Page 1

SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart
XI 3.2, version for SAP solutions - User
Guide
Version 12.2.0.0
Page 2

October 2009
Copyright
Trademarks
© Copyright 2009 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or for any purpose
without the express permission of SAP AG. The information contained herein may be
changed without prior notice.
Some software products marketed by SAP AG and its distributors contain proprietary
software components of other software vendors.
All rights reserved. SAP, R/3, SAP NetWeaver, Duet, PartnerEdge, ByDesign, SAP Business
ByDesign, and other SAP products and services mentioned herein as well as their respective
logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP AG in Germany and other countries.
Business Objects and the Business Objects logo, BusinessObjects, Crystal Reports, Crystal
Decisions, Web Intelligence, Xcelsius, and other Business Objects products and services
mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks
of Business Objects S.A. in the United States and in other countries. Business Objects is an
SAP company.
All other product and service names mentioned are the trademarks of their respective
companies. Data contained in this document serves informational purposes only. National
product specifications may vary.
These materials are subject to change without notice. These materials are provided by SAP
AG and its affiliated companies ("SAP Group") for informational purposes only, without
representation or warranty of any kind, and SAP Group shall not be liable for errors or
omissions with respect to the materials. The only warranties for SAP Group products and
services are those that are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such
products and services, if any. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty.
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction 11
What is a Rapid Mart? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Rapid Marts packages accelerate Time to Value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
SAP BusinessObjects Rapid Marts packages architecture . . . . . . . . . 14
About this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Chapter 2 Overview 17
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
What you can do with this Rapid Mart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Supported analyses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Related Rapid Marts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Sharing components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions schema
24
Where the Rapid Mart fits in the customer order management cycle . . . . 25
Chapter 3 Subject Areas 27
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Sales Order Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Rapid Mart Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Backlog Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Schedule Lines Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Delivery Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 3
Page 4

Contents
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Billing Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Sales Order History Preservation Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Document Flow Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Rapid Mart Processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Rapid Mart Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
On Time Delivery Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Rapid Mart Processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Document Validation Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
Rapid Mart Processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
Rapid Mart Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Chapter 4 Reports 79
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Sales Orders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Recommended table joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .92
Deliveries and On-Time Delivery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Recommended table joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
Billing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
Summary Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
Recommended table joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Backlog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123
Sample report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123
Recommended table joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .125
Schedule Lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .126
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .126
4 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 5

Contents
Recommended table joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Sales Order History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Recommended table joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Document Flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Invalid Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
SAP Master Data Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Data Discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Data Auditing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Recommended table joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Chapter 5 Universe 163
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Universe Design Principles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Universe Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Universe Table Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Join Strategy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Techniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Hierarchies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Hierarchies Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Geographic Hierarchies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Time Dimension and Fiscal Period Hierarchies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Material Product Hierarchy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Horizontal & Vertical Hierarchies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Hierarchy Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
SAP Sales Analysis Universe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Universe Objects & Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Common Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Fact Table Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 5
Page 6

Contents
Sales Orders & Backlog Subject Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Schedule Lines Subject Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Deliveries Subject Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .204
Billings Subject Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .209
Sales Order History Subject Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .212
Document Flow Subject Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .215
Current On Time Delivery Subject Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .217
History On Time Delivery Subject Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .221
Invalid Documents Subject Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
Universe Validation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .226
Using Fact Tables as Dimensions to Other Fact Tables . . . . . . . . . . .227
SAP Master Data Universe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .230
Universe Objects & Classes - Master Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .230
Universe Validation - Master Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
Customizing the SAP Sales Analysis Universe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .267
Chapter 6 Installing the Rapid Mart 269
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .270
System Prerequisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
Personnel Prerequisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .272
Rapid Mart product components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
Preparing your environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .275
Preparing Data Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .275
Preparing Target Database Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .275
Preparing Source Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .276
Preparing BusinessObjects Enterprise . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
Performance Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .276
The Rapid Mart Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .278
Install the Rapid Mart Target Schema . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .279
Create Target Schema . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .279
Install the Data Services Job(s) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
Renaming the Data Stores . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .282
Import ATL File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .284
6 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 7

Contents
Adjusting the Data Stores . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
Using Auxiliary Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
Using ABAP Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 294
Final Steps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 298
Installing Rapid Mart Reporting Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
Import Wizard for Reporting Content BIAR File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
Creating Universe Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316
Chapter 7 Using the Rapid Mart 319
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
Recovery framework . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
Data Services automatic recovery feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
Rapid Mart recovery framework . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 321
Execution status framework . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 322
The execution status table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 322
The execution status API . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 323
Executing a job with the Reset option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 324
Extraction, transformation and loading process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 324
Global Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
Global Variable Cross-Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
Used in All Rapid Marts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
Used in 2 to 10 Rapid Marts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Used in Only 1 Rapid Mart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
Setting Global Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 353
Executing the job . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
Initial (First) Extraction and Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
Incremental (Delta) Extraction and Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 358
Customizing the Rapid Mart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
Chapter 8 Technical Implementation 361
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 362
Sales order section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 362
Dimension Table Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 7
Page 8

Contents
Initial load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 366
Incremental load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .369
Processes completed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .370
Delivery section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .373
Dimension table load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .373
Initial load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 376
Incremental load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .377
Processes completed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .377
Billing section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 379
Dimension table load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .379
Initial load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 382
Incremental load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .383
Backlog section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .384
Dimension table load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .384
Initial and incremental load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
Schedule lines section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .393
Dimension load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
Initial and incremental load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 395
Sales order history preservation section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .396
Dimension load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 396
Initial and Incremental Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
On Time Delivery Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .400
Dimension Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .400
On Time Delivery Processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .402
Optimization Techniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .407
Table Partitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .407
Data Transfer Transform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .409
Hierarchy Optimizations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 411
Dealing with NULL values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .413
Fact Table Stored Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 415
Fiscal Periods & Time Dim Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 416
8 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 9

Contents
Chapter 9 Documentation References 419
Data Services Documentation References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 420
BusinessObjects Enterprise Documentation References . . . . . . . . . . . . 420
Appendix A Rapid Mart Data Schema 423
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 9
Page 10

Contents
10 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 11
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Introduction
chapter
Page 12

Introduction
1
What is a Rapid Mart?
What is a Rapid Mart?
SAP BusinessObjects Rapid Marts packages are blueprints for building data
marts with SAP BusinessObjects technology:
• Data Services
• Universe Designer
• Web Intelligence.
Rapid Marts packages deliver jump-start ETL (extract, transform & load)
mappings, schema, and initial reporting content, accelerating the deployment
of BI (business intelligence) for enterprise applications from SAP, PeopleSof t,
Oracle, and Siebel.
Each Rapid Mart is designed to address the reporting needs of a specific
business area (or department) like accounting, sales, or purchasing. A
component-based framework allows conducting analysis across these
selected business areas by combining different packages within the same
source application suite.
Rapid Marts focus on basic standard configuration of the enterprise
applications. They are country and industry neutral templates meant to be
easily modified and extended to suit customer specific application
implementation and reporting needs.
Rapid Marts incorporate best practices, and provide easily modifiable
templates. With Rapid Marts total development time of a data mart solution is
greatly reduced.
Each customer situation is different. You will probably encounter one or more
of these:
• Customizations you have made to SAP solutions the Rapid Mart does not
cover.
• Standard SAP solutions data fields important for your specific business,
but not included in the Rapid Mart templates.
• Optimization and performance challenges unique to your environment.
• Reporting requirements not covered within the Rapid Mart template
reports.
Rapid Marts are flexible templates that you can adjust to account for these
unique situations. It is expected that some customization and optimization will
be needed to suit your individual environment. Rapid Marts are not an out-ofthe-box solution.
12 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 13

BI tools and analytic tools can access Rapid Mart data through SQL queries.
Rapid Marts can be implemented individually, or in any combination, to form a
single platform that delivers the infrastructure for your company’s internal and
external information needs. They can also serve as a staging area for
enterprise analytic applications.
Rapid Marts provide your business with an accelerated time to value through
rapid BI deployments because you can implement them quickly and easily
customize them to meet specific analytic requirements.
Rapid Marts packages accelerate Time to Value
Rapid Marts are packaged data solutions that you can quickly deploy to
address specific areas of business analysis.
Available Rapid Marts packages for SAP solutions include:
Financial Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects General Ledger Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Accounts Payable Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Accounts Receivable Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Cost Center Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
Operational Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects Inventory Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Purchasing Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
Manufacturing Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects Plant Maintenance Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Project Systems Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
Human Capital Management (HCM) Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects Human Resources Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
Introduction
What is a Rapid Mart?
1
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 13
Page 14

Introduction
1
What is a Rapid Mart?
You can combine multiple Rapid Marts packages into a single environment to
build the foundation for your data warehouse or use them as a staging area
for business intelligence applications.
SAP BusinessObjects Rapid Marts packages architecture
Rapid Marts architecture is driven by SAP BusinessObjects technology.
Rapid Mart Architecture:
Rapid Marts packages include the following components:
14 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 15

Introduction
What is a Rapid Mart?
• Data Movement Jobs - packaged source-to-target mappings and data
transformations. Each job is designed to perform initial and incremental
data movement;
• Data Model & Schema - set of dat a mart database objects designed with
dimensional data modeling approach. Rapid Marts packages for SAP
solutions has a single integrated data model. The schema are available
for Oracle, SQL Server IBM DB2, and Teradata;
• Semantic Layer (Universes) - SAP BusinessObjects metadata packages
for efficient query generation. There can be one or more universes per
Rapid Mart. Each universe is developed using Rapid Marts design
principles to ensure compatibility, code readability, and component reuse. In addition, there is one Master universe for development/
maintenance of multiple use objects (like Customer, Material, Currency,
etc.);
• Reports (Samples) - set of 15-20 Web Intelligence reports per Rapid
Mart. They represent answers to mostly asked business questions (for
example, in the SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions - 'What is the monthly Revenue trend by Division for this
year?'). The reports are developed using Rapid Mart color/layout
templates. Reports are examples of Web Intelligence best practice
development (trends, listing, guided analysis, roll ups and downs, etc.).
1
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 15
Page 16

Introduction
1
About this document
About this document
This document describes the SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart,
version for SAP solutions. This document contains information for a variety of
users—information that helps you understand the use of the Rapid Mart, the
data in the Rapid Mart, the reports you can create with the Rapid Mart, and
how to use and update the Rapid Mart.
This document contains the following chapters:
• Chapter 2: Overview — Describes the business problems you can solve
and the types of analyses you can do with this Rapid Mart
• Chapter 3: Subject Areas — Contains detailed information about each
section in the Rapid Mart, including the processes each section captures
• Chapter 4: Reports — Provides examples of reports you can produce
• Chapter 5: Universe — Describes SAP BusinessObjects Universe upon
which the reports are based
• Chapter 6: Installing the Rapid Mart — Contains the information you need
to install the Rapid Mart
• Chapter 7: Using the Rapid Mart — Describes how to execute the Rapid
Mart, including information about initializing variables and considerations
you need to make when customizing the Rapid Mart
• Chapter 8: Technical Implementation — Describes each section and the
work flows that run to load that section
• Chapter 9: Documentation References — Information about where to find
related to the Rapid Mart technical documentation on Data Services and
BusinessObjects Enterprise
• Appendix A: Rapid Mart Data Schema — Contains a detailed list of the
tables and views in the Rapid Mart
16 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 17

SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Overview
chapter
Page 18

Overview
2
Overview
Overview
This chapter describes the business problems you can solve with the SAP
BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions and the types
of analyses you can do with this Rapid Mart. The information in this chapter is
useful for those who want a business-level overview of the Rapid Mart and its
benefits.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• What you can do with this Rapid Mart
• Supported analyses
• Related Rapid Marts
• SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
schema
• Where the Rapid Mart fits in the customer order management cycle
What you can do with this Rapid Mart
The SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
supports analysis of data in the Sales and Distribution (SD) module of SAP
solutions. This module allows businesses to manage products, sales, and
services and to manage their performance with customers and other business
partners.
Using this Rapid Mart, you can:
• Analyze sales trends
• Determine customer behavior
• Forecast product sales with greater accuracy
• Plan product life cycles
• Track deliveries you make to your customers
• Track On Time Delivery Performance
• Report Bookings, Billings, Backlog in SAP solutions Document Currency
or your Global Currency
The SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
addresses three sub-modules of SD:
• Sales (SD-SLS)
• Shipping (SD-SHP)
• Billing (SD-BIL)
18 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 19

