SAP BusinessObjects Production Business Guide

SAP BusinessObjects Production
Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2, version for
SAP solutions - Business Guide
Version 12.2.2.0

October 2009
Copyright
Trademarks
© Copyright 2009 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or for any purpose
without the express permission of SAP AG. The information contained herein may be
changed without prior notice.
Some software products marketed by SAP AG and its distributors contain proprietary
software components of other software vendors.
All rights reserved. SAP, R/3, SAP NetWeaver, Duet, PartnerEdge, ByDesign, SAP Business
ByDesign, and other SAP products and services mentioned herein as well as their respective
logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP AG in Germany and other countries.
Business Objects and the Business Objects logo, BusinessObjects, Crystal Reports, Crystal
Decisions, Web Intelligence, Xcelsius, and other Business Objects products and services
mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks
of Business Objects S.A. in the United States and in other countries. Business Objects is an
SAP company.
All other product and service names mentioned are the trademarks of their respective
companies. Data contained in this document serves informational purposes only. National
product specifications may vary.
These materials are subject to change without notice. These materials are provided by SAP
AG and its affiliated companies ("SAP Group") for informational purposes only, without
representation or warranty of any kind, and SAP Group shall not be liable for errors or
omissions with respect to the materials. The only warranties for SAP Group products and
services are those that are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such
products and services, if any. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty.

Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction 7
What is a Rapid Mart? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Rapid Marts packages accelerate Time to Value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
SAP BusinessObjects Rapid Marts packages architecture . . . . . . . . . 10
About this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Chapter 2 Overview 13
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
What is production planning? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
What you can do with this Rapid Mart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Supported analyses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Related Rapid Marts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Sharing components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
The Rapid Mart schema . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Where the Rapid Mart fits in the production planning process . . . . . . . . . . 22
Chapter 3 Subject Areas 23
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Work Center section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Basic Data in a Work Center: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Integration of Work Centers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Capacity section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide 3

Contents
MRP results section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Planned Order section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Reservation section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Rapid Mart Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Routing section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Bills of Material (BOM) section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Production Order section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Production Operation section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Rapid Mart processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Rapid Mart data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Chapter 4 Reports 79
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Work Center Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Capacity Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
MRP Results Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Planned Order Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
4 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide

Contents
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Reservation Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Routing Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Bill Of Materials Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Production Order Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Production Operation Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Recommended Table Joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
SAP Master Data Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Data Discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Data Auditing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Recommended table joins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide 5

Contents
6 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide
Introduction
chapter

Introduction
1
What is a Rapid Mart?
What is a Rapid Mart?
SAP BusinessObjects Rapid Marts packages are blueprints for building data
marts with SAP BusinessObjects technology:
• Data Services
• Universe Designer
• Web Intelligence.
Rapid Marts packages deliver jump-start ETL (extract, transform & load)
mappings, schema, and initial reporting content, accelerating the deployment
of BI (business intelligence) for enterprise applications from SAP, PeopleSoft,
Oracle, and Siebel.
Each Rapid Mart is designed to address the reporting needs of a specific
business area (or department) like accounting, sales, or purchasing. A
component-based framework allows conducting analysis across these
selected business areas by combining different packages within the same
source application suite.
Rapid Marts focus on basic standard configuration of the enterprise
applications. They are country and industry neutral templates meant to be
easily modified and extended to suit customer specific application
implementation and reporting needs.
Rapid Marts incorporate best practices, and provide easily modifiable
templates. With Rapid Marts total development time of a data mart solution is
greatly reduced.
Each customer situation is different. You will probably encounter one or more
of these:
• Customizations you have made to SAP solutions the Rapid Mart does not
cover.
• Standard SAP solutions data fields important for your specific business,
but not included in the Rapid Mart templates.
• Optimization and performance challenges unique to your environment.
• Reporting requirements not covered within the Rapid Mart template
reports.
Rapid Marts are flexible templates that you can adjust to account for these
unique situations. It is expected that some customization and optimization will
be needed to suit your individual environment. Rapid Marts are not an
out-of-the-box solution.
8 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide

