
Original Operating Manual
Assembly and Operating Manual
GSM-P
Rotary gripping module with parallel gripper

Imprint
2
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
Imprint
Copyright:
This manual is protected by copyright. The author is SCHUNK GmbH & Co. KG. All rights reserved. Any reproduction, processing, distribution (making available to third parties),
translation or other usage - even excerpts - of the manual is especially prohibited and requires our written approval.
Technical changes:
We reserve the right to make alterations for the purpose of technical improvement.
Document number: 389104
Version: 07.00|26/04/2018|en
© SCHUNK GmbH & Co. KG
All rights reserved.
Dear Customer,
thank you for trusting our products and our family-owned company, the leading techno-
logy supplier of robots and production machines.
Our team is always available to answer any questions on this product and other solutions.
Ask us questions and challenge us. We will find a solution!
Best regards,
Your SCHUNK team
SCHUNK GmbH & Co. KG
Spann- und Greiftechnik
Bahnhofstr. 106 – 134
D-74348 Lauffen/Neckar
Tel. +49-7133-103-0
Fax +49-7133-103-2399
info@de.schunk.com
schunk.com

Table of contents
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
3
Table of contents
1 General.................................................................................................................... 5
1.1 About this manual ................................................................................................5
1.1.1 Presentation of Warning Labels ...............................................................5
1.1.2 Applicable documents ..............................................................................6
1.1.3 Sizes ..........................................................................................................6
1.1.4 Variants.....................................................................................................6
1.2 Warranty .............................................................................................................. 6
1.3 Scope of delivery ..................................................................................................6
1.4 Accessories ........................................................................................................... 6
2 Basic safety notes ................................................................................................... 7
2.1 Intended use......................................................................................................... 7
2.2 Not intended use.................................................................................................. 7
2.3 Constructional changes ........................................................................................7
2.4 Spare parts ........................................................................................................... 7
2.5 Environmental and operating conditions .............................................................7
2.6 Personnel qualification......................................................................................... 8
2.7 Personal protective equipment............................................................................ 8
2.8 Notes on safe operation....................................................................................... 9
2.9 Transport .............................................................................................................. 9
2.10 Malfunctions......................................................................................................... 9
2.11 Disposal .............................................................................................................. 10
2.12 Fundamental dangers......................................................................................... 10
2.12.1 Protection during handling and assembly ..............................................10
2.12.2 Protection during commissioning and operation ...................................11
2.12.3 Protection against dangerous movements.............................................11
2.12.4 Protection against electric shock............................................................12
2.13 Notes on particular risks..................................................................................... 12
3 Technical data.........................................................................................................15
4 Assembly ................................................................................................................16
4.1 Mechanical connection ...................................................................................... 16
4.2 Pneumatic connections ......................................................................................18
4.3 Mounting the sensor .......................................................................................... 20
4.3.1 Overview of sensors ...............................................................................20
4.3.2 Switch-off hysteresis...............................................................................20
4.3.3 Assembly and setup of the MMS-P 22....................................................21
4.3.4 Inductive monitoring via INW 40............................................................25
4.4 Mounting a customized construction................................................................. 30
4.5 Adjusting the end positions................................................................................ 31
5 Commissioning .......................................................................................................34

Table of contents
4
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
5.1 Setting the speed................................................................................................ 34
5.2 Adjustment of the shock absorber stroke ..........................................................35
5.3 Restart after long standstill ................................................................................36
6 Troubleshooting .....................................................................................................37
6.1 Product does not achieve the opening and closing times.................................. 37
6.2 Swivel movement is not executed immediately................................................. 37
7 Maintenance ..........................................................................................................38
7.1 Notes ..................................................................................................................38
7.2 Maintenance and care intervals .........................................................................38
7.3 Grease/greasing areas........................................................................................ 39
7.4 Screw tightening torques ................................................................................... 40
7.5 Disassembly/assembly of the unit in the basic modules.................................... 40
7.6 Disassembly/assembly of the gripping module.................................................. 41
7.6.1 Version without maintenance of gripping force unit GSM-P..................41
7.6.2 Version with maintenance of gripping force unit...................................42
7.6.3 Mounting orientation of the magnets, item 120....................................44
7.7 Disassembly/assembly of the DKM feed-through compact module (item 40) ..44
7.8 Replacing a shock absorber for S variants ..........................................................46
7.9 Replacing an elastomer for E variants ................................................................47
7.10 Disassembly/assembly of the FAN rotor drive (50) ............................................ 48
7.11 Servicing and assembling the product................................................................ 49
8 Drawings.................................................................................................................50
8.1 Assembly drawing of the basic module.............................................................. 50
8.2 Assembly drawing of the DKM and FAN modules ..............................................51
8.3 Assembly drawing of the gripping modules .......................................................52
9 Seal kit....................................................................................................................53
9.1 Sealing kit lists for the FAN 40 - 64 rotor drive...................................................53
9.2 Sealing kit lists for the P-32 - P-64 gripping modules .........................................54
10 Accessory pack rotational speed rotor FAN .............................................................56
11 Translation of original declaration of incorporation ................................................57
12 Annex to Declaration of Incorporation....................................................................58

General
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
5
1 General
1.1 About this manual
This manual contains important information for a safe and appropriate use of the product.
This manual is an integral part of the product and must be kept accessible for the personnel at all times.
Before starting work, the personnel must have read and understood this operating manual. Prerequisite for safe working is the
observance of all safety instructions in this manual.
Illustrations in this manual are provided for basic understanding
and may differ from the actual product design.
In addition to these instructions, the documents listed under Ap-
plicable documents [}6] are applicable.
1.1.1 Presentation of Warning Labels
To make risks clear, the following signal words and symbols are
used for safety notes.
DANGER
Danger for persons!
Non-observance will inevitably cause irreversible injury or death.
WARNING
Dangers for persons!
Non-observance can lead to irreversible injury and even death.
CAUTION
Dangers for persons!
Non-observance can cause minor injuries.
NOTICE
Material damage!
Information about avoiding material damage.

General
6
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
1.1.2 Applicable documents
• General terms of business*
• Catalog data sheet of the purchased product *
• Assembly and operating manuals of the accessories *
The documents marked with an asterisk (*) can be downloaded on
our homepage schunk.com
1.1.3 Sizes
This operating manual applies to the following sizes:
• GSM-P 32
• GSM-P 40
• GSM-P 50
• GSM-P 64
1.1.4 Variants
This operating manual applies to the following variations:
• GSM-P without gripping force maintenance
• GSM-P with gripping force maintenance "O.D. gripping" (AS)
• GSM-P with gripping force maintenance "I.D. gripping" (IS)
1.2 Warranty
If the product is used as intended, the warranty is valid for 24
months from the ex-works delivery date under the following conditions:
• Observe the specified maintenance and lubrication intervals
• Observe the ambient conditions and operating conditions
Parts touching the workpiece and wear parts are not included in
the warranty.
1.3 Scope of delivery
The scope of delivery includes
• Rotary gripping module with parallel gripper GSM-P in the version ordered
• Assembly and Operating Manual
• Accessory pack
1.4 Accessories
A wide range of accessories are available for this product
For information regarding which accessory articles can be used
with the corresponding product variants, see catalog data sheet.

Basic safety notes
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
7
2 Basic safety notes
2.1 Intended use
The product was designed for swiveling, gripping and time-limited
holding of workpieces or other objects.
The functions "actuate gripper" and "swivel" must be executed alternately.
• The product may only be used within the scope of its technical
data, Technical data [}15].
• The product is intended for installation in a machine/system.
The applicable guidelines must be observed and complied with.
• The product is intended for industrial and industry-oriented use.
• Appropriate use of the product includes compliance with all instructions in this manual.
2.2 Not intended use
It is not intended use if the product is used, for example, as a
pressing tool, stamping tool, lifting gear, guide for tools, cutting
tool, clamping device or a drilling tool.
• Any utilization that exceeds or differs from the appropriate use
is regarded as misuse.
2.3 Constructional changes
Implementation of structural changes
By conversions, changes, and reworking, e.g. additional threads,
holes, or safety devices can impair the functioning or safety of the
product or damage it.
• Structural changes should only be made with the written approval of SCHUNK.
2.4 Spare parts
Use of unauthorized spare parts
Using unauthorized spare parts can endanger personnel and damage the product or cause it to malfunction.
• Use only original spare parts or spares authorized by SCHUNK.
2.5 Environmental and operating conditions
Required ambient conditions and operating conditions
Incorrect ambient and operating conditions can make the product
unsafe, leading to the risk of serious injuries, considerable material
damage and/or a significant reduction to the product's life span.
See also Environmental and operating conditions [}7].
• Make sure that the product and the top jaws are a sufficient
size for the application.
• Observe maintenance and lubrication intervals, Maintenance
and care intervals [}38].