Overview
What you can do with this Rapid Mart
With the SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
you can answer the following kinds of questions:
• How are new product features affecting sales?
• How do sales vary by region?
• What is the average delivery time for a product?
• How well are we meeting our scheduled deliveries to customers?
• How well are we planning our deliveries for our customers?
• How do distribution, pricing, and promotional activities compare across
geographically diverse locations and various time periods?
• Are we fulfilling our commitments to customers in a timely fashion?
• What would our revenue have been if all originally entered sales orders
had been fulfilled?
• What are the trends in my sales orders history?
• What are my monetary exchange rate variances between my document
currency and Global currency?
• How do my bookings (sales orders) compare to my billings in a given
time period?
• How many credit memos are we issuing?
• What impact do credit memos have on revenue?
2
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 19
Page 20
Overview
2
Supported analyses
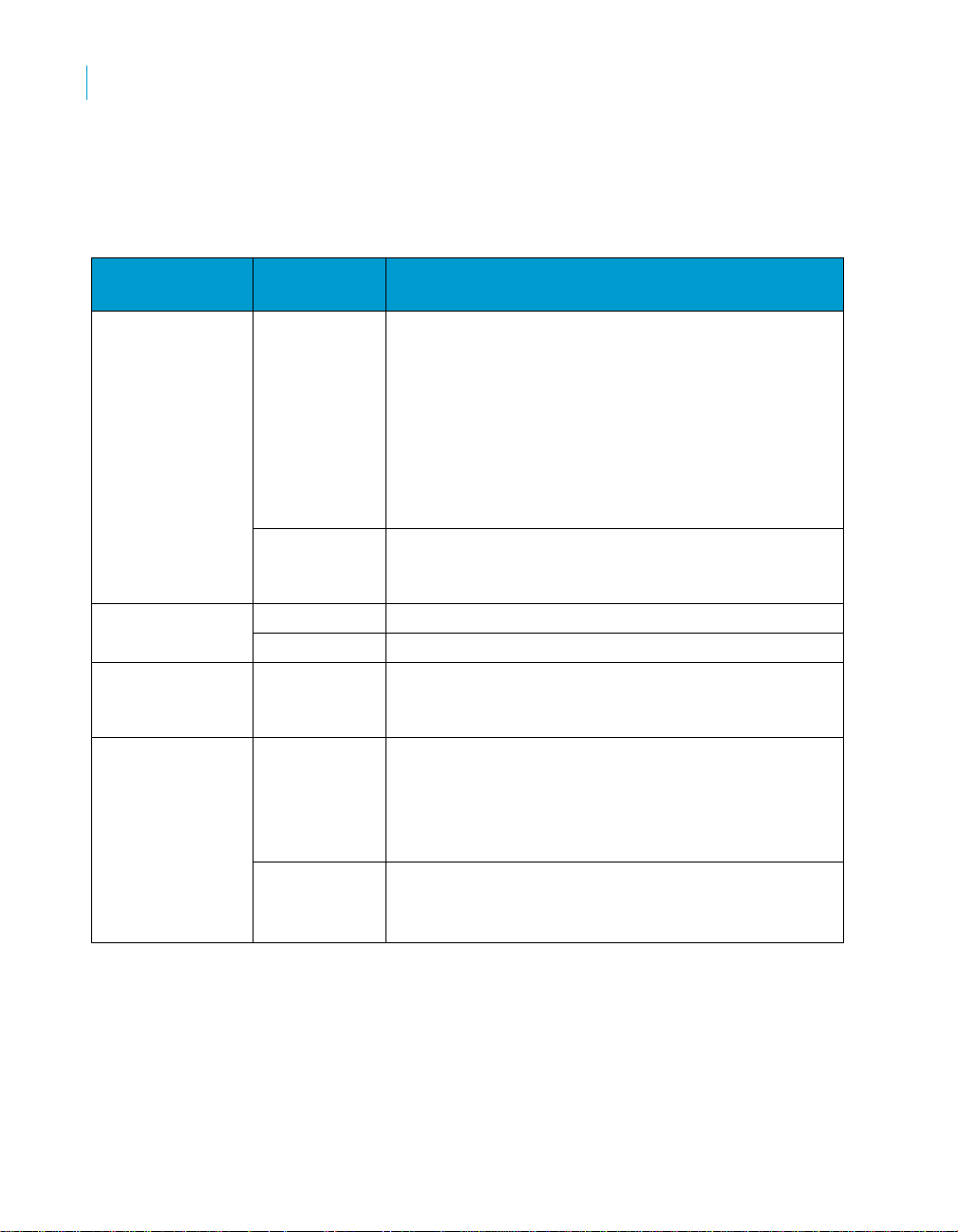
Supported analyses
The SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
supports several types of analyses.
Business
function
Sales Orders
(Bookings)
Backlog By Delivery
Schedule Lines Planning
Delivery Efficiency
Types of
analysis
Sales
Returns
By Billing
Service Level
Measures available in the Rapid Mart
• Sales order volumes and trends across time at
summary level for the enterprise or any level down
to individual line-item information
• Sales ranking by customer, product, sales
representative, region, or sales type
• Detailed sales order analysis by customer, product,
sales representative, region, sales type
• Customer requests fulfillment in terms of delivery
dates and quantities
• Sales orders of return category
• Return trends over time by customer, product,
region, sales type
• Un-delivered sales orders
• Un-billed sales orders
• Days Early or Late (Customer Requested Delivery
Date vs. Planned Delivery Dates).
• Compare Returns vs. Sales (booking) Trends
• Average order-to-delivery cycle time
• Cycle time patterns between order and delivery by
customer, product, sales office
• Comparison of scheduled and actual material
availability, loading, goods issue, and delivery dates
• Backlog quantities by customer, product, region
• Completion status by customer, product, region
• Shipped products for revenue recognition
20 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 21
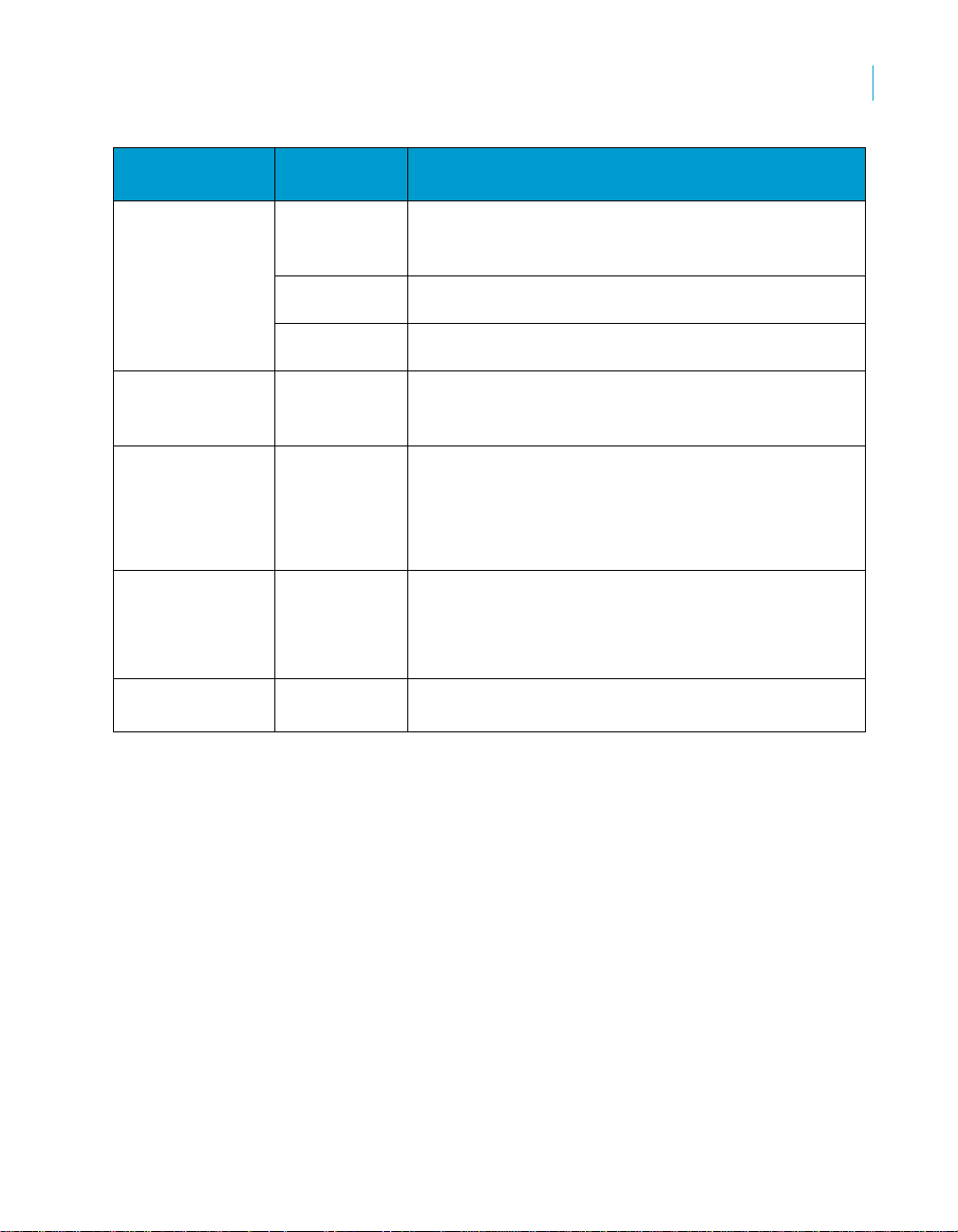
Overview
Supported analyses
2
Business
function
Billing Discounting
Sales Order
History
Document Flow Sales Order
On Time Delivery By Schedule
Invalid Documents by Sales Order
Types of
analysis
Margins
Revenue
Sales order
changes
preservation
Lifecycle
Line or
Delivery
or Billing
Measures available in the Rapid Mart
• Trends for discounting by product over time for
different customers
• Relationship between discounting and sales volume
• Base price to discount price and product cost
comparisons to identify margins and time by product
• Revenue over time by customer, product, sales
organizations
• What if revenue analysis
• Deletion of sales orders by sales person, by product,
by customer
• Unfulfilled Sales Orders
• Sales Order fulfillment Lifecycle (sales order
creation to billing time)
• Lifecycle by customer , product, sales representative,
region, sales type
• Average Days Delivery is Early or Late
• Quantities Early or Late
• Net Value Early or Late
• On Time Delivery Performance
• Sales Orders rejected by the Data Services
• Billings rejected by the Data Services
To support these analyses, the SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart,
version for SAP solutions contains a number of dimension tables. Tables
extracted from SAP solutions master data and customizable tables include
enterprise entities such as country, region, currency, plant, customer, and
material data. Tables extracted from the SD module include pricing,
organizational elements and their hierarchies (sales organization, division,
distribution channel, sales office, sales group, sales person), and sales
documents.
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 21
Page 22

Overview
2
Related Rapid Marts
Related Rapid Marts
Each Rapid Mart is composed of multiple components. A component is a
stand-alone work flow that completes a particular task, such as loading a
specific dimension table. Components can contain other components. A
section is a set of components that address a particular business problem or
subject area. A section is itself a component.
Components of the SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions are related to other SAP BusinessObjects Rapid Mart components.
For example:
• Sales orders for make-to-order materials are included in the:
• SAP BusinessObjects Inventory Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions - linked by material movements.
• SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for
SAP solutions - linked by reservations, and production orders.
These linkages give a complete view of the manufacturing process.
• Sales orders for Purchased materials are tracked in the:
• SAP BusinessObjects Purchasing Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions. - linked by purchasing documents, goods receipts, and
invoice receipts.
• SAP BusinessObjects Accounts Payable Rapid Mart, version for
SAP solutions - linked by purchasing documents (financial view) and
vendor financial documents.
• Tracking of customer payments for sales billings are included in the SAP
BusinessObjects Accounts Receivable Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions.
Sharing components
The same components can be used in multiple Rapid Marts. For example, a
component that extracts information about materials bought, produced, and
sold is needed for a Rapid Mart that supports sales analysis and also for a
Rapid Mart that supports inventory analysis. Work flows that extract star
schema “dimensions” are components. You can add a component to any
Rapid Mart using a simple import procedure.
A Data Services job can include multiple instances of a component. For
example, each section includes all the required dimension components.
Therefore, a job with several sections may include several instances of a
particular dimension component. Components are set to execute only once
within a job. This “execute once” feature ensures that shared components do
22 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 23

Overview
Related Rapid Marts
not cause duplicate data extraction from SAP solutions. For more information
about the “execute once” feature, see the Data Integrator/Data Services
Designer Guide.
Each of the sections listed in “What you can do with this Rapid Mart” on
page 18 are considered components. You can identify a component within an
Data Services job by a “C_” prefix before its name. For example, the
component that contains sales order and the associated reporting dimensions
is named C_SalesOrder_Section.
2
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 23
Page 24

Overview
2
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions schema
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart,
version for SAP solutions schema
The following diagram shows an overview of the SAP BusinessObjects Sales
Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions Star Schema Layout. Tables in the
center of the diagram are the fact tables and correspond to particular
sections; the side boxes contain dimension tables that may apply to multiple
sections.
24 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 25

Where the Rapid Mart fits in the customer order management cycle
Additionally the Sales Rapid Mart includes the following hierarchy, staging,
validation, and auxiliary tables that are not organized as a star schema:
Where the Rapid Mart fits in the customer
order management cycle
The SAP solutions customer order management cycle consists of the
following elements:
• Pre-sales activities (such as quotations, inquiries, contracts, and
scheduling agreements)
• Sales order processing
• Inventory sourcing
• Delivery
• Billing
• Payment
Overview
2
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 25
Page 26

Overview
2
Where the Rapid Mart fits in the customer order management cycle
Other Rapid Marts (see “Related Rapid Marts” on page 22) fit into the Order
Management Cycle as shown below:.
26 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 27
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Subject Areas
chapter
Page 28

Subject Areas
3
Overview
Overview
Each section in the SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions pertains to a particular subject area. This chapter describes each
section and the processes each section captures.
The information in this chapter is useful to understand the data in the Rapid
Mart and how it relates to SAP solutions.
This chapter discusses:
• Sales Order Section
• Backlog Section
• Schedule Lines Section
• Delivery Section
• Billing Section
• Sales Order History Preservation Section
• Document Flow Section
• On Time Delivery Section
• Document Validation Section
Sales Order Section
A sales order is a document that captures and records customer commitment
to purchase goods or services. The sales order contains all the information
needed to process the customer commitment throughout the SD module.
The SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions has
no restrictions on sales document categories. The sales order section
captures:
• sales orders,
• returns,
• credit and debit memo requests,
• pre-sales documents, such as
• quotes,
• inquiries,
• contracts,
• scheduling agreements.
When creating a sales order, SAP solutions copies default information from
the following:
28 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 29

Subject Areas
Sales Order Section
• Customer master
• Material master
• Condition records for pricing
• Pre-set configuration for shipping point and route
SAP solutions can create a sales order that references another sales
document, such as a quote, an inquiry, scheduling agreement, or a contract.
SAP solutions can overwrite copied information for a particular sales order.
SAP solutions supports many types of sales transactions within sales order
processing, including:
• Standard order — Product request from a customer with 'normal' delivery
requirements
• Rush order — Product request from a customer with immediate delivery
• Returns authorization — Product return from a customer
• Delivery free of charge — Product delivered to a customer with no charge
• Consignment — Product sent to a customer but p aid for only as it is used
• Service Contracts — Used by the SAP solutions Service Module
• Quotation — Initial quote to a customer before sales order is created.
Can be turned into a sales order once the sale is agreed to.
• Debit Memo Request — A precursor to a Debit Memo. These are
instructions for additional charges to a customer.
• Credit Memo Request — A precursor to Credit Memo. These are
instructions to reduce charges to a customer.
• Inquiries — A precursor to a quotation. A Customer can ask for detailed
information about specific goods, in particular their prices.
The sales order section extracts order-related data from SAP solutions
header and line item tables. The section stores the transactions for individual
sales order documents in the SALES_ORDER_F ACT table. This section does
not store the history of data changes to sales orders.
Sales order processing in Data Services for the Rapid Mart has two major
branches. The first is the initial load. This is a full refresh of all sales orders in
the SAP solutions system. Typically, you will run this refresh only once when
you first implement the Rapid Mart.
The second branch is the incremental or “delta” load of the sales orders. The
Data Services keeps track of the run date for each Rapid Mart refresh,
including the first. Subsequent refreshes load only those sales orders that
have been added, deleted, or changed in SAP solutions since the previous
refresh.
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 29
Page 30

