Schumacher 98026053 User Manual

GASLESS
WIRE FEED WELDER
USER’S GUIDE
GUIDE DE L’UTILISATEUR
Form 00-99-000378/1003
98026053
© 2003
800034584 Rev.00

2
SAFETY INFORMATION
The following safety information is provided as a guideline to help you operate your new welder under
the safest possible conditions. Any equipment that uses electrical power can be potentially dangerous
to use when safety or safe handling instructions are not known or not followed. The following safety
information is provided to give you the information necessary for safe use and operation.
When a WARNING precedes a procedure step, it is an indication that the step contains a procedure
that might be injurious to a person if proper safety precautions are not heeded. When a procedure
step is preceded by a CAUTION, it is an indication that the step contains a procedure that might
damage the equipment being used. A NOTE may be used before or after a procedure step to highlight
or explain something in that step.
READ ALL SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY before attempting to install, operate, or service
this welder. Failure to comply with these instructions could result in personal injury and/or property
damage.
Published standards on safety are available. They are listed in ADDITIONAL SAFETY
INFORMATION at the end of this SAFETY SUMMARY. The National Electrical Code, Occupational
Safety and Health Act regulations, local industrial codes and local inspection requirements also
provide a basis for equipment installation, use, and service.
SHOCK HAZARDS
WARNING
Electric shock can kill! To reduce the risk of death or serious injury from shock, read,
understand, and follow the following safety instructions. In addition, make certain that
anyone else who uses this welding equipment, or who is a bystander in the welding
area understands and follows these safety instructions as well.
IMPORTANT! TO REDUCE THE RISK OF DEATH, INJURY, OR PROPERTY
DAMAGE, DO NOT ATTEMPT OPERATION of this welding equipment until you have
read and understand the following safety summary.
• Do not, in any manner, come into physical contact with any part of the welding current circuit.
The welding current circuit includes: a. the work piece or any conductive material in contact
with it, b. the ground clamp, c. the electrode or welding rod, d. any metal parts on the
electrode holder.
• Do not weld in a damp area or come in contact with a moist or wet surface.
• Do not attempt to weld if any part of clothing or body is wet.
• Do not allow the welding equipment to come in contact with water or moisture.
• Do not drag welding cables, wire feed gun, or welder power cord through or allow them to
come into contact with water or moisture.
• Do not touch welder, attempt to turn welder on or off if any part of the body or clothing is moist
or if you are in physical contact with water or moisture.
• Do not attempt to plug the welder into the power source if any part of body or clothing is
moist, or if you are in physical contact with water or moisture.
• Do not connect welder ground clamp to or weld on electrical conduit.
• Do not alter power cord or power cord plug in any way.
• Do not attempt to plug the welder into the power source if the ground prong on power cord
plug is bent over, broken off, or missing.
• Do not allow the welder to be connected to the power source or attempt to weld if the welder,
welding cables, welding site, or welder power cord are exposed to any form of atmospheric
precipitation, or salt water spray.
• Do not carry coiled welding cables around shoulders, or any other part of the body, when they
are plugged into the welder.
• Do not modify any wiring, ground connections, switches, or fuses in this welding equipment.
3
• Wear welding gloves to help insulate hands from welding circuit.
• Keep all liquid containers far enough away from the welder and work area so that if spilled,
the liquid can not possibly come in contact with any part of the welder or electrical welding
circuit.
• Replace any cracked or damaged parts that are insulated or act as insulators such as
welding cables, power cord, or electrode holder IMMEDIATELY.
EMF INFORMATION
WARNING
Welding current will cause electromagnetic fields as it flows through welding cables and internal
wiring. There has been and continues to be some concern and research about such fields. Until the
final conclusions of the research are reached, you may wish to minimize your exposure to
electromagnetic fields when welding or cutting.
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace:
• Keep cables close together by twisting or taping them.
• Arrange cables to one side and away from you.
• Do not coil or drape cables around your body.
• Keep welding power source and cables as far away from you as practical.
• Connect work clamp to workpiece as close to the weld as possible.
About Pacemakers:
Pacemaker wearers consult your doctor first. If cleared by your doctor, then following the above
procedures is recommended.
FLASH HAZARDS
WARNING
ARC RAYS CAN INJURE EYES AND BURN SKIN! To reduce risk of injury from arc
rays, read, understand, and follow the following safety instructions. In addition, make
certain that anyone else that uses this welding equipment, or is a bystander in the
welding area, understands and follows these safety instructions as well.
