Schneider Electric USA GWA242F User Manual

ConneXium WiFi
TCSG, TCSN
User Installation Manual
TCSGWA272, TCSNWA271, TCSNWA2A1, TCSNWA271F,
TCSGWA242, TCSGWC241, TCSGWA242F, TCSNWA241,
TCSNWA241F
8/2010
S1A31526.00
www.schneider-electric.com

S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010 – 19.8.10

Contents
About this Manual 6
Key 9
Safety instructions 10
1 System Planning 18
1.1 WiFi devices 18
1.1.1 WiFi access points 18
1.1.2 WiFi clients 19
1.2 Frequency Bands 19
1.2.1 The ISM Bands 19
1.2.2 Government Regulation of the ISM Bands 22
1.2.3 Anticipating Radio Wave Behavior 22
2 Device description 25
2.1 Properties and functions 25
2.1.1 IP67 types 26
2.1.2 Rail / IP40 types 26
2.1.3 802.11 a/b/g/h/i types 26
2.1.4 802.11 a/b/g/h/i/n types 26
2.2 Interfaces and control elements 28
2.2.1 TCSGWA272 28
2.2.2 TCSNWA271, TCSNWA271F and TCSNWA2A1 29
2.2.3 TCSGWA242 and TCSGWA242F 30
2.2.4 TCSGWC241 31
2.2.5 TCSNWA241 and TCSNWA241F 32
2.3 Device models 33
2.3.1 TCSGWA272 devices 33
2.3.2 TCSGWA242.../TCSGWC241 devices 33
2.3.3 TCSNWA271... and TCSNWA241... devices 34
3 Assembly and start-up 35
3.1 Safety instructions 35
3.2 Overview of installation 35
3.3 Unpacking and checking 36
3.4 Assembling components (IP67 types) 36
3.5 Selecting the location for mounting/
setting up 37

3.6 Mounting outdoors (IP67 types) 37
3.6.1 Lightning protection 38
3.6.2 Pole mounting 38
3.7 DIN rail mounting (Rail-/IP40 types) 39
3.8 Flat surface mounting 39
3.8.1 IP67 types 39
3.9 Selecting the Right Antenna 40
3.9.1 Antenna Characterisitics 40
3.9.2 Omnidirectional Antennas 40
3.9.3 Directional Antennas 41
3.9.4 Leaky Cable 42
3.10 Mounting/connecting external antennas 42
3.10.1 Connectors for external antennas on IP67 types 42
3.10.2 Connectors for external antennas on Rail/IP40 types 44
3.10.3 Mounting external antennas 45
3.11 Connecting LAN and WLAN connectors 45
3.11.1 IP67 types 45
3.11.2 Rail / IP40 types 46
3.12 Grounding 46
3.12.1 IP67 types 46
3.12.2 Rail / IP40 types 47
3.13 Connecting the supply voltage 47
3.13.1 5-pin M12 connector (IP67 types) 48
3.13.2 4-pin terminal block (Rail-/IP40 types) 48
3.13.3 Power over Ethernet (PoE) -
power supply via the LAN cable 49
3.14 Connecting the data lines 49
3.14.1 10/100 Mbit/s twisted pair connection 49
3.14.2 10/100 Mbit/s twisted pair connection 51
3.15 Installing the TCSNWA2A1 housing cover 52
3.16 Startup procedure 54
3.16.1 IP67 types 54
3.16.2 Rail / IP40 types 54
3.17 Finding and configuring devices 55
3.18 Installing external antennas 55
3.19 Display elements 57
3.20 Operation element (reset button) 60
3.20.1 Functions 61
4
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010

3.20.2 IP67 types 61
3.20.3 Rail / IP40 types 61
3.21 Basic set-up 63
3.22 Disassembly 64
4 Technical data 65
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010
5

