
3. Adjustment and Color
Memory
Color Balance
This function allows you to control the overall color tone of copies by adjusting
the Yellow, Magenta, Cyan and Black color balance. Nine levels of tone are available.
Note
❒ The color balance will return to the default when:
• The machine is automatically reset.
• The {Clear Modes} key is pressed.
• The operation switch is turned off.
• The main power switch is turned off.
❒ You can store and adjustments you make in memory and recall them later.
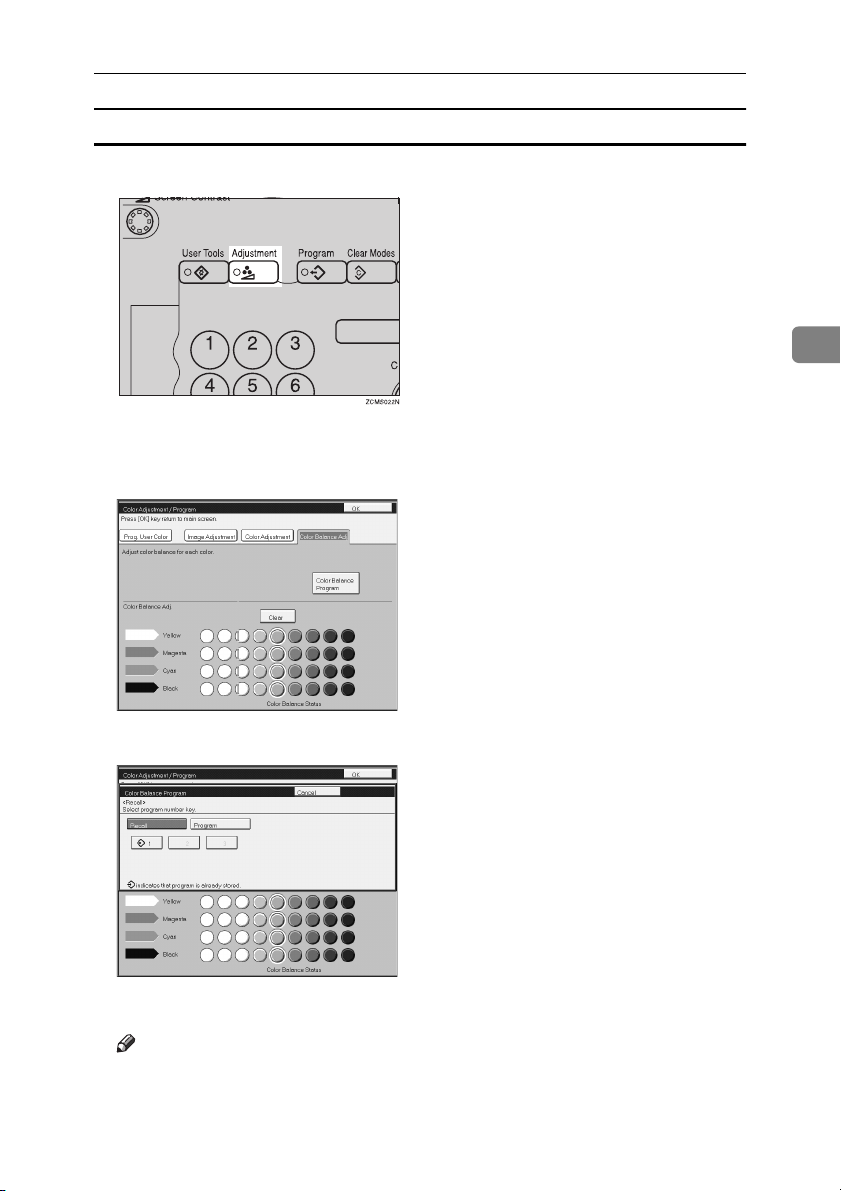
Color Balance Adjustment
Press the {{{{Adjustment}}}} key.
A
Zcms022n.eps
Make sure that the [Color Balance] key is selected.
B
copy80.tif
Adjust the color balance, then press the [OK] key.
C
103

Adjustment and Color Memory
Color Balance Program
You can store the color balance setting in memory and recall it when you want
to use it.
Note
❒ You can store up to three color balances.
Storing the adjusted color balance
3
Change the color balance (⇒⇒⇒⇒ P.103 “Color Balance Adjustment”), but don't
A
press the [OK] key.
Press the [Color Balance Program] key.
B
copy80.tif
Press the [Program] key.
C
Select a number for this setting.
D
copy81.tif
104
Recalling the color balance
Press the {{{{Adjustment}}}} key.
A
Zcms022n.eps
Make sure that the [Color Balance] key is selected.
B
Press the [Color Balance Program] key.
C
copy80.tif
Color Balance
3
Make sure that the [Recall] key is selected.
D
copy82.tif
Select the setting you want to recall.
E
Note
❒ Only color balance programs marked with m contain a color balance.
105
Adjustment and Color Memory
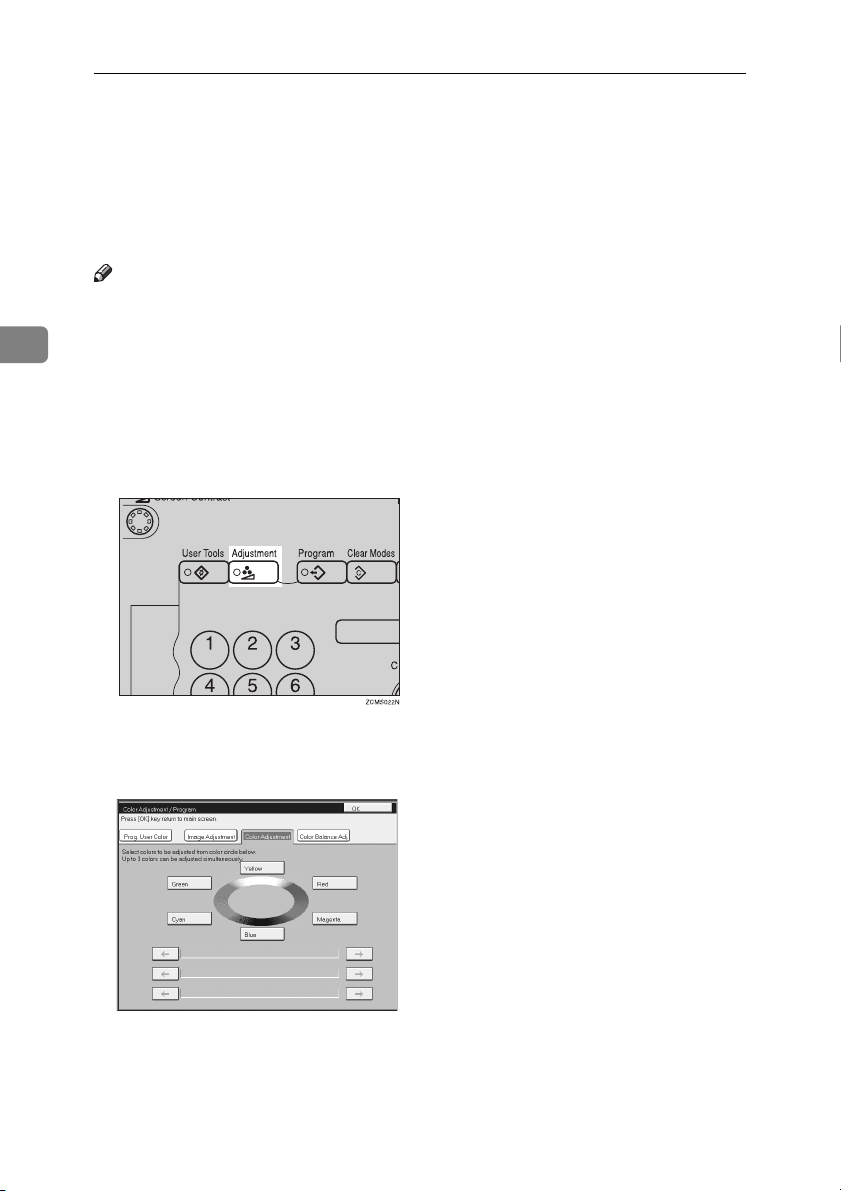
Color Adjustment
This function lets you alter up to three single colors by mixing them with adjacent colors in the color circle. For example, yellow can be shifted towards red to
make orange, or towards green to make a yellow green. Note that only areas of
the image containing this color will be modified.
Note
❒ This function is only available in Full Color mode or Auto Color Select mode.
❒ The single color adjustment will return to the default when:
3
• The machine is automatically reset.
• The {Clear Modes} key is pressed.
• The operation switch is turned off.
• The main power switch is turned off.
Press the {{{{Adjustment}}}} key.
A
Zcms022n.eps
106
Press the [Color Adjustment] key.
B
Select the color key that you want to adjust from the color circle.
C
copy83.tif

Color Adjustment
Adjust the color with the keys.
D
copy84.tif
Note
❒ For example, if you wish to make yellow appear more red, press the [→→→→]
key.
❒ If you wish to make yellow appear more green, press the [←←←←] key.
Press the [OK] key.
E
3
107
Adjustment and Color Memory
Image Adjustment
You can change the following default settings for image adjustment:
Soft/Sharp You can adjust the edges of the image to make the image sharper or
Contrast You can adjust the contrast between light parts and dark parts of the
3
Background Density You can adjust the background density control.
Pastel You can make copies in pastel tones.
U.C.R. Adjustment You can adjust the black toner density to make the black parts clearer
A.C.S. (Auto Color Selection) Sensitivity
Auto Text/Photo Sensitivity
softer.