BI tools and analytic tools can access Rapid Mart data through SQL queries.
Rapid Marts can be implemented individually, or in any combination, to form a
single platform that delivers the infrastructure for your company’s internal and
external information needs. They can also serve as a staging area for
enterprise analytic applications.
Rapid Marts provide your business with an accelerated time to value through
rapid BI deployments because you can implement them quickly and easily
customize them to meet specific analytic requirements.
Rapid Marts packages accelerate Time to Value
Rapid Marts are packaged data solutions that you can quickly deploy to
address specific areas of business analysis.
Available Rapid Marts packages for SAP solutions include:
Financial Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects General Ledger Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Accounts Payable Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Accounts Receivable Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Cost Center Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
Operational Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects Inventory Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Purchasing Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
Manufacturing Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects Plant Maintenance Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
• SAP BusinessObjects Project Systems Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
Human Capital Management (HCM) Suite:
• SAP BusinessObjects Human Resources Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions
Introduction
What is a Rapid Mart?
1
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide 9
Introduction
1
What is a Rapid Mart?
You can combine multiple Rapid Marts packages into a single environment to
build the foundation for your data warehouse or use them as a staging area
for business intelligence applications.
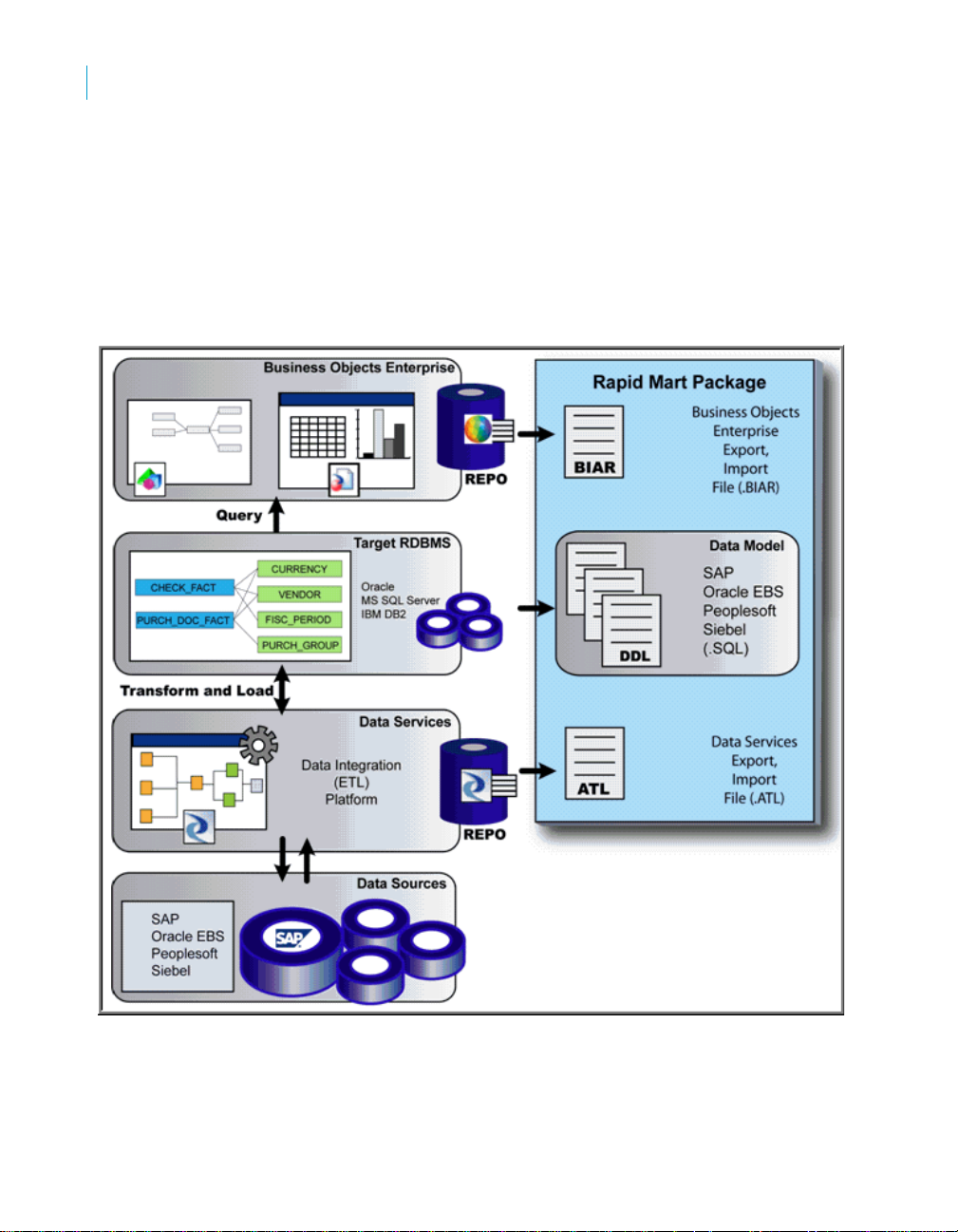
SAP BusinessObjects Rapid Marts packages architecture
Rapid Marts architecture is driven by SAP BusinessObjects technology.
Rapid Mart Architecture:
Rapid Marts packages include the following components:
10 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide

