
SAP BusinessObjects Production
Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2, version for
SAP solutions - User Guide
Version 12.2.2.0

October 2009
Copyright
Trademarks
© Copyright 2009 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or for any purpose
without the express permission of SAP AG. The information contained herein may be
changed without prior notice.
Some software products marketed by SAP AG and its distributors contain proprietary
software components of other software vendors.
All rights reserved. SAP, R/3, SAP NetWeaver, Duet, PartnerEdge, ByDesign, SAP Business
ByDesign, and other SAP products and services mentioned herein as well as their respective
logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP AG in Germany and other countries.
Business Objects and the Business Objects logo, BusinessObjects, Crystal Reports, Crystal
Decisions, Web Intelligence, Xcelsius, and other Business Objects products and services
mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks
of Business Objects S.A. in the United States and in other countries. Business Objects is an
SAP company.
All other product and service names mentioned are the trademarks of their respective
companies. Data contained in this document serves informational purposes only. National
product specifications may vary.
These materials are subject to change without notice. These materials are provided by SAP
AG and its affiliated companies ("SAP Group") for informational purposes only, without
representation or warranty of any kind, and SAP Group shall not be liable for errors or
omissions with respect to the materials. The only warranties for SAP Group products and
services are those that are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such
products and services, if any. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty.

SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User
Guide
Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction 11
What is a Rapid Mart? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Rapid Marts packages accelerate Time to Value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
SAP BusinessObjects Rapid Marts packages architecture . . . . . . . . . 14
About this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Chapter 2 Overview 17
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
What is production planning? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
What you can do with this Rapid Mart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Supported analyses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Related Rapid Marts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Sharing components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
The Rapid Mart schema . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Where the Rapid Mart fits in the production planning process . . . . . . . . . . 26
Chapter 3 Subject Areas 27
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Work Center section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Basic Data in a Work Center: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Integration of Work Centers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Capacity section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 3

Contents
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
MRP results section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Planned Order section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Reservation section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Rapid Mart Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Routing section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Bills of Material (BOM) section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Production Order section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Production Operation section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Chapter 4 Reports 83
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Work Center Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Capacity Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
MRP Results Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
4 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Contents
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Planned Order Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Reservation Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Routing Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Bill Of Materials Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Production Order Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Production Operation Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
SAP Master Data Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Data Discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Data Auditing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Recommended table joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Chapter 5 Universe 175
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Universe Design Principles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Universe Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Universe Table Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Join Strategy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Techniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Hierarchies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Hierarchies Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 5

Contents
Geographic Hierarchies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Time Dimension and Fiscal Period Hierarchies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .183
Material Product Hierarchy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .183
Horizontal & Vertical Hierarchies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Hierarchy Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .190
Production Planning Specific Hierarchies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .195
Accounting Hierarchies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .195
Additional Hierarchies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .195
SAP Production Planning Universe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .197
Universe Objects & Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .198
Common Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .199
Planned Order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .214
Production Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .216
Production Order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .220
Reservation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
Filters & Techniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
Universe Validation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .226
SAP Capacity Planning and MRP Universe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .228
Universe Objects & Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .229
Common Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .231
Capacity Interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
Capacity Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .244
MRP Result . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
Work Center Cost Assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .249
Filters & Techniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
Universe Validation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .254
SAP Production Routing and BOM Universe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .255
Universe Objects & Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .256
Common Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .258
Production BOM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .269
Production BOM Explosion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .271
Routing BOM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .274
Routing Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
6 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Contents
Filters & Techniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
Universe Validation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 281
SAP Master Data Universe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
Universe Objects & Classes - Master Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
Universe Validation - Master Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318
Customizing the Universe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
Splitting the SAP Capacity Planning and MRP Universe . . . . . . . . . . 320
Chapter 6 Installing the Rapid Mart 323
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 324
System Prerequisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
Personnel Prerequisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
Rapid Mart product components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 327
Preparing your environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 329
Preparing Data Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 329
Preparing Target Database Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 329
Preparing Source Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
Preparing BusinessObjects Enterprise . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
Performance Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
The Rapid Mart Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 332
Install the Rapid Mart Target Schema . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Create Target Schema . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Install the Data Services Job(s) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336
Renaming the Data Stores . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336
Import ATL File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
Adjusting the Data Stores . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340
Using Auxiliary Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 347
Using ABAP Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
Final Steps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 352
Installing Rapid Mart Reporting Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354
Import Wizard for Reporting Content BIAR File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354
Creating Universe Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 370
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 7

Contents
Chapter 7 Using the Rapid Mart 373
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .374
Recovery framework . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .374
Data Services automatic recovery feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .374
Rapid Mart recovery framework . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 375
Execution status framework . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .376
The execution status table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .376
The execution status API . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .377
Executing a job with the Reset option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 378
Extraction, transformation and loading process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .378
Global Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .380
Global Variable Cross-Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 380
Used in All Rapid Marts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .384
Used in 2 to 10 Rapid Marts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .387
Used in Only 1 Rapid Mart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
Setting Global Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .407
Executing the job . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .411
Initial (First) Extraction and Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 411
Incremental (Delta) Extraction and Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .412
Customizing the Rapid Mart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .414
Chapter 8 Technical Implementation 415
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .416
Work Center section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .416
Capacity section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 418
Capacity Intervals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .421
Capacity Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .421
Routing section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .422
Routing Line Fact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 425
Routing BOM Fact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .426
MRP Results section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .427
Initial (First) Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 429
Incremental (Delta) Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .430
8 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Contents
Planned Order section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 430
Initial (First) Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433
Incremental (Delta) Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433
Production Order section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 434
Initial (First) Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438
Incremental (Delta) Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 439
Bill of Materials (BOM) section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 439
Production BOM Fact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 441
Production BOM Explosion Fact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 443
Reservation section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 445
Reservation Fact Load Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 448
Production Operation section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 449
Initial (First) Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 453
Incremental (Delta) Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 453
Dimensions with Incremental Loads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 453
Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 453
Routing Material . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 454
Routing Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 455
Optimization Techniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 455
Table Partitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 456
Data Transfer Transform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 457
Hierarchy Optimizations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 459
Dealing with NULL values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 461
Fact Table Stored Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 463
Fiscal Periods & Time Dim Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 464
Chapter 9 Documentation References 467
Data Services Documentation References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 468
BusinessObjects Enterprise Documentation References . . . . . . . . . . . . 468
Appendix A Rapid Mart Data Schema 471
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 9

Contents
10 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Introduction
chapter

Introduction
1
What is a Rapid Mart?
What is a Rapid Mart?
SAP BusinessObjects Rapid Marts packages are blueprints for building data
marts with SAP BusinessObjects technology:
• Data Services
• Universe Designer
• Web Intelligence.
Rapid Marts packages deliver jump-start ETL (extract, transform & load)
mappings, schema, and initial reporting content, accelerating the deployment
of BI (business intelligence) for enterprise applications from SAP, PeopleSoft,
Oracle, and Siebel.
Each Rapid Mart is designed to address the reporting needs of a specific
business area (or department) like accounting, sales, or purchasing. A
component-based framework allows conducting analysis across these
selected business areas by combining different packages within the same
source application suite.
Rapid Marts focus on basic standard configuration of the enterprise
applications. They are country and industry neutral templates meant to be
easily modified and extended to suit customer specific application
implementation and reporting needs.
Rapid Marts incorporate best practices, and provide easily modifiable
templates. With Rapid Marts total development time of a data mart solution is
greatly reduced.
Each customer situation is different. You will probably encounter one or more
of these:
• Customizations you have made to SAP solutions the Rapid Mart does not
cover.
• Standard SAP solutions data fields important for your specific business,
but not included in the Rapid Mart templates.
• Optimization and performance challenges unique to your environment.
• Reporting requirements not covered within the Rapid Mart template
reports.
Rapid Marts are flexible templates that you can adjust to account for these
unique situations. It is expected that some customization and optimization will
be needed to suit your individual environment. Rapid Marts are not an
out-of-the-box solution.
12 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

BI tools and analytic tools can access Rapid Mart data through SQL queries.
Rapid Marts can be implemented individually, or in any combination, to form a
single platform that delivers the infrastructure for your company’s internal and
external information needs. They can also serve as a staging area for
enterprise analytic applications.
Rapid Marts provide your business with an accelerated time to value through
rapid BI deployments because you can implement them quickly and easily
customize them to meet specific analytic requirements.
Rapid Marts packages accelerate Time to Value
Rapid Marts are packaged data solutions that you can quickly deploy to
address specific areas of business analysis.
Available Rapid Marts packages for SAP solutions include:
Financial Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects General Ledger Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Accounts Payable Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Accounts Receivable Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Cost Center Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
Operational Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects Inventory Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Purchasing Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
Manufacturing Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects Plant Maintenance Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Project Systems Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
Human Capital Management (HCM) Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects Human Resources Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
Introduction
What is a Rapid Mart?
1
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 13
Introduction
1
What is a Rapid Mart?
You can combine multiple Rapid Marts packages into a single environment to
build the foundation for your data warehouse or use them as a staging area
for business intelligence applications.
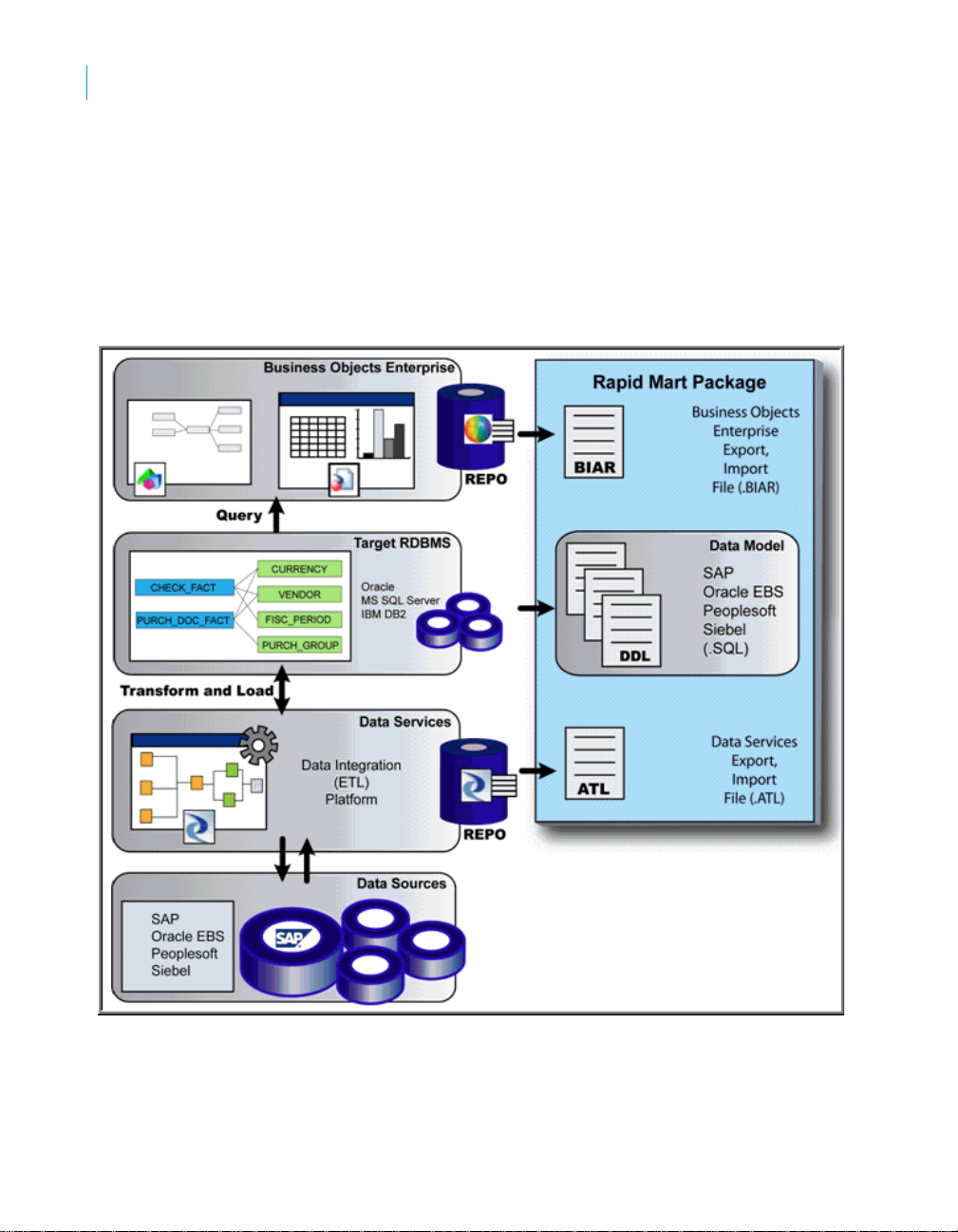
SAP BusinessObjects Rapid Marts packages architecture
Rapid Marts architecture is driven by SAP BusinessObjects technology.
Rapid Mart Architecture:
Rapid Marts packages include the following components:
14 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Introduction
About this document
• Data Movement Jobs - packaged source-to-target mappings and data
transformations. Each job is designed to perform initial and incremental
data movement;
• Data Model & Schema - set of dat a mart database objects designed with
dimensional data modeling approach. Rapid Marts packages for SAP
solutions has a single integrated data model. The schema are available
for Oracle, SQL Server IBM DB2, and Teradata;
• Semantic Layer (Universes) - SAP BusinessObjects metadata packages
for efficient query generation. There can be one or more universes per
Rapid Mart. Each universe is developed using Rapid Marts design
principles to ensure compatibility, code readability, and component
re-use. In addition, there is one Master universe for
development/maintenance of multiple use objects (like Customer,
Material, Currency, etc.);
• Reports (Samples) - set of 15-20 Web Intelligence reports per Rapid
Mart. They represent answers to mostly asked business questions (for
example, in the SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions - 'What is the monthly Revenue trend by Division for this
year?'). The reports are developed using Rapid Mart color/layout
templates. Reports are examples of Web Intelligence best practice
development (trends, listing, guided analysis, roll ups and downs, etc.).
1
About this document
This document describes the SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning
Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions. This document contains information for
a variety of users—information that helps you understand the use of the
Rapid Mart, the data in the Rapid Mart, the reports you can create with the
Rapid Mart, and how to use and update the Rapid Mart.
This document contains the following chapters:
• Chapter 2: Overview — Describes the business problems you can solve
and the types of analyses you can do with this Rapid Mart
• Chapter 3: Subject Areas — Contains detailed information about each
section in the Rapid Mart, including the processes each section captures
• Chapter 4: Reports — Provides examples of reports you can produce
• Chapter 5: Universe — Describes the SAP BusinessObjects Universes
upon which the reports are built.
• Chapter 6: Installing the Rapid Mart — Cont ains the information you need
to install the Rapid Mart
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 15

Introduction
1
About this document
• Chapter 7: Using the Rapid Mart — Describes how to execute the Rapid
Mart, including information about initializing variables and considerations
you need to make when customizing the Rapid Mart
• Chapter 8: Technical Implementation — Describes each section and the
work flows that run to load that section
• Chapter 9: Documentation References — Information about where to find
related to the Rapid Mart technical documentation on Data Services and
BusinessObjects Enterprise
• Appendix A: Rapid Mart Data Schema — Contains a detailed list of the
tables and views in the Rapid Mart
16 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Overview
chapter

Overview
2
Overview
Overview
This chapter describes the business problems you can solve with the SAP
BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
and the types of analyses you can do with this Rapid Mart. The information in
this chapter is useful for those who want a business-level overview of the
Rapid Mart and its benefits.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
• What is production planning?
• What you can do with this Rapid Mart
• Supported analyses
• Related Rapid Marts
• The Rapid Mart schema
• Where the Rapid Mart fits in the production planning process
What is production planning?
Within SAP solutions, the process of production planning and control (PP)
determines what to produce, how much to produce, and when to produce it.
Production quantities and scheduling are constrained by machine time, labor ,
material availability, and storage space. These resources are in turn
constrained by budget and other financial considerations. By balancing
resource constraints with demand and scheduling requirements, an effective
production plan optimizes factory lead times, improves customer delivery
performance, and reduces time consumed by work in progress (WIP).
Planning processes in SAP solutions generate time-based demands for
materials based on sales order planning, long term forecasts, stock
replenishment quantities, customer order requirements, backlog, safety stock
levels, and other anticipated sources of demand. The SAP solutions materials
requirements planning (PP-MRP) component combines lead time scheduling
information with independent and dependent requirements (based on bill of
materials) for a material and produces a production and procurement
proposal—a planning proposal—that satisfies current and projected demand
requirements.
The planning proposal that SAP solutions produces does not account for
material availability or work center capacity until a production order is created.
When creating a production order, SAP solutions explodes a bill of materials,
18 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

