Page 1
▬▬▬▬
SBIG
ASTRONOMICAL
INSTRUMENTS
Operating Manual
CCD Camera Models
ST-7XE/XME, ST-8XE, ST-9XE,
ST-10XE/XME and ST-2000XM/XCM
With High Speed USB Interface
Santa Barbara Instrument Group
147A Castilian Drive
Santa Barbara, CA 93117
Phone (805) 571-7244 • Fax (805) 571-1147
Web:<www.sbig.com> • Email:<sbig@sbig.com>
Page 2

Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is
no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning
the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the receiver and the equipment.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Shielded I/O cables must be used when operating this equipment.
You are also warned, that any changes to this certified device will void your legal right to
operate it.
OPERATION Manual for ST-XE/ST-8XE/ST-9XE/ST-10XE/ST-10XME/ST-2000XM
Revision 1.4
June, 2004
Page 3

Section 1 - Introduction
1.
1.1. Getting Started.................................................................................................................. 4
1.2. Installing the USB Drivers for the First Time...............................................................4
1.2.3. Getting Started with CCDOPS ....................................................................................... 22
1.2.4. To try some functions with sample images:................................................................. 22
1.2.5. Capturing Images with the CCD Camera ....................................................................22
2.
2.1. Cameras in General ....................................................................................................... 25
2.2. How CCD Detectors Work ........................................................................................... 25
2.3. Camera Hardware Architecture ..................................................................................26
2.4. CCD Special Requirements........................................................................................... 29
2.5. Electronic Imaging ......................................................................................................... 32
2.6. Black and White vs. Color............................................................................................. 33
Introduction .....................................................................................................................3
1.2.1. Installing the CCDOps and the Driver Checker ......................................5
1.2.2.1. Add New Hardware Wizard for Windows XP Users............................. 6
1.2.2.2. Add New Hardware Wizard for Window 95/98/Me Users ............... 13
1.2.2.3. Add New Hardware Wizard for Windows 2000 Users........................ 18
Introduction to CCD Cameras .................................................................................... 25
2.2.1. Full Frame and Frame Transfer / Interline CCDs ................................. 26
2.4.1. Cooling.........................................................................................................29
2.4.2. Double Correlated Sampling Readout ....................................................30
2.4.3. Dark Frames ................................................................................................ 30
2.4.4. Flat Field Images......................................................................................... 30
2.4.5. Pixels vs. Film Grains................................................................................. 31
2.4.6. Guiding ........................................................................................................ 32
3.
3.1. Step by Step with a CCD Camera................................................................................ 35
3.2. Attaching the Camera to the Telescope ...................................................................... 35
3.3. Establishing a Communications Link .........................................................................36
3.4. Focusing the CCD Camera ...........................................................................................36
3.5. Finding and Centering the Object ............................................................................... 38
3.6. Taking an Image............................................................................................................. 38
3.7. Displaying the Image .................................................................................................... 38
3.8. Processing the Image..................................................................................................... 39
3.9. Advanced Capabilities .................................................................................................. 39
4.
4.1. System Components...................................................................................................... 43
4.2. Connecting the Power ................................................................................................... 43
4.3. Connecting to the Computer........................................................................................ 43
4.4. Connecting the Relay Port to the Telescope............................................................... 43
At the Telescope with a CCD Camera....................................................................... 35
3.9.1. Crosshairs Mode (Photometry and Astrometry) ................................... 39
3.9.2. Sub-Frame Readout in Focus.................................................................... 39
3.9.3. Track and Accumulate...............................................................................40
3.9.4. Autoguiding and Self Guiding................................................................. 40
3.9.5. Auto Grab .................................................................................................... 41
3.9.6. Color Imaging ............................................................................................. 41
Camera Hardware .........................................................................................................43
Page 1
Page 4

Section 1 - Introduction
4.4.1 Using Mechanical Relays............................................................................... 44
4.5. Modular Family of CCD Cameras............................................................................... 46
4.6 Connecting accessories to the Camera........................................................................ 50
4.7 Battery Operation...........................................................................................................51
5.
5.1. Lunar and Planetary Imaging ...................................................................................... 53
5.2. Deep Sky Imaging..........................................................................................................53
5.3. Terrestrial Imaging ........................................................................................................53
5.4. Taking a Good Flat Field............................................................................................... 54
5.5. Building a Library of Dark Frames.............................................................................. 54
5.6. Changing the Camera Resolution................................................................................ 54
5.7. Flat Fielding Track and Accumulate Images ............................................................. 55
5.8. Tracking Functions ........................................................................................................56
6.
6.1. Water Cooling................................................................................................................. 59
6.2. Tri-color Imaging ...........................................................................................................60
6.3. Camera Lens Adapters and Eyepiece Projection....................................................... 60
6.4. Focal Reducers................................................................................................................60
6.5. AO-7 and Lucy-Richardson Software ......................................................................... 60
6.6. SGS - Self-Guided Spectrograph.................................................................................. 60
6.7. Third Party Products and Services .............................................................................. 61
6.8. SBIG Technical Support ................................................................................................61
Advanced Imaging Techniques ................................................................................. 53
Accessories for your CCD Camera............................................................................. 59
6.7.1. Windows Software ..................................................................................... 61
6.7.2. Image Processing Software ....................................................................... 61
6.7.3. Getting Hardcopy....................................................................................... 61
7.
8.
A.
A.1. Connector Pinouts for the AO7/CFW8/SCOPE port:.............................................. 69
A.2. Connector Pinouts for the power jack:........................................................................ 69
A.3. Connector Pinouts for the I2C AUX port:................................................................... 69
A.4. SBIG Tracking Interface Cable (TIC-78)...................................................................... 70
B.
B.1. Cleaning the CCD and the Window ........................................................................... 71
B.2. Regenerating the Desiccant ..........................................................................................71
C.
C.1. Technique........................................................................................................................ 72
D.
E.
Common Problems .......................................................................................................63
Glossary .......................................................................................................................... 65
Appendix A - Connector and Cables......................................................................... 69
Appendix B - Maintenance.......................................................................................... 71
Appendix C - Capturing a Good Flat Field .............................................................. 72
Appendix D - Use and Maintenance of the Cooling Booster ...............................73
Appendix E – Third Party Vendors Supporting SBIG Products.......................... 75
Page 2
Page 5

Section 1 - Introduction
1. Introduction
Congratulations and thank you for buying one of Santa Barbara Instrument Group's CCD cameras.
The model ST-7XE/XME, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE/XME, and ST-2000XM/XCM are SBIG's fifth
generation CCD cameras and represent the state of the art in CCD camera systems with their low
noise and advanced capabilities, including Kodak's new Blue Enhanced E series of CCDs and high
speed USB interface. We feel that these cameras will expand your astronomy experience by being
able to easily take images like the ones you've seen in books and magazines, of structure never seen
through the eyepiece. SBIG CCD cameras offer convenience, high sensitivity, and advanced image
processing techniques that film just can't match. While CCDs will probably never replace film in its
large format, CCDs allow a wide range of scientific measurements and have established a whole
new field of amateur astronomy that is growing by leaps and bounds.
These cameras include several exciting new features: improved self-guiding (US Patent
5,525,793), high speed USB interface, improved cooling design and more. These cameras have two
CCDs inside, one for guiding and a large one for imaging. The low noise of the read out electronics
virtually guarantees that a usable guide star will be within the field of the guiding CCD for
telescopes with F/numbers F/6.3 or faster. The new cooling design is capable of performance
similar to that which used to require an optional second stage cooling booster. The relay output
plugs directly into most recent commercial telescope drives and is easily modifiable to virtually any
drive system. As a result, you can take hour long guided exposures with ease, with no differential
deflection of guide scope relative to main telescope, and no radial guider setup hassles, all from the
computer keyboard. This capability, coupled with the phenomenal sensitivity of the CCD, will
allow the user to acquire observatory class images of deep sky images with modest apertures! The
technology also makes image stabilization possible through our AO-7, or self-guided spectroscopy
with our SGS.
The new ST-X series of cameras incorporate the following design improvements over their
parallel based predecessors:
Uses High Speed USB vs. Parallel Port for 10X to 15X faster downloads.
Adds a new I2C bi-directional AUX port for future use.
LEDs on the Digital Board show Relay Activations (helpful for troubleshooting).
New Heat Exchanger with Water Circulation Capability built-in.
No firmware ROM to update, software uploads to camera at boot-up.
New capabilities can be added to the camera by replacing the loader driver.
New Boot sequence, LED flashes and fan comes on when firmware upload is complete.
LED flashes when initializing shutter.
Mechanical/electronic design work to reduce shutter errors and stray light.
TC237 autoguider CCD added to the ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE and ST-10XME.
Premier software, CCDSoftV5 and TheSky included with each camera.
CCDOPS version 5 camera control software included with major improvements
o Support for USB cameras
o Support for Ethernet (Ethernet to Parallel) for parallel cameras
o Read FITS files
o Save in several formats (including ASCII format that imports to Excel).
o Multiple images open at once
o New universal drivers
Page 3
Page 6

Section 1 - Introduction
o Works with all 32-bit Windows OS (95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP).
o Version 5 (Gold Icon) can co-exist with Version 4 (Black Icon).
o Focus Mode Dialog has big numbers for peak brightness to aid focusing.
o Added 1xN, 2xN and 3N readout modes to ST-7/8/9/10/1001
o Magnified preview in crosshairs window
o Sharpen preview in contrast dialog.
o Dockable Icon bar.
1.1. Getting Started.
This manual describes the ST-7XE/XME, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE/XME and ST-2000XM/XCM
CCD Camera Systems from Santa Barbara Instrument Group. The first section contains USB driver
installation instructions. The USB driver installation process must be completed by anyone
installing an SBIG USB camera for the first time on a particular computer. If you wish to run your
SBIG USB camera from more than one computer, you must go through the USB driver installation
process for each computer you intend to use.
For users new to the field of CCD Astronomy, Sections 2, 3 and 4 offer introductory material
about CCD Cameras and their applications in Astronomy. Users who are familiar with CCD
cameras may wish to skip section 2 and browse through sections 3 and 4, reading any new material.
Thoroughly experienced SBIG customers may wish to jump right to the separate Software
Manual, which gives detailed and specific information about the SBIG software. Sections 5 and 6
offer hints and information about advanced imaging techniques and accessories for CCD imaging
that you may wish to read after your initial telescope use of the CCD camera. Finally, section 7 may
be helpful if you experience problems with your camera, and the Appendices provide a wealth of
technical information about these systems.
1.2. Installing the USB Drivers for the First Time
If you are installing an SBIG USB camera for the first time use this section to walk you through the
driver installation process. To operate the camera you must first install camera control software
onto your computer or laptop. Your camera comes with two programs: CCDOPS from SBIG and
CCDSoftV5, which was jointly written by Software Bisque and SBIG. CCDSoftV5 is a very
comprehensive program that incorporates many of the camera control functions of CCDOPS.
However, because we use CCDOPS solely to develop and test our cameras we are able to post more
frequent updates for CCDOPS at our web site for free download. You can use either program to
control the camera but we suggest starting with CCDOPS to install the USB drivers and to make
sure everything is working properly and then move to CCDSoftV5 when you are more familiar
with the operations of the camera. Follow the instructions below to install and run the CCDOPS
software and display and process sample images found at our web site.
Please follow these directions IN SEQUENCE. Do not connect the camera to the PC or turn it on
until instructed to do so below. USB drivers can be difficult to install if you don’t follow the
instructions.
Page 4
Page 7
Section 1 - Introduction
1.2.1. Installing the CCDOps and the Driver Checker
The first thing you should do in all cases is to install CCDOps version 5 and the Driver Checker
utility. This is relatively simple:
1. Make sure the camera is not connected to the computer. You will do this later.
2. Run the CCDOps Installer. It can be found in the CCDOps directory of the CD-ROM that
came with your camera. Follow the onscreen instructions to complete the installation.
3. First make sure you are the Administrator or have Administrator privileges if you’re
running under Windows 2000, or Windows XP. On Windows XP Home edition you are the
administrator so you don’t have to worry about that. Next run the Driver Checker Installer.
It can be found in the Driver Checker folder of the CD-ROM.
4. Towards the end of the Driver Checker installation the installer will run the utility. This
utility checks to make sure you have the latest version of the SBIG camera drivers installed
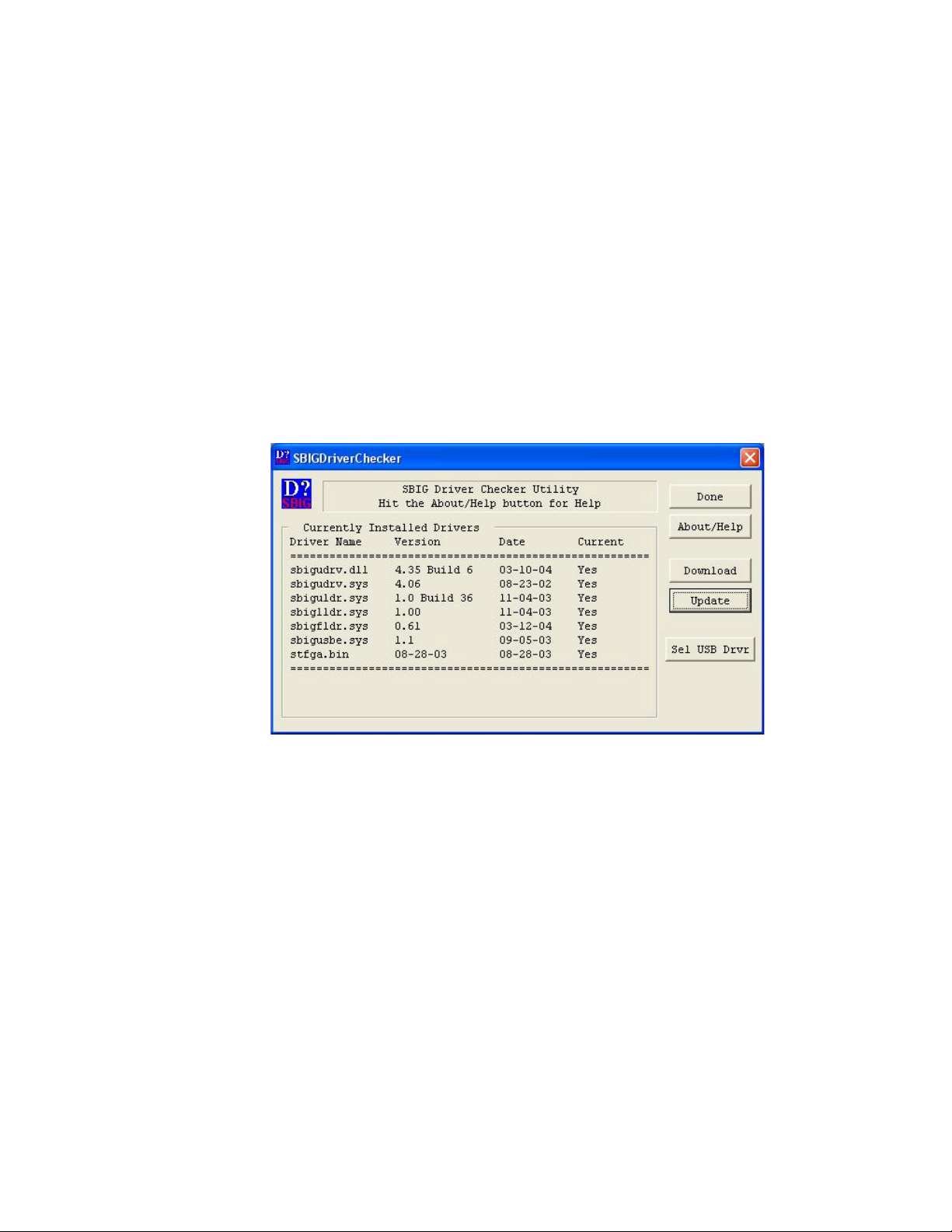
on your system. When the SBIGDriverChecker utility is run you’ll see a dialog like:
If you have previously installed CCDOPS you’ll see some entries in the table. Most likely
one or more drivers is not installed or is not up to date. Also if this is the first time you’ve
run the Driver Checker you may get a warning something like “The sbigudrv service can
not be found”. Just ignore this error.
Page 5
Page 8
Section 1 - Introduction
5. Using the Driver Checker to update your drivers is a two-step process:
A. If you have an internet connection, Click on the
instructions to download the current drivers from SBIG’s Servers. If you don’t have an
internet connection on this machine then make sure you have downloaded the latest Driver
Checker Installer from SBIG’s web site, copied it to this machine and run it.
B. Whether you have an internet connection or not then click the
copy the current drivers to your system and make sure they are properly installed. Some
new computers without parallel ports will report that the SBIGUDRV.SYS was not started.
Don’t worry about that. The SBIGUDRV.SYS is the parallel port camera driver and is not
use with USB cameras.
You may be asked to reboot your system as well. If so, click Done and do so. Otherwise
simply click Done.
6. Follow the instruction in Sections 1.2.2.1, 1.2.2.2 or 1.2.2.3 below depending on the version of
Windows you have on your computer.
Download
button then follow the
Update
button. This will
1.2.2.1. Add New Hardware Wizard for Windows XP Users
1. With the camera disconnected from the computer, plug in the power to the camera and if
your power supply has a power switch turn on the power to the camera.
2. Plug the camera into the computer with the supplied USB cable. The computer will then
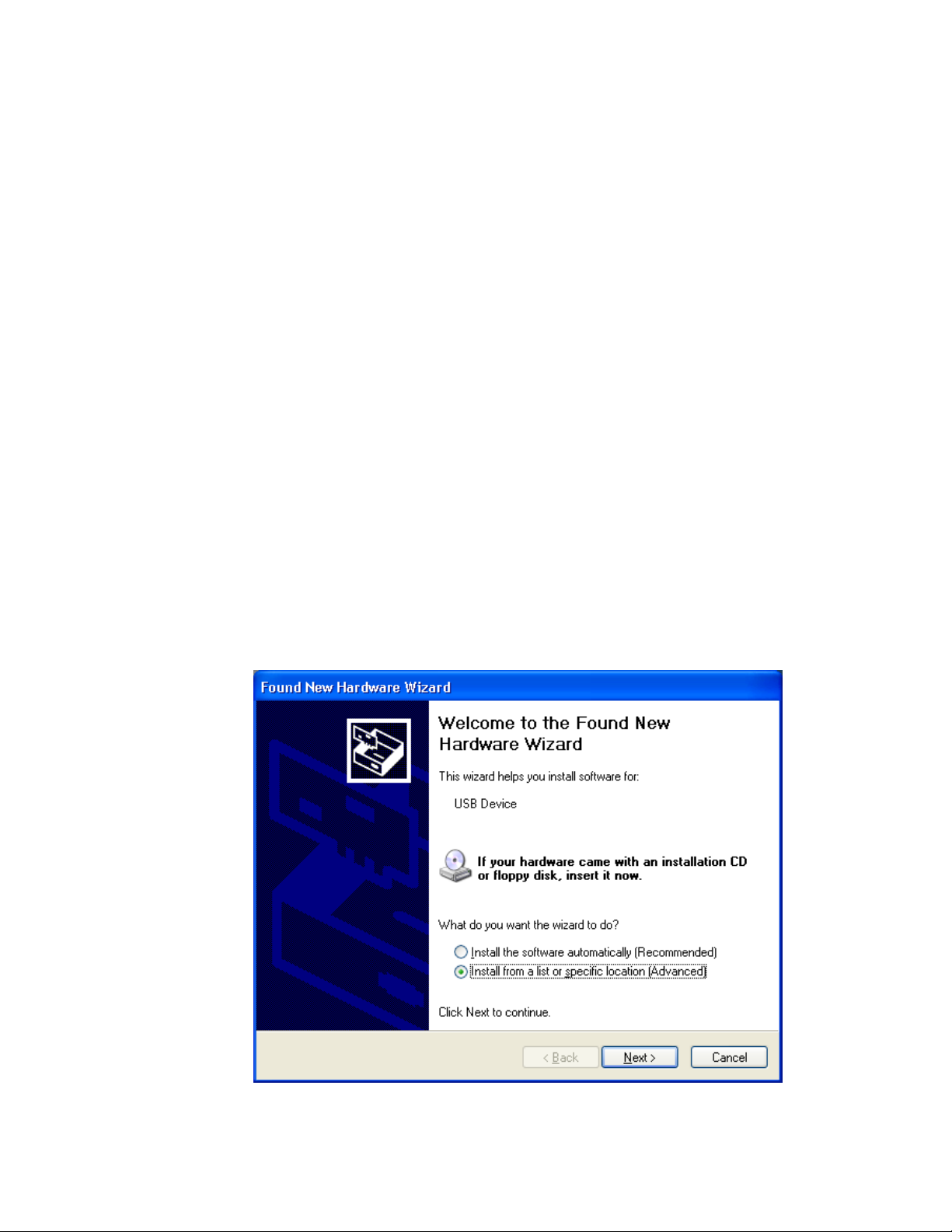
present you with the Found New Hardware Wizard. Click the “
button then click the
Next
button.
Install from a list…
” radio
Page 6
Page 9
Section 1 - Introduction
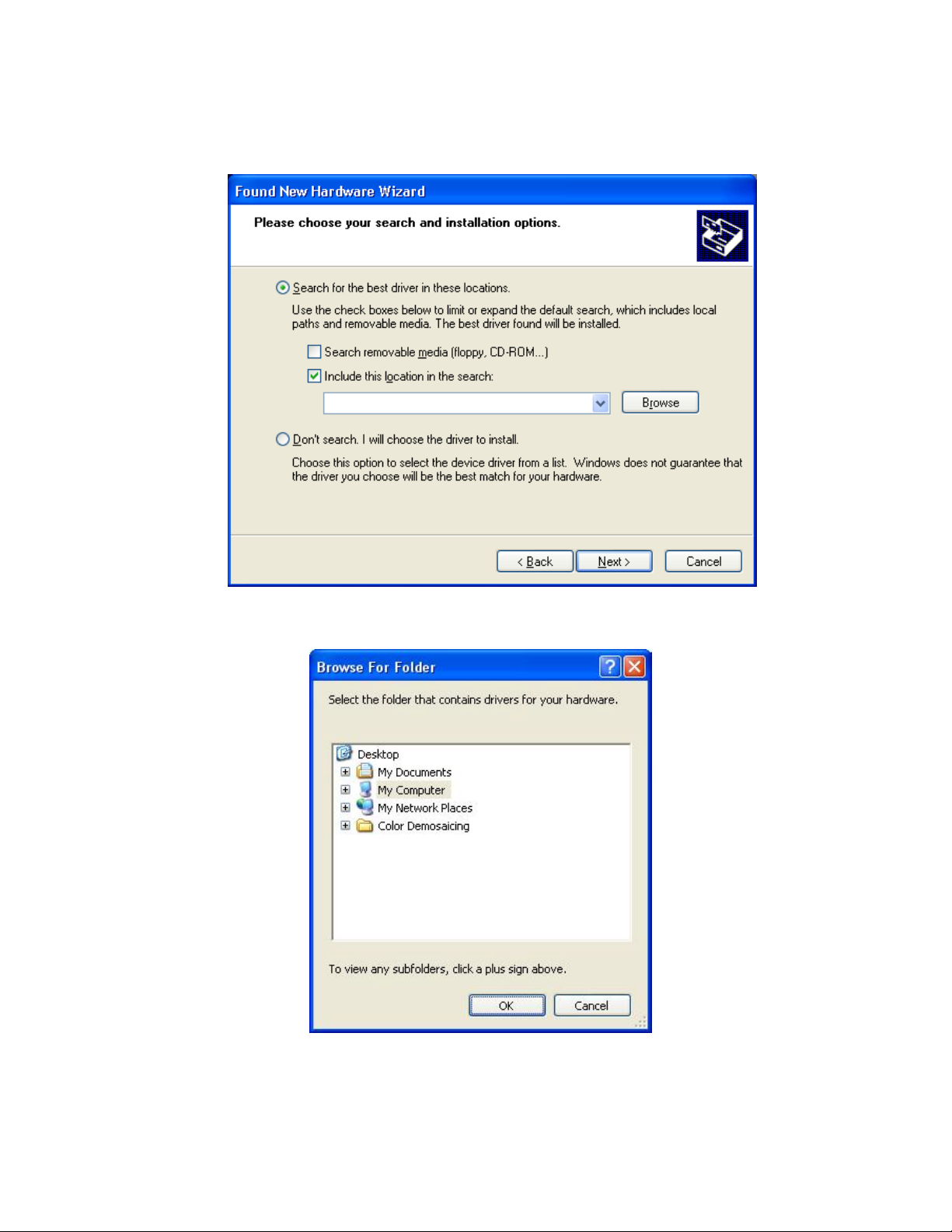
3. As shown below, click the “
Include this location…
“
” checkbox then click the
Search for the best driver…
Browse
” radio button then check the
button.
You will see the
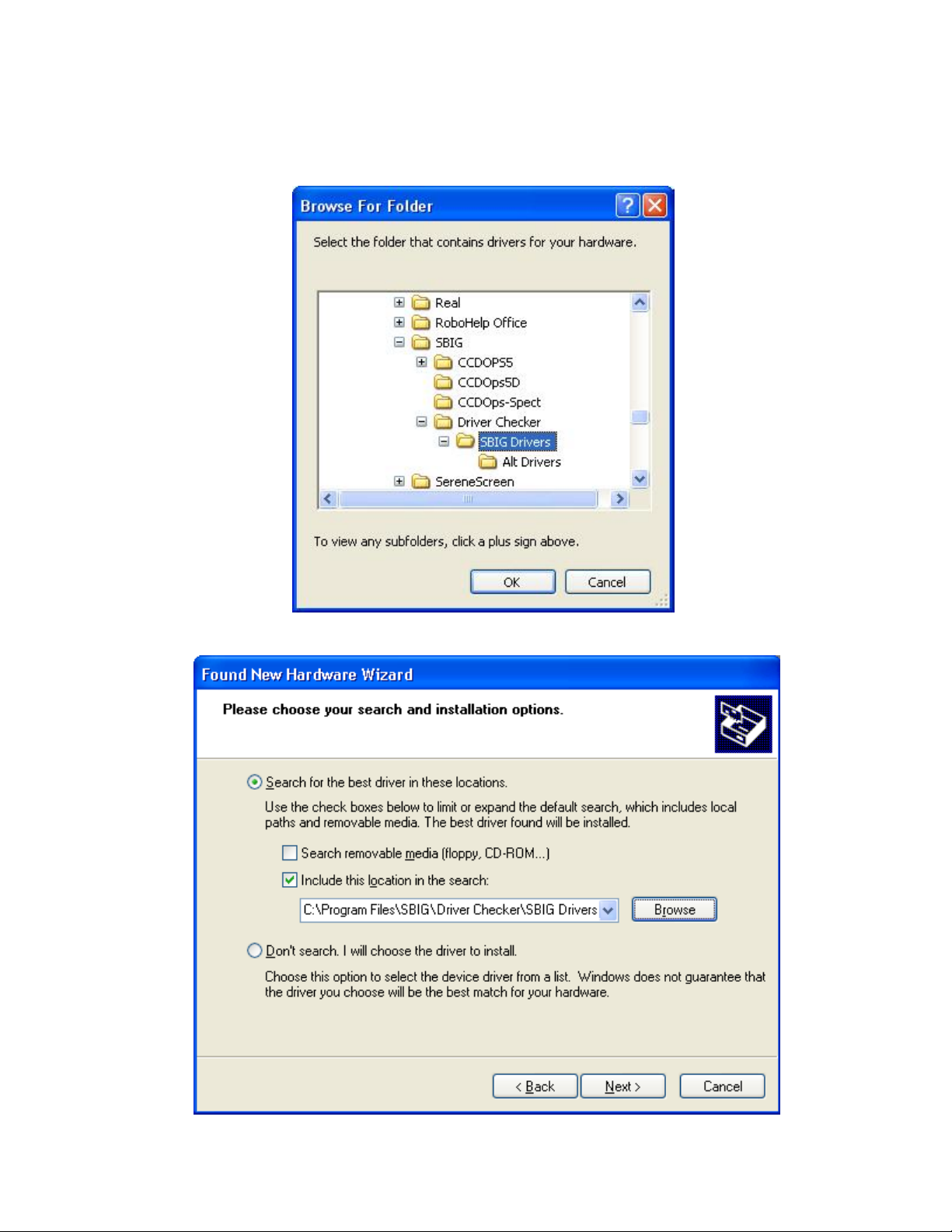
Navigate through the directory structure of you hard drive to the:
My Computer\C:\Program Files\SBIG\Driver Checker\SBIG Drivers
Browse for Folder
dialog shown below:
Page 7
Page 10
Section 1 - Introduction
directory. Expand each section by clicking on the “+” next to the name. For example scroll
to the top and click the “+” next to My Computer, then click the “+” next to C:, etc. Finally
click on the
SBIG Drivers
folder to select it (it will turn blue as shown below) then click OK.
You’ll then be back in the Found New Hardware Wizard. Click the
Next
button.
Page 8
Page 11