Subject Areas
3
Sales Order Section
Note: The Rapid Mart treats deleted sales orders differently than SAP
solutions. In SAP solutions the sales orders are physically deleted from the
database. However, the Rapid Mart does not delete the records, but assigns
them a reject code.
Both the first and incremental refreshes use a staging table to prepare sales
order information for the Rapid Mart. The table is named
SALES_ORDER_STAGE. Data extracted from SAP solutions is loaded here
first.
Further transformations of the data take place in the stage table. These
include lookup of Global Currency exchange rates and of the ship to address
for each sales order
Once the staging table is fully updated, the global currency exchange rates
lookups are validated using a Validation transform in the Rapid Mart. Rows
that do not validate are written to the SALES_ORDER_FACT_BAD table.
Rows that pass validation update the SALES_ORDER_FACT table. See the
Document Validation Section later in this chapter for more details.
Rapid Mart processing
Sales orders are stored in the SALES_ORDER_FACT table of the target
database. Additionally, this section captures the following dimensional
attributes and their associated dimension tables.
Attribute Dimension Table Names
Billing Block BILLING_BLOCK
Central Address CENTRAL_ADDRESS
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Credit Control Area CREDIT_CONTROL_AREA
Credit Management Risk Class CREDIT_MGMT_RISK_CLASS
Monetary Currency CURRENCY
Customer CUSTOMER
Customer Group CUSTOMER_GROUP
Delivery Block DELIVERY_BLOCK
Delivery Route DELIVERY_ROUTE
Distribution Channel DISTRIBUTION_CHANNEL
Division DIVISION
30 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 31

Subject Areas
Sales Order Section
Attribute Dimension Table Names
Document Category DOCUMENT_CATEGORY
Document Type DOCUMENT_TYPE &
DOCUMENT_CATEGORY
Inter Company Terms INTER_COMPANY_TERM01
Material & Product Hierarchy MATERIAL,
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
Material Alternate Unit of Measure MATERIAL_ALT_UOM
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Material Group MATERIAL_GROUP
Order Reason ORDER_REASON
Payment Term PAYMENT_TERM
Plant PLANT
Pricing Procedure (Horizontal &
Vertical)
Profit Center & Hierarchy PROFIT_CENTER,
Reject Reason REJECT_REASON
Sales District SALES_DISTRICT
Sales Group SALES_GROUP
Sales Office SALES_OFFICE
Sales Order Status SALES_ORDER_STATUS
Sales Organization & Hierarchy SALES_ORGANIZATION,
Sales Person SALES_PERSON
Shipping Point SHIPPING_POINT
Storage Location STORAGE_LOCATION
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
PRICING_PROCEDURE_HZ,
PRICING_PROCEDURE_VR
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_BAD,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_VR
SALES_ORGANIZATION_HIER
3
Fact Table Fields
The SALES_ORDER_FACT table contains the following measures
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 31
Page 32

Subject Areas
3
Sales Order Section
Note: The suffix GBL is for Global Currency . The suf fix TRX is for transaction
(or Document) Currency.:
Col. Name Description
AMT_NET_PRICE_GBL VBAP-NETPR - Net Price -after discounts
and surcharges are applied, but excluding
tax - Global Currency
AMT_NET_PRICE_TRX VBAP-NETPR - Net Price -after discounts
and surcharges are applied, but excluding
tax - Transaction Currency
AMT_NET_VALUE_GBL VBAP-NETWR - Net value of the order line
item in Global currency
AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL VBAK-NETWR - Net value of the order (all
line items) in Global currency
AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_TRX VBAK-NETWR - Net value of the order (all
line items) in transaction currency
AMT_NET_VALUE_TRX VBAP-NETWR - Net value of the order line
item in transaction currency
AMT_RECEIVED_GBL Calculated field: for sales documents of
categories A or B it is 0, for sales
documents of categories H or K without
rejection reasons it is set to a negative of
the net item value, for the rest sales
documents without rejection reasons it is
the net item value - In Global Currency
AMT_RECEIVED_TRX Calculated field: for sales documents of
categories A or B it is 0, for sales
documents of categories H or K without
rejection reasons it is set to a negative of
the net item value, for the rest sales
documents without rejection reasons it is
the net item value - In Transaction Currency
AMT_STD_COST_GBL VBAP-WAVWR - Cost in transaction
currency
AMT_STD_COST_TRX VBAP-WAVWR - Cost in transaction
currency
AMT_SUBTTL_01_GBL VBAP-KZWI1 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 1
AMT_SUBTTL_01_TRX VBAP-KZWI1 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 1
32 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 33

Subject Areas
Sales Order Section
Col. Name Description
AMT_SUBTTL_02_GBL VBAP-KZWI2 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 2
AMT_SUBTTL_02_TRX VBAP-KZWI2 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 2
AMT_SUBTTL_03_GBL VBAP-KZWI3 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 3
AMT_SUBTTL_03_TRX VBAP-KZWI3 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 3
AMT_SUBTTL_04_GBL VBAP-KZWI4 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 4
AMT_SUBTTL_04_TRX VBAP-KZWI4 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 4
AMT_SUBTTL_05_GBL VBAP-KZWI5 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 5
AMT_SUBTTL_05_TRX VBAP-KZWI5 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 5
AMT_SUBTTL_06_GBL VBAP-KZWI6 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 6
AMT_SUBTTL_06_TRX VBAP-KZWI6 - Customer-configurable
subtotal 6
AMT_TRGT_GBL VBAP-ZWERT - Target value for outline
agreement in transaction currency
AMT_TRGT _TRX VBAP-ZWERT - Target value for outline
agreement in transaction currency
QTY_CONFIRM_SLSUOM VBAP-KBMENG - Cumulative confirmed
quantity in sales unit
QTY_ORDER_SLSUOM VBAP- KWMENG - Cumulative Order
Quantity in Sales Units
QTY_PRICE_UNIT VBAP-KPEIN - Condition pricing unit
QTY_RECEIVED_SLSUOM Calculated field: for sales documents of
categories A or B it is 0, for sales
documents of categories H or K without
rejection reasons it is set to a negative of
the sales qty, for the rest sales documents
without rejection reasons it is the sales qty
QTY_TRGT_SLSUOM VBAP-ZMENG - Target quantity in sales
units
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 33
Page 34

Subject Areas
3
Sales Order Section
Status fields (for the whole document and for each line item) for tracking sales
orders include:
Col. Name Description
BILL_STATUS_ID VBUP-FKSAA - Billing Status of ORder-Related
BIlling Document
BILL_STATUS_ID_HDR VBUK-FKSAK - Billing Status of ORder-Related
Billing Document (lookup)
DELIV_STATUS_ID VBUP-LFGSA - Overall Delivery Status of the
Item
DELIV_STATUS_ID_HDR VBUK-LFGSK - Overall Delivery Status of the
Item (lookup)
INCOMPLT_STATUS_ID VBUP-UVALL - General Incompletion Status of
the Item
INCOMPLT_STATUS_ID
_HDR
PROCESS_STATUS_ID VBUP-GBSTA - Overall Processing Status of the
PROCESS_STATUS_ID
_HDR
REF_STATUS_ID VBUP-RFGSA - Overall status of reference
REF_STATUS_ID_HDR VBAK-RFGSK - Total reference status of all
REJECT_STATUS_ID VBAP-ABSTA - Rejection status for SD item
REJECT_STATUS_ID_H
DR
SALES_DOC_STATUS_
KEY
VBUK-UVALL - General Incompletion Status of
the Item
SD item
VBUK-GBSTK - Overall Processing Status of the
SD item (lookup)
items
VBUK-ABSTK - Rejection status
Concatenated values of Sales Document Status
fields
Other important attributes (fields) of the SALES_ORDER_FACT table are:
Col. Name Description
CURR_ID_GBL Global Currency (Global Variable Set in Rapid
Mart Job)
CURR_ID_STATS VBAK-STWAE - Stati s tics currency
CURR_ID_TRX VBAP-WAERK - Line Item transaction currency
CURR_ID_TRX_HDR VBAK-WAERK - Document header Currency
code
34 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 35

Subject Areas
Sales Order Section
Col. Name Description
CUSTOMER_ID_BILLTO VBPA-KUNNR - Bill-to Customer Number
(lookup)
CUSTOMER_ID_SHIPTO VBPA-KUNNR - Ship-to Customer Number
(lookup)
CUSTOMER_ID_SOLD
TO
EXCH_RA TE_GBL TCURR.UKURS - Exchange rate from transaction
EXCH_RATE_STATS VBAP-STCUR - Exchange rate for statistics
EXCH_TYPE_ID_GBL Global Exchange Rate Type (Global Variable Set
EXCH_TYPE_ID_STATS VBAK.KURST - Exchange rate type
VBAK-KUNNR - Sold-to Customer Number
currency to Global Currency
(Exch.rate at time of creation)
in Rapid Mart Job)
3
SALES_TO_BASE_DIVI
SOR
SALES_TO_BASE_MUL
TIPLR
VALID_FROM_DATE VBAK-GUEBG - Valid-from date (outline
VALID_TO_DATE VBAK-GUEEN - Valid-to date (outline
VBAP-UMVKN - Denominator (divisor) for
conversion of sales qty. into Stock-keeping unit of
measure
VBAP-UMVKZ - Numerator (factor) for conversion
of sales quantity into Stock-keeping unit of
measure
agreements, product proposals)
agreements, product proposals)
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 35
Page 36

Subject Areas
3
Sales Order Section
Rapid Mart Data
The sales order section includes sales transaction detail. The
SALES_ORDER_FACT stores these details. SALES_ORDER_FACT and
associated dimensions are organized as a star schema as shown below:
36 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 37

Analysis
Subject Areas
Sales Order Section
With the tables in this section, you can analyze sales orders along several
dimensions:
• By material
• By customer
• By sales organization elements
• By order reason
• By rejection reason
• By billing or delivery blocking codes
• By various sales order statuses
• By profit center and associated hierarchy
• By various sales order operational dimensions
• By time period vs. previous period, quarter vs. previous quarter, year vs.
previous year
Typical queries include:
• What was the top selling product in the line last quarter, last year?
• Who is our top sales rep. in the company?
• What are our sales trends in this region for the last 5 years?
• How have our sales numbers per sales office changed since the sales
groups reassignments?
• How well do we honor our contract obligations?
• Who are our 10 biggest customers by bookings value?
• How do my sales vary seasonally (or quarterly)?
• Which customers are most satisfied / dissatisfied (as measured by
returns)?
• Which materials (or products) are my best sellers?
• Which products are not well received by my customers (as measured by
slow sales and high rate of returns)?
• Which factories (or plants) are processing the most bookings?
• Which operating company had the most sales this quarter? This year?
• What are the gross margins on each product line we sell?
• Which sales district generated the most bookings last year?
• Did our bookings numbers look better using last year’s sales organization
structure or this years?
• How do my bookings compare to my billings for this quarter? This year?
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 37
Page 38

Subject Areas
3
Backlog Section
Backlog Section
The backlog section stores backlog quantities for open sales orders. The
section calculates the backlog as the difference between booked quantities
and shipped quantities.
All backlog processing takes place in the Rapid Mart. It is important that Sales
Orders, Deliveries, and Billings be loaded before backlog processing, as
backlog relies on data from those subject ares.
The backlog section calculates backlog using the SALES_ORDER_FACT
and DELIVERY_FACT tables. Additionally, in the case of drop shipment or
intangible delivery orders, the backlog section also uses the BILLING_FACT
table.
For a sales order item line item, the backlog is the quantity that has not been
delivered yet (the ordered quantity less
section stores this data in the BACKLOG_FACT table.
The section uses several rules when calculating backlog:
• Includes sales orders of category 'C.'
• Excludes contracts and scheduling agreements.
• Excludes billed line items with no delivery information.
the delivered quantity.) The backlog
The Rapid Mart makes use of the fact that a delivery line item refers to
one and only one sales order line item.
Contracts are sales orders that eventually turn into category 'C' orders.
You can customize the Rapid Mart to include contracts and scheduling
agreements by allowing categories 'E' and 'G.'
Note: Drop Shipments / Intangible Deliveries
Some companies use drop shipments (third-party delivery). In this case,
a sales order line item has the “Billing Relevant” indicator set to “B” or “F”.
No Delivery document is generated in your SAP solutions system (as the
third party does that). However, an invoice is produced and backlog is
reduced by the invoice rather than the delivery.
The Billing Relevant indicator is also set to “B” or “F” in cases of an
intangible delivery. That is a delivery where no physical material is
delivered, such as when a service is purchased.
If you use drop shipments or intangible deliveries, set the
$G_DROP_SHIP global variable to “Y” (yes). The Rapid Mart will
segregate these orders and reduce backlog when invoices are generated
for these orders (ordered quantity less
invoice quantity).
38 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 39

With every incremental load, the section removes deleted or cancelled orders
from the BACKLOG_FACT table. It also removes orders that are fully
delivered and therefore no longer backlog.
As an alternative backlog calculation you can use
SALES_DOC_FLOW_VIEW. The view represents a union of
SALES_ORDER_FACT, DELIVERY_FACT, and BILLING_FACT. It has fact
table common attribute fields such as sales order number, customer id,
material id, sales document category id. In addition, it contains fact table
measurement fields, such as sales order requested quantity, net item value,
delivery quantity, billing document quantity and net item value. Aggregating
by common fields you can calculate the difference between ordered,
delivered, and billed quantities and amounts by sales order number, by
customer, by material.
Rapid Mart processing
Backlog is stored in the BACKLOG_FACT table. Which is associated with the
following dimensional attributes and dimension tables. Additionally, in the
universe, BACKLOG_FACT is joined to SALES_ORDER_FACT as both
tables have the same primary key. This allows the use of any Sales Order
dimension with Backlog.
Subject Areas
Backlog Section
3
Attribute Dimension Table Name
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Customer CUSTOMER
Material & Product
Hierarchy
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Plant PLANT
Profit Center & Hierarchy PROFIT_CENTER, PROFIT_CENTER_HIER,
Storage Location STORAGE_LOCATION
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
MA TERIAL, PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_BAD,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_VR
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 39
Page 40

