Data Services Migration
Considerations
BusinessObjects Data Services XI 3.0 (12.0.0)

Copyright
© 2008 Business Objects. All rights reserved. Business Objects owns the following
U.S. patents, which may cover products that are offered and licensed by Business
Objects: 5,555,403; 5,857,205; 6,289,352; 6,247,008; 6,490,593; 6,578,027;
6,831,668; 6,768,986; 6,772,409; 6,882,998; 7,139,766; 7,299,419; 7,194,465;
7,222,130; 7,181,440 and 7,181,435. Business Objects and the Business Objects
logo, BusinessObjects, Business Objects Crystal Vision, Business Process On
Demand, BusinessQuery, Crystal Analysis, Crystal Applications, Crystal Decisions,
Crystal Enterprise, Crystal Insider, Crystal Reports, Desktop Intelligence, Inxight,
the Inxight Logo, LinguistX, Star Tree, Table Lens, ThingFinder, Timewall, Let
there be light, Metify, NSite, Rapid Marts, RapidMarts, the Spectrum Design, Web
Intelligence, Workmail and Xcelsius are trademarks or registered trademarks in
the United States and/or other countries of Business Objects and/or affiliated
companies. All other names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Third-party
Contributors
Business Objects products in this release may contain redistributions of software
licensed from third-party contributors. Some of these individual components may
also be available under alternative licenses. A partial listing of third-party
contributors that have requested or permitted acknowledgments, as well as required
notices, can be found at: http://www.businessobjects.com/thirdparty
2008-03-16

Contents
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide 7Chapter 1
Introduction..................................................................................................8
Using the migration tool.............................................................................25
How Data Quality repository contents migrate..........................................37
How transforms migrate.............................................................................55
Welcome to Data Services.....................................................................8
Overview of migration...........................................................................14
Overview of the migration utility...........................................................25
Migration checklist................................................................................26
Connection information........................................................................27
Running the dqmigration utility ............................................................29
dqmigration utility syntax and options..................................................31
Migration report ...................................................................................35
How projects and folders migrate.........................................................37
How connections migrate.....................................................................43
How substitution files and variables migrate........................................49
How data types migrate........................................................................54
How Data Quality attributes migrate.....................................................55
Overview of migrated transforms.........................................................55
Address cleansing transforms..............................................................63
Reader and Writer transforms..............................................................73
How Data Quality integrated batch Readers and Writers migrate.....109
How Data Quality transactional Readers and Writers migrate...........116
Matching transforms...........................................................................120
UDT-based transforms.......................................................................129
Other transforms................................................................................139
Data Services Migration Considerations 3

Contents
Suggestion Lists options....................................................................153
Post-migration tasks................................................................................154
Further cleanup .................................................................................154
Improving performance .....................................................................161
Troubleshooting..................................................................................166
Migration Considerations Guide 175Chapter 2
Introduction..............................................................................................176
Behavior changes in version 12.0.0........................................................177
Case transform enhancement............................................................177
Data Quality projects in Data Integrator jobs ....................................178
Data Services web address................................................................178
Large object data type enhancements...............................................179
License keycodes...............................................................................181
Locale selection..................................................................................182
ODBC bigint data type........................................................................183
Persistent and pageable cache enhancements.................................184
Row delimiter for flat files...................................................................184
Behavior changes in version 11.7.3.........................................................185
Data flow cache type..........................................................................185
Job Server enhancement...................................................................186
Logs in the Designer..........................................................................186
Pageable cache for memory-intensive data flows..............................186
Behavior changes in version 11.7.2.........................................................187
Embedded data flows.........................................................................187
Oracle Repository upgrade................................................................187
Solaris and AIX platforms...................................................................189
Behavior changes in version 11.7.0.........................................................189
Data Quality........................................................................................190
Distributed data flows.........................................................................192
JMS Adapter interface........................................................................193
4 Data Services Migration Considerations

Contents
XML Schema enhancement...............................................................193
Password management......................................................................193
Web applications................................................................................194
Web services......................................................................................194
Behavior changes in version 11.6.0.........................................................195
Netezza bulk loading..........................................................................195
Conversion between different data types...........................................196
Behavior changes in version 11.5.1.5......................................................196
Behavior changes in version 11.5.1.........................................................196
Behavior changes in version 11.5.0.0......................................................197
Web Services Adapter........................................................................197
Varchar behavior................................................................................197
Central Repository..............................................................................198
Behavior changes in version 11.0.2.5......................................................198
Teradata named pipe support............................................................198
Behavior changes in version 11.0.2.........................................................198
Behavior changes in version 11.0.1.1......................................................199
Statistics repository tables..................................................................199
Behavior changes in version 11.0.1.........................................................199
Crystal Enterprise adapters................................................................200
Behavior changes in version 11.0.0.........................................................200
Changes to code page names...........................................................201
Data Cleansing...................................................................................202
License files and remote access software.........................................203
Behavior changes in version 6.5.1..........................................................203
Behavior changes in version 6.5.0.1.......................................................204
Web services support.........................................................................204
Sybase bulk loader library on UNIX...................................................205
Behavior changes in version 6.5.0.0.......................................................205
Browsers must support applets and have Java enabled....................205
Execution of to_date and to_char functions.......................................206
Data Services Migration Considerations 5

Contents
Changes to Designer licensing..........................................................207
License files and remote access software.........................................207
Administrator Repository Login..........................................................208
Administrator Users............................................................................209
Business Objects information resources.................................................210
Documentation...................................................................................210
Index 211
6 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Introduction
Introduction
Welcome to Data Services
Welcome
Data Services XI Release 3 provides data integration and data quality
processes in one runtime environment, delivering enterprise performance
and scalability.
The data integration processes of Data Services allow organizations to easily
explore, extract, transform, and deliver any type of data anywhere across
the enterprise.
The data quality processes of Data Services allow organizations to easily
standardize, cleanse, and consolidate data anywhere, ensuring that end-users
are always working with information that's readily available, accurate, and
trusted.
Documentation set for Data Services
You should become familiar with all the pieces of documentation that relate
to your Data Services product.
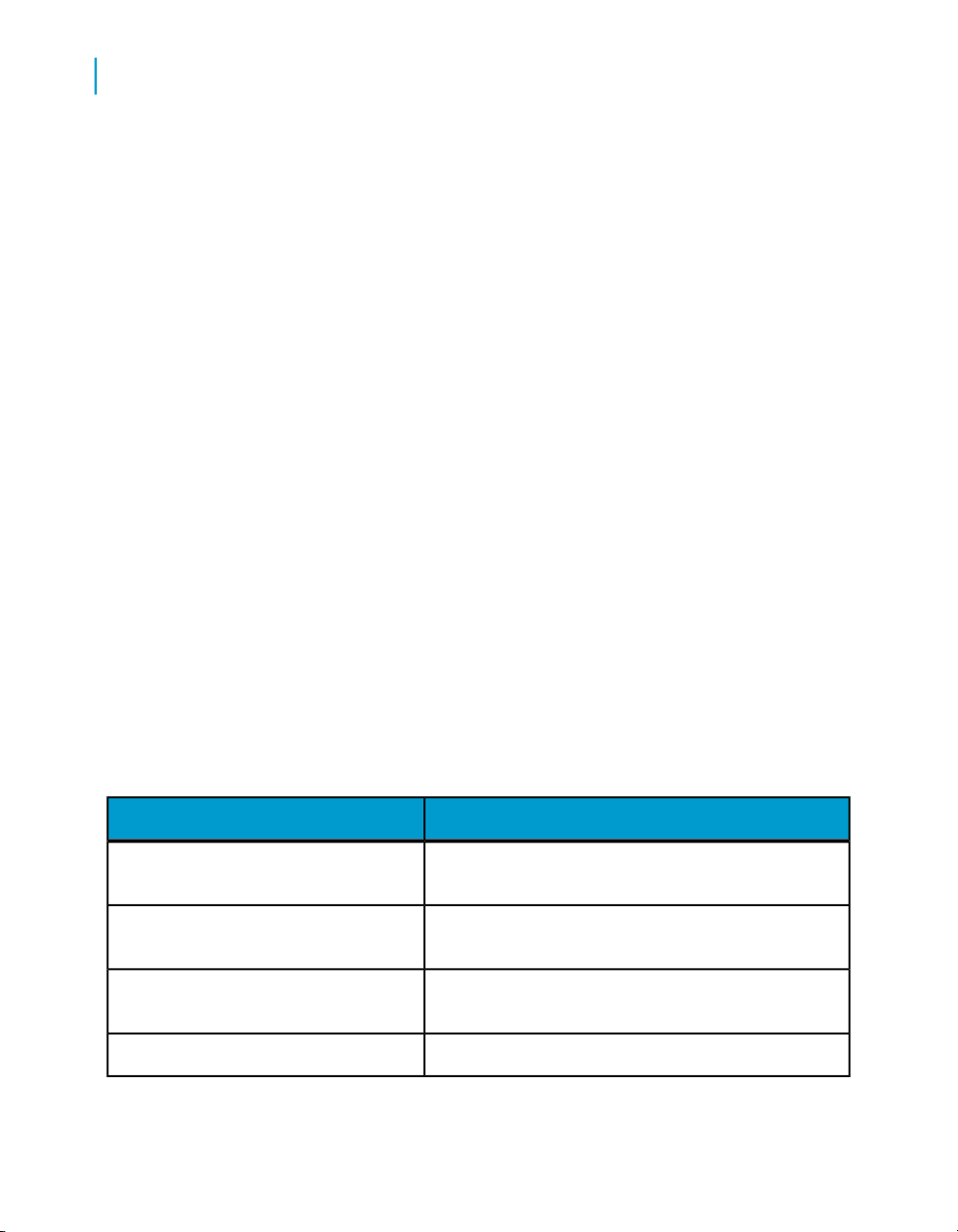
What this document providesDocument
Documentation Map
Release Summary
Release Notes
Getting Started Guide
8 Data Services Migration Considerations
Information about available Data Services books,
languages, and locations
Highlights of key features in this Data Services release
Important information you need before installing and
deploying this version of Data Services
An introduction to Data Services
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Introduction
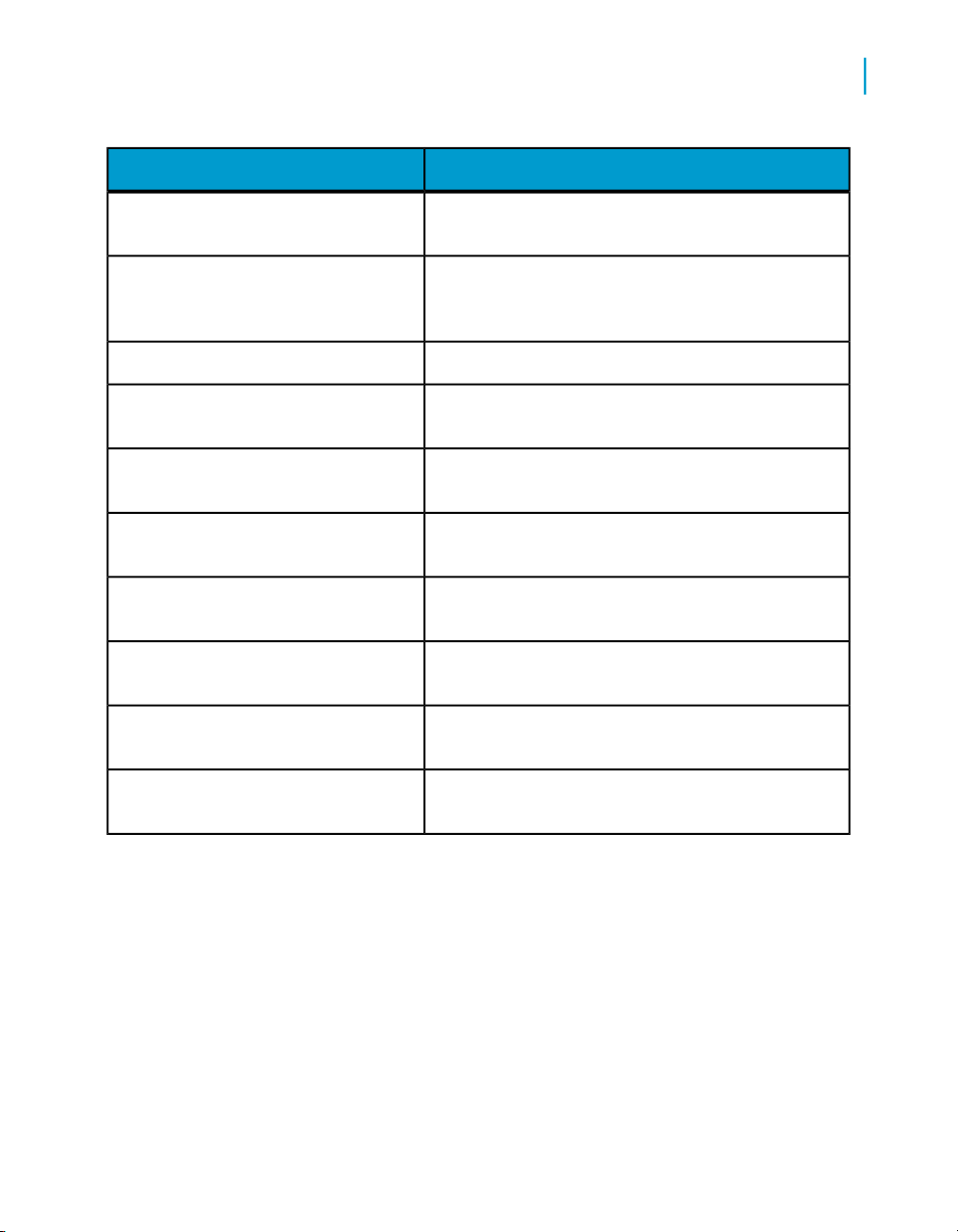
What this document providesDocument
1
Installation Guide
Advanced Development Guide
Designer Guide
Integrator's Guide
Management Console: Administrator
Guide
Management Console: Metadata Reports Guide
Migration Considerations
Migration Guide
Performance Optimization Guide
Information about and procedures for installing Data
Services
Guidelines and options for migrating applications including information on multi-user functionality and
the use of the central repository for version control
Information about how to use Data Services Designer
Information for third-party developers to access Data
Services functionality
Information about how to use Data Services Administrator
Information about how to use Data Services Metadata
Reports
Release-specific product behavior changes from
earlier versions of Data Services to the latest release
Information about how to migrate from Data Quality
to Data Services
Information about how to improve the performance
of Data Services
Reference Guide
Detailed reference material for Data Services Designer
Data Services Migration Considerations 9
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Introduction
Technical Manuals
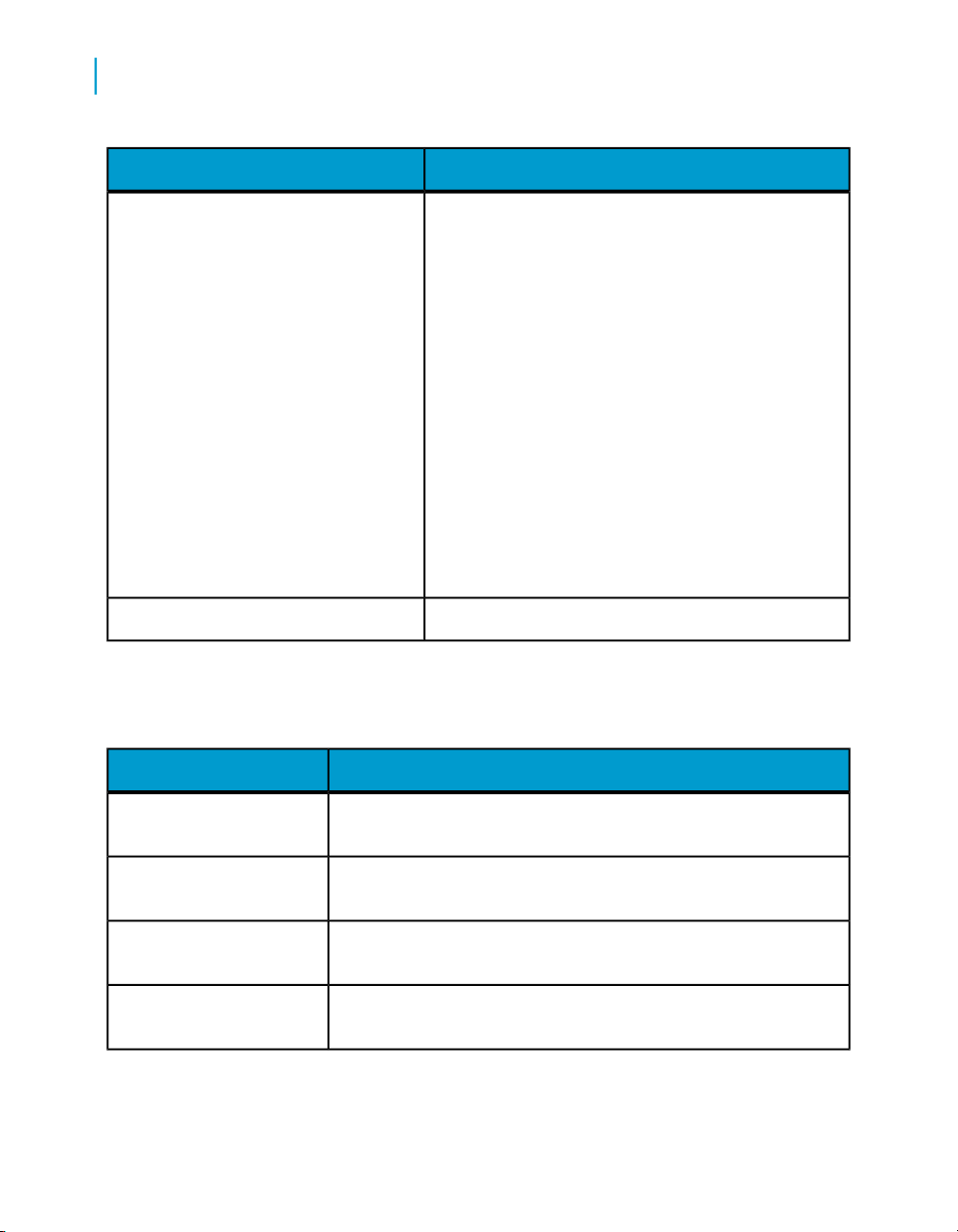
What this document providesDocument
A compiled “master” PDF of core Data Services books
containing a searchable master table of contents and
index:
• Installation Guide
• Getting Started Guide
• Designer Guide
• Reference Guide
• Management Console: Metadata Reports Guide
• Management Console: Administrator Guide
• Performance Optimization Guide
• Advanced Development Guide
• Supplement for J.D. Edwards
• Supplement for Oracle Applications
• Supplement for PeopleSoft
• Supplement for Siebel
• Supplement for SAP
Tutorial
A step-by-step introduction to using Data Services
In addition, you may need to refer to several Adapter Guides and
Supplemental Guides.
What this document providesDocument
JMS Adapter Interface
Salesforce.com Adapter
Interface
Supplement for J.D. Edwards
Supplement for Oracle Applications
10 Data Services Migration Considerations
Information about how to install, configure, and use the Data
Services Adapter for JMS
Information about how to install, configure, and use the Data
Services Salesforce.com Adapter Interface
Information about license-controlled interfaces between Data
Services and J.D. Edwards World and J.D. Edwards OneWorld
Information about the license-controlled interface between Data
Services and Oracle Applications
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Introduction
What this document providesDocument
1
Supplement for PeopleSoft
Supplement for SAP
Supplement for Siebel
Information about license-controlled interfaces between Data
Services and PeopleSoft
Information about license-controlled interfaces between Data
Services, SAP ERP and R/3, and SAP BI/BW
Information about the license-controlled interface between Data
Services and Siebel
Accessing documentation
You can access the complete documentation set for Data Services in several
places.
Note: For the latest tips and tricks on Data Services, access our Knowledge
Base on the Customer Support site at http://technicalsupport.businessob
jects.com. We have posted valuable tips for getting the most out of your Data
Services product.
Accessing documentation on Windows
After you install Data Services, you can access the documentation from the
Start menu.
1. Choose Start > Programs > BusinessObjects XI 3.0 >
BusinessObjects Data Services > Data Services Documentation.
Note: Only a subset of the documentation is available from the Start
menu. The documentation set for this release is available in
LINK_DIR\Doc\Books\en.
2. Click the appropriate shortcut for the document that you want to view.
Accessing documentation on UNIX
After you install Data Services, you can access the online documentation by
going to the directory where the printable PDF files were installed.
1. Go to LINK_DIR/doc/book/en/.
Data Services Migration Considerations 11
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Introduction
2. Using Adobe Reader, open the PDF file of the document that you want
to view.
Accessing documentation from the Web
You can access the complete documentation set for Data Services from the
Business Objects Customer Support site.
1.
Go to www.businessobjects.com
2. From the "Support" pull-down menu, choose Documentation.
3. On the "Documentation" screen, choose Product Guides and navigate
to the document that you want to view.
You can view the PDFs online or save them to your computer.
Business Objects information resources
Customer support, consulting, and training
A global network of Business technology experts provides customer support,
education, and consulting to ensure maximum business intelligence benefit
to your business.
Useful addresses at a glance
Product information
http://www.businessob
jects.com
Product documentation
http://www.businessob
jects.com/support
Documentation mailbox
documentation@businessobjects.com
12 Data Services Migration Considerations
ContentAddress
Information about the full range of Business
Objects products.
Business Objects product documentation, including the Business Objects Documentation
Roadmap.
Send us feedback or questions about your
Business Objects documentation.
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
ContentAddress
Introduction
1
Online Customer Support
http://www.businessob
jects.com/support
Online Developer Community
http://diamond.businessob
jects.com/
Consulting services
http://www.businessob
jects.com/services/consulting/
Education services
http://www.businessob
jects.com/services/training
Online Customer Support
The Business Objects Customer Support web site contains information about
Customer Support programs and services. It also has links to a wide range
of technical information including Knowledge Base articles, downloads, and
support forums. http://www.businessobjects.com/support
Information on Customer Support programs,
as well as links to technical articles, downloads, and online forums.
An online resource for sharing and learning
about Data Services with your developer colleagues.
Information about how Business Objects can
help maximize your business intelligence investment.
Information on Business Objects training options and modules.
Looking for training options?
From traditional classroom learning to targeted e-learning seminars, Business
Objects can offer a training package to suit your learning needs and preferred
learning style. Find more information on the Business Objects Education
web site: http://www.businessobjects.com/services/training
Send us your feedback
Do you have a suggestion on how we can improve our documentation? Is
there something that you particularly like or have found useful? Drop us a
line, and we will do our best to ensure that your suggestion is considered for
the next release of our documentation: documentation@businessobjects.com.
Data Services Migration Considerations 13