• Do not look at an electric arc without proper protection. A welding arc is
extremely bright and intense and, with inadequate or no eye protection, the
retina can be burned, leaving a permanent dark spot in the field of vision. A shield or helmet
with a number 10-shade filter lens (minimum) must be used.
• Do not strike a welding arc until all bystanders and you (the welder) have welding shields
and/or helmets in place.
• Do not wear a cracked or broken helmet and replace any cracked or broken filter lenses
IMMEDIATELY.
• Do not allow the uninsulated portion of the wire feed gun to touch the ground clamp or
grounded work to prevent an arc flash from being created on contact.
• Provide bystanders with shields or helmets fitted with a number 10-shade filter lens.
• Wear protective clothing. The intense light of the welding arc can burn the skin in much the
same way as the sun, even through lightweight clothing. Wear dark clothing of heavy
material. The shirt worn should be long sleeved and the collar kept buttoned to protect chest
and neck.
• Protect against REFLECTED ARC RAYS. Arc rays can be reflected off shiny surfaces such
as a glossy painted surface, aluminum, stainless steel, and glass. It is possible for your eyes
to be injured by reflected arc rays even when wearing a protective helmet or shield. If welding
with a reflective surface behind you, arc rays can bounce off the surface, then off the filter
lens on the inside of your helmet or shield, then into your eyes. If a reflective background
4
exists in your welding area, either remove it or cover it with something nonflammable and
non-reflective. Reflected arc rays can also cause skin burn in addition to eye injury.
FIRE HAZARDS
WARNING
FIRE OR EXPLOSION CAN CAUSE DEATH, INJURY, AND PROPERTY DAMAGE!
To reduce risk of death, injury, or property damage from fire or explosion, read,
understand, and follow the following safety instructions. In addition, make certain that
anyone else that uses this welding equipment, or is a bystander in the welding area,
understands and follows these safety instructions as well. REMEMBER! Arc welding
by nature produces sparks, hot spatter, molten metal drops, hot slag, and hot metal
parts that can start fires, burn skin, and damage eyes.
• Do not wear gloves or other clothing that contain oil, grease, or other flammable substances.
• Do not wear flammable hair preparations.
• Do not weld in an area until it is checked and cleared of combustible and/or flammable
materials. BE AWARE that sparks and slag can fly 35 feet and can pass through small cracks
and openings. If work and combustibles cannot be separated by a minimum of 35 feet,
protect against ignition with suitable, snug-fitting, fire resistant, covers or shields.
• Do not weld on walls until checking for and removing combustibles touching the other side of
the walls.
• Do not weld, cut, or perform other such work on used barrels, drums, tanks, or other
containers that had contained a flammable or toxic substance. The techniques for removing
flammable substances and vapors, to make a used container safe for welding or cutting, are
quite complex and require special education and training.
• Do not strike an arc on a compressed gas or air cylinder or other pressure vessel. Doing so
will create a brittle area that can result in a violent rupture immediately or at a later time as a
result of rough handling.
• Do not weld or cut in an area where the air may contain flammable dust (such as grain dust),
gas, or liquid vapors (such as gasoline).
• Do not handle hot metal, such as the workpiece or electrode stubs, with bare hands.
• Wear leather gloves, heavy long sleeve shirt, cuffless trousers, high-topped shoes, helmet,
and cap. As necessary, use additional protective clothing such as leather jacket or sleeves,
fire resistant leggings, or apron. Hot sparks or metal can lodge in rolled up sleeves, trouser
cuffs, or pockets. Sleeves and collars should be kept buttoned and pockets eliminated from
the shirtfront.
• Have fire-extinguishing equipment handy for immediate use! A portable chemical fire
extinguisher, type ABC, is recommended.
• Wear earplugs when welding overhead to prevent spatter or slag from falling into ear.
• Make sure welding area has a good, solid, safe floor, preferably concrete or masonry, not
tiled, carpeted, or made of any other flammable material.
• Protect flammable walls, ceilings, and floors with heat resistant covers or shields.
• Check welding area to make sure it is free of sparks, glowing metal or slag, and flames before
leaving the welding area.