Note
❒
image.
Default:
level 4
Note
❒
Default:
level 5
Note
❒
❒
❒
level 5
Default:
If copying a newspaper or an original with a dark background, adjust the background density to a lighter setting.
If part of the original is marked with a highlighting pen, adjust the
background density to a darker setting. However, because the color
of a highlighting pen is difficult to duplicate, it might be copied in
different colors or some colors might not be copied.
Note
❒
in Full Color mode.
level 9 which yields a normal color copy
Default:
Note
❒
❒
❒
You can adjust the sensitivity when detecting whether the original has
color areas in Auto Color Select mode. When set to “B&W” values, the
machine will be more likely to detect originals as black originals. “Full
Color” values will cause the machine to be more likely to detect originals as color originals.
level 5
Default:
Adjust this setting to a darker setting when you want to copy letter
parts clearly in black.
Adjust this setting to a lighter setting when the original image is
dark.
Note
❒
You can adjust the sensitivity when detecting letter and photo parts of
an original in Auto Text/Photo mode. If letter parts photo parts of an
original are not differentiated correctly, adjust this setting.
Default:
level 3
108
❒
Note
Default:
level 5
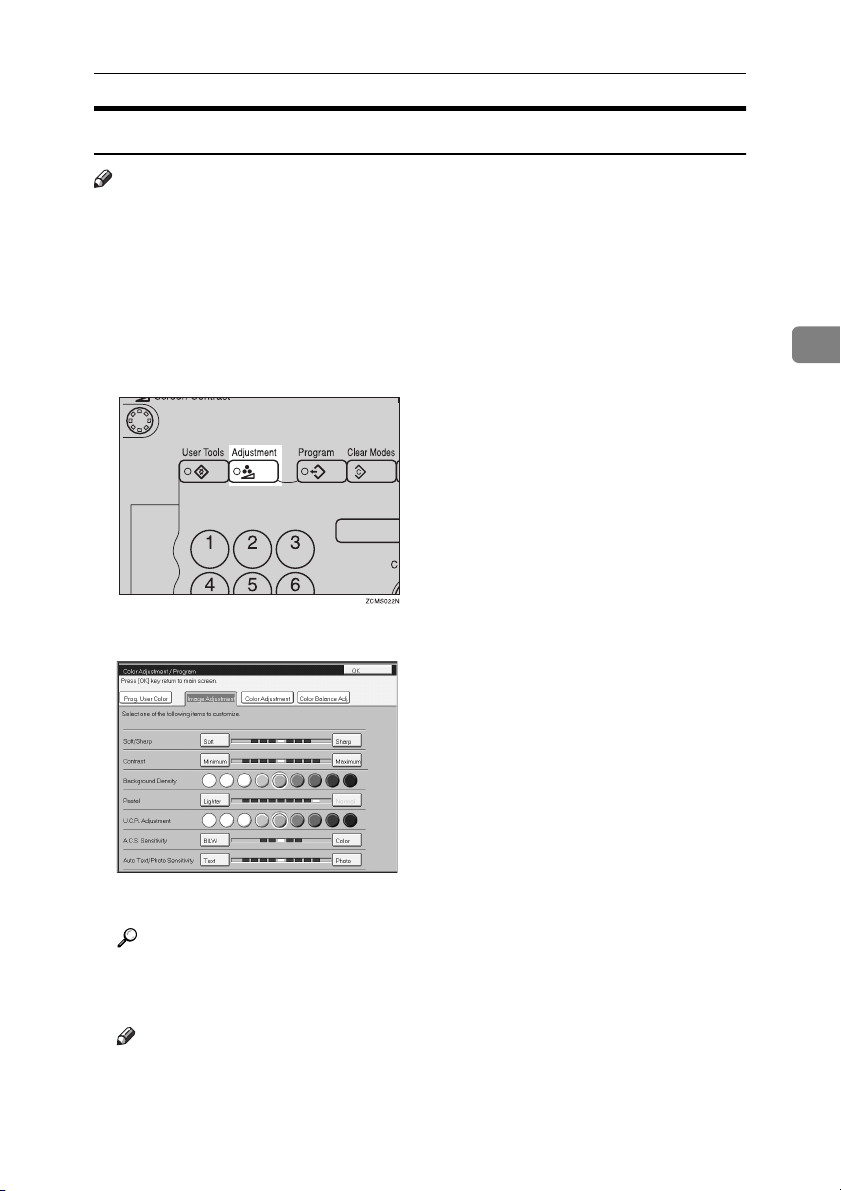
Image Adjustment
Soft/Sharp, Contrast, Background Density, and Pastel
Note
❒ Any settings you make with the Sharp/Soft, Contrast, Background Density
and Pastel functions will be canceled under the following conditions:
• The machine is automatically reset.
• The {Clear Modes} key is pressed.
• The operation switch is turned off.
• The main power switch is turned off.
Press the {{{{Adjustment}}}} key.
A
Zcms022n.eps
Press the [Image Adjustment] key.
B
copy85.tif
3
Adjust the settings.
C
Reference
For details, ⇒ P.108 “Image Adjustment”.
Press the [OK] key.
D
Note
❒ If you do not press the [OK] key, you can still make copies, but the Image
Adjustment settings you have just entered will not used. However, any
settings or featured you chose before pressing the {Adjustment} key will
still apply.
109
Adjustment and Color Memory
U.C.R. Adjustment, A.C.S. Sensitivity and Auto Text/Photo
Sensitivity
Note
❒ Any settings you make with the U.C.R. Adjustment, A.C.S. Sensitivity, and
Auto Text/Photo Sensitivity functions are not cleared by turning the power
off or by pressing the {Clear Modes} key. They are canceled only when you
overwrite them with new settings.
Press the {{{{Adjustment}}}} key.
A
3
Zcms022n.eps
Press the [Image Adjustment] key.
B
copy85.tif
110
Adjust the settings.
C
Reference
For details, ⇒ P.108 “Image Adjustment”.
Press the [OK] key.
D
Note
❒ If you do not press the [OK] key, you can still make copies, but the Image
Adjustment settings you have just entered will not used. However, any
settings or featured you choose before pressing the {Adjustment} key will
still apply.
Program User Color
Program User Color
In addition to the base colors, you can store up to 15 customized colors into
memory (User Color).
Reference
For color samples ⇒ P.10 “Color Sample Chart”.
If your machine has an option, you can sample the user color. ⇒ P.115 “Sam-
pling the User Color (Option)”.
Note
❒ There are two ways to make user colors as follows:
• Adjusting a selected base color
• Mixing colors manually with number keys
❒ Up to 15 colors can be stored.
❒ The total percentages of the mixed colors must be 255% or less.
❒ If the total percentage of the mixed color is over 255%, the copier cannot cre-
ate the color properly and the results will appear different.
❒ If the total percentage of the mixed colors is too low, toner may not bond to
the paper properly resulting in a change in image density.
❒ The appearance of user colors might vary slightly according to the image type
you have selected (Photo, Text, etc.).
Adjusting Colors Based on the Selected Color
Press the {{{{Adjustment}}}} key.
A
Zcms022n.eps
3
Press the [Prog. User Color] key.
B
111

Adjustment and Color Memory
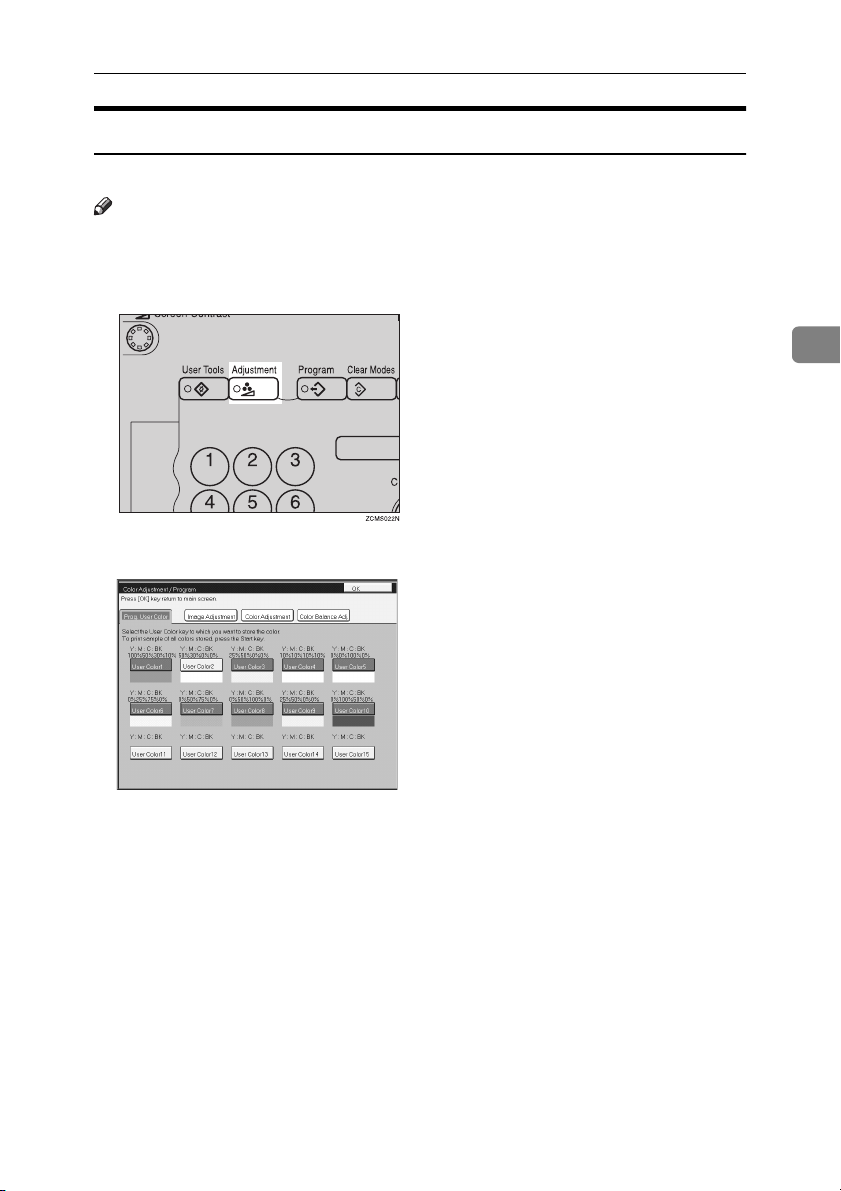
Select the key you wish to store the color in.