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Introduction
Note: If your issue concerns a Business Objects product and not the
documentation, please contact our Customer Support experts.
Overview of migration
About this guide
The Data Quality Migration Guide provides information about:
• migrating your Data Quality Projects into Data Services
• understanding some of the benefits of using Data Services
• seeing the differences between previous versions of Data Quality and
Data Services
• using best practices during migration
• learning how to troubleshoot during migration
Who should migrate?
Anyone who is using Data Quality XI and Data Services as standalone
applications should migrate to Data Services.
The migration utility works with these versions of software:
• Data Integrator 11.7.x
• Data Quality XI 11.7.x and 11.6.x
• Data Integrator XI R2
• Data Quality XI R2 11.5 and newer
• Firstlogic IQ8 8.05c and newer
Those who are using the Firstlogic Data Quality Suite (Job file, RAPID, Library
and/or eDataQuality) cannot use the migration utility to convert the existing
projects into Data Services. The only option is to create the projects again
in Data Services.
1
Some manual steps are required.
2
Some manual steps are required.
14 Data Services Migration Considerations
1
2

Why migrate?
You may have seen some literature that includes a comprehensive list of
reasons to migrate. Here are a handful of the main reasons why you should
migrate.
Performance
The new platform utilizes the past Data Integrator features with the improved
Data Quality features in one user interface.
Data profiling of source and target
You can monitor, analyze, and report on the quality of information contained
in the data marts, data warehouses, and any other data stored in databases.
You can test business rules for validity and prioritize data quality issues so
that investments can be made in the high impact areas.
Improved multi-user support
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Introduction
1
With Data Services, you have access to both a central repository (if
purchased) for multi-user storage and a local repository for each user. Version
control for the repository objects keeps you in control by labeling and
comparing objects. This version includes top-notch security with
authentication to access the central repository, authorization for group-based
permissions to objects, and auditing for changes to each object.
Powerful debugging capabilities
You can set break points, view the data before and after each transform, set
filters when previewing data and save and print the preview data.
Repository management
You can easily manage your fully relational repository across systems and
have the ability to import repository objects from a file. You can also import
source and target metadata for faster UI response times. With datastore
configurations, you can define varying connection options for similar
datastores between environments, use different relational database
technology between environments without changing your jobs, and use
different database owners between systems without making changes during
Data Services Migration Considerations 15

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Introduction
migration to each environment. With system configurations, you can associate
substitution configurations per system configuration by associating different
substitution parameter values by environment.
Import and export metadata
You can import and export metadata with Common Warehouse Model (CWM)
1.0/1.1 support and ERWIN (Computer Associates) 4.x XML. You can also
export on Meta Integration Model Bridge (MiMB), if you have it installed.
Auditing
You can audit your projects with statistics collection, rule definitions, email
notification, and audit reporting.
Reports and dashboards
With the reporting tool, you can view daily and historical execution results
and duration statistics. With the data validation dashboard, you can view the
results of validation rules, organize the validation rules across jobs into
functional areas and drill down statistics to a functional area's validation
rules. You can also define high-level business rules based on results of
validation rules.
With impact and lineage analysis, you can understand the cost and impact
of other areas when the datasource is modified. You can view, analyze and
print jobs, work flows, and data flow details, view table/file usage based on
the source and target, view a summary of job variables and parameters,
generate PDF/Word documents on a job-by-job basis, and view a transform
option and field mapping summary.
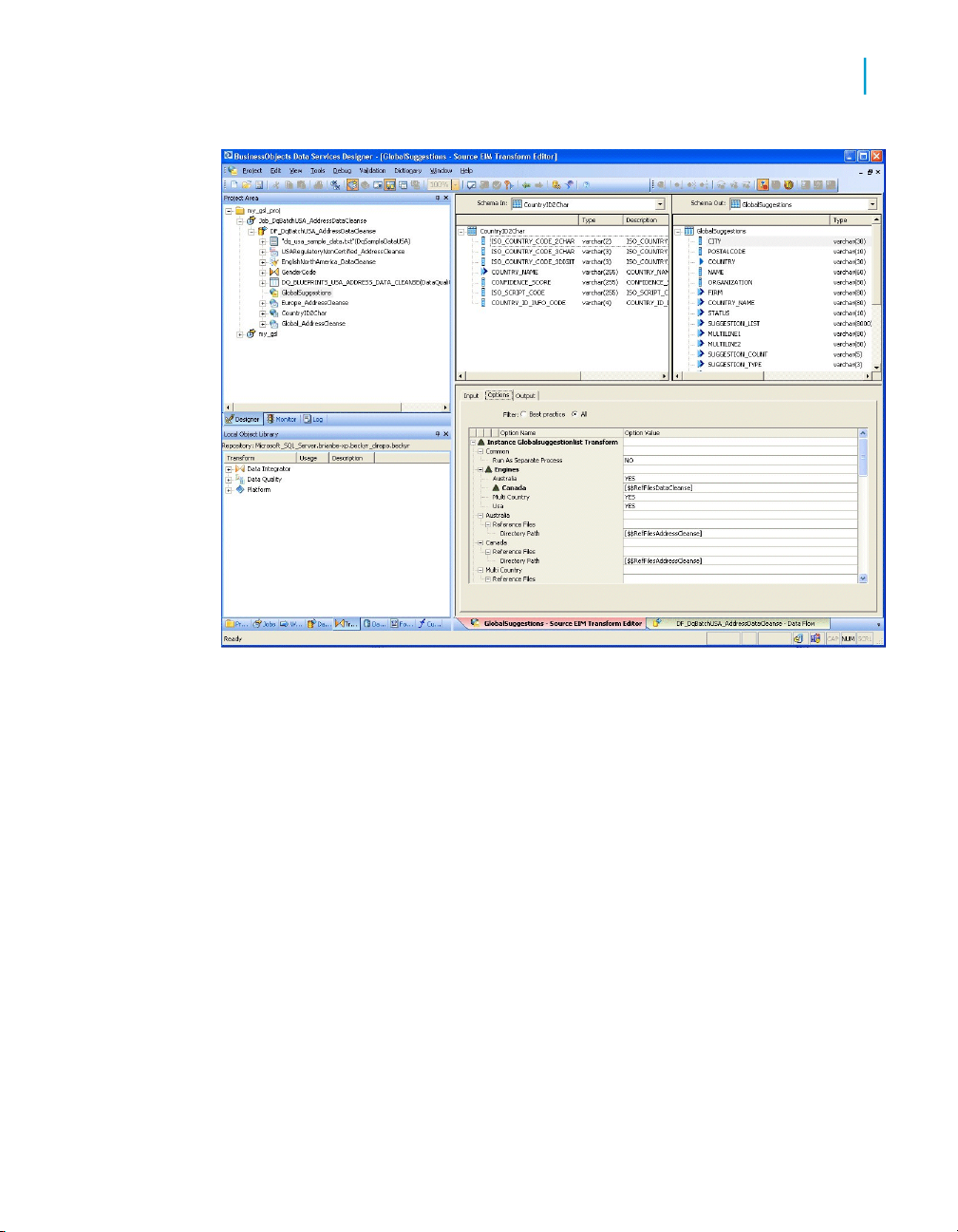
Introduction to the interface
The Data Services user interface is different from the Data Quality user
interface. It has similar elements, but in a different presentation.
16 Data Services Migration Considerations
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Introduction
1
Note: The window shows a project named my_gsl_proj open on the left
portion of the screen. The right portion shows the GlobalSuggestions
transform input and output fields and the Option groups.
In the upper left corner of the Data Services UI, you can see the Project
Area. You can see your project folders and any jobs that you have. It's a
hierarchical view of the objects used in each project.
Below the Project Area is the is the Local Object Library where you have
access to all of the reusable objects in your jobs. It is a view into your
repository, so that you do not need to access the repository directly. There
are tabs at the bottom so that you can view projects, jobs, work flows, data
flows, transforms, data sources, file formats and functions.
The right side of the window is the workspace. The information presented
here will differ based on the objects you have selected. For example, when
you first open Data Services, you will see a Business Objects banner followed
by Getting Started options, Resources, and Recent Projects. In the example,
the workspace has the GlobalSuggestions transform open to the object editor.
Data Services Migration Considerations 17

