive Models
ST2000NM0021
ST1000NM0021
ST500NM0021
SED FIPS 140-2 Models
ST2000NM0041
ST1000NM0041
ST500NM0041
100650925
Rev. E
March 2012

Revision history
Revision Date Sheets affected or comments
Rev. A 02/18/11 Initial release.
Rev. B 03/23/11 42-43 & 47-48.
Rev. C 04/28/11 fc, 2, 5 & 55
Rev. D 08/11/11 2, 11, 41-42, 56 & back cover.
Rev. E 03/26/12 fc, 2, 11, 41, 43-45, 56 & 58-59.
© 2012, Seagate Technology LLC All rights reserved.
Publication number: 100650925, Rev. E March 2012
Seagate, Seagate Technology and the Wave logo are registered trademarks of Seagate Technology LLC
in the United States and/or other countries. Constellation ES.1 and SeaTools are either trademarks or
registered trademarks of Seagate Technology LLC or one of its affiliated companies in the United States
and/or other countries. The FIPS logo is a certification mark of NIST, which does not imply product
endorsement by NIST, the U.S., or Canadian governments.All other trademarks or registered trademarks
are the property of their respective owners.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without written permission of Seagate Technology LLC. Call 877-PUB-TEK1(877-782-8351) to request permission.
When referring to drive capacity, one gigabyte, or GB, equals one billion bytes and one terabyte, or TB,
equals one trillion bytes. Your computer’s operating system may use a different standard of measurement
and report a lower capacity. In addition, some of the listed capacity is used for formatting and other functions, and thus will not be available for data storage. Actual quantities will vary based on various factors,
including file size, file format, features and application software. Actual data rates may vary depending on
operating environment and other factors. The export or re-export of hardware or software containing
encryption may be regulated by the U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (for
more information, visit www.bis.doc.gov), and controlled for import and use outside of the U.S. Seagate
reserves the right to change, without notice, product offerings or specifications.

Contents
1.0 Seagate Technology support services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2.0 Scope. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
3.0 Applicable standards and reference documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
3.1 Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
3.1.1 Electromagnetic compatibility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
3.1.2 Electromagnetic compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
3.1.3 European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
3.1.4 China Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
3.2 Reference documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
4.0 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4.1 Standard features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
4.2 Media description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
4.3 Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
4.4 Reliability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.5 Formatted capacities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.6 Programmable drive capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.7 Factory-installed options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
5.0 Performance characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.1 Internal drive characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.2 Seek performance characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.2.1 Access time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.2.2 Format command execution time for 512-byte sectors (minutes) . . . . . . . . . . . 11
5.2.3 General performance characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
5.3 Start/stop time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
5.4 Prefetch/multi-segmented cache control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.5 Cache operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.5.1 Caching write data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.5.2 Prefetch operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
6.0 Reliability specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.1 Error rates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.1.1 Recoverable Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.1.2 Unrecoverable Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.1.3 Seek errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
6.1.4 Interface errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
6.2 Reliability and service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
6.2.1 Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) and Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) . . . . 15
6.2.2 Preventive maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
6.2.3 Hot plugging the drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
6.2.4 S.M.A.R.T. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
6.2.5 Thermal monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
6.2.6 Drive Self Test (DST) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.2.7 Product warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
7.0 Physical/electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.1 PowerChoiceTM power management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.1.1 PowerChoice reporting methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.2 AC power requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.3 DC power requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.3.1 Conducted noise immunity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
7.3.2 Power sequencing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
7.3.3 Current profiles. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E i

7.4 Power dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
7.5 Environmental limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
7.5.1 Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
7.5.2 Relative humidity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
7.5.3 Effective altitude (sea level) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
7.5.4 Shock and vibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
7.5.5 Acoustics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
7.5.6 Air cleanliness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
7.5.7 Corrosive environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
7.5.8 Electromagnetic susceptibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
7.6 Mechanical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.0 About FIPS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
9.0 About self-encrypting drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
9.1 Data encryption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
9.2 Controlled access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
9.2.1 Admin SP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
9.2.2 Locking SP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
9.2.3 Default password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.3 Random number generator (RNG). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.4 Drive locking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.5 Data bands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.6 Cryptographic erase. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.7 Authenticated firmware download . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.8 Power requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
9.9 Supported commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
9.10 RevertSP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
10.0 Defect and error management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
10.1 Drive internal defects/errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
10.2 Drive error recovery procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
10.3 SAS system errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
10.4 Background Media Scan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
10.5 Media Pre-Scan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
10.6 Deferred Auto-Reallocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
10.7 Idle Read After Write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
10.8 Protection Information (PI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
10.8.1 Levels of PI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
10.8.2 Setting and determining the current Type Level. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
10.8.3 Identifying a Protection Information drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
11.0 Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
11.1 Drive orientation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
11.2 Cooling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
11.3 Drive mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
11.4 Grounding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
12.0 Interface requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
12.1 SAS features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
12.1.1 task management functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
12.1.2 task management responses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
12.2 Dual port support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
12.3 SCSI commands supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
12.3.1 Inquiry data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
12.3.2 Mode Sense data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
12.4 Miscellaneous operating features and conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
ii Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E

12.4.1 SAS physical interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
12.4.2 Physical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
12.4.3 Connector requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
12.4.4 Electrical description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
12.4.5 Pin descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
12.4.6 SAS transmitters and receivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
12.4.7 Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
12.5 Signal characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
12.5.1 Ready LED Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
12.5.2 Differential signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
12.6 SAS-2 Specification Compliance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
12.7 Additional information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E iii

iv Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E

List of Figures
Figure 1. 2TB model current profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Figure 2. 1TB model current profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Figure 3. 500GB model current profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Figure 4. 2TB models (3Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Figure 5. 2TB models (6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Figure 6. 1TB models (3Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Figure 7. 1TB models (6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Figure 8. 500GB models (3Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Figure 9. 500GB models (6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Figure 10. Location of the HDA temperature check point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Figure 11. Recommended mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Figure 12. Mounting configuration dimensions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Figure 13. Example of FIPS tamper evidence labels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Figure 14. Physical interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Figure 15. Air flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Figure 16. Physical interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Figure 17. SAS device plug dimensions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Figure 18. SAS device plug dimensions (detail). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Figure 19. SAS transmitters and receivers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E v