Section 1 - Introduction
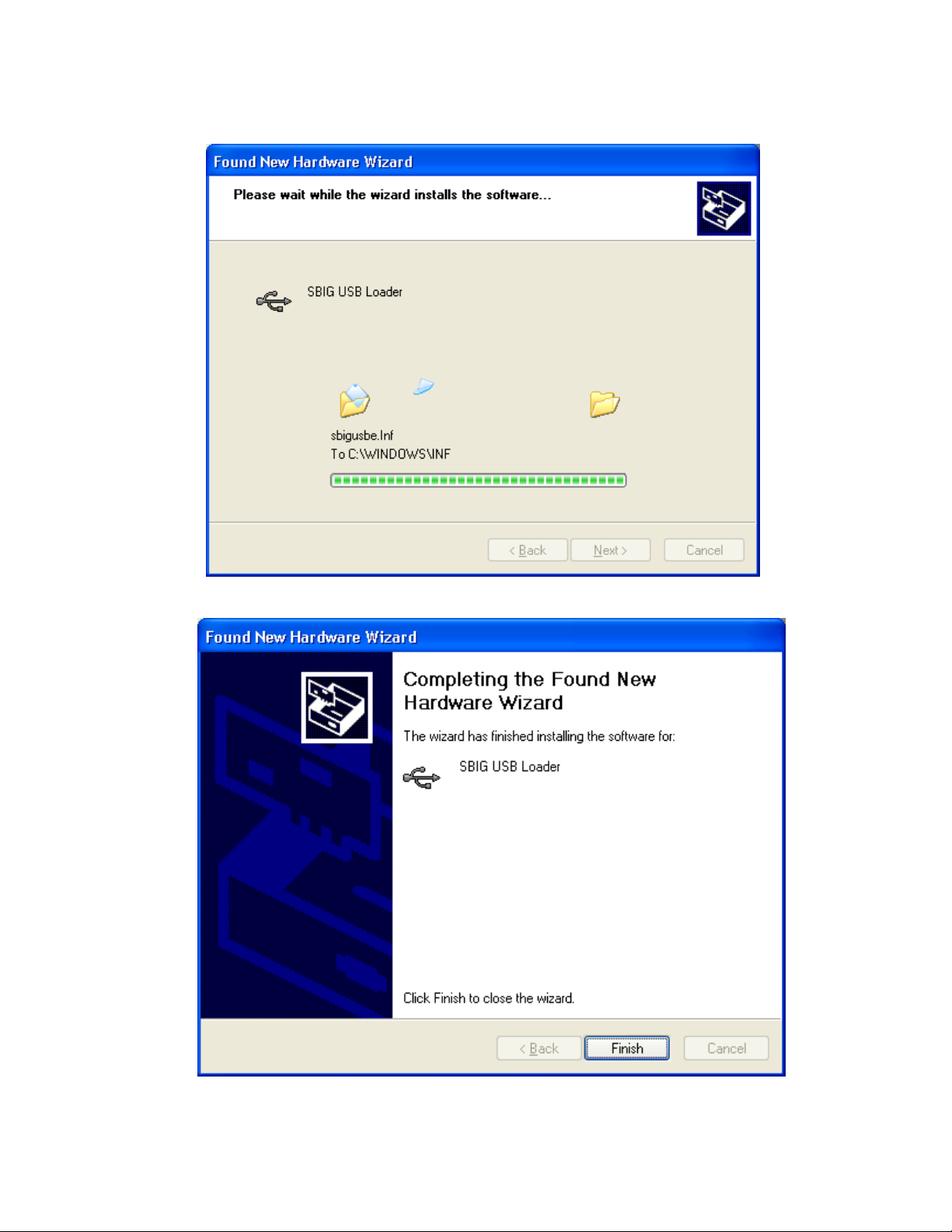
4. Windows will show the dialog below while it is copying the driver:
5. You may be presented with the dialog below warning you the SBIG USB Loader driver has
not passed the Windows Logo testing procedure. At this point click the
Continue Anyway
button.
Page 9
Page 12
Section 1 - Introduction
6. Windows will continue installing the driver as shown in the dialog below:
7.
Windows will finish installing the SBIG USB Loader driver as shown in the dialog below
Hit the
Finish
button.
You are half-way through the installation of the drivers.
At this point the Camera’s Fan and LED should come on.
Page 10
Page 13
Section 1 - Introduction
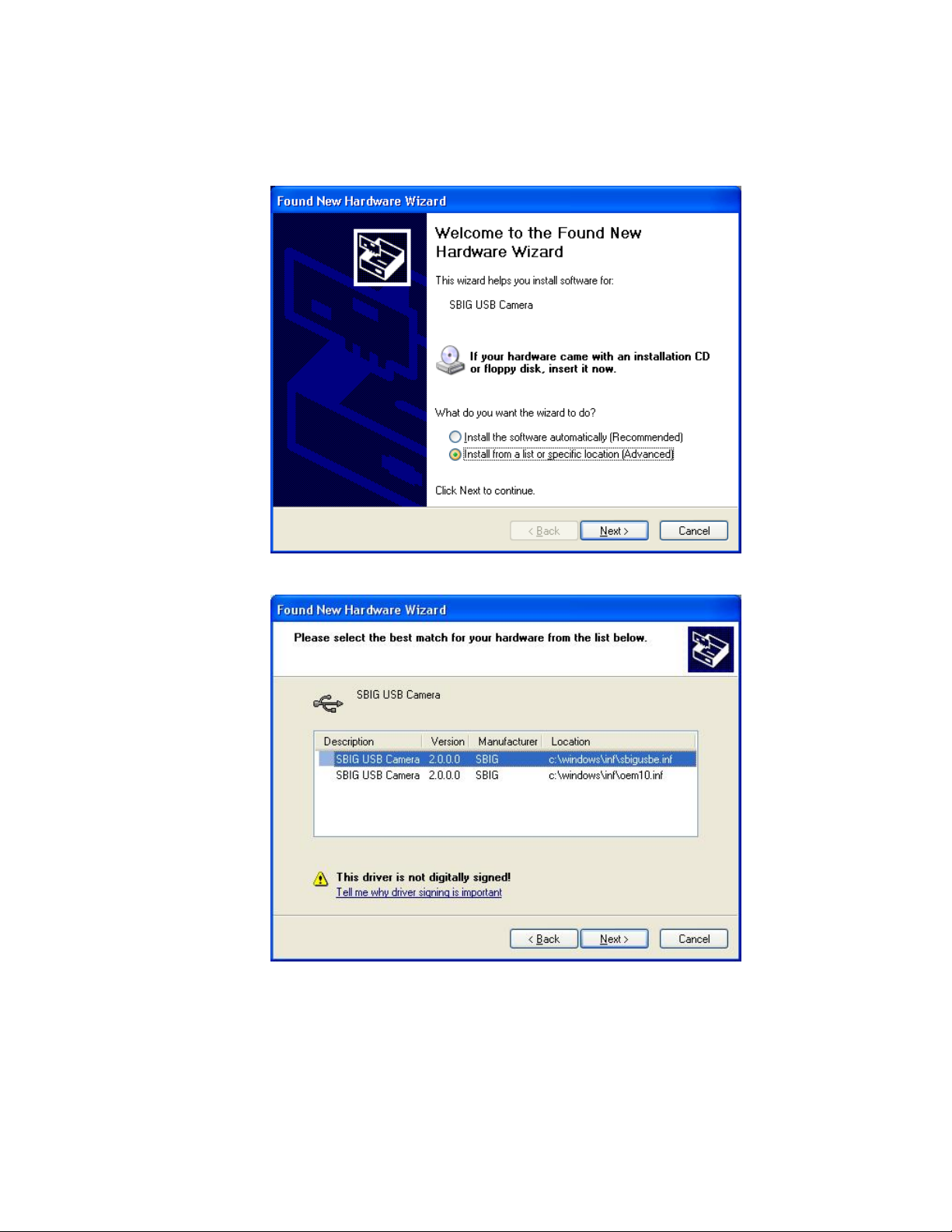
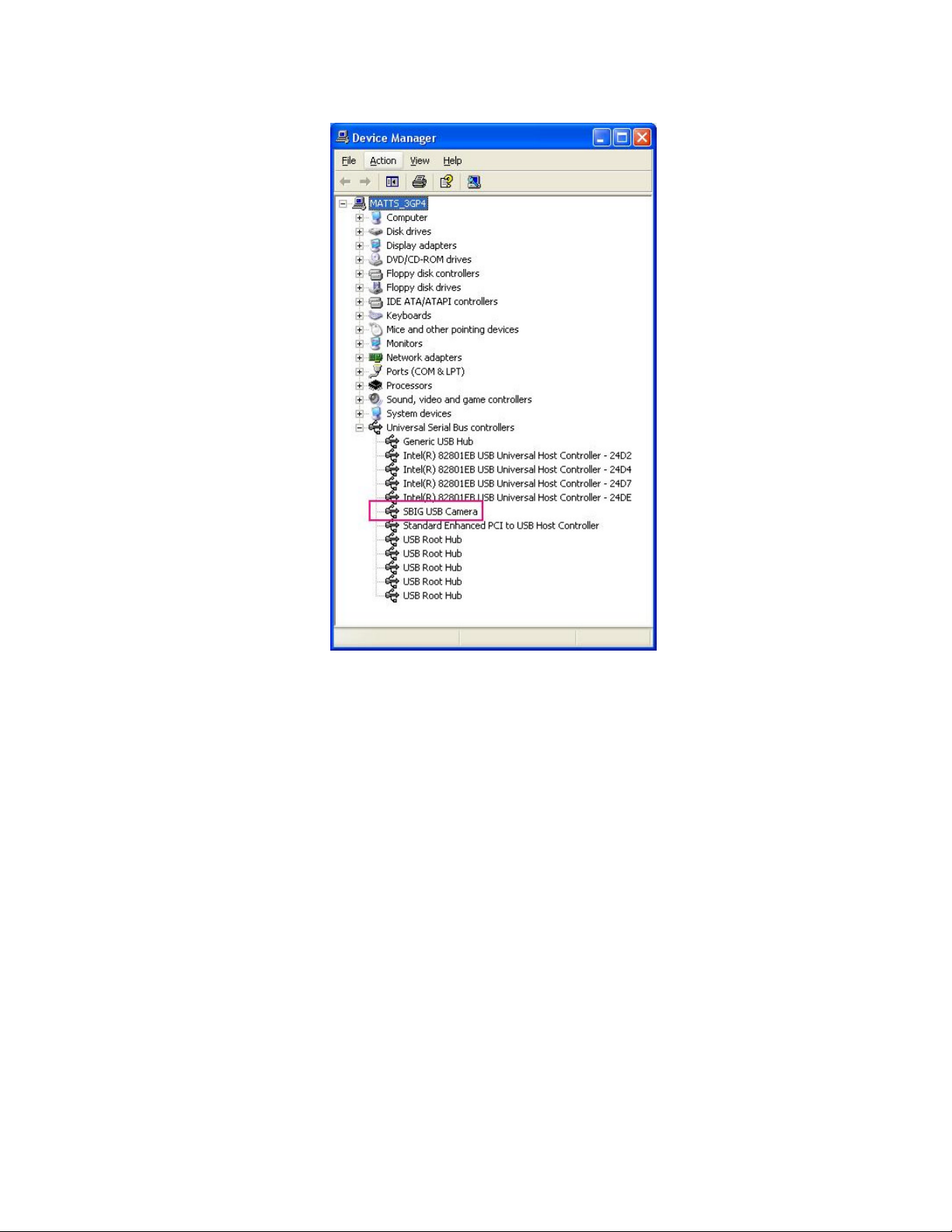
8. Again you will be presented with the Found New Hardware wizard for the SBIG USB
Camera driver as shown in the dialog below. Repeat steps 3 through 7 for this driver just
like you did before.
9. At one point you may be presented with the following dialog:
Select the top entry and hit the
Control Panel
from the
Start Menu
button and finally expand the
Next
button. When you’re all done if you open the
, select the
Universal Serial Bus Controllers
Hardware
tab then click the
section at the bottom you
should see the SBIG USB Camera entry as shown below:
System
Device Manager
Page 11
Page 14
Section 1 - Introduction
Page 12
Page 15
Section 1 - Introduction
1.2.2.2. Add New Hardware Wizard for Window 95/98/Me Users
1. With the camera disconnected from the computer, plug in the power to the camera and if
your power supply has a power switch turn on the power to the camera.
2. Plug the camera into the computer with the supplied USB cable. The computer will then
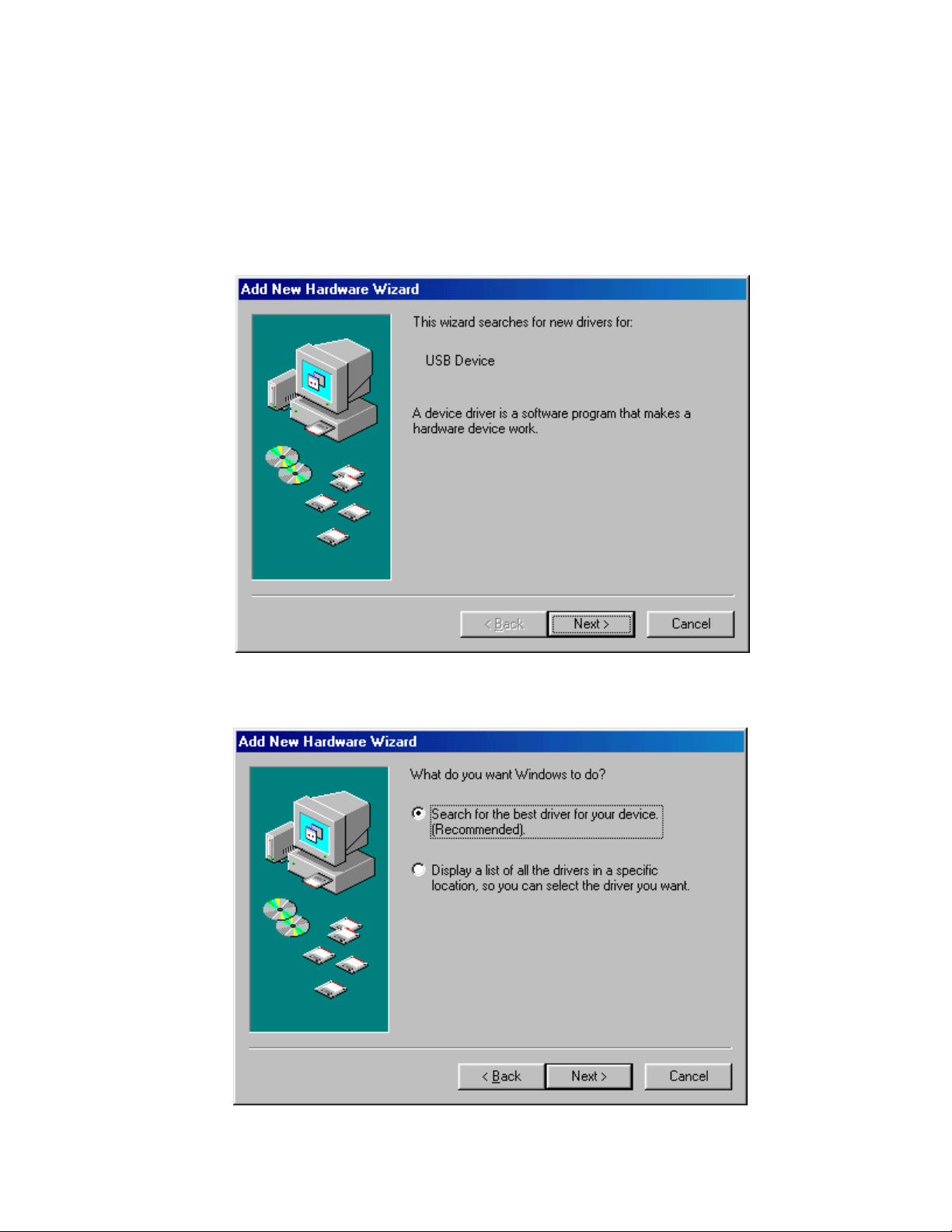
present you with the Found New Hardware Wizard shown below:
Click the
3.
Click “
Next
button.
Search for the best driver..
” then click the
Next
button as shown below:
Page 13
Page 16
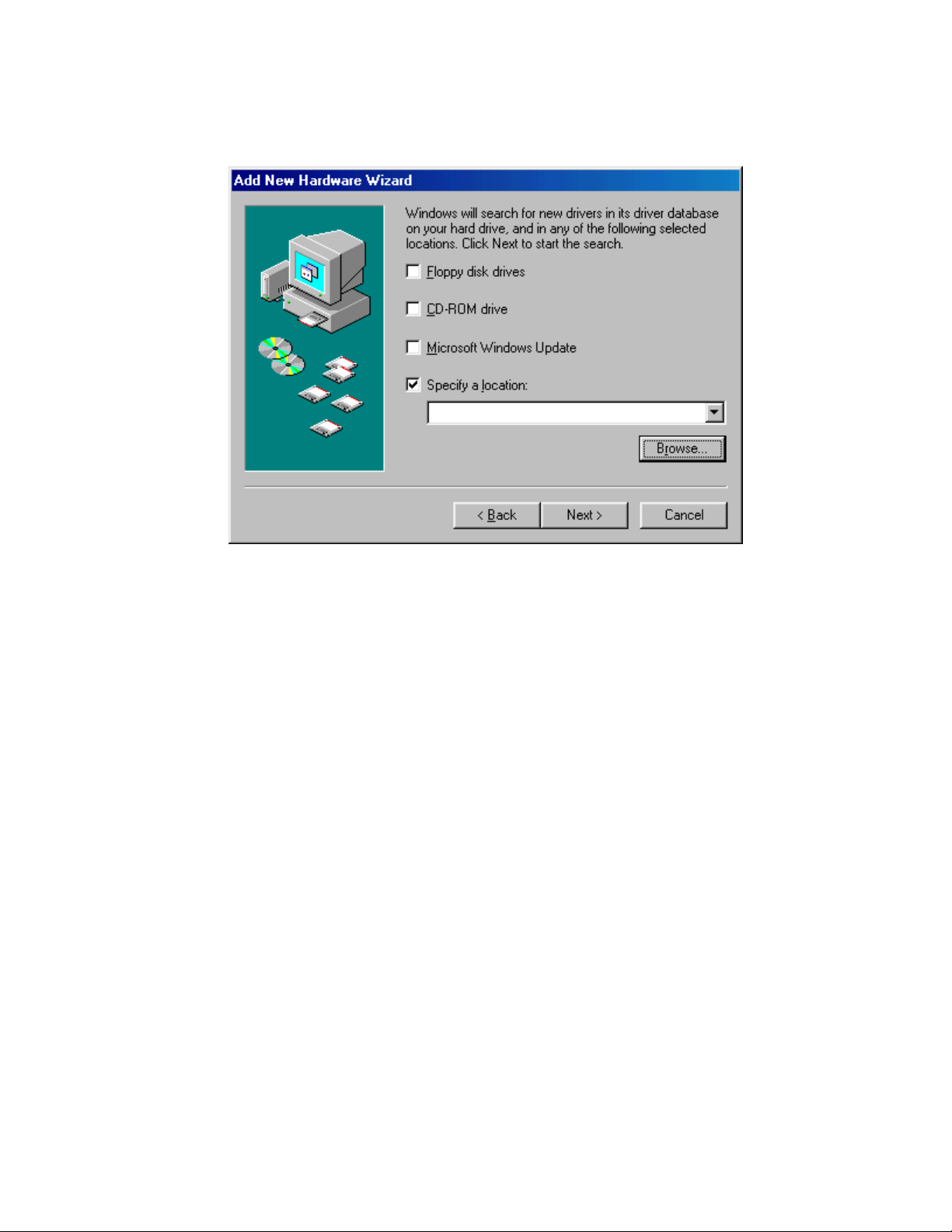
Section 1 - Introduction
4.
Uncheck all the options except “
Specify a location
” as shown below then click the Browse
button
Page 14
Page 17
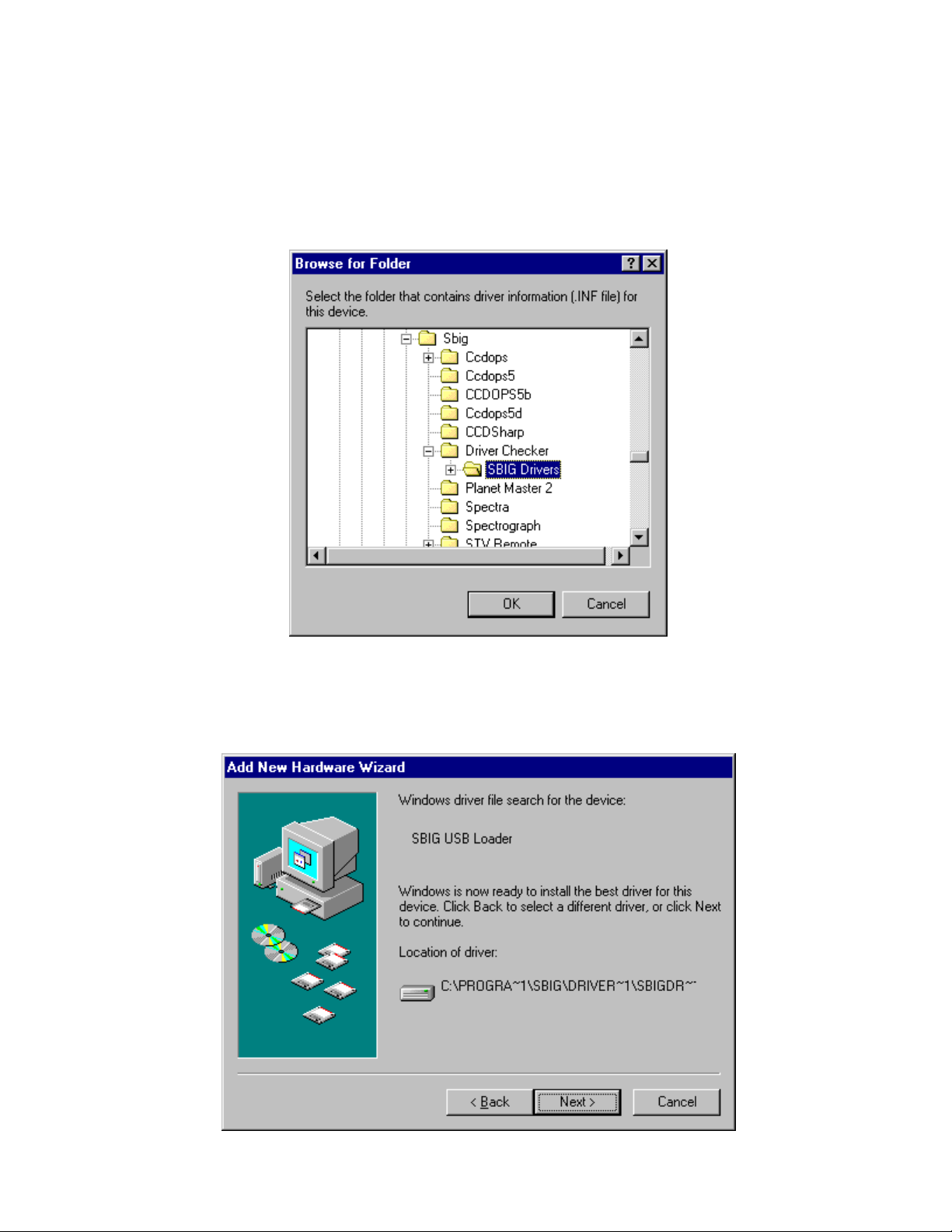
Section 1 - Introduction
5. Navigate through the Browser window to the
My Computer\C:\Program Files\SBIG\Driver Checker\SBIG Drivers
directory as shown below. Expand each section by clicking on the “+” next to the name.
For example scroll to the top and click the “+” next to My Computer, then click the “+” next
to C:, etc.:
Click on the
SBIG Drivers
folder until it is highlighted as shown above then click the OK
button. This will get you back to the dialog shown above in step 4 but with the location
filled out. Click the
6.
You’ll see the dialog below. Click the
Next
button.
Next
button.
Page 15
Page 18
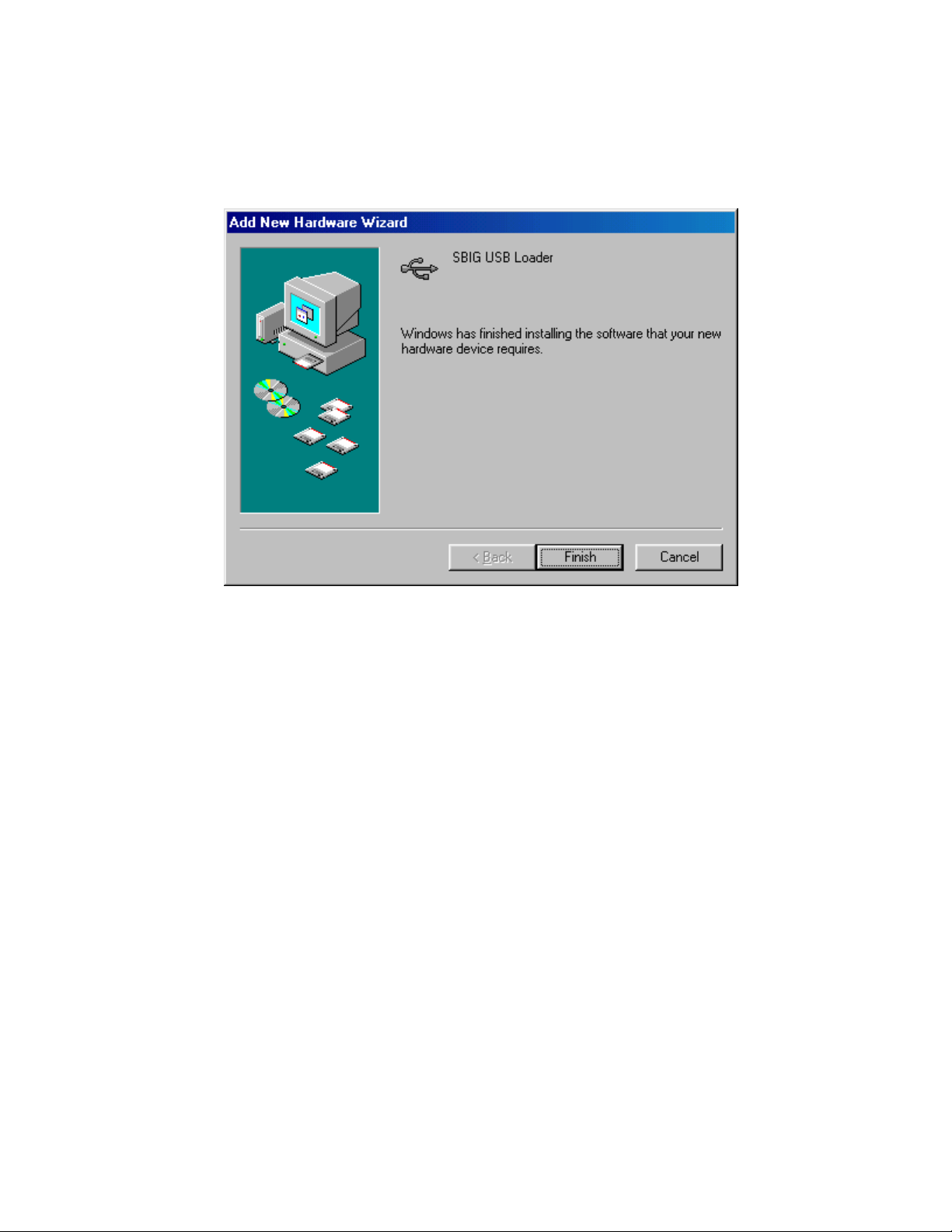
Section 1 - Introduction
7.
Windows will spin for a while and then present you with the dialog below. Click the
button and you’re done. The SBIG cameras actually use two drivers and after you click
Finish the system will automatically install the second driver.
LED should come on in the camera
.
At this point the Fan and
Finish
Page 16
Page 19
Section 1 - Introduction
8.
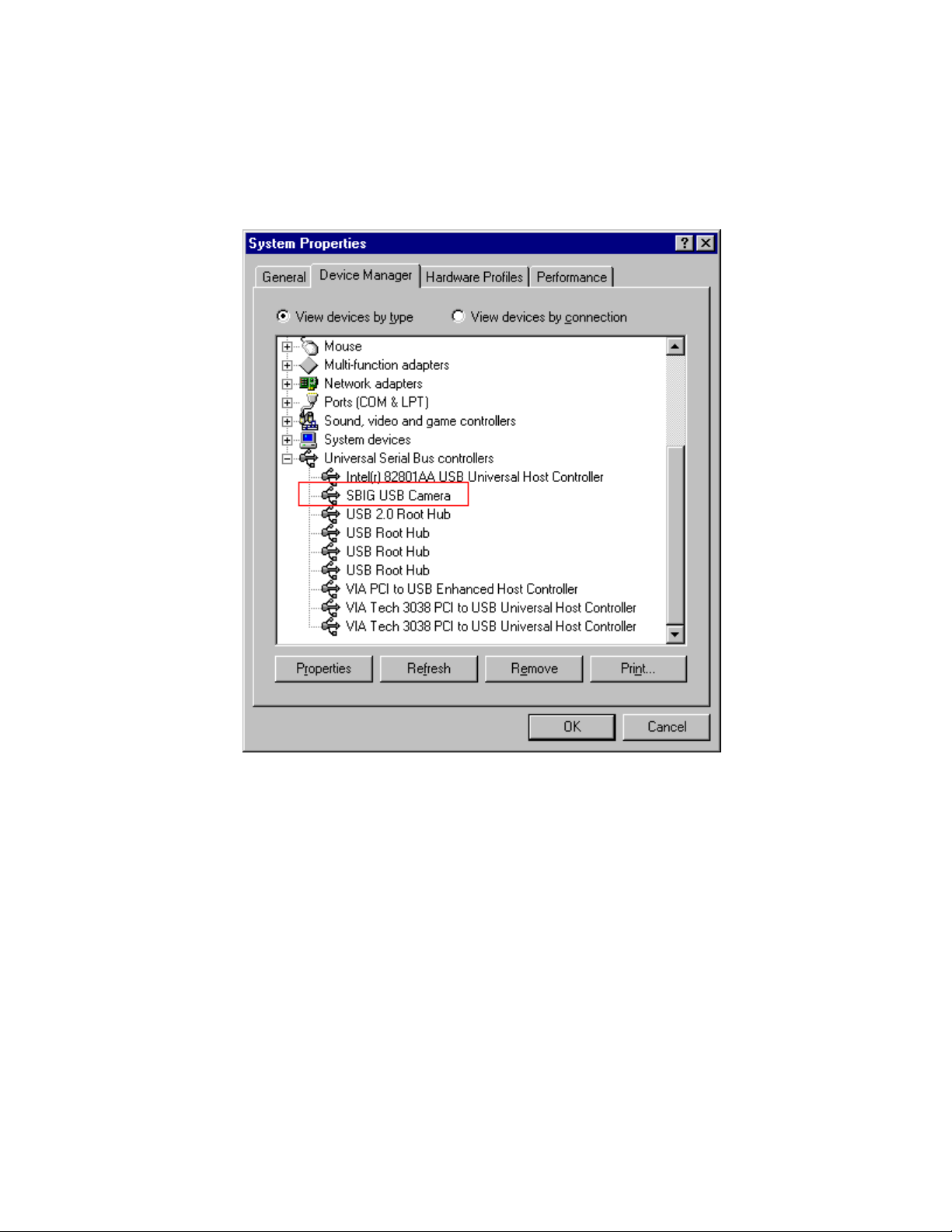
If you have any question about whether the drivers were installed correctly open the Device
Manager tab of the System Control Panel. Click the “View devices by type” button and
expand the “Universal Serial Bus controllers” section by clicking the “+” to the left. You
should see something like the dialog below where we have highlighted the SBIG USB
Camera in red outline:
Page 17
Page 20
Section 1 - Introduction
1.2.2.3. Add New Hardware Wizard for Windows 2000 Users
1. With the camera disconnected from the computer, plug in the power to the camera and if
your power supply has a power switch turn on the power to the camera.
2.
Plug the camera into the computer with the supplied USB cable. The computer will then
present you with the Found New Hardware Wizard shown below. Click the
Next
button.
Page 18
Page 21
Section 1 - Introduction
3. Click the “
then click the
Search for suitable driver…
Next
button.
” radio button as shown below:
Uncheck all the options other than “Specify a location” as shown below:
4.
then click the
Next
button.
Page 19
Page 22
Section 1 - Introduction
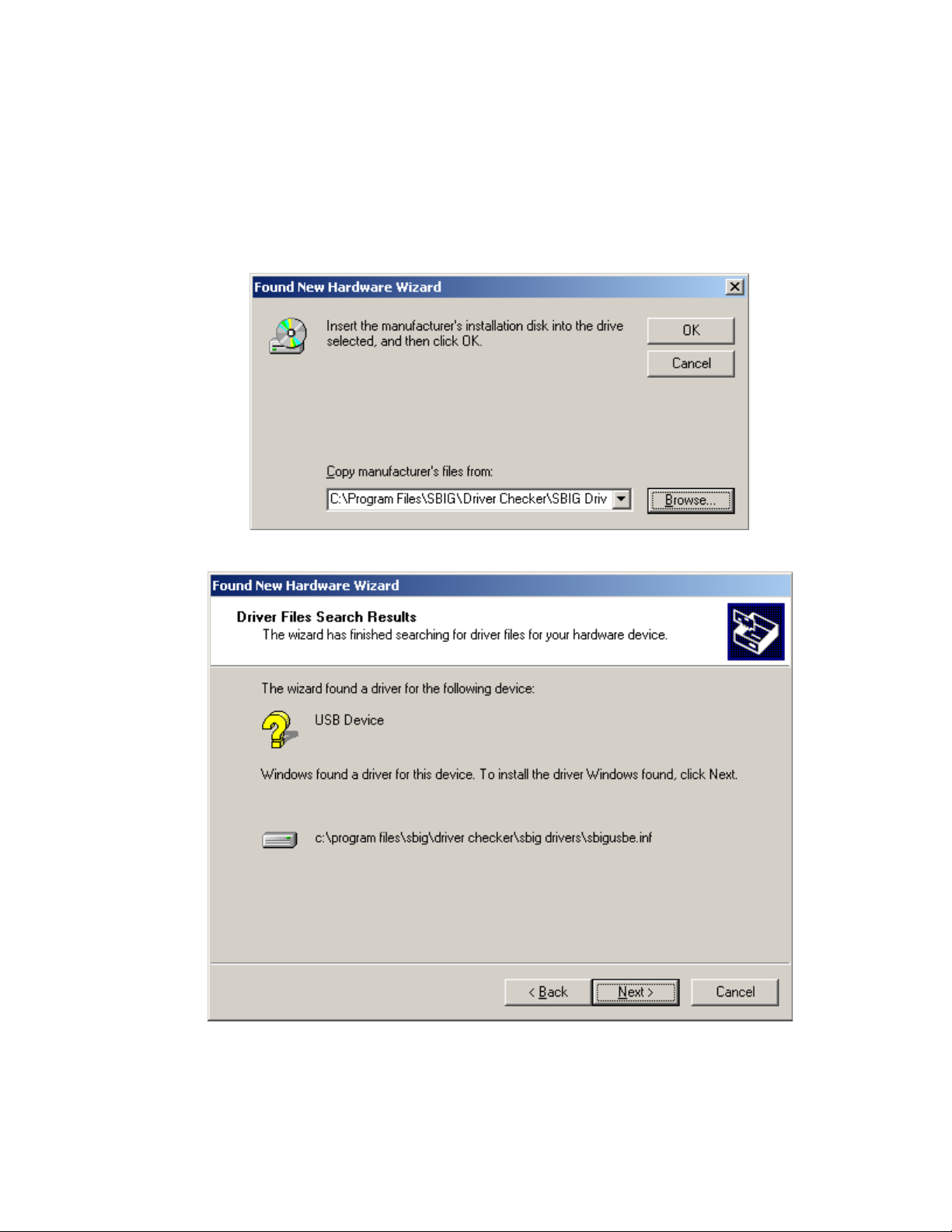
5.
As shown below click the Browse button then navigate to the
My Computer\C:\Program Files\SBIG\Driver Checker\SBIG Drivers
directory. Expand each section by clicking on the “+” next to the name. For example scroll
to the top and click the “+” next to My Computer, then click the “+” next to C:, etc. Click on
SBIG Drivers
the
folder to highlight it then Click OK in the Find File dialog then click OK
back at the New Hardware Wizard.
6. Windows will find the driver and present you with the dialog below:
Click the
Next
button.
Page 20
Page 23
Section 1 - Introduction
7.
Windows will spin for a while, then present you with the dialog below. Click the
button and you’re done. The SBIG cameras actually use two drivers and after you click
Finish the system will automatically install the second driver.
Finish
Page 21
Page 24