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Introduction
The editor displays the input and output schemas for the object and the panel
below lists the options for the object.
See the Data Services Designer Guide: Designer User Interface for
information.
Related Topics
• Introduction to the interface on page 16
Downloading blueprints and other content objects
We’ve identified a number of common scenarios that you are likely to perform
with Data Services. Instead of creating your own job from scratch, look
through the blueprints. If you find one that is closely related to your particular
business problem, you can simply use the blueprint and tweak the settings
in the transforms for your specific needs.
For each scenario, we’ve included a blueprint that is already set up to solve
the business problem in that scenario. Each blueprint contains the necessary
Data Services project, jobs, data flows, file formats, sample data, template
tables, and custom functions to run the data flows in your environment with
only a few modifications.
You can download all of the blueprints or only the blueprints and other content
that you think you will find useful from the Business Objects Diamond
Developer website. On the Diamond website, we periodically post new and
updated blueprints, custom functions, best practices, white papers, and other
Data Services content. You can refer to this site frequently for updated content
and use the forums to provide us with any questions or requests you may
have. We've also provided the ability for you to upload and share any content
you've developed with the rest of the Data Services development community.
Instructions for downloading and installing the content objects are also located
on the Diamond website.
1. To access the Business Objects Diamond Developer website, go to
http://diamond.businessobjects.com/dataservices/blueprints in your web
browser.
2. Log in to your Diamond account using your username and password, or
create a new account.
18 Data Services Migration Considerations

3. Open the Content Objects User's Guide to view a list of all of the available
blueprints and content objects and their descriptions, and instructions for
downloading and setting up the blueprints.
4. Use the filters at the top of the Data Services Blueprints page to search
for the blueprint or content objects that you want to download.
5. Select the blueprint that you want to download. To download all blueprints,
select Data Quality Blueprints - All.
6. Follow the instructions in the user's guide to download the files to the
appropriate location and make the necessary modifications in Data
Services to run the blueprints.
Introduction to the migration utility
The Data Quality Migration Utility is a Windows-based utility command line
that migrates your Data Quality repository to the Data Services repository.
The utility is in the LINK_DIR\DQMigration folder. It uses an XML-based
configuration file.
You can set options on this Windows-based utility to migrate the entire
repository (recommended) or on a project-by-project or
transform-by-transform basis. You can also set the utility to Analyze Mode
where the utility identifies errors and warning during migration so that you
can either fix them in Data Quality before fully migrating.
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Introduction
1
After running the utility you can optionally view the Migration Report in a web
broswer for details of possible errors and warnings. We highly recommend
you fix these before trying to run the job in Data Services.
In addition, if your Data Quality jobs were published as Web services, after
running the utility you can publish the migrated jobs as Data Services Web
services. For information on publishing jobs as Web services, see the Data
Services Integrator's Guide.
Related Topics
• Running the dqmigration utility on page 29
Data Services Migration Considerations 19
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Introduction
• dqmigration utility syntax and options on page 31
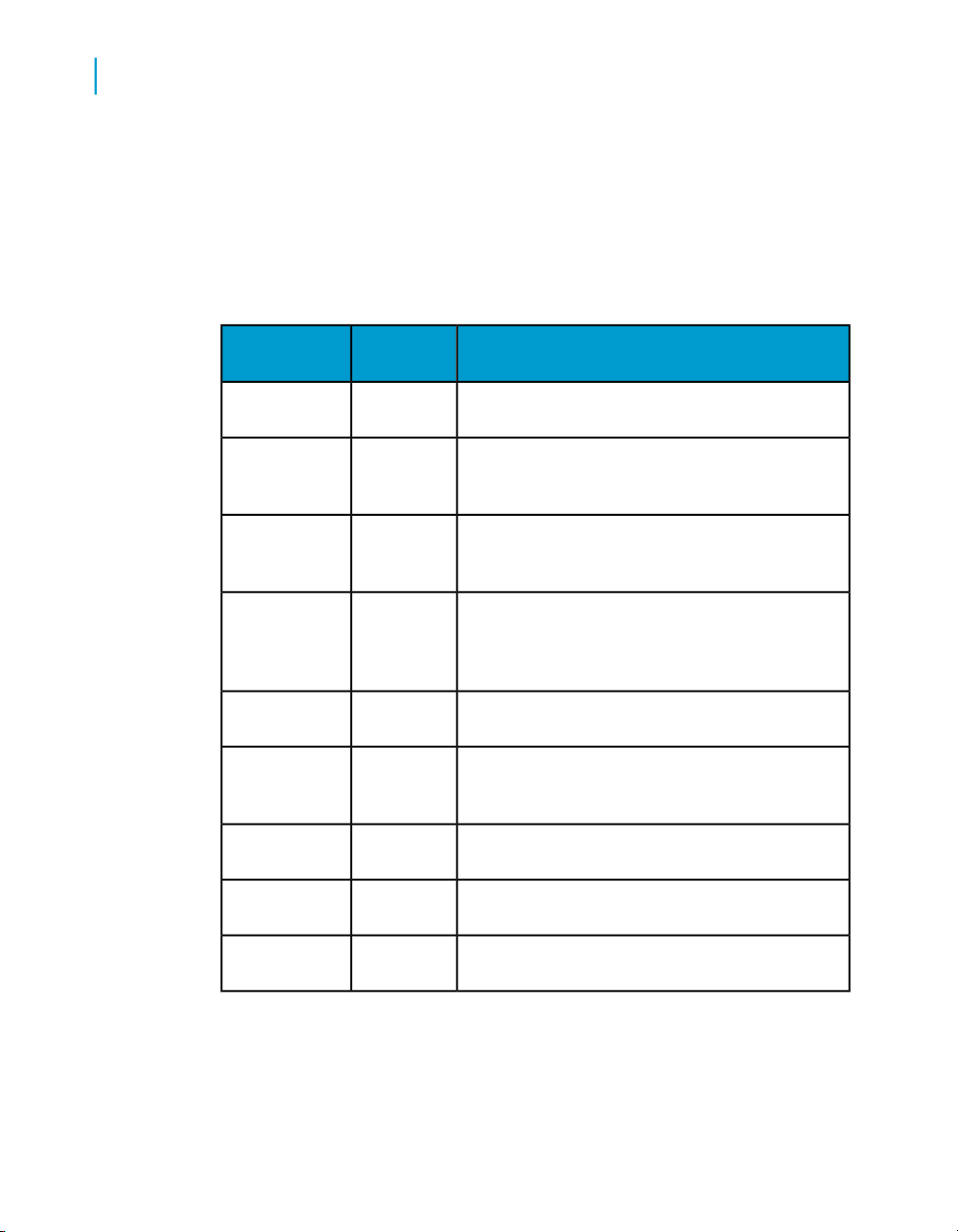
Terminology in Data Quality and Data Services
Several terms are different between Data Quality and Data Services.
Data Quality
er/option editor
vices
projectfolder
jobproject
workspacecanvas
data flowdataflow
object editoroption explor-
real timetransactional
sourcereader
DescriptionData Ser-
Terms are different, but it holds the project or job
that runs.
In Data Quality, a project is able to run. In Data
Services, a project is a level higher. The project
contains the job, and the job is able to run.
In Data Quality, you dragged a transform onto a
canvas. In Data Services, you drag a transform
onto a workspace.
In Data Quality, a dataflow is a series of transforms hooked together, that may or may not run.
In Data Services, the data flow includes everything that will extract, transform and load data.
The terms are different, but you do the same
things: set your options.
The terms are different, but they mean the same
thing: processing one or many records at a time,
usually through a web service.
The terms are different, but they mean the same
thing: a place where the incoming data is held.
targetwriter
substitution
variables
substitution
parameters
In Data Quality, you had a few basic layers: a folder, a project, and a dataflow
that contains a series of transforms which may or may not run.
20 Data Services Migration Considerations
The terms are different, but they mean the same
thing: a place where the output data is held.
The terms are different, but they mean the same
thing: a text string alias.
In Data Services, the top layer is called a project. The next layer is a job that
runs. The job may hold a work flow which is where you can set up conditional
processing. The work flow, if you use one, will contain the data flow that
contains a series of transforms.
See the Data Services Designer Guide: Designer User Interface for
information.
Naming conventions
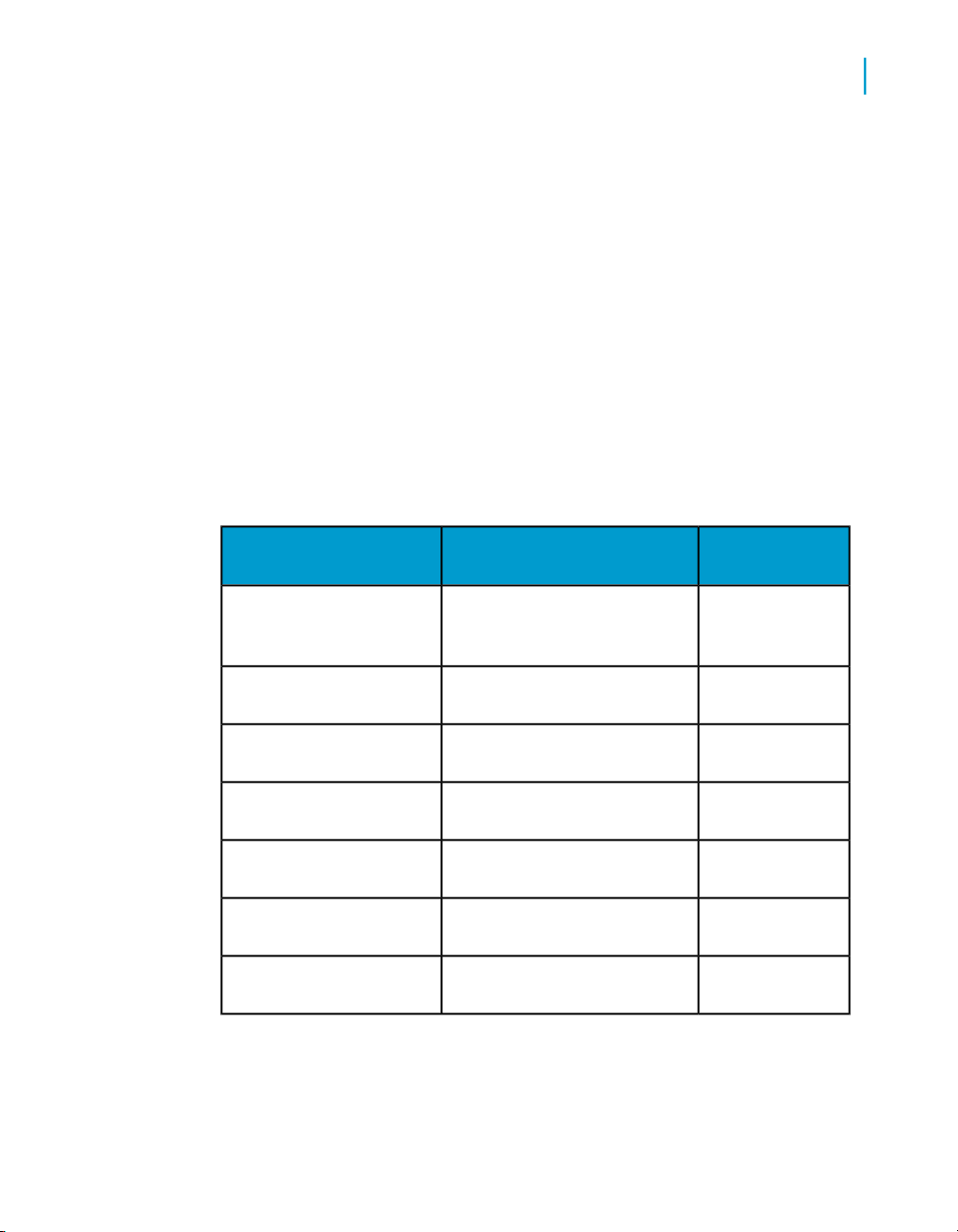
Object names
Your objects, when migrated, will have the prefix DQM_. If the name of the
object is longer than 64 characters, then a numeric suffix will be added (for
example, _001) to preserve the unique names.
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Introduction
1
Object
uration
named_connections
Datastores created from
Reater/Writer settings
named_connections
File formats created from
Reader/Writer settings
tions
and jobs
Pre-migrated Data Quality
name
dqserver1_substitutions.xmlSubstitution variable config-
Project first.xml with Reader
called My_DB_Reader
Project first.xml with Reader
called Cust_Det
my_usa_reg_addr_cleanseSDK transform configura-
Migrated Data
Services name
DQM_dqserver1_substitutions.xml
DQM_first_connfirst_connDatastores created from
DQM_first_My_DB_Reader
DQM_CRM_usaCRM_usaFile formats created from
DQM_first_Cust_Detect
DQM_my_usa_reg_addr_cleanse
DQM_firstfirst.xmlData Integrator data flows
Data Services Migration Considerations 21

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Introduction
Input and output field names
Data Quality input and output fields have a period in their names. However,
Data Services does not allow a period (.) in the column names. Therefore,
the dqmigration utility replaces the period with an underscore (_).
For example, suppose your Data Quality Reader transform has input field
names input.field1, input.field2, and input.field3. After migration,
these field names become input_field1, input_field2, and input.field3.
Deprecated objects
Differences between Data Quality and Data Services
While this list is not exhaustive, it lists the major differences that you will see
between Data Quality and Data Services.
There are also changes to transform options and option groups. See each
transform section in this document for details.
• Web Services
The .Net deployment is deprecated.
• Match transforms
The Aggregator, Sorter3, Candidate Selector, Match or Associate, Group
Statistics, Unique ID, and Best Record transforms are now included
together in one Match transform. You will also notice the performance
improvement in the Match and UDT transforms.
• GAC transform
Support for Australia, Canada, Global Address, EMEA, Japan and USA
engines. There is also a new Suggestion List option group.
• URAC transform
You can only output one Suggestion Lists output field within URAC.
• Search/Replace transform
The Search/Replace Transform is replaced by a Query transform using
a new search_replace() function call.
3
The Sorter transform only becomes part of the Match transform when it is migrated in a specific
transform order like Sorter, Aggreator and then Match.
22 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Introduction
• Data Cleanse transform
New dictionary connection management window.
• Global Suggestion Lists transform
New Suggestion List Option group.
• Phonetic Key transform
The Phonetic Key transform is replaced by a query transform with either
a double_metaphone() or soundex() function call.
• Substitution variables and files
Substitution variables are now referred to as Substitution parameters.
• Python changes
Several Python methods have been deprecated.
Deprecated objects
The improved technology in Data Services requires the depreciation of certain
aspects of Data Quality.
• Compound Transforms
• Shared options
• Candidate Selector's Unique ID record stem support
• Some options and behaivours related to pre/post SQL operations in the
database Reader and Writer transforms
• UDT's per dataflow mode (use a workflow and scripts as a workaround)
• Disabled transforms
1
Note: Disabled transforms in Data Quality projects are enabled after
migration. If you don't want to the enable the transform, then removed
them prior to migration.
• Flat Files
• Binary file type support in fixed-width files in versions of Data Quality
earlier than 11.7
• Logical and packed field support in versions of Data Quality earlier
than 11.7.
• Data collections
• Thread and watermark settings on a per-transform basis
• Observer transform
Data Services Migration Considerations 23