Basic safety notes
8
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
2.6 Personnel qualification
Inadequate qualifications of the personnel
If the personnel working with the product is not sufficiently qualified, the result may be serious injuries and significant property
damage.
• All work may only be performed by qualified personnel.
• Before working with the product, the personnel must have read
and understood the complete assembly and operating manual.
• Observe the national safety regulations and rules and general
safety instructions.
The following personal qualifications are necessary for the various
activities related to the product:
Trained electrician
Due to their technical training, knowledge and experience, trained
electricians are able to work on electrical systems, recognize and
avoid possible dangers and know the relevant standards and regulations.
Qualified personnel
Due to its technical training, knowledge and experience, qualified
personnel is able to perform the delegated tasks, recognize and
avoid possible dangers and knows the relevant standards and regulations.
Instructed person
Instructed persons were instructed by the operator about the delegated tasks and possible dangers due to improper behaviour.
Service personnel of
the manufacturer
Due to its technical training, knowledge and experience, service
personnel of the manufacturer is able to perform the delegated
tasks and to recognize and avoid possible dangers.
2.7 Personal protective equipment
Use of personal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment serves to protect staff against
danger which may interfere with their health or safety at work.
• When working on and with the product, observe the occupational health and safety regulations and wear the required personal protective equipment.
• Observe the valid safety and accident prevention regulations.
• Wear protective gloves to guard against sharp edges and
corners or rough surfaces.
• Wear heat-resistant protective gloves when handling hot surfaces.
• Wear protective gloves and safety goggles when handling hazardous substances.
• Wear close-fitting protective clothing and also wear long hair in
a hairnet when dealing with moving components.

Basic safety notes
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
9
2.8 Notes on safe operation
Incorrect handling of the personnel
Incorrect handling and assembly may impair the product's safety
and cause serious injuries and considerable material damage.
• Avoid any manner of working that may interfere with the function and operational safety of the product.
• Use the product as intended.
• Observe the safety notes and assembly instructions.
• Do not expose the product to any corrosive media. This does
not apply to products that are designed for special environments.
• Eliminate any malfunction immediately.
• Observe the care and maintenance instructions.
• Observe the current safety, accident prevention and environmental protection regulations regarding the product's application field.
2.9 Transport
Handling during transport
Incorrect handling during transport may impair the product's
safety and cause serious injuries and considerable material damage.
• When handling heavy weights, use lifting equipment to lift the
product and transport it by appropriate means.
• Secure the product against falling during transportation and
handling.
• Stand clear of suspended loads.
2.10 Malfunctions
Behavior in case of malfunctions
• Immediately remove the product from operation and report the
malfunction to the responsible departments/persons.
• Order appropriately trained personnel to rectify the malfunction.
• Do not recommission the product until the malfunction has
been rectified.
• Test the product after a malfunction to establish whether it still
functions properly and no increased risks have arisen.

Basic safety notes
10
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
2.11 Disposal
Handling of disposal
The incorrect handling of disposal may impair the product's safety
and cause serious injuries as well as considerable material and environmental harm.
• Follow local regulations on dispatching product components for
recycling or proper disposal.
2.12 Fundamental dangers
General
• Observe safety distances.
• Never deactivate safety devices.
• Before commissioning the product, take appropriate protective
measures to secure the danger zone.
• Disconnect power sources before installation, modification,
maintenance, or calibration. Ensure that no residual energy remains in the system.
• If the energy supply is connected, do not move any parts by
hand.
• Do not reach into the open mechanism or movement area of
the product during operation.
2.12.1 Protection during handling and assembly
Incorrect handling and assembly
Incorrect handling and assembly may impair the product's safety
and cause serious injuries and considerable material damage.
• Have all work carried out by appropriately qualified personnel.
• For all work, secure the product against accidental operation.
• Observe the relevant accident prevention rules.
• Use suitable assembly and transport equipment and take precautions to prevent jamming and crushing.
Incorrect lifting of loads
Falling loads may cause serious injuries and even death.
• Stand clear of suspended loads and do not step into their swiveling range.
• Never move loads without supervision.
• Do not leave suspended loads unattended.

Basic safety notes
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
11
2.12.2 Protection during commissioning and operation
Falling or violently ejected components
Falling and violently ejected components can cause serious injuries
and even death.
• Take appropriate protective measures to secure the danger
zone.
• Never step into the danger zone during operation.
2.12.3 Protection against dangerous movements
Unexpected movements
Residual energy in the system may cause serious injuries while
working with the product.
• Switch off the energy supply, ensure that no residual energy remains and secure against inadvertent reactivation.
• Never rely solely on the response of the monitoring function to
avert danger. Until the installed monitors become effective, it
must be assumed that the drive movement is faulty, with its action being dependent on the control unit and the current operating condition of the drive. Perform maintenance work, modifications, and attachments outside the danger zone defined by
the movement range.
• To avoid accidents and/or material damage, human access to
the movement range of the machine must be restricted. Limit/
prevent accidental access for people in this area due through
technical safety measures. The protective cover and protective
fence must be rigid enough to withstand the maximum possible
movement energy. EMERGENCY STOP switches must be easily
and quickly accessible. Before starting up the machine or automated system, check that the EMERGENCY STOP system is
working. Prevent operation of the machine if this protective
equipment does not function correctly.

Basic safety notes
12
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
2.12.4 Protection against electric shock
Possible electrostatic energy
Components or assembly groups may become electrostatically
charged. When the electrostatic charge is touched, the discharge
may trigger a shock reaction leading to injuries.
• The operator must ensure that all components and assembly
groups are included in the local potential equalisation in accordance with the applicable regulations.
• While paying attention to the actual conditions of the working
environment, the potential equalisation must be implemented
by a specialist electrician according to the applicable regulations.
• The effectiveness of the potential equalisation must be verified
by executing regular safety measurements.
2.13 Notes on particular risks
DANGER
Risk of fatal injury from suspended loads!
Falling loads can cause serious injuries and even death.
• Stand clear of suspended loads and do not step within their
swiveling range.
• Never move loads without supervision.
• Do not leave suspended loads unattended.
• Wear suitable protective equipment.
WARNING
Risk of injury from objects falling and being ejected!
Falling and ejected objects during operation can lead to serious
injury or death.
• Take appropriate protective measures to secure the danger
zone.
WARNING
Risk of injury due to unexpected movements!
If the power supply is switched on or residual energy remains in
the system, components can move unexpectedly and cause serious injuries.
• Before starting any work on the product: Switch off the power
supply and secure against restarting.
• Ensure that no residual energy remains in the system.

Basic safety notes
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
13
WARNING
Risk of injury from crushing and impacts!
Serious injury could occur during the base jaw procedure and
when breaking or loosening the gripper fingers.
• Wear suitable protective equipment.
• Do not reach into the open mechanism or the movement area
of the product.
WARNING
Risk of injury due to spring forces!
Parts are under spring tension on products which clamp using
spring force or which have gripping force maintenance. While disassembling components can move unexpectedly and cause serious injuries.
• Disassemble the product cautiously.
• Make sure that no residual energy remains in the system.
WARNING
Risk of injury from objects falling during energy supply failure
Products with a mechanical gripping force maintenance can, during energy supply failure, still move independently in the direction specified by the mechanical gripping force maintenance.
• Secure the end positions of the product with SCHUNK SDV-P
pressure maintenance valves.
WARNING
Danger of injury due to uncontrolled movements!
Due to incorrect control and incorrect operation, loss of workpieces and uncontrolled movement of the product may occur and
can cause serious injuries.
• Take checks in the user's program.
• The danger zone must be secured by suitable measures.
WARNING
Risk of injury from rotating components!
In the case of swivel units or rotary tables with a rotary drive, serious injuries can be caused by rotating components.
• Take appropriate protective measures to secure the danger
zone.

Basic safety notes
14
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
WARNING
Risk of injury by parts becoming detached and destruction of
the rotary actuator if the shock absorbers are defective.
Avoidance measures: Regular visual inspections of individual
components for wear and damage.

Technical data
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
15
3 Technical data
Designation GSM-P 32 GSM-P 40 GSM-P 50 GSM-P 64
IP rating 30
Noise emission [dB(A)] ≤ 70
Pressure medium Compressed air, compressed air quality according
to ISO 8573-1:7 4 4
Nominal working pressure [bar] 6
Min. pressure [bar] for gripping
without gripping force maintenance
with gripping force maintenance
2
4
Min. pressure [bar] for swiveling 3.5 4 3
Max. pressure [bar] 6.5
More technical data is included in the catalog data sheet.
Whichever is the latest version.

Assembly
16
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
4 Assembly
4.1 Mechanical connection
Mounting the GSM on the side and base side
Item GSM - SFL basic size 40 64
1A
1B
1C
Centering sleeve for lateral mounting of the unit and
fitting depth in the mounting plate
Ø8
2.5 deep
Item 206
Ø10
3 deep
Item 205
2 Centering sleeve for mounting the unit on the base side
and fitting depth in the mounting plate
Ø6
2.5 deep
Item 205
Ø10
3 deep
Item 205
3A
3B
3C
Thread diameter for screwing through for mounting
the unit at the side
M4
Item 232
M5
Item 232
4A
4B
4C
Thread diameter and max. depth of engagement for
screw connection for lateral mounting
M5
19 deep
Item 231
M6
25 deep
Item 231
5 Thread diameter for screwing through for mounting
the unit on the base side
M3 M5
6 Thread diameter and maximum depth of engagement
for screw connection for mounting on the base side
M4
8 deep
M6
11 deep
** To ensure the function of the sensors, the A2 screws from the
accessory pack are to be used.
For process-reliable monitoring, adapter plates should be
made of non-ferromagnetic material.