Section 1 - Introduction
1.2.3. Getting Started with CCDOPS
• Use Camera->Establish Com Link
lower-right corner of CCDOPS main window where ST-10 is the camera model. You are
now talking to the camera.
• From this point you should follow the software instructions / help menus to Set Up the
camera’s cooling, Focus, Grab images, etc.
. After a few seconds should see “Link:[ST-10]USB” in
1.2.4. To try some functions with sample images:
• Double-click on the CCDOPS icon to launch the program.
• Use the Open command in the File menu to load one of the sample images. A window
showing the exposure time, etc. will appear. Click in it to make it disappear. The image will
show up in its own window.
• Try using the crosshairs. Use the Crosshairs command in the Display menu.
• Use the mouse to move the crosshair around in the image and see the pixel values.
• Close the crosshairs and try inverting the image. Click the Invert item in the Contrast
window.
• Try the photo display mode. Use the Photo Mode command in the Display menu. Click the
mouse to return to the menus.
• Load up the other sample images and display them using the photo display mode. You
have to close any existing image first.
• If you find that the display is too dark or bright, try setting Auto Contrast in the Contrast
window or adjust the background and range parameters to achieve the best display. You may
have to hit the Apply button in the Contrast window to see changes in the Background and
Range
1.2.5. Capturing Images with the CCD Camera
Unfortunately there really aren't many shortcuts you can take when using the CCD camera to
capture images. The instructions below refer you to various sections of the manual.
• Find some relatively bright object like M51, the Ring Nebula (M57) or the Dumbbell Nebula
(M27) (refer to section 3.5).
• Take a 1 minute exposure using the Grab command with the Dark frame option set to Also
(refer to Section 3.6).
• Display the image (refer to Section 3.7).
• Process the image (refer to Section 3.8).
You can use the SBIG Test Lens to take indoor test exposures and get familiar with the camera
operation. Also, if you happened to have purchased a camera lens adapter for your CCD Camera
you can also use that to take test images during the day:
Page 22
Page 25

Section 1 - Introduction
Camera lens daytime exposure guidelines:
• Close the F stop all the way to F/16 or F/22.
• Set the focus based upon the object and the markings on the lens.
• Take a short (<1 second) exposure with the Grab command.
• Display the image.
• Process the image.
Page 23
Page 26

Page 27

Section 2 - Introduction to CCD Cameras
2. Introduction to CCD Cameras
This section introduces new users to CCD (Charge Coupled Device) cameras and their
capabilities and to the field of CCD Astronomy and Electronic Imaging.
2.1. Cameras in General
The CCD is very good at the most difficult astronomical imaging problem: imaging small, faint
objects. For such scenes long film exposures are typically required. The CCD based system has
several advantages over film: greater speed, quantitative accuracy, ability to increase contrast
and subtract sky background with a few keystrokes, the ability to co-add multiple images
without tedious dark room operations, wider spectral range, and instant examination of the
images at the telescope for quality. Film has the advantages of a much larger format, color, and
independence of the wall plug (the SBIG family of cameras can be battery operated in
conjunction with a laptop computer, though, using a power inverter). After some use you will
find that film is best for producing sensational large area color pictures, and the CCD is best for
planets, faint objects, and general scientific work such as variable star monitoring and position
determination.
2.2. How CCD Detectors Work
The basic function of the CCD detector is to convert an incoming photon of light to an electron
which is stored in the detector until it is read out, thus producing data which your computer
can display as an image. It doesn't have to be displayed as an image. It could just as well be
displayed as a spreadsheet with groups of numbers in each cell representing the number of
electrons produced at each pixel. These numbers are displayed by your computer as shades of
gray for each pixel site on your screen thus producing the image you see. How this is
accomplished is eloquently described in a paper by James Janesick and Tom Elliott of the Jet
Propulsion Laboratory:
"Imagine an array of buckets covering a field. After a rainstorm, the buckets are
sent by conveyor belts to a metering station where the amount of water in each
bucket is measured. Then a computer would take these data and display a
picture of how much rain fell on each part of the field. In a CCD the "raindrops"
are photons, the "buckets" the pixels, the "conveyor belts" the CCD shift registers
and the "metering system" an on-chip amplifier.
Technically speaking the CCD must perform four tasks in generating an image.
These functions are 1) charge generation, 2) charge collection, 3) charge transfer,
and 4) charge detection. The first operation relies on a physical process known
as the photoelectric effect - when photons or particles strikes certain materials
free electrons are liberated...In the second step the photoelectrons are collected in
the nearest discrete collecting sites or pixels. The collection sites are defined by
an array of electrodes, called gates, formed on the CCD. The third operation,
charge transfer, is accomplished by manipulating the voltage on the gates in a
systematic way so the signal electrons move down the vertical registers from one
pixel to the next in a conveyor-belt like fashion. At the end of each column is a
horizontal register of pixels. This register collects a line at a time and then
Page 25
Page 28