Subject Areas
3
Backlog Section
Fact Table Fields
Rapid Mart data
The Backlog table includes the following measures:
Col. Name Description
QTY_BACKLOG_SLSUOM
• Regular Backlog:
SALES_ORDER_FACT.QTY_ORDER_SLSUOM DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_DELIV_SLSUOM
• Third Party (Drop Ship) Backlog:
SALES_ORDER_FACT.QTY_ORDER_SLSUOM BILLING_FACT.QTY_BILL_SLSUOM
QTY_DELIV_SLSUOM DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_DELIV_SLSUOM - Actually
QTY_ORDER_SLSUOM SALES_ORDER_FACT.QTY_ORDER_SLSUOM -
BACKLOG_FACT and associated dimensions are organized as a star
schema as shown below.
Delivered Qty
Cumulative Sales Order Qty
40 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 41

Analysis
Subject Areas
Backlog Section
With the dimensions in this section, plus sales order dimensions you can
analyze backlog along several dimensions:
• By customer
• By material
• By sales organization elements
• By period vs. previous period, quarter vs. previous quarter, year vs.
previous year
• By any sales order attribute.
Typical queries include:
• What was ordered but not delivered yet, listed by customer and product?
• What was ordered, delivered but not billed yet by plant?
• What is the gap between ordered and delivered products in this quarter?
• Which products have the greatest delivery backlog?
• Who is the most unsatisfied customer in terms of unfulfilled orders?
• Where is my greatest revenue potential as measured by backlog? By
customer? By Sales Organization? By material?
• How old is my backlog? (How long are customers waiting for delivery?)
All dimensions associated with sales orders can be used with backlog. Refer
to the Sales Order Section -Analysis in this chapter for more details.
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 41
Page 42

Subject Areas
3
Schedule Lines Section
Schedule Lines Section
The schedule lines section extracts detailed information about scheduled
deliveries for sales orders.
In SAP solutions, all sales documents have the same structure—a document
header with any number of items. The items can have any number of
schedule lines.
A schedule line contains all the data needed for a delivery. For example,
suppose a customer orders 20 units of a particular material. You enter this as
one item in the sales order. Suppose, however, that you can only deliver 15
pieces now. The customer wants the remaining 5 pieces next month. In this
case, you need to schedule two deliveries. SAP solutions stores the data for
these deliveries (dates, confirmed quantities, and so forth) in two separate
schedule lines. These schedule lines differ by delivery date and quantity.
Schedule lines can also have different control elements. For example,
material requirements planning might be completed for some schedule lines
but not other schedule lines. Similarly, schedule lines defined in a returns
document post a goods receipt, not a goods issue.
Data recorded in schedule lines includes:
• Schedule line quantity
• Schedule Line Date
• Delivery Date (also called Planned Delivery Date in SAP solutions)
• Goods Issue Date (also called Planned Goods Issue Date in SAP
solutions)
• Sales Order Create Date
• Requested Delivery Date (from the sales order)
42 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 43

Subject Areas
Schedule Lines Section
• Loading Date
• Material Available Date
• Transportation Planning Date
• Confirmed Quantity
• Order Quantity
• Rounded Quantity
• Required Quantity
For sales documents where delivery data is not relevant—for example, in
contracts, credit and debit memo requests—SAP solutions does not create
schedule lines.
The schedule lines section extracts detailed scheduled delivery information
for sales orders from SAP solutions table VBEP into the
SALES_SCHED_LINE_FACT table. This table only contains information for
relevant sales orders. Some sales documents, such as inquiries, quotations,
and contracts, do not contain delivery data, and therefore have not schedule
lines.
The section uses the same approach SAP solutions uses for handling deleted
schedule lines information. When SAP solutions removes an existing sales
order or sales order line item and all related schedule lines, the Rapid Mart
removes the corresponding records from the schedule line fact table.
This section only extracts current information. This section does not store
historical information.
The section uses an initial full load strategy, followed by subsequent
incremental (delta) loads. Only schedule lines added, changed, or deleted
since the previous Rapid Mart refresh are loaded in an incremental load.
3
Rapid Mart processing
Schedule Lines include the following dimensional attributes and associated
dimension tables:
Attribute Dimension Table Name
Delivery Block DELIVERY_BLOCK
Material & Product Hierarchy MATERIAL,
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
Material Alternate Unit of Measure MATERIAL_ALT_UOM
Material by Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Material Group MATERIAL_GROUP
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 43
Page 44

Subject Areas
3
Schedule Lines Section
Fact Table Fields
Attribute Dimension Table Name
Plant PLANT
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Unit of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
The schedule lines include the following measures:
Column Name Description
DAYS_EARLY_LATE Difference between Requested Deliv. Date
(VBAK.VDATU) and Planned Goods Issue
Date (VBEP.WADAT). A negative number
indicates Late Delivery. A positive number
indicates Early Delivery.
QTY_ADJUST_SLSUOM VBEP-CMENG - Corrected quantity in sales
unit
QTY_CONFIRM_BASEUOM Confirmed quantity in Base Units
QTY_CONFIRM_SLSUOM VBEP-BMENG - Confirmed quantity - sales
units
QTY_ORDER_BASEUOM Order quantity in Base Units
QTY_ORDER_SLSUOM VBEP-WMENG - Order quantity in sales units
These are additional important attributes for the Schedule Line:
Column Name Description
DELIV_DATE
GI_DATE
MTRL_AVAIL_DATE
RQST_DELIV_DATE
SCHED_LOAD_DATE
TRANSPORT_SCHED_DATE
Additional information on these attributes:
VBEP-EDATU - Delivery date for the
schedule line
VBEP-WADAT - Goods issue date
VBEP-MBDAT - Material availability date
VBAK-VDATU - Proposed schedule line
date
VBEP-LDDAT - Scheduled Loading date
VBEP-TDDAT - Transportation scheduling
date
• DELIV_DATE (also called Planned Delivery Date in SAP solutions)
A requested delivery date or confirmed delivery date. This is the date you
expect the customer to receive the goods.
44 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 45

Subject Areas
Schedule Lines Section
For most sales orders, SAP solutions creates schedule lines
automatically . When you enter a requested delivery date for a sales order
or a sales order line item, SAP solutions runs a material availability check
to calculate a confirmed delivery date. If the requested quantity can be
delivered on the requested date, SAP solutions creates one schedule
line. If the requested quantity cannot be delivered as requested, SAP
solutions creates multiple schedule lines. The first line contains the
requested delivery date in the DELIVERY_DATE field. Subsequent lines
have confirmed delivery dates in this field.
• GI_DATE (also called Planned Goods Issue Date in SAP solutions)
The date when the goods should leave the shipping point. Calculated by
adding loading lead time to the loading date.
• MTRL_AVAIL_DATE
The date when the goods are available and the delivery process can
begin.
• RQST_DELIV_DATE
The requested delivery date from the sales order header. This is used to
calculate the delivery date (above). It is also used in measuring how well
we are planning vs. customer requests.
• SCHED_LOAD_DATE
The date when the goods are scheduled to be loaded for transport. SAP
solutions calculates by adding the pick, pack, and stage lead times to the
material availability date.
• TRANSPORT_SCHED_DATE
The date when transportation planning is scheduled to start. Calculated
by subtracting transportation lead time from the load date.
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 45
Page 46

Subject Areas
3
Schedule Lines Section
Rapid Mart data
Analysis
SALES_SCHED_LINE_FACT and associated dimensions are organized as a
star schema as shown below
With the tables in this section, you can analyze scheduled deliveries for sales
orders along several dimensions:
• By material and its product hierarchy
• By customer
• By sales organization elements
• By time period vs. previous period, quarter vs. previous quarter, or year
vs. previous year.
Typical queries include:
• How many sales orders can not meet the customer’s requested delivery
date?
• How often do we need to schedule multiple deliveries for a single order
line item because we do not have enough quantity in stock to satisfy the
demand?
• How well are we planning to meet customer requested delivery date?
• When are our deliveries scheduled? (By month, quarter, or year)
• What are our average days early (or late) meeting customer requested
delivery dates?
46 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 47

Delivery Section
This section extracts information about deliveries, return deliveries,
shipments, and shipping notifications from SAP solutions.
Creating the delivery document signals the start of the shipping activities for
the sales order. It is the electronic means to manage all the activities of
delivery processing, including picking product, packing, planning and
monitoring shipments, preparing shipping papers, and goods issue
documents.
Delivery includes several shipping processes that take place within the plant.
When the product is available and ready to be processed in the warehouse, a
shipping scheduler creates a delivery document so that the warehouse can
efficiently pick, stage, and release (goods issue) the product to the customer.
When creating a delivery document that references a sales order, SAP
solutions copies critical shipping information from the sales order into the
delivery document. SAP solutions can overwrite some of this information
(such as quantities to deliver) on a particular delivery document.
The delivery section extracts delivery information from the SAP solutions
tables at the header (Table LIKP) and line-item levels (table LIPS). The
section stores the extracted data in a fact table called DELIVERY_FACT. The
section extracts all categories of delivery documents, including delivery,
returns delivery, shipment, and shipping notification. The section stores the
latest version of each delivery. This section does not store the history of data
changes to deliveries.
The Rapid Mart has an initial (first) load and an incremental (delta) load.
Unlike the Sales Orders section, this load does not use a Stage table. Both
the initial and incremental loads are direct to the Delivery Fact table.
Note: This section follows the convention of SAP solutions for handling
deleted delivery information. Existing deliveries or delivery line items that are
deleted within SAP solutions are also removed from the delivery fact table.
Note: The Rapid Mart does not maintain global currency values for
deliveries. However, the SAP BusinessObjects Universe calculates global
currency values using the exchange rates from the associated sales order.
Subject Areas
Delivery Section
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 47
Page 48

Subject Areas
3
Delivery Section
Rapid Mart processing
Deliveries include the following dimensional attributes and associated
dimension tables.
Attribute Name Dimension Table
Billing Block BILLING_BLOCK
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Credit Control Area CREDIT_CONTROL_AREA
Credit Mgmt Risk Class CREDIT_MGMT_RISK_CLASS
Monetary Currency CURRENCY
Customer CUSTOMER
Customer Group CUSTOMER_GROUP
Delivery Block DELIVERY_BLOCK
Delivery Priority DELIVERY_PRIORITY
Delivery Route DELIVERY_ROUTE
Delivery Status DELIVERY_STATUS
Distribution Channel DISTRIBUTION_CHANNEL
Division DIVISION
Document Category DOCUMENT_CATEGORY
Document Type DOCUMENT_TYPE &
Inter Company Terms INTER_COMPANY_TERM01
Material & Product Hierarchy MATERIAL,
Material Alternative Unit of Measure MATERIAL_ALT_UOM
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Material Group MATERIAL_GROUP
Plant PLANT
Pricing Procedure (Horizontal &
Vertical)
DOCUMENT_CATEGORY
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
PRICING_PROCEDURE_VR,
PRICING_PROCEDURE_HZ
48 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 49

Attribute Name Dimension Table
Profit Center & Hierarchy PROFIT_CENTER,
Sales Group SALES_GROUP
Sales Office SALES_OFFICE
Sales Organization & Sales
Organization Hierarchy
Shipping Point SHIPPING_POINT
Storage Location STORAGE_LOCATION
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
Fact Table Fields
Deliveries contain the following measures:
Column Name Description
AMT_STD_COST_TRX LIPS-WAVWR - Cost in Document
AMT_SUBTTL_01_TRX LIPS-KZWI1 - Customer-
AMT_SUBTTL_02_TRX LIPS-KZWI2 - Customer-
AMT_SUBTTL_03_TRX LIPS-KZWI3 - Customer-
AMT_SUBTTL_04_TRX LIPS-KZWI4 - Customer-
AMT_SUBTTL_05_TRX LIPS-KZWI5 - Customer-
AMT_SUBTTL_06_TRX LIPS-KZWI6 - Customer-
QTY_DELIV_BASEUOM LIPS-LGMNG - Actual Quantity
QTY_DELIV_SLSUOM LIPS-LFIMG - Actual Quantity
QTY_GROSS_WEIGHT LIPS-BRGEW - Gross weight
Subject Areas
Delivery Section
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_BAD,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_V
SALES_ORGANIZATION &
SALES_ORGANIZATION_HIER
Currency
Configurable Subtotal 1
Configurable Subtotal 2
Configurable Subtotal 3
Configurable Subtotal 4
Configurable Subtotal 5
Configurable Subtotal 6
Delivered (in Base Units)
Delivered (in Sales Units)
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 49
Page 50

Subject Areas
3
Delivery Section
Column Name Description
QTY_NET_WEIGHT LIPS-NTGEW - Net weight
QTY_VOLUME LIPS-VOLUM - Volume
Note: AMT_SUBTTL_01_TRX - AMT_SUBTTL_06_TRX: These
subtotals (in sales document currency) contain the values of certain
pricing conditions used in a specific pricing procedure. T ypically, Subtotal
1 is the List Price. Price calculation in SAP solutions depends on various
factors such as:
• Customer
• Sales order type
• Sales organization
• Quantity
Each delivery can have its own definition for what is contained in subtotal
1-6 fields. The descriptions of these fields are in the Pricing Procedure
tables.
Additional important fields in the DELIVERY_FACT table are:
Column Name Description
Status Columns
Val u es:
• Blank = Not Applicable
• A = Not yet processed
• B = Partially processed
• C = Completely Processed
BILL_STATUS_DELIV_RELTD_ID VBUP-FKSTA - Billing Status of
Delivery-Related Billing Documents
DELIV_STATUS_KEY Concatenated values of Sales
Document Status fields
GI_STATUS_ID VBUP-WBSTA - Goods Issue status
(indicates whether goods have left the
warehouse)
PACKNG_STATUS_ID VBUP-PKSTA - Packing status
PICKNG_CONFIRM_STATUS_ID VBUP.KOQUA - Picking confirmation
status
PICKNG_STATUS_ID VBUP-KOSTA - Picking Status
PROCESS_STATUS_ID VBUP-GBSTA - Overall processing
status of the SD document item
Date/Day Columns
50 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 51