About this Manual
Validity Note
The data and illustrations found in this book are not binding. We reserve the
right to modify our products in line with our policy of continuous product
development. The information in this document is subject to change without
notice and should not be construed as a commitment by Schneider Electric.
Product Related Information
Schneider Electric assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear
in this document. If you have any suggestions for improvements or
amendments or have found errors in this publication, please notify us.
No part of this document may be reproduced in any form or by any means,
electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, without express written
permission of Schneider Electric.
All pertinent state, regional, and local safety regulations must be observed
when installing and using this product. For reasons of safety and to ensure
compliance with documented system data, only the manufacturer should
perform repairs to components.
When devices are used for applications with technical safety requirements,
please follow the relevant instructions.
Failure to use Schneider Electric software or approved software with our
hardware products may result in improper operating results.
Failure to observe this product related warning can result in injury or
equipment damage.
User Comments
We welcome your comments about this document. You can reach us by
e-mail at techpub@schneider-electric.com
6
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010

Related Documents
Title of Documentation Reference-
Number
ConneXium WiFi TCSG,TSCN Configuration and Administration Guide S1A31559
ConneXium WiFi TCSG,TCSN Operation and Maintenance Guide S1A31553
ConneXium WiFi TCSG,TCSN Quick Start Guide S1A31547
ConneXium WiFi TCSG, TCSN User Installation Guide S1A31526
ConneXium WiFi TCSG,TCSN Command Line Interface S1A31521
ConneXium WiFi TCSG, TCSN Outdoor Installation Guide S1A31531
ConneXium WiFi TCSG, TSCN Antenna Guide S1A56438
ConneXium WiFi 2.4 GHz Omni Directional Antenna -
TCSWAB2O Mounting Instructions
ConneXium WiFi 5 GHz Omni Directional Antenna -
TCSWAB5O Mounting Instructions
ConneXium WiFi Dual band Hemispherical Antenna -
TCSWABDH Mounting Instructions
ConneXium WiFi 2.4 GHz Directional Antenna -
TCSWAB2D Mounting Instructions
ConneXium WiFi 5 GHz Medium & Very Directional Antennas -
TCSWAB5x Mounting Instructions
ConneXium WiFi 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz Dual Slant , MiMo 11n Antennas -
TCSWABxS, TCSAB5DN Mounting Instructions
ConneXium WiFi Dual band Omni Directional 11n Antenna -
TCSWABDON Mounting Instruction
ConneXium WiFi Over Voltage Protector - Antenna -
TCSWABP Mounting Instructions
ConneXium WiFi Over Voltage Protector - LAN/PoE -
TCSWABP68 Mounting Instructions
ConneXium WiFi Memory Card IP40,IP67 and ATEX Modules -
TCSWAMCD, TCSWAMC67
S1A50472
S1A50473
S1A50474
S1A50475
S1A50476
S1A50480
S1A50481
S1A50482
S1A50483
S1A50484
Note: The Glossary is located in the TSCG, TSCN Configuration and
Administration Guide.
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010
7

TCSG,TSCN Configuration and Administration Guide
The ”TCSG,TSCN Configuration and Administration Guide” contains
information about creating basic configurations for specific use cases and
detailed information regarding all the configurable parameters.
TCSG,TCSN Operation and Maintenance Guide
The ”TCSG,TCSN Operation and Maintenance Guide” contains information
about using the LANConfig, Webconfig and local area LANmonitor software
tools to operate and maintain ConneXium WiFi Devices.
TCSG,TCSN Quick Start Guide
The ”TCSG,TCSN Quick Start Guide” contains information about how to get
started with a new out of the box Connexium WiFi Device.
TCSG,TCSN User Installation Guide
The “TCSG, TCSN User Installation Guide” contains a device description,
safety instructions, a description of the display, and the other information that
you need to install the device.
TCSG,TCSN Command Line Interface Reference Manual
The "TCSG, TCSN Command Line Interface Reference Manual” contains
detailed information on using the Command Line Interface to operate the
individual functions of the device.
TCSG, TCSN Outdoor Installation Guide
The "TCSG, TCSN Outdoor Installation Guide" contains basic information
about planing, mounting and installing wireless LAN systems in an outdoor
environment.
Antenna Mounting Instruction
The antenna mounting instructions contain information you need to mount
the antennas/accessories.
TCSG, TCSN Antenna Guide
The "TCSG, TCSN Antenna Guide" contains an overview of the available
antennas, over voltage protectors, adaptor cable and antenna cables. This
guide helps you to find the suitable accessories for your wireless LAN
application.
8
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010

