Page 1

SD Specifications
Part E1
SDIO Simplified Specification
Version 2.00
February 8, 2007
Technical Committee
SD Card Association
Page 2
©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Revision History
Date Version Changes compared to previous issue
April 3, 2006 1.10 Simplified Version Initial Release
February 8, 2007 2.00 (1) Added method to change bus speed (Normal Speed up to 25MHz
and High Speed up to 50 MHz)
(2) Operational Voltage Requirement is extended to 2.7-3.6V
(3) Combine sections 12 (Physical Properties) and 13 (Mechanical
Extensions) and add miniSDIO to the new section 13 (Physical
Properties)
(4) Add Embedded SDIO ATA Standard Function Interface Code
(5) Reference of Physical Ver2.00 supports SDHC combo card.
(6) Some typos in Ver1.10 are fixed.
i
Page 3

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Release of SD Simplified Specification
The following conditions apply to the release of the SD simplified specification ("Simplified Specification") by
the SD Card Association. The Simplified Specification is a subset of the complete SD Specification which is
owned by the SD Card Association.
Publisher:
SD Association
2400 Camino Ramon, Suite 375
San Ramon, CA 94583 USA
Telephone: +1 (925) 275-6615
Fax: +1 (925) 886-4870
E-mail: office@sdcard.org
Copyright Holder:
The SD Card Association
Notes:
This Simplified Specification is provided on a non-confidential basis subject to the disclaimers below. Any
implementation of the Simplified Specification may require a license from the SD Card Association or other
third parties.
Disclaimers:
The information contained in the Simplified Specification is presented only as a standard specification for SD
Cards and SD Host/Ancillary products and is provided "AS-IS" without any representations or warranties of
any kind. No responsibility is assumed by the SD Card Association for any damages, any infringements of
patents or other right of the SD Card Association or any third parties, which may result from its use. No
license is granted by implication, estoppel or otherwise under any patent or other rights of the SD Card
Association or any third party. Nothing herein shall be construed as an obligation by the SD Card
Association to disclose or distribute any technical information, know-how or other confidential information to
any third party.
ii
Page 4
©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Conventions Used in This Document
Naming Conventions
Some terms are capitalized to distinguish their definition from their common English meaning. Words not
capitalized have their common English meaning.
Numbers and Number Bases
Hexadecimal numbers are written with a lower case “h” suffix, e.g., FFFFh and 80h.
Binary numbers are written with a lower case “b” suffix (e.g., 10b).
Binary numbers larger than four digits are written with a space dividing each group of four digits, as in 1000 0101
0010b.
All other numbers are decimal.
Key Words
May: Indicates flexibility of choice with no implied recommendation or requirement.
Shall: Indicates a mandatory requirement. Designers shall implement such mandatory requirements to
ensure interchangeability and to claim conformance with the specification.
Should: Indicates a strong recommendation but not a mandatory requirement. Designers should give strong
consideration to such recommendations, but there is still a choice in implementation.
Application Notes
Some sections of this document provide guidance to the host implementers as follows:
Application Note:
This is an example of an application note.
iii
Page 5

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Table of Contents
1. General Description ................................................................................................................................. 1
1.1 SDIO Features .................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Primary Reference Document ............................................................................................................. 1
1.3 Standard SDIO Functions.................................................................................................................... 1
2. SDIO Signaling Definition........................................................................................................................ 2
2.1 SDIO Card Types ................................................................................................................................ 2
2.2 SDIO Card modes............................................................................................................................... 2
2.2.1 SPI (Card mandatory support) ..................................................................................................... 2
2.2.2 1-bit SD Data Transfer Mode (Card Mandatory Support) ............................................................. 2
2.2.3 4-bit SD Data Transfer Mode (Mandatory for High-Speed Cards, Optional for Low-Speed)......... 2
2.3 SDIO Host Modes ............................................................................................................................... 2
2.4 Signal Pins .......................................................................................................................................... 3
3. SDIO Card Initialization............................................................................................................................ 4
3.1 Differences in I/O card Initialization..................................................................................................... 4
3.2 The IO_SEND_OP_COND Command (CMD5)................................................................................. 10
3.3 The IO_SEND_OP_COND Response (R4)........................................................................................11
3.4 Special Initialization considerations for Combo Cards....................................................................... 12
3.4.1 Re-initialize both I/O and Memory .............................................................................................. 12
3.4.2 Using a Combo Card as SDIO only or SD Memory only after Combo Initialization.................... 12
3.4.3 Acceptable Commands after Initialization .................................................................................. 12
3.4.4 Recommendations for RCA after Reset ..................................................................................... 12
3.4.5 Enabling CRC in SPI Combo Card............................................................................................. 14
4. Differences with SD Memory Specification.......................................................................................... 15
4.1 SDIO Command List ......................................................................................................................... 15
4.2 Unsupported SD Memory Commands............................................................................................... 15
4.3 Modified R6 Response ...................................................................................................................... 16
4.4 Reset for SDIO.................................................................................................................................. 16
4.5 Bus Width.......................................................................................................................................... 16
4.6 Card Detect Resistor......................................................................................................................... 17
4.7 Timings.............................................................................................................................................. 17
4.8 Data Transfer Block Sizes................................................................................................................. 18
4.9 Data Transfer Abort ............................................................................................................
4.9.1 Read Abort ................................................................................................................................. 18
4.9.2 Write Abort ................................................................................................................................. 18
4.10 Changes to SD Memory Fixed Registers .......................................................................................... 18
4.10.1 OCR Register............................................................................................................................. 19
4.10.2 CID Register............................................................................................................................... 19
4.10.3 CSD Register ............................................................................................................................. 19
4.10.4 RCA Register ............................................................................................................................. 19
4.10.5 DSR Register ............................................................................................................................. 19
4.10.6 SCR Register ............................................................................................................................. 19
4.10.7 SD Status ................................................................................................................................... 19
4.10.8 Card Status Register .................................................................................................................. 19
5. New I/O Read/Write Commands............................................................................................................ 21
5.1 IO_RW_DIRECT Command (CMD52) .............................................................................................. 21
5.2 IO_RW_DIRECT Response (R5) ......................................................................................................22
5.2.1 CMD52 Response (SD modes).................................................................................................. 22
5.2.2 R5, IO_RW_DIRECT Response (SPI mode) ............................................................................. 23
5.3 IO_RW_EXTENDED Command (CMD53) ........................................................................................ 24
5.3.1 CMD53 Data Transfer Format.................................................................................................... 25
............... 18
iv
Page 6

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
5.3.2 Special Timing for CMD53 Multi-Block Read.............................................................................. 25
6. SDIO Card Internal Operation................................................................................................................ 26
6.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 26
6.2 Register Access Time........................................................................................................................ 26
6.3 Interrupts ........................................................................................................................................... 26
6.4 Suspend/Resume.............................................................................................................................. 27
6.5 Read Wait.......................................................................................................................................... 27
6.6 CMD52 During Data Transfer............................................................................................................ 27
6.7 SDIO Fixed Internal Map................................................................................................................... 27
6.8 Common I/O Area (CIA) .................................................................................................................... 28
6.9 Card Common Control Registers (CCCR)......................................................................................... 28
6.10 Function Basic Registers (FBR) ........................................................................................................ 35
6.11 Card Information Structure (CIS)....................................................................................................... 37
6.12 Multiple Function SDIO Cards........................................................................................................... 37
6.13 Setting Block Size with CMD53......................................................................................................... 37
6.14 Bus State Diagram ............................................................................................................................ 38
7. Embedded I/O Code Storage Area (CSA) ............................................................................................. 39
7.1 CSA Access....................................................................................................................................... 39
7.2 CSA Data Format .............................................................................................................................. 39
8. SDIO Interrupts....................................................................................................................................... 40
8.1 Interrupt Timing ................................................................................................................................. 40
8.1.1 SPI and SD 1-bit Mode Interrupts .............................................................................................. 40
8.1.2 SD 4-bit Mode ............................................................................................................................ 40
8.1.3 Interrupt Period Definition .......................................................................................................... 40
8.1.4 Interrupt Period at the Data Block Gap in 4-bit SD Mode (Optional) .......................................... 40
8.1.5 Inhibited Interrupts (Removed Section)...................................................................................... 40
8.1.6 End of Interrupt Cycles............................................................................................................... 40
8.1.7 Terminated Data Transfer Interrupt Cycle .................................................................................. 41
8.1.8 Interrupt Clear Timing................................................................................................................. 41
9. SDIO Suspend/Resume Operation........................................................................................................ 42
10. SDIO Read Wait Operation..................................................................................................................... 43
11. Power Control..................................................................................................................
11.1 Power Control Overview.................................................................................................................... 44
11.2 Power Control support for SDIO Cards ............................................................................................. 44
11.2.1 Master Power Control ................................................................................................................ 44
11.2.2 Power Selection ......................................................................................................................... 45
11.2.3 High-Power Tuples..................................................................................................................... 45
11.3 Power Control Support for the SDIO Host.........................................................................................45
11.3.1 Version 1.10 Host....................................................................................................................... 45
11.3.2 Power Control Operation............................................................................................................ 46
12. High-Speed Mode ................................................................................................................................... 47
12.1 SDIO High-Speed Mode.................................................................................................................... 47
12.2 Switching Bus Speed Mode in a Combo Card................................................................................... 47
13. SDIO Physical Properties ...................................................................................................................... 48
13.1 SDIO Form Factors ........................................................................................................................... 48
13.2 Full-Size SDIO .................................................................................................................................. 48
13.3 miniSDIO........................................................................................................................................... 48
14. SDIO Power............................................................................................................................................. 48
14.1 SDIO Card Initialization Voltages ...................................................................................................... 48
14.2 SDIO Power Consumption ................................................................................................................ 48
15. Inrush Current Limiting.......................................................................................................................... 50
16. CIS Formats ............................................................................................................................................ 51
16.1 CIS Reference Document ................................................................................................................. 51
....................... 44
v
Page 7

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
16.2 Basic Tuple Format and Tuple Chain Structure ................................................................................. 51
16.3 Byte Order Within Tuples .................................................................................................................. 51
16.4 Tuple Version .................................................................................................................................... 52
16.5 SDIO Card Metaformat...................................................................................................................... 52
16.6 CISTPL_MANFID: Manufacturer Identification String Tuple .............................................................. 53
16.7 SDIO Specific Extensions.................................................................................................................. 53
16.7.1 CISTPL_FUNCID: Function Identification Tuple......................................................................... 53
16.7.2 CISTPL_FUNCE: Function Extension Tuple .............................................................................. 54
16.7.3 CISTPL_FUNCE Tuple for Function 0 (common)....................................................................... 54
16.7.4 CISTPL_FUNCE Tuple for Function 1-7 .................................................................................... 55
16.7.5 CISTPL_SDIO_STD: Function is a Standard SDIO Function..................................................... 58
16.7.6 CISTPL_SDIO_EXT: Tuple Reserved for SDIO Cards............................................................... 58
Appendix A..................................................................................................................................................... 59
A.1 SD and SPI Command List.................................................................................................................... 59
Appendix B..................................................................................................................................................... 61
B.1 Normative References........................................................................................................................... 61
Appendix C..................................................................................................................................................... 62
Abbreviations and Terms................................................................................................................... 62
C.1
Appendix D..................................................................................................................................................... 64
vi
Page 8

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Table of Tables
Table 3-1 OCR Values for CMD5 ..................................................................................................................... 10
Table 4-1 Unsupported SD Memory Commands ............................................................................................. 16
Table 4-2 R6 response to CMD3 ..................................................................................................................... 16
Table 4-3 SDIO R6 Status Bits......................................................................................................................... 16
Table 4-4 Combo Card 4-bit Control ................................................................................................................ 17
Table 4-5 Card Detect Resistor States............................................................................................................. 17
Table 4-6 is blanked......................................................................................................................................... 17
Table 4-7 SDIO Status Register Structure ....................................................................................................... 20
Table 5-1 Flag data for IO_RW_DIRECT SD Response.................................................................................. 23
Table 5-2 IO_RW_ EXTENDED command Op Code Definition....................................................................... 24
Table 5-3 Byte Count Values ........................................................................................................................... 25
Table 6-1 Card Common Control Registers (CCCR) ....................................................................................... 29
Table 6-2 CCCR bit Definitions ........................................................................................................................ 34
Table 6-3 Function Basic Information Registers (FBR).................................................................................... 35
Table 6-4 FBR bit and field definitions ............................................................................................................. 36
Table 6-5 Card Information Structure (CIS) and reserved area of CIA.............................................................37
Table 11-1 Reference Tuples by Master Power Control and Power Select...................................................... 45
Table 16-1 Basic Tuple Format........................................................................................................................ 51
Table 16-2 Tuples Supported by SDIO Cards.................................................................................................. 52
Table 16-3 CISTPL_MANFID: Manufacturer Identification Tuple.....................................................................53
Table 16-4 CISTPL_FUNCID Tuple................................................................................................................. 53
Table 16-5 CISTPL_FUNCE Tuple General Structure ..................................................................................... 54
Table 16-6 TPLFID_FUNCTION Tuple for Function 0 (common) .................................................................... 54
Table 16-7 TPLFID_FUNCTION Field Descriptions for Function 0 (common)................................................. 54
Table 16-8 TPLFID_FUNCTION Tuple for Function 1-7 .................................................................................. 55
Table 16-9 TPLFID_FUNCTION Field Descriptions for Functions 1-7............................................................. 57
Table 16-10 TPLFE_FUNCTION_INFO Definition........................................................................................... 57
Table 16-11 TPLFE_CSA_PROPERTY Definition ........................................................................................... 57
Table 16-12 CISTPL_SDIO_STD: Tuple Reserved for SDIO Cards................................................................ 58
Table 16-13 CISTPL_SDIO_EXT: Tuple Reserved for SDIO Cards................................................................. 58
Table A-14 SD Mode Command List................................................................................................................ 59
Table A-15 SPI Mode Command List............................................................................................................... 60
vii
Page 9

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Table of Figures
Figure 2-1 Signal connection to two 4-bit SDIO cards ....................................................................................... 3
Figure 3-1 SDIO response to non-I/O aware initialization.................................................................................. 4
Figure 3-2 Card initialization flow in SD mode (SDIO aware host) .................................................................... 7
Figure 3-3 Card initialization flow in SPI mode (SDIO aware host).................................................................... 9
Figure 3-4 IO_SEND_OP_COND Command (CMD5)..................................................................................... 10
Figure 3-5 Response R4 in SD mode...............................................................................................................11
Figure 3-6 Response R4 in SPI mode ..............................................................................................................11
Figure 3-7 Modified R1 Response ....................................................................................................................11
Figure 3-8 Re-Initialization Flow for I/O Controller........................................................................................... 13
Figure 3-9 Re-Initialization Flow for Memory controller ................................................................................... 13
Figure 5-1 IO_RW_DIRECT Command........................................................................................................... 21
Figure 5-2 R5 IO_RW_DIRECT Response (SD modes)..................................................................................22
Figure 5-3 IO_RW_DIRECT Response in SPI Mode....................................................................................... 23
Figure 5-4 IO_RW_EXTENDED Command..................................................................................................... 24
Figure 6-1 SDIO Internal Map.......................................................................................................................... 28
Figure 6-2 State Diagram for Bus State Machine............................................................................................. 38
viii
Page 10

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
1. General Description
The SDIO (SD Input/Output) card is based on and compatible with the SD memory card. This compatibility
includes mechanical, electrical, power, signaling and software. The intent of the SDIO card is to provide
high-speed data I/O with low power consumption for mobile electronic devices. A primary goal is that an SDIO
card inserted into a non-SDIO aware host shall cause no physical damage or disruption of that host or it’s
software. In this case, the SDIO card should simply be ignored. Once inserted into an SDIO aware host, the
detection of the card proceeds via the normal means described in this specification with some extensions. In this
state, the SDIO card is idle and draws a small amount of power (15 mA averaged over 1 second). During the
normal initialization and interrogation of the card by the host, the card identifies itself as an SDIO card. The host
software then obtains the card information in a tuple (linked list) format and determines if that card’s I/O
function(s) are acceptable to activate. This decision is based on such parameters as power requirements or the
availability of appropriate software drivers. If the card is acceptable, it is allowed to power up fully and start the
I/O function(s) built into it.
1.1 SDIO Features
• Targeted for portable and stationary applications
• Minimal or no modification to SD Physical bus is required
• Minimal change to memory driver software
• Extended physical form factor available for specialized applications
• Plug and play (PnP) support
• Multi-function support including multiple I/O and combined I/O and memory
• Up to 7 I/O functions plus one memory supported on one card.
• Allows card to interrupt host
• Operational Voltage range: 2.7-3.6V (Operational Voltage is used for Initialization)
• Application Specifications for Standard SDIO Functions.
• Multiple Form Factors:
• Full-Size SDIO
• miniSDIO
1.2 Primary Reference Document
This specification is based on and refers extensively to the SDA document:
SD Memory Card Specifications
Part 1 PHYSICAL LAYER SPECIFICATION Version 2.00 May 9, 2006
The reader is directed to this document for more information on the basic operation of SD cards. In addition,
other documents are referenced in this specification. A complete list can be found in appendix B.1.
This specification can apply to any released versions of Physical Layer Specification after Version 2.00.
1.3 Standard SDIO Functions
Associated with the base SDIO specification, there are several Application Specifications for Standard SDIO
Functions. These common functions such as cameras, Bluetooth cards and GPS receivers have a standard
register interface, a common operation method and a standard CIS extension. Implementation of the standard
interfaces are optional for any card vendor, but compliance with the standard allows the use of standard drivers
and applications which will increase the appeal of these cards to the consumer. Full information on these
standard interfaces can be found in the Application Specifications for Standard SDIO Functions maintained by
the SDA.
1
Page 11