Subject Areas
Delivery Section
Column Name Description
ACTL_GI_DA TE LIKP.WADAT_IST - Actual Goods Issue
Date. The date the goods actually left
the shipping point.
DAYS_FIXED_PROCESS LIPS-VBEAF - Fixed Shipping
Processing Time in Days (setup time).
This field contains a fixed shipping
processing time in days. This time is
needed in shipping to process a specific
quantity of a material in base units. An
example is the time required to load a
van that transports the material to a
customer
DAYS_SHIP_PROCESS LIPS-VBEAV - Variable Shipping
Processing Time in Days. This field
contains the processing time in days for
shipping a particular quantity of an item.
It is used for capacity planning for
deliveries. Formula:
Confirmed_Qty x Processing_Time /
BASE_QTY
DELIV_DATE LIKP-LFDAT - Delivery Date. The date
by which the delivery should be
received by the customer.
DELIV_LOAD_DATE LIKP-LDDAT - Loading Date. The date
by which picking and packing must be
completed so that the goods are ready
for loading and for the delivery to the
customer
MTRL_AVAIL_DATE LIPS-MBDAT - Material Availability
Date. The date by which sufficient
quantities of the item must be available
for picking to begin
PICKNG_DATE LIKP-KODAT - Picking Date. The date
by which picking must begin for the
delivery item to reach the customer on
time.
PLAN_GI_DATE LIKP-WADAT - Planned Goods Issue
Date. The date on which the goods
must physically leave the shipping point
to reach the customer on time.
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 51
Page 52

Subject Areas
3
Delivery Section
Rapid Mart data
The Delivery Fact and its associated dimensions form a Star Schema as
shown below:
Analysis
With the tables in this section, you can analyze deliveries along several
dimensions:
• By material
• By customer
• By sales organization elements
• By region
• By plant
• By billing or delivery blocking codes
• By delivery priority
52 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 53

Subject Areas
Delivery Section
Typical queries include:
• Which customers did not receive deliveries on the requested date?
• What is the average delivery time by product, by customer?
• How big are my shipments in terms of volume and weight monthly?
• What is the value of my deliveries, in global currency or document
currency?
• How long between planned goods issue and actual goods issue?
• Which deliveries are in process right now?
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 53
Page 54

Subject Areas
3
Billing Section
Billing Section
The billing section extracts billing information from SAP solutions. The section
extracts information about invoices, pro forma invoices, credit memos, and
debit memos.
After a material is shipped, an invoice is sent to the customer and a billing
document is created. In the SD module, order processing ends with billing.
SAP solutions creates a billing document by copying billing information from
the sales order and/or delivery document. For example, copied information
includes the name of the business partner who receives and verifies the
invoice address, the name of the business partner who pays the invoice, the
address and payment terms, and material and delivered quantity. SAP
solutions can overwrite some of the copied data, such as price and quantity,
for a particular billing document.
Typically, when creating a billing document, SAP solutions automatically
updates general ledger accounts. For example, SAP solutions debits the
customer receivable account and credits the revenue account.
The billing section extracts billing information from SAP solutions at header
(table VBRK) and line item level (table VBRP). The section stores the
extracted data in a fact table called BILLING_FACT.
The section extracts all categories of billing documents, including invoices,
credit and debit memos, pro-forma items, intercompany invoices, and
intercompany credit memos. It also captures any cancellation documents
such as a cancelled credit memo or invoice. The section stores the latest
version of each billing document. The section does not store changes as a
billing document history.
Billings have an initial full load where all billing records are transferred from
SAP solutions. Subsequent loads are incremental (Delta) loads where only
changed, or cancelled billing documents are loaded into the Rapid Mart.
Like sales orders, billings are first loaded to a BILLING_STAGE table. Here
transforms such as the lookup of Global Currency exchange rates occur.
Once the staging table is fully updated, these changes are validated using a
Validation transform in the Rapid Mart. Rows that do not validate are written
to the BAD_BILLING_FACT table. Rows that do pass validation update the
BILLING_FACT table. See the Document Validation Section later in this
chapter for more details.
54 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 55

Rapid Mart processing
Billings include the following dimensional attributes and associated dimension
tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Credit Control Area CREDIT_CONTROL_AREA
Monetary Currency CURRENCY
Customer CUSTOMER
Customer Group CUSTOMER_GROUP
Distribution Channel DISTRIBUTION_CHANNEL
Division DIVISION
Document Category DOCUMENT_CATEGORY
Document Type DOCUMENT_TYPE &
Fiscal Period FISC_PERIOD
Inter Company Terms INTER_COMPANY_TERM01
Material & Product Hierarchy MATERIAL,
Material Alternative Unit of Measure MATERIAL_ALT_UOM
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Material Group MATERIAL_GROUP
Payment Term PAYMENT_TERM
Plant PLANT
Pricing Procedure PRICING_PROCEDURE_HZ,
Profit Center & Hierarchy PROFIT_CENTER,
Sales Document Status SALES_DOC_STATUS
Sales Group SALES_GROUP
Sales Office SALES_OFFICE
Subject Areas
Billing Section
DOCUMENT_CATEGORY
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
PRICING_PROCEDURE_VR
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_BAD,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_V
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 55
Page 56

Subject Areas
3
Billing Section
Fact Table Fields
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Sales Organization & Sales
Organization Hierarchy
Shipping Point SHIPPING_POINT
Storage Location STORAGE_LOCATION
Time Dim TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
Billings contain the following measures:
Column Name Description
AMT_NET_VALUE_GBL VBRP-NETWR - Net Value (Global
Currency)
AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL Net value in document currency (Global
Currency)
AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_TRX VBRK-NETWR - Net Value of the billing
document in Document Currency
AMT_NET_VALUE_TRX VBRP-NETWR - Net value of the line item
in document currency
AMT_REVENUE_GBL Calculated field (Global Currency): for sales
documents of categories U or 5 or 6 it 0, for
sales documents of categories N or O it set
to a negative of the net item value, for the
rest sales documents it the net item value
AMT_REVENUE_TRX Calculated field: for sales documents of
categories U or 5 or 6 it 0, for sales
documents of categories N or O it set to a
negative of the net item value, for the rest
sales documents it the net item value
AMT_STD_COST_GBL VBRP-WAVWR - Cost in Global Currency
AMT_STD_COST_TRX VBRP-WAVWR - Cost in Document
Currency
AMT_SUBTTL_01_GBL VBRP-KZWI1 - Customer Configurable
Subtotal 1 (Global Currency)
AMT_SUBTTL_01_TRX VBRP-KZWI1 - Customer-Configurable
Subtotal 1
SALES_ORGANIZATION &
SALES_ORGANIZATION_HIER
56 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 57

Subject Areas
Billing Section
Column Name Description
AMT_SUBTTL_02_GBL VBRP-KZWI2 - Customer Configurable
Subtotal 2 (Global Currency)
AMT_SUBTTL_02_TRX VBRP-KZWI2 - Customer-Configurable
Subtotal 2
AMT_SUBTTL_03_GBL VBRP-KZWI3 - Customer Configurable
Subtotal (Global Currency)
AMT_SUBTTL_03_TRX VBRP-KZWI3 - Customer-Configurable
Subtotal 3
AMT_SUBTTL_04_GBL VBRP-KZWI4 - Customer Configurable
Subtotal 4 (Global Currency)
AMT_SUBTTL_04_TRX VBRP-KZWI4 - Customer-Configurable
Subtotal 4
AMT_SUBTTL_05_GBL VBRP-KZWI5 - Customer Configurable
Subtotal 5 (Global Currency)
AMT_SUBTTL_05_TRX VBRP-KZWI5 - Customer-Configurable
Subtotal 5
AMT_SUBTTL_06_GBL VBRP-KZWI6 - Customer Configurable
Subtotal 6 (Global Currency)
AMT_SUBTTL_06_TRX VBRP-KZWI6 - Customer-Configurable
Subtotal 6
QTY_BILL_SLSUOM Calculated field = QTY_BILL_STOCKUOM
X SALES_TO_BASE_DIVISOR /
SALES_TO_BASE_MULTIPLR
QTY_BILL_STOCKUOM VBRP-FKLMG - Billing Qty in Stock-
keeping Unit of Measure
3
Note: AMT_SUBTTL_01_TRX - AMT_SUBTTL_06_TRX and
AMT_SUBTTL_01_GBL- AMT_SUBTTL_06_GBL: These subtotals (in
transaction or global currency) contain the values of certain pricing
conditions used in a specific pricing procedure. Typically, Subtotal 1 is the
List Price. Price calculation in SAP solutions depends on various factors
such as:
• Customer
• Sales order type
• Sales organization
• Quantity
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 57
Page 58

Subject Areas
3
Billing Section
Each billing can have its own definition for what is contained in subtotal 16 fields. The descriptions of these fields are in the Pricing Procedure
tables.
Additional important fields in the BILLING_FACT table are:
Column Name Description
BILL_DATE VBRK.FKDAT - Billing Date or Invoice Date.
BILL_DOC_ID_CANCEL VBRK-SFAKN - Cancelled billing document
number. This field references either an invoice, a
credit memo, or a credit memo list that has been
cancelled by the current billing document. This
field is only populated for billing documents of
type cancellation,
DOC_CANCEL_FLAG Calculated field - If the Billing document line item
is cancelled it is set to “1”
PROCESS_STATUS_ID VBUP-GBSTA - Overall Processing S tatus of the
SD item. This field allows you to monitor whether
a line item is open, being processed, or
complete.
REF_DOC_ID VBRP-VGBEL - Document number of the
reference document (allows you to monitor a
referenced delivery.)
REF_LINE_ITEM_ID VBRP-VGPOS - Item number of the reference
item (allows you to monitor a referenced
delivery.)
58 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 59

Rapid Mart data
The following diagram shows the billing tables organized as a star schema.
Subject Areas
Billing Section
3
Analysis
With the tables in this section, you can analyze billing documents along
several dimensions:
• By material
• By customer
• By payer (can be different from Customer who placed a sales order)
• By sales organization elements
• By plant
• By billing document type
• By period vs. previous period, quarter vs. previous quarter, year vs.
previous year via Fiscal Period Dimension
• By period vs. previous period, quarter vs. previous quarter, year vs.
previous year via Time Dimension
Typical queries include:
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 59
Page 60

Subject Areas
3
Billing Section
•
What is the average time between booking a sales order and issuing a
bill by customer and product?
• What are discount/margin trends by customer and product?
• What is the company revenue by month, quarter, and year?
• What is the difference between bookings and expected revenue?
• What are my gross margins? By material? By factory (plant)?
• Which customers have the most credit memos?
• What are billings by company code? By Sales Office?
• How do foreign currency exchange variances affect the bottom line?
• Are there seasonal variations in my revenue (Billings) flow?
• Who are my top 10 customers by revenue (Billings generated)?
60 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 61

Sales Order History Preservation Section
Sales Order History Preservation Section
The sales order history preservation section tracks changes to sales orders.
By using this section, you can avoid querying SAP solutions’s transaction log
tables (CDHDR - the change document header table and CDPOS - the
change line item table) to determine changes. In most cases, querying SAP
solutions transaction logs is very resource intensive. Therefore, most SAP
solutions sites avoid such queries.
All Sales Order History Preservation processing takes place in the Rapid
Mart.
The sales order history preservation section extracts changes to a sales order
and stores the changes in the SALES_ORDER_HISTORY table. In p articular ,
the section stores these changes:
• A sales order (or a sales order line item) is deleted and the requested
quantity of the deleted line items and their net value become 0.
• The quantity of a sales order line item is increased or reduced.
• The line item net value is increased or reduced.
There are limitations to the captured changes:
• When multiple changes occur in the same field of a sales order between
two incremental loads, the Rapid Mart only captures the net effect of all
the changes.
• The Rapid Mart does not detect deleted line items for free goods (goods
with a net item value of 0) because the SAP solutions sales order header
table does not change when such line items are deleted.
• The Rapid Mart does not capture sales orders that are created and
deleted between two incremental loads.
See Chapter 8: Sales order history preservation section for more details
about how the section captures changes.
Subject Areas
3
Rapid Mart processing
Sales Order History includes the following dimensional attributes and
associated dimension tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Table
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Currency CURRENCY
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 61
Page 62

Subject Areas
3
Sales Order History Preservation Section
Attribute Name Dimension Table
Customer CUSTOMER
Plant PLANT
Profit Center & Hierarchy PROFIT_CENTER,
Sales Organization SALES_ORGANIZATION
Sales Person SALES_PERSON
Storage Location STORAGE_LOCATION
Time Dim TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
Fact table fields
Sales Order History contains the following measures:
Column Name Description
AMT_NET_VALUE_DELTA_TRX Calculated change in net item value
AMT_NET_VALUE_TRX VBAP-NETWR - Net Value of the Order
QTY_ORDER_DELTA_SLSUOM Calculated change in quantity since last
QTY_ORDER_SLSUOM VBAP- KWMENG - Cumulative Order
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_BAD,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_V
since last run. (A negative number
indicates a decrease in net value)
Line Item in Document Currency for
validity dates shown on this record. This
is set to zero on a deleted record.
run. (A negative number indicates the
quantity decreased on the sales order.)
Quantity In Sales Units for validity dates
shown on this record. This is set to zero
on a deleted record.
62 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 63