FUME HAZARDS
WARNING
FUMES, GASSES, AND VAPORS CAN CAUSE DISCOMFORT, ILLNESS, AND
DEATH! To reduce risk of discomfort, illness, or death, read, understand, and follow
the following safety instructions. In addition, make certain that anyone else that uses
this welding equipment or is a bystander in the welding area, understands and follows
these safety instructions as well.
5

• Do not weld in an area until it is checked for adequate ventilation as described in ANSI
standard #Z49.1. If ventilation is not adequate to exchange all fumes and gasses generated
during the welding process with fresh air, do not weld unless you (the welder) and all
bystanders are wearing air-supplied respirators.
• Do not heat metals coated with, or that contain, materials that produce toxic fumes (such as
galvanized steel), unless the coating is removed. Make certain the area is well ventilated, and
the operator and all bystanders are wearing air-supplied respirators.
• Do not weld, cut, or heat lead, zinc, cadmium, mercury, beryllium, or similar metals without
seeking professional advice and inspection of the ventilation of the welding area. These
metals produce EXTREMELY TOXIC fumes that can cause discomfort, illness, and death.
• Do not weld or cut in areas that are near chlorinated solvents. Vapors from chlorinated
hydrocarbons, such as trichloroethylene and perchloroethylene, can be decomposed by the
heat of an electric arc or its ultraviolet radiation. These actions can cause PHOSGENE, a
HIGHLY TOXIC gas to form, along with other lung and eye-irritating gasses. Do not weld or
cut where these solvent vapors can be drawn into the work area or where the ultraviolet
radiation can penetrate to areas containing even very small amounts of these vapors.
• Do not weld in a confined area unless it is being ventilated or the operator (and anyone else
in the area) is wearing an air-supplied respirator.
• Stop welding if you develop momentary eye, nose, or throat irritation as this indicates
inadequate ventilation. Stop work and take necessary steps to improve ventilation in the
welding area. Do not resume welding if physical discomfort persists.
ADDITIONAL SAFETY INFORMATION
For additional information concerning welding safety, refer to the following standards and comply with
them as applicable.
• ANSI Standard Z49.1 — SAFETY IN WELDING AND CUTTING — obtainable from the American
Welding Society, 550 NW Le Jeune Road, Miami, FL 33126 Telephone (800) 443-9353, Fax (305)
443-7559 - www.amweld.org or www.aws.org
• ANSI Standard Z87.1 — SAFE PRACTICE FOR OCCUPATION AND EDUCATIONAL EYE AND
FACE PROTECTION — obtainable from the American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd
St., New York, NY 10036 Telephone (212) 642-4900, Fax (212) 398-0023 - www.ansi.org
• NFPA Standard 51B — CUTTING AND WELDING PROCESS — obtainable from the National Fire
Protection Association, 1 Batterymarch Park, P.O. Box 9101, Quincy, MA 02269-9101 Telephone
(617) 770-3000, Fax (617) 770-0700 - www.nfpa.org
• OSHA Standard 29 CFR, Part 1910, Subpart Q., WELDING, CUTTING AND BRAZING —
obtainable from your state OSHA office or U. S. Dept. of Labor OSHA, Office of Public Affairs, Room
N3647, 200 Constitution Ave. NW Washhington, DC 20210 - www.osha.gov
• CSA Standard W117.2 — Code for SAFETY IN WELDING AND CUTTING. — obtainable from
Canadian Standards Association, 178 Rexdale Blvd. Etobicoke, Ontario M9W 1R3 - www.csa.ca
• American Welding Society Standard A6.0. WELDING AND CUTTING CONTAINERS WHICH HAVE
HELD COMBUSTIBLES. — obtainable from the American Welding Society, 550 NW Le Jeune Road,
Miami, FL 33126 Telephone (800) 443-9353, Fax (305) 443-7559 - www.amweld.org or www.aws.org
6
INTRODUCTION
DESCRIPTION
Your new welder is designed for repair, maintenance, and sheet metal fabrication. The welder
consists of a single-phase power transformer, and a unique built-in control/feeder.
Now you can weld 18-gauge steel sheet metal up to 3/16 inch with a single pass. Welds thicker metal
with beveling and multiple pass.
Your new wirefeed welder is equipped with infinite wire speed control to accurately select the proper
wire feed rate needed for various welding conditions. Internal components are thermostatically
protected.