vi Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E

1.0 Seagate Technology support services
SEAGATE ONLINE SUPPORT and SERVICES
For information regarding products and services, visit http://www.seagate.com/www/en-us/about/contact_us/
Available services include:
Presales & Technical support
Global Support Services telephone numbers & business hours
Authorized Service Centers
For information regarding Warranty Support, visit
http://www.seagate.com/www/en-us/support/warranty_&_returns_assistance
For information regarding Data Recovery Services, visit http://www.i365.com
For Seagate OEM & Distribution partner portal, visit
For Seagate reseller portal, visit
http://spp.seagate.com
https://direct.seagate.com/portal/system
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E 1
2.0 Scope
This manual describes Seagate Technology® LLC, Constellation® ES.1 Series SAS (Serial Attached SCSI)
disk drives.
Constellation ES.1 drives support the SAS Protocol specifications to the extent described in this manual. The
SAS Interface Manual (part number 100293071) describes the general SAS characteristics of this and other
Seagate SAS drives. The Self-Encrypting Drive Reference Manual, part number 100515636, describes the
interface, general operation, and security features available on Self-Encrypting Drive models.
Product data communicated in this manual is specific only to the model numbers listed in this manual. The data
listed in this manual may not be predictive of future generation specifications or requirements. If you are
designing a system which will use one of the models listed or future generation products and need further
assistance, please contact your Field Applications Engineer (FAE) or our global support services group as
shown in Section 1.0.
Unless otherwise stated, the information in this manual applies to standard and Self-Encrypting Drive models.
Model Number Self-Encrypting Drive (SED) FIPS 140-2 Level 2
ST2000NM0001 No No
ST2000NM0021 Yes No
ST2000NM0041 Yes Yes
ST1000NM0001 No No
ST1000NM0021 Yes No
ST1000NM0041 Yes Yes
ST500NM0001 No No
ST500NM0021 Yes No
ST500NM0041 Yes Yes
Note. Previous generations of Seagate Self-Encrypting Drive models were called Full Disk Encryption
(FDE) models before a differentiation between drive-based encryption and other forms of encryption was necessary.
Note. The Self-Encrypting Drive models indicated on the cover of this product manual have provisions for
“Security of Data at Rest” based on the standards defined by the Trusted Computing Group (see
www.trustedcomputinggroup.org).
For more information on FIPS 140-2 Level 2 certification see Section 8.0 on page 41.
2 Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E

3.0 Applicable standards and reference documentation
The drives documented in this manual have been developed as system peripherals to the highest standards of
design and construction. The drives depends on host equipment to provide adequate power and environment
for optimum performance and compliance with applicable industry and governmental regulations. Special
attention must be given in the areas of safety, power distribution, shielding, audible noise control, and temperature regulation. In particular, the drive must be securely mounted to guarantee the specified performance
characteristics. Mounting by bottom holes must meet the requirements of Section 11.3.
3.1 Standards
The Constellation ES.1 family complies with Seagate standards as noted in the appropriate sections of this
manual and the Seagate SAS Interface Manual, part number 100293071.
The drives are recognized in accordance with UL 60950-1 as tested by UL, CSA 60950-1 as tested by CSA,
and EN60950-1 as tested by TUV.
The security features of Self-Encrypting Drive models are based on the “TCG Storage Architecture Core Specification” and the “TCG Storage Workgroup Security Subsystem Class: Enterprise_A” specification with additional vendor-unique features as noted in this product manual.
3.1.1 Electromagnetic compatibility
The drive, as delivered, is designed for system integration and installation into a suitable enclosure prior to
use. The drive is supplied as a subassembly and is not subject to Subpart B of Part 15 of the FCC Rules and
Regulations nor the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
The design characteristics of the drive serve to minimize radiation when installed in an enclosure that provides
reasonable shielding. The drive is capable of meeting the Class B limits of the FCC Rules and Regulations of
the Canadian Department of Communications when properly packaged; however, it is the user’s responsibility
to assure that the drive meets the appropriate EMI requirements in their system. Shielded I/O cables may be
required if the enclosure does not provide adequate shielding. If the I/O cables are external to the enclosure,
shielded cables should be used, with the shields grounded to the enclosure and to the host controller.
3.1.1.1 Electromagnetic susceptibility
As a component assembly, the drive is not required to meet any susceptibility performance requirements. It is
the responsibility of those integrating the drive within their systems to perform those tests required and design
their system to ensure that equipment operating in the same system as the drive or external to the system
does not adversely affect the performance of the drive. See Table 2, DC power requirements.
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E 3