Section 2 - Introduction to CCD Cameras
transports the charge packets in a serial manner to an on-chip amplifier. The
final operating step, charge detection, is when individual charge packets are
converted to an output voltage. The voltage for each pixel can be amplified offchip and digitally encoded and stored in a computer to be reconstructed and
displayed on a television monitor."
1
Readout Register
Output
Y=1
Amplifier
Y=N
X=1 X=M
Figure 2.1 - CCD Structure
2.2.1. Full Frame and Frame Transfer / Interline CCDs
In the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE and ST-10XME, the CCD is read out electronically by
shifting each row of pixels into a readout register at the Y=0 position of the CCD (shown in
Figure 2.1), and then shifting the row out through an amplifier at the X=0 position. The entire
array shifts up one row when a row is shifted into the readout register, and a blank row is
inserted at the bottom. The electromechanical shutter built into the camera covers the CCD
during the readout to prevent streaking of the image. Without a shutter the image would be
streaked due to the fact that the pixels continue to collect light as they are being shifted out
towards the readout register. CCDs with a single active area are called Full Frame CCDs.
For reference, the ST-5C, ST-237A, STV and guiding CCDs in the ST-X series of cameras
use a different type of CCD, which is known as a Frame Transfer CCD. In these devices all
active pixels are shifted very quickly into a pixel array screened from the light by a metal layer,
and then read out. This makes it possible to take virtually streak-free images without a shutter.
This feature is typically called an electronic shutter. The interline CCD used in the ST-2000XM is
similar to a frame transfer except that the protected pixels are interlaced with the active pixels.
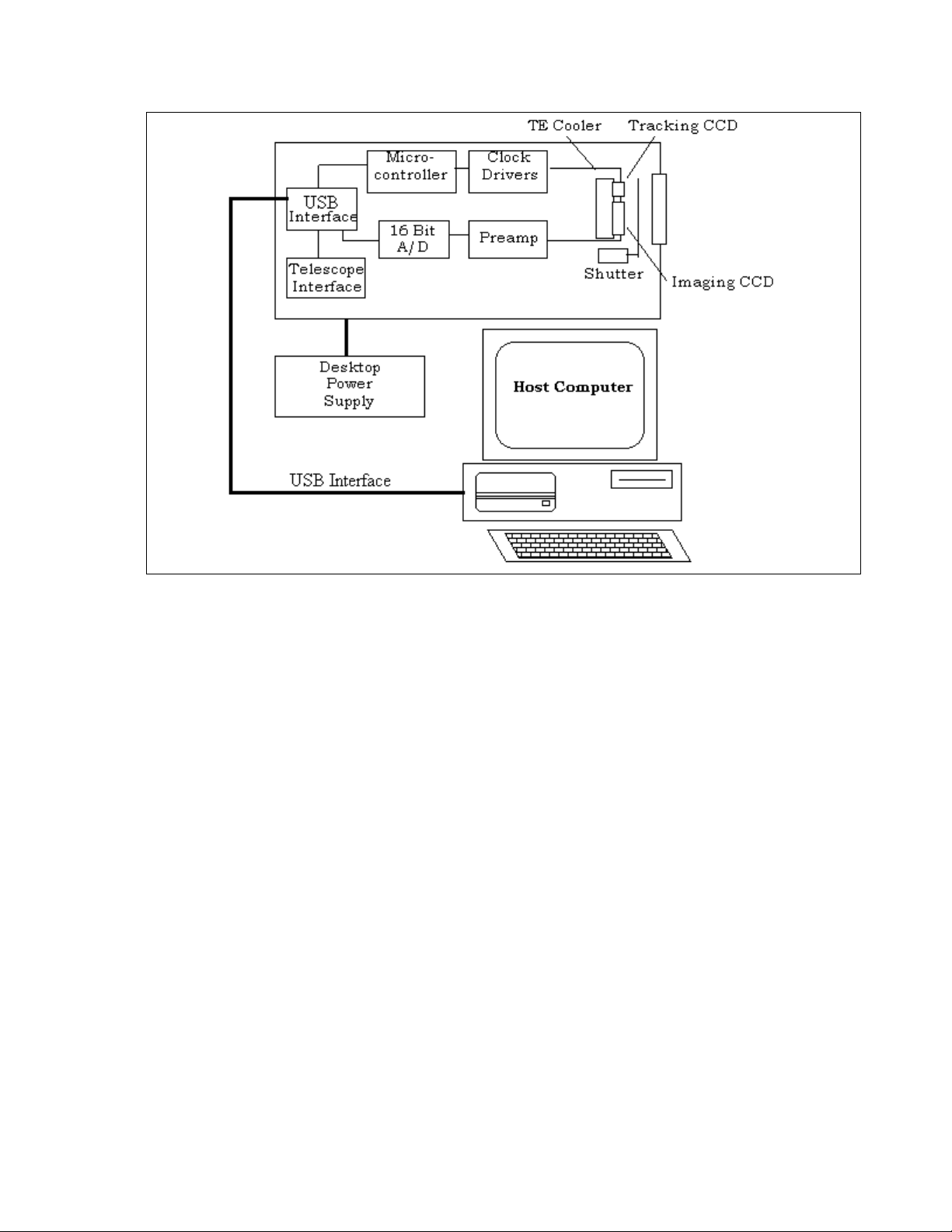
2.3. Camera Hardware Architecture
This section describes the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM CCD
cameras from a systems standpoint. It describes the elements that comprise a CCD camera and
the functions they provide. Please refer to Figure 2.2 below as you read through this section.
1
"History and Advancements of Large Area Array Scientific CCD Imagers", James Janesick, Tom
Elliott. Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, CCD Advanced Development
Group.
Page 26
Page 29
Section 2 - Introduction to CCD Cameras
Figure 2.2 - CCD System Block Diagram
As you can see from Figure 2.2, the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST2000XM are completely self-contained. Unlike our previous products, the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM contain all the electronics in the optical head. There
is no external CPU like the ST-5C, ST-237, ST-6 and STV.
At the "front end" of any CCD camera is the CCD sensor itself. As we have already
learned, CCDs are a solid-state image sensor organized in a rectangular array of regularly
spaced rows and columns. The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM
use two CCDs, one for imaging (Kodak KAF series) and one for tracking (TI TC211 or TC237).
Page 27
Page 30

Table 2.1 below lists some interesting aspects of the CCDs used in the various SBIG
cameras.
Section 2 - Introduction to CCD Cameras
Camera
TC211 Tracking CCD TC211 2.6 x 2.6 mm 192 x 164 13.75 x 16 µ
TC237 Tracking CCD TC237 4.9 x 3.7 mm 657 x 495 7.4 x 7.4 µ
ST-5C TC255 3.2 x 2.4 mm 320 x 240 10 x 10 µ
ST-237A TC237 4.9 x 3.7 mm 640 x 480 7.4 x 7.4 µ
STV/STV Deluxe TC237 4.7 x 3.0 mm 320 x 200 14.8 x 14.8 µ
ST-6B TC241 8.6 x 6.5 mm 375 x 242 23 x 27 µ
ST-7E/XE KAF0401E 6.9 x 4.6 mm 765 x 510 9 x 9 µ
ST-8E/XE KAF1602E 13.8 x 9.2 mm 1530 x 1020 9 x 9 µ
ST-9E/XE KAF0261E 10.2 x 10.2 mm 512 x 512 20 x 20 µ
ST-10E/XE/XME KAF3200E 14.9 x 10.0 mm 2184 x 1472 6.8 x 6.8 µ
ST-1001E KAF1001E 24.6 x 24.6 mm 1024 x 1024 24 x 24 µ
ST-2000XM KAI2000M 11.8 x 8.9 mm 1600 x 1200 7.4 x 7.4 µ
The CCD is cooled with a solid-state a thermoelectric (TE) cooler. The TE cooler pumps heat
out of the CCD and dissipates it into a heat sink, which forms part of the optical head's
mechanical housing. In the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM
cameras this waste heat is dumped into the air using a new heat exchanger and a small fan. The
heat exchanger is also capable of water circulation for additional efficiency if needed in hot
climates. An inlet and outlet are provided at the back of the camera head for passing water
through the heat exchanger. Only a very small flow is required and an ordinary aquarium
pump is sufficient if it will pull the flow up the length of tubing you might require at your
installation. An optional 110VAC pump and tubing are also available from SBIG.
Since the CCD is cooled below 0°C, some provision must be made to prevent frost from
forming on the CCD. The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM have
the CCD/TE Cooler mounted in a windowed hermetic chamber sealed with an O-Ring. The
hermetic chamber does not need to be evacuated, another "ease of use" feature we employ in the
design of our cameras. Using a rechargeable desiccant in the chamber keeps the humidity low,
forcing the dew point below the cold stage temperature.
Other elements in the self contained ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and
ST-2000XM include the preamplifier and an electromechanical shutter. The shutter makes
taking dark frames a simple matter of pushing a button on the computer and provides streakfree readout. Timing of exposures in ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST2000XM cameras is controlled by this shutter.
The Clock Drivers and Analog to Digital Converter interface to the CCD. The Clock
Drivers convert the logic-level signals from the micro controller to the voltage levels and
sequences required by the CCD. Clocking the CCD transfers charge in the array and is used to
clear the array or read it out. The Analog to Digital Converter (A/D) digitizes the data in the
CCD for storage in the Host Computer.
The micro controller is used to regulate the CCD's temperature by varying the drive to
the TE cooler. The external Power Supply provides +5V and ±12V to the cameras. Finally, the
CCD
Table 2.1 - Camera CCD Configurations
Array
Dimensions
Number of
Pixels
Pixel Sizes
Page 28
Page 31

Section 2 - Introduction to CCD Cameras
cameras contain a TTL level telescope interface port to control the telescope and the optional
CFW-6A motorized color filter wheel.
Although not part of the CCD Camera itself, the Host Computer and Software are an
integral part of the system. SBIG provides software for the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE,
ST-10XME and ST-2000XM cameras for the IBM PC and Compatible computers running
Windows 95/98/2000/Me/NT/XP. The software allows image acquisition, image processing,
and auto guiding with ease of use and professional quality. Many man-years and much
customer feedback have gone into the SBIG software and it is unmatched in its capabilities.
2.4. CCD Special Requirements
This section describes the unique features of CCD cameras and the special requirements that
CCD systems impose.
2.4.1. Cooling
Random readout noise and noise due to dark current combine to place a lower limit on the
ability of the CCD to detect faint light sources. SBIG has optimized the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM to achieve readout noises below 20 electrons rms for
two reads (light - dark). This will not limit most users. The noise due to the dark current is
equal to the square root of the number of electrons accumulated during the integration time.
For these cameras, the dark current is not significant until it accumulates to more than 280
electrons. Dark current is thermally generated in the device itself, and can be reduced by
cooling. All CCDs have dark current, which can cause each pixel to fill with electrons in only a
few seconds at room temperature even in the absence of light. By cooling the CCD, the dark
current and corresponding noise is reduced, and longer exposures are possible. In fact, for
roughly every 5 to 6° C of additional cooling, the dark current in the CCD is reduced to half.
The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM have a single stage TE
cooler, efficient heat exchanger and water circulation capability. A temperature sensing
thermistor on the CCD mount monitors the temperature (Earlier parallel models offered a
cooling booster which used a second TE cooler but we feel that the new design provides similar
performance without the need for a second power supply). The micro controller controls the
temperature at a user-determined value for long periods. As a result, exposures hours long are
possible, and saturation of the CCD by the sky background typically limits the exposure time.
At 0 °C the dark current in the ST-7XE, ST-8XE and ST-10XE, high-resolution mode, is only 60
electrons per minute! The ST-9XE, with bigger pixels, has roughly 8 times this amount of dark
current due largely to the larger pixel area but also due to the inherent higher bulk dark current
in the devices.
The sky background conditions also increase the noise in images, and in fact, as far as
the CCD is concerned, there is no difference between the noise caused by dark current and that
from sky background. If your sky conditions are causing photoelectrons to be generated at the
rate of 100 e
current is roughly half that amount will not improve the quality of the image. This very reason
is why deep sky filters are so popular with astrophotography. They reduce the sky background
level, increasing the contrast of dim objects. They will improve CCD images from very light
polluted sights.
-
/pixel/sec, for example, increasing the cooling beyond the point where the dark
Page 29
Page 32

Section 2 - Introduction to CCD Cameras
2.4.2. Double Correlated Sampling Readout
During readout, the charge stored in a pixel is stored temporarily on a capacitor. This capacitor
converts the optically generated charge to a voltage level for the output amplifier to sense.
When the readout process for the previous pixel is completed, the capacitor is drained and the
next charge shifted, read, and so on. However, each time the capacitor is drained, some
residual charge remains.
This residual charge is actually the dominant noise source in CCD readout electronics.
This residual charge may be measured before the next charge is shifted in, and the actual
difference calculated. This is called double correlated sampling. It produces more accurate data
at the expense of slightly longer read out times (two measurements are made instead of one).
The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM utilize double correlated
sampling to produce the lowest possible readout noise. At 10e
cameras are unsurpassed in performance.
-
to 15e- rms per read these
2.4.3. Dark Frames
No matter how much care is taken to reduce all sources of unwanted noise, some will remain.
Fortunately, however, due to the nature of electronic imaging and the use of computers for
storing and manipulating data, this remaining noise can be drastically reduced by the
subtraction of a dark frame from the raw light image. A dark frame is simply an image taken at
the same temperature and for the same duration as the light frame with the source of light to
the CCD blocked so that you get a "picture" of the dark. This dark frame will contain an image
of the noise caused by dark current (thermal noise) and other fixed pattern noise such as read
out noise. When the dark frame is subtracted from the light frame, this pattern noise is
removed from the resulting image. The improvement is dramatic for exposures of more than a
minute, eliminating the many "hot" pixels one often sees across the image, which are simply
pixels with higher dark current than average.
2.4.4. Flat Field Images
Another way to compensate for certain unwanted optical effects is to take a "flat field image"
and use it to correct for variations in pixel response uniformity across the area of your darksubtracted image. You take a flat field image of a spatially uniform source and use the
measured variations in the flat field image to correct for the same unwanted variations in your
images. The Flat Field command allows you to correct for the effects of vignetting and
nonuniform pixel responsivity across the CCD array.
The Flat Field command is very useful for removing the effects of vignetting that may
occur when using a field compression lens and the fixed pattern responsivity variations present
in all CCDs. It is often difficult to visually tell the difference between a corrected and
uncorrected image if there is little vignetting, so you must decide whether to take the time to
correct any or all of your dark-subtracted images. It is always recommended for images that are
intended for accurate photometric measurements.
Appendix D describes how to take a good flat field. It's not that easy, but we have
found a technique that works well for us.
Page 30
Page 33

Section 2 - Introduction to CCD Cameras
2.4.5. Pixels vs. Film Grains
Resolution of detail is determined, to a certain degree, by the size of the pixel in the detector
used to gather the image, much like the grain size in film. The pixel size of the detector in the
ST-10XE is 6.8 x 6.8 microns (1 micron = 0.001mm, 0.04 thousandths of an inch). In the ST-7XE
and ST-8XE it is 9 x 9 microns, in the ST-9XE it's 20 x 20 microns and in the ST-2000XM it is 7.4 x
7.4 microns. However, the effects of seeing are usually the limiting factor in any good
photograph or electronic image. On a perfect night with excellent optics an observer might
hope to achieve sub-arcsecond seeing in short exposures, where wind vibration and tracking
error are minimal. With the average night sky and good optics, you will be doing well to
achieve stellar images in a long exposure of 3 to 6 arcseconds halfwidth. This will still result in
an attractive image, though.
Using an ST-7XE or ST-8XE camera with their 9 micron pixels, an 8" f/10 telescope will
produce a single pixel angular subtense of 0.9 arcsecond. An 8" f/4 telescope will produce
images of 2.5 arcseconds per pixel. If seeing affects the image by limiting resolution to 6
arcseconds, you would be hard pressed to see any resolution difference between the two focal
lengths as you are mostly limited by the sky conditions. However, the f/4 image would have a
larger field of view and more faint detail due to the faster optic. The ST-9XE, with its 20 micron
pixels would have the same relationship at roughly twice the focal length or a 16 inch f/10
telescope. See table 4.4 for further information.
A related effect is that, at the same focal length, larger pixels collect more light from
nebular regions than small ones, reducing the noise at the expense of resolution. While many
people think that smaller pixels are a plus, you pay the price in sensitivity due to the fact that
smaller pixels capture less light. For example, the ST-9XE with its large 20 x 20 micron pixels
captures five times as much light as the ST-7XE and ST-8XE's 9 micron square pixels. For this
reason we provide 2x2 or 3x3 binning of pixels on most SBIG cameras. With the ST-7XE and ST8XE, for instance, the cameras may be configured for 18 or 27-micron square pixels. Binning is
selected using the Camera Setup Command. It is referred to as resolution (High = 9µ
Medium = 18µ
2
pixels, Low = 27µ2 pixels). When binning is selected the electronic charge from
groups of 2x2 or 3x3 pixels is electronically summed in the CCD before readout. This process
adds no noise and may be particularly useful on the ST-10XE with its very small 6.8 micron
pixels. Binning should be used if you find that your stellar images have a halfwidth of more
than 3 pixels. If you do not bin, you are wasting sensitivity without benefit. Binning also
shortens the download time.
The halfwidth of a stellar image can be determined using the crosshairs mode. Find the
peak value of a relatively bright star image and then find the pixels on either side of the peak
where the value drops to 50% of the peak value (taking the background into account, if the star
is not too bright). The difference between these pixel values gives the stellar halfwidth.
Sometimes you need to interpolate if the halfwidth is not a discrete number of pixels.
Another important consideration is the field of view of the camera. For comparison, the
diagonal measurement of a frame of 35mm film is approximately 43mm, whereas the diagonal
dimension of the ST-7XE chip is approximately 8 mm. The relative CCD sizes for all of the SBIG
cameras and their corresponding field of view in an 8" f/10 telescope are given below:
2
pixels,
Page 31
Page 34

Section 2 - Introduction to CCD Cameras
Camera Array Dimensions Diagonal Field of View at 8" f/10
TC211 Tracking CCD 2.64 x 2.64 mm 3.73 mm 4.5 x 4.5 arcminutes
TC237 Tracking CCD 4.93 x 3.71 mm 6.17 mm 8.2 x 6.2 arcminutes
ST-5C 3.20 x 2.40 mm 4.00 mm 5.6 x 4.2 arcminutes
ST-237A 4.93 x 3.71 mm 6.17 mm 8.2 x 6.2 arcminutes
STV 4.74 x 2.96 mm 5.58 mm 8.2 x 5.1 arcminutes
ST-7XE 6.89 x 4.59 mm 8.28 mm 11.9 x 7.9 arcminutes
ST-8XE 13.8 x 9.18 mm 16.6 mm 23.8 x 15.8 arcminutes
ST-9XE 10.2 x 10.2 mm 14.4 mm 17.6 x 17.6 arcminutes
ST-10XE (XME) 14.9 x 10.0 mm 17.9 mm 25.1 x 16.9 arcminutes
ST-1001E 24.6 x 24.6 mm 34.8 mm 41.5 x 41.5 arcminutes
ST-2000XM 11.8 x 9.0 mm 14.8 mm 20.0 x 15.0 arcminutes
35mm Film 36 x 24 mm 43 mm 62 x 42 arcminutes
Table 2.2 - CCD Array Dimensions
2.4.6. Guiding
Any time you are taking exposures longer than several seconds, whether you are using a film
camera or a CCD camera, the telescope needs to be guided to prevent streaking. While modern
telescope drives are excellent with PEC or PPEC, they will not produce streak-free images
without adjustment every 30 to 60 seconds. The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME
and ST-2000XM allow simultaneous guiding and imaging, called self-guiding (US Patent
5,525,793). This is possible because of the unique design employing 2 CCDs. One CCD guides
the telescope while the other takes the image. This resolves the conflicting requirements of
short exposures for guiding accuracy and long exposures for dim objects to be met, something
that is impossible with single CCD cameras. Up to now the user either had to set up a separate
guider or use Track and Accumulate to co-add several shorter images. The dual CCD design
allows the guiding CCD access to the large aperture of the main telescope without the
inconvenience of off-axis radial guiders. Not only are guide stars easily found, but the
problems of differential deflection between guide scope and main scope eliminated.
Track and Accumulate is another SBIG patented process (US #5,365,269) whereby short
exposures are taken and added together with appropriate image shifts to align the images. It is
supported by the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM camera
software, but will generally not produce as good as results as self guiding, where the
corrections are more frequent and the accumulated readout noise less. It is handy when no
connection to the telescope drive is possible and also works best on cameras with larger pixels
like the ST-9XE or for cameras with smaller pixels in binned mode. For cameras with smaller
pixels imaging in high resolution mode such as the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and
ST-2000XM, SBIG is proud to make self-guiding available to the amateur, making those long
exposures required by the small pixel geometry easy to achieve!
2.5. Electronic Imaging
Electronic images resemble photographic images in many ways. Photographic images are
made up of many small particles or grains of photo sensitive compounds which change color or
become a darker shade of gray when exposed to light. Electronic images are made up of many
Page 32
Page 35

Section 2 - Introduction to CCD Cameras
small pixels which are displayed on your computer screen to form an image. Each pixel is
displayed as a shade of gray, or in some cases a color, corresponding to a number which is
produced by the electronics and photo sensitive nature of the CCD camera. However,
electronic images differ from photographic images in several important aspects. In their most
basic form, electronic images are simply groups of numbers arranged in a computer file in a
particular format. This makes electronic images particularly well suited for handling and
manipulation in the same fashion as any other computer file.
An important aspect of electronic imaging is that the results are available immediately.
Once the data from the camera is received by the computer, the resulting image may be
displayed on the screen at once. While Polaroid cameras also produce immediate results,
serious astrophotography ordinarily requires hypersensitized or cooled film, a good quality
camera, and good darkroom work to produce satisfying results. The time lag between exposure
of the film and production of the print is usually measured in days. With electronic imaging,
the time between exposure of the chip and production of the image is usually measured in
seconds.
Another very important aspect of electronic imaging is that the resulting data are
uniquely suited to manipulation by a computer to bring out specific details of interest to the
observer. In addition to the software provided with the camera, there are a number of
commercial programs available that will process and enhance electronic images. Images may
be made to look sharper, smoother, darker, lighter, etc. Brightness, contrast, size, and many
other aspects of the image may be adjusted in real time while viewing the results on the
computer screen. Two images may be inverted and electronically "blinked" to compare for
differences, such as a new supernova, or a collection of images can be made into a large mosaic.
Advanced techniques such as maximum entropy processing will bring out otherwise hidden
detail.
Of course, once the image is stored on a computer disk, it may be transferred to another
computer just like any other data file. You can copy it or send it via modem to a friend, upload
it to your favorite bulletin board or online service, or store it away for processing and analysis
at some later date.
We have found that an easy way to obtain a hard copy of your electronic image is to
photograph it directly from the computer screen. You may also send your image on a floppy
disk to a photo lab that has digital photo processing equipment for a professional print of your
file. Make sure the lab can handle the file format you will send them. Printing the image on a
printer connected to your computer is also possible depending on your software/printer
configuration. There are a number of software programs available, which will print from your
screen. However, we have found that without specialized and expensive equipment, printing
images on a dot matrix or laser printer yields less than satisfactory detail. However, if the
purpose is simply to make a record or catalog the image file for easy identification, a dot matrix
or laser printer should be fine. Inkjet printers are getting very good, though.
2.6. Black and White vs. Color
The first and most obvious appearance of a CCD image is that it is produced in shades of gray,
rather than color. The CCD chip used in SBIG cameras itself does not discriminate color and the
pixel values that the electronics read out to a digital file are only numbers proportional to the
Page 33
Page 36

Section 2 - Introduction to CCD Cameras
number of electrons produced when photons of any wavelength happen to strike its sensitive
layers.
Of course, there are color video cameras, and a number of novel techniques have been
developed to make the CCD chip "see" color. The most common way implemented on
commercial cameras is to partition the pixels into groups of three, one pixel in each triplet
"seeing" only red, green or blue light. The results can be displayed in color. The overall image
will suffer a reduction in resolution on account of the process. A newer and more complicated
approach in video cameras has been to place three CCD chips in the camera and split the
incoming light into three beams. The images from each of the three chips, in red, green and
blue light is combined to form a color image. Resolution is maintained. For normal video
modes, where there is usually plenty of light and individual exposures are measured in small
fractions of a second, these techniques work quite well. However, for astronomical work,
exposures are usually measured in seconds or minutes. Light is usually scarce. Sensitivity and
resolution are at a premium. The most efficient way of imaging under these conditions is to
utilize all of the pixels, collecting as many photons of any wavelength, as much of the time as
possible.
In order to produce color images in astronomy, the most common technique is to take
three images of the same object using a special set of filters and then recombine the images
electronically to produce a color composite or RGB color image. SBIG offers as an option an
integrated motorized color filter wheel. The CFW8A color filter wheel is attached to the front of
the camera in such a way that light entering the camera passes through the colored filter before
it strikes the CCD. An object is then exposed using a red filter. The wheel is commanded to
insert the green filter in place, and another image taken. Finally a blue image is taken. When
all three images have been saved, they may be merged into a single color image using SBIG or
third party color software.
Page 34
Page 37