C
copy86.tif
3
Select the base color.
D
copy87.tif
112
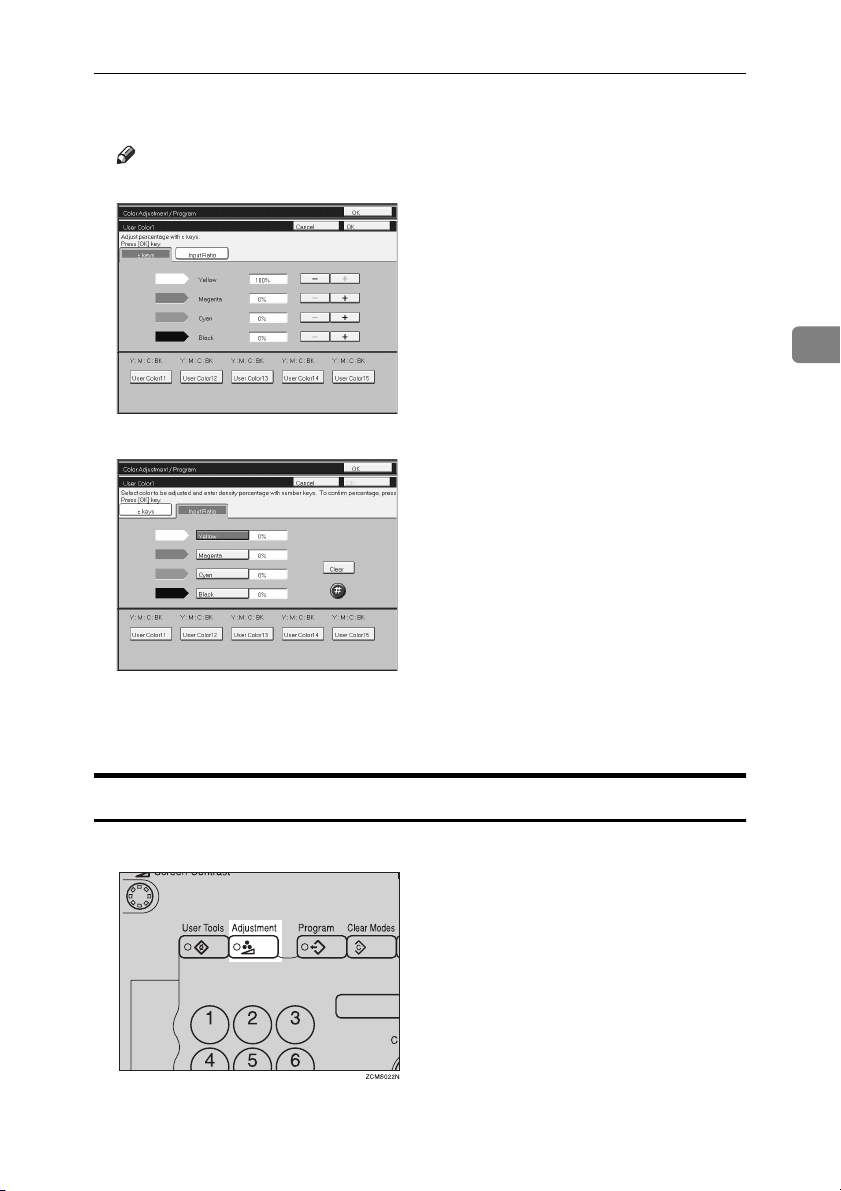
Program User Color
You can change the color density in two ways— press the [
E
Note
❒ Increase or decrease in steps with the [+] or [-] key. Press the [+ - keys] key.
copy88.tif
❒ Enter the percentage with the number keys.—Press the [Input Ratio] key.
copy89.tif
+ - keys
] key.
3
Repeat step EEEE for each color, then press the [OK] key.
F
Press the [OK] key.
G
Mixing Colors Manually with the Number Keys
Press the {{{{Adjustment}}}} key.
A
Zcms022n.eps
113

Adjustment and Color Memory
Press the [
B
Select the number that you want to store the user color in.
C
copy86.tif
Prog. User Color
] key.
3
Press the [Input Ratio] key.
D
copy87.tif
Select the color that you want to adjust.
E
114
Enter the density with the number keys, then press the [#] key.
F
copy89.tif
Note
❒ To change the number, press the [
Repeat steps EEEE and FFFF for each color then press the [OK] key.
G
Press the [OK] key.
H
Clear
] key.
Program User Color
Sampling the User Color (Option)
You can print out a sample of User Colors to check the colors you have made.
Note
❒ The sample will be copied on a A4K, 8
17"L sheet.
Press the {{{{Adjustment}}}} key.
A
Zcms022n.eps
Press the [Prog. User Color] key.
B
copy90.tif
1
/2" × 11"K sheet or a A3L, 11" ×
3
Press the {{{{Start}}}} key.
C
115

Adjustment and Color Memory
3
116
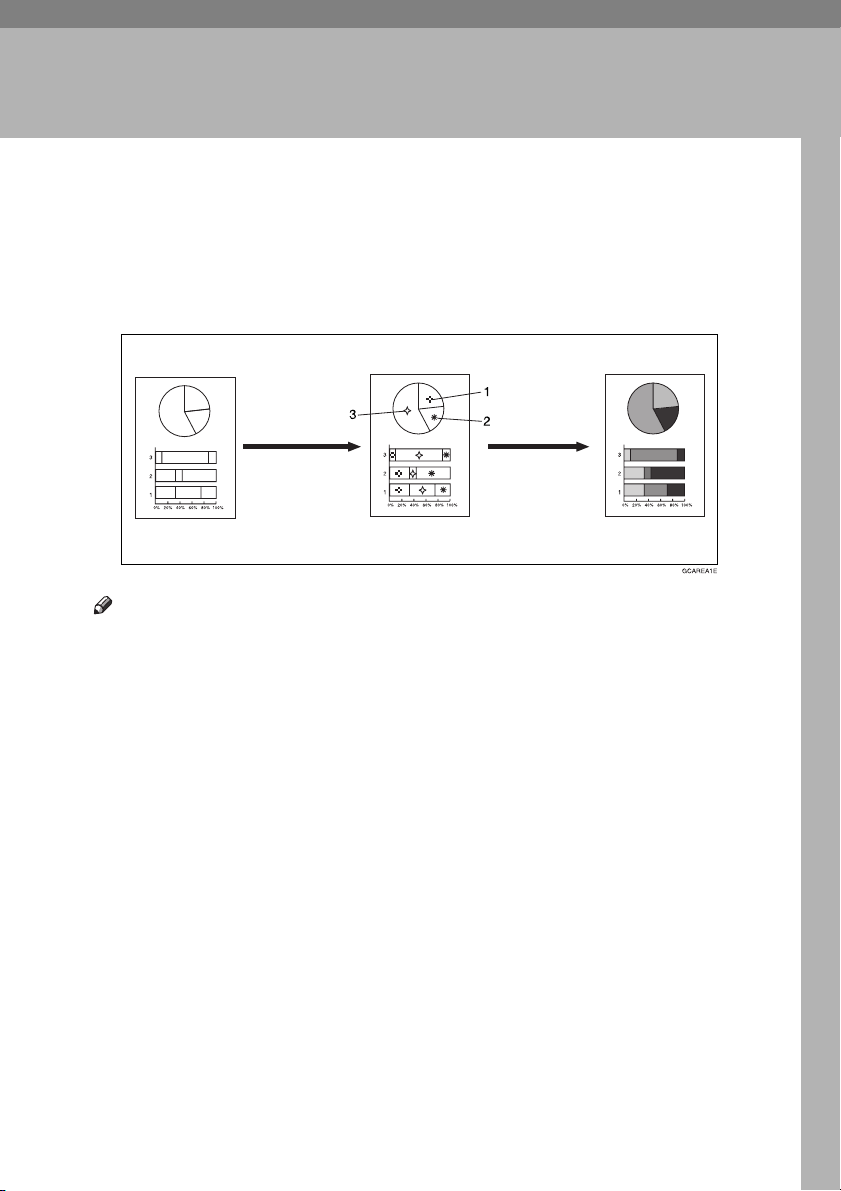
4. Area Editing (Option)
What is Area Editing?
If your machine has an Area Editing (Option), you can select areas of an image
to be treated differently or have effects applied to them. An example is shown
below.
Example:
Gcarea1e.eps
Note
❒ In this chapter, multiple areas of the image that you wish to apply the same
effects to are referred to as a “Group”.
117

Area Editing (Option)
How to Edit Areas
Editing an image involves scanning it in to memory, choosing areas to edit and
how those areas will be re-produced.
The basic steps are summarized below. Details are given in the rest of this section.