Introduction
About this document
• Data Movement Jobs - packaged source-to-target mappings and data
transformations. Each job is designed to perform initial and incremental
data movement;
• Data Model & Schema - set of data mart database objects designed with
dimensional data modeling approach. Rapid Marts packages for SAP
solutions has a single integrated data model. The schema are available
for Oracle, SQL Server IBM DB2, and Teradata;
• Semantic Layer (Universes) - SAP BusinessObjects metadata packages
for efficient query generation. There can be one or more universes per
Rapid Mart. Each universe is developed using Rapid Marts design
principles to ensure compatibility, code readability, and component
re-use. In addition, there is one Master universe for
development/maintenance of multiple use objects (like Customer,
Material, Currency, etc.);
• Reports (Samples) - set of 15-20 Web Intelligence reports per Rapid
Mart. They represent answers to mostly asked business questions (for
example, in the SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions - 'What is the monthly Revenue trend by Division for this
year?'). The reports are developed using Rapid Mart color/layout
templates. Reports are examples of Web Intelligence best practice
development (trends, listing, guided analysis, roll ups and downs, etc.).
1
About this document
This document describes the SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning
Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions. This document contains information for
a variety of users—information that helps you understand the use of the
Rapid Mart, the data in the Rapid Mart, the reports you can create with the
Rapid Mart, and how to use and update the Rapid Mart.
This document contains the following chapters:
• Chapter 2: Overview — Describes the business problems you can solve
and the types of analyses you can do with this Rapid Mart
• Chapter 3: Subject Areas — Contains detailed information about each
section in the Rapid Mart, including the processes each section captures
• Chapter 4: Reports — Provides examples of reports you can produce
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide 11

Introduction
1
About this document
12 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide

Overview
chapter

Overview
2
Overview
Overview
This chapter describes the business problems you can solve with the SAP
BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions
and the types of analyses you can do with this Rapid Mart. The information in
this chapter is useful for those who want a business-level overview of the
Rapid Mart and its benefits.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
• What is production planning?
• What you can do with this Rapid Mart
• Supported analyses
• Related Rapid Marts
• The Rapid Mart schema
• Where the Rapid Mart fits in the production planning process
What is production planning?
Within SAP solutions, the process of production planning and control (PP)
determines what to produce, how much to produce, and when to produce it.
Production quantities and scheduling are constrained by machine time, labor ,
material availability, and storage space. These resources are in turn
constrained by budget and other financial considerations. By balancing
resource constraints with demand and scheduling requirements, an effective
production plan optimizes factory lead times, improves customer delivery
performance, and reduces time consumed by work in progress (WIP).
Planning processes in SAP solutions generate time-based demands for
materials based on sales order planning, long term forecasts, stock
replenishment quantities, customer order requirements, backlog, safety stock
levels, and other anticipated sources of demand. The SAP solutions materials
requirements planning (PP-MRP) component combines lead time scheduling
information with independent and dependent requirements (based on bill of
materials) for a material and produces a production and procurement
proposal—a planning proposal—that satisfies current and projected demand
requirements.
The planning proposal that SAP solutions produces does not account for
material availability or work center capacity until a production order is created.
When creating a production order, SAP solutions explodes a bill of materials,
14 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide

What you can do with this Rapid Mart
creates requisitions for externally procured materials, selects a routing for
produced materials, reserves materials and resources, and calculates
capacity requirements for work centers.
What you can do with this Rapid Mart
The SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions enables you to analyze the planning components that automate the
production process. The data that supports these planning
components—work centers, routings, planning strategies, bill of materials,
capacities, and MRP results—can provide insight into the production process
and help you improve and streamline both the planning process and the
actual production and procurement of goods and services.
The SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions is made up of several components or sections. Each section
supports a subject related to planning analysis:
• Work center section — S tores data about work centers—the machines,
production lines, or labor pools capable of producing units of work as
output. The amount of work that a work center can produce during a
given time is its capacity . Basic work center data includes category (labor ,
machine, etc.), description, location (plant), and standard values for
queue times. This section also contains the work center hierarchy, which
allows you to roll up work center capacity to accumulate capacities at
various levels. This section also contains the work center assignment to
cost center.
• Capacity section— Stores standard shift times and operating times for
various capacity categories (machine, labor). Work centers have one or
more capacities, measured in terms of units of time, associated with
them. The combination of operating hours, utilization rate, and number of
capacities determines the standard available cap acity for the work center .
Additional capacity, called interval available capacity, might be available
for certain intervals of time. Capacity requirements generated by
production orders and planned orders using lead time scheduling are
also included in this section.
• Materials requirement planning (MRP) results section — Stores the
results tables from MRP and master production scheduling (MPS)
planning runs.
• Planned order section — Stores detailed routing and operation
information for planned orders. Planned Orders are transient in the SAP
solutions system (they are deleted once converted to a Production Order
Overview
2
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide 15