This welder is designed for use with Flux Core Welding (Gasless) wire only. As delivered from the
factory, this welder can weld with .030” (.8mm) diameter flux-cored wire. A starter spool of .030” fluxcored wire is included.
WELDER PERFORMANCE
Your welder has been designed to weld on steel from approximately 18 gauge up to 3/16 inch thick.
Thinner and thicker material can be welded depending on the experience and technique of the welder
and the type of welding wire being used. From the factory, this welder is set up to run .030" flux-cored
steel welding wires (a starter spool of .030” wire is included).
SPECIFICATIONS
Input Voltage 120 volt 60 Hz. Single
Phase
Input Amps @
Rated Output
Input Plug Style 120 volt 15 amp
Power Cord Length 8-ft.
Rated Output Amps 80 AAC
Max Output Amps 90 AAC
Rated Output Volts 21 VAC
Rated Duty Cycle 10%
Max Open Circuit
Voltage
Agency Listing cCSAus
Output Settings 2
Wire Feed System Two-roll system with
Wire Spool
Capacity
20 AAC
30 VAC
quick reset tension, top
load
4-in. diameter spools –
up to 2.5 lbs.
ASSEMBLY
UNPACKING YOUR WELDER
1. Remove the welder from the carton. .
2. Remove any cartons or bags containing accessories. Open the side hood and remove all
loose parts and accessories packed inside the welder.
3. Open the cartons or bags packed with your welder and inspect their contents for damage.
4. Lay out the parts and compare them to any illustrations in this manual to familiarize yourself
with them and what they are called. This will help you when reading the manual.
POWER REQUIREMENTS
This welder is designed to operate on a properly grounded power source fused with a minimum 20
amp fuse or circuit breaker. If you modify the power cord in any way, other than attaching the proper
input plug, you will void the manufacturer’s warranty. It is recommended that a qualified electrician
verify the actual voltage at the receptacle into which the welder will be plugged and confirm that the
receptacle is properly fused and grounded. The use of the proper circuit size can eliminate nuisance
circuit breaker tripping while welding.
7
DO NOT OPERATE THIS WELDER if the actual power source voltage is less than 100 volts AC or
greater than 125 volts AC. Contact a qualified electrician if this problem exists. Improper performance
and/or damage to the welder will result if operated on inadequate or excessive power.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL! FIRE CAN KILL, INJURE, AND CAUSE PROPERTY DAMAGE!
• To reduce the risk of electric shock and fire, connect only to properly grounded
and fused outlets.
• Never alter the AC power cord provided on the welder. Never alter an extension
cord or extension cord plugs.
EXTENSION CORD USE
For optimum welder performance, an extension cord should not be used unless absolutely necessary.
If necessary, care must be taken in selecting an extension cord appropriate for use with your specific
welder.
Select a properly grounded extension cord that will mate the AC power cord of the welder with the AC
power source receptacle directly, without the use of adapters. Make sure the extension cord is
properly wired and in good electrical condition.
For an extension cord not exceeding 25 feet in length, choose the same AWG wire size as that of the
power cord on the welder. Extension cord lengths longer than 25 feet will require heavier wire gauges
to compensate for voltage losses.
ASSEMBLE HANDLE STRAP
1. Thread the handle strap through the slot in the front of the unit, then through the slot in the
back.
2. Thread the loose end of the strap through the buckle making sure the fabric contacts the
teeth in the buckle.
INSTALLING THE WELDING GUN
The welding gun comes factory-installed to the welder. To remove the gun for maintenance, refer to
maintenance instructions later in this manual.
CHANGING THE DRIVE ROLLER
1. Remove drive tension.
2. If there is wire already installed in the welder, roll it back onto the wire spool by hand-turning
the spool clockwise, but be careful not to allow the wire to come out of the tail piece of the gun
without holding onto it, or it will unspool itself. Put the end of the wire into the hole on the
outside edge of the spool and bend it over to hold the wire in place, and then remove the
spool of wire from the welder.
3. Remove the drive roller bracket from the drive assembly. Two Phillips head screws hold the
bracket.
4. Remove the drive roller by pulling it straight out and off of the drive motor shaft.
5. Find the drive roller that is stamped with the same wire diameter as that of the wire being
installed. Push the drive roller onto the drive motor shaft so that the desired groove is to the
inside. Make sure the groove of the roller is lined up with the wire guides and the roller is flush
with the drive assembly.