A Enter Area Editing mode.
Press the [Area Editing] key.
B Designate areas.
⇒ P.119 “Designating Areas”.
Select modes.
C
⇒ P.130 “Selecting Modes for Designated Areas”.
4
D Specify more areas to be treated differently (optional).
Repeat C and D.
E Copy image.
Press the {Start} key.
118
Designating Areas
Designating Areas
Several tools are provided for designating areas of an image.
Area Shapes
• Rectangle: Specify two points defining the opposite diagonals of a rectangle.
• Right Angle Polygon/Polygon: Specify a sequence of points defining a poly-
gon.
• Closed Loop: If your image contains a shape outlined in black and that outline forms a closed loop, specify a point inside the shape to designate it.
• Multi-Closed Loop: If your image contains a closed loop and that outline
forms another closed loop, specify points inside of the closed loop to designate it.
Frame/Line
• Rectangle frame: Specify areas defined by a rectangular frame.
• Right Angle Polygon/Polygon frame: Specify areas defined by a polygon or
right-angled polygon.
• Line: Specify a series of points linked together by straight lines.
Note
❒ You can designate many areas and apply the same changes to them all by
placing them in the same Group.
❒ Different areas may be treated differently by placing them in different
Groups.
4
119
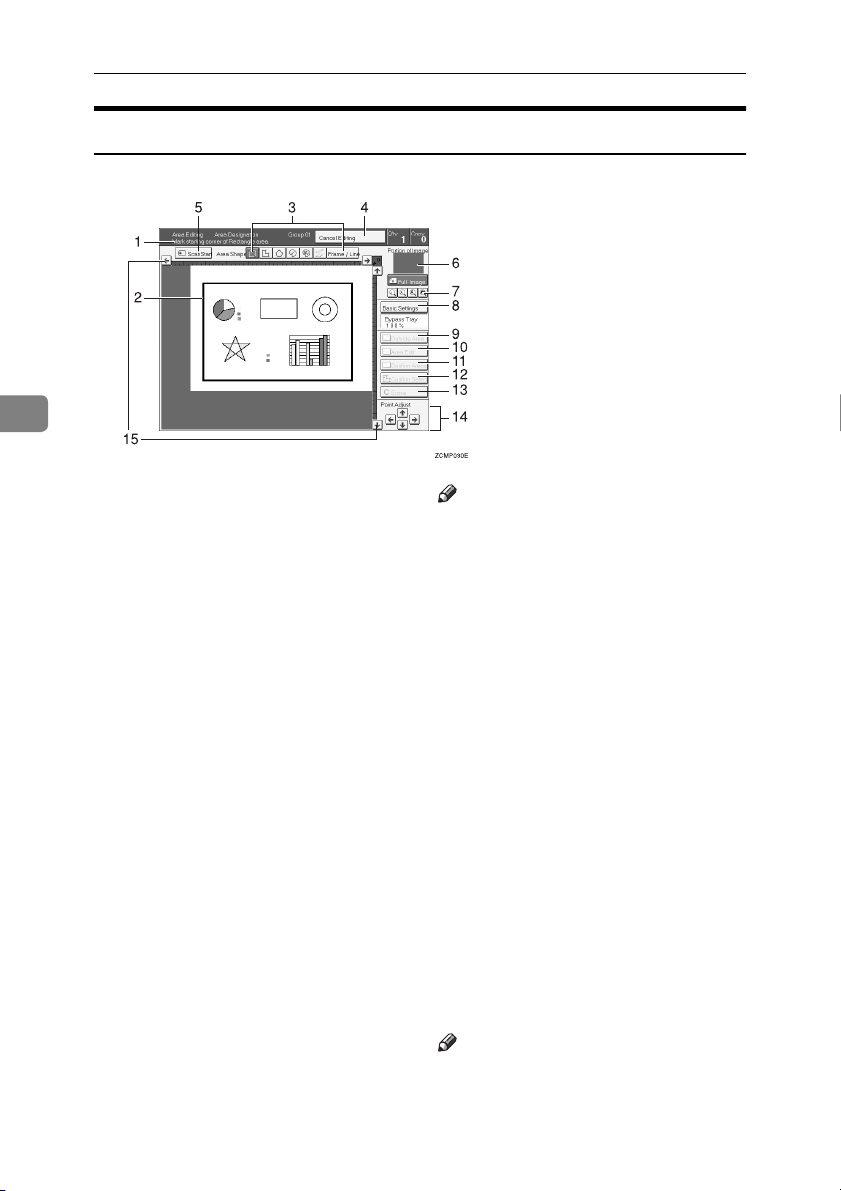
Area Editing (Option)
Designate Area Display
Zcmp030e.eps
4
1.
Message Area
Messages and instructions appear here.
2.
Display Area
The image is displayed.
3.
Area Shape/Frame/Line
Select the area shape or frame shape and
line.
4.
Cancel Editing
Exit area editing.
5.
Scan Start
Scan in the original again.
6.
Portion of Image
Shows the portion of the original that is
currently being viewed or is enlarged.
7.
Enlarge
Enlarge 4
Enlarge by about 528%
Enlarge 3
Enlarge by about 394%
Enlarge 2
Enlarge by about 264%
Enlarge 1
Enlarge by about 200%
Full Image
Note
❒ After pressing the [Enlarge] key, mark
a point in the displayed image to
zoom in on.
8.
Basic Settings
Change the job settings for the entire image.
9.
Outside Area
Set modes for outside areas.
10.
Area Edit
Edit inside the area.
11.
Confirm Areas
Show selected areas, modes, and groups.
12.
Confirm Selection
Complete a designated area.
13.
Erase
Cancel last point selected.
14.
Arrow keys
Move cursor in small steps.
15.
Scroll key
Move the portion of the original.
Note
❒ Do not press the touch panel display
with any hard or sharp object.
120
Designating Areas
Designate Area Tools
Note
❒ There are nine tools to designate areas.
Area Editing Area Shape Rectangle (⇒ P.122
Right Angle Polygon (⇒ P.123
Polygon”
.)
Polygon (⇒ P.123
Closed Loop (⇒ P.124
Multi Closed Loop (⇒ P.124
Frame/Line Rectangle frame (⇒ P.122
Right Angle Polygon frame (⇒ P.126
gon frame and Polygon frame”
Polygon frame (⇒ P.126
Polygon frame”
Line (⇒ P.127
Note
❒ You cannot use the optional document feeder with this function.
❒ The relationships between the position of the original and the orientation of
the scanned image on the display are as follows:
Set on the exposure
glass
Display
“Rectangle”
“Right Angle Polygon and Polygon”
.)
“Line”
.)
.)
“Right Angle Polygon and
“Closed Loop”
“Rectangle”
“Right Angle Polygon frame and
.)
“Multi-Closed Loop”
.)
“Right Angle Poly-
.)
.)
.)
4
Exposure glass
R
Display
R
GCAREA5E
121
Area Editing (Option)
Area Shapes
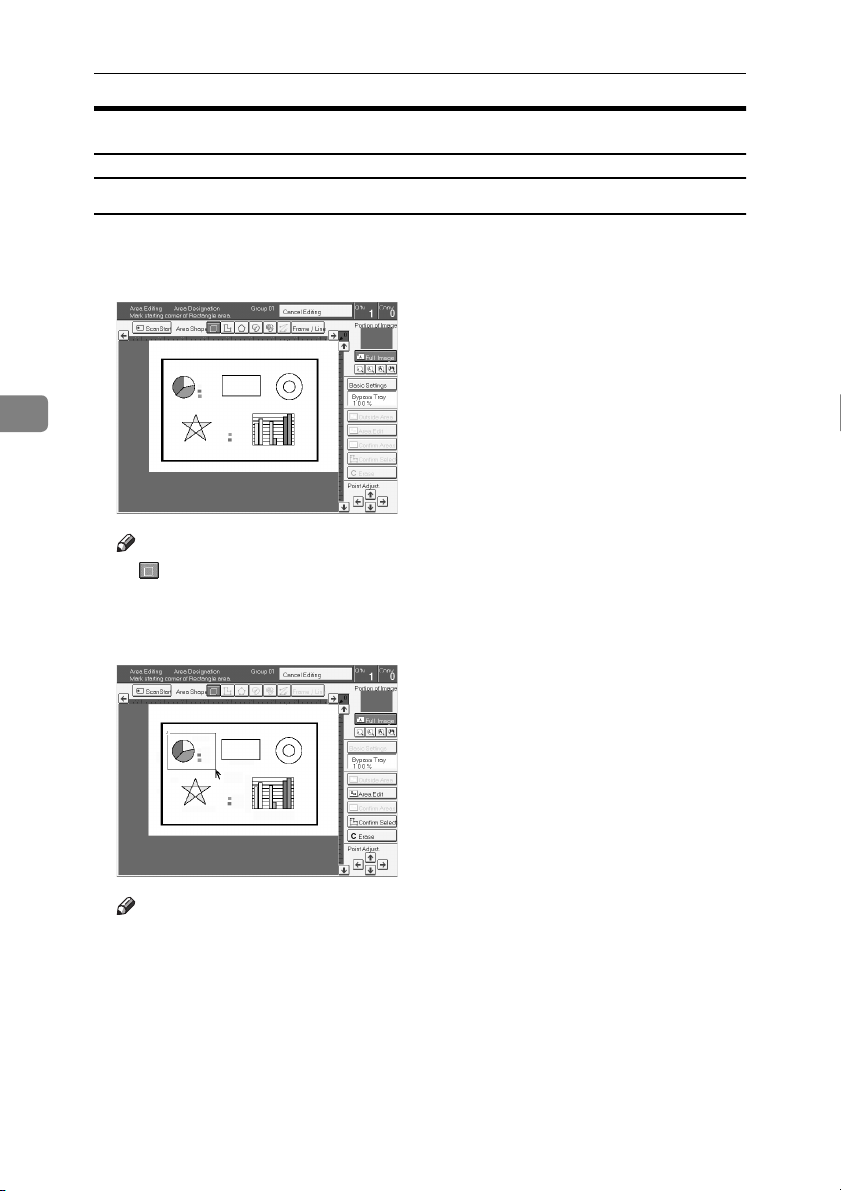
Rectangle
Set your original on the exposure glass.