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
2. SDIO Signaling Definition
2.1 SDIO Card Types
This specification defines two types of SDIO cards. The Full-Speed card supports SPI, 1-bit SD and the 4-bit SD
transfer modes at the full clock range of 0-25MHz. The Full-Speed SDIO cards have a data transfer rate of over
100 Mb/second (10 MB/Sec). A second version of the SDIO card is the Low-Speed SDIO card. This card
requires only the SPI and 1-bit SD transfer modes. 4-bit support is optional. In addition, Low-Speed SDIO cards
shall support a full clock range of 0-400 KHz. The intended use of Low-Speed cards is to support low-speed I/O
capabilities with a minimum of hardware. The Low-Speed cards support such functions as modems, bar-code
scanners, GPS receivers etc. If a card is a ‘Combo card’ (memory plus SDIO) then Full-Speed and 4-bit
operation is mandatory for both the memory and SDIO portions of the card.
2.2 SDIO Card modes
There are 3 signaling modes defined for SD memory cards that also apply to SDIO Card:
2.2.1 SPI (Card mandatory support)
The SPI bus topology is defined in section 3.5.2 and the protocol is defined in sections 3.6.2 and 7 of the SD
Physical Specification Version 2.00. In this mode pin 8, which is undefined for memory, is used as the
interrupt pin. All other pins and signaling protocols are identical to the SD Physical Specification.
2.2.2 1-bit SD Data Transfer Mode (Card Mandatory Support)
This mode is identical to the 1 data bit (narrow) mode defined for SD Memory in section 3.6.1 of the SD
Physical Specification. In this mode, data is transferred on the DAT[0] pin only. In this mode pin 8, which is
undefined for memory, is used as the interrupt pin. All other pins and signaling protocols are identical to the
SD Memory specification.
2.2.3 4-bit SD Data Transfer Mode (Mandatory for High-Speed Cards, Optional for Low-Speed)
This mode is identical to the 4 data bit mode (wide) defined for SD Memory in section 3.6.1 of the SD
Physical Specification. In this mode, data is transferred on all 4 data pins (DAT[3:0]). In this mode the
interrupt pin is not available for exclusive use as it is utilized as a data transfer line. Thus, if the interrupt
function is required, a special timing is required to provide interrupts. See section 8.1.2 for details of this
operation. The 4-bit SD mode provides the highest data transfer possible, up to 100 Mb/sec.
2.3 SDIO Host Modes
If a SDIO aware host supports the SD transfer mode, it is recommended that both the 1-bit and 4-bit modes be
supported. While a SDIO host that supports only the 4-bit transfer mode is possible, its performance with a
Low-Speed SDIO card may be reduced. This is because the only means to transfer data to and from a
Low-Speed card would be the single byte per command transfer (using the IO_RW_DIRECT command
(CMD52) see 5.1).
2
Page 12
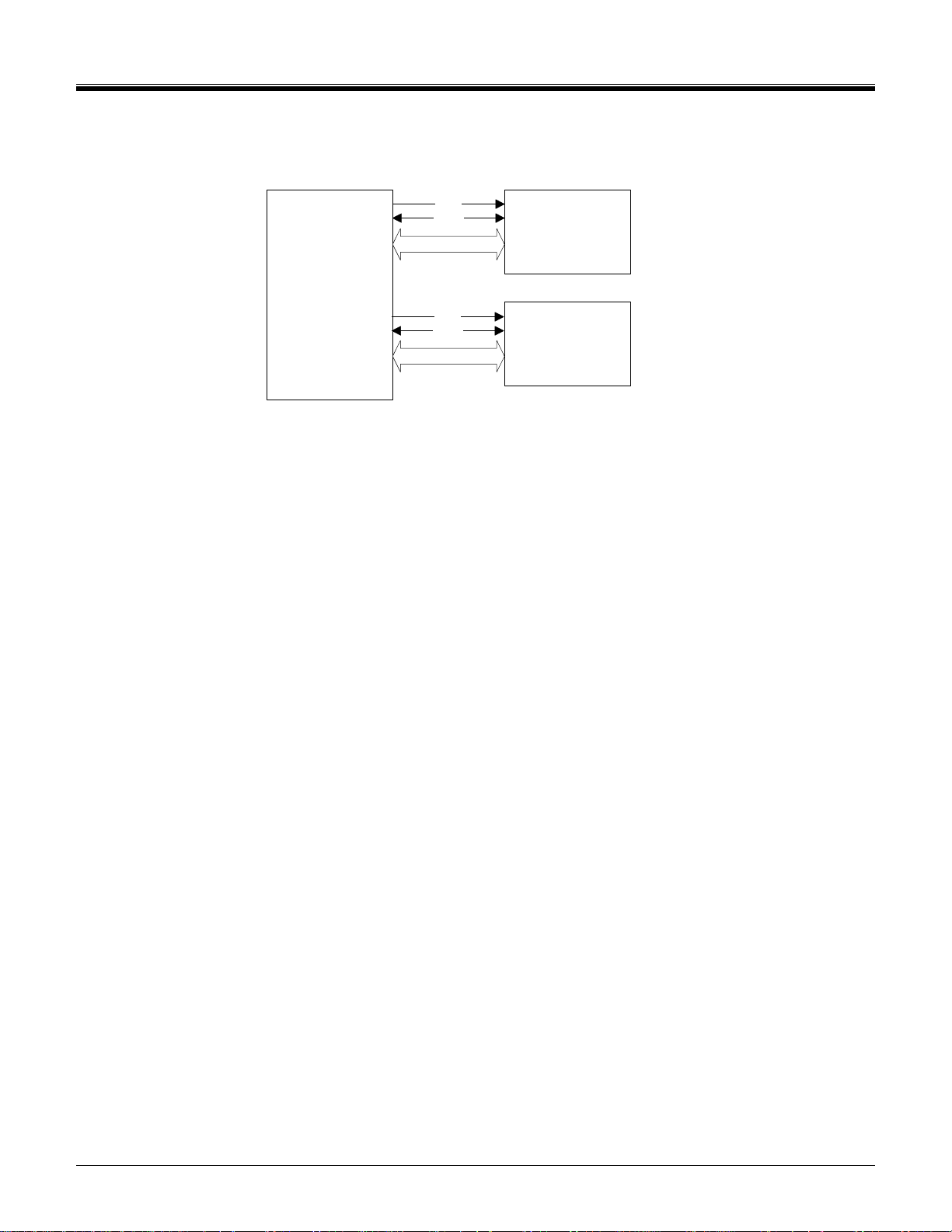
©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
2.4 Signal Pins
CLK
CMD
DAT[3:0]
SD Host
CLK
CMD
DAT[3:0]
Figure 2-1 Signal connection to two 4-bit SDIO cards
The rest of this chapter is not included in the Simplified Specification.
SD I/O Card
SD I/O Card
3
Page 13
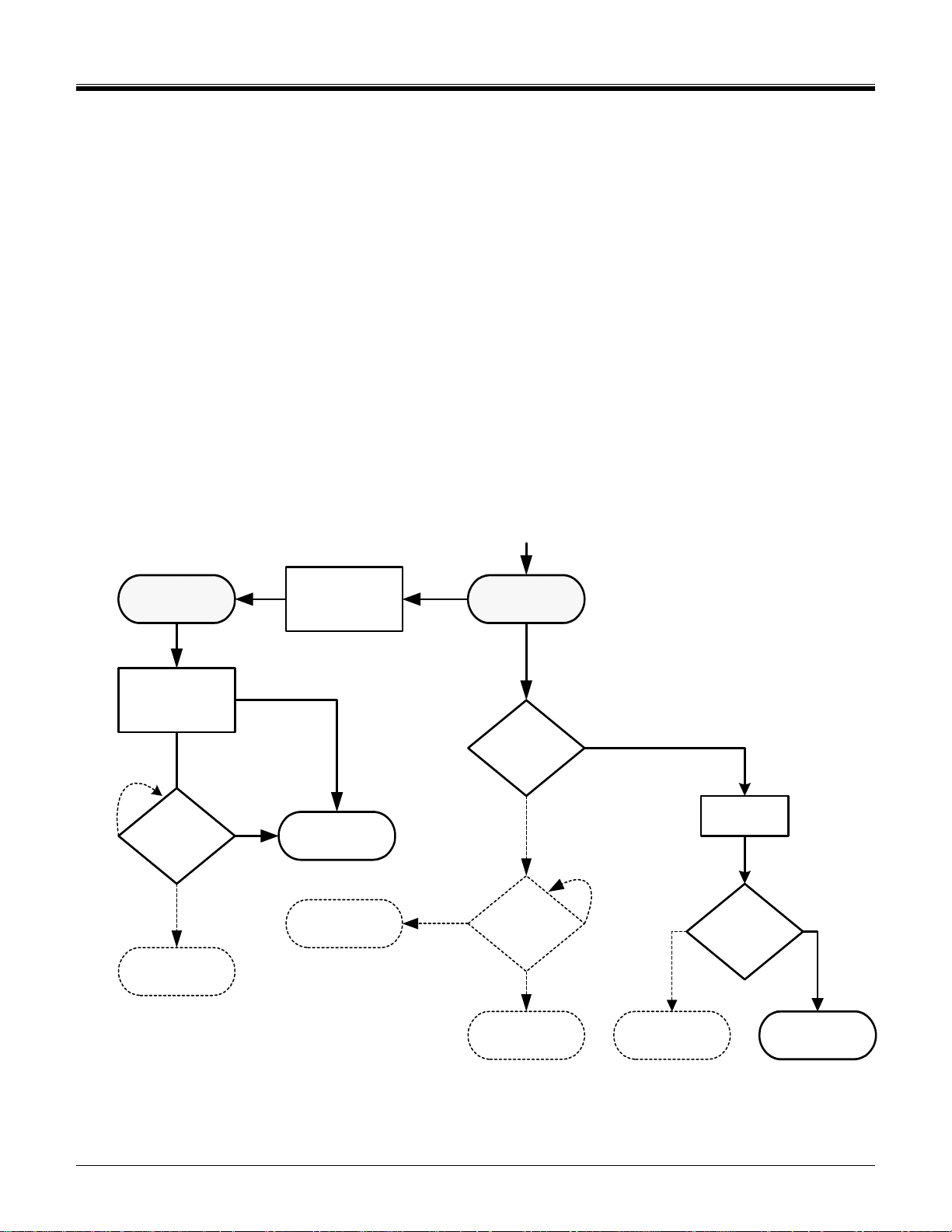
©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
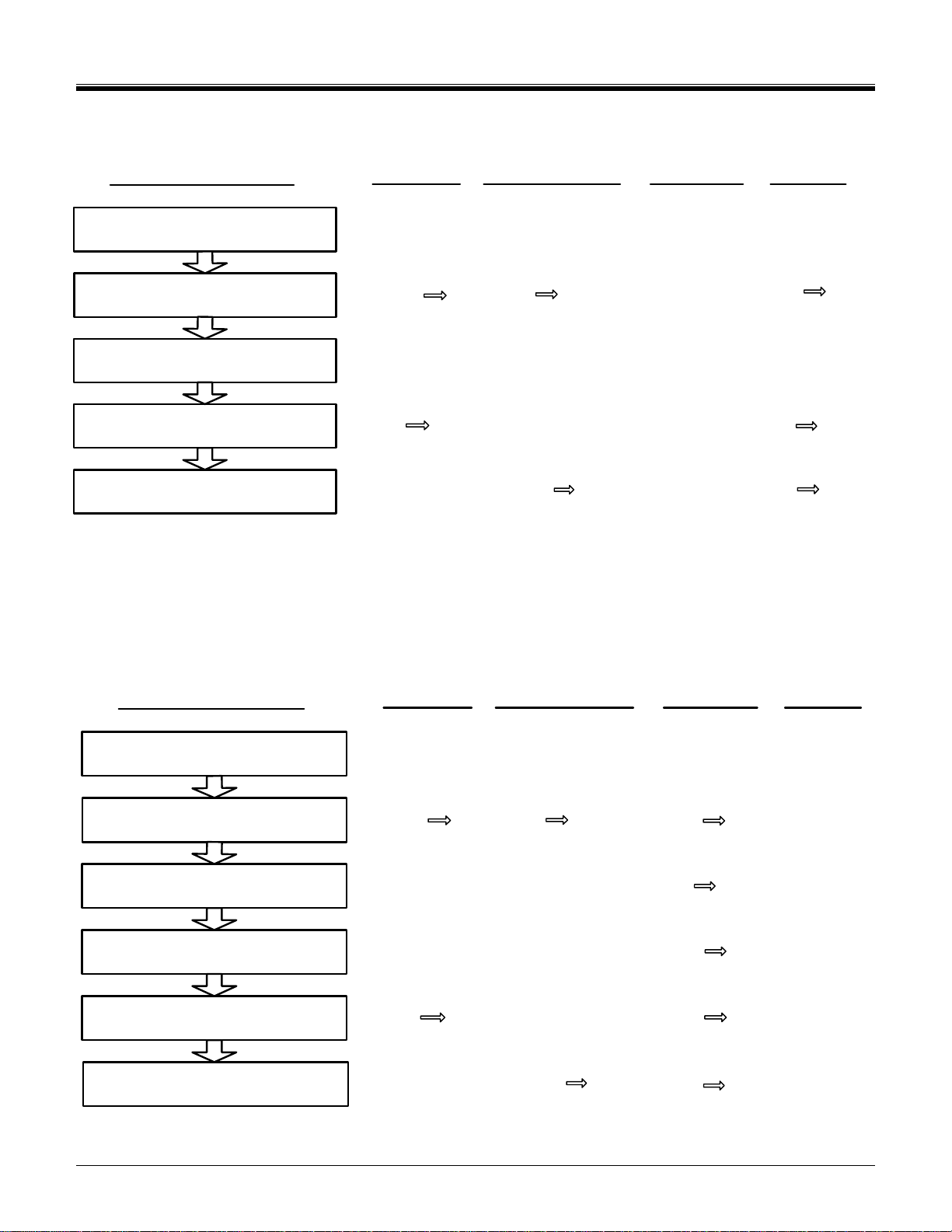
3. SDIO Card Initialization
3.1 Differences in I/O card Initialization
A requirement for the SDIO specification is that an SDIO card shall not cause non-I/O aware hosts to fail when
inserted. In order to prevent operation of I/O functions in non-I/O aware hosts, a change to the SD card
identification mode flowchart is needed. A new command (IO_SEND_OP_COND, CMD5) is added to replace
the ACMD41 for SDIO initialization by I/O aware hosts (see 3.2).
After reset or power-up, all I/O functions on the card are disabled and the I/O portion of the card shall not
execute any operation except CMD5 or CMD0 with CS=low. If there is SD memory installed on the card (also
called a combo card), that memory shall respond normally to all normal mandatory memory commands.
An I/O only card shall not respond to the ACMD41 and thus appear initially as an MMC card (See appendix B.1
for information on the MMC specification). The I/O only card shall also not respond to the CMD1 used to initialize
the MMC cards and appear as a non-responsive card. The host then gives up and disables this card. Thus, the
non-aware host receives no response from an I/O only card and force it to the inactive state. The operation of an
I/O card with a non-I/O aware host is shown in Figure 3-1 Note that the solid lines are the actual paths taken
while the dashed lines are not executed.
Reset
SPI Mode Idle
State
CMD58
(optional)
Busy
CMD1 or
ACMD41
Normal SPI
memory operation
Invalid
Cmd
Invalid
Cmd
CMD0 + CS
asserted (0)
SDIO card is
Rejected
Inactive State
SPI
Response
No
Response
Idle State
SD
ACMD41
(arg = 00)
Busy
ACMD41
arg = working
voltage
Response
Normal SD
memory operation
No
Response
Response
Card is MMC
CMD0
CMD1
No
Response
SDIO card is
Reject ed
Figure 3-1 SDIO response to non-I/O aware initialization
4
Page 14