Assembly
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
17
Mounting the Unit Mounting the unit on the base side
(with adapter plate similar to A, B or C; see "Mounting the GSM at
the side and on the base side")
The assembly of the unit can be carried out from the side of the
unit using the screws (6).
There are threads in the housings for mounting from the customer-specific opposite side (screws 5 and 6 are not included in
the scope of delivery).
Centering sleeves (2) are to be used for the secure transmission of
shearing forces and positioning of the unit.
Mounting the unit at the side
(with adapter plate similar to A, B or C)
The assembly of the unit can be carried out from the side of the unit
using the A2 screws included in the accessory pack (3A, 3B or 3C).
For mounting from the customer-specific opposite side, there are
threads in the housings (the A2 screws (4A, 4B or 4C) are included
in the accessories pack).
Centering sleeves (1A, 1B or 1C) are to be used for the secure
transmission of shearing forces and positioning of the unit.
NOTE
In order to guarantee process reliability for monitoring with magnetic switches, most especially the adapter plates and the attachments located near the unit should be made of non-ferromagnetic
material. Otherwise, monitoring with magnetic sensors could be
impaired considerably Accessories [}6].
NOTE
When monitoring with magnetic switches, a minimum distance of
10 mm is to be observed between the units in the event of the assembly of several units next to each other Accessories [}6].

Assembly
18
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
4.2 Pneumatic connections
WARNING
Risk of injury during connection!
• Switch off the energy supply.
NOTICE
The central air unit must be equipped with a maintenance unit
that is located as near as possible to the consumer.
NOTICE
If the end positions of the stroke and swivel movements are not
impact-free and bounce-free, the respective movements must
be adjusted with the exhaust throttle.
NOTICE
Observe the requirements for the air supply
Technical data [}15].
Pneumatic connections

Assembly
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
19
"A" - "D" are main connections, "a" - "d" are direct connections
Connection Function
Hose connection A Swivel toward 180° or 90°
position
Hose-free direct connection a
Hose connection B Swivel toward 0° position
Hose-free direct connection b
Hose connection C Move gripper into »OPEN«
position
Hose-free direct connection c
Hose connection D Move gripper into »CLOSED«
position
Hose-free direct connection d
Connections “C” and “D” for the modules with a base cross section
of 25x25 are slightly offset from center
If direct connections "a" – "d" are used, use the locking screws included in the accessory pack for the corresponding main connections "A" – "D".
If air connections "a" – "d" are used, ensure sufficient throttling,
which can be set by means of exhaust air throttling. To do this, the
throttle reductions for the main connections, which are designed
for a medium load, can be attached to the adapter plate, for example.
• Open only the air connections that are needed.
• Close unused main air connections using the screw plugs from
the enclosed pack.
• For a hose-free direction connection, use the O-rings from the
enclosed pack.

Assembly
20
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
4.3 Mounting the sensor
NOTE
Observe the assembly and operating manual of the sensor for
mounting and connecting.
The product is prepared for the use of sensors.
• For the exact type designations of suitable sensors, please see
catalog datasheet and Link Übersicht Sensoren.
• For technical data for the suitable sensors, see assembly and
operating manual and catalog datasheet.
– The assembly and operating manual and catalog datasheet
are included in the scope of delivery for the sensors and are
available at schunk.com.
• Information on handling sensors is available at schunk.com or
from SCHUNK contact persons.
4.3.1 Overview of sensors
Designation GSM-P
22 32 42 52
Magnetic switch MMS 30 X X X X
Inductive proximity switch IN 80 X X X X
Flexible position sensor FPS-S 13 X X X
4.3.2 Switch-off hysteresis
Sensors MMS 22, MMS-P 22, MMS 22-PI1 and MMS 22-PI2
The smallest detectable difference in stroke is defined in the following table:
The smallest detectable difference in stroke based on the nominal stroke
For grippers with X mm
nominal stroke per jaw
Min. query range per jaw/
min. queried stroke difference per jaw
X ≤ 5 mm 30% of the nominal stroke per jaw
X > 5 mm to X ≤ 10 mm 20% of the nominal stroke per jaw
X > 10 mm 10% of the nominal stroke per jaw
Example: Product with 7 mm nominal stroke per jaw
7 mm * 20 % = 1.4 mm

Assembly
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
21
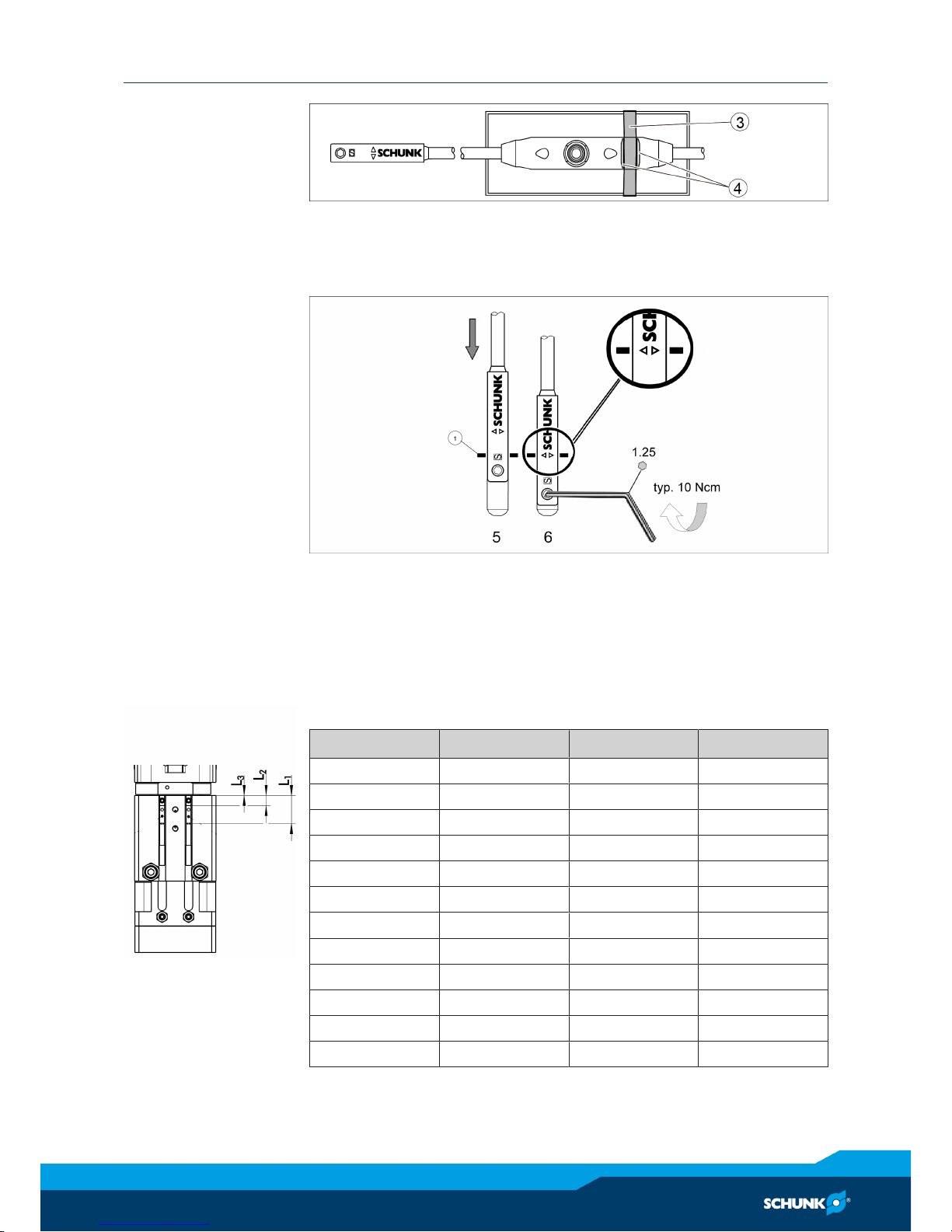
4.3.3 Assembly and setup of the MMS-P 22
Position and installation of the MMS-P magnetic switches
1 Sensor MMS-P
(left groove)
Monitoring gripper position 1 and gripper
position 2 in the left rotating angle end position (signals SGL1 and SGL2)
2 Sensor MMS-P
(right groove)
Monitoring gripper position 1 and gripper
position 2 in the right rotating angle end
position (signals SGR1 and SGR2)
3 Stop for MMS-P Determining the clamping position of the
MMS-P sensor
Monitoring GSM locations/positions/end positions:
SGL1: left rotating angle end position, gripper position 1
SGL2: left rotating angle end position, gripper position 2
SGR1: right rotating angle end position, gripper position 1
SGR2: right rotating angle end position, gripper position 2
The monitoring of swiveling and grasping movements with an
magnetic switch can yield reliable results only in the ranges of 0°
±3° and 180°±3° or 0°±3° and 90°±3°.