A
Press the [Area Editing] key.
B
copy58.tif
4
Note
❒ [Rectangle] key is selected by default.
Mark the first point.
C
122
Mark the diagonally opposite corner of the area you wish to select.
D
copy59.tif
Note
❒ When you make a mistake, press the [
❒ Repeat D and E to add more rectangles.
❒ When you continue to add areas, you can select other shapes (except
Closed Loop Multi-Closed Loop, Line, Frame).
Press the [Confirm Selection] key.
E
Erase
] key.
Designating Areas
Press the [
F
Reference
For details, ⇒ P.130 “Selecting Modes for Designated Areas”.
Press the {{{{Start}}}} key.
G
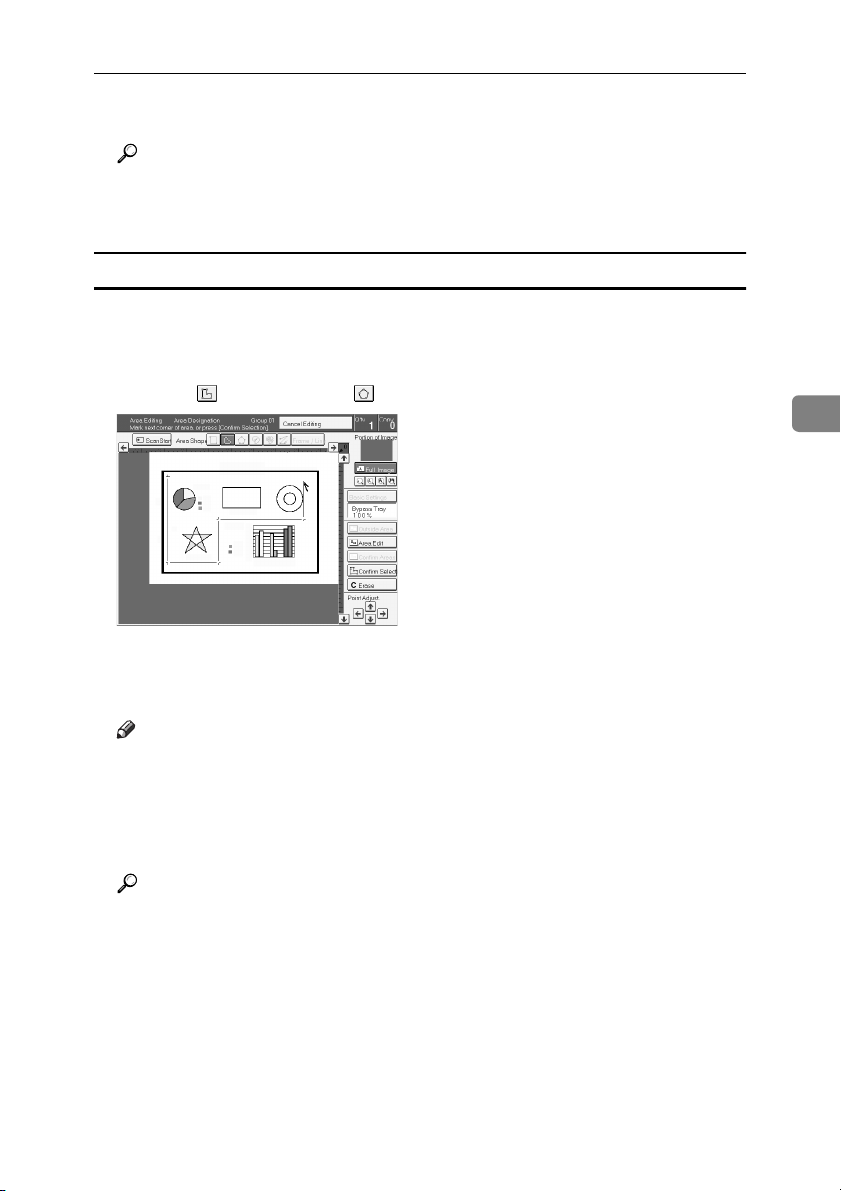
Right Angle Polygon and Polygon
Set your original on the exposure glass.
A
Press the [Area Editing] key.
B
Press the [
C
copy60.tif
Mark the first point.
D
Mark the next points.
E
Area Edit
] key, specify your settings, then press the [OK] key.
R.A. Polygon
] or [
Polygon
] key.
4
Note
❒ When you use Right Angle Polygon mode, mark points that make right an-
gles.
After making the last point, press the [Confirm Selection] key.
F
Press the [
G
Reference
For details, ⇒ P.130 “Selecting Modes for Designated Areas”.
Press the {{{{Start}}}} key.
H
Area Edit
] key, specify your settings, then press the [OK] key.
123

Area Editing (Option)
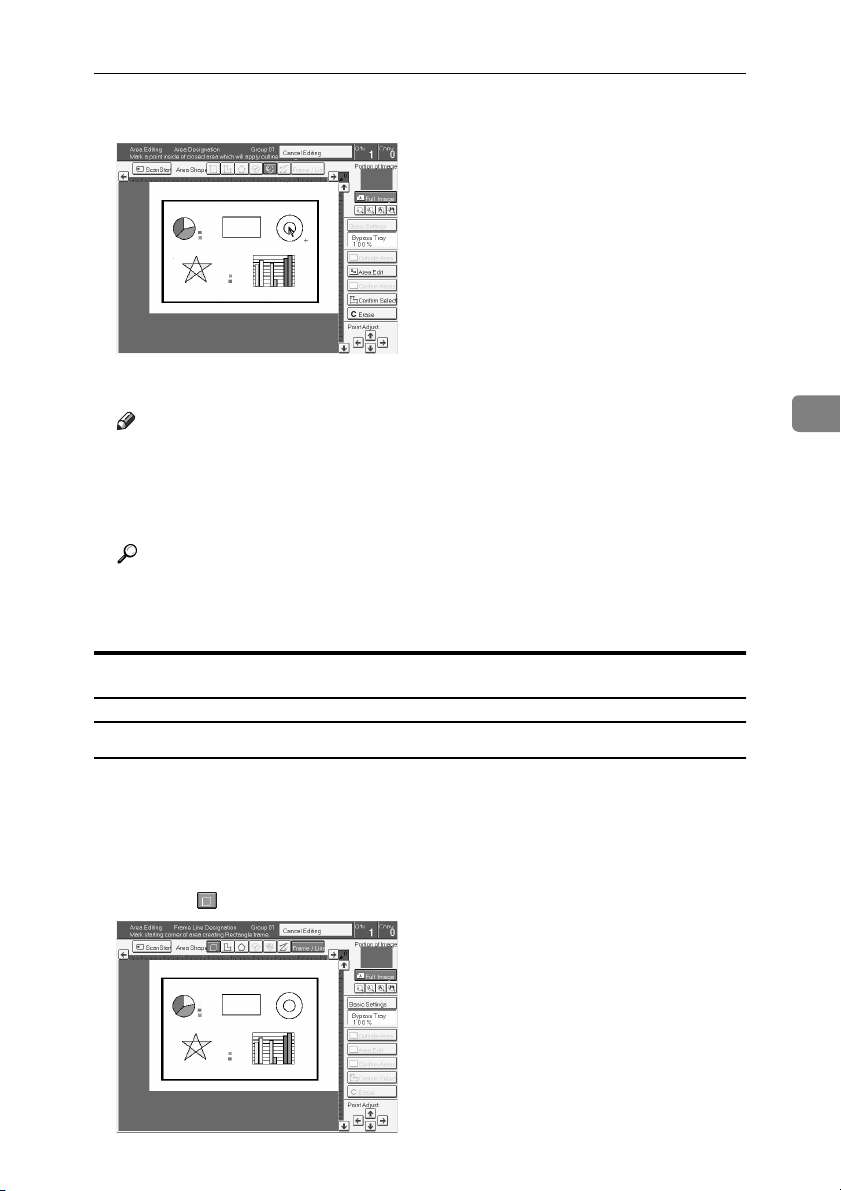
Closed Loop
Limitation
❒ If you specify an area with Closed Loop, you cannot specify any additional
areas with other selection tools.
Note
❒ When you color areas with the Closed Loop, the area boundary may shift de-
pending on the image.
Set your original on the exposure glass.
A
Press the [Area Editing] key.
B
Press the (Closed Loop) key.
4
C
Touch on a point inside a closed loop.
D
copy61.tif
Press the [Confirm Selection] key.
E
Press the [Area Edit] key, specify your settings, then press the [OK] key.
F
Reference
For details, ⇒ P.130 “Selecting Modes for Designated Areas”.
Press the {{{{Start}}}} key.
G
Multi-Closed Loop
Limitation
❒ If you specify an area with Multi-Closed Loop, you cannot specify any addi-
tional areas with other selection tools.
Set your original on the exposure glass.
A
Press the [Area Editing] key.
B
Press the (Multi-Closed loop) key.
C
124
Designating Areas
Press on a point inside the exterior area you wish to specify.