3.1.2 Electromagnetic compliance
Seagate uses an independent laboratory to confirm compliance with the directives/standards for CE Marking
and C-Tick Marking. The drive was tested in a representative system for typical applications. The selected system represents the most popular characteristics for test platforms. The system configurations include:
• Typical current use microprocessor
• Keyboard
• Monitor/display
• Printer
• Mouse
Although the test system with this Seagate model complies with the directives/standards, we cannot guarantee
that all systems will comply. The computer manufacturer or system integrator shall confirm EMC compliance
and provide the appropriate marking for their product.
Electromagnetic compliance for the European Union
If this model has the CE Marking it complies with the European Union requirements of the Electromagnetic
Compatibility Directive 2004/108/EC as put into place on 20 July 2007.
Australian C-Tick
If this model has the C-Tick Marking it complies with the Australia/New Zealand Standard AS/NZ CISPR22 and
meets the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Framework requirements of Australia’s Spectrum Management Agency (SMA).
Korean KCC
If these drives have the Korean Communications Commission (KCC) logo, they comply with paragraph 1 of
Article 11 of the Electromagnetic Compatibility control Regulation and meet the Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) Framework requirements of the Radio Research Laboratory (RRL) Communications Commission,
Republic of Korea.
These drives have been tested and comply with the Electromagnetic Interference/Electromagnetic
Susceptibility (EMI/EMS) for Class B products. Drives are tested in a representative, end-user system by a
Korean-recognized lab.
• Family name: Constellation ES
• Certificate number: STX-ST2000NM0001 (B)
• Date of Certification: 22 December 2010
• Manufacturer/nationality: USA, Singapore and China
Taiwanese BSMI
If this model has two Chinese words meaning “EMC certification” followed by an eight digit identification number, as a Marking, it complies with Chinese National Standard (CNS) 13438 and meets the Electromagnetic
Compatibility (EMC) Framework requirements of the Taiwanese Bureau of Standards, Metrology, and Inspection (BSMI).
4 Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E
3.1.3 European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS)
The European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive, restricts the presence of chemical substances, including Lead, Cadmium, Mercury, Hexavalent Chromium, PBB and PBDE, in electronic products, effective July 2006. This drive is manufactured with components and materials that comply with the RoHS
Directive.
A number of parts and materials in Seagate products are procured from external suppliers. We rely on the representations of our suppliers regarding the presence of RoHS substances in these parts and materials. Our
supplier contracts require compliance with our chemical substance restrictions, and our suppliers document
their compliance with our requirements by providing material content declarations for all parts and materials for
the disk drives documented in this publication. Current supplier declarations include disclosure of the inclusion
of any RoHS-regulated substance in such parts or materials.
Seagate also has internal systems in place to ensure ongoing compliance with the RoHS Directive and all laws
and regulations which restrict chemical content in electronic products. These systems include standard operating procedures that ensure that restricted substances are not utilized in our manufacturing operations, laboratory analytical validation testing, and an internal auditing process to ensure that all standard operating
procedures are complied with.
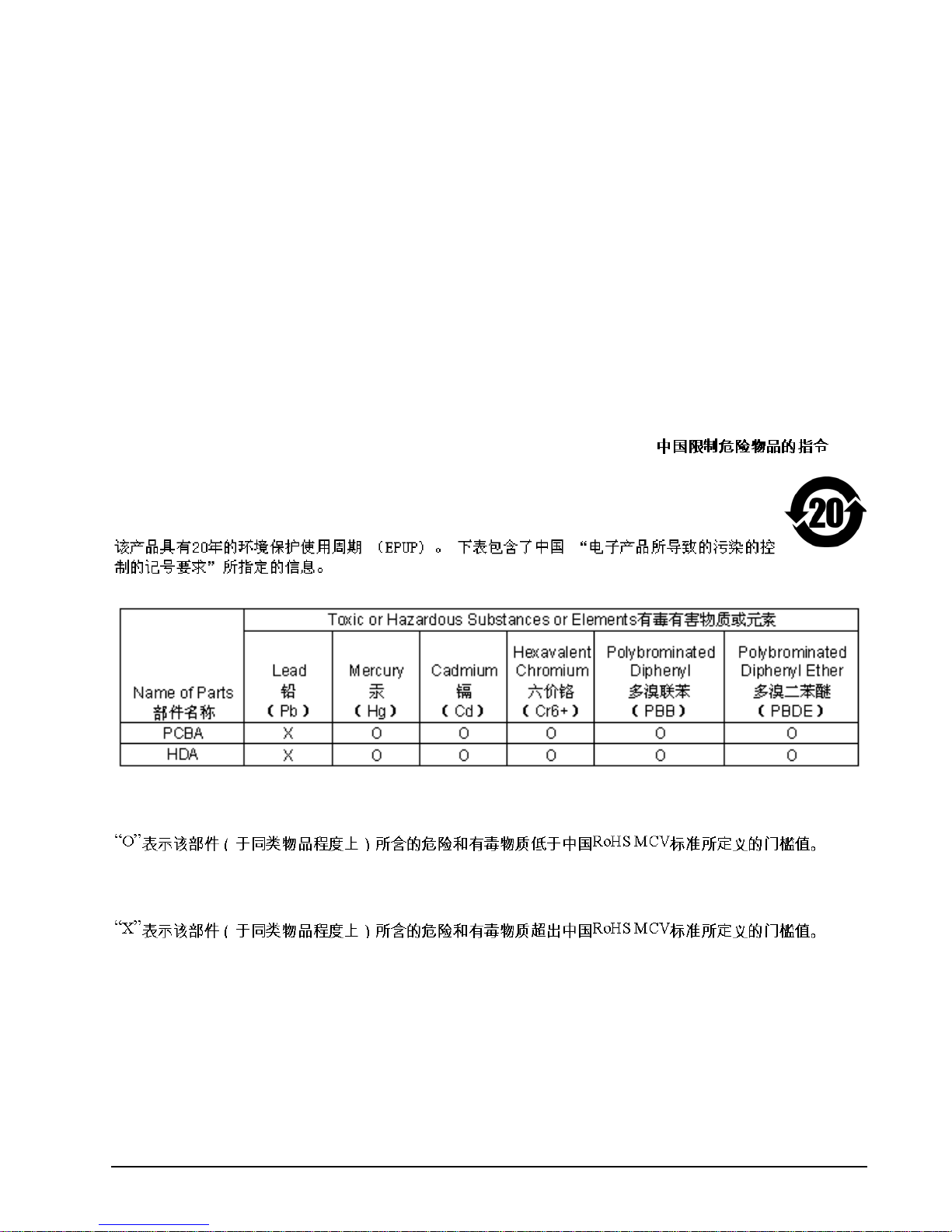
3.1.4 China Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive
This product has an Environmental Protection Use Period (EPUP) of 20 years. The following
table contains information mandated by China's "Marking Requirements for Control of Pollution
Caused by Electronic Information Products" Standard.
"O" indicates the hazardous and toxic substance content of the part (at the homogenous material level) is lower
than the threshold defined by the China RoHS MCV Standard.
"X" indicates the hazardous and toxic substance content of the part (at the homogenous material level) is over
the threshold defined by the China RoHS MCV Standard.
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E 5

3.2 Reference documents
SAS Interface Manual
Seagate part number: 100293071
SCSI Commands Reference Manual
Seagate part number: 100293068
Self-Encrypting Drives Reference Manual
Seagate part number: 100515636
ANSI SAS Documents
SFF-8323 3.5” Drive Form Factor with Serial Connector
SFF-8460 HSS Backplane Design Guidelines
SFF-8470 Multi Lane Copper Connector
SFF-8482 SAS Plug Connector
ANSI INCITS.xxx Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) Standard (T10/1562-D)
ISO/IEC 14776-xxx SCSI Architecture Model-3 (SAM-3) Standard (T10/1561-D)
ISO/IEC 14776-xxx SCSI Primary Commands-3 (SPC-3) Standard (T10/1416-D)
ISO/IEC 14776-xxx SCSI Block Commands-2 (SBC-2) Standard (T10/1417-D)
ANSI Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) Documents
X3.270-1996 (SCSI-3) Architecture Model
Trusted Computing Group (TCG) Documents (apply to Self-Encrypting Drive models only)
TCG Storage Architecture Core Specification, Rev. 1.0
TCG Storage Security Subsystem Class Enterprise Specification, Rev. 1.0
Specification for Acoustic Test Requirement and Procedures
Seagate part number: 30553-001
In case of conflict between this document and any referenced document, this document takes precedence.
6 Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E