Assembly
22
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
Swivel range
Adjustment range of start angle
Adjustment range of end angle
Switching range of sensor
end angle
start angle
start angle
end angle
Swivel range
Adjustment range of start angle
Adjustment range of end angle
Switching range of sensor
Rotating angle setting and monitoring range GSM
By each of the two sensors MMS-P, 2 gripper positions can be
monitored. If the gripper is in a third position, the rotation angle
end position can only be monitored by additional sensors.
• The left rotating angle end position is always reached, when a
swichting point of the sensor of the left groove (SGL1 or SGL2) is
active.
• The right rotating angle end position is always reached, when a
swichting point of the sensor of the right groove (SGR1 or SGR2)
is active.
The sequence of the swivel and closing movements (process sequence) defined during the teach process must also be followed
during operation. Otherwise, incorrect sensor signals may be outputted.
With many GSM variants, it is possible to combine magnetic switch
monitoring with inductive monitoring, Inductive monitoring via
INW 40 [}25].
• If you require further information on sensor operation, contact
your SCHUNK contact person or download information from our
homepage.
• Technical data for the sensors can be found in the data sheets
(included in the scope of delivery).
Assembly
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
23
Mounting of the
sensor
Ø To relieve the cable, the electronics have to be fixed in place us-
ing cable ties (7). There are ribs (6) in place on the electronics
for mounting purposes.
Ø Orient the sensor towards the mark on the housing (1) of the
pneumatic module
OR
Ø Insert it up to the clamping stop (many SCHUNK products are
prepared for this)
Ø Fix the sensor with the Allen key.
Should there be no mark on the housing, insert the magnetic switch according to dimension l2 or according to dimension l1 and then fix it with an Allen key.
Installation dimensions for MMS-P
GSM Type Dimension l1 Dimension l2 Dimension l3
GSM-P-32 8.9 0 GSM-P-32-AS 8.9 0 GSM-P-32-IS 20.05 11.15 6.15
GSM-P-40 13.9 5 0
GSM-P-40-AS 13.9 5 0
GSM-P-40-IS 31.5 22.6 17.6
GSM-P-50 16.9 8 3
GSM-P-50-AS 16.9 8 3
GSM-P-50-IS 36.7 27.8 23
GSM-P-64 13.9 5 0
GSM-P-64-AS 13.9 5 0
GSM-P-64-IS 26.25 16.35 11.35

Assembly
24
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
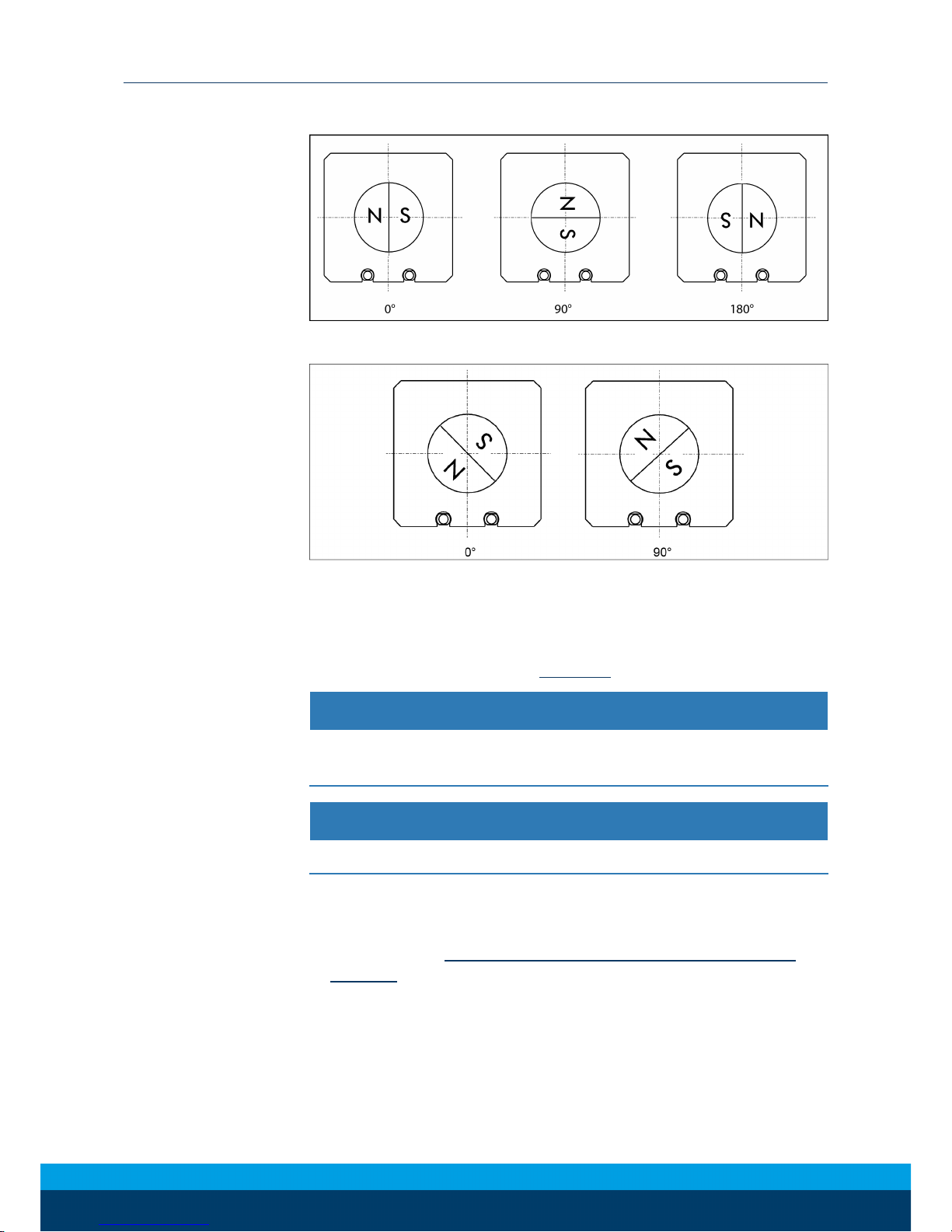
Setting up the switching points
Ø Press the Teach button (4) for 2 seconds.
✓ After 2 seconds LED 1 (3) is flashing.
Ø Move the gripper into position 1 (e.g. "open").
Ø Press the Teach-Button (4) briefly.
✓ LED 1 (3) lights up and LED 2 (5) is flashing.
Ø Move the gripper into position 2 (e.g. „-2mm“).
✓ LED 1 (3) should turn out as soon as the switching point 1 is
left.
Ø Press the Teach-Button (4) briefly.
✓ LED 2 (5) lights up.
✔ The switching points are set.
Adjusting the
hysteresis
The hysteresis to both switching points will be adjusted automatically corresponding to the characteristics of the magnetic field.
The user can set the switching and trigging points of each position
a little bit closer than for the automatic mode. The trigging point is
closer to the switching point. At the same time the susceptibility to
trouble and damage increases. In the mode of the lowest hysteresis, an error signal (such as jitter or untimely switch off) can be
avoided, if the sensor is protected against all types of disturbances
(i.e. by shielding). Frequent types of disturbances are change in
temperature and electro-magnetic influences.
Within the closest fine-teach mode, SCHUNK cannot guarantee
EMC-compatibility any more.
The hysteresis adjustment is used for the manual adjustment of
the switching points (if necessary).
In case that the hysteresis automatically determined by the sensor
should be too high or too low after “the adjustment of the switching points”, you may correct the value as follows.
The sensor avoids a too small hysteresis during hysteresis adjustment.

Assembly
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
25
4.3.4 Inductive monitoring via INW 40
Mounting kits for INW 40
GSM-P Mounting kit for INW 40 ID number
AS-GSM-P-32, mounting kit for INW 40 0304934
AS-GSM-P-40, mounting kit for INW 40 0304935
AS-GSM-P-50, mounting kit for INW 40 0304936
AS-GSM-P-64, mounting kit for INW 40 0304937
NOTE
The monitoring of swiveling and grasping movements with an inductive proximity switch can yield reliable results only in the
ranges of 0°±3° and 180°±3° or 0°±3° and 90°±3°.
Swivel range
Adjustment range of start angle
Adjustment range of end angle
Switching range of sensor
end angle
start angle
start angle
end angle
Swivel range
Adjustment range of start angle
Adjustment range of end angle
Switching range of sensor
Rotating angle setting and monitoring range

Assembly
26
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
Schematic diagram of
inductive monitoring
with INW 40 for GSM
for 090 variants
Schematic diagram of inductive monitoring with INW 40 of GSM
Dampened sensor
[1] Rotating angle end position in counterclockwise direction with opened gripper
[2] Rotating angle end position in counterclockwise direction with closed gripper
[3] Rotating angle end position in clockwise direction with opened gripper
[4] Rotating angle end position in clockwise direction with closed gripper

Assembly
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
27
Schematic diagram of
inductive monitoring
with INW 40 for GSM
for 180 variants
Schematic diagram of inductive monitoring with INW 40 of GSM
Dampened sensor
[1] Rotating angle end position in counterclockwise direction with opened gripper
[2] Rotating angle end position in counterclockwise direction with closed gripper
[3] Rotating angle end position in clockwise direction with opened gripper
[4] Rotating angle end position in clockwise direction with closed gripper