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Introduction
• Progress Service transform
• Integrated batch API
• Admin methods in real-time API
• Netscape and Firefox browsers
• JIS_Encoding for flat files
• Some less popular code page support (most used code pages are
supported)
• Several Python methods
• Web Services .Net deployment
• Several Web Services functions
• Sun Java application server for web tier
Related Topics
• Introduction to the interface on page 16
• Overview of migrated transforms on page 55
Premigration checklist
To ensure a smooth migration, make sure you have completed the following
tasks.
• Upgrade to Data Quality XI 11.7, if possible.
Being on the most current version ensures that the latest options and
functionality are properly installed and named. The options will more
easily map to the Data Services options. Upgrade the repository using
RepoMan.
• Verify that you have permissions to both the Data Quality and Data
Services repositories.
If you don't have a connection to the repositories or permissions to access
the repositories, then you will not be able to migrate to Data Services.
• Back up your Data Quality and Data Services repositories.
Your projects will look different in Data Services. You may want to keep
a backup copy of your repository so that you can compare the Data Quality
and/or Data Services setup with Data Services.
• Clean your repository.
24 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Delete any unused projects or projects that have verification errors.
Projects that do not run on Data Quality XI will not migrate well and will
not run on Data Services without making some changes in Data Services.
Projects that have verification errors due to input or output fields will not
migrate. Remove any custom transforms, compound transforms and
projects that you do not use anymore from the file system repository.
• Verify that your support files are accessible.
If you have a flat file reader or writer, ensure that the corresponding FMT
or DMT file is in the same directory location as the flat file reader or writer.
• Install Data Services.
Follow the installation instructions in the BusinessObjects Data Services
XI 3.0 Installation Guide.
Using the migration tool
Overview of the migration utility
Using the migration tool
1
You invoke the Data Quality migration utility with the dqmigration command
and specify a migration configuration file name. The utility is only available
on Windows. If your repository is on UNIX, you must have a shared system
to the repository, or FTP the repository file to a Windows system prior to
running the utility.
The configuration file specifies the Data Quality repository to migrate from,
the Data Services repository to migrate to, and processing options for the
migration utility. Data Services provides a default migration configuration file
named dqmig.xml in the directory LINK_DIR\DQMigration. You can either
edit this file or copy it to customize it. For details, see Running the dqmigration
utility on page 29.
The value of the LINK_DIR system variable is the path name of the directory
in which you installed Data Services.
The dqmigration utility creates the following files:
•
Migration report in LINK_DIR \DQMigration\mylogpath
Data Services Migration Considerations 25

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Using the migration tool
This migration report provides the status of each object that was migrated
and displays the informational, warning, and error messages from the
migration utility. After the dqmigration utility completes, it displays a
prompt that asks you if you want to view the migration report. Always
open the file in Internet Explorer.
• Work files
The dqmigration utility creates a directory LINK_DIR
\DQMigration\work_files that contains the following files. Use these files
if you need to troubleshoot any errors in the migration report.
• Directories configuration_rules_1 and configuration_rules_2 – These
directories contain a copy all of the intermediate XML created during
migration.
• .atl files – These files contain the internal language that Data Services
uses to define objects.
The last step of the dqmigration utility imports the .atl files and creates the
equivalent jobs, data flows, and connections in the Data Services repository.
Related Topics
• Running the dqmigration utility on page 29
• dqmigration utility syntax and options on page 31
• Migration report on page 35
Migration checklist
During migration, follow these steps.
• Complete the steps in the premigration checklist.
• Run the migration utility on your entire repository (recommended) or on
your project that has all verification errors fixed.
• Follow the utility prompts to complete the migration steps.
• Review the view the migration report by selecting to view the report at
the end of the migration.
• If you have errors or warnings that can be fixed in Data Quality 11.7, then
fix them and run the utility again. The files for the repository (or project,
as the case may be) will be overwritten in Data Services when the utility
is rerun.
26 Data Services Migration Considerations

• Fix any other errors or warnings in Data Services.
• Follow the recommendations in each transform section to optimize
performance.
• Test the jobs in Data Services and compare the results with Data Quality
results.
• Make changes in Data Services, as appropriate.
After you have your jobs migrated to Data Services, you should set aside
some time to fully analyze and test your jobs in a pre-production environment.
Related Topics
• Premigration checklist on page 24
Connection information
The database connection options may be confusing, especially for
<DATABASE_SERVER_NAME> which may be the name of the server, or
the name of the database. To set your database connection information,
open the dqmig.xml file in the directory LINK_DIR \DQMigration.
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Using the migration tool
1
Locate the <DI_REPOSITORY_OPTIONS> section.
Based on your database type, you would enter information similar to the
following.
Example: DB2
<DATABASE_TYPE>DB2</DATABASE_TYPE> <!-- Note here that Server name
is actually database name-->
<DATABASE_SERVER_NAME>REPORTS1</DATABASE_SERVER_NAME>
<DATABASE_NAME>REPORTS1</DATABASE_NAME>
<WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>NO</WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>
Example: MS SQL
<DATABASE_TYPE>Microsoft_SQL_Server</DATABASE_TYPE> <!-- Note
here that Server name is actual machine if it is default instance.-->
Data Services Migration Considerations 27

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Using the migration tool
<DATABASE_SERVER_NAME>MACHINE-XP2</DATABASE_SERVER_NAME> <--If
you have separate instance then you have to mention something like
IQ8TEST-XP2\MSSQL2000 -->
<DATABASE_NAME>REPORTS_MDR</DATABASE_NAME>
<WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>NO</WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>
Example: MySQL
<DATABASE_TYPE>MySQL</DATABASE_TYPE> <!-- Note here that Server
name is actually ODBC DSN name created by installer.-->
<DATABASE_SERVER_NAME>BusinessObjectsEIM</DATABASE_SERVER_NAME>
<DATABASE_NAME>BusinessObjectsEIM</DATABASE_NAME>
<WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>NO</WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>
Example: Oracle
<DATABASE_TYPE>Oracle</DATABASE_TYPE> <!-- Note here that Server
name is actually database name-->
<DATABASE_SERVER_NAME>DSORA103.COMPANY.NET</DATABASE_SERV
ER_NAME>
<DATABASE_NAME>DSORA103.COMPANY.NET </DATABASE_NAME>
<WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>NO</WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>
Example: Sybase
<DATABASE_TYPE>Sybase</DATABASE_TYPE> <!-- Note here that Server
name is actually machine name-->
<DATABASE_SERVER_NAME>sjds003</DATABASE_SERVER_NAME>
<DATABASE_NAME>test_proj </DATABASE_NAME>
<WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>NO</WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>
28 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Running the dqmigration utility
When you run the dqmigration utility, you can specify the options in one of
the following ways:
• Run the dqmigration utility and specify all options on the command line.
• Specify all options in a configuration file and run the dqmigration utility
and select only the option that references that file on the command line.
• Specify default values for the options in the configuration file and run the
dqmigration utility with some options specified on the command line.
The command line options override the values specified in the
configuration file.
To run the dqmigration utility:
1. Make sure the PATH system environment variable contains
%LINK_DIR%/bin. The utility will not run if it is not there.
2. Set up the configuration file that contains the options for the dqmigration
utility.
For example, create a customized configuration file named
dqmig_repo.xml and copy the contents of file dqmig.xml file to
dqmig_repo.xml.
Using the migration tool
1
3. Specify the information for the Data Quality repository that you want to
migrate.
a. In the DQ_REPOSITORY_OPTIONS section of the configuration file,
specify the following options.
• Absolute path name of your Data Quality repository configuration
file in the <CONFIGURATION_RULES_PATH> option.
• Path name, relative to the absolute path name, of your Data Quality
substitution file in the <SUBSTITUTION_FILE_NAME> option.
Note: Business Objects recommends that when you run the dqmigra
tion utility the first time, you migrate the entire Data Quality repository
instead of an individual project file to ensure that all dependent files
are also migrated. Therefore, do not specify a value in the
<FILE_OR_PATH> option the first time you run the utility. However,
it is possible that after you migrate the entire repository and you fix
errors in the resulting Data Services jobs, you might find an error that
is easier to fix in Data Quality. In this case, you can run the migration
utility on just the project after fixing it in Data Quality.
Data Services Migration Considerations 29

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Using the migration tool
b. Specify the information for the Data Services repository to which you
want to migrate.
For example, change the options in the dqmig_repo.xml configuration file
to migrate the Data Quality repository at location D:\dqxi\11_7\repos
itory\configuration_rules to the Data Services repository repo.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-16"?>
<REPOSITORY_DOCUMENT FileType = "MigrationConfiguration">
<MIGRATION_OPTIONS>
<PROCESSING_OPTIONS>
<LOG_PATH>mylogpath</LOG_PATH>
<ANALYZE_ONLY_MODE>YES</ANALYZE_ONLY_MODE>
</PROCESSING_OPTIONS>
<DQ_REPOSITORY_OPTIONS>
<CONFIGURATION_RULES_PATH>D:\dqxi\11_7\repository\configu
ration_rules</CONFIGURATION_RULES_PATH>
<SUBSTITUTION_FILE_NAME>dqxiserver1_substitutions.xml</SUB
STITUTION_FILE_NAME>
<FILE_OR_PATH></FILE_OR_PATH>
</DQ_REPOSITORY_OPTIONS>
<DI_REPOSITORY_OPTIONS>
<DATABASE_TYPE>Microsoft_SQL_Server</DATABASE_TYPE>
<DATABASE_SERVER_NAME>my_computer</DATABASE_SERVER_NAME>
<DATABASE_NAME>repo</DATABASE_NAME>
<WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>NO</WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION>
</DI_REPOSITORY_OPTIONS>
</MIGRATION_OPTIONS>
</REPOSITORY_DOCUMENT>
<USER_NAME>repo</USER_NAME>
<PASSWORD>repo</PASSWORD>
4. Open a command window and change directory to LINK_DIR\DQMigration
where the dqmigration executable is located.
5. Run the dqmigration utility in analyze mode first to determine the status
of objects within the Data Quality repository.
Specify the value YES for <ANALYZE_ONLY_MODE> in the configuration
file, or use the option -a when you run the dqmigration utility. For example,
type the following command and options in a command window:
dqmigration -cdqmig_repo.xml -aYES
Note: There is no space between the option -a and the value YES.
This step does not update the Data Services repository.
6. When the migration utility displays the prompt that asks if you want to
view the migration report, reply y.
7. In the migration report, review any messages that have type Error.
30 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Using the migration tool
You should migrate a production Data Quality repository where all of
•
the projects have executed successfully. If your Data Quality repository
contains unverifiable or non-runnable projects, then they will likely not
migrate successfully. Delete these types of projects before you run
the dqmigration utility with <ANALYZE_ONLY_MODE> set to NO.
Note: To delete a project in Data Quality, you delete its .xml file from
the directory \repository\configuration_rules\projects.
• If your Data Quality repository contains objects that the migration utility
currently does not migrate (for example dBase3 data sources), you
need to take some actions before you migrate. For details, see Trou
bleshooting on page 166.
Other errors, such as a Reader or Writer that contains a connection string,
can be fixed in Data Services after you run the migration utility with
<ANALYZE_ONLY_MODE> set to NO.
For information about how to fix errors listed in the migration report, see
Troubleshooting on page 166.
8. After you have fixed the serious errors that pertain to the Data Quality
projects that you want to migrate, run the dqmigration utility with
<ANALYZE_ONLY_MODE> set to NO.
This step imports the migrated objects into the Data Services repository.
1
Some of the Data Services jobs and data flows that result from the migration
from Data Quality might require clean-up tasks before they can execute. For
details, see Further cleanup on page 154.
Other migrated jobs or data flows might require changes to improve their
performance. For details, see Improving performance on page 161.
dqmigration utility syntax and options
Use the dqmigration utility to migrate the contents of a Data Quality
repository to a Data Services repository. You can also specify an individual
project file or folder.
Note: Business Objects recommends that when you run the utility the first
time, migrate the entire Data Quality repository instead of an individual project
file to ensure that all dependent files are also migrated. You would need to
Data Services Migration Considerations 31

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Using the migration tool
obtain the names of these dependent files (click View > Referenced File
Explorer in the Project Architect) and run the migration utility multiple times,
once for each file.
If you specify an option in the command line, it overrides the value in the
configuration file.
Note: If your configuration file is invalid, the command line options will not
be processed.
The following table describes the dqmigration utility options.
Option
-h or /h or /?
-cmig_conffile_path
name
-lmig_logfile_path
XML tag in dqmig configuration file
None
None
<LOG_PATH> mig_log
file_path </LOG_PATH>
Description
Prints the options available for this
utility.
Name of the configuration file for this
utility.
Default value is dqmig.xml which
is in the LINK_DIR\DQMigration
directory.
Path for the log file that this dqmigration utility generates.
Default value is migration_logs
which is in the current directory
from which you run this utility.
32 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Using the migration tool
1
Option
-amode
-ttimeout_in_seconds
XML tag in dqmig configuration file
<ANALYZE_ONLY_MODE>
mode</ANALYZE_ONLY_MODE>
<IMPORT_TIMEOUT> time
out_in_seconds </IMPORT_TIMEOUT>
Description
Analyze mode.
Specify YES to analyze the Data
Quality repository and provide
warning and error messages for
objects that will require manual
steps to complete the migration,
but do not update the Data Services repository.
Specify NO to also update the Data
Services repository with the migrated objects.
Default value is NO.
Amount of time that the migration
utility waits to import one Data Quality project into the Data Services
repository. If one project times out,
the migration utility will continue with
the next project. If a timeout occurs,
the migration log indicates which
object was being processed.
-ridq_input_re
pos_path
<CONFIGURATION_RULES_PATH> dq_in
put_repos_path</CONFIGURATION_RULES_PATH>
Data Services Migration Considerations 33
Default value is 300 seconds.
Path of the Data Quality repository
files.
Default value blank, but the sample
has the value
dq_directory\repository\con
figuration_rules
where dq_directory is the directory
in which you installed Data Quality.

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Using the migration tool
Option
-rsdq_substitu
tion_file
-fidq_input_re
pos_file
-dtds_repo_db_type
XML tag in dqmig configuration file
<SUBSTITUTION_FILE_NAME> dq_substi
tution_file</SUBSTITUTION_FILE_NAME>
<FILE_OR_PATH>dq_input_re
pos_file</FILE_OR_PATH>
<DATABASE_TYPE>ds_re
po_db_type</DATABASE_TYPE>
Description
Name of the substitution file to use
during migration.
Default value is blank, but the
sample has the value
dqxiserver1_substitutions.xml
Optional. Name of XML file or folder
to migrate. If you specify a file, only
that file migrates. If you specify a
folder, all the contents of the folder
and its subfolders migrate.
Default value is NULL which
means migrate the entire Data
Quality repository.
Database type for Data Services
repository. Values can be one of the
following:
• ODBC
• Oracle
• Microsoft_SQL_Server
• Sybase
• MySQL
• DB2
<DATABASE_SERV
-dsdi_repo_db_server
34 Data Services Migration Considerations
ER_NAME>di_repo_db_serv
er</DATABASE_SERV
ER_NAME>
Database server name for a Data
Services repository that is Microsoft
SQL Server or Sybase ASE.