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
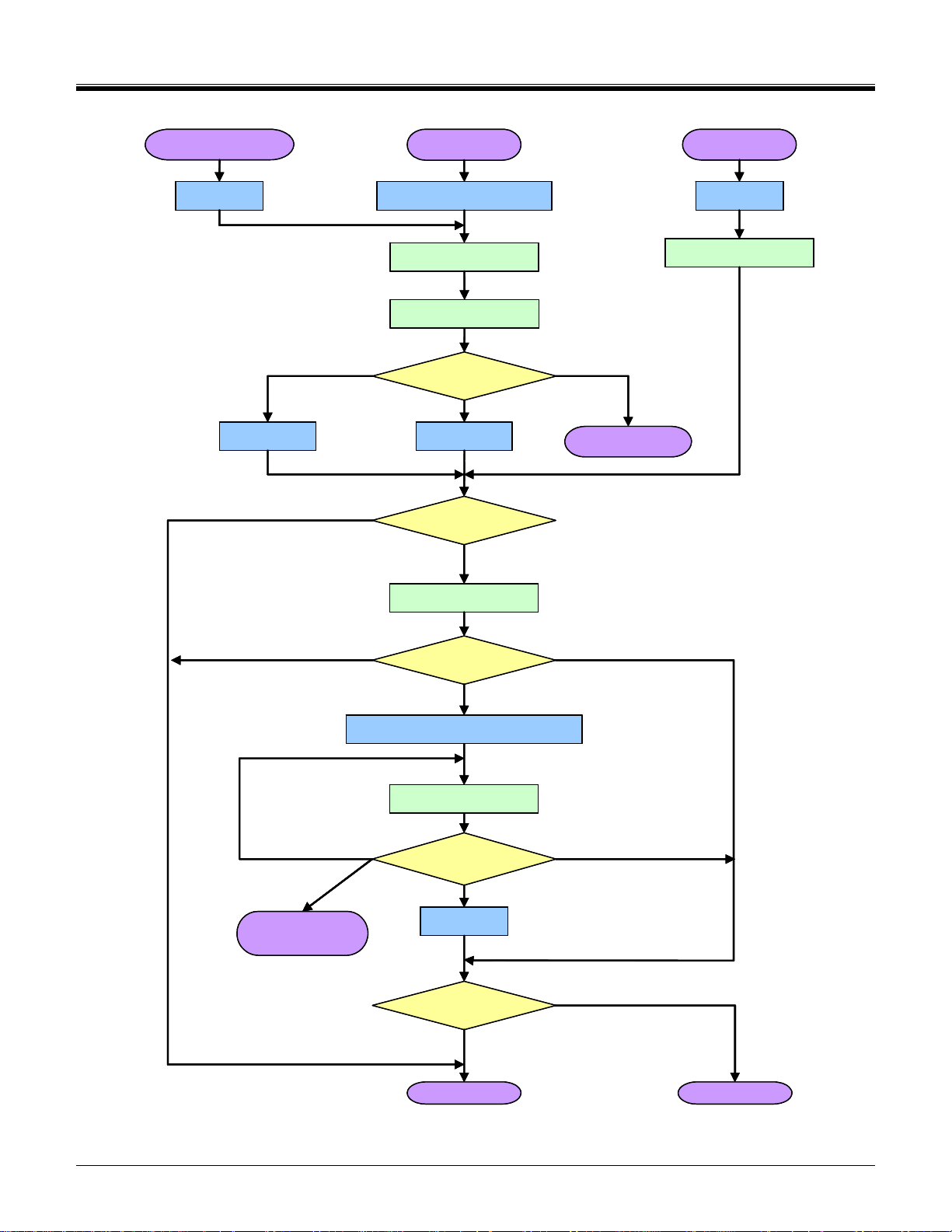
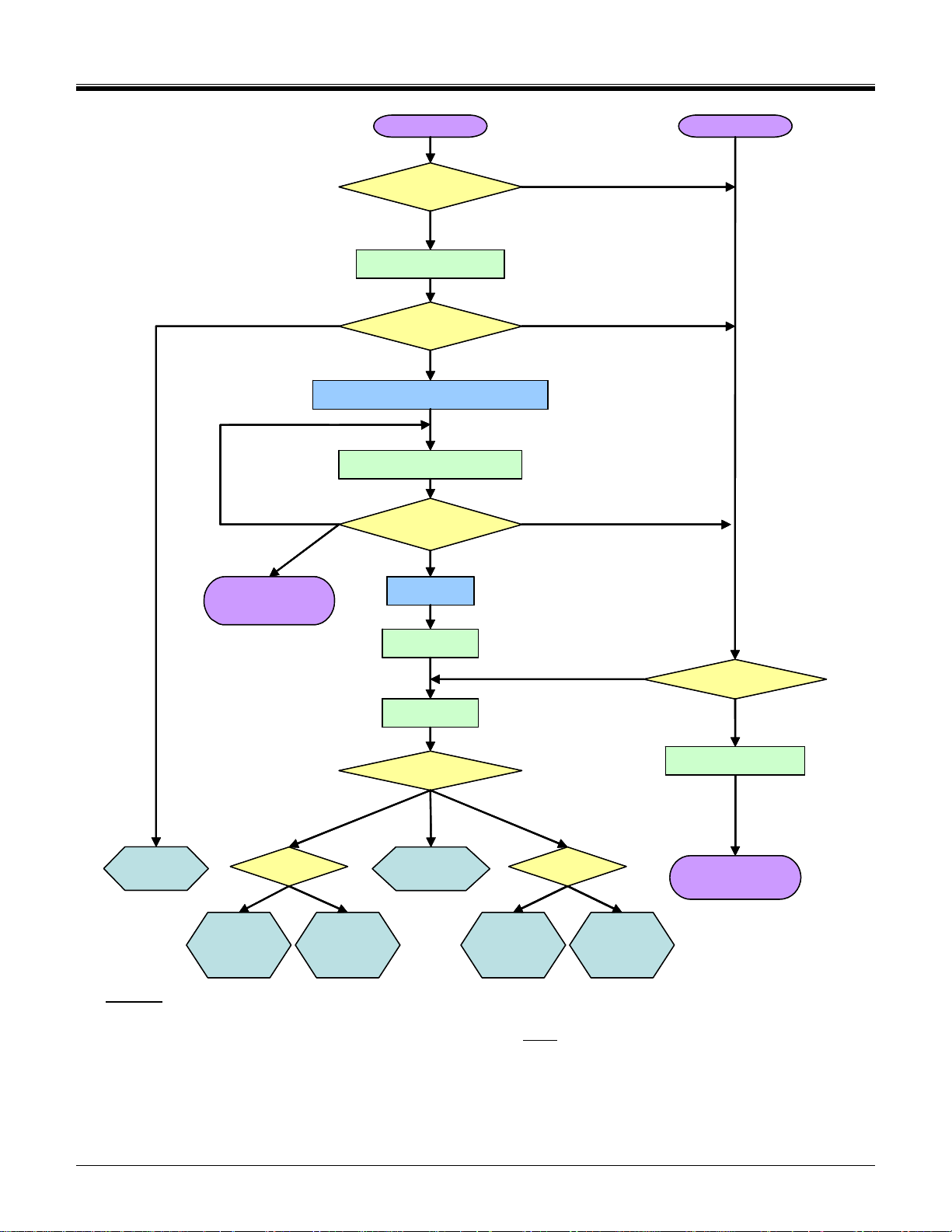
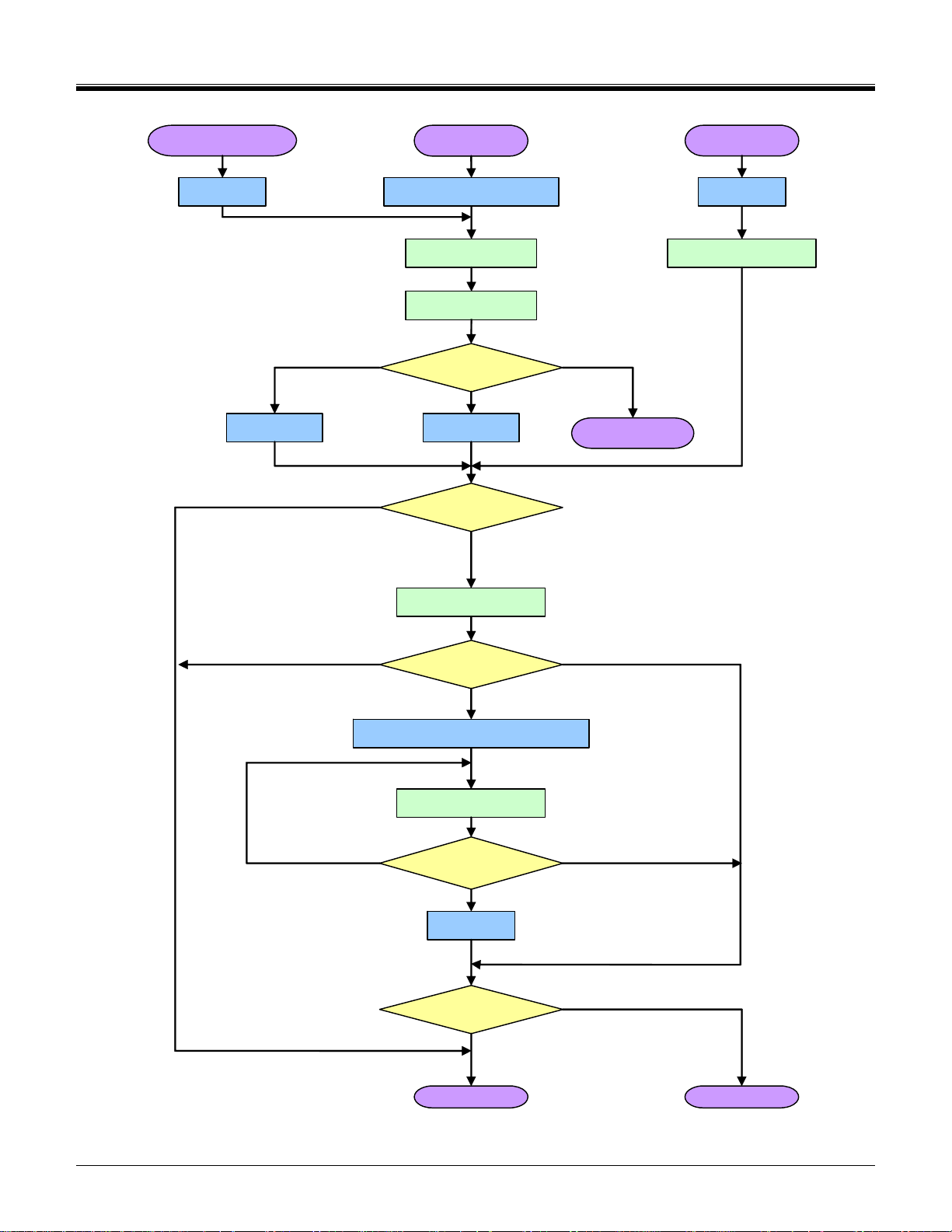
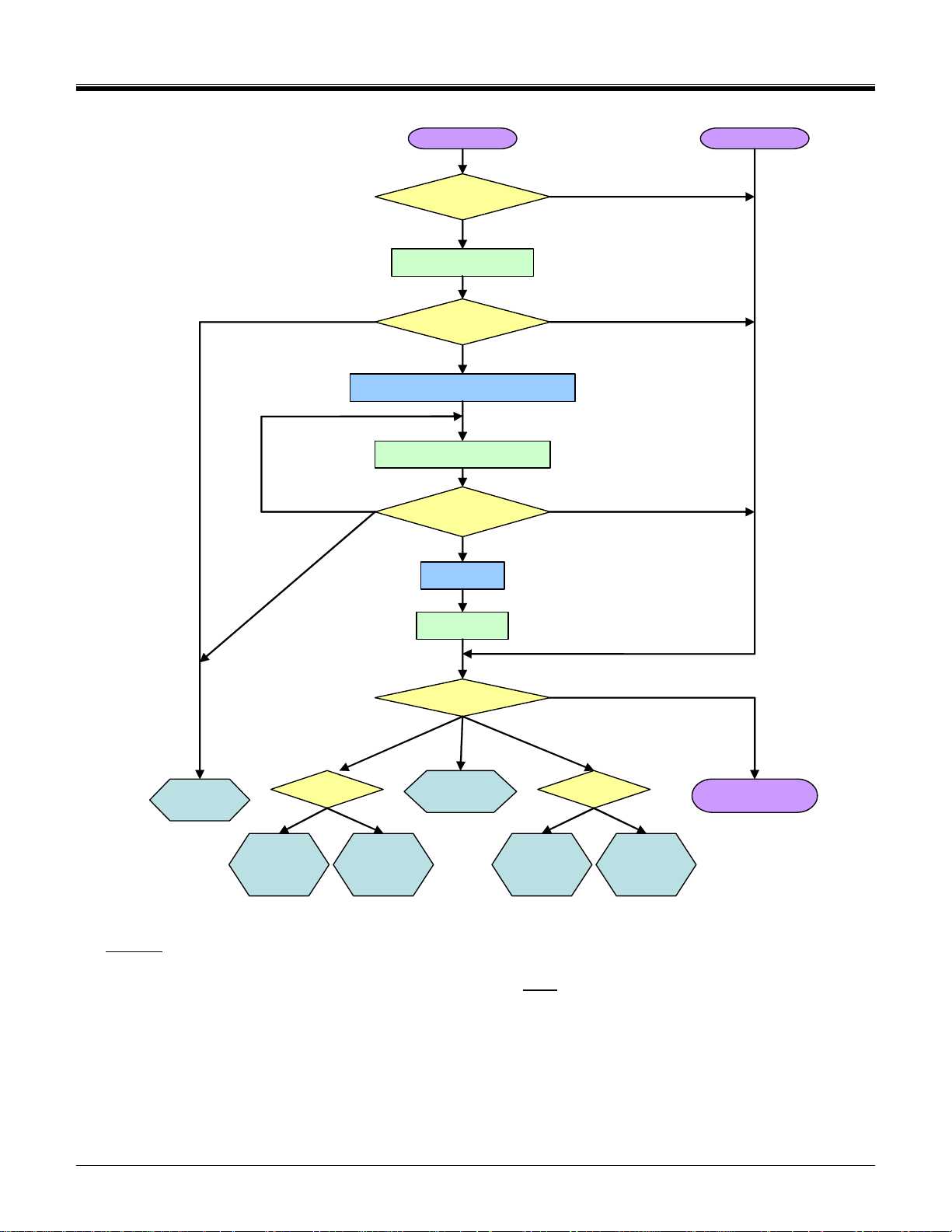
An SDIO aware host sends CMD5 prior to the CMD55/ACMD41 pair, and thus would receive a valid OCR in the
R4 response to CMD5 and continue to initialize the card. Figure 3-2 shows the operation of an SDIO aware host
operating in the SD modes and Figure 3-3 shows the same operation for a host that operates in the SPI mode.
If the I/O portion of a card has received no CMD5, the I/O section remains inactive and shall not respond to any
command except CMD5. A combo card stays in the memory-only mode. If no memory is installed on the card
(i.e. an I/O only card in a non-SDIO aware host) the card would not respond to any memory command. This
satisfies the condition where a user uses some I/O function on the card such as Ethernet to load a music file to
the memory function of that card. The card is then removed and inserted into a non-SDIO aware host. That host
would not enable the I/O function (no CMD5) so would appear to the player as a memory-only card. If the host
were I/O aware, it would send the CMD5 to the card and the card would respond with R4. The host reads that R4
value and knows the number of available I/O functions and about the existence of any SD memory.
After the host has initialized the I/O portion of the card, it then reads the Common Information Area (CIA) of the
card (see 6.8). This is done by issuing a read command, starting with the byte at address 0x00, of I/O function 0.
The CIA contains the Card Common Control Registers (CCCR) and the Function Basic Registers (FBR). Also
included in the CIA are pointers to the card’s common Card Information Structure (CIS) and each individual
function’s CIS. The CIS structure is defined in section 16. The CIS includes information on power, function,
manufacturer and other things the host needs to determine if the I/O function(s) is appropriate to power-up. If the
host determines that the card should be activated, a register in the CCCR area enables the card and each
individual function. At this time, all functions of the I/O card are fully available. In addition, the host can control
the power consumption and enable/disable interrupts on a function-by-function basis. This access to I/O does
not interfere with memory access to the card if present.
Combo Cards can accept CMD15 with RCA=0000, as described in, but there is an exception for SD memory
only cards. Memory only cards require a non-zero RCA before the host may issue CMD15. Thus, CMD15 shall
be issued after CMD3 in the Standby state. In the case of ACMD41, it shall accept RCA=0x0000.
As shown in Figure 3-2 and Figure 3-3, an SDIO aware host shall send CMD5 arg=0 as part of the initialization
sequence after either Power On or a CMD 52 with write to I/O Reset. Sending CMD5 arg=0 that has not been
preceded by one of these two reset conditions shall not result in either the host or card entering the initialization
sequence.
5
Page 15
©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Re-init Memory
Re-init Memory
Power On
Power On
Re-init IO
Re-init IO
MEM=0
MEM=0
IO=0IO=0, MEM=0
IO=0IO=0, MEM=0
CMD0 Pin1=High
CMD0 Pin1=High
CMD52 IO Reset
CMD52 IO Reset
CMD8
CMD8
CMD8 is required to support
CMD8 is required to support
High Capacity Memory.
High Capacity Memory.
No Response
No Response
Check Response
Check Response
Error Response
Error Response
Good Response
Good Response
F8=1F8=0
F8=1F8=0
Unusable card
Unusable card
Skip IO Initialize or IO=1
Skip IO Initialize or IO=1
Test IO Flag
Test IO Flag
No Response
No Response
IORDY=0 1sec Timeout
IORDY=0 1sec Timeout
No Response
No Response
Unusable card
Unusable card
(Inactive State)
(Inactive State)
Execute IO Initialize & IO=0
Execute IO Initialize & IO=0
Get IO OCR
CMD5 Arg=0
CMD5 Arg=0
Check Response
Check Response
NF>0 & OCR valid
NF>0 & OCR valid
Set New Voltage (if needed)
Set New Voltage (if needed)
CMD5 Arg=WV
CMD5 Arg=WV
Check Response
Check Response
IORDY=1
IORDY=1
IO=1
IO=1
Test MP Flag
Test MP Flag
Get IO OCR
IO Initialized
IO Initialized
NF=0 or OCR invalid
NF=0 or OCR invalid
MP=0
MP=0
MP=1
MP=1
A
A
B
B
6
Page 16
©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
A
A
B
B
Test MEM Flag
Test MEM Flag
Skip memory initialize or MEM=1
Skip memory initialize or MEM=1
Execute memory initialize & MEM=0
Execute memory initialize & MEM=0
ACMD41 Arg=0
ACMD41 Arg=0
Get memory OCR
Get memory OCR
No Response
No Response
Check Response
Check Response
OCR valid
OCR valid
OCR invalid
OCR invalid
Set New Voltage (if needed)
Set New Voltage (if needed)
ACMD41 Arg=HCS, WV
ACMD41 Arg=HCS, WV
High Capacity Support Host: HCS=1
High Capacity Support Host: HCS=1
MRDY=0 1sec Timeout
No Response
No Response
MRDY=0 1sec Timeout
Unusable card
Unusable card
(Inactive State)
(Inactive State)
Check Response
Check Response
MRDY=1
MRDY=1
MEM=1
MEM=1
CMD2
CMD2
CMD3
CMD3
Memory Initialized
Memory Initialized
If F8=1, CCS is valid
If F8=1, CCS is valid
IO=1
IO=1
Test IO Flag
Test IO Flag
IO=0
IO=0
CMD15 RCA=0
IO=0, MEM=1
IO=0, MEM=1
Test Flags
Test Flags
Not SD
Not SD
Card
Card
Only Card
Only Card
Var iables
NF: Number of I/O Functions (CMD5 Response)
MP: Memory Present Flag (CMD5 Response)
IORDY: I/O Power-up Status (C bit in the CMD5 response)
MRDY: Memory Power-up Status (OCR Bit31)
HCS: Host Capacity Support (ACMD41 Argument)
Test CCS Test CCS
Test CCS Test CCS
CCS=0 CCS=1 CCS=0 CCS=1
CCS=0 CCS=1 CCS=0 CCS=1
Standard
Standard
Capacity
Capacity
Memory
Memory
High
High
Capacity
Capacity
Memory
Memory
Only Card
Only Card
IO Only
IO Only
Card
Card
IO=1, MEM=0
IO=1, MEM=0
IO=1,
IO=1,
MEM=1
MEM=1
Standard
Standard
Capacity
Capacity
Combo
Combo
High
High
Capacity
Capacity
Combo
Combo
Card
Card
CCS: Card Capacity Status (ACMD41 Response)
Flags
IO: I/O Functions Initialized Flag
MEM: Memory Initialized Flag
F8: CMD8 Flag
Card
Card
CMD15 RCA=0
Unusable card
Unusable card
(Inactive State)
(Inactive State)
Figure 3-2 Card initialization flow in SD mode (SDIO aware host)
7
Page 17
©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Re-init Memory
MEM=0
Illegal Command
Skip IO Initialize or IO=1
Execute IO Initialize & IO=0
Power On
CMD0 CS=Low
CMD8
Check Response
Good Response
F8=1F8=0
Test IO Flag
Re-init IO
IO=0IO=0, MEM=0
CMD52 IO Reset
CMD8 is required to support
High Capacity Memory.
Error Response
Unusable card
Illegal Command
IORDY=0 1sec Timeout
CMD5 Arg=0
Get IO OCR
Check Response
NF>0 & OCR valid
Set New Voltage (if needed)
CMD5 Arg=WV
Check Response
IORDY=1
IO=1
IO Initialized
Test MP
MP=1
NF=0 or OCR invalid
MP=0
C
D
8
Page 18
©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
C
D
Test MEM Flag
Execute memory initialize & MEM=0
CMD58
Skip memory initialize or MEM=1
Get memory OCR
Illegal Command
Check Response
OCR valid
OCR invalid
Set New Voltage (if needed)
ACMD41 Arg= HC S, WV
High Capacity Support Host: HCS=1
IDLE=1 1sec Timeout
Check Response
IDLE=0
MEM=1
Memory Initialized
Illegal Command
CMD58
If F8=1, CMD58 is required
to get CCS. If F8=0, CSS=0.
IO=0, MEM=1
Not SD
Card
Test CCS Test CCS
CCS=0 CCS=1 CCS=0 CCS=1
Standard
Capacity
Memory
Only Card
High
Capacity
Memory
Only Card
Test Flags
IO=1,
MEM=0
IO Only
Card
IO=1, MEM=1
Standard
Capacity
Combo
Card
IO=0, MEM=0
Unusable card
High
Capacity
Combo
Card
Var iables
NF: Number of I/O Functions (CMD5 Response)
MP: Memory Present Flag (CMD5 Response)
IORDY: I/O Power-up Status (C bit in the CMD5 response)
MRDY: Memory Power-up Status (OCR Bit31)
HCS: Host Capacity Support (ACMD41 Argument)
CCS: Card Capacity Status (ACMD41 Response)
Flags
IO: I/O Functions Initialized Flag
MEM: Memory Initialized Flag
F8: CMD8 Flag
Figure 3-3 Card initialization flow in SPI mode (SDIO aware host)
9
Page 19
©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
D
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
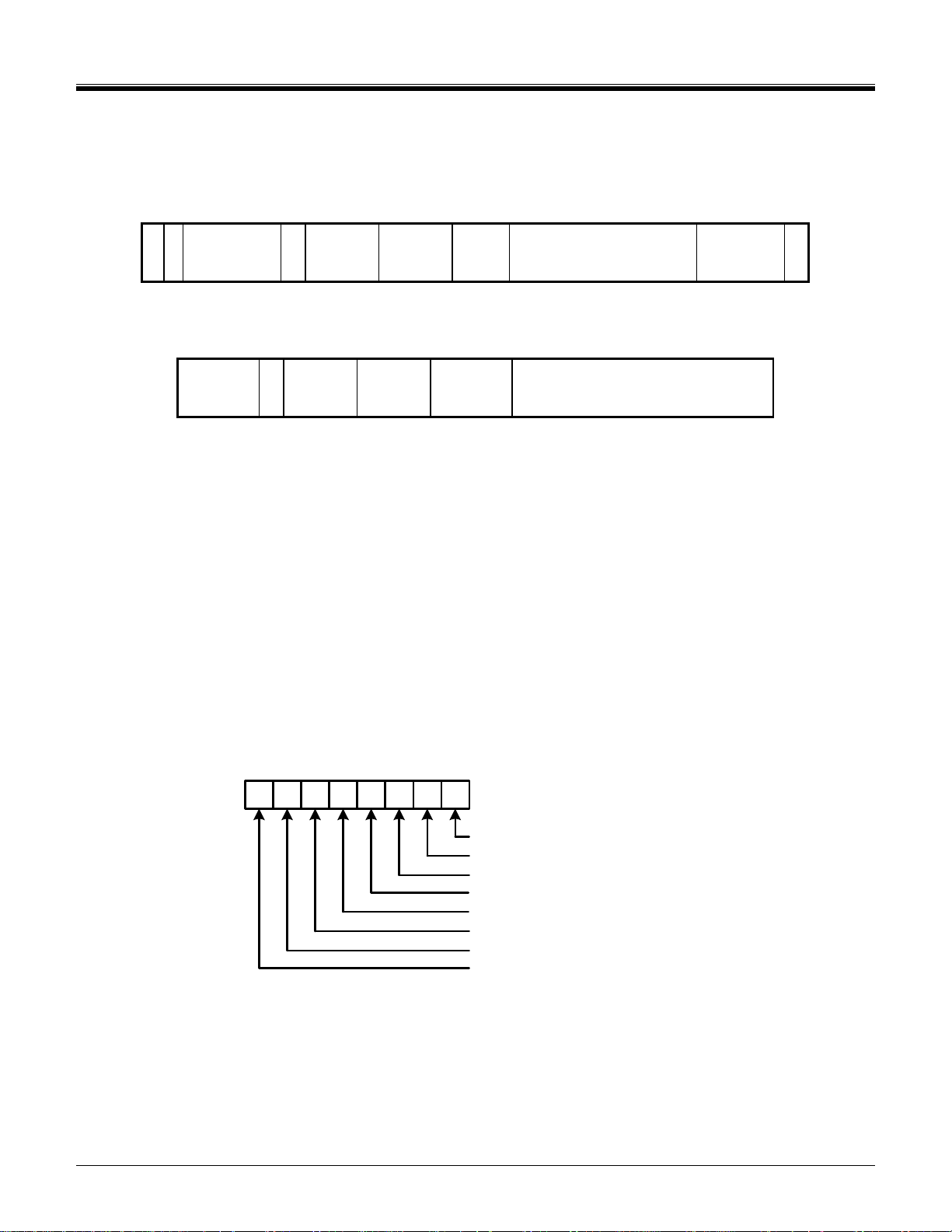
3.2 The IO_SEND_OP_COND Command (CMD5)
Figure 3-4 shows the format of the IO_SEND_OP_COND command (CMD5). The function of CMD5 for SDIO
cards is similar to the operation of ACMD41 for SD memory cards. It is used to inquire about the voltage range
needed by the I/O card. The normal response to CMD5 is R4 in either SD or SPI format. The R4 response in SD
mode is shown in Figure 3-5 and the SPI version is shown in Figure 3-6.
S
Command Index
000101b
1 1 6 8 24 7 1
Figure 3-4 IO_SEND_OP_COND Command (CMD5)
The IO_SEND_OP_COND Command contains the following fields:
S(tart bit): Start bit. Always 0
D(irection): Direction. Always1 indicates transfer from host to card.
Command Index: Identifies the CMD5 command with a value of 000101b
Stuff Bits: Not used, shall be set to 0.
I/O OCR:
CRC7: 7 bits of CRC data
E(nd bit): End bit, always 1
Stuff
Bits
I/O OCR CRC7 E
Operation Conditions Register. The supported minimum and maximum values
for VDD. The layout of the OCR is shown in Table 3-1. See section 4.10.1 for
additional information.
I/O OCR bit
position
0-3 Reserved
4 Reserved
5 Reserved
6 Reserved
7 Reserved
8 2.0-2.1
9 2.1-2.2
10 2.2-2.3
11 2.3-2.4
12 2.4-2.5
13 2.5-2.6
14 2.6-2.7
15 2.7-2.8
16 2.8-2.9
17 2.9-3.0
18 3.0-3.1
19 3.1-3.2
20 3.2-3.3
21 3.3-3.4
22 3.4-3.5
23 3.5-3.6
VDD Voltage Window
(in Volts)
Table 3-1 OCR Values for CMD5
The SDIO Version 2.00 cards shall support the operational voltage range 2.7-3.6V and are not necessary to
support the voltage range 2.0-2.7V for basic communication. The hosts, which support SDIO Version 2.00, shall
not use voltage range 2.0-2.7V for basic communication.
10
Page 20
©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
D
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
3.3 The IO_SEND_OP_COND Response (R4)
An SDIO card receiving CMD5 shall respond with a SDIO unique response, R4. The format of R4 for both the
SD and SPI modes is:
S
Reserved C Number
of I/O
functions
1 1 6 1 3 1 3 24 7 1
Figure 3-5 Response R4 in SD mode
Modified
R1
C
Number
of I/O
functions
8 1 3 1 3 24
Figure 3-6 Response R4 in SPI mode
The Response, R4 contains the following data:
S(tart bit): Start bit. Always 0
D(irection): Direction. Always 0. Indicates transfer from card to host.
Reserved: Bits reserved for future use. These bits shall be set to 1.
C: Set to 1 if Card is ready to operate after initialization
I/O OCR:
Operation Conditions Register. The supported minimum and maximum values
for VDD. The layout of the OCR is shown in Table 3-1. See section 4.10.1 for
additional information.
Memory Present: Set to 1 if the card also contains SD memory. Set to 0 if the card is I/O only.
Number of I/O Functions: Indicates the total number of I/O functions supported by this card. The range is 0-7.
Note that the common area present on all I/O cards at Function 0 is not included in
this count. The I/O functions shall be implemented sequentially beginning at
function 1.
Modified R1: The SPI R1 response byte as described in the SD Physical Specification modified
for I/O as follows:
Memory
Present
Memory
Present
Stuff
I/O OCR Reserved E
Bits
Stuff Bits I/O OCR
00 0
1 = in idle state
RFU (always 0)
1 = illegal command
1 = COM CRC error
1 = Function number error
RFU (always 0)
1 = parameter error
Start Bit (always 0)
Figure 3-7 Modified R1 Response
Stuff Bits: Not used, shall be set to 0.
11
Page 21

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Once an SDIO card has received a CMD5, the I/O portion of that card is enabled to respond normally to all
further commands. This I/O enable of the functions within the I/O card shall remain set until a reset, power cycle
or CMD52 with write to I/O reset is received by the card. Note that a SD memory only card may respond to a
CMD5. The proper response for a memory only card would be Memory Present = 1 and Number of I/O
Functions = 0. A memory only card built to SD Memory Card specification version 1.01 would detect the CMD5
as an illegal command and not respond. Note that unlike the similar memory command ACMD41, The SPI
response to CMD5 does contain the OCR value from the card.
The I/O aware host sends CMD5. If the card responds with response R4 within the timeout value of Ncr as
defined in the SD Physical Specification, the host determines the card’s configuration based on the data
contained within the R4.
3.4 Special Initialization considerations for Combo Cards
The host must be aware of some special situations when initializing a Combo card (SDIO plus SD Memory on
the same card). This is caused because an implementation of the Combo card could actually use 2 separate
controllers (Memory and I/O) in the same package and sharing the same bus lines. It important for the host to
both detect and properly configure both parts (controllers) of a Combo card in order to prevent conflicts between
the SDIO and the SD memory controller. These concerns are caused due to the different response to a reset
(hard or soft) by the two controllers. Another concern is the value of the RCA (Relative Card Address) that exists
within the Memory controller.
Note that this consideration is for the SD 1-bit and SD 4-bit modes only. In The SPI mode, card select/de-select
is accomplished using the hardware CS line rather than the RCA.
3.4.1 Re-initialize both I/O and Memory
When the host re-initializes both I/O and Memory controllers, it is strongly recommended that the host either
execute a power reset (power off then on) or issues a reset commands to both controllers prior to any other
operation. If the host chooses to use the reset commands, it shall issue CMD52 (I/O Reset) first, because it
cannot issue CMD52 after CMD0 (see 4.4). After the reset, the host shall re-initialize both the I/O and Memory
controller as defined in Figure 3-2.
3.4.2 Using a Combo Card as SDIO only or SD Memory only after Combo Initialization
If a host intends to use only the SDIO or the Memory portion of a Combo Card, it is strongly recommended that
the host power reset (power off then on) or issues reset commands to both controllers prior to any other
operation. If the host chooses to use the reset commands, it shall issue CMD52 (I/O Reset) first, because it
cannot issue CMD52 after CMD0 (see 4.4). After the resets, the host re-initializes either the I/O and Memory
controller as defined in Figure 3-2.
3.4.3 Acceptable Commands after Initialization
When the host re-initializes a Combo card, the acceptable commands that the host can issue are restricted until
the I/O controller is placed into the command state and memory controller enters the transfer state. The kinds of
prohibited commands are identified in the next section. Combo cards may not work correctly when the host
issues these prohibited commands. The proper command sequence for the I/O controller and the memory
controller are shown below. Note that CMD15 (GO_INACTIVE_STATE) can be sent at any time after
initialization in order to send any addressed memory controller to the inactive state.
3.4.4 Recommendations for RCA after Reset
Important Note: The RCA specification was not fully defined in SDIO Specification Ver1.0. There are two types
of card (SDIO or Combo) with different responses to CMD0 or SDIO reset. The possible responses are:
12
Page 22
©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
The card clears RCA to 0x0000
The card keeps current RCA value
Command Sequence
Combo Init
(After CMD7 with the correct RCA)
Issue CMD52 (Reset I/O)
Re-initialize I/O (CMD5)
Issue CMD3
Issue CMD7 with the correct RCA
(and Data Transfer)
Figure 3-8 Re-Initialization Flow for I/O Controller
Figure 3-8 shows the re-initialization flow for the I/O controller of a Combo card. The flow of commands on the
left side is matched with the RCA and controller states on the right side. The RCA value of xxxx denotes an RCA
value of either 0x0000 or the prior RCA value. For new controller designs, a reset RCA value of 0x0000 is
recommended. The host shall not issue any commands to the Combo Card except for CMD0, CMD5, CMD3 or
CMD7 until the I/O controller has transitioned to the cmd state.
Command Sequence
Card RCA Select/Deselect Mem State I/O State
Select tran cmd
Sel Desel
Deselect
Deselect
Desel Sel
tran
tran
tran
tran
cmd idle
stby cmd
idle
RCA1
xxxx
RCA1
xxxx
xxxx
RCA2
RCA2
Card RCA Select/Deselect Mem State I/O State
stbyidle
Combo Init
(After CMD7 with the correct RCA)
Issue CMD0 (Reset Memory)
Re-initialize Memory (ACMD41)
Issue CMD2
Issue CMD3)
Issue CMD7 with the correct RCA
(and Data Transfer)
Figure 3-9 Re-Initialization Flow for Memory controller
13
RCA1 Select tran cmd
RCA1
xxxxh
xxxxh
xxxxh
xxxxh
RCA2
RCA2 Desel Sel
Sel Desel
Deselect
Deselect
Deselect
tran
idle
idle ready
ready ident
stbyident
stby tran
cmd
cmd
cmd
cmd
cmd
Page 23