What you can do with this Rapid Mart
creates requisitions for externally procured materials, selects a routing for
produced materials, reserves materials and resources, and calculates
capacity requirements for work centers.
What you can do with this Rapid Mart
The SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions enables you to analyze the planning components that automate the
production process. The data that supports these planning
components—work centers, routings, planning strategies, bill of materials,
capacities, and MRP results—can provide insight into the production process
and help you improve and streamline both the planning process and the
actual production and procurement of goods and services.
The SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions is made up of several components or sections. Each section
supports a subject related to planning analysis:
• Work center section — Stores data about work centers—the machines,
production lines, or labor pools capable of producing units of work as
output. The amount of work that a work center can produce during a
given time is its capacity . Basic work center data includes category (labor ,
machine, etc.), description, location (plant), and standard values for
queue times. This section also contains the work center hierarchy, which
allows you to roll up work center capacity to accumulate capacities at
various levels. This section also contains the work center assignment to
cost center.
• Capacity section— Stores standard shift times and operating times for
various capacity categories (machine, labor). Work centers have one or
more capacities, measured in terms of units of time, associated with
them. The combination of operating hours, utilization rate, and number of
capacities determines the standard available cap acity for the work center .
Additional capacity, called interval available capacity, might be available
for certain intervals of time. Capacity requirements generated by
production orders and planned orders using lead time scheduling are
also included in this section.
• Materials requirement planning (MRP) results section — Stores the
results tables from MRP and master production scheduling (MPS)
planning runs.
• Planned order section — Stores detailed routing and operation
information for planned orders. Planned Orders are transient in the SAP
solutions system (they are deleted once converted to a Production Order
Overview
2
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 19

Overview
2
Supported analyses
or Purchase Requisition). The Rapid Mart can capture quasi complete
history of Planned Orders, (including those deleted) depending on how
often the Rapid Mart is refreshed.
• Reservation section — A request to the warehouse or stores to keep a
material ready for issue at a future date for a certain purpose. The
purpose of a reservation is to ensure that a material is available when
required. A material can be reserved for a cost center, a plant, or a
production order.
• Routing section — Stores routing information for production operations.
Manufactured goods require a routing to describe the steps required to
produce a quantity of output. Routings for a material are time-dependent
and may be lot size-dependent. This section contains a material-plant
level routing description including setup, processing, and teardown times
used for basic date scheduling. The routing header associated with each
material routing contains information on lot sizing, status, and usage. The
routing header links to a table containing the individual operations with
time parameters required for detailed scheduling of each stage of the
operation. An additional table contains a link between the routing and bill
of materials of the base material.
• Production BOM section — The Production Bill Of Materials (BOM)
Section of this Rapid Mart stores data that describes what materials are
used in planning production of a given material and the quantity needed
of each of its constituents. The BOM usage supported in this component
is production. BOM tables included are single level, BOM explosion with
quantities, and BOM explosion with materials-only for where-used
reporting.
• Production order section — Stores data about production orders.
When goods are required, planned orders are converted to production
orders. The production order specifies how much to produce, the routing,
the bill of material used to reserve, produce or procure dependent
materials, the scheduled and actual start and end dates, and the status of
the order.
• Production operation section — Operations are the activities to be
performed in the production process. They are a basis for determining
dates, capacity requirements, and costs. They enumerate the use of
materials, work centers, and quality checks during production.
Chapter 3: Subject Areas discusses each of these sections in more detail and
how to link them together for a complete analysis of production planning.
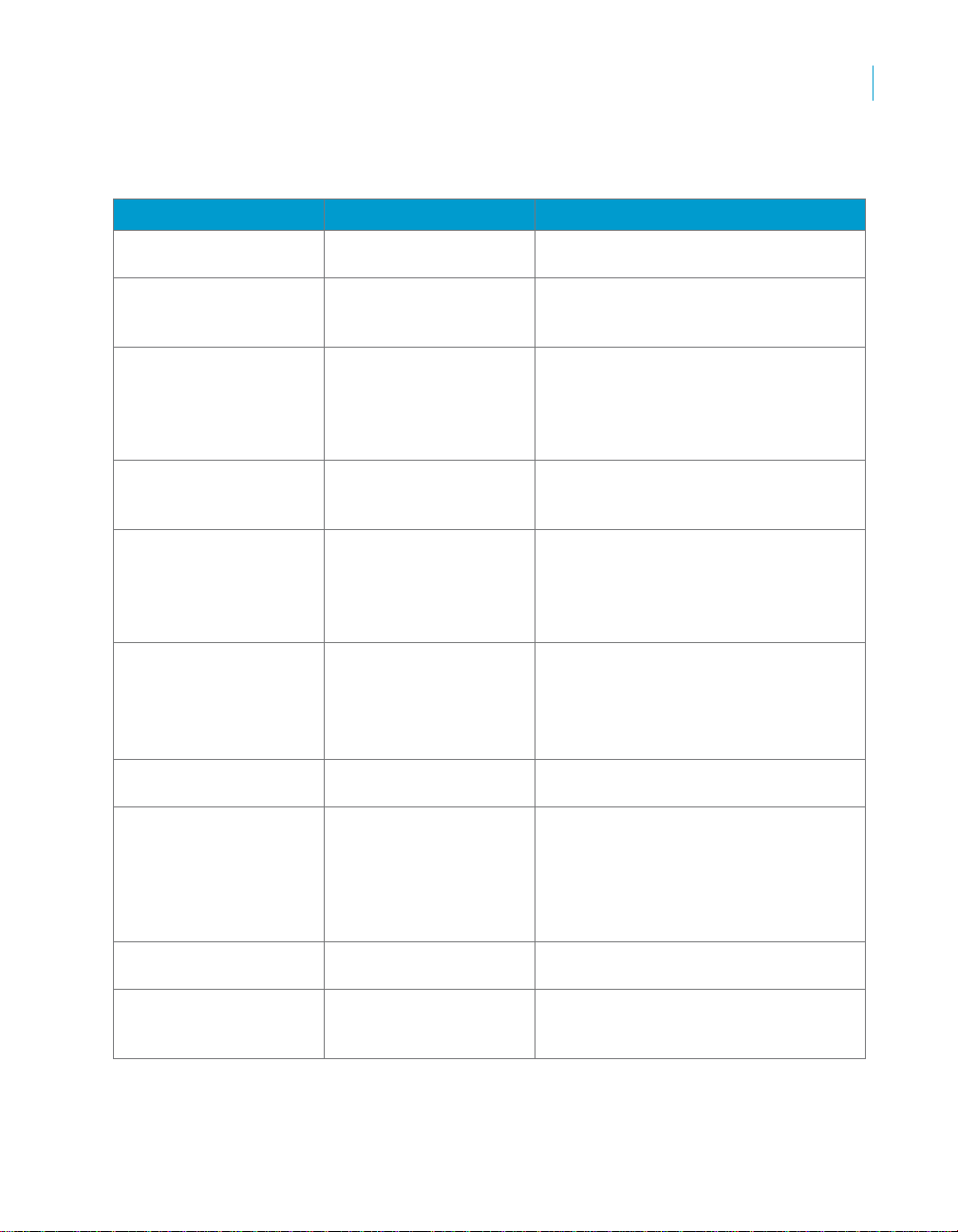
Supported analyses
20 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Overview
Supported analyses
The SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions supports several types of analyses.
Business function Types of analysis Measures available in the Rapid Mart
Bill of material Explosion
Where-used
Routing explosion
Work center Hierarchy
Capacity planning
Cost analysis
Routing/operations Lead time
Where-used
MRP results MRP requirements list
Planned orders Pegged requirements
Planned versus actual
scheduling
• Report dependent requirements for
production bill of materials
• Single, top, and multi-level listings
of bills of materials where a
particular component is used
• Accumulation of operations required
to produce a multi-level material
displayed hierarchically by
aggregating the operation times of
BOM components
• Calculate accumulated work center
capacity using work center
hierarchies
• Evaluate standard work center
capacity and shifts. Assess the
need for alternative interval capacity
based on factory calendar and
percent utilization.
• Analysis of production costs by work
center (requires purchase of Cost
Analysis (CA) Rapid Mart)
• Report and aggregate
manufacturing lead time by activity
• Find materials using a routing or
routing using a material
• Report results of materials
requirements planning (MRP) and
master production scheduling
(MPS) planning runs, including
materials requirements at the time
of the planning run
• Planned capacity requirements by
sales order
• Compare planned operation start
times, finish times, and lead times
with actual
2
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 21

Overview
2
Related Rapid Marts
Business function Types of analysis Measures available in the Rapid Mart
Planned versus actual
yield
To support these analyses, the SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning
Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions includes a number of dimension tables.
Reporting dimensions include material master data, planning data,
plant-specific material master data, error texts, capacity parameters formulas,
and production version, as well as time-related dimensions, such as factory
calendar, time buckets, and calendar year.
• Compare planned yield with actual
Related Rapid Marts
Each Rapid Mart is composed of multiple components. A component is a
stand-alone work flow that completes a particular task, such as loading a
specific dimension table. Components can contain other components. A
section is a set of components that address a particular business problem or
subject area. A section is itself a component.
Components of the SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart,
version for SAP solutions are related to other SAP BusinessObjects Rapid
Mart components. For example:
• Inventory positions in the SAP BusinessObjects Inventory Rapid Mart,
version for SAP solutions.
• Account assignment by work center, controlling area, and activity along
with actual cost information for production orders in the SAP
BusinessObjects Cost Center Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions.
• Purchase requisitions and purchase orders in the SAP BusinessObjects
Purchasing Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions.
• Equipment maintenance scheduling by work center in the Plant
Maintenance Rapid Mart.
• Demand from sales documents in the SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid
Mart, version for SAP solutions.
Sharing components
The same components can be used in multiple Rapid Marts. For example, a
component that extracts information about materials bought, produced, and
sold is needed for a Rapid Mart that supports sales analysis and also for a
22 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Rapid Mart that supports inventory analysis. Work flows that extract star
schema “dimensions” are components. You can add a component to any
Rapid Mart using a simple import procedure.
A Data Services job can include multiple instances of a component. For
example, each section includes all the required dimension components.
Therefore, a job with several sections may include several instances of a
particular dimension component. Components are set to execute only once
within a job. This “execute once” feature ensures that shared components do
not cause duplicate data extraction from SAP solutions. For more information
about the “execute once” feature, see the Data Integrator/Data Services
Designer Guide.
Each of the sections listed in “What you can do with this Rapid Mart” on
page 19 are considered components. You can identify a component within a
Data Services job by a “C_” prefix before its name. For example, the
component that contains work centers and the associated reporting
dimensions is named C_WorkCenter_Section.
The Rapid Mart schema
The following diagrams show an overview of the SAP BusinessObjects
Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions components and
their relationships in Star Schema Format, and then the associated
hierarchies and auxiliary tables. As an overall picture, these diagrams are
challenging to understand. They are broken down into additional diagrams by
subject area in Chapter 3: Subject Areas.
Overview
The Rapid Mart schema
2
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 23

Overview
2
The Rapid Mart schema
Overview Star Schema (1 of 2):
24 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Overview Hierarchies and Auxiliary Tables:
Overview
The Rapid Mart schema
2
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 25
Overview
2
Where the Rapid Mart fits in the productio n planning process
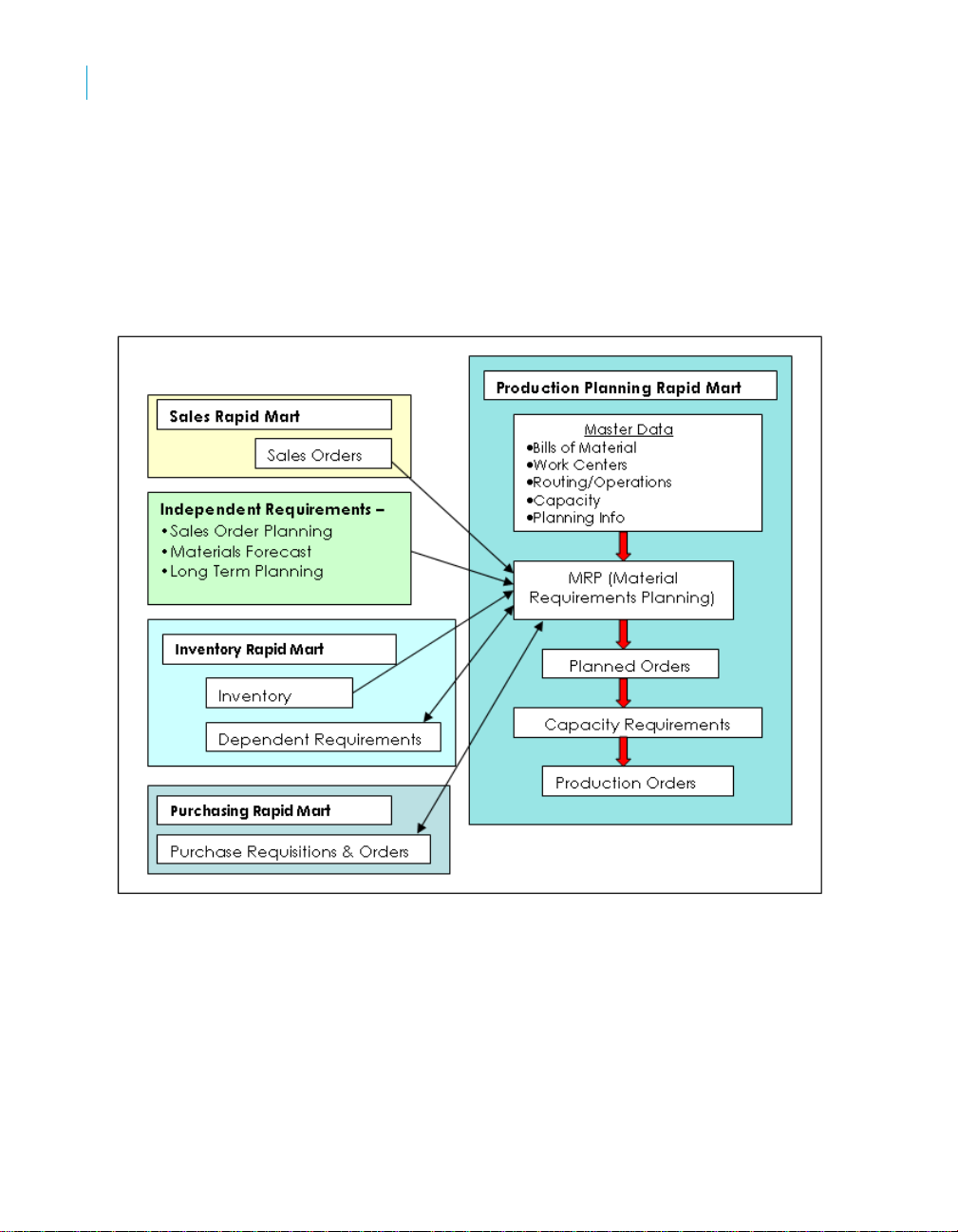
Where the Rapid Mart fits in the production
planning process
To create a comprehensive view of SAP solutions logistics modules, you can
combine the SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version
for SAP solutions components with components from other Rapid Marts.
26 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
chapter

Subject Areas
3
Overview
Overview
Each section in the SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart,
version for SAP solutions pertains to a particular subject area. This chapter
describes each section and the processes each section captures.
The information in this chapter is useful for readers who use the Rapid Mart to
design and support a real-time system, such as a Web application, and need
to understand the data in the Rapid Mart and how it relates to SAP solutions.
This chapter discusses:
• Work Center section
• Capacity section
• MRP results section
• Planned Order section
• Reservation section
• Routing section
• Bills of Material (BOM) section
• Production Order section
• Production Operation section
Work Center section
Production operations are carried out at a work center. In SAP solutions work
centers represent the following:
• Machines, machine groups
• Production lines
• Assembly work centers
• Employees, groups of employees
Work centers are used in task list (routing) operations and production orders.
Work centers contain the following types of information:
• Scheduling
Operating times and formulas are entered in the work center, so that the
duration of an operation can be calculated.
• Costing
Formulas are entered in the work center, so that the costs of an operation
can be calculated. A work center is also assigned to a cost center.
• Capacity planning
28 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
(Routings)
Work Center section
The available capacity and formulas for calculating capacity requirements
are entered in the work center.
• Simplifying operation maintenance
Various default values for operations can be entered in the work center.
The following graphic illustrates the use of work center data.
3
A work center is created for a plant (a plant can have many work centers).
The work center category, which you define in Customizing the work center,
determines which data can be maintained in the work center.
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 29