6. Replace the drive roller bracket and secure the screws.
INSTALLING THE WELDING WIRE
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL!
8

• Always turn the power switch to the OFF position and unplug the welder’s power
cord from the AC power source before installing wire.
1. Remove the nozzle and contact tip from the end of the gun assembly.
2. Release the wire tension arm by flipping the drive tension knob out. Move the wire tension
arm up and away from the drive roller.
3. Make sure that the wire diameter stamped on the
drive roller is the same as the diameter of the wire
being installed. If it is not the same, change the
drive roller as specified in the preceding section.
4. Remove the wire spindle spring/spool tension
hardware to allow the spool to be mounted.
5. Unwrap the spool of wire and find the leading end
of the wire (it goes through a hole in the outer
edge of the spool, and is bent over the spool
edge to prevent the wire from unspooling), but do
not unhook it yet!
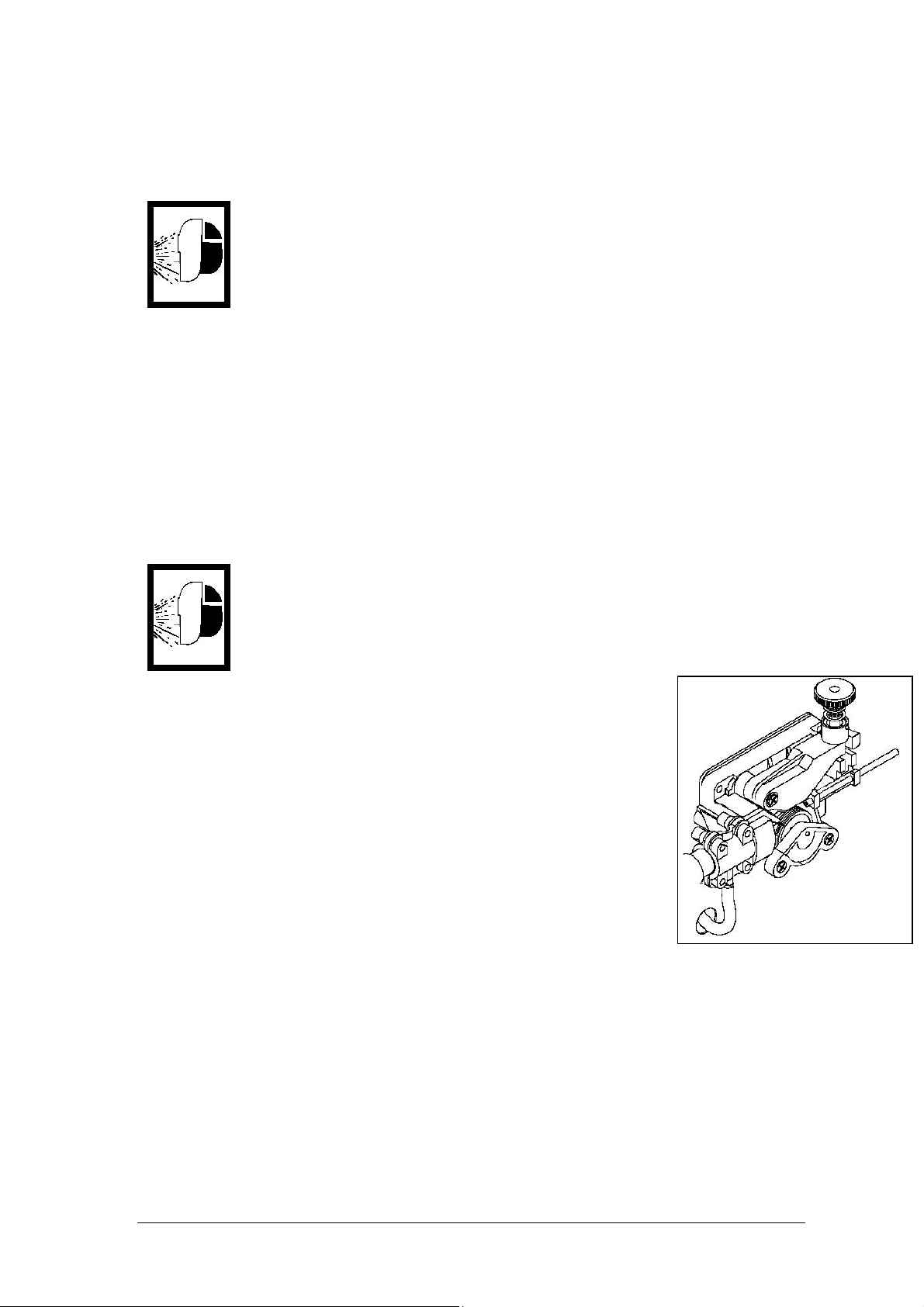
6. Place the spool on the spindle in such a manner
that when the wire comes off the spool, it enters
the wire drive assembly in a straight line (see
photograph)
7. After checking to make sure that your welder is
disconnected from the AC power source, free the
leading end of the wire from the spool, but do not
let go of it until told to do so in step 11, or the wire
will unspool itself.