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Figure 3-9 shows the equivalent command flow to re-initialize the memory controller of a Combo card. The RCA
value of xxxxh denotes an RCA value of either 0x0000 or the prior RCA value. For new controller designs, a
reset value of 0x0000 is recommended. The important fact for the host designer to note is that the host shall not
issue any commands except for CMD0, ACMD41 (with RCA=0x0000), CMD2, CMD3 or CMD7 to the Combo
Card until the memory controller has transitioned to the tran state.
3.4.5 Enabling CRC in SPI Combo Card
When receiving CMD59, Combo cards shall synchronize CRC enable in both SDIO and memory portions of the
card. If a host enables CRC using CMD59 and subsequently re-initializes either the I/O or memory controller,
the CRC for that controller will be off by default and the host shall issue a CMD59 to re-enable CRC. When
CMD59 is received, Combo Cards return the R1 response token while SDIO only cards return the modified R1
response token.
14
Page 24

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
4. Differences with SD Memory Specification
4.1 SDIO Command List
Table A-14 shows the list of commands accepted by SD memory and SDIO cards when using the SD bus
interface. Table A-15 shows the list of commands accepted by SD memory and SDIO cards when using the SPI
bus interface.
4.2 Unsupported SD Memory Commands
Several commands required for SD Memory cards are not supported by either SDIO-only cards or the I/O
portion of Combo cards. Some of these commands have no use in SDIO cards such as Erase commands and
thus are not supported in SDIO. In addition, there are several commands for SD memory cards that have
different commands when used with the SDIO section of a card. Table 4-1 lists these SD Memory commands
and the equivalent SDIO commands. For a complete list of supported and unsupported commands, see Table
A-14 and Table A-15.
SD Memory
Command
CMD0 CMD52 (write to
CMD12 CMD52 (write to
CMD16 CMD52 (write to
CMD2 NONE The CID register does not exist in an SDIO only card
CMD4 NONE The DSR register does not exist in an SDIO only card
CMD9 NONE The CSD register does not exist in an SDIO only card
CMD10 NONE The CID register does not exist in an SDIO only card
CMD13 NONE An SDIO only card or the I/O portion of a combo card does not
ACMD6 CMD52 (write to
ACMD13 NONE The SD Status register does not exist in an SDIO only card
ACMD41 CMD5 SDIO cards and hosts use the IO_SEND_OP_COND
ACMD42 CMD52 In the SD mode, the pull-up resistor on DAT[3] is controlled by
ACMD51 NONE The SCR register does not exist in an SDIO only card
CMD17, CMD53 I/O block operations use CMD53, rather than memory block
SDIO
Command
I/O reset in
CCCR)
I/O abort)
I/O Block
Length)
Bus_Width [1:0]
in CCCR)
Comment
The reset command (CMD0) is only used for memory or the
memory portion of Combo cards. In order to reset an I/O only
card or the I/O portion of a combo card, use CMD52 to write a
1 to the RES bit in the CCCR (bit 3 of register 6). Note that in
the SD mode, CMD0 is only used to indicate entry into SPI
mode and shall be supported. An I/O only card or the I/O
portion of a combo card is not reset with CMD0
In order to abort the block transfer of data, SD memory use
CMD12. In order to abort an I/O transaction, use CMD52 to
write to the abort register in the CCCR (bits 2:0 of register 6)
See 4.8 for details.
CMD16 sets the block length for SD memory. In order to set
the block length for each I/O function, use CMD52 to write the
block length in the FBR
support the same SEND_STATUS (CMD13) protocol the SD
memory uses. See 4.10.8.
SET_BUS_WIDTH is handled by a write to the CCCR. See
4.4 for details.
Command (CMD5). See 3.2
writing to the
this resistor is enabled unless both the memory and the I/O
control registers are set to disable the resistor. For details, see
section 4.6
CD Disable bit in the CCCR. For Combo Cards,
15
Page 25

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
SD Memory
Command
CMD18,
SDIO
Command
Comment
read/write commands.
CMD24,
CMD25
Table 4-1 Unsupported SD Memory Commands
4.3 Modified R6 Response
The normal response to CMD3 by a memory card is R6 as shown in Table 4-2. The card status bits (23-8) are
changed when CMD3 is sent to an I/O only card. In this case, the 16 bits of response shall be the SDIO-only
values shown in Table 4-3
Bit position 47 46 [45:40] [39:8] Argument field [7:1] 0
Width (bits) 1 1 6 16 16 7 1
Value ‘0’ ‘0’ X X X X ‘1’
Description Start
Bits Identifier Type Value Description Clear
15 COM_CRC_ERROR E R ’0’= no error
14 ILLEGAL_COMMAND E R ’0’= no error
13 ERROR E R X ’0’= no error
12: 0 Undefined. Should read as 0 for SDIO only cards. Host should ignore these bits.
Note: Please refer to sections 7.3.4 of the SD Physical Specification for explanation of the entries in the Type
and Clear Condition columns.
bit
Direction
bit
Command
index
(‘000011’)
New published RCA
[31:16] of the card
Table 4-2 R6 response to CMD3
The CRC check of the previous
’1’= error
’1’= error
’1’= error
command failed
Command not legal for the card
state
A general or an unknown error
occurred during the operation
[15:0] Card status
(see
Table 4-3)
CRC7 end
bit
Condition
B
B
C
Table 4-3 SDIO R6 Status Bits
4.4 Reset for SDIO
In order to reset all functions within an SDIO card or the SDIO portion of a combo card, a method different than
that used for SD memory is defined. The reset command (CMD0) is only used for memory or the memory
portion of Combo cards. In order to reset an I/O only card or the I/O portion of a combo card, use CMD52 to write
a 1 to the RES bit in the CCCR (bit 3 of register 6). Note that in the SD mode, CMD0 is only used to indicate
entry into SPI mode and shall be supported. An I/O only card or the I/O portion of a combo card is not
reset by
CMD0.
4.5 Bus Width
For a SD memory card, the bus width for SD mode is set using ACMD6. The SDIO card uses a write to the
CCCR using CMD52 to select bus width. In the case of a combo card, both selection methods exist. In this case,
the host shall set the bus width in both locations by issuing both the ACMD6 and the CCCR write using CMD52
with the same width before starting any data transfers. For details on changing the bus for an SDIO card, see
Table 6-2. . For a Combo Card, changing bus width is handled as shown in Table 4-4.
16
Page 26

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
I/O Memory Control Method
Initialized Not
Initialized
Not
Initialized
Initialized Initialized CCCR & ACMD6
Initialized ACMD6
CCCR
Table 4-4 Combo Card 4-bit Control
As shown in Table 4-4, if only the I/O function of a combo card is active, only writing to the CCCR is required
change the bus width mode. If only memory is active then ACMD6 is all that is needed to change bus widths. If
both I/O and Memory are active then both CCCR and ACMD6 are needed to change the bus width. In the
combo card, both the memory and I/O controllers shall be set to the same bus width
Note that Low-Speed SDIO cards support 4-bit transfer as an option. When communicating with a Low-Speed
SDIO card, the host shall first determine if the card supports 4-bit transfer prior to attempting to select that mode.
If a Combo card supports the lock/unlock operation, it cannot change bus width of a locked card and returns an
illegal command error to a bus width switch command. The host needs to unlock the card by CMD42 before
changing bus width. This also implies that the host should not change bus width during initialization before
managing a locked card.
4.6 Card Detect Resistor
SD memory and I/O cards use a pull-up resistor on DAT[3] to detect card insertion. The procedure to
enable/disable this resistor is different between SD memory and SDIO. SD memory uses ACMD42 to control
this resistor while SDIO uses writes to the CCCR using CMD52. In the case of a combo card, both control
locations exist and shall be managed by the host. For a combo card, the resistor is enabled only when both
memory and the I/O control registers have the resistor enabled. That is, after a power on, the host shall disable
the resistor using ACMD42 to the memory controller or a CCCR write to the SDIO controller since the resistor
enable is a logical AND of the two enables. Table 4-5 shows the effect of each resistor enable on the card’s
resistor. After power-up, both locations default to resistor enabled. Note that after an I/O reset, the I/O resistor
enable is not changed. Note that the SDIO Specification Version 1.00 required that both the SDIO and Memory
resistor be disabled in order for the resistor to actually be disabled (logical OR of the 2 enables). Combo cards
built to that specification require the host to disable both enables. It is recommended the host disable both
enables of any combo card to avoid problems with the difference between 1.0 and current specification based
cards.
I/O Resistor Memory Resistor Card Resistor
Enabled Enabled Resistor Connected
Enabled Disabled Resistor Disconnected
Disabled Enabled Resistor Disconnected
Disabled Disabled Resistor Disconnected
the
Table 4-5 Card Detect Resistor States
4.7 Timings
This section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
Table 4-6 is blanked
17
Page 27

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
4.8 Data Transfer Block Sizes
SDIO cards may transfer data in either a multi-byte (1 to 512 bytes) or an optional block format, while the SD
memory cards are fixed in the block transfer mode. The SD Physical Specification limits the block size for data
transfer to powers of 2 (i.e. 512, 1024, 2048) unless using partial read and write. The SDIO Specification allows
any block size from 1 byte to 2048 bytes in order to accommodate the various natural block sizes for I/O
functions. Note that an SDIO card function may define a maximum block size or byte count in the CIS that is
smaller than the maximum values described above.
4.9 Data Transfer Abort
A host communicating with a SD memory card uses CMD12 to abort the transfer of read or write data to/from the
card. For an SDIO card, CMD12 abort is replaced by a write to the ASx bits in the CCCR. Normally, the abort is
used to stop an infinite block transfer (block count=0). If an exact number of blocks are to be transferred, it is
recommended that the host issue a block command with the correct block count, rather than using an infinite
count and aborting the data at the correct time.
4.9.1 Read Abort
The host may issue an I/O abort by writing to the CCCR at any time during I/O extended read operation. The
data transmission stops 2 clocks cycles after the end bit of the I/O abort command, even If the card has already
begun transferring an unwanted data block while the host is issuing the abort.
The rest of this section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
4.9.2 Write Abort
The host may issue an I/O abort by writing to the CCCR at any time between data blocks during I/O extended
write operation. In this case, the final block transfer (including the CRC response from the card) shall have been
completed. This requires that the end bit of the I/O abort command should appear a maximum of two clocks
before the end bit of the CRC response to the last data block. Note that the I/O abort command may be sent any
time after the CRC response to the last data block. The host shall not abort in the middle of a write block. After
the I/O abort is sent to the card, the card signals ‘Busy’ (by pulling DAT[0] line to ‘0’) until it has finished
processing the last transferred data block. During that Busy period, the host may release the bus by writing to
the CCCR BR bit. There exist some special cases when the abort is issued near the end of the CRC response to
a write multiple command.
The rest of this section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
4.10 Changes to SD Memory Fixed Registers
The SD Physical Specification Version 1.01 defines 7 fixed card registers. They are:
OCR Register (32 bits)
1.
2. CID Register (128 bits)
3. CSD Register (128 bits)
4. RCA Register (16 bits)
5. DSR Register (16 bits, optional)
SCR Register (64 bits)
6.
SD_CARD_STATUS (512 bits)
7.
In addition, within an SD memory card there is a status register whose value is returned to the host in the form of
several responses (i.e. the R1b response). An SDIO only card eliminates some registers and changes some of
the bits in the remaining registers. The description of these register changes follows:
18
Page 28

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
4.10.1 OCR Register
All SD cards (memory, I/O and combo) shall have at least one OCR register. If the card is a combo card, it may
have two OCR’s (one for memory and one for I/O). The memory portion of a combo card has an OCR accessed
using ACMD41 and CMD58. The I/O portion of a card has an OCR with the same structure that is accessed via
CMD5. If there are multiple OCR’s the voltage range may not be identical. Some I/O functions may have a wider
VDD range than that reflected in the I/O OCR register. The I/O OCR shall be the logical AND of the voltage
ranges(s) of all I/O functions. Note that the I/O OCR format is different from the memory version in that it is only
24 bits long. For details, see Table 3-1. The per-function voltage for each I/O function can be read in the CIS for
the card.
4.10.2 CID Register
There shall be a maximum of one CID register per SD card. If the card contains both memory and I/O, the CID
register information is unchanged from the SD 1.01 version and reflects the information from the memory
portion of the card. If the card is I/O only, the CID register and the associated access command (CMD10) are
not supported. If the host attempts to access this register in an I/O only card, a card in SPI mode shall respond
with an "Invalid Command" error response and a card in SD mode shall not respond.
4.10.3 CSD Register
There shall be a maximum of one CSD register per SD card. If the card contains both memory and I/O, the CSD
register information is unchanged from the SD 1.01 version and reflects the information from the memory
portion of the card. If the card is I/O only, the CSD register and the associated access command (CMD9) are not
supported. If the host attempts to access this register in an I/O only card, a card in SPI mode shall respond with
an "Invalid Command" error response and a card in SD mode shall not respond.
4.10.4 RCA Register
There shall only be one RCA register per SD card. The RCA value shall apply to the card as a whole. All
functions and any memory share the same card address.
4.10.5 DSR Register
SDIO only cards do not support the DSR register. In the case of combo cards, support is optional as defined in
the SD Physical Specification.
4.10.6 SCR Register
There shall be a maximum of one SCR register per SD card. If the card contains both memory and I/O, the SCR
register information is unchanged from the SD 1.01 version and reflects the information from the memory
portion of the card. If the card is I/O only, the SCR register and the associated access command (ACMD51) are
not supported. If the host attempts to access this register in an I/O only card, a card in SPI mode shall respond
with an "Invalid Command" error response and a card in SD mode shall not respond.
4.10.7 SD Status
There shall be a maximum of one SD Status register per SD card. If the card contains both memory and I/O, the
SD Status register information is unchanged from the SD 1.01 version and reflects the information from the
memory portion of the card. If the card is I/O only, the SD Status register and the associated access command
(ACMD13) are not supported. If the host attempts to access this register in an I/O only card, a card in SPI mode
shall respond with an "Invalid Command" error response and a card in SD mode shall not respond.
4.10.8 Card Status Register
The structure of the SDIO status register is shown in Table 4-7. For SDIO specific operations in the SD mode
that return the card status register contents (i.e. the response to CMD7), some bits are not applicable to I/O
operations and shall be returned as 0. These unused bits are identified as type N/A. For combo cards, the
values returned shall reflect the memory status. The CURRENT_STATE bits (12:9) shall reflect the memory
Controller State. For an I/O only card, the unused bits are 0 and the Current_State bits (12:9) shall be 0xF (15) to
19
Page 29

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
identify it as an I/O only response.
I/O specific status is reported by I/O response and Memory specific status is reported by Memory response
except for the following case: In the SD bus mode, the card shall not respond to an Illegal Command or a
command with a CRC error. The indication of those two error cases shall be given by the card in the following
command’s response. This is true for an I/O only card as well as for combo cards, even in cases where the
erroneous command and the command that follows are not targeting the same card module (Memory or I/O).
Bit
31 OUT_OF_RANGE E R ’0’= no error
Identifier
Type
Value
’1’= error
The command’s argument was out
of the allowed range for this card.
Description
Clear
Condition
C
30 ADDRESS_ERROR N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
29 BLOCK_LEN_ERROR N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
28 ERASE_SEQ_ERROR N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
27 ERASE_PARAM N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
26 WP_VIOLATION N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
25 CARD_IS_LOCKED N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
24 LOCK_UNLOCK_FAILED N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
23 COM_CRC_ERROR E R ’0’= no error
’1’= error
22 ILLEGAL_COMMAND E R ’0’= no error
’1’= error
The CRC check of the previous
command failed. (Note 1)
Previous command not legal for the
card state. (Note 2)
B
B
21 CARD_ECC_FAILED N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
20 CC_ERROR N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
19 ERROR E R ’0’= no error
’1’= error
A general or an unknown error
occurred during the operation.
C
18 UNDERRUN N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
17 OVERRUN N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
16 CID/ CSD_OVERWRITE N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
15 WP_ERASE_SKIP N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
14 CARD_ECC_DISABLED N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
13 ERASE_RESET N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
12:9 CURRENT_STATE S X 15=I/O only
For an I/O only card, the current
state shall be fixed at a value of
0x0F. This indicates that it is an I/O
only card and the normal memory
states do not apply
B
8 READY_FOR_DATA N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
7:6 Reserved
5 APP_CMD N/A 0 CMD55 not used in SDIO operation C
4 Reserved
3 AKE_SEQ_ERROR (SD
Memory Card app. spec.)
N/A 0 Not used with SDIO operation C
2 Reserved for application specific commands
1, 0 Reserved for manufacturer test mode
Table 4-7 SDIO Status Register Structure
Note 1: In the SPI mode, if the card detects a CRC error, it returns a com CRC error in the R1 response
immediately following the command (see Figure 3-7). In this situation, the note that the CRC error is for the
previous command does not apply.
Note 2: In the SPI mode, if the card detects an Illegal Command, it returns an Illegal Command error in the R1
response immediately following the command (see Figure 3-7). In this situation, the note that the Illegal
Command error is for the previous command does not apply.
20
Page 30

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
5. New I/O Read/Write Commands
Two additional data transfer instructions have been added to support I/O. IO_RW_DIRECT, a direct I/O
command similar to the MMC 'Fast I/O' command, and IO_RW_EXTENDED, which allows fast access with byte
or block addresses. Both commands are in class 9 (I/O Commands).
5.1 IO_RW_DIRECT Command (CMD52)
The IO_RW_DIRECT is the simplest means to access a single register within the total 128K of register space in
any I/O function, including the common I/O area (CIA). This command reads or writes 1 byte using only 1
command/response pair. A common use is to initialize registers or monitor status values for I/O functions. This
command is the fastest means to read or write single I/O registers, as it requires only a single
command/response pair.
S D Command
Index
110100b
1 1 6 1 3 1 1 17 1 8 7 1
R/W
flag
Function
Number
RAW
flag
Figure 5-1 IO_RW_DIRECT Command
Stuff Register Address Stuff Write Data
or Stuff Bits
CRC7 E
The IO_RW_DIRECT Command contains the following fields:
S(tart bit): Start bit. Always 0
D(irection): Direction. Always1 indicates transfer host to card.
Command Index: Identifies the “IO_RW_DIRECT” command with a value of 110100b
R/W Flag: This bit determines the direction of the I/O operation. If this bit is 0, this command
shall read data from the SDIO card at the address specified by the Function Number
and the Register Address to the host. The data byte is returned in the response, R5.
If this bit is set to 1, the command shall write the bytes in the Write Data field to the
I/O location addressed by the Function Number and the Register Address. If the
RAW flag is 0, then the data in the register that was written shall be read and that
value returned in the response.
RAW Flag: The Read after Write flag. If this bit is set to 1 and the R/W flag is set to 1, then the
command shall read the value of the register after the write. This is useful to allow
writing to a control register and reading the status at the same address. If this bit is
cleared, the value returned in the R5 response shall be the same as the write data in
the command. If this bit is set, the data field of the R5 response shall contain the
value read from the addressed register after the write operation.
Function Number: The number of the function within the I/O card you wish to read or write. Note that
function 0 selects the common I/O area (CIA).
Register Address: This is the address of the byte of data inside of the selected function to read or write.
There are 17 bits of address available so the register is located within the first 128K
(131,072) addresses of that function.
Write Data/Stuff Bits: For a direct write command (R/W=1), this is the byte that is written to the selected
address. For a direct read (R/W=0), this field is not used and shall be set to 0.
CRC7: 7 bits of CRC data
E(nd bit): End bit, always 1
21
Page 31

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
5.2 IO_RW_DIRECT Response (R5)
The SDIO card’s response to CMD52 shall be in one of two formats. If the communication between the card and
host is in the 1-bit or 4-bit SD mode, the response shall be in a 48-bit response (R5) as described in 5.2.1. If the
communication is using the SPI mode, the response shall be a 16-bit R5 response as described in 5.2.2.
5.2.1 CMD52 Response (SD modes)
The SDIO card’s response to CMD52 in the SD mode is shown in Figure 5-2. If the operation was a read
command, the data being read is returned as an 8-bit value. In addition, 15 bits of status information is returned.
The format of the SD response is as follows:
S D
1 1 6 16 8 8 7 1
Command
Index
110100b
Figure 5-2 R5 IO_RW_DIRECT Response (SD modes)
The IO_RW_DIRECT response (R5) contains the following fields:
S(tart bit): Start bit. Always 0
D(irection): Direction. 0 indicates transfer card to host (Response)
Command Index: Identifies the “IO_RW_DIRECT” command with a value of 110100b
Stuff Bits Not used, shall be set to 0
Response Flags 8 Bits of flag data indicating the status of the SDIO card. Table 5-1 shows the format
of these flag bits.
Read or Write Data: For an I/O write (R/W=1) with the RAW Flag set (RAW=1) this field shall contain the
value read from the addressed register after
command. Note that in this case, the read-back data may not be the same as the
data written to the register, depending on the design of the hardware. For an I/O
write with the RAW bit=0, the SDIO function shall not
and the data in this field shall be identical to the data byte in the write command. For
an I/O read (R/W=0), the actual value read from that I/O location is returned in this
field.
CRC7: 7 bits of CRC data
E(nd bit): End bit, always 1
Bits Identifier Type Value Description Clear
7 COM_CRC_ERROR E R ’0’= no error
6 ILLEGAL_COMMAND E R ’0’= no error
Stuff Response Flags
Bit
7--------------------------0
The CRC check of the previous
’1’= error
’1’= error
command failed.
Command not legal for the card
State.
Read or Write
Data
the write of the data contained in the
do a read after write operation,
CRC7 E
Condition
B
B
22
Page 32

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Bits Identifier Type Value Description Clear
Condition
5-4 IO_CURRENT_STATE S 00=DIS
01=CMD
02=TRN
03=RFU
3 ERROR E R
E R X
’0’= no error
’1’= error
DIS=Disabled:
Initialize, Standby and Inactive
States (card not selected)
CMD=DAT lines free:
1. Command waiting (No
transaction suspended)
2. Command waiting (All
CMD53 transactions
suspended)
3. Executing CMD52 in CMD
State
TRN=Transfer:
Command executing with data
transfer using DAT[0] or DAT[3:0]
lines
A general or an unknown error
occurred during the operation.
Type “E R” shall be used for
CMD52
Type “E R X” shall be used for
CMD53
B
C
2 RFU -- Fixed at 0 Reserved for Future Use C
1 FUNCTION_NUMBER E R ’0’= no error
’1’= error
0 OUT_OF_RANGE E R ’0’= no error
’1’= error
An invalid function number was
requested
The command’s argument was out
of the allowed range for this card.
C
C
Table 5-1 Flag data for IO_RW_DIRECT SD Response
5.2.2 R5, IO_RW_DIRECT Response (SPI mode)
The SDIO card’s response to CMD52 in the SPI mode is shown in Figure 5-3. If the operation was a read
command, the data being read is returned as an 8-bit value. In addition, 8 bits of status information is returned in
a SPI R1 response byte as described in Fig 47 of the SD Physical Specification modified for I/O as shown in
Figure 5-3.
R/W Data (8 Bits)00 0
1 = in idle state
RFU (always 0)
1 = illegal command
1 = COM CRC error
1 = Function number error
RFU (always 0)
1 = parameter error
Start Bit (always 0)
Figure 5-3 IO_RW_DIRECT Response in SPI Mode
Note the read/write (R/W) data is identical to the read/write data described for the SD R5 response (see 5.2.1).
Parameter error status in SPI mode corresponds to OUT_OF_RANGE and ERROR in the SD mode response.
In the case of CMD53, Data Error Token should also be used to indicate OUT_OF_RANGE and ERROR.
23
Page 33