Subject Areas
3
Work Center section
Basic Data in a Work Center:
• Assignments (to cost centers, etc.)
• Capacities
• Scheduling
• Default values
• Hierarchy
• Technical data
Integration of Work Centers
Task Lists (Routings)
Work centers are assigned to operations in task lists (routings). If you change
default values in a work center, the changes are effective in the task list if a
reference indicator has been set for the default value.
Work Center Hierarchies
Work centers can be arranged in hierarchies. These are important in capacity
planning. You use hierarchies to cumulate available capacities and capacity
requirements in a hierarchy work center.
Rapid Mart processing
The Rapid Mart extracts data from SAP solutions tables
• CRHD - Work Center Header
• CRCO - Assignment of Work Center to Cost Center
Data from these tables is used to populate target table
• WORKCENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT
The fact table contains descriptive information and basic data needed for
routing, costing, and capacity calculations.
30 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
Work Center section
The section captures the following dimensional attributes and their associated
dimension tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Activity & Hierarchy ACTIVITY, ACTIVITY_HIER,
ACTIVITY_HIER_HZ,
ACTIVITY_HIER_VR,
ACTIVITY_HIER_BAD
Chart of Accounts CHART_OF_ACCOUNTS
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Control Key CONTROL_KEY
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Cost Center & Hierarchy COST_CENTER,
COST_CENTER_HIER,
COST_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
COST_CENTER_HIER_VR,
COST_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Plant PLANT
Plant Location PLANT_LOCATION
Purchasing Organization PURCH_ORGANIZATION
Standard Text Key STANDARD_TEXT_KEY
Standard Value Key STANDARD_VALUE_KEY
Task List Usage TASK_LIST_USAGE
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Valuation Area VALUATION_AREA
Work Center & Hierarchy WORK_CENTER,
WORK_CENTER_HIER,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_VR,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Work Center Category WORK_CENTER_CATEGORY
Work Center Formula WORK_CENTER_FORMULA
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 31

Subject Areas
3
Work Center section
Fact Table Fields
A work center is master data information. Therefore, classic “measures”
(monetary and quantity values) are not found in the
WORKCENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT table. However, these fields are of
key importance:
Column Name Description
ACTIVITY_ID CRCO.LSTAR - Activity Type
CURRENT_FLAG “X” indicates record is currently in
effect
DAYS_VALID_ASSIGN Number of days assignment is valid
FORMULA_ID CRCO.FORML - Formula key for
costing
GROUP_USG_ID CRHD.PLANV - Key for task list
usage
LOCATN_ID CRHD.STAND - Work center location
PURCH_ORG_ID T001W.EKORG Purchasing
organization (lookup)
VALID_FROM_DATE Start date of validity period for this
record (calculated)
VALID_TO_DATE End date of validity period
(calculated)
WORK_CNTR_CATEG_ID CRHD.VERWE - Work center
category
32 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Rapid Mart data
The following diagram shows the tables in the work center section as a star
schema.
Work Centers:
Subject Areas
Work Center section
3
With the tables in this section you can analyze Work Centers along several
dimensions:
• Activity & Hierarchy
• Chart of Accounts
• Company Code
• Control Key
• Controlling Area
• Cost Center & Hierarchy
• Plant
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 33

Subject Areas
3
Capacity section
• Plant Location
• Purchasing Organization
• Standard Text Key
• Standard Value Key
• Task List Usage
• Time Dimension
• Valuation Area
• Work Center & Hierarchy
• Work Center Category
• Work Center Formula
Note: As Work Center Cost Assignment is a cross-reference fact table, both
work centers and cost centers appear as dimensions with their associated
hierarchies.
Typical queries for this section include:
• What Activities are associated with this work center?
• Which Work Centers are associated with each plant?
• What Cost Centers are associated with my work centers today vs. a year
ago?
Capacity section
The capacity section stores available capacity information by work center,
available interval capacity by date, and capacity requirements for planned
orders.
Work center capacities measure the amount of work output that a work center
can produce during a period of time. Capacity categories subdivide capacity
into types, such as machine, labor, or electrical output. More than one
capacity category can exist at a work center.
Capacities have standard operating times based on shift lengths, break times,
number of individual capacities, and percentage utilization rates. Additional
data items include the formulas and parameters used when calculating the
amount of capacity required for an operation during order scheduling and
capacity planning. Intervals of available capacity can be used to
accommodate deviations from standard available capacities. These intervals
are identified by a version and are delimited with beginning and ending
effective dates.
34 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Capacity planning uses planned order start dates and other work center
scheduling information to calculate capacity requirements for each operation
in the order. The operation capacity requirements consist of the sum of the
time required to set up, process, and teardown after each operation.
Comparison of required capacity to available capacity may necessitate
changes to planned orders before production begins.
Rapid Mart processing
in the Rapid Mart, Capacity Intervals and Capacity Requirements are two
separate fact tables.
Capacity Intervals
Capacity Intervals are sourced from these SAP solutions tables
• KAZY - Interval of Available Capacity
• TC36T - Available Capacity Descriptive Texts
• TC37A - Shift Definitions
• KAPA - Shift Parameters For Available Capacity
• KAKO - Capacity Header Segment
Data from these tables is used to populate target database tables:
• CAPACITY_INTERVAL_STAGE - from KAZY and TC36T. we use the
Data Services Effective Date transform to generate the Valid From Date
not available in the SAP solutions source tables.
• SHIFT_DEFINITION - from TC37A. This table defines the valid periods
(date ranges) of work shifts, and the hours of operation within those
validity periods
• CAPACITY_INTERVAL_FACT - from CAPACITY_INTERVAL_STAGE,
SHIFT_DEFINITION, KAKO, and KAPA
CAPACITY_INTERVAL_STAGE and SHIFT_DEFINITION are intermediate
staging tables, not used for reporting in the Rapid Mart universe (semantic
layer).
The final step of the load process outer-joins CAP ACITY_INTER VAL_STAGE
with data extracted from KAPA and KAKO tables (using
CAPACITY_INTERVAL_STAGE as the outer source). This ensures that all
capacity records are represented in the target table, regardless if intervals
have been defined for them or not. The SHIFT_DEFINITION table is used as
a lookup to determine validity dates and operating hours.
Subject Areas
Capacity section
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 35

Subject Areas
3
Capacity section
The calculation of shift start times, end times, hours of availability are
calculated for either Standard Available Capacity or Non-Standard Available
Capacity.
Capacity Requirements
Capacity Requirements are sourced from these SAP solutions tables
• KBKO - Header Record for Capacity Requirements
• KBED - Capacity Requirements Records
Data from these tables is used to populate target database table:
• CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT- contains results of capacity
Dimensional Attributes
The section captures the following dimensional attributes and their associated
dimension tables
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Capacity CAPACITY
Capacity By Work Center CAPACITY_BY_WORK_CENTER
Capacity Category CAPACITY_CATEGORY
Capacity Object Type CAPACITY_OBJECT_TYPE
Capacity Planning Group CAPACITY_PLANNING_GROUP
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Internal Order & Hierarchy INTERNAL_ORDER,
Object Number Type OBJECT_NUMBER_TYPE
Object Status OBJECT_STATUS,
Order Operation ORDER_OPERATION
Plant PLANT
Purchasing Organization PURCH_ORGANIZATION
Routing ROUTING
planning when a routing is included in a planned order or a production
order.
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_HZ,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_VR,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_BAD
OBJECT_STATUS_HZ
36 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Routing Operation ROUTING_OPERATION
Routing Sequence ROUTING_SEQUENCE
Scheduling Error SCHEDULING_ERROR
Scheduling Type SCHEDULING_TYPE
Task List Type (Routing Type) TASK_LIST_TYPE
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
Valuation Area VALUATION_AREA
Work Center Category WORK_CENTER_CATEGORY
Work Center & Hierarchy WORK_CENTER,
Fact Table Fields
Important measures for Capacity Intervals and Requirements are time
oriented, and mostly presented in days, hours, minutes, etc.
Subject Areas
Capacity section
WORK_CENTER_HIER,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_VR,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_BAD
3
Table Name Column Name Description
CAPACITY_INTERVAL_
FACT
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 37
DAYS_INTERVAL_CYCLE KAZY.ANZTG - Number of days in interval cycle of
HOURS_AVAIL KAPA.KAPAZ -Interval available capacity in hours
HOURS_BREAK KAKO.PAUSE - Cumulative break time in Hours
HOURS_OPRTN KAPA.EINZT - Operating time in hours
NUM_CAPACITY_INDIVID KAPA.ANZHL - Number of individual capacities
PRCNT_UTILIZATN_RATE KAPA.NGRAD - Capacity utilization rate (percent)
STD_CAPACITY_FLAG KAZY.KKOPF - Standard capacity is valid for this
SURROGATE_DOC_ID Alternate key generated in the Rapid Mart for reporting
WORK_DAYS_FLAG KAPA.FABTG - Indicator: Workdays
available capacity
interval
purposes

Subject Areas
3
Capacity section
Table Name Column Name Description
CAPACITY_REQUIREM
ENT_FACT
HOURS_OPRTN_DURTN_
ACTL
HOURS_OPRTN_DURTN_
EARLY
HOURS_OPRTN_DURTN_
LATE
HOURS_OPRTN_DURTN_
SCHED
HOURS_SCHED_TTL Sum of setup time, processing time and teardown time
MINS_OPRTN_DURTN_ACTLCalculated Operation Duration in Min - based on
MINS_OPRTN_DURTN_EA
RLY
MINS_OPRTN_DURTN_LATECalculated Operation Duration in Min - based on
MINS_OPRTN_DURTN_SC
HED
MINS_SCHED_PRCSS KBED.KBEASOLL - Scheduled cap. requirements for
MINS_SCHED_SETUP KBED.KRUESOLL - Scheduled cap. requirements for
MINS_SCHED_TEARDWN KBED.KABRSOLL - Scheduled cap. requirements for
MINS_SCHED_TTL Sum of setup time, processing time and teardown time
QTY_OPRTN KBED.MGVRG- Operation quantity pr oduced
Calculated Operation Duration in Hours- based on
Actual Start date time
Calculated Operation Duration in Hours- based on
Earliest Start date time
Calculated Operation Duration in Hours- based on
Latest Start date time
Calculated Operation Duration in Hours- based on
Scheduled Start date time
in Hours
Actual Start date time
Calculated Operation Duration in Min - based on
Earliest Start date time
Latest Start date time
Calculated Operation Duration in Min - based on
Scheduled Start date time
the op. segment "processing converted to minutes
the op. segment "setup" converted to minutes
the op. segment teardown converted to minutes
in minutes
38 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Rapid Mart data
The following diagrams show the tables in the Capacity section as a star
schema.
Capacity Intervals
Subject Areas
Capacity section
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 39

Subject Areas
3
Capacity section
Capacity Requirements
With the tables in this section you can analyze Work Centers along several
dimensions:
• Capacity
• Capacity By Work Center
• Capacity Category
• Capacity Object Type
• Capacity Planning Group
• Company Code
• Controlling Area
• Internal Order & Hierarchy
• Object Number Type
• Object Status
• Order Operation
• Plant
• Purchasing Organization
• Routing
• Routing Operation
40 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
MRP results section
• Routing Sequence
• Scheduling Error
• Scheduling Type
• Task List Type (Routing Type)
• Time Dimension
• Unit Of Measure
• Valuation Area
• Work Center Category
• Work Center & Hierarchy
Typical queries for this section include:
• What are capacity requirements by work center by weekly or monthly
time buckets?
• What are the sum individual capacities by work center according to work
center hierarchy?
• How productive are Capacity Intervals scheduled around holidays as
compared to regular intervals?
• Which are the top 10 routing operations in terms of actual operation
hours?
3
MRP results section
The MRP results section stores the results tables from material requirements
planning (MRP) and master production scheduling (MPS) planning runs.
Material requirements planning (MRP) combines production master data with
demand forecasts, sales orders, and material availability to arrive at a plan for
how much material to procure through production, purchase requisition, stock
transfer, or other means. Depending on user inputs, the bill of materials may
be exploded as well to generate requirements lists for dependent materials.
The MRP requirements list contains the amount of stock on hand, the
demands by requirement date, planned order quantities, procurement
quantities, scrap output, and exception warnings indicating errors.
The MRP process generates rough-cut capacity requirements if the
scheduling type selected at planning time is type 2 (lead time scheduling and
capacity planning).
The MRP results table also includes materials planned using master
production scheduling (MPS) strategies.
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 41