Key
The symbols used in this manual have the following meanings:
Listing
Work step
Subheading
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010
9
Safety instructions
Important Information
Notice: Read these instructions carefully, and look at the equipment to
become familiar with the device before trying to install, operate, or
maintain it. The following special messages may appear throughout this
documentation or on the equipment to warn of potential hazards or to call
attention to information that clarifies or simplifies a procedure.
The addition of this symbol to a Danger or Warning safety label
indicates that an electrical hazard exists, which will result in
personal injury if the instructions are not followed.
This is the safety alert symbol. It is used to alert you to potential
personal injury hazards. Obey all safety messages that follow
this symbol to avoid possible injury or death.
DANGER
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
can result in death or serious injury.
PLEASE NOTE: Electrical equipment should be installed, operated,
serviced, and maintained only by qualified personnel.
No responsibility is assumed by Schneider Electric for any consequences
arising out of the use of this material.
© 2010 Schneider Electric. All Rights Reserved.
Usage
The device may only be employed for the purposes described in the
catalog, technical description, and manuals.
Supply voltage
Apply supply voltage to the device if terminal blocks are wired and
installed correctly as described in chapter “Connecting the supply
voltage“ on page 47.
10
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010
The devices are designed for operation with extra-low voltage (SELV).
Accordingly, SELV circuits with voltage restrictions in accordance with
IEC/EN 60950-1 may be connected to the supply voltage connectors.
Use undamaged parts.
For TCSNWA241 and TCSNWA241F: The DC power supply line
should not exceed 3 meters (118.11 inches).
WARNING
LOSS OF CONTROL
Berücksichtigen Sie bei der Planung der Steuerungsschemata mögliche
Ausfälle der Steuerungspfade. Stellen Sie dabei für bestimmte kritische
Steuerungsfunktionen entsprechende Mittel bereit, um während und nach
einem Pfadausfall einen sicheren Zustand zu gewährleisten. Beispiele für
kritische Steuerungsfunktionen sind Notfall-Stopp, Überfahr-Stopp,
Stromausfall und Neustart.
Für kritische Steuerungsfunktionen müssen getrennte oder redundante
Steuerungspfade verfügbar sein.
Systemsteuerungspfade können Datenlinks enthalten. Berücksichtigen Sie
deshalb die Auswirkungen von unvorhergesehenen
Übertragungsverzögerungen oder -ausfällen der Links.
Beachten Sie die Unfallverhütungsvorschriften und die lokalen
Sicherheitsrichtlinien.
a
Überprüfen Sie jede Implementierung dieser Anlage einzeln gründlich auf
Funktionsfähigkeit und Betriebssicherheit, bevor Sie sie in Betrieb nehmen.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury,
or equipment damage.
a. Weitere Informationen finden Sie in den Richtlinien NEMA ICS 1.1 (neueste Ausgabe),
„Safety Guidelines for the Application, Installation, and Maintenance of Solid State Control“,
sowie NEMA ICS 7.1 (neueste Ausgabe),„Safety Standards for Construction and Guide for
Selection, Installation and Operation of Adjustable-Speed Drive Systems“, bzw. in den
entsprechenden vor Ort geltenden Bestimmungen.
Use a cable cross-section of at least 1.0 mm² (for North America, AWG
16) for the current conductor at the voltage input.
Relevant for North America: For use in Class 2 circuits.
Only use copper wire/conductors of class 1, 75 °C (167 °F).
Relevant for North America: For use in Class 2 circuits.
The device may only be connected to a supply voltage of class 2 that
fulfills the requirements of the National Electrical Code, Table 11(b). If
the voltage is being supplied redundantly (two different voltage
sources), the combined supply voltages must fulfill the requirements of
the National Electrical Code, Table 11(b).
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010
11