Section 3 - At the Telescope with a CCD Camera
3. At the Telescope with a CCD Camera
This section describes what goes on the first time you take your CCD camera out to the
telescope. You should read this section throughout before working at the telescope. It will help
familiarize you with the overall procedure that is followed without drowning you in the details.
It is recommended you first try operating the camera in comfortable, well lit surroundings to
learn its operation.
3.1. Step by Step with a CCD Camera
In the following sections we will go through the steps of setting up and using your CCD
camera. The first step is attaching the camera to the telescope. The next step is powering up the
camera and establishing a communication link to your computer. Then you will want to focus
the system, find an object and take an image. Once you have your light image with a dark
frame subtracted, you can display the image and process the results to your liking. Each of
these steps is discussed in more detail below.
3.2. Attaching the Camera to the Telescope
ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM cameras are similar in
configuration. The CCD head attaches to the telescope by slipping it into the eyepiece holder or
attaching it via t-threads. A fifteen-foot cable runs from the head to the host computer's USB
port. The camera is powered by a desktop power supply. Operation from a car or marine
battery is possible using the optional 12V power supply or with a 12V to 110V power inverter.
Connect the CCD head to the USB port of your computer using the supplied cable and
insert the CCD Camera's nosepiece into your telescope's eyepiece holder. Fully seat the camera
against the end of the draw tube so that once focus has been achieved you can swap out and
replace the camera without having to refocus. Orient the camera so that the CCD's axes are
aligned in Right Ascension and Declination. Use Figure 3.1 below showing the back of the
optical head as a guide for the preferred orientation. Any orientation will work, but it is
aggravating trying to center objects when the telescope axes don't line up fairly well with the
CCD axes.
Next, connect the power cable and plug in the desktop power supply. A few seconds
after you establish a link using CCDOPS software, the red LED on the rear of the camera should
glow and the fan should spin indicating that the firmware has been uploaded to the camera and
it is ready for operation. We recommend draping the cables over the finderscope, saddle or
mount to minimize cable perturbations of the telescope, and guard against the camera falling
out of the drawtube to the floor. In the alternative, there is a ¼-20 threaded hole on the side
plate of the camera used for tripod mounting. This is also a convenient place to attach a safety
strap to prevent the camera from accidentally falling from the telescope. (Note that there are
electronics inside the chassis that can be damaged by long bolts. Make sure nothing threaded
into the tripod hole is longer than 0.200” / 5mm.) When possible, we also recommend using
the T-Ring attachments for connecting the camera to the telescope, as the cameras are heavy.
Page 35
Page 38

Section 3 - At the Telescope with a CCD Camera
Figure 3.1 Orientation of the Optical Head Viewed from Back.
(Pixel 1,1 is at the upper left in this view)
3.3. Establishing a Communications Link
After setting up the software and the camera as described in the previous sections, using
CCDOPS software, establish a link to the camera by clicking on the “Establish Comm Link”
command from the Camera menu. If the software is successful the "Link" field in the Status
Window is updated to show the type of camera found. If the camera is not connected, powered
up, or the USB port has not yet been properly selected, a message will be displayed indicating
that the software failed to establish a link to the camera. If this happens, use the
Communications Setup command in the Misc menu to configure the CCDOPS software for the
USB. Then use the Establish COM Link command in the Camera Menu to establish
communications with the camera.
Note: It is not necessary to have a camera connected to your computer to run the software and
display images already saved onto disk. It is only necessary to have a camera connected
when you take new images.
Once the COM link has been established you may need to set the camera's setpoint temperature
in the Camera Setup command. The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST2000XM power up regulating to whatever temperature the CCD is at, which in this case will be
the ambient temperature. Use the Camera Setup command and choose a setpoint temperature
approximately 30°C below the ambient temperature. Type in the setpoint, set the temperature
control to active, and hit ENTER.
3.4. Focusing the CCD Camera
Focusing a CCD camera can be a tedious operation, so a few hints should be followed. Before
using the software to focus the camera the first time you should place a diffuser (such as scotch
tape or ground glass) at the approximate location of the CCD's sensitive surface behind the
Page 36
Page 39

Section 3 - At the Telescope with a CCD Camera
eyepiece tube and focus the telescope on the moon, a bright planet or a distant street lamp. This
preliminary step will save you much time in initially finding focus. The approximate distance
behind the eyepiece tube for each of our CCD cameras is listed in Table 3.1 below:
Camera Distance
Diffuser
ST-7/8/9/10XE ~0.92 inch
ST-2000XM ~0.92 inch
Table 3.1 - Camera Back Focus
Back Focus Distance
from Table 3.1
To achieve fine focus, insert the CCD head into the eyepiece tube, taking care to seat it,
and then enter the CCDOPS FOCUS mode. The Focus command automatically displays
successive images on the screen as well as the peak brightness value of the brightest object in
the field of view. Point the telescope at a bright star. Center the star image in the CCD, and
adjust the focus until the star image is a small as can be discerned. Next, move the telescope to
a field of fainter stars that are dimmer so the CCD is not saturated. Further adjust the focus to
maximize the displayed star brightness in counts and minimize the star diameter. This can be
tedious. It helps considerably if a pointer or marker is affixed to the focus knob so you can
rapidly return to the best focus once you've gone through it.
An exposure of 1 to 3 seconds is recommended to smooth out some of the atmospheric
effects. While you can use the Full frame mode to focus, the frame rate or screen update rate
can be increased significantly by using Planet mode. In Planet mode the Focus command takes
a full image and then lets you position a variable sized rectangle around the star. On
subsequent images the Planet mode only digitizes, downloads, and displays the small area you
selected. The increase in frame rate is roughly proportional to the decrease in frame size,
assuming you are using a short exposure.
The telescope focus is best achieved by maximizing the peak value of the star image.
You should be careful to move to a dimmer star if the peak brightness causes saturation. The
saturation levels of the various resolution modes are shown in Table 3.2 below. Another point
you should also be aware of is that as you approach a good focus, the peak reading can vary by
30% or so. This is due to the fact that as the star image gets small, where an appreciable
percentage of the light is confined to a single pixel, shifting the image a half a pixel reduces the
peak brightness as the star's image is split between the two pixels. The Kodak CCD pixels are
so small that this is not likely to be a problem.
Resolution Saturation Counts
High Res ~20,000 for ST-7XE/8XE ABG Cameras,
~40,000 for ST-7XE/8XE Non ABG cameras,
~50,000 for ST-10XE Camera
~65,000 for ST-9XE/2000XM Cameras
Med/Low Res ~65,000 for ST-7/8/9/10/2000
Table 3.2 - Saturation Values
Page 37
Page 40

Section 3 - At the Telescope with a CCD Camera
Once the best focus is found, the focusing operation can be greatly shortened the second time
by removing the CCD head, being careful not to touch the focus knob. Insert a high power
eyepiece and slide it back and forth to find the best visual focus, and then scribe the outside of
the eyepiece barrel. The next time the CCD is used the eyepiece should be first inserted into the
tube to the scribe mark, and the telescope visually focused and centered on the object. At f/6
the depth of focus is only 0.005 inch, so focus is critical. An adapter may be necessary to allow
the eyepiece to be held at the proper focus position. SBIG sells extenders for this purpose.
3.5. Finding and Centering the Object
Once best focus is achieved, we suggest using "Dim" mode to help center objects. This mode
gives a full field of view, but reduces resolution in order to increase the sensitivity, and
digitization and download rate. If you have difficulty finding an object after obtaining good
focus, check to be sure that the head is seated at best focus, then remove the head and insert a
medium or low power eyepiece. Being careful not to adjust the focus knob on the telescope,
slide the eyepiece in or out until the image appears in good focus. Then visually find and center
the object, if it is visible to the eye. If not, use your setting circles carefully. Then, re-insert the
CCD head and use FOCUS mode with an exposure time of about ten seconds, if it is dim.
Center the object using the telescope hand controls.
Note: With a 10 second exposure, objects like M51 or the Ring Nebula (M57) are easily
detected with modest amateur telescopes. The cores of most galactic NGC objects can also
be seen.
3.6. Taking an Image
Take a CCD image of the object by selecting the Grab command and setting the exposure time.
Start out with the Image size set to full and Auto Display and Auto contrast enabled. The
camera will expose the CCD for the correct time, and digitize and download the image. One
can also take a dark frame immediately before the light image using the Grab command.
Because the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM have
regulated temperature control, you may prefer to take and save separate dark images, building
up a library at different temperatures and exposure times, and reusing them on successive
nights. At the start it's probably easiest to just take the dark frames when you are taking the
image. Later, as you get a feel for the types of exposures and setpoint temperatures you use,
you may wish to build this library of dark frames.
3.7. Displaying the Image
The image can be displayed on the computer screen using the graphics capability of your PC.
Auto contrast can be selected and the software will pick background and range values which
are usually good for a broad range of images or the background and range values can be
optimized manually to bring out the features of interest.
The image can also be displayed as a negative image, or can be displayed with
smoothing to reduce the graininess. Once displayed, the image can be analyzed using
crosshairs, or can be cropped or zoomed to suit your tastes.
Page 38
Page 41

Section 3 - At the Telescope with a CCD Camera
3.8. Processing the Image
If not done already, images can be improved by subtracting off a dark frame of equal exposure.
You will typically do this as part of the Grab command although it can also be done manually
using the Dark Subtract command. By subtracting the dark frame, pixels which have higher
dark current than the average, i.e., "hot" pixels, are greatly suppressed and the displayed image
appears much smoother. Visibility of faint detail is greatly improved.
The CCDOPS program also supports the use of flat field frames to correct for vignetting
and pixel to pixel variations, as well as a host of other image processing commands in the
Utility menu. You can smooth or sharpen the image, flip it to match the orientation of
published images for comparison, or remove hot or cold pixels.
3.9. Advanced Capabilities
The following sections describe some of the advanced features of SBIG cameras. While you
may not use these features the first night, they are available and a brief description of them is in
order for your future reference.
3.9.1. Crosshairs Mode (Photometry and Astrometry)
Using the crosshair mode enables examination of images on a pixel by pixel basis for such
measurements as Stellar and Diffuse Magnitude, and measurement of stellar positions. The 16
bit accuracy of SBIG systems produces beautiful low-noise images and allows very accurate
brightness measurements to be made. With appropriate filters stellar temperature can be
measured.
In the crosshair mode, you move a small cross shaped crosshair around in the image
using the keyboard or the mouse. As you position the crosshair, the software displays the pixel
value beneath the crosshair and the X and Y coordinates of the crosshair. Also shown is the
average pixel value for a box of pixels centered on the crosshair. You can change the size of the
averaging box from 3x3 to 31x31 pixels to collect all the energy from a star.
3.9.2. Sub-Frame Readout in Focus
The Focus command offers several frame modes for flexibility and increased frame throughput.
As previously discussed, the Full frame mode shows the entire field of view of the CCD with
the highest resolution, digitizing and displaying all pixels.
The "Dim" mode offers the same field of view but offers higher frame rates by reducing
the image's resolution prior to downloading. The resolution is reduced by combining a
neighboring block of pixels into a "super pixel". This reduces the download and display times
proportionately, as well as improving sensitivity. It is great for finding and centering objects.
The Planet mode is suggested if high spatial resolution is desired for small objects like
planets. The Planet mode allows you to select a small sub-area of the entire CCD for image
acquisition. The highest resolution is maintained but you don't have to waste time digitizing
and processing pixels that you don't need. Again, the image throughput increase is
proportional to the reduction in frame size. It can be entered from Auto mode.
Page 39
Page 42

Section 3 - At the Telescope with a CCD Camera
2
Another aspect of the Focus command and its various modes is the Camera Resolution
setting in the Camera Setup command. Briefly, the Resolution setting allows trading off image
resolution (pixel size) and image capture time while field of view is preserved. High resolution
with smaller pixels takes longer to digitize and download than Low resolution with larger
pixels. The cameras support High, Medium, Low and Auto resolution modes. The Auto mode
is optimized for the Focus command. It automatically switches between Low resolution for Full
frame mode to provide fast image acquisition, and High resolution for Planet mode to achieve
critical focus. While Auto resolution is selected all images acquired using the GRAB command
will be high resolution.
3.9.3. Track and Accumulate
An automatic Track and Accumulate mode (SBIG patented) is available in CCDOPS which
simplifies image acquisition for the typical amateur with an accurate modern drive. These
drives, employing PEC or PPEC technology and accurate gears, only need adjustment every 30
to 120 seconds. With Track and Accumulate the software takes multiple exposures and
automatically co-registers and co-adds them. The individual exposures are short enough such
that drive errors are not objectionable and the accumulated image has enough integrated
exposure to yield a good signal to noise ratio.
Operationally the camera will take an exposure, determine the position of a preselected
star, co-register and co-add the image to the previous image, and then start the cycle over again.
The software even allows making telescope corrections between images to keep the object
positioned in the field of view. The resulting exposure is almost as good as a single long
exposure, depending on the exposure used and sky conditions. The great sensitivity of the
CCD virtually guarantees that there will be a usable guide star within the imaging CCD's field
of view. This feature provides dramatic performance for the amateur, enabling long exposures
with minimal setup!
3.9.4. Autoguiding and Self Guiding
The CCDOPS software allows the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST2000XM cameras to be used as autoguiders and self-guiders through the commands in the
Track menu. While these systems are not stand-alone like the ST-4, but require a host
computer, they can accurately guide long duration astrophotographs and CCD images with
equal or superior accuracy. Their sensitivity is much greater than an ST-4, and the computer
display makes them easier to use.
When functioning as an autoguider, the CCD camera repeatedly takes images of a guide
star, measures the star's position to a fraction of a pixel accuracy, and corrects the telescope's
position through the hand controller. While autoguiding alleviates the user of the tedious task
of staring through an eyepiece for hours at a time, it is by no means a cure to telescope drive
performance. All the things that were important for good manually guided exposures still exist,
including a good polar alignment, rigid tubes that are free of flexure and a fairly good stable
mount and drive corrector. Remember that the function of an auto guider is to correct for the
small drive errors and long term drift, not to slew the telescope.
2
The Resolution setting in the Camera Setup command combines pixels before they are digitized.
This is referred to as on-chip binning and offers increases in frame digitization rates.
Page 40
Page 43

Section 3 - At the Telescope with a CCD Camera
One of the reasons that SBIG autoguiders are often better than human guiders is that,
rather than just stabbing the hand controller to bump the guide star back to the reticule, it gives
a precise correction that is the duration necessary to move the guide star right back to its
intended position. It knows how much correction is necessary for a given guiding error
through the Calibrate Track command. The Calibrate Track command, which is used prior to
autoguiding, exercises the telescope's drive corrector in each of the four directions, measuring
the displacement of a calibration star after each move. Knowing the displacement and the
duration of each calibration move calibrates the drive's correction speed. Once that is known,
the CCD tracker gives the drive corrector precise inputs to correct for any guiding error.
When self guiding is selected by invoking the Self Guiding command under the Track
Menu, the computer prompts the user for the exposure time for the tracking and imaging
CCDs. Once these are entered, the computer takes and displays an image with the tracking
CCD, and the user selects a guide star using the mouse. Guide stars that are bright, but not
saturating, and isolated from other stars are preferred. Once the star is selected, the computer
starts guiding the telescope. When the telescope corrections settle down (usually once the
backlash is all taken up in the declination drive) the user starts the exposure by striking the
space bar. The computer then integrates for the prescribed time while guiding the telescope,
and downloads the image for display.
A calibration star should be chosen that is relatively bright and isolated. The calibration
software can get confused if another star of comparable brightness moves onto the tracking
CCD during a move. The unit will self guide on much fainter stars. Tests at SBIG indicate that
the probability of finding a usable guide star on the tracking CCD is about 95% at F/6.3, in
regions of the sky away from the Milky Way. If a guide star is not found the telescope position
should be adjusted, or the camera head rotated by a multiple of 90 degrees to find a guide star.
We recommend that the user first try rotating the camera 180 degrees. Rotating the camera will
require recalibration of the tracking function. [Note: CCDSoftV5 software allows SBIG cameras
to calibrate and track in any orientation, similar to the STV video autoguider].
3.9.5. Auto Grab
The Auto Grab command allows you to take a series of images at a periodic interval and log the
images to disk. This can be invaluable for monitoring purposes such as asteroid searches or
stellar magnitude measurements. You can even take sub-frame images to save disk space if you
don't need the full field of view.
3.9.6. Color Imaging
The field of CCD color imaging is relatively new but expanding rapidly. Since all SBIG cameras
are equipped with monochromatic CCDs, discriminating only light intensity, not color, some
provision must be made in order to acquire color images. SBIG offers a color filter wheel, the
CFW-8, which provides this capability for the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and
ST-2000XM.
The color filter wheel allows remotely placing interference filters in front of the CCD in order to
take multiple images in different color bands. These narrow band images are then combined to
form a color image. With the SBIG system, a Red, Green and Blue filter are used to acquire
Page 41
Page 44

Section 3 - At the Telescope with a CCD Camera
three images of the object. The resulting images are combined to form a tri-color image using
CCDOPS, CCDSoftV5 or third party software.
Color imaging places some interesting requirements on the user that bear mentioning.
First, many color filters have strong leaks in the infrared (IR) region of the spectrum, a region
where CCDs have relatively good response. If the IR light is not filtered out then combining the
three images into a color image can give erroneous results. If your Blue filter has a strong IR
leak (quite common) then your color images will look Blue. For this reason, SBIG incorporates
an IR blocking filter stack with the three color band filters.
Second, since you have narrowed the CCD's wavelength response with the interference
filters, longer exposures are required to achieve a similar signal to noise compared to what one
would get in a monochrome image with wide spectral response. This is added to the fact that
tri-color images require a higher signal to noise overall to produce pleasing images. With black
and white images your eye is capable of pulling large area detail out of random noise quite
well, whereas with color images your eye seems to get distracted by the color variations in the
noisy areas of the image. The moral of the story is that while you can achieve stunning results
with CCD color images, it is quite a bit more work.
Page 42
Page 45

Section 4 – Camera Hardware
4. Camera Hardware
This section describes the modular components that make up the CCD Camera System and how
they fit into the observatory, with all their connections to power and other equipment.
4.1. System Components
The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM CCD cameras consist of four
major components: the CCD Sensors and Preamplifier, the Readout/Clocking Electronics, the
Microcontroller, and the power supply. All the electronics are packaged in the optical head in
these cameras with an external desktop power supply.
The CCDs, Preamplifier, and Readout Electronics are mounted in the front of the optical
head. The optical head interfaces to the telescope through a 1.25 inch (or larger) draw tube,
sliding into the telescope's focus mechanism. The placement of the preamplifier and readout
electronics close to the CCD is necessary to achieve good noise performance. The
Microcontroller is housed in the rear of the Optical Head along with the interface logic to the PC
and Telescope.
4.2. Connecting the Power
The desktop power supply is designed to run off voltages found in most countries (90 to 240
VAC). In the field however, battery operation may be the most logical choice. In that case you
need to use the optional 12V power supply or a 12VDC to 110 VAC power inverter.
4.3. Connecting to the Computer
The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM CCD Cameras are supplied
with a 15 foot cable to connect the system to the host computer. The connection is between the
camera and the Host Computer's USB port. If it is necessary or desirable to extend the distance
between the camera and the computer, third party USB extenders such as the “Ranger” made
by Icron (http://www.icron.com
) may be used for remote operation up to 500 meters.
4.4. Connecting the Relay Port to the Telescope
The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM camera systems can be used
as autoguiders where the telescope's position is periodically corrected for minor variations in
the RA and DEC drives. The host software functions as an autoguider in three modes: the
Track mode, the SBIG patented Track and Accumulate mode, and the SBIG patented Self
Guided mode (except for the ST-1001E).
In the Track mode and Self Guided mode the host software corrects the telescope as
often as once every second to compensate for drift in the mount and drive system. The host
software and the CCD camera operate in tandem to repeatedly take exposures of the designated
guide star, calculate its position to a tenth of a pixel accuracy, and then automatically activate
the telescope's controller to move the star right back to its intended position. It does this
tirelessly to guide long duration astrophotographs.
In the Track and Accumulate mode the software takes a series of images and
automatically co-registers and co-adds the images to remove the effects of telescope drift.
Page 43
Page 46

Section 4 – Camera Hardware
Typically you would take ten 1 minute "snapshots" to produce an image that is comparable to a
single 10 minute exposure except that no guiding is required. The reason no guiding is required
is that with most modern telescope mounts the drift over the relatively short 1 minute interval
is small enough to preserve round star images, a feat that even the best telescope mounts will
not maintain over the longer ten minute interval. The Track and Accumulate software does
allow correction of the telescope position in the interval between snapshots to keep the guide
star grossly positioned within the field of view, but it is the precise co-registration of images
that accounts for the streakless images.
The host software and the CCD camera control the telescope through the 9-pin
Telescope port on the camera. This port provides active low open collector signals to the
outside world. By interfacing the camera to the telescope's controller the CPU is able to move
the telescope as you would: by effectively closing one of the four switches that slews the
telescope.
Note: You only need to interface the camera's Telescope port to your telescope if you are
planning on using the camera system as an autoguider or selfguider, or feel you need to
have the Track and Accumulate command make telescope corrections between images
because your drive has a large amount of long term drift.
Some recent model telescopes (like the Celestron Ultima and the Meade LX200) have connectors
on the drive controller that interface directly to the camera's TTL level Telescope port. All that's
required is a simple cable to attach the 9 pin Telescope port to the telescope's telephone jack
type CCD connector. SBIG includes its TIC-78 (Tracking Interface Cable Adapter) for this
express purpose although it is easy to modify a standard 6-pin telephone cable for interface to
the Telescope port (see Appendix A for specific pin outs, etc.). The TIC-78 plugs into the 9-pin
port on the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM, and a standard
phone cable, which we supply, connects the adapter to the telescope drive. Note: phone cables
come in a few variations. We use the six-pin cable, and the pin order is reversed left to right
relative to the connector from one end to the other. This is identical to what is typically sold at
Radio Shack stores as an extension cable.
4.4.1 Using Mechanical Relays
Older telescopes generally require modifying the hand controller to accept input from the
camera's Telescope port. The difficulty of this task varies with the drive corrector model and
may require adding external relays if your drive corrector will not accept TTL level signals. We
maintain a database of instructions for the more popular telescopes that we will gladly share
with you. For a minimal charge will also modify your hand controllers if you feel you do not
have the skills necessary to accomplish such a task. We sell a mechanical relay box that
interfaces to the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM, and will
interface to the older drives. Contact SBIG for more information.
In general, the camera has four signals that are used in tracking applications. There is
one output line for each of the four correction directions on the hand controller (North, South,
East and West). Our previous cameras had internal relays for the telescope interface, but with
the proliferation of TTL input telescopes the relays were removed (We do offer an external relay
adapter accessory). The following paragraphs describe the general-purpose interface to the
telescope which involves using external relays.
Page 44
Page 47