Overview
2
Supported analyses
or Purchase Requisition). The Rapid Mart can capture quasi complete
history of Planned Orders, (including those deleted) depending on how
often the Rapid Mart is refreshed.
• Reservation section — A request to the warehouse or stores to keep a
material ready for issue at a future date for a certain purpose. The
purpose of a reservation is to ensure that a material is available when
required. A material can be reserved for a cost center, a plant, or a
production order.
• Routing section — Stores routing information for production operations.
Manufactured goods require a routing to describe the steps required to
produce a quantity of output. Routings for a material are time-dependent
and may be lot size-dependent. This section contains a material-plant
level routing description including setup, processing, and teardown times
used for basic date scheduling. The routing header associated with each
material routing contains information on lot sizing, status, and usage. The
routing header links to a table containing the individual operations with
time parameters required for detailed scheduling of each stage of the
operation. An additional table contains a link between the routing and bill
of materials of the base material.
• Production BOM section — The Production Bill Of Materials (BOM)
Section of this Rapid Mart stores data that describes what materials are
used in planning production of a given material and the quantity needed
of each of its constituents. The BOM usage supported in this component
is production. BOM tables included are single level, BOM explosion with
quantities, and BOM explosion with materials-only for where-used
reporting.
• Production order section — Stores data about production orders.
When goods are required, planned orders are converted to production
orders. The production order specifies how much to produce, the routing,
the bill of material used to reserve, produce or procure dependent
materials, the scheduled and actual start and end dates, and the status of
the order.
• Production operation section — Operations are the activities to be
performed in the production process. They are a basis for determining
dates, capacity requirements, and costs. They enumerate the use of
materials, work centers, and quality checks during production.
Chapter 3: Subject Areas discusses each of these sections in more detail and
how to link them together for a complete analysis of production planning.
Supported analyses
16 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide
Overview
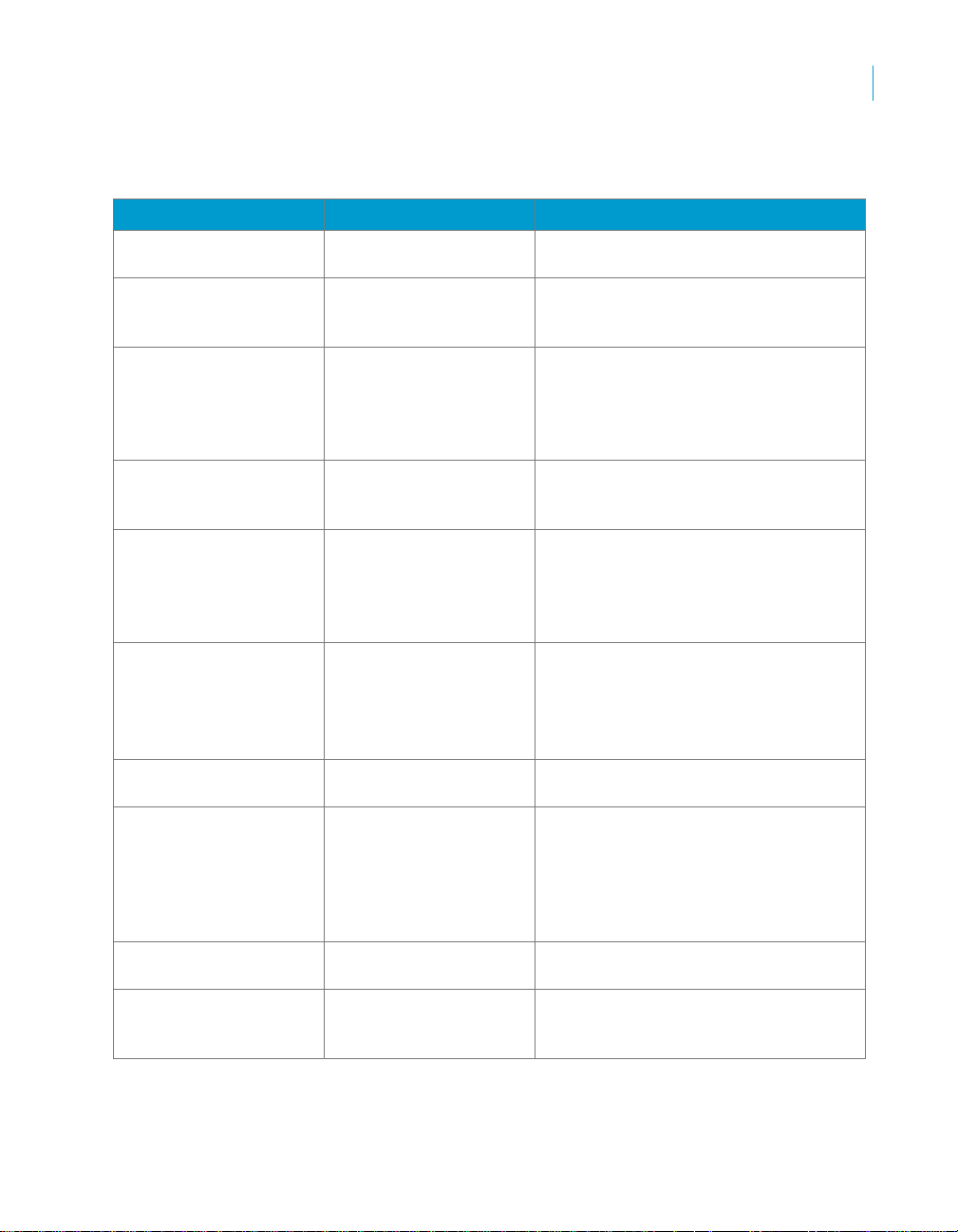
Supported analyses
The SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP
solutions supports several types of analyses.
Business function Types of analysis Measures available in the Rapid Mart
Bill of material Explosion
Where-used
Routing explosion
Work center Hierarchy
Capacity planning
Cost analysis
Routing/operations Lead time
Where-used
MRP results MRP requirements list
Planned orders Pegged requirements
Planned versus actual
scheduling
• Report dependent requirements for
production bill of materials
• Single, top, and multi-level listings
of bills of materials where a
particular component is used
• Accumulation of operations required
to produce a multi-level material
displayed hierarchically by
aggregating the operation times of
BOM components
• Calculate accumulated work center
capacity using work center
hierarchies
• Evaluate standard work center
capacity and shifts. Assess the
need for alternative interval capacity
based on factory calendar and
percent utilization.
• Analysis of production costs by work
center (requires purchase of Cost
Analysis (CA) Rapid Mart)
• Report and aggregate
manufacturing lead time by activity
• Find materials using a routing or
routing using a material
• Report results of materials
requirements planning (MRP) and
master production scheduling
(MPS) planning runs, including
materials requirements at the time
of the planning run
• Planned capacity requirements by
sales order
• Compare planned operation start
times, finish times, and lead times
with actual
2
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide 17