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
5.3 IO_RW_EXTENDED Command (CMD53)
In order to read and write multiple I/O registers with a single command, a new command, IO_RW_EXTENDED
is defined. This command is included in command class 9 (I/O Commands). This command allows the reading
or writing of a large number of I/O registers with a single command. Since this is a data transfer command, it
provides the highest possible transfer rate.
S D Command
Index
110101b
1 1 6 1 3 1 1 17 9 7 1
The IO_RW_EXTENDED Command contains the following fields:
S(tart bit): Start bit. Always 0
D(irection): Direction. Always1 indicates transfer host to card.
Command Index: Identifies the “IO_RW_EXTENDED” command with a value of 110101b
R/W Flag: This bit determines the direction of the I/O operation. If this bit is 0, this command
Function Number: The number of the function within the I/O card you wish to read or write. Note that
Block Mode (Optional) this bit, if set to 1, indicates that the read or write operation shall be
OP code Defines the read/write operation as described in Table 5-2
R/W
flag
Function
Number
Block
Mode
OP
Code
Register Address Byte/Block
Count
CRC7 E
Figure 5-4 IO_RW_EXTENDED Command
reads data from the SDIO card at the address specified by the Function Number and
the Register Address to the host. The read data shall be returned on the DAT[x]
lines. If this bit is set to 1, the command shall write the bytes from the DAT[x] lines to
the I/O location addressed by the Function Number and the Register Address.
function 0x00 selects the common I/O area (CIA).
performed on a block basis, rather than the normal byte basis. If this bit is set, the
Byte/Block count value shall contain the number of blocks to be read/written. The
block size for functions 1-7 is set by writing the block size to the I/O block size
register in the FBR (See Table 6-3 and Table 6-4). The block size for function 0 is set
by writing to the FN0 Block Size register in the CCCR. Card and host support of the
block I/O mode is optional. The host can determine if a card supports block I/O by
reading the Card supports MBIO bit (SMB) in the CCCR (see Table 6-2). The block
size used when Block Mode = 1 and the maximum byte count per command used
when Block Mode = 0 can be read from the CIS in the tuple
TPLFE_MAX_BLK_SIZE (see 16.7.4) on a per-function basis.
OP code Command operation
0 Multi byte R/W to fixed address
1 Multi byte R/W to incrementing address
Table 5-2 IO_RW_ EXTENDED command Op Code Definition
• OP Code 0 is used to read or write multiple bytes of data to/from a single I/O register
address. This command is useful when I/O data is transferred using a FIFO inside of
the I/O card. In this case, multiple bytes of data are transferred to/from a single
register address. For this operation, the address of the register is set into the
Register Address field. Data is transferred on the DAT[0] or DAT[3:0] lines as defined
for SD memory cards.
• OP Code 1 is used to read or write multiple bytes of data to/from an I/O register
24
Page 34

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
address that increment by 1 after each operation. This command is used when large
amounts of I/O data exist within the I/O card in a RAM like data buffer. In this
operation, the start address is loaded into the Register Address field. The first
operation occurs at that address within the I/O card. The next operation shall occur
at address+1 with the address incrementing by 1 until the operation has completed.
As with OP Code 0, the number of bytes is set in the Byte Count field of the
command.
Register Address: Start Address of I/O register to read or write. Range is [0x1FFFF:0]
Byte/Block Count If the command is operating on bytes (Block Mode = 0), this field contains the
number of bytes to read or write. A value of 0x000 shall cause 512 bytes to be read
or written.
Count Value 0x000 0x001 0x002 ---- 0x1FF
Bytes Transferred 512 1 2 511
Block Transferred ∞ 1 2 511
Table 5-3 Byte Count Values
If the command is in block mode (Block Mode=1), the Block Count field specifies the
number of Data Blocks to be transferred following this command. A value of 0x000
indicates that the count set to infinite. In this case, the I/O blocks shall be transferred
until the operation is aborted by writing to the I/O abort function select bits (ASx) in
the CCCR (see Table 6-1 and Table 6-2). Table 5-3 shows the relationship between
the value in the command and the actual number of bytes transferred.
CRC7: 7 bits of CRC data
E(nd bit): End bit, always 1
The response from the SDIO card to CMD53 shall be R5 (the same as CMD52) as defined in 5.2. For CMD53,
the 8-bit data field shall be stuff bits and shall be read as 0x00.
X” (see
Table 5-1).
Also, the ERROR response bit shall be type “E R
5.3.1 CMD53 Data Transfer Format
When executing the IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53), the multi-byte or multi-block data transfer is similar to the
data transfer for memory. For the multi-byte transfer modes (block mode=0) the following applies:
IO_RW_EXTENDED byte read is similar to CMD17 (READ_SINGLE_BLOCK)
IO_RW_EXTENDED byte write is similar to CMD24 (WRITE_BLOCK)
Note that the byte count for this transfer is set in the command, rather than the fixed block size. Thus, the size of
the data payload is in the range of 1-512 bytes. The block mode is similar to the following memory commands:
IO_RW_EXTENDED block read is similar to CMD18 (READ_MULTIPLE_BLOCK)
IO_RW_EXTENDED block write is similar to CMD25 (WRITE_MULTIPLE_BLOCK)
For the block mode the only difference is that for a fixed block count, the host does not need to stop the transfer,
as it continues until the block count is satisfied. If the block count is set to zero, the operation is identical to the
memory mode in that the host must stop the transfer.
5.3.2 Special Timing for CMD53 Multi-Block Read
This section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
25
Page 35

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
6. SDIO Card Internal Operation
I/O access differs from memory in that the registers can be written and read individually and directly without a
FAT file structure or the concept of blocks (although block access is supported). These registers allow access to
the I/O data, control of the I/O function and report on status or transfer I/O data to/from the host. The SD memory
relies on the concept of a fixed block length with commands reading/writing multiples of these fixed size blocks.
I/O may or may not have fixed block lengths and the read size may be different from the write size. Because of
this, I/O operations may be based on either a length (byte count) or a block size.
6.1 Overview
Each SDIO card may have from 1 to 7 functions plus one memory function built into it. A function is a self
contained I/O device. I/O functions may be identical or completely different from each other. All I/O functions are
organized as a collection of registers. There is a maximum of 131,072 (2
function. These registers and their individual bits may be read Only (RO), Write Only (WO) or Read/Write (R/W).
These registers can be 8, 16 or 32 bits wide within the card. All addressing is based on byte access. These
registers can be written and/or read one at a time, multiply to the same address or multiply to an incrementing
address. The single R/W access is often used to initialize the I/O function or to read a single status or data value.
The multiple reads to a fixed address are used to read or write data from a data FIFO register in the card. The
read to incrementing addresses is used to read or write a collection of data to/from a RAM area inside of the
card. Figure 6-1 shows the mapping of the CIA and optional CSA space for an SDIO card.
6.2 Register Access Time
All registers in SDIO only cards and the SDIO portion of Combo cards shall complete read and write data
transfer in less than 1 second. This timeout value relates to the time for the requested data to be transferred
to/from the host on the DAT[x] lines and not the timing between the command and the response. This wait time
is signaled to the host by the card using busy for a write or delaying the start bit for a read operation. The host
can use 1 second as the timeout value for a non-responding location. If a functions needs to support an access
time greater than 1 second, the card maker may use some function specific method that is not defined in this
specification.
6.3 Interrupts
All SDIO hosts should support hardware interrupts. If a host does not support interrupts, it may have difficulties
working with SDIO cards that expect fast response to interrupt conditions. Each function within an SDIO or
Combo card may implement interrupts as needed. The interrupt used on SDIO functions is a type commonly
called “level sensitive”. Level sensitive means that any function may signal for an interrupt at any time, but once
the function has signaled an interrupt, it shall not release (stop signaling) the interrupt until the cause of the
interrupt is removed or commanded to do so by the host. Since there is only 1 interrupt line, it may be shared by
multiple interrupt sources. The function shall continue to signal the interrupt until the host responds and clears
the interrupt. Since multiple interrupts may be active at once, it is the responsibility of the host to determine the
interrupt source(s) and deal with it as needed. This is done on the SDIO function by the use of two bits, the
interrupt enable and interrupt pending. Each function that may generate an interrupt has an interrupt enable bit.
In addition, the SDIO card has a master interrupt enable that controls all functions. An interrupt shall only be
signaled to the SD bus if both the function’s enable and the card’s master enable are set. The second interrupt
bit is called interrupt pending. This read-only bit tells the host which function(s) may be signaling for an interrupt.
There is an interrupt pending bit for each function that can generate interrupts. These bits are located in the
CCCR area. For more details, see Table 6-1 and Table 6-2. Interrupt operation is described more fully in section
8.
17
) registers possible for each I/O
26
Page 36

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
6.4 Suspend/Resume
Within a multi-function SDIO or a Combo card, there are multiple devices (I/O and memory) that share access to
the SD bus. In order to allow the sharing of access to the host among multiple devices, SDIO and combo cards
can implement the optional concept of suspend/resume. If a card supports suspend/resume, the host may
temporarily halt a data transfer operation to one function or memory (suspend) in order to free the bus for a
higher priority transfer to a different function or memory. Once this higher-priority transfer is complete, the
original transfer is re-started where it left off (resume). Support of suspend/resume is optional on a per-card
basis. If suspend/resume is implemented, it shall be supported by the memory (if any) of a Combo card and all
I/O functions except 0 (the CIA). Note that the host can suspend multiple transactions and resume them in any
order desired. I/O function 0 does not support suspend/resume. Suspend/Resume is described in more detail in
section 9. Any card that supports Suspend/Resume shall also support Read Wait and Direct Commands (
SDC = 1) Note that Suspend/Resume is defined only for the SD 1 and 4-bit modes. It does not apply to SPI
and
transfers.
SRW
6.5 Read Wait
Host devices built to the SD Physical Specification shall control the SDCLK to stop the read data block output
from a card executing a multiple read command whenever the host cannot accept more data. During the time
that the host has stopped the SDCLK, a CMD52 cannot be issued. This limitation causes a problem in that a
host device built to the SD Physical Specification cannot perform the I/O command during a multiple read cycle.
In order to eliminate this limitation, the SDIO Specification adds the Read Wait control to enable the host to issue
CMD52 during a multiple read cycle. Read Wait uses the DAT[2] line to allow the host to signal the card to
temporarily halt the sending of read data by a card. This feature is optional for an SDIO or combo card. However,
if an SDIO or combo supports Read Wait, all functions and any memory shall support Read Wait. Read Wait is
described in more detail in section 10. Any card that supports Suspend/Resume shall also support Read Wait.
Note that Read Wait is defined only for the SD 1 and 4-bit modes. It does not apply to SPI transfers.
6.6 CMD52 During Data Transfer
A card may accept CMD52 during data transfer
and SPI modes
reset regardless of this bit value
, if an error occurs during data transfer the SDIO card shall accept CMD52 to allow I/O abort and
of the value of SDC.
if it supports Direct Commands (see SDC, Table 6-3). For both SD
6.7 SDIO Fixed Internal Map
The SDIO card has a fixed internal register space and a function unique area. The fixed area contains
information about the card and certain mandatory and optional registers in fixed locations. The fixed locations
allow any host to obtain information about the card and perform simple operations such as enable in a common
manner. The function unique area is a per-function area, which is defined either by the Application
Specifications for Standard SDIO functions or by the vendor for non-standard functions. Figure 6-1 shows the
internal map of an SDIO card with multiple functions.
27
Page 37

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
CIA (Function 0)
0x000000-0x0000FF
0x000200-0x0002FF
0x000300-0x0003FF
0x000700-0x0007FF
0x000800-0x000FFF
0x001000-0x017FFF
0x018000-0x01FFFF
0x000000-0x01FFFF
CCCR
FBR (Function 1)0x000100-0x0001FF
FBR (Function 2)
FBR (Function 3)
FBR (Function 7)
RFU
CIS Area
(common and per-function)
RFU
Window
Window
Window
Window
128K Register Space
(function 1-7)
Function Unique
X
X
CIS Pointers
16 MB optional
Code Storage
Area
(CSA)
Figure 6-1 SDIO Internal Map
6.8 Common I/O Area (CIA)
The Common I/O Area (CIA) shall be implemented on all SDIO cards. The CIA is accessed by the host via I/O
reads and writes to function 0. The registers within the CIA are provided to enable/disable the operation of the
I/O function(s), control the generation of interrupts and optionally load software to support the I/O functions. The
registers in the CIA also provide information about the function(s) abilities and requirements. There are three
distinct register structures supported within the CIA. They are:
1. Card Common Control Registers (CCCR)
2. Function Basic Registers (FBR)
3. Card Information Structure (CIS)
6.9 Card Common Control Registers (CCCR)
The Card Common Control Registers allow for quick host checking and control of an I/O card’s enable and
interrupts on a per card (master) and per function basis. The bits in the CCCR are mixed Read/Write and read
only. If any of the possible 7 functions are not provided on an SDIO card, the bits corresponding to unused
functions shall all be read-only and read as 0. All reserved for future use bits (RFU) shall be read-only and return
a value of 0. All writeable bits are set to 0 after power-up or reset. Access to the CCCR is possible even after
initialization when the I/O functions are disabled. Access is performed using the I/O read and write commands
defined in section 5. This allows the host to enable functions after initialization. The CCCR is organized as
follows:
28
Page 38

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Address Register Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0x00 CCCR/SDIO
Revision
0x01 SD Specification
Revision
0x02 I/O Enable
0x03 I/O Ready
0x04 Int Enable
0x05
Int Pending
0x06 I/O Abort
0x07 Bus Interface
Control
0x08 Card Capability
0x09-
0x0B
Common CIS
Pointer
0x0C Bus Suspend
0x 0D Function Select
0x 0E Exec Flags
0x 0F Ready Flags
0x10-
FN0 Block Size
SDIO
bit 3
RFU RFU RFU RFU SD
IOE7 IOE6 IOE5 IOE4 IOE3 IOE2 IOE1 RFU
IOR7 IOR6 IOR5 IOR4 IOR3 IOR2 IOR1 RFU
IEN7 IEN6 IEN5 IEN4 IEN3 IEN2 IEN1
INT7 INT6 INT5 INT4 INT3 INT2 INT1 RFU
RFU RFU RFU RFU RES AS2 AS1 AS0
CD
Disable
4BLS LSC E4MI S4MI SBS SRW SMB SDC
RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU BR BS
DF RFU RFU RFU FS3 FS2 FS1 FS0
EX7 EX6 EX5 EX4 EX3 EX2 EX1 EXM
RF7 RF6 RF5 RF4 RF3 RF2 RF1 RFM
SDIO
bit 2
SCSI ECSI RFU RFU RFU
Pointer to card’s common Card Information Structure (CIS)
SDIO
bit 1
SDIO
bit 0
I/O block size for Function 0
CCCR
bit 3
bit 3
CCCR
bit 2
SD
bit 2
CCCR
bit 1
SD
bit 1
Bus
Width 1
CCCR
bit 0
SD
bit 0
IENM
Bus
Width 0
0x11
0x 12 Power Control
0x 13 High-Speed
0x14-
RFU
RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU EHS SHS
Reserved for Future Use (RFU) EMPC SMPC
Reserved for Future Use (RFU)
0xEF
0xF0-
0xFF
Reserved for
Vendors
Area Reserved for Vendor Unique Registers
Table 6-1 Card Common Control Registers (CCCR)
Field Type Description
CCCRx R/O CCCR Format Version number. These 4 bits contain the version of the CCCR and
FBR format that this card supports. Any change to the CCCR and/or the FBR
structure shall cause a new version code to be assigned. The codes for the
CCCR/FBR formats are as follows:
Value CCCR/FBR Format Version
0x00 CCCR/FBR Version 1.00
0x01 CCCR/FBR Version 1.10
0x02 CCCR/FBR Version 1.20
0x03-0x0F Reserved for Future Use
SDIOx R/O SDIO Specification Revision number. These 4 bits contain the version of the SDIO
Specification that this card supports. The codes for the SDIO Specifications are as
follows:
Value SDIO Specification
0x00 SDIO Specification Version 1.00
0x01 SDIO Specification Version 1.10
0x02 SDIO Specification Version 1.20 (unreleased)
0x03 SDIO Specification Version 2.00
0x04-0x0F Reserved for Future Use
29
Page 39

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Field Type Description
SDx R/O SD Format Version number. These 4 bits contain the version of the SD Physical
Specification that this card supports. The codes for the SD Physical Specification are
as follows:
Value SD Physical Specification
0x00 SD Physical Specification Version 1.01 (March 2000)
0x01 SD Physical Specification Version 1.10 (October 2004)
0x02 SD Physical Specification Version 2.00 (May 2006)
0x03-0x0F Reserved for Future Use
IOEx R/W Enable Function - If this bit is reset to 0, the function is disabled. If this bit is set to 1,
the function is enabled to start its initialization. The completion of initialization is
indicated in IORx. On power up or after a reset, the card shall reset this bit to 0. The
host can also use IOEx as a per function reset for error recovery. The host sequence
for a per function reset is to reset IOEx to 0, wait until IORx becomes 0 and then set
IOEx to 1 again. If the error is not recovered by this sequence, SDIO reset should be
used noting that the operation of all functions will be aborted. See section 11 for
relation to Master Power Control and Power Select.
IORx R/O I/O Function Ready- If this bit is reset to 0, the function is not ready to operate. This
may be caused by the function being disabled or not ready due to internal causes
such as a built-in self-test in progress. If this bit is set to 1, the function is ready to
operate. The functions shall set this bit to 1 within the timeout value defined in the
TPLFE_ENABLE_TIMEOUT_VAL tuple. On power up or after a reset, this bit shall
be set to 0. For any function that is not implemented on an SDIO card, this bit shall
always be 0.
IENx R/W Interrupt Enable for function x. If this bit is cleared to 0, any interrupt from this function
shall not be sent to the host. If this bit is set to 1, then this function’s interrupt shall be
sent to the host if the master Interrupt Enable (bit 0) is also set to 1.
IENM R/W Interrupt Enable Master. If this bit is cleared to 0, no interrupts from this card shall be
sent to the host. If this bit is set to 1, then any function’s interrupt shall be sent to the
host.
INTx R/O Interrupt Pending for function x. If this bit is cleared to 0, this indicates that no
interrupts are pending from this function. If this bit is set to 1, then this function has
interrupt pending. Note that if the IENx or IENM bits are not set, the host cannot
receive this pending interrupt.
ASx W/O Abort Select In order to abort an I/O read or write and free the SD bus, the function
that is currently transferring data must be addressed. These 3 bits define which
function’s transfer to stop. For example, the abort the transfer to function number 3,
the value of 0x03 would be written to these bits using CMD52 only. If the abort is
addressed to a suspended function, it does not affect current data transaction. Note
that this is an abort, not a reset. The addressed function shall return to the CMD state
and data transfer pending to that function shall be halted. This abort procedure does
not work for SPI write operations. To abort an SPI write data transfer use the
STOP_TRAN token as defined in section 7.3.3 of the SD Physical Specification. This
form of abort applies only to the functions of an SDIO card. For the memory of a
combo card, the abort methods defined in the SD Physical Specification shall be used
to abort transfers to/from memory
RES
W/O I/O CARD RESET: Setting the RES to 1 shall cause all I/O functions in an SDIO or
Combo card to perform a soft reset. Setting the RES to 1 does not affect the current
card protocol selection(SD vs. SPI mode) and CD Disable. Setting of the RES bit
shall only be performed using CMD52. When RES=1, the values of AS2-0 are
don’t-cares. The RES bit is auto cleared, so there is no need to rewrite a value of 0.
This bit is write-only, any read returns an undetermined value. Memory in a combo
card is not affected.
30
Page 40

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Field Type Description
Bus Width
1:0
CD Disable R/W Connect[0]/Disconnect[1] the 10K-90K ohm pull-up resistor on CD/DAT[3] (pin 1) of
SCSI R/O Support Continuous SPI interrupt. This read-only bit is set to indicate that this SDIO
ECSI R/W Enable Continuous SPI Interrupt. If the SCSI bit is set, then this R/W bit is used to
SDC R/O Card Supports Direct Commands during data transfer. This bit applies only to the SD
SMB R/O Card Supports Multi-Block. This flag bit reports the SDIO card’s ability to execute the
SRW R/O Card Supports Read Wait. This bit applies only to the SD modes, it does not apply to
SBS R/O Card supports Suspend/Resume. This bit applies only to the SD modes, it does not
S4MI R/O Supports interrupt between blocks of data in 4-bit SD mode. This flag bit reports the
R/W Defines the data bus width (’00’=1-bit or’10’=4-bit bus) to be used for data transfer. All
Full-Speed SDIO cards support both 1 and 4-bit bus. A Low-Speed SDIO card’s
support of 4-bit bus is optional. On reset or power-on these bits are cleared to 00.
the card. The pull-up may be used for card detection. This bit is cleared to 0 on
power-on (connected). Its state is not affected by a reset command.
card supports the assertion of interrupts in the SPI mode at any time, irrespective of
the status of the card select (CS) line. If this bit is zero, then this SDIO card can only
assert the interrupt line in the SPI mode when the CS line is asserted. This bit signals
the capability of all functions in the SDIO card.
allow the SDIO card to assert the interrupt line in the SPI mode at any time,
irrespective of the state of the CS line. This bit is cleared to zero on reset or power-up.
If the SCSI bit is clear, this bit shall be read only and set to zero. This bit controls the
assertion of interrupts in the SPI mode for all functions in the SDIO card.
modes, it does not apply to SPI mode. This flag bit reports the SDIO card’s ability to
execute CMD52 while data transfer is in progress. If this bit is set, all I/O functions
shall accept and execute the CMD52 while data transfer is underway on the DAT[x]
lines. Also, any memory in a combo card shall allow the CMD52 to execute while it is
transferring data. Since the CMD52 does not use the DAT[x] lines, it is possible to
execute while data transfer to a different address on the card is underway. CMD52 is
described in 5.1. In any case, SD or SPI mode, if an error occurs during data transfer
the SDIO card shall accept CMD52 to allow I/O abort and reset regardless of this bit
value. If the card supports suspend/resume then it shall also support this bit.
IO_RW_EXTENDED command (CMD53) in the block mode. If this bit is set, all I/O
functions (0-7) shall accept and execute CMD53 with the optional block mode bit set.
The IO_RW_EXTENDED command is described in 5.3
SPI mode. This flag bit reports the SDIO card’s ability to support the Read Wait
Control (RWC) operation. If set, all functions on the card are able to accept the wait
signal on DAT[2]. RWC operation is described in section 6.5.
Suspend/Resume shall also support Read Wait
apply to SPI mode. This flag bit reports the SDIO card’s ability to Suspend and
Resume operations at the request of the host. If this bit is set, all functions except 0
shall accept a request to suspend operations and resume under host control.
Suspend/Resume operation is described in 6.4. If this bit is 0, registers (0x0C-0x0F)
shall not be supported.
SDIO card’s ability to generate interrupts during a 4-bit multi-block data transfer. If
this bit is 0, then the SDIO card is not able to signal an interrupt during a multi-block
data transfer in 4-bit mode. In this case, the interrupt is not signaled until after the
data transfer is complete. If this bit is 1, then the SDIO card is able to signal an
interrupt between blocks while data transfer is in progress. This operation is
described in 8.1.4 Note, even if a card does not support the interrupt during 4-bit
block transfer (S4MI=0), the card may signal interrupts during all other Interrupt
Periods while the interrupt is enabled (IENx=1).
Any card that supports
31
Page 41