4.0 General description
Constellation ES.1 drives provide high performance, high capacity data storage for a variety of systems including engineering workstations, network servers, mainframes, and supercomputers. The Serial Attached SCSI
interface is designed to meet next-generation computing demands for performance, scalability, flexibility and
high-density storage requirements.
Constellation ES.1 drives are random access storage devices designed to support the Serial Attached SCSI
Protocol as described in the ANSI specifications, this document, and the SAS Interface Manual (part number
100293071) which describes the general interface characteristics of this drive. Constellation ES.1 drives are
classified as intelligent peripherals and provide level 2 conformance (highest level) with the ANSI SCSI-1 standard. The SAS connectors, cables and electrical interface are compatible with Serial ATA (SATA), giving future
users the choice of populating their systems with either SAS or SATA hard disk drives. This allows you to continue to leverage your existing investment in SCSI while gaining a 6Gb/s serial data transfer rate.
The Self-Encrypting Drive models indicated on the cover of this product manual have provisions for “Security
of Data at Rest” based on the standards defined by the Trusted Computing Group (see www.trustedcomputinggroup.org).
The head and disk assembly (HDA) is sealed at the factory. Air recirculates within the HDA through a nonreplaceable filter to maintain a contamination-free HDA environment.
Note. Never disassemble the HDA and do not attempt to service items in the sealed enclosure (heads,
media, actuator, etc.) as this requires special facilities. The drive does not contain user-replaceable
parts. Opening the HDA for any reason voids your warranty.
Constellation ES.1 drives use a dedicated load/unload zone at the outermost radius of the media to eliminate
the possibility of destroying or degrading data by landing in the data zone. The heads automatically go to the
ramp load/unload when power is removed from the drive.
An automatic shipping lock prevents potential damage to the heads and discs that results from movement during shipping and handling. The shipping lock disengages and the head load process begins when power is
applied to the drive.
Constellation ES.1 drives decode track 0 location data from the servo data embedded on each surface to eliminate mechanical transducer adjustments and related reliability concerns.
The drives also use a high-performance actuator assembly with a low-inertia, balanced, patented, straight arm
design that provides excellent performance with minimal power dissipation.
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E 7

4.1 Standard features
Constellation ES.1 drives have the following standard features:
• Perpendicular recording technology
• 1.5 / 3 / 6 Gb Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) interface
• Integrated dual port SAS controller supporting the SCSI protocol
• Support for SAS expanders and fanout adapters
• Firmware downloadable using the SAS interface
• 128 - deep task set (queue)
• Supports up to 32 initiators
• Jumperless configuration.
• User-selectable logical block size (512, 520 or 528 bytes per logical block).
• Industry standard 3.5-inch dimensions
• Programmable logical block reallocation scheme
• Flawed logical block reallocation at format time
• Programmable auto write and read reallocation
• Reallocation of defects on command (Post Format)
• ECC maximum burst correction length of 400 bits
• No preventive maintenance or adjustments required
• Embedded servo design
• Dedicated head load/unload zone
• Self diagnostics performed when power is applied to the drive
• Vertical, horizontal, or top down mounting
• 64 Mbyte data buffer (see Section 5.5).
• Drive Self Test (DST)
• Background Media Scan (BMS)
• Idle Read After Write (IRAW)
• Power Save
Constellation ES.1 SAS Self-Encrypting Drive models have the following additional features:
• Automatic data encryption/decryption
• Controlled access
• Random number generator
• Drive locking
• 16 independent data bands
• Cryptographic erase of user data for a drive that will be repurposed or scrapped
• Authenticated firmware download
4.2 Media description
The media used on the drive has a aluminum substrate coated with a thin film magnetic material, overcoated
with a proprietary protective layer for improved durability and environmental protection.
4.3 Performance
• Programmable multi-segmentable cache buffer
• 600MB/s maximum instantaneous data transfers.
• 7200 RPM spindle. Average latency = 4.16ms
• Background processing of queue
• Supports start and stop commands (spindle stops spinning)
• Adaptive seek velocity; improved seek performance
Note. There is no significant performance difference between Self-Encrypting Drive and standard (non-
Self-Encrypting Drive) models.
8 Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E
4.4 Reliability
• Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) of 0.73%
• Mean time between failures (MTBF) of 1,200,000 hours
• Balanced low mass rotary voice coil actuator
• Incorporates industry-standard Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.)
• 5-year warranty
4.5 Formatted capacities
Standard OEM models are formatted to 512 bytes per block. The block size is selectable at format time and
must be a multiple of 4 bytes. Users having the necessary equipment may modify the data block size before
issuing a format command and obtain different formatted capacities than those listed.
To provide a stable target capacity environment and at the same time provide users with flexibility if they
choose, Seagate recommends product planning in one of two modes:
1. Seagate designs specify capacity points at certain block sizes that Seagate guarantees current and future
products will meet. We recommend customers use this capacity in their project planning, as it ensures a
stable operating point with backward and forward compatibility from generation to generation. The current
guaranteed operating points for this product are:
Capacity (Blocks)
Sector
Size
ST2000NM0001
ST2000NM0021
ST2000NM0041
Decimal Hex Decimal Hex Decimal Hex
512 3,907,029,168 E8E088B0 1,953,525,168 74706DB0 976,773,168 3A386030
520 3,824,358,992 E3F31650 1,923,076,936 729FD348 961,538,472 394FE9A8
528 3,719,165,192 DDADF508 1,876,331,336 6FD68B48 938,165,672 37EB45A8
ST1000NM0001
ST1000NM0021
ST1000NM0041
ST500NM0001
ST500NM0021
ST500NM0041
4.6 Programmable drive capacity
Using the Mode Select command, the drive can change its capacity to something less than maximum. See the
Mode Select (6) parameter list table in the SAS Interface Manual, part number 100293071. A value of zero in
the Number of Blocks field indicates that the drive will not change the capacity it is currently formatted to have.
A number other than zero and less than the maximum number of LBAs in the Number of Blocks field changes
the total drive capacity to the value in the Number of Blocks field. A value greater than the maximum number of
LBAs is rounded down to the maximum capacity.
4.7 Factory-installed options
You may order the following items which are incorporated at the manufacturing facility during production or
packaged before shipping. Some of the options available are (not an exhaustive list of possible options):
• Other capacities can be ordered depending on sparing scheme and sector size requested.
• Single-unit shipping pack. The drive is normally shipped in bulk packaging to provide maximum protection
against transit damage. Units shipped individually require additional protection as provided by the single unit
shipping pack. Users planning single unit distribution should specify this option.
• The Safety and Regulatory Agency Specifications, part number 75789512, is usually included with each
standard OEM drive shipped, but extra copies may be ordered.
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E 9