Subject Areas
Sales Order History Preservation Section
Additional important fields in Sales Order History are:
Column Name Description
CURRENT_FLAG C = Current version, H = Historical version (older
version)
SURROGATE_KEY_ID A surrogate primary key generated by Data
Services. (The natural primary key would be
composed of the SALES_ORDER_NUMBER,
SALES_LINE_ITEM_ID, and
VALID_FROM_DATE columns.)
VALID_FROM_DATE Calculated date - Starting Validity Date for this
Record
VALID_TO_DATE Calculated date - Ending Validity Date for this
Record
Example: history for a sales order: Original order is for 10 items at 10.00
each. (Total net value 100.00.) This is followed by a change in quantity, then a
change in price, and finally order cancellation.
3
Surrogate
Key Id
1 H 01-Jan-
2 H 04-Jan-
3 H 10-Jan-
4 C 17-Jan-
Current
Flag
Valid
From
Date
2009
2009
2009
2009
The initialization values of these fields in the First Load (or for the new rows in
incremental load) is configured with the $G_INIT_HIST_CHG global variable:
they can be set to 0 if you want to be able to sum and obtain the total changes
made to the orders, or they can be set to the values of the
QTY_RECEIVED_SLSUOM and AMT_RECEIVED_TRX fields if you want to
obtain the current values by summing.
See Chapter 8: Sales order history preservation section for details about how
this global variable is used.
Valid To
Date
03-Jan2009
09-Jan2009
16-Jan2009
31-Dec9999
Qty
Order
Slsuom
Amt
Net
Value
Trx
10 100.00 10 100.00 Original Order
7 70.00 -3 -30.00 Quantity Decreased by 3
7 84.00 0 14.00 Price Increased by 2.00
0 0.00 -7 -84.00 Order Cancelled
Qty
Order
Delta
Slsuom
Amt Net
Value
Delta
Trx
Comment
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 63
Page 64

Subject Areas
3
Sales Order History Preservation Section
Rapid Mart data
The sales order history preservation section complements the sales order
section with an additional fact table as shown below:
Analysis
You can analyze deleted or changed sales orders along several dimensions:
• By customer
• By sales organization
• By sales person
• By time period vs. previous period, quarter vs. previous quarter, or year
vs. previous year
64 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 65

Subject Areas
Sales Order History Preservation Section
Typical queries posed with the Sales Order History table include:
• How many sales orders or line items have been deleted per customer?
• Which sales person has the most sales orders or line items deleted?
• What would our revenue have been if all deleted sales orders and line
items had been delivered and the quantities of other orders and line items
had not been reduced?
• Which time periods show the most deleted sales orders?
• Which companies or plants are most affected by order changes and
deletions?
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 65
Page 66

Subject Areas
3
Document Flow Section
Document Flow Section
The Document Flow is a view (SALES_DOC_FLOW_VIEW) in the Rapid
Mart database creates a union of information from Sales Orders, Deliveries,
and Billings. This section allows you to see query related sales order , delivery
and billing documents. You can see the entire order fulfillment lifecycle.
This view has fact tables common attribute fields such as sales order number,
customer id, material id, sales document category id. In addition, it contains
fact table measurement fields, such as sales order requested quantity, net
item value, delivery quantity, billing document quantity and net item value.
Aggregating by common fields you can trace sales orders history. For
example what quantities and amounts were delivered and billed for each
sales order. All Document Flow processing takes place in the Rapid Mart.
The Rapid Mart simply contains a database view that creates a union of the 3
fact tables (SALES_ORDER_FACT, DELIVERY_FACT, & BILLING_FACT)
together. The join is on the Sales Order Number and Sales Order Line Item.
These two fields are the primary key to the Sales Orders Fact, and are foreign
keys in Delivery Fact and Billing Fact.
Rapid Mart Processing
Document Flow includes the following dimensional attributes and associated
dimension tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Currency CURRENCY
Customer CUSTOMER
Distribution Channel DISTRIBUTION_CHANNEL
Division DIVISION
Document Category DOCUMENT_CATEGORY
Material MATERIAL
Material Alternative Unit of Measure MATERIAL_ALT_UOM
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Plant PLANT
66 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 67

View Fields
Subject Areas
Document Flow Section
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Profit Center & Hierarchy PROFIT_CENTER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_BAD,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_V
Sales District SALES_DISTRICT
Sales Group SALES_GROUP
Sales Office SALES_OFFICE
Sales Organization & Hierarchy SALES_ORGANIZATION,
SALES_ORGANIZATION_HIER
Sales Person SALES_PERSON
Storage Location STORAGE_LOCATION
The Document Flow View contains the following measures:
Col. Name Description
AMT_BILL_NET_VALUE_GBL Net value (Global Currency)
AMT_BILL_NET_VALUE_TRX Net value in document currency
AMT_BILL_REVENUE_GBL Calculated field: for sales
documents of categories U or 5 or 6
it is 0, for sales documents of
categories N or O it is set to a
negative of the net item value, for
the rest sales documents it is the net
item value - Global Currency
AMT_BILL_REVENUE_TRX Calculated field: for sales
documents of categories U or 5 or 6
it is 0, for sales documents of
categories N or O it is set to a
negative of the net item value, for
the rest sales documents it is the net
item value - Transaction Currency
AMT_SALES_NET_VALUE_GBL Net value in Global currency
AMT_SALES_NET_VALUE_TRX Net value in document currency
3
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 67
Page 68

Subject Areas
3
Document Flow Section
Col. Name Description
AMT_SALES_RECEIVED_GBL Calculated field: for sales
documents of categories A or B it is
0, for sales documents of categories
H or K without rejection reasons it is
set to a negative of the net item
value, for the rest sales documents
without rejection reasons it is the net
item value - Global Currency
AMT_SALES_RECEIVED_TRX Calculated field: for sales
documents of categories A or B it is
0, for sales documents of categories
H or K without rejection reasons it is
set to a negative of the net item
value, for the rest sales documents
without rejection reasons it is the net
item value - Transaction Currency
QTY_BILL_SLSUOM Calculated field as QTY_INVOICED
* SLS_TO_BASE_DIVISOR /
SLS_TO_BASE_NUMERATOR
QTY_DELIV_SLSUOM LIPS-LFIMG - Actual Quantity
Delivered (in Sales Units)
QTY_ORDER_SLSUOM Cumulative Order Quantity in Sales
Units
68 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 69

Rapid Mart Data
The Document Flow Union View links the Sales Orders, Deliveries, and
Billings as shown below
Subject Areas
Document Flow Section
3
Analysis
Document Flow allows you analyze along several dimensions:
• By bill-to, ship-to, or sold-to customer
• By sales order create date
• By sales organization attributes
• By material and factory attributes
• By financial organization attributes.
• By sales organization attributes
• By Profit center and hierarchy
Typical queries on document flow include:
• How many deliveries were issued for this sales order?
• What is the average number of deliveries for a sales order?
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 69
Page 70

Subject Areas
3
On Time Delivery Section
•
Which sales orders are delivered, but not yet invoiced?
• What is the value of deliveries or billings vs. the booked value of the sales
orders?
On Time Delivery Section
This section uses information derived from the Schedule Lines and Deliveries
sections described earlier in this chapter. On Time Delivery allows you to
track how well you are delivering to schedule by calculating the days a
delivery is early or late.
On Time Delivery focuses on a subset of Schedule Line and Delivery
information. The idea is focus on the deliveries that are due in the near future
or near past. The default range is 15 days past and 15 days future. The range
is configured with global variable $G_ONTIME_DELIV_WINDOW.
On Time Delivery also has a history table that keeps a copy of all previous
runs. This allows you to see how delivery schedules have changed over time.
Example:
your current snapshot of On Time Delivery shows a sales order delivered
on schedule. But when you examine the history table you find the sales
order was rescheduled several times over a period of weeks and was
originally planned to be delivered weeks earlier. By this measure the
delivery is late.
All On Time Delivery processing occurs in the Rapid Mart. Sales Orders,
Schedule Lines, and Deliveries must be loaded before On Time Delivery
processing can occur. Data from the Schedule Lines is merged with data from
the deliveries. The delivery quantity is allocated to the schedule line.
When there is more than one schedule line or more than one delivery (or
both) for an item, we distribute the total delivered quantity for the item across
the schedule lines. The earliest schedule line is assigned the quantity from
the earliest delivery.
Example:
A sales order item has three schedule lines, each with an order quantity
of 50 pieces. You make two deliveries: the first for 20 pieces, the second
for 60 pieces.
The delivered quantity allocated to the first schedule line is 50 pieces (20
from the first delivery and 30 from the second delivery). This leaves 30
pieces remaining on the second delivery , which is a llocated to the second
schedule line. The allocation quantity for the third schedule line is zero.
70 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 71

Subject Areas
On Time Delivery Section
If you delete the first delivery (20 pieces), the delivered quantity for this
schedule line is still 50 pieces, but now this allocated from the second
delivery. There are still 10 pieces available on the second delivery to
further allocate. The system allocates the remaining 10 pieces to the next
schedule line. The third schedule, still has zero allocated.
The tables below illustrate this example:
With Both Deliveries:
3
Sched
Line
Number
First Delivery
Second Delivery
Delivery
Number
1 1 50 20 20
2 1 50 20 0
3 1 50 20 0
1 2 50 60 30
2 2 50 60 30
3 2 50 60 0
Sched
Line Qty
Delivery
Qty
With First Delivery Deleted:
Sched
Line
Number
Second Delivery Only
1 2 50 60 50
2 2 50 60 10
3 2 50 60 0
Delivery
Number
Sched
Line Qty
Delivery
Qty
Allocated
Delivery
Qty
Allocated
Delivery
Qty
The Rapid Mart also calculates if a delivery is on time, late, or early. The
formula uses the Planned Goods Issue Date from the Schedule Line and the
Actual Goods Issue Date from the Delivery. These correspond to the SAP
solutions fields VBEP.WADAT and LIKP.WADAT_IST, respectively. If the
Planned Goods Issue Date is in the past and there is no Delivery, we use the
current system date instead to the Actual Goods Issue Date.
The formula is:
Days Early or Late =
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 71
Page 72

Subject Areas
3
On Time Delivery Section
Planned Goods Issue Date - Actual Goods Issue Date
A late delivery will be a negative number, and an early delivery will be a
positive number. Zero indicates an on time delivery.
Each schedule line is also assigned a delivery status based on these two
dates.
• EARLY - The Actual Goods Issue Date is before the Planned Goods
Issue Date
• ON TIME - Actual Goods Issue Date and Planned Goods Issue Date are
the same
• LATE - Actual Goods Issue Date is after the Planned Goods Issue Date
• DND - (Did Not Deliver) Planned Goods Issue Date is in the Past and
there is no Delivery. This is a missed delivery.
• N/A - (Not Applicable) Planned Goods Issue Date is in the future and
there is no Delivery. No delivery is due yet
The Rapid Mart also relies on a global variable that sets the date range
window. The default setting is 15 days. This tells the system to look only at
schedule lines that have a Planned Goods Issue Date 15 days in the past or
future from today . This allows you to focus on the immediate deliveries due or
past due. This date range is expandable, but keep in mind that the loading job
will run longer as the window expands.
The final feature in On Time Delivery is the ability to focus on changes
between runs. The Rapid Mart initially loads data to a staging table and
compares this stage table to the results of the last run. A change status is
assigned by doing this comparison:
• NEW - The schedule line / delivery combination was not included in the
previous run, but is in the current run. This may be because the record is
new in the SAP solutions system or because, until now, the Planned
Goods Issue Date was outside the date range set by the global variable.
On the very first run of On Time Delivery all records will be assigned
status “NEW”.
• CHANGE - The schedule line / delivery information has changed since
the previous run. A change in any of the fields in the On Time Delivery
fact table when compared to the previous run will generate this change
status.
• NO CHANGE - The schedule line / delivery information has not changed
since the previous run.
• DELETED - The schedule line / delivery combination was in the previous
run, but not the current run. This may be because of physical deletion of
records in SAP solutions, or because the Planned Goods Issue Date has
changed and is now outside the date range set by the global variable.
72 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 73

Rapid Mart Processing
On Time Delivery has two fact tables.
• ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT - A picture of the current delivery status
within the On Time Delivery window.
• ONTIME_DELIVERY_HISTORY - Historical snapshots of previous runs
of On Time Delivery. The contents of ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT are
appended to ONTIME_DELIVERY_HISTORY before each refresh of the
data.
On Time Delivery & On Time Delivery History include the following
dimensional attributes and associated dimension tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Monetary Currency CURRENCY
Customer CUSTOMER
Delivery Block DELIVERY_BLOCK
Distribution Channel DISTRIBUTION_CHANNEL
Division DIVISION
Inter Company Terms INTER_COMPANY_TERM01
Material & Product Hierarchy MATERIAL,
Material Alternative Unit of Measure MATERIAL_ALT_UOM
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Plant PLANT
Sales Office SALES_OFFICE
Sales Organization SALES_ORGANIZATION
Sales Person SALES_PERSON
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
On Time Delivery Section
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
Subject Areas
3
On Time Delivery and On Time Delivery History contain the following
Measures
Column Name Description
AMT_NET_PRICE_GBL VBAP-NETPR - Net Price
AMT_NET_PRICE_TRX VBAP-NETPR - Net Price
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 73
Page 74

Subject Areas
3
On Time Delivery Section
Column Name Description
DAYS_EARLY_LATE Calculated - difference between
Sched. Goods Issue Date and
Actual Goods Issue Date. A positive
number indicates an early delivery.
A negative number indicates a late
delivery.
QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM Calculated - Sched Line Quantity
allocated to the Delivery
QTY_DELIV_SLSUOM LIPS-LFIMG - Actual Quantity
Delivered (in Sales Units)
QTY_ORDER_SLSUOM VBAP- KWMENG - Cumulative
Order Quantity in Sales Units
QTY_SCHED_CONFIRM_SLSUOM Schedule line confirmed quantity
74 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 75

Rapid Mart data
The On Time Delivery section is composed of two fact tables
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT and ONTIME_DELIVERY_HISTORY. There is
also a staging table called ONTIME_DELIVERY_STAGE. The fact tables
share the same set of dimensions. They are organized as a star schema as
shown below:
Subject Areas
On Time Delivery Section
3
Analysis
With the tables in this section, you can analyze billing documents along
several dimensions
• By Material
• By Plant
• By Division, Distribution Channel, or Sales Organization
• By Sales Person
• By Inter-Company Terms
Typical queries include:
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 75
Page 76