Subject Areas
3
MRP results section
Rapid Mart processing
MRP results can be stored in either clustered or transparent MRP detail
tables in SAP solutions. The Rapid Mart selects from both tables to ensure a n
accurate representation of MRP results.
The source tables in SAP solutions are:
• MDKP - Header Data for MRP Document
• MDTB - MRP Details (transparent)
• MDTC - Aggregated MRP table items (clustered)
The target table in the Rapid Mart is:
• MRP_RESULT_FACT
The clustered MDTC table is accessed via a Custom ABAP transform called
MRPCluster.
You can choose to maintain only the last set of MRP results or to accumulate
them over time. If you choose to preserve old results during incremental
loads, you should periodically clean the MRP_RESULT_FACT table so that
performance is not adversely affected.
The section captures the following dimensional attributes and their associated
dimension tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Exception Text EXCEPTION_TEXT
Material & Product Hierarchy MATERIAL,
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Material Group MATERIAL_GROUP
Material Type MATERIAL_TYPE
MRP Controller MRP_CONTROLLER
MRP Element Type MRP_ELEMENT_TYPE
MRP Group MRP_GROUP
MRP Lot Size MRP_LOT_SIZE
MRP Profile MRP_PROFILE
MRP Type MRP_TYPE
Plant PLANT
42 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Procurement Type PROCUREMENT_TYPE
Purchasing Group PURCH_GROUP
Purchasing Organization PURCH_ORGANIZATION
Storage Location STORAGE_LOCATION
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
Valuation Area VALUATION_AREA
Fact Table Fields
Important measures for MRP Results are both quantity and time oriented, and
presented in base unit of measure and days.
Column Name Description
DAYS_GR_PROCESS MDTB.WEBAZ - Goods receipt processing
DAYS_RECPT_COVERAGE MDKP.BERW2 - Receipt range of coverage
DAYS_STOCK_COVERAGE MDKP.BERW1 - Stock coverage without
QTY_MRP MDTB.MNG01 - Quantity received or
QTY_SCRAP MDTB.MNG02 - Variable scrap quantity
QTY_SHORTAGE MDTB.MNG03 - Shortage quantity
QTY_STOCK_EXCESS MDTB.RDMNG - Excess stock quantity
time in days
receipts
quantity required
Subject Areas
MRP results section
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 43
Subject Areas
3
MRP results section
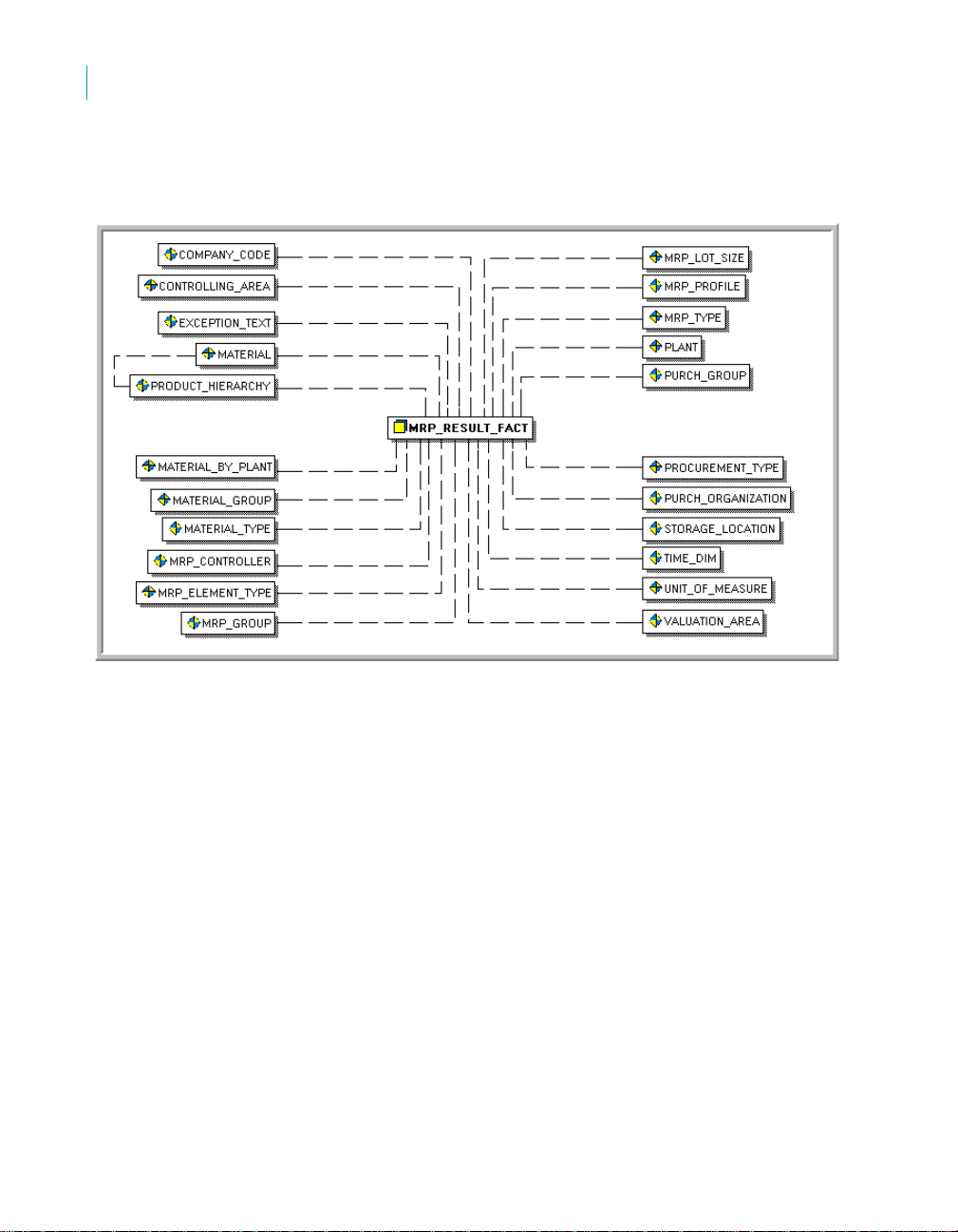
Rapid Mart data
The following diagram shows the tables in the MRP results section.
With the tables in this section you can analyze Work Centers along several
dimensions:
• Company Code
• Controlling Area
• Exception Text
• Material & Product Hierarchy
• Material By Plant
• Material Group
• Material Type
• MRP Controller
• MRP Element Type
• MRP Group
• MRP Lot Size
• MRP Profile
• MRP Type
44 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
Planned Order section
• Plant
• Procurement Type
• Purchasing Group
• Purchasing Organization
• Storage Location
• Time Dimension
• Unit Of Measure
• Valuation Area
Typical queries for this section include:
• What is my planned scrap production for next month?
• What is the planned total quantity of purchase requisitions for next
month?
• List MRP requirements by requirement type.
• Which materials have the highest external procurement rate by quantity?
• Which plants have excess stock?
• Which materials consistently show a shortage by plant at the end of each
quarter?
3
Planned Order section
The planned order section extracts detailed information for planned orders.
Materials Requirements Planning results in planned orders that suggest the
amount of material to produce and when to produce it in order to meet the
demand requirements.
Conversion of a planned order to a production order creates orders for all the
material components needed to complete the planned order. Material
reservations are created if existing stocks will be used for components. A
routing and a bill of materials is required to create a planned order.
Planned orders that have been converted to production orders are removed
from the planned order table once the quantity to be produced is covered by
production orders. Only planned orders marked as convertible can be
converted to production orders.
The Rapid Mart facilitates maintaining a partial history of the planned orders
that have been removed. The Rapid Mart delta (incremental) load does not
delete Planned Orders that exist in the target table.
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 45

Subject Areas
3
Planned Order section
if a planned order is created and then subsequently converted to a production
order between Rapid Mart refreshes, the planned order will not appear in the
Rapid Mart target table as it was deleted in SAP solutions before it could be
captured by the Rapid Mart.
Additionally, a final set of changes to a planned order just before it is
converted (and deleted) may not be captured in the target Rapid Mart table.
Planned orders do not have creation or change dates associated with them.
Thus, there is no way to tell when a change or deletion of a planned order
occurs in SAP solutions.
The Rapid Mart does a full extract of all planned orders in either the first
(initial) load or delta (incremental) loads.
In an initial load, the planned order target table is truncated (all data deleted)
before data from SAP solutions is loaded.
In a delta load, no data is deleted in the target, and the Table Comparison
transform is used to add or updated existing records. Table Comparison does
not delete existing records in the target. Thus, the partial history detailed
above can be preserved.
Rapid Mart processing
Planned orders are sourced from SAP solutions table
• PLAF - Planned Orders
The data populates target table
• PLANNED_ORDER_FACT - Planned order details
The section captures the following dimensional attributes and their associated
dimension tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Account Assignment Category ACCT_ASSIGNMENT_CATEGORY
Bill Of Materials Status BILL_OF_MATERIALS_STATUS
Bill Of Materials Usage BILL_OF_MATERIALS_USAGE
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Document Type DOCUMENT_TYPE &
DOCUMENT_CATEGORY
Material & Product Hierarchy MATERIAL &
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
46 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
Planned Order section
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Material Group MATERIAL_GROUP
Production Material MATERIAL_PRODUCTION
Material Type MATERIAL_TYPE
MRP Controller MRP_CONTROLLER
Object Type OBJECT_TYPE
Plant PLANT
Procurement Type PROCUREMENT_TYPE
Production Scheduler PRODUCTION_SCHEDULER
Project PROJECT
Project Element & Hierarchy PROJECT_ELEMENT,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_HZ,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_VR,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_BAD
Purchasing Organization PURCH_ORGANIZATION
Routing ROUTING
Scheduling Error SCHEDULING_ERROR
Storage Location STORAGE_LOCATION
Task List Type TASK_LIST_TYPE
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
Valuation Area VALUATION_AREA
3
Fact Table Fields
Important measures for planned orders are both quantity and time oriented:
Column Name Description
DAYS_ORD_DURTN_PLAN Calculated Order to Completion time
in Days- based on Planned Start date
time
HOURS_ORD_DURTN_PLAN Calculated Order to Completion time
in Hours - based on Planned Start
date time
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 47
Subject Areas
3
Planned Order section
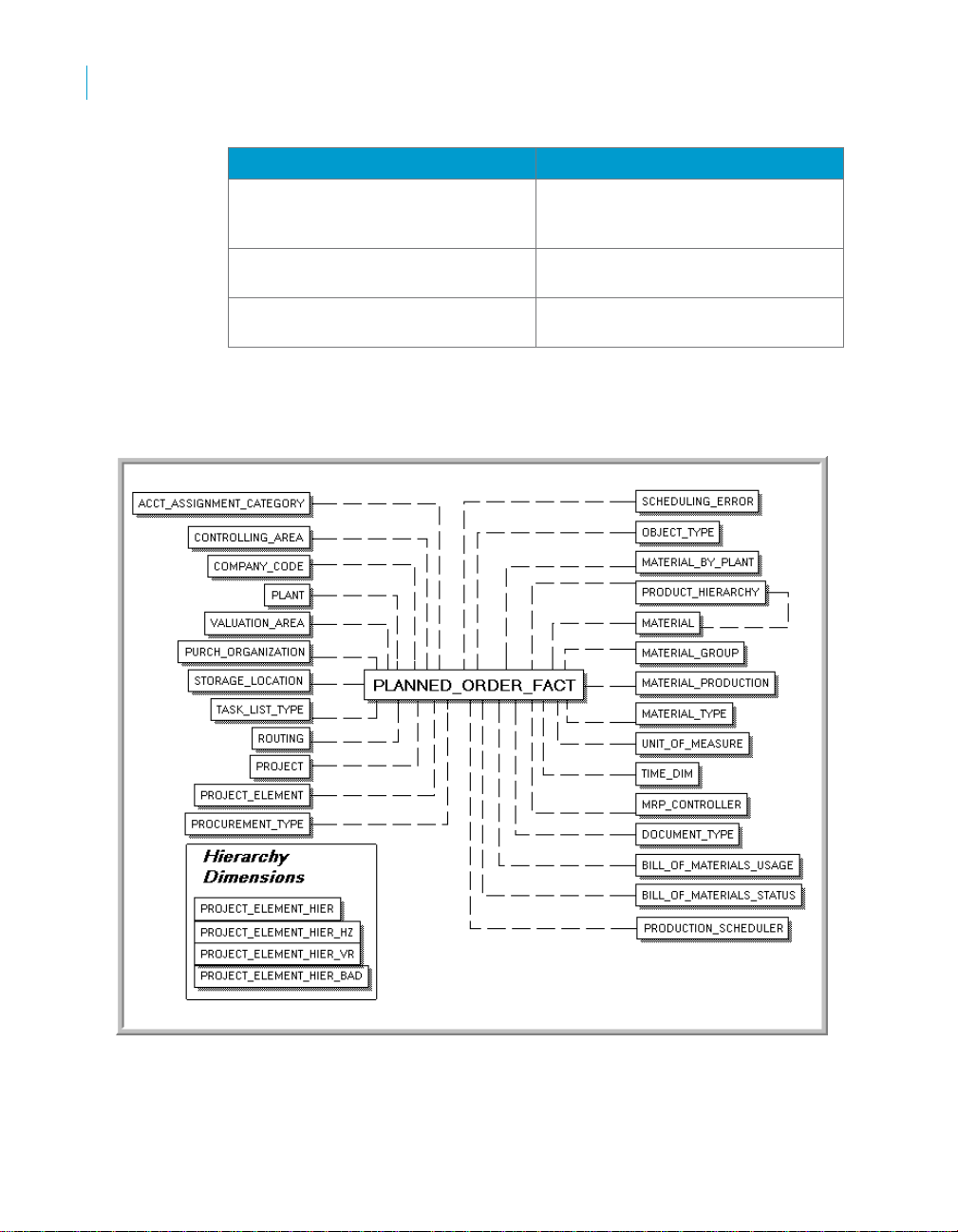
Rapid Mart data
Column Name Description
MINS_ORD_DURTN_PLAN Calculated Order to Completion time
in Min - based on Planned Start date
time
QTY_REDUCED PLAF.ABMNG - Reduced quantity in
the planned order
QTY_TTL PLAF.GSMNG - Total planned order
quantity
The following diagram shows the tables in the planned order section.
With the tables in this section you can analyze Planned Orders along several
dimensions:
48 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
Planned Order section
• Account Assignment Category
• Bill Of Materials Status
• Bill Of Materials Usage
• Company Code
• Controlling Area
• Document Type
• Material & Product Hierarchy
• Material By Plant
• Material Group
• Production Material
• Material Type
• MRP Controller
• Object Type
• Plant
• Procurement Type
• Production Scheduler
• Project
• Project Element & Hierarchy
• Purchasing Organization
• Routing
• Scheduling Error
• Storage Location
• Task List Type
• Time Dimension
• Unit Of Measure
• Valuation Area
Typical queries for this section include:
• Show planned production quantities by material, and by week
• Which MRP controllers have the most Planned Orders by month?
• What did this planned order looked like before it was deleted in SAP
solutions?
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 49

Subject Areas
3
Reservation section
Reservation section
In SAP solutions, a reservation or dependent requirement is a request to the
warehouse to keep materials ready for use on a particular date. A reservation
ensures that a material is available when the material is needed. The MRP
process can make reservations automatically , or users can make reservations
manually. Any check on material availability must consider prior reservations
for the material. Reservations are allowed only if the material is available to
promise (ATP).
The reservation’s timing determines when goods issues (for consumption in a
production order, or for delivery in a sales order) are allowed for reserved
items. This may be manually overridden using the “movement allowed”
indicator. A goods issue appears in the material movements table and
references the reservation. At this point, SAP solutions reduces inventory by
the amount of the goods issue.
If the reservation is for a particular customer order, the sales order and sales
line item numbers are stored on the reservation. In this case, the goods issue
document in the material movements table also contains references to the
sales order. These fields provide a link to the sales and distribution functions
of the Sales Rapid Mart.
SAP solutions marks reservations as deleted when their retention periods
have been exceeded. Reservations marked deleted are not moved into the
Rapid Mart reservations table.
Rapid Mart processing
In the Rapid Mart, reservations are sourced from SAP solutions tables:
• RKPF - Document Header: Reservation
• RESB - Reservation/dependent requirements details
The target table in the Rapid Mart is:
• RESERVATION_FACT
The section captures the following dimensional attributes and their associated
dimension tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Acct Assignment Category ACCT_ASSIGNMENT_CATEGORY
Activity & Hierarchy ACTIVITY, ACTIVITY_HIER,
ACTIVITY_HIER_HZ,
ACTIVITY_HIER_VR,
ACTIVITY_HIER_BAD
50 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Subject Areas
Reservation section
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Bill Of Materials & Hierarchy BILL_OF_MATERIALS,
BILL_OF_MATERIALS_HZ,
BILL_OF_MATERIALS_VR
BOM Item Category BOM_ITEM_CATEGORY
Business Area BUSINESS_AREA
Chart Of Accounts CHART_OF_ACCOUNTS
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Cost Center & Hierarchy COST_CENTER,
COST_CENTER_HIER,
COST_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
COST_CENTER_HIER_VR,
COST_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Currency CURRENCY
Customer CUSTOMER
Debit Credit Indicator DEBIT_CREDIT_INDICATOR
Internal Order & Hierarchy INTERNAL_ORDER,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_HZ,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_VR,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_BAD
Material, Product Hierarchy MATERIAL,
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
Material Batch MATERIAL_BATCH
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Material Group MATERIAL_GROUP
Material Type MATERIAL_TYPE
Object Number Type OBJECT_NUMBER_TYPE
Object Status & Hierarchy OBJECT_STATUS,
OBJECT_STATUS_HZ
Order Operation ORDER_OPERATION
Plant PLANT
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 51

Subject Areas
3
Reservation section
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Profit Center & Hierarchy PROFIT_CENTER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_VR,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Project PROJECT
Project Element & Hierarchy PROJECT_ELEMENT,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_HZ,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_VR,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_BAD
Purchasing Group PURCH_GROUP
Purchasing Organization PURCH_ORGANIZATION
Special Stock Indicator SPECIAL_STOCK_INDICATOR
Storage Location STORAGE_LOCATION
Supply Area SUPPLY_AREA
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
Valuation Area VALUATION_AREA
Warehouse WAREHOUSE
Fact Table Fields
Important measures in Reservations include quantities and monetary values
(amounts) of the reserved materials:
Column Name Description
AMT_PRICE RESB.GPREIS - Price in component
currency
AMT_WITHDRAWN RESB.ENWRT - Value withdrawn
AMT_WITHDRAWN_SIGN RESB.ENWRT - Value withdrawn
(negative for Credit, positive for
Debit)
QTY RESB. BDMNG - Requirements
quantity
QTY_SIGN RESB. BDMNG - Requirements
quantity (negative for Credit, positive
for Debit)
52 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Column Name Description
QTY_WITHDRAWN RESB.ENMNG - Quantity withdrawn
QTY_WITHDRAWN_SIGN RESB.ENMNG - Quantity withdrawn
Rapid Mart Data
The following diagram shows the tables in the Reservations section:
Subject Areas
Reservation section
(negative for Credit, positive for
Debit)
3
With the tables in this section your can analyze Reservations along several
dimensions:
• Acct Assignment Category
• Activity & Hierarchy
• Bill Of Materials & Hierarchy
• BOM Item Category
• Business Area
• Chart Of Accounts
• Company Code
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 53