Overview
2
Related Rapid Marts
Business function Types of analysis Measures available in the Rapid Mart
Planned versus actual
yield
To support these analyses, the SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning
Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions includes a number of dimension tables.
Reporting dimensions include material master data, planning data,
plant-specific material master data, error texts, capacity parameters formulas,
and production version, as well as time-related dimensions, such as factory
calendar, time buckets, and calendar year.
• Compare planned yield with actual
Related Rapid Marts
Each Rapid Mart is composed of multiple components. A component is a
stand-alone work flow that completes a particular task, such as loading a
specific dimension table. Components can contain other components. A
section is a set of components that address a particular business problem or
subject area. A section is itself a component.
Components of the SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart,
version for SAP solutions are related to other SAP BusinessObjects Rapid
Mart components. For example:
• Inventory positions in the SAP BusinessObjects Inventory Rapid Mart,
version for SAP solutions.
• Account assignment by work center, controlling area, and activity along
with actual cost information for production orders in the SAP
BusinessObjects Cost Center Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions.
• Purchase requisitions and purchase orders in the SAP BusinessObjects
Purchasing Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions.
• Equipment maintenance scheduling by work center in the Plant
Maintenance Rapid Mart.
• Demand from sales documents in the SAP BusinessObjects Sales Rapid
Mart, version for SAP solutions.
Sharing components
The same components can be used in multiple Rapid Marts. For example, a
component that extracts information about materials bought, produced, and
sold is needed for a Rapid Mart that supports sales analysis and also for a
18 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide