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Using the migration tool
1
Option
-dndi_repo_db_name
-dwwin_auth
-dudi_repo_us
er_name
-dpdi_repo_password
XML tag in dqmig configuration file
<DATABASE_NAME>di_re
po_db_name</DATABASE_NAME>
<WINDOWS_AUTHENTICA
TION>win_auth</WIN
DOWS_AUTHENTICATION>
<USER_NAME>di_repo_us
er_name </USER_NAME>
<PASSWORD>di_repo_pass
word </PASSWORD>
Description
Connection name for a Data Services repository that is Oracle.
Data source name for a Data Services repository that is DB2 or
MySQL.
Database name for a Data Services repository that is Microsoft
SQL Server or Sybase ASE.
Whether or not to use Windows Authentication (instead of SQL Server
authentication) for Microsoft SQL
Server. Values can be Yes or No.
The default is No.
User name of authorized user to the
Data Services repository.
Password for the user authorized to
the Data Services repository.
Migration report
When you run the dqmigration utility, it generates a migration report in your
LINK_DIR\DQMigration\mylogpath directory.
The dqmigration utility displays the name of the migration report and a
prompt that asks if you want to view it. The dqmigration log file has a name
with the following format:
dqmig_log_processID_threadID_yyyymmdd_hhmmssmmm.xml
For example: dqmig_log_005340_007448_20080619_092451642.xml
The migration report consists of the following sections:
Data Services Migration Considerations 35

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
Using the migration tool
• Migration Summary
• Migration Settings – Lists the configuration option values used for this
migration run.
• General Processing Messages – Lists the status message of every
.xml file processed in the Data Quality repository. Possible message
types are:
• Info when the .xml file was processed successfully.
• Error when the .xml file was not processed successfully, and you
will need to take corrective action.
• Warning when the .xml file was processed and migrated, but you
might need to take additional actions after migration to make the
resulting data flow run successfully in Data Services. For example,
a substitution variable is not migrated and you would need to enter
the actual value in the Data Services object after migration.
The dqmigration utility executes in the following three stages, and
this General Processing section displays a different color background
for the messages that are issued by each stage.
• Stage 1 — Determines the version of the source Data Quality
repository. If the Data Quality repository is a version prior to 11.7,
this stage migrates it to version 11.7. The background color of
these stage 1 messages is beige.
• Stage 2 — Migrates Global Address Cleansing and Match family
transforms. The background color of these stage 2 messages is
light pink.
• Stage 3 — Migrates all other Data Quality objects and creates the
.atl file to import into the Data Services repository. The background
color of these stage 3 messages is the background color set for
your Web browser.
• General Objects – Lists the status of substitution files and connection
files.
• Transform Configurations – Lists the status of each transform
configuration that was migrated.
• Jobs – Lists the status of each job that was migrated.
• Migration Details
This section provides detailed migration status for each of the following
objects:
• Each substitution file
36 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
• Each named connection in the named_connections.xml file.
• Each transform configuration
• Each job (project)
How Data Quality repository contents
migrate
This section describes how the dqmigration utility migrates the following
Data Quality Repository components which consist mainly of different XML
files and folders:
• Projects and folders
• Substitution files and variables
• Named connections
• Data types
• Content type
1
Related Topics
• Deprecated objects on page 22
How projects and folders migrate
In Data Quality, folders contain objects, and the folder hierarchy can be
multiple levels. After migration to Data Services, the utility prefixes each
object with DQM_, and then they appear together in the Local Object Library.
The "Properties" of the migrated object indicates its source Data Quality
project.
Note: All of the files are not migrated. For example, the contents of the
blueprints folder, and the sample transforms that are automatically installed
in Data Quality. If you want to migrate a file from that folder, move the
contents to another folder that is migrated.
In Data Quality, you can create three types of projects:
Data Services Migration Considerations 37

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
• Batch – A batch project executes at a specific time and ends after all data
in the specified source is processed. See How batch projects migrate on
page 38.
• Transactional – A transactional project receives data from a calling
application (such as Web services or SDK calls) and processes data as
it arrives. It remains active and ready for new requests. See How
transactional projects migrate on page 40.
• Integrated Batch -- A project run using batch processing with an Integrated
Batch Reader and an Integrated Batch Writer transform. This type of
project can be used to pass data to and from an integrated application,
including Data Integrator XI Release 2 Accelerated (11.7). See How
integrated batch projects migrate on page 41.
Related Topics
• How database Reader transforms migrate on page 73
• How database Writer transforms migrate on page 83
• How flat file Reader transforms migrate on page 93
• How flat file Writer transforms migrate on page 101
• How transactional Readers and Writers migrate on page 116
How batch projects migrate
The dqmigration utility migrates a Data Quality Batch project to the following
two Data Services objects:
•
Data Flow -- A Data Services data flow is the equivalent of a Data Quality
project. Everything having to do with data, including reading sources,
transforming data, and loading targets, occurs inside a data flow.
•
Job -- A job is the only object you can execute in Data Services. Therefore,
the migration utility creates a job to encompass the migrated data flow.
The dqmigration utility also creates additional objects, such as a datastore
or file format, as sections How database Reader transforms migrate on page
73 and How flat file Reader transforms migrate on page 93 describe.
For example, suppose you have the following Data Quality
my_address_cleanse_usa project.
38 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
The dqmigration utility migrates this batch project to a Data Services job
named DQM_my_address_cleanse_usa which contains a data flow with the
same name. The dqmigration utility adds a DQM_ prefix to your project name
from Data Quality to form the Data Services job and data flow name.
1
The Project Area shows that the data flow DQM_my_address_cleanse_usa
contains the following migrated transforms:
• The Data Quality Reader transform has become the following Data
Services objects:
• Source object named Reader_Reader, which reads data from file
format DQM_my_address_cleanse_usa_Reader_Reader. The file
format is visible on the Formats tab of the Local Object Library.
• Query transform named Reader_Reader_Query, which maps fields
from the file format to the field names used by the rest of the data flow.
• The Data Quality UsaRegAddressCleanseCass transform has become
the Data Services UsaRegAddressCleanseCass_UsaRegAddressCleanse
transform.
• The Data Quality Writer transform has become the following Data Services
objects:
• Query transform named Writer_Writer_Query
• Target object named Writer_Writer, which maps fields from field
names used in the data flow to the file format DQM_my_ad
Data Services Migration Considerations 39

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
dress_cleanse_usa_Writer_Writer (visible in the Local Object
Library).
When the dqmigration utility creates the Data Services objects, it updates
each object's description to indicate its source Data Quality project and
transform. The description also contains the original Data Quality description.
For example, in the Data Services Designer, the Formats tab in the Local
Object Library shows the following descriptions.
To view the full description, select a name in the Format list, right-click, and
select Properties.
Related Topics
• How database Reader transforms migrate on page 73
• How database Writer transforms migrate on page 83
• How flat file Reader transforms migrate on page 93
• How flat file Writer transforms migrate on page 101
How transactional projects migrate
The dqmigration utility migrates a Data Quality transactional project to a
Data Services real-time job that consists of the following objects:
• Initialization — Starts the real-time process. The initialization component
can be a script, work flow, data flow, or a combination of objects. It runs
only when a real-time service starts.
• A data flow which contains the resulting Data Services objects from the
Data Quality project:
• A single real-time source — XML message
40 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
• A single real-time target — XML message
• Clean-up -- Ends the real-time process. The clean-up component (optional)
can be a script, work flow, data flow,or a combination of objects. It runs
only when a real-time service is shut down.
For example, suppose you have the following Data Quality project
my_trans_address_suggestions_usa.xml.
The dqmigration utility migrates this transactional project
my_trans_address_suggestions_usa to a Data Services real-time job named
DQM_my_trans_address_suggestions_usa which contains a data flow with
the same name.
1
Related Topics
• How transactional Readers and Writers migrate on page 116
• Post-migration tasks for transactional Readers and Writers on page 120
How integrated batch projects migrate
In Data Integrator XI Release 2 Accelerated (version 11.7), a Data Quality
integrated batch project passed data from a job in Data Integrator, cleansed
the data in Data Quality, and passed the data back to the Data Integrator
job. These Data Quality projects were imported into Data Integrator 11.7
through a Data Quality datastore and the imported Data Quality project was
used as a cleansing transform within a Data Integrator data flow.
Data Services Migration Considerations 41

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
The Data Quality transforms are now integrated into Data Services, and you
can use them just like the regular Data Integrator transforms in a data flow.
You no longer need to create a Data Quality datastore and import the
integrated batch projects.
If you used imported Data Quality projects in Data Integrator 11.7, you will
see them in Data Services.
• Data Quality datastores are still visible, but you cannot edit them and you
cannot create new ones. You can delete the Data Quality datastores.
• You cannot connect to the Data Quality Server and browse the integrated
batch projects.
• The previously imported Data Quality projects are still visible:
• under each Data Quality datastore, but you cannot drag and drop them
into data flows. You can use the option View Where Used to see what
existing data flows use each imported Data Quality project.
• as a Data Quality transform within the data flow, and you can open
this transform to view the field mappings and options.
To use your existing Data Integrator 11.7 integrated batch projects in Data
Services, you must modify them in one of the following ways:
• If your Data Integrator 11.7 data flow contains a small number of imported
Data Quality transforms, modify your data flow in Data Services to use
the new built-in Data Quality transforms.
• If your Data Integrator 11.7 data flow contains a large number of Data
Quality transforms, migrate the Data Quality integrated batch project and
replace the resulting placeholder Readers and Writers with the appropriate
sources and targets. A large number of Data Quality transforms can exist
as either:
• An imported Data Quality project that contains a large number of Data
Quality transforms.
• Multiple imported Data Quality projects that each contain a few Data
Quality transforms.
Related Topics
• Modifying Data Integrator 11.7 Data Quality projects on page 112
• Migrating Data Quality integrated batch projects on page 109
• How batch projects migrate on page 38
42 Data Services Migration Considerations

How connections migrate
The dqmigration utility migrates Data Quality connections to one of the
following Data Services objects, depending on whether the data source is a
file or a database:
•
Datastores when the connection is a database -- Datastores represent
connection configurations between Data Services and databases or
applications.
•
File Formats when the connection is a flat file -- A file format is a set of
properties describing the structure of a flat file (ASCII). File formats
describe the metadata structure, which can be fixed or delimited. You
can use one file format to access multiple files if they all have the same
metadata structure.
For a named connection, the dqmigration utility generates the name of the
resulting datastore or file format as follows:
DQM_connectionname
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
1
For connections that are not named (the Reader or Writer transform provides
all of the connection information instead of the file named_connections.xml),
the resulting name of the datastore or file format is:
DQM_projectname_readername_Reader
DQM_projectname_writername_Writer
The following table shows to which Data Services objects each specific
Driver_Name value is migrated.
Table 1-4: Mapping of Data Quality Driver_Name options
Value of Data Quality connection Driver_Name option
FLDB_DBASE3
Data Services Migration Considerations 43
Data Services object
Placeholder Fixed width File Format
DatastoreFLDB_STD_DB2
File Format for a flat fileFLDB_DELIMITED

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
Value of Data Quality connection Driver_Name option
Rather than not migrate the Data Quality xml file, the dqmigration utility
creates a placeholder file format or placeholder datastore that you can fix
after migration in situations that include the following:
• The flat file type or database type (such as dBase3) is not supported in
Data Services.
• A substitution variable was used in the Data_Source_Name and the file
that the substitution variable refers to was not found.
For information about how to change the placeholder objects, see Table
1-51: on page 167 in Troubleshooting on page 166.
Data Services object
File Format for a flat fileFLDB_FIXED_ASCII
ODBC DatastoreFLDB_STD_MSSQL
Placeholder ODBC DatastoreFLDB_STD_MYSQL
DatastoreFLDB_STD_ODBC
DatastoreFLDB_STD_ORACLE9
DatastoreFLDB_STD_ORACLE10
The following table shows how the Data Quality connection options are
mapped to the Data Services datastore options.
Note: If the dqmigration utility cannot determine the database type from a
named connection (for example, the connection name specified in the Data
Quality Reader does not exist), then the utility creates an Oracle 9 datastore.
Table 1-5: Connection_Options mapping
Data Quality Connection_Options option
44 Data Services Migration Considerations
Data Services datastore
option
Datastore nameNamed_Connection

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
1
Data Quality Connection_Options option
FLDB_STD_DB2
FLDB_STD_MYSQL
Data_Source_
Name
Connection string
Data Services datastore
option
Data Source
Data SourceFLDB_STD_MSSQL
Cleanup required. See Fixing
invalid datastores on
page 154.
Data SourceFLDB_STD_ODBC
Connection nameFLDB_STD_ORACLE9
Connection nameFLDB_STD_ORACLE10
Cleanup required. See Fixing
invalid datastores on
page 154.
Data Services Migration Considerations 45

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
Data Quality Connection_Options option
FLDB_STD_DB2
FLDB_STD_MYSQL
Driver_Name
FLDB_STD_ODBC
FLDB_STD_ORACLE9
Data Services datastore
option
Database type:DB2
Database version:DB2 UDB
8.x
Database type:ODBCFLDB_STD_MSSQL
A placeholder ODBC datastore is created. Cleanup required. See Fixing invalid
datastores on page 154.
Database type:ODBC
Driver_name in ODBC Data
Source Administration
Database type:Oracle
Database version:Oracle
9i
Database type:Oracle
FLDB_STD_ORACLE10
Host_Name
PORT_NUMBER
For example, suppose your Data Quality projects use the following named
connections:
46 Data Services Migration Considerations
Database version:Oracle
10g
Ignored, but the dqmigra
tion log displays a warning.
Ignored, but the dqmigra
tion log displays a warning.
In Edit Datastore, User nameUser_Name
In Edit Datastore, PasswordPassword

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
The following Formats tab in the local object library in the Data Services
Designer shows:
• The Data Quality named connection namedoutff is now the Data Services
file format DQM_namedoutff.
Note: A Data Quality named connection can have two contexts: Client
and Server. The dqmigration utility migrates the Server named
connection and ignores the Client one.
For a named connection, the description of the resulting file format refers
to named_connections.xml.
• Other Data Quality connections migrated to file formats in addition to the
namedoutff flat file connection.
1
These other Reader and Writers do not use named connections; therefore,
the description indicates the name of the Data Quality project from which
it was created.
To view the connection information, select a name in the Format list,
right-click, and select Edit.
Data Services Migration Considerations 47

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
• The Data Quality Driver Name FLDB_FIXED_ASCII becomes the Data
Services File Format Type Fixed width.
• The Data Quality connection Name namedoutff becomes the Data
Services File Format Name DQM_namedoutff.
• The Data Quality Data Source Name D:\dq_files\outff.txt becomes
the Data Services File name(s).
The following Datastores tab in the local object library in the Data Services
Designer shows:
• The Data Quality named connection orcl is now the Data Services
datastore DQM_orcl.
For a named connection, the description of the resulting datastore refers
to named_connections.xml. Otherwise, the description indicates the name
of the Data Quality project from which it was created.
• Other Data Quality connections migrated to datastores in addition to the
orcl database connection.
48 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
To view the connection information, select a datastore name in the datastore
list, right-click, and select Edit .
• The Data Quality connection Name orcl becomes the Data Services
Datastore name DQM_orcl.
• The Data Quality Data Source Name orcl becomes the Data Services
Connection name orcl.
1
How substitution files and variables migrate
The dqmigration utility migrates Data Quality substitution files and variables
as follows :
• Each Data Quality substitution file becomes a Data Services substitution
configuration in the Substitution Parameter Store. The name of the
resulting substitution configuration has the following format:
DQM_substitutionfilename
• Each Data Quality substitution variable becomes a Data Services
substitution parameter. The name of the resulting substitution parameter
is the same as the substitution variable. Afer migration, the substitution
parameter is enclosed in square brackets ([]) when used in the data flow.
Data Services Migration Considerations 49