WARNING
CUTTING WIRE CAN BE A HAZARD TO YOUR EYES.
• The end of the wire being cut can fly up at you - wear eye protection when cutting
wire.
8. Using a wire cutter, cut the bent end off the leading end of the wire so that only a straight
leading end remains.
9. With the wire tension arm pulled away from the drive roller, insert the leading end of the wire
into the inlet guide tube, push it across the drive roller and into the gun assembly, then hand
feed it about six inches into the gun.
10. Line the wire up in the groove of the drive roller, then rotate the wire tension arm to drop onto
the drive roller. Flip the tension-adjusting lever up and into place.
11. Tighten (turn clockwise) the drive tensioner knob until the drive-bearing roller is applying
enough force on the wire to prevent it from slipping out of the drive assembly. Now you can let
go of the wire.
12. Plug the welder's power cord into the AC power source, set the VOLTAGE selector to the
desired welding setting, and set the WIRE SPEED control to the middle of the wire speed
range.
9
13. Pull the trigger on the welding gun to feed the wire through the gun assembly.
WARNING
ARC FLASH CAN INJURE EYES!
To reduce the risk of arc flash, make certain that the welding wire, when it finally
comes out of the end of the gun, does not touch the ground clamp or any grounded
piece of metal.
14. When at least an inch of wire sticks out past the end of the gun, release the trigger.
15. Select a contact tip stamped with the same wire diameter as the diameter of the wire being
used.
16. Slide the contact tip over the wire (protruding from the end of the gun), thread it into the end of
the gun, and hand tighten securely.
17. Install the nozzle on the end of the gun assembly.
18. Cut off excess wire that extends more than 1/4" past the end of the nozzle.
SET THE WIRE DRIVE TENSION.
WARNING
ARC FLASH CAN INJURE EYES!
• To reduce the risk of arc flash, make certain that the welding wire, when it finally
comes out of the end of the gun, does not touch the ground clamp or any grounded
piece of metal during the drive tension settling process.
1. Pull the trigger on the gun.
2. Turn the drive tension adjustment knob clockwise, increasing the drive
tension until the wire seems to feed smoothly without slipping.
3. Block the end of the nozzle by holding it up against something that
doesn't conduct electricity, such as a block of wood or a concrete floor,
then trigger the gun again. The wire should slip at the drive roller. If the
wire bird-nests at the drive roller, decrease the drive tension by turning
the drive tension adjustment knob counterclockwise and try again after
rethreading the welding wire. When set correctly, there should be no
slippage between the wire and the drive roller under normal conditions,
but if an obstruction occurs along the wire feed path, the wire should
then slip on the drive roller.
OPERATION
GETTING TO KNOW YOUR NEW WELDER
Whether or not you have welded before, it is important that you become familiar with your welder, its
controls, and the results achieved at different settings. We strongly recommend that you practice with
your new welder on scrap metal, trying a variety of heat settings, base metal thicknesses, and welding
positions for each type and size of wire that you will be using. By doing this you will gain a feel for how
changes in these welding variables affect the weld.
If you have not welded before, you will need to develop welding skills and techniques as well. The selftaught welder learns through a process of trial and error. The best way to teach yourself how to weld is
with short periods of practice at regular intervals.
Do not attempt to weld on any valuable equipment until you have made practice welds on scrap metal
that can be discarded. The scrap metal should be of the same type and thickness as that of the item
10

to be welded. Only after you are satisfied that your practice welds are of good strength and
appearance, should you attempt your actual welding job.