5.0 Performance characteristics
This section provides detailed information concerning performance-related characteristics and features of Constellation ES.1 drives.
5.1 Internal drive characteristics
ST2000NM0001 ST1000NM0001 ST500NM0001
ST2000NM0021 ST1000NM0021 ST500NM0021
ST2000NM0041 ST1000NM0041 ST500NM0041
Drive capacity 2TB 1TB 500GB (formatted, rounded off value)
Read/write data heads 8 4 2
Bytes per track 1,012,608 1,012,608 1,012,608 Bytes (average, rounded off values)
Bytes per surface 250,000 250,000 250,000 MB (unformatted, rounded off value)
Tracks per surface (total) 248,600 248,600 248,600 Tracks (user accessible)
Tracks per inch 237,000 237,000 237,000 TPI (average)
Peak bits per inch 1,523,000 1,523,000 1,523,000 BPI
Areal density 324 324 324 Gb/in
Internal data rate 95 - 212 95 - 212 95 - 212 MB/s (variable with zone)
Disk rotation speed 7200 7200 7200 rpm
Avg rotational latency 4.16 4.16 4.16 ms
5.2 Seek performance characteristics
2
See Section 12.4.1, "SAS physical interface" on page 66 and the SAS Interface Manual (part number
100293071) for additional timing details.
5.2.1 Access time
1
Not including controller overhead2 (ms)
,
Including controller overhead
Read Write Read Write
43
Average Typical
Single track Typical
Full stroke Typical
,
8.3 9.3 8.5 9.5
3,4
0.5 0.8 0.7 1.0
3,4
18 19 18.2 19.2
1. Execution time measured from receipt of the Command to the Response.
2. Assumes no errors and no sector has been relocated.
3. Typical access times are measured under nominal conditions of temperature, voltage, and horizontal orientation as
measured on a representative sample of drives.
4. Access time = controller overhead + average seek time and applies to all data transfer commands.
Access to data = access time + latency time.
1, 2
(ms)
10 Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E

5.2.2 Format command execution time for 512-byte sectors (minutes)
2TB models 1TB models 500GB models
Maximum (with verify)
Maximum (without verify)
627 345 173
314 173 86
Execution time measured from receipt of the last byte of the Command Descriptor Block (CDB) to the request
for a Status Byte Transfer to the Initiator (excluding connect/disconnect).
When changing sector sizes, the format times shown above may need to be increased by 30 minutes.
5.2.3 General performance characteristics
Minimum sector interleave 1 to 1
Data buffer to/from disk media (one 512-byte logical block)* 95 to 212 MB/s
Sustained transfer rate 60 to 147 MB/s
SAS Interface maximum instantaneous transfer rate 600MB/s* per port
Logical block sizes
512 (default), 520 or 528.
Read/write consecutive sectors on a track Yes
Flaw reallocation performance impact (for flaws reallocated at format time using the
spare sectors per sparing zone reallocation scheme.)
Average rotational latency 4.16ms
*Assumes no errors and no relocated logical blocks. Rate measured from the start of the first logical block transfer to or
from the host.
(dual port = 1200MB/s*)
Negligible
5.3 Start/stop time
The drive accepts the commands listed in the SAS Interface Manual less than 3 seconds after DC power has
been applied.
If the drive receives a NOTIFY (ENABLE SPINUP) primitive through either port and has not received a START
STOP UNIT command with the START bit equal to 0, the drive becomes ready for normal operations within 30
seconds (excluding the error recovery procedure).
If the drive receives a START STOP UNIT command with the START bit equal to 0 before receiving a NOTIFY
(ENABLE SPINUP) primitive, the drive waits for a START STOP UNIT command with the START bit equal to 1.
After receiving a START STOP UNIT command with the START bit equal to 1, the drive waits for a NOTIFY
(ENABLE SPINUP) primitive. After receiving a NOTIFY (ENABLE SPINUP) primitive through either port, the
drive becomes ready for normal operations within 30 seconds (excluding the error recovery procedure).
If the drive receives a START STOP UNIT command with the START bit and IMMED bit equal to 1 and does
not receive a NOTIFY (ENABLE SPINUP) primitive within 5 seconds, the drive fails the START STOP UNIT
command.
The START STOP UNIT command may be used to command the drive to stop the spindle. Stop time is 20 seconds (maximum) from removal of DC power. SCSI stop time is 20 seconds. There is no power control switch
on the drive.
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E 11