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
After migration, you need to take additional steps to ensure that the migrated
substitution parameters use the correct values. For details, see Setting
substitution parameter configuration on page 158.
Note: In Data Quality, the substitution variables are case-sensitive. However,
in Data Services, the substitution parameters are case-insensitive. Therefore,
if two substitution variables exist with the same name but different casing,
only the first substitution variable migrates and the dqmigration utility issues
a warning message in the migration report.
Related Topics
• Name differences with substitution parameters for reference files on
page 51
• How built-in substitution variables migrate on page 50
• Example of how substitution files and variables migrate on page 53
How built-in substitution variables migrate
The following table shows that $$Dataflow_Name is the only Data Quality
11.7 built-in substitution variable that migrates to Data Services . The dqmi
gration utility replaces all instances of $$Dataflow_Name with the Data
Quality project name.
50 Data Services Migration Considerations
Migrate to Data ServicesData Quality built-in substitution variable
Yes$$Dataflow_Name
No$$Dataflow_XML_Path
No$$Log_Path
No$$Report_Path
No$$Stat_Path
No$$Time_Stamp
No$$Dataflow_ID
No$$Runtime_Metadata_Path

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
Migrate to Data ServicesData Quality built-in substitution variable
No$$Repos_Path
The dqmigration utility leaves the unsupported built-in substitution variables
as they are in the migrated data flow and issues warning messages in the
Migration Report. You must change these substitution variables to the actual
values in the Data Services data flow. If you do not change them, Data
Services produces run-time errors.
Note: If any of these built-in substitution variables are in places that the ATL
syntax does not allow substitution variables, the import of the generated .atl
file will fail. You must take one of the following actions before you migrate
the project:
• Delete or change these variables to the actual values.
• Remove the references to these variables.
When $$Dataflow_Name is used in a flat file Reader transform, the dqmigra
tion utility does the following:
• Replaces the substitution variable with the actual value.
• Locates the .fmt or .dmt file with the dataflow name.
• Creates a corresponding file format.
However, $$Dataflow_Name is no longer a substitution variable. Therefore,
if the name of the dataflow changed, you must change the actual value to
avoid unexpected results.
1
Name differences with substitution parameters for reference files
The installation of Data Services creates a substitution configuration that
includes substitution parameters for Data Quality reference files used by
various content transforms. Most of the Data Quality substitution variables
have been replaced by a single Data Services substitution parameter. These
substitution parameter settings are now part of the base configurations for
various content transforms.
The Data Services names of these substitution parameters differ from the
names of the corresponding substitution variables in Data Quality as the
following table shows.
Data Services Migration Considerations 51

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
Table 1-7: Name differences for substitution parameters for reference files
Data Quality substitution variable name
$$DIR_PATH_GLOBAL_ADDRESS
$$DIR_PATH_AUSTRALIA
$$DIR_PATH_CANADA
$$DIR_PATH_JAPAN
$$DIR_PATH_MULTI_COUNTRY
$$DIR_PATH_USA
$$DIR_PATH_USA_DPV
$$DIR_PATH_USA_ELOT
$$DIR_PATH_USA_EWS
$$DIR_PATH_USA_GEO
$$DIR_PATH_USA_LACS
$$DIR_PATH_USA_RDI
Data Services substitution parameter name
$$RefFilesAddressCleanse
$$DIR_PATH_USA_Z4CHANGE
Note: Ensure that you install the directories and other reference files in the
path pointed to by these substitution parameters.
52 Data Services Migration Considerations
$$RefFilesDataCleansePart of $$DCT_PATH
$$ReportsAddressCleanseDid not exist in Data Quality
$$ReportsMatchDid not exist in Data Quality
$$SamplesInstallDid not exist in Data Quality

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
Example of how substitution files and variables migrate
Suppose you have the following Data Quality substitution file
"dqxiserver1_substitutions" that contains the following substitution variables.
dqmigration utility migrates this Data Quality substitution file and variables
to the following Data Services substitution configuration.
1
Data Services Migration Considerations 53

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How Data Quality repository contents migrate
How data types migrate
The following table shows how the dqmigration utility maps the Data Quality
field types to the Data Services data types.
Table 1-8: Mapping of data types
54 Data Services Migration Considerations
Data Services data typeData Quality data type
decimal (38,7)NUMBER
doubleDOUBLE
dateDATE
datetimeDATETIME
timeTIME
decimalINT, UNIT
varcharSTRING

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Data Services data typeData Quality data type
varcharBINARY
varcharBYTEARRAY
Note: Data Quality does not distinguish between an integer and a decimal.
It represents and stores both data types as number. However, Data Services
makes this distinction. The dqmigration utility converts a number data type
to decimal(38,7) which accommodates both decimal and integer values. After
migration, verify that this decimal(38,7) is appropriate for your data. If it is
not, change the data type.
How Data Quality attributes migrate
The Data_Record_Field_Type and Data_Record_Field_Length are
automatically mapped in each transforms' Schema Out Type column.
How transforms migrate
1
Likewise, the Content_Type attribute is automatically mapped in each
transform's Schema Out Content Type column. If a content type cannot be
automatically mapped, then the content type will be blank.
You can change the attribute values for an output field by right-clicking the
field and selecting Properties.
How transforms migrate
Overview of migrated transforms
This topic lists the Data Quality transforms, how Data Services implements
each transform after it is migrated, and the new equivalent Data Services
transform if you create a new Data Services data flow.
Data Services Migration Considerations 55

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Data Quality
transform
Candidate Selector
Copier
Country_id
Data Cleanse
Data Services objects after
migration
Match transformAggregator
Associate transformAssociate
Match transformBest Record
Match transform.
Query transform with multiple
output pipes.
How Country ID transforms
migrate on page 63
Similar to Data Cleanse in
Data Quality.
Equivalent Data Services
transform
Part of the Group Forming prematch operations in the Match
transform. (Break Group)
Part of the match-level postmatch processing operations.
Part of the Group Forming prematch operations in the Match
transform. (Candidate Selection)
Built-in functionality
See Table 1-11: Country_ID
transform family on page 59
See Table 1-12: Data Cleanse
transform family on page 59
Python-based User-Defined
Filter
Global Address
Cleanse
Global Suggestion Lists
Group Statistics
56 Data Services Migration Considerations
and Case transform to support multiple pipes
User-Defined transformFormatter
How Global Address Cleanse
transforms migrate on
page 64
Similar to Global Suggestion
Lists in Data Quality.
Match transform.
Case transform
Query transform. See Formatter
transform on page 132
See Table 1-13: Global Address
Cleanse transform family on
page 60
See Table 1-14: Global Sugges-
tion Lists transform family on
page 61
Group Statistics post-match
processing per match level.

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality
transform
Phonetic Key
Progress Service
Database
Reader
Flat File
Reader
Read
er
Transactional
Reader
Data Services objects after
migration
Match transformMatch
Query transformObserver
Query with Soundex or Double-Metaphone function
Database source and SQL
transform with Query. See
How database Reader transforms migrate on page 73.
Flat file source and Query
transform. See How flat file
Reader transforms migrate
on page 93.
XML message source,
Query_Reader transform,
Row_Generation transform,
Query_Driver transform. See
How transactional Readers
and Writers migrate on
page 116.
Equivalent Data Services
transform
Query transformUser-Defined transformList/Source
See Table 1-15: Match trans-
form family (non-priority) on
page 61
Not supported because this
transform does not exist in Data
Quality 11.5 and above.
No longer a transform.
Not supportedNot migrated
Database source imported from
database datastore
Flat file source imported from
file format
XML message source imported
from file format
Scan and Split
Search and Replace
User Defined transform with
replace_substr function
Search_replace function in
Query transform
Data Services Migration Considerations 57
Query transform with replace_substr function
Query transform with
search_replace function

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Data Quality
transform
Sorter
Unique ID Plugin
USA Regulatory Address
Cleanse
User-Defined
transform
Database
Writer
Data Services objects after
migration
Order By option in Query
transform. In some cases,
part of Match transform options.
Match transform.Unique ID
Match transform.
How USA Regulatory Address Cleanse transforms
migrate on page 68
User-Defined transform
Query transform and dummy
target table. See How
database Writer transforms
migrate on page 83.
Equivalent Data Services
transform
Order By option in Query transform
Part of the match-level postmatch processing operations.
Part of the Unique ID postmatch processing operation.
See Table 1-16: USA Regulato-
ry Address Cleanse transform
family on page 63
See How User-Defined trans-
forms migrate on page 129
Database target imported or
created from database datastore
Query transform and flat file
Writ
er
Flat File
Writer
Transactional
Writer
target. See How flat file Writ-
er transforms migrate on
page 101.
Query transform and XML
schema target. See How
transactional Readers and
Writers migrate on page 116.
The following section discusses each transform family and maps the Data
Quality transform to the equivalent Data Services transform.
Note: The migration utility only processes transforms that are created by
the user. If a transform was part of the Data Quality installation, it will not be
migrated because the equivalent transform will be installed as part of the
Data Services installation.
58 Data Services Migration Considerations
Flat file source imported or created from file format
XML message source imported
or created from file format

Table 1-10: Associate transform family
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality transform
assoc_match_sets
Table 1-11: Country_ID transform family
Data Quality transform
Table 1-12: Data Cleanse transform family
Data Quality transform
data_cleanse_en
Equivalent Data Services
transform
AssociateGroupStatistics_Asso
ciateBatch
Base_Associateassoc_trans
Wizard_AssociateBatchassociate
Equivalent Data Services
transform
CountryID2Charcountry_id_country_ code
Equivalent Data Services
transform
EnglishNorthAmerica_Data
Cleanse
Spanish_DataCleansedata_cleanse_es
French_DataCleansedata_cleanse_fr
Portuguese_DataCleansedata_cleanse_pt
Data Services Migration Considerations 59

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Table 1-13: Global Address Cleanse transform family
Data Quality transform
australia_plugin
canada_plugin
Equivalent Data Services
transform
Global_AddressCleanse
Note: The Australia plugin is
now the Australia engine within
the Global Address Cleanse
Transform.
Global_AddressCleanse
Note: The Canada plugin is now
the Canada engine within the
Global Address Cleanse Transform.
Global_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse
Australia_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_australia
Brazil_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_brazil
Canada_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_canada
Canada_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_canada_ suggest
60 Data Services Migration Considerations
France_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_france
Germany_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_germany
Italy_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_italy
Japan_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_japan
Portugal_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_portugal
Spain_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_spain
UK_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_uk
USA_AddressCleanseglobal_address_ cleanse_usa

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality transform
global_address_ cleanse_suggest
multi_country_ plugin
usa_plugin
Table 1-14: Global Suggestion Lists transform family
Equivalent Data Services
transform
Global_AddressCleanse
Note: Set options under Sugges-
tion List Options.
Japan_AddressCleansejapan_plugin
Global_AddressCleanse
Note: Multi-country plugin is
now the EMEA engine and the
Global Address engine within the
Global Address Cleanse transform.
Global_AddressCleanse
Note: USA plugin is now the
USA engine within the Global
Address Cleanse transform.
Data Quality transform
Table 1-15: Match transform family (non-priority)
Data Quality transform
Data Services Migration Considerations 61
Equivalent Data Services
transform
GlobalSuggestionsglobal_suggest_lists_ global
UKSuggestions
Equivalent Data Services
transform
Address_MatchBatchmatch_address

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Data Quality transform
match_comsumr_ househld_res_fam_ind
match_comsumr_ househld_res_ind
match_corporate_ househld
Equivalent Data Services
transform
AddressJapan_MatchBatchmatch_address_japan
ConsumerHouseholdResFa
mInd_MatchBatch
ConsumerHousehol
dResInd_MatchBatch
CorporateHousehold
FirmInd_MatchBatch
FirmAddress_MatchBatchmatch_firm_address
FirmAddressJapan_MatchBatchmatch_firm_address_ japan
IndividualId_MatchBatchmatch_individual_id
NameAddress_MatchBatchmatch_name_address
NameDate_MatchBatchmatch_name_date
NameEmail_MatchBatchmatch_name_email
match_name_firm_ address_japan
62 Data Services Migration Considerations
NameFirmAddress_MatchBatchmatch_name_firm_ address
NameFirmAddressJapan_Match
Batch
NameIndividualId_MatchBatchmatch_name_ individual_id
NamePhone_MatchBatchmatch_name_phone
ProductDescription_MatchBatchmatch_ product_desc

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Table 1-16: USA Regulatory Address Cleanse transform family
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality transform
usa_reg_address_ cleanse_cass_ews
usa_reg_address_ cleanse_cass_geo
usa_reg_address_ cleanse_cass_rdi
usa_reg_address_ cleanse_cass_z4c
usa_reg_address_ cleanse_suggest
Address cleansing transforms
Equivalent Data Services
transform
USARegulatory_AddressCleanseusa_reg_address_ cleanse_CASS
USARegulatoryEWS_Address
Cleanse
USARegulatoryGeo_AddressCle
anse
USARegulatoryRDI_AddressCle
anse
USARegulatoryZ4Change_Ad
dressCleanse
USARegulatorySuggestions_Ad
dressCleanse
How Country ID transforms migrate
The dqmigration utility migrates Data Quality Country ID transform directly
to Country ID transform in Data Services.
Best Practice
You may notice that the Input, Options, and Output tabs contain options at
the top of the tab to filter the fields listed. Filter options are Best Practice,
In Use, and All . For migrated transforms, any fields or options that were set
in the original transform are listed when you select either Best practice or
In use.
Data Services Migration Considerations 63

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Related Topics
• Overview of migrated transforms on page 55
• Migrating Data Quality output fields on page 68
How Global Address Cleanse transforms migrate
The dqmigration utility migrates Data Quality Global Address Cleanse
transforms to a Global Address Cleanse transform in Data Services.
Most elements of the transform migrate to Data Services without any changes.
For example, all of the options in the Standardization group migrate to the
Global Address Cleanse transform in Data Services.
However, there are some aspects of the Data Quality Global Address Cleanse
transform that change after migration to Data Services.
Note: Global Address Cleanse migration error
In certain circumstances, when you migrate a Global Address Cleanse from
Data Quality to Data Services, a validation error appears regarding the
transforms output schema.
[EIM transform Source:<name of Data Quality transform>] BODI-1111071:
Output column <name of output column> is not mapped.
When this error appears, open the transform and remap the field named in
the error.
Related Topics
• Migration of Global Address Cleanse transform options on page 64
Migration of Global Address Cleanse transform options
When the dqmigration utility migrates your Global Address Cleanse
transforms to Data Services, there are changes to certain options and option
groups. The table below describes the changes to expect for Global Address
Cleanse.
64 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality Global Address Cleanse option
Plugins
Multicountry plugin
Field attributes
Suggestion lists
Country Map
Description
Defines the options for
processing addresses
from different countries.
Assigns the correct postal
code for addresses from
many different countries.
Defines the type of data
a field contains as well as
other aspects of the field.
Settings that define the
type of suggestion list information that is generated.
Option group that maps
a country and script to a
plugin for processing.
Data Services Global
Address Cleanse option
Now called engines. You
define engine settings in
the Options tab.
Replaced with the EMEA
engine.
Column headings in the
Output tab of the transform that includes field
name, field class, field
category, type, and content type.
Settings that indicate
whether or not to include
certain suggestion list information.
Deprecated and the migrated settings are
mapped to the country
and script code so that
the best engine available
processes the data.
Common option group
Component_Output_Fields, Standardized_Output_Fields, and
Suggestion_Output_Fields
Option group that contains settings for transform performance.
Option groups that define
output field attributes.
Data Services Migration Considerations 65
Contains only one option;
Run as Separate Process.
Field attribute named
Generated_Field_Category for output fields. Categories include Component, Standardized, and
Suggestion.