Subject Areas
3
Document Validation Section
•
How is my On Time delivery performance?
• Are we meeting delivery schedules?
• Which customers are getting the most late deliveries?
• Which plants are producing the most late deliveries?
• Which plants are delivering early? (may indicate unused capacity).
• What sales orders must I prepare to ship in the next week? Month?
• Which sales orders need to be expedited because they did not ship as
scheduled?
Document Validation Section
The Data Services load job validates that sales orders and billings meet
certain validation criteria. The Rapid Mart validates both sales orders and
billings for accurate exchange rates and conversion of monetary values to
global currency. Invalid records are not loaded into the Sales Orders Fact or
Billing Fact tables. Instead, they are loaded to two special tables that can be
queried in the SAP BusinessObjects Universe. You must make corrections to
the sales order or billings in SAP solutions and then re-load the Rapid Mart
with the corrected records. All validation occurs in the Rapid Mart.
The Rapid Mart uses the Data Services validation transform to check that
documents in the BILLING_STAGE and SALES_ORDER_STAGE tables
have correct global currency and exchange rates. Documents passing this
check are loaded to the BILLING_FACT and SALES_ORDER_FACT tables.
Documents failing this check are loaded to the BILLING_FACT_BAD and
SALES_ORDER_FACT_BAD instead.
Rapid Mart Processing
The Rapid Mart data consists of two tables
• SALES_ORDER_FACT_BAD
• BILLING_FACT_BAD
They have these associated dimensions
Attribute Table Names
Customer CUSTOMER
Material MATERIAL
Plant PLANT
76 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 77

Attribute Table Names
Sales Organization SALES_ORGANIZATION
Division DIVISION
Distribution Channel DISTRIBUTION_CHANNEL
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Fact Table Fields
SALES_ORDER_FACT_BAD and BILLNG_FACT_BAD tables are almost
identical to the SALES_ORDER_FACT and BILLING_FACT tables.
The differences are:
Subject Areas
Document Validation Section
• They each include two additional fields:
• ETL_ERROR_ACTN - An error message describing the why the
validation failed
• ETL_ERROR_COLUMN - Lists the column names that caused
validation to fail
• The primary keys also includes the LOAD_DATE (includes load date
and timestamp). This allows multiple versions of the invalid
documents can be loaded and gives you an audit trail of how often
the same document has failed validation.
3
Rapid Mart Data
The Validation tables for Sales Orders and Billings can be organized as star
schemas with the same dimensions as the Sales Order Fact and Billing Fact
tables:
“Rapid Mart Data” on page 36 for Sales Orders
“Rapid Mart data” on page 59 for Billings.
Analysis
You can analyze the invalid documents by several dimensions.
• By Material and Product Hierarchy
• By Plant
• By Sales Organization, Division, Distribution Channel
• By Document (or Transaction) Currency
• By Global Currency
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 77
Page 78

Subject Areas
3
Document Validation Section
Typical queries include:
• Which sales orders and billings failed validation?
• What errors caused the validation to fail?
• Which fields caused the validation to fail?
78 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 79

SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Reports
chapter
Page 80

Reports
4
Overview
Overview
You can use the SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions to produce many kinds of reports. This chapter provides examples
of reports you could generate using the Sales Rapid Mart universe. The
information in this chapter is useful for those who design reporting solutions
for Sales Analysis.
This chapter provides reports and the recommended joins for each section in
the Rapid Mart:
• Sales Orders
• Deliveries and On-Time Delivery
• Billing
• Backlog
• Schedule Lines
• Sales Order History
• Document Flow
• Invalid Documents
• SAP Master Data Reports
Note that all report SQL is located in the Rapid Mart installation directory
under "\Sample\DML".
Sales Orders
The sales order section captures sales orders, returns, credit and debit memo
requests, and pre-sales documents, such as quotes, inquiries, contracts, and
scheduling agreements.
Reports
Using the sales order information, you can complete numerous analyses and
generate different reports. For example, reports you can generate include:
• Sales Order Discount Analysis
• Number of Deals Trend Analysis
• Bookings vs Returns
• Returns Trend Analysis
• Top 10 Bookings
• Booking Trends
80 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 81

• Top Sales Reps by Quarter
Sales Order Discount Analysis
This report analyzes sales order discounts by Product Hierarchy, Company
Code, and Sales Rep.
By Company Code
View overall trend summaries by Company Code based on net value and also
on Discount %. The report also includes a section for each Company Code
with detailed discount information.
Reports
Sales Orders
4
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 81
Page 82

Reports
4
Sales Orders
By Product Hierarchy
View the Top 10 discounts by Product Hierarchy Level 1. This report uses the
Web Intelligence ranking feature to limit displayed results to Top 10 by
Discount %.
.
By Sales Rep
View Peer Performance and detailed discount information for each Sales
Rep.
82 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 83

Report SQL
All report SQL is located in the Rapid Mart installation directory under
"\Sample\DML".
Number of Deals Trend Analysis
This report analyzes Number of Deals trends; providing a high-level summary
analysis and detailed analysis by Sales Rep and Company Code
Summary
View dashboard-style summary for Number of Deals for the entire enterprise.
Reports
Sales Orders
4
Report SQL
SELECT
COMPANY_CODE.CMPNY_CODE_NAME,
SALES_ORGANIZATION.SALES_ORG_DESCR,
DIVISION.DIVISION_DESCR,
sum(SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_SUBTTL_01_GBL),
SALES_PERSON.SALES_PERSON_FIRST_NAME,
SALES_PERSON.SALES_PERSON_LAST_NAME,
sum(SALES_ORDER_F ACT.AMT_SUBTTL_01_GBL -
SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_GBL),
TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALENDAR_YEAR,
sum(SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL),
MATERIAL.MTRL_TYPE_DESCR,
CUSTOMER_SOLDTO.CUSTOMER_NAME_01,
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 83
Page 84

Reports
4
Sales Orders
CUSTOMER_SOLDTO.CUSTOMER_NAME_02,
TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALENDAR_QUARTER,
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY.LVL_01_DESCR,
CURRENCY_GLOBAL.CURR_ISO_CODE,
avg(SALES_ORDER_FACT.QTY_ORDER_SLSUOM),
sum(SALES_ORDER_FACT.QTY_ORDER_SLSUOM),
sum(SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_GBL -
SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_STD_COST_GBL),
case when SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL < 200 then 'Small
Order (less than 200.00)' else
case when SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL >= 200 and
SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL < 500 then 'Medium
Order(200.00 to 499.99)' else
case when SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL >= -30 and
SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL < 0 then '1 - 30 Days
Late' else
case when SALES_ORDER_F ACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL >= 500 then 'Large
Order (500.00 or more)' else
'N/A'
end end end end ,
COUNT( DISTINCT SALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_DOC_ID)
FROM
COMPANY_CODE,
SALES_ORGANIZATION,
DIVISION,
SALES_ORDER_FACT,
SALES_PERSON,
TIME_DIM TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE,
MATERIAL,
CUSTOMER CUSTOMER_SOLDTO,
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY,
CURRENCY CURRENCY_GLOBAL
WHERE
(
SALES_ORDER_FACT.CREATE_DATE=TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALEND
AR_DATE )
AND (
SALES_ORGANIZATION.SALES_ORG_ID=SALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_O
RG_ID )
AND (
SALES_PERSON.SALES_PERSON_ID=SALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_PERSO
N_ID )
AND ( DIVISION.DIVISION_ID=SALES_ORDER_FACT.DIVISION_ID )
AND (
CUSTOMER_SOLDTO.CUSTOMER_ID=SALES_ORDER_FACT.CUSTOMER_I
D_SOLDTO )
AND ( SALES_ORDER_FACT.MATERIAL_ID=MATERIAL.MATERIAL_ID )
AND (
COMPANY_CODE.CMPNY_CODE_ID=SALES_ORDER_FACT.CMPNY_COD
E_ID )
AND ( MATERIAL.PROD_HIER_ID=PRODUCT_HIERARCHY.PROD_HIER_ID )
AND ( CURRENCY_GLOBAL.CURR_ID=SALES_ORDER_FACT.CURR_ID_GBL
)
AND ( SALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_DOC_ID<> '?' )
AND
(
84 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 85

Reports
Sales Orders
( (SALES_ORDER_FACT.DOC_CATEG_ID= 'C' or
SALES_ORDER_FACT.DOC_CATEG_ID= 'I') )
AND
TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALENDAR_YEAR In @prompt('Calendar
Year:','N','Doc. Creation Date Time Dim\Calendar
Year',Multi,Free,Persistent,,User:0)
)
GROUP BY
COMPANY_CODE.CMPNY_CODE_NAME,
SALES_ORGANIZATION.SALES_ORG_DESCR,
DIVISION.DIVISION_DESCR,
SALES_PERSON.SALES_PERSON_FIRST_NAME,
SALES_PERSON.SALES_PERSON_LAST_NAME,
TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALENDAR_YEAR,
MATERIAL.MTRL_TYPE_DESCR,
CUSTOMER_SOLDTO.CUSTOMER_NAME_01,
CUSTOMER_SOLDTO.CUSTOMER_NAME_02,
TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALENDAR_QUARTER,
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY.LVL_01_DESCR,
CURRENCY_GLOBAL.CURR_ISO_CODE,
case when SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_V ALUE_HDR_GBL < 200 then 'Small
Order (less than 200.00)' else
case when SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL >= 200 and
SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL < 500 then 'Medium
Order(200.00 to 499.99)' else
case when SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL >= -30 and
SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL < 0 then '1 - 30 Days
Late' else
case when SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL >= 500 then 'Large
Order (500.00 or more)' else
'N/A'
end end end end
HAVING
sum(SALES_ORDER_F ACT.AMT_SUBTTL_01_GBL -
SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_GBL) <> 0
4
Bookings vs Returns
This report analyzes company Bookings vs Returns trends by Company Code
and Plant for selected Calendar Years. This report uses two synchronized
queries, one to retrieve Bookings data and the other for Returns data.
Common dimensions are merged and the Net V alue amount from each query
is used in the report.
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 85
Page 86

Reports
4
Sales Orders
Report SQL
All report SQL is located in the Rapid Mart installation directory under
"\Sample\DML".
86 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 87

Returns Trend Analysis
View Returns Trend Analysis for a selected set of Calendar Years by:
• Company Code
• Sales Org
• Plant
Reports
Sales Orders
4
Report SQL
All report SQL is located in the Rapid Mart installation directory under
"\Sample\DML".
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 87
Page 88

Reports
4
Sales Orders
Top 10 Bookings
View summary of top bookings for the enterprise over the selected Calendar
Year, including Top 10:
• Customers
• Sales Reps
• Products
This report uses the Web Intelligence ranking feature to limit displayed results
to Top 10.
Report SQL
SELECT
TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALENDAR_QUARTER,
TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALENDAR_YEAR,
CUSTOMER_SOLDTO.CUSTOMER_NAME_01,
CUSTOMER_SOLDTO.CUSTOMER_NAME_02,
SALES_PERSON.SALES_PERSON_FIRST_NAME,
SALES_PERSON.SALES_PERSON_LAST_NAME,
88 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 89

Sales Orders
sum(SALES_ORDER_FACT.AMT_NET_VALUE_HDR_GBL),
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY.LVL_01_DESCR
FROM
SALES_ORDER_FACT,
TIME_DIM TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE,
SALES_PERSON,
CUSTOMER CUSTOMER_SOLDTO,
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
WHERE
(
SALES_ORDER_FACT.CREATE_DATE=TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALEND
AR_DATE )
AND (
SALES_PERSON.SALES_PERSON_ID=SALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_PERSO
N_ID )
AND (
CUSTOMER_SOLDTO.CUSTOMER_ID=SALES_ORDER_FACT.CUSTOMER_I
D_SOLDTO )
AND (
SALES_ORDER_FACT.PROD_HIER_ID=PRODUCT_HIERARCHY.PROD_HIE
R_ID )
AND ( SALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_DOC_ID<> '?' )
AND
(
TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALENDAR_YEAR = @prompt('Calendar
Year:','N','Doc. Creation Date Time Dim\Calendar
Year',Mono,Free,Persistent,,User:0)
AND
( (SALES_ORDER_FACT.DOC_CATEG_ID= 'C' or
SALES_ORDER_FACT.DOC_CATEG_ID= 'I') )
)
GROUP BY
TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALENDAR_QUARTER,
TIMEDIM_CREATE_DATE.CALENDAR_YEAR,
CUSTOMER_SOLDTO.CUSTOMER_NAME_01,
CUSTOMER_SOLDTO.CUSTOMER_NAME_02,
SALES_PERSON.SALES_PERSON_FIRST_NAME,
SALES_PERSON.SALES_PERSON_LAST_NAME,
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY.LVL_01_DESCR
Reports
4
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 89
Page 90

Reports
4
Sales Orders
Booking Trends
This report analyzes Booking Trends for the entire enterprise over the
selected set of Calendar Years by:
• Company Code
• Sales Org
• Product Hierarchy
Report SQL
All report SQL is located in the Rapid Mart installation directory under
"\Sample\DML".
90 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 91

Top Sales Reps by Quarter
View Top Sales Reps for the selected Calendar Years. Bookings amounts are
displayed for each quarter. Sales Reps are sorted according to highest
Bookings amount
Reports
Sales Orders
4
Report SQL
All report SQL is located in the Rapid Mart installation directory under
"\Sample\DML".
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 91
Page 92