5.4 Prefetch/multi-segmented cache control
The drive provides a prefetch (read look-ahead) and multi-segmented cache control algorithms that in many
cases can enhance system performance. Cache refers to the drive buffer storage space when it is used in
cache operations. To select this feature, the host sends the Mode Select command with the proper values in
the applicable bytes in page 08h. Prefetch and cache operations are independent features from the standpoint
that each is enabled and disabled independently using the Mode Select command; however, in actual operation, the prefetch feature overlaps cache operation somewhat as described in sections 5.5.1 and 5.5.2.
All default cache and prefetch mode parameter values (Mode Page 08h) for standard OEM versions of this
drive family are given in Table 10.
5.5 Cache operation
Note. Refer to the SAS Interface Manual for more detail concerning the cache bits.
Of the 64MB physical buffer space in the drive, approximately 30,000 kbytes can be used as a cache. The buffer is divided into logical segments from which data is read and to which data is written.
The drive keeps track of the logical block addresses of the data stored in each segment of the buffer. If the
cache is enabled (see RCD bit in the SAS Interface Manual ), data requested by the host with a read command
is retrieved from the buffer, if possible, before any disk access is initiated. If cache operation is not enabled, the
buffer is still used, but only as circular buffer segments during disk medium read operations (disregarding
Prefetch operation for the moment). That is, the drive does not check in the buffer segments for the requested
read data, but goes directly to the medium to retrieve it. The retrieved data merely passes through some buffer
segment on the way to the host. All data transfers to the host are in accordance with buffer-full ratio rules. See
the explanation provided with the information about Mode Page 02h (disconnect/reconnect control) in the SAS
Interface Manual.
The following is a simplified description of the prefetch/cache operation:
Case A—read command is received and all of the requested logical blocks are already in the cache:
1. Drive transfers the requested logical blocks to the initiator.
Case B—A Read command requests data, and at least one requested logical block is not in any segment of
the cache:
1. The drive fetches the requested logical blocks from the disk and transfers them into a segment, and then
from there to the host in accordance with the Mode Select Disconnect/Reconnect parameters, page 02h.
2. If the prefetch feature is enabled, refer to section 5.5.2 for operation from this point.
Each cache segment is actually a self-contained circular buffer whose length is an integer number of logical
blocks. The drive dynamically creates and removes segments based on the workload. The wrap-around capability of the individual segments greatly enhances the cache’s overall performance.
Note. The size of each segment is not reported by Mode Sense command page 08h, bytes 14 and 15.
The value 0XFFFF is always reported regardless of the actual size of the segment. Sending a size
specification using the Mode Select command (bytes 14 and 15) does not set up a new segment
size. If the STRICT bit in Mode page 00h (byte 2, bit 1) is set to one, the drive responds as it does
for any attempt to change an unchangeable parameter.
12 Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E

5.5.1 Caching write data
Write caching is a write operation by the drive that makes use of a drive buffer storage area where the data to
be written to the medium is stored while the drive performs the Write command.
If read caching is enabled (RCD=0), then data written to the medium is retained in the cache to be made available for future read cache hits. The same buffer space and segmentation is used as set up for read functions.
The buffer segmentation scheme is set up or changed independently, having nothing to do with the state of
RCD. When a write command is issued, if RCD=0, the cache is first checked to see if any logical blocks that
are to be written are already stored in the cache from a previous read or write command. If there are, the
respective cache segments are cleared. The new data is cached for subsequent Read commands.
If the number of write data logical blocks exceed the size of the segment being written into, when the end of the
segment is reached, the data is written into the beginning of the same cache segment, overwriting the data that
was written there at the beginning of the operation; however, the drive does not overwrite data that has not yet
been written to the medium.
If write caching is enabled (WCE=1), then the drive may return Good status on a write command after the data
has been transferred into the cache, but before the data has been written to the medium. If an error occurs
while writing the data to the medium, and Good status has already been returned, a deferred error will be generated.
The Synchronize Cache command may be used to force the drive to write all cached write data to the medium.
Upon completion of a Synchronize Cache command, all data received from previous write commands will have
been written to the medium. Table 10 shows the mode default settings for the drive.
5.5.2 Prefetch operation
If the Prefetch feature is enabled, data in contiguous logical blocks on the disk immediately beyond that which
was requested by a Read command are retrieved and stored in the buffer for immediate transfer from the buffer to the host on subsequent Read commands that request those logical blocks (this is true even if cache
operation is disabled). Though the prefetch operation uses the buffer as a cache, finding the requested data in
the buffer is a prefetch hit, not a cache operation hit.
To enable Prefetch, use Mode Select page 08h, byte 12, bit 5 (Disable Read Ahead - DRA bit). DRA bit = 0
enables prefetch.
The drive does not use the Max Prefetch field (bytes 8 and 9) or the Prefetch Ceiling field (bytes 10 and 11).
When prefetch (read look-ahead) is enabled (enabled by DRA = 0), the drive enables prefetch of contiguous
blocks from the disk when it senses that a prefetch hit will likely occur. The drive disables prefetch when it
decides that a prefetch hit is not likely to occur.
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E 13

6.0 Reliability specifications
The following reliability specifications assume correct host and drive operational interface, including all inter-
face timings, power supply voltages, environmental requirements and drive mounting constraints.
Seek error rate: Less than 10 errors in 108seeks
Read Error Rates
Recovered Data Less than 10 errors in 1012 bits transferred (OEM default settings)
Unrecovered Data Less than 1 sector in 1015 bits transferred
Miscorrected Data Less than 1 sector in 1021 bits transferred
Interface error rate: Less than 1 error in 1012 bits transferred
Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF): 1,200,000 hours
Annualized Failure Rate (AFR): 0.73%
Preventive maintenance: None required
1. Error rate specified with automatic retries and data correction with ECC enabled and all flaws reallocated.
6.1 Error rates
The error rates stated in this manual assume the following:
• The drive is operated in accordance with this manual using DC power as defined in paragraph 7.3, "DC
power requirements."
• Errors caused by host system failures are excluded from error rate computations.
• Assume random data.
• Default OEM error recovery settings are applied. This includes AWRE, ARRE, full read retries, full write
retries and full retry time.
1
6.1.1 Recoverable Errors
Recoverable errors are those detected and corrected by the drive, and do not require user intervention.
Recoverable Data errors will use correction, although ECC on-the-fly is not considered for purposes of recovered error specifications.
Recovered Data error rate is determined using read bits transferred for recoverable errors occurring during a
read, and using write bits transferred for recoverable errors occurring during a write.
6.1.2 Unrecoverable Errors
An unrecoverable data error is defined as a failure of the drive to recover data from the media. These errors
occur due to head/media or write problems. Unrecoverable data errors are only detected during read operations, but not caused by the read. If an unrecoverable data error is detected, a MEDIUM ERROR (03h) in the
Sense Key will be reported. Multiple unrecoverable data errors resulting from the same cause are treated as 1
error.
14 Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E