Section 4 – Camera Hardware
y
In our older camera models and in the optional relay adapter accessory, each of the
relays has a Common, a Normally Open, and a Normally Closed contact. For example, when
the relay is inactivated there is a connection between the Common and the Normally Closed
contact. When the relay is activated (trying to correct the telescope) the contact is between the
Common and the Normally Open contacts.
If your hand controller is from a relatively recent model telescope it probably has four
buttons that have a "push to make" configuration. By "push to make" we mean that the
switches have two contacts that are shorted together when the button is pressed. If that's the
case then it is a simple matter of soldering the Common and Normally Open leads of the
appropriate relay to the corresponding switch, without having to cut any traces, as shown in
Figure 4.1 below.
A: Unmodified Push to Make Switch
switch
B: Modified Push to Make Switch
switch
normally open
common
c
relay
nonc
Figure 4.1 - Push to Make Switch Modification
Another less common type of switch configuration (although it seems to have been used more
often in older hand controllers) involve hand controller buttons that use both a push to make
contact in conjunction with a push to break contact. The modification required for these
switches involves cutting traces or wires in the hand controller. Essentially the relay's Normally
Open is wired in parallel with the switch (activating the relay or pushing the hand controller
button closes the Normally Open or Push to Make contact) while at the same time the Normally
Closed contact is wired in series with the switch (activating the relay or pushing the hand
controller button opens the Normally Closed or the Push to Break contact). This type of switch
modification is shown in Figure 4.2 below.
A: Unmodified Push to Make/Break Switch
c
switch
nonc
common
normally open
normall
closed
B: Modified Push to Make/Break Switch
c
nonc
c
nc
common
relay
no
normally open
normally closed
Figure 4.2- Push to Make/Break Modification
The last type of hand controller that is moderately common is the resistor joystick. In this
joystick each axis of the joystick is connected to a potentiometer or variable resistor. Moving the
joystick handle left or right rotates a potentiometer, varying the resistance between a central
"wiper" contact and the two ends of a fixed resistor. The relays can be interfaced to the joystick
Page 45
Page 48

Section 4 – Camera Hardware
as shown in Figure 4.3 below. Essentially the relays are used to connect the wire that used to
attach to the wiper to either end of the potentiometer when the opposing relays are activated.
A
wiper
B
+ relay
A
C
nccno
- relay
nccno
potentiometer
A: Unmodified Joystick
BC
B: Modified Joystick
Figure 4.3 - Joystick Modification
A slight variation on the joystick modification is to build a complete joystick eliminator as
shown in Figure 4.4 below. The only difference between this and the previous modification is
that two fixed resistors per axis are used to simulate the potentiometer at its mid position. You
do not need to make modifications to the joystick; you essentially build an unadjustable version.
This may be easier than modifying your hand controller if you can trace out the wiring of your
joystick to its connector.
A
- relay
nccno
wiper
B
R
potentiometer
+ relay
c
A
nc
no
C
BC
R/2 R/2
A: Unmodified Joystick
B: Joystick Eliminator
Figure 4.4- Joystick Eliminator
4.5. Modular Family of CCD Cameras
With the introduction of the ST-6 CCD Camera in 1992 SBIG started a line of high quality, low
noise, modular CCD cameras. The ST-7E, ST-8E and ST-9E were a second family of modular
CCD cameras. The ST-10E allowed for upgrades to a faster USB interface and larger tracking
CCD.
The benefits of a modular line of CCD Cameras are many fold. Users can buy as much
CCD Camera as they need or can afford, with the assurance that they can upgrade to higher
performance systems in the future. With a modular approach, camera control software like
CCDOPS can easily support all models. This last point assures a wide variety of third party
Page 46
Page 49

Section 4 – Camera Hardware
software. Software developers can produce one package for the many users across the model
line instead of different packages for each of the cameras.
While the SBIG cameras have many similarities, there are also important differences
between the products. Table 4.2 below highlights the differences from a system's standpoint:
Camera
A/D
Resolution
Temperature
Regulation
Electromechanical
Shutter/Shutter
Electronic
Shutter
Wheel/Vane
ST-5C 16 bits Closed Loop Shutter Wheel
ST-237A 16 bits Closed Loop Shutter Wheel
STV 10+2 bits Closed Loop Shutter Wheel
ST-6 16 bits Closed Loop Vane
ST-7/8/9/10/1001/2000 16 bits Closed Loop Shutter None
0.01
0.01
0.001
0.01
second
second
second
second
Table 4.2 - System Features
How these features affect the average user are discussed in the paragraphs below:
A/D Resolution - This is a rough indication of the camera's dynamic range. Higher precision
A/D Converters are able to more finely resolve differences in light levels, or for
larger CCDs with greater full well capacities, they are able to handle larger total
charges with the same resolution.
Temperature Regulation - In an open loop system like the original ST-4 the CCD cooling is
either turned on or turned off. While this provides for adequate cooling of the
CCD, the CCD's temperature is not regulated which makes it important to take
dark frames in close proximity to the associated light frame. Closed loop
systems regulate the CCD's temperature to an accuracy of ±0.1° C making dark
frames useful over longer periods.
Electromechanical Vane - Having the vane in the ST-6 means the host software can effectively
"cover the telescope" and take dark frames remotely, without the user having to
get up and physically cover the telescope.
Electromechanical Shutter - Having the shutter in the ST-7E/8E/9E/10E/1001E gives streak-
free readout and allows taking dark frames without having to cover the
telescope. While the minimum exposure is 0.11 seconds, repeatability and area
uniformity are excellent with SBIG's unique unidirectional shutter.
Shutter Wheel - The Shutter Wheel, used in conjunction with the camera's Electronic shutter,
allows you to cover the CCD for taking dark frames and in the case of the
ST-5C/237/237A allows replacement with a mini internal color filter wheel.
Electronic Shutter - Having an electronic shutter involves having a CCD with a frame transfer
region. These CCDs actually have an array that has twice the number of rows
advertised, where the bottom half is open to the light (referred to as the Image
Area), and the top half is covered with a metalization layer (referred to as the
Storage Area). In frame transfer CCDs at the end of the exposure, the pixel data
from the Image Area is transferred into the Storage Area very rapidly where it
can be read out with a minimum of streaking.
Page 47
Page 50

Section 4 – Camera Hardware
In addition to the system level differences between the various cameras, Table 4.3 below
quantifies the differences between different CCDs used in the cameras:
Camera CCD Used Number of
Pixels
TC211 Tracking CCD TC-211 192 x 164 13.75 x 16 µ 2.6 x 2.6 mm
TC237 Tracking CCD TC-237 657 x 495 7.4 x 7.4 µ 4.9 x 3.7 mm 12e- rms 20Ke-
ST-5C TC-255 320 x 240 10 x 10 µ 3.2 x 2.4 mm
ST-237A TC-237 657 x 495 7.4 x 7.4 µ 4.9x 3.7 mm
STV TC-237 320 x 200 14.8 x 14.8 µ 4.7 x 3.0 mm
ST-7XE KAF0401E 765 x 510 9 x 9 µ 6.9 x 4.6 mm 15e- rms
ST-8XE KAF1602E 1530 x 1020 9 x 9 µ 13.8 x 9.2 mm 15e- rms
ST-9XE KAF0261E 512 x 512 20 x 20 µ 10.2 x 10.2 mm 13e- rms 180Ke-
ST-10XE, XME KAF3200E 2184 x 1472 6.8 x 6.8 µ 14.9 x 10.0 mm 11e- rms 77Ke-
ST-1001E KAF1001E 1024 x 1024 24 x 24 µ 24.6 x 24.6 mm 16e- rms 180Ke-
ST-2000XM KAI2000M 1600 x 1200 7.4 x 7.4 µ 11.8 x 9.0 mm 15e- rms 45Ke-
Pixel
Dimensions
Array
Dimension
Read
Noise
12e- rms 150Ke-
20e- rms 50Ke-
15e- rms 20Ke-
17e- rms
Full Well
Capacity
20Ke-
50/100Ke-3
50/100Ke-4
Table 4.3- CCD Differences
How these various specifications affect the average user is described in the following
paragraphs:
Number of Pixels - The number of pixels in the CCD affects the resolution of the final images.
The highest resolution device is best but it does not come without cost. Larger
CCDs cost more money and drive the system costs up. They are harder to cool,
require more memory to store images, take longer to readout, etc. With typical
PC and Macintosh computer graphics resolutions, the CCDs used in the SBIG
cameras offer a good trade off between cost and resolution, matching the
computer's capabilities well.
Pixel Dimensions - The size of the individual pixels themselves really plays into the user's
selection of the system focal length. Smaller pixels and smaller CCDs require
shorter focal length telescopes to give the same field of view that larger CCDs
have with longer focal length telescopes. Smaller pixels can give images with
higher spatial resolution up to a point. When the pixel dimensions (in
arcseconds of field of view) get smaller than roughly half the seeing, decreasing
the pixel size is essentially throwing away resolution. Another aspect of small
pixels is that they have smaller full well capacities.
For your reference, if you want to determine the field of view for a pixel
or entire CCD sensor you can use the following formula:
Field of view (arcseconds) =
Field of view (arcseconds) =
8.12x size (µm)
focal length (inches)
20.6x size(um)
focal length(cm)
3
The Kodak CCDs (KAF0400 and KAF1600) are available with or without Antiblooming Protection.
Units with the Antiblooming Protection have one-half the full well capacity of the units without it.
Page 48
Page 51

Section 4 – Camera Hardware
where size is the pixel dimension or CCD dimension in millimeters and the focal
length is the focal length of the telescope or lens. Also remember that 1° = 3600
arcseconds.
Read Noise - The readout noise of a CCD camera affects the graininess of short exposure
images. For example, a CCD camera with a readout noise of 30 electrons will
give images of objects producing 100 photoelectrons (very dim!) with a Signal to
Noise (S/N) of approximately 3 whereas a perfect camera with no readout noise
would give a Signal to Noise of 10. Again, this is only important for short
exposures or extremely dim objects. As the exposure is increased you rapidly get
into a region where the signal to noise of the final image is due solely to the
exposure interval. In the previous example increasing the exposure to 1000
photoelectrons results in a S/N of roughly 20 on the camera with 30 electrons
readout noise and a S/N of 30 on the noiseless camera. It is also important to
note that with the SBIG CCD cameras the noise due to the sky background will
exceed the readout noise in 15 to 60 seconds on the typical amateur telescopes.
Even the $30,000 priced CCD cameras with 10 electrons of readout noise will not
produce a better image after a minute of exposure!
Full Well Capacity - The full well capacity of the CCD is the number of electrons each pixel can
hold before it starts to loose charge or bleed into adjacent pixels. Larger pixels
hold more electrons. This gives an indication of the dynamic range the camera is
capable of when compared to the readout noise, but for most astronomers this
figure of merit is not all that important. You will rarely takes images that fill the
pixels to the maximum level except for stars in the field of view. Low level
nebulosity will almost always be well below saturation. While integrating longer
would cause more build up of charge, the signal to noise of images like these is
proportional to the square-root of the total number of electrons. To get twice the
signal to noise you would have to increase the exposure 4 times. An ST-5C with
its relatively low full well capacity of 50,000e
-
could produce an image with a
S/N in excess of 200!
Antiblooming - Most SBIG CCD cameras have antiblooming protection. The TI CCDs used in
the ST-5C, ST-237, ST-237A, TC-237 autoguider and TC-211 autoguider have
antiblooming built into the CCDs. The Kodak CCDs used in the ST-7XE and ST8XE have Antiblooming versions of the CCDs available and the CCD used in the
ST-2000XM only comes with antiblooming. Blooming is a phenomenon that
occurs when pixels fill up. As charge continues to be generated in a full pixel, it
has to go somewhere. In CCDs without antiblooming protection the charge
spills into neighboring pixels, causing bright streaks in the image. With the
CCDs used in the SBIG cameras the excess charge can be drained off saturated
pixels by applying clocking to the CCD during integration. This protection
allows overexposures of 100-fold without blooming. The trade off is sensitivity.
Antiblooming CCDs are less sensitive than non-antiblooming CCDs. In the case
of the ST-7XE and ST-8XE, for example, the non-antiblooming versions are very
roughly twice as sensitive.
The CCDs used in the ST-9XE, ST-10XE and ST-10XME and ST-1001E
detectors do not come in an antiblooming version.
Page 49
Page 52

Section 4 – Camera Hardware
From the telescope's point of view, the different models offer differing fields of view for a given
focal length, or turned around, to achieve the same field of view the different models require
differing focal lengths. Tables 4.4 and 4.5 below compare the fields of view for the cameras at
several focal lengths, and vice versa.
C8, 8" f/10
Camera
TC211 Tracking CCD 4.2x4.2 1.3x1.5 11.7x11.7 3.7x4.3 2.3x2.3 0.7x0.8
TC237 Tracking CCD 8.2x6.2 0.75x0.75 21.9x16.5 2.0x2.0 4.3x3.2 0.39x0.39
ST-5C 5.4x4.1 1.0x1.0 14.4x10.8 2.7x2.7 2.8x2.1 0.5x0.5
ST-237A 8.2x6.2 0.75x0.75 21.9x16.5 2.0x2.0 4.3x3.2 0.39x0.39
STV 8.0x5.0 1.5x1.5 21.6x13.5 4.0x4.0 4.0x2.5 0.75x0.75
ST-7XE 11.9x7.9 0.9x0.9 31.2x20.8 2.4x2.4 6.1x4.1 0.5x0.5
ST-8XE 23.8x15.8 0.9x0.9 62.4x41.6 2.4x2.4 12.2x8.2 0.5x0.5
ST-9XE 17.6x17.6 2.0x2.0 46.2x46.2 5.3x5.3 9.1x9.1 1.1x1.1
ST-10XE 25.1x16.9 0.7x0.7 67.0x45.2 1.8x1.8 13.0x8.8 0.36x0.36
ST-1001E 41.6x41.6 2.4x2.4 111x111 6.5x6.5 21.6x21.6 1.27x1.27
ST-2000XM 20.0x15.0 0.75x0.74 53.4x40.1 2.0x2.0 10.4x7.8 0.39x0.39
Field of
View
(arcmins)
Pixel Size
(arcsecs)
LX200, 10" f/34
Field of View
(arcmins)
Pixel Size
(arcsecs)
Field of
View
(arcmins)
14" f/11
Pixel Size
(arcsecs)
Table 4.4 - Field of View
Object
Moon 0.5° 275mm = 11 inches 760mm = 30 inches
Jupiter 40 arcseconds 13000mm = 510 inches 34000mm = 1350 inches
Size
Focal Length to fill 211
Tracking CCD
Focal Length
to fill ST-7XE
M51-Whirlpool Galaxy 8x5 arcminutes 1040mm = 41 inches 3700mm = 145 inches
M27-Dumbell Nebula 8.5 x 5.5 arcminutes 1040mm = 41 inches 3700mm = 145 inches
M57-Ring Nebula 1.3 x 1 arcminutes 6400mm = 250 inches 23000mm = 900 inches
Table 4.5 - Focal Length Required
From these numbers you can deduce that the popular C8, an 8" f/10 telescope will nicely frame
many popular objects with the ST-7XE whereas a much shorter system (f/3, perhaps achieved
with a focal reducer) will frame the same objects for the tracking CCD. Another point to bear in
mind is that, except for planetary images, you'll rarely take images where the pixel size in
seconds of arc is down near the seeing limit. Most objects are relatively large, where the field of
view is more important than whether the individual pixels are less than half the seeing.
4.6 Connecting accessories to the Camera
There are two 9 pin accessory ports on the ST-X series of cameras. The first is labeled “AO7 /
CFW8/ SCOPE.” This is the port that supports our AO-7 Adaptive optics device, CFW8A color
4
f/6.3 telescope with an f/6.3 focal reducer and star diagonal.
Page 50
Page 53

Section 4 – Camera Hardware
filter wheel and relay adapter box. It is also the relay output for direct connection to many
popular telescopes’ “CCD” autoguiding port. (Note: This is not the same thing as the
telescope’s RS232 port that is commonly used to point and slew the telescope). The second
accessory port on the camera is labeled I2C AUX (“I squared C”) and is for future accessories.
Be sure to keep the static safe cap over this port to insure that you do not accidentally plug in an
accessory that is intended for the AO7/CFW8/SCOPE port. Plugging in the wrong accessory to
the I2C port could cause damage.
More than one accessory can be connected to the accessory ports by using multiple plug
adapters provided with the accessory.
4.7 Battery Operation
The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM can be operated off of
a 12 volt car or marine battery using a the optional 12V power supply or using a power inverter.
We have used the Radio Shack model 22-132A, 12 volt DC to 115 volt AC Portable Power
Inverter (140 watt) with good success. The camera draws 2.2 amps from the battery with this
inverter, which should enable an evening's operation from a single battery. If your camera has
the older two-stage cooling booster, it will, when connected, draw another 2 amps. We
recommend a separate battery for the camera; using your vehicle's battery with the engine
running may add undesirable readout noise, and using your vehicle's battery without the
engine running may result in a long walk home in the dark!
Page 51
Page 54

Page 55

Section 5 – Advanced Imaging Techniques
5. Advanced Imaging Techniques
With practice, you will certainly develop methods of your own to get the most from your CCD
camera. In this section we offer some suggestions to save you time getting started in each of the
different areas outlined below, but these suggestions are by no means exhaustive.
5.1. Lunar and Planetary Imaging
When imaging the moon using most focal lengths available in astronomical telescopes, you will
note that the moon's image typically fills the CCD. The image is also very bright. The best way
to image the moon is to use neutral density filters to attenuate the light.
You may also try an aperture mask to reduce the incoming light. If you feel that an
aperture mask reduces resolution to an unacceptable degree, consider using a full aperture solar
filter. This will result in an optimum exposure of only a few seconds. Another way to reduce
the incoming light is to increase the effective focal length of your telescope by using a barlow
lens or eyepiece projection. This is very desirable for planetary imaging since it also increases
the image size.
5.2. Deep Sky Imaging
Ordinarily, with telescopes of 8" aperture or larger, a ten second exposure in focus mode, with a
dark frame subtracted, will show most common deep sky objects except for the very faintest.
This is a good starting point for finding and centering deep sky objects. If you find ten seconds
to be insufficient, a one-minute exposure will clearly show nearly any object you wish to image,
particularly if 2x2 or 3x3 binning is selected. Using the Grab command, exposures of five
minutes will generally give you a clear image with good detail. Of course, longer exposures are
possible and desirable, depending on your telescope's tracking ability or your desire to guide.
Once you have determined the longest exposure possible with your particular drive error, try
Track and Accumulate exposures of a duration less than your measurable error. We have found
that exposures of thirty seconds to two minutes are best depending on the focal length of
telescope one is using. With the self guiding feature of the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE,
ST-10XME and ST-2000XM, one can take long integrations while the internal tracking CCD
guides the telescope.
We highly recommend that you initially pursue deep sky imaging with a fast telescope,
or focal reducer to produce a final F number of F/6.3 or faster at the CCD. The sensitivity
advantage is considerable!
5.3. Terrestrial Imaging
An optional accessory for the SBIG cameras is the camera lens adapter. These accessories are
made to accommodate most popular camera models. You may attach a camera lens in place of
your telescope and use the CCD camera for very wide angle images of the night sky or for
terrestrial views in daylight. Begin with a tenth second exposure at f/16 for scenes at normal
room light and adjust as necessary for your conditions.
Page 53
Page 56

Section 5 – Advanced Imaging Techniques
5.4. Taking a Good Flat Field
If you find that flat field corrections are necessary due to vignetting effects, CCD sensitivity
variations, or for more accurate measurements of star magnitudes, try either taking an image of
the twilight sky near the horizon or take an image of a blank wall or neutral grey card. The
Kodak CCDs may have a low contrast grid pattern visible in the sky background. A flat field
will eliminate this.
Finding areas of the sky devoid of stars is very difficult after twilight. Therefore, you
should take flat field images of the night sky after sunset, but long before you can see any stars.
If this is not possible, take an image of a featureless wall or card held in front of the telescope.
However, if using this second method, be sure that the wall or card is evenly illuminated.
Appendix D describes how to do this. You will know if the flat field is good if the sky
background in your images has little variation across the frame after flat fielding, displayed
using high contrast (a range of 256 counts is good for showing this).
If you plan on flat fielding Track and Accumulate images you should also refer to
section 6.8. Since the same flat field is added to itself a number of times, be sure that you do not
saturate the flat field image by starting with pixel values too high. Typically try to keep the
pixel values between 10% to 20% of saturation for this purpose. For single flat field images, try
to keep the values to approximately 50% of saturation.
5.5. Building a Library of Dark Frames
The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM have regulated temperature
control, and therefore it is possible to duplicate temperature and exposure conditions on
successive nights. You can set the camera TE cooler temperature to a value comfortably within
reach on your average night, and then take and save on disk a library of dark frames for later
use. This is a good project for a rainy night. We recommend you build a file of 5, 10, 20 ,40, and
60 minute dark frames at zero degrees Centigrade for a start. Otherwise you will find yourself
wasting a clear night taking hour long dark frames!
Note:
Dark frames taken the same night always seem to work better. The adaptive
dark subtract will help if the ambient temperature changes slightly.
5.6. Changing the Camera Resolution
The Camera Setup command allows you to select the resolution mode you wish to use for
taking and displaying images. The ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST2000XM cameras have High, Medium, Low and Auto modes. The High Resolution mode is the
best for displaying the greatest detail since it utilizes the maximum number of pixels for your
particular camera. The Medium Resolution Mode operates by combining 2x2 pixels giving the
same field of view as High Resolution Mode, but with 1/4 the resolution. This results in
significantly faster digitization and download times. Also, in Medium Resolution Mode, with
larger pixels and comparable readout noise there is a better signal to noise ratio for very dim
diffuse objects. This improved signal to noise ratio combined with faster digitization and
download times makes Medium Resolution Mode ideal for finding and centering dim objects,
and for imaging most objects. Additionally, a Low resolution mode is provided which bins the
CCD 3x3 before readout. Low resolution mode is sensational for displaying faint nebulosity
Page 54
Page 57

Section 5 – Advanced Imaging Techniques
with short exposure times. In Auto Resolution Mode, the camera and software will always use
High Resolution for all imaging and display functions except when you are in Full Frame Focus
Mode. It will then automatically switch to Low Resolution Mode. If you further select Planet
Mode for focusing, the camera will switch back to High Resolution on the selected box area.
The small pixel size, is best for critical focusing. Planet mode will result in fast digitization and
download times since only a small portion of the frame is read out.
In general, you should pick a binning mode that yields stars with two to three pixels full
width at half maximum. This is easily measured by using the crosshairs to determine the peak
brightness of a relatively bright star, and determining the number of pixels between the 50%
values on either side of the peak. More than 3 pixels per stellar halfwidth merely wastes
sensitivity without improved resolution.
5.7. Flat Fielding Track and Accumulate Images
This section gives the step by step procedure for flat field correcting images taken using the
Track and Accumulate command.
Flat field correcting images allow the user to remove the effects of CCD response nonuniformity (typically less than a few percent) and optical vignetting which for some optical
systems can be as much as a 50% effect from center to edge. The CCDOPS software allows flat
field correcting images using the Flat Field command, but some preparation must be made to
use that command with Track and Accumulate images. Essentially you must prepare a special
flat field correction image for Track and Accumulate images. This special preparation is
necessary to have the same set of alignment and co-addition operations apply to the flat field
file that have occurred in acquiring the Track and Accumulate image. In general, the following
procedure should be followed when flat field correction of Track and Accumulate images is
desired:
1. Take a normal flat field image using the Grab command. You can use the dusk
sky or a neutral gray or white card held in front of the telescope. Try to adjust
the illumination and/or exposure so that the build up of light in the image yields
values that when co-added several times will not overflow 65,000 counts. The
number of times the image will need to be co-added without overflowing is set
by how many snapshots you intend to use in Track and Accumulate. A good
goal is to try and attain a maximum level in the flat field image of 1,000 to 2,000
counts which will allow co-addition 32 times without overflow.
Note: You will have to take a new flat field image anytime you change the optical
configuration of your telescope such as removing and replacing the optical head in the
eyepiece holder.
2. Save the flat field image on your disk using the Save command. In the following
discussions this flat field file will be referred to as FLAT.
3. Take your Track and Accumulate image using the Track and Accumulate
command and save it on the disk using the Save command. In the following
discussions this Track and Accumulate image file will be referred to as IMAGE.
4. Immediately after saving the IMAGE use the Save Track List command on the
PC or activate the Track List window on the Mac and use the Save command to
Page 55
Page 58