Reports
4
Sales Orders
Recommended table joins
When analyzing data from the sales order section, you need to create joins
between different tables. Specifically, you need to create joins between the
SALES_ORDERS_FACT table and other dimension tables in the Rapid Mart
Note: BACKLOG_FACT and SALES_ORDER_FACT are joined because
they share the same primary key. This allows Backlog and Sales Orders to
share the same set of dimensions in the universe.
Dimension Table Join Expression
BACKLOG_FACT
allows Backlog Orders to be used as
a dimension to Sales Orders)
BILLING_BLOCK BILLING_BLOCK.BILL_BLOCK_ID=SALES
CENTRAL_ADDRESS CENTRAL_ADDRESS.ADDRESS_ID=
COMPANY_CODE COMPANY_CODE.CMPNY_CODE_ID=SAL
CONTROLLING_AREA CONTROLLING_AREA.CTRL_AREA_ID=S
CREDIT_CONTROL_AREA SALES_ORDER_FACT.CR_CTRL_AREA_I
CREDIT_MGMT_RISK_CLASSSALES_ORDER_FACT.CR_CTRL_AREA_I
CURRENCY CURRENCY.CURR_ID=SALES_ORDER_F
CURRENCY CURRENCY.CURR_ID=SALES_ORDER_F
CURRENCY CURRENCY.CURR_ID=SALES_ORDER_F
(Fact to Fact -
BACKLOG_FACT.SALES_DOC_ID=SALES
_ORDER_FACT.SALES_DOC_ID AND
BACKLOG_FACT.SALES_LINE_ITEM_ID=S
ALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_LINE_ITEM_I
D
_ORDER_FACT.BILL_BLOCK_ID
SALES_ORDER_FACT.ADDRESS_ID_SHI
PTO
ES_ORDER_FACT.CMPNY_CODE_ID
ALES_ORDER_FACT.CTRL_AREA_ID
D =
CREDIT_CONTROL_AREA.CR_CTRL_AR
EA_ID
D =
CREDIT_MGMT_RISK_CLASS.CR_CTRL_
AREA_ID and
SALES_ORDER_FACT.CR_MGMT_RISK_C
LASS_ID =
CREDIT_MGMT_RISK_CLASS.CR_MGMT
_RISK_CLASS_ID
ACT.CURR_ID_GBL
ACT.CURR_ID_STATS
ACT.CURR_ID_TRX
92 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 93

Reports
Sales Orders
Dimension Table Join Expression
CUSTOMER CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_ID=SALES_ORD
ER_FACT.CUSTOMER_ID_BILLTO
CUSTOMER CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_ID=SALES_ORD
ER_FACT.CUSTOMER_ID_SHIPTO
CUSTOMER CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_ID=SALES_ORD
ER_FACT.CUSTOMER_ID_SOLDTO
CUSTOMER_GROUP SALES_ORDER_FACT.CUSTOMER_GRP_
01_ID=CUSTOMER_GROUP.CUSTOMER_
GRP_ID
DELIVERY_BLOCK DELIVERY_BLOCK.DELIV_BLOCK_ID=SA
LES_ORDER_FACT.DELIV_BLOCK_ID
DELIVERY_ROUTE SALES_ORDER_FACT.DELIV_ROUTE_ID=
DELIVERY_ROUTE.DELIV_ROUTE_ID
DISTRIBUTION_CHANNEL DISTRIBUTION_CHANNEL.DISTRIBTN_C
HANNEL_ID=SALES_ORDER_FACT.DISTR
IBTN_CHANNEL_ID
DIVISION DIVISION.DIVISION_ID=SALES_ORDER_F
ACT.DIVISION_ID
DOCUMENT_CATEGORY SALES_ORDER_FACT.DOC_CATEG_ID=D
OCUMENT_CATEGORY.DOC_CATEG_ID
and
DOCUMENT_CATEGORY.DIM_SRC_ID =
'SALES'
DOCUMENT_TYPE SALES_ORDER_FACT.DOC_CATEG_ID=D
OCUMENT_TYPE.DOC_CATEG_ID and
SALES_ORDER_FACT.DOC_TYPE_ID=DO
CUMENT_TYPE.DOC_TYPE_ID and
DOCUMENT_TYPE.DIM_SRC_ID =
'SALES'
INTER_COMPANY_TERM01 SALES_ORDER_FACT.INTER_CMPNY_TE
RM01_ID=INTER_COMPANY_TERM01.INT
ER_CMPNY_TERM01_ID
MA TERIAL SALES_ORDER_FACT.MATERIAL_ID=MAT
ERIAL.MATERIAL_ID
MATERIAL_ALT_UOM SALES_ORDER_FACT.MATERIAL_ID=MAT
ERIAL_ALT_UOM.MATERIAL_ID and
MATERIAL_ALT_UOM.UOM_ID_ALT =
@Prompt('Enter Alt. Unit of Meas.','A',
,MONO,FREE)
4
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 93
Page 94

Reports
4
Sales Orders
Dimension Table Join Expression
MATERIAL_BY_PLANT MATERIAL_BY_PLANT.PLANT_ID=SALES
_ORDER_FACT.PLANT_ID and
MATERIAL_BY_PLANT.MATERIAL_ID=SAL
ES_ORDER_FACT.MATERIAL_ID
MATERIAL_GROUP SALES_ORDER_FACT.MTRL_GRP_ID=MA
TERIAL_GROUP.MTRL_GRP_ID
ORDER_REASON SALES_ORDER_FACT.ORDER_REASON_I
D=ORDER_REASON.ORDER_REASON_I
D
PAYMENT_TERM SALES_ORDER_FACT.PAYMNT_TERM_ID
=PAYMENT_TERM.PAYMNT_TERM_ID
AND
PAYMENT_TERM.PAYMNT_TERM_DAY_LI
MIT = '?'
PLANT PLANT.PLANT_ID=SALES_ORDER_FACT.
PLANT_ID
PRICING_PROCEDURE_HZ SALES_ORDER_FACT.PRICE_PROCEDU
RE_ID=PRICING_PROCEDURE_HZ.PRICE
_PROCEDURE_ID and
PRICING_PROCEDURE_HZ.APPLICTN_ID
= 'V' and
PRICING_PROCEDURE_HZ.USAGE_ID =
'A'
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY SALES_ORDER_FACT.PROD_HIER_ID=P
RODUCT_HIERARCHY.PROD_HIER_ID
PROFIT_CENTER SALES_ORDER_FACT.PROFIT_CNTR_ID
= PROFIT_CENTER.PROFIT_CNTR_ID
AND
SALES_ORDER_FACT.CTRL_AREA_ID =
PROFIT_CENTER.CTRL_AREA_ID
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ SALES_ORDER_FACT.PROFIT_CNTR_ID
=
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ.PROFIT_CNT
R_ID AND
SALES_ORDER_FACT.CTRL_AREA_ID =
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ.CTRL_AREA_
ID
94 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 95

Reports
Sales Orders
Dimension Table Join Expression
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_VR SALES_ORDER_FACT.PROFIT_CNTR_ID
= PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_VR.CHILD_ID
AND
SALES_ORDER_FACT.CTRL_AREA_ID =
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_VR.CTRL_AREA
_ID
REJECT_REASON SALES_ORDER_FACT.REJECT_REASON_
ID=REJECT_REASON.REJECT_REASON_
ID
SALES_DISTRICT SALES_DISTRICT.SALES_DISTRICT_ID=S
ALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_DISTRICT_I
D
SALES_GROUP SALES_GROUP.SALES_GRP_ID=SALES_
ORDER_FACT.SALES_GRP_ID
SALES_OFFICE SALES_OFFICE.SALES_OFFICE_ID=SALE
S_ORDER_FACT.SALES_OFFICE_ID
SALES_ORDER_FACT SALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_DOC_ID<>
'?'
SALES_ORDER_STATUS SALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_DOC_STAT
US_KEY=SALES_ORDER_STATUS.SALES
_DOC_STATUS_KEY
SALES_ORGANIZATION SALES_ORGANIZATION.SALES_ORG_ID=
SALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_ORG_ID
4
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 95
Page 96

Reports
4
Sales Orders
Dimension Table Join Expression
SALES_ORGANIZATION_HIERSALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_ORG_ID=S
ALES_ORGANIZATION_HIER.SALES_OR
G_ID and
SALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_GRP_ID=S
ALES_ORGANIZATION_HIER.SALES_GRP
_ID and
SALES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_OFFICE_ID
=SALES_ORGANIZATION_HIER.SALES_O
FFICE_ID and
SALES_ORDER_FACT.DISTRIBTN_CHAN
NEL_ID=SALES_ORGANIZATION_HIER.DI
STRIBTN_CHANNEL_ID and
SALES_ORDER_FACT.DIVISION_ID_HDR
=SALES_ORGANIZATION_HIER.DIVISION
_ID and @Prompt('Enter Sales Org
Hierarchy Date','D',,MONO,FREE) between
SALES_ORGANIZATION_HIER.VALID_FR
OM_DATE and
SALES_ORGANIZATION_HIER.VALID_TO_
DATE
SALES_PERSON SALES_PERSON.SALES_PERSON_ID=SA
LES_ORDER_FACT.SALES_PERSON_ID
SHIPPING_POINT SALES_ORDER_FACT.SHIP_POINT_ID=S
HIPPING_POINT.SHIP_POINT_ID
STORAGE_LOCATION STORAGE_LOCATION.STORAGE_LOCAT
N_ID=SALES_ORDER_FACT.STORAGE_L
OCATN_ID and
STORAGE_LOCATION.PLANT_ID=SALES_
ORDER_FACT.PLANT_ID
TIME_DIM SALES_ORDER_FACT.CREATE_DATE=TI
ME_DIM.CALENDAR_DATE
TIME_DIM SALES_ORDER_FACT.DOC_DATE=TIME_
DIM.CALENDAR_DATE
TIME_DIM SALES_ORDER_FACT.RQST_DELIV_DAT
E_HDR=TIME_DIM.CALENDAR_DATE
UNIT_OF_MEASURE UNIT_OF_MEASURE.UOM_ID=SALES_OR
DER_FACT.UOM_ID_BASE
UNIT_OF_MEASURE UNIT_OF_MEASURE.UOM_ID=SALES_OR
DER_FACT.UOM_ID_SALES
UNIT_OF_MEASURE UNIT_OF_MEASURE.UOM_ID=SALES_OR
DER_FACT.UOM_ID_TRGT
96 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 97

Deliveries and On-Time Delivery
The delivery and on-time delivery section contains information about all
deliveries; including returns, shipments, shipment notifications, and
information for tracking delivery status.
Reports
Using the delivery information, you can complete numerous analyses and
generate different reports, including:
• On-time Delivery Trends
• On-time Delivery Details
• On-Time Delivery Summary
• On-Time Delivery Top 10 Customers
• On-Time Delivery Top 10 Documents
On-time Delivery Trends
This report analyzes On-Time delivery trends for selected Calendar Years by:
• Plant
• Division
Reports
Deliveries and On-Time Delivery
4
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 97
Page 98

Reports
4
Deliveries and On-Time Delivery
Report SQL
SELECT
PLANT.PLANT_ID,
PLANT.PLANT_NAME_01,
DIVISION.DIVISION_ID,
DIVISION.DIVISION_DESCR,
MATERIAL.MTRL_DESCR,
TIMEDIM_GOODS_ISSUE_DATE.CALENDAR_YEAR,
TIMEDIM_GOODS_ISSUE_DATE.CALENDAR_QUARTER,
AVG(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE),
AVG(case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < -60 then
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM) else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE >= -60 and
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM) else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE >= -30 and
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM) else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE = 0 then
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM) else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 0 and
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM) else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 30 and
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM) else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 60 then
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM) else
0.0
end end end end end end end
),
SUM(case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < -60 then
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM *
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE >= -60 and
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM *
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE >= -30 and
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM *
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE = 0 then
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM *
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 0 and
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM *
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 30 and
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM *
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 60 then
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < -30 then
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < 0 then
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE <= 30 then
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE <= 60 then
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.AMT_NET_PRICE_TRX) else
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < -30 then
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.AMT_NET_PRICE_TRX) else
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < 0 then
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.AMT_NET_PRICE_TRX) else
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.AMT_NET_PRICE_TRX) else
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE <= 30 then
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.AMT_NET_PRICE_TRX) else
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE <= 60 then
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.AMT_NET_PRICE_TRX) else
98 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Page 99

Reports
Deliveries and On-Time Delivery
(ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.QTY_ALLOCTN_SLSUOM *
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.AMT_NET_PRICE_TRX) else
0.0
end end end end end end end
),
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < -60 then 'More than
60 Days Late' else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE >= -60 and
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < -30 then '31 - 60 Days Late'
else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE >= -30 and
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < 0 then '1 - 30 Days Late'
else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE = 0 then 'On Time'
else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 0 and
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE <= 30 then '1 - 30 Days
Early' else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 30 and
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE <= 60 then '31 - 60 Days
Early' else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 60 then 'More than
60 Days Early' else
'N/A'
end end end end end end end
FROM
PLANT,
DIVISION,
MATERIAL,
TIME_DIM TIMEDIM_GOODS_ISSUE_DATE,
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT
WHERE
(
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.SCHED_GI_DATE=TIMEDIM_GOODS_ISSUE_D
ATE.CALENDAR_DATE )
AND ( ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DIVISION_ID=DIVISION.DIVISION_ID )
AND ( PLANT.PLANT_ID=ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.PLANT_ID )
AND ( MATERIAL.MATERIAL_ID=ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.MATERIAL_ID )
AND
TIMEDIM_GOODS_ISSUE_DATE.CALENDAR_YEAR In @prompt('Calendar
Year(s):','N','Planned Goods Issue Date Time Dim\Calendar
Year',Multi,Free,Persistent,,User:0)
GROUP BY
PLANT.PLANT_ID,
PLANT . PLANT_NAME_01,
DIVISION.DIVISION_ID ,
DIVISION.DIVISION_DESCR,
MATERIAL.MTRL_DESCR,
TIMEDIM_GOODS_ISSUE_DATE.CALENDAR_YEAR,
TIMEDIM_GOODS_ISSUE_DATE.CALENDAR_QUARTER,
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < -60 then 'More than
60 Days Late' else
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE >= -60 and
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < -30 then '31 - 60 Days Late'
else
4
SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 99
Page 100

Reports
4
Deliveries and On-Time Delivery
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE >= -30 and
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE = 0 then 'On Time'
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 0 and
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 30 and
case when ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE > 60 then 'More than
'N/A'
end end end end end end end
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE < 0 then '1 - 30 Days Late'
else
else
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE <= 30 then '1 - 30 Days
Early' else
ONTIME_DELIVERY_FACT.DAYS_EARLY_LATE <= 60 then '31 - 60 Days
Early' else
60 Days Early' else
100 SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
 Loading...
Loading...