Subject Areas
3
Reservation section
• Controlling Area
• Cost Center & Hierarchy
• Currency
• Customer
• Debit Credit Indicator
• Internal Order & Hierarchy
• Material, Product Hierarchy
• Material Batch
• Material By Plant
• Material Group
• Material Type
• Object Number Type
• Object Status & Hierarchy
• Order Operation
• Plant
• Profit Center & Hierarchy
• Project
• Project Element & Hierarchy
• Purchasing Group
• Purchasing Organization
• Special Stock Indicator
• Storage Location
• Supply Area
• Time Dimension
• Unit Of Measure
• Valuation Area
• Warehouse
Typical queries for this section include:
• What materials are reserved for a particular sales order?
• What materials are reserved for a particular production order?
• What is the value of materials in a particular cost center?
• Which requirements for a certain material are due in the next week?
54 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Routing section
The routing section stores master data that describes material routings,
routing header data, and detailed routing operations, as well as a table linking
routing to bill of materials components. These are presented as two fact
tables in the Rapid Mart:
• ROUTING_LINE_FACT
• ROUTING_BOM_FACT
SAP solutions stores routing information as a list of operations which are
required to produce a material. A routing is identified by a task list type, a
group, and a group counter. A routing consists of a header with status
information, descriptive information, effective dates, and lot size constraints.
Operations consist of a sequence number, activity number, effective dates,
and a set of associated activities. The operations list also specifies additional
times required to setup, process, wait, or move materials.
Before you can produce a material, you must assign it to a routing. A routing
can be specified for each component of a bill of materials (BOM).
Note: In SAP solutions, task lists are a super-set of routings. They can
include other types of tasks organized into lists, such as inspection plans for
the Quality Management (QM) module. SAP solutions distinguishes the
different task lists by task list type. The Production Planning Rapid Mart
limits the data extracted from SAP solutions to two task list types:
• “N” - Routings
• “R” - Rate Routings
Subject Areas
Routing section
3
Rapid Mart processing
In the Rapid Mart, Routings has two separate fact tables:
• ROUTING_LINE_FACT, sourced from SAP solutions tables:
• PLFL - Task list - sequences
• PLAS - Task list - selection of operations/activities
• PLPO - Task list - operation/activity
• ROUTING_BOM_FACT, source from SAP solutions table:
• PMLZ - Allocation of bill of material items to operations
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 55

Subject Areas
3
Routing section
The section captures the following dimensional attributes and their associated
dimension tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Activity & Hierarchy ACTIVITY, ACTIVITY_HIER,
ACTIVITY_HIER_HZ,
ACTIVITY_HIER_VR,
ACTIVITY_HIER_BAD
Bill Of Materials & Hierarchy BILL_OF_MATERIALS,
BILL_OF_MATERIALS_HZ,
BILL_OF_MATERIALS_VR
Capacity Category CAPACITY_CATEGORY
Chart Of Accounts CHART_OF_ACCOUNTS
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Control Key CONTROL_KEY
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Cost Center & Hierarchy COST_CENTER,
COST_CENTER_HIER,
COST_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
COST_CENTER_HIER_VR,
COST_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Cost Element & Hierarchy COST_ELEMENT,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_HZ,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_VR,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_BAD
Factory Calendar, Factory Calendar
Period
Monetary Currency CURRENCY
Operation Suitability OPERATION_SUITABILITY
Plant PLANT
Project PROJECT
Project Element & Hierarchy PROJECT_ELEMENT,
Purchasing Organization PURCH_ORGANIZATION
Routing ROUTING
FACTORY_CALENDAR,
FACTORY_CALENDAR_PERIOD
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_HZ,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_VR,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_BAD
56 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Routing Material ROUTING_MATERIAL
Routing Operation ROUTING_OPERATION
Routing Sequence ROUTING_SEQUENCE
Standard Text Key STANDARD_TEXT_KEY
Task List Type TASK_LIST_TYPE
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
Valuation Area VALUATION_AREA
Work Center & Hierarchy WORK_CENTER,
Work Center Category WORK_CENTER_CATEGORY
Fact Table Fields
Routings are essentially master data. In ROUTING_BOM_FACT table, the
two measures are BOM and Routing counts.
In ROUTING_LINE_FACT, many important measures are time oriented and
presented in hours. Traditional values (such as cost s and quantities) are also
included.:
Subject Areas
Routing section
WORK_CENTER_HIER,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_VR,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_BAD
3
Table Name Column Name Description
ROUTING_BOM_FACT BOM_COUNT Values are 1 for a the first occurrence
of BOM_ID and 0 for the rest for
Number of BOMs measure
ROUTING_COUNT Values are 1 for a the first occurrence
of ROUTING_ID and 0 for the rest for
Number of Routings measure
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 57

Subject Areas
3
Routing section
Table Name Column Name Description
ROUTING_LINE_FACT AMT_COST PLPO.PRKST -Costs in the activity
HOURS_MOVE_MIN PLPO.ZTMIN - Minimum move time
converted to hours
HOURS_MOVE_STD PLPO.ZTNOR - Standard move time
converted to hours
HOURS_OVERLAP_MIN PLPO.ZMINU - Minimum overlap time
converted to hours
HOURS_PRCSS_MIN PLPO.ZMINB - Minimum processing
time converted to hours
HOURS_QUEUE_MIN PLPO.ZWMIN - Minimum queue time
converted to hours
HOURS_QUEUE_STD PLPO.ZWNOR - Standard queue time
converted to hours
HOURS_STD_01 PLPO.VGW01 - Standard value in
hours
HOURS_STD_02 PLPO.VGW02 - Standard value in
hours
HOURS_STD_03 PLPO.VGW03 - Standard value in
hours
HOURS_STD_04 PLPO.VGW04 - Standard value of
activity in hours
HOURS_STD_05 PLPO.VGW05 - Standard value in
hours
HOURS_STD_06 PLPO.VGW06 - Standard value in
hours
HOURS_WAIT_MAX PLPO.ZLMAX - Maximum wait time
converted to hours
HOURS_WAIT_MIN PLPO.ZLPRO - Minimum wait time
converted to hours
NUM_SPLITS PLPO.SPLIM - Number of splits
PRCNT_SCRAP_FACTORPLPO.AUFAK - Scrap factor in pct
QTY_SENDAHEAD_MIN PLPO.MINWE - Minimum send-ahead
quantity
QTY_STD PLPO.BMSCH - Quantity of the
material to be produced to which the
standard values of the operation refer
58 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Rapid Mart data
The following diagram shows the tables in the routing section.
Subject Areas
Routing section
3
With the tables in this section you can analyze Routings along several
dimensions:
• Activity & Hierarchy
• Bill Of Materials & Hierarchy
• Capacity Category
• Chart Of Accounts
• Company Code
• Control Key
• Controlling Area
• Cost Center & Hierarchy
• Cost Element & Hierarchy
• Currency
• Factory Calendar & Factory Calendar Period
• Operation Suitability
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 59

Subject Areas
3
Bills of Material (BOM) section
• Plant
• Project
• Project Element & Hierarchy
• Purchasing Organization
• Routing
• Routing Material
• Routing Operation
• Routing Sequence
• Standard Text Key
• Task List Type
• Time Dimension
• Unit Of Measure
• Valuation Area
• Work Center & Hierarchy
• Work Center Category
Typical queries for this section include:
• What are the routings where a particular material is used?
• What are routing operations standard activities by controlling area?
• What are routing costs by cost center and associated hierarchy?
• What are the routing BOMs for a particular material?
Bills of Material (BOM) section
Bills of Material (BOMs) are formally structured lists of the components that
make up a product or assembly. The list contains the object number of each
component, together with the quantity and unit of measure.
BOMs are used in their different forms in various situations where a finished
product is assembled from several component parts or materials. Depending
on the industry sector, they can also be called recipes or lists of ingredients
and so on.
They contain important basic data for numerous areas of a company, for
example:
• MRP (Material Requirements Planning)
• Material provisions for production
• Product costing
• Plant maintenance
60 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
Bills of Material (BOM) section
You can create the following categories of BOMs in the SAP solutions
system:
• Material BOMs (scope of this Rapid Mart)
• Equipment BOMs
• Functional location BOMs
• Document structures
• Order BOM
• Work breakdown structure (WBS) BOM
The Rapid Mart limits data extracted to:
• BOM Category “M” - Material BOMs
These are the BOMs that describe which component materials are used in
planning production of a given material (assembly material) and the quantity
needed of each of its components.
Within SAP solutions, a bill of materials is assigned to a plant. Plants can
have alternative BOMs within a plant for production of different lot sizes of the
same material. The header record contains the base quantity produced and
the production unit of measure. All component quantities are calculated
based on these parameters. The header record also contains information on
the overall status and validity period for the BOM.
Item records in a BOM describe the components of the assembly, and the
quantities required to produce the base quantity of the BOM material. BOM
items also have validity periods associated with them. Other item properties
include pricing information, dimensions, by-products, and scrap production.
The latter two items are created as a result of the production process and are
listed as negative quantities in the BOM.
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 61

Subject Areas
3
Bills of Material (BOM) section
The process of generating a hierarchical listing of all the components needed
to produce an item is called the BOM explosion. Because each component or
assembly in a BOM may have its own BOM, the BOM explosion continues to
grow exponentially until the final (lowest level) components have no
constituent parts. The BOM explosion process must also account for
differences between the quantity needed when an item is a component in a
BOM, and the base quantity produced when the item is the BOM item in a
subsequent level explosion.
The following example shows an SAP solutions three-level BOM explosion:
Rapid Mart processing
The Rapid Mart presents BOM’s as two separate fact tables:
• PRODUCTION_BOM_EXPLOSION_FACT
This table explodes BOMs allowing you to display BOMs in the Rapid
Mart in the same manner as shown in example above.
• PRODUCTION_BOM_FACT
This table allows you to view a more complete single level BOM detail.
62 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