Assembly
28
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
NOTE
One of the two inductive proximity switches for the "gripping"
monitoring is briefly crossed over during swiveling action by
"second switching lug gripping".
NOTICE
The maximum tightening torque for the clamping screws (301
and/or 303) at the holder (300) is 125 Ncm. Remove bracket (8).
NOTICE
Risk of damage due to incorrect adjustment of the proximity
switches!
Disconnect the energy supply before installing or adjusting the inductive proximity switches.
Installation steps for assembly of the mounting kit and mounting
of the proximity switch
Ø Mount the plastic holders (300) onto the designated spaces
with the screws (301 and/or 303). Depending on the mounting
kit, offset pieces (94) may have to be installed.
Ø Remove the retaining plate (8) and the distance plate (7).
Mount switching lug(s) grippers (91+92) onto the base jaw
which lies in the 0° swivel position exactly above the 0° swivel
position.
Ø Mount the inductive proximity switch INW 40 into the plastic
holders (300).
It is advised to set the switching distance of all four proximity
switches under the swiveling switching lug (93).
By gently applying the clamping screws (301 or 303), the proximity switch can be lightly clamped. A feeler gauge tape with a
thickness of 0.5 mm can be very helpful as well, because the
proximity switch can thus be installed on "blocked/stop", which
prevents a collision during a swiveling movement.
Ø Move the unit with the energy supply switched off in the re-
spective rotating angle end position and set two of the proximity switches on the swiveling switching lug (93) and tighten the
clamping screws (301 or 303).
CAUTION: observe permissible tightening torque.
When setting the switching distances, make sure that none of
the switching flags can collide with a proximity switch.
Ø Check the function of each proximity switch and check the out-
put signals of the proximity switch by moving to different gripper positions in the two rotating angle end positions with connected energy supply.

Assembly
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
29
Ø Should one or more proximity switches not send a signal, repeat
step 3 of the setting instructions and slightly reduce the switching distance until the desired function is achieved.
Ø Should a signal be received "too early", this can be corrected by
increasing the switching distance, which, however, also affects
the sensitivity of the switching function.
Assembly of GSM
with inductive monitoring with INW 40
Assembly of GSM 090 variants with inductive monitoring
* Only included in the mounting kit for P-50
** In P-32, item 92 is identical to item 91
*** Item 112 is not a component of the mounting kit, it
is part of the gripping module

Assembly
30
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
Assembly of GSM 180 variants with inductive monitoring
* Only included in the mounting kit for P-50
** In P-32, item 92 is identical to item 91
*** Item 112 is not a component of the mounting kit, it
is part of the gripping module
4.4 Mounting a customized construction
NOTICE
Damage to the unit during assembly!
When inserting the cylindrical pins or centering sleeves, the unit
must not be subjected to any impact.
Mounting of a customized construction to the gripper fingers
GSM-P
It is recommended to use the width of the gripper finger which is
designed as the fit size for the centering of the customized top
jaws. It is also recommended to use the upper contact surface of
the gripper finger to support the customized top jaws.
No mounting screws are included in the scope of delivery.

Assembly
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
31
4.5 Adjusting the end positions
Position of the item numbers Drawings [}50]
Adjusting the end position for elastomer cushioning:
Ø Connect connections A and B to the compressed air supply.
Ø Load connections A and B alternately and allow the unit to
swivel.
Ø Load connection B, the rotary actuator reaches the limit posi-
tion by turning counterclockwise.
Ø Place the unit on a measuring table on its side, with the air con-
nections facing up.
Ø Undo the lock nut (124) and twist the stop (83). To increase the
area of the angle of traverse, unscrew the stop, but only to the
max. projection dimension B. (For the projection dimensions A and
B see following table "Total rotating angle range").
Once you have set the angle of traverse, tighten the lock nut (124).
Ø Load connections A and B alternately and allow the unit to
swivel.
Ø Repeatedly check the angle of traverse that you set. Repeat
steps 5 and 6 until the desired position is reached reliably, even
after swiveling several times.
Ø To set the second limit position, proceed as for steps 5 to 7, but
this time load connection A.
Stepless angular adjustment with balls
For angles between “0°” and “180°”, or “0°” and “90°” place additional steel balls, (108) , in the ball guideway. The number of steel
balls needed for this and the permissible minimum and maximum
projections for the stops are given in the following table "Total rotating angle range".

Assembly
32
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
Adjusting the end position for hydraulic cushioning using shock
absorbers:
Proceed as for steps 1 to 8 of the elastomer cushioning, but instead of the stops (83) - use shock absorbers (120) and instead of
the lock nut (124) - use the shock absorber nut (121).
For angles between “0°” and “180°”, or “0°” and “90°” place additional steel balls (108), in the ball guideway. The number of steel
balls needed for this and the permissible minimum and maximum
projections (for the shock absorbers for S-versions) /(stops for Eversions) are given in table "Total rotating angle range"
The insertion of the balls is described in the following chapters:
• for S-Versions Replacing a shock absorber for S variants [}46]
• for E-Versions Replacing an elastomer for E variants [}47]
NOTICE
The permissible minimum and maximum projections are to be
strictly observed; if a rotating angle should not be achieved by
adjusting the shock absorbers (120) or stops (83), it must be
achieved by inserting or removing steel balls (108). There must,
however, be at least one ball inserted on each side.
Total rotating angle range
Basic size 40 Basic size 64
Standard
total rotating angle range
90° or 180°
Minimum rotating angle range Can be reduced down to 0° for any position within
the total rotating angle range of the standard unit
Angle limitation per ball [°] 19 13.5
Min. projection A [mm], E variants 3 4.5
Max. projection B [mm], E variants 7 9.5
Min. projection A [mm], S variants 19.5 28
Max. projection B [mm], S variants 23.5 33

Assembly
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
33
Swivel range
Adjustment range of start angle
Adjustment range of end angle
Switching range of sensor
end angle
start angle
start angle
end angle
Swivel range
Adjustment range of start angle
Adjustment range of end angle
Switching range of sensor
Rotating angle setting and monitoring range with GSM-P
Total rotating angle range

Commissioning
34
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
5 Commissioning
NOTICE
Damage to the rotary module possible!
The rotary module can be damaged if it arrives too abruptly in
the end position.
• The rotary motion must reach the end position without jerk or
bounce.
• Therefore flow control valves and shock absorbers must be
used, Setting the speed [}34] and Adjustment of the shock
absorber stroke [}35].
• Please observe the information in the catalog pages.
5.1 Setting the speed
NOTICE
Risk of damage to the product!
If the end position is approached too hard, the product may be
damaged.
• Adjust exhaust throttle valve and shock absorber so that the
movement is braked smoothly.
Ø Close exhaust throttle valve completely.
Ø Open exhaust throttle valve until the product starts to move.
Ø Continue to open the exhaust throttle valve incrementally until
the movement decelerates smoothly.
✓ If the speed is too low, the product will brake too soon and
the end position will be reached too slowly.
✓ If the speed is too high, the product will impact against the
end position and the shock absorber will be overloaded.

Commissioning
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
35
NOTE
A smooth motion may also be too slow in many use-cases.
Further settings can be made via the shock absorbers, Adjustment
of the shock absorber stroke [}35].
5.2 Adjustment of the shock absorber stroke
NOTE
When received from the factory, the unit is set to utilize the maximum shock absorber stroke.
Movement
Target position
End position
Target time
Time T
Dampening
The shock absorber stroke is too long and the end position is
reached too slowly.
Movement
Target position
End position
Target time
Time T
Dampening
The shock absorber stroke is too short and the unit arrives in the
end position too abruptly.
Movement
Target position
End position
Target time
Time T
Dampening
Optimal shock absorber stroke.

Commissioning
36
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
5.3 Restart after long standstill
During a longer standstill no compressed air must be allowed to be
present at the gripper.
If problems occur during restart, see Swivel movement is not ex-
ecuted immediately [}37].