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Field Type Description
E4MI R/W Enable interrupt between blocks of data in 4-bit SD mode. Enable the multi-block IRQ
during 4-bit transfer for the SDIO card. When this bit is 0, the card shall not signal
interrupts during a 4-bit multi-block data transfer. If this bit is 1, the card shall generate
interrupts during 4 bit multi-block data transfers as described in 8.1.4 If this SDIO card
does not support 4 bit multi-block IRQs (S4MI=0), then this bit shall be R/O and
always read as 0. This bit shall be cleared to 0 by any reset
LSC R/O Card is a Low-Speed card. If this bit is set, it indicates that the SDIO card is a
Low-Speed card (see 2.1). If this bit is clear, the SDIO card is a Full-Speed card.
4BLS R/O 4-bit support for Low-Speed cards. If the SDIO card is a Low-Speed card (LSC=1)
and it supports 4-bit data transfer, then this bit shall be set. If the card is not
Low-Speed or if the card does not support 4-bit transfer, then this bit shall be zero.
Pointer to
card’s
common CIS
BS
BR
R/O This 3-byte pointer points to the start of the card’s common CIS. The common CIS
contains information relation to the entire card. The card common CIS shall be
located within the CIS space of function 0 (0x001000- 0x017FFF) as described in
section 6.11. A card common CIS is mandatory for all SDIO cards. This pointer is
stored in little-endian format (LSB first).
R/O Bus status: If this bit is set to 1, then the currently addressed function (selected by
FSx or by the function number in an I/O command) is currently executing a command
which transfers data on the DAT[x] line(s). If this bit is 0, then the addressed function
is not using the data bus. This bit is used by the host to determine which function of a
multi-function or combo card is currently performing data transfer. Note that this bit is
a part of the optional Suspend/Resume protocol. If the card does not support
Suspend/Resume, this bit shall be read as 0. Any access to the CIA may not be
suspended, so in this case, BS shall always be set to 1, irrespective of the host
setting BR to 1.
R/W Bus Release Request/Status: This bit is used to request that the addressed function
(selected by FSx or by the function number in CMD53 or Memory commands using
DAT line) release the Data lines and suspend operation. If the host sets this bit to 1,
the addressed function shall temporarily halt data transfer on the DAT[x] lines and
suspend the command that is in process. The BR bit shall remain set to 1 until the
release is complete. If the card can never accept the suspend request while
executing transactions, the card shall return response with BR cleared to 0 and BS
set to 1. This indicates that the suspend request is cancelled by the card and thus the
host should not issue a cancel suspend command.
The followings are the cases where the card can cancel a suspend request:
Transaction addressed to function 0.
The card knows the transfer will terminate soon.
The card knows the transfer is timing critical (i.e. If suspended, the transfer cannot
proceed).
A Multi function card that indicates SBS=1, but contains a function that does not
support suspend/resume.
Once the function is in suspend, it shall signal the host by clearing the BS and BR
bits. The host can monitor the status of the suspend request by reading the BR bit. If
it is set, the suspend request is still in progress. A pending suspend request can be
cancelled by the host by writing 0 to the BR bit.
The Standard Host Specification defines following suspend sequence:
If the suspend request is not accepted, the host retries with a cancel suspend request
command. Even if the card received a cancel suspend command, it should accept
suspend if possible. If the card does not accept suspend, the host considers the
function to have never suspend.
However, the host should monitor the BR, BS and EXx bits to confirm that the
suspend request was cancelled rather that granted. If SBS=0, this bit shall be R/O
and read as 0.
32
Page 42

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Field Type Description
FSx R/W Select Function bits 3:0 These four bits are used to select a function number (0-7) or
the memory of a combo card (8) for Suspend/Resume. There are 2 means to write
the value of FSx. First, an I/O writes to the register in the CCCR and second, a new
I/O command causes the FSx to be set to the function number in that command. The
value of FSx shall remain until overwritten. If a function or memory is currently
suspended, the writing of it’s number to FSx shall re-start (resume) the data transfer
operation When reading FSx, the value returned shall be the number of the currently
addressed function. Note that when reading FSx, if the Bus Status is 0 (BS=0), the
FSx value is undefined. The FSx bits are coded as follows:
FSx Current Transaction
0000
0001-0111 Transaction to functions 1-7
1000
1001-1111 Not defined, reserved for future use
If SBS=0 these bits shall be R/O.
DF R/O Resume Data Flag: A data transaction is resumed by writing its number to FSx. Once
the transaction is resumed, the DF indicates if more data will be transferred. If DF is
cleared to 0, then no additional data will be transferred after the function or memory is
resumed. If DF is set to 1, then there is more data to transfer that will begin after the
function or memory in resumed. The DF flag can be used to control the interrupt cycle
in 4-bit mode. If DF=1, there is more data to transfer after restoring the function. In
this case, the interrupt cycle should be disabled. If DF=0, the function or memory was
suspended at end of data transfer (during busy). In this case, no data transfer shall
begin after resume so the host can detect a start interrupt cycle after restore. When
resuming, if the suspended function cannot continue data transfer the card shall
return DF=0 to abort the transfer.
EXx R/O Execution Flag bits 7:0 These bits are used by the host to determine the current
execution status of all functions (1-7) and memory (0). The bit is set to 1 for each
function or memory that is currently executing a command. The EXx bits tell the host
that a function or memory is currently executing a command so no additional
command should be issued to that function/memory. These bits are only defined if
SBS=1. This bit is set if the function is active (either currently executing or
suspended). If SBS=0 these bits shall be read as zero.
RFx R/O Ready Flag bits 7:0 These bits tell the host the read or write busy status for functions
(1-7) and memory (0). If a function or memory is executing a write transaction, an RFx
bit cleared to 0 indicates the function/memory is busy and not ready to accept more
data. If the RFx bit is set to 1, then the function/memory can accept write data. If a
function/memory is executing a read command, if the RFx bit is cleared to 0, it
indicates that read data is NOT available. If the bit is set to 1, it indicates that read
data is ready to be transferred. These bits are only defined if SBS=1. Setting a bit to 1
indicates the function is ready to accept the resume command. There are two
conditions where the function will set the bit to 1. One is when the function (executing
or suspended) is ready to continue data transfer. The other is when the suspended
function cannot continue data transfer. If SBS=0 these bits shall be read as zero.
FN0 Block
Size
R/W This 16-bit register sets the block size for I/O block operations for Function 0 only. If
this card does not support I/O block operations (SMB=0), then this register becomes
read-only and shall always read 0x0000. The maximum block size is 2048 (0x0800)
and the minimum is 1. At power-up or reset, this register shall be initially loaded with a
value of 0x0000. The host is responsible for setting the appropriate value for the
block size supported by function 0. This pointer is stored in little-endian format (LSB
first).
Transaction of function 0 (CIA)
Transaction of memory in combo card
33
Page 43

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Field Type Description
SMPC R/O Support Master Power Control These bits tell the host if the card supports Master
Power Control.
SMPC=0 : The total card current is less than 200mA, even if all functions
are active (IOEx=1). EMPC,SPS and EPS shall be zero.
SMPC=1 :The total card current may exceed 200mA.
EMPC, SPS and EPS are available.
EMPC R/W Enable Master Power Control
EMPC=0(default): The total card current shall be less than 200mA.
The card automatically switches the mode of function(s) to lower current or does not
allow some functions to become enabled, regardless of the value of EPS, so that total
card current is 200mA or less. (The card manufacturer determines which functions
operate and their modes to guarantee this limit.)
EMPC=1: The total card current may exceed 200mA and SPS and EPS are available.
The host uses SPS, EPS in FBR and IOEx to enable higher current function modes
based on the host’s ability to supply the necessary current.
SHS R/O Support High-Speed
This flag bit reports the card’s ability to operate in High-Speed mode
SHS=0: The card does not support High-Speed mode
SHS=1: The card supports High-Speed mode. The host enables High-Speed mode
via the EHS bit. See section 12 for details on switching between default and
High-Speed mode.
EHS R/W Enable High-Speed
EHS=0 (default): The card operates in default timing mode with a clock rate up to
25MHz.
EHS=1 : High-Speed Mode
The card operates in High-Speed timing mode with a clock rate up to 50MHz. See
section 12 for details on switching between default and High-Speed mode.
When SHS is set to 0, writing to this bit is ignored and always indicates 0.
RFU R/O Any bit defined as Reserved for Future Use (RFU) shall be read-only and shall be
read as 0.
Reserved
for Vendors
R/W These 16 registers are reserved for the maker of the I/O card to be used for any
operations that are defined by and specific to any vendor unique operation.
Information about the use of these optional registers needs to be obtained from the
SDIO card maker. Reading and/or writing these registers without understanding the
vendor’s definitions may cause unexpected behavior or even damage to the card.
Table 6-2 CCCR bit Definitions
34
Page 44

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
6.10 Function Basic Registers (FBR)
In addition to the CCCR, each supported I/O function has a 256-byte area used to allow the host to quickly
determine the abilities and requirements of each function, enable power selection for each function and to
enable software loading. The address of this area is from 0x00n00 to 0x00nFF where n is the function number
(0x1 to 0x7). This per-function area is structured as follows:
Address 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0x100 Function 1
CSA
enable
0x101 Function 1 Extended standard SDIO Function interface code
0x102 RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU EPS SPS
0x103-0x108 Reserved for Future Use (RFU)
0x109-0x10B Pointer to Function 1 Card Information Structure (CIS)
0x10C-0x10E Pointer to Function 1 Code Storage Area (CSA)
0x10F Data access window to Function 1 Code Storage Area (CSA)
0x110-0x111 I/O block size for Function 1
0x112-0x1FF Reserved for Future Use
0x200-0x7FF Function 2 to 7 Function Basic Information Registers (FBR)
0x800-0xFFF Reserved for Future Use
Function 1
supports
CSA
RFU RFU Function 1 Standard SDIO Function
interface code
Table 6-3 Function Basic Information Registers (FBR)
The Individual bits and fields in the FBA are defined below in Table 6-4.
Field Type Description
SDIO
Standard
Function
interface
code
Function
Supports
CSA
R/O The SDIO Standard Function code identifies those I/O functions, which implement the
recommended standard interface as defined in a separate Application Specification. A
complete and current list of assigned standard codes shall be maintained and published
in any addendums to this specification. The codes assigned to those standard interfaces
at the time this specification was published are:
0x0 No SDIO standard interface supported by this function
0x1 This function supports the SDIO Standard UART
0x2 This function supports the SDIO Type-A for Bluetooth standard interface
0x3 This function supports the SDIO Type-B for Bluetooth standard interface
0x4 This function supports the SDIO GPS standard interface
0x5 This function supports the SDIO Camera standard interface
0x6 This function supports the SDIO PHS standard interface
0x7 This function supports the SDIO WLAN interface
0x8 This function supports the Embedded SDIO-ATA standard interface
(Embedded SDIO-ATA shall be implemented only on devices following the
“Embedded SDIO Specification”).
0x9-0x0E Not assigned, reserved for future use
0xF This function supports an SDIO standard interface number greater than 0xE. In this
case, the value in byte 0x101 identifies the standard SDIO interfaces type.
R/O If this function supports and contains a Code Storage Area (CSA), this bit shall be set to 1.
If this function does not support a CSA, this bit shall be cleared to 0. CSA enable is
controlled by bit 7 of register 0xn00.
35
Page 45

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Field Type Description
Function
CSA
Enable
Extended
SDIO
Standard
Function
interface
code
SPS
(Support
Power
Selection)
EPS
(Enable
Power
Selection)
Address
pointer to
Function
CIS
Address
pointer to
Function
CSA
Data
access
window to
CSA
Function
1-7 I/O
Block Size
R/W This bit controls access to the Code Storage Area for this function. If this bit is cleared to
0, then any read or write access to the CSA shall be blocked. If this bit is set to 1, then
access to the CSA is allowed. This bit is cleared to 0 upon reset. If this function does not
support CSA (0xn00 bit 6=0), then this bit shall be R/O and always read as 0.
R/O This is the extension of the SDIO Standard Function interface code. If the SDIO Standard
Function interface code is greater than 0xE, then this byte shall contain the code and the
standard code (0x100 bits 3-0) shall contain a value of 0xF. If the standard code is less
than 0xF, then this byte shall be 0x00.
R/O This bit indicates if the function has Power Selection.
SPS=0 :This function has no Power Selection. EPS shall be zero.
SPS=1 :This function has 2 power modes which are selected by EPS.
R/W EPS=0(default): The function operates in Higher Current Mode
The maximum current for the function shall be given in TPLFE_HP_MAX_PWR_3.3V
EPS=1: The function works in Lower Current Mode
The maximum current for the function shall be given in TPLFE_LP_MAX_PWR_3.3V
This bit shall be reset when IOEx=0.
R/O These three bytes make up a 24-bit pointer (only the lower 17 bits are used) to the start of
the Card Information Structure (CIS) that is associated with each function. The CIS is
defined in section 6.11. A CIS is mandatory for each function on an SDIO card. This
pointer is stored in little-endian format (LSB first). This register points to the End of Chain
tuple if the function is not supported on the card.
R/W These three bytes make up a 24-bit pointer to the desired byte in the CSA to read or write.
After any read or write to the CSA access window register, this pointer shall be
automatically incremented by 1. If this function does not support CSA (0xn00 bit 6=0),
then these 24 bits shall be R/O and always read as 0x000000. This pointer is stored in
little-endian format (LSB first).
R/W Any read or write to this address when the CSA is enabled (0xn00 bit 7=1), shall pass
data to/from the byte addressed by the CSA address pointer. If this function does not
support CSA (0xn00 bit 6=0), then these 8 bits shall be R/O and always read as 0x00.
R/W This 16-bit register sets the block size for I/O block operations for each function (1-7). If
this card does not support I/O block operations (SMB=0), then this register becomes
read-only and shall always read 0x0000. The maximum block size is 2048 (0x0800) and
the minimum is 1 (0x0001). At power-up or reset, this register shall be initially loaded with
a value of 0x0000. The host is responsible for setting the appropriate value for the block
size supported by each function. This pointer is stored in little-endian format (LSB first).
Table 6-4 FBR bit and field definitions
36
Page 46

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
6.11 Card Information Structure (CIS)
The Card Information Structure provides more complete information about the card and the individual functions.
The CIS is the common area to read information about all I/O functions that exist in a card. The design is based
on the PC Card16 design standardized by PCMCIA. All cards that support I/O shall have a common CIS and a
CIS for each function. The CIS is accessed by reads to a fixed area as shown in Table 6-5 This one area serves
the card as a Common CIS and also as the storage area for each function. The common area and each function
have a pointer to the start of its CIS within this memory space.
Address 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0x0001000
- 0x017FFF
0x018000-
0x01FFFF
Card Common Card Information Structure (CIS) area for card common and all functions
Reserved for Future Use
Table 6-5 Card Information Structure (CIS) and reserved area of CIA
The valid tuples (storage structures) from the PCMCIA specification and new tuples created for SDIO are
defined in section 16.7.
6.12 Multiple Function SDIO Cards
Multiple Function SDIO Cards shall have a separate set of Configuration registers for each function on the card.
Multiple Function SDIO Cards shall use a combination of a CIS common to all functions on the card and a
separate function-specific CIS specific to each function on the card. The common CIS describes features that
are common to all functions on the card. Each function-specific CIS describes features specific to a particular
function on the SDIO Card. Functions are numbered sequentially beginning with 1.
The CMD5 response indicates the total number of functions, which includes ‘dummy’ functions. The host shall
iterate through the CIS entries based on the CMD5 response.
The ERROR status flag of an R5 response is type “E R X”, (see section 5.2.1) and can indicate an error in the
previous command. Since the host software needs a method to determine which function detected the error, a
Multiple Function SDIO cards shall only return the R5 ERROR status flag in the subsequent command issued to
the same function.
6.13 Setting Block Size with CMD53
The host sets the block size for a function’s multiple block transfers by writing to the 16-bit Function I/O Block
Size register in the FBR (see Table 6-4). The host shall not write this register using CMD53 with Block Mode set
to 1. If the card detects an invalid block size before executing CMD53 with Block Mode set to 1, it shall indicate
an OUT_OF_RANGE error in the current response and shall not perform data transfer. This will also stop the
interrupt period (see section 8.1.3)
37
Page 47

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
6.14 Bus State Diagram
Figure 6-2 shows the Bus State Diagram for an SDIO card. It shows the bus states and their relations to SDIO
commands and Suspend/Resume.
Commands
accepted in “INI”
CMD5, CMD3
Power On
Initialization
State
CMD15
Commands
accepted in “STB”
CMD3, CMD7,
CMD15
Standby
State
CMD7 with
correct RCA
Commands
accepted in “CMD”
CMD7, CMD52,
CMD53, CMD15
CMD3
CMD52 Reset
CMD52 Reset
Transfer
State
(Dat Bus Active)
BS=1
Function Suspend
CMD52 Abort
CMD7 with
incorrect RCA
Command
CMD53 (to valid
function)
Function
Resume
Execution complete
State
(Dat Bus Free)
BS=0
CMD7 with correct
RCA
CMD53 to invalid
function
CMD15 or OCR
mismatch
CMD53 to invalid function can be:
y I/O Disable or I/O Not Ready (IORDY=0)
y I/O Function number error in response
y I/O Function already Suspended
Figure 6-2 State Diagram for Bus State Machine
Commands
accepted in “TRN”
CMD52
Inactive
State
38
Page 48

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
7. Embedded I/O Code Storage Area (CSA)
In order to support the concept of “Plug-and-Play” for SDIO cards, each function contained in a card may need
to contain a block of memory for the storage of drivers and/or applications. In addition, since the same SDIO
card may be used on multiple different host platforms, several different versions of the code may be needed for
each function. One option is to store these programs in a standard SD Memory section of a combo card.
Alternately, a standard access means to load the code is contained in the optional Code Storage Area (CSA).
The CSA is a separate 16MB memory area that is accessed using the CSA address pointer and the CSA
window register contained in the FBR registers. Note that each function may have it’s own CSA to support it. The
CSA data can be read only or R/W. The actual storage method for the CSA is not a part of this specification and
left to the implementers.
7.1 CSA Access
In order for the host to access a function’s CSA, it first shall determine if that function supports a CSA. The host
reads the FBR register at address 0x00n00 where n is the function number (0x1 to 0x7). If bit 6=1, then the
function supports a CSA and the host enables access by writing bit 7=1. The next step is for the host to load the
24 bit address to start reading or writing. This is accomplished by writing the 24 bits (A23-0) to registers
0x00n0C to 0x00n0E where n is the function number (0x1 to 0x7). Once the start address is written, data can be
read or written by accessing register 0x00n0F, the CSA data window register. If more than 1 byte needs to be
read or written, an extended I/O command (byte or block) can be performed with an OP code of 0 (fixed
address). The address pointer shall be automatically incremented with each access to the window register, so
the access will be to sequential addresses within the CSA. Once the operation is complete, the address of the
NEXT operation shall be held in the 24 bit address register for the host to read.
7.2 CSA Data Format
The data stored in the CSA shall be structured using the FAT12/FAT16 format. This format is defined in the ISO
specification: ISO/IEC9293:1994 Information technology - Volume and file structure of disk cartridges for
information interchange. This specification is also the basis for the SD memory cards. The information on the
SD memory implementation can be found in the SDA publication: Part 2 FILE SYSTEM SPECIFICATION
Version 2.00 May 9, 2006. The actual layout of files within the CSA is undefined by this specification.
The use of the CSA for program or data storage for different host types requires that the SDIO card
manufacturer load the programs and data in a file format that may be recognized by the host. An example of this
would be the use of a specific file name saved within a specific subdirectory that is recognized and executed by
a particular host operating system. Such formats are specific and sometimes proprietary to different host
implementations and operating systems.
The rest of this chapter is not included in the Simplified Specification.
39
Page 49

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
8. SDIO Interrupts
In order to allow the SDIO card to interrupt the host, an interrupt function is added to a pin on the SD interface.
Pin number 8, which is used as DAT[1] when operating in the 4-bit SD mode, is used to signal the card’s
interrupt to the host. The use of interrupt is optional for each card or function within a card. The SDIO interrupt is
“level sensitive”, that is, the interrupt line shall be held active (low) until it is either recognized and acted upon by
the host or de-asserted due to the end of the Interrupt Period (see 8.1.2). Once the host has serviced the
interrupt, it is cleared via some function unique I/O operation. All hosts shall provide pull-up resistors on all data
lines DAT[3:0] as described in section 6 of the SD Physical Specification.
8.1 Interrupt Timing
The operation of the interrupt pin is different between the SPI mode and the SD mode. The operation of the
interrupt pin is defined as follows:
8.1.1 SPI and SD 1-bit Mode Interrupts
In the SPI and 1-bit SD mode, Pin 8 is dedicated to the interrupt function. Thus, in the SPI and SD 1-bit modes
there are no timing constraints on interrupts. A card in the SPI or 1-bit SD mode signals an interrupt to the host
at any time by asserting pin 8 low. The host detects this pending interrupt using a level sensitive input. The host
is responsible for clearing the interrupt. If the SDIO card is operating in the SPI mode, the interrupt from the card
may not be asserted if the card is not selected.(CS=0). The exception to this requirement occurs only if the card
is both capable of interrupting when not selected (the SCSI bit in the CCCR = 1), and has that feature turned on
(the ECSI bit = 1). In this case, the card may assert the interrupt irrespective of the state of the CS line. For more
information, see Table 6-1.
8.1.2 SD 4-bit Mode
Since Pin 8 is shared between the IRQ and DAT[1] use in the 4-bit SD mode, an interrupt shall only be sent by
the card and recognized by the host during a specific time. The time that a low on Pin 8 shall be recognized as
an interrupt is defined as the Interrupt Period.
An SDIO host shall only sample the level on Pin 8 (DAT[1]/IRQ) into the interrupt detector during the Interrupt
Period. At all other times, the host interrupt controller shall ignore the level on Pin 8. Note that the Interrupt
Period is applicable for both memory and I/O operations
The definition of the Interrupt Period is different for operations with single block and multiple block data transfer.
8.1.3 Interrupt Period Definition
This section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
8.1.4 Interrupt Period at the Data Block Gap in 4-bit SD Mode (Optional)
This section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
8.1.5 Inhibited Interrupts (Removed Section)
This section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
8.1.6 End of Interrupt Cycles
This section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
40
Page 50