The source tables for BOMs in SAP solutions are:
Subject Areas
Bills of Material (BOM) section
3
SAP solutions
Table
MARA General Material Data
MAST Material to BOM Link
STAS BOMs - Item Selection
STKO BOM Header
STPO BOM item
T001W Plants/Branches
The Rapid Mart first extracts data to populate PRODUCTION_BOM_FACT.
Then, PRODUCTION_BOM_FACT serves as the source table for
PRODUCTION_BOM_EXPLOSION_FACT.
The section captures the following dimensional attributes and their associated
dimension tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Bill Of Materials & Hierarchy BILL_OF_MATERIALS,
BOM Item Category BOM_ITEM_CATEGORY
Bill Of Materials Status BILL_OF_MATERIALS_STATUS
Bill Of Materials Usage BILL_OF_MATERIALS_USAGE
Chart Of Accounts CHART_OF_ACCOUNTS
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Cost Element & Hierarchy COST_ELEMENT,
Monetary Currency CURRENCY
Material, Product Hierarchy MATERIAL,
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Material Group MATERIAL_GROUP
Material Type MATERIAL_TYPE
Table Description
BILL_OF_MATERIALS_HZ,
BILL_OF_MATERIALS_VR
COST_ELEMENT_HIER,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_HZ,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_VR,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_BAD
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 63
Subject Areas
3
Bills of Material (BOM) section
Fact Table Fields
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Object Type OBJECT_TYPE
Plant PLANT
Purchasing Group PURCH_GROUP
Purchasing Organization PURCH_ORGANIZATION
Spare Part Indicator SPARE_PART_INDICATOR
Storage Location STORAGE_LOCATION
Supply Area SUPPLY_AREA
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
Valuation Area VALUATION_AREA
Vendor VENDOR
Vendor By Company VENDOR_BY_COMPANY
Important measures for Bills of Material are component and assembly
quantities, pricing information, and counts of number of times a component is
referenced:
PRODUCTION_BOM_EXPLOSION_FACT:
Column Name Description
LVL_01_NUM_TIMES_USED Count number of times component is
referenced in BOM to see if special
handling is required - Level 1
LVL_01_QTY STPO-MENGE - Component quantity -
Level 1
LVL_02_NUM_TIMES_USED Count number of times component is
referenced in BOM to see if special
handling is required - Level 2
LVL_02_QTY STPO-MENGE - Component quantity -
Level 2
LVL_03_NUM_TIMES_USED Count number of times component is
referenced in BOM to see if special
handling is required - Level 3
LVL_03_QTY STPO-MENGE - Component quantity -
Level 3
64 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
Bills of Material (BOM) section
Column Name Description
LVL_04_NUM_TIMES_USED Count number of times component is
referenced in BOM to see if special
handling is required - Level 4
LVL_04_QTY STPO-MENGE - Component quantity -
Level 4
LVL_05_NUM_TIMES_USED Count number of times component is
referenced in BOM to see if special
handling is required - Level 5
LVL_05_QTY STPO-MENGE - Component quantity -
Level 5
LVL_06_NUM_TIMES_USED Count number of times component is
referenced in BOM to see if special
handling is required - Level 6
LVL_06_QTY STPO-MENGE - Component quantity -
Level 6
QTY_BOM STKO-BMENG - Base quantity for BOM
Material
3
PRODUCTION_BOM_FACT:
Column Name Description
AMT_PRICE STPO-PREIS - Price
DAYS_DELIV STPO-LIFZT - Delivery time in days
PRCNT_SCRAP STPO.AUSCH - Component scrap in
percent
PRICE_UNIT STPO-PEINH - Price unit
QTY STPO-MENGE - Component quantity
QTY_BOM STKO-BMENG - Base quantity for BOM
Material
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 65
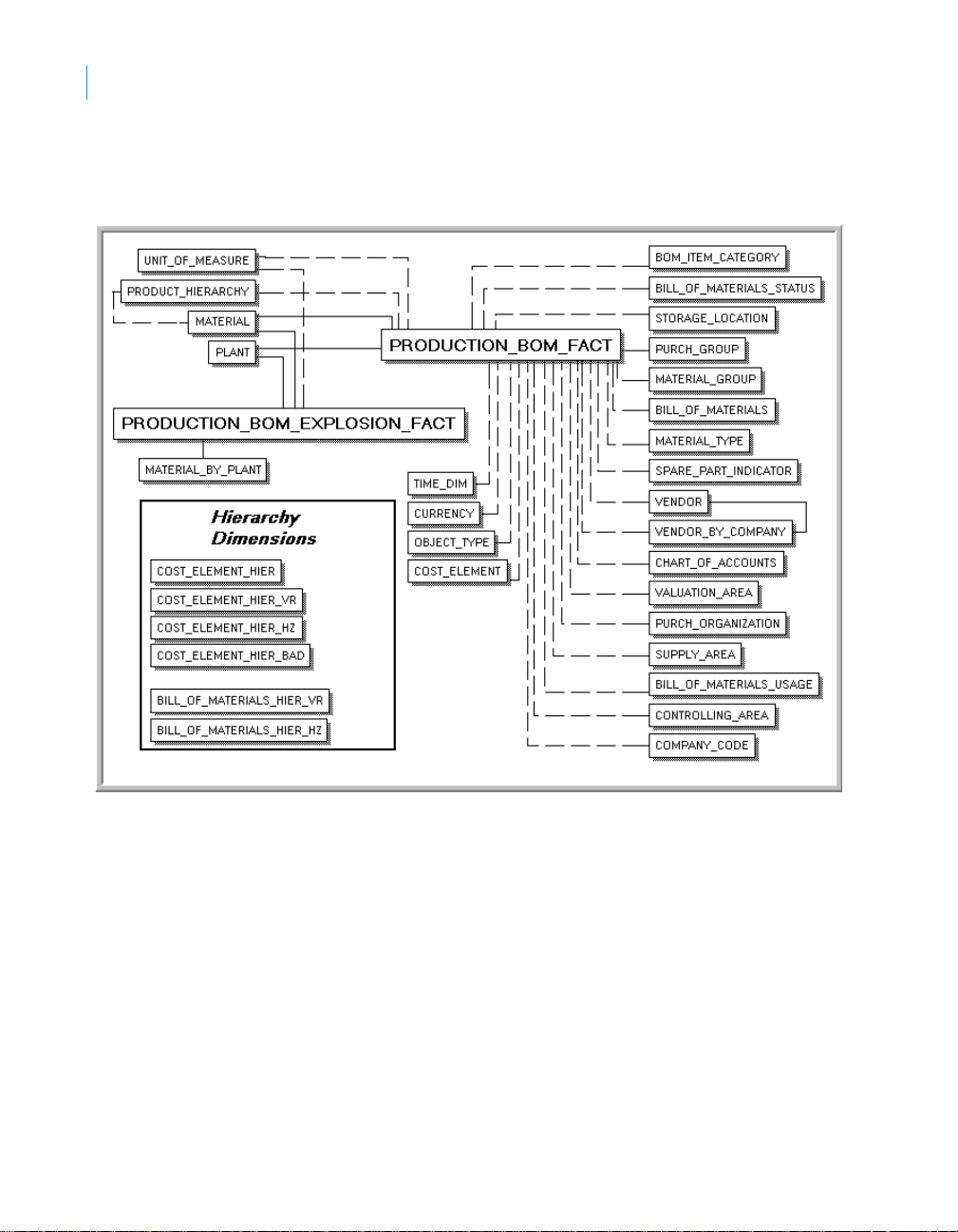
Subject Areas
3
Bills of Material (BOM) section
Rapid Mart data
The following diagram shows the tables in the bill of materials section.
With the tables in this section you can analyze Bills of Material along several
dimensions:
• Bill Of Materials & Hierarchy
• BOM Item Category
• Bill Of Materials Status
• Bill Of Materials Usage
• Chart Of Accounts
• Company Code
• Controlling Area
• Cost Element & Hierarchy
• Monetary Currency
66 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
Production Order section
• Material, Product Hierarchy
• Material By Plant
• Material Group
• Material Type
• Object Type
• Plant
• Purchasing Group
• Purchasing Organization
• Spare Part Indicator
• Storage Location
• Supply Area
• Time Dimension
• Unit Of Measure
• Valuation Area
• Vendor
• Vendor By Company
Typical queries for this section include:
• Display exploded bill of materials by plant and material
• On which bills of materials is a particular component is used?
• Are the BOMs for a material produced at two separate plants identical?
• Which BOMs have the highest and lowest scrap percentages?
• What components does a certain purchasing organization procure?
3
Production Order section
Production orders are a fundamental part of Production Planning and Control
(PP). PP is fully integrated in the Logistics (LO) component and has, among
others, interfaces to:
• Sales and Distribution (SD)
• Materials Management (MM)
• Controlling (CO)
A production order defines which material is to be processed, at which
location, at what time and how much work is required. It also defines which
resources are to be used and how the order costs are to be settled.
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 67
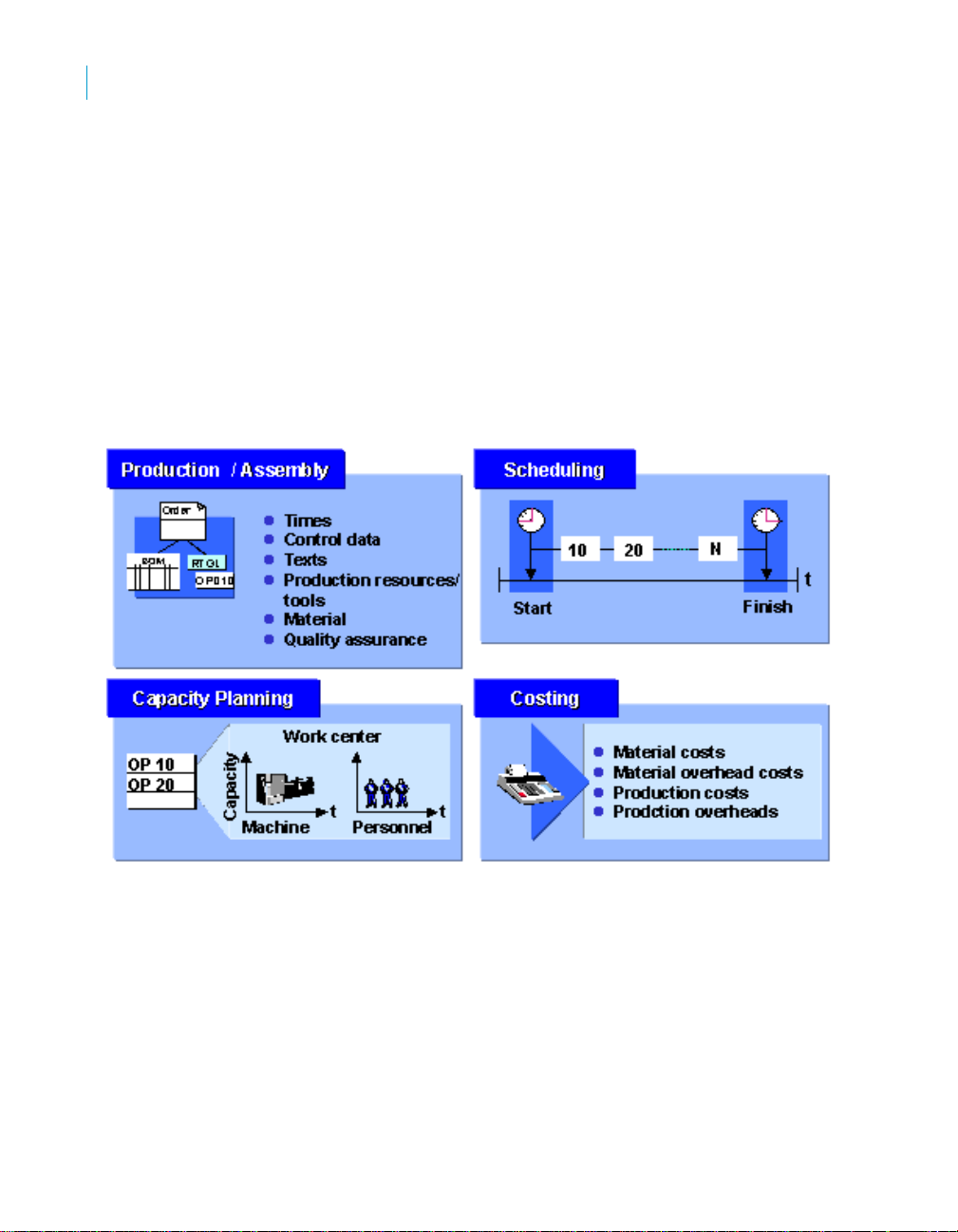
Subject Areas
3
Production Order section
As soon as a planned order or other request is generated from material
requirements planning, the information is passed on to shop floor control; the
order-relevant data is also added to ensure complete order processing.
Production orders are used to control production within a company and also
to control cost accounting.
You can use the production order to specify:
• What is to be produced (Production / Assembly)
• When production is to take place (Scheduling)
• Which capacity is to process the order (Capacity Planning)
• How much production costs (Costing)
This is illustrated graphically below:
Production orders can be generated in the following ways:
• From a requirement generated in requirements planning, that is, by
converting a planned order to a production order
• Using an assembly order
• Without any previous requirement, that is, by creating it manually
When a production order is created the following actions are carried out:
• A routing is selected, its operations and sequences are transferred to the
order
68 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
Production Order section
• The bill of materials is exploded and the items in the bill of material are
transferred to the order
• Reservations are generated for bill of material items held in stock
• The planned costs for the order are generated
• The capacity requirements are generated for the work centers
• Purchase requisitions are generated for non-stock items and
externally-processed operations
In the Rapid Mart, the production order section stores data about production
orders. When goods are required, planned orders are converted to production
orders. The production order specifies how much to produce, the routing, the
bill of material used to reserve, produce or procure dependent materials, the
scheduled and actual start and end dates, and the status of the order.
The SAP solutions PP-MRP materials requirements planning system
converts planned orders into production orders based on material demand.
When a production order is created, the system automatically creates a
reservation for the necessary material components.
The availability of the components can also be dependent on a production
order. In-stock components can be issued, or purchase requisitions
generated to procure external materials. Resources and tools for production
must be scheduled. Conversion of a planned order to a production order
initiates these processes.
There are two basic types of production orders:
• Make-to-order production orders — Orders that fulfill a specific sales
order. Records for make-to-order production orders contain a reference
to a sales order and sales line item.
• Make-to-stock production orders — Orders that replenish stock.
Customer orders are typically filled from existing stock. Make-to-stock
production orders replenish that stock. Make-to-stock production orders
can also increase stock in anticipation of future customer demand.
Make-to-stock production orders do not reference specific sales orders.
3
Rapid Mart processing
Production orders are a shared component. They are used in the following
Rapid Marts:
• SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions - Extracts only Order Category “10” (Standard Production
Orders).
• SAP BusinessObjects Project Systems Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions - Extracts only Order Category “20” (Network Orders)
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 69

Subject Areas
3
Production Order section
There is more information on how this shared component is used in Chapter
8: Technical Implementation of this user guide.
Production orders are source from these SAP solutions tables:
• AUFK - Order master data
• AFKO - Order header data PP orders
• AFPO - Order item
The target table for Production Orders is:
• PRODUCTION_ORDER_FACT
The section captures the following dimensional attributes and their associated
dimension tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Account Assignment Category ACCT_ASSIGNMENT_CATEGORY
Business Area BUSINESS_AREA
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Cost Center & Hierarchy COST_CENTER,
COST_CENTER_HIER,
COST_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
COST_CENTER_HIER_VR,
COST_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Cost Element & Hierarchy COST_ELEMENT,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_HZ,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_VR,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_BAD
Document Type DOCUMENT_TYPE &
DOCUMENT_CATEGORY
Functional Area & Hierarchy FUNCTIONAL_AREA,
FUNCTIONAL_AREA_HIER,
FUNCTIONAL_AREA_HIER_HZ,
FUNCTIONAL_AREA_HIER_VR,
FUNCTIONAL_AREA_HIER_BAD
Internal Order & Hierarchy INTERNAL_ORDER,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_HZ,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_VR,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_BAD
Internal Order Status INTERNAL_ORDER_STATUS
70 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
Production Order section
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Material Batch MATERIAL_BATCH
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Material Group MATERIAL_GROUP
Material Production MATERIAL_PRODUCTION
Material Type MATERIAL_TYPE
Material, Product Hierarchy MATERIAL,
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
Monetary Currency CURRENCY
MRP Controller MRP_CONTROLLER
Object Class OBJECT_CLASS
Object Number Type OBJECT_NUMBER_TYPE
Object Status & Hierarchy OBJECT_STATUS,
OBJECT_STATUS_HZ
Plant PLANT
Plant Location PLANT_LOCATION
Production Scheduler PRODUCTION_SCHEDULER
Profit Center & Hierarchy PROFIT_CENTER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_VR,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Project PROJECT
Project Element & Hierarchy PROJECT_ELEMENT,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_HZ,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_VR,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_BAD
Purchasing Organization PURCH_ORGANIZATION
Routing ROUTING
Service Person SERVICE_PERSON
Special Procurement Type SPECIAL_PROCUREMENT_TYPE
Storage Location STORAGE_LOCATION
Task List Type TASK_LIST_TYPE
Task List Usage TASK_LIST_USAGE
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 71

Subject Areas
3
Production Order section
Fact Table Fields
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
Valuation Area VALUATION_AREA
Important measures for Production Orders are both quantity and time
oriented:
Column Name Description
DA YS_COMPLT_ACTL Number of Days to actually complete
a service order (Calculated)
DAYS_COMPLT_BASIC Number of Days to Basic complete a
service order (Calculated)
DAYS_COMPLT_FCST Number of Forecast Days to
complete a service order (Calculated)
DAYS_COMPLT_SCHED Number of Days scheduled to
complete a service order (Calculated)
DAYS_GR_PROCESS AFPO.WEBAZ -Goods receipt
processing time in days
DA YS_RELEASE_ACTL Number of Days to actually release a
service order (Calculated)
DAYS_RELEASE_SCHED Number of Days scheduled to
release a service order (Calculated)
HOURS_COMPLT _BASIC Number of Hours to Basic complete a
service order (Calculated)
HOURS_COMPLT_FCST Number of Forecast Hours to
complete a service order (Calculated)
HOURS_COMPLT_SCHED Number of Hours scheduled to
complete a service order (Calculated)
MINS_COMPLT_ACTL Number of Minutes to actually
complete a service order (Calculated)
MINS_COMPL T_BASIC Number of Minutes to Basic complete
a service order (Calculated)
MINS_COMPLT_FCST Number of Forecast Minutes to
complete a service order (Calculated)
MINS_COMPLT_SCHED Number of Minutes scheduled to
complete a service order (Calculated)
72 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Column Name Description
QTY AFPO.PSMNG - Order item quantity
QTY_PROD AFPO.WEMNG - Quantity of goods
QTY_SCRAP AFPO.PSAMG - Scrap quantity in
Rapid Mart data
The following diagram shows the tables in the production order section.
Subject Areas
Production Order section
produced and received for the order
item
item
3
With the tables in this section you can analyze Production Orders along
several dimensions:
• Account Assignment Category
• Business Area
• Company Code
• Controlling Area
• Cost Center & Hierarchy
• Cost Element & Hierarchy
• Monetary Currency
• Document Type
• Functional Area & Hierarchy
• Internal Order & Hierarchy
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 73

Subject Areas
3
Production Order section
• Internal Order Status
• Material, Product Hierarchy
• Material Batch
• Material By Plant
• Material Group
• Material Production
• Material Type
• MRP Controller
• Object Class
• Object Number Type
• Object Status & Hierarchy
• Plant
• Plant Location
• Production Scheduler
• Profit Center & Hierarchy
• Project
• Project Element & Hierarchy
• Purchasing Organization
• Routing
• Service Person
• Special Procurement Type
• Storage Location
• Task List Type
• Task List Usage
• Time Dimension
• Unit Of Measure
• Valuation Area
Typical queries for this section include:
• What is the average time to complete a production order?
• Is one plant faster at completing production orders than another for the
same material?
• Which production orders have the lowest / highest scrap yields?
• Are my production orders for a certain product line evenly distributed
between plants?
74 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

• Which MRP Controllers have the greatest / lowest shares of production in
a given plant?
Production Operation section
The Production Operation section extracts information about operations. An
operation is an activity in a work-step of the Production Order. Operations are
line items in a Production Order . They are copied into a production order from
the routing master data for the material to be produced.
The operations keep track of completion dates and times for the various steps
in executing the production order.
This fact table also indicates the status of the Operation, such as released,
partially confirmed, finally confirmed, technically completed, deleted.
Additionally some dimensional attributes carried on the Production Order are
also available on the Production Operation.
Rapid Mart processing
The operation section extracts operation level data from these SAP solutions
tables:
• AFVC - Operation within an order
• AFVV - DB structure of the quantities/dates/values in the operation
The section stores the data in the fact table
• PRODUCTION_OPERATION_FACT
The section captures the following dimensional attributes and their associated
dimension tables
Subject Areas
Production Operation section
3
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Activity & Hierarchy ACTIVITY, ACTIVITY_HIER,
ACTIVITY_HIER_HZ,
ACTIVITY_HIER_VR,
ACTIVITY_HIER_BAD
Business Area BUSINESS_AREA
Chart Of Accounts CHART_OF_ACCOUNTS
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Control Key CONTROL_KEY
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 75
Subject Areas
3
Production Operation section
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Cost Center & Hierarchy COST_CENTER,
COST_CENTER_HIER,
COST_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
COST_CENTER_HIER_VR,
COST_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Cost Element & Hierarchy COST_ELEMENT,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_HZ,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_VR,
COST_ELEMENT_HIER_BAD
Document Type DOCUMENT_TYPE &
DOCUMENT_CATEGORY
Functional Area & Hierarchy FUNCTIONAL_AREA,
FUNCTIONAL_AREA_HIER,
FUNCTIONAL_AREA_HIER_HZ,
FUNCTIONAL_AREA_HIER_VR,
FUNCTIONAL_AREA_HIER_BAD
Internal Order & Hierarchy INTERNAL_ORDER,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_HZ,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_VR,
INTERNAL_ORDER_HIER_BAD
Material & Product Hierarchy MATERIAL,
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY
Material By Plant MATERIAL_BY_PLANT
Material Group MATERIAL_GROUP
Material Type MATERIAL_TYPE
Monetary Currency CURRENCY
Object Class OBJECT_CLASS
Object Number Type OBJECT_NUMBER_TYPE
Object Status & Hierarchy OBJECT_STATUS,
OBJECT_STATUS_HZ
Object Type OBJECT_TYPE
Operation Suitability OPERATION_SUITABILITY
Order Operation ORDER_OPERATION
Plant PLANT
Plant Location PLANT_LOCATION
76 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
Production Operation section
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Profit Center & Hierarchy PROFIT_CENTER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_VR,
PROFIT_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Project PROJECT
Project Element & Hierarchy PROJECT_ELEMENT,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_HZ,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_VR,
PROJECT_ELEMENT_HIER_BAD
Purchasing Group PURCH_GROUP
Purchasing Organization PURCH_ORGANIZATION
Routing ROUTING
Routing Operation ROUTING_OPERATION
Routing Sequence ROUTING_SEQUENCE
System Condition SYSTEM_CONDITION
Task List Type TASK_LIST_TYPE
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Unit Of Measure UNIT_OF_MEASURE
Valuation Area VALUATION_AREA
Vendor VENDOR
Vendor By Company VENDOR_BY_COMPANY
Work Center & Hierarchy WORK_CENTER,
WORK_CENTER_HIER,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_VR,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Work Center Category WORK_CENTER_CATEGORY
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 77