Troubleshooting
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
37
6 Troubleshooting
6.1 Product does not achieve the opening and closing times
Possible cause Corrective action
Compressed air lines are not installed optimally.
If present: Open the flow control couplings
on the product to the maximum that the
movement of the jaws occurs without bouncing and hitting.
Check compressed air lines.
Inner diameters of compressed air lines are
of sufficient size in relation to compressed
air consumption.
Keep compressed air lines between the
product and directional control valve as
short as possible.
Flow rate of valve is sufficiently large relative to the compressed air consumption.
NOTICE!The throttle check valve must not
be removed, even if the product has not
reached the opening and closing times.
If you still cannot achieve the open and close
times mentioned in the latest catalog, we recommend the use of quick-air-vent-valves
directly at the product.
Loading too large. Check permissible weight and length of the
gripper fingers.
6.2 Swivel movement is not executed immediately
Possible cause Corrective action
Product stood still for a longer time. • Vent piston chamber
• Open and close gripper 1x
• Depressurise gripper

Maintenance
38
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
7 Maintenance
7.1 Notes
Original spare parts
Use only original spare parts of SCHUNK when replacing spare and
wear parts.
Replacement of the housing and base jaws
The cover housing (35), fingers (3), and needle rollers (13, 14, 15)
are adapted to each other. To replace these parts, send the complete module together with a repair order to SCHUNK or order the
housing with base jaws as a set.
NOTICE
The needle rollers are suitable only for this gripper and cannot
be replaced with needle rollers belonging to another gripper of
the same type and size.
7.2 Maintenance and care intervals
NOTICE
Material damage due to hardening lubricants!
Lubricants harden more quickly at temperatures above 60°C,
leading to possible product damage.
• Reduce the lubricant intervals accordingly.
Maintenance and care intervals GSM-P
Size GSM-P 32 - 64
Interval [Mio. cycles] 2
Maintenance and care intervals DKM
Size DKM 40 / 64
Interval [Mio. cycles] 2
Maintenance and care intervals FAN
Size FAN 40 / 64
Interval [Mio. cycles] 2

Maintenance
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
39
7.3 Grease/greasing areas
Position of the item numbers Drawings [}50]
Types of grease used
Designation PGM DKM FAN
Renolit HLT 2
(not on surfaces that assume a function on the
rotary feed-through)
Item 100
Item 101
Item 102
Item 42
Item 43
Item 44
Item 46
Item 109
Item 131
GP303-P - - Isoflex-Topas NCA 52 (MPG grease) Item 3
Item 4
Item 15
Item 35
Item 85
Item 122
-
Mixture of Interflon Fin assembly grease for Interflon Fin Lupe EP (mass ratio 1:1)
Item 103 Item 11
Item 82
Item 42
Item 43
Item 44
Item 46 *
Item 51
Item 52
Item 53
Item 58
Item 59
Item 109
Item 110
* Especially seals of the rotary feed-through and therefore ad-
joining surfaces
Adhesives used
Designation GSM-P DKM
Activator from Weicon for all magnets Item 120 Adhesive from Weicon, 302-10 for all magnets Item 120 Item 123
Adhesive from Weicon, 302-43 for all screws Item 110/ 111/112 Item 104/140
Equivalent adhesives and activators from other manufacturers
may be used.

Maintenance
40
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
7.4 Screw tightening torques
Position of the item numbers Drawings [}50]
Screw tightening torques GSM-P
GSM-P Item 110 Item 111 Item 112 Item 115
32 2.7 Nm 2.7 Nm 0.7 Nm 5.8 Nm
40 5.8 Nm 5.8 Nm 0.7 Nm 5.8 Nm
50 5.8 Nm 12 Nm 0.7 Nm 5.8 Nm
64 6 Nm 12 Nm 1.3 Nm 12 Nm
DKM screw tightening torques
Rotary gripping
module
Item 121/124 Item 133 Item 140 Item 231 Item 232
GSM-P-32/-P-40 Basic size
40x40
1.2 Nm - 2 Nm 6 Nm 3 Nm
GSM-P-50/-P-64 Basic size
64x64
2.0 Nm - 4 Nm 10 Nm 6 Nm
Tightening torques for screws FAN
Rotor drive Item 101 Item 104
FAN 40 1.3 Nm
FAN 64 3.1 Nm
7.5 Disassembly/assembly of the unit in the basic modules
Position of the item numbers Drawings [}50]
Disassembly
Ø Remove the compressed air lines.
Ø Turn the gripping module (GSM) into the middle position.
Ø Remove the screws (104) and pull the DKM feed-through com-
pact module (40) off the FAN rotor drive (50).
Assembly
Ø Turn the rectangular section of the rotor drive (53) with the
longer side towards the center of the air connections A and B.
Ø Turn the DKM back stop 1 (81) with the magnet towards the 90°
position, i.e. with the 090 version, one magnet has to point towards the 90° position and the other one towards the 180° position.
Ø Put the DKM feed-through compact module (40) on the FAN ro-
tor drive (50) and secure the two modules with the screws
(104). Observe the permissible tightening torques Screw tight-
ening torques [}40].

Maintenance
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
41
7.6 Disassembly/assembly of the gripping module
For disassembly/assembly of the gripping modules, observe the assembly drawing Drawings [}50].
For assembly, observe the permissible tightening torques as well
as the greases and adhesives to be used; Screw tightening torques
[}40] and Grease/greasing areas [}39].
7.6.1 Version without maintenance of gripping force unit GSM-P
NOTICE
The needle rollers are suitable only for this gripper and cannot
be replaced with needle rollers belonging to another gripper of
the same type and size.
Disassembly
Ø Remove the compressed air lines.
Ø Loosen the screws (111) and remove the bushing (44).
Ø Remove the magnet (120) Mounting orientation of the mag-
nets, item 120 [}44].
Ø Unscrew the screw (110) and pull off the piston (39).
Ø Remove the seal rings (102) from the piston.
Ø Loosen the screws (112) and remove the holders (8).
Ø Take the needle rollers (15) out of the cover housing and re-
move the needle rollers (13 and 14).
Ø Use the piston rod (4) to pull the fingers (3) upwards out of the
cover housing (35).
Ø Loosen the quad ring (101) from the cover housing.
Ø Remove the O-ring (100) from the cover housing (35).
Assembly
For assembly, observe the permissible tightening torques as well
as the greases and adhesives to be used Screw tightening torques
[}40] and Grease/greasing areas [}39].
Ø Lubricate the seals (101) and mount them into the cover hous-
ing (35).
Ø Grease the guide grooves in the cover housing (35).
Ø Lubricate the running surfaces of the fingers (3).
Ø Grease the piston rod (4) in the diagonal pull area, separately from
the lower part of the piston rod (4) Grease/greasing areas [}39].
Ø Install the fingers (3) onto the piston rod (4) and insert the parts
into the cover housing (35).
Ø Fit the needle rollers (13 and 14) between the fingers (3) and
the cover housing (35) into the guiding grooves intended for
this purpose.

Maintenance
42
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
Ø Lubricate the needle rollers (15) and fit them between the fin-
gers (3).
Ø Mount the bracket and the collar (8) with screws (112) onto the
fingers.
Ø Lubricate the O-ring (100) and mount it onto the cover housing (35).
Ø Fasten the piston (39) to the piston rod (4) using the screw (110).
Ø Grease the seals (102) and mount them on the piston (39).
Ø Glue the magnet into the piston Mounting orientation of the
magnets, item 120 [}44].
Ø Carefully fit the cover housing (35) with the mounted parts into
the bushing (44).
Ø Screw the cover housing (35) into the bushing (44) using the
screws (111).
7.6.2 Version with maintenance of gripping force unit
WARNING
Risk of injury due to spring forces
With the "O.D. gripping" version, the bushing (46) or cover housing (35) is under spring tension.
WARNING
Risk of injury due to spring forces
With the "I.D. gripping" version, the piston (36) is under spring
tension.
NOTICE
The needle rollers are suitable only for this gripper and cannot
be replaced with needle rollers belonging to another gripper of
the same type and size.
"O.D. gripping" version GSM-P-...-AS:
Disassembly
Ø Repeat steps 1 to 11 of the gripper disassembly without main-
tenance of the gripping force Version without maintenance of
gripping force unit GSM-P [}41]. However, the bushing has item
46 and a spring (121) is installed to maintain the gripping force.
Ø Carefully clamp the gripping module between the cover housing
(35) and the bushing (46) when loosening the screws (111),
since the two parts are under spring tension.

Maintenance
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
43
Assembly
For assembly, observe the permissible tightening torques as well
as the greases and adhesives to be used Screw tightening torques
[}40] and Grease/greasing areas [}39].
Ø Repeat steps 1 to 14 of the gripper assembly without mainten-
ance of the gripping force Version without maintenance of grip-
ping force unit GSM-P [}41]. However, the bushing has item 46
and a spring (121) is installed to maintain the gripping force.
Ø With the variant with maintenance of the gripping force, make
sure the spring (121) is inserted in the bushing (46) between
steps 12 and 13 of the assembly without maintenance of the
gripping force.
"I.D. gripping" version GSM-P-...-IS:
Disassembly
Ø Repeat steps 1 to 11 of the gripper disassembly without main-
tenance of the gripping force Version without maintenance of
gripping force unit GSM-P [}41]. However, the bushing has item
46 and a spring (121) is installed to maintain the gripping force.
Ø Carefully clamp the gripping module between the cover housing
(35) and piston (36), since the two parts are under spring tension.
Assembly
For assembly, observe the permissible tightening torques as well
as the greases and adhesives to be used Screw tightening torques
[}40] and Grease/greasing areas [}39].
Ø Repeat steps 1 to 14 of the gripper assembly without mainten-
ance of the gripping force Version without maintenance of grip-
ping force unit GSM-P [}41]. However, the bushing has item 46
and a spring (121) is installed to maintain the gripping force.
Ø With the variant with maintenance of the gripping force, make
sure the spring (121) is put on the piston (36) between steps 9 and
10 of the assembly without maintenance of the gripping force.
Maintenance
44
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
7.6.3 Mounting orientation of the magnets, item 120
Top view in rotating angle position for 0°-180° variants
Top view in rotating angle position for 0°-90° variants
7.7 Disassembly/assembly of the DKM feed-through compact
module (item 40)
Position of the item numbers Drawings [}50]
NOTICE
If the housing (11), bearing ring (82), or bushing (44 or 46) is replaced, a new set of fitting disks (111 and 112) must be ordered.
NOTICE
The balls (142) lie loosely in the DKM GSM ball guide (85).
Disassembly
Ø In order to start disassembling the DKM, the steps of disas-
sembly/assembly of the unit must have been carried out in the
basic modules Disassembly/assembly of the unit in the basic
modules [}40].
Ø Remove the O-rings (109) and ball guide rail DKM GSM (85)
from the DKM GSM housing.
Ø Remove the balls (142).
Ø Turn the screws (140) from the bushing of the gripping module
(31-34) and pull DKM GSM stop 1 (81) and the set of fitting disks
(111/112) off the bushing (44 or 46).