D
copy62.tif
Press on a point inside the interior area you wish to treat differently.
E
Note
❒ Be sure to select a point inside of the exterior area you wish to define.
Press the [Confirm Selection] key.
F
Press the [Area Edit] key, specify your settings, then press the [OK] key.
G
Reference
For details, ⇒ P.130 “Selecting Modes for Designated Areas”.
Press the {{{{Start}}}} key.
H
4
Frame/Line
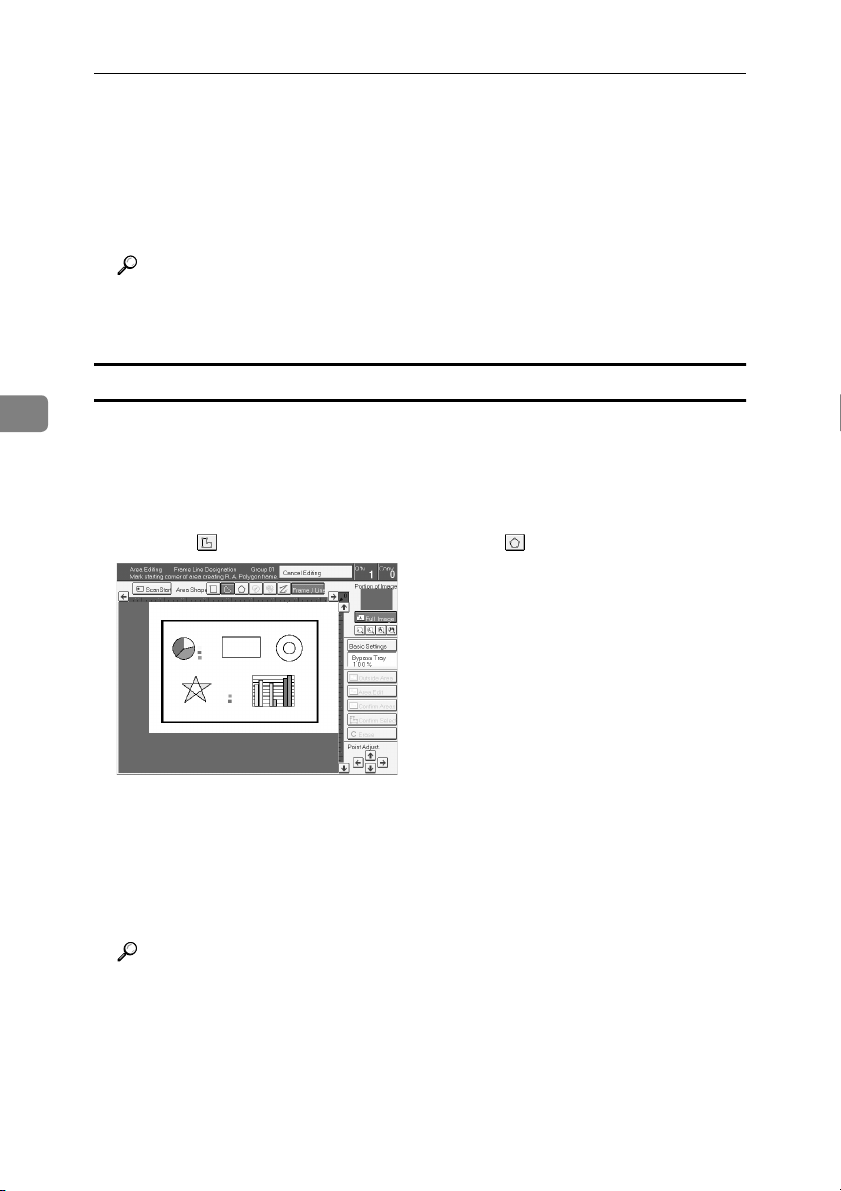
Rectangle frame
Set your original on the exposure glass.
A
Press the [Area Editing] key.
B
Press the [Frame / Line] key.
C
Press the (Rectangle) key.
D
copy65.tif
125
Area Editing (Option)
Mark the first point.
E
Mark the diagonally opposite corner of the area you wish to select.
F
Press the [Confirm Selection] key.
G
Press the [Area Edit] key, specify your settings, then press the [OK] key.
H
Reference
For details, ⇒ P.130 “Selecting Modes for Designated Areas”.
Press the {{{{Start}}}} key.
I
Right Angle Polygon frame and Polygon frame
4
Set your original on the exposure glass.
A
Press the [Area Editing] key.
B
Press the [Frame / Line] key.
C
Press the (Right Angle Polygon) key or the (Polygon) key.
D
copy64.tif
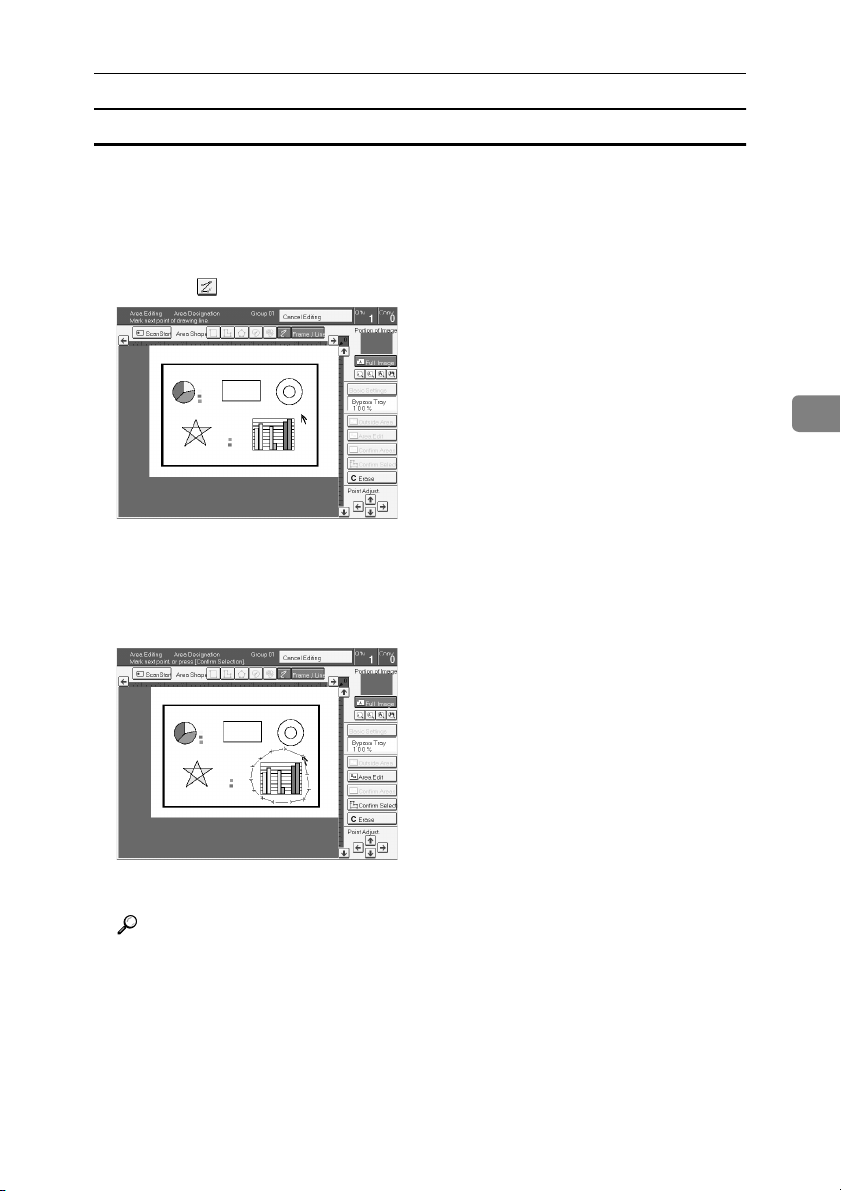
Mark the first point.
E
Mark the next points.
F
After making the last point, press the [Confirm Selection] key.
G
Press the [
H
Reference
For details, ⇒ P.130 “Selecting Modes for Designated Areas”.
Area Edit
] key, specify your settings, then press the [OK] key.
126
Press the {{{{Start}}}} key.
I
Line
Set your original on the exposure glass.
A
Designating Areas
Press the [
B
Press the [Frame / Line] key.
C
Press the (Line) key.
D
copy63.tif
Mark the first point.
E
Mark the next points.
F
After marking the last point, press the [Confirm Selection] key.
G
copy66.tif
Area Editing
] key.
4
Press the [Area Edit] key, specify your settings, then press the [OK] key.
H
Reference
For details, ⇒ P.130 “Selecting Modes for Designated Areas”.
Press the {{{{Start}}}} key.
I
127
Area Editing (Option)
Notes for Designating Areas
The number of the points, areas, and groups that can be designated
Note
❒ Maximum number of points: 500
❒ In Right Angle Polygon mode, Polygon mode, or Line mode, the maximum
number of points for one area is 30.
❒ The number of areas that can be designated is as follows:
• Rectangle mode: maximum 250 areas
4
• Right Angle Polygon mode, Polygon mode, Line mode: 500 points maxi-
mum. For example, if 10 points are designated for each area, the maximum
number of areas that can be designated is 50.
• Closed Loop mode, Multi-Closed Loop mode: maximum 500 areas
❒ Maximum number of groups: 20 (“Group” means a set of areas that you want
to do same editions.)