Subject Areas
3
Production Operation section
Fact Table Fields
Important measures for Production Operations are both quantity and time
oriented:
Column Name Description
AMT_COST_MTRL AFVC.MAT_PRKST - Material
planning in networks: primary costs
AMT_COST_TTL AFVC.PRKST - Total Costs in the
activity - Planned
AMT_PRICE AFVC.PREIS - Price
DAYS_EXECUTN_ACTL Calculated Days of Operation
execution/startup time (as Actl Start
and Actl End datetime)
DAYS_EXECUTN_SCHED Calculated Days of Operation
execution/startup time (as Sched
Start and Sched End datetime)
HOURS_EXECUTN_ACTL Calculated Hours of Operation
execution/startup time (as Actl Start
and Actl End datetime)
HOURS_EXECUTN_SCHED Calculated Hours of Operation
execution/startup time (as Sched
Start and Sched End datetime)
MINS_EXECUTN_ACTL Calculated Mins of Operation
execution/startup time (as Actl Start
and Actl End datetime)
MINS_EXECUTN_SCHED Calculated Mins of Operation
execution/startup time (as Sched
Start and Sched End datetime)
PRICE_UNIT AFVC.PEINH - Price Unit
QTY_DURTN AFVV.DAUNO - Normal duration of
the activity
QTY_WORK_ACTL AFVV-ISMNW - Actual work
QTY_WORK_FCST AFVV-ORMNW - Forecasted work
(actual + remaining)
QTY_WORK_SCHED AFVV-ARBEI - Work involved in the
activity
78 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Rapid Mart data
The following diagram shows the tables in the Production Operation section:
Subject Areas
Production Operation section
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 79

Subject Areas
3
Production Operation section
Additionally, the following hierarchies are available:
With the tables in this section you can analyze Production Operations along
several dimensions:
• Activity & Hierarchy
• Business Area
• Chart Of Accounts
• Company Code
• Control Key
• Controlling Area
• Cost Center & Hierarchy
• Cost Element & Hierarchy
• Document Type
• Functional Area & Hierarchy
• Internal Order & Hierarchy
• Material & Product Hierarchy
• Material By Plant
80 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Subject Areas
Production Operation section
• Material Group
• Material Type
• Monetary Currency
• Object Class
• Object Number Type
• Object Status & Hierarchy
• Object Type
• Operation Suitability
• Order Operation
• Plant
• Plant Location
• Profit Center & Hierarchy
• Project
• Project Element & Hierarchy
• Purchasing Group
• Purchasing Organization
• Routing
• Routing Operation
• Routing Sequence
• System Condition
• Task List Type
• Time Dimension
• Unit Of Measure
• Valuation Area
• Vendor
• Vendor By Company
• Work Center & Hierarchy
• Work Center Category
Typical queries for this section include:
• How may Operations are un-released?
• Are there any trends in operations taking more than 10 days to complete
across a particular functional location and associated hierarchy?
• Do operations for certain materials t ake longer in one plant than another?
• Which production orders have the most steps (operations)?
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 81

Subject Areas
3
Production Operation section
• Which operations are only partially confirmed and more than 6 months
old?
• Is there a trend by functional location on partially confirmed operations
more than 6 months old?
82 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Reports
chapter

Reports
4
Overview
Overview
You can use the SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart,
version for SAP solutions to produce many kinds of reports. This chapter
provides examples of reports you could produce. The information in this
chapter is useful for those who analyze and produce reports with the Rapid
Mart data.
This chapter provides a sample report and the recommended joins for each
section in the Rapid Mart:
• Work Center Section
• Capacity Section
• MRP Results Section
• Planned Order Section
• Reservation Section
• Routing Section
• Bill Of Materials Section
• Production Order Section
• Production Operation Section
• SAP Master Data Reports
Work Center Section
Production operations are carried out at a work center. In SAP solutions work
centers represent the following:
• Machines, machine groups
• Production lines
• Assembly work centers
• Employees, groups of employees
Work centers are used in task list (routing) operations and production orders.
The work center section allows you to analyze data and produce reports by
work center and to aggregate data according to work center hierarchy.
Reports
There is one Sample Report for Work Centers:
84 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Work Center Cost Details
View Work Center cost assignment details for the selected Plant and Work
Center. The report mimics SAP solutions transaction CR03, Work Center
Costing tab.
Work Center Cost
Reports
Work Center Section
4
Report SQL
SELECT DISTINCT
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.PLANT_ID,
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.WORK_CNTR_ID,
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.VALID_FROM_DATE,
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.VALID_TO_DATE,
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.CTRL_AREA_I D,
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.DAYS_VALID_ASSIGN,
WORK_CENTER.WORK_CNTR_DESCR,
COST_CENTER.COST_CNTR_FULL_NAME,
CONTROLLING_AREA.CTRL_AREA_FULL_NAME,
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.INCENTIVE_WAGE_ID,
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.INCENTIVE_WAGE_DESCR,
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.REF_FLAG,
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.FORMULA_ID,
WORK_CENTER_FORMULA.FORMULA_DESCR,
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.RECORD_TYPE_GRP_DESCR,
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.ACTIVITY_ID,
ACTIVITY.ACTIVITY_DESCR,
ACTIVITY.UOM_ID_OUTPUT
FROM
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT,
WORK_CENTER,
COST_CENTER,
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 85

Reports
4
Work Center Section
CONTROLLING_AREA,
WORK_CENTER_FORMULA,
ACTIVITY
WHERE
(
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.CTRL_AREA_ID=COST_CENTE
R.CTRL_AREA_ID and
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.COST_CNTR_ID=COST_CENTE
R.COST_CNTR_ID )
AND (
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.FORMULA_ID=WORK_CENTE
R_FORMULA.FORMULA_ID )
AND (
CONTROLLING_AREA.CTRL_AREA_ID=WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSI
GN_FACT.CTRL_AREA_ID )
AND (
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.WORK_CNTR_ID=WORK_CEN
TER.WORK_CNTR_ID and
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.PLANT_ID=WORK_CENTER.PL
ANT_ID )
AND (
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.CTRL_AREA_ID=ACTIVITY.CT
RL_AREA_ID and
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.ACTIVITY_ID=ACTIVITY.ACTI
VITY_ID )
AND
(
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.WORK_CNTR_ID = 'R-G07'
AND
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.PLANT_ID In ('1000')
)
Recommended Table Joins
To analyze Work Center Cost Assignment data you will need to create joins
between the WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGNMENT_FACT and dimension
tables as follows.
86 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Additional joins between dimension and hierarchy tables are shown in
“Recommended table joins” on page 27 for master reports.
Fact Table Dimension Table Join Expression
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
ACTIVITY WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.CTRL_AREA_ID=ACTIVITY.CTRL_AR
EA_ID and
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.ACTIVITY_ID=ACTIVITY.ACTIVITY_ID
ACTIVITY_HIER_HZ WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.CTRL_AREA_ID=ACTIVITY_HIER_HZ
.CTRL_AREA_ID and
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.ACTIVITY_ID=ACTIVITY_HIER_HZ.A
CTIVITY_ID
ACTIVITY_HIER_VR WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.CTRL_AREA_ID =
ACTIVITY_HIER_VR.CTRL_AREA_ID
and
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.ACTIVITY_ID =
ACTIVITY_HIER_VR.CHILD_ID
CHART_OF_ACCOUNTSCHART_OF_ACCOUNTS.CHART_OF_
ACCT_ID=WORK_CENTER_COST_AS
SIGN_FACT.CHART_OF_ACCT_ID
COMPANY_CODE COMPANY_CODE.CMPNY_CODE_ID=
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.CMPNY_CODE_ID
CONTROL_KEY CONTROL_KEY.CTRL_KEY_ID=WORK
_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.CTRL
_KEY_ID
CONTROLLING_AREA CONTROLLING_AREA.CTRL_AREA_ID
=WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FA
CT.CTRL_AREA_ID
COST_CENTER WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.CTRL_AREA_ID=COST_CENTER.CT
RL_AREA_ID and
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.COST_CNTR_ID=COST_CENTER.CO
ST_CNTR_ID
Reports
Work Center Section
4
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 87

Reports
4
Work Center Section
Fact Table Dimension Table Join Expression
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
COST_CENTER_HIER
_HZ
COST_CENTER_HIER
_VR
PLANT WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
PLANT_LOCATION PLANT_LOCATION.PLANT_ID=WORK_
PURCH_ORGANIZATIONPURCH_ORGANIZATION.PURCH_ORG
STANDARD_TEXT_KEYSTANDARD_TEXT_KEY.STD_TEXT_KE
STANDARD_VALUE_KEYSTANDARD_VALUE_KEY.STD_VALUE_
TASK_LIST_USAGE TASK_LIST_USAGE.GROUP_USG_ID=
TIME_DIM TIME_DIM_DOCDATE.CALENDAR_DAT
UNIT_OF_MEASURE UNIT_OF_MEAS_BASE.UOM_ID=WOR
VALUATION_AREA VALUATION_AREA.VALUATN_AREA_ID
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.CTRL_AREA_ID=COST_CENTER_HI
ER_HZ.CTRL_AREA_ID and
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.COST_CNTR_ID=COST_CENTER_HI
ER_HZ.COST_CNTR_ID
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.CTRL_AREA_ID=COST_CENTER_HI
ER_VR.CTRL_AREA_ID and
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.COST_CNTR_ID=COST_CENTER_HI
ER_VR.CHILD_ID
T.PLANT_ID=PLANT.PLANT_ID
CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.PLANT
_ID and
PLANT_LOCATION.LOCATN_ID=WORK
_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.LOCA
TN_ID
_ID=WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_
FACT.PURCH_ORG_ID
Y_ID=WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN
_FACT.STD_TEXT_KEY_ID
KEY_ID=WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSI
GN_FACT.STD_V ALUE_KEY_ID
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.GROUP_USG_ID
E=WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_F
ACT.VALID_FROM_DATE
K_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT.UO
M_ID
=WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FA
CT.VALUATN_AREA_ID
88 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Fact Table Dimension Table Join Expression
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER_COS
T_ASSIGN_FACT
WORK_CENTER WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.WORK_CNTR_ID=WORK_CENTER.W
ORK_CNTR_ID and
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.PLANT_ID=WORK_CENTER.PLANT_I
D
WORK_CENTER_CAT
EGORY
WORK_CENTER_FOR
MULA
WORK_CENTER_HIER
_HZ
WORK_CENTER_HIER
_VR
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.WORK_CNTR_CATEG_ID=WORK_CE
NTER_CATEGORY.WORK_CNTR_CAT
EG_ID
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.FORMULA_ID=WORK_CENTER_FOR
MULA.FORMULA_ID
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.WORK_CNTR_ID=WORK_CENTER_
HIER_HZ.WORK_CNTR_ID and
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.PLANT_ID=WORK_CENTER_HIER_H
Z.PLANT_ID
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.WORK_CNTR_ID=WORK_CENTER_
HIER_VR.CHILD_ID AND
WORK_CENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FAC
T.PLANT_ID=WORK_CENTER_HIER_V
R.PLANT_ID
Reports
Capacity Section
4
Capacity Section
The capacity section stores available capacity information by work center,
available interval capacity by date, and capacity requirements for planned
orders.
Work center capacities measure the amount of work output that a work center
can produce during a period of time. Capacity categories subdivide capacity
into types, such as machine, labor, or electrical output. More than one
capacity category can exist at a work center.
The capacity section allows you to analyze data and produce reports for
capacity requirements and availability scheduling.
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 89

Reports
4
Capacity Section
Reports
Sample Reports for the Capacity include:
• Capacity Requirements Listing
• Capacity Intervals of Availability
Capacity Requirements Listing
View Capacity Requirements for the specified Work Center Id, Capacity
Category Id, and Order Id. Mimics SAP solutions transaction IW33 > Go To >
Planning Board functionality.
Report SQL
All report SQL is located in the Rapid Mart installation directory under
“\Sample\DML”
90 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
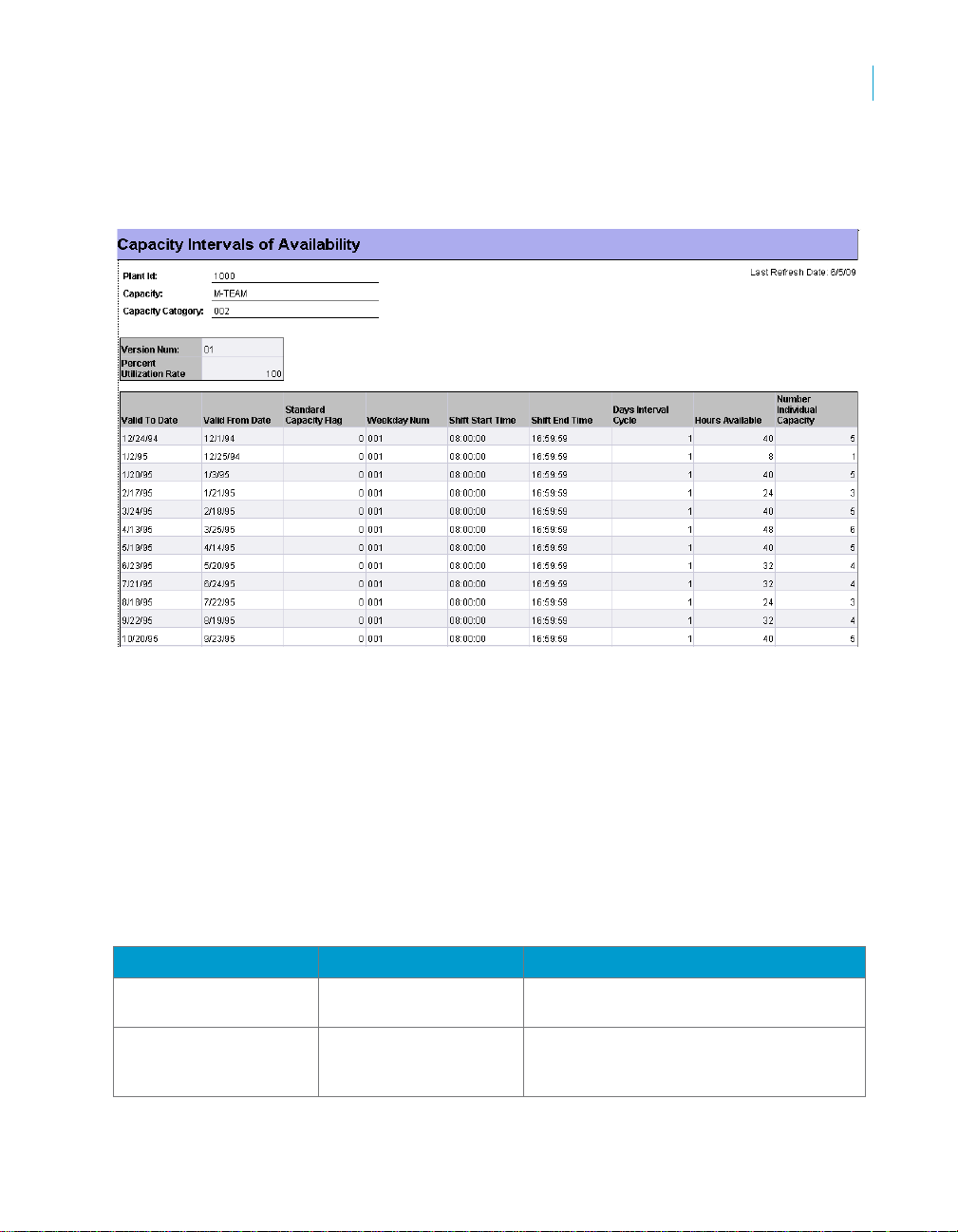
Capacity Intervals of Availability
View Capacity Intervals for the specified Plant, Capacity, and Capacity
Category. Report mimics SAP solutions transaction CR13. Y.
Reports
Capacity Section
4
Report SQL
All report SQL is located in the Rapid Mart installation directory under
“\Sample\DML”
Recommended Table Joins
To analyze Work Center Cost Assignment data you will need to create joins
between the CAPACITY_INTERVAL_FACT and
CAP ACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT and dimension tables as follows.
Additional joins between dimension and hierarchy tables are shown in
“Recommended table joins” on page 27 for master reports.
Fact Table Dimension Table Join Expression
CAPACITY_INTERVAL
_FACT
CAPACITY_INTERVAL
_FACT
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 91
CAPACITY CAPACITY_INTERVAL_FACT.CAPACIT
Y_ID=CAPACITY.CAPACITY_ID
CAPACITY_CATEGORYCAPACITY_INTERVAL_FACT.CAPACIT
Y_CATEG_ID=CAPACITY_CATEGORY.
CAPACITY_CATEG_ID
Reports
4
Capacity Section
Fact Table Dimension Table Join Expression
CAPACITY_INTERVAL
_FACT
CAPACITY_INTERVAL
_FACT
CAPACITY_INTERVAL
_FACT
CAPACITY_INTERVAL
_FACT
CAPACITY_INTERVAL
_FACT
CAPACITY_INTERVAL
_FACT
CAPACITY_INTERVAL
_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_PLANNING
_GROUP
COMPANY_CODE COMPANY_CODE.CMPNY_CODE_ID=
CONTROLLING_AREA CONTROLLING_AREA.CTRL_AREA_ID
PLANT PLANT.PLANT_ID=CAPACITY_INTERV
PURCH_ORGANIZATIONPURCH_ORGANIZATION.PURCH_ORG
TIME_DIM TIME_DIM.CALENDAR_DATE=CAPACI
VALUATION_AREA VALUATION_AREA.VALUATN_AREA_ID
CAPACITY CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.CAP
CAPACITY_BY_WORK
_CENTER
CAPACITY_CATEGORYCAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.CAP
CAPACITY_OBJECT_T
YPE
CAPACITY_PLANNING
_GROUP
CAPACITY_INTERVAL_FACT.CAPACIT
Y_PLANNG_GRP_ID=CAPACITY_PLAN
NING_GROUP.CAPACITY_PLANNG_G
RP_ID
CAPACITY_INTERVAL_FACT.CMPNY_
CODE_ID
=CAPACITY_INTERVAL_FACT.CTRL_A
REA_ID
AL_FACT.PLANT_ID
_ID=CAPACITY_INTERVAL_FACT.PUR
CH_ORG_ID
TY_INTERVAL_FACT.VALID_FROM_DA
TE
=CAPACITY_INTERVAL_FACT.VALUAT
N_AREA_ID
ACITY_ID=CAPACITY.CAPACITY_ID
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.CAP
ACITY_ID=CAPACITY_BY_WORK_CEN
TER.CAPACITY_ID and
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.RES
OURCE_ID=CAPACITY_BY_WORK_CE
NTER.RESOURCE_ID
ACITY_CATEG_ID=CAPACITY_CATEG
ORY.CAPACITY_CATEG_ID
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.CAP
ACITY_OBJ_TYPE_ID=CAPACITY_OBJ
ECT_TYPE.CAPACITY_OBJ_TYPE_ID
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.CAP
ACITY_PLANNG_GRP_ID=CAPACITY_
PLANNING_GROUP.CAPACITY_PLANN
G_GRP_ID
92 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Fact Table Dimension Table Join Expression
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
COMPANY_CODE COMPANY_CODE.CMPNY_CODE_ID=
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.CMP
NY_CODE_ID
CONTROLLING_AREA CONTROLLING_AREA.CTRL_AREA_ID
=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.CT
RL_AREA_ID
INTERNAL_ORDER CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.INT
ERNAL_ORDER_ID=INTERNAL_ORDE
R.INTERNAL_ORDER_ID
INTERNAL_ORDER_HI
ER_HZ
INTERNAL_ORDER_HI
ER_VR
OBJECT_NUMBER_TYPEOBJECT_NUMBER_TYPE.OBJ_NUM_T
OBJECT_STATUS_HZ OBJECT_STATUS_HZ.OBJ_ID=CAPACI
ORDER_OPERATION ORDER_OPERATION.OPERATN_ROU
PLANT PLANT.PLANT_ID=CAPACITY_REQUIR
PURCH_ORGANIZATIONPURCH_ORGANIZATION.PURCH_ORG
ROUTING ROUTING.ROUTING_ID=CAPACITY_R
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.INT
ERNAL_ORDER_ID=INTERNAL_ORDE
R_HIER_HZ.INTERNAL_ORDER_ID
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.INT
ERNAL_ORDER_ID=INTERNAL_ORDE
R_HIER_VR.CHILD_ID
YPE_ID=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_F
ACT.OBJ_NUM_TYPE_ID
TY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.OBJ_ID
TING_ID=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_
FACT.OPERATN_ROUTING_ID and
ORDER_OPERATION.OPERATN_SEQ_
ID=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.
OPERATN_SEQ_ID
EMENT_FACT.PLANT_ID
_ID=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.
PURCH_ORG_ID
EQUIREMENT_FACT.ROUTING_ID
Reports
Capacity Section
4
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 93