Maintenance
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
45
Ø Pull the gripping module (31-34) from the DKM GSM housing.
Ø For elastomer variants, proceed as follows:
Remove the back stops (83) after loosening the nuts (124).
Also remove the needle rollers (122).
Ø For shock absorber variants, proceed as follows:
Remove the dampers (120) after loosening the nuts (121).
Also remove the sleeves (122).
Assembly
For assembly, observe the permissible tightening torques as well
as the greases and adhesives to be used; Screw tightening torques
[}40] and Grease/greasing areas [}39].
Ø Lubricate the DKM GSM housing (11) and the bushing (44 or 46)
on the running surfaces and bearings.
Ø Grease the bearing ring (82).
Ø Insert the bearing ring with the outer chamfer downwards into
the DKM GSM housing.
Ø Lubricate the O-rings (103) and mount them into the recesses
on the bushing (44 or 46).
Ø Insert the gripping module into the DKM GSM housing.
Ø Adjust the axial bearing seat of the bushing with the fitting disks
(111 or 112).
Ø Set DKM stop 1 (81) onto the bushing and fasten it to the bush-
ing using the screws (140).
Ø Grease the DKM ball guide (85).
Ø Turn the bushing so that DKM stop 1 (81) is pointing 180° away
from the bore holes for the damper.
Ø Lubricate the needle rollers (122) and put them into the appro-
priate fits.
Ø For elastomer variants, proceed as follows:
Lubricate the needle rollers (122) and put them into the appropriate fits.
Place one ball (142) in the housing in front of each needle roller
(122) and screw the DKM back stop 2 (83) into the housing.
Ø For shock absorber variants, proceed as follows:
Grease the sleeves (122) and put them on the dampers (120).
Insert the sleeve into the provided fit in the DKM GSM housing
(11) and screw the damper into the housing.
Place one ball (142) in the housing in front of each sleeve (122).
Ø Mount the locknut (124) onto the stops/shock absorbers.
Ø Connect the DKM module (11) to the FAN rotor drive using the
screws (104). When doing this, pay attention to the assembly of
the basic modules Disassembly/assembly of the unit in the basic
modules [}40].

Maintenance
46
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
7.8 Replacing a shock absorber for S variants
Position of the item numbers Drawings [}50]
The shock absorbers have a limited lifespan, depending on the
load. For this reason, their function should be checked regularly.
The shock absorber is working correctly if the unit moves gently to
the end positions. When replacing it, observe the control number
"-446" at the end of the damper designation. These specially
tested shock absorbers are only to be ordered from SCHUNK.
When replacing a damper, the complete additional parts list for
hydraulic dampening should be ordered.
Proceed as follows with the replacement:
Ø Remove the compressed air lines.
Ø Loosen the counter nut (124).
Ø Remove the shock absorber (121) from the unit and remove the
sleeve (122). If the latter cannot be loosened from the shock absorber, it may be helpful to use a small bar magnet or turn the
unit by hand.
NOTE
If the shock absorbers are installed vertically (horizontal axis of rotation of the module), make sure that the sleeve (122) and the
ball (142) are secured against falling out.
Clean all parts thoroughly and check all parts for defects and wear.
The unit is assembled in reverse order; finish by re-adjusting the
end positions Adjusting the end positions.

Maintenance
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
47
7.9 Replacing an elastomer for E variants
Position of the item numbers Drawings [}50]
The elastomers have a limited lifespan, depending on the load. For
this reason, their function should be checked regularly. The elastomer is working correctly if the unit moves gently to the end positions. When replacing an elastomer, the complete additional parts
list for elastomer dampening should be ordered.
Proceed as follows with the replacement:
Ø Remove the compressed air lines.
Ø Loosen the counter nut (124).
Ø Remove the shock absorber (121) from the unit and remove the
sleeve (122). If the latter cannot be loosened from the shock absorber, it may be helpful to use a small bar magnet or turn the
unit by hand.
NOTE
If the shock absorbers are installed vertically (horizontal axis of rotation of the module), make sure that the sleeve (122) and the
ball (142) are secured against falling out.
Clean all parts thoroughly and check all parts for defects and wear.
The unit is assembled in reverse order; finish by re-adjusting the
end positions Adjusting the end positions.

Maintenance
48
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
7.10 Disassembly/assembly of the FAN rotor drive (50)
Position of the item numbers Drawings [}50]
Disassembly
Ø Remove the compressed air lines.
Ø Loosen the screws (101) and take the upper housing (51) off the
lower housing (52).
Ø Remove the O-rings (109) and the centering sleeve (108).
Ø Take the rotor (53) out of the housing (52) and pull the bearing
(100) off the rotor.
Ø Pull the O-rings (110) off the rotor.
Ø Remove the stop rotor (58) and pull the stop seal (59) off the
stop rotor.
Ø Clean all parts thoroughly and check all parts for defects and
wear.
Ø Renew the seals listed in the seal set.
Assembly
Ø Lubricate the upper and lower housing (51 and 52) from the in-
side.
Ø Grease the entire stop rotor (58).
Ø Pull the stop seal (59) into the correct position on the stop rotor
(58) and grease the two parts completely again.
Ø Put the stop rotor in the correct position in the intended fit in
the upper rotor housing (51).
Ø Grease the entire rotor (53) except for the rectangular section.
Ø Pull both O-rings (110) onto the rotor and lubricate them.
Ø Stick the ball bearing onto the rotor.
Ø Stick the rotor with the rectangular part facing down into the
upper housing. Move the rotor into the 90° position, which
means opposite the stop rotor (53).
Ø Put the centering sleeve (108) in the upper housing (51) for as-
sembly with the lower housing (52).
Ø Lubricate four O-rings (109) and place them into the provided
mirrored views in the lower housing (52).
Ø Mount the upper housing with the lower housing and attach
both with screws (101). The screws (101) are to be tightened
"crosswise".
Ø Lubricate two O-rings (109) and fit them into the upper housing
(51) into the appropriate counterbores.
Ø Mount the centering sleeve (108) or cylindrical pin (107) onto
the upper housing (51).

Maintenance
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
49
7.11 Servicing and assembling the product
Maintenance
• Clean all parts thoroughly and check for damage and wear.
• Treat all greased areas with lubricant.
Grease/greasing areas [}39]
• Oil or grease bare external steel parts.
• Replace all wear parts / seals.
– Position of the wearing parts Drawings [}50]
– Seal kit Seal kit [}53]
Assembly
Assembly takes place in the opposite order to disassembly. Observe the following:
• Unless otherwise specified, secure all screws and nuts with Loc-
tite no. 243 and tighten with the appropriate tightening
torque.Screw tightening torques [}40]

Drawings
50
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
8 Drawings
The following figures are example images.
They serve for illustration and assignment of the spare parts.
Variations are possible depending on size and variant.
8.1 Assembly drawing of the basic module
Basic module overview
34 PGM gripping module
40 DKM feed-through compact module
50 FAN rotor drive

Drawings
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
51
8.2 Assembly drawing of the DKM and FAN modules
DKM and FAN overview
* Included in the seal kit. Seal kit can only be ordered completely.
** Only for the basic sizes 40 x 40 and 64 x 64

Drawings
52
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
8.3 Assembly drawing of the gripping modules
Assembly drawing of the basic modules
* Included in the parts list for the DKM feed-through compact module
** Item 113 only available for the sizes P-40, P-50, and P-64

Seal kit
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
53
9 Seal kit
9.1 Sealing kit lists for the FAN 40 - 64 rotor drive
Position of the item numbers Drawings [}50]
FAN 40
ID.-No. of the seal kit 5516256
Item ID number Quantity Designation
53 5514529 1 Rotor FLU 40
59 9939734 1 Stop seal SFL 40
109 9611155 2 O-ring DIN3771
NBR70 2.5x1
131 9611155 4 O-ring DIN3771
NBR70 2.5x1
132 9611086 2 O-ring DIN3771
NBR70 6x2
FAN 64
ID.-No. of the seal kit 5516257
Item ID number Quantity Designation
53 5514530 1 Rotor FLU 64
59 9939735 1 Stop seal SFL 64
109 9611163 2 O-ring DIN3771
NBR70 4x1
131 9611163 4 O-ring DIN3771
NBR70 4x1
132 9939882 2 O-ring DIN3771
NBR70
11.3x2.40