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Data Quality Global Address Cleanse option
Data_Record_Field_Type
and Data_Record_Field_Length
Content_Type
Remove Primary Name
Apostrophe
Engines
Description
Attributes for the output
fields.
Attributes for the output
fields.
Specifies whether to include punctuation in certain street names that include a DE L' or D'.
A generated output field.Building_Name
Assigns the plugins to
use for processing.
Data Services Global
Address Cleanse option
Field attributes that are
listed in each transforms'
Schema Out Type column.
Field attribute that is listed in the Schema Out
section in the Content
Type column.
Attribute name changed
to Remove Address
Apostrophes.
Output field name
changed to Building_Name1.
Deprecated and options
migrated to respective
engine group settings.
Best Practice
You may notice that the Input, Options, and Output tabs contain options at
the top of the tab to filter the fields listed. Filter options are Best Practice,
In Use, and All. For migrated projects, any fields or options that were set in
the original transforms are listed when you select either Best practice or In
use.
Related Topics
• Example of Global Address Cleanse migration on page 67
• Reference Guide: Description of column headings in the Output tab
• Reference Guide: Content types
66 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Example of Global Address Cleanse migration
To give you a better idea of the changes in the Global Address Cleanse
transform, suppose you have a Data Quality data flow that includes a Reader
transform, a Global Address Cleanse France transform, and a Writer
transform. Also included in the setup are plugins for Australia, Multi country,
and Japan. The data flow in Data Quality looks like the following illustration:
How transforms migrate
1
The dqmigration utility creates a Data Services data flow that will not include
plugins in the data flow. The dqmigration utility migrates the settings in the
Data Services plugins to settings in the Global Address Cleanse France
transform.
Also, the multi-country plugin settings are migrated to the EMEA engine
setup.
The rest of the option settings in the Data Quality plugins migrate to the
Global Address Cleanse transform into the applicable country sections. For
example, the illustration below shows the Japan options.
Data Services Migration Considerations 67

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
How USA Regulatory Address Cleanse transforms migrate
The dqmigration utility migrates Data Quality USA Regulatory Address
Cleanse transform to the Data Services USA Regulatory Address Cleanse
transform.
Note: If you used DPV or LACSLink in Data Quality, and did not purchase
these options in Data Services, you must disable these options before
migrating. If you do not disable them, your job will not run in Data Services.
Related Topics
• Migrating Data Quality output fields on page 68
• Migrating USA Regulatory Address Cleanse Options on page 71
Migrating Data Quality output fields
After you migrate the Data Quality USA Regulatory Address Cleanse
transform to Data Services using the dqmigration utility, you will notice
changes in how output fields are listed, mapped, and defined.
Best Practice
You may notice that the Input, Options, and Output tabs contain options at
the top of the tab to filter the fields listed. Filter options are Best Practice,
In Use, and All . For migrated projects, any fields or options that were set
in the original project are listed when you select either Best practice or In
use.
68 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
Output field types
All output fields, Component, Standardized, Suggestion, and Suggestion
List, are migrated to the Output tab in Data Services. The Output tab lists
the output fields and their attributes, which are populated with the settings
in Data Quality. Attributes are listed under the following column headings:
Generated_Field_Name, Generated_Field_Class,
Generated_Field_AddrClass, Generated_Field_Category, Type, and Content
Type.
Example:
1
Note: You can change attributes such as field length by double-clicking the
name of the field in the Output Schema portion of the transform. For more
information about changing field attributes, see the Getting Started Guide.
Output_Fields/Field
The following fields migrate to the Schema Out section of Data Services.
Data Quality transform option
Content_Type
Specifies the type of
data in the field.
Data Services Migration Considerations 69
Data Services optionDescription
Schema Out Content Type.

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Data Quality transform option
Specifies the number
Data_Record_
Field_Length
Data_Record_
Field_Type
Transform options: All transform options (Assignment, Standardization, and
so on) appear under the Options tab in Data Services.
Example:
of characters to make
available for the posted
data in this field.
Specifies the kind of
data this output field
will contain.
Data Services optionDescription
Schema Out Type
Schema Out Type
Related Topics
• Reference Guide: Generated field types
• Reference Guide: Content types
70 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
Migrating USA Regulatory Address Cleanse Options
The following table shows how dqmigration utility maps the Data Quality
USA Regulatory Address Cleanse options to Data Services.
1
Data Quality USA Regulatory Address Cleanse
option
Option Group settings
(values)
Suggestion_Lists_Out
put_Fields
Component_Output_Fields, Standardized_Output_Fields, and
Suggestion_Output_Fields
Description
Options that you set in
the transform to specify
how you want the transform to process your data
Options that you set in
the transform to specify
what information to include in suggestion list
output.
In Data Quality, there are
option groups for Component, Standardized, and
Suggestion output fields.
Data Services USA
Regulatory Address
Cleanse option
The values are migrated
to the Options tab. Each
category of options make
up a group of options. For
example, the assignment
options are in a group labeled Assignment Options.
The values are migrated
to the Options tab under
the Suggestion List Options group. Each group
is divided into Lastline
Components, Primary
Address Components,
and Secondary Address
Components.
In Data Services, output
fields are listed in the
Output tab, and they are
assigned a Generated_Field_Category of
Component, Standardized, or Suggestion.
Data Services Migration Considerations 71

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Data Quality USA Regulatory Address Cleanse
option
Data_Record_Field_Type,
Content_Type, and Data_Record_Field_Length
Best Practice
You may notice that the Input, Options, and Output tabs contain options at
the top of the tab to filter the fields listed. Filter options are Best Practice,
In Use, and All. For migrated projects, any fields or options that were set in
the original project are listed when you select either Best practice or In use.
Pre-migration task for jobs with LACSLink and DPV
Read this section only if you have purchased the LACSLink and DPV features
in Data Quality, but you did not purchase these features in Data Services.
If you migrate a Data Quality job to Data Services that has LACSLink and
DPV enabled, but you haven't purchased the LACSLink and DPV features
in Data Services, you may need to build the job in Data Services manually.
Description
In Data Quality, these
three attributes are set in
the Output Fields groups.
Data Services USA
Regulatory Address
Cleanse option
In Data Services, these
fields don't exist. Instead,
the settings are migrated
into the Type field attribute, which is a column
in the Output tab.
For example, suppose you have purchased LACSLink and DPV for Data
Quality XI, and you have jobs that are set up for LACSLink and DPV
processing. Then suppose you upgrade to Data Services, but you do not
have LACSLink and DPV features. The dqmigration utility migrates the
jobs successfully. However, when you import the jobs into Data Services
Designer, the LACSLink and DPV features become disabled.
In addition, if you open the job that contains the LACSLink and DPV transform
configuration, the transform corresponding to that configuration on the canvas
will have a red X on the corner indicating that it is broken. If this occurs, you
must delete the job and create a new one.
To avoid creating a new job, disable LACSLink and DPV in Data Quality
before you migrate to Data Services. Then the dqmigration utility migrates
72 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
the job successfully, and you can import the job to Data Services Designer
without ruining the job.
If you have migrated and opened your job, and the transform is disabled
(has a red X on the node in the canvas), you can purchase the LACSLink or
DPV features (and activate them with the assigned keycode) and then use
the jobs.
Related Topics
• Migrating Data Quality output fields on page 68
Reader and Writer transforms
How database Reader transforms migrate
The dqmigration utility migrates a Reader transform with a database data
source to the following Data Services objects:
• SQL transform -- Performs the indicated SQL query operation.
• Query transform -- Maps the Reader fields to the Data Quality input fields.
How transforms migrate
1
Note: After migration, open the resulting SQL transform in the migrated data
flow and click Update Schema to sequence the columns in the order of the
SQL query, and open each downstream transform to update the columns to
correspond to the updated SQL transform schema.
This section covers the following topics:
•
Mapping database Reader transform options on page 73
•
Example of migrated database Reader on page 77
•
Database Reader with Pre and Post SQL Statements on page 82
Mapping database Reader transform options
The following tables show how database Reader options map to the Data
Services object and options.
Data Services Migration Considerations 73

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Table 1-20: Transform_Performance option
Data Quality
database
Reader option
Bulk_Read_
Size_Recs
Table 1-21: Connection_Options
Data Quality
database Reader
option
Data_Source_
Name
Driver_Name
Description
Specifies the bulk factor and controls
whether or not bulk
reading is used. This
option is for relational
databases only.
Description
Specifies the name and path to the
data source.
Specifies the database driver to use
when connecting from the Reader
to the data source.
Data Services
object and option
SQL transform
Array fetch size
Description of Data Services option
Indicates the number of rows retrieved in a single
request to a source
database.
Data Services object
and option
Datastore Data
source
See table in How con-
nections migrate on
page 43
Specifies the server name where the
Host_Name
Named_ Connection
Password
74 Data Services Migration Considerations
data source resides. This option is
for relational databases only.
Specifies the name of a pre-configured data source connection to either a relational database or a flat
file.
Specifies the password appropriate
to the user name in order to access
the relational database.
Ignored
Becomes part of the
name of the datastore.
Datastore Password

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality
database Reader
option
Port_Number
User_Name
Table 1-22: Misc_Options
Data Quality
database Reader
option
Data_Source_ID
Description
Specifies the port number used for
connections. This option is for relational databases only.
Specifies the login name required to
access the relational database.
Max_Records_Per_
Collection
Description
Adds a new column and
value that you specify before it passes to the next
transform.
Specifies the number of
records allowed in each
collection before it is sent
to the next transform.
Data Services object
and option
Ignored
Datastore User name
Data Services object and
option
Query transform Schema Out
column DATA_SOURCE_ID,
which contains the constant
value defined in this option in
the Data Quality Reader.
Ignored
Max_Records_
Processed
Starting_Record_
Num
Specifies the total number
of records used for processing.
Specifies the record number that you want to include first. This option is
for flat files only.
Data Services Migration Considerations 75
Ignored
Ignored

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Data Quality
database Reader
option
Unique_Record_ID_
Stem
Table 1-23: SQL_Options
Data Quality
database
Reader option
Description
Sets the action that you
Post_SQL_Error_ Action
want to occur if a
Post_SQL_Statement
has failed.
Description
Adds a new column and
value that you specify
used for sequencing.
Data Services
object and option
Data Services object and
option
Query transform Schema
Out column
UNIQUE_RECORD_ID_STEM
which contains the constant
value defined in this option
in the Data Quality Reader.
Description of Data Services option
Not applicableIgnored
Post_SQL_
Statement
Specifies the SQL to exe-
cute after the Se-
lect_SQL_Statement.
Sets the action that you
Pre_SQL_Error_ Action
want to occur if a
Pre_SQL_Statement
has failed.
76 Data Services Migration Considerations
Post-Dataflow
Script that contains SQL function
SQL function runs
a SQL operation
against tables in
the specified
database
Not applicableIgnored

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality
database
Reader option
Description
Specifies the SQL to exPre_SQL_
Statement
ecute before the Se-
lect_SQL_Statement
begins.
Specifies the records
Select_SQL_
Statement
that are selected from
the input source, which
has a driver that accepts
SQL commands.
Example of migrated database Reader
This example shows how the dqmigration utility migrates a Data Quality
project with a database Reader.
Data Services
object and option
Pre-dataflow
script that contains SQL function
SQL Transform
SQL Text
Description of Data Services option
SQL function runs
a SQL operation
against tables in
the specified
database
Text of the SQL
query that is
passed to the
database server
This database Reader transform uses a Named_Connection orcl. The
dqmigration utility migrates the Named_Connection to the datastore
DQM_orcl. For details about how the named connection options map to the
datastore options, see How connections migrate on page 43.
Data Services Migration Considerations 77

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
This sample Reader has the following SQL_Options group. Option Se
lect_SQL_Statement selects the input database columns F1, F2, and F3.
The dqmigrationutility migrates this SELECT statement to the Data Services
SQL transform. In the following SQL Transform Editor, the SQL transform
named Reader_Reader contains this SELECT statement in the SQL Text
78 Data Services Migration Considerations

option.
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Services Migration Considerations 79

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
The Data Quality Reader maps the database columns f1 , f2, and f3 to input
fields input.f1, input.f2 , and input.f3.
The dqmigration utility migrates this mapping to a Data Services query
transform.
However, Data Services does not allow a period (.) in the column names.
Therefore, the dqmigration utility replaces the period with an underscore
(_). The sample Data Services query transform named
Reader_Reader_Query maps the input field names F1, F2, and F3 to column
80 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
names input_f1, input_f2, and input_f3.
How transforms migrate
1
The following table shows how the data types from the sample Data Quality
Reader input fields map to the data types in Data Services.
Table 1-24: Mapping of input data types
Data Quality database
Reader input field option
Data
Quality
Value
F1Input_Field_Name
input.f1Data_Record_Field_Name
100Data_Record_Field_Length
StringData_Record_Field_Type
Data Services
Query transform
option
Schema Out column
name
Data Services Migration Considerations 81
Data Services
Value
input_F1
varchar(100)Column data type

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Data Quality database
Reader input field option
Related Topics
• How connections migrate on page 43
• How data types migrate on page 54
Data
Quality
Value
F2Input_Field_Name
input.f2Data_Record_Field_Name
38Data_Record_Field_Length
NumberData_Record_Field_Type
Data Services
Query transform
option
Schema Out column
name
Database Reader with Pre and Post SQL Statements
If your Data Quality transform contains pre or post SQL statements, the
dqmigration utility migrates them to pre or post scripts around the Data
Services data flow.
Example: How a database reader with pre and post SQL statements
migrate
Data Services
Value
input_F2
decimal(38,7)Column data type
Suppose your Data Quality project db_reader_db_writer has a
Pre_SQL_Statement option that creates a test table and a
Post_SQL_Statement that drops the table.
The resulting migrated job DQM_db_reader_db_writer contains a
DQM_Pre_Script and DQM_Post_Script around the data flow
DQM_db_reader_db_wrtier.
82 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
The resulting migrated DQM_Pre_Script contains the Pre_SQL_Statement
value:
sql('DQM_db_reader_db_writer_My_DB_Reader_Reader',
'CREATE TABLE TestTable (DFID int NOT NULL ,
STSCNTER varchar2(256) ,
SRCIDFLD varchar2(256) )');
1
The resulting migrated DQM_Post_Script contains the Post_SQL_Statement
value :
sql('DQM_db_reader_db_writer_My_DB_Reader_Reader',
'drop table TestTable');
How database Writer transforms migrate
The dqmigration utility migrates a database Writer transform to the following
Data Services objects:
• Query transform -- Maps the fields from the previous transform to the
Target columns.
The generated name for this query has the format:
DataQualityWriterName_Writer_Query
Data Services Migration Considerations 83