Shielding ground
The shield of the connectable twisted pair cables is connected to the
metal casing of the device as a conductor.
Housing
Relevant for Rail-/IP40 types:
CAUTION
EQUIPMENT OVERHEATING
When installing the device, make sure any ventilation slots remain free.
Maintain a clearance of at least 10 cm (3.94 in).
Failure to follow these instructions can result in injury or equipment
damage.
Only technicians authorized by the manufacturer are permitted to open
the housing.
Make sure that the electrical installation meets local or nationally
applicable safety regulations.
IP67 types:
A separate screw connector on the housing is provided for the functional
ground (FE). This is indicated by the functional ground symbol ( ). The
functional ground is electrically connected to the switching ground and the
metal housing of the device.
Rail / IP40 types:
The lower panel of the device housing is grounded by means of the DIN
rail.
Environment
Refer to Chapter 4“Technical data“ for environmental considerations.
Relevant for use in Ex zone 2 according to ATEX 95 (ATEX 100a):
Only products labeled accordingly may be operated in Ex zone 2.
When operating the TCSNWA2A1 types in Ex zone 2, the following
applies:
II 3G
Ex nA II T4 -20°C ... +55°C
KEMA 10 ATEX 0133 X
12
Temperature Code T4 Ambient –20 °C … +55 °C
List of Standards EN 60079-0: 2006
EN 60079-15: 2005
CLC/TR 50427: Dez. 2004
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010

DO NOT OPEN THE DEVICE WHEN IT IS ELECTRICALLY CHARGED.
DO NOT DETACH ANY CONNECTORS WHEN THE DEVICE IS
ELECTRICALLY CHARGED.
DO NOT REMOVE THE LABELED HOUSING COVER.
DANGER
EXPLOSIVE ENVIRONMENT
Do not open this device or detach any connectors when the device is
electrically charged.
Do not remove the labeled housing cover.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death, serious injury,
or equipment damage.
The TCSNWA2A1 modules are delivered with the housing cover
installed. Remove the cover to make connections, then replace the
cover prior to operation.
Special conditions for safe use
Provisions shall be made to prevent the rated voltage from being
exceeded by transient disturbances of more than 40 %.
When the temperature under rated conditions exceeds 70 °C at the
cable or conduit entry point, or 80 °C at the branching point of the
conductors, the temperature specification of the selected cable shall
be in compliance with the actual measured temperature values.
Lightning protection
When you mount devices and / or antennas outdoors, there is a risk of
them being struck by lightning. Additionally, there is the risk of voltage
surges being transmitted into the interior of the building. It is your
responsibility to take appropriate measures to mitigate the effects of
lightning strikes. Make sure the equipment is installed by a licensed
electrician in accordance with local, regional and national regulations for
codes and standards (such as VDE 0182 and IEC 62305) and according
to best practices for your application and environment.
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010
13

DANGER
LIGHTNING STRIKE AND VOLTAGE SURGES
Protect devices or antennas installed outdoors using lightning arrester
devices, such as lightning rods.
Install over voltage protector devices on every cable.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death, serious injury,
or equipment damage.
CE marking
The devices comply with the regulations contained in the following
European directive:
1999/5/EC
Directive of the European Parliament and the council for radio
installations and telecommunication systems and for the mutual
recognition of their conformity.
This directive also contains the goals of directive 2004/108/EC of the
European Parliament and the council for standardizing the regulations of
member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility, and directive
2006/95/EC of the European Parliament and the council for standardizing
the regulations of member states relating to electrical equipment to be
used within specific voltage ranges, but without applying the lower voltage
threshold.
This product may be operated in all EU states (EU = European
Union) under the condition that it has been configured correctly.
In accordance with the above-named EC directive (EC = European
Community), the EC conformity declaration will be at the disposal of the
relevant authorities at the following address:
Schneider Electric
35 rue Josep Monier
CS 30323
92506 Rueil-Malmaison
France
This product can be used in living areas (living area, place of business,
small business) and in industrial areas.
Information on using devices in motor vehicles (E1)
Some variants of the devices are E1-certified. Only operate suitably
labeled products in motor vehicles.
14
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010