Reports
4
Capacity Section
Fact Table Dimension Table Join Expression
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
ROUTING_OPERATIONROUTING_OPERATION.GROUP_TYPE
_ID=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.
GROUP_TYPE_ID and
ROUTING_OPERATION.GROUP_ID=C
APACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.GRO
UP_ID and
ROUTING_OPERATION.GROUP_NODE
_ID=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.
GROUP_NODE_ID
ROUTING_SEQUENCE ROUTING_SEQUENCE.ROUTING_ID=
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.ROU
TING_ID and
ROUTING_SEQUENCE.GROUP_LINE_I
D=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.G
ROUP_LINE_ID
SCHEDULING_ERROR SCHEDULING_ERROR.SCHED_ERRO
R_ID=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FAC
T.SCHED_ERROR_ID
SCHEDULING_TYPE SCHEDULING_TYPE.SCHED_TYPE_ID
=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.SC
HED_TYPE_ID
TASK_LIST_TYPE TASK_LIST_TYPE.GROUP_TYPE_ID=C
APACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.GRO
UP_TYPE_ID
TIME_DIM TIME_DIM_DOCDATE.CALENDAR_DAT
E=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.C
REATE_DATE
UNIT_OF_MEASURE UNIT_OF_MEASURE.UOM_ID=CAPACI
TY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.UOM_ID
VALUATION_AREA VALUATION_AREA.VALUATN_AREA_ID
=CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.VA
LUATN_AREA_ID
WORK_CENTER CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.PLA
NT_ID=WORK_CENTER.PLANT_ID and
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.WO
RK_CNTR_ID=WORK_CENTER.WORK
_CNTR_ID
WORK_CENTER_CAT
EGORY
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.WO
RK_CNTR_CATEG_ID=WORK_CENTE
R_CATEGORY.WORK_CNTR_CATEG_I
D
94 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

Fact Table Dimension Table Join Expression
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
CAPACITY_REQUIRE
MENT_FACT
WORK_CENTER_HIER
_HZ
WORK_CENTER_HIER
_VR
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.WO
RK_CNTR_ID=WORK_CENTER_HIER_
HZ.WORK_CNTR_ID and
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.PLA
NT_ID=WORK_CENTER_HIER_HZ.PLA
NT_ID
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.WO
RK_CNTR_ID=WORK_CENTER_HIER_
VR.CHILD_ID AND
CAPACITY_REQUIREMENT_FACT.PLA
NT_ID=WORK_CENTER_HIER_VR.PLA
NT_ID
Reports
Capacity Section
4
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 95

Reports
4
MRP Results Section
MRP Results Section
The MRP results section stores the results tables from material requirements
planning (MRP) and master production scheduling (MPS) planning runs.
The MRP results section allows you to list and compare results of materials
requirement planning runs for various materials.
MRP Listing
View the MRP listing for the specified Material and Plant. Mimics SAP
solutions transaction MD05.
MRP Listing
Report SQL
All report SQL is located in the Rapid Mart installation directory under
“\Sample\DML”
Recommended Table Joins
To analyze Work Center Cost Assignment data you will need to create joins
between the MRP_RESULT_FACT and dimension tables as follows.
96 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
Reports
MRP Results Section
Additional joins between dimension and hierarchy tables are shown in
“Recommended table joins” on page 27 for master reports.
Fact Table Dimension Table Join Expression
MRP_RESULT_FACT COMPANY_CODE COMPANY_CODE.CMPNY_CODE_ID=
MRP_RESULT_FACT.CMPNY_CODE_I
D
MRP_RESULT_FACT CONTROLLING_AREA CONTROLLING_AREA.CTRL_AREA_ID
=MRP_RESULT_FACT.CTRL_AREA_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT EXCEPTION_TEXT EXCEPTION_TEXT.EXCEPTN_ID=MRP
_RESULT_FACT.EXCEPTN_ID_01
MRP_RESULT_FACT MATERIAL MRP_RESULT_FACT.MATERIAL_ID=M
ATERIAL.MATERIAL_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT MATERIAL_BY_PLANT MRP_RESULT_FACT.MATERIAL_ID=M
A TERIAL_BY_PLANT.MA TERIAL_ID and
MRP_RESULT_FACT.PLANT_ID=MATE
RIAL_BY_PLANT.PLANT_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT MATERIAL_GROUP MRP_RESULT_FACT.MTRL_GRP_ID=M
ATERIAL_GROUP.MTRL_GRP_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT MATERIAL_TYPE MRP_RESULT_FACT.MTRL_TYPE_ID=
MATERIAL_TYPE.MTRL_TYPE_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT MRP_CONTROLLER MRP_RESULT_FACT.MRP_CTRLLER_I
D=MRP_CONTROLLER.MRP_CTRLLE
R_ID and
MRP_RESULT_FACT.PLANT_ID=MRP_
CONTROLLER.PLANT_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT MRP_ELEMENT_TYPE MRP_RESULT_FACT.MRP_ELEM_TYP
E_ID=MRP_ELEMENT_TYPE.MRP_EL
EM_TYPE_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT MRP_GROUP MRP_RESULT_FACT.MRP_GRP_ID=M
RP_GROUP.MRP_GRP_ID and
MRP_RESULT_FACT.PLANT_ID=MRP_
GROUP.PLANT_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT MRP_LOT_SIZE MRP_RESULT_FACT.MRP_LOT_SIZE_I
D=MRP_LOT_SIZE.MRP_LOT_SIZE_ID
MRP_RESULT _FACT MRP_PROFILE MRP_RESULT_FACT.MRP_PROFILE_I
D=MRP_PROFILE.MRP_PROFILE_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT MRP_TYPE MRP_RESULT_FACT.MRP_TYPE_ID=M
RP_TYPE.MRP_TYPE_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT PLANT PLANT.PLANT_ID=MRP_RESULT_FAC
T.PLANT_ID
4
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 97

Reports
4
Planned Order Section
Fact Table Dimension Table Join Expression
MRP_RESULT_FACT PROCUREMENT_TYPEPROCUREMENT_TYPE.PROCUREMN
T_TYPE_ID=MRP_RESULT_FACT.PRO
CUREMNT_TYPE_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT PRODUCT_HIERARCHYMRP_RESULT_FACT.PROD_HIER_ID=
PRODUCT_HIERARCHY.PROD_HIER_I
D
MRP_RESULT_FACT PURCH_GROUP PURCH_GROUP.PURCH_GRP_ID=MR
P_RESULT_FACT.PURCH_GRP_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT PURCH_ORGANIZATIONPURCH_ORGANIZATION.PURCH_ORG
_ID=MRP_RESULT_FACT.PURCH_OR
G_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT STORAGE_LOCATION STORAGE_LOCATION.STORAGE_LOC
ATN_ID=MRP_RESULT_FACT.STORAG
E_LOCATN_ID and
STORAGE_LOCATION.PLANT_ID=MRP
_RESULT_FACT.PLANT_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT TIME_DIM TIME_DIM.CALENDAR_DATE=MRP_R
ESULT_FACT.MRP_DATE
MRP_RESULT_FACT UNIT_OF_MEASURE UNIT_OF_MEASURE.UOM_ID=MRP_R
ESULT_FACT.UOM_ID
MRP_RESULT_FACT VALUATION_AREA VALUATION_AREA.VALUATN_AREA_ID
=MRP_RESULT_FACT.VALUATN_AREA
_ID
Planned Order Section
Materials Requirements Planning results in planned orders that suggest the
amount of material to produce and when to produce it in order to meet the
demand requirements.
Conversion of a planned order to a production order creates orders for all the
material components needed to complete the planned order. Material
reservations are created if existing stocks will be used for components. A
routing and a bill of materials is required to create a planned order.
The planned order section allows you to analyze and display planned orders.
Reports
Sample Reports for the Capacity include:
• Planned Order Analysis
98 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide

• Planned Order Listing
Planned Order Analysis
Analysis of planned orders for the selected Company Code and Calendar
Year. Provides a Summary analysis comparing all plants, Top 3 Plants, and
Top 10 Materials for each Plant.
This report contains three tabs for distinct analysis of the data.
Summary
Analyze planned order metrics (including order count, days order planned
duration, and average quantity) summary analysis by Plant.
Reports
Planned Order Section
4
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide 99
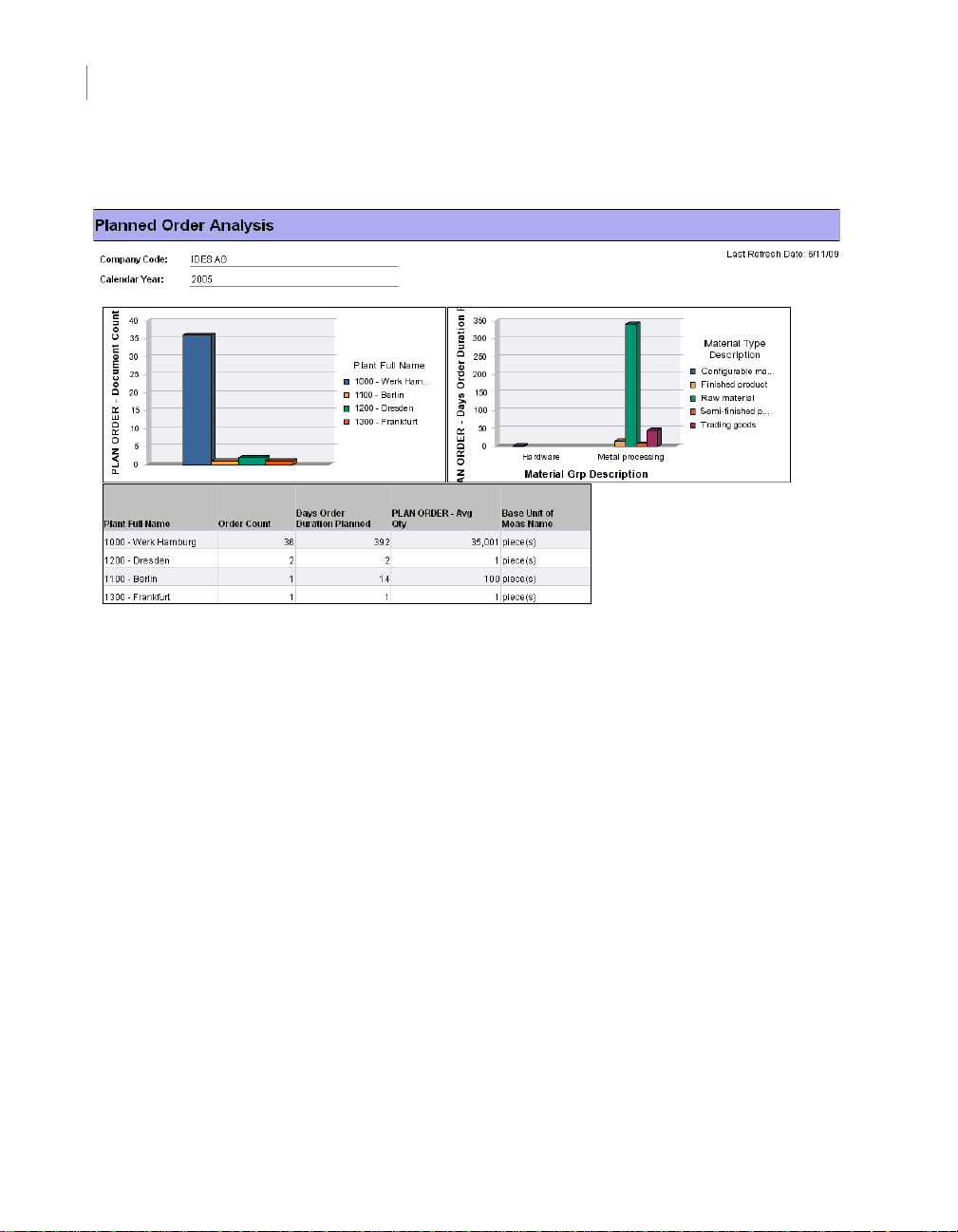
Reports
4
Planned Order Section
Top 3 Plants
View top 3 plants (according to order count).
100 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions User Guide
 Loading...
Loading...