6.1.3 Seek errors
A seek error is defined as a failure of the drive to position the heads to the addressed track. After detecting an
initial seek error, the drive automatically performs an error recovery process. If the error recovery process fails,
a seek positioning error (Error code = 15h or 02h) will be reported with a Hardware error (04h) in the Sense
Key. Recoverable seek errors are specified at Less than 10 errors in 108 seeks. Unrecoverable seek errors
(Sense Key = 04h) are classified as drive failures.
6.1.4 Interface errors
An interface error is defined as a failure of the receiver on a port to recover the data as transmitted by the
device port connected to the receiver. The error may be detected as a running disparity error, illegal code, loss
of word sync, or CRC error.
6.2 Reliability and service
You can enhance the reliability of Constellation ES.1 disk drives by ensuring that the drive receives adequate
cooling. Section 7.0 provides temperature measurements and other information that may be used to enhance
the service life of the drive. Section 11.2 provides recommended air-flow information.
6.2.1 Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) and Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF)
The production disk drive shall achieve an AFR of 0.73% (MTBF of 1,200,000 hours) when operated in an
environment that ensures the HDA case temperatures do not exceed the values specified in Section 7.5. Operation at case temperatures outside the specifications in Section 7.5 may increase the product AFR (decrease
the MTBF). The AFR (MTBF) is a population statistic not relevant to individual units.
The AFR (MTBF) specification is based on the following assumptions for Enterprise Storage System environments:
• 8,760 power-on hours per year.
• 250 average on/off cycles per year.
• Operations at nominal voltages.
• Systems will provide adequate cooling to ensure the case temperatures specified in Section 7.5 are not
exceeded. Temperatures outside the specifications in Section 7.5 will increase the product AFR and
decrease the MTBF.
6.2.2 Preventive maintenance
No routine scheduled preventive maintenance is required.
6.2.3 Hot plugging the drive
When a disk is powered on by switching the power or hot plugged, the drive runs a self test before attempting
to communicate on its’ interfaces. When the self test completes successfully, the drive initiates a Link Reset
starting with OOB. An attached device should respond to the link reset. If the link reset attempt fails, or any
time the drive looses sync, the drive initiated link reset. The drive will initiate link reset once per second but
alternates between port A and B. Therefore each port will attempt a link reset once per 2 seconds assuming
both ports are out of sync.
If the self-test fails, the drive does not respond to link reset on the failing port.
Note. It is the responsibility of the systems integrator to assure that no temperature, energy, voltage haz-
ard, or ESD potential hazard is presented during the hot connect/disconnect operation. Discharge
the static electricity from the drive carrier prior to inserting it into the system.
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E 15

Caution. The drive motor must come to a complete stop prior to changing the plane of operation. This time is
required to insure data integrity.
6.2.4 S.M.A.R.T.
S.M.A.R.T. is an acronym for Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology. This technology is intended
to recognize conditions that indicate imminent drive failure and is designed to provide sufficient warning of a
failure to allow you to back up the data before an actual failure occurs.
Note. The drive’s firmware monitors specific attributes for degradation over time but can’t predict instanta-
neous drive failures.
Each monitored attribute has been selected to monitor a specific set of failure conditions in the operating performance of the drive and the thresholds are optimized to minimize “false” and “failed” predictions.
Controlling S.M.A.R.T.
The operating mode of S.M.A.R.T. is controlled by the DEXCPT and PERF bits on the Informational Exceptions
Control mode page (1Ch). Use the DEXCPT bit to enable or disable the S.M.A.R.T. feature. Setting the DEXCPT bit disables all S.M.A.R.T. functions. When enabled, S.M.A.R.T. collects on-line data as the drive performs
normal read and write operations. When the PERF bit is set, the drive is considered to be in “On-line Mode
Only” and will not perform off-line functions.
You can measure off-line attributes and force the drive to save the data by using the Rezero Unit command.
Forcing S.M.A.R.T. resets the timer so that the next scheduled interrupt is in one hour.
You can interrogate the drive through the host to determine the time remaining before the next scheduled measurement and data logging process occurs. To accomplish this, issue a Log Sense command to log page 0x3E.
This allows you to control when S.M.A.R.T. interruptions occur. Forcing S.M.A.R.T. with the RTZ command
resets the timer.
Performance impact
S.M.A.R.T. attribute data is saved to the disk so that the events that caused a predictive failure can be recreated. The drive measures and saves parameters once every one hour subject to an idle period on the drive
interfaces. The process of measuring off-line attribute data and saving data to the disk is interruptable. The
maximum on-line only processing delay is summarized below:
Maximum processing delay
On-line only delay
DEXCPT = 0, PERF = 1
S.M.A.R.T. delay times 233 ms 560 ms
Fully-enabled delay
DEXCPT = 0, PERF = 0
Reporting control
Reporting is controlled by the MRIE bits in the Informational Exceptions Control mode page (1Ch). An example, if the MRIE is set to one, the firmware will issue to the host an 01-5D00 sense code. The FRU field contains the type of predictive failure that occurred. The error code is preserved through bus resets and power
cycles.
Determining rate
S.M.A.R.T. monitors the rate at which errors occur and signals a predictive failure if the rate of degraded errors
increases to an unacceptable level. To determine rate, error events are logged and compared to the number of
total operations for a given attribute. The interval defines the number of operations over which to measure the
rate. The counter that keeps track of the current number of operations is referred to as the Interval Counter.
16 Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E