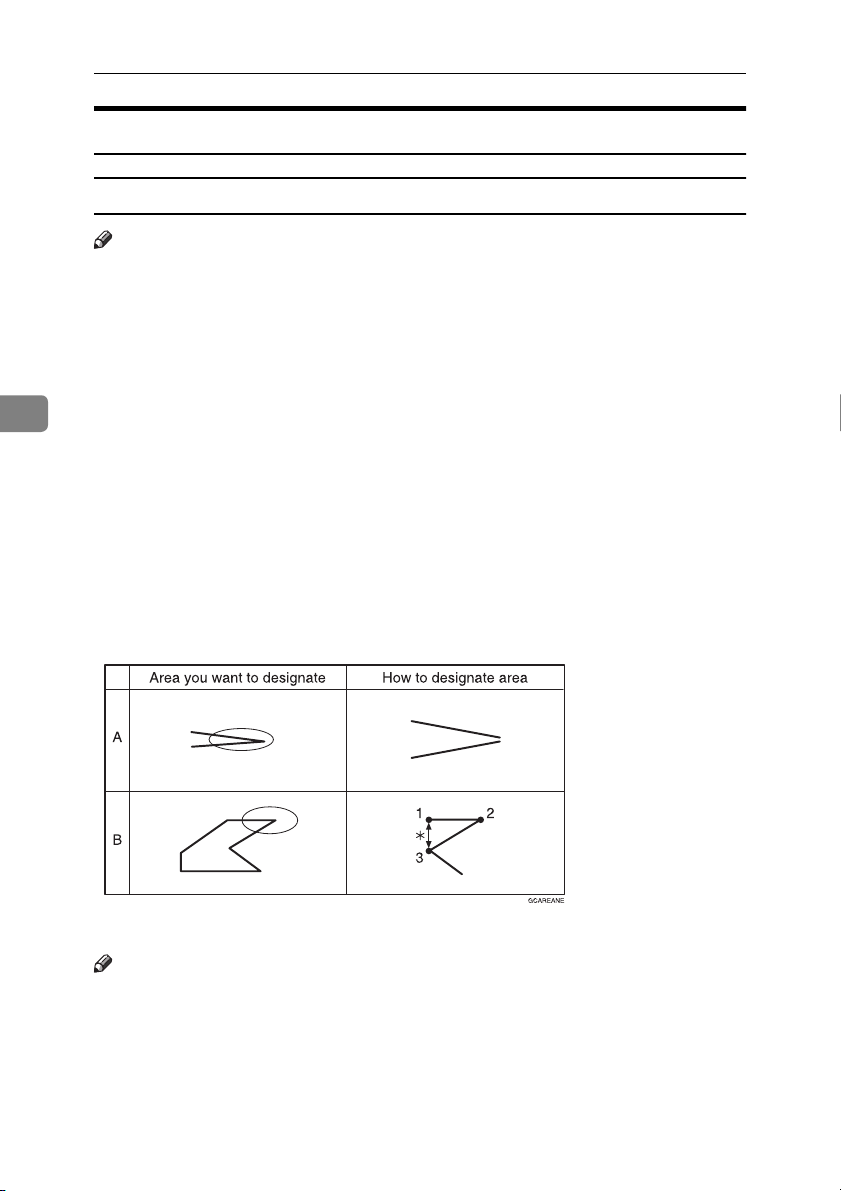
❒ If you want to designate area shape like an acute angle by using Polygon
mode or Line mode, see the following instructions.
• Use two separate lines to create angle(A).
• The first designated point(1) and the next designate point(3) should have
distance of more than 4mm(0.2")(B).
*:4mm(0.2”)
Note
❒ Do not designate an area or line which overlaps part of another area or line.
If an area overlaps another one, the job settings specified last will be applied
to the overlapped portion or those areas might not be copied.
128
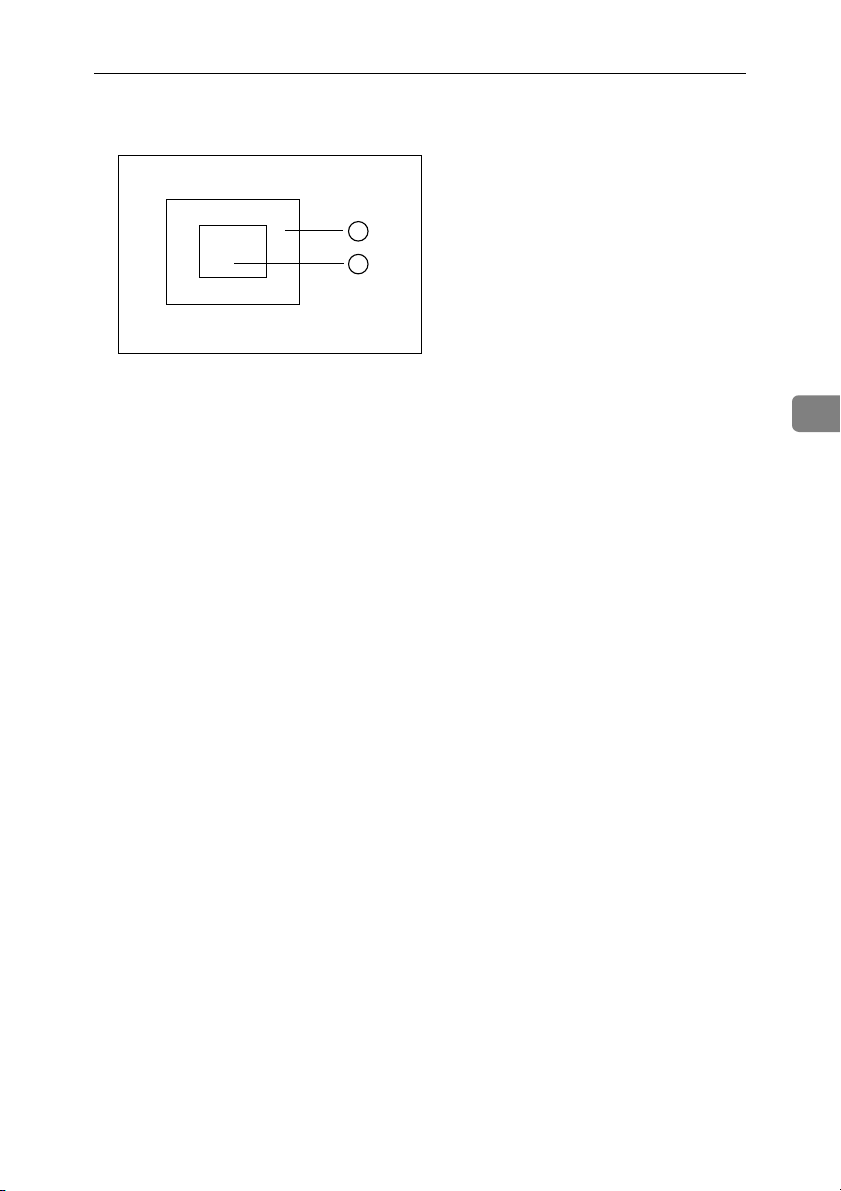
Designating Areas
❒ However, areas containing areas (see below) are permitted. Designate start-
ing with the outermost area.
GCAREA4E.eps
1
2
GCAREA4E
❒ These operations are available, however, under the following conditions:
• When designating areas with Closed Loop mode, Multi-closed Loop or
Frame/Line mode.
❒ If you mark a line and it overlaps another line you have previously marked,
the last point you marked will be canceled automatically.
❒ If you designate an area in Right Angle Polygon mode, make sure to mark
points that make right angles. If you mark a point which does not match, the
editor will automatically correct it to make a right angle.
❒ If you want to designate a triangular area, use Polygon mode.
❒ In Closed Loop mode or Multi-Closed Loop mode, the machine might not de-
tect a closed loop area or multi-closed loop area completely under the following conditions:
• The outline is not completely closed, it is too light to detect, or the thickness
is uneven.
• The outline is thinner than 0.3mm.
• The outline is not black.
• The space between two closed loop outlines is less than 1mm.
• The closed loop can be up to 2 meters long.
• The area enclosed by the outline is not white.
❒ The more areas you designate, the more time copying will take.
❒ If you erase an area, group, or job setting, it is cleared from the display. How-
ever, the points are still stored in memory and are not cleared until you exit
Area Editing. This affects the maximum number of areas you can designate.
❒ Closed Loop mode Multi-Closed Loop mode and Frame/Line mode cannot
be used with Rectangle mode, Right Angle Polygon mode, and Polygon mode
for one group at a time.
❒ If you need to align areas precisely, you can have a grid shown on the en-
larged display. The grid spacing matches the scale of the display.
4
129
Area Editing (Option)
Selecting Modes for Designated Areas
Reference
The available modes for area editing depend on the area shape. ⇒ P.146
“Combination Chart for Area Editing”.
Regarding functions that cannot be used together in area editing, ⇒ P.146
“Combination Chart for Area Editing”.
More than one mode can be set for designated area, however, there are some
limitations, ⇒ P.146 “Combination Chart for Area Editing”. And up to 7 patterns
of modes can be set together.
Note
4
❒ Up to 20 groups of multiple areas can be edited. All the areas should belong
to groups 1 ∼ 20. You can select up to seven job patterns for at most 20 groups.
After you have set seven patterns, the copier will only allow you to choose the
pattern of a previous group. If you change the settings for one group, it will
change the settings for all other groups with the same job pattern. However,
if you have set a Paint, Color Background, or Frame/ Line, changing the color
in one group will not affect other groups. (Up to 15 colors can be selected.)
❒ The modes that can be set for inside areas as follows:
• Color/Image Adjustment: Image Density, Color Mode, Original Type, Im-
age Adjustment, Color Adjustment, Color Balance Adjustment
• Color Creation: Color Conversion, Color Erase, Color Background, Paint,
Type Mask
Note
❒ The editing functions available when specifying area with Frame/Line mode
are Width and Color.