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
8.1.7 Terminated Data Transfer Interrupt Cycle
This section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
8.1.8 Interrupt Clear Timing
Since the SDIO card uses level sensitive interrupts, the host shall clear pending interrupts with an I/O read or
write to some function unique area. In some host implementations, the sending of a CMD52 to the card is
handled by host adapter hardware while the host CPU can execute other operations. This condition may allow
an interrupt that has already been handled to re-interrupt the host if the timing of the interrupt clear is not
controlled. To prevent this condition, Any SDIO card that implements interrupts shall follow some required timing
with respect to removing the interrupt from the DAT[1] line after the write to the function unique area that clears
the interrupt. The clearing of the interrupt can be caused by an I/O write in a function unique method, or by a
function unique I/O read. An example of clearing an interrupt using an I/O read would be a function where the
reading of a data register may automatically clear the data ready interrupt.
The rest of this section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
41
Page 51

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
9. SDIO Suspend/Resume Operation
The procedure used to perform the Suspend/Resume operation on the SD bus is:
1. The host determines which function is currently using the DAT[3:0] line(s).
2. The host requests the lower priority or slower transaction to suspend.
3. The host checks for the transaction suspension to complete.
4. The host begins the higher priority transaction.
5. The host waits for the completion of the higher priority transaction.
6. The host restores the suspended transaction.
If the current transaction can accept suspend and the card receives a suspend command during Read Wait, it
shall accept the suspend request.
The rest of this chapter is not included in the Simplified Specification.
42
Page 52

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
10. SDIO Read Wait Operation
The optional Read Wait (RW) operation is defined only for the SD 1-bit and 4-bit modes. The read Wait
operation allows a host to signal a card that is executing a read multiple (CMD53) operation to temporarily stall
the data transfer while allowing the host to send commands to any function within the SDIO card. To determine
if a card supports the Read Wait protocol, the host shall test
CCCR (see Table 6-1). The timing for Read Wait is based on the Interrupt Period that is defined in section 8.1
If a card does not support the Read Wait protocol, the only means a host has to stall (not abort) data in the
middle of a read multiple command is to control the SDCLK. Read wait support is mandatory for the card to
support suspend/resume.
The rest of this chapter is not included in the Simplified Specification.
SRW capability bit in the Card Capability byte of the
43
Page 53

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
11. Power Control
11.1 Power Control Overview
The concept of high-power SDIO cards was introduced in Version 1.10 of the SDIO Specification. Power Control
supports following two features:
• High-Power Support
SDIO cards created prior to Version 1.10 of the SDIO Specification were limited to a maximum current of
200mA at any time, irrespective of the number or types of functions supported. With the creation of wireless
communication devices in the SDIO form factor, a need was seen to provide more current to accommodate
the higher power requirements of some SDIO cards. Since backward compatibility is a primary concern for
any changes made to this specification, a method was chosen to prevent a high-power card from drawing
excessive amounts of current from hosts designed to only support the SDIO 1.0 cards. Master Power
Control allows standard and high-power cards to be inserted into any host without causing excessive
current damage to the host. It is important to note that there exists the possibility of trying to use a card that
requires high-power in a standard power host and having that card fail to operate. Master Power Control is
supported on a per card basis and available to the host in the CCCR. A high-power card may have a mix of
both high and standard power functions.
• Power Selection Support
Not all hosts can supply enough current for all SDIO cards. A host may choose to use the SDIO card in a
lower power mode to increase operation time. Power Selection enables the host to switch the card to a
lower power mode. It is important to note that there exists the possibility of trying to use a standard power
card in a host that does not have enough power to meet the card’s requirement. In this case the card will fail
to operate. Cards supporting Power Selection will enable the widest range of host support. Power Selection
is supported on a per function basis and available to the host in the FBR.
11.2 Power Control support for SDIO Cards
11.2.1 Master Power Control
SDIO version 1.10 cards indicate their support for the new power control functions with the SMPC (Support
Master Power Control) bit in the CCCR (See section 6.9). Hosts enable the card’s power control functions with
EMPC (Enable Master Power Control) bit.
the
SMPC can be set to 0 if the card maximum current is less than 200mA and Power Selection (see section 11.2.2)
is not supported. A SDIO version 1.10 card which has
EMPC is set to 0. A SDIO version 1.0 host may not be aware of EMPC, which will remain 0 (its default state).
In the case where
200mA shall not set IORx to 1 and TPLFE_OP_MAX_PWR shall be set to 0. If a multi-function card’s total power
exceeds 200mA the card shall not set all IORx to 1, even if all IOEx are set to 1. Some of the functions’ IORx can
be set to 1 as long as the card’s total current is less than 200mA. If the host tries to enable a function (IOEx =1)
that will cause the card’s total current to exceed 200mA, the card shall disable (IORx=0) one or more functions
to keep the card’s total current less than 200mA. Which functions are enabled depends on the design of the card
vendor.
In the case where
should be designed, where possible, to not require the maximum current , thus functioning in as many hosts as
possible with sufficient power.
EMPC is set to 0, the card total current shall not exceed 200mA. Functions that exceed
EMPC is set to 1, the card current can exceed 200mA, up to a maximum of 500mA. Card
SMPC set to 1 shall maintain backward compatibility when
44
Page 54

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
11.2.2 Power Selection
Power Selection defines two power modes for a function: Lower Current Mode and Higher Current Mode. A card
implementing Power Selection gives the host the choice between these two power modes. These modes can be
used for functions, such as a radio, which can operate in full performance (Higher Current Mode) or reduced
performance (Lower Current Mode). A card’s support of Power Selection is indicated with the SPS bit (Support
Power Selection) in the FBR. The host enables Power Selection with the EPS bit (Enable Power Selection) in
the FBR.
11.2.3 High-Power Tuples
Six new tuples are defined in version 1.10 for each function tuple.
• Average power required when Master Power Control is not enabled (TPLFE_SP_AVG_PWR_3.3V)
• Peak power required when Master Power Control is not enabled (TPLFE_SP_MAX_PWR_3.3V)
• Average power required in Higher Current Mode (TPLFE_HP_AVG_PWR_3.3V)
• Peak power required in Higher Current Mode (TPLFE_HP_MAX_PWR_3.3V)
• Average power required in Lower Current Mode (TPLFE_LP_AVG_PWR_3.3V)
• Peak power required in Lower Current Mode (TPLFE_LP_MAX_PWR_3.3V)
These values are 16 bits long with a 1mA/step resolution. This allows a value of 0 to 65,535 mA to be used.
Current varies depending on the voltage. These tuples are defined in 3.1-3.5V or 2.7-3.6V range. When a new
voltage range is added in future specification, another six tuples will be added.
Table 11-1 shows which tuples a host shall refer to depending on the host version and the settings of
EPS bits.
Host
Ver 1.0 Don’t care Don’t care TPLFE_OP_MIN_PWR
Ver 1.1 0 Don’t care TPLFE_SP_AVG_PWR_3.3V
Ver 1.1 1 0 TPLFE_HP_AVG_PWR_3.3V
Ver 1.1 1 1 TPLFE_LP_AVG_PWR_3.3V
EMPC EPS Reference TPLs Comments
TPLFE_OP_AVG_PWR
TPFLE_OP_MAX_PWR
Same as TPLFE_OP_AVG_PWR
TPLFE_SP_MAX_PWR_3.3V
TPLFE_HP_MAX_PWR_3.3V
TPLFE_LP_MAX_PWR_3.3V
Same as TPFLE_OP_MAX_PWR
Non zero value is required when
SMPC=1
Non zero value is required when
SPS=1
EMPC and
Table 11-1 Reference Tuples by Master Power Control and Power Select
A version 1.10 SDIO card shall implement the six new tuples. A card which has SMPC set to 1, shall set a
non-zero value to TPLFE_HP_AVG_PWR_3.3V and TPLFE_HP_MAX_PWR_3.3V. A card which has SPS set
to 1, shall set a non-zero value to TPLFE_LP_AVG_PWR_3.3V and TPLFE_LP_MAX_PWR_3.3V.
TPLFE_SP_AVG_PWR_3.3V and TPLFE_SP_MAX_PWR_3.3V should be set to the same value as
TPFLE_OP_AVG_PWR and TPLFE_OP_MAX_PWR respectively.
11.3 Power Control Support for the SDIO Host
11.3.1 Version 1.10 Host
The following are requirements for a version 1.10 host:
• The host shall recognize new Power Control registers and tuples as defined in SDIO Specification
Version 1.10.
• Power Control bits (
• Power Selection bits (SPS, EPS) in the FBR
• High-Power Tuples
• The host shall know its own power supply ability
45
SMPC, EMPC) in the CCCR
Page 55

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
• The host shall have the ability to manage power by calculating maximum current shown in the tuples
and control EMPC, EPS and IOEx not to exceed total current that the host can supply. If the host does
not have enough power to use the card, the host shall not enable the card.
11.3.2 Power Control Operation
A host reads the
card’s support of Power Selection. If
SMPC to see if the card supports Power Control additions. If so, the host checks SPS to see the
SMPC is set to 1, a version 1.10 host should set EMPC to 1.
Power Selection provides the host with the choice of two power modes for the function. A host that can supply
enough power to the card does not need to use Power Selection.
If SMPC is set to 1 and SPS is set to 1, the host can utilize Power Selection by setting EMPC to 1. If EPS is set
to 0 (default mode of the card), Higher Current Mode is selected. If EPS is set to 1, Lower Current Mode is
selected. For example, a wireless function may offer a power mode with reduced transmission range and
corresponding reduced current requirements. As the host knows how much current it can supply to the card, it
reads the appropriate tuples and decides whether or not to enable each function (with IOEX), and if so in what
Current Mode. The host shall verify that the total current required by the card shall not exceed the current of host
can supply. A version 1.10 host should read new tuples as shown in Table 11-1.
46
Page 56

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
12. High-Speed Mode
High-Speed mode increases the bus clock rate to 50MHz and the SD bus throughput from 12.5MB/sec to
25MB/sec. For information on High-Speed mode for SD memory cards see Part 1 Physical Layer Specification
Version 2.00, sections 4.3.10, 4.3.11 and 6.8. SDIO and combo cards may also support High-Speed mode.
12.1 SDIO High-Speed Mode
SDIO version 1.20 cards indicate their support for High-Speed mode with the SHS (Support High-Speed) bit in
the CCCR (See section 6.9). Hosts switch between default and High-Speed mode with the EHS (Enable
High-Speed) bit in the CCCR by CMD52. Following a command to set or clear EHS, cards shall switch speed
mode within 8 clocks after the end bit of the corresponding response.
When switching from default to High-Speed mode the host can try to set EHS without first checking SHS. The
host issues CMD52 in RAW mode, setting EHS to one, and after getting the response of CMD52 the host
checks SHS and EHS. If SHS=0 or EHS=0, the command will be ignored and the card is still in default mode. If
SHS=1 and EHS=1, the card is in High-Speed Mode.
12.2 Switching Bus Speed Mode in a Combo Card
A combo card that supports High-Speed shall support it for both memory and IO. Two bus speed switch
commands are defined; SD memory command (CMD6) and SDIO command (EHS in CCCR is changed using
CMD52).
A part of this section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
When one bus speed switch commands is executed successfully, the card switches the card bus speed mode.
If two bus speed switch commands are executed in turn (to the same bus speed mode), only the first successful
command is effective to switch bus speed mode.
The host needs to check success of executing bus speed switch command and then the host can switch the
host bus speed mode to the same one.
Success of switching bus speed mode is determined by checking receipt of a good response and the result of
switching bus speed mode is the same as the switch requested.
The status of current bus speed mode is read by bus speed switch commands. For example, when bus speed
mode is switched by CMD6, the result can be read from EHS. If switching by RAW mode of CMD52 has failed,
there are two kinds of responses. One is no response with illegal command error. The other is that CMD52 is
accepted and the status of RAW mode indicates EHS is not changed.
A reset of either the memory or IO portion of a combo card will also reset both portions to default speed mode.
Within 8 clocks after response of a reset by CMD52 (write to RES in CCCR) or CMD0 the card shall change the
speed mode to default speed mode.
Note that when changing the bus speed the host bus driver should treat a bus speed change request from any
driver as an atomic operation. The host should mask interrupts and not issue any command to the card until the
bus speed change is complete.
If a combo card supports the Lock/unlock function, a locked card cannot change bus speed mode. A locked card
indicates an illegal command error to a bus speed switch command. The host needs to unlock the card by
CMD42 before changing bus speed. It also implies that a host should not change bus speed mode during
initialization before managing a locked card.
47
Page 57

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
13. SDIO Physical Properties
This chapter is not included in the Simplified Specification.
13.1 SDIO Form Factors
The SDIO definition encompasses different form factors:
• Full-Size SDIO — compatible with host sockets designed for SD memory cards
• miniSDIO — compatible with host sockets designed for miniSD memory cards
13.2 Full-Size SDIO
The SDIO card is compatible with host sockets designed for SD memory cards. In addition, the SDIO cards can
be extended to allow for external connectors, antennas etc. With the exception of the write protect switch, all
SDIO cards shall meet the mechanical specifications described in the SD Physical Specification for that portion
of the card that is not extended. The WP switch is not supported by hosts for SDIO only cards.
The rest of this section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
13.3 miniSDIO
The miniSDIO card is compatible with host sockets designed for miniSD memory cards. In addition, the
miniSDIO cards can be extended to allow for external connectors, antennas etc. All miniSDIO cards shall meet
the mechanical specifications described in miniSD Card Addendum Version 2.00, Part 1 Physical Layer
Specification Version 2.00 for that portion of the card that is not extended.
When a miniSDIO card is inserted into a miniSD to SD memory card adaptor, and plugged-into an SDIO host
slot, it shall appear to the host as an SDIO card.
The rest of this section is not included in the Simplified Specification.
14. SDIO Power
14.1 SDIO Card Initialization Voltages
SDIO Version 2.00 eliminate the voltage range 2.0-2.7V for basic communication because the SD Physical
Specification Version 2.00 eliminates it. SDIO cards follow the same voltage and current requirements as SD
memory cards. This means that an SDIO or combo card shall be used at an operating voltage range of 2.7 to
3.6V. The hosts shall not supply the voltage range 2.0-2.7V for basic communication to the SDIO Version 2.00
cards.
14.2 SDIO Power Consumption
The SDIO cards are intended to operate in mobile devices that have limited power sources available. Because
the host’s battery life may be significantly reduced if the SDIO card draws excessive power, a primary goal of
SDIO designers should be low power. By reducing power consumption to a minimum, Host battery life and
consumer satisfaction will be enhanced. The following power data represents the maximum that a SDIO card
may draw. It is important for designers to note that a low power host may reject any SDIO card that identifies
48
Page 58

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
itself as drawing more power that the host is willing to supply, thus lower power cards may have a competitive
advantage in the market.
The rest of this chapter is not included in the Simplified Specification.
49
Page 59

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
15. Inrush Current Limiting
This chapter is not included in the Simplified Specification.
50
Page 60

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
16. CIS Formats
16.1 CIS Reference Document
The CIS used by SDIO is based directly upon the metaformat specification used by PCMCIA and Compact
Flash. The user of this specification is directed to:
PC Card Standard
Volume 4
Metaformat Specification
Published by:
PCMCIA (Personal Computer Memory Card International Association)
2635 North First Street, Suite 209
San Jose, CA 95134 USA
+1-408-433-2273
+1-408-433-9558 (Fax)
16.2 Basic Tuple Format and Tuple Chain Structure
The Card Information Structure is one or more chains (or linked lists) of data blocks or tuples. The basic format
of tuples is shown in Table 16-1.
Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0x00 TPL_CODE Tuple code: CISTPL_xxx
0x01 TPL_LINK Offset to next tuple in chain. This is the number of bytes in the tuple body. (n)
0x02..
(n+2)
The tuple body. (n bytes)
Table 16-1 Basic Tuple Format
Byte 0 of each tuple contains a tuple code. A tuple code of 0xFF is a special mark indicating that there are no
more tuples in the chain. There are 2 tuples with only a tuple code, the CISTPL_NULL and the CISTPL_END
(see Table 16-2). These tuples do not have any additional bytes. For all other tuples, byte 1 of each tuple
contains a link to the next tuple in the chain. If the link field is 0, then the tuple body is empty. If the link field
contains 0xFF, then this tuple is the last tuple in its chain. There are two ways of marking the end of a tuple chain
for SDIO cards: a tuple code of 0xFF, or a tuple link of 0xFF. The use of an FFH link value is allowed in SDIO
cards, but it is recommended to use the End of Chain tuple. System software shall use the link field to validate
tuples. No SDIO card tuple can be longer than 257 bytes: 1 byte TPL_CODE + 1 byte TPL_LINK + FFH byte
tuple body (and this 257 byte tuple ends the chain). Some tuples provide a termination or stop byte that marks
the end of the tuple. In this case, the tuple can effectively be shorter than the value implied by its link field.
However, software shall not scan beyond the implied length of the tuple, even if a termination byte has not been
seen.
16.3 Byte Order Within Tuples
Within tuples, all multi-byte numeric data shall be recorded in little-endian order. That is, the least-significant
byte of a data item shall be stored in the first byte of a given field. Within tuples, all character data shall be stored
in the natural order. That is, the first character of the field shall be stored in the first byte of the field. Fixed-length
character fields shall be padded with null characters, if necessary.
51
Page 61

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
16.4 Tuple Version
With the introduction of SDIO Specification Version 1.10, a different format for the tuple information is possible
based on the changes made by each specification revision. These changes could be added fields in a tuple or
entirely new tuples. In order to maintain backward compatibility, new data fields are added after existing fields in
order to maximize backward compatibility. It is the responsibility of the host program that is scanning the tuple
chain (sometimes called “walking the tuples”) to first determine the SDIO specification version that the card was
designed to. The program shall be designed to anticipate that SDIO cards will be encountered that are built to a
later version of the specification. This requires the program to ignore the additional data existing in SDIO cards
built to a later specification. Specifically, the program shall first read the SDIO specification version that the card
was designed to meet from the SDIOx field in the CCCR area. If the version is less than or equal to the version
of the tuple scan program, then the program shall know and properly decode all tuple information. If the card
version is greater than the scan program’s version, the scan program may need to ignore additional information
fields or tuples. The unknown tuples can be ignored by simply skipping those tuples with unrecognized codes.
Skipping is accomplished by using the TPL_LINK field (always the second byte) to jump over the unknown tuple.
In a similar manner, the additional data fields in tuples should be ignored using the link field. For example, if a
scan program is expecting 0x15 bytes of data and the TPL_LINK field indicates a size of 0x19 bytes, the scan
program should ignore and skip over the last 4 bytes of data.
16.5 SDIO Card Metaformat
Unlike the PCMCIA card, the SDIO card has multiple CIS areas. There is a common CIS for the entire card and
a CIS assigned to each function. Because of the multiple CIS areas, the SDIO card does not need to support the
CISTPL_LONGLINK_MFC tuple or the CISTPL_LINKTARGET as described in section 2.3.6 of the PCMCIA
spec. Table 16-2 lists the tuple codes supported by SDIO cards. The type field indicates if a tuple is Optional (O),
Mandatory (M), Recommended (R), or not applicable (n/a) for the common (function 0) tuple and for each
function (1-7) supported by the card. For more details on each tuple, see the PCMCIA metaformat specification
section referenced.
Code Name Description PCMCIA
Reference
0x00 CISTPL_NULL Null tuple 3.1.9 O O
0x10 CISTPL_CHECKSUM Checksum control 3.1.1 R R
0x15 CISTPL_VERS_1 Level 1
version/product-information
0x16 CISTPL_ALTSTR The Alternate Language String
Tuple
0x20 CISTPL_MANFID Manufacturer Identification
String Tuple
0x21 CISTPL_FUNCID Function Identification Tuple 3.2.7 n/a M
0x22 CISTPL_FUNCE Function Extensions 3.2.6 n/a M
0x800x8F
0x91 CISTPL_SDIO_STD Additional information for
0x92 CISTPL_SDIO_EXT Reserved for future use with
0xFF CISTPL_END The End-of-chain Tuple 3.1.2 M M
Vendor Unique Tuples None O O
functions built to support
application specifications for
standard SDIO functions.
SDIO devices.
3.2.10 O O
3.2.1 O O
3.2.9 M O
6.1.2 n/a M
6.1.3 n/a n/a
Type
Common
Type Function
1
:Standard
SDIO Function
1
:non-Standard
O
SDIO Function
Table 16-2 Tuples Supported by SDIO Cards
52
Page 62

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Note 1: the use of CISTPL_SDIO_STD is mandatory for all functions that claim to support a SDIO standard
interface specification (see 1.3). If the function does not support a standard SDIO interface, this tuple should be
used with a value of 0.
16.6 CISTPL_MANFID: Manufacturer Identification String Tuple
The manufacturer identification tuple contains information about the manufacturer of a SDIO Card. Two types of
information are provided: the SDIO Card's manufacturer and a manufacturer card number. This tuple shall be
present in the card common CIS.
This should also be present in each function’s CIS. This allows a function to override the card common
manufacturer information so the driver can take advantage of unique features.
Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0x00 TPL_CODE CISTPL_MANFID (20H)
0x01 TPL_LINK Link to next tuple (at least 4)
0x02-0x03 TPLMID_MANF SDIO Card manufacturer code
0x04-0x05 TPLMID_CARD manufacturer information (Part Number and/or Revision)
Table 16-3 CISTPL_MANFID: Manufacturer Identification Tuple
The TPLMID_MANF field identifies the SDIO Card's manufacturer. New codes are assigned by both PCMCIA
and JEIDA. The first 256 identifiers (0x0000 through 0x00FF) are reserved for manufacturers who have JEDEC
IDs assigned by JEDEC Publication 106. Manufacturers with JEDEC IDs may use their eight-bit JEDEC
manufacturer code as the least significant eight bits of their SDIO Card manufacturer code. In this case, the
most significant eight bits shall be zero (0). For example, if a JEDEC manufacturer code is 89H, their SDIO Card
manufacturer code is 0x0089. If a SDIO card manufacturer does not currently have a TPLMID_MANF assigned,
one can be obtained at little or no cost from the PCMCIA. The TPLMID_CARD field is reserved for the use of the
SDIO Card's manufacturer. It is anticipated that the field will be used to store card identifier and revision
information.
16.7 SDIO Specific Extensions
SDIO cards use two to four tuples to provide additional information about the card (common) and each function.
The first is the Function ID tuple. The changes for SDIO are detailed in the next sections.
16.7.1 CISTPL_FUNCID: Function Identification Tuple
To identify an SDIO card, the CISTPL_FUNCID tuple shall exist in all CIS areas. This means there shall be a
CISTPL_FUNCID in the common CIS space chain and one in each function’s CIS space chain. The format of
this tuple is shown in
Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0x00 TPL_CODE CISTPL_FUNCID (0x21)
0x01 TPL_LINK Link to next tuple (0x02)
0x02 TPLFID_FUNCTION Card function code (0x0C)
0x03 TPLFID_SYSINIT System initialization bit mask. (Not used, set to 0x00)
Table 16-4 CISTPL_FUNCID Tuple
The function identification tuple contains information about the functionality provided by an SDIO Card.
Information is also provided to enable system utilities to decide if the SDIO Card should be configured during
system initialization. Since additional function specific information is available, one or more function extension
tuples follow this tuple. The TPLFID_FUNCTION field contains an identifier assigned by PCMCIA (0x0C) to
identify the SDIO device class.
53
Page 63