Rapid Mart that supports inventory analysis. Work flows that extract star
schema “dimensions” are components. You can add a component to any
Rapid Mart using a simple import procedure.
A Data Services job can include multiple instances of a component. For
example, each section includes all the required dimension components.
Therefore, a job with several sections may include several instances of a
particular dimension component. Components are set to execute only once
within a job. This “execute once” feature ensures that shared components do
not cause duplicate data extraction from SAP solutions. For more information
about the “execute once” feature, see the Data Integrator/Data Services
Designer Guide.
Each of the sections listed in “What you can do with this Rapid Mart” on
page 15 are considered components. You can identify a component within a
Data Services job by a “C_” prefix before its name. For example, the
component that contains work centers and the associated reporting
dimensions is named C_WorkCenter_Section.
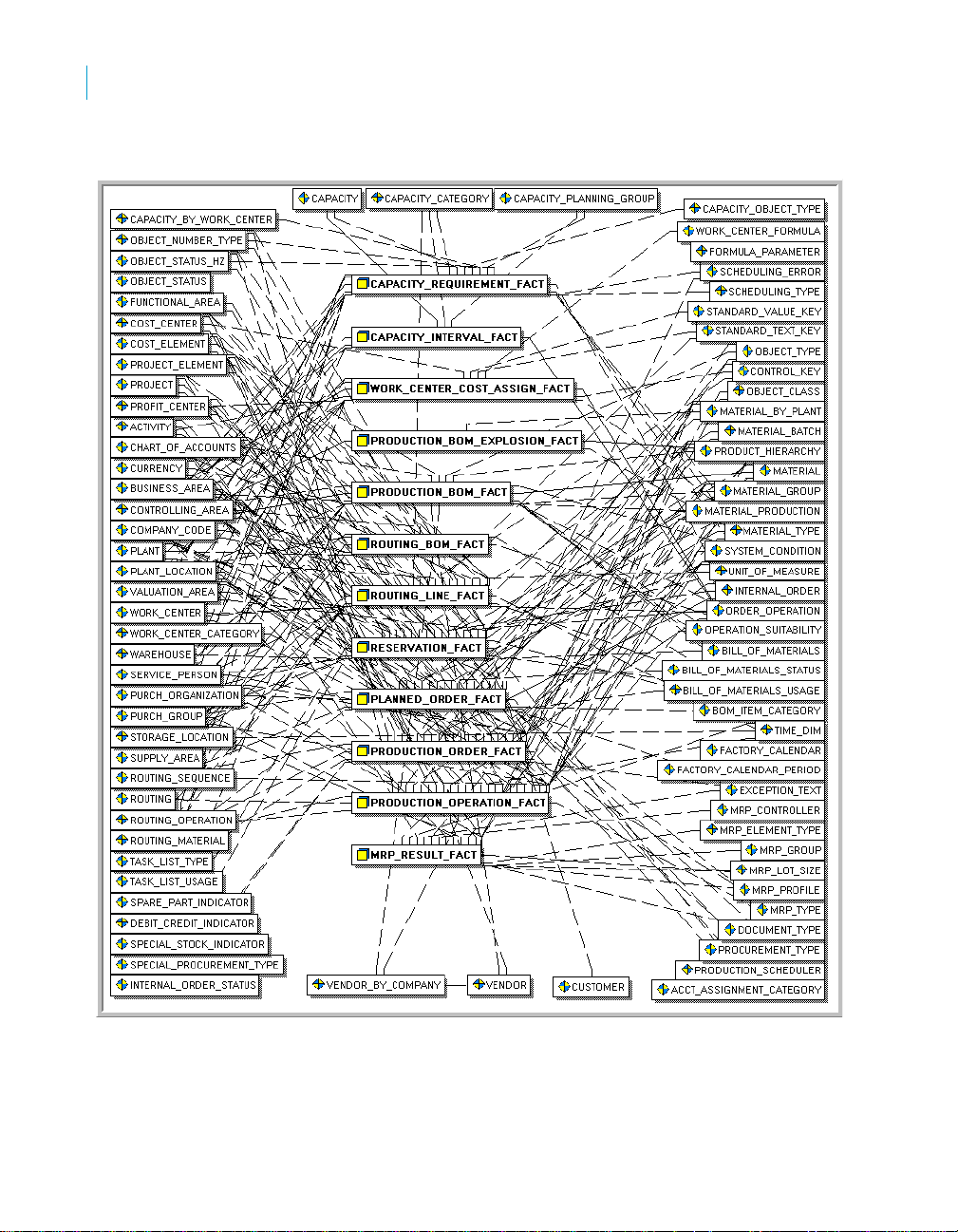
The Rapid Mart schema
The following diagrams show an overview of the SAP BusinessObjects
Production Planning Rapid Mart, version for SAP solutions components and
their relationships in Star Schema Format, and then the associated
hierarchies and auxiliary tables. As an overall picture, these diagrams are
challenging to understand. They are broken down into additional diagrams by
subject area in Chapter 3: Subject Areas.
Overview
The Rapid Mart schema
2
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide 19
Overview
2
The Rapid Mart schema
Overview Star Schema (1 of 2):
20 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide

Overview Hierarchies and Auxiliary Tables:
Overview
The Rapid Mart schema
2
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide 21

Overview
2
Where the Rapid Mart fits in the productio n planning process
Where the Rapid Mart fits in the production
planning process
To create a comprehensive view of SAP solutions logistics modules, you can
combine the SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart, version
for SAP solutions components with components from other Rapid Marts.
22 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide
Subject Areas
chapter