❒ Color/Image Adjustment's default setting:
• Image Density - Manual Image Density
• Color Mode - Black & White
• Original Type - Text
❒ You can change the default settings. ⇒ P.173 “User Tools”.
❒ Depending on the shapes of the areas, coloring or deleting near the outlines
of the areas might not do well, or the outlines might become uneven.
❒ The way to set modes is basically the same as for the entire image. For details,
refer to each page.
• To fill an area with a selected color, select the Paint.
• Image Density (⇒ P.26 “Adjusting Copy Image Density”.)
• Original Type (⇒ P.33 “Selecting the Original Image Type”.)
• Color Adjustment (⇒ P.106 “Color Adjustment”.)
• Color Conversion (⇒ P.83 “Color Conversion”.)
130
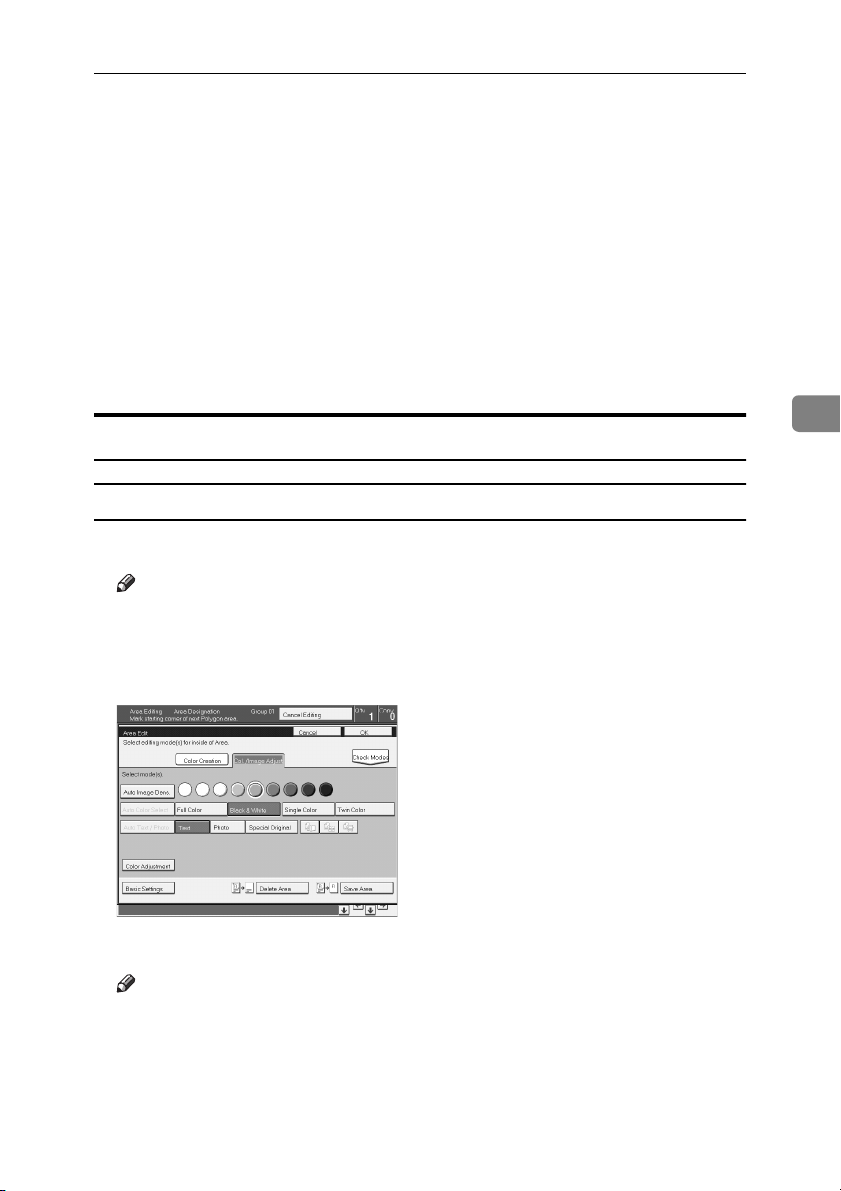
Selecting Modes for Designated Areas
• Color Background (⇒ P.86 “Color Background”.)
• Color Mode (⇒ P.28 “Selecting a Color Mode”.)
• Image Adjustment (⇒ P.108 “Image Adjustment”.)
• Color Balance Adjustment (⇒ P.103 “Color Balance Adjustment”.)
• Color Erase (⇒ P.85 “Color Erase”.)
• Save Area (⇒ P.133 “Save Area”.)
• Changing Basic Settings for the Entire Image (⇒ P.138 “Changing Basic Set-
tings for the Entire Image”.)
• Change Modes (⇒ P.140 “Change Modes”.)
• Adding Areas (⇒ P.141 “Adding Areas”.)
• Erasing a Group (⇒ P.143 “Erasing a Group”.)
Area Editing
Basic modes
Designate the areas you wish to modify.
A
Note
❒ For how to designate areas, ⇒ P.119 “Designating Areas”.
4
Press the [Area Edit] key.
B
Press the [Col. /Image Adjust.], [Color Creation] key.
C
copy67.tif
Select the effects you wish to apply.
D
Note
❒ Image Density, ⇒ P.26 “Adjusting Copy Image Density”.
❒ Color Mode, ⇒ P.28 “Selecting a Color Mode”.
❒ Original Type, ⇒ P.33 “Selecting the Original Image Type”.
❒ Color Adjustment, ⇒ P.106 “Color Adjustment”.
❒ Color Creation, ⇒ P.83 “Color Creation”.
131
Area Editing (Option)
Press the [OK] key.
E
Press the [Start] key.
F
Delete Area
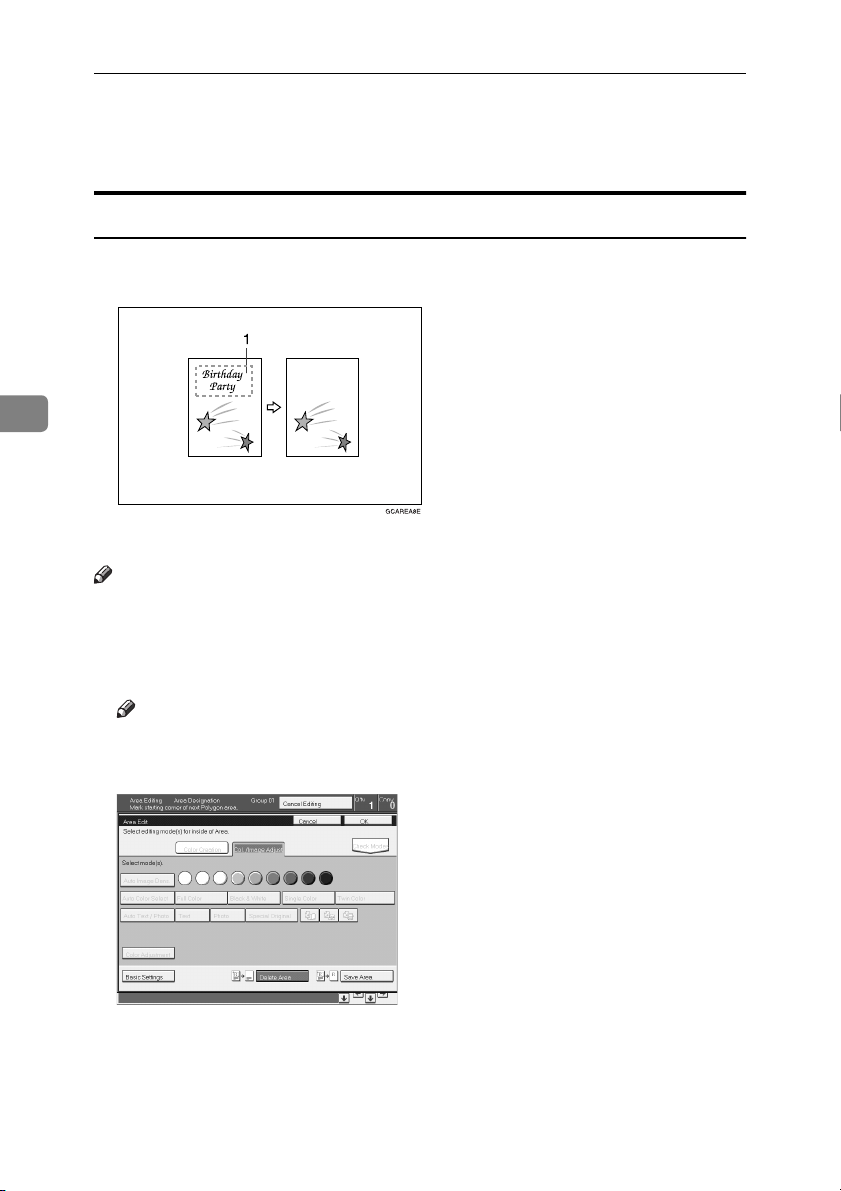
This function blanks out designated areas.
GCAREA8E.eps
4
1.
Designated area
Note
❒ When you select Delete Area mode, previously selected modes are canceled.
Designate the areas you wish to modify.
A
132
Press the [Area Edit] key.
B
Note
❒ For how to designate areas, ⇒ P.119 “Designating Areas”.
Press the [
C
copy68.tif
Press the [OK] key.
D
Press the
E
Delete Area
Start
{{{{
key.
}}}}
] key.
 Loading...
Loading...