DANGER
HAZARD OF ELECTRIC SHOCK, EXPLOSION OR ARC FLASH
Remove the Ethernet cable that provides PoE to disconnect power before
installing or removing any hardware and cables.
Always use a properly rated voltage sensing device to confirm that power is
off.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death, serious injury,
or equipment damage.
CAUTION
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
In a PoE installation, use only devices that adhere to the 802.3af standard.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in injury or equipment
damage.
Note: To meet the requirements of directive 1999/5/EG (R&TTE
directive) when operating the device in a motor vehicle, do one of the
following:
Supply the power to the device via a Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Switch or via a power unit that conforms to IEEE 802.3af.
You will find information on PoE-compatible Switches from Schneider
Electric at www.schneider-electric.com
Install an upstream filter on the 24V DC power supply. You will find
information on suitable filters at www.schneider-electric.com.
Note: If you are using an E1-certified device in a vehicle and want to be
able to drive the vehicle freely within the EU, set the country profile for
Germany. This country profile is identical to all the country profiles for EU
countries. Do not, however, use any special frequencies, such as BFWA.
FCC note:
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
This device may not cause harmful interference, and
This device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010
15

Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct
the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Important note:
This equipment complies with FCC and IC RSS-102 radiation exposure
limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be
installed and operated with minimum distance 40 cm (15.8 in) between
the radiator and your body.
The antenna used for this transmitter must not be co-located with any
other transmitters within a host device, except in accordance with FCC
multi-transmitter product procedures.
This transmitter is restricted to indoor use only within the 5.15-5.25 GHz
band to reduce potential for harmful interference to co-channel mobile
satellite systems.
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003
du Canada.
To reduce potential radio interference to other users, the antenna type
and its gain should be so chosen that the equivalent isotropically radiated
power (e.i.r.p.) is not more than that permitted for successful
communication.
This device has been designed to operate with the antennas listed below
in point-to-multipoint systems, and having a maximum gain of 9 dBi:
16
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010

Device model Antennas operating with this device model
TCSGWA242F TCSWAB2O
TCSWAB5O
TCSWABDH
TCSWAB2S
TCSWAB5S
TCSWABC5
TCSWABC10
Table 1: Antennas for use in point-to-multipoint systems
The antennas listed below have been designed for use exclusively in fixed
point-to-point systems operating in the 2400 MHz to 2483 MHz band:
Device model Antennas operating with this device model
TCSGWA242F TCSWAB2D
Table 2: Antennas for use in fixed point-to-point systems
Antennas not included in this list are strictly prohibited for use with this
device. The required antenna impedance is 50 ohms.
Recycling note
After usage, this product must be disposed of properly as electronic
waste, in accordance with the current disposal regulations of your county,
state and country.
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010
17

1 System Planning
1.1 WiFi devices
1.1.1 WiFi access points
Within the ConneXium WiFi offer are several access point devices, providing
a choice of:
1 or 2 radios inside the device
throughput
environmental ruggedness/ingress protection
conformance to government-mandated bandwidth restrictions
Access Point
Model
TCSNWA241 1 up to 300 Mb/s rated for IP40
TCSGWA242 2 up to 54 Mb/s rated for IP40
TCSNWA241F 1 up to 300 Mb/s rated for IP40 in U.S. and Canada
TCSGWA242F 2 up to 54 Mb/s rated for IP40
TCSGWA271 1 up to 300 Mb/s rated for IP67
TCSGWA272 2 up to 54 Mb/s rated for IP67
TCSGWA271F 1 up to 300 Mb/s rated for IP67 in U.S. and Canada
TCSNWA2A1 1 up to 300 Mb/s rated for IP67
Number of
Radios
Nominal
Throughput
Environmental
Ruggedness
a
b
and ATEX
c
Country Restrictions
outside U.S. and Canada
outside U.S. and Canada
outside U.S. and Canada
Table 3: ConneXium WiFi Access Point Characteristics
a. IP40 indicates that the module has ingress protection against solid particles with a diameter
greater than 1 mm (.04 inch). No special protection against ingress of liquids.
b. IP67 indicates that the module has ingress protection against dust and immersion in water
up to 1 m (3.3 ft).
c. ATEX indicates that the device is designed to operate in potentially explosive atmospheres.
Devices rated for IP67 are often used for outdoor installations because of
their ability to withstand rain, snow and dust storms. IP40 devices are
designed primarily for indoor use, but they can be used outdoors when they
are installed inside weather-resistant IP67 enclosures.
Effective throughput for a WiFi device is heavily affected by overhead
considerations, particularly power loss due to the distance between the
access point and its power source. Often the real throughput over a WiFi link
is only half of the specified nominal throughput.
Each radio that operates in an access point requires an antenna.
18
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010