Section 5 – Advanced Imaging Techniques
save the Track and Accumulate track list. The track list is a file that describes
what alignment operations were done to the individual components of IMAGE
to achieve the end result. In the following discussions this track list file will be
referred to as TRACK.
5. Repeat steps 3 and 4 as many times as desired for all the objects you wish to
image, each time choosing a set of corresponding new names for the IMAGE and
TRACK files.
6. You will now create a combined flat field image for each Track and Accumulate
image you captured. Invoke the Add by Track List command. The software will
bring up a file directory dialog showing all the track list files. Select the TRACK
file corresponding to the image you wish to correct. The software will load the
TRACK file and present you with another file directory dialog showing all the
images. Select the appropriate FLAT image. The software will align and co-add
the FLAT image using the same operations it performed on the Track and
Accumulate image. Finally save the combined flat field image using the Save
command. In the following discussions this combined flat field image will be
referred to as COMBINED-FLAT. Repeat this step for each of the TRACK files
using a corresponding name for the COMBINED-FLAT image.
7. You will now flat field correct the Track and Accumulate image with the
combined flat field image. Use the Open command to load the IMAGE file, then
use the Flat Field command. The software will present you with a file directory
dialog where you should select the corresponding COMBINED-FLAT image.
After the software has finished correcting the image you can view the results and
save the flat field corrected image with the Save command. This image will be
referred to as the CORRECTED-IMAGE file. Repeat this step for each of the
IMAGE files using the corresponding COMBINED-FLAT image.
At SBIG we have adopted the following naming convention for our various image and related
files. If it helps you organize your files please feel free to adopt it or any method you feel helps
sort out the process of naming files:
Image type Name
Uncorrected image (IMAGE) XXXXXXXX. (blank extension)
Flat field file (FLAT) FLATXXXX. (blank extension)
Track list file (TRACK) XXXXXXXX.TRK
Combined flat field (COMBINED-FLAT) FLATXXXX.C
Flat field corrected image (CORRECTED-IMAGE) XXXXXXXX.F
5.8. Tracking Functions
The CCDOPS software allows your ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST2000XM to be used as an autoguider or self-guided imager. It does not function as a standalone autoguider like the ST-4, but instead requires using a PC to perform the function. These
cameras have considerably better sensitivity than the ST-4.
Page 56
Page 59

Section 5 – Advanced Imaging Techniques
CCD autoguiders alleviate you from having to stare down the eyepiece for hours at a
time while guiding astrophotographs. They are not the end-all, cure-all approach to telescope
mechanical problems, though. You still need a good polar alignment and a rigid mount
between the guide scope and the main scope or you need to use an off-axis guider, with all its
inherent difficulties. A good declination drive, free of backlash, is desirable although not
absolutely necessary. Finally, modern drive correctors with periodic error correction (PEC) or
permanent periodic error correction (PPEC) will ease the difficulty of achieving good results.
The moral of the story is don't count on the CCD autoguider to fix all your problems.
The better the drive, the better results you will obtain.
Using the CCD as an autoguider requires interfacing the CPU's relay port to your hand
controller (as discussed in section 4.4) and then training the CCD system on your telescope.
This is done with the Calibrate Track command. Focus your system and then find and center
on a moderately bright calibration star (1000 to 20,000 peak counts will do) without any nearby
neighboring stars of similar brightness. Then execute Calibration command. It takes a
sequence of five images. In the first image it determines the pixel position of the calibration
star. In the four subsequent images, the software, in sequence, activates each of the telescope's
four correction directions, measuring the displacement of the calibration star. From this
calibration information, the software is able to calculate a precise correction when the guide star
moves away from its intended position.
At the start, you should pick a calibration star with roughly the same declination as the
intended object since the telescope's correction speeds vary with declination. As you get used
to the tracking functions you can calibrate on a star near the celestial equator and have the
software adjust for different declinations for you.
The tracking functions in CCDOPS are accessed through the Track menu. The Calibrate
Track command, as described above, is used to calibrate your telescope's drive corrector. Once
that is done, the Track command, which you would use for autoguiding astrophotographs,
allows you to select a guide star in the field of view, and then repeatedly takes images,
measuring the guide star's position and hence guiding error, and corrects the telescope.
The Track and Accumulate command, discussed in section 3.9.2, also has provisions for
making telescope corrections between images. This is necessary only if your drive has a large
amount of long term drift, which results in Track and Accumulate images that are reduced in
width.
Finally, the Tracking Parameters command allows you to fine tune the CCDOPS
tracking performance. You can deactivate the RA or DEC corrections or even deactivate both, a
feature that can be used to monitor the uncorrected tracking accuracy of your drive. You can
also fine tune the correction speeds if you find the telescope is consistently over or under
correcting.
Page 57
Page 60

Page 61

Section 6 – Accessories for your CCD Camera
6. Accessories for your CCD Camera
This section briefly describes the different accessories available for your CCD camera.
6.1. Water Cooling
Your camera is equipped with a new heat exchanger design that is ready to accept water
circulation for additional cooling efficiency, if needed in warm climates.
The camera can be used either with or without flowing water. Water-cooling is
probably not necessary for most users when the air temperature is below 10 degrees C (50
degrees F), since the dark current is fairly low already. Think of it as a summertime accessory!
We do not recommend use of water cooling below freezing temperatures, where antifreeze
must be added to the water. It is simply not necessary then.
There is no problem using the camera at any time without water circulation. Adding
water circulation simply improves the cooling performance. With water circulation the
improvement in cooling is about 10 degrees C better than with air only.
You may supply your own pump and tubing or use the optional pump and tubing
available from SBIG. To operate the camera with water circulation using the optional pump
available from SBIG, start with the camera at the same level as the water reservoir. Connect all
the hoses, and make sure the water return goes back into the reservoir. Push the ¼ inch internal
diameter (ID) hoses onto the nipples on the back of the camera so they seal. Attach one hose to
the nipple onto the reducing connector that adapts the ¼ inch ID hose to the ½ inch diameter
hose from the pump.
Turn on the pump, and let the flow establish itself through the hoses. Next, mount the
camera to the telescope. If you always keep the return hose outlet near the reservoir level the
pump will have no problem raising the water 2 meters (6 feet) off the floor. The limited
pressure capacity of the pump is only a problem when you let the water fall back into the
reservoir from a significant height above it, such a 0.3 meter (12 inches). Lastly, check for leaks!
Once you have established water circulation, turn on the TE cooler to 100% by giving it a
target temperature of –50 degrees. Wait for about 10 to 20 minutes for the system to stabilize at
the lowest temperature it can achieve. Examine the camera temperature, and reset the set point
to 3 degrees C above the current temperature. This 3 degree temperature margin will enable
the camera to regulate the temperature accurately.
When using water cooling, avoid the temptation to put ice in the water to get the camera
even colder. If colder water is used, the head may fog or frost up, depending on the dew point.
At the end of the evening, stop the pump, and raise the outlet hose above the camera to let all
the water drain out of the system. Blowing it out with gently pressure helps clear the water.
You can leave the hoses full of water, but if a leak occurs while you’re not there you may have a
problem.
When packing the camera for a long time, or at the end of summer, disconnect the hoses
and blow out the heat sink to allow the enclosed spaces to dry out and minimize long term
corrosion.
Page 59
Page 62

Section 6 – Accessories for your CCD Camera
6.2. Tri-color Imaging
You can make splendid color images with your CCD camera by using the optional CFW-8 color
filter wheel. The CFW-8 attaches to the front of the CCD head and allows you to take images in
red, green and blue light of the same object. When these images are aligned and processed a
full color image results.
6.3. Camera Lens Adapters and Eyepiece Projection
Camera Lens adapters are available for the ST-7XE, 8XE, 9XE, 10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM.
The camera lens adapter allows you to mount your camera lens in place of the telescope for
very wide field views of the night sky or for daytime terrestrial imaging. The adapters are
available for a variety of the most common camera lenses in use.
The cameras themselves can be used for eyepiece projection assuming you already have
a T-thread eyepiece projection adapter for. Instead of attaching a 35mm camera to the T-thread
camera adapter you can attach the CCD camera by unscrewing the T-Thread nosepiece fom the
front of the camera.
6.4. Focal Reducers
Several third party vendors, including Optec, Celestron and Meade, make focal reducers for
their telescopes that could be used with the ST-7XE, 8XE, 9XE, 10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM
cameras. While most will work with the ST-7XT some may have slight amounts of vignetting
when used on the larger 8XE, 9XE, 10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM.
Note
: Many very fast (F/3.3) commercial units will not accommodate a filter wheel.
6.5. AO-7 and Lucy-Richardson Software
The AO-7 is the world's only Adaptive Optics accessory for the amateur CCD market and it
works only with the self guided feature of the ST-7XE, 8XE, 9XE, 10XE, ST-10XME and ST2000XM. The AO-7 is essentially an electromechanical driven diagonal mirror that goes
between the camera and the telescope. Using the AO-7 allows corrections to be made at rates
up to 40 Hz. This yields perfect, backlash-free guiding and allows removal of some
atmospheric effects. When used in conjunction with the CCDSharp software stellar peak
brightness can double and stellar half-widths can shrink by 25%.
6.6. SGS - Self-Guided Spectrograph
The SGS Self Guided Spectrograph takes the tedium out of spectroscopy by allowing you to
image and guide the source on the tracking CCD while acquiring its spectra on the imaging
CCD. No more hunting around to place the object on the slit! With the SGS you can measure
galactic redshifts, stellar classifications and determine nebular constituency. This is another
example of the value of a self-guided camera like the ST-7XE, 8XE, 9XE, 10XE, ST-10XME and
ST-2000XM.
Page 60
Page 63

Section 6 – Accessories for your CCD Camera
6.7. Third Party Products and Services
There are numerous third party products and services available directed to the CCD user.
Appendix E mentions a few vendors who have supported SBIG products just to give you an
idea of the ever increasing interest in this new technology.
6.7.1. Windows Software
Our CCDOPS version 5 software is compatible with Windows 95/98/2000/Me/NT/XP.
However, many users also want additional image processing or analytical features not found in
CCDOPS. Therefore, since January 2001, all SBIG cameras also include CCDSoftV5 which is a
joint software development of SBIG and Software Bisque. There are also several other
commercial Windows programs available which include a stellar database, telescope control for
computerized telescopes like the Meade LX200, and CCD camera functions in an integrated
package.
6.7.2. Image Processing Software
There are a host of image processing software packages capable of reading and processing FITS
and TIFF files and many packages will read and process native SBIG image formats as well. In
addition to commercial software, a number of web sites offer public domain and shareware
programs.
6.7.3. Getting Hardcopy
One older way of producing a hard copy of images taken with the CCD camera is to simply
take a photograph of the computer screen while the image is displayed. It is best to use a long
lens and step back from the monitor to reduce the appearance of the curvature of the edges of
the screen, and use an exposure longer than 1/30th of a second to avoid the video refresh rate of
your monitor. Darken the room, and use a brighter background than is visually optimum.
For the best quality hard copy, save the files in TIFF format and send a copy of the file on a disk
to a photo lab which offers printing of digital images. The Windows version of CCDOPS allows
for printing of the images, and there are a number of third party software programs for the PC
such as Pizzaz Plus which will capture and print the display on your computer screen. These
programs, however, do not produce very detailed prints and are useful only to a very limited
degree. Recently, photo quality color desktop printers have become commonplace. Many of
these printers will do a reasonable job with commercial image processing programs such as
Adobe Photoshop.
6.8. SBIG Technical Support
If you have any unanswered questions about the operation of your CCD camera system or have
suggestions on how to improve it please don't fail to contact us. We appreciate all your
comments and suggestions. Additionally if you are interested in writing software supporting
SBIG cameras, we offer technical support regarding our file formats found in Appendix B, and
Page 61
Page 64

Section 6 – Accessories for your CCD Camera
Technical Notes regarding the camera command protocol which we will make available upon
request.
Page 62
Page 65

Section 8 – Glossary
7. Common Problems
This section discusses some of the more common problems others have encountered while
using our CCD cameras. You should check here if you experience difficulties, and if your
problem still persists please contact us to see if we can work it out together.
Achieving Good Focus
with CCD cameras due to the lack of real time feedback when focusing. Focus can take a
good deal of time, and as with all forms of imaging, focus is critical to getting the most
out of your camera.
Once you have achieved a good focus with your system, it can be very useful for
future observing sessions to scribe an eyepiece or mark down or log positions of each
component so the next time you will at least be close to focus at the start.
If you know where the focal plane lies for your telescope, you can use Table 3.1
to calculate exactly where the CCD is with respect to your system. By placing the CCD
close to the focal plane initially, you can save a lot of time.
The best kind of object to focus on is a star. As you converge towards focus, more
light from the star will be concentrated onto one pixel. Thus, watching your peak
reading while focusing and focusing for a maximum reading is a good way to get best
focus. This is how we do it. It helps to have a dial or indicator on the focus knob so you
can rapidly return to the best point after going through focus.
Elongated Guided Images
guiding errors resulting in elongated star images, you are probably using too long a
snapshot time. If the snapshot time is longer than the amount of time your drive can
track unguided with acceptable guiding errors, you will see elongated stars in your final
images. If your snapshot times are getting down to 30 seconds or less you should
improve your drive.
- Achieving a good focus is one of the most difficult areas in working
- When using Track and Accumulate or Self Guiding, if you notice
If you are using your camera as an autoguider for film photography and are noticing
unacceptable guiding errors, please check the following before calling SBIG:
1. Can you move the telescope using the Move command? This is an
indicator as to whether or not you are properly connected to your
drive system via the relay cable from the CPU.
2. Be sure that your calibration time gives at least 10 to 50 pixels of
movement for each step of the Calibrate Track command.
3. Check for flexure between the CCD camera head and your system.
Check for flexure between the guide scope or off-axis guider and your
telescope system. This is a very common source of guiding errors. A
very small movement of the CCD head with respect to the guide
scope during an exposure can cause unacceptable streaking.
4. If your mount is stable, try longer exposure times while tracking to
average out the atmospheric effects.
Finding Objects
finding objects a little difficult. If you experience this problem you might try the
- The size of the CCD used in the ST-7 (roughly 8mm diagonal) can make
Page 63
Page 66

Section 8 – Glossary
following suggestions.
The easiest method of finding objects is to use a reticule eyepiece, if the object is
bright enough to see. Pull the CCD optical head from the eyepiece holder and insert a
12-20mm eyepiece, focusing the eyepiece by sliding it in and out of the eyepiece holder,
not by adjusting the telescope's focus mechanism. Center the object carefully (to within
10% of the total field) and then replace the CCD optical head. Since the head was fully
seated against the eyepiece holder when you started, fully seating it upon replacement
will assure the same focus.
If the object is too dim to see visually you will have to rely on your setting circles.
Go to a nearby star or object that is easily visible and center that object in the CCD
image. Calibrate your RA setting circle on the known object's RA and note any DEC
errors. Reposition the telescope at the intended object, using the correct RA setting and
the same DEC offset noted with the calibration object. Try a ten second or one minute
exposure and hopefully you will have winged the object. If not you will have to hunt
around for the object. You can use the Focus mode in Low resolution mode for this and
hopefully you won't have to search too far. Check in DEC first, as DEC setting circles
are often smaller and less accurate.
Telescope Port doesn't Move Telescope
Tracking, Track and Accumulate or Self Guiding you should use the Move Telescope
command with a several second period to isolate the problem down to a specific
direction or directions. If you set the Camera Resolution to the Low mode in the Camera
Setup Command, you can move the telescope and Grab an image fairly quickly to detect
movement of the telescope pointed at a moderately bright star. Try each of the four
directions and see which ones move and which ones don't. At this point the most likely
culprit is the hand controller modification. Trace the signals from the camera's telescope
connector back through the hand controller, paying particular attention to the offending
wires.
Can't Reach Low Setpoint Temperatures
expected the problem is probably increased ambient temperatures. While these cameras
have temperature regulation, they still can only cool a fixed amount below the ambient
temperature (30 to 40 °C). Lowering the ambient temperature allows the cameras to
achieve lower setpoint temperatures.
CCD Frosts
No Image is Displayed
- If your camera starts to frost after a year of use it's time to regenerate the desiccant
as described in Appendix C. This is a simple matter of unscrewing the desiccant
container and baking it (without the little O-ring) in an oven at 350°F for 4 hours.
- Try the Auto Contrast setting or use the crosshairs to examine the
image pixel values and pick appropriate values for the Background and Range
parameters.
- If you find the camera is not moving the telescope for
- If you find that the camera isn't getting as cold as
Horizontal Faint Light Streaks in Image
maskable interrupts when moved. These interrupts can slightly brighten the line being
read out. If this occurs, do not move the mouse during read out.
- some PCs apparently have the mouse generate non-
Page 64
Page 67

8. Glossary
Section 8 – Glossary
Antiblooming Gate
effectively spill over into an adjoining pixel. This is referred to as blooming. Kodak
CCDs with the antiblooming option can be used to help stop or at least reduce blooming
when the brighter parts of the image saturate.
Astrometry
Autoguider
CCD
- The CCD (Charged Coupled Device) is a flat, two dimensional array of very small light
Dark Frame
- Astrometry is the study of stellar positions with respect to a given coordinate
system.
- All SBIG CCD cameras have auto guiding or "Star Tracker" functions. This is
accomplished by using the telescope drive motors to force a guide star to stay precisely
centered on a single pixel of the CCD array. The camera has four relays to control the
drive corrector system of the telescope. The CCD camera head is installed at the guide
scope or off axis guider in place of a guiding eyepiece.
detectors referred to as pixels. Each pixel acts like a bucket for electrons. The electrons
are created by photons (light) absorbed in the pixel. During an exposure, each pixel fills
up with electrons in proportion to the amount of light entering the pixel. After the
exposure is complete, the electron charge buildup in each pixel is measured. When a
pixel is displayed at the computer screen, its displayed brightness is proportional to the
number of electrons that had accumulated in the pixel during the exposure.
- The user will need to routinely create image files called Dark Frames. A Dark
Frame is an image taken completely in the dark. The shutter covers the CCD. Dark
Frames are subtracted from normal exposures (light frames) to eliminate fixed pattern
and dark current noise from the image. Dark Frames must be of the same integration
time and temperature as the light frame being processed.
- When a CCD pixel has reached its full well capacity, electrons can
Dark Noise
Double Correlated Sampling
False Color
FITS Image File Format
- Dark Noise or Dark Current is the result of thermally generated electrons building
up in the CCD pixels during an exposure. The number of electrons due to Dark Noise is
related to just two parameters; integration time and temperature of the CCD. The longer
the integration time, the greater the dark current buildup. Conversely, the lower the
operating temperature, the lower the dark current. This is why the CCD is cooled for
long integration times. Dark noise is a mostly repeatable noise source, therefore it can be
subtracted from the image by taking a "Dark Frame" exposure and subtracting it from
the light image. This can usually be done with very little loss of dynamic range.
digitization errors due to residual charge in the readout capacitors. This results in lower
readout noise.
- False Color images are images that have had colors assigned to different
intensities instead of gray levels.
- The FITS image file format (which stands for Flexible Image
Transport System) is a common format supported by professional astronomical image
processing programs such as IRAF and PC Vista. CCDOPS can save image files in this
format but can not read them..
- Double Correlated Sampling (DCS) is employed to lower the
Page 65
Page 68

Flat Field
An image taken this way is called a flat field image and is used with CCDOPS to correct
images for vignetting.
Section 8 – Glossary
- A Flat Field is a image with a uniform distribution of light entering the telescope.
Focal Reducer
- A Focal Reducer reduces the effective focal length of an optical system. It
consists of a lens mounted in a cell and is usually placed in front of an eyepiece or
camera. With the relatively small size of CCDs compared to film, focal reducers are
often used in CCD imaging.
Frame Transfer CCDs
portion (usually half) of the pixel array. The unmasked portion is used to collect the
image. After the exposure is complete, the CCD can very quickly shift the image from
the unmasked portion of the CCD to the masked portion, thus protecting the image
from light which may still be impinging on the CCD. This acts as an electronic shutter.
Full Well Capacity
- Full Well Capacity refers to the maximum number of electrons a CCD
pixel can hold. This number is usually directly proportional to the area of the pixel.
Histogram
- The Histogram is a table of the number of pixels having a given intensity for each
of the possible pixel locations of the image file. Remember that, in the end, the image file
is nothing more than a list of pixel values, one for each CCD pixel. These value numbers
can be displayed in two formats; as a table or plotted as a graph.
Light Frame
- The Light Frame is the image of an object before a Dark Frame has been
subtracted.
Photometry
Pixel Size
- Photometry is the study of stellar magnitudes at a given wavelength or bandpass.
- The smallest resolution element of a CCD camera is the CCD pixel. The pixel sizes
for each of the SBIG cameras are as follows:
- Frame Transfer CCDs are CCDs that have a metal mask over some
Camera Pixel Size (microns)
TC-211 Tracking CCD 13.75 x 16
TC-237 Tracking CCD 7.4 x 7.4
ST-5C 10 x 10
ST-237/237A 7.4 x 7.4
STV 14.8 x 14.8
ST-7XE/ST-8XE 9 x 9
ST-9XE 20 x 20
ST-10XE, ST-10XME 6.8 x 6.8
ST-1001E 24 x 24
ST-2000XM 7.4 x 7.4
Planet Mode
- Planet Mode is the most useful way to achieve focus. When you select Planet
mode, a full frame is exposed, downloaded, and displayed on the computer monitor. A
small window can be placed anywhere in the image area and the size of the window can
be changed. Subsequent downloads will be of the area inside the box resulting in a much
faster update rate.
Quantum Efficiency
in the CCD pixel for a given number of photons. Quantum Efficiency is usually plotted
as a function of wavelength.
- Quantum Efficiency refers to the fractional number of electrons formed
Page 66
Page 69

Readout Noise
and readout of each of the CCD pixels at the end of an exposure. This is the result of
fixed pattern noise in the CCD, residual charge in the readout capacitors and to a small
extent the noise from the A/D converter and preamplifier.
Section 8 – Glossary
- Readout noise is associated with errors generated by the actual interrogation
Resolution Mode
be increased by combining or binning more than one pixel and displaying it as one pixel.
Doing so decreases the effective resolution but speeds up the download time of the
image. Maximum resolution is determined by the size of the individual CCD pixel. The
ST-7XE, 8XE, 9XE, 10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM can run in High, Medium, Low and
Auto resolution modes.
Response Factor
given telescope for photometric calculations. The Response Factor multiplied by 6700 is
the number of photoelectrons generated in the CCD for a 0th magnitude star per second
per square inch of aperture.
Saturation
- Saturation refers to the full well capacity of a CCD pixel as well as the maximum
counts available in the A/D converter. The pixel is saturated when the number of
electrons accumulated in the pixel reaches its full well capacity. The A/D is saturated
when the input voltage exceeds the maximum. The saturation values for the various
cameras are shown in the table below.
Camera
ST-5C 50,000 e- 65,535 1.25
ST-237 20,000 e- 4,095 3.4
ST-237A 20,000 e- 65,535 0.7
ST-7XE/ST-8XE
ST-7XE/ST-8XE Med/Low Res 100,000 e- 65,535 2.3
ST-9XE 180,000 e- 65,535 2.8
ST-10XE, ST-10XME 77,000 e- 65,535 1.5
ST-1001E 180,000e- 65,535 2.8
ST-2000XM 45,000e- 65,535 0.72/1.4
TC-211 Tracking CCD 150,000 e- 65,535 1.3
TC-237 Tracking CCD 20,000 e- 65,535 0.72
- The resolution of a CCD camera is determined by pixel size. Pixel size can
- Response Factor is a multiplier used by CCDOPS to calibrate CCDOPS to a
Full Well
Capacity
9
ABG High Res 50,000 e- 20,000 2.3
Maximum
A/D Counts
Electrons
per A/D
count5
Sky Background
- The sky background illumination or brightness is the number of counts in
the image in areas free of stars or nebulosity and is due to city lights and sky glow.
High levels of sky background can increase the noise in images just like dark current.
For some objects deep sky filters can be used to reduce the sky background level.
5
The e-/Count shown are for the High Resolution readout mode. These numbers can be different for other
readout modes. Use the Parameters command in the Display menu to see the actual value for images acquired
in other readout modes.
The non-ABG versions of the ST-7E/8E have twice the full well capacity of the values shown. ABG version may
9
also vary from camera to camera with maximum counts being as high as ~30,000.
Page 67
Page 70