Subject Areas
3
Overview
Overview
Each section in the SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart,
version for SAP solutions pertains to a particular subject area. This chapter
describes each section and the processes each section captures.
The information in this chapter is useful for readers who use the Rapid Mart to
design and support a real-time system, such as a Web application, and need
to understand the data in the Rapid Mart and how it relates to SAP solutions.
This chapter discusses:
• Work Center section
• Capacity section
• MRP results section
• Planned Order section
• Reservation section
• Routing section
• Bills of Material (BOM) section
• Production Order section
• Production Operation section
Work Center section
Production operations are carried out at a work center. In SAP solutions work
centers represent the following:
• Machines, machine groups
• Production lines
• Assembly work centers
• Employees, groups of employees
Work centers are used in task list (routing) operations and production orders.
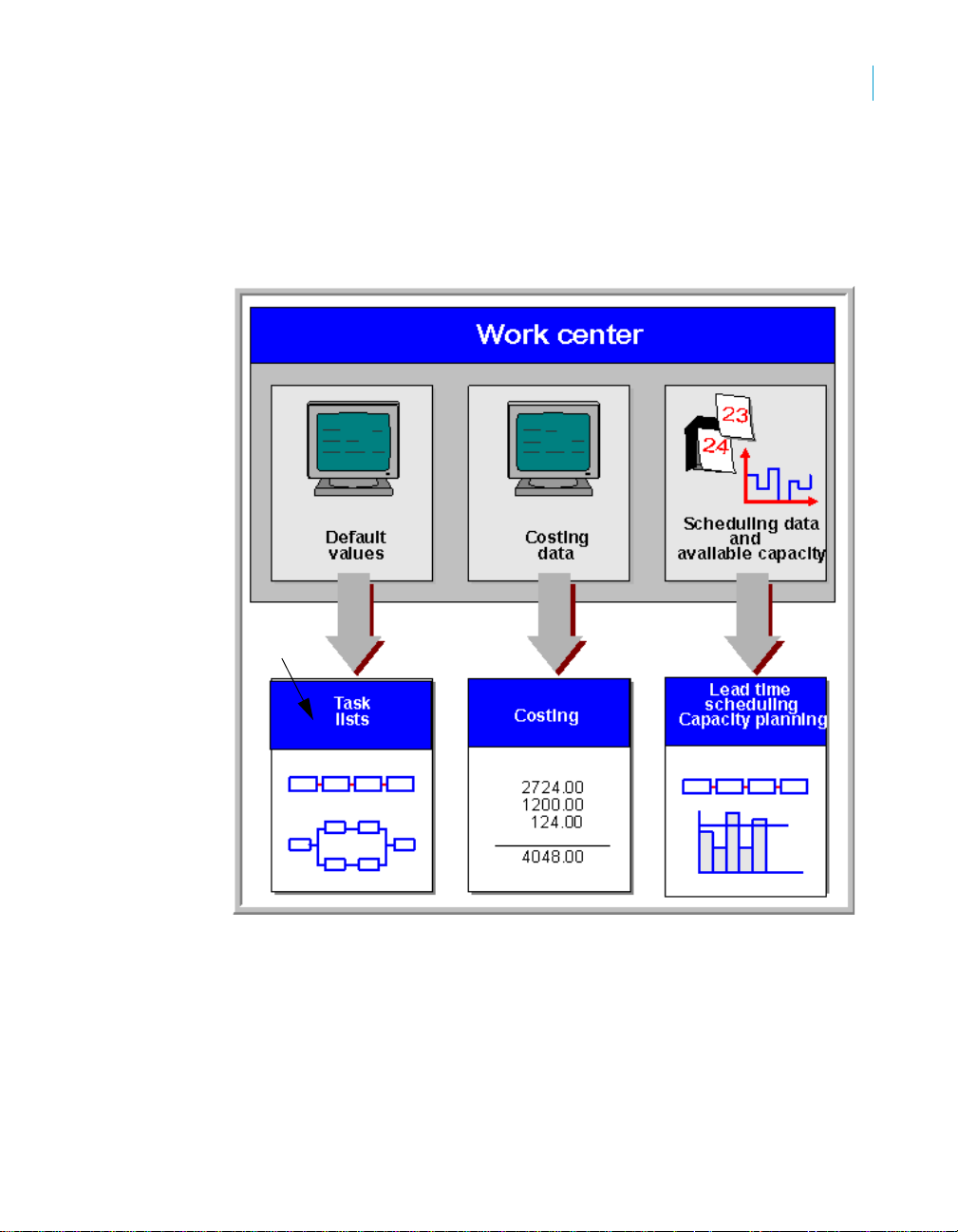
Work centers contain the following types of information:
• Scheduling
Operating times and formulas are entered in the work center, so that the
duration of an operation can be calculated.
• Costing
Formulas are entered in the work center, so that the costs of an operation
can be calculated. A work center is also assigned to a cost center.
• Capacity planning
24 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide
Subject Areas
(Routings)
Work Center section
The available capacity and formulas for calculating capacity requirements
are entered in the work center.
• Simplifying operation maintenance
Various default values for operations can be entered in the work center.
The following graphic illustrates the use of work center data.
3
A work center is created for a plant (a plant can have many work centers).
The work center category, which you define in Customizing the work center,
determines which data can be maintained in the work center.
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide 25