1.1.2 WiFi clients
A client is a radio device that resides in or is connected to a station. The client
allows the station to communicate wirelessly with an access point. The
PCMCIA card in a laptop that enables the computer to operate wirelessly is
a client, and the laptop is the station. Other types of stations might be moving
vehicles such as forklifts or I/O modules used in a machine such as a
conveyor belt. A client enables its station to operate wirelessly and may
enable the station to roam through a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
environment without loosing its network connection by switching to the next,
strongest signal in the access point array.
Any of the ConneXium WiFi access points can be configured as a client. Also
offered is two pure limited-functionality client devices, the TCSGWC241 and
the TCSGWC241F. These module each have 1 radio, a nominal throughput
of 54 Mb/s, and an IP40 rating. The TCSGWC241 is designed for use outside
the U.S. and Canada; the TCSGWC241F can be used in the U.S. and
Canada.
Each radio in a client device also requires an antenna. Laptop computers
frequently have an antenna built into the screen. If you are using a
ConneXium WiFi device as a client, you need to select the appropriate
ConneXium WiFi antenna(s) for the station. For example, a TCSWABDH
hemispherical antenna is designed to mount onto a moving station, e.g., on
the roof of a vehicle such as a forklift.
1.2 Frequency Bands
ConneXium WiFi devices communicate in the radio spectrum. They operate
in defined bandwidths, and they often share that bandwidth space with other
devices. The requirements of your application will determine the frequency
band in which you choose to operate and the types of ConneXium WiFi
devices to select.
1.2.1 The ISM Bands
The IEEE manages a series of specifications for local area networking called
the 802 family. WiFi devices fall under four 802.11 standards:
Standard Frequency Band Transmission Rate
802.11a 5 GHz up to 54 Mb/s
802.11b 2.4 GHz 5.5 Mb/s
11 Mb/s
802.11g 2.4 GHz up to 54 Mb/s
802.11n 2.4 and 5 GHz up to 300 Mb/s
Table 4: WiFi Frequencies and Speeds
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010
19
The 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands are reserved for industrial, scientific and
medical (ISM) equipment, which uses the radio spectrum for transmitting and
receiving data. They are called the ISM bands. Devices operating within the
bandwidths shared by ConneXium WiFi devices are usually unlicensed.
Working in the 2.4 GHz Band
Signals in the lower-frequency 2.4 GHz band (802.11b, 802.11g, and
sometimes 802.11n) can propagate through obstacles such as wood,
untempered glass and drywall better than 5 GHz signals. Therefore lower
frequency transmissions can travel longer distances and are sometimes
needed in locations where clients are separated from access points by
walls, windows, high shelves, etc.
The 2.4 MHz bandwidth is such that network throughput often suffers
because of device density in the band. Other ISM devices, such as
microwave ovens and cordless phones, operate in the band and can take
space in the band away from the ConneXium WiFi network.
Another consideration that can make communications slow, particularly
when a WLAN requires many access points for coverage, is the limited
channel capacity of the 2.4 GHz band. Each access point in the WLAN
operates on a channel that you assign it in the configuration process. As
a roaming client traverses the WLAN from access point to access point, it
should maintain uninterrupted communication.
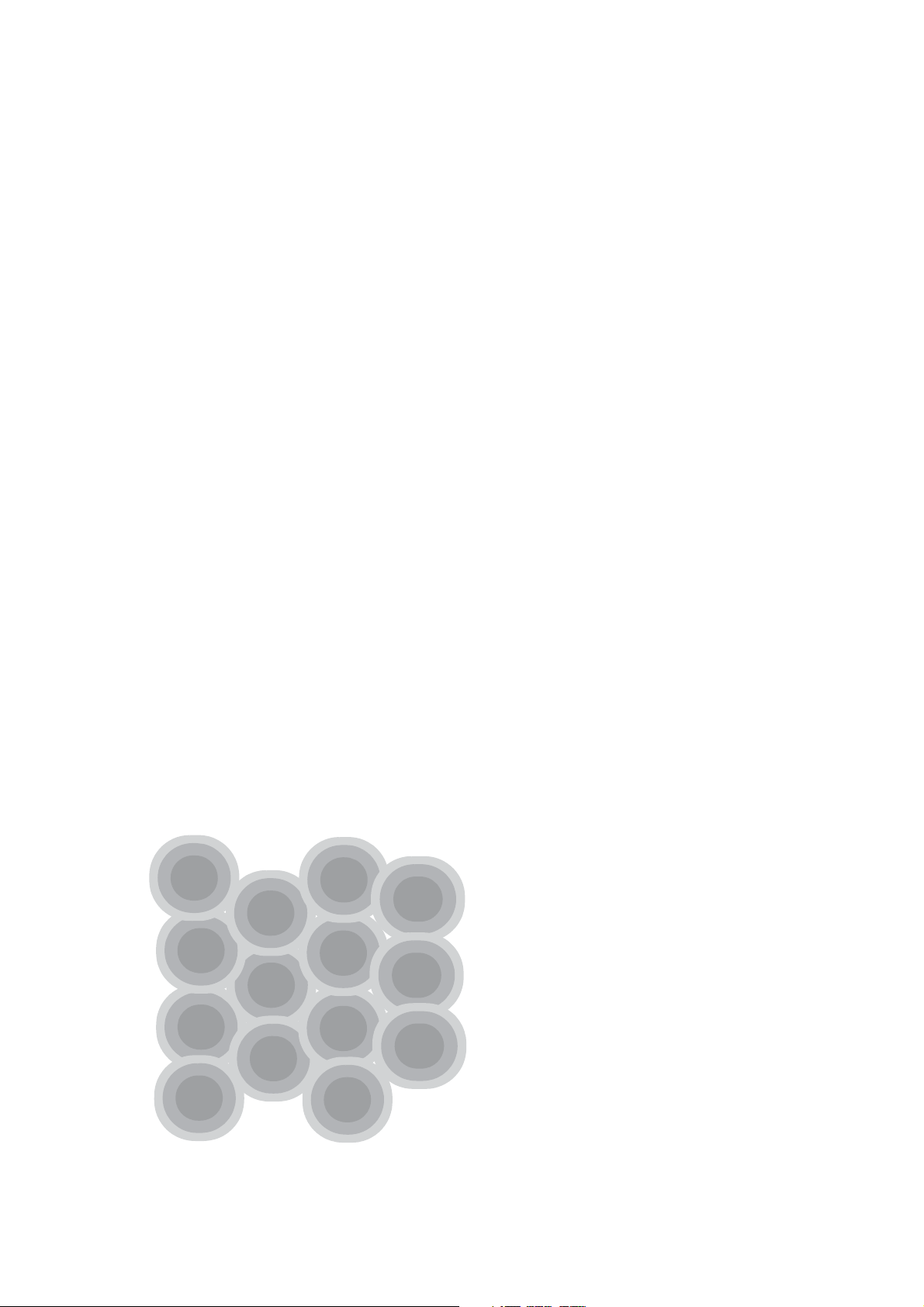
The 2.4 GHz band provides only 13 channels (only 11 are available in
North America), To reduce interference from channel overlap, adjacent
channels in the WLAN should be separated by at least 25 MHz. Most
users choose to run 3 channels, channels 1, 6, and 11. The illustration
below shows an ideal coverage plan where a series of ConneXium WiFi
access points broadcasting with omnidirectional antennas are arranged
by channel to limit the channel overlap.
1
1
11
11
6
1
11
6
1
11
6
6
1
1
20
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010