Seeing
Section 8 – Glossary
- Seeing refers to the steadiness and the clarity of the atmosphere during an observing
session.
TE Cooler
TIFF Image File Format
Track and Accumulate
Track List
Tri-Color
- The TE Cooler is a Thermal Electric cooling device used to cool the CCD down to
operating temperature. The CCD is mounted to the TE Cooler which is mounted to a
heat sink, usually the camera head housing.
Format) was developed jointly by Microsoft and Aldus Corporations to allow easy
interchange of graphics images between programs in areas such as presentation and
desktop publishing. CCDOPS can save image files in this format but it can not read
them.
CCDOPS that allows the user to automatically co-register and co-add (including dark
frame subtraction) a series of images of an object. These exposures can be taken
unguided as long as the "Snapshot time" does not exceed the length of time before
tracking errors of your clock drive become apparent. This allows you to image and track
without guiding or the need to connect the CCD Relay port to your drive motors.
- The Track List is an ASCII file generated by CCDOPS during a Track and
Accumulate session. The Track List logs all the corrections made by CCDOPS for each of
the images. Track lists are required when flat fielding Track and Accumulate images.
- Tri-Color refers to color images created using three different colors mixed into a
balanced color image using red, green and blue filters. An object is imaged three times,
once with each color filter. The three images are then co-added and color balanced with
the appropriate software.
- The TIFF image file format (which stands for Tagged Interchange File
- The Track and Accumulate function is a SBIG patented feature of
Vignetting
an uneven illumination of the image plane. The effects of vignetting can be corrected
using flat field images.
- Vignetting is obstruction of the light paths by parts of the instrument. It results in
Page 68
Page 71

Appendix A - Connector Pinouts
A. Appendix A - Connector and Cables
A.1. Connector Pinouts for the AO7/CFW8/SCOPE port:
Pin Number Function
1 Chassis Ground
2 CFW-8 Pulse/AO-7 Data Out
3 Plus X (Active Low Open Drain) 6
4 Plus Y (Active Low Open Drain)
5 Signal Ground
6 Minus X (Active Low Open Drain)
7 Minus Y (Active LowOpen Drain)
8 +12 Volts Out (100mA max shared with I2C AUX)
9 +5 Volts Out (300 mA max shared with I2C AUX)
Shell Chassis Ground
Table A1 Telescope Connector
A.2. Connector Pinouts for the power jack:
Pin Number Function
6, Shell Earth Ground
5 DC Ground
4 -12V DC, 100mA
3 No contact
2 +12V DC, 500mA
1 +5V DC, 2A
Table A2 Power Connector Power Jack
A.3. Connector Pinouts for the I2C AUX port:
Pin Number Function
1 +5V DC (300 mA max shared with AO7/CFW8)
2 No Contact
3 Serial Clock
4 Serial Data
5 Signal Ground
6 No Contact
7 No Contact
8 +12V DC (100mA max shared with AO7/CFW8)
9 +3.3V DC (500mA max)
Shell Chassis Ground
Table A3 I2C Accessory Port
6
The Open Drain outputs can sink 100 mA maximum
Page 69
Page 72

Appendix A - Connector Pinouts
A.4. SBIG Tracking Interface Cable (TIC-78)
Many of the newer telescopes have a phone-jack connector on the drive corrector for connecting
directly to the ST-7XE, 8XE, 9XE, 10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM Camera's Telescope Port.
These include the Celestron Ultima, Losmandy CG11 and Meade LX-200. You can interface
these telescopes to the Telescope port with our TIC-78 (Tracking Interface Cable), or you can
make your own cable. Figure A1 below shows the pinouts on some of these telescopes.
Hand Controller
Button
Special
Common
Left
Down
Up
Right
Modular Phone
Wire Color
White
Black
Red
Green
Yellow
Blue
Telescope Port Pin
None
5
6
7
4
3
Figure A1 - CCD Connector for TIC Mating
Telescope electronic designs are changing rapidly. You should check with the manufacturer
of your telescope for the actual pinouts of your particular model. If this TIC cable does not
match your drive port, then you can use the information in Table A1 to make a cable to work
with your specific telescope/drive system.
Page 70
Page 73

Appendix B - Maintenance
B. Appendix B - Maintenance
This appendix describes the maintenance items you should know about with your CCD camera
system.
B.1. Cleaning the CCD and the Window
The design of SBIG cameras allows for cleaning of the CCD. The optical heads are not
evacuated and are quite easy to open and clean. When opening the CCD chamber, one should
be very careful not to damage the structures contained inside.
To open the CCD Chamber, remove the six screws that hold the 5 inch front cover in
place. Remove the six screws and lift the front cover, exposing the structures inside. There is a
rubber O-Ring that sets in the groove on the top of the Chamber housing.
The CCD array is protected by a thin cover glass that can be cleaned with Q-Tips and
Isopropyl Alcohol. Do not get alcohol on the shutter. Dust on the CCD should be blown off. Use
alcohol only if necessary. The optical window of the chamber housing can be cleaned the same
way. When reinstalling the chamber housing, be very careful to make sure the O-ring is in the
groove when seated.
B.2. Regenerating the Desiccant
This section describes the regeneration procedure for the desiccant used in the ST-7XE, 8XE,
9XE, 10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM. The desiccant absorbs moisture in the CCD chamber,
lowering the dew point below the operating temperature of the cooled CCD, thus preventing
the formation of frost. The desiccant is contained in a small cylindrical plug that screws into the
chamber from the rear. In normal operation the useful life of the desiccant is over a year. If the
CCD chamber is opened often, the desiccant should be regenerated when frosting is noticed.
Follow the procedure below to regenerate the desiccant:
1. Unscrew the brass desiccant container from the rear of the camera and
remove the O-ring.
2. Plug the resulting hole by screwing in the supplied bolt or plug 2 or 3 turns.
Finger tight is adequate. Don't put a wrench on it.
3. Heat the desiccant container in an oven at 350°F (175 deg C) for 4 hours. The
solder used to seal the can melts at 460 degrees F, so be sure to stay at least 50
degrees below this number. Preheating the oven to avoid hot spots is
advised.
4. Replace the desiccant container into the rear of the camera, being careful to
reinstall the O-ring and insure that it does not get pinched.
5. Expect the camera to take an hour or two to reach the frost free state. If it
does seem to frost and you need to capture images, reduce your cooling to
the zero degree C range - the CCD dark current will still be quite low.
Page 71
Page 74

Appendix C – Capturing a Good Flat Field
C. Appendix C - Capturing a Good Flat Field
This appendix describes how to take a good flat field. A good flat field is essential for
displaying features little brighter than the sky background. The flat field corrects for
pixel non-uniformity, vignetting, dust spots (affectionately called dust doughnuts), and
stray light variations. If the flat field is not good it usually shows up as a variation in
sky brightness from on side of the frame to the other.
C.1. Technique
The first consideration in capturing a flat field is to use the telescope-CCD combination
in exactly the configuration used to collect the image. This means you probably have to
capture the flat field at the telescope. Do not rotate the head between image and flat
field, since the vignetting is usually slightly off center. Do not be tempted to build a
little LED into the telescope or camera for doing flat fields; it doesn't work at all. The
dust debris shadows would be different!
Arrange a light source such as a flashlight, two white cards, the telescope and
CCD as shown in Figure D-1.
Figure D-1: Flat Field Geometry
Telescope
CCD
Flat White
Surface
The key aspects of this geometry are that the reflection off two diffuse surfaces is used,
and the large flat surface is square to the illumination from the small flat surface. When
we do this, the first flat surface is typically a white T-shirt worn by the operator! Take
care that no apparent shadows are cast onto the larger flat white surface. Use an
exposure at the camera that yields an average light level equal to about half of full scale.
Flashlight
Flat White
Surface
Page 72
Page 75

Appendix D – Use and Maintenance of the Cooling Booster
D. Appendix D - Use and Maintenance of the Cooling Booster
The cooling booster was an option or included accessory for the parallel versions of the
ST-7E, ST-8E, ST-9E, ST-10E and ST-10XME. When a parallel camera with this accessory is
upgraded to the USB version, the cooling booster is left in place instead of changing to the new
cooling design. The cooling booster is a second TE cooling module that goes inside the back
compartment of the camera. It requires a second power supply. This memo is a step-by-step
guide to using the booster for those upgraded cameras that kept the earlier design.
CAUTION! Please be sure that whenever the cooling booster is on (i.e., plugged into
12VDC), the camera is also powered up so that the fan is running. The fan is needed to
dissipate the heat generated by the cooling booster. If you power up the booster by plugging it
into 12VDC without the camera fan running it can overheat and damage the cooling booster
system. This won't happen immediately if you happen to accidentally power up the booster
before turning on the camera, but running it more than few minutes without the fan could
damage the unit.
For users with fixed sites, or small observatories, water circulation and the attendant
tubes and pump are easier to manage. For field use, however, you may wish to forgo water
circulation and use the cooling booster with 12VDC only to simplify the setup. When using
water circulation, the major problem one must deal with is routing the rather heavy water tubes
off the mount to minimize perturbations to the mount during tracking. In general, try to route
tubes (and wires) over the mount, rather than just let the tubes dangle from the end of a long
tube. Water cooling is probably not necessary for most users when the air temperature is below
10 degrees C (50 degrees F), since the dark current is fairly low already. Think of it as a
summertime accessory! We do not recommend use of water cooling below freezing
temperatures, where antifreeze must be added to the water. It is simply not necessary then.
There is no problem with using the cooling booster with only air cooling in the winter, though.
With the cooling booster installed on your camera, you have a choice of three levels of
cooling. First, you can ignore the booster and operate the camera with single stage cooling only
by simply not connecting 12VDC to the booster's power plug. Second, with the camera power
on and fan funning, you can also power up the cooling booster by plugging in 12VDC to
increase the cooling capability of the camera without using any water circulation. Third, you
can power up the cooling booster with 12VDC and use water circulation to further increase the
cooling capability of the camera.
cooling improvement is about 15 degrees C. If you plan to use it without the water then you
should disconnect the hoses from the camera and shake out the water trapped in the heat sink.
Disconnecting the hoses will reduce the potential perturbation to your telescope mount.
as before and simply plug the auxiliary 12 volt supply jack into the connection on the camera
back plate. Turn on the TE cooling to 100% by giving it a target temperature of –50 degrees.
After 10 minutes examine the camera temperature, and reset the set point to 3 degrees C above
Without flowing water the cooling improvement is about 6 degrees C. With it the
To operate the cooling booster without water cooling, mount the camera to the telescope
Page 73
Page 76

Appendix D – Use and Maintenance of the Cooling Booster
the current temperature. This 3 degree temperature margin will enable the ST-7/8 to regulate
the temperature accurately.
To operate the camera with water cooling, the procedure is the same except that the
water flow must be established before mounting the camera to the telescope, since the water
pumps have limited pressure capability. To do this, put the camera at the same level as the
water reservoir. Connect all the hoses, and make sure the water return goes back into the
reservoir. Push the ¼ inch internal diameter (ID) hoses onto the nipples on the back of the
camera so they seal. Attach one hose to the nipple onto the reducing connector which adapts
the ¼ inch ID hose to the ½ inch diameter hose from the pump.
Turn on the pump, and let the flow establish itself through the hoses. Next, mount the
camera to the telescope. If you always keep the return hose outlet near the reservoir level the
pump will have no problem raising the water 2 meters (6 feet) off the floor. The limited
pressure capacity of the pump is only a problem when you let the water fall back into the
reservoir from a significant height above it, such a 0.3 meter (12 inches). Lastly, check for leaks!
When using water cooling, avoid the temptation to put ice in the water to get the camera
even colder. As the cooling booster is designed, the camera will not be cooled below ambient
temperature if ambient temperature water is used. If colder water is used, the head may fog or
frost up, depending on the dew point. . The exposed electronics inside the ST-7/8 will get wet,
and corrode. The hoses will start dripping condensation, and you will have a mess. Keep the
ice for a cold drink!
At the end of the evening, stop the pump, and raise the outlet hose above the camera to
let all the water drain out of the system. Blowing it out with gently pressure helps clear the
water. You can leave the hoses full of water, but if a leak occurs while you’re not there you may
have a problem. When packing the camera for a long time, or at the end of summer, disconnect
the hoses and blow out the heat sink to allow the enclosed spaces to dry out and minimize long
term corrosion.
A 110VAC to 12VDC transformer is supplied with the cooling booster. The booster
requires approximately 2 amps at 12VDC.
polarity of the DC Power Jack on back plate of camera.
from the camera body.
If you wish to connect direct to 12VDC, please note
The power jack is electrically isolated
+12VDC on outside
Ground in Center
Mating plug is 5.5mm
outside and 2.1mm inside
Figure A - DC Power Jack
Page 74
Page 77

Appendix E – Third Party Vendors Supporting SBIG Products
E. Appendix E – Third Party Vendors Supporting SBIG Products
Company / Author Product Notes
Software Bisque
912 12th Street Golden, CO 80401-1114 USA
Sales: (800) 843-7599 International: (303) 278-4478
Facsimile: (303) 278-0045
E-mail Sales: bisque@bisque.com
E-mail Support: support@bisque.com
Web site: www.bisque.com
Diffraction Ltd.
100 Craig Henry Drive,
Unit 106, Ottawa, ON, K2G 5W3, Canada
Telephone (613) 225-2732 FAX (613) 225-9688
E-mail Sales: sales@cyanogen.com
E-mail Support: support@cyanogen.com
Web site: www.cyanogen.com
Axiom Research
1830 East Broadway Blvd, Suite 124-202
Tucson, AZ 85719
Voice 520-323-8600 Fax 520-822-1435
E-mail Sales sales@axres.com
E-mail Support support@axres.com
Web http://www.axres.com
Axilone Multimedia
18, ch. des Ajoncs, 31470 Saint-Lys FRANCE
Phone: +33 5 34 47 20 52 Fax: +33 5 34 47 10 20
E-mail: prism@axilone.com
M.S.B. di Fabio Cavicchio, Via Romea Vecchia 67,
Classe, 48100 Ravenna RA. P.IVA 01379350398,
TEL/FAX +39 0544 473589 Mobile +39 0339 2739548
E-Mail msbsoftware@tin.it, msb@sira.it
Web site: http://www.msb-astroart.com
New Astronomy Press, Ron Wodaski
PO Box 1766, Duvall, WA 98019
E-mail: support@newastro.com
FAX: 425-844-1535
Web site: http://www.newastro.com
The Minor Planet Observer, Brian Warner
e-mail: brianw_mpo@compuserve.com
Web site: http://www.minorplanetobserver.com
CCDSoftV5,
TheSky,
Orchestrate,
T-point,
Paramount
Maxim
DL.CCD
Mira
software
Prism 5 Image processing, camera
Astroart Image processing
The New
Astronomy
Minor Planet
Observer
software
Camera control, Image
Processing, Astrometry,
Minor Planet Searches,
Planetarium and
Charting, Scripting,
Remote operation and
telescope control.
Robotic mounts.
Authorized SBIG Dealer
Image Processing,
Camera Control software
Authorized SBIG Dealer
Camera control, Image
processing, analysis,
spectroscopy
control
software and camera
control. FITS viewer
Book: Basics of CCD
Imaging, background and
techniques.
Astrometry, Minor planet
searches
Page 75
Page 78

Appendix E – Third Party Vendors Supporting SBIG Products
Bruce Johnston Computing
7124 Cook Rd.
Swartz Creek, MI 48473 U.S.A.
Phone: 810-635-9191 Fax: 1-810-750-1761
E-mail: BJohns7764@aol.com
Web site: http://members.aol.com/bjohns7764
Phase Space Technology
Phone: +61 3 9735 2270 Fax:: +61 3 9739 4996
Web site: http://www.phasespace.com.au
E-mail Support: support@phasespace.com.au
E-mail General: pst@phasespace.com.au
E-mail Orders: orders@phasespace.com.au
Steve Mandel
Hidden Valley Observatory
1425 Hidden Valley Rd., Soquel, CA 95073
E-mail: steve@galaxyimages.com
Web: http://www.galaxyimages.com/ccdwidefield.html
Dr. Brady Johnson
E-mail: bradydjohnson@rogers.com
Web site:
http://members.rogers.com/bradydjohnson/widefield.htm
Astro-Physics, Inc.
11250 Forest Hills Road, Rockford, IL 61115, U.S.A.
Phone: 815-282-1513 Fax: 815-282-9847
E-mail:
Web site:
RC Optical Systems
Brad Ehrhorn
3507 Kiltie Loop, Flagstaff, AZ 86001
Tel: (928) 773-7584
E-mail: info@rcopticalsystems.com
Web site: http://www.rcopticalsystems.com/index.html
Astro Works Corporation
P.O. Box 699, Aguila, Arizona 85320
Tel: (928) 685-2422
Web site: http://www.astroworks.com
Disclaimer: Mention is made of third party vendors in this section as a courtesy only. These
vendors are independent companies and/or individuals. SBIG does not endorse or support any
particular company, product or service by virtue of mentioning them in this section. SBIG is not
responsible for the use of any product or service mentioned in this section that is not manufactured
or made by SBIG.
info@astro-physics.com
http://www.astro-physics.com
MexaFix
Software
Astra Image Image Processing
Mandel Wide
Field Adapter
Johnson
Wide Field
Adapter
APO
Refractors
and mounts
RitcheyChretien
telescopes
Centurion 18
telescope
Image processing
Software
Nikon lens adapter for
SBIG color filter wheel
Pentax, Olympus and
Minolta lens adapters for
SBIG color filter wheel
4” to 6” APO refractors
and GOTO mounts.
Authorized SBIG OEM
RC Telescopes and
accessories for CCD
imaging. Authorized
SBIG OEM
18” F/2.8 telescope made
specifically for CCD
imaging. Authorized
SBIG OEM
Page 76
Page 79

Index
A/D converter, 28, 49
accessories, 63
adaptive optics, 62
antiblooming, 51, 67
Antiblooming Gate (def), 67
AO-7, 62
astrometric measurements, 67
Astrometry (def), 67
astrophotography, 33
atmospheric effects, 39
auto contrast, 40
Auto Grab Command, 43
autoguider, 29, 42, 45, 58, 67
Autoguider (def), 67
background parameter, 40
battery operation, 37, 45
binning, 31
Calibrate Track Command, 43, 59
calibration star, 59
camera lens adapter, 55, 62
Camera Setup Commands, 42
CCD, 28, 32
(def), 67
cameras, 25, 26, 29, 37, 45, 48, 49, 50
cleaning, 73, 74
detector, 25, 27, 45
orientation, 37
CCDCOLOR software, 44
CCDOPS software, 29
centering objects, 40
cleaning the CCD, 73, 74
clock drivers, 28
co-add images, 25, 42, 45
cold pixels, 41
color filter wheel, 43, 62
color images, 34, 43
color table, 67
commands
Auto Grab, 43
Calibrate Track, 43, 59
Dark Subtract, 41
Focus, 39, 41
Grab, 40, 41, 55
Track, 59
Track and Accumulate, 42, 55, 59
Tracking Parameters, 59
Commands
Establish COM Link, 38
PC Setup, 38
communications link, 38
connector
Telescope, 71, 72
connector (CPU)
RELAYS, 45, 59
cooling, 29, 70
co-register images, 42, 45
crop, 40
crosshairs, 40
dark current, 29
dark frame, 28, 30, 37, 40, 41
Dark Frame (def), 67
Dark Noise (def), 67
Dark Subtract Command, 41
dark subtracted, 30, 37, 41
DCS, 30, 67
Declination, 37, 45, 59, 66
desiccant, 73
Diffuse Magnitude, 41
diffuser, 38
Dim mode, 41
displaying images, 40
double correlated sampling, 30
Double Correlated Sampling (def), 67
drive corrector, 42
electromechanical shutter, 49
electromechanical vane, 49
electronic images, 33
electronic shutter, 49
Establish COM Link Command, 38
eyepiece, 40
eyepiece holder, 37
eyepiece projection, 62
eyepiece tube, 39
False Color (def), 67
field of view, 31, 50, 51, 52, 59
film, 25, 31
film grain, 31
filter wheel, 34
filters, 34, 41, 43, 62
finding objects, 40
fine focus, 39
FITS format (def), 67
flat field, 30, 41, 56, 57
Flat Field (def), 68
77
Page 80

Index
flip, 41
focal length, 52
focal reducer, 62
Focal Reducer (def), 68
focus
Dim mode, 40, 41
fine, 39
Full frame mode, 39
Full Frame mode, 41
peak, 39
Planet mode, 39, 41, 68
Focus Command, 39, 41
focus mode, 39, 41
Focusing, 38
Frame Transfer CCDs, 26
Frame Transfer CCDs (def), 68
frost, 28
Full Frame CCDs, 26
full well capacity, 51
Full Well Capacity (def), 68
Grab Command, 40, 41, 55
graphics, 40
guiding, 32
guiding error, 42, 59
hand controller, 40, 42, 45, 46
hermetic chamber, 28
Histogram (def), 68
host computer, 29, 37, 45
hot pixels, 41
IBM PC, 29
image processing, 29, 33, 41, 63
interference, ii
IR blocking filter, 44
joystick, 47
joystick modification, 48
library of dark frames, 40, 56
light frame, 30, 37, 40
light frame (def), 68
Link, 38
LPT port, 37, 38, 45
magnitude
diffuse, 41
stellar, 41
maintenance, 73, 74
microcontroller, 29
modifying hand controller, 46
moon, 39, 52, 55
negative image, 40
nosepiece, 37
observatory, 45
optical head, 37, 45
optical head orientation, 38
O-ring, 28
PC, 29
PC Setup Command, 38
PEC drive correctors, 42, 59
photometric measurements, 68
Photometry (def), 68
pixel nonuniformity, 41
pixel size, 31, 50
Pixel Size (def), 68
pixel uniformity, 30
planet mode, 41
Planet mode (def), 68
planets, 25, 39, 52, 55
POWER connector, 37
power supply, 29, 37
power supplyr, 45
PPEC drive correctors, 42, 59
preamp, 28, 45
printing images, 33, 63
push to make switch modification, 47
push to make/break switch modification,
47
Quantum Efficiency (def), 68
range parameter, 40
readout
electronics, 45
noise, 51
Noise (def), 69
register, 26
regenerating desiccant, 73
RELAYS connector, 45, 59
resolution, 31, 42, 56
Resolution (def), 69
Response factor (def), 69
Right Ascension, 37, 45, 59, 66
Saturation (def), 69
scribing the eyepiece, 40
seeing, 31, 39, 42, 52
Seeing (def), 70
self guiding, 45
separations, 41
setup, 37
SGS-Self Guided Spectrograph, 62
sharpen, 41
78
Page 81

Index
shutter, 28
signal to noise ratio, 44, 51
sky background, 25, 42
smoothing, 41
snapshot, 46
software, 49, 63
spectral range, 25
spectrograph, 62
Status Window, 38
Link field, 38
stellar magnitude, 41
stellar temperature, 41
super pixel, 41
taking images, 40
TE cooler, 29
TE Cooler, 28
TE Cooler (def), 70
Technical Support, 63
telescope, 31, 37, 40, 42
Telescope connector, 71, 72
telescope hand controller, 40, 42, 45, 46
temperature regulation, 40, 49
thermistor, 29
TIC, 72
TIC-78, 46
TIFF format (def), 70
Track and Accumulate (def), 70
Track and Accumulate Command, 42, 55, 59
Track and Accumulate mode, 45, 57
Track Command, 59
track list, 58
Track List (def), 70
track mode, 45
tracking interface cable (TIC), 46, 72
Tracking Parameters Command, 59
Tri-Color (def), 70
tri-color images, 62
T-Thread, 62
vane, 49
vignetting, 30, 41
Vignetting (def), 70
zoom, 40
79
 Loading...
Loading...