Seal kit
54
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
9.2 Sealing kit lists for the P-32 - P-64 gripping modules
Position of the item numbers Drawings [}50]
P-32
ID.-No. of the seal kit 5516260
Item ID number Quantity Designation
100 9936332 1 O-ring DIN3771
NBR70 16x2
101 9610005 1 Quad ring AS568A NBR70
6.07x1.78 4010
102 9612610 2 Cylinder seal 16x10x2.55 /
Z8-1610N3580
103 9939719 3 O-ring DF-coated
18x1 NBR70
P-40
ID.-No. of the seal kit 5516261
Item ID number Quantity Designation
100 9611115 1 O-ring DIN3771
NBR70 18x1
101 9610111 1 Quad ring AS568A NBR70
8.20x1.78
4012A
102 9907469 2 Cylinder seal 20x14x2.55 /
Z8-2014N3580
103 9939717 3 O-ring DF-coated
22x1 NBR70

Seal kit
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
55
P-50
ID.-No. of the seal kit 5516262
Item ID number Quantity Designation
100 9907474 1 O-ring DIN3771
NBR70 22x1
101 9610111 1 Quad ring AS568A NBR70
8.20x1.78
4012A
102 9937411 2 Cylinder seal 25x19x3.25 /
Z8-2519N3580
103 9937577 3 O-ring DF-coated
26.70x1.76
NBR70
P-64
ID.-No. of the seal kit 5516263
Item ID number Quantity Designation
100 9907605 1 O-ring DIN3771
NBR70 25x1
101 9610111 1 Quad ring AS568A NBR70
8.20x1.78
4012A
102 9936473 1 Quad ring AS568A NBR70
23.52x1.78
4021
103 9937322 3 O-ring DF-coated
30x2 NBR70

Accessory pack rotational speed rotor FAN
56
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
10 Accessory pack rotational speed rotor FAN
Position of the item numbers Drawings [}50]
Content of the accessory pack:
• Centering sleeves (205 or 206)
• O-rings (207)
• Steel balls (108)
• Locking screws (230)
• Screws (231 / 232)
Rotational speed rotor FAN
Rotational speed rotor ID number
FAN 40 5514441
FAN 64 5514442

Translation of original declaration of incorporation
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
57
11 Translation of original declaration of incorporation
in terms of the Directive 2006/42/EG, Annex II, Part 1.B of the European Parliament and of
the Council on machinery.
Manufacturer/
Distributor
SCHUNK GmbH & Co. KG Spann- und Greiftechnik
Bahnhofstr. 106 – 134
D-74348 Lauffen/Neckar
We hereby declare that on the date of the declaration the following partly completed machine complied with all basic safety and health regulations found in the directive 2006/42/
EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on machinery. The declaration is
rendered invalid if modifications are made to the product.
Product designation: Rotary gripping module with parallel gripper / GSM-P /
ID number 304630 / 304730 / 304631 / 304731 / 304632 / 304732 /
304640 / 304740 / 304641 / 304741 / 304642 / 304742 /
304650 / 304750 / 304651 / 304751 / 304652 / 304752 /
304660 / 304760 / 304661 / 304761 / 304662 / 304762 /
303830 / 303930 / 303831 / 303931 / 303832 / 303932 /
303840 / 303940 / 303841 / 303941 / 303842 / 303942 /
303850 / 303950 / 303851 / 303951 / 303852 / 303952 /
303860 / 303960 / 303861 / 303961 / 303862 / 303962
The partly completed machine may not be put into operation until conformity of the machine into which the partly completed machine is to be installed with the provisions of the
Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) is confirmed.
Applied harmonized standards, especially:
EN ISO 12100:2010 Safety of machinery - General principles for design -
Risk assessment and risk reduction
The manufacturer agrees to forward on demand the relevant technical documentation for
the partly completed machinery in electronic form to national authorities.
The relevant technical documentation according to AnnexVII, Part B, belonging to the
partly completed machinery, has been created.
Person authorized to compile the technical documentation:
Robert Leuthner, Address: see manufacturer's address
Lauffen/Neckar, April 2018 p.p. Ralf Winkler,
Manager for development
of gripping system components
Annex to Declaration of Incorporation
58
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
12 Annex to Declaration of Incorporation
according 2006/42/EG, Annex II, No. 1 B
1.Description of the essential health and safety requirements pursuant to 2006/42/EC, Annex I that are applicable and that have been fulfilled with:
Product designation Rotary gripping module with parallel gripper
Type designation GSM-P
ID number 304630 / 304730 / 304631 / 304731 / 304632 / 304732 / 304640 /
304740 / 304641 / 304741 / 304642 / 304742 / 304650 / 304750 /
304651 / 304751 / 304652 / 304752 / 304660 / 304760 / 304661 /
304761 / 304662 / 304762 / 303830 / 303930 / 303831 / 303931 /
303832 / 303932 / 303840 / 303940 / 303841 / 303941 / 303842 /
303942 / 303850 / 303950 / 303851 / 303951 / 303852 / 303952 /
303860 / 303960 / 303861 / 303961 / 303862 / 303962
To be provided by the System Integrator for the overall machine ⇓
Fulfilled for the scope of the partly completed machine ⇓
Not relevant ⇓
1.1 Essential Requirements
1.1.1 Definitions X
1.1.2 Principles of safety integration X
1.1.3 Materials and products X
1.1.4 Lighting X
1.1.5 Design of machinery to facilitate its handling X
1.1.6 Ergonomics X
1.1.7 Operating positions X
1.1.8 Seating X
1.2 Control Systems
1.2.1 Safety and reliability of control systems X
1.2.2 Control devices X
1.2.3 Starting X
1.2.4 Stopping X
1.2.4.1 Normal stop X
1.2.4.2 Operational stop X
1.2.4.3 Emergency stop X
1.2.4.4 Assembly of machinery X
1.2.5 Selection of control or operating modes X
1.2.6 Failure of the power supply X

Annex to Declaration of Incorporation
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
59
1.3 Protection against mechanical hazards
1.3.1 Risk of loss of stability X
1.3.2 Risk of break-up during operation X
1.3.3 Risks due to falling or ejected objects X
1.3.4 Risks due to surfaces, edges or angles X
1.3.5 Risks related to combined machinery X
1.3.6 Risks related to variations in operating conditions X
1.3.7 Risks related to moving parts X
1.3.8 Choice of protection against risks arising from moving parts X
1.3.8.1 Moving transmission parts X
1.3.8.2 Moving parts involved in the process X
1.3.9 Risks of uncontrolled movements X
1.4 Required characteristics of guards and protective devices
1.4.1 General requirements X
1.4.2 Special requirements for guards X
1.4.2.1 Fixed guards X
1.4.2.2 Interlocking movable guards X
1.4.2.3 Adjustable guards restricting access X
1.4.3 Special requirements for protective devices X
1.5 Risks due to other hazards
1.5.1 Electricity supply X
1.5.2 Static electricity X
1.5.3 Energy supply other than electricity X
1.5.4 Errors of fitting X
1.5.5 Extreme temperatures X
1.5.6 Fire X
1.5.7 Explosion X
1.5.8 Noise X
1.5.9 Vibrations X
1.5.10 Radiation X
1.5.11 External radiation X
1.5.12 Laser radiation X
1.5.13 Emissions of hazardous materials and substances X
1.5.14 Risk of being trapped in a machine X
1.5.15 Risk of slipping, tripping or falling X
1.5.16 Lightning X
1.6 Maintenance
1.6.1 Machinery maintenance X

Annex to Declaration of Incorporation
60
07.00 | GSM-P | Assembly and Operating Manual | en | 389104
1.6 Maintenance
1.6.2 Access to operating positions and servicing points X
1.6.3 Isolation of energy sources X
1.6.4 Operator intervention X
1.6.5 Cleaning of internal parts X
1.7 Information
1.7.1 Information and warnings on the machinery X
1.7.1.1 Information and information devices X
1.7.1.2 Warning devices X
1.7.2 Warning of residual risks X
1.7.3 Marking of machinery X
1.7.4 Instructions X
1.7.4.1 General principles for the drafting of instructions X
1.7.4.2 Contents of the instructions X
1.7.4.3 Sales literature X
The classification from Annex 1 is to be supplemented from here forward.
2 Supplementary essential health and safety requirements for certain
categories of machinery
X
2.1 Foodstuffs machinery and machinery for cosmetics or pharmaceutical
products
X
2.2 Portable hand-held and/or guided machinery X
2.2.1 Portable fixing and other impact machinery X
2.3 Machinery for working wood and material with similar physical characteristics
X
3 Supplementary essential health and safety requirements to offset haz-
ards due to the mobility of machinery
X
4 Supplementary essential health and safety requirements to offset haz-
ards due to lifting operations
X
5 Supplementary essential health and safety requirements for machinery
intended for underground work
X
6 Supplementary essential health and safety requirements for machinery
presenting particular hazards due to the lifting of persons
X
 Loading...
Loading...