This coverage illustration is considered an ideal WLAN layout, but quite
often it cannot be installed so cleanly. Walls inside a building or
geographical barriers outdoors often deflect the radio wave transmission.
The floor plan in your building, the terrain and landscape in an outdoor
application, and the presence of other non-WiFi noise in the band need to
be anticipated as part of a network plan before your equipment is
purchased, then tested thoroughly as part of the installation process.
Schneider Electric recommends that you commission a professional site
survey (an independent study of your site requirements) to prepare for the
installation of a WLAN (see page 37).
Working in the 5 MHz Band
One clear advantage that a signal in the higher-frequency 5 GHz band
(802.11a and sometimes 802.11n) has is the availability of multiple
channels that do not overlap. In this radio spectrum, at least 8 channels
can be supported cleanly. Another advantage is that the band is not
populated by legacy ISM devices, so interference is much less likely.
There are some disadvantages though. Signals in the 5 MHz band
operate well when there is a clear and unobstructed line of sight. They do
not propagate well through physical obstacles such as interior walls and
doors and outdoor traffic and terrain. Also, some client devices, such as
the built-in wireless adapters in many laptops, operate only in the 2.4 GHz
band.
All of the ConneXium WiFi access point devices are dual-band, i.e., they
operate in both the 2.4 MHz and 5 MHz frequency bands. However, you
need to be aware of any bandwidth restrictions at your site when you
select your antennas because several of them are band-specific.
Here is how the access points perform in terms of transmission rate:
AP Device 802.11a 802.11b 802.11g 802.11n
TCSNWA241 Yes Yes Yes Yes (up to 300 Mb/s)
TCSNWA241F
TCSGWA242 Yes Yes Yes No (up to 54 Mb/s)
TCSGWA242F
TCSGWA271 Yes Yes Yes Yes (up to 300 Mb/s)
TCSGWA271F
TCSGWA272 Yes Yes Yes No (up to 54 Mb/s)
TCSGWA2A1 Yes Yes Yes Yes (up to 300 Mb/s)
Table 5: ConneXium WiFi access point transmission rates
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010
21