Subject Areas
3
Work Center section
Basic Data in a Work Center:
• Assignments (to cost centers, etc.)
• Capacities
• Scheduling
• Default values
• Hierarchy
• Technical data
Integration of Work Centers
Task Lists (Routings)
Work centers are assigned to operations in task lists (routings). If you change
default values in a work center, the changes are effective in the task list if a
reference indicator has been set for the default value.
Work Center Hierarchies
Work centers can be arranged in hierarchies. These are important in capacity
planning. You use hierarchies to cumulate available capacities and capacity
requirements in a hierarchy work center.
Rapid Mart processing
The Rapid Mart extracts data from SAP solutions tables
• CRHD - Work Center Header
• CRCO - Assignment of Work Center to Cost Center
Data from these tables is used to populate target table
• WORKCENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT
The fact table contains descriptive information and basic data needed for
routing, costing, and capacity calculations.
26 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide

Subject Areas
Work Center section
The section captures the following dimensional attributes and their associated
dimension tables:
Attribute Name Dimension Tables
Activity & Hierarchy ACTIVITY, ACTIVITY_HIER,
ACTIVITY_HIER_HZ,
ACTIVITY_HIER_VR,
ACTIVITY_HIER_BAD
Chart of Accounts CHART_OF_ACCOUNTS
Company Code COMPANY_CODE
Control Key CONTROL_KEY
Controlling Area CONTROLLING_AREA
Cost Center & Hierarchy COST_CENTER,
COST_CENTER_HIER,
COST_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
COST_CENTER_HIER_VR,
COST_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Plant PLANT
Plant Location PLANT_LOCATION
Purchasing Organization PURCH_ORGANIZATION
Standard Text Key STANDARD_TEXT_KEY
Standard Value Key STANDARD_VALUE_KEY
Task List Usage TASK_LIST_USAGE
Time Dimension TIME_DIM
Valuation Area VALUATION_AREA
Work Center & Hierarchy WORK_CENTER,
WORK_CENTER_HIER,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_HZ,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_VR,
WORK_CENTER_HIER_BAD
Work Center Category WORK_CENTER_CATEGORY
Work Center Formula WORK_CENTER_FORMULA
3
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide 27
Subject Areas
3
Work Center section
Fact Table Fields
A work center is master data information. Therefore, classic “measures”
(monetary and quantity values) are not found in the
WORKCENTER_COST_ASSIGN_FACT table. However, these fields are of
key importance:
Column Name Description
ACTIVITY_ID CRCO.LSTAR - Activity Type
CURRENT_FLAG “X” indicates record is currently in
effect
DAYS_VALID_ASSIGN Number of days assignment is valid
FORMULA_ID CRCO.FORML - Formula key for
costing
GROUP_USG_ID CRHD.PLANV - Key for task list
usage
LOCATN_ID CRHD.STAND - Work center location
PURCH_ORG_ID T001W.EKORG Purchasing
organization (lookup)
VALID_FROM_DATE Start date of validity period for this
record (calculated)
VALID_TO_DATE End date of validity period
(calculated)
WORK_CNTR_CATEG_ID CRHD.VERWE - Work center
category
28 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide

Rapid Mart data
The following diagram shows the tables in the work center section as a star
schema.
Work Centers:
Subject Areas
Work Center section
3
With the tables in this section you can analyze Work Centers along several
dimensions:
• Activity & Hierarchy
• Chart of Accounts
• Company Code
• Control Key
• Controlling Area
• Cost Center & Hierarchy
• Plant
SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide 29

Subject Areas
3
Capacity section
• Plant Location
• Purchasing Organization
• Standard Text Key
• Standard Value Key
• Task List Usage
• Time Dimension
• Valuation Area
• Work Center & Hierarchy
• Work Center Category
• Work Center Formula
Note: As Work Center Cost Assignment is a cross-reference fact table, both
work centers and cost centers appear as dimensions with their associated
hierarchies.
Typical queries for this section include:
• What Activities are associated with this work center?
• Which Work Centers are associated with each plant?
• What Cost Centers are associated with my work centers today vs. a year
ago?
Capacity section
The capacity section stores available capacity information by work center,
available interval capacity by date, and capacity requirements for planned
orders.
Work center capacities measure the amount of work output that a work center
can produce during a period of time. Capacity categories subdivide capacity
into types, such as machine, labor, or electrical output. More than one
capacity category can exist at a work center.
Capacities have standard operating times based on shift lengths, break times,
number of individual capacities, and percentage utilization rates. Additional
data items include the formulas and parameters used when calculating the
amount of capacity required for an operation during order scheduling and
capacity planning. Intervals of available capacity can be used to
accommodate deviations from standard available capacities. These intervals
are identified by a version and are delimited with beginning and ending
effective dates.
30 SAP BusinessObjects Production Planning Rapid Mart XI 3.2 for SAP solutions Business Guide
 Loading...
Loading...