S.M.A.R.T. measures error rates. All errors for each monitored attribute are recorded. A counter keeps track of
the number of errors for the current interval. This counter is referred to as the Failure Counter.
Error rate is the number of errors per operation. The algorithm that S.M.A.R.T. uses to record rates of error is to
set thresholds for the number of errors and their interval. If the number of errors exceeds the threshold before
the interval expires, the error rate is considered to be unacceptable. If the number of errors does not exceed
the threshold before the interval expires, the error rate is considered to be acceptable. In either case, the interval and failure counters are reset and the process starts over.
Predictive failures
S.M.A.R.T. signals predictive failures when the drive is performing unacceptably for a period of time. The firmware keeps a running count of the number of times the error rate for each attribute is unacceptable. To accomplish this, a counter is incremented each time the error rate is unacceptable and decremented (not to exceed
zero) whenever the error rate is acceptable. If the counter continually increments such that it reaches the predictive threshold, a predictive failure is signaled. This counter is referred to as the Failure History Counter.
There is a separate Failure History Counter for each attribute.
6.2.5 Thermal monitor
Constellation ES.1 drives implement a temperature warning system which:
1. Signals the host if the temperature exceeds a value which would threaten the drive.
2. Signals the host if the temperature exceeds a user-specified value.
3. Saves a S.M.A.R.T. data frame on the drive which exceeds the threatening temperature value.
A temperature sensor monitors the drive temperature and issues a warning over the interface when the temperature exceeds a set threshold. The temperature is measured at power-up and then at ten-minute intervals
after power-up.
The thermal monitor system generates a warning code of 01-0B01 when the temperature exceeds the specified limit in compliance with the SCSI standard. The drive temperature is reported in the FRU code field of
mode sense data. You can use this information to determine if the warning is due to the temperature exceeding
the drive threatening temperature or the user-specified temperature.
This feature is controlled by the Enable Warning (EWasc) bit, and the reporting mechanism is controlled by the
Method of Reporting Informational Exceptions field (MRIE) on the Informational Exceptions Control (IEC)
mode page (1Ch).
The current algorithm implements two temperature trip points. The first trip point is set at 65°C which is the
maximum temperature limit according to the drive specification. The second trip point is user-selectable using
the Log Select command. The reference temperature parameter in the temperature log page (see Table 1) can
be used to set this trip point. The default value for this drive is 65°C, however, you can set it to any value in the
range of 0 to 65°C. If you specify a temperature greater than 65°C in this field, the temperature is rounded
down to 65°C. A sense code is sent to the host to indicate the rounding of the parameter field.
Table 1: Temperature Log Page (0Dh)
Parameter Code Description
0000h
0001h
Primary Temperature
Reference Temperature
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E 17

6.2.6 Drive Self Test (DST)
Drive Self Test (DST) is a technology designed to recognize drive fault conditions that qualify the drive as a
failed unit. DST validates the functionality of the drive at a system level.
There are two test coverage options implemented in DST:
1. Extended test
2. Short test
The most thorough option is the extended test that performs various tests on the drive and scans every logical
block address (LBA) of the drive. The short test is time-restricted and limited in length—it does not scan the
entire media surface, but does some fundamental tests and scans portions of the media.
If DST encounters an error during either of these tests, it reports a fault condition. If the drive fails the test,
remove it from service and return it to Seagate for service.
6.2.6.1 DST failure definition
The drive will present a “diagnostic failed” condition through the self-tests results value of the diagnostic log
page if a functional failure is encountered during DST. The channel and servo parameters are not modified to
test the drive more stringently, and the number of retries are not reduced. All retries and recovery processes
are enabled during the test. If data is recoverable, no failure condition will be reported regardless of the number
of retries required to recover the data.
The following conditions are considered DST failure conditions:
• Seek error after retries are exhausted
• Track-follow error after retries are exhausted
• Read error after retries are exhausted
• Write error after retries are exhausted
Recovered errors will not be reported as diagnostic failures.
6.2.6.2 Implementation
This section provides all of the information necessary to implement the DST function on this drive.
6.2.6.2.1 State of the drive prior to testing
The drive must be in a ready state before issuing the Send Diagnostic command. There are multiple reasons
why a drive may not be ready, some of which are valid conditions, and not errors. For example, a drive may be
in process of doing a format, or another DST. It is the responsibility of the host application to determine the “not
ready” cause.
While not technically part of DST, a Not Ready condition also qualifies the drive to be returned to Seagate as a
failed drive.
A Drive Not Ready condition is reported by the drive under the following conditions:
• Motor will not spin
• Motor will not lock to speed
• Servo will not lock on track
• Drive cannot read configuration tables from the disk
In these conditions, the drive responds to a Test Unit Ready command with an 02/04/00 or 02/04/03 code.
6.2.6.2.2 Invoking DST
To invoke DST, submit the Send Diagnostic command with the appropriate Function Code (001b for the short
test or 010b for the extended test) in bytes 1, bits 5, 6, and 7.
18 Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E

6.2.6.2.3 Short and extended tests
DST has two testing options:
1. short
2. extended
These testing options are described in the following two subsections.
Each test consists of three segments: an electrical test segment, a servo test segment, and a read/verify scan
segment.
Short test (Function Code: 001b)
The purpose of the short test is to provide a time-limited test that tests as much of the drive as possible within
120 seconds. The short test does not scan the entire media surface, but does some fundamental tests and
scans portions of the media. A complete read/verify scan is not performed and only factual failures will report a
fault condition. This option provides a quick confidence test of the drive.
Extended test (Function Code: 010b)
The objective of the extended test option is to empirically test critical drive components. For example, the seek
tests and on-track operations test the positioning mechanism. The read operation tests the read head element
and the media surface. The write element is tested through read/write/read operations. The integrity of the
media is checked through a read/verify scan of the media. Motor functionality is tested by default as a part of
these tests.
The anticipated length of the Extended test is reported through the Control Mode page.
6.2.6.2.4 Log page entries
When the drive begins DST, it creates a new entry in the Self-test Results Log page. The new entry is created
by inserting a new self-test parameter block at the beginning of the self-test results log parameter section of the
log page. Existing data will be moved to make room for the new parameter block. The drive reports 20 parameter blocks in the log page. If there are more than 20 parameter blocks, the least recent parameter block will be
deleted. The new parameter block will be initialized as follows:
1. The Function Code field is set to the same value as sent in the DST command
2. The Self-Test Results Value field is set to Fh
3. The drive will store the log page to non-volatile memory
After a self-test is complete or has been aborted, the drive updates the Self-Test Results Value field in its SelfTest Results Log page in non-volatile memory. The host may use Log Sense to read the results from up to the
last 20 self-tests performed by the drive. The self-test results value is a 4-bit field that reports the results of the
test. If the field is set to zero, the drive passed with no errors detected by the DST. If the field is not set to zero,
the test failed for the reason reported in the field.
The drive will report the failure condition and LBA (if applicable) in the Self-test Results Log parameter. The
Sense key, ASC, ASCQ, and FRU are used to report the failure condition.
6.2.6.2.5 Abort
There are several ways to abort a diagnostic. You can use a SCSI Bus Reset or a Bus Device Reset message
to abort the diagnostic.
You can abort a DST executing in background mode by using the abort code in the DST Function Code field.
This will cause a 01 (self-test aborted by the application client) code to appear in the self-test results values
log. All other abort mechanisms will be reported as a 02 (self-test routine was interrupted by a reset condition).
Constellation ES.1 SAS Product Manual, Rev. E 19
 Loading...
Loading...