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
• Target -- Contains the SQL statements from the Data Quality Writer
transform options Write_SQL_Statement, Pre_Write_SQL_Statement,
and Post_Write_SQL_Statement.
A target is an object to which Data Services loads extracted and
transformed data in a data flow. However, the target table that results
from a migrated Data Quality Writer is not the object that is loaded. The
SQL statement in Write_SQL_Statement identifies the table into which
you insert, update, or delete, and this table might be created by the
Pre_Write_SQL_Statement. When you execute the migrated job, Data
Services executes these SQL statements.
The generated name for this target has the format:
DataQualityWriterName_Writer
For example, if your Data Quality Writer name is My_DB_Writer, it
becomes the target named My_DB_Writer_Writer after migration to Data
Services.
• Datastore -- Fulfills the target object requirement for a table defined in a
datastore.
A Data Services Target object requires a table and schema defined in a
datastore. The dqmigration utility creates a dummy table and datastore
and places their names in the target object. This target table does not
appear in the imported table list of the datastore. You can ignore this
generated datastore unless you have defined a similarly named table that
is accessed by SQL statements elsewhere and you want to change the
name for clarity.
The following topics describe the mapping of the Data Quality database
Writer options to the Data Services Query and Target options.
•
Mapping database Writer Connection_Options on page 85
•
Mapping Per_Write_SQL_Options on page 88
•
Mapping Per_Write_SQL_Options on page 88
•
Mapping Output_Field_Options on page 91
•
Mapping Transform_Performance, Misc_Options, and Field option groups
on page 93
84 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
Mapping database Writer Connection_Options
The Connection_Options option group includes information about accessing
the output destination, which can be a flat file or a relational database. The
following table shows how the dqmigration utility maps these Data Quality
options to Data Services datastore options.
Table 1-25: Mapping Connection_Options
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality
database Writer option
Data_Source_
Name
Driver_Name
Host_Name
Description of Data
Quality option
Specifies the name and
path to the data
source.
Specifies the database
driver to use when
connecting from the
Writer to the output
destination.
Specifies the server
name where the output destination resides.
This option is for relational databases only.
Data Services
object and option
Datastore Data
source for DB2,
MSSQL, ODBC
Datastore
Connection
name for Ora-
cle
See table in
How connections migrate on
page 43
Ignored, but the
dqmigration
log displays a
warning.
Description of
Data Services option
Datastores represent connection
configurations between Data Services and databases or applications.
Database type and
database version
Not applicable
Data Services Migration Considerations 85

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Data Quality
database Writer option
Named_ Connection
Password
Port_Number
User_Name
Description of Data
Quality option
Specifies the name of
a pre-configured data
source connection to
either a relational
database or a flat file.
Specifies the password
appropriate to the user
name in order to access the relational
database for output.
Specifies the port number used for connections. This option is for
relational databases
only.
Specifies the login
name required to access the relational
database for output.
Data Services
object and option
Datastore Connection name
File Format
Name
Datastore Password
Ignored, but the
dqmigration
log displays a
warning.
Datastore User
name
Description of
Data Services option
Descriptive name
for the database
connection
Descriptive name
for the file format
User’s password
Not applicable
User name of the
account through
which Data Services accesses the
database.
Mapping Once_Per_Writer_SQL_Options
The SQL statements in the Once_Per_Writer_SQL_Options are executed
only once per Writer transform.
Note: Migrated jobs ignore all *_Error_Action options. If an SQL statement
fails, the Data Services job fails.
86 Data Services Migration Considerations

Table 1-26: Once_Per_Writer_SQL_Options
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality
database Writer
option
Post_Connection_ Error_Action
Post_Connection_
SQL_Statement
Post_SQL_ Error_Action
Post_SQL_
Statement
Pre_SQL_ Error_Action
Description
Sets the action that you want to occur if a Post_Connection_SQL_Statement has failed.
Specifies the SQL statement to execute after a connection to the
database is established.
Sets the action that you want to occur if a Post_SQL_Statement has
failed.
Specifies the SQL statement to execute after the Select_SQL_Statement.
Sets the action that you want to occur if a Pre_SQL_Statement has
failed.
Data Services object
and option
Ignored
In Target object, on
Pre-Load Commands tab, first part
of SQL Commands
text box
Ignored
In Target object, on
Post-Load Commands tab, part of
SQL Commands text
box
Ignored
In Target object, on
Pre_SQL_
Statement
Specifies the SQL to execute before
the Select_SQL_Statement begins.
Pre-Load Commands tab, first part
of SQL Commands
For example, suppose your Writer transform contains the following values
for the Once_Per_Writer_SQL_Options.
• Pre_SQL_Statement option:
CREATE TABLE test_unique_id
(
DATA_SOURCE_ID VARCHAR(10) ,
Data Services Migration Considerations 87

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
astset VARCHAR(256) ,
dataflowid NUMERIC(10) ,
mtlvlname VARCHAR(256) ,
mtset VARCHAR(256) ,
transformid NUMERIC(10) ,
UNIQUE_RECORD_ID_STEM VARCHAR(10)
);
• Post_SQL_Statement option:
DELETE SOMETABLE
The dqmigration utility produces the following dummy Target object with
the Pre-Load Commands tab that contains the Pre_SQL_Statement value.
The following Post-Load Commands tab shows the Post_SQL_Statement
value.
Mapping Per_Write_SQL_Options
In Data Quality, any SQL statements entered in Per_Write_SQL_Options
options are processed for each data collection. In Data Services, data
collections do not exist and these SQL statements are processed for the
entire data set.
Note: Migrated jobs ignore all *_Error_Action options. If an SQL statement
fails, the Data Services job fails.
88 Data Services Migration Considerations

Table 1-27: Per_Write_SQL_Options
Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality
database Writer option
Placehold
er_Mode
Post_Write_SQL_
Error_Action
Post_Write_SQL_
Statement
Pre_And_Post_
SQL_Frequency
Pre_Write_SQL_
Error_Action
Description
Specifies whether you want placeholders in your SQL statements,
and if so, the type of placeholder.
Sets the action that you want to
occur if a Post_Write_SQL_Statement has an error.
Specifies the SQL to execute after
the file is written.
Specifies how often the
Pre_Write_SQL_Statement and
Post_Write_SQL_Statement
should be invoked.
Sets the action that you want to
occur if a
Pre_Write_SQL_Statement has
an error.
Data Services object
and option
In Target object, on Op
tions tab, option Column comparison is set
to Compare by name
Ignored
In Target object, on Load
Triggers tab, third SQL
statement
Ignored
Ignored
Pre_Write_SQL_
Statement
Write_SQL_Error_ Action
Specifies database operations before writing a record.
Sets the action that you want to
occur if a Write_SQL_Statement
has an error.
Data Services Migration Considerations 89
In Target object, on Load
Triggers tab, first SQL
statement
Ignored

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Data Quality
database Writer option
Write_SQL_
Statement
Writer_Mode
Description
Specifies the records that are
placed into the output destination,
which has a driver that accepts
SQL commands.
Sets a mode for performing SQL
commands.
Data Services object
and option
In Target object, on Load
Triggers tab, second
SQL statement
In Target object, on Load
Triggers tab, option On
Operation
For example, suppose your Writer transform contains the following values
for the Per_Write_SQL_Options to insert into the test_unique_id table
(created by the Pre_SQL_Statement ) with Placeholder_Mode value Named.
Option Pre_Write_SQL_Statement contains the following SQL statement:
insert into othertable (column1, column2) values (:ds, :at)
Option Write_SQL_Statement contains an insert into the test_unique_id
table:
INSERT INTO test_unique_id
(DATA_SOURCE_ID,
astset,
dataflowid,
mtlvlname,
mtset,
transformid,
UNIQUE_RECORD_ID_STEM)
90 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
VALUES
(:ds,
:at,
:df,
:mtlvl,
:mt,
:tf,
:unq);
Option Post_Write_SQL_Statement contains the following SQL statement:
insert into someothertable (c1, c2) values (:mtlvl, :unq)
The dqmigration utility produces the following Target object with the
Load_Triggers tab that contains these three SQL statements:
• The Pre_Write_SQL_Statement value as the first statement
• The Write_SQL_Statement value as the second statement
• The Post_Write_SQL_Statement value as the third statement
1
Mapping Output_Field_Options
The Output_Field_Options option group creates the output fields that hold
the data that this transform creates. For example, the following
Output_Field_Options show the input field name in each Field option. The
Placeholder_Mode option in the Per_Write_SQL_Options option group has
a value Named (which is the default value) that indicates the Writer should
Data Services Migration Considerations 91

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
map each input field name to the Output_Field_Placeholder_Name.
After the dqmigration utility migrates this Writer transform, the Data Services
Query transform maps the input field names to the placeholder names.
However, a colon (:) is not allowed in Data Services names. Therefore, the
dqmigration utility removes the colon.
Table 1-28: Mapping of input field names to output placeholder names
Data Quality Output_Field_Options Field
92 Data Services Migration Considerations
Data Quality Output_Field_ Placeholder
name
Data Services
column name
ds:dsData_Source_ID
at:atinput.astset
df:dfinput.dataflowid
mtlvl:mtlvlinput.mtlvlname
mt:mtinput.mtset
tf:tfinput.transformid

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality Output_Field_Options Field
The dqmigration utility produces the following Query transform named
My_DB_Writer_Writer_Query which shows:
• The input field names are in the Schema In area of the Query transform.
• The modified placeholder names are in the Schema Out area.
• The Mapping column in Schema Out contains the name of the input field,
prefaced with the name of the object before this Query.
Data Quality Output_Field_ Placeholder
name
Data Services
column name
unq:unqUnique_Record_ID_Stem
Mapping Transform_Performance, Misc_Options, and Field option groups
How flat file Reader and Writer transforms migrate
How flat file Reader transforms migrate
The dqmigration utility migrates Reader transforms with flat file inputs to
the following Data Services objects:
• File Format -- A file format is a set of properties describing the structure
of a flat file (ASCII). File formats describe the metadata structure which
can be fixed or delimited. You can use one file format to access multiple
files if they all have the same metadata structure.
Data Services Migration Considerations 93

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
• Source -- A source is an object from which Data Services reads data. In
this case, it is the specific flat file from which the migrated Data Quality
Reader transform reads data.
• Query transform -- A Query transform maps the Reader fields to the Data
Quality input fields.
The following topics describe the mapping of the Data Quality flat file Reader
options to the Data Services Source and Query options.
•
Migration of flat file Reader Connection_Options on page 94
•
Mapping flat file Reader Misc_Options on page 96
•
Mapping Native_Flat_File_Options on page 97
•
Mapping Input_Field_Options on page 99
•
Ignored flat file Reader options on page 100
Migration of flat file Reader Connection_Options
The Connection_Options group includes information about accessing the
input source for a flat file Reader transform. The input source can be a flat
file such as fixed-length ASCII or delimited.
The following table shows how the dqmigration utility maps the flat file
Reader Connection_Options to the Data Service File Format options.
Data Quality
database Reader
option
Named_ Connection
94 Data Services Migration Considerations
Description
Specifies the
name of a preconfigured data
source connection
to either a relational database or a
flat file.
Data Services File Format section
and option
General section, Name contains the
connection name prefaced with DQM.
File Name(s) contains the Data_Source_Name to which the named
connection refers.

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality
database Reader
option
Data_
Source_Name
Driver_Name
Description
Specifies the
name and path to
the data source.
Contains a substitution variable for
the name and path
to the data source.
Specifies the flat
file driver to use
when connecting
from the Reader to
the data source.
For flat files, this
value is either
FLDB_DELIMITED or
FLDB_FIXED_ASCII.
Data Services File Format section
and option
General section, Name contains the
data source name.
Data File(s) section, File Name(s)
contains the path.
General section, Name contains the
data source name.
Data File(s) section, File Name(s)
contains the substitution parameter.
Note: The term substitution variable
is changed to substitution parameter
to avoid confusion with existing Data
Services variables.
General section, Type contains Delim
ited or Fixed Width.
For example, suppose you have a Data Quality project ff_named.xml that
has the following Connection_Options values. The named connection dfmt
is for data source e:\Titan\ff.txt.
Data Services Migration Considerations 95

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Using the information in the named_connections file, the dqmigration utility
creates a Data Services file format with the following values for this Reader
transform:
• Name: DQM_Dfmt
• Type: Delimited
• File Name(s): e:\Titan\ff.txt
Mapping flat file Reader Misc_Options
The Misc_Options group includes various information about record size,
unique records, and more.
The following table shows how the dqmigration utility maps the Data Quality
Misc_Options to the Data Service Query transform and File Format options.
Data Quality flat file
Reader option
Data_Source_ID
Max_Records_Per_Collec
tion
96 Data Services Migration Considerations
Data Services object and option
Query transform, Schema Out column DATA_SOURCE_ID which contains the constant value
defined in this option in the Data Quality Reader.
Ignored
IgnoredMax_Records_ Processed

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
1
Data Quality flat file
Reader option
Starting_Record_Num
Unique_Record_ID_Stem
Example: How Starting_Record_Num migrates
Suppose you have a Data Quality project named ff_input.xml and the
value of Starting_Record_Num is 1000. After migration:
• The new Data Services File Format has the name DQM_ff_input_2.
• The value of Skipped rows is 999.
Data Services object and option
A File Format that:
• has option Skipped rows set to this Data
Quality option value minus one. Therefore, this
File Format starts with this record number. If
another flat file Reader has a different value for
Starting_Record_Num set, then migration creates a new File Format.
• Has a name with "_2" appended to it.
See example below.
Query transform, Schema Out column
UNIQUE_RECORD_ID_STEM which contains the
constant value defined in this option in the Data
Quality Reader.
Mapping Native_Flat_File_Options
The Native_Flat_File_Options options group provides information about
fixed-length ASCII or delimited files.
Note: dBASE3 files are not supported in Data Services. The dqmigration
utility migrates a dBASE3 file to a Fixed width file type in Data Services.
The following table shows how the dqmigration utility maps the
Native_Flat_File_Options to the Data Service File Format options.
Data Services Migration Considerations 97

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
Default_Flat_File_Schema_Location
Data Services object and optionData Quality flat file Reader option
The dqmigration utility looks in this
location for the fmt or dmt file to define the File Format in Data Services.
Character_Encoding
For example, suppose you have a Data Quality project ff_namedout.xml
that has the following Native_Flat_File_Options values.
The following Data Services File Format Editor shows that the option
Character_Encoding value utf-8 migrated to the Data Services Code
Page option and the other options are ignored.
File Format , Locale section Code
Page
IgnoredUnassigned_Character_Action
IgnoredUnassigned_Character_Default
IgnoredIllegal_Character_Action
IgnoredIllegal_Character_Default
IgnoredUnicode_To_ASCII_Table
98 Data Services Migration Considerations

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
How transforms migrate
Mapping Input_Field_Options
The Input_Field_Options option group maps the input fields to use in this
Reader transform.
1
The following table shows how the dqmigration utility maps the
Input_Field_Options to the Data Service Query transform schema attributes.
Data Services Query schema attributeData Quality Reader Field option
Schema Out Content TypeContent_Type
Schema Out Type contains lengthData_Record_Field_Length
Schema Out column nameData_Record_Field_Name
Schema Out TypeData_Record_Field_Type
Schema In column nameInput_Field_Name
For example, suppose you have a Data Quality project my_ad
dress_cleanse_usa.xml that has the following Input_Field_Options and
options for Field (input.contact).
Data Services Migration Considerations 99

Data Quality to Data Services Migration Guide
1
How transforms migrate
The following sample Data Services Query Editor shows:
• The Data Quality Input_Field_Name value Contact migrates to a Schema
In column in the Data Services Query transform.
• The Data Quality Data_Record_Field_Name value input.custid
migrates to a Schema Out column in the Data Services Query transform.
• The Data Quality Data_Record_Field_Length and
Data_Record_Field_Type values are combined into the Type attribute
in Schema Out.
• The Data Quality Content_Type migrates to the Content Type attribute
in Schema Out.
Ignored flat file Reader options
The dqmigration utility ignores the following flat file Reader option groups.
100 Data Services Migration Considerations
 Loading...
Loading...