1.2.2 Government Regulation of the ISM Bands
Governments control and regulate the allotment of radio spectrum in their
airspace. In Europe, for example, band allocation is managed by the
European Radiocommunications Office (ERO), and in the United States and
Canada by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
If your ConneXium WiFi network is being designed to operate in the United
States or Canada, different access point modules are needed than if your
network is located in Europe, Asia, or Australia:
AP Device U.S./Canada Other Countries IP67
TCSNWA241 No Yes No No
TCSGWA242
TCSNWA241F Yes No No No
TCSGWA242F
TCSGWA271 No Yes Yes No
TCSGWA272
TCSGWA271F Yes No Yes No
TCSGWA2A1 No Yes Yes Yes
Table 6: ConneXium WiFi access points by country and application environment
a. IP67 indicates that the module has ingress protection against dust and immersion in water
up to 1 m.
b. ATEX indicates that the device is designed to operate in potentially explosive atmospheres.
a
ATEX
b
1.2.3 Anticipating Radio Wave Behavior
Because WiFi relies on radio bands for data transmission and reception, you
need to expect some network behaviors that differ from those on the wired
network. These behaviors include:
the ways that the transmissions propagate through physical impediments
and the atmosphere
the unbounded nature of radio signals
the inherent half-duplex nature of radio transmission and reception
Propagation can be hindered by both visible and invisible impediments.
Visible impediments
Visible impediments include walls, doors, windows and stacked material
inside a building. If you have chosen to operate at 2.4 GHz in order to get
the signal to propagate through a wall, you also need to know what is
behind the wall. A steel reinforcing beam or a mortar and cement fireblock
(a physical wall, not a network firewall) will deflect (or block) the radio
signal more severely than you might have expected if you assumed you
were passing through drywall.
22
S1A31526 - Draft - 8/2010
 Loading...
Loading...