CONTROLS & THEIR FUNCTIONS
ON-OFF – THERMAL INDICATOR
To turn the power on to the welder, push the main switch to ON. Your welder has a lighted main
switch. This light will come on if the welder has overheated. The light indicates that a thermostat has
shut off the power within the welder. Once the welder has cooled, the thermostat will turn the welder
back on and the light will go out. Over heating is usually caused by exceeding the welder duty cycle.
Note that whenever the switch is set to ON, the welding wire installed in the welder is electrically
active. Make sure the wire is not in contact with the ground clamp or a metal surface connected to the
ground clamp.
VOLTAGE SELECTOR
Two heat settings can be selected. The lower setting is for thinner material, the higher setting for
thicker materials.
WIRE SPEED
The wire speed control adjusts the speed at which the wire is fed out of the gun. The wire speed
needs to be matched, or “tuned-in”, to the rate at which it is being melted off. Some things that affect
wire speed selection are the type and diameter of the wire to be used, the desired heat setting, and
the welding position to be used.
DUTY CYCLE
The duty cycle rating of a welder is a measure of how long the welder can weld and how long it must
be rested to cool. It is expressed as a percentage of ten minutes (the industry recognized cycle time)
and represents the maximum welding time allowed, with the balance of the ten minute cycle required
for cooling.
INTERNAL THERMAL PROTECTION
If you exceed the duty cycle of your welder, an internal thermal protector will open and shut off all
welder functions except the cooling fan. If this ever happens to you, do not shut off the welder! Leave it
turned on with the fan running. After cooling a while, the thermal protector will automatically reset and
the welder will function again. However, you should wait at least 10 minutes after the thermal protector
opens before resuming welding, even if the protector resets itself sooner, or you may experience less
than specified duty cycle performance.
If you find that your welder will not weld for 1 minute without stopping, reduce the wire speed slightly
and tune the welder in at the lowest wire setting that still produces a smooth arc. Welding with the wire
speed too high causes excessive current draw and shortens the unit duty cycle.
CAUTION!
DO NOT CONSTANTLY EXCEED THE DUTY CYCLE OR DAMAGE TO THIS WELDER WILL
RESULT!
TUNING IN THE WIRE SPEED
This is one of the most important parts of MIG welder operation and must be done before starting
each welding job, or whenever any of the following variables are changed: heat setting, wire diameter,
or wire type.
1. Set up and ground a scrap piece of the same type of metal that you will be welding. It should
be equal to or greater than the thickness of the actual work piece and free of paint, oil, rust,
etc.
2. Select a VOLTAGE setting.
3. Hold the gun in one hand allowing the nozzle to rest on the edge of the work piece farthest
away from you and at an angle similar to that which will be used when actually welding.
4. With your free hand, turn the WIRE SPEED control to maximum and continue to hold onto
the knob.
11

5. Lower your welding helmet and pull the trigger on the gun to start an arc, then begin to drag
the gun toward you while turning down on the WIRE SPEED control knob at the same time.
6. Listen! As you decrease the wire speed, the sound that the arc makes will change from a
sputtering to a smooth, high-pitched buzzing sound and then will begin sputtering again if you
decrease the wire speed too far — very similar to tuning in a radio. The points on the WIRE
SPEED control where this high-pitched buzzing sound is achieved is the best-sounding
range.
You can use the wire speed control to slightly increase or decrease heat and penetration for a given
heat setting by selecting higher or lower wire speed settings within the best-sounding range.
Repeat this tune-in procedure if you select a new voltage setting, a different diameter wire, or a
different type of wire.
CONNECT WELDER GROUND
Attach the ground clamp to the work piece making sure that the work piece is cleaned of dirt, oil, rust,
scale, oxidation, and paint at the point of connection. It is best to connect the ground clamp directly to
the work piece and as close to the weld as possible. If it is impractical to connect the ground clamp
directly to the work piece, connect it to metal that is securely attached to the work piece, but not
electrically insulated from it. Also, make sure this other metal is of similar or greater thickness than that
of the work piece.
CAUTION!
RISK OF ELECTRONIC COMPONENT DAMAGE!
If the ground clamp is being connected to an automobile or other equipment with on-board computer
systems, solid state electronic controls, solid state sound systems, etc., do not weld until
disconnecting the cable from the battery that is attached to chassis ground. Failure to do so may result
in electronic component damage!
12
 Loading...
Loading...