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
16.7.2 CISTPL_FUNCE: Function Extension Tuple
The CISTPL_FUNCE tuple provides standard information about the card (common) and each individual
function. There shall be one CISTPL_FUNCE in each function’s CIS immediately following the
CISTPL_FUNCID tuple. The format of the CISTPL_FUNCE is shown in Table 16-5.
Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0x00 TPL_CODE CISTPL_FUNCE (0x22)
0x01 TPL_LINK Link to next tuple (see following sections)
0x02 TPLFE_TYPE Type of extended data (see following sections)
0x03-n TPLFE_DATA Function information (see following sections)
Table 16-5 CISTPL_FUNCE Tuple General Structure
There are two versions of the CISTPL_FUNCE tuple, one for the common CIS (function 0) and a version used
by the individual function’s CIS (1-7). Both types are described below.
16.7.3 CISTPL_FUNCE Tuple for Function 0 (common)
This version of the CISTPL_FUNCE tuple gives the host common information about the card. There shall be
only one of these tuples, located in the CIS for function 0 following the CISTPL_FUNCID. The format of this
tuple is shown in Table 16-6.
Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0x00 TPL_CODE CISTPL_FUNCE (0x22)
0x01 TPL_LINK Link to next tuple (0x04)
0x02 TPLFE_TYPE Type of extended data (0x00)
0x03-0x04 TPLFE_FN0_BLK_SIZE
0x05 TPLFE_MAX_TRAN_SPEED
Table 16-6 TPLFID_FUNCTION Tuple for Function 0 (common)
The fields in this tuple have the following definition:
Field Description
TPLFE_FN0_BLK_SIZE This is both the maximum block size and byte count that function 0 can
support. A value of zero is not valid and shall not be used.
TPLFE_MAX_TRAN_SPEED This byte indicates the maximum transfer rate per one data line during
data transfer. This value applies to all functions in the SDIO card. This
value shall be 25 Mb/Sec (0x32) for all Full-Speed SDIO cards. The
minimum value for Low-Speed SDIO cards shall be 400 Kb/Sec (0x48).
The format is identical to the TRAN_SPEED value stored in the CSD of
SD memory cards. The maximum data transfer rate is coded according
to the following method:
Bits 2:0 contain the transfer rate unit coded as follows:
0=100kbit/s, 1=1Mbit/s, 2=10Mbit/s, 3=100Mbit/s, 4... 7=reserved
Bits 6:3 contain the time value codes as follows:
0=reserved, 1=1.0, 2=1.2, 3=1.3, 4=1.5, 5=2.0, 6=2.5, 7=3.0, 8=3.5,
9=4.0, A=4.5, B=5.0, C=5.5, D=6.0, E=7.0, F=8.0
Bit 7 is reserved and shall be zero
A Combo Card shall support 25MHz clock (0x32)
Table 16-7 TPLFID_FUNCTION Field Descriptions for Function 0 (common)
54
Page 64

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
16.7.4 CISTPL_FUNCE Tuple for Function 1-7
This version of the CISTPL_FUNCE tuple gives the host common information about each individual function on
a per-function basis. There shall be one of these tuples, located in the CIS for each function following the
CISTPL_FUNCID. The format of this tuple is shown in Table 16-8.
Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0x00 TPL_CODE CISTPL_FUNCE (0x22)
0x01 TPL_LINK Link to next tuple (0x2A)
0x02 TPLFE_TYPE Type of extended data (0x01)
0x03 TPLFE_FUNCTION_INFO
0x04 TPLFE_STD_IO_REV
0x05-0x08 TPLFE_CARD_PSN
0x09-0x0C TPLFE_CSA_SIZE
0x0D TPLFE_CSA_PROPERTY
0x0E-0x0F TPLFE_MAX_BLK_SIZE
0x10-0x13 TPLFE_OCR
0x14 TPLFE_OP_MIN_PWR
0x15 TPLFE_OP_AVG_PWR
0x16 TPLFE_OP_MAX_PWR
0x17 TPLFE_SB_MIN_PWR
0x18 TPLFE_SB_AVG_PWR
0x19 TPLFE_SB_MAX_PWR
0x1A-0x1B TPLFE_MIN_BW
0x1C-0x1D TPLFE_OPT_BW
0x1E-0x1F TPLFE_ENABLE_TIMEOUT_VAL
0x20-0x21 TPLFE_SP_AVG_PWR_3.3V
0x22-0x23 TPLFE_SP_MAX_PWR_3.3V
0x24-0x25 TPLFE_HP_AVG_PWR_3.3V
0x26-0x27 TPLFE_HP_MAX_PWR_3.3V
0x28-0x29 TPLFE_LP_AVG_PWR_3.3V
0x2A-0x2B TPLFE_LP_MAX_PWR_3.3V
Table 16-8 TPLFID_FUNCTION Tuple for Function 1-7
The fields in this tuple have the following definition:
Field Description
TPLFE_FUNCTION_INFO Bit significant information about the Function The bits are defined in Table
16-10
TPLFE_STD_IO_REV This 8-bit value contains the version level of the Application Specification
for Standard SDIO Functions that this function supports. The format is x.y
where x is the major version (4-bits) and y is the minor version level. For
example if the version is 2.4 the value would be 0x24. If this function does
not support an SDIO standard function, the value shall be 0x00.
TPLFE_CARD_PSN The Product Serial Number is a 32 bit unsigned binary integer. Support of
a serial number is optional, if there is no serial number, this field shall be
0x00000000 While a unique serial number is not required for all devices,
it is strongly recommended that SDIO card vendors place a unique serial
number in this field to assist the operating systems is differentiating
multiple cards of the same type. Also note that some Application
Specifications for Standard SDIO Functions require a unique serial
number in this field. The individual Application Specification will indicate if
support of this field is mandatory.
55
Page 65

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
TPLFE_CSA_SIZE Size of the CSA space available for this function in bytes
TPLFE_CSA_PROPERTY This byte contains flags identifying properties of this function’s CSA. The
bits are defined in Table 16-11
TPLFE_MAX_BLK_SIZE This is both the maximum block size and byte count that this function can
support. A value of zero is not valid and shall not be used.
TPLFE_OCR This is the OCR value for this function. The format is identical to the 32-bit
OCR format used by SD memory devices. For more details, see section
5.1 of the SD Physical Specification.
TPLFE_OP_MIN_PWR This is the minimum current, in mA, required by this function when
operating. This value is valid for all voltages supported by this function. If
the required current exceeds 200mA, this value shall be zero.
TPLFE_OP_AVG_PWR This is the average current, in mA, required by this function when
operating. This value is valid for all voltages supported by this function. If
the required current exceeds 200mA, this value shall be zero
TPLFE_OP_MAX_PWR This is the maximum (peak) current, in mA, required by this function when
operating. This value is valid for all voltages supported by this function. If
the required current exceeds 200mA, this value shall be zero
TPLFE_SB_MIN_PWR This is the minimum current, in mA, required by this function when in the
standby condition. If this function does not support standby, this value
shall be 0x00. The method to place this function in the standby state and
the capabilities it has while in standby are vendor defined. This value is
valid for all voltages supported by this function. Note that this value is
valid only for standard power SDIO cards or high-power cards when
EMPC is 0. With an 8-bit field, the range is from 0 to 254 mA. A value of
255 (0xFF) is used to indicate a value of 255mA or greater.
TPLFE_SB_AVG_PWR This is the average current, in mA, required by this function when in the
standby condition. If this function does not support standby, this value
shall be 0x00. The method to place this function in the standby state and
the capabilities it has while in standby are vendor defined. This value is
valid for all voltages supported by this function. Note that this value is
valid only for standard power SDIO devices cards or high-power cards
EMPC is 0. With an 8-bit field, the range is from 0 to 254 mA. A
when
value of 255 (0xFF) is used to indicate a value of 255mA or greater.
TPLFE_SB_MAX_PWR This is the maximum current, in mA, required by this function when in the
standby condition. If this function does not support standby, this value
shall be 0x00. The method to place this function in the standby state and
the capabilities it has while in standby are vendor defined. This value is
valid for all voltages supported by this function. Note that this value is
valid only for standard power SDIO devices cards or high-power cards
EMPC is 0. With an 8-bit field, the range is from 0 to 254 mA. A
when
value of 255 (0xFF) is used to indicate a value of 255mA or greater.
TPLFE_MIN_BW This is the minimum data transfer bandwidth, in KB/sec, needed by this
function to successfully operate. If this function has no minimum
necessary bandwidth, these bytes shall be 0x0000.
TPLFE_OPT_BW This is the data transfer bandwidth, in KB/sec, needed by this function to
function at an optimum level. If this function has no optimum bandwidth,
these bytes shall be 0x0000.
TPLFE_ENABLE
TIMEOUT_VAL
(Added in SDIO Rev 1.1) This 16-bit value indicates the function’s
required time-out value for coming ready after being enabled. This
per-function value indicates the time a host should wait from asserting
IOEx until expecting the card to indicate ready by asserting IORx.
Different SDIO functions take different amounts of time to become ready
after being enabled due to different internal initialization requirements.
The required time-out limit is in 10mS steps, allowing a range of 0-655.35
56
Page 66

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
seconds. If the cards required no time-out, this field shall be set to
0x0000.
TPLFE_SP_AVG_PWR_3.3V This value is the same as that of TPLFE_OP_AVG_PWR.
TPLFE_SP_MAX_PWR_3.3V This value is the same as that of TPLFE_OP_MAX_PWR.
TPLFE_HP_AVG_PWR_3.3V This 16-bit value indicates the average current, in mA, required by this
function when operating in the Higher Current Mode (
This value indicates a current range from 1 to 65535 mA.
TPLFE_HP_MAX_PWR_3.3V This 16-bit value indicates the peak current, in mA, required by this
function when operating in the Higher Current Mode. This value indicates
a current range from 1 to 65535 mA.
TPLFE_LP_AVG_PWR_3.3V This 16-bit value indicates the average current, in mA, required by this
function when operating in the Lower Current Mode (
This value indicates a current range from 1 to 65535 mA
TPLFE_LP_MAX_PWR_3.3V This 16-bit value indicated the maximum (peak) current, in mA, required
by this function when operating in the Lower current mode (
EPS=1). This value indicates a current range from 1 to 65535 mA
EMPC=1 & EPS=0).
EMPC=1 & EPS=1).
EMPC=1 &
Table 16-9 TPLFID_FUNCTION Field Descriptions for Functions 1-7
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU FN_WUS
Table 16-10 TPLFE_FUNCTION_INFO Definition
The FN_WUS (Wake Up Support) bit signals the function’s support of wake-up when the function is placed into
a low power state and the SDCLK is stopped. The intent is to allow a SDIO card to be placed into a low power
condition and still signal the host of a wake-up event. If this bit is set to 1, then this function may be placed into
a low power state using some function standard or vendor defined method and the SDCLK can be stopped with
the power remaining applied to the card. Irrespective of the state of this bit, the host may stop the SDCLK as
allowed by the SD Physical Specification.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU CSA_NF CSA_WP
Table 16-11 TPLFE_CSA_PROPERTY Definition
The CSA_WP bit is used to write protect the CSA for this function, or identifies it as read-only. If this bit is set to
1, then the CSA of this function is either write protected or read-only. If this bit is clear, then the host may write
the CSA. Setting of this bit for R/W devices is handled in a vendor-defined method.
The CSA_NF bit is used to indicate to the host that the CSA area should not be reformatted. If the bit is set to 1,
the host may not format the CSA file structure. If this bit is cleared to 0, then the host may reformat the file
system of the CSA.
57
Page 67

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
16.7.5 CISTPL_SDIO_STD: Function is a Standard SDIO Function
This tuple code (0x91) has been reserved for use by SDIO devices that conform to the application specifications
for standard SDIO functions, as defined in those separate specifications. The exact format for this tuple can be
found in those specifications. The basic format only is provided here and the reader is directed to the
appropriate Application Specification for Standard SDIO Functions for more complete details:
Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0x00 TPL_CODE CISTPL_SDIO_STD (91h)
0x01 TPL_LINK Link to next tuple (2 ≤ n ≤ 255)
n is the number of bytes in the tuple body
0x02 TPLSDIO_STD_ID
0x03 TPLSDIO_STD_TYPE
0x04 ... (n+1) TPLSDIO_STD_DATA
If n = 2, TPLSDIO_STD_DATA does not exist.
Table 16-12 CISTPL_SDIO_STD: Tuple Reserved for SDIO Cards
The fields in this tuple have the following definition:
Field Description
TPLSDIO_STD_ID This 8-bit code identifies the Standard SDIO Function type for which this
tuple supplies additional information. The available codes can be found in
the I/O device interface code entry of the FBR (see 6.10)
TPLSDIO_STD_TYPE This 8-bit value identifies the format and type of data contained within the
body of this tuple. If this value is 0x00, then only 1 standard data structure
has been defined for this Standard SDIO Function. If this value is
non-zero, then this byte identifies which tuple data format is being used for
the data. This code is defined in the Application Specification for Standard
SDIO Functions.
TPLSDIO_STD_DATA The data component of this tuple (n-2 bytes). The format of this data
structure is defined in the Application Specification for Standard SDIO
Functions.
16.7.6 CISTPL_SDIO_EXT: Tuple Reserved for SDIO Cards
This tuple code (0x92) has been reserved for future use by SDIO cards. The actual format of the data has not
been established at this time. The basic format of this tuple is:
Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0x00 TPL_CODE CISTPL_SDIO_EXT (92h)
0x01 TPL_LINK Link to next tuple (0 ≤ n ≤ 255)
n is the number of bytes in the tuple body
0x02 ... (n+1) TPLSDIO_EXT_DATA The data component of this tuple (n bytes)
If n=0, TPLSDIO_EXT_DATA does not exist.
Table 16-13 CISTPL_SDIO_EXT: Tuple Reserved for SDIO Cards
58
Page 68

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Appendix A
(Normative)
A.1 SD and SPI Command List
Table A-14 and Table A-15 show the commands that are supported by SD memory and SDIO devices in both
SPI and SD modes. If a command is not identified as either mandatory or optional, then it is not supported by
that device.
Supported
Commands
CMD0 GO_IDLE_STATE Mandatory Mandatory Used to change from SD to SPI mode
CMD2
CMD3 SEND_RELATIVE_ADDR Mandatory Mandatory
CMD4 SET_DSR Optional DSR not supported by SDIO
CMD5 IO_SEND_OP_COND Mandatory
CMD6 SWITCH_FUNC Mandatory1 Mandatory1 Added in Part 1 v1.10
CMD7 SELECT/DESELECT_CARD Mandatory Mandatory
CMD9 SEND_CSD Mandatory CSD not supported by SDIO
CMD10 SEND_CID Mandatory CID not supported by SDIO
CMD12 STOP_TRANSMISSION Mandatory
CMD13 SEND_STATUS Mandatory Card Status includes only SDMEM information
CMD15 GO_INACTIVE_STATE Mandatory Mandatory
CMD16 SET_BLOCKLEN Mandatory
CMD17 READ_SINGLE_BLOCK Mandatory
CMD18 READ_MULTIPLE_BLOCK Mandatory
CMD24 WRITE_BLOCK Mandatory
CMD25 WRITE_MULTIPLE_BLOCK Mandatory
CMD27 PROGRAM_CSD Mandatory CSD not supported by SDIO
CMD28 SET_WRITE_PROT Optional
CMD29 CLR_WRITE_PROT Optional
CMD30 SEND_WRITE_PROT Optional
CMD32 ERASE_WR_BLK_START Mandatory
CMD33 ERASE_WR_BLK_END Mandatory
CMD38 ERASE Mandatory
CMD42 LOCK_UNLOCK Optional
CMD52 IO_RW_DIRECT Mandatory
CMD53 IO_RW_EXTENDED Mandatory Block mode is optional
CMD55
CMD56 GEN_CMD Mandatory
CMD6 SET_BUS_WIDTH Mandatory
CMD13 SD_STATUS Mandatory
CMD22 SEND_NUM_WR_BLOCKS Mandatory
CMD23 SET_WR_BLK_ERASE_COUNT Mandatory
CMD41 SD_APP_OP_COND Mandatory
CMD42 SET_CLR_CARD_DETECT Mandatory
CMD51 SEND_SCR Mandatory SCR not supported by SDIO
LL_SEND_CID Mandatory CID not supported by SDIO
PP_CMD Mandatory
Abbreviation
SDMEM
System
SDIO
System
Comments
Table A-14 SD Mode Command List
1
For Part 1 v1.10 or higher Memory or Combo Cards
59
Page 69

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Supported
Commands
CMD0 GO_IDLE_STATE Mandatory Mandatory Used to change from SD to SPI mode
CMD1 SEND_OP_COND Mandatory
CMD5 IO_SEND_OP_COND Mandatory
CMD6 SWITCH_FUNC Mandatory1 Mandatory1 Added in Part 1 v1.10
CMD9 SEND_CSD Mandatory CSD not supported by SDIO
CMD10 SEND_CID Mandatory CID not supported by SDIO
CMD12 STOP_TRANSMISSION Mandatory
CMD13 SEND_STATUS Mandatory Card Status includes only SDMEM information.
CMD16 SET_BLOCKLEN Mandatory
CMD17 READ_SINGLE_BLOCK Mandatory .
CMD18 READ_MULTIPLE_BLOCK Mandatory
CMD24 WRITE_BLOCK Mandatory
CMD25 WRITE_MULTIPLE_BLOCK Mandatory
CMD27 PROGRAM_CSD Mandatory CSD not supported by SDIO.
CMD28 SET_WRITE_PROT Optional
CMD29 CLR_WRITE_PROT Optional
CMD30 SEND_WRITE_PROT Optional
CMD32 ERASE_WR_BLK_START Mandatory
CMD33 ERASE_WR_BLK_END Mandatory
CMD38 ERASE Mandatory
CMD42 LOCK_UNLOCK Optional
CMD52 IO_RW_DIRECT Mandatory
CMD53 IO_RW_EXTENDED Mandatory Block mode is optional
CMD55
CMD56 GEN_CMD Mandatory
CMD58 READ_OCR Mandatory
CMD59 CRC_ON_OFF Mandatory Mandatory
CMD13 SD_STATUS Mandatory
CMD22 SEND_NUM_WR_BLOCKS Mandatory
CMD23 SET_WR_BLK_ERASE_COUNT Mandatory
CMD41 SD_APP_OP_COND Mandatory
CMD42 SET_CLR_CARD_DETECT Mandatory
CMD51 SEND_SCR Mandatory SCR includes only SD-MEM information.
PP_CMD Mandatory
Abbreviation
SDMEM
System
SDIO
System
Comments
Table A-15 SPI Mode Command List
1
For Part 1 v1.10 or higher Memory or Combo Cards
60
Page 70

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Appendix B
(Normative)
B.1 Normative References
The following documents are referenced by this specification.
This specification can apply to any released versions of below SD Specifications after Version 2.00.
1) SD Specifications Part 1 PHYSICAL LAYER SPECIFICATION
Version 2.00 May 9, 2006
2) SD Specifications Part 1 miniSD Card Addendum
Version 2.00 January 30, 2007
3) SD Specifications Part 2 FILE SYSTEM SPECIFICATION
Version 2.00 May 9, 2006
4) ISO/IEC9293:1994
Information technology - Volume and file structure of disk cartridges for information interchange
5) PC CARD STANDARD Release 8.1 2002
Volume 4 Metaformat Specification
61
Page 71

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Appendix C
C.1 Abbreviations and Terms
3C The original 3 companies that established the SDA and the SD card
specification
ACMD Application CommanD An additional set of commands created to support SD
specific requirements.
Block A number of bytes, basic data transfer unit
CCCR Common Card Control Registers
CD Connect/Disconnect
CIA Common Information Area
CID Card IDentification number register
CIS Card Information Structure
CLK Clock signal
CMD Command line or SD bus command (if extended CMDXX)
Combo Card A card that includes both SDIO and SD memory
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check
CS Chip or Card Select
CSA Code Storage Area
CSD Card Specific Data register
DAT[x] Data line where x is in the range of 0 to 3
DSR Driver Stage Register
ECC Error Correction Code
Embedded SDIO I/O or combo devices that are embedded in a host device that utilize the SDIO
electrical and command interface, but are not intended to be removed.
EMI Electro-Magnetic Interference
ESC External Signal Contacts
ESD Electro-Static Discharge
FAT File Allocation Table
FBR Function Basic Registers
FIFO First In-First Out buffer
Flash A type of multiple time programmable non volatile memory
Full-Size SDIO Card A SDIO card with physical dimensions based on SD Physical Specification
Version 1.01
Function An I/O device contained within an SDIO card
High-Power SDIO A SDIO device that requires up to 500 mA rather than the standard 200 mA
allowed for a Standard-Power SDIO device
hi-Z A three-state driver in the high-impedance state
Interrupt A signal from the SDIO device to the host signaling the need for attention
Interrupt Period The times that a card may generate an interrupt signal on the SD bus
Legacy Slot SD Slot that supports only the SD Physical Specification Version 1.01
62
Page 72

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
LOW, HIGH Binary interface states with defined assignment to a voltage level
MBIO Multi-Block I/O
miniSDIO Card A SDIO card based on the miniSD card form factor.
MMC MultiMedia Card
MSB, LSB The Most Significant Bit or Least Significant Bit
OCR Operation Conditions Register
PCMCIA Personal Computer Memory Card International Association
PnP Plug and Play a means to identify an SDIO device and optionally load
applications and/or drivers without user intervention
R/O Read Only
R/W Read or Write
RAW Read After Write
RCA Relative Card Address register
Resume Re-starting the temporarily halted data transfer
RFU Reserved for Future Use. Normally Read-Only and set to 0
ROM Read Only Memory
RWC Read Wait Control
SCR SD Configuration Register
SDA SD Association
SDCLK SD clock signal
SDIO SD Input/Output
SDIO aware A host designed to support the signals and protocol of SDIO devices
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface
Standard-Power SDIO A SDIO device that operates with 200 mA or less of current at all times.
Stuff bit(s) Filling bit(s) to ensure fixed length frames for commands and responses.
Suspend Temporarily halting the transfer of data
TBD To Be Determined (in the future)
Three-state driver A driver stage which has three output driver states: HIGH, LOW and high
impedance (which means that the interface does not have any influence on the
interface level)
Tuple Data blocks in a linked list or chain format
VDD + Power supply
VSS Power supply ground
W/O Write Only
WP Write Protect
63
Page 73

©Copyright 2000-2007 SD Card Association
SDIO Simplified Specification Version 2.00
Appendix D
(Informative)
Appendix D is not included in the Simplified Specification.
64
The Last Page
